Page 1

Service Training
Audi TT Coupé ´07 - Body
Self-Study Programme 383
Page 2

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi-Space-Frame ASF® of the Audi TT Coupé
The development targets for the bodyshell of the Audi TT
With a weight advantage of 48 % over a comparable all-steel bodyshell, in addition to an optimised weight
distribution, the new composite aluminium-steel spaceframe body of the Audi TT marks yet another milestone in the development of modern Audi bodyshells.
Crash safety of the bodyshell is enhanced by means of load-bearing structures at the front end, sides and rear
end, with a heavy emphasis on pedestrian safety.
To ensure efficient volume bodyshell production, various new joining and production techniques are
employed.
The repair concept is based heavily on the well-known aluminium repair concept. However, of course, the
materials combination of aluminium and steel necessitated that new approaches be taken.
383_001
Page 3

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Contents
Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Technological concept . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Contact corrosion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Combination of steel and aluminium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Comparison of ASF concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Joining techniques and production processes
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Punch riveting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Clinching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
MIG welding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Resistance spot welding and MAG welding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Structural bonding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
New joining technique: solid punch riveting (Kerb-Konus riveting) . . . . . . . . . . 16
New joining technique: Flow Drill screwing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
New joining technique: aluminium laser welding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Repair concept
Aluminium repairs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Steel repairs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Aluminium-steel repairs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Workshop equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Qualification of aluminium. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Bodyshell safety concept
Head-on collision, side impact and rear collision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Pedestrian safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Electromechanical rear spoiler
The self-study programme teaches the design and function of new vehicle models,
new automotive parts or new technologies.
The self-study programme is not a repair manual!
All values given are intended as a guideline only and refer to the software version valid at the time of
preparation of the SSP.
For maintenance and repair work, always refer to the current technical literature.
NoteReference
Page 4
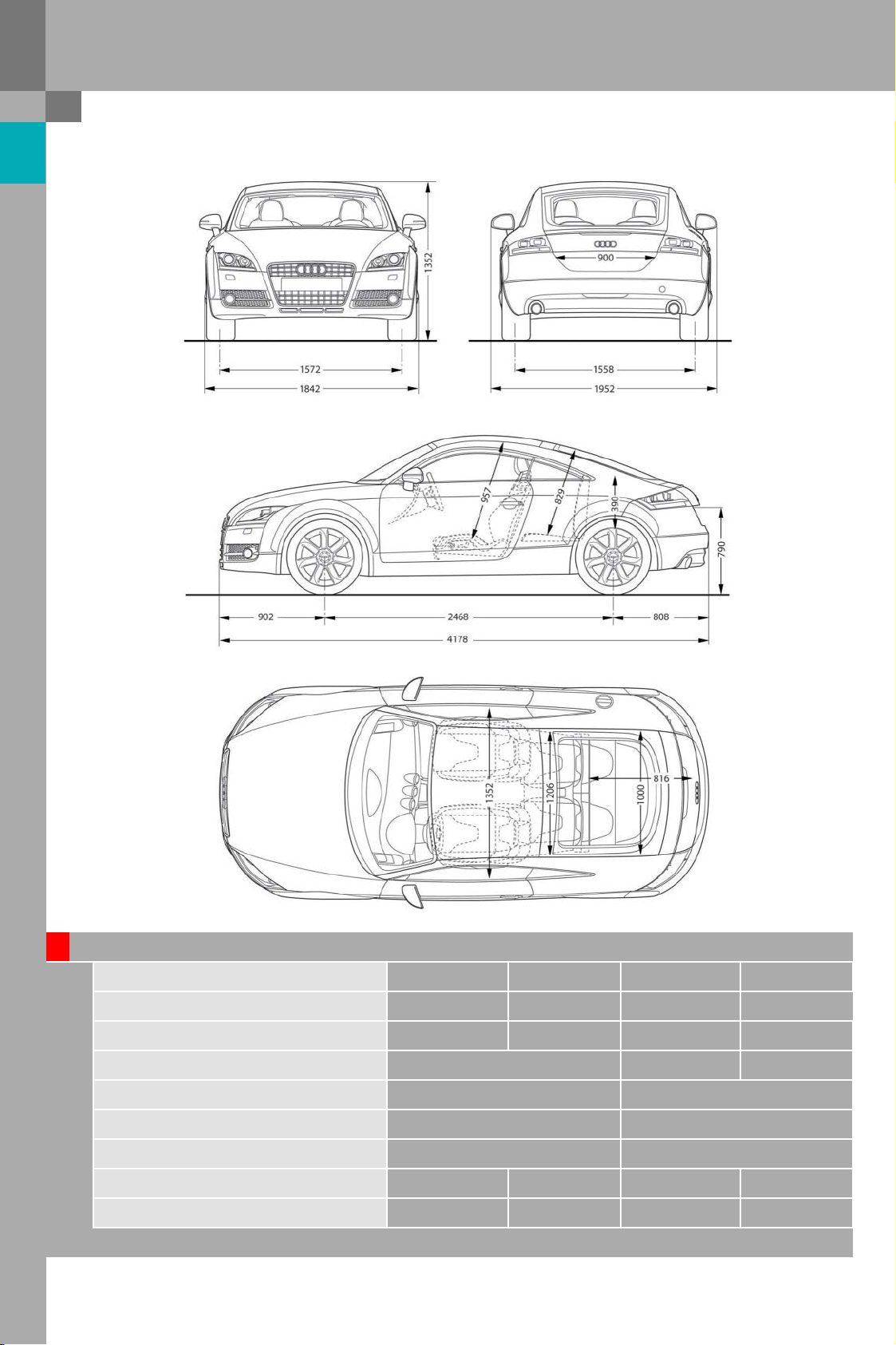
Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
Dimensions
383_002
Audi TT Coupé ’ 07 2,0 3,2 quattro
Transmission Manual gearbox S tronic Manual gearbox S tronic
Kerb weight without driver in kg 1260 1280 1410 1430
Max. perm. gross weight in kg 1660 1680 1810 1830
cw (rear spoiler extended) 0.3 0.3 0.31
Boot capacity in l 290 (700*) 290 (700*)
Max. power output in kW 147 (200 bhp) 184 (250 bhp)
vmax in kph 240 250
Acceleration 0-100 kph in s 6.6 6.4 5.9 5.7
Fuel consumption in l/100 km 7.7 7.7 10.3 9.4
* with the rear-seat back folded forward
4
Page 5

