Page 1
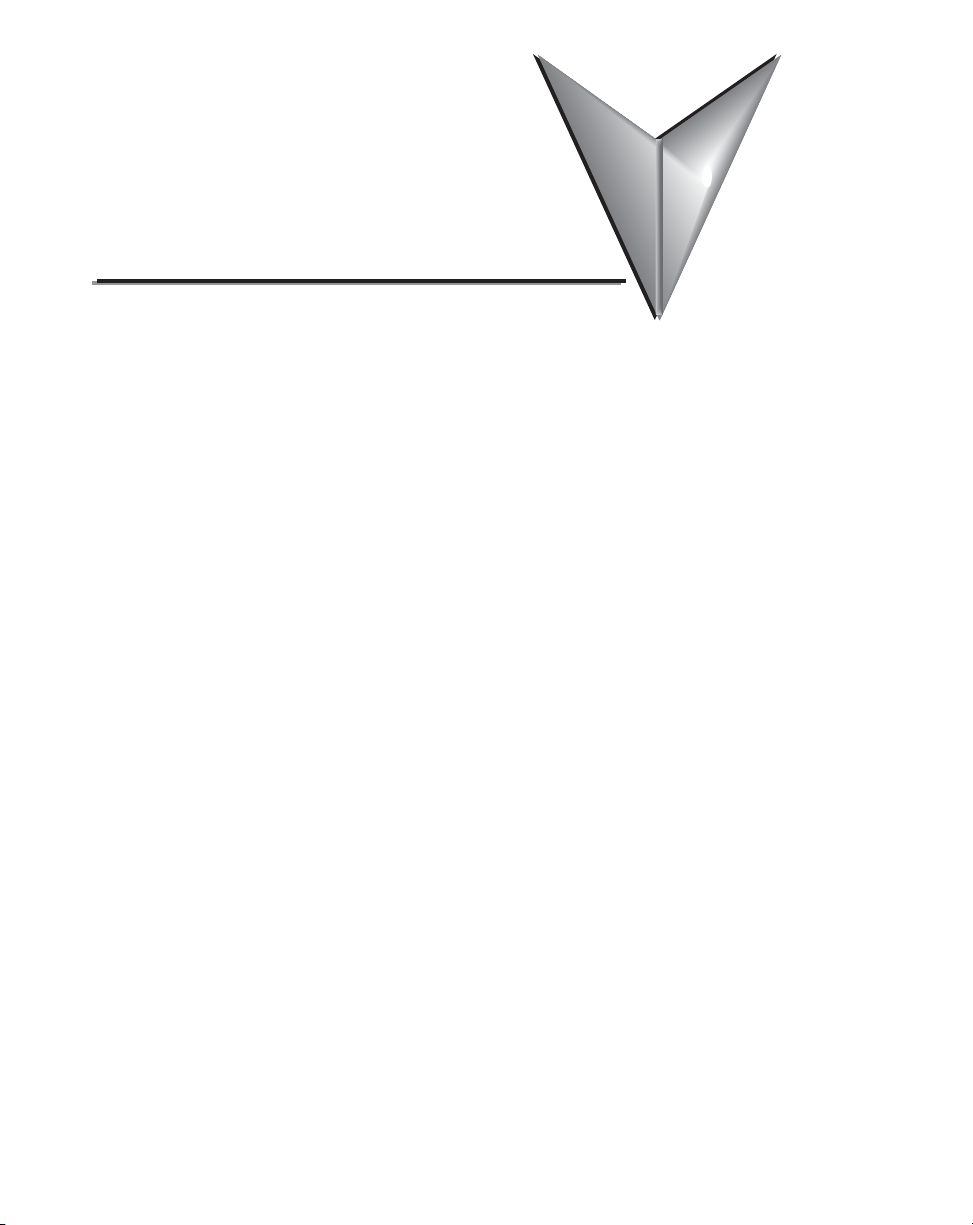
F0-4AD2DA-1,
4-ChAnnel In/2-Ch.
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Out AnAlOg Current
COmbInAtIOn
11
11
11
In This Chapter...
Module Specifications .............................................................................................11–2
Setting the Module Jumper .....................................................................................11–4
Connecting and Disconnecting the Field Wiring ...................................................11–5
Wiring Diagram .......................................................................................................11–6
Module Operation ................................................................................................... 11–7
Special V-memory Locations ...................................................................................11–8
Using the Pointer in Your Control Program ......................................................... 11–11
Scale Conversions .................................................................................................. 11–13
Special Relays ......................................................................................................... 11–16
Module Resolution .................................................................................................11–18
Analog Input Ladder Logic Filter ..........................................................................11–19
Page 2
Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Module Specifications
The F0-4AD2DA-1 Analog Combination module offers the following features:
• The analog input and output channels are updated in one scan.
• The removable terminal block makes it possible to remove the
module without disconnecting the field wiring.
• Analog inputs can be used as process variables for the four (4)
PID loops in the DL05 and the eight (8) PID loops in the DL06
CPUs.
• On-board active analog filtering and RISC-like microcontroller
provide digital signal processing to maintain precise analog
measurements in noisy environments.
R
W
P
N
U
R
U
P
C
1
X
T
1
X
R
2
X
T
2
X
R
11–2
NOTE: The DL05 CPU’s analog feature for this module requires DirectSOFT32 Version 3.0c (or later) and
firmware version 3.30 (or later). The DL06 requires DirectSOFT32 version V4.0, build 16 (or later) and
firmware version 1.00 (or later). See our website for more information: www.automationdirect.com.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 3
Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
The following tables provide the specifications for the F0–4AD2DA–1 Analog Combination
Module. Review these specifications to make sure the module meets your application
requirements.
Input Specifications
Number of Channels
Input Range
Resolution
Step Response
Crosstalk
Active Low-pass Filtering
Input Impedance
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Converter type
Linearity Error (End to End)
Input Stability
Full Scale Calibration Error
(Offset error not included)
Offset Calibration Error
Maximum Inaccuracy
Accuracy vs Temperature
Recommended Fuse (external)
*One count in the specification table is equal to one least significant bit of the analog data value (1 in 4096).
4, single ended (one common)
0 to 20mA or 4 to 20mA (jumper selectable)
12 bit (1 in 4096) for 0–20 mA, scaled for 4–20 mA
25.0 ms (typ) to 95% of full step change
-80dB, 1/2 count maximum*
-3dB at 40Hz (-12dB per octave)
125 Ohm _0.1%, 1/8 W current input
-30mA to +30mA current input
Successive approximation
±2 counts
±1 count*
±10 counts maximum @ 20mA current input*
±5 counts maximum @ 0mA current input*
±0.4% @ 25°C (77°F)
±0.85% 0 to 60°C (32 to 140°F)
±100ppm typical full scale calibration
(Including maximum offset change)
0.032 A Series 217 fast-acting, current inputs
Output Specifications
Number of Channels 2, single ended (one common)
Output Range 4 to 20mA or 0 to 20mA (jumper selectable)
Output Type Current sourcing
Resolution 12 bit (1 in 4096) for 0 to 20mA, scaled for 4 to 20mA
Maximum Loop Voltage 30VDC
Load (ohms)/Loop Power Supply 0–300/18–30 V
Linearity Error (end to end) ± 2 counts (± 0.050% of full scale) maximum*
Conversion Settling Time 400µS max. full scale change
Full Scale Calibration Error
Note: Error depends on the load from
source terminal to ground.
Offset Calibration Error
Max. Full Scale Inaccuracy
(% of full scale) all errors included
* One count in the specification tables is equal to one least significant bit of the analog data value (1 in 4096).
± 26 counts max. @ 300q load
± 18 counts max. @ 250q load
± 12 counts max. @ 125q load
± 10 counts max. @ 300q load
± 8 counts max @ 250q load
± 6 counts max. @ 125q load
300q load 0.4% @ 60°C
250q load 0 3%@60°C
125q load 0.2% @ 60°C
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–3
Page 4
Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
General Specifications
PLC Update Rate
16-bit Data Word
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Relative Humidity
Environmental Air
Vibration
Shock
Noise Immunity
Power Budget Requirement
Connector
Connector Wire Size
Connector Screw Torque
Connector Screwdriver Size
4 input channels per scan, 2 output channels per scan
12 binary data bits
0 to 60°C (32 to 140°F)
-20 to 70°C (-4 to 158°F)
5 to 95% (non-condensing)
No corrosive gases permitted
MIL STD 810C 514.2
MIL STD 810C 516.2
NEMA ICS3-304
100mA @ 5VDC (supplied by base)
Phoenix Mecano, Inc., Part No. AK1550/8-3.5 - green
28–16 AWG
3.5 inch-pounds (0.4 N·m)
DN-SS1 (recommended)
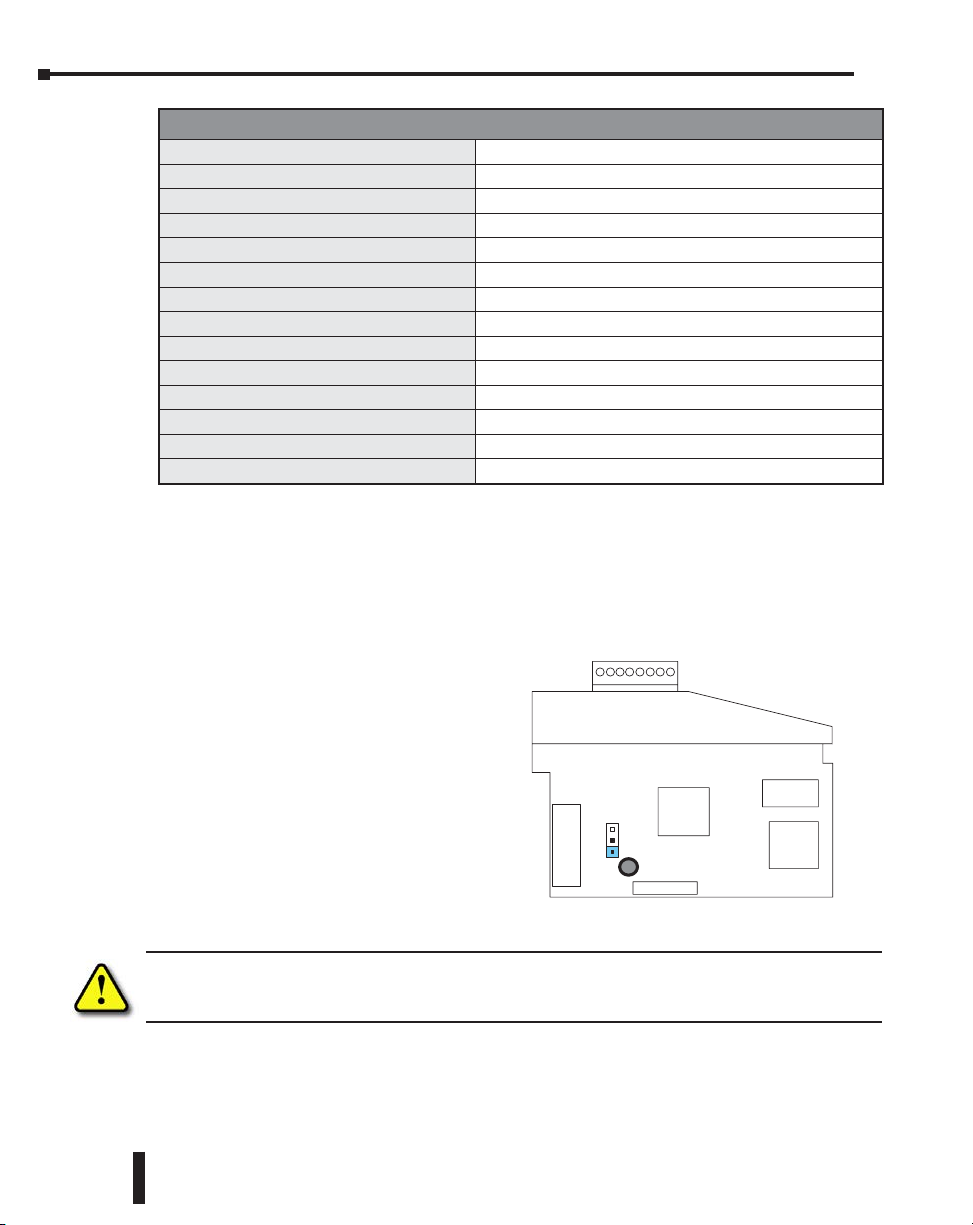
Setting the Module Jumper
The position of the J2 jumper determines the input and output signal level. You can choose
between 0–20 mA and 4–20 mA signal levels. The module ships without the jumper connecting
the pins (pins not jumpered). In this position, the input and output signal level is 4–20 mA. To
select 0–20 mA signal level, install the jumper, connecting the pins.
11–4
The J2 jumper is shown in the 4–20 mA
position (not installed). Install the jumper
for the 0–20 mA position.
WARNING: Before removing the analog module or the terminal block on the face of the module,
disconnect power to the PLC and all field devices. Failure to disconnect power can result in damage to
the PLC and/or field devices.
J2
C14
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 5

