Page 1
Service Training
Audi Q7 - New Driver Assistance Systems
z Audi side assist
z Optical parking system (OPS)
z Reversing camera
Self-study programme 375
Page 2

Driver assistance systems
The continuous improvement of vehicle safety is one of the foremost objectives in the development of new
vehicles. New driver assistance systems that have been introduced into series production for the first time on
board the Audi Q7 make a considerable contribution in this regard. On request, a number of innovative driver
assistance systems are also available in the Q7, for example the radar-based Audi side assist, the optical
parking system with audible and visual information and the reversing camera.
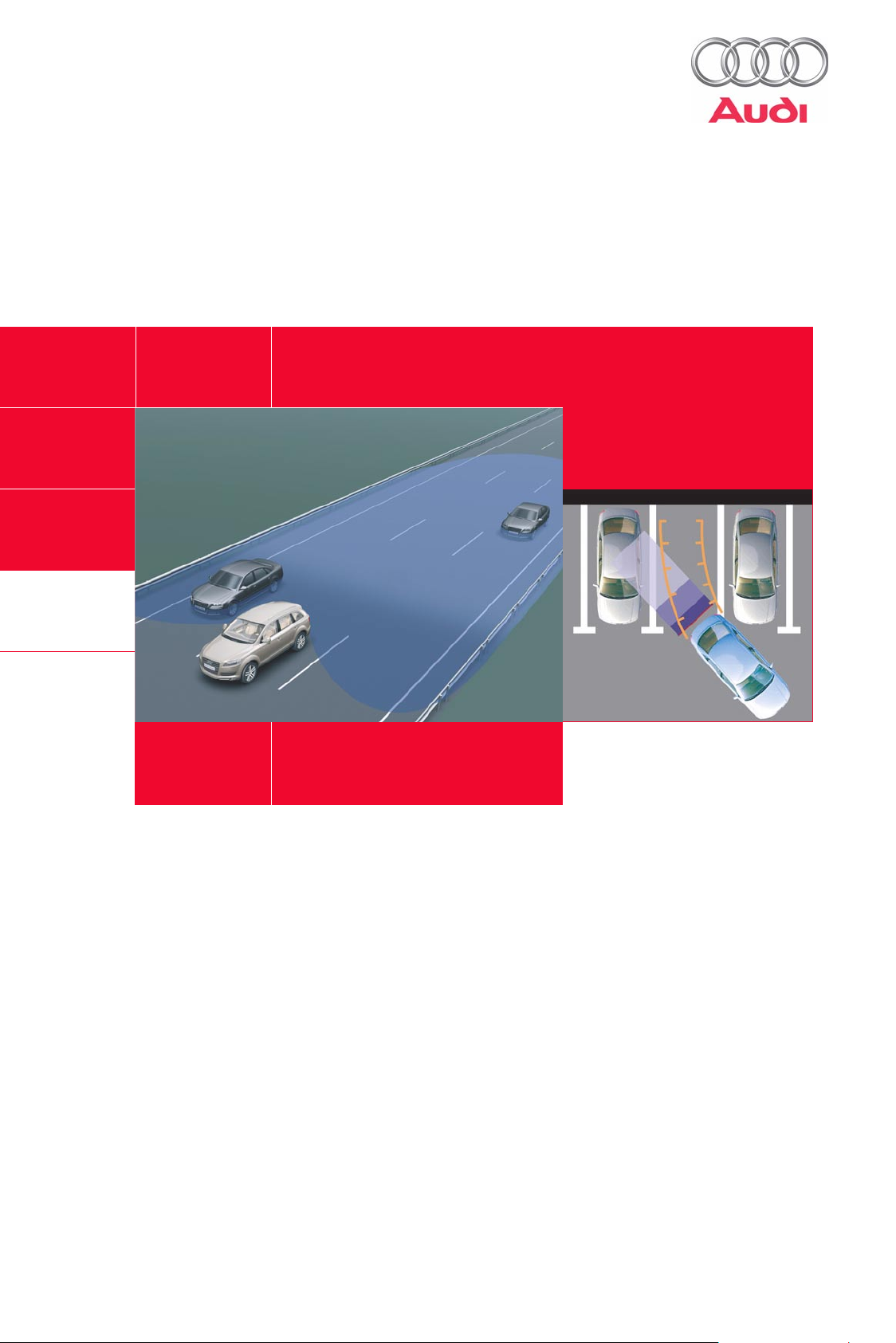
A frequent cause of accidents when changing lanes is that other vehicles are overlooked.
By continuously monitoring the adjacent lanes, in particular the area to the rear of the vehicle, the Audi side
assist supports the driver during overtaking and lane-change manoeuvres and thus makes a contribution to
active safety. The driver is alerted if one of the adjacent lanes is occupied by one or more road users. Despite
the system’s capability, the driver must always be aware that the system serves as an aid, but cannot take the
responsibility away from the driver for his/her own decisions. Despite the Audi side assist, it is still necessary
for the driver to turn his/her head, look in the side mirror and observe the traffic.
The electronic parking aid system has been further improved. Two new functions are now available to the
customer. The familiar acoustic parking aid system has been expanded by a graphic screen display in the
MMI. Using bar diagrams this provides the customer with a detailed depiction of the point at which a collision
may occur. The bar diagrams permit the distance from the obstacle to be estimated with precision.
The familiar acoustic feedback is retained.
Drivers who would prefer to get a picture of the situation behind the rear of the vehicle for themselves, can
have the image from a reversing camera displayed on the MMI screen. The camera which has been
integrated into the tailgate handle provides an ideal overview of the situation behind the vehicle. The camera
image appears automatically when reverse gear is engaged.
Taking the lead: With design & performance
Page 3

Contents
Audi side assist. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Optical parking system (OPS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Reversing camera. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
The self-study programme provides basic information on the design and function of new vehicle models,
new vehicle components or new technologies.
The self-study programme is not intended as a workshop manual.
The specified values only serve for better understanding and relate to
the software versions applicable at the time the SSP was compiled.
For maintenance and repair operations it is essential that you refer to the current technical literature.
NoteReference
Page 4

Audi side assist
Audi side assist in the Audi Q7
Introduction
The purpose of the Audi side assist is to monitor the area behind and to the side the vehicle using radar
sensors and assist the driver when changing lanes. The area monitored also includes the so-called "blind
spot" on the driver side and the front passenger side. Each vehicle side is fitted with a radar sensor for this
purpose.
If the Audi side assist detects a critical situation that could cause an accident during a lane change,
the system alerts and warns the driver. The driver is alerted through activation of the warning lamps in the
relevant exterior mirror and warned through the warning lamps flashing rapidly.
375_040
4
Page 5
Radar sensors and control units
The Audi side assist is equipped with two control
units, the side assist control unit J769 (master
control unit) and the side assist control unit 2 J770
(slave control unit). The master control unit forms a
single module with the right radar sensor, while the
slave control unit forms a single module with the
left radar sensor.
The master and slave control units are identical in
design. The main component is an electronic circuit
board with a digital signal processor as the central
processing unit. Among other functions, it is used
to record and track objects detected by means of
the radar sensors. The system is manufactured by
Hella.
375_001
The aerial circuit board with integrated transmitting
and receiving aerials is connected to the electronic
circuit board via a connector console.
The transmitting aerial comprises 40 copper
squares, whereas the 3 receiving aerials comprise 8
or 16 copper squares. The technical term for the
copper squares is "patch".
The physical properties of the reflected beams
picked up by the receiving aerials are evaluated by
the digital signal processor. Based on these
properties, the size, position and speed of the
object reflecting the beams is calculated.
A plastic cover, referred to as the "radom", is fitted
on the control unit.
This is made from a special plastic which is ideal for
allowing the radar beams to pass through, without
causing any significant losses.
Receiving aerials Transmitting aerial
375_002
375_003
5
Page 6

