Page 1

ATTO Technology, Inc.
ATTO BridgeTools
TM
for ATTO FibreBridgeTM 1100, 2100, 3100, 2200, 3200
Installation & Operations Manual
Copyright © 2002 A TTO Technology, Incorporated. All brand or product names are trademarks of their
respective holders. No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means without the
expressed wri tte n permission of ATT O Technology, Incorporated.
Jan. 2002.....................................................2.10.....Document Control Number: PRMA–0312-000MD
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
1 ATTO FibreBridge supports diverse SAN needs .............................1
2 BridgeTools aids FibreBridge management ....................................3
Glossary
3 Installing the BridgeTools program ..................................................5
Requirements
Installation step by step
4 The BridgeTools graphical interface is ready ..................................7
4.1 FibreBridge connection pages ............................................9
Welcome page
In-Band Fibre Channel connection page
Ethernet connection page
Serial port connection page
4.2 General panel ........................................................................11
4.3 SCSI Port configuration panel .............................................12
4.4 Ethernet port configuration panel .......................................13
4.5 Serial port configuration panel ............................................14
4.6 Firmware updater panel ........................................................15
4.7 Fibre Channel port configuration panel ..............................16
4.8 Mapping panel .......................................................................19
4.9 Events panel ..........................................................................21
4.10 Save/Restore panel .............................................................22
Appendix A Available products and accessories ...............................i
Appendix B How to contact ATTO Technology, Inc. ..........................iii
Page 4

1 ATTO FibreBridge supports diverse SAN needs
The ATTO FibreBridge
TM
family of products provides a Fibre Channel-to-SCSI bridge available as a
Compact PCI board, a stand alone enclosure that can be fitted for rackmount integration, or a desktop
unit, depending on the model and your needs.
The ATTO FibreBridge family of products share
common forms and functions to provide the most
versatile connectivity options available. Each
product has been engineered to address specific
customer needs. New capabilities are integrated
into products throughout the FibreBridge family
as much as possible, requiring only an upgrade of
firmware to incorporate them into your SAN.
All A TTO FibreBridge models include full duplex
Please refer to the Technical Specifications and
the FibreBridge Installation and Operation
Manual for complete information about your
FibreBridge model.
Exhibit 1-1 provides an overview of the features
and capabilities for current FibreBridge models.
Contact your authorized ATTO representative or
visit ATTO Technology’s website,
www.attotech.com, for additional information.
mode, Class 2 transfers, Intermix transfers and
direct fabric connect capabilities.
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
1
Page 5
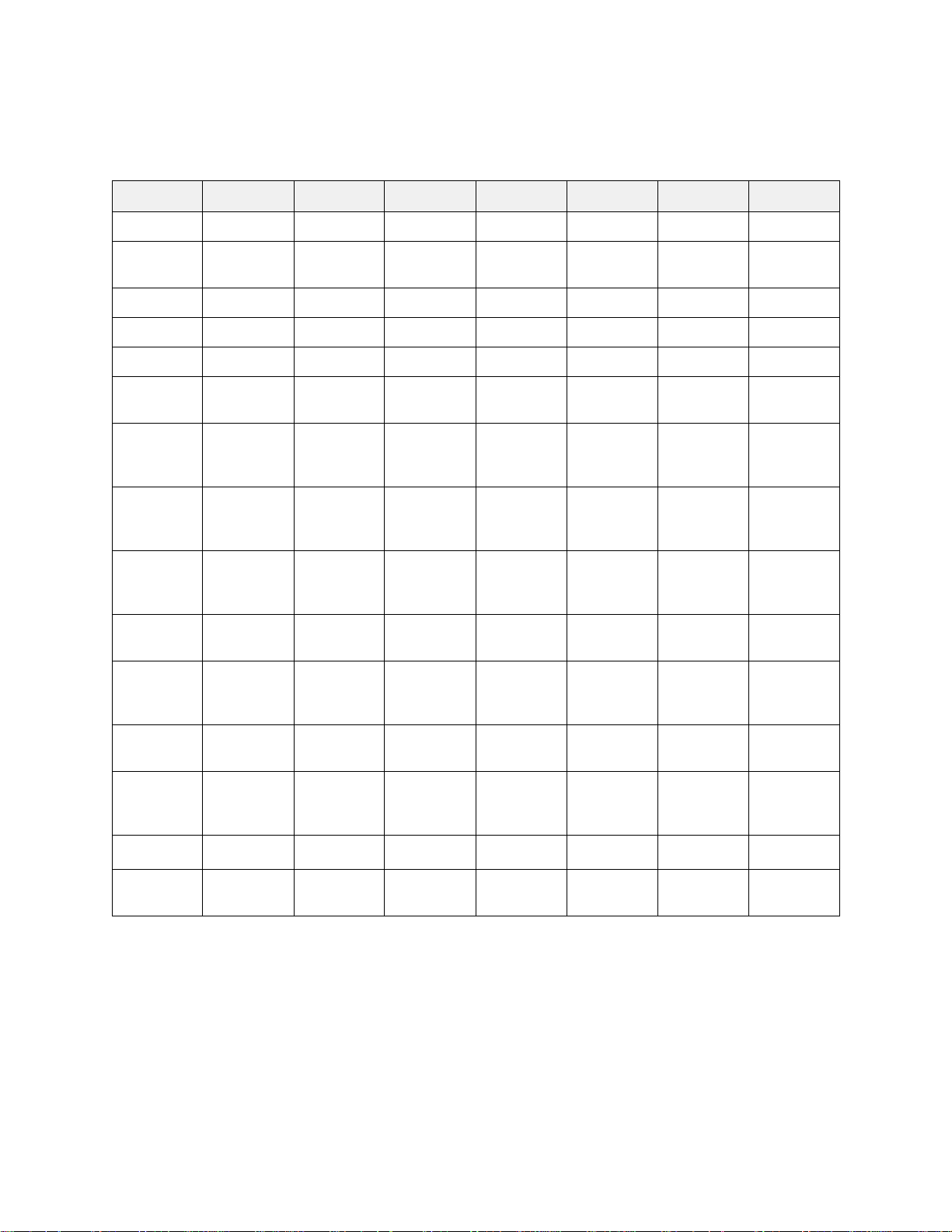
Exhibit 1-1 ATTO Technology Inc. has a complete line of FibreBridge products to fit your needs.
ATTO FibreBridgeTM feature availability matrix
1180E/D 1190E 2200R/D 2300E/R/D 3200R 3300R 4500C/R/D
FC Ports1111113
FC port
number (fp)
FC interface DB9/SC DB9/SC GBIC
Data transfer 1 Gigabit 1 Gigabit 1 Gigabit 2 Gigabit 1 Gigabit 2 Gig abit 1 Gigabit
SCSI ports 1 2 2
SCSI bus
number (sb)
Configuration Board
Error chec king
& correction
memory
Serial
management
interface
000
0 0, 1 0, 1
Board Desktop
Desktop
Rackmount
✓✓ ✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓✓✓✓
0000, 1, 2
SFP GBIC SFP SC
2224
0, 1 0, 1 0, 1 0, 1, 2, 3
Board
Desktop
Rackmount
Rackmount Rackmount Board
Desktop
Rackmount
FibreBridge family
Management
via Telnet/FTP
In-band SCSI
management
interface
Menu
interface
BridgeTools
management
interface
In-band CLI
Serverless
backup
✓✓✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓✓✓✓
2
Page 6