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Connecting and Disconnecting the Field Wiring
Wiring Guidelines
Your company may have guidelines for wiring and cable installation. If so, you should check
those before you begin the installation. Here are some general things to consider:
• Use the shortest wiring route whenever possible.
• Use shielded wiring and ground the shield at the transmitter source. Do not ground the shield at
both the module and the source.
• Do not run the signal wiring next to large motors, high current switches, or transformers. This may
cause noise problems.
• Route the wiring through an approved cable housing to minimize the risk of accidental damage.
Check local and national codes to choose the correct method for your application.
A separate transmitter power supply may be required, depending on the type of transmitter
being used.
This module has a removable connector to make wiring and module removal easier. To remove
the terminal block, disconnect power to the PLC and the field devices. Pull the terminal block
firmly until the connector separates from the module.
The analog module can be removed from the PLC by folding out the retaining tabs at the top
and bottom of the module. As the retaining tabs pivot upward and outward, the module’s
connector is lifted out of the PLC socket. Once the connector is free, you can lift the module
out of its slot.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–5
Page 6
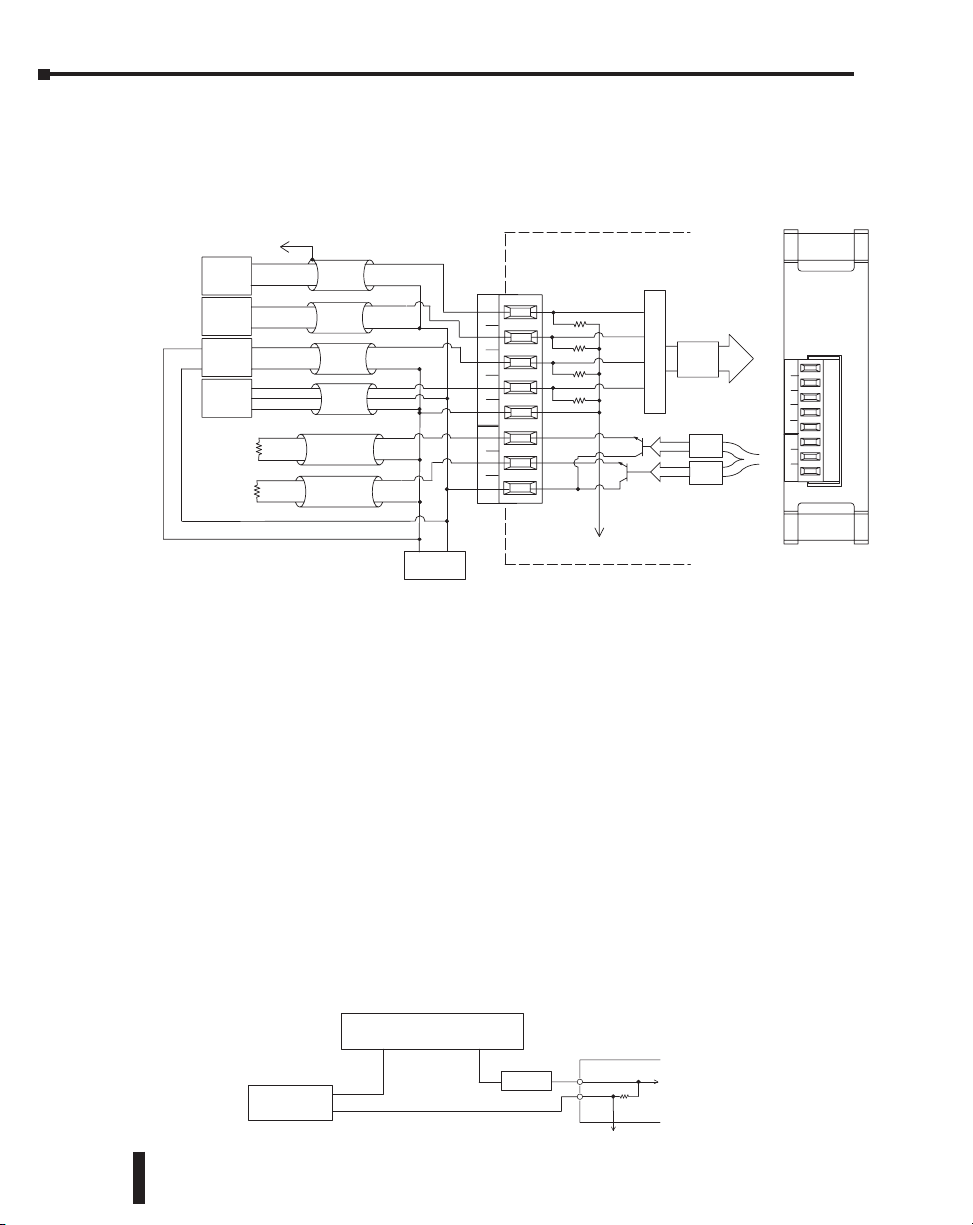
Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
commons.
0V
Wiring Diagram
Use the following diagram to connect the field wiring. If necessary, the terminal block can be
removed to make removal of the module possible without disturbing field wiring.
Typical User Wiring
125Ω
125Ω
125Ω
125Ω
Internal
Module
Wiring
OV
Analog Switch
A to D
Converter
D to A
Converter
D to A
Converter
See NOTE 1
–
CH1
2–wire
+
Current
Transmitter
–
CH2
2–wire
Current
+
Transmitter
–
+
NOTE 1: Shields should be grounded at the signal
NOTE 2: Connect all external power supply
CH3
4–wire
Current
Transmitter
CH4
3–wire
Current
Transmitter
CH 1 load
300Ω
maximum
resistance
CH 2 load
300Ω
maximum
resistance
source.
+
–
+
+
–
–
Transmitter
Power Supply
IN
1
2
3
4
0V
1
2
24V
OUT
+
Analog
4–In/2–Out
0–20mA
4–20mA
IN
1
2
3
4
0V
1
2
+V
OUT
F0–4AD2DA–1
In/Out
11–6
Current Loop Transmitter Impedance
Manufacturers of transmitters and transducers specify a wide variety of power sources for their
products. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
In some cases, manufacturers specify a minimum loop or load resistance that must be used with
the transmitter. The F0-04AD2DA-1 provides 125 ohm resistance for each channel. If your
transmitter requires a load resistance below 125 ohms, you do not have to make any changes.
However, if your transmitter requires a load resistance higher than 125 ohms, you need to add
a resistor in series with the module.
Consider the following example for a transmitter being operated from a 30VDC supply with a
recommended load resistance of 750 ohms. Since the module has a 125 ohm resistor, you need
to add an additional resistor.
R = Tr–Mr R = resistor to add
R = 750–125 Tr = Transmitter Requirement
R M 625 Mr = Module resistance (internal 125 ohms)
Two-wire Transmitter
+–
DC Supply
+30V
0V
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
R
Module Channel 1
CH1
COM
125 ohms
Page 7

