Page 1

®
General PurPose
DC Motors user Manual
Manual Number: IH-MTPM-DC_UMW
Page 2

BLANK
PAGE
Page 3
~ WARNING ~
Thank you for purchasing automation equipment from Automationdirect.com®, doing business as
AutomationDirect. We want your new automation equipment to operate safely. Anyone who installs or uses
this equipment should read this publication (and any other relevant publications) before installing or operating
the equipment.
To minimize the risk of potential safety problems, you should follow all applicable local and national codes
that regulate the installation and operation of your equipment. These codes vary from area to area and usually
change with time. It is your responsibility to determine which codes should be followed, and to verify that the
equipment, installation, and operation is in compliance with the latest revision of these codes.
At a minimum, you should follow all applicable sections of the National Fire Code, National Electrical
Code, and the codes of the National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association (NEMA). There may be local
regulatory or government offices that can also help determine which codes and standards are necessary for
safe installation and operation.
Equipment damage or serious injury to personnel can result from the failure to follow all applicable codes
and standards. We do not guarantee the products described in this publication are suitable for your particular
application, nor do we assume any responsibility for your product design, installation, or operation.
Our products are not fault-tolerant and are not designed, manufactured or intended for use or resale as on-line
control equipment in hazardous environments requiring fail-safe performance, such as in the operation
of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication systems, air traffic control, direct life support
machines, or weapons systems, in which the failure of the product could lead directly to death, personal
injury, or severe physical or environmental damage (“High Risk Activities”). AutomationDirect specifically
disclaims any expressed or implied warranty of fitness for High Risk Activities.
For additional warranty and safety information, see the Terms and Conditions section of our catalog. If
you have any questions concerning the installation or operation of this equipment, or if you need additional
information, please call us at 770-844-4200.
This publication is based on information that was available at the time it was printed. At AutomationDirect
we constantly strive to improve our products and services, so we reserve the right to make changes to the
products and/or publications at any time without notice and without any obligation. This publication may also
discuss features that may not be available in certain revisions of the product.
Trademarks
This publication may contain references to products produced and/or offered by other companies. The
product and company names may be trademarked and are the sole property of their respective owners.
AutomationDirect disclaims any proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
Copyright 2007–2019 Automationdirect.com® Incorporated
All Rights Reserved
No part of this manual shall be copied, reproduced, or transmitted in any way without the prior, written
consent of Automationdirect.com® Incorporated. AutomationDirect retains the exclusive rights to all
information included in this document.
Page W–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 4

~ AVERTISSEMENT ~
Nous vous remercions d’avoir acheté l’équipement d’automatisation de Automationdirect.com®, en faisant
des affaires comme AutomationDirect. Nous tenons à ce que votre nouvel équipement d’automatisation
fonctionne en toute sécurité. Toute personne qui installe ou utilise cet équipement doit lire la présente
publication (et toutes les autres publications pertinentes) avant de l’installer ou de l’utiliser.
Afin de réduire au minimum le risque d’éventuels problèmes de sécurité, vous devez respecter tous les codes
locaux et nationaux applicables régissant l’installation et le fonctionnement de votre équipement. Ces codes
diffèrent d’une région à l’autre et, habituellement, évoluent au fil du temps. Il vous incombe de déterminer les
codes à respecter et de vous assurer que l’équipement, l’installation et le fonctionnement sont conformes aux
exigences de la version la plus récente de ces codes.
Vous devez, à tout le moins, respecter toutes les sections applicables du Code national de prévention des
incendies, du Code national de l’électricité et des codes de la National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association
(NEMA). Des organismes de réglementation ou des services gouvernementaux locaux peuvent également
vous aider à déterminer les codes ainsi que les normes à respecter pour assurer une installation et un
fonctionnement sûrs.
L’omission de respecter la totalité des codes et des normes applicables peut entraîner des dommages à
l’équipement ou causer de graves blessures au personnel. Nous ne garantissons pas que les produits décrits
dans cette publication conviennent à votre application particulière et nous n’assumons aucune responsabilité à
l’égard de la conception, de l’installation ou du fonctionnement de votre produit.
Nos produits ne sont pas insensibles aux défaillances et ne sont ni conçus ni fabriqués pour l’utilisation ou
la revente en tant qu’équipement de commande en ligne dans des environnements dangereux nécessitant une
sécurité absolue, par exemple, l’exploitation d’installations nucléaires, les systèmes de navigation aérienne ou
de communication, le contrôle de la circulation aérienne, les équipements de survie ou les systèmes d’armes,
pour lesquels la défaillance du produit peut provoquer la mort, des blessures corporelles ou de graves
dommages matériels ou environnementaux («activités à risque élevé»). La société AutomationDirect nie toute
garantie expresse ou implicite d’aptitude à l’emploi en ce qui a trait aux activités à risque élevé.
Pour des renseignements additionnels touchant la garantie et la sécurité, veuillez consulter la section
Modalités et conditions de notre documentation. Si vous avez des questions au sujet de l’installation ou
du fonctionnement de cet équipement, ou encore si vous avez besoin de renseignements supplémentaires,
n’hésitez pas à nous téléphoner au 770-844-4200.
Cette publication s’appuie sur l’information qui était disponible au moment de l’impression. À la société
AutomationDirect, nous nous efforçons constamment d’améliorer nos produits et services. C’est pourquoi
nous nous réservons le droit d’apporter des modifications aux produits ou aux publications en tout temps, sans
préavis ni quelque obligation que ce soit. La présente publication peut aussi porter sur des caractéristiques
susceptibles de ne pas être offertes dans certaines versions révisées du produit.
Marques de commerce
La présente publication peut contenir des références à des produits fabriqués ou offerts par d’autres
entreprises. Les désignations des produits et des entreprises peuvent être des marques de commerce et
appartiennent exclusivement à leurs propriétaires respectifs. AutomationDirect nie tout intérêt dans les autres
marques et désignations.
Copyright 2007–2019 Automationdirect.com® Incorporated
Tous droits réservés
Nulle partie de ce manuel ne doit être copiée, reproduite ou transmise de quelque façon que ce soit sans le
consentement préalable écrit de la société Automationdirect.com® Incorporated. AutomationDirect conserve
les droits exclusifs à l’égard de tous les renseignements contenus dans le présent document.
Page W–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 5
History
History
History
User ManUal revision
History
H
H
H
Please include the Manual Number and the Manual Issue, both shown below, when communicating with
Technical Support regarding this publication.
Manual Number: IH-MTPM-DC_UMW
Issue: Second Edition, Revision D
Issue Date: 01/06/2020
Publication History
Issue Date Description of Changes
First Edition 02/2010 Original Issue
1st Ed, Rev A 06/2011 Chapter 4: Added accessory brush part # MTPM-BRUSH-3
1st Ed, Rev B 08/2012 Chapter 5: Added motor performance curves and data
Second Edition 03/2014 Added new small-frame PMDC motors
Ch1, pg5 form factor 1.35 > 1.40.
2nd Ed, Rev A 11/2017
2nd Ed, Rev B 09/2018
2nd Ed, Rev C 02/2019 Ch5: Added “Typical Motor Perfomance Data” tables
2nd Ed, Rev D 01/2021 Ch1: Added Inductance to MTPM motor performance data table
Chapter 1: Added resistance and inductance values. Added rotor inertia values.
Chapter 4: Changed usage of MTPM-BRUSH-3 and MTPM-BRUSH-2.
User Manual file name change to IH-MTPM-DC_UMW (was IH-MTPM-DC-User-M-WO)
Ch3: 56C drive bearing
Page H–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 6

Revision History
BLANK
PAGE
Page H–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 7
Table of ConTenTs
Contents
Contents
Contents
MTPM DC MoTors User ManUal
Warnings W–1
~ Warning ~ W–1
TraDeMarks W–1
~ aVerTisseMenT ~ W–2
MarqUes De CoMMerCe W–2
User ManUal reVision HisTory H–1
MTPM DC MoTors User ManUal Table of ConTenTs ToC–1
CHaPTer 1: geTTing sTarTeD 1–1
ManUal oVerVieW 1–2
oVerVieW of THis PUbliCaTion 1–2
WHo sHoUlD reaD THis ManUal 1–2
TeCHniCal sUPPorT 1–2
sPeCial syMbols 1–2
reCeiVing anD insPeCTion 1–2
UnPaCking 1–2
aVailable MoDels 1–3
ironHorse MoTors ParT nUMber inforMaTion 1–3
PerManenT MagneT DC MoTors feaTUres anD sPeCifiCaTions 1–3
resHiPPing 1–6
long TerM sTorage 1–6
WarranTy 1–6
TOC–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 8

Table of Contents
CHaPTer 2: MoUnTing anD iniTial sTarTUP 2–1
safeTy inforMaTion 2–2
Danger! 2–2
Wiring noTes: Please reaD Prior To insTallaTion 2–2
aPPliCable CoDes 2–2
MoTor DiMensions 2–3
TerMinal DiagraM anD Wiring 2–5
MoTor MoUnTing 2–5
sTable sliDe bases 2–5
ProPer insTallaTion ConDiTions 2–6
CoUPling alignMenT 2–6
MoTor naMePlaTe anD sTarTer inforMaTion 2–7
TyPiCal ironHorse MoTor naMePlaTe 2–7
MoTor ConTrol inforMaTion 2–7
insPeCTion before sTarTUP 2–7
iniTial sTarTUP insPeCTion 2–7
CHaPTer 3: MainTenanCe anD TroUblesHooTing 3–1
roUTine MainTenanCe 3–2
bearing size inforMaTion 3–2
rePlaCing brUsHes 3–3
TroUblesHooTing 3–4
CHaPTer 4: aCCessories 4–1
sTable sliDe bases 4–2
sliDe base seleCTion 4–2
sliDe base DiMensions 4–2
rePlaCeMenT aCCessories 4–3
TOC–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 9

Table of Contents
CHaPTer 5: referenCe 5–1
inTroDUCTion To PerManenT MagneT DC MoTors 5–2
inTroDUCTion 5–2
forM faCTor 5–2
enClosUre anD eleCTriCal insUlaTion sysTeMs 5–3
PerManenT MagneTs 5–3
brUsHes 5–4
PoWer sUPPly 5–5
DC MoTor TyPes 5–6
PerManenT MagneT MoTors 5–6
ConTrolling sPeeD 5–6
loaD ConsiDeraTions 5–6
HigH TeMPeraTUre ConsiDeraTions 5–7
ConTaMinaTion ConsiDeraTions 5–7
VibraTion ConsiDeraTions 5–7
alTiTUDe ConsiDeraTions 5–7
aMbienT TeMPeraTUre 5–8
TyPiCal PerforManCe DaTa for sMall-fraMe PMDC MoTors 5–9
12/24VDC sMall-fraMe PMDC MoTors 5–9
90VDC sMall-fraMe PMDC MoTors 5–14
180VDC sMall-fraMe PMDC MoTors 5–16
JUnCTion box DiMensions for 56C-fraMe MoTors 5–18
sHiPPing CraTe DiMensions for 56C-fraMe MoTors 5–18
DeCibel leVels for 56C-fraMe MoTors 5–18
PerforManCe CUrVes for 56C-fraMe MoTors 5–19
MTPM-P33-1l18 5–19
MTPM-P50-1l18 5–20
MTPM-P75-1l18 5–21
MTPM-001-1l18 5–22
MTPM-1P5-1l18 5–23
MTPM-P33-1M18 5–24
MTPM-P50-1M18 5–25
MTPM-P75-1M18 5–26
MTPM-001-1M18 5–27
MTPM-1P5-1M18 5–28
MTPM-002-1M18 5–29
TOC–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 10

Table of Contents
BLANK
PAGE
TOC–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 11
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
GettinG Started
1
1
1
Table of ConTenTs
Manual Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Overview of this Publication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Who Should Read This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Special Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Receiving and Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Unpacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Available Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
IronHorse Motors Part Number Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Permanent Magnet DC Motors Features and Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Reshipping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–6
Long Term Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–6
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–6
Page 1–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 12