Audi side assist
Fitting locations
In the Audi Q7, the two control unit modules are located in the area of the rear bumper and fastened to the
end plate. The end plate is clipped to the bumper cover and bolted to the body. The bumper conceals the
modules, making them invisible from the outside, unlike the parking aid sensors. Because the bumper cover is
made of plastic, it does not represent an obstacle to radar beams.
The modules are installed at an angle of 22 degrees with respect to the vehicle transversal axis, providing
better coverage for scanning the side areas. They are inclined upwards at an angle of approx. 3 degrees.
Once fastened to the vehicle, precise calibration is conducted using the diagnostic tester and special
calibration tools.
Calibration and the tools required are described in more detail in a later chapter.
A mechanical fine adjustment, as familiar from the ACC, is not possible for the side assist sensors.
375_004
6
Page 7
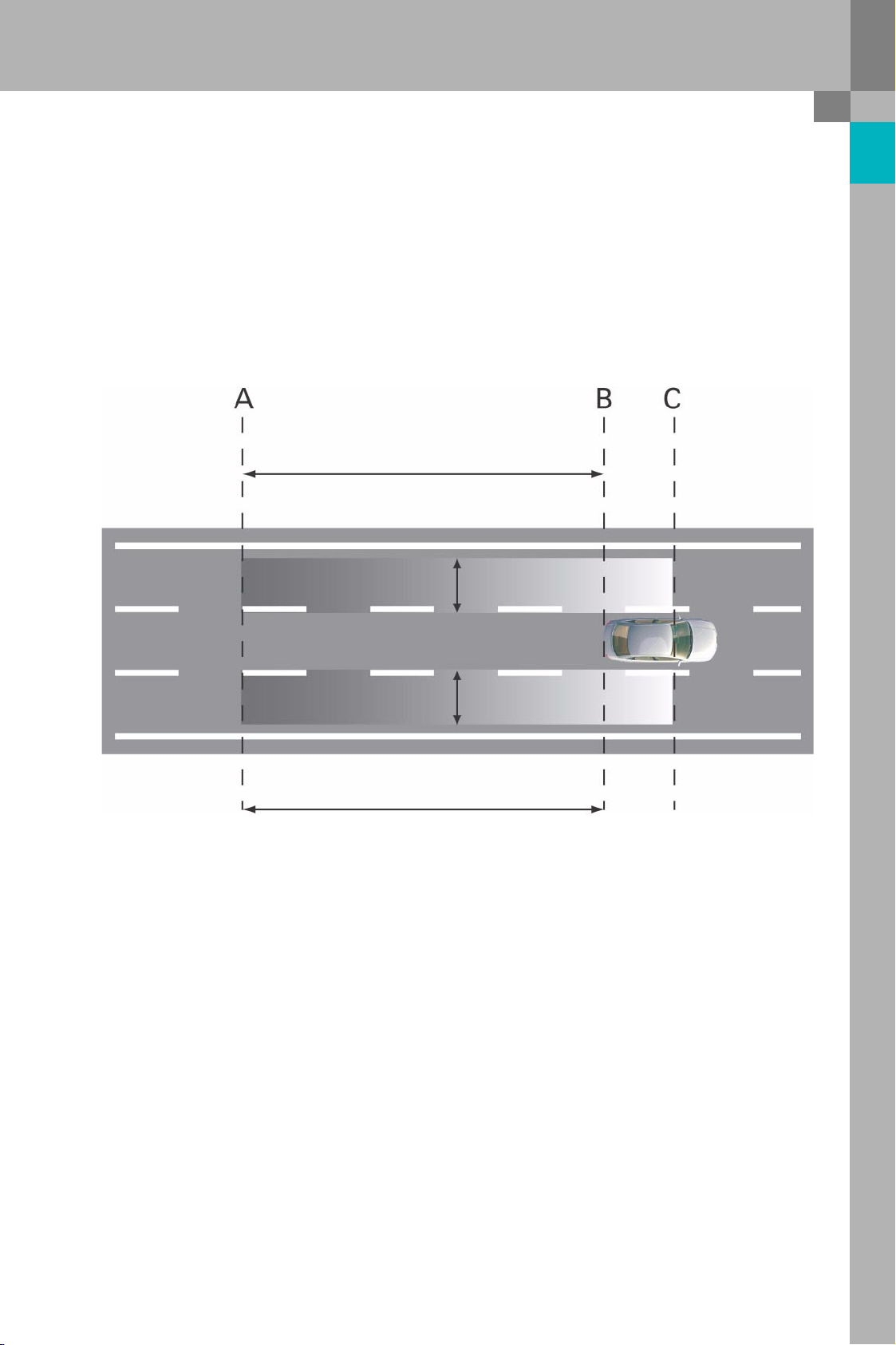
Radar sensor detection zone
The detection zone consists of areas to the rear and to both sides of the vehicle. The rear detection area
extends from the rear edge of the vehicle to approx. 50 metres rearwards. This corresponds to the grey area
between lines A and B. The side area extends from the rear edge of the vehicle to approximately the line of the
B-pillar, which corresponds to the grey area between lines B and C. The width of the grey areas measures
approximately 3.60 metres.
50 m
3.6 m
3.6 m
50 m
Sensor detection zone
375_005
The illustration of the sensor detection zone shows a straight stretch of road. On curved road sections,
the Audi side assist operates above a minimum curve radius of approx. 170 metres. If the radius of the curve
drops below the 170 m limit, the Audi side assist is deactivated because the emitted radar beams can no
longer monitor the full 50 metres of the rear detection zone. This deactivation threshold is provided with a
hysteresis of 30 metres. This means that if the Audi side assist has been deactivated due to the radius of the
curve, it is reactivated when the radius of a curve exceeds 200 m.
The course of the road is calculated by the side assist control unit by means of the yaw rate and the individual
wheel speeds from the ABS control unit J104. The curved detection zone during cornering is represented as a
straight road section by the software. This ensures that the basis of the assessment for the warning algorithm
used to determine whether or not the driver needs to be alerted is the same for straight roads and bends.
7
Page 8