2 BridgeTools aids FibreBridge management
ATTO BridgeToolsTM is a Java-based configuration utility designed to flash firmware and manage the
configuration of your ATTO FibreBridge.
Fibre Channel is a serial communications
technology designed to transfer large amounts of
data between a variety of hardware systems over
long distances. It is a key technology for
applications that require shared, high bandwidth
access to storage.
Fibre Channel provides a logical point-to point
serial channel for the transfer of data between a
buffer at a source device and a buffer at a
destination device. It moves buffer contents from
one port to another, without regard to the format
or meaning of the data so different upper level
protocols are able to run over Fibre Channel
hardware.
The Fibre Channel architecture is structured as a
hierarchica l set of pro tocol laye rs. Def ined with in
these layers are rules for signal interfaces, serial
encoding and decoding, error control, frame
format and communications protocols.
All ATTO FibreBridge models can be used in a
SAN (Storage Area Network) to connect a variety
of Fibre Channel and SCSI devices to meet your
needs.
A SAN is a shared storage architecture connecting
computers and storage devices for online data
access. Each connected system can directly access
any attached storage device. Storage devices
could includ e RA ID, tape backup, ta pe libr a ry,
CD-ROM library or JBOD.
ATTO FibreBridge models provide the interface
between SCSI and Fibre Channel resources in
SANs. Possible configurations depend upon your
current hardware and what you need to do.
The FibreBridge allows parallel SCSI devices to
participate in a Fibre Channel arbitrated loop or
on a fabric. Fibre Channel and SCSI
configurations address devices differently, and the
FibreBridge translates between these addressing
models.
The simplest way to communicate with the A TT O
FibreBridge is to use ATTO BridgeTools, a Java-
based graphical interface configuration utility
designed to fla sh firmwa re and m a nag e the
configuration for all models of the FibreBridge.
BridgeTools detects which FibreBridge model is
available and presents you with the applicable
configuration options.
At the startup, a wizard-type interface will ask
you how you want to communicate with the
ATTO FibreBridge. You can choose between an
in-band connection direct over the Fibre Channel
link, an RS-232 port or an Ethernet port.
A tabbed panel interface presents configuration
parameters in a simple, one-window display.
Message boxes, icons, drop-down boxes, menu
bars and other common graphical constructs will
lead you through the configuration process.
Refer to the ATTO FibreBridge Installation and
Operation Manual for more information about
other methods to manage your FibreBridge.
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
3
Page 7

Glossary
Some terms used in the Fibre Channel industry are defined below . More information is available through
the F ibre C hannel Industry Assoc iation (www.fibrechannel.com), the Storage Area Networking Industry
Association (www.snia.org) and the Fibre Channel Consortium (www.iol.unh.edu).
Term Definition
fabric A Fibre Channel s witch or two or m ore Fibre Channe l s witche s interconnec ted to
physically transmit data between any two N_Ports on a switch or switches.
failover The substitution of a working system for one which has failed.
FC-AL Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop: A Fibre Channel network in which up to 126
systems and devices are connected in a loop topology, with each transmitter
connecting to the receiver of the device to its logical right. The Fibre Channel
Arbitrated Loop protocol used for transmission is different from Fibre Channel
switche d and point to point prot ocols. Multiple FC-A L loops can be conn ected via
a fabric switch to extend the network.
firmware Software stored in read-only memory (ROM) or programmable ROM (PROM).
Firmware is often resp onsible f or the beha vior of a sy stem when it is fi rst switc hed
on.
F_port A port in the Fibre Channel fabric where a N_port may attach
FL-port A port in the Fibre Channel fabric where a NL_port may attach in an arbitrated
loop
Glossary
initiator device A component which originates a command
LED Light-emitting diode , a type of dio de that emits li ght when current pas ses through
it. Visible LEDs are used as indicator lights on all sorts of electronic devices.
LUN Logical Unit Number: a SCSI or Fibre Channel identifier of a device
NL port a port attached to a node in Fibre Channel arbitrated loop or fabric loop
configurations
N_port a port attached to a node used with point to point or fabric configurations
SCSI Small Computer Systems Interface: a processor-independent standard for
system-le v el interf ac e betw een a compute r and in telligent d e vices i ncluding hard
disks, floppy disks, CD-ROM, printers, scanners, etc.
topology logical layout of the parts of a computer system or network and their
interconnections
4
Page 8

3 Installi ng the BridgeTools program
The installation and startup procedures are the same for all FibreBridge models except for the
configuration pa ne ls .
ATTO FibreBridge models provide the interface
between SCSI and Fibre Channel resources in
SANs. Possible configurations depend upon your
current hardware and what you need to do.
BridgeTools detects which FibreBridge model is
available and presents you with the applicable
configuration options.
Requirements
1 BridgeTools installed on a computer
running any of the approved operating
systems
Windows NT 4.0
✛
Windows 2000
✛
Mac OS 8.X, 9.X and Mac OS X
✛
Solaris 2.7 and 2.8
✛
2 One or more FibreBridge models.
3 Java Virtual Machine software
4 Any of the following three connections
between your computer and one or more
FibreBridge:
One Fibre Channel host adapter connected
✛
to the FibreBridge with a Fibre Channel cable
(ATTO ExpressPCI FC HBA is recommended).
An RS-232 null modem serial cable
✛
connected between your computer and the
FibreBridge.
An Ethernet connection between your
✛
computer and the FibreBridge. A direct
connection requires a crossover cable.
Refer to the FibreBridge installation and
operation manual for complete instructions on
how to access the FibreBridge.
Installation step by step
Windows NT 4.0 & Windows 2000
1 Place the ATTO BridgeTools CD in the CD
drive. An installation wizard will guide
installation.
2 Choose a location for program files
installation. The default location is
C:\Program Files\BridgeTools.
“Choose” button to select an alternative
location.
3 The installer will ask where you want a
shortcut. Choices include:
New Program Group
Existing Program Group
Start Menu
Desktop
Other
No Shortcut Icon
4 Java Virtual Machine software is required
BridgeTools execution. If it is already
installed, select it to run BridgeTools. If Jav a
VM software is not already installed, select
the option to have the installer pr ogram load
the Java software from the BridgeTools CD.
5 The installer will set up Prog ram Gr oup and
load necessary files. A message will appear
indicating completion.
Click the
Note: An uninstaller program can be found in
the Program Group.
Macintosh
1 Place ATTO BridgeTools CD in CD drive.
Double click on the installation program and
an installation wizard will guide installation.
2 Choose a location for program files
installation. The default location is to create
a
BridgeTools
folder on the Macintosh drive. Click the
“Choose” button to select an alternative
location.
3 The installer will ask you to select where to
create an alias. Choices include:
Apple Menu
Desktop
Other
Create no alias
folder within the Applications
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
5
Page 9