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Module Operation
Input/Output Channel Update Sequence
The DL05 and DL06 will read four channels of input data and two channels of output data
during each scan. Each CPU supports special V-memory locations that are used to manage the
data transfer. This is discussed in more detail beginning on the next page, “Special V-memory
Locations”.
Scan
Read Inputs
DL05/DL06 PLC
Execute Application Progr
Read the data
Store data
Write to Outputs
am
Scan N
Scan N+1
Scan N+2
Scan N+3
Scan N+4
Ch 1, 2, 3, 4 IN; Ch 1,2 OUT
Ch 1, 2, 3, 4 IN; Ch 1,2 OUT
Ch 1, 2, 3, 4 IN; Ch 1,2 OUT
Ch 1, 2, 3, 4 IN; Ch 1,2 OUT
Ch 1, 2, 3, 4 IN; Ch 1,2 OUT
Analog Module Updates
Even though the channel updates to the CPU are synchronous with the CPU scan, the module
asynchronously monitors the analog transmitter signals and converts each signal into a 12-bit
binary representation. This enables the module to continuously provide accurate measurements
without slowing down the discrete control logic in the RLL program.
The module takes approximately 25 milliseconds to sense 95% of the change in the analog
signal. For the vast majority of applications, the process changes are much slower than these
updates.
NOTE: If you are comparing other manufacturers’ update times (step responses) with ours, please be aware
that some manufacturers refer to the time it takes to convert the analog signal to a digital value. Our analog
to digital conversion takes only a few microseconds. It is the settling time of the filter that is critical in
determining the full update time. Our update time specification includes the filter settling time.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–7
Page 8