Audi side assist
Warning lamps in the exterior mirrors
The Audi side assist warns or alerts the driver, as appropriate, of potential hazards during a lane change by
means of warning lamps integrated into the two exterior mirrors.
The usual service designations for these are: Side assist warning lamp in driver side exterior mirror K233 and
side assist warning lamp in front passenger side exterior mirror K234.
The two warning lamps K233 and K234 can be replaced individually, without having to remove the mirror
housing. This procedure is described in the Workshop Manual.
The warning lamps are activated directly by the side assist slave control unit J770.
They comprise four yellow LEDs.
375_006
If the Audi side assist recognises a critical situation in one of the two lanes, and no imminent lane change is
indicated, the driver is informed of this situation through illumination of the warning lamp in the relevant
exterior mirror. If an intended change of lane is indicated through actuation of a turn signal and the adjacent
lane is occupied, the driver is warned by the warning lamp flashing on and off four times.
The customer can adjust the brightness of the warning lamps to 5 different levels via the MMI.
The current ambient brightness measured by the rain and light sensor G397 is also used for determining the
brightness of the warning lamps.
8
Page 9
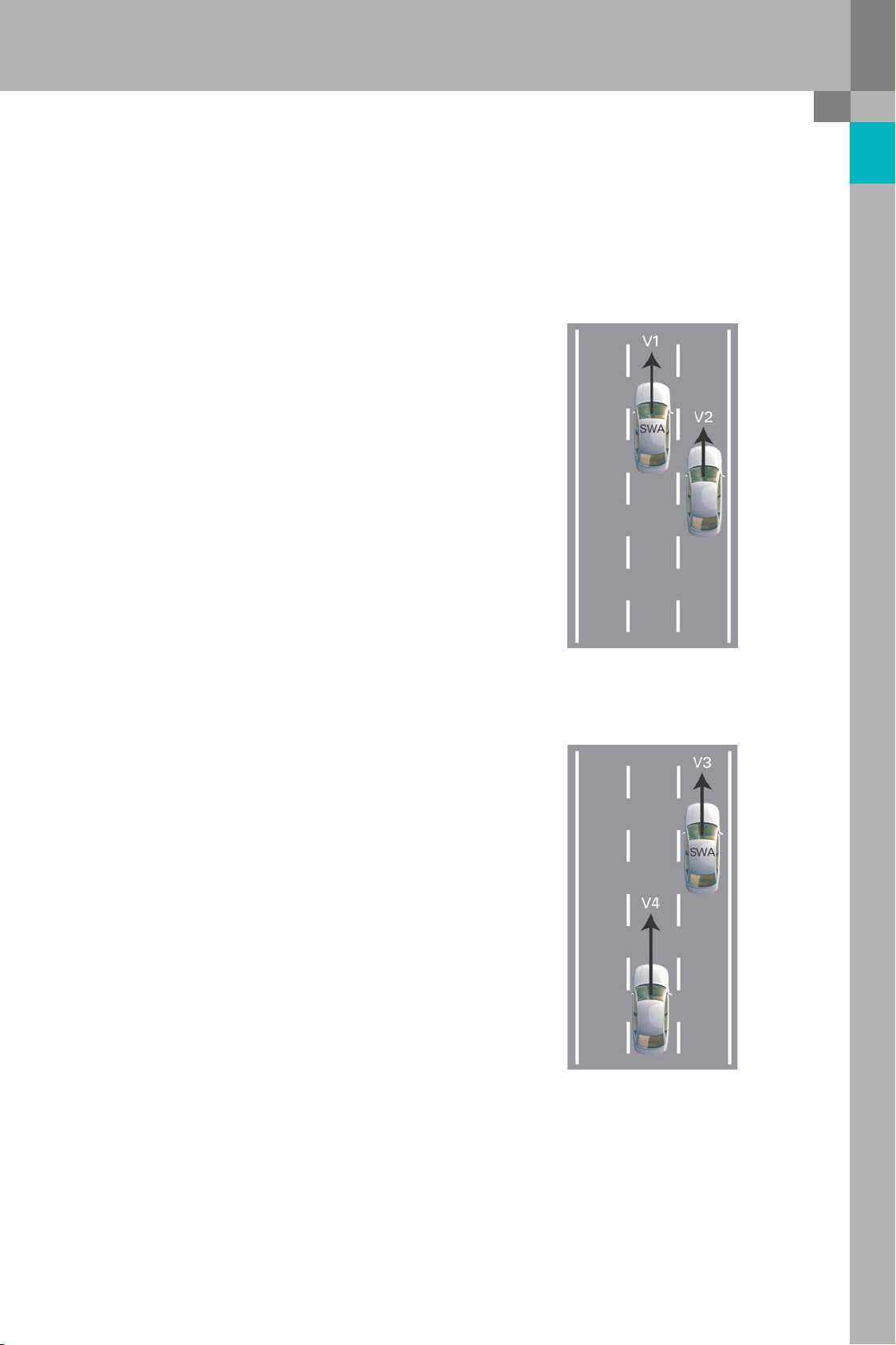
Two specific traffic situations
By way of an example, two typical traffic situations
resulting in a warning being provided by the Audi
side assist are described below:
Scenario 1
The vehicle with the Audi side assist is being driven
in the centre lane of a three-lane motorway and is
currently overtaking the vehicle on the right-hand
side. The speed difference between the vehicle with
Audi side assist (SWA) and the vehicle being
overtaken is less than 15 km/h. This small difference
in speed means that the overtaking manoeuvre will
take some time and that the vehicle being overtaken
will disappear into the "blind spot" at a certain
point. In this situation, the warning lamp in the right
exterior mirror must alert the driver that the
right-hand lane is occupied. If the driver of the
vehicle equipped with Audi side assist then
activates the right turn signal, the driver is warned
by four flashes in the right exterior mirror.
Scenario 2
The vehicle with the Audi side assist (SWA) is being
driven at a moderate speed in the right-hand lane of
the three-lane motorway. A vehicle in the centre
lane approaches from behind at a much faster
speed. The approaching vehicle is detected by the
Audi side assist, which activates the warning lamp
in the left exterior mirror. If the left turn signal is
now actuated nonetheless, the driver is warned of a
potential collision before changing lanes by means
of a flashing warning lamp.
The maximum distance between the two vehicles at
which the warning lamps are activated depends on
the speed difference between the two vehicles.
The greater the difference in speed, the greater the
maximum distance between the two vehicles at
which the driver is alerted to the imminent collision.
At the earliest, however, a warning can be issued
from a distance of 50 m, as 50 m is the upper limit of
the detection range of the radar sensors.
375_007
375_008
9
Page 10

Audi side assist
Operating the system
The side assist button E530 is located in the driver door, to the right of the central locking switch. The button
is used for switching the Audi side assist on and off. A red LED in the button indicates its current status. If the
LED is illuminated, this means that the Audi side assist is switched on. If the LED is not illuminated, the system
is either switched off or faulty. Every time the system is restarted it readopts the last valid system status.
When switched on, the Audi side assist may be either active or inactive.
Two conditions must be met in order for the system to be activated: the road speed must exceed a minimum
speed of 60 km/h and the current curve radius must not be less than 170 metres during cornering. If one of the
two conditions is no longer met, the Audi side assist switches to the inactive mode.
It should be noted, however, that the driver is not
provided with any indication as to whether the
system is in the active or inactive state.
375_009
10
Page 11