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Technological concept
Sheet-steel parts are used for the first time in the
ASF of the new Audi TT in addition to aluminium
castings, aluminium extruded sections and aluminium sheet-metal parts. Collectively, they make up
the body structure. Vehicle weight distribution has
been optimised by using sheet-steel parts in the
rear body section. This has a direct bearing on
sporting characteristics, such as driving dynamics
and acceleration as well as safety characteristics,
such as stopping distance and driving stability
In spite of the partial use of sheet-steel parts, the
total body weight of 277 kg, including attachments
such as doors and lids, is considerably less than
that of a comparable all-steel body.
Although the new TT has grown in size, the gross
weight of the vehicle has been reduced through the
use of the aluminium-steel bodyshell.
The body structure of the new Audi TT has higher
strength and 50 % higher torsional rigidity than its
predecessor.
Aluminium extruded sections
Sheet-aluminium parts
Aluminium castings
Sheet-steel parts
383_003
5
Page 6

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
Contact corrosion
Aluminium has a passivating oxide surface layer
which protects the material underneath from corrosion. This is why an unpainted aluminium part normally does not corrode.
However, if there is contact between aluminium and
a metal higher up in the electrochemical series than
aluminium and if an electrolyte, such as salt water,
is present in this region, contact corrosion will
occur.
Contact corrosion
The greater the difference in potential, the greater
the contact corrosion. As aluminium is normally the
lesser noble metal, it degrades.
383_005
Schematic of contact corrosion with example
Contact corrosion can only be prevented by taking
measures to stop the flow of electrical current
induced by the potential difference between
the two metals. This is best achieved by painting the
surfaces. However, the risk of corrosion is high even
if a tiny amount of paint damage occurs.
Reference
For detailed information on contact corrosion,