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Manual Overview
Overview of this Publication
The IronHorse General Purpose DC Motor User Manual describes the installation, maintenance
and use of all IronHorse General Purpose DC Motors.
Who Should Read This Manual
This manual contains important information for those who will install, maintain, use and/or resell
any of the IronHorse motors.
Technical Support
By Telephone: 770-844-4200
(Mon.-Fri., 9:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. E.T.)
On the Web: support.automationdirect.com
Our technical support group is glad to work with you in answering your questions. If you cannot
find the solution to your particular application, or, if for any reason you need additional technical
assistance, please call technical support at 770-844-4200. We are available weekdays from 9:00
a.m. to 6:00 p.m. Eastern Time.
We also encourage you to visit our web site where you can find technical and non-technical
information about our products and our company. Visit us at www.automationdirect.com.
Special Symbols
NOTE: When you see the “notepad” icon in the left-hand margin, the
paragraph to its immediate right will be a special note.
WARNING: WheN you see the “exclAmAtIoN mARk” IcoN IN the left-hANd mARGIN, the
pARAGRAph to Its ImmedIAte RIGht WIll be A WARNING. thIs INfoRmAtIoN could pReveNt
INjuRy, loss of pRopeRty, oR eveN deAth (IN extReme cAses).
Receiving and Inspection
Unpacking
After receiving an IronHorse motor, please check for the following:
• Open the motor packaging and inspect for damage during shipment.
• Make sure the part number indicated on the motor nameplate corresponds with the part
number on your order.
• For all 56C-frame motors, make sure that the shipment contains the motor, with attached
removable mounting foot and two spare brushes.
Motor Nameplate
Extra set of brushes
(56C motors only)
Page 1–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Mounting foot
(not available on all models)
Page 13
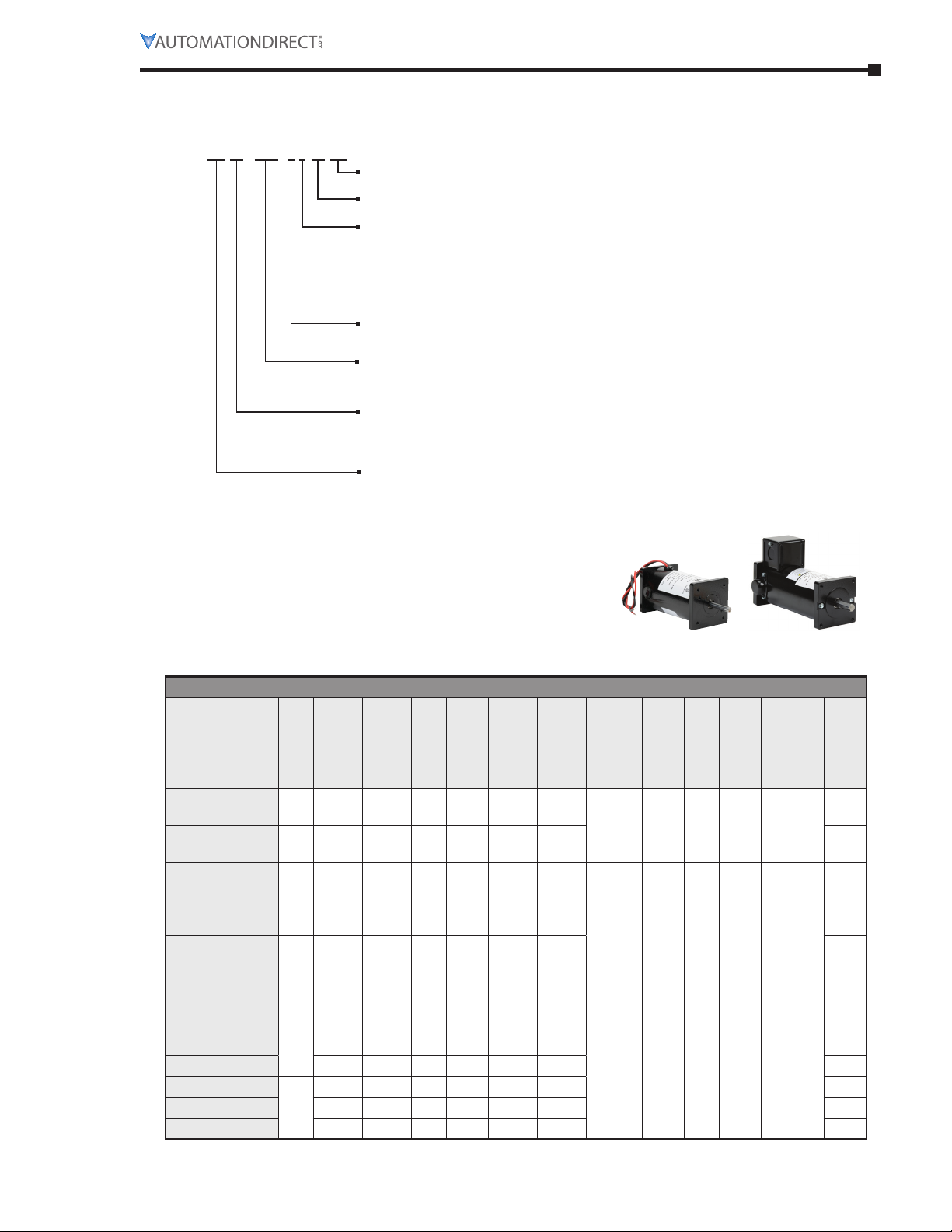
Available Models
IronHorse Motors Part Number Information
MT PM - 1P5 - 1 M 18
Optional Identifier
CK: C-face cast iron motor
Nominal RPM
Two digits representing 100s of rpm
Voltage Class (multiple letters possible)
A: 115 VAC
B: 208-230 VAC
D: 460 VAC
J: 12 VDC
K: 24 VDC
L: 90 VDC
M: 180 VDC
Phase
1: Single phase
3: Three phase
Rated Horsepower
P: Decimal point
# left of P: Rated full hp
# right of P: Rated fractional hp (expressed as decimal)
Motor type
A: Motor accessory
C: AC Motor with cast iron frame
R: AC Motor with rolled steel frame
PM: DC Permanent magnet
IronHorse Motors Series Designation
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Permanent Magnet DC Motors Features and Specifications
Small-Frame Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) Motors
IronHorse small-frame PMDC motors are available from
1/3 hp to 1/4 hp. All models have a TENV rolled steel
frame. Motors have easy-access brushes.
Small-Frame PMDC Motor Specifications
Motor Specifications – Small-Frame DC Motors
Part Number
MTPM-P10-1JK43
MTPM-P13-1JK42
MTPM-P17-1JK43
MTPM-P25-1JK40
MTPM-P25-1JK44
MTPM-P03-1L18
MTPM-P04-1L17
MTPM-P05-1L19
MTPM-P13-1L19
MTPM-P14-1L19
MTPM-P07-1M24
MTPM-P13-1M19
MTPM-P14-1M18
12 241/20
12 241/17
12 241/13
12 241/6
12 241/5
90
180
HP
Voltage (VDC)
Speed (rpm)
1746
1/10
4252
1825
1/8
4224
1841
1/16
4290
1732
1/4
3996
1854
1/4
4375
(oz·in)
F.L. Torque
F.L. Current (A)
Resistance (Ω)
28 4.83 0.603 1.33
32 5.39 0.459 1.18 3.25
42 7.54 0.324 1.58
96 8014.3
113 7018.1
0.101 0.472 7.8
12.2
6.91 0.383 9
11.9
1/31 1797 18 0.39 41.3 96.0
1/26 1749 22 0.46 31.6 85.5 3.25
(mH)
Inductance
Shaft Dia (in)
0.3125 1.00 85 70
0.50 2.02 130 150
0.3125 1.00 85 70
1/19 1917 28 0.68 17.0 66.3
1/8 1917 73 1.4 5.16 30.2 7.8
1/7 1740 86 1.61 5.65 29.6 9
1/15 2440 28 0.42 44.1 177 5.3
0.50 2.02 130 150
1/8 1865 73 0.73 25.0 111 7.8
1/7 1828 84 0.83 30.0 129 9
Pilot Shaft (in)
Load (lb)
Overhung
Axial/ Thrust
Load (lb)
junction
junction
Wiring Type
flying
leads
box
flying
leads
box
(lb)
Motor Weight
2.75
5.3
2.75
5.3
Page 1–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 14
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Rolled Steel 56C Frame Permanent Magnet DC (PMDC) Motors
IronHorse 56C frame PMDC motors are available from 1/3
hp to 2hp. All models have a TEFC or TENV rolled steel
frame, cast aluminum end bell and removable mounting
bases. Motors have easy-access brushes.
Rolled Steel 56C Frame PMDC Motor Specifications
Motor Specifications – DC 56C Frame Motors – 1800 RPM
Part Number HP
MTPM-P33-1L18
MTPM-P50-1L18
MTPM-P75-1L18
MTPM-001-1L18
MTPM-1P5-1L18
MTPM-P33-1M18
MTPM-P50-1M18
MTPM-P75-1M18
MTPM-001-1M18
MTPM-1P5-1M18
MTPM-002-1M18
Note: Please review the AutomationDirect Terms & Conditions for warranty and service on this product.
1/3
1/2 5.2 20.74 22
3/4
1 10.4 28.36 30
1-1/2 15.4 34.97 37
1/3
1/2 2.6 20.74 22
3/4
1 5.2 28.32 30
1-1/2 7.7 35.70 37
2 9.8 61.95 65
Base
RPM
1800
Armature
Voltage
90 VDC
180 VDC
Housing
TENV
TEFC
TENV
TEFC
NEMA
Frame
56C
flange
mount
Service
Factor
1.0
F.L.
Amps
Motor
Weight
(lb)
Approx Ship
Weight
3.5 17.70 19
7.8 25.30 27
1.75 17.60 19
3.9 25.58 27
(lb)
Rolled Steel 56C Frame PMDC Performance Data
Performance Data * – DC 56C Frame Motors – 1800 RPM
Part
Number
MTPM-P33-1L18
MTPM-P50-1L18
MTPM-P75-1L18
MTPM-001-1L18
MTPM-1P5-1L18
MTPM-P33-1M18
MTPM-P50-1M18
MTPM-P75-1M18
MTPM-001-1M18
MTPM-1P5-1M18
MTPM-002-1M18
HP
Armature Resistance (Ω)
Armature Voltage (VDC)
1/3
1.85 13.23 0.97
1/2 1.31 9.21 1.46 0.02365 80
90
3/4 0.86 6.26 2.19 0.02795 80
1 0.67 4.98 2.92 0.03225 80
1-1/2 1.45 3.74 4.38 0.04945 81
1/3
7.6 52.23 0.97 0.01956 79
1/2 5.25 37.02 1.46 0.02365 80
3/4 3.23 26.02 2.19 0.02795 80
180
1 2.63 19.86 2.92 0.03225 80
1-1/2 1.45 14.08 4.38 0.04945 81
2 1.45 11.26 5.84 0.09675 85
* For performance curves and additional data, refer to Chapter 5: Reference.
** See the discussion of Form Factor in the following section of this chapter.
Inductance (mH)
Full
Load
Torque (lb·ft)
DC Power Form Factor **
1.35
Ambient Temp. ( °C [°F] )
40°C
(104°F)
Ball Bearings
Insulation Class
DE
ODE
F 6203
Mounting
Wire / Housing
Junction Box
Top Mounted
Shaft
Overall Speed Range
Constant Torque Speed Range
Keyed
0-2000 RPM
90-1800 RPM
Base / Type
Rigid Removable
Paint Color
Gray
Rotor
Inertia
(kG/m2)
Efficiency (%)
0.01956 79
Page 1–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 15
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Permanent Magnet DC Motors Features and Specifications (continued)
Form Factor
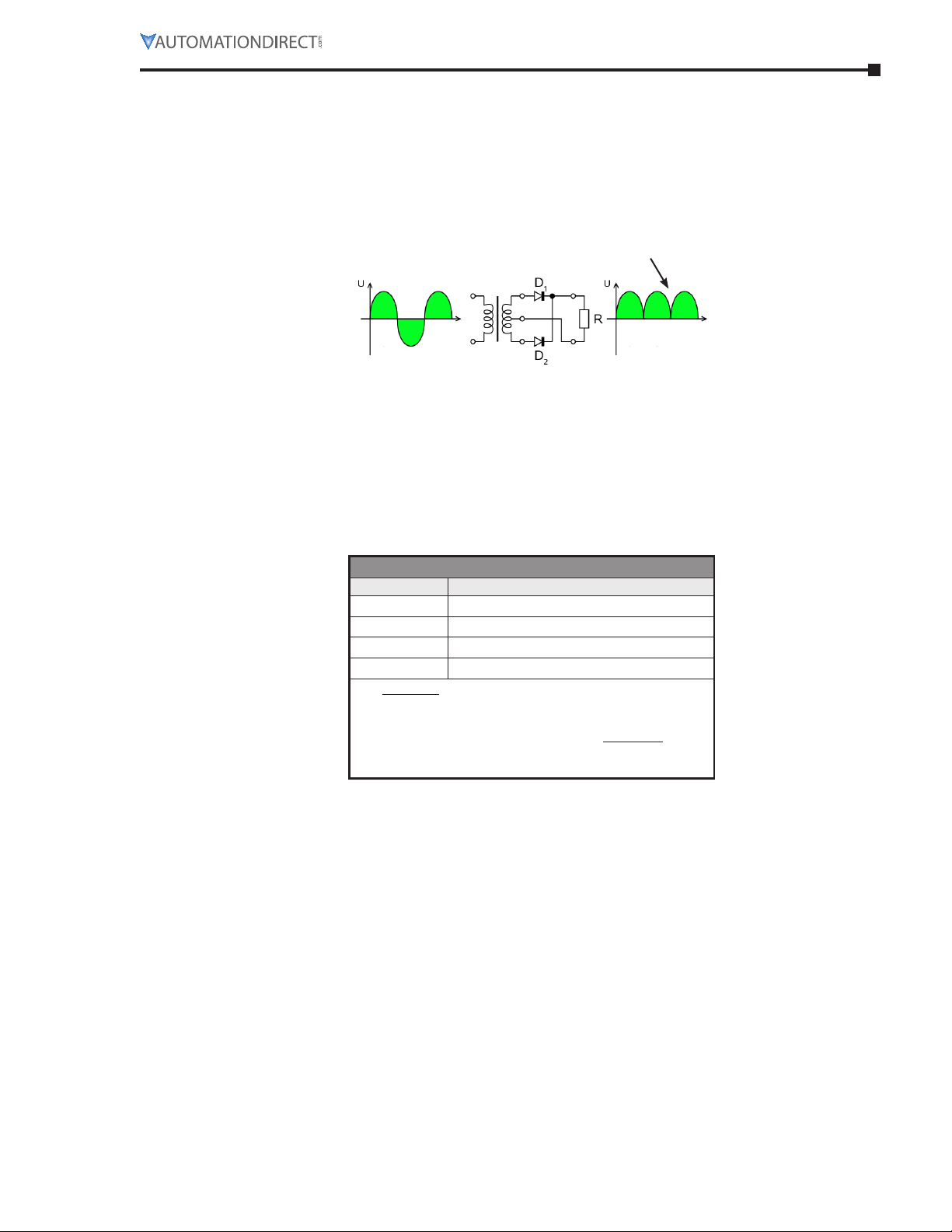
The voltage normally used to power a permanent magnet (PM) DC motor is not pure DC. It is
derived by rectifying a supplied AC voltage. The resulting DC voltage has a ripple that is related
to the frequency of the AC input, as shown in the example below.
Current Fluctuations
Cause Ripple Current
(Full Wave
Rectication)
Rectied DC Rectier Circuit Single Phase AC
Form factor is the ratio of I
to Idc and indicates how close the driving voltage is to pure DC.
rms
The form factor for a DC battery is 1.0. The higher the form factor is above 1.0, the more it
deviates from pure DC. The Form Factor Table shows examples of commonly used voltages.
Form factor should not exceed 1.40 for continuous operation. Half wave rectification is not
recommended as it increases form factor.
Operating Ironhorse PMDC motors with DC voltages with form factors higher than 1.40 can
result in premature brush failure and excessive motor heating.
Form Factor Table
Form factor DC voltage source
1.0 Battery (pure DC)
1.05 * Pulse width modulation (PWM)
1.40 ** Full wave rectification (single phase)
1.9 *** Half wave rectification (single phase)
* All DC-input IronHorse GSD series DC drives are 1.05.
* IronHorse AC-input GSD5 DC drive is 1.05.
** Single phase full wave rectification is the most common
form of DC drive in 0.33–2 hp range. All AC-input
IronHorse GSD series DC drives are 1.40 or better.
*** Not Recommended.
Page 1–5IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 16