Adjusting the brightness of the warning lamps
Using the MMI, the customer can individually adjust
the brightness of the warning lamps in the exterior
mirrors. For this purpose, the "Audi side assist"
menu item in the Car menu of the MMI must be
selected and activated by pressing the rotary
control.
The brightness of the warning lamp can be set to
5 different levels. The third level is the factory
default. Having completed the selection, the
warning lamps are switched on for 2 s at the
selected brightness.
Personalisation
At the end of a journey, the brightness setting
selected by the driver is stored in the side assist
control unit J769 (master control unit) under the
vehicle key last used. This setting is reactivated for
the next journey made with this vehicle key.
User Log book
Display brightness
brighter darker
Systems Version
Car
375_010
11
Page 12
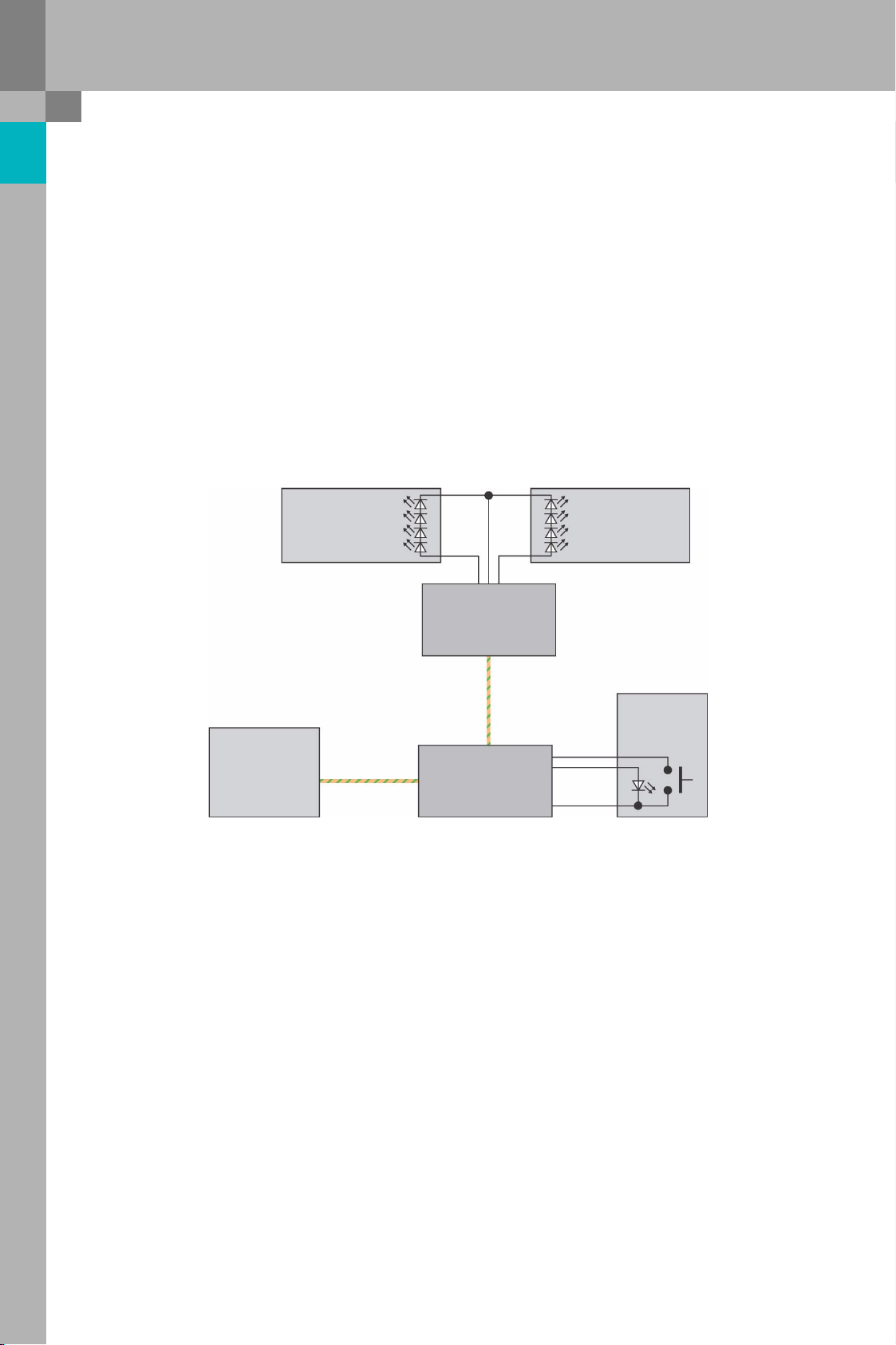
Audi side assist
Implementation of function in hardware and software
System circuit diagram
The master and slave control units exchange data via a dedicated high-speed CAN bus.
The master control unit is connected to the extended CAN, enabling data exchange with other bus modules
via the data bus diagnostic interface J533. The master control unit is also responsible for reading in the side
assist button E530, while the slave control unit actuates the two warning lamps K233 and K234 in the exterior
mirrors.
Data bus
diagnostic
interface
J533
Side assist
warning lamp
in driver side
exterior mirror
K233
Extended CAN
Side assist
control unit 2
- slave J770
Dedicated CAN
Side assist control unit
- master J769
Side assist
warning lamp in front
passenger side
exterior mirror
K234
Side assist
button
E530
375_011
12
Page 13

Allocation of tasks between master and slave control units
The two control units emit radar beams using the transmitting aerials. The emitted radar beams are reflected
by objects. Depending on the nature of the object, many, few or no beams at all are reflected.
The reflected beams are measured in the two control units by means of three receiving aerials. Based on the
physical properties of the reflected beams, the control units are able to obtain a variety of information
regarding the reflection objects. These physical properties include, for example, the time delay between
transmitting and receiving the radar signal, the frequency shift between the transmitted and received signal
and also the different phase position at the receiving aerials. Based on these, the current position, the speed
and also the direction of travel of different objects can be calculated.
Each control unit is independently able to detect fixed reflection objects, such as the crash barrier, structures
at the edge of the road or stationary vehicles. As these objects must not result in a warning, they are not
tracked further by the control units.
Objects that have been recognised as moving vehicles are tracked in the master control unit.
Curved road sections are also transformed into a straight road section in this control unit. This makes it easier
for the warning algorithm to assess the prevailing situation.
Side assist control unit
(master control unit)
Coordinate transformation
onto straight road section
Uniform tracking
of moving objects
Recognition and deletion
of stationary objects
(e.g. crash barrier)
Evaluation of
reflected beams
Emission of
radar beams
Side assist control unit 2
(slave control unit)
Activation of left or right
warning lamp depending on
prevailing situation
Evaluation of transferred
objects for warning criteria
Recognition and deletion
of stationary objects
(e.g. crash barriers)
Evaluation of
reflected beams
Emission of
radar beams
375_012
The data processed in this manner is supplied via the dedicated CAN to the slave control unit J770 where the
warning algorithm is implemented. If the slave control unit recognises a collision hazard based on the
predetermined warning criteria if lanes were to be changed, it activates the warning lamp on the relevant
side. If despite this the driver actuates the turn signal on the critical side, the lower intensity continuous light
changes to a flashing light at an increased intensity.
13
Page 14

Audi side assist
Communication structure of the Audi side assist
The Audi side assist requires a large amount of information from a number of different control units which are
in turn connected to the various bus systems. Below is a description of the control units that exchange data
with the Audi side assist via bus systems and the information and variables in question.
Side assist
warning lamp in
driver side
exterior mirror
K233
Rain and light
sensor
G397
Side assist control
unit 2 - slave
J770
Onboard
supplycontrol unit
J519
Convenience system
central control unit
J393
warning lamp in
passenger side
exterior mirror
Side assist CAN
Access and start
authorisation
control unit
J518
Convenience CAN
Side assist
K234
control unit - master
Extended CAN
Side assist
J769
Data bus
diagnostic
interface
J533
MOST bus
Dash panel
insert CAN
Drive CAN
Side assist
button
E530
Control unit
in dash panel
insert
J285
ABS control
unit
J104
Trailer recognition
control unit
J345
14
Front information
display and
operating unit
control unit
J523
375_013
Page 15

Rain and light sensor G397
Convenience system central control unit J393
Supplies the Audi side assist with the
instantaneously measured ambient brightness via
its LIN master, the onboard supply control unit J519.
This enables the brightness of the warning lamp to
be perfectly adapted to the ambient conditions.
Control unit in dash panel insert J285
Informs the driver by means of error messages in
the event of faults in the Audi side assist and also
outputs an acoustic signal to this effect.
ABS control unit J104
Supplies the Audi side assist with the yaw rate and
the current wheel speeds. These variables are used
to calculate the current vehicle speed and the curve
radius during cornering, etc.
Trailer recognition control unit J345
Informs the Audi side assist whether a trailer is
attached to the vehicle or not. If a trailer is attached
to the vehicle, the function is deactivated because
there is a risk of the scanning range of the sensor
being impaired. A corresponding message is
displayed in the dash panel insert.
Transmits the information as to whether the right or
left turn signal has been actuated. The Audi side
assist infers from this that a lane change is
intended. The convenience control unit also informs
the Audi side assist whether or not the reversing
lights are currently switched on. The Audi side assist
is deactivated during reversing.
Access and start authorisation control unit J518
Transmits the key number of the vehicle key
currently being used. This ensures that the
personalised brightness setting is adopted for the
warning lamps after "ignition ON".
Front information display and operating unit control
unit J523
The customer is able to use this to set the desired
brightness for the warning lamps. The value is
stored in the side assist control unit J769 together
with the corresponding key.
15
Page 16

Audi side assist
Diagnostics
In the diagnostics tester, the address word 3C is assigned to the side assist control unit (master) J769.
The side assist slave control unit J770 is not addressable separately using the diagnostics tester and thus
does not have its own address word. The fault memory, the measured value blocks, the code and the adaption
channels of the Audi side assist are all to be found in the side assist master control unit J769.
The following variables can be found in the
measured value blocks:
● Supply voltage and internal temperature of
master and slave
● Communication status of dedicated CAN bus
between master and slave
● Current system status (on / off)
● Input variables of the function, which are
transmitted by other control units via the CAN
bus
● Calculated current radius of curve
● Status of side assist button and its LED
● Status of both warning lamps in the exterior
mirrors
● X and Y coordinates of the nearest object in the
left, centre and right lane
● Relative speed of the nearest object in the left,
centre and right lane
● Current status of auto-calibration; calibration
information
● Status of communication with the control units
involved in the overall function
The following information is encoded into the code:
● Vehicle model equipped with Audi side assist
● Country in which the vehicle is operated
● Left or right-hand drive
● Whether or not a trailer control unit is installed in
the vehicle
The following variables can be adapted in the
adaption channels:
● The brightness of the warning lamps
It is possible to actuate the following components
via final control diagnosis:
● LED in side assist button
● Side assist warning lamp in driver side exterior
mirror
● Side assist warning lamp in front passenger side
exterior mirror
16
Page 17