please refer to Self-Study Programme 239 "Audi
A2 - Body" .
383_004
In the case of the Audi TT, the following anti-corrosion measures have been taken:
– coating of all steel screws and fasteners such as
self-piercing rivets
– Galvanising of all sheet-metal parts (zinc and alu-
minium have a smaller potential difference than
steel and aluminium)
– Insulation by means of adhesive
– Sealing of aluminium-steel joints
6
Page 7
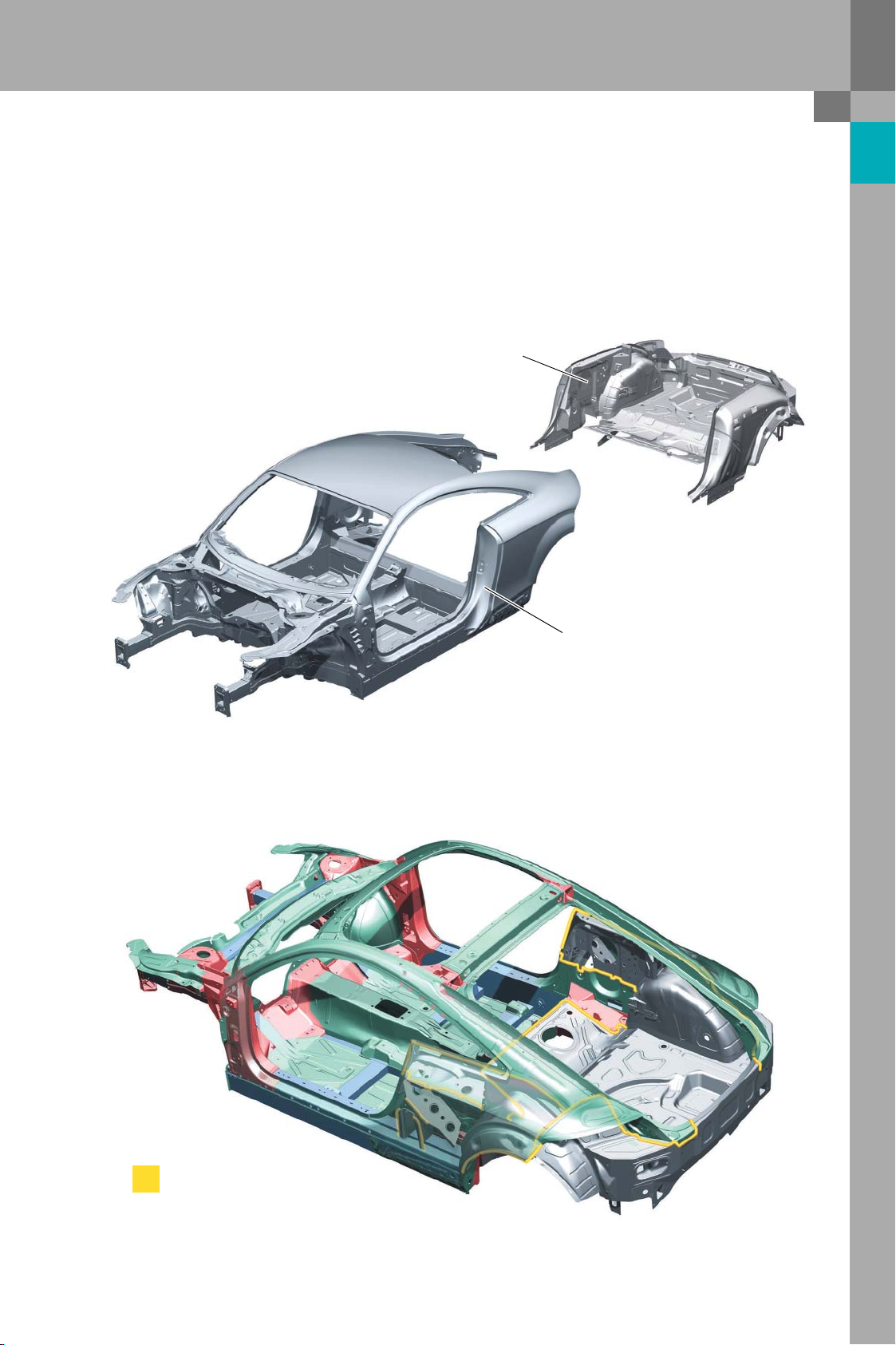
Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Joining steel and aluminium
One of the challenges for the development of the
Audi TT bodyshell was the attachment of the sheetsteel rear-end parts to the aluminium body assemblies.
Thermal joining processes such as MIG welding can
be ruled out because it is not possible by these
means to make a joint which has the requisite structural and dynamic strength and will not result in
contact corrosion.
Steel
Aluminium
383_011
Aluminium-steel connections
383_006
7
Page 8
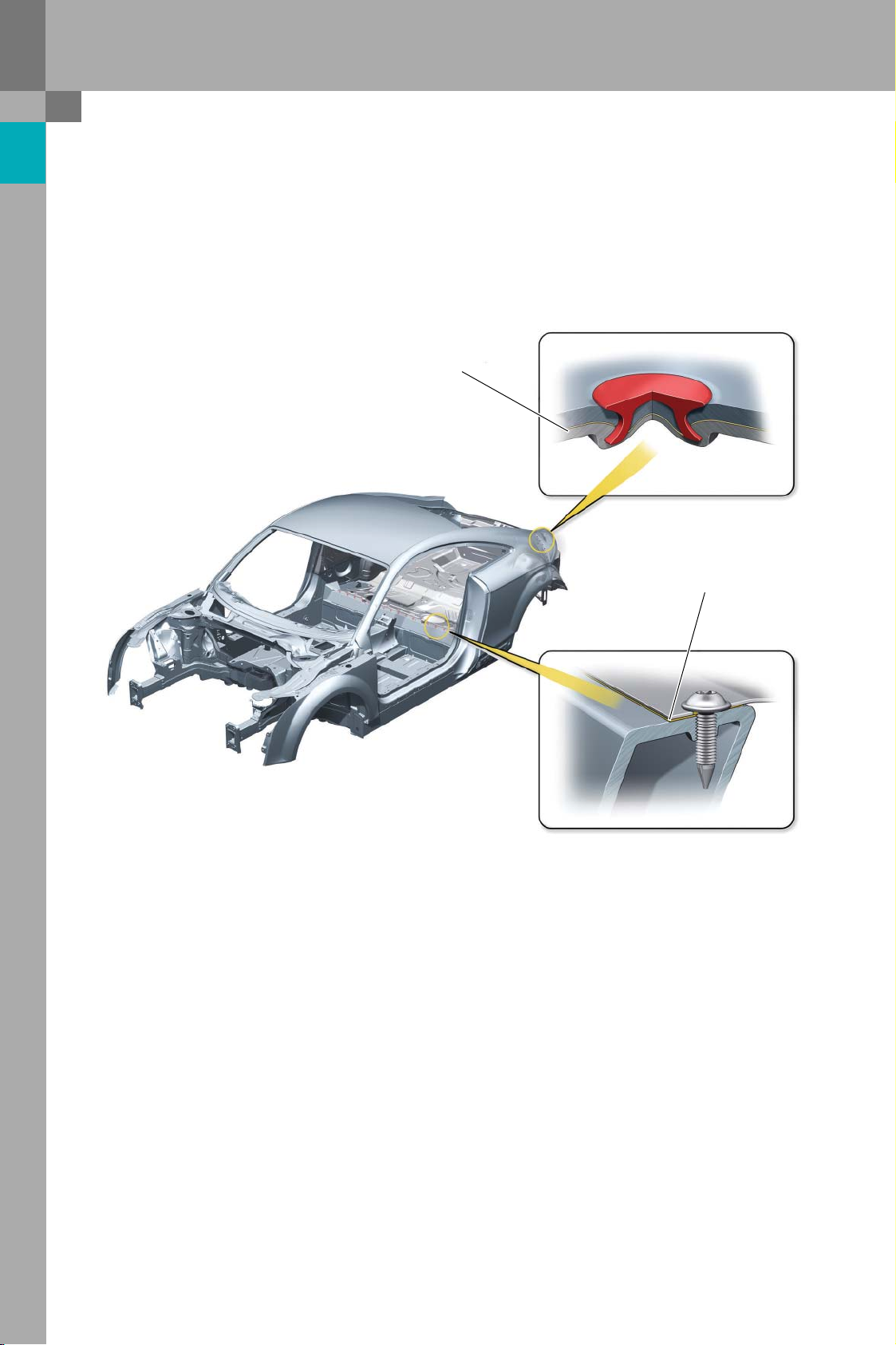
Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
Special requirements are made with regard to the
strength and corrosion protection of the joints
between aluminium body parts and steel parts.
Adhesive
This is ensured by non-thermal joining of parts
using coated self-piercing rivets and special screws
in combination with bonding.
Adhesive
Aluminium and steel joints with faulty corrosion protection can exhibit much higher corrosion rates than
all-aluminium joints or all-steel joints.When making
aluminium-steel joints, therefore, highest standards
of quality must be maintained at all times during the
production process and in the service workshop.
383_012
Adhesive bonding is the basis for the corrosion protection of corrosion-susceptible aluminium/galvanised steel joints in the bodyshell of the Audi TT.In
this way, the mating materials are superficially insulated, thus suppressing corrosion processes at the
point of contact. As a further measure, all composite joints either sealed with PVC or coated with wax
preservative after the cataphoretic dip coating (KTL)
process.
8
Page 9