4 The installer will set up Program Group and
load necessary files. A message will appear
indicating completion.
Note: An uninstaller program can be found in
the Pro gr a m Group.
5 Java Virtual Machine software, built in to the
Mac OS, is required for BridgeTools to
execute. An updated version is f ound on the
BridgeTools CD.
Sun Solaris
Unix platform operation of BridgeTools requires
general UNIX shell experience. You must have a
Java 2 runtime en vironment installed and running
before attempting to install BridgeTools. Java
runtime environments for certain platforms are on
the BridgeTo ols CD. Java 2 environments are also
available on the Internet at java.sun.com. The
latest versions of Solaris include Java 2.
1 T ype java –version from a command shell to
determine if Java is installed. A version of
or later should be reported if it is
1.2.0
installed. If not, you must install Java and
add it to your path.
2 Log in.
Note: Being root is not required to install and
operate BridgeTools.
3 Place A TTO BridgeT ools CD in CD drive. The
CD will automatically appear on the screen.
4Open folders
to the instdata/unix/solaris direct or y.
Double click on the
installer.
instdata, unix
bt200.bin
and
file to start the
solaris
to get
5 Click OK on the SUN execution options
window. An installation wizard will
automatically appear to guide installation.
6 Choose a location for program files
installation. The default location is the home
directory. Click the
an alternative location.
7 The installer will ask you where to create a
link. Choices include:
Home folder
Other
Create no link
8 Java Virtual Machine software is required
for BridgeT ools to execute. The installer will
search your system to see if a compatible
version of Java VM software is already
installed. If it is installed on your system,
select this software to run BridgeTools. If
not, an updated version is found on the
BridgeTools CD.
9 The installer will set up Prog ram Gr oup and
load necessary files. A message will appear
indicating completion.
10 From a command shell, go to the directory
where you installed BridgeTools and untar
the
start.tar
create a file called
will have the proper permissions to run
BridgeTools with a Java 2 virtual machine.
11 Type
file by typing
startBridgeTools
Choose
startBridgeTools.
button to select
tar –xf start.tar
to launch the program.
to
The file
Note: An uninstaller program can be found in
the Program Group.
Installing the program
6
Page 10

4 The BridgeTools graphical interface is ready
Once you have connected your computer to the FibreBridge, installed BridgeTools and started the
progr am, the graphical interface is available to configure and monitor your FibreBridge.
CAUTION
BridgeTools must be saved to the FibreBridge and the
bridge must either be power cycled or a
Firmware
other FibreBridg e activity. Do not run BridgeTools when
the FibreBridge is executing applications.
To take effect, changes made with
Restart
command must be issued which will disrupt
Once the computer is connected to the
FibreBridge, apply power to the bridge, power up
your computer and launch BridgeTools. The
startup splash screen will appear, followed by the
Welcome Page.which displays the version of
BridgeTools installed. Ch e ck th e ATTO
Technology, Inc. web site, www.attotech.com, to
verify yo u ar e us in g th e late st v e r sio n.
The Graphical Interface
ATTO BridgeT ools uses a graphical user interface
based on various common components. At the
startup, a wizard-type interface will ask how you
wish to communicate with the ATTO
FibreBridge. You can choose either an RS-232,
Ethernet, or in-band connection (direct over the
Fibre Channel link) for updating and/or
configuring your FibreBridge. You will then be
guided through all the available flash and
configuration options.
A tabbed panel interface presents configuration
parameters in a simple, one-window manner.
Click on the tab selection button to view the panel.
At the bottom of each panel is a message box that
displays useful hints and suggestions to lead you
through the program. The top menu bar includes a
help icon . This will g i ve a det aile d ex plana tion of
each parameter, the possible values that can be
entered and how the FibreBridge will respond to
your selection.
Other common graphical constructs include drop
down list boxes to present choices and radio boxes
for mutually exclusive choices. Some parameters
will be “ gray ed out” if e ith er the y do not app ly to
your model of the FibreBridge or if they have no
effect based upon the selected value of a related
parameter.
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
7
Exhibit 4-1 The BridgeTools
Welcome screen.
Page 11

Exhibit 4-2 Typical use of tabs, panels
and information across the bottom of the
screen. Top screen shot: Connection
through FibreChannel. Similar screens
show parameters for connecting through
Ethernet and the serial port.
Exhibit 4-3 The General Panel for a serial
port connection. Tabs show the other panels
available for management and
configuration of the FibreBridge.
Starting up
Exhibit 4-4 The F ibr e Channel P ort pane l
for an in-band connection.
8
Page 12

4.1 FibreBridge connection pages
Welcome page
The W elcome Page asks you to select the interface
you are using to connect to the FibreBridge:
Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or Serial Por t, depending
on the physical connection. Not all bridge models
support all types of connections. Check the
Installation and Operations manual for details.
Options will vary depending upon the connection.
Once you have selected a communication
interface, the FibreBridge Connection page for
that interface will appear.
In-Band Fibre Channel connection page
Click on the Scan button to detect all connected
FibreBridge units. A list will appear with the
following information for each ATTO
FibreBridge:
➔
Vendor
➔
Model – Reports the model of the
FibreBridge that is currently connected
➔
Version –current version of firmware
➔
World Wide Name –unique identifier
➔
Location – Identifies the FibreBridge in a
SAN.
The first digit is the SCSI port and indicates the
➔
PCI slot the connected Fibre Channel host
adapter is in.
The second digit is the PCI Bus of the
➔
connected Fibre Channel host adapter.
(Usually set to 0 unless your computer has
more than one PCI bus.).
The third digit is the Fibre Channel ID (AL-PA)
➔
of the FibreBridge. The fourth digit is the Fibre
Channel LUN of the FibreBridge.
Even though BridgeTools will list every visible
ATTO FibreBridge from the computer, only one
can be modified at a time. Highlight the one you
wish to modify and click the Connect button.
After a few moments, the General page will
appear.
If a link cannot be established, BridgeTools will
time out and an error message will be displayed.
If this happens or only a partial listing of
FibreBridge units appears, verify the following
items:
➔
The FibreBridge(s) is powered up
➔
Cables have a secure connection.
➔
Y our operating system recognizes the Fibre
Channel host adapter.
➔
Your operating system recognizes the
ATTO FibreBridge?
Ethernet connection page
The Ethernet Connection page will ask for the
FibreBridge IP address. A convenient pull down
window displays the last 10 connected IP
addresses. Once the address is selected hit the
select button to complete a connection.
The defa ult address of th e FibreBridge i s 10.0.0.1.
If you changed the address and have forgotten it,
connect the computer to the FibreBridge with the
serial port, establish a link, and issue a
getipaddress command.
If an Ethernet link cannot be established,
BridgeTools will time out and an error message
will be displayed . If th is happens, ve rify the
following items:
➔
The FibreBridge(s) is powered up
➔
Cables have a secure connection. A direct
connection between the computer and
FibreBridge requires a crossover cable.
➔
Your Network Interface Card is configured
properly.
➔
The link and activity LEDs are illuminated
on the Ethernet ports of the FibreBridge(s)
and the host.
➔
A T elnet link between the FibreBridge and
the computer has been established.
Serial port connection page
The serial port connection page will ask you to
configure the RS-232 protocol to connect to your
FibreBridge. The parameters you choose here will
temporarily override any previous configurations
chosen using the standard operating system
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
9
Page 13