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Reshipping
If an IronHorse motor needs to be reshipped from the initial shipping point, the following
procedures should be followed to protect the motor from damage.
1)
If the original packaging is to be used for reshipment, inspect the packaging for previous
shipping damage and repackage if necessary. Take care to protect the motor body, fan cover and
shaft.
2)
It is a good idea to bolt or strap the motor to a platform that fits securely in the bottom of the
shipping crate or box. This helps prevent the motor from shifting during transport and thus
protects the bearings from damage.
Long Term Storage
The following preventative measures should be taken when storing IronHorse motors for a long
period of time.
1)
Store motors in a controller temperature, dry atmosphere free of excess dirt, dust and airborne
particles.
2)
Rotate the motor shaft every sixty days to prevent hardening of the bearing grease.
Warranty
IronHorse 56C-frame PMDC motors carry a two year warranty from the date of invoice, and the
small-frame PMDC motors carry our standard one year warranty.
Page 1–6 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 17
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Mounting and
initial Startup
2
2
2
Table of ConTenTs
Safety Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Danger! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Wiring Notes: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO INSTALLATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Applicable Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Motor Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Terminal Diagram and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
Motor Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
STABLE Slide Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
Proper Installation Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
Coupling Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
Motor Nameplate and Starter Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Typical IronHorse Motor Nameplate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Motor Control Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Inspection Before Startup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Initial Startup Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Page 2–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 18

Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
Safety Information
Danger!
Hazardous Voltage! Before making any connection to tHe motor, disconnect all power to tHe
motor.
warning: any electrical or mecHanical modification to tHis equipment witHout prior written
consent of automationdirect.com, inc. will Void all warranties, may result in a safety Hazard,
and may Void tHe
warning: to aVoid pHysical injury, keep your Hands and clotHing away from all moVing parts.
1)
During installation, follow all local electrical, construction, and safety codes for the country in
which the motor is to be installed.
2)
Make sure the appropriate protective devices (circuit breaker or fuses) are connected between
the power source and motor controller.
3)
Make sure that the leads are connected correctly and the motor is properly grounded. (Ground
resistance should not exceed 0.1Ω.)
csaus listing.
c
4)
Use ground leads that comply with AWG/MCM standards and keep them as short as possible.
5)
Make sure that the power source is capable of supplying the correct voltage and required current
to the motor.
6)
Do not attach or remove wiring when power is applied to the motor.
All IronHorse small-frame PMDC motors are UL recognized (E365956) and CSA approved.
Therefore they comply with the requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and the
Canadian Electrical Code (CEC).
Installations intended to meet the UL or CSA requirements must follow the instructions provided
in the “Wiring Notes” as a minimum standard. Follow all local codes that exceed UL or CSA
requirements. Refer to the technical data on the motor nameplate for electrical and performance
data.
IronHorse small-frame PMDC motors are RoHS compliant.
All IronHorse 56C-frame PMDC motors are cCSAus listed, and therefore comply with the
requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC).
Installations intended to meet the cCSAus requirements must follow the instructions provided
in the “Wiring Notes” as a minimum standard. Follow all local codes that exceed cCSAus
requirements. Refer to the technical data on the motor nameplate for electrical and performance
data.
IronHorse 56C-frame PMDC motors are CE compliant.
Page 2–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 19
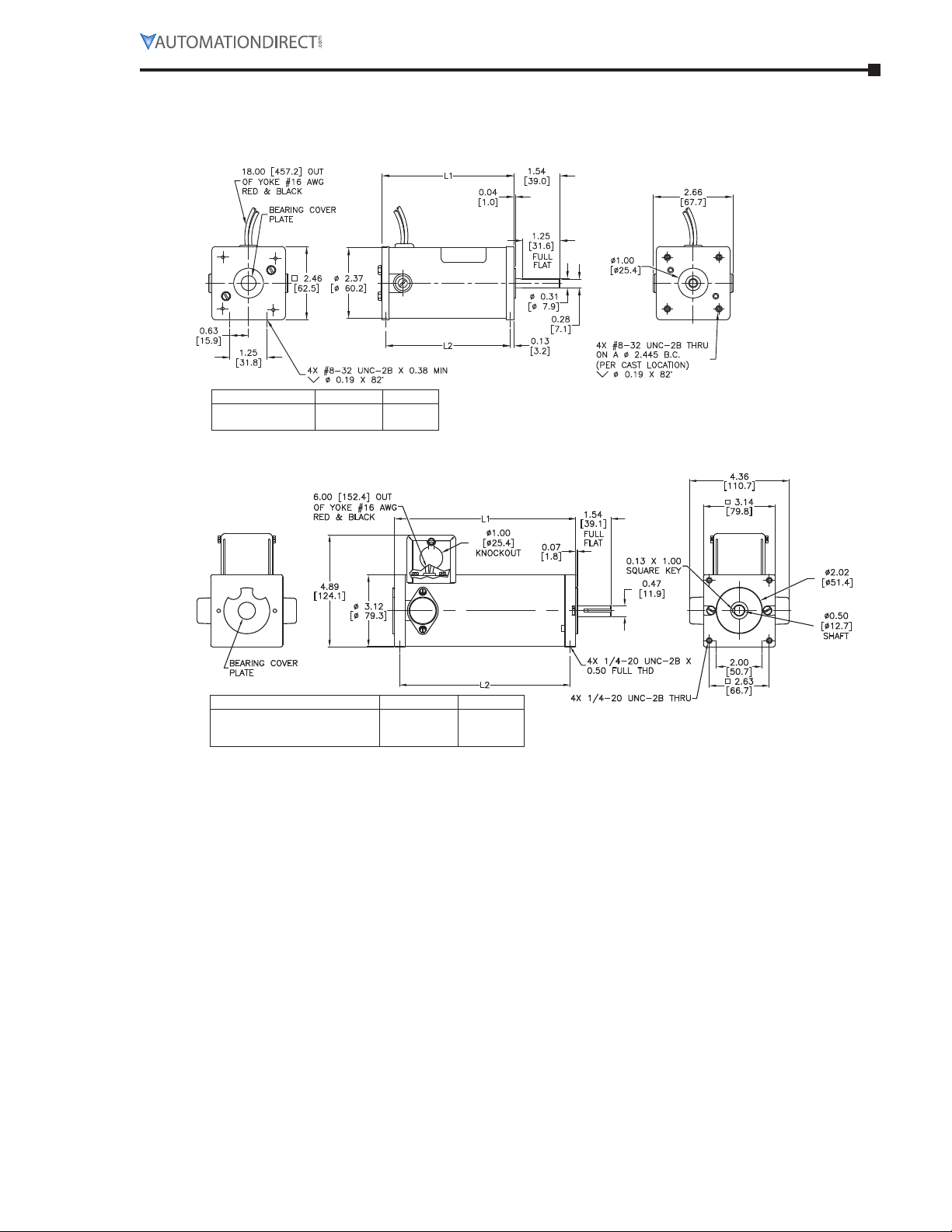
Motor Dimensions
Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
MTPMP03-1L18, P10-1JK34
P04-1L17, P13-1JK42
L1
4.44 [112.8]
4.94 [125.5]
L2
4.19 [106.4]
4.69 [119.1]
MTPM-
P05-1L19, P07-1M24, P17-JK43
P13-1L19, P13-1M19, P25-1JK40
P14-1L19, P14-1M18, P25-1JK44
L1
4.92 [125.0]
6.92 [175.8]
7.92 [201.2]
L2
4.56 [115.8]
6.46 [164.1]
7.46 [189.5]
Page 2–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 20
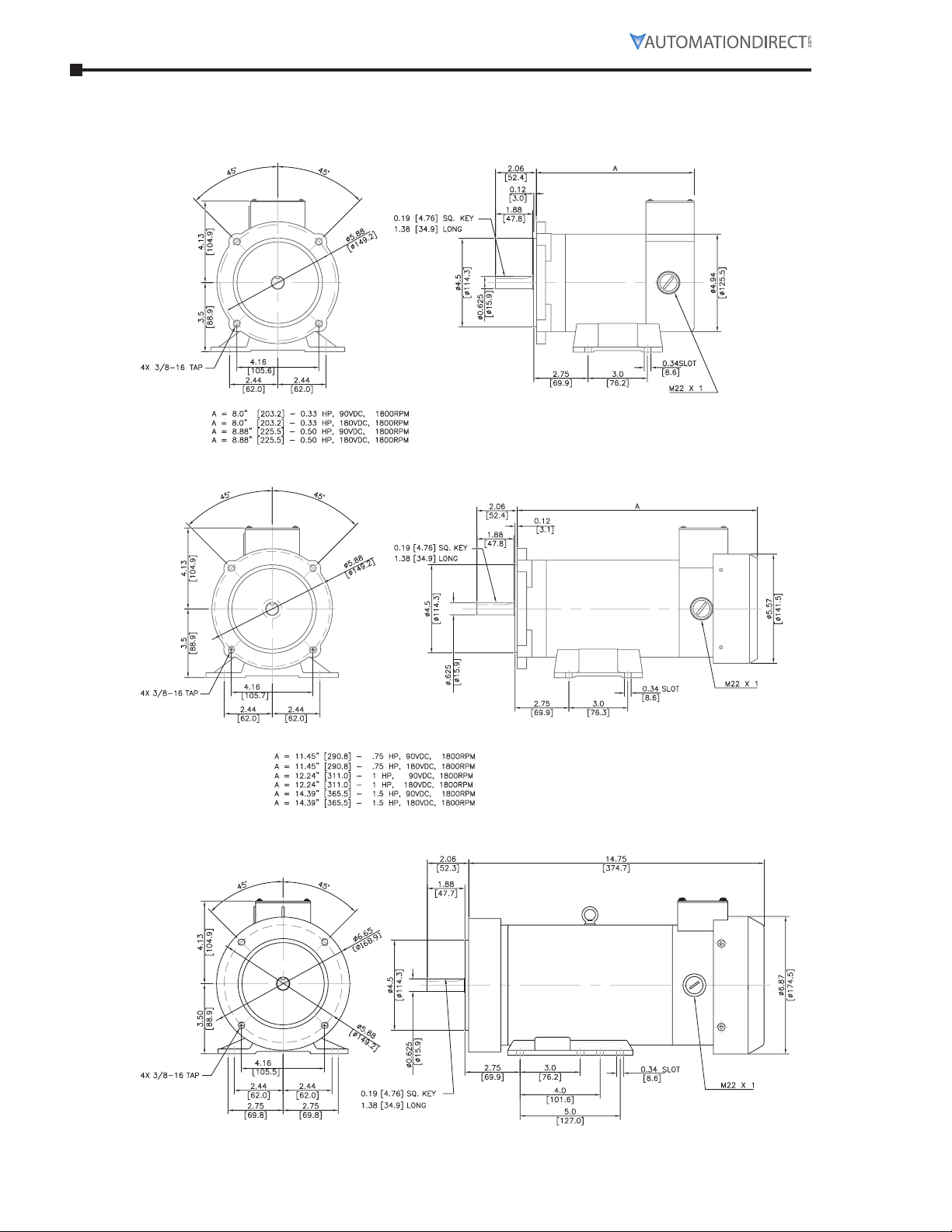
Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
Page 2–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 21