Special tools for system calibration
Special tools have been developed for calibrating
the radar sensors. These are a calibration board
with a Doppler generator VAS 6350, wheel centre
markers VAS 6350/1 and a distance measuring
device VAS 6350/2 featuring laser measuring
technology. The calibration board is used for
calibrating the radar sensors of the Audi side assist
and also for calibrating the reversing camera.
The first step is to correctly position the calibration
board, which is described in detail in the calibration
instructions. This document is available as a
Workshop Manual. First, the calibration board is
aligned at a defined distance from the two rear
wheels. For this purpose, the wheel centre markers,
also referred to as "paddles", are attached to the
wheel nuts using a special device. Gravity aligns the
movable paddles perpendicular to the ground.
Using an electronic distance meter, the calibration
board is then adjusted to the specified distance on
both sides.
375_014
375_015
Using a laser liner located centrally on the calibration board, the calibration board is then centred along the
longitudinal axis of the vehicle, without the distance already set being altered.
The laser projects a vertical line onto the rear of the vehicle, which when aligned correctly divides,
for example, the Audi emblem on the rear end into two equal halves.
Once the alignment is complete, the calibration procedure can be started using the diagnostics tester.
The rest of the procedure is fully automatic. The black circles on the calibration board are only required for
calibrating the reversing camera. The so-called "Doppler generator" is used for calibrating the radar sensors.
Using a rotating fan wheel, it simulates a moving object, the nominal position of which is known to the control
unit. Based on the difference between the actual position and the nominal position, the control unit learns the
correction values required to make the subsequent adjustments to the measured positions.
17
Page 18

Audi side assist
Applied radar technology
Radar sensor system
The word RADAR is an acronym and stands for RAdio Detection And Ranging.
The technology is used in stationary objects for determining positions as a function of distance and angle.
In moving objects, the movement is detected as a function of current position, speed and direction of travel.
This occurs through the emission of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation, i.e. "microwaves",
and evaluation the radiation reflected by objects. The reflection characteristics of the objects is of crucial
importance. Metallic objects reflect the radiation very well, whereas plastic materials, for example, are almost
entirely permeable to it.
Consequently, motor vehicles are very well-suited for detection by radar sensors.
Advantages of radar sensors over other sensor systems
When selecting the sensors, it was decided to use radar technology rather than rival technologies such as
video, ultrasound or infrared technology.
Ultrasonic sensors have the disadvantage of a very limited range and are highly sensitive to environmental
effects. Moreover, ultrasonic sensors always need to have direct contact with the propagation medium, i.e. air,
which means they would have to be positioned in a visible location.
Infrared sensors, in contrast, are particularly well-suited for detecting lateral movements but are very poor at
detecting movements towards or away from the sensor. It is this direction of movement in particular, however,
that is crucial for the Audi side assist. Moreover, infrared sensors are also very sensitive to environmental
effects such as rain.
The sensitivity to environmental effects is also the reason why video sensors were not chosen for this
application. Other reasons against video sensors are their range and inaccuracy. The inaccuracy stems from
the fact that the video image has to be interpreted in order to determine a distance. It is an indirect
measurement process compared to the direct measurement method of radar sensors.
Radar sensors lend themselves to this type of task because they are insensitive to environmental effects and
penetrate non-metallic materials, enabling the sensors to be concealed by the bumper cover. Radar
applications have also become much more reasonably priced in recent years, making it feasible to use them
on a large scale.
18
Page 19

19
Page 20

Optical parking system (OPS)
Optical parking system (OPS) in the Audi Q7
Introduction
The optical parking system (OPS) is an innovative
extension of previous Audi parking aid systems.
The 4-channel (rear only parking aid) and the
8-channel (front and rear parking aid) systems are
already familiar. In these systems, an acoustic signal
provides the customer with information about the
distance of the vehicle from an obstacle.
The new optical parking system (OPS) is only
available as an 8-channel system. In addition to the
existing acoustic sensor evaluation, it provides the
customer with an image in the MMI display which
schematically depicts the current distance value of
each individual parking aid sensor from an obstacle.
Additional hardware is not required for this
extended function. The optical parking system can
be ordered with or without a reversing camera.
One major advantage to the customer over the
purely acoustic system is that he/she can now
accurately ascertain the point at which the vehicle is
approaching an obstacle. In the purely acoustic
version, based on the signal frequency, it is only
possible to distinguish whether an obstacle has
been detected by the front 4 parking aid sensors or
the rear 4 parking aid sensors.
Parking aid system
Check roadway too!
375_016
20
Page 21

Parking aid control unit J446
The purpose of the parking aid control unit is to:
● Provide the supply voltage for the parking aid
sensors
● Evaluate and process the signals from the
parking aid sensors
● Activate the two parking aid warning buzzers H15
and H22
● Transmit the information required for displaying
the OPS image on the MMI screen to the front
information display and operating unit control
unit J523
● Store the settings with respect to the remote
control key when locking the vehicle (rear/front
volume, rear/front frequency)
● Diagnose the system; manage the fault memory
● Read in the parking aid button E266
● Control the LED in the parking aid button E266
● Communicate with other control units for
transmitting and receiving messages
375_017
Schematic circuit diagram of the parking aid control unit J446
J446
Rear parking aid
warning buzzer
To the r ea r
CAN node
Convenience CAN
Convenience CAN low
Front parking aid
warning buzzer
H22
Ter mina l 15
Ter mina l 30
Ter mina l 31
Parking aid control unit
H15
Parking aid button
E266
Rear parking aid sensor Front parking aid sensor
375_018
21
Page 22

Optical parking system (OPS)
Fitting location
The parking aid control unit J446 is fitted at the rear
right, underneath the load floor.
It can be addressed using the diagnostics tester
under address word 76.
375_019
Parking aid sensors
Fourth generation
parking aid sensor
Fifth generation
parking aid sensor
The Audi Q7 is the first vehicle to use fifth
generation parking aid sensors. They are much
smaller compared to the dimensions of fourth
generation sensors. The solid plastic housing,
which surrounded the vibrating mass of the fourth
generation sensors has been discontinued for the
Plastic housing
new sensor generation.
Vibrating mass
(ultrasonic transmitter and receiver)
Vibrating mass
(ultrasonic transmitter and receiver)
375_020
The function of the optical parking system (OPS)
Parking system detection zone
Like the previous 8-channel systems, the optical parking system (OPS) monitors the area around the vehicle
using 4 parking aid sensors integrated in the front bumper and 4 in the rear bumper. The acoustic warning is
given by one warning buzzer in the front section of the vehicle and one in the rear. The visual display is
provided in the MMI display, with both the Basic and the High version supporting OPS.
Depending on their fitting location, the parking aid sensors recognise distinct obstacles as follows:
● Rear side parking aid sensor: from approx. 60 cm
● Front side parking aid sensor: from approx. 90 cm
● Rear centre parking aid sensor: from approx. 160 cm
● Front centre parking aid sensor: from approx. 120 cm
On reaching the following distances, the signal changes to a continuous tone:
● Front: from approx. 25 cm
● Rear without trailer hitch: from approx. 30 cm
with trailer hitch: from approx. 35 cm
22
Page 23