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
MSB LSB
HIGH BYTE
Special V-memory Locations
Formatting the Module Data
The DL05 and DL06 PLCs have three special V-memory locations assigned to their respective
option slots. These V-memory locations allow you to:
• Specify the data format (binary or BCD)
• Specify the number of input and output channels to scan.
• Specify the V-memory locations to store the input data
• Specify the V-memory locations to store the output data
DL05 Data Formatting
The table below shows the special V-memory locations used by the DL05 PLC for the analog
combination module.
Analog Combination Module
DL05 Special V-memory Locations
Data Type and Number of I/O Channels V7700
Input Storage Pointer V7701
Output Storage Pointer V7702
Structure of V7700
V-memory location 7700 is used for identifying the number of output channels, the number of
input channels and the data type (binary or BCD). The low byte equals the number of output
channels and the high byte equals the number of input channels. Enter a 1 through 4 to select
the number of input channels and a 1 through 2 to
select the number of output channels to be used. A
zero (0) entered for channel selection will cause the
channel, either input or output, to be inoperative.
Loading a constant of 402 into V7700 identifies
four input and two output analog channels, and
sets the I/O data type to BCD.
Loading a constant of 8482 into V7700 identifies four input and two output analog channels,
and sets the I/O data type to binary.
MSB LSB
LOW BYTE
Structure of V7701
V7701 is a system parameter that points to a V-memory location used for storing analog
input data. The V-memory location loaded in V7701 is an octal number identifying the first
V-memory location for the analog input data. This V-memory location is user selectable. For
example, loading O2000 causes the pointer to write Ch 1’s data value to V2000, Ch 2’s data
value to V2001, CH 3’s data value to V2002 and Ch 4’s data value to V2003.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–8
Page 9