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
This illustration shows clearly what effects contact
corrosion can have if adequate corrosion protection
is not provided. A this joint, the flange was sealed in
the bodyshell without using adhesive.
Seal
Seal
The aluminium sheet shown here exhibits severe
contact corrosion, which has resulted in mechanical
failure of the punch riveted joint.
383_007
By way of a comparison, this illustration shows the
same flange with an adhesive bond and sealing.
Seal
Adhesive
Seal
In this case, the aluminium sheet showed no damage due to contact corrosion after exposure to identical environmental conditions.
383_008
9
Page 10
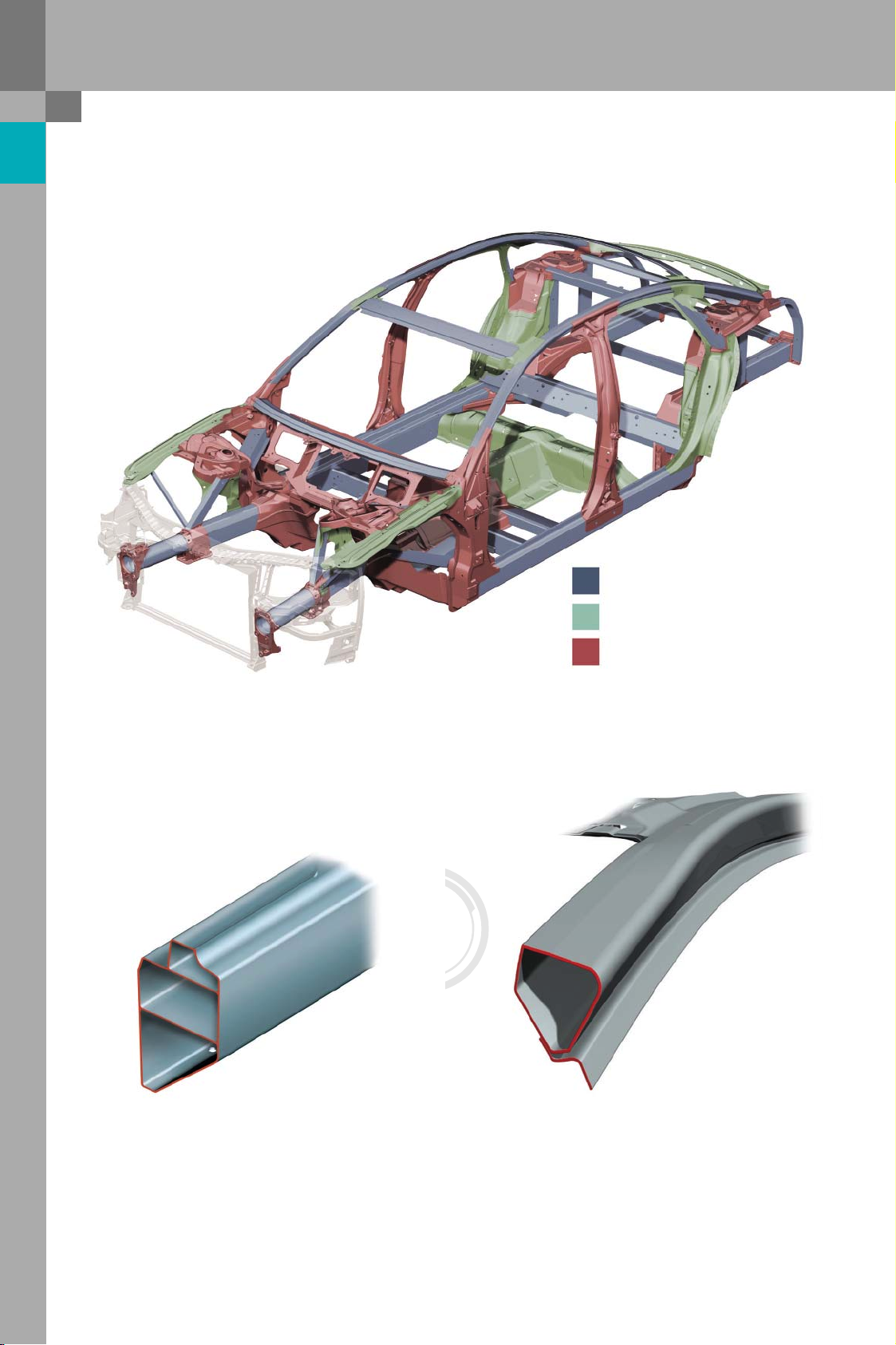
Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
Comparison of ASF concepts
Audi A8 (2003 ➔)
Aluminium extruded sections
Sheet aluminium parts
Aluminium castings
383_013
383_014
Sill section Audi A8
Three-chamber extruded section
10
383_017
A-post, Audi A8
Single-chamber extruded section
Page 11