Operation of the parking aid system
The driver is only given audible and visual information if the parking system is activated. Activation is
automatic when reverse gear is engaged.
During forward parking or when moving forwards towards an obstacle, the parking system must be activated
manually by pressing the parking aid button. Activation of the system is always signalled to the driver by a
confirmation tone. It is also possible to recognise that the parking system is activated from the illuminated
LED in the parking aid button.
Activating the system automatically switches the MMI to the optical parking system display. If the vehicle is
also equipped with the reversing camera system, it is possible to select which of the two displays is to appear
on the screen in the Car menu of the MMI under the item "Audi parking system". The setting options available
to the customer in the MMI are explained in greater detail in the chapter on the reversing camera system.
375_021
375_021
An activated parking aid system is deactivated when
● a speed of approx. 15 km/h is exceeded (forwards),
● the ignition is switched off,
● the parking aid button is pressed.
Following deactivation, the LED in the button extinguishes and the MMI switches back to the image source set
before the system was activated.
23
Page 24

Optical parking system (OPS)
Information to the driver
If an obstacle has been detected inside the warning
zone while the parking aid system is activated,
the distance warning is triggered. As the distance to
the obstacle decreases, the time between the sound
pulses also diminishes until it becomes a
continuous tone when a critical distance is reached.
In the case of the optical parking system (OPS),
the current distance measurement values for the
parking aid sensors are shown in the MMI display in
addition to the audible warning. For this purpose,
a sector is assigned to each sensor, with the
8-channel system this corresponds to 4 sectors at
the front and 4 at the rear. A red segment within a
sector represents the current distance between an
obstacle and the vehicle, i.e. the sensor making the
measurement. If an obstacle moves towards the
vehicle, the red segment also moves towards the
vehicle in the diagram.
OPS display in the MMI High
Parking system
Segment
Sector
Sound off Check roadway too! Rear View
375_022
OPS display in the MMI Basic
375_023
Trailer operation
If, based on the code, the parking aid control unit
recognises that a trailer hitch is installed, the range
for the continuous tone is extended by 5 cm to
35 cm. This is necessary because the trailer hitch
increases the vehicle length at the rear.
24
Parking system
Check roadway too!
375_024
Page 25

Communication structure of the optical parking system
In order to operate correctly, the parking aid control unit also requires information from other control units.
The control unit receives this information via the convenience CAN. Information required from the modules of
other bus systems is made available on the convenience CAN by the data bus diagnostic interface and is thus
accessible to the parking aid control unit.
Front information
display and operating
unit control unit
Onboard supply
control unit
J519
J523
Park ing aid
control unit
J446
Convenience CAN
Trailer
recognition
control unit
J345
Access and start
authorisation
control unit
J518
Automatic gearbox
control unit
J217
Data bus
diagnostic interface
J533
MOST bus
ABS
control unit
J104
375_025
25
Page 26

Optical parking system (OPS)
The following information is supplied to the parking
aid control unit J446 by the control units listed
below:
Onboard supply control unit J519
The reversing lights are on. It can be deduced from
this that reverse gear is engaged and that the
parking aid system needs to be activated.
(CAN-message is only evaluated in vehicles with
manual gearbox.)
Trailer recognition control unit J345
Trailer is currently recognised or not recognised. If a
trailer is currently recognised, the rear parking
system is deactivated.
Access and start authorisation control unit J518
The current terminal status and the number of the
key currently being used are transmitted.
The number of the current key is used to activate
driver-specific settings, such as the volume and
frequency of the audible warning.
ABS control unit J104
Transmits the current vehicle speed. This is needed
because the front parking aid system is only
available up to a speed threshold of v=15 km/h when
the parking aid system is activated. If this threshold
is exceeded, the system is deactivated. As the
vehicle speed is only required for the front parking
aid system, the message from the ABS control unit
J104 is only evaluated in the case of an 8-channel
system.
Front information display and operating unit control
unit J523
Transmits the driver-specific settings to the parking
aid control unit, which stores the settings under the
current vehicle key. Moreover, the J523 serves as a
driver display unit for showing the distances
determined by the parking aid sensors in the form
of a segment diagram.
Automatic gearbox control unit J217
Transmits the information as to whether the
selector lever is in the “R” position. If this is the
case, the parking aid system is activated.
26
Page 27

Diagnostics
In the diagnostics tester, the address word 76 is assigned to the parking aid control unit.
The following variables can be found in the measured value blocks:
● Distance of the individual rear sensors from an obstacle
● Distance of the individual front sensors from an obstacle
● Minimum distance for the 4 rear sensors
● Minimum distance for the 4 front sensors
● Vehicle speed
● Voltage supply for parking aid sensors
● Reverse gear engaged yes / no
● Trailer attached yes / no
● Operation of function key
● Set volume and frequency, rear
● Set volume and frequency, front
● Decay times of the individual rear sensors
● Decay times of the individual front sensors
● Applicable vehicle key number
● Setting stored for the current vehicle key
The following information is encoded into the code:
● Vehicle derivative (saloon, Avant, coupe, etc.)
● USA or Rest of world
● Type of gearbox installed (manual gearbox / automatic gearbox)
● Installation of a reversing camera in the vehicle
● Installation of a trailer hitch in the vehicle
● Optical parking system (OPS) or only 8-channel acoustic parking system
The following variables can be adapted in the adaption channels:
● Confirmation tone for activation of parking aid system on / off
● Resetting volume and frequency to factory default
It is possible to actuate the following components via final control diagnosis:
● Rear parking aid warning buzzer H15
● Front parking aid warning buzzer H22
● Parking aid warning lamp K136
27
Page 28

Reversing camera (rear-view)
Reversing camera (rear-view) in the Audi Q7
Introduction
The AUDI reversing camera provides the customer with an improved view to the rear by capturing the area
behind the vehicle and depicting this on the MMI screen. This makes it much easier for customers to reverse
and reverse park.
The reversing camera makes it possible to get much closer to obstacles. The customer can direct his/her line
of vision forwards for the most part and does not need to keep turning his/her head all the time. Static and
dynamic reference lines that are superimposed on the video image further simplify reverse parking.
In principle, the reversing camera can be ordered as a separate parking system, together with the acoustic
rear parking system or with the optical parking system (OPS). The order options available depend largely on
the particular market.
375_032
28
Page 29

Reversing camera
The Audi reversing camera is a PANASONIC camera. It weighs 40 g and measures 27 mm x 24.5 mm x 35 mm.
Due to its compact design, it was possible to integrate the camera into the tailgate handle.
375_026
It is a wide-angle camera with a horizontal detection
angle of 130° and a vertical detection angle of 95°.
Owing to the wide-angle lens used, the camera
image is greatly distorted and this distortion must
be eliminated before the image is displayed on the
MMI display. The distorted image is corrected in the
reversing camera system control unit J772.
The chip used for capturing the image has a
horizontal resolution of 510 pixels and a vertical
375_027
resolution of 492 pixels, which results in an overall
resolution of 250K pixels
The camera lens has a dirt-repellent coating. Dirt on the camera lens is not detected by the reversing camera
system control unit, but is identified by the driver due to the quality of the image on the MMI screen.
The driver is responsible for cleaning the dirty lens. The recommended method is to moisten the lens using a
commercially available alcohol-based glass cleaner and clean it with a dry cloth.
375_028
29
Page 30

Reversing camera (rear-view)
Reversing camera system control unit J772
Tasks of the control unit
The reversing camera system control unit J772 is connected to the convenience CAN.
The purpose of the reversing camera system control unit is to:
● Supply the reversing camera with voltage
● Remove distortion from the camera’s wide-angle image
● Superimpose static and dynamic reference lines onto the camera image
● Provide a video input for the camera signal
● Provide a video input for the TV tuner
● Switch to the desired video signal using an integrated video switch
● Supply a video output for the incoming video signal
● Perform a self-diagnosis of the control unit
● Diagnose the incoming camera signals
● Perform the system calibration using VAS tester and calibration board
The TV tuner is available as special equipment.
If there is no TV tuner in the vehicle, then the
second video input of the reversing camera system
control unit remains unused.
Fitting location
The reversing camera system control unit is located
in the rear of the vehicle, on the right near the wheel
housing. For transferring the image, the reversing
camera is connected to the control unit via a
screened wire. This wire is used for transmitting the
entire video signal including colour, brightness,
blanking and synchronising information.
375_029
375_030
30
Page 31