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Structure of V7702
V7702 is a system parameter that points to a V-memory location used for storing analog
output data. The V-memory location loaded in V7702 is an octal number identifying the first
V-memory location for the analog output data. This V-memory location is user selectable. For
example, loading O2010 causes the pointer to read Ch 1’s data value at V2010 and Ch 2’s data
value at V2011.
You will find an example program that loads appropriate values to V7700, V7701and V7702
on page 11–11.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–9
Page 10

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
HIGH BYTE
DL06 Data Formatting
Special V-memory locations are assigned to the four option module slots of the DL06 PLC.
The table below shows these V-memory locations which can be used by the F0–4AD2DA–1.
Analog Combination Module
DL06 Special V-memory Locations
Slot No. 1 2 3 4
Data Type and Number of Channels V700 V710 V720 V730
Input Storage Pointer V701 V711 V721 V731
Output Storage Pointer V702 V712 V722 V732
Setup Data Type and Number of Channels
V-memory locations 700, 710, 720 and 730 are used to set the number of output channels, the
number of input channels and the data type (binary or BCD). The low byte equals the number
of output channels and the high byte equals the number of input channels. Enter a 1 through
4 to select the number of input channels and a 1 through 2 to select the number of output
channels to be used. A zero (0) entered for channel selection will cause the channel, either input
or output, to be inoperative.
Consider the F0–4AD2DA–1 to be installed in slot
2 . Loading a constant of 402 into V710 identifies
four input and two output analog channels, and
sets the I/O data type to BCD.
Loading a constant of 8482 into V710 identifies
four input and two output analog channels, and
sets the I/O data type to binary.
MSB LSB
LOW BYTE
MSB LSB
11–10
Input Storage Pointer Setup
V-memory locations 701, 711, 721 and 731 are special locations used as a storage pointer for
the analog input data. With the analog module installed in slot 2, the V-memory location
loaded in V711 is an octal number identifying the first user V-memory location to write the
analog input data to. This V-memory location is user selectable. For example, loading O2000
causes the pointer to write Ch 1’s data value to V2000, Ch 2’s data value to V2001, CH 3’s
data value to V2002 and Ch 4’s data value to V2003.
Output Storage Pointer Setup
V-memory locations 702, 712, 722 and 732 are special locations used as a storage pointer for
the analog output data. With the analog module installed in slot 2, the V-memory location
loaded in V712 is an octal number identifying the first user V-memory location to read the
analog output data from. This V-memory location is user selectable. For example, loading
O2010 causes the pointer to read Ch 1’s data value at V2010 and Ch 2’s data value at V2011.
You will find an example program that loads appropriate values to V710, V711 and V712 on
page 11–12.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 11