Terminal Diagram and Wiring
DC motors are very easy to wire. There are only two terminals; one for the positive (red) lead
and one for the negative (black) lead.
If wired correctly, the motor will turn clockwise when you are facing the motor shaft. If the
motor turns counterclockwise, reverse the positive and negative leads.
+
M
-
NOTE: These motors do not have connectors for installing encoders or
tachometers.
Motor Mounting
Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
IronHorse motors should be properly mounted to prevent premature motor and/or bearing failure.
There are no limitations on mounting orientation; that is, the motor can be installed vertically,
horizontally, upside down, or at any angle. When necessary, use motor shims to level the motor
at all mounting bolt holes. Use proper diameter bolts of the highest grade material available for
the application. Use the chart below to select the correct size bolt for each frame size.
A mounted motor must operate vibration free. Each motor installation should be checked for
potential vibration situations. Base shims should also be used when necessary for level mounting.
Motor Mounting Bolt Sizes
A
Frame
Size
Small
Frame
56
Bolt
Diameter
5/16 in 0.45 in 0.88 in
Minimum Usable
Thread Length (A)
Face mounting only; no mounting feet
Minimum Exposed
Anchor Length (B)
B
AutomationDirect offers STABLE slide bases for simple mounting of NEMA standard frame
motors. STABLE slide bases are manufactured from heavy-duty steel and allow motor position
adjustment when mounting any NEMA framed motor. See Chapter 4 (Accessories) for complete
details.
Page 2–5IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 22

Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
IronHorse small-frame motors should be properly mounted to prevent premature motor and/
or bearing failure. There are no limitations on mounting orientation; that is, the motor can be
installed vertically, horizontally, upside down, or at any angle. Use proper diameter bolts of the
highest grade material available for the application, as shown on the dimension diagrams.
A mounted motor must operate vibration free. Each motor installation should be checked for
potential vibration situations.
Care should be taken to make sure that an IronHorse 56C-frame motor is mounted at least
thirty inches from a wall or structure that would prevent proper ventilation of the motor. The
installation area should be free of dust and smoke particles. Any air contaminate could inhibit
proper operation of the motor fan.
If an IronHorse motor is to be installed in a high altitude or in a low temperature location, use the
Altitude / Ambient Temperature Derating chart below for proper motor sizing.
Altitude / Ambient Temperature Derating Chart
Altitude – Meters (Feet) Above Sea Level
1000
(3281)
10 (50) 1.50
1500
(4921)
2000
(6562)
2500
(8202)
3000
(9842)
3500
(11,483)
4000
(13,123)
15 (59) 1.05 0.99
20 (68) 1.05 0.99 0.93
25 (77) 1.05 0.98 0.93 0.88
30 (86) 1.05 0.97 0.92 0.87 0.82
40 (104) 1.00 0.94 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72
Temperature – °C (°F)
50 (122) 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 0.68 0.65 0.62
60 (140) 0.71 0.67 0.64 0.60 0.57 0.55 0.52
Example: 1hp @ 60 °C and 2000 meters
1 / 0.64 = 1.56 hp
The motor should be a 2hp motor.
Correct coupling alignment is very important to the life of the motor. Coupling misalignment is
the major cause of motor bearing failure. In belt driven applications, pulleys should be installed
correctly. Belt tension, alignment and wear should be checked at installation and at regular
maintenance intervals. Install motor couplings per the manufacturers instructions. Whenever
possible, direct couple or flange mount IronHorse motors in their application. Doing so can
greatly extend the bearing life.
Page 2–6 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 23

Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
Motor Nameplate and Starter Information
Starting System Information
Frame Size
Small-Frame
56C (1Ø)
Number of
Internal Leads
2 16 AWG
2 16 AWG 6 in 90/180 VDC
Internal
Lead Size
Internal
Lead Length
6 in (with junction box)
18 (without junction box)
Voltage
12–24/90/180 VDC
DC Motor
Type
Permanent
Magnet
Inspection Before Startup
1)
Turn the shaft by hand and make sure the shaft turns freely. Listen for any unusual noises and
feel for any interruption in the shaft as it turns.
2)
Perform a final check on the installation of all parts in the assembly. Check the motor mounting
bolts, coupling, belt drive, C-face mount, alignment, etc.
3)
Verify all electrical connections for the motor and drive. Make sure all terminal screws are
tightened properly.
4)
Make sure that all electrical components used in the installation are rated for the locked rotor
amperage.
5)
Make sure the motor is properly grounded. Use the grounding lug provided in the motor
terminal box.
Initial Startup Inspection
1)
At initial startup monitor the start-up voltage and the running voltage of the motor. The full load
voltage should never exceed the line voltage on the motor nameplate multiplied by the service
factor of the motor.
Example: 180 VDC x 1.00 = 180 VDC.
2)
Check the full load running amperage of the motor. The full load running amperage should not
be more than the amount indicated on the motor nameplate
3)
Listen for any unusual noises at motor start-up and in the first hour of operation. Listen for any
unusual bearing noise in the drive end and opposite drive end of the motor. Abnormal bearing
noise can be an indication of a defective bearing. Ironhorse PMDC motors have sealed bearings.
Page 2–7IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 24

Chapter 2: Mounting and Initial Startup
BLANK
PAGE
Page 2–8 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 25

Chapter
Chapter
Maintenance and
troubleshooting
Table of ConTenTs
Routine Maintenance � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3–2
Bearing Size Information � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3–2
Replacing Brushes � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3–3
Troubleshooting � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3–4
Chapter
3
3
3
Page 3–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 26

Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
A routine maintenance schedule should be developed for every IronHorse motor installation
based on the individual application. Motors installed in a harsh running environment should be
serviced more frequently than those installed in a clean, climate controlled area. The following
list should be used as a basis for creating the routine maintenance schedule.
A)
Clean the motor housing using a brush, soft cloth or compressed air. Remove any dirt and dust
from the fan and fan cover vents.
B)
Frequently monitor the bearing temperature on the motor. It should not exceed 60°C (140°F).
C)
Have the insulation checked periodically by an authorized motor specialist.
D)
Replace the motor brushes after every 2500 hours of operation.
Bearing Size Information
Bearing Chart
Frame Size Drive End Bearing SKF Type Opposite Drive End Bearing SKF Type
Small-Frame
56C
All IronHorse 56C-frame motors use premium sealed SKF brand bearings.
not user serviceable
6203ZZ or equivalent
Page 3–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 27

Replacing Brushes
warning: to preVent serious personal injury and damage to your equipment, always disconnect
input power Before replacing BrusHes.
A spare set of brushes ship in each 56C-frame PMDC motor box, and the brushes should be
replaced after every 2500 hours of operation. Small-frame PMDC motor brushes should be
replaced as needed. If you visually inspect the brushes, the minimum acceptable length is 6mm.
See “Chapter 4: Accessories” for replacement brush ordering information. Make sure you install
the correct replacement brushes; check the part numbers carefully. Ensure that the replacement
brushes are the same width as the brushes being removed from the motor. DO NOT install
smaller brushes in a larger motor. There is no break-in period with new brushes.
Replacement brush and spring assembly sets:
NOTE: The brushes are spring-loaded. Be careful when removing the
brush cover.
Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Motor has two brushes; one on each side of the motor.
Always replace the brushes in pairs.
A)
Remove the brush cover using a flathead screwdriver as
shown. Turn the brush cover counterclockwise to remove.
B)
Carefully remove the old brush and spring assembly and install
the replacement.
C)
Reinstall the brush cover, turning clockwise.
D)
Replace the other motor brush and spring following the same
steps.
Page 3–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 28

Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
To prevent serious damage, faults observed when a motor first goes into service or during
subsequent operation should be investigated and repaired immediately. These troubleshooting
tables cover most common PMDC motor problems.
warning: to preVent serious personal injury and damage to your equipment, always disconnect
input power Before inspecting or repairing your motor.
Mechanical Problems – Noise While Running
Problem Possible Causes Solutions
Defective transmission components, or
Motor vibrates or
runs noisily when
coupled up, but
runs okay when
uncoupled.
Motor runs rough
when uncoupled.
Problem Possible Causes Solutions
Scratching, rubbing,
or rumbling noise
from bearing.
Whistling noise from
bearing.
Excessive bearing
wear.
Scoring when motor
is inoperative.
Scoring when motor
running.
* Bearings in the small-frame PMDC motors are not user replaceable; replace motor instead of bearings.
problem with the machine being driven.
Foundation has become unlevel.
Problem with gear drive.
Incorrectly balanced drive or driven
machine components.
Bearing damage. See Bearing Problems troubleshooting table.
Mounting bolts are loose. Re-tighten and lock mounting bolts.
Fitted drive components (coupling or
pulleys) affecting rotor balance.
Mechanical Problems – Roller Bearing Problems
Bearing is defective. Replace bearing. *
Bearing has run dry. Replace bearing. *
Faulty cage. Replace bearing. *
Bearing overloaded.
Bearing is being subjected to vibration
from outside source.
Current leakage.
Inspect transmission and drive components.
Check alignment.
Realign machine set. Check and repair
foundation level.
Align drive, check driving and driven gear
pitch circles.
Re-balance drive and/or driven components.
Balance rotor with coupling or pulley fitted.
Check alignment, belt tension, gear pressure,
coupling thrust. Reduce bearing load. If
needed, reduce additional axial load.
Isolate motor from source of vibration or
keep motor turning over.
Remove motor from service. Repair or
replace motor.
Page 3–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 29

Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Possible Causes Solutions
Motor shaft rotates in
wrong direction (should
rotate clockwise when
facing shaft).
Motor fails to start off-load.
Jerky starting.
Motor will not run under
load.
Motor overspeeding and
hunting while under load.
Motor overheating.
Positive (+) and negative
(-) input power leads are
reversed.
Break in the armature supply. Check and repair connection.
Fuse is blown. Replace fuse.
Controller damaged or
incorrectly connected.
Armature coils burned out or
short-circuiting.
Brushes not bearing down
correctly.
Break in starter circuit. Repair break.
Armature short-circuit.
Commutator short-circuit. Check commutator and repair short-circuit.
Short circuit in the supply. Locate short circuit and repair.
Overloading. Check current input and remedy overload.
Voltage drop. Increase supply line cross section.
Controller.
Overloading.
Insufficient airflow. Improve cooling conditions.
Cooling air temperature too
high.
Armature winding shortcircuit.
Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Electrical Problems
Switch the input power connections.
Check starter for break in circuit and repair break.
Correct short circuit. This may require bringing
the motor to a repair shop.
Check brush position and bearing pressure.
Replace worn brushes.
Correct short circuit. This may require bringing
the motor to a repair shop.
Decrease IR compensation.
Check speed potentiometer wiring and signal,
and repair if needed.
Check voltage and current levels, and correct
overload condition.
If TEFC model, inspect the fan for damage.
Check windings and soldered connections. Repair
coils or windings.
Page 3–5IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 30

Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
BLANK
PAGE
Page 3–6 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 31
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Accessories
4
4
4
Table of ConTenTs
STABLE Slide Bases � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4–2
Slide Base Selection � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4–2
Slide Base Dimensions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4–2
Replacement Accessories � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4–3
Page 4–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 32

Chapter 4: Accessories
STABLE Slide Bases
AutomationDirect offers STABLE motor slide bases for mounting NEMA motor frame sizes
from 56 to 449. These heavy-duty steel bases are primed with an oven-baked primer ready for
painting. The motor mounting bolts are welded to the exact motor foot pattern to prevent the
bolts from spinning. The motor position is adjustable along the long axis.
Slide Base Selection
Part Number Fits Frame Type Shipping Weight (lb) IronHorse Model
MTA-BASE-W56
Motor Slide Bases
56 3.5
MTPM-xxx-1L18
MTPM-xxx-1M18
Slide Base Dimensions
J
M
E E
G G
W56 - W145T Motor Slide Base Dimensions
Dimensions [inches, except as noted] – STABLE Motor Slide Bases
MTA-BASE-W56
A
A B C D E F G
10-5/8 6-1/2 1-1/8 4-1/2 2-7/16 1-1/2 3-13/16
H I J K (mm) L M N
2-7/8 3/8 3 2 mm 7/8 5/16 x 1 3/8 x 4
L
H
F
B
D
N
F
H
I
K(mm)
C
Page 4–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 33

Replacement Accessories
Replacement brushes and spare/replacement parts can be ordered at www.automationdirect.com.
Replacement DC Motor Brushes
All small-frame IronHorse® DC motors ship with brushes installed, and the brushes should be
replaced as needed. (Minimum brush length is 6mm.)
Brushes for 56C-frame motors should be changed after every 2500 hours of use. Each 56C-frame
motor ships with brushes installed, plus one extra set of spare/replacement brushes.
Match the replacement brush part number against the motor horsepower carefully to insure you
order the correct brushes for your motor. When replacing brushes, pay special attention that
the correct brush is inserted into the motor (especially if you have multiple motor sizes at your
facility). Verify that the width of the brush you remove matches the width of the replacement
brush. DO NOT install smaller brushes into a larger motor.
Chapter 4: Accessories
See “Chapter 3: Maintenance and Troubleshooting” for brush replacement procedure.
DC Motor Replacement Brushes
Part Number Description Motor Type
MTPM-BRUSH-1
MTPM-BRUSH-2
MTPM-BRUSH-3
MTPM-BRUSH-4
MTPM-BRUSH-5
MTPM-BRUSH-6
MTPM-BRUSH-7
All IronHorse DC motors ship with one set of brushes installed.
All IronHorse 56C-frame DC motors ship with one set of brushes installed and one extra set in the box.
Brushes with
springs
(one set of 2)
Brushes with
springs and
caps
(one set of 2)
IronHorse
MTPM
Rated
Voltage
90 VDC
180 VDC
180 VDC 2
90 VDC 1.5
12/24
VDC
90VDC
180VDC
90VDC
180VDC
Motor HP Brush Materials
0.33–1.5
1/4 @ 24VDC
1/10–1/6 @ 24VDC
1/8–1/7 @ 90VDC
1/8–1/7 @ 180VDC
1/31–1/19 @ 90VDC
1/15 @ 180VDC
Resin class
Graphite
Copper Graphite
Carbon Graphite
Spare/Replacement Parts Kit for Small-Frame DC Motors
Small-Frame DC Motors Spare Parts Kit
Part Number Description For Motors MTPM-
DC motor spare parts kit, for certain MTPM series
MTGA-KIT-1
MTGA-KIT-1 includes spare/replacement parts only.
All parts in the kit are included with the applicable motors.
permanent magnet DC motors as listed.
Includes: two metal brush cap covers, one terminal box,
one 1/8 (0.125 inch) shaft key, and one 3/16 (0.187 inch)
shaft key.
P05-1L19, P13-1L19, P14-1L19;
P17-1JK43, P25-1JK40, P25-1JK44;
Pxx-1Mxx
Page 4–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 34

Chapter 4: Accessories
BLANK
PAGE
Page 4–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 35

Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
RefeRence
5
5
5
Table of ConTenTs
Introduction to Permanent Magnet DC Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–2
Introduction� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–2
Form Factor � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–2
Enclosure and Electrical Insulation Systems � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–3
Permanent Magnets � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–3
Brushes� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–4
Power Supply � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–5
DC Motor Types � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–6
Permanent Magnet Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–6
Controlling Speed � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–6
Load Considerations � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–6
High Temperature Considerations � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–7
Contamination Considerations � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–7
Vibration Considerations � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–7
Altitude Considerations � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–7
Ambient Temperature � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–8
Typical Performance Data for Small-Frame PMDC Motors � � � � � � � � � � 5–9
12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–9
90VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–14
180VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–16
Junction Box Dimensions for 56C-Frame Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–18
Shipping Crate Dimensions for 56C-Frame Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–18
Decibel Levels for 56C-Frame Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–18
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–19
MTPM-P33-1L18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–19
MTPM-P50-1L18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–20
MTPM-P75-1L18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–21
MTPM-001-1L18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–22
MTPM-1P5-1L18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–23
MTPM-P33-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–24
MTPM-P50-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–25
MTPM-P75-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–26
MTPM-001-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–27
MTPM-1P5-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–28
MTPM-002-1M18 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5–29
Page 5–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 36

Chapter 5: Reference
Introduction to Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Introduction
Permanent magnet DC motors are useful in a range of applications from conveyors to pumps.
PMDC motors have a linear speed-torque curve well suited to adjustable speed applications
where the motor will operate at less than 3000 rpm.
Inside these motors, permanent magnets replace the field windings found in shunt motors. A
wound armature and commutator brushes complete the motor.
Permanent magnets supply the field flux, eliminating the need for external field current. This
design yields a smaller, lighter, energy-efficient motor.
The PMDC motor’s field has a high reluctance (low permeability) that eliminates significant
armature interaction. High reluctance yields a constant field, permitting linear operation over
the motor’s entire speed-torque range. In operation with a constant armature voltage, as speed
decreases, available torque increases. As armature voltage increases, the linear speed-torque
curves shift upwards. Thus, a series of parallel speed-torque curves, for different armature
voltages, represents the speed-torque properties of a PMDC motor. Speed is proportional to
voltage and torque is proportional to current.
Form Factor
The voltage used to power a PMDC motor is not a pure DC. It is derived DC voltage by
rectifying an AC voltage. Thus, the DC voltage has a ripple component related to the frequency
of the AC input.
Form factor is the ratio of I
to Idc and indicates how close the driving voltage is to pure DC.
rms
Form factor for a pure DC source, such as a battery, is 1.0. The higher the form factor is above
1.0, the more it deviates from pure DC. The table here shows typical form factors for common
voltage sources.
Form Factor: Comparing Driving Voltage to Pure DC
Form Factor DC Voltage Source
1.0 Battery – Pure DC
1.05 * Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
1.35 ** Full Wave Rectification (Single Phase)
1.9 *** Half Wave Rectification (Single Phase)
* All DC-input IronHorse GSD series DC drives are 1.05.
IronHorse AC-input GSD5 DC drive is 1.05.
** Single phase full wave rectification is the most common form of DC drive in 0.33–2 hp range. All
IronHorse GSD series DC drives are 1.35 or better.
*** Not Recommended.
For Ironhorse PMDC motors it is recommended that form factor not exceed 1.4 for continuous
operation. Half wave rectification is not recommended because it increases the form factor.
Driving a Ironhorse PMDC motor with a higher form factor control than intended can cause
premature brush failure and excessive internal heating.
PMDC motors can generate high momentary starting and acceleration torques, typically 10 to 12
times full rated torque. Thus, they suit applications requiring high starting torques or momentary
bursts of power. However, they are not intended for continuous operation at these higher levels
of torque. This can cause overheating, which can result in non-reversible demagnetization of the
field magnets.
Torque (current) limiting in the drive limits stall conditions and current draw, particularly during
high torque demand, and protects against detrimental overload.
Page 5–2 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 37

Chapter 5: Reference
Enclosure and Electrical Insulation Systems
Other considerations for PMDC motor selection include proper choice of enclosure and electrical
insulation system. If safety factors dictate a totally enclosed motor, it may be non-ventilated
(TENV) or fan-cooled (TEFC).
Electrical insulation systems, as shown is the following table, are tested for 20,000 hours at a
rated temperature without degradation (as recognized by UL, CSA, BSI, and VDE). Subtract
ambient temperatures (usually 25 °C or 40 °C) to determine allowable rise.
Electrical Insulation Systems
Class A
Class B
Class F
Class H
105 °C
130 °C
155 °C
180 °C
Permanent Magnets
A number of magnetic materials are available for permanent magnets. These include ceramic
oriented ferrites, rare earth permanent magnets, and Alnico. The following table compares
common magnet materials.
Comparing Permanent Magnet Motor Materials
Type Cost Demagnetizing Resistance Energy Product
Ceramic Oriented Ferrites *
Samarium Cobalt
Neodymium Iron Boron
* Ironhorse PMDC motors contain ceramic oriented ferrite magnets.
Low Medium Low
High High High
High High High
Ceramic oriented ferrites, typically made with barium or strontium have become the material
of choice in most PM motors, replacing Alnico, because of their greater resistance to
demagnetization and low cost.
Rare earth magnets may allow a downsized PM motor or boost its power rating. They include
samariumcobalt and neodymium-iron-boron. Their characteristics, include high energy and low
susceptibility to demagnetization; however, the cost of these materials remains high.
Page 5–3IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 38

Chapter 5: Reference
Brushes
PMDC motors use a mechanical commutator to switch current to the armature winding.
Commutator bars connect to the armature windings. Spring loaded brushes make mechanical
contact with the commutator bars, carrying the current to the armature. The armature commutator
and the brushes act as a rotary switch for energizing the windings.
The ideal brush offers low voltage loss, negligible dust formation, no arcing, little commutator
wear, and generates little noise.
Commonly used brush materials include carbon and carbon graphite, graphite, electro-graphitic,
and metal-graphite. The following table compares these brush materials.
Material Type Voltage Drop Current Capacity Limitations of Use
Carbon, Carbon-Graphite * High Low High Voltage, Low Speed, Fractional hp Only
Natural Graphite Medium Medium Medium Speed / High Voltage
Electro-Graphitic Medium High Medium to High Speed / High Voltage
Copper Graphite Low Low Low Voltage / Low Speeds
Silver Graphite Very Low Very Low Very Low Voltage / Low Speeds
Comparing Motor Brush Materials
* PMDC motors use resin-class graphite brushes, which puts them in the category of carbon-graphite brushes.
Resin-Bonded Brushes (Including resin-class graphite / carbon-graphite brushes)
The raw material is graphite, bonded with resin, which is pressed and heat treated in a special
process. The advantage of special graphite brushes is their high contact drop and low internal
resistance. They also have good oxidation resistance. These properties are very valuable for
machines with high commutating requirements. The main field of application for special graphite
brushes covers machines with high commutating requirements, but with relatively low brush
current. These include small PMDC motors.
Other factors also affect brush life and performance, including temperature, humidity, altitude,
spring pressure, control form factor, size and duty cycle.
If spring pressure is too low, excessive electrical wear may occur. If it is too high, excessive
mechanical wear may occur. The optimal spring-pressure range for minimal wear is between the
high electrical and mechanical wear regions.
Low humidity, high temperature or high altitude environments may not have enough moisture
present to form the necessary lubricating film between brush and commutator bar. Special
lubricant impregnated brushes can correct the problem.
Under light load conditions, the low current draw can cause poor lubrication of the commutator.
Smutting of the commutator and uneven commutation often result.
Ironhorse PMDC brushes have been specifically manufactured for optimal
performance with the Ironhorse PMDC motors.
We do not recommend using other manufacturer’s brushes.
Page 5–4 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 39

