AUSTN AS5SS128K36DQ-12-XT, AS5SS128K36DQ-12-IT, AS5SS128K36DQ-11-XT, AS5SS128K36DQ-11-IT Datasheet

Austin Semiconductor, Inc.
SRAM
AS5SS128K36
128K x 36 SSRAM
SYNCHRONOUS ZBL SRAM
FLOW-THRU OUTPUT
FEATURES
• High frequency and 100% bus utilization
• Fast cycle times: 11ns & 12ns
• Single +3.3V +5% power supply (VDD)
• Advanced control logic for minimum control signal interface
• Individual BYTE WRITE controls may be tied LOW
• Single R/W\ (READ/WRITE) control pin
• CKE\ pin to enable clock and suspend operations
• Three chip enables for simple depth expansion
• Clock-controlled and registered addresses, data I/Os and
control signals
• Internally self-timed, fully coherent WRITE
• Internally self-timed, registered outputs to eliminate the
need to control OE\
• SNOOZE MODE for reduced-power standby
• Common data inputs and data outputs
• Linear or Interleaved Burst Modes
• Burst feature (optional)
• Pin/function compatibility with 2Mb, 8Mb, and 16Mb ZBL
SRAM
• Automatic power-down
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing (Access/Cycle/MHz)
8.5ns/11ns/90 MHz -1 1
9ns/12ns/83 MHz -1 2
• Packages
100-pin TQFP DQ No. 1001
• Operating T emperature Ranges
Military (-55oC to +125oC) XT
Industrial (-40oC to +85oC) IT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Austin Semiconductor, Inc. Zero Bus Latency SRAM
family employs high-speed, low-power CMOS designs using an advanced CMOS process.
ASI’s 4Mb ZBL SRAMs integrate a 128K x 36 SRAM core
with advanced synchronous peripheral circuitry and a 2-bit burst
counter. These SRAMS are optimized for 100 percent bus utilization,
eliminating any turnaround cycles for READ to WRITE, or WRITE
to READ, transitions. All synchronous inputs pass through registers
controlled by a positive-edge-triggered single clock input (CLK). The
synchronous inputs include all addresses, all data inputs, chip enable
(CE\), two additional chip enables for easy depth expansion (CE2,
CE2\), cycle start input (ADV/LD\), synchronous clock enable (CKE\),
byte write enables (BW a\, BWb\, BWc\, and BWd\) and read/write (R/
W\).
Asynchronous inputs include the output enable (OE\, which
may be tied LOW for control signal minimization), clock (CLK) and
snooze enable (ZZ, which may be tied LOW if unused). There is also
a burst mode pin (MODE) that selects between interleaved and linear
burst modes. MODE may be tied HIGH, LOW or left unconnected if
burst is unused. The flow-through data-out (Q) is enabled by OE\.
WRITE cycles can be from one to four bytes wide as controlled by the
write control inputs.
All READ, WRITE and DESELECT cycles are initiated by
the ADV/LD\ input. Subsequent burst addresses can be internally
generated as controlled by the burst advance pin (ADV/LD\). Use of
burst mode is optional. It is allowable to give an address for each
individual READ and WRITE cycle. BURST cycles wrap around
after the fourth access from a base address.
To allow for continuous, 100 percent use of the data bus,
the flow-through ZBL SRAM uses a LATE WRITE cycle. For example, if a WRITE cycle begins in clock cycle one, the address is
present on rising edge one. BYTE WRITEs need to be asserted on the
same cycle as the address. The write data associated with the address
is required one cycle later, or on the rising edge of clock cycle two.
Address and write control are registered on-chip to simplify
WRITE cycles. This allows self-timed WRITE cycles. Individual
byte enables allow individual bytes to be written. During a BYTE
WRITE cycle, BWa\ controls DQa pins; BWb\ controls DQb pins;
BWc\ controls DQc pins; and BWd\ controls DQd pins. Cycle types
can only be defined when an address is loaded, i.e., when ADV/LD\ is
LOW . Parity/ECC bits are available on this device.
Austin’s 4Mb ZBL SRAMs operate from a +3.3V V
power supply, and all inputs and outputs are LVTTL-compatible.