utilities. Upon exiting BridgeT ools, the COM port
will return to its previous setting.
To connect to the FibreBridge, select the
appropriate COM port. If no choices are available,
the bios or operati ng syste m ma y no t be
configured for a serial port. Refer to your
computer or OS manuals for instructions. Once
this is done, configure the remaining serial port
settings.
The default values for the FibreBridge are:
➔
Baud Rate = 9600
➔
Data Bits = 8
➔
Parity = None
➔
Stop Bits = 1
➔
Flow Control = None
If a link cannot be established, BridgeTools will
time out and an error message will be displayed.
If this happens, verify the following items:
➔
The FibreBridge(s) is powered up
➔
Cables have a secure connection. Make
sure a crossover serial cable is being used.
➔
The COM port on the computer is
config ur e d pr op e rly.
➔
Hyperlink or some other serial program is
able to communicate between the
FibreBridge and the computer.
Connection pages
10
Page 14

4.2 General panel
The general panel provides some basic information about the Fibr eBridge. A message box at the bottom
of the panel displays useful hints and suggestions. Clicking on the help icon will give a detailed
explana tion of eac h parameter, th e possible values t o enter and how t he Fi breBr idge will r espond to ea ch
selection. Some parameters will be “grayed out” if they do not apply to your model of the FibreBridge
or if they have no effect based upon the selected value of a related parameter.
Blink Ready LED (default = disabled)
Enabling this option causes the Ready LED on the front
panel of the FibreBridge to blink until you disable the
parameter. Helps to identify the particular FibreBridge you
are connected to in the SAN.
FibreBridge Name
An eight-character name assigned by the user to identify
each FibreBridge on the network to help identify and select
a specific FibreBridge.
FibreBridge Type
Read only: reports the type of FibreBridge in use.
Minimum Alarm Temperature
Sets and displays the enclosure temperature minimum
threshold value. An alarm will trigger if the enclosure
temperature drops below this value. Valid entries are
between 5 and 40 degrees C and must be below the
Maximum Alarm Temperature value.
Maximum Alarm Temperature
Sets and displays the enclosure temperature maximum
threshold value. An alarm will trigger if the enclosure
temperature goes above this value. V alid entries are between
5 and 40 degrees C and must be above the Minimum Alarm
Temperature value.
NVRAM Version
Read only: reports the revision level of the NVRAM within
the FibreBr i dge.
Power Status A
Read only: allows remote monitoring of Power Supply A
status. BridgeTools will report it as either OK or
Unavailable.
Power Status B
Read only: allows remote monitoring of Power Supply B
status. BridgeTools will report it as either OK or
Unavailable.
Serial Number
Read only: serial number of FibreBr i dg e currently
connected to BridgeTools.
Temperature
Read only: allows remote monitoring of the FibreBridge
internal temperature.
World Wide Name (WWN)
Read only: provides a guaranteed unique identifier for each
Fibre Channel port on the network. This information can be
used to persistently bind the port to a host target ID.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
Blink Ready LED
FibreBridge name
FibreBridge type
Maximum Temperature
Minimum Temperature
NVRAM version
Power Status A
Power Status B
Serial number
Temperature
World Wide Name
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
11
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●
●●●●●●
2200/3200
serial port
●●●●●
●●
●●
●● ●●
4500
in-band
●●●
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
Page 15

4.3 SCSI Port configuration panel
This panel is used to modify the SCSI parameters for the FibreBridge. Some parameters will be “grayed
out” if they do not apply to your model of the FibreBridge or if they have no effect based upon the
selected value of a related parameter.
Each SCSI port on FibreBridge models with more than one
port must be configured separately. Each has its own subpanel marked as SCSI port 1, SCSI port 2, etc.
Force SCSI Negotiation Rate (default = Ultra2 Wide
SCSI)
The FibreBridge is designed to negotiate the most efficient
SCSI transfer rate with the attached SCSI devices. Some
devices and applications work better if you force the transfer
rate to a slower speed. Leaving the FibreBridge at the
default Ultra2/Wide SCSI rate will allow the autonegotiation function to determine the transfer rate.
Reset SCSI Bus on Startup (default = Enabled)
Disables the function to reset the SCSI Bus upon startup of
the FibreBridge. Even though it is called out in the SCSI-3
specification, some devices do not react very well to a bus
reset when the initiator is powered up. Set this field to
disabled if the host cannot detect connected SC SI devices.
SCSI Initiator ID (default = 7)
If the ‘Use SCSI Initiator Soft ID’ is enabled, used to enter
the ID for the SCSI Initiator Port of the FibreBridge. Th e
SCSI port on the FibreBridge is similar to a SCSI host
adapter in that it needs to have a SCSI ID that is different
than the SCSI devices connected to it.
Selection Timeout (d efault = 256 ms)
Sets the amount of time the FibreBridge will wait for a SCSI
device to respond after a selection request. The timeout
periods that can be selected are 256 ms, 128 ms, 64 ms, 32
ms, 16 ms, 8 ms, 4 ms, 2 ms and 1 ms.
Tagged Command Queuing (default = Enabled)
Leaving Tagged Command Queuing for the SCSI Ports of
the FibreBridge enabled allows maximum perform ance.
T agged Command Queuing is an optional SCSI II command
scheme in which multiple tagged commands are sent to the
drive for processing. The tagged commands are kept in the
drive's command buffer where they are sorted into an
optimal sequence by the drive's microprocessor and then
executed. Optimization orders the commands to require the
least amount of seeking and rotational latency in the drives.
TCQ additionally cuts down on the SCSI overhead by
buffering the incoming SCSI commands.
Some devices do not support Tagged Command Queuing
and do not react properly whe n the initiator attempts. Try
setting this field to disabled if you have trouble reading and
writing to SCSI devices connected to the FibreBridge.
Use SCSI Initiator Soft ID (default = Disabled)
Enables selection of the SCSI Initiator ID for the SCSI Bus
of the FibreBridge. When disabled, the SCSI ID is taken
from the jumper settings on the FibreBridge circuit board.
The factory default value is SCSI ID 7.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
Force SCSI Negotiation Rate
Reset SCSI Bus
SC Initiator ID
Selection Timeout
Tagged Command Queuing
Use SCSI Initiator Soft ID
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●
2200/3200
serial port
4500 in-
band
4500
Ethernet
4500 serial
port
12
Page 16