System circuit diagram
The reversing camera and the corresponding control unit are connected together by 4 wires.
These are the wire for the camera’s power supply and the corresponding earth wire, a screened wire for the
video signal and the screening of the video signal connected to earth.
The camera is switched on and off via the voltage supply.
The camera voltage supply is 6.5 V and is generated in the reversing camera system control unit by means of
a switching power supply. When in operation, it requires an output of approx. 500 mW.
The camera’s power supply is switched off at speeds above 25 km/h, as the function is not active at speeds
higher than this.
Reversing
camera R189
Term in a l 30
Term in a l 31
Camera VCC
Camera earth
Convenience CAN-high
Convenience CAN-low
... screened wire
Reversing camera syst em
control unit
J772
Front information
display and operating
unit control unit
J523
Image
processing
TV tuner
R78
375_031
The front information display and operating unit control unit J523 has only one video input, even though there
may be two video signal sources present in the vehicle: the TV tuner R78 and the reversing camera R189.
For this reason, the reversing camera system control unit J772 has 2 video inputs and a video switch which
patches through the image from the TV tuner or the image from the reversing camera to its video output,
as required. The video output of the reversing camera system control unit J772 is connected to the video input
of the front information display and operating unit control unit J523.
The illustration above depicts the off-position of the video switch in J772: this transmits the video signal of the
TV tuner to the video output. The video splitter only switches to the reversing camera if the reversing image is
needed in the MMI. The image from the reversing camera must first be processed in the reversing camera
system control unit before it reaches the front information display and operating unit control unit J523 via the
video switch and video output.
31
Page 32

Reversing camera (rear-view)
Parking modes
With the Audi reversing camera, there are two different parking modes - the “transverse parking” mode and
the “parallel parking” mode. Depending on the parking situation, the customer can opt for one of the two
modes. The “transverse parking” mode is defined as the standard mode. To change the mode that is currently
active, in the MMI control panel the softkey assigned to the displayed term “Mode” must be pressed.
If the vehicle is also equipped with the optical parking system (OPS), the OPS diagram can also be selected
using the softkey assigned to the term “Diagram”.
Parking mode 1: transverse parking
Parking mode 1, “transverse parking”, is, as shown
in the adjacent illustration, particularly suitable for
reverse parking. It is also particularly suitable for
reversing up narrow paths, such as relatively long
driveways, for example. The blue area represents a
vehicle contour that has been lengthened by 5 m.
The vehicle would drive over the blue area shown,
if it was reversed a further 5 m without turning the
steering wheel.
The different shades of blue make it easier for the
driver to estimate the distance from obstacles. The
first transition from the dark-blue to the mid-blue
area is around 1 m from the rear bumper, the next
transition is at about 2 m. The following light-blue
area extends to a distance of about 5 m.
The red line which delimits the dark blue area is
about 40 cm away from the rear of the vehicle. If this
line touches an obstacle, then the driver should not
reverse any further.
As the alignment of the reference field does not
depend on the steering angle and only depends on
the instantaneous vehicle position, this is known as
a static reference field.
In contrast, the orange reference lines indicate the
path the vehicle will follow for the next 5 m if the
steering angle remains the same. As the radius of
the line is dependent on the steering angle, these
are known as “dynamic reference lines”. The side
markings along the dynamic reference lines are
provided at approx. 1 m intervals.
375_032
Mode
Check roadway too!
32
Diagram
375_033
Page 33

Parking mode 2: parallel parking
Parking mode 2, “parallel parking”, makes it easier for the driver to reverse park alongside the kerb. Two blue
fields are depicted - a light-blue field for reverse parking on the right-hand side and a dark-blue field for
reverse parking on the left. The static blue lines shown, indicate the ideal point at which the driver should
adjust the steering angle.
Procedure for reverse parking
If the dark-blue area fits between the two vehicles,
between which the driver intends to park, then the
space is large enough. Now reverse in a straight line
until the end of the dark-blue area touches the rear
of the vehicle (see the upper of the two
illustrations). Then reverse with the steering wheel
turned to left full lock. The driver must ensure that
he/she does not touch the vehicle he/she is parking
behind. When the dark-blue line touches the kerb
(see the lower of the two illustrations), the steering
wheel must be turned to right full lock and reversing
continued until the vehicle is parallel to the kerb.
The vehicle should then be driven forward slightly
and the vehicle will be parked perfectly.
Check roadway too!
375_034
Mode
Diagram
375_035
Mode
Check roadway too!
Diagram
375_036
33
Page 34

Reversing camera (rear-view)
Operating the system
Activating the reversing camera
The display of the reversing camera image on the
MMI screen is activated automatically as soon as
terminal 15 is active and reverse gear has been
engaged.
On vehicles with the optical parking system (OPS),
the reversing camera display may also be activated
using the parking aid button in the centre console.
This is possible when driving forwards at speeds
< 10 km/h.
Deactivating the reversing camera
The display of the reversing camera in the MMI is
switched off when terminal 15 is switched off, if
another hardkey in the MMI is operated or the
vehicle is travelling forwards at a speed > 10 km/h.
In vehicles with OPS, pressing the parking aid
button also terminates display of the reversing
camera on the screen.
Setting options in the MMI
As is already familiar from other Audi models with a
parking aid system, the customer has the option of
storing individual settings for the frequency and
volume of the front and rear warning tone. For this
purpose, the “Audi parking system” menu item in
the Car menu of the MMI must be selected.
As there are two possible parking aid systems
available in vehicles with optical parking system
(OPS) and reversing camera, the settings listed in
the adjacent table for the MMI display when a
parking cycle begins can be selected under the item
“Display APS”.
The settings are active for the next parking cycle.
375_021
User Log book
Audi parking system
Display APS
Front volume
Front frequency
Rear volume
Rear frequency
Systems Version
Settings of MMI display
1 Off there is no display of the parking
2 Diagram the diagram of the optical parking
3 Rear View the image of the reversing camera is
4 Automatic when reversing, the image from the
Car
Off
Diagram
Rear View
Automatic
375_038
system function in the MMI display
system (OPS) is displayed in the MMI
display
shown in the MMI display
reversing camera is displayed in the
MMI display, when driving forwards the
OPS diagram is shown
34
Page 35

Communication structure of the reversing camera system
The reversing camera system control unit exchanges information with various control units.
This information is required for the correct operation of the overall function and is described below:
Reversing camera
K189
Onboard supply
control unit
J519
Parking aid control
unit
J446
Trailer recognition
control unit
J345
ABS control
unit
J104
Drive CAN
Convenience system
central control unit
Access and start
authorisation
control unit
Steering angle
sender
G85
J393
J518
Convenience CAN
Data bus diagnostic
interface
J533
Reserving camera
system control unit
J772
Front information
display and operating
unit control unit
J523
MOST bus
TV tuner
R78
375_039
35
Page 36