SP0
Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Using the Pointer in Your Control Program
DL05 Pointer Method
The DL05 CPU examines the pointer values (the memory locations identified in V7700,
V7701 and V7702) on the first scan only.
The example program below shows how to setup these locations for 4 input channels and 2
output channels. This rung can be placed anywhere in the ladder program or in the initial stage
if you are using stage programming instructions.
This is all that is required to read the analog input and output data into V-memory locations.
Once the data is in V-memory you can perform math on the data, compare the data against
preset values, and so forth. V2000 and V2010 are used in the example, the V-memory locations
are user selectable.
LD
K402
- or -
LD
K8482
OUT
V7700
Loads a constant that specifies the number of channels to scan and the
data format. The upper byte selects the input data format (i.e. 0=BCD,
8=Binary) and the number of input channels (set to 4). The lower byte
selects the output data format (i.e. 0=BCD, 8=Binary) and the number
of output channels (set to 2).
The binary format is used for displaying data on some operator
interface
Special V-memory location assigned to the option slot contains the
data format and the number of channels to scan.
units. The DL05 PLCs support binary math functions.
LDA
O2000
OUT
V7701
LDA
O2010
OUT
V7702
This loads an octal value for the first V-memory location that will be used
to store the incoming data. For example, the O2000 entered here would
designate the following addresses:
Ch1 – V2000, Ch2 – V2001, Ch3 – V2002, Ch4 – V2003
The octal address (O2000) is stored here. V7701 is assigned to the
option slot and acts as a pointer, which means the CPU will use the
octal value in this location to determine exactly where to store the
incoming
This loads an octal value for the first V-memory location that will be used
to store the output data. For example, the O2010 entered here would
designate the following addresses:
Ch1 – V2010, Ch2 – V2011
The octal address (O2010) is stored here. V7702 is assigned to the
option slot and acts as a pointer, which means the CPU will use the
octal value in this location to determine exactly where to get the output
data.
data.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–11
Page 12

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
data.
DL06 Pointer Method
Use the special V-memory table as a guide to setup the pointer values in the following example
for the DL06. Slot 1 is the left most option slot. The CPU will examine the pointer values at
these locations only after a mode transition, first scan only.
Analog Combination Module
DL06 Special V-memory Locations
Slot No. 1 2 3 4
No. of Channels V700 V710 V720 V730
Input Pointer V701 V711 V721 V731
Output Pointer V702 V712 V722 V732
The F0–4AD2DA–1 can be installed in any available DL06 option slot. Using the example
program from the previous page, but changing the V-memory addresses, the ladder diagram
below shows how to setup these locations for 4 input channels and 2 output channels with the
module installed in slot 2 of the DL06. Use the above table to determine the pointer values if
locating the module in any of the other slot locations. Place this rung anywhere in the ladder
program or in the initial stage if you are using stage programming instructions.
Like the DL05 example, this logic is all that is required to read the analog input data into
V-memory locations. Once the data is in V-memory you can perform mathematical calculations
with the data, compare the data against preset values, and so forth. V2000 and V2010 is used
in the example but you can use any user V-memory location.
11–12
SP0
LD
K402
- or -
LD
K8482
OUT
V710
LDA
O2000
OUT
V71
1
LDA
O2010
OUT
V712
Loads a constant that specifies the number of channels to scan and the
data format. The upper byte selects the input data format (i.e. 0=BCD,
8=Binary) and the number of input channels (set to 4). The lower byte
selects the output data format (i.e. 0=BCD, 8=Binary) and the number
of output channels (set to 2).
The binary format can be used for displaying data on some
operator interface units and on the DL06 LCD display. The DL06
PLCs support binary math functions.
Special V-memory location, V710, assigned to the option slot
contains the data format and the number of channels to scan.
This loads an octal value for the first V-memory location that will be used
to store the incoming data. For example, the O2000 entered here would
designate the following addresses:
Ch1 – V2000, Ch2 – V2001, Ch3 – V2002, Ch4 – V2003
The octal address (O2000) is stored here. V711 is assigned to the
option slot and acts as a pointer, which means the CPU will use the
octal value in this location to determine exactly where to store the
data.
incoming
This loads an octal value for the first V-memory location that will be used
to store the output data. For example, the O2010 entered here would
designate the following addresses:
Ch1 – V2010, Ch2 – V2011
The octal address (O2010) is stored here. V712 is assigned to the
option slot and acts as a pointer, which means the CPU will use the
octal value in this location to determine exactly where to get the output
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 13