The device is ideally suited for systems requiring high bandwidth and
zero bus turnaround delays.
DD
AS5SS128K36
Rev. 2.0 12/00
For more products and information
please visit our web site at
www.austinsemiconductor .com
Austin Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
1
Austin Semiconductor, Inc.
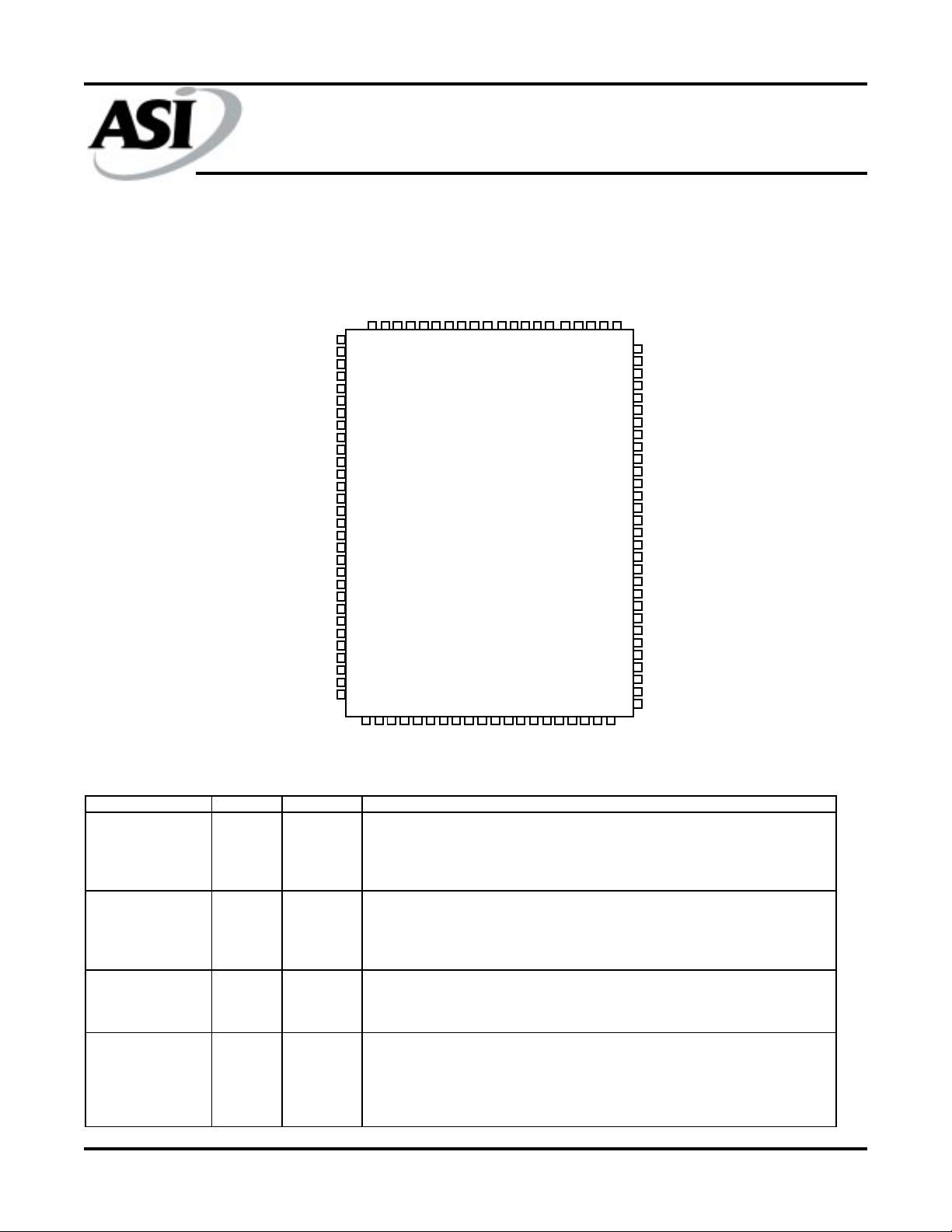
PIN ASSIGNMENT
(T op Vie w)
100-pin TQFP (DQ)
SS
DD
R/W\
CLK
V
V
CE2\
BWa\
BWb\
BWc\
BWd\
CE2
CE\
SA
SA
100 99 98 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81
DQc
1
DQc
2
DQc
3
VDDQ
4
V
5
SS
DQc
6
DQc
7
DQc
8
DQc
9
10
V
SS
11
VDDQ
12
DQc
13
DQc
14
V
SS
15
V
DD
16
V
DD
17
V
SS
18
DQd
19
DQd
20
VDDQ
21
V
SS
22
DQd
23
DQd
24
DQd
25
DQd
26
V
SS
27
VDDQ
28
DQd
29
DQd
30
DQd
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
SS
DD
SA
SA
SA
SA
SA1
SA0
DNU
DNU
V
SA
V
DNU
DNU
CKE\
SA
ADV/LD\
OE\ (G\)
SA
SA
NF
SRAM
AS5SS128K36
SA
SA
NF
DQb
80
DQb
79
DQb
78
VDDQ
77
V
76
SS
DQb
75
DQb
74
DQb
73
DQb
72
V
71
SS
VDDQ
70
69
DQb
68
DQb
67
V
SS
66
V
SS
65
V
DD
64
ZZ
63
DQa
62
DQa
61
VDDQ
60
V
SS
59
DQa
58
DQa
57
DQa
56
DQa
55
V
SS
54
VDDQ
53
DQa
52
DQa
51
DQa
SA
SA
SA
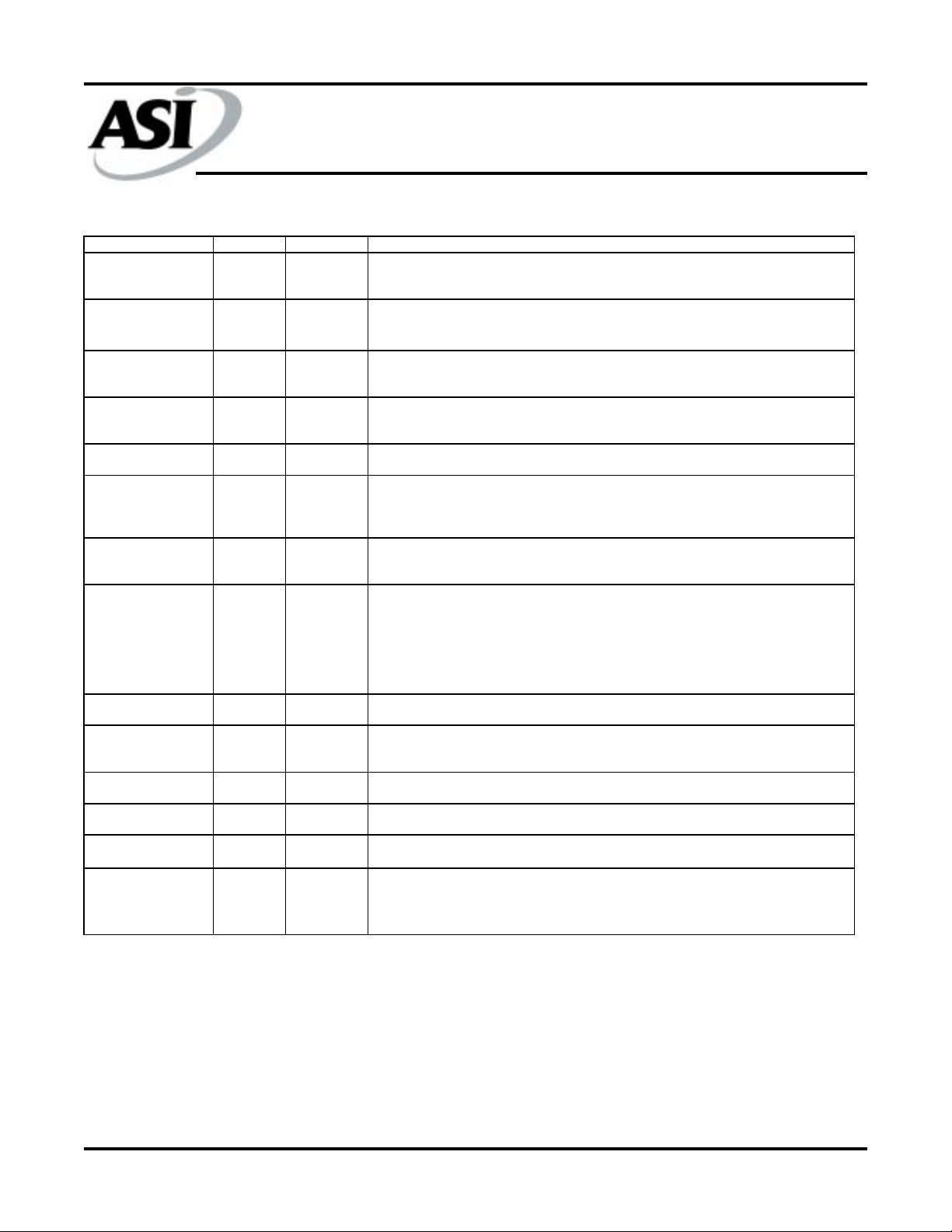
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
MODE (LBO\)
TQFP PINS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
37
36
32-35, 44-50,
81, 82, 99, 100
93
94
95
96