4.4 Ethernet port configuration panel
The Ethernet panel is used to configure the communication parameters for the Ethernet link on the
FibreBridge. Some parameters will be “grayed out” if they do not apply to your model of the
FibreBridge or if they have no effect based upon the selected value of a related parameter.
DHCP Server (default = Auto detect)
The FibreBridge Ethernet port is capable of receiving its IP
address from a DHCPP Server. Select “DHCP” to enable
this capability. If autodetect is selected, the FibreBridge will
use the ID address entered using IP Address.
Ethernet Speed (default = Automatic Detection)
Configures the Ethernet port on the FibreBridge to either
10Base-T, 100Base-T or for autom atic detectio n.
IP Address (default = 10.0.0.1)
Sets and displays t he current IP address of the Fibre Bridge .
If DHCP is enabled, this field will display the IP address
assigned by the name server.
IP Gatewa y (default = 0.0.0.0)
Sets and displays the current IP Gateway of the FibreBridge.
IP Subnet Mask (default = 255.255.255.0)
Sets and displays the current IP Subnet Mask of the
FibreBridge. If DHCP is enabled, this field will display the
Subnet Mask assigned by the name server.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
DHCP Server
Ethernet Speed
IP Address
IP Gateway
IP Subnet Mask
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
2200/3200
serial port
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
13
Page 17

4.5 Serial port configuration panel
The Serial Port Configuration panel configures the communication parameters for the RS-232 link on
the Fibr eBridge. These settings must match settings selected on your host computer in order to establish
a link. Some parameters will be “grayed out” if they do not apply to your model of the FibreBridge or
if they have no effect based upon the selected value of a related parameter.
The number of data bits is fixed at eight for the FibreBridge.
Parity is always disabled.
Baud Rate (default = 9600)
Modifies the baud rate. The FibreBridge is capable of 2400,
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 or 115200 bits per second.
Flow Control (default = None)
FibreBridge and the host computer. Serial port flow control
can be managed using either hardware flow control,
software flow control (Xon/Xoff) or no flow control.
Stop Bits (default = 1)
Configures the number of stop bits per character to either
one or two.
Selects the method for data handshaking b etween the
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
Baud rate
Flow control
Stop bits
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
2200/3200
serial port
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
14
Page 18

4.6 Firmware updater panel
This panel is used to flash the updated FibreBridge firmware.
Firmware for FibreBridge products is distributed in a .JAR
file, a compressed file containing the firmware image file
(*.IMA) and supporti ng readme documents. It is not
necessary to decompress the JAR file before flashing.
If necessary, BridgeTools will flash the FibreBridge with
.IMA files.
1 Download the latest firmware, a .JAR file,
from the ATTO Technology, Inc. web site at
www.attotech.com
. Store it in a convenient
location, possibly in the BridgeTools
directory.
2 Click on the BROWSE button to locate the
.JAR file.
3 Highlight the file and click the SELECT
button. The file selected will be displayed in
the ‘Select firmware to flash’ window.
4 Click on the VIEW DOCUMENTA TION button
to read about this version of firmware, new
features and any recommendations from
ATTO Technology, Inc.
5 Click on the FLASH button to erase the
current version of firmware and install the
new version. BridgeT ools will indicate when
the process is completed.
W ARNING
Do not cycle power on the Fib reBridge w h ile
the unit is being flashed.
6 The new firmware will not execute until
power is cycled on the FibreBridge or a
Restart firmware command is issued from
the Save/Restore panel. Once one
FibreBridge has been flashed, BridgeTools
will be able to recall the firmware file. The
firmware will be found in the ‘Select
Firmware to Flash’ pull-down window.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
Firmware updater utility
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●● ●●
2200/3200
serial port
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
15
Page 19

4.7 Fibre Channel port configuration panel
This panel is used to modify the Fibre Channel parameters for the FibreBridge. Some parameters will
be “grayed out” if they do not apply to your model of the FibreBridge or if they have no effect based
upon the selected value of a related parameter.
ACK Mode (default = ACK1)
ACK 0 and ACK 1 are the two dif ferent methods for sending
the acknowledgment during Class 2 transfers. ACK 0 sends
an acknowledgement at the end of a sequence of data
packets. When ACK 1 is selected, an acknowledgement will
be sent after every data packet. The method of ACK must
match that of the initiator.
Addressing Mode (default = Soft)
Select either the Hard or Soft Fibre Channel Addressing
Mode. Hard Addressing enables the FibreBridge to always
use the AL-P A (Fibre Channel ID) value entered in the Hard
Address fi eld. Soft Addr essing will re sult in the FibreBridge
taking a soft address in which the FibreBridge will be
assigned an AL-PA by the loop master during loop
initialization. This may cause the FibreBridge, and
connected SCSI devices, to be identified by a different ALPA each time the loop is rebooted.
Address Translation (default = Disabled)
Used to enable the Addressing Translation Mode within the
FibreBridge. Setting Address Translation to Disabled will
result in the FibreBridge using the default bit pattern of
LLLL TTTB to address your SCSI devices.
Setting the Address Translation to Enabled allows users to
configure the BTL pattern (FibreBridge Bu s, Target ID,
LUN) for a configuration that matches the intended
installation.
A Fibre Channel host computer will address the
FibreBridge using a Fibre Channel ID and a Fibre Channel
LUN (ex. ID 4 LUN 7). The SCSI devices connected to the
FibreBridge will be addressed as Fibre Channel LUNs of
the FibreBridge ID (ex. ID 4 LUNs 0-6). The FibreBridge
has two independent busses that can each contain SCSI
targets 0 through 15 with multiple LUNs for each target.
The BTL translation method is used to co mbine each of
these unique SCSI device IDs into one Fibre Channel LUN,
while maintaining the requirement that each SCSI device
have an unique identifier.
Each SCSI device connected to the FibreBridge can be
identified by the FibreBridge Bus (B) it is connected to, the
SCSI Target ID (T) the device is set at and the SCSI LUN
(L). The selected bit pattern uses a binary translation to
combine the BTL information into one Fibre Channel LUN.
Leaving this field disabled is usually acceptable if you have
four or fewe r SCSI tar get de vic es on FibreBr idge Bus 1 (se t
to SCSI IDS 0, 1, 2 and 3) a nd four or fe wer on Fi breBridg e
Bus 2 (set to SCSI IDs 0, 1, 2 and 3). Configurat i ons using
SCSI RAID contro llers o r th ose th at re quir e more than four
devices per bridge bus will require you to set this field to
enabled and to modify the Addressing Meth od field. Refer
to the Fibre Channel to SCSI Addressing ch apter in the
FibreBridge manual or co ntact ATTO Technical Support if
you need further assistance.
Hard Address (default = 3)
Used to set the decimal value of the FC-AL hard address
after the Addressing Mode field is set to Hard. Allowable
values are between 0 and 126. Be sure to select an AL-PA
not in use by any other Fibre Channel device in the
arbitrated loop.
Arbitration Fairness (default = Enabled)
Used to enable or disable Arbitration Loop Fairness.
Fairness is an algorithm that assures all NL_Ports on an
arbitrated loop will have equal access to the loop. Each
NL_Port has an arbitration priority assigned to it based on
its AL_P A. When enabled, the fairness algorithm creates an
access window in which all NL_Ports are given an
opportunity to win access to the loop, regardless of assigned
priority. When disabled, a device with a high priority may
dominate the loop.
Some Fibre Channel devices are not compatible in the
execution of arbitration fairness algorithms. If you
experience intermittent behavior in terms of FibreBridge
performance or certain SCSI devices connec ted to th e
FibreBridge are not detected by the host computer, try
disabling this setting.
Class 2 (default = Disabled)
Used to enable Class 2 Fibre Channel transfers. When
enabled, the target device (FibreBridge) will send an
acknowledge to the initiator indicating that data has been
received. The default mode of the FibreBridge uses Class 3
transfers in which the responsibility of verifying that data
has been properly transferred is left to the app lication
program. While Class 2 will result is fewer retries from the
application program, it requires more overhead to send the
actual acknowledge. Only set the bridge for Class 2
transfers if the initiating device also supports it.
FibreBridge Soft Fibre LUN (de fault = 7)
If Address Translation has been enabled, the value selected
will be the Fibre Channel LUN of the FibreBridge as
identified by all host computers. For example, if a value of
5 exists in this field and the FibreBridge hard address is set
16
Page 20