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Audi TT (2006 ➔)
Aluminium extruded sections
383_016
Sill section, Audi TT
Four-chamber extruded section
Sheet aluminium parts
Aluminium castings
Sheet-steel parts
383_009
383_015
A-post, Audi TT
Sheet-aluminium sections (interior/exterior)
11
Page 12

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Joining techniques and production processes
Overview
In addition to well-known processes such as MIG welding or punch riveting, the joining techniques of Flow
Drill screwing and Kerb-taper riveting are used for the first time on the Audi TT.
In the production process, a laser cleaning method is used for cleaning before the roof drip moulding is
attached by welding.
Riveted joint
383_019
Flow-Drill screw connection
Clean Laser
Technology Process Quantity per vehicle
383_018
383_020
Mechanical
joining techniques
Thermal
joining techniques
Punch riveting
Flow Drill screwing
Solid punch riveting (Kerb-Konus)
Clinching
MIG welding
Laser welding
Resistance spot welding
MAG welding
Stud welding
1615 pce.
229 pce.
96 pce.
164 pce.
21462 mm
5309 mm
1287 spots
809 mm
234 pce.
Bonding technology Bonding 97156 mm
Machining technology Milling
12
Drilling
Thread cutting
Brushing
Roll seaming
Clean lasering
188 mm
16 pce.
8 pce.
2300 mm
26737 mm
4000 mm
Page 13