87 CKE\ Input Synchronous Clock Enable: This active LOW input permits CLK to propagate
88 R/W\ Input Read/Write: This input determines the cycle type when ADV/LD\ is LOW and is the
AS5SS128K36
Rev. 2.0 12/00
SA0
SA1
SA
BWa\
BWb\
BWc\
BWd\
Input Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must meet the setup
and hold times around the rising edge of CLK. Pins 83 and 84 are reserved as
address bits for the higher-density 8Mb and 16Mb ZBL SRAMs, respectively. SA0 and
SA1 are the two least significant bits (LSB) of the address field and set the internal
burst counter if burst is desired.
Input Synchronous Byte Write Enables: These active LOW inputs allow individual bytes to
be written when a WRITE cycle is active and must meet the setup and hold times
around the rising edge of CLK. BYTE WRITEs need to be asserted on the same cycle
as the address. BWa\ controls DQa pins; BWb\ controls DQb pins; BWc\ controls
DQc pins; BWd\ controls DQd pins.
throughout the device. When CKE is HIGH, the device ignores the CLK input and
effectively internally extends the previous CLK cycle. This input must meet setup and
hold times around the rising edge of CLK.
only means for determining READs and WRITEs. READ cycles may not be converted
into WRITEs (and vice versa) other than by loading a new address. A LOW on this pin
permits BYTE WRITE operations and must meet the setup and hold times around the