Reversing camera (rear-view)
Steering angle sender G85
Supplies the current steering angle, which is
needed for calculating the dynamic reference lines
in the camera image.
Parking aid control unit J446
Supplies information as to whether the parking aid
system is currently active based on the button or
based on the reverse gear being engaged and
whether the parking aid control unit is defective.
Trailer recognition control unit J345
Informs the reversing camera system whether or
not a trailer is currently attached to the vehicle. If a
trailer is attached to the vehicle, then the reference
lines and the reference field are disabled.
Convenience system central control unit J393
Transmits the information as to whether the tailgate
is open or closed. If the tailgate is open,
the reference lines and the reference field are
deactivated.
Access and start authorisation control unit J518
Front information display and operating unit control
unit J523
It depicts the reversing camera image on its display.
In addition, system settings for the reversing
camera can also be made.
Onboard supply control unit J519
This transmits the information as to whether the
reversing light is currently actuated. In vehicles
without a parking aid control unit, it can be deduced
from this that the reverse gear is currently engaged
and that the camera image must be displayed on
the MMI screen accordingly.
ABS control unit J104
The “current vehicle speed” information is required
by the J104 for detecting the conditions for
switching the reversing camera on and off.
Data bus diagnostic interface J533
This directs the required CAN messages from other
bus systems onto the convenience CAN. Transmits
freeze-frame information if an entry is made in the
fault memory of the reversing camera system
control unit.
Transmits the current status of terminal 15 to the
reversing camera.
Remarks
The following control units are optional and
therefore not installed in every Audi Q7:
● Parking aid control unit J446
● Trailer recognition control unit J345
● TV tuner R78
36
Page 37

Diagnostics
In the diagnostics tester, the address word 6C is assigned to the reversing camera control unit.
The following variables can be read out in the measured value blocks:
● S-contact status and terminal 15 status
● Reverse gear engaged yes / no
● Voltage supply for control unit
● Voltage supply for camera
● Tailgate open / closed
● Current vehicle speed
● Calibration active / not active
● Status of last calibration
● Cause of a failed calibration
The following characteristics are encoded in the code:
● Vehicle manufacturer VW / Audi
● Country version
● OPS (optical parking system) installed - yes / no
● Trailer hitch installed - yes/no
● Steering installed
● Camera height above ground (dependent on chassis and tyres)
● Vehicle model
The following variables can be adapted in the adaption channels:
● Start of calibration
● Coordinate information for calibrating the camera
● Brightness, contrast and colour settings for video image
37
Page 38
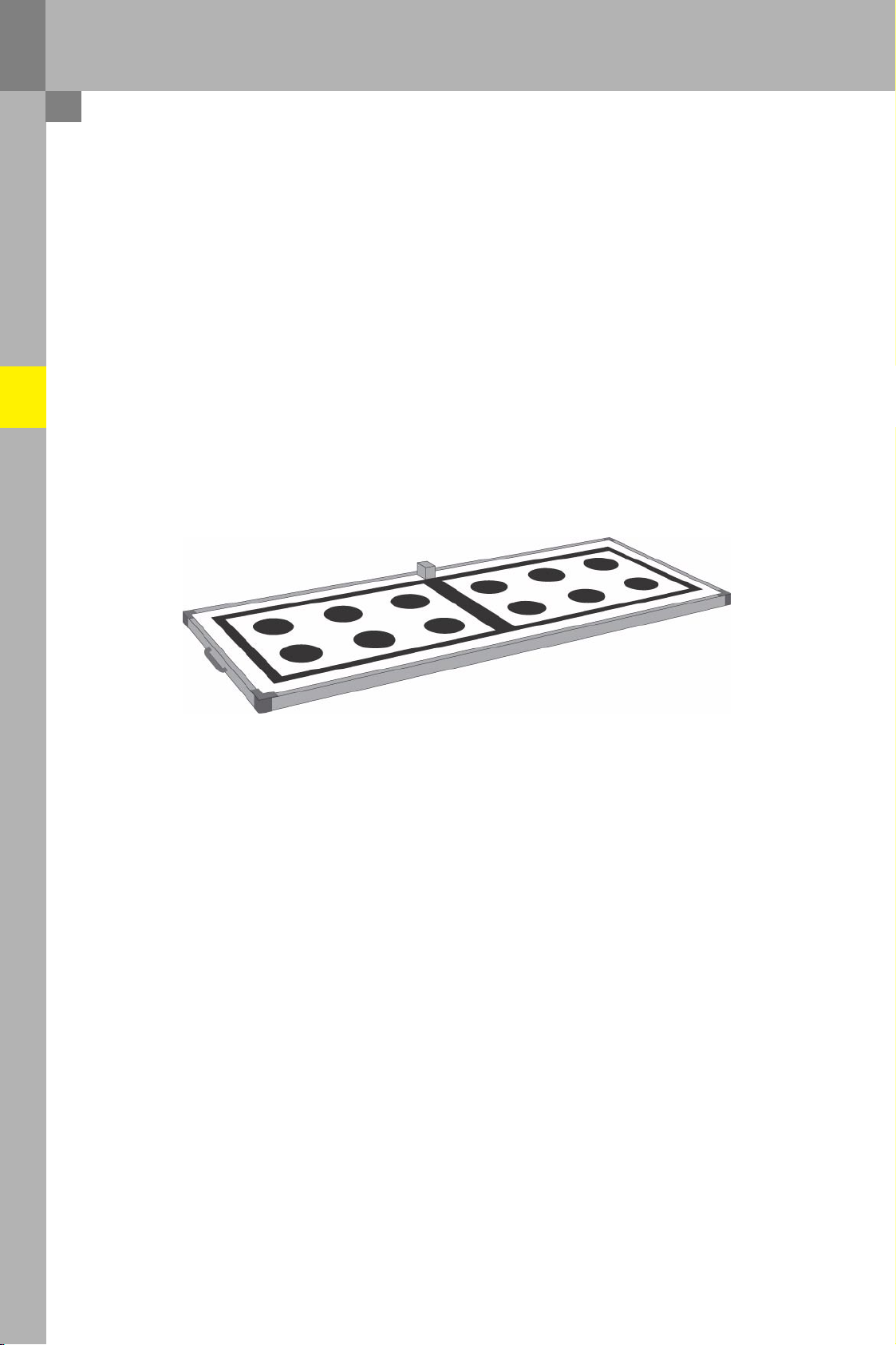
Reversing camera (rear-view)
Special tool for system calibration
The same calibration board is used for calibrating the reversing camera as is also used for calibrating the Audi
side assist. The Doppler generator is however not required.
The way in which the calibration board must be aligned to the vehicle is described in detail in the
corresponding Workshop Manual and is also briefly outlined in the chapter on calibrating the Audi side assist.
It should also be noted that the board must be perfectly level, which is achieved via the three adjustable feet
under the calibration board. A built-in spirit level on the calibration board indicates whether the required
position has been achieved.
The distance of the surface of the calibration board from the ground must be determined using a tape
measure and entered into the tester before starting the calibration procedure. A bore has been provided next
to the spirit level to measure the distance.
375_037
The calibration must be carried out according to the calibration instructions available in the guided
fault-finding.
Once the calibration device has been aligned correctly, the calibration program can be started in the guided
fault-finding.
The purpose of calibrating the reversing camera is to correct the distortion of the camera image. For this
purpose, the system first searches for the two rectangles on the calibration board outlined in black.
Once these have been found, the system then finds the 6 black circles in each of these rectangles and
determines their centre points. Then the actual position of the centre of the circle that has been determined is
compared with the specified position stored in the control unit. From this information the correction
parameters can be calculated, which are used to continuously correct the distortion of the camera image.
38
Page 39

Self-study programme for the Audi Q7
SSP 312 Audi A3 ‘04
– Control units
– Distributed functions
– Infotainment
– Passenger protection
Order number: A03.5S00.03.20
375_041
SSP 326 Audi A6 ´05 Electrical system
375_042
–Networking
–Bus topologies
– Convenience electrics
– Infotainment
Order number: A04.5S00.09.20
SSP 364 Audi Q7 Electrical system
–Networking
– Fitting locations
– Convenience control units
– Vehicle electrical system
Order number: A05.5S00.17.20
375_043
Page 40

Vorsprung durch Technik www.audi.de
375
All rights reserved, including
the right to make technical
modifications.
Copyright
AUDI AG
I/VK-35
Service.training@audi.de
Fax +49-841/89-36367
AUDI AG
D-85045 Ingolstadt
Technical status 10/05
Printed in Germany
A05.5S00.21.20
 Loading...
Loading...