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Punch riveting
Punch riveting is one of the principal joining techniques used on the bodyshell of the new Audi TT. This technique is used for joining aluminium body parts and for joining aluminium body parts to steel body parts.
The process has been in use since launch of the Audi A2. Self piercing rivets with two different diameters and
lengths are used in the Audi TT.
383_032
Punch riveting process
Applications of punch riveting
383_051
Clinching
With clinching, the metal sheets to be joined are clamped between a die and a blankholder. The sheets are
then pushed down into the die by a punch to form an interlocking joint. However, joints produced in this way
is not as strong as joints produced by punch riveting, for example.
In the Audi TT, this technology is used on attachments such as doors and lids. Several clinched joints are also
located in the area of the B-post and rear wheel arch. In this area, aluminium sheets as well as steel and aluminium sheets are clinched together.
Clinching process
383_052
Applications of clinching
383_053
13
Page 14

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Joining techniques and production processes
MIG welding
Aluminium parts have largely been joined by means of metal inert gas welding since the launch of the Audi
aluminium bodyshell in the Audi A8 (1994) . This technique is principally used to make joints between castings
and extruded sections, as well as sheet-metal parts.
This joining technique is notable for producing high-strength joints, but it introduces a great deal of heat into
the joint and has a relatively slow process speed.
383_054
MIG welding process
Applications of MIG welding
383_055
Resistance spot welding and MAG welding
The usual techniques of resistance spot welding and, to a lesser extent, metal active gas welding (MAG welding) are used for joining sheet steel body parts in steel body manufacturing.
383_056
Resistance spot welding process
Applications of MAG welding
Applications of resistance spot welding
14
383_057
Page 15

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Structural bonding
In certain areas, adhesive bonding is used supplementary to clinched joints and punch riveted joints, solid
punch riveted joints, Flow Drill screw connections and resistance spot welds. This improves joint strength.
Adhesive bonding is also used for strengthening of seam joints, e.g. in the rear wheel arch. In other areas of
the body, adhesive beads are used for sealing and insulation between aluminium and steel sheets, as well as
for noise reduction.
Structural bonding process in production
383_058
Applications of structural adhesive
383_059
15
Page 16

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Joining techniques and production processes
New joining technique: solid punch riveting (Kerb-Konus riveting)
Solid punch riveting or Kerb-Konus riveting involves the use of aluminium or coated stainless steel rivets. In
contrast to punch riveting, the rivet is punched through both sheets to be joined.
Unlike steel rivets, aluminium solid punch rivets can be reworked mechanically. This is the case with the joint
between the body side section and the drip moulding. However, the strength of solid punch riveted joints is
inferior to that of punch riveted joints.
383_060
383_073
Solid punch riveting process in production
Solid punch riveting process
383_061
Micrograph of a solid punch riveted joint
Information on the repair concept
Aluminium solid punch rivets are used in the C-post drip moulding area, while coated stainless steel solid
punch rivets are used in the region of the roof frame. Stainless steel rivets must not be drilled out or ground,
due to the risk of corrosion.
Applications of solid punch riveting
16
383_048
Page 17

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
New joining technique: Flow Drill screwing
Automatic direct screwing enables joints to be made between any materials, even if these materials can be
accessed from one side only. A special coated screw is driven under high surface pressure through a hole in
the outer part to be joined. The lower part is not predrilled. The pressure and rotational speed soften the
material and allow the screw to be inserted.
383_062
Flow Drill screwing process
Flow Drill
Screw
383_074
Screwing process in production
383_063
Micrograph of a Flow Drill screw connection
Information on the repair concept
Flow Drill screws can be removed in the service workshop and replaced with new screws. In case of thread
damage, screws are also available in oversize (M6 instead of M5) . For use in new parts, it may be necessary to
predrill the material.
Applications of Flow Drill screwing
383_064
17
Page 18

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Joining techniques and production processes
New joining technique: aluminium laser welding
(invisible roof seam)
Laser welding has been used for joining aluminium body parts since the launch of the Audi A2. In most cases,
sheet-metal parts are welded onto castings or extruded parts. The invisible joint in the roof area is joined
using a new joining technique: laser welding.
Laser beam
Evaporating metal vapour
Laser-induced plasma
Liquid melt zone
Solid melt zone
Welding wire
Vapour / plasma / channel
Direction of welding
383_066
Laser welding process in production
Micrograph of the roof frame and roof panel joint
383_065
383_025
Applications of laser beam welding
Invisible roof seam
Applications of laser beam welding
18
383_067
Page 19

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
To ensure consistent laser welding of aluminium parts, the parts to be welded must have a perfectly clean surface. This is achieved either by washing the component parts followed by chemical pickling or by using the
new Laser Clean process.
A controlled laser beam removes all residues from the surface by heating it for a short time. Parts cleaned
using this method can be directly laser-welded.
383_069
383_068
Laser Clean process in production
Micrograph of a laser-welded seam with
Laser Clean (above) and without cleaning (below)
383_075
The joint between the roof frame and roof panel is reworked and surface finished automatically in the production line by means of a brushing process.
383_071
Brushing process in production
383_070
383_072
Laser weld seam before (above) and
after the brushing process (below)
19
Page 20