rising edge of CLK. Full bus-width WRITEs occur if all byte write enables are LOW.
Austin Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
2
SRAM
AS5SS128K36
Austin Semiconductor, Inc.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
TQFP PINS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
64 ZZ Input Snooze Enable: This active HIGH, asynchronous input causes the device to enter a
89 CLK Input Clock: This signal registers the address, data, chip enables, byte write enables and
98, 92 CE\, CE2\ Input Synchronous Chip Enable: These active LOW inputs are used to enable the device
97 CE2 Input Synchronous Enable: This active HIGH input is used to enable the device and is
86 OE\
85 ADV/LD\ Input Synchronous Address Advance/Load: When HIGH, this input is used to advance the
31 MODE
(a) 51, 52, 53, 56-59,
62, 63
(b) 68, 69, 72-75, 78,
79, 80
(c)1, 2, 3, 6-9, 12, 13
(d) 18, 19, 22-25, 28,
29, 30
15, 16, 41, 65, 91
5, 10, 14, 17, 21, 26
40, 55, 60, 66, 67, 71
76, 90
4, 11, 20, 27, 54, 61
70, 77
38, 39, 42, 43, 83, 84 64NC ---- No Connect: These pins can be left floating or connected to GND to minimize thermal
(G\)
(LBO\)
DQa
DQb
DQc
DQd
V
DD
Vss Ground Ground: GND
Q
V
DD
38, 39, 42, 43 DNU
83, 84 NF
Input Output Enable: This active LOW, asynchronous inputs enables the data I/O output
Input Mode: This inputs selects the burst sequence. A LO W on this pin selects linear burst.