Chapter 5: Reference
Power Supply
Ironhorse PMDC motors are designed for use with NEMA code K power supplies, but can be
supplied by five basic types of power sources: batteries, generators, six-step SCR, three-step
SCR, and single phase SCR. These types of supplies are divided into four NEMA codes, based
on the quality of the output power as shown below.
Common PMDC Power Supplies
NEMA Code Description Power Quality Use Form Factor
A Batteries, Generators Excellent Limited 1.0
C
D D: 1.13
E 3 Phase / 3-Step SCR (Solid State) Average Limited 1.05
K 1 Phase SCR (Solid State) Poor High (for low hp) 1.35
3 Phase / 6-Step SCR (Solid State) Excellent High (for high hp)
The most common way to provide DC voltage to a motor from an AC line is through the use of an
electronic drive. Depending on the construction, a drive will provide a pulse wave form similar
to the voltage from a battery. These pulses are characterized by a form factor which is defined
by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers’ Association) as a power supply code. Codes are
based on the quality of the power output. Application concerns include drive cost, operational
cost (efficiency), reliability, and output power quality.
C: 1.04
NEMA Power Code A
This power supply is a pure DC power supply such as a battery or a generator. High frequency
PWM power supplies will approach NEMA power code A.
NEMA Power Codes C and D
This power supply is close to being pure and consists of six silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRS)
connected in a three phase, full-wave bridge configuration.
NEMA Power Code E
This power supply has average quality and consists of three controlled rectifiers (SCRS)
connected in a three phase, halfwave bridge configuration. Most DC motors will require some
derating when used on this type of power supply.
NEMA Power Code K
This power supply has limited applications and consists of two controlled rectifiers (SCRs)
and two diode style rectifiers connected in a single phase full-wave bridge configuration. A
freewheeling rectifier may be used across the motor armature terminals. This type of power
supply is normally used for motors rated up to 7-1/2 HP.
Ironhorse MTPM series motors are rated for use with Code K DC power supplies.
Single-Phase Power Supply Considerations
This type of power supply is limited to motors fractional through 7-1/2hp. Drive application is
limited due to simplicity of power supply.
Page 5–5IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 40
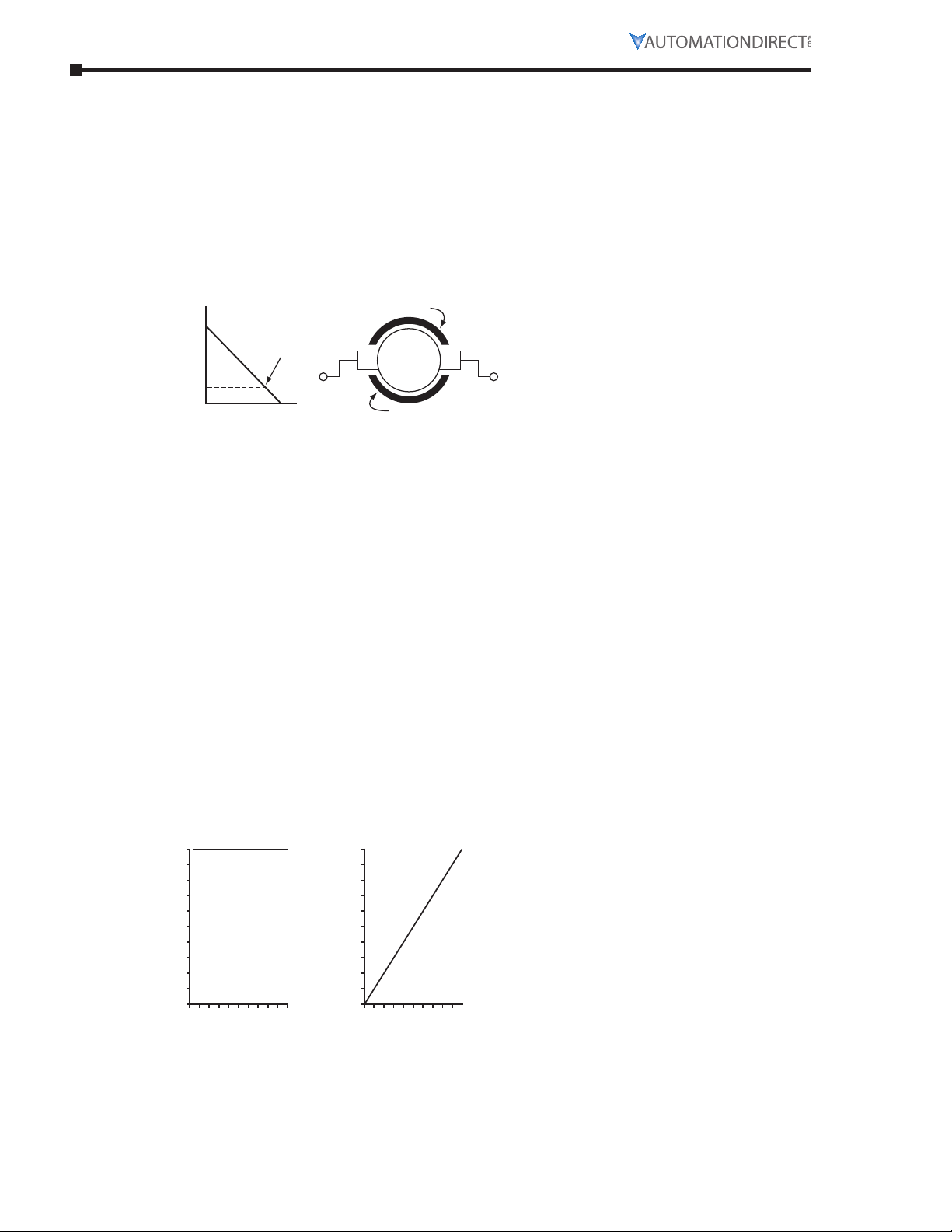
Chapter 5: Reference
DC Motor Types
There are four kinds of DC motors commonly used in industrial applications: shunt, series,
compound wound or stabilized shunt, and permanent magnet. Ironhorse MTPM series motors are
permanent magnet DC motors.
Permanent Magnet Motors
Permanent magnet motors are generally used where response time is a factor. They are built
with a conventional type of armature, but have permanent magnets in the field section rather than
windings. Permanent magnet motors are considered less expensive to operate as they require no
field supply.
Magnet
Magnet
%
Rated
Torque
150%
100%
Maximum
Permissible
Torque
100%
% Rated Speed
Controlling Speed
The method of controlling the speed of a PM direct current motor is armature voltage control.
Armature Voltage Control
For this type of speed control the armature voltage is varied. The output torque of a DC motor is
proportional to the product of the main pole flux, armature current, and a machine constant which
is a function of armature windings. With armature voltage speed control, the torque is dependent
upon the armature current only; that is, at rated armature current the torque is constant.
A DC motor, operated with armature voltage control and fixed field excitation, will develop rated
torque at rated armature current independent of the speed. This is commonly called constant
torque operation.
Load Considerations
Constant Torque
Many industrial applications such as conveyors, mixers, squeeze rolls, continuous processing
machinery, etc., require nearly constant torque over their operating speed range. Direct current
motors operated with fixed shunt field excitation and adjustable armature voltage have an
approximately constant torque capacity over their speed range as shown below.
100
80
60
40
%Torque
20
0 20 40 60 80 100
%Speed %Speed
100
80
60
40
%Horsepower
20
0 20 40 60 80 100
Page 5–6 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 41

Chapter 5: Reference
High Temperature Considerations
Overload is only one cause of over-temperature problems. High ambient temperatures or
improper cleaning of filters on the machine itself contribute to short service life by increasing
operating temperatures. This in turn causes abnormally high differential expansion stress
resulting in cracks in the insulation which usually propagate through to the bare conductor,
opening the circuit to contamination failure. In addition, the commonly known effect is the more
rapid degradation of the insulation materials which shrink and harden, then gradually lose both
strength and insulating characteristics.
Ambient temperatures greater than 40°C are also harmful to grease, cables, brushes, and
commutation.
Contamination Considerations
Nonconducting contaminants such as factory dust and sand gradually promote over-temperature
by restricting cooling air circulation. In addition, these may erode the insulation and the varnish,
gradually reducing their effectiveness.
Conducting contaminants such as metal dust, carborundum, carbon, and salt, in addition to
promoting over-temperature, also provide immediate conducting paths for shorting or grounding
leakage currents wherever the electrical circuit is contacted. Normal differential expansion,
rotational stresses, and thermal expansion of trapped air in voids within the insulation system
eventually open the insulated circuit at unpredictable locations. Depending on the severity of the
operating voltage, service life may be measured in years, months, days, or hours.
Oil deposits promote easy adhesion of contaminants to the internal insulated and exposed
un-insulated surfaces to promote early service life problems.
Water from splashing or condensation seriously degrades an insulation system. The water
alone is conducting. Nonconducting contaminants are readily converted into leakage current
conductors. Intermittent or occasional wetness ultimately causes service failure because
successive leakage situations gradually deposit a permanent path for continuation of the
damaging shorting or grounding currents.
Vibration Considerations
High vibration promotes service life problems by subjecting the shaft to stress, which finally
results in actual shorting of conductors between turns or between layers. In addition, the severe
stress causes fissures and cracks in the conductor insulation exposing the electrical circuit to
contamination failure. Another important factor is the work hardening effect that this vibration
has on the conductor itself, resulting in an open circuit by conduction or cracking. Commutation
problems may arise because of brush bouncing. Continued severe vibration fatigues metals and
could cause failure in casting or bearings.
Altitude Considerations
Standard motor ratings are based on operation at any altitude up to 3300 feet (1000 meters). All
altitudes up to and including 3300 feet are considered to be the same as sea level. High altitude
derating is required because of lower air density which requires a greater amount of cooling.
DC motors are derated by 3% per 1000 feet above the 3300 feet. In some cases, a blower will be
sufficient to cool the motor instead of using a larger frame motor.
Page 5–7IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 42

Chapter 5: Reference
Ambient Temperature
Motors for use in abnormally hot places are usually designed to accommodate the higher ambient
by having a lower winding temperature rise. If the ambient temperature is above 50°C, special
consideration must also be made of the lubricant. Although it’s possible to operate in ambients
above 50°C, application should be referred to the manufacturer to determine what steps must be
taken.
In general, the simplest method of derating for high ambient temperatures is to derate the
horsepower rating of the motor. In this way, the armature will operate at reduced current. For
ambients lower than 40°C, a standard 40°C machine is normally used at rated load. In the case
when the ambient is maintained well below 40°C, a standard ambient motor may be used at
overload, provided the following factors are known:
1)
The ambient is known always to be low.
2)
Shaft stresses, bearing loading and commutation are approved by the factory.
3)
Overload protection for the motor from an over load or stalled condition is available and used.
Operation of motors in ambients below 0°C results in severe duty on the machine component
parts. Of major concern are the lubrication system and the insulation system.
Page 5–8 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 43

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for Small-Frame PMDC Motors
12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P10-1JK43
Powered with 12VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2407 0.54 0.000 0.00
5.0 2292 1.30 0.011 54.17
10.0 2178 2.07 0.022 64.80
15.0 2063 2.83 0.031 67.19
20.0 1948 3.60 0.039 66.60
25.0 1833 4.37 0.045 64.60
30.0 1718 5.13 0.051 61.82
35.0 1604 5.90 0.056 58.56
40.0 1489 6.66 0.059 54.99
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
28.0 1764 4.83 0.049 63.00
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
28.0 1764 4.83 0.049 63.00
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
104.83 (for reference only)
16.60 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
4.8240 ±10%
6.5269 ±10%
0.6025 ±7.5%
0.7230 ±12.5%
3.5000
6.0000
0.0066
1.3294
1.8387
15.7504
16005
10.10
Powered with 24VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 4895 0.54 0.000 0.00
10.0 4665 2.07 0.046 69.41
20.0 4436 3.60 0.088 75.83
30.0 4206 5.13 0.125 75.66
40.0 3976 6.66 0.157 73.44
50.0 3747 8.20 0.185 70.33
60.0 3517 9.73 0.209 66.75
70.0 3287 11.26 0.228 62.89
80.0 3058 12.79 0.242 58.85
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
28.0 4252 4.83 0.118 75.92
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
28.0 4252 4.83 0.118 75.92
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
213.6 (for reference only)
33.20 (for reference only)
4.8240 ±10%
6.5269 ±10%
0.6025 ±7.5%
0.7230 ±12.5%
3.5000
6.0000
0.0066
1.3294
1.8387
15.7504
32544
10.10
Page 5–9IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 44
Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P13-1JK42
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2328 0.66 0.000 0.00
5.0 2249 1.40 0.011 49.32
10.0 2171 2.14 0.021 62.37
15.0 2092 2.88 0.031 67.05
20.0 2014 3.62 0.040 68.48
25.0 1935 4.36 0.048 68.31
30.0 1856 5.10 0.055 67.25
35.0 1778 5.84 0.062 65.62
40.0 1699 6.57 0.067 63.62
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
32.0 1825 5.39 0.058 66.65
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
32.0 1825 5.39 0.058 66.65
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Powered with 12VDC
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
148.04 (for reference only)
22.54 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
5.0025 ±10%
6.7684 ±10%
0.4590 ±7.5%
0.5325 ±12.5%
4.5000
7.0000
0.0081
1.1882
2.2316
13.3887
18209
11.89
Powered with 24VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 4727 0.66 0.000 0.00
10.0 4570 2.14 0.045 65.64
20.0 4412 3.62 0.087 75.03
30.0 4255 5.10 0.126 77.07
40.0 4098 6.57 0.162 76.73
50.0 3941 8.05 0.195 75.30
60.0 3783 9.53 0.225 73.31
70.0 3626 11.01 0.251 70.97
80.0 3469 12.48 0.275 68.41
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
32.0 4224 5.39 0.134 77.13
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
32.0 4224 5.39 0.134 77.13
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
300.57 (for reference only)
45.07 (for reference only)
5.0025 ±10%
6.7684 ±10%
0.4590 ±7.5%
0.5325 ±12.5%
4.5000
7.0000
0.0081
1.1882
2.2316
13.3887
36971
11.89
Page 5–10 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 45