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Repair concept
Aluminium repair
The repair concept for the all-aluminium body parts
is similar to that for the repair of previous Audi aluminium-bodied vehicles.
The front end of the vehicle is designed in such a
way that the bumper beams and bolted crash boxes
can be replaced after minor collisions up to approx.
15 kph.
Bumper beam 1
Crash box
If the vehicle structure is damaged, beam 1 can also
be replaced by undoing the screw connection. All further damage to the vehicle front end can only be
repaired by welding suitable genuine parts into place.
Bumper beam
Screw connections
Bumper beam 2
383_023
383_024
Joint between beam 1 and beam 2
20
Page 21

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
The four-chamber extruded section is located
beneath the sill moulding.A special repair method
was developed for damaged outer chambers. When
repair work is needed, the extruded section is split
vertically so that the two rear chambers including
the centre ridge of the four-chamber profile remain.
A dual-chamber genuine part developed specially
for this repair solution is welded to the remainder of
the sill profile using a continuous MIG weld seam at
the top and bottom. In addition, the U-shaped channel in the genuine part is filled with an adhesive
bead which provides additional strength and eliminates noise transmission between the two sills.
New part
MIG weld seam
Adhesive bead
383_039
21
Page 22

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Repair concept
Steel repairs
The rear end of the Audi TT is only area where it is
possible to carry out repair work involving only steel
parts and where the aluminium-steel joint is fully
intact.
This repair work can be carried out on the
– rear end section
– rear side member (body side section undamaged)
– rear floorpan
Basically, the repair procedure is the same as for allsteel-bodied vehicles. Due to the danger of contact
corrosion in aluminium body parts, however, special
safety precautions must be taken. Grinding dust of
steel parts, particularly flying sparks caused by cutting or welding work, must not be allowed to drop
onto the aluminium parts.
This also applies to painted aluminium parts! Red
hot steel parts can damage the paintwork and steel
particles can come into contact with the aluminium
body parts, leading to contact corrosion on the
undamaged aluminium body.
Therefore, the complete bodyshell must be protected carefully when carrying out steel repairs. This
is done by using suitable protective covers and by
masking the body with masking tape. Furthermore,
cutting work may only be performed using a body
saw. If grinding work is needed, this must be done
using grinding discs which produce little or no flying sparks. The spot welding machine should be
used for welding work where possible, because it
produces less weld spatter during the welding process.
body parts which must be covered when carrying out steel repairs
Damage to be
repaired
383_040
22
Page 23

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Aluminium-steel repairs
In the case of body side or rear-end damage, both
aluminium and steel body parts may become damaged. This is the case, for example, when the body
side section (aluminium) and rear wheel arch (steel)
are damaged. After removing the damaged parts,
the new genuine parts are installed in accordance
with the repair procedures described in the previous
sections. Joining of steel and aluminium parts must
be carried out with the greatest care in order to
eliminate the possibility of future contact corrosion.
Two-component car body adhesive DA 001 730 A1
and rivets or screws are used for joining. As in
series production, an insulating layer is placed
between the two materials to prevent contact corrosion. When welding steel body parts, the aluminium
parts must be carefully covered and masked!
Reference
All body repair work must be performed in
accordance with the guidelines set out in the
current workshop literature!
23
Page 24

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Repair concept
Workshop equipment
A special tool is required for repair work on aluminium-bodied vehicles. The basis is work scope 2010.
In addition to the special equipment and machines
for stud welding, dent removal, bonding and riveting, the aluminium welding technology is of special
importance.
383_026
Aluminium body dent removal tools VAS 5196 and VAS 6049
383_028
Aluminium inert gas welder V.A.G 2001B
Aluminium inert gas welder VAS 6388
383_076
Cordless punch riveter VAS 5279A
383_029
There are now two appliances with modern control
systems which
are ideal for welding work on the Audi aluminium
body.
Reference
For further information on the workshop equip-
The welding appliances, when used properly, produce perfect aluminium welded joints which have
optimum strength.
ment for Audi aluminium-bodied vehicles, refer
to the workshop literature and the Audi Service
Net.
24
Page 25

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Qualification of aluminium
A special knowledge and special skills are required
to repair aluminium bodyshells. A prerequisite for
successful body repairs is participation in the relevant training courses.
Particularly for welding work, certification of
employees according to international standard DIN
EN ISO 9606-2 is important.
EX 351
Welding
Aluminium Certificate
Repeat exam
AB 352
Aluminium technology
BT 350
Welding
Aluminium technology
Welding Certificate
EX 353
Audi TT
Aluminium technology
BT 351
Basics
Body
BT 352
Basics
Vehicle electrical
systems for car body
technology
BS 301 Occupant protection, airbags and belt ten-
sioners
BS 310 Selective use of technical information
BS 360 Vehicle diagnosis, testing and information
system VAS 5051
Reference
For further information on the qualifications in
aluminium technology, refer to the Audi Service
Net.
383_049
25
Page 26