Input/Output SRAM Data I/Os: Byte "a" is DQa pins; Byte "b" is DQb pins; Byte "c" is DQc pins;
Supply Power Supply: See DC Electrical Characteristics and Operating Conditions for range.
Supply Isolated Output Buffer Supply: See DC Electrical Characteristics and Operating
----
----
low-power standby mode in which all data in the memory array is retained. When ZZ
is active, all other inputs are ignored.
burst control inputs on its rising edge. All synchronous inputs must meet setup and
hold times around the clock's rising edge.
and are sampled only when a new external address is loaded (ADV/LD\ LOW). CE2\
can be used for memory depth expansion.
sampled only when a new external address is loaded (ADV/LD\ LOW). This input can
be used for memory depth expansion.
drivers. G\ is the JEDEC-standard term for OE\.
internal burst counter, controlling burst access after the external address is loaded.
When ADV/LD\ is HIGH, R/W\ is ignored. A LOW on ADV/LD\ clocks a new address
at the CLK rising edge.
NC or HIGH on this pin selects interleaved burst. Do not alter input state while device
is operating. LBO\ is the JEDEC-standard term for MODE.
Byte "d" is DQd pins. Input data must meet setup and hold times around the rising
edge CLK.
Conditions for range.
impedance.
Do Not Use: These signals may with be unconnected or wired to GND to
minimize thermal impedance.
No Function: These pins are internally connected to the die and will have the
capacitance of an input pin. It is allowable to leave these pins unconnected or
driven by signals. Pins 83 and 84 are reserved for address expansion.
AS5SS128K36
Rev. 2.0 12/00
Austin Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
3
Austin Semiconductor, Inc.
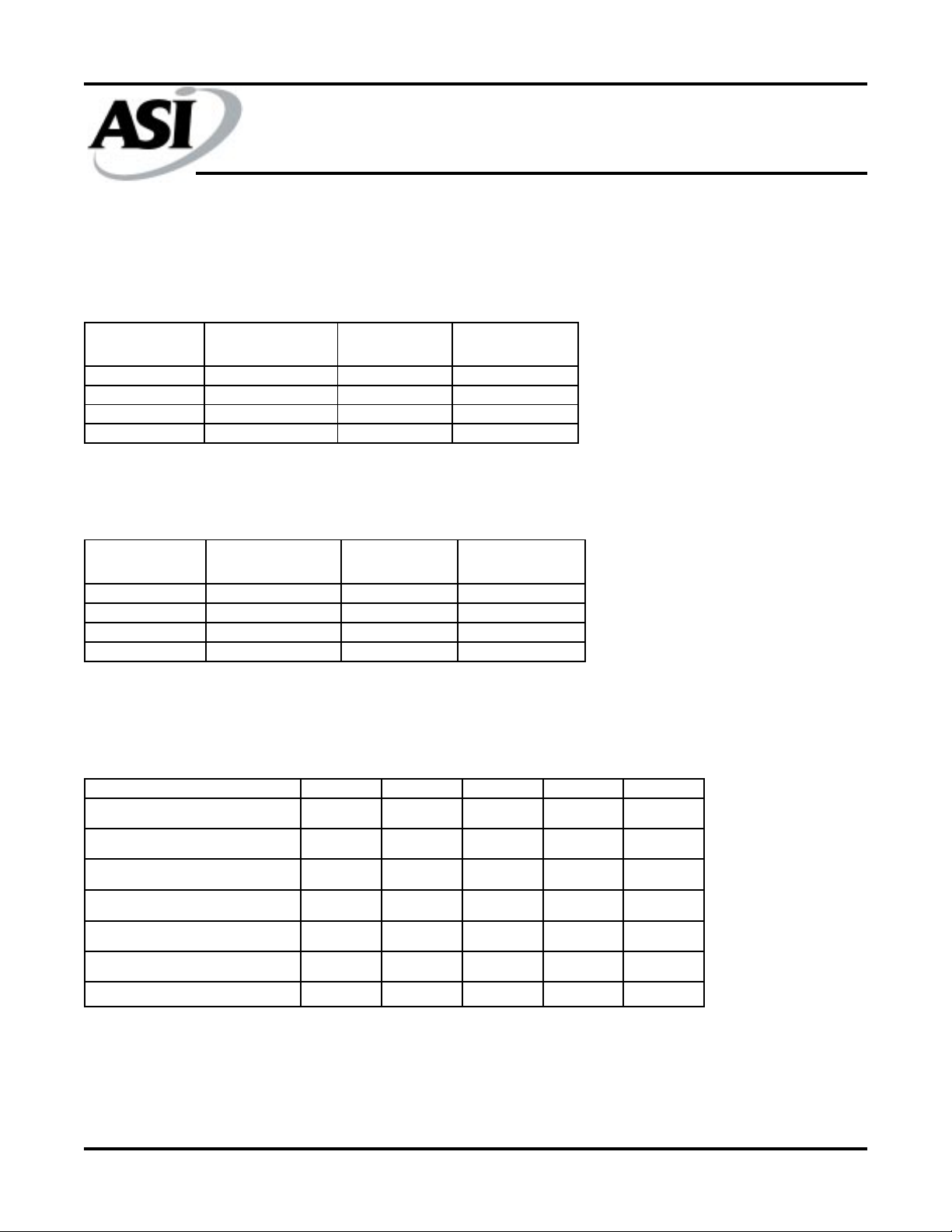
INTERLEAVED BURST ADDRESS TABLE (MODE = NC OR HIGH)