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P17-JK43
Powered with 12VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2352 1.21 0.000 0.00
10.0 2230 2.72 0.022 50.56
20.0 2109 4.22 0.042 61.46
30.0 1987 5.73 0.059 64.01
40.0 1865 7.24 0.074 63.43
50.0 1744 8.75 0.086 61.34
60.0 1622 10.26 0.096 58.40
70.0 1500 11.77 0.104 54.95
80.0 1379 13.27 0.109 51.15
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
42.0 1841 7.54 0.077 63.10
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
42.0 1841 7.54 0.077 63.10
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
193.37 (for reference only)
30.38 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
4.8997 ±10.0%
6.6293 ±10.0%
0.2634 ±7.5%
0.3951 ±12.5%
8.0000
12.0000
0.0173
1.0366
2.6240
22.0216
11184
7.23
Powered with 24VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 4801 1.21 0.000 0.00
10.0 4679 2.72 0.046 53.04
20.0 4558 4.22 0.090 66.42
30.0 4436 5.73 0.132 71.45
40.0 4314 7.24 0.171 73.35
50.0 4193 8.75 0.208 73.74
60.0 4071 10.26 0.242 73.29
70.0 3950 11.77 0.274 72.31
80.0 3828 13.27 0.303 71.00
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
42.0 4290 7.54 0.178 73.52
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
42.0 4290 7.54 0.178 73.52
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
394.73 (for reference only)
60.75 (for reference only)
4.8997 ±10.0%
6.6293 ±10.0%
0.2634 ±7.5%
0.3951 ±12.5%
8.0000
12.0000
0.0173
1.0366
2.6240
22.0216
22830
7.23
Page 5–11IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 46

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P25-1JK40
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2151 1.35 0.000 0.00
25.0 2042 4.73 0.051 66.41
50.0 1933 8.11 0.096 73.33
75.0 1823 11.49 0.135 73.25
100.0 1714 14.87 0.170 70.95
125.0 1605 18.25 0.199 67.66
150.0 1496 21.63 0.222 63.84
175.0 1386 25.01 0.240 59.71
200.0 1277 28.39 0.253 55.38
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
96.0 1732 14.33 0.165 71.40
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
96.0 1732 14.33 0.165 71.40
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Powered with 12VDC
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
492.23 (for reference only)
67.89 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
5.4672 ±10.0%
7.3971 ±10.0%
0.1010 ±7.5%
0.1767 ±12.5%
10.0000
15.0000
0.0411
0.4720
2.6703
18.8191
11971
8.46
Powered with 24VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 4346 1.35 0.000 0.0
50.0 4128 8.11 0.204 78.30
100.0 3909 14.87 0.387 80.90
150.0 3691 21.63 0.548 78.76
200.0 3472 28.39 0.688 75.28
250.0 3254 35.15 0.805 71.22
300.0 3035 41.91 0.901 66.86
350.0 2816 48.67 0.976 62.34
400.0 2598 55.43 1.029 57.70
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
80.0 3996 12.17 0.317 80.87
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
80.0 3996 12.17 0.317 80.87
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
994.45 (for reference only)
135.79 (for reference only)
5.4672 ±10.0%
7.3971 ±10.0%
0.1010 ±7.5%
0.1767 ±12.5%
10.0000
15.0000
0.0411
0.4720
2.6703
18.8191
24184
8.46
Page 5–12 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 47

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 12/24VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P25-JK44
Powered with 12VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2303 1.74 0.000 0.00
25.0 2204 5.36 0.055 63.30
50.0 2104 8.98 0.104 72.14
75.0 2005 12.60 0.149 73.48
100.0 1906 16.22 0.189 72.33
125.0 1806 19.83 0.224 70.06
150.0 1707 23.45 0.253 67.19
175.0 1607 27.07 0.279 63.95
200.0 1508 30.69 0.299 60.48
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
113.0 1854 18.10 0.207 71.25
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
113.0 1854 18.10 0.207 71.24
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
579.45 (for reference only)
85.63 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
5.1050 ±10.0%
6.9071 ±10.0%
0.0801 ±7.5%
0.1401 ±12.5%
12.0000
15.0000
0.0531
0.3825
2.7294
22.1208
10902
7.19
Powered with 24VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 4654 1.74 0.000 0.00
50.0 4455 8.98 0.221 76.37
100.0 4256 16.22 0.421 80.78
150.0 4057 23.45 0.603 79.86
200.0 3859 30.69 0.764 77.38
250.0 3660 37.93 0.906 74.24
300.0 3461 45.17 1.028 70.75
350.0 3263 52.41 1.131 67.05
400.0 3064 59.65 1.213 63.23
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
70.0 4375 11.87 0.303 79.40
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.05 Bandwidth (Hz)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
70.0 4375 11.87 0.303 79.40
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
1170.90 (for reference only)
171.26 (for reference only)
5.1050 ±10.0%
6.9071 ±10.0%
0.0801 ±7.5%
0.1401 ±12.5%
12.0000
15.0000
0.0531
0.3825
2.7294
22.1208
22030
7.19
Page 5–13IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 48

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
90VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P03-1L18
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2130 0.06 0.000 0.00
5.0 2038 0.15 0.010 54.57
10.0 1945 0.24 0.019 65.60
15.0 1853 0.33 0.028 68.39
20.0 1760 0.42 0.035 68.20
25.0 1667 0.51 0.041 66.60
30.0 1575 0.60 0.047 64.21
35.0 1482 0.69 0.051 61.36
40.0 1390 0.78 0.055 58.19
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
18.0 1797 0.39 0.032 68.50
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
18.0 1797 0.39 0.032 68.50
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
115.09 (for reference only)
2.14 (for reference only)
Horse-
power (hp)
Powered with 90VDC
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
41.0040 ±10.0%
55.4784 ±10.0%
41.2764 ±7.5%
42.1019 ±12.5%
3.5000
6.0000
0.0066
96.0471
2.2813
12.6947
17572
12.54
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P04-1L17
Powered with 90VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2047 0.08 0.000 0.00
5.0 1979 0.16 0.010 49.38
10.0 1911 0.25 0.019 62.49
15.0 1844 0.34 0.027 67.22
20.0 1776 0.42 0.035 68.71
25.0 1708 0.51 0.042 68.60
30.0 1640 0.60 0.049 67.60
35.0 1572 0.68 0.054 66.03
40.0 1504 0.77 0.060 64.09
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
22.0 1749 0.46 0.038 68.81
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
22.0 1749 0.46 0.038 68.81
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
150.82 (for reference only)
2.69 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
42.6880 ±10.0%
57.7569 ±10.0%
31.5737 ±7.5%
33.4681 ±12.5%
4.5000
7.0000
0.0081
86.5239
2.5853
11.5569
18550
13.77
Page 5–14 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 49

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 90VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P05-1L19
Powered with 90VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2212 0.15 0.000 0.00
10.0 2106 0.34 0.021 50.93
20.0 2001 0.53 0.040 62.21
30.0 1896 0.72 0.056 65.13
40.0 1790 0.91 0.071 64.93
50.0 1685 1.09 0.083 63.21
60.0 1579 1.28 0.094 60.65
70.0 1474 1.47 0.102 57.57
80.0 1368 1.66 0.108 54.15
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
28.0 1917 0.68 0.053 64.88
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
28.0 1917 0.68 0.053 64.88
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
209.82 (for reference only)
4.11 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
39.1976 ±10.0%
53.0343 ±10.0%
16.9866 ±7.5%
21.9127 ±12.5%
8.0000
12.0000
0.0173
66.3453
3.0277
19.0855
12136
8.34
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P13-1L19
Powered with 90VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2041 0.17 0.000 0.00
50.0 1956 1.01 0.097 79.15
100.0 1871 1.86 0.185 82.60
150.0 1786 2.70 0.265 81.31
200.0 1701 3.55 0.337 78.67
250.0 1616 4.39 0.400 75.46
300.0 1531 5.24 0.455 71.95
350.0 1446 6.08 0.501 68.28
400.0 1361 6.93 0.539 67.49
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
73.0 1917 1.40 0.139 81.87
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
73.0 1917 1.40 0.139 81.87
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
1201.00 (for reference only)
20.46 (for reference only)
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
43.7376 ±10.0%
59.1770 ±10.0%
5.1647 ±7.5%
4.3979 ±12.5%
10.0000
15.0000
0.0411
30.2054
6.8681
7.3169
29207
21.75
Page 5–15IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 50

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 90VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P14-1L19
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 1971 0.20 0.000 0.00
25.0 1904 0.61 0.047 64.18
50.0 1837 1.02 0.091 73.90
75.0 1770 1.43 0.131 76.11
100.0 1703 1.84 0.169 75.84
125.0 1636 2.25 0.202 74.45
150.0 1569 2.67 0.233 72.45
175.0 1502 3.08 0.260 70.10
200.0 1435 3.49 0.284 67.51
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
86.0 1740 1.61 0.148 76.19
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
86.0 1740 1.61 0.148 76.19
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Powered with 90VDC
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
734.58 (for reference only)
12.28 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
44.9240 ±10.0%
60.7822 ±10.0%
5.6800 ±7.5%
7.3272 ±12.5%
12.0000
15.0000
0.0531
29.6208
4.0426
14.9355
13821
10.66
180VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P07-1M24
Powered with 180VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2727 0.09 0.000 0.00
10.0 2625 0.21 0.026 51.87
20.0 2522 0.32 0.050 64.09
30.0 2420 0.44 0.072 67.95
40.0 2317 0.55 0.092 68.69
50.0 2215 0.67 0.110 67.91
60.0 2112 0.78 0.125 66.29
70.0 2010 0.90 0.139 64.16
80.0 1907 1.02 0.151 61.67
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
28.0 2440 0.42 0.068 67.51
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
28.0 2440 0.42 0.068 67.51
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
266.01 (for reference only)
3.16 (for reference only)
Efficiency
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
64.0730 ±10.0%
88.6908 ±10.0%
44.1455 ±7.5%
56.9477 ±12.5%
8.0000
12.0000
0.0173
177.2726
3.1129
18.5632
15385
8.57
Page 5–16 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 51