to 3, the FibreBridge will be at AL-PA 3 LUN 5 on all host
computers. The ran ge of v alid LUNs is 0 throug h 255. Mo st
operating systems can only scan for the LUNs 0 through
31and you should choose between these values.
If Address Translation is off, the FibreBridge LUN is set
from jumpers on the circuit board. The factory default
jumper value is LUN 14.
Fibre Channel Connect Mode (default = Arbitrated
Loop (FL_Port))
Sets the FibreBridge to either Arbitrated Loop (FL_ Port)
mode or Point to Point (F_Port) mode. F_ Port mode can
only be used when connecting directly to a F_Port on a host
adapter or a switch. FL_Port mode must be used when the
FibreBridge is connected to a hub or there are other devices
daisy chained off of the second GBIC port of the
FibreBridge. F_Port mode will result in slight performance
improvements. The initiator must be set to the same mode
as the FibreBridge for proper operation.
Fibre Channel Frame Length (default = 2048)
Modifies the maximum number of payload data bytes in a
Fibre Channel frame. Select 512 bytes, 1024 bytes or 2048
bytes. Experimenting with this value may increase
performance depending on both the application and
connected devices.
Open Full Duplex (default = Enabled)
Used to enable or disable Full Duplex transfer, a mode in
which a Fibre Channel port can receive and transmit data at
the same time, resulting in improved performance under
certain conditions. The initiator must also be set for Full
Duplex transfers.
Physical Device Addressing Method (default = LLLL
TTTB)
If the Address Translation field is set to enabled, modifies
the SCSI Address translation pattern for the Fibre Br idg e.
The number of B, T and L bits defined in the pattern will
determine the number of FibreBridge busses, targets, and
LUNs addressed. The position of the B, T and L bits will
determine how they are mapped into the Fibre Channel
LUN. A binary translation is used to convert the eight BTL
bits into 256 possible unique F ib re Channel LUNs.
Using the default pattern of LLLL TTTB will allow two
FibreBridge busses to be addressed. One B bit can have a
value of 0 or 1. With three T bits, there is a possibility for
eight unique targets on each bus. Four LUN bits allow
sixteen LUNs on each target, on each bus. The decimal
value of this BTL byte is what is used to determine the Fibre
Channel LUN value of your connected SCSI device.
For example, if the addressing pattern is set to LLLL TTTB
and a SCSI drive is set at Target ID 4 LUN 0 connected to
FibreBridge bus 1. The B bit is set to binary 1, the T bits are
set to binary 4 (100), the L bits are set to binary 0 (000 0) .
The LLLL TTTB pattern will be filled in as 0000 1001
which translates to Fibre Channel LUN 9.
T o modify the BTL patter n, click on the bar that con tains the
BTL bits. An edit window will pop up.
Use the tool to select the position and number of bits for the
Bus, Target, and LUN bits. BridgeTools will indicate if an
inappropriate bit pattern is selected. Each BTL designator
can hav e any num ber of def ined bits . Do not lea ve und efined
bits unless they are at the most significant positions. For
example, if only 5 bits need to be defined they must be in
positions 0 through 4. Leaving bit 0 undefined and then
assigning bits 1 through 5 is not allowed. Any one bit
position cannot be assigned to more than one BTL
designator. When more than one bit is required for any of
the B, T or L designators, they must be next to each other.
Three T bits must be assigned in consecutive positions.
A translation tool will help determine the Fibre Ch ann e l
LUN for a dev ice. Cl ick on the
View FC LUNs
tab. Find the
SCSI Target ID the device is set at down the left-hand
column. Find the SCSI LUN the device is set at (usually 0)
along the top. The Fibre Channel LUN is the value in the
green field that coincides with the devices SCSI ID and
LUN.
The table calculates the Fibre LUN based upon the current
BTL pattern set within the
tab, with a separate table
Editor
for devices connected to FibreBridge bus 1 and bus 2. The
grayed out LUNs are “unreachable” because this is the SCSI
ID the bridge SCSI po rt is set to. The Fi bre Channel LUN i n
red is the ID the FibreBridge itself will assume.
Refer to the Fibre Channel to SCSI Addressing chapter in
the FibreBridge manual or contact A TTO T echnical Support
for further assistance.
Unprocessed SCSI Command Returns (default =
Queue Full)
Used to select the SCSI status command returned by the
FibreBridge when it is unable to accept a new command
from a host because of a temporary lack of internal
resources, a rare condition. This option is available because
some UNIX operating systems do not use the Queue Full
command and the FibreBridge will ne ed to send a Busy
instead. Using Busy instead of Queue Full slows data
transfer rates.
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
17
Page 21

Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
ACK Mode
Addressing Mode
Address Translation
Arbitration Fairness
Class 2 transfers
FB Soft Fiber LUN
FC Connection Mode
FC Frame Length
FC Initiator Mode
FC Port LUN
Hard Address
Open Full Duplex
Physical Dev. Addressing
Translation tool
Unprocessed SCSI Command
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●
●●●
●●●●●●
2200/3200
serial port
●●●●●
4500
in-band
●●●
●●●
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
FC port configuration
18
Page 22

4.8 Mapping panel
The mapping panel assigns LUNs, maps SCSI devices to FibreChannel ports and troubleshoots FC ports
and connected SCSI devices. The number of ports available depends on the particular model of the
FibreBridge.
In order for a host computer to comm u nicate to a SCSI
storage device connected to the FibreBridge, the host must
be able to identify the storage device (target). To the host,
each SCSI target is identified as a Fibre Channel ID and a
LUN (ex. ID 0 LUN 1). The Fibre Channel ID is the actual
ID of the bridge’s Fibre Channel port (set on the Fibre
Channel Panel). The LUN can be set to virtually any value
using this panel.
The FibreBridge moves data between a Fibre Channel port
and a connected SCSI storage device (target). The best way
to achieve maximum throughput to the SCSI devices is to
balance the connected SCSI devices among the Fibre
Channel and SCSI ports. This is done by mapping, or
assigning each SCSI device to any of the Fibre Channel
ports.
When you first open the Mapping panel after launching
BridgeT ools, the device window will be empty. Clicking the
button at the bottom of the panel will instruct the
SCAN
bridge to detect all of the connected SCSI targets.
Informatio n for each SCSI tar ge t foun d will be disp laye d in
a row within the window: the make and model of the device,
the SCSI bus or port of the bridge the device is connected to,
and the Target ID and LUN the device is physically set to.
Each detected SCSI target will be assigned a LUN and will
be mapped to the Fibre Channel port(s).
The port assignment and LUN value can be changed by
simply clicking in the cell of the table. A pull down list will
appear showing the available choices. It is important to
remember that every target on each Fibre port must be
assigned a u niq ue I D. You may have a LUN 0 on Fibre por t
0 and a LUN 0 on Fibre port 1, but an error will occur if
there are multiple LUN 0s on the same Fibre port.
The Fibre Channel port(s) of the FibreBridge will also be
displayed in the device window. Each of these ports is also
considered a target device for Serverless Backup
applications or when BridgeTools is communicating with
the bridge over the in-band connection. Because of this, the
LUNs assigned to the SCSI targets must be different than
the LUN assigned to the bridge port itself. The Fibre
Channel Port LUN can be assigned using the Fibre Channel
panel within BridgeTools.
The device window also contains an ACTION for each
SCSI target detected to set a target to either Online or
Offline. The target must be set to Online for the bridge to
pass through SCSI commands. If the target is set to Offline,
SCSI commands to that target will be rejected. Offline can
be used for balancing hou rs of use between tape drives.
➔
The read-only STATUS column in the
device window is used to report the status
of each mapped SCSI target.
➔
ONLINE indicates the device is online and
is able to accept SCSI commands.
➔
UNAVAILABLE indicates that no device
is present at a particular mapping.
➔
OFFLINE indicates that a device is not
able to accept SCSI commands
➔
GOING OFFLINE indicates that a device
was set to Offline in the Action column, but
queued commands to the device have not
yet completed.
New SCSI devices will automatically be assigned a LUN
and mapped to one of the Fibre Channel ports but will be set
to OFFLINE. The ACTION for each target device must be
set to ONLINE before a host computer will be able to access
it.
Once all of the mappings and actions have been completed,
the
APPLY
take effect. If there is an error with the mappings (for
example, two targets were assigned the same LUN on the
same Fibre port), BridgeTools will display a warning in the
message box at the bottom of the pag e. Unlike mo difying
the other parameters using Br idg eTools, mapping changes
take affect immediately after hitting APPLY. However, the
changes will not remain after a power cycle unless they are
saved using the Save/Restore panel.
The Mapping Panel also contains features to add a map or
remove a map. Clicking the
blank row to the device window. This can be useful for
mapping devices that will be connected to the FibreBridge
in the future. The future device can be mapped by filling in
the Fibre Port and Fibre LUN mapping fields. In addition,
information for the intended SCSI Bu s, SCSI Target and
SCSI LUN fields must also be entered. All information must
be filled in or an error message will appear when the APPLY
button is selected.
The mapping for any device can be deleted by highlighting
the row in the device window and clicking the
MAP
button must be selected to make the changes
ADD MAP
button.
button will add a
REMOVE
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
19
Page 23

Trouble shooting
The mapping panel is also very useful for troubleshooting.
Clicking the SCAN button displays a list of the Fibre
Channel port(s) and the SCSI Target devices, as well their
status (online/offline).
If a target is not detected or is listed as offline in the
ST ATUS field, check the device itself, the SCSI cabling, and
the SCSI termination.
If all targets for a particular SCSI Bus are not detected or are
all listed as offline in the STATUS field, chances are the
SCSI Bus within the bridge itself has failed. Call the place
of purchase for a repair order.
If a Fibre Port is listed as offline in the STATUS field,
chances are the Fibre Port within the bridge itself has failed.
Call the place of purchase for a repair order.
Mapping
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Options
Mapping Panel
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/Access method
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
2200/3200
serial port
●● ●●
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
20
Page 24

4.9 Events panel
Event logs help to troubleshoot hardware failur es. This panel configures the event logging features of
the FibreBridge. Some parameters will be “grayed out” if they do not apply to your model of the
FibreBridge or if they have no effect based upon the selected value of a related parameter.
If the SAN is unable to detect or communicate with SCSI
devices connected to the FibreBridge, you can examine the
Event Log to determine if there is a hardware issue with the
FibreBridge or if the problem is due to a configuration error.
If the FibreBridge is configured to log all events, the log can
be lengthy and difficult to interpret. Log events as ef ficiently
as possible by enabling logging for that section of the
FibreBridge.
Use BridgeTools to configure the type of event logging
desired. To view the actual events, use either Serial or
Ethernet communications tools such as FTP or Hyper
Terminal. Refer to the Fib reB ridge manual for further
details.
Event Level (default = all active)
Selects the level of monitoring and logging.
Event Logging (default = active)
Disables Event logging.
Event Subsystem (default = all active)
Selects which hardware subsystems are to be monitored.
Select as many of the hardware systems as needed:
➔
Fibre Channel
➔
SCSI, Ethernet
➔
GBIC
➔
NVRAM hardware systems
Clear all Events
Erases all previously recorded event log entries.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Access method
Options
Clear All Events
Event Level
Event Logging
Event Subsystem
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
2200/3200
serial port
●● ●●
●● ●●
●● ●●
●● ●●
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
21
Page 25