SRAM
AS5SS128K36
First Address
(external)
X...X00 X...X01 X...X10 X...X11
X...X01 X...X00 X...X11 X...X10
X...X10 X...X11 X...X00 X...X01
X...X11 X...X10 X...X01 X...X00
Second Address
(internal)
Third Address
(internal)
Fourth Address
(internal)
LINEAR BURST ADDRESS TABLE (MODE = LOW)
First Address
(external)
X...X00 X...X01 X...X10 X...X11
X...X01 X...X10 X...X11 X...X00
X...X10 X...X11 X...X00 X...X01
X...X11 X...X00 X...X01 X...X10
Second Address
(internal)
Third Address
(internal)
Fourth Address
(internal)
PARTIAL TRUTH TABLE FOR READ/WRITE COMMANDS*
FUNCTION R/W\ BWa\ BWb\ BWc\ BWd\
READ H XXXX
Write Abort/NOP L HHHH
Write Byte a (DQa, DQPa)
Write Byte b (DQb, DQPb)
Write Byte c (DQc, DQPc)
Write Byte d (DQd, DQPd)
2
2
2
2
LLHHH
LHLHH
LHHLH
LHHHL
Write all bytes LLLLL
* NOTE: Using R/W\ and byte write(s), any one or more bytes may be written.
AS5SS128K36
Rev. 2.0 12/00
4
Austin Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.

Austin Semiconductor, Inc.
17
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIA GRAM
SRAM
AS5SS128K36
SA0, SA1, SA
CLK
CKE\
17 17 15 17
ADDRESS
REGISTER
MODE
K
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER
ADV/LD\
BWa\
BWb\ DQs
BWc\
BWd\
R/W\
OE\
CE\
CE2
CE2\
WRITE REGISTRY AND
DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
READ
LOGIC
ADV/LD\
SA1
SA0
K
D1
D0
BURST
LOGIC
SA1'
Q1
SA0'
Q0
17
WRITE
DRIVERS
128K X 9 X 4
MEMORY
ARRAY
INPUT
REGISTER
O
D
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
E
A
T
A
S
T
E
E
R
I
N
G
U
T
P
U
T
B
U
F
F
E
R
S
E
NOTE: The Functional Block Diagram illustrates simplified device operation. See Truth Table, pin descriptions and timing diagrams for detailed
information.
AS5SS128K36
Rev. 2.0 12/00
5
Austin Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
 Loading...
Loading...