Chapter 5: Reference
Typical Performance Data for 180VDC Small-Frame PMDC Motors (continued)
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P13-1M19
Powered with 180VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2113 0.09 0.000 0.00
25.0 2028 0.31 0.050 67.43
50.0 1943 0.53 0.096 75.38
75.0 1859 0.75 0.138 76.33
100.0 1774 0.97 0.176 75.05
125.0 1689 1.19 0.209 72.78
150.0 1604 1.41 0.238 69.99
175.0 1519 1.63 0.263 66.88
200.0 1434 1.85 0.284 63.57
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
73.0 1865 0.73 0.135 76.36
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
73.0 1865 0.73 0.135 76.36
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
622.44 (for reference only)
5.58 (for reference only)
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
83.8304 ±10.0%
113.4225 ±10.0%
25.0243 ±7.5%
32.2813 ±12.5%
10.0000
15.0000
0.0411
110.9630
3.4374
14.6195
15137
10.89
Typical Small-Frame PMDC Motor Performance Data – MTPM-P14-1M18
Powered with 180VDC
Torque
(oz·in)
0.0 2065 0.10 0.000 0.00
25.0 1995 0.32 0.049 64.17
50.0 1924 0.53 0.095 73.88
75.0 1854 0.75 0.138 76.09
100.0 1783 0.97 0.177 75.81
125.0 1713 1.18 0.212 74.41
150.0 1642 1.40 0.244 72.40
175.0 1572 1.61 0.272 70.04
200.0 1501 1.83 0.297 67.44
Primary Load Point Tm (mechanical time const) (ms)
84.0 1828 0.83 0.152 76.17
Continuous Duty Rating – Form Factor = 1.40 Bandwidth (Hz)
84.0 1828 0.83 0.152 76.17
Stall Torque (oz·in)
Stall Current (A)
Speed
(rpm)
Current
(A)
Horse-
power (hp)
Efficiency
732.74 (for reference only)
6.42 (for reference only)
(%)
Motor Design Data and Constants
Ke (V/krpm)
Kt (oz·in/A)
Ra (Ω)
Rt (Ω)
Friction Torque (nominal) (oz·in)
Friction Torque (maximum) (oz·in)
Ja (inertia) (oz·in·s2)
La (inductance) (mH)
Te (electric time const) (ms)
Theoretical Accel at Stall (rad/s2)
85.7640 ±10.0%
116.0387 ±10.0%
21.7410 ±7.5%
28.0459 ±12.5%
12.0000
15.0000
0.0531
107.9568
3.8493
15.6853
13786
10.15
Page 5–17IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 52

Chapter 5: Reference
Junction Box Dimensions for 56C-Frame Motors
XC
(Length)
AA (Conduit Hole
Diameter)
Junction Box Dimensions
Frame Size XD Width XC Length HH Depth AA Conduit Hole (NPT)
56
2.5 in 2.76 in 1.55 in 1/2 in
XD
(Width)
HH (Depth)
Shipping Crate Dimensions for 56C-Frame Motors
Nominal Shipping Crate Dimensions
Frame Size HP Width x Depth x Height (in)
1/3
1/2
56C
Motor and shipping weights are listed in the Motor
Specifications tables in “Chapter 1: Getting Started.”
3/4 15.2 x 7.5 x 8.5
1 15.9 x 7.5 x 8.5
1-1/2 18.1 x 7.5 x 8.5
2 18.7 x 9.8 x 10.6
13.2 x 7.5 x 8.5
Decibel Levels for 56C-Frame Motors
The decibel (sound) level of an IronHorse PMDC motor should be measured after initial startup,
after 30 days, and after six months of use. Decibel levels should remain fairly consistent, and
can be an indication of misalignment and premature bearing wear. If the measured decibel
level for your IronHorse model exceeds the value listed below by more than 10%, contact
AutomationDirect or a local motor service technician found at www.easa.com.
Average Decibel Levels
Frame Size HP Noise Level: Lw dB (A)
56
All 55.0
Page 5–18 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 53

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors
MTPM-P33-1L18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-P33-1L18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 90.23 0.850 76.71 0.083 1828 15.92 20.7
Rated 90.07 3.752 337.9 1.422 1678 250.0 73.9
Max Eff 90.03 4.680 421.4 1.869 1630 319.9 75.6
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 89.91 8.502 764.4 3.640 1435 546.9 71.5
89.91 8.502 764.4 3.640 1435 546.9 71.5
89.91 8.502 764.4 3.640 1435 546.9 71.5
Page 5–19IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 54

Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-P50-1L18
Performance Data – MTPM-P50-1L18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 90.67 0.690 62.60 0.077 1896 15.40 24.6
Rated 90.40 5.146 465.3 2.115 1693 375.0 80.5
Max Eff 90.41 5.067 458.1 2.092 1696 371.4 81.0
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 90.30 8.576 774.5 3.684 1551 598.3 77.2
90.30 8.576 774.5 3.684 1551 598.3 77.2
90.30 8.576 774.5 3.684 1551 598.3 77.2
Page 5–20 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 55

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-P75-1L18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-P75-1L18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 90.44 0.615 55.68 0.071 1833 13.66 24.5
Rated 90.11 7.519 677.5 3.244 1619 550.0 81.1
Max Eff 90.17 5.634 508.1 2.383 1673 417.4 82.1
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 90.05 9.803 882.8 4.313 1555 702.2 79.5
90.05 9.803 882.8 4.313 1555 702.2 79.5
90.05 9.803 882.8 4.313 1555 702.2 79.5
Page 5–21IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 56

Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-001-1L18
Performance Data – MTPM-001-1L18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 90.67 0.816 73.99 0.082 1887 16.35 22.1
Rated 90.30 10.16 918.4 4.345 1647 750.0 81.6
Max Eff 90.34 8.131 734.6 3.418 1694 606.2 82.5
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 90.30 10.21 922.2 4.364 1647 752.9 81.6
90.30 10.21 922.2 4.364 1647 752.9 81.6
90.30 10.21 922.2 4.364 1647 752.9 81.6
Page 5–22 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 57

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-1P5-1L18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-1P5-1L18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 90.51 0.852 77.18 0.086 1917 17.42 22.5
Rated 90.01 14.75 1328 6.373 1686 1125 84.7
Max Eff 90.13 9.510 857.2 3.992 1765 737.8 86.0
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 89.77 25.07 2251 11.110 1537 1787 79.4
89.77 25.07 2251 11.110 1537 1787 79.4
89.77 25.07 2251 11.110 1537 1787 79.4
Page 5–23IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 58
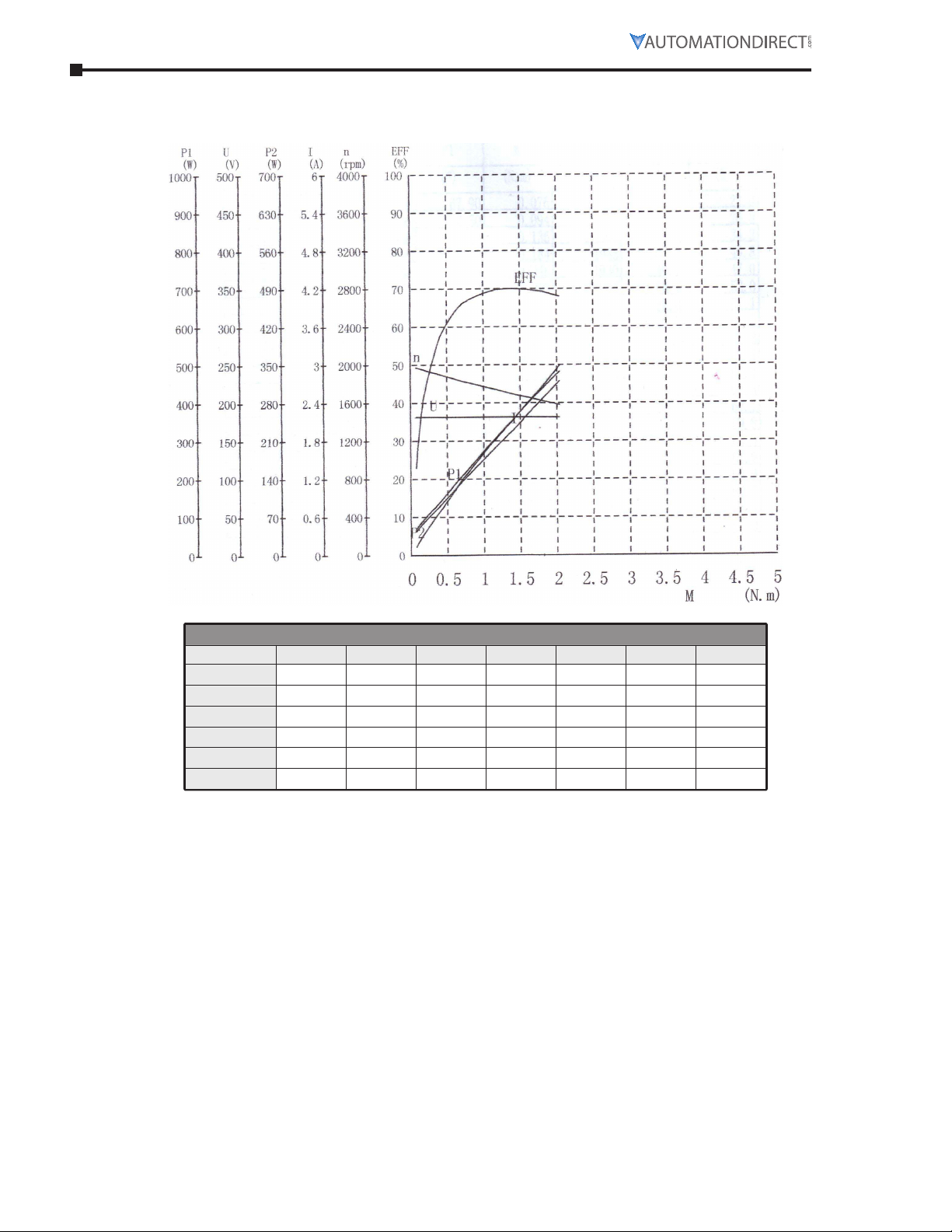
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-P33-1M18
Performance Data – MTPM-P33-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.6 0.375 67.90 0.076 1966 15.64 23.0
Rated 180.5 1.980 357.5 1.414 1687 250.0 69.9
Max Eff 180.5 1.980 357.5 1.414 1687 250.0 69.9
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 180.4 2.744 495.2 2.046 1573 337.0 68.0
180.4 2.744 495.2 2.046 1573 337.0 68.0
180.4 2.744 495.2 2.046 1573 337.0 68.0
Page 5–24 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 59

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-P50-1M18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-P50-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.2 0.391 70.66 0.106 1905 21.22 30.0
Rated 180.1 2.554 460.2 2.044 1752 375.0 81.4
Max Eff 180.0 2.812 506.4 2.278 1734 413.6 81.6
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 180.0 3.142 565.9 2.571 1710 460.4 81.3
180.0 3.142 565.9 2.571 1710 460.4 81.3
180.0 3.142 565.9 2.571 1710 460.4 81.3
Page 5–25IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 60

Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-P75-1M18
Performance Data – MTPM-P75-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.8 0.333 60.35 0.081 1858 15.87 26.3
Rated 180.5 3.547 640.7 3.081 1704 550.0 85.8
Max Eff 180.6 3.164 571.4 2.736 1722 493.3 86.3
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 180.5 4.272 771.4 3.766 1672 659.3 85.4
180.5 4.272 771.4 3.766 1672 659.3 85.4
180.5 4.272 771.4 3.766 1672 659.3 85.4
Page 5–26 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 61

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-001-1M18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-001-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.6 0.434 78.52 0.075 1792 14.10 17.9
Rated 180.4 5.026 909.7 4.412 1623 750.0 82.4
Max Eff 180.4 5.026 909.7 4.412 1623 750.0 82.4
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 180.4 5.026 909.7 4.412 1623 750.0 82.4
180.4 5.026 909.7 4.412 1623 750.0 82.4
180.4 5.026 909.7 4.412 1623 750.0 82.4
Page 5–27IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 62

Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-1P5-1M18
Performance Data – MTPM-1P5-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.3 0.492 88.87 0.084 1927 17.02 19.1
Rated 180.0 7.198 1296 6.099 1761 1125 86.8
Max Eff 180.1 5.337 961.5 4.427 1804 836.2 86.9
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 179.8 14.40 2590 12.261 1612 2069 79.8
179.8 14.40 2590 12.261 1612 2069 79.8
179.8 14.40 2590 12.261 1612 2069 79.8
Page 5–28 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 63

Performance Curves for 56C-Frame Motors (continued)
MTPM-002-1M18
Chapter 5: Reference
Performance Data – MTPM-002-1M18
Description U (V) I (A) P1 (W) M (N·m) n (rpm) P2 (W) Eff
No Load 180.7 0.690 124.8 0.07 1933 14.16 11.3
Rated 180.3 10.58 1910 8.25 1733 1500 78.5
Max Eff 180.4 8.374 1510 6.54 1763 1207 79.9
Max P
out
Max Torque
End 180.1 18.00 3244 12.82 1502 2017 62.1
180.1 18.00 3244 12.82 1502 2017 62.1
180.1 18.00 3244 12.82 1502 2017 62.1
Page 5–29IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 64

Chapter 5: Reference
BLANK
PAGE
Page 5–30 IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 65

BLANK
PAGE
Page CR–1IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
Page 66

IronHorse® General Purpose DC Motors User Manual – 2nd Ed. Rev D – 01/06/2021
 Loading...
Loading...