4.10 Save/Restore panel
This panel saves the new configuration changes in FibreBridge NVRAM, restores values to the factory
defaults, or exits without saving the changes.
CAUTION
New settings and newly flashed firmware will
not take affect until the FibreBridge power is cycled.
Save Current Settings
Saves any changes made to the configuration parameters.
The FibreBridge will use these options the next time it is
Leave This Session
Closes the current connection with the FibreBridge and
exits BridgeTools. Changed parameters during this se ssio n
will not take effect unless they were sav ed before closing the
connection.
Make Use of Saved Changes
Issues a restart firmware command to the FibreBridge. This
powered up.
Set to Factory Defaults
Sets configuration settings to the factory defaults.
Undo Changes
Ignores any changes made since entering the BridgeTools
program and returns configurations to the last saved values.
is the same as cycling power on the FibreBridge. Any
freshly saved configuration parameters or new firmware
will now be in effect.
Some options will be “grayed out” on the panel: they are not available because of the type of access mode or FibreBridge model or they have no effect based on other
Make use of saved changes
selections. The chart below shows options available based on model and access method.
Model/access method
Options
Leave this session
Save current settings
Set to factory defaults
Undo changes
2200/3200
in-band
2200/3200
Ethernet
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
●●●●●●
2200/3200
serial port
●● ●●
4500
in-band
4500
Ethernet
4500
serial port
22
Page 26

Appendix A Available products and accessories
The following Fibre Channel accessories are available through ATTO Technology. Contact an ATTO
Technology authorized sales representative to order.
Embedded
FibreBridge 1180
FCBR-1180-ELC Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Embedded Board with Copper DB9
FCBR-1180-ELS Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Embedded Board with Optical SC
FibreBridge 1190
FCBR-1190-ELC Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Embedded Board with Copper DB9
FCBR-1190-ELS Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Embedded Board with Optical SC
FibreBridge 2300
FCBR-2300-EL0 2-gigabit Fibre Channel to HVD Ultra SCSI Bridge Embedded Board
FibreBridge 4500
FCBR-4500-CH0 Fibre Channel to HVD Ultra SCSI Bridge CPCI Board
FCBR-4500-CL0 Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge CPCI Board
Destop/Rackmount
FibreBridge 1180
FCBR-1180-DLC Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Embedded Board with Copper DB9
FibreBridge 2200
FCBR-2200-DH0…… Fibre Channel to HVD Ultra SCSI Bridge Desktop or Rackmount
……
FCBR-2200-DL0
FibreBridge 2300
FCBR-2300-DL0 2-Gigaabit Fibre Channel to HVD Ultra SCSI Bridge Desktop or Rackmount
FibreBridge 4500
FCBR-4500-DH0 Fibre Channel to HVD Ultra SCSI Bridge Desktop or Rackmount
FCBR-4500-DL0 Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Desktop or Rackmount
Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra2 SCSI Bridge Desktop or Rackmount
ATTO FC Rack System (build to order)
FC Rack Enclosures with Power Supplies
FCRS-BAS1-000…… Rack System with Single Power Supply
FCRS-BAS2-000
FibreBridge 3200
FCBR-3200-RH0…… ATTO FibreBridge 3200R HVD
FCBR-3200-RL0
FibreBridge 3300
FCBR-3300-RL0 2-Gigabit Fibre Channel to LVD Ultra SCSI Bridge
ATTO Technology BridgeTools Installation and Ope ration Manual
i
……
Rack System with Redundant Power Supplies
……
ATTO FibreBridge 3200R LVD
Page 27

Field Replacement Units (FRU)
PWRA-0000-FRU Power Module for ATTO FC Rack System
FCBR-3200-RHF
FCBR-3200-RLF ATTO FibreBridge 3200R LVD Replacement Unit
FCBR-3300-RLF ATTO FibreBridge 3300R LVD Replacement Unit
MIAs
ADAP-MIAS-BLK MIA Adapter-Short Wave
GBICS
GBIC-DB90-000 GBIC – DB9 Active Copper Interface
GBIC-HSDC-000 GBIC – HSSDC Active Copper Interface
GBIC-SWFO-000 GBIC – Short Wave Optical Duplex SC Interface
SFP2-0000-000 SFP – Optical LC
Cables/Copper
CBL-FCCU-003 DB9 Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 3m.
CBL-FCCU-010 DB9 Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 10m.
CBL-FCCE-020 DB9 Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Equalized) – 20m.
CBL-HSDB-003 HSSDC to DB9 Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 3m.
CBL-HSDB-010 HSSDC to DB9 Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 10m.
CBL-HSHS-003 HSSDC to HSSDC Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 3m.
CBL-HSHS-010 HSSDC to HSSDC Copper Fibre Channel Cable (Unequalized) – 10m.
…
ATTO FibreBridge 3200R HVD Replacement Unit
Appendix D
Cables/Optical
CBL-FCFI-005 5 Meter Cable-Duplex 50 Micron Multi-mode FC/Optical
CBL-FCFI-010 10 Meter Cable-Duplex 50 Micron Multi-mode FC/Optical
CBL-FCFI-030 30 Meter Cable- Duplex 50 Micron Multi-mode FC/Optical
Cables/FibreChain
CBL-FCFC-001 FibreChain 24” Cable
Cables/SCSI
CBL-FP68-C3 68-pin “P” / 50-pin Centronics – 1m
CBL-FP68-C6 68-pin “P” / 50-pin Centronics – 2m
CBL-FP68-C25 68-pin “P” / 50-pin Centronics – 8m
CBL-FP68-C79 68-pin “P” / 50-pin Centronics – 24m
CBL-F68E-00X 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 1ft
CBL-U68E-681 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 1m
CBL-F68E-686 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 2m
CBL-F68E-003 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 3m
CBL-F68E-010 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 10m
CBL-F68E-025 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 25m
CBL-F68E-68X 68-pin “P” / 68-pin fine pitch “P” – 16m.
CBL-V68E-48 68-pin offset VHDCI to 68-pin VHDCI
ii
Page 28

Appendix B How to contact ATTO Technology, Inc.
Customer service, sales information and technical support are available by phone Monday through Friday,
Eastern Standard Time 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., or by fax and web site 24-hours a day.
ATTO Technology, Inc.
155 CrossPoint Parkway
Amherst, New York 14068
(716) 691-1999 • voice
(716) 691-9353 • fax
http://www.attotech.com
ATTO Technology can also be reached via e-mail at the following addresses:
Sales Support
Technical Support
: sls@attotech.com
: techsupp@attotech.com
ATTO T echnology BridgeTools Installation and Operation Manual
iii
 Loading...
Loading...