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Scale Conversions
Scaling the Input Data
Many applications call for measurements in
engineering units, which can be more meaningful
than raw data. Convert to engineering units using
the formula shown to the right.
You may have to make adjustments to the
formula depending on the scale you choose for the
engineering units.
For example, if you wanted to measure pressure (PSI)
from 0.0 to 100.0 then you would have to multiply
the analog value by 10 in order to imply a decimal place when you view the value with the
programming software or a handheld programmer. Notice how the calculations differ when
you use the multiplier.
Analog Value of 2024, slightly less than half scale, should yield 49.4 PSI
Example without multiplier Example with multiplier
Units =A
Units=2024
Units= 49
H – L
4095
100 – 0
4095
+ L
+ 0
Units=10 A
Units=20240
Units=494
unit range
unit range
+ L
4095
H – L
4095
+ 0
+ L
Units =A
H = High limit of the engineering
L = Low limit of the engineering
A = Analog value (0 – 4095)
H – L
4095
100 – 0
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–13
Page 14

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
SP1
The Conversion Program
The following example shows how you would write the program to perform the engineering
unit conversion from input data formats 0–4095. This example assumes the raw input data
read at V2000 is in BCD format.
Note: this example uses SP1, which is always on. You could also use an X, C, etc., permissive
contact.
SP1
LD
V2000
MUL
K1000
DIV
K4095
OUT
V2100
When SP1 is on, load channel 1 data to the accumulator (for
a range of 0–1000).
Multiply the accumulator by 1000.
Divide the accumulator by 4095 (the module resolution).
Store the result in V2100.
Output Conversion Program
The following example program shows how you would write the program to perform the
engineering unit conversion to output data formats 0–4095. This example assumes you have
calculated or loaded the engineering unit values between 0–1000 in BCD format and stored
them in V2300 and V2301 for channels 1 and 2 respectively. Both the DL05 and DL06 offer
instructions that allow you to perform math operations using BCD format. It is usually easier
to perform any math calculations in BCD and then convert the value to binary before you send
the data to the module.
LD
V2300
MUL
K4095
DIV
K1000
The LD instruction loads the engineering units used with channel 1 into
the accumulator. This example assumes the numbers are BCD. Since
SP1 is used, this rung automatically executes on every scan. You could
also use an X, C, etc. permissive contact.
Multiply the accumulator by 4095.
Divide the accumulator by 1000 (this is the maximum value of
V2300).
11–14
Store the BCD result in V2010; the V–memory location set up to
send the data to Ch 1 output.
The LD instruction loads the engineering units used with Ch 2 into the
accumulator. This example assumes the numbers are BCD. Since SP1 is
used, this rung automatically executes on every scan. You could also use
an X, C, etc. permissive contact.
Multiply the accumulator by 4095.
Divide the accumulator by 1000 (this is the maximum value of
V2301).
Store the BCD result in V2011; the V–memory location set up to send
the data to Ch 2 output.
SP1
OUT
V2010
LD
V2301
MUL
K4095
DIV
K1000
OUT
V2011
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 15

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
4095
Analog and Digital Value Conversions
Sometimes it is useful to convert between the signal levels and the digital values. This is
especially helpful during machine startup or troubleshooting. The following tables provide
formulas to make this conversion easier.
Range If you know the digital value If you know the analog signal level
4 to 20mA
A =
4095
For example, if you have measured the signal as
10mA, you can use the formula to determine
the digital value (D) that will be stored in the
V-memory location that contains the data.
16D
+ 4
D =
16
4095
D =
16
4095
D =
16
D = (255.93) (6) D = 1536
Range If you know the digital value If you know the analog signal level
0 to 20mA
A =
4095
20D
D =
20
4095
(A – 4)
(10mA – 4)
4095
(A - 4)
(A)
This example shows the result for the 0 to 20mA
range.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
20
4095
20
(A)
(10mA)
D =
D =
D = (204.75) (10)
D = 2047.5
11–15
Page 16

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
Special Relays
The list of other Special Relays associated with the DL05 and DL06 PLCs are contained in the
DL05 User Manual and the DL06 User Manual. The following special relays are new and
relate to the status of the F0–04AD2DA–1 module or one of its input channels.
DL05 Special Relays
DL05 Special Relays
SP600
SP601
SP602
SP603
SP610
SP611
SP612
SP613
DL06 Special Relays
SP140
SP141
SP142
SP143
SP150
SP151
SP152
SP153
Chan 1 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 2 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 3 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 4 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 1 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 2 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 3 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 4 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
DL06 Special Relays
SLOT 1
Chan 1 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 2 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 3 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 4 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 1 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 2 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 3 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 4 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
11–16
SLOT 2
SP240
SP241
SP242
SP243
SP250
SP251
SP252
SP253
Chan 1 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 2 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 3 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 4 input type 0 = 0–20mA 1 = 4–20mA
Chan 1 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 2 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 3 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 4 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 17