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Car body safety concept
Head-on collision, side impact and rear collision
Likewise, in terms of crash safety, the new TT makes
no compromises. The front beams consist of aluminium extruded sections and aluminium castings.
In combination with the front beams and a subframe, they reduce and distribute the forces which
act on the car body during a head-on collision.
Large-sized beams in the rear end protect the occupant cell.High-strength aluminium beams in the
doors provide side impact protection. The aluminium bonnet is designed to all requirements for
pedestrian safety.
The simulation provides information on the collision
behaviour of the body structure at a very early stage
in the development process. For this purpose, calculations are done on the basis of the available car
body data using the Finite Elements Method. The
results are incorporated into the ongoing design
process, thus allowing the body structure design to
be optimised in respect of the relevant crash loads.
Simulation Euro NCAP head-on collision
383_031
26
Page 27

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
To check the theoretical results and to meet statutory requirements, actual tests are conducted.
Euro NCAP head-on collision (64 kph with partial overlap)
Various test conditions are simulated on the basis of
the applicable standard.
383_041
Euro NCAP side impact (50 kph)
383_042
ECE and Japan rear collision (50 kph)
383_043
27
Page 28

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Car body safety concept
Pedestrian safety
Pedestrian safety is an increasingly important factor. Various measures were implemented in the new
Audi TT in order to meet the safety requirements.
When designing the bonnet, importance was
attached to a stable design which yields to absorb
head impacts. This is achieved by the honeycomblike structure of the car body inner panelling.
The overall concept provides for deformation zones
between the bonnet and the units or car body structural parts.
383_034
To reduce leg impact force at the front end, the
bumper cover has been decoupled and an impactabsorbing foam part has been integrated between
the bumper beam and bumper cover.
383_044
28
Page 29

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
The development tools "Simulation" and "Testing" were used for design.
Headform
(head impact)
Lower legform
(leg impact)
Head impact
383_035
To test the head impact a hemisphere which represents the head is catapulted onto the bonnet.
The relevant physical variables are determined, on
the basis of which conclusions are drawn regarding
impact loads.
Leg impact
Leg impact is simulated by means of a test configuration in which a test body similar to the actual body
part impacts the vehicle bumper.
383_036
383_037
29
Page 30

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Electromechanical rear spoiler
The new Audi TT has as standard an electrically
extendable rear spoiler. The extended rear spoiler
significantly increases driving stability at high
speeds. The spoiler extends automatically at a
speed of 120 kph and retracts at a speed of 80 kph.
At speeds of less then 120 kph, the rear spoiler can
be actuated manually with a switch in the centre
console.
The unit consisting of the rear spoiler module and
the spoiler wing is integrated in the boot lid of the
Audi TT. The rear spoiler module with drive unit,
input shaft and reversing mechanism (hinge) is
bolted with self-adjusting elements to the sheetsteel spoiler wing painted in the body colour.
Reference
For further information on operation, function
and diagnosis, refer to Self-study
Programme 382 "Audi TT Coupé ‘07 Electrical and Infotainment Systems“.
383_038
383_045
When repair work is needed, the spoiler wing can
be replaced separately. The rear spoiler module is
replaced completely in case of damage.
30
Page 31

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
SSP 380 Audi TT Coupé ‘07
–Body
– Occupant protection
–Engine
– Suspension system
– Electrical system
– Air conditioning
– Infotainment
Order number: A06.5S00.25.20
SSP 381 Audi TT Coupé ‘07 - Suspension System
–Front axle
–Rear axle
– Shock absorber system
– Brake system
Order number: A06.5S00.26.20
SSP 382 Audi TT Coupé ‘07 Electrical and Infotainment Systems
–Networking
–Bus topology
– Convenience electronics
– Infotainment
Order number: A06.5S00.27.20
SSP 383 Audi TT Coupé ‘07 - Body
– Audi Space Frame of the Audi TT
– Joining techniques and production processes
– Repair concept
– Car body safety concept
– Electromechanical rear spoiler
Order number: A06.5S00.28.20
Page 32

Protected by copyright. Copying for private or commercial purposes, in part or in whole, is not
permitted unless authorised by AUDI AG. AUDI AG does not guarantee or accept any liability
with respect to the correctness of information in this document. Copyright by AUDI AG.
Vorsprung durch Technik www.audi.de
383
All rights reserved. Technical
specifications subject to
change without notice.
Copyright
AUDI AG
I/VK-35
Service.training@audi.de
Fax +49-841/89-36367
AUDI AG
D-85045 Ingolstadt
Technical status: 05/06
Printed in Germany
A06.5S00.28.20
 Loading...
Loading...