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
DL06 Special Relays (cont’d)
SLOT 3
SP340
SP341
SP342
SP343
SP350
SP351
SP352
SP353
SP440
SP441
SP442
SP443
SP450
SP451
SP452
SP453
Chan 1 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 2 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 3 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 4 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 1 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 2 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 3 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 4 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
SLOT 4
Chan 1 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 2 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 3 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 4 input type 0 = 0–20 mA 1 = 4–20 mA
Chan 1 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 2 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 3 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
Chan 4 input open 1 = xmitter signal open 0 = xmitter signal good
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–17
Page 18

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
53211 2048
MSB LSB
Module Resolution
Analog Data Bits
The first twelve bits represent the analog data in binary format.
Bit Value BitV
alue
01664
127 128
248 256
389 512
= data bits
41610 1024
Resolution Details
Since the module has 12-bit resolution, the analog signal is converted from 4096 counts
ranging from 0–4095 (212). For example, a 4mA signal would be 0 and 20mA signal would be
4095. This is equivalent to a binary value of 0000 0000 0000 to 1111 1111 1111, or 000 to
FFF hexadecimal. The diagrams below show how this relates to the two signal ranges.
20mA
4mA
20mA
0mA
4 – 20mA
0 Counts
0 – 20mA
0 Counts
4095
4095
Resolution =
H = high limit of the signal range
L = low limit of the signal range
16mA / 4095 = 3.907µA per count
20mA / 4095 = 4.884µA per count
H
4095
– L
01110987654321
11–18
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
Page 19

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
SP1
Analog Input Ladder Logic Filter
PID Loops / Filtering
Please refer to the “PID Loop Operation” chapter in the DL06 or DL05 User Manual for
information on the built-in PV filter (DL05/06) and the ladder logic filter (DL06 only) shown
below. A filter must be used to smooth the analog input value when auto tuning PID loops to
prevent giving a false indication of loop characteristics.
Smoothing the Input Signal (DL06 only)
The filter logic can also be used in the same way to smooth the analog input signal to help
stabilize PID loop operation or to stabilize the analog input signal value for use with an operator
interface display, etc.
WARNING: The built-in and logic filters are not intended to smooth or filter noise generated by improper
field device wiring or grounding. Small amounts of electrical noise can cause the input signal to bounce
considerably. Proper field device wiring and grounding must be done before attempting to use the filters
to smooth the analog input signal.
Using Binary Data Format
LDD
V2000
BTOR
SUBR
V1400
MULR
R0.2
ADDR
V1400
OUTD
V1400
RTOB
OUT
V2100
Loads the analog signal, which is in binary format
and has been loaded from V–memory location
V2000 – 2001, into the accumulator. Contact SP1
is always on.
Converts the binary value in the accumulator
to a real number.
Subtracts the real number stored in location
V1400 from the real number in the accumulator,
and stores the result in the accumulator. V1400
is the designated workspace in this example.
Multiplies the real number in the accumulator by
0.2 (the filter factor), and stores the result in the
accumulator. This is the filtered value. The filter
range is 0.1 to 0.9. Smaller filter factors
increase filtering. (1.0 eliminates filtering.)
Adds the real number stored in location V1400
to the real number filtered value in the
accumulator, and stores the result in the accumulator.
Copies the value in the accumulator to
location V1400.
Converts the real number in the
accumulator to a binary value, and
stores the result in the accumulator.
Loads the binary number filtered value from
the accumulator into location V2100 to use in
your application or PID loop.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
11–19
Page 20

Chapter 11: F0-4AD2DA-1, 4-Ch. In/2-Ch. Out Analog Current Combination
SP1
.
NOTE: Be careful not to do a multiple number conversion on a value. For example, if you are using the pointer
method in BCD format to get the analog value, it must be converted to binary (BIN) as shown below. If you
are using the pointer method in Binary format, the conversion to binary (BIN) instruction is not needed.
Using BCD Data Format
LD
V2000
BIN
BTOR
SUBR
V1400
MULR
R0.2
ADDR
V1400
OUTD
V1400
RTOB
BCD
Loads the analog signal, which is in BCD format
and has been loaded from V–memory location
V2000, into the accumulator. Contact SP1
is always on.
Converts the BCD value in the accumulator
to binary.
Converts the binary value in the accumulator
to a real number.
Subtracts the real number stored in location
V1400 from the real number in the accumulator,
and stores the result in the accumulator. V1400
is the designated workspace in this example.
Multiplies the real number in the accumulator by
0.2 (the filter factor), and stores the result in the
accumulator. This is the filtered value. The filter
range is 0.1 to 0.9. Smaller filter factors
increase filtering. (1.0 eliminates filtering.)
Adds the real number stored in location V1400
to the real number filtered value in the
accumulator, and stores the result in the accumulator
Copies the value in the accumulator to
location V1400.
Converts the real number in the
accumulator to a binary value, and
stores the result in the accumulator.
Converts the binary value in the accumulator
to a BCD number. Note: The BCD instruction
is not needed to PID loop PV (loop PV is a
binary number).
11–20
OUT
V1402
Loads the BCD number filtered value from
the accumulator into location V1402 to use in
your application or PID loop.
DL05/06 Option Modules User Manual; 7th Ed. Rev. E
 Loading...
Loading...