Page 1

SE5416A Series
Industrial Serial Device Server
User’s Manual
v. 1.0
April, 2013
Page 2

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Important Announcement
The information contained in this document is the sole property of Atop Technologies, Inc. and
is supplied for the sole purpose of operation and maintenance of Atop Technologies, Inc.
products. No part of this publication is to be used for any other purposes, and is not to be
reproduced, copied, disclosed, transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
human or computer language, in any form, by any means, in whole or in part, without the prior
explicit written consent of Atop Technologies, Inc., offenders will be held liable for damages. All
rights, including rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility model or design, are
reserved.
Disclaimer
We have checked the contents of this manual for agreement with the hardware and software
described. Since deviations cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full agreement.
However, the data in this manual is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections included
in subsequent editions. Suggestions for improvement are welcomed. All other product names
referenced herein are registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Published and Printed by
Atop Technologies, Inc.
2F, No. 146, Sec. 1, Tung-Hsing Rd.
Jubei, Hsinchu 30261
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-3-5508137
Fax: 886-3-5508131
www.atop-tech.com
www.atop.com.tw
Copyright © 2013 Atop Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Technical data is subject to
change.
ii
Page 3

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Content
1 Preface ..................................................................................................... 8
2 Introduction ............................................................................................ 10
2.1 Product Overview ................................................................................................... 10
2.2 Features ................................................................................................................... 11
3 Getting Started ....................................................................................... 12
3.1 Model Comparison ................................................................................................. 12
3.2 Inside the Package ................................................................................................. 13
3.3 Panel Layout and Dimensions .............................................................................. 14
3.4 First Time Installation ............................................................................................ 15
3.5 User Interface Overview ........................................................................................ 16
3.6 Factory Default Settings ........................................................................................ 17
4 LCM Configuration ................................................................................ 18
4.1 Welcome Screen ..................................................................................................... 18
4.2 Main Menu Structure .............................................................................................. 18
4.2.1 Overview ........................................................................................................ 19
4.2.2 Network Settings ............................................................................................ 19
4.2.3 Serial Settings ................................................................................................ 20
4.2.4 Server State ................................................................................................... 23
4.2.5 Restart............................................................................................................ 23
5 Web Configuration ................................................................................ 24
5.1 Administrator Login ............................................................................................... 24
5.2 Overview ................................................................................................................. 25
5.3 Network Configuration .......................................................................................... 28
5.4 Serial ........................................................................................................................ 34
5.4.1 COM Configuration ........................................................................................ 35
iii
Page 4

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.4.2 COM Configuration: Advanced Settings ........................................................ 37
5.5 Alert Settings .......................................................................................................... 40
5.5.1 Email Settings ................................................................................................ 40
5.5.2 Alert Event ..................................................................................................... 41
5.6 System Configuration ............................................................................................ 42
5.6.1 Link State ....................................................................................................... 42
5.6.2 Log Settings ................................................................................................... 43
5.6.3 System Log .................................................................................................... 45
5.6.4 COM Log ........................................................................................................ 45
5.6.5 Time Settings ................................................................................................. 46
5.6.6 Security Configuration .................................................................................... 47
5.6.7 Import/Export ................................................................................................. 48
5.6.8 Set to Default ................................................................................................. 49
5.6.9 Restart............................................................................................................ 49
6 CLI Configuration .................................................................................. 50
6.1 Accessing the CLI .................................................................................................. 50
6.1.1 Serial Console ................................................................................................ 50
6.1.2 Telnet Console ............................................................................................... 50
6.2 General Information ............................................................................................... 51
6.3 Networking Configuration ..................................................................................... 59
6.3.1 LAN 1 / LAN 2 Settings .................................................................................. 59
6.3.2 DNS Settings ................................................................................................. 60
6.3.3 SNMP Settings ............................................................................................... 60
6.3.4 Bridge Settings ............................................................................................... 61
6.3.5 ERPS Settings ............................................................................................... 61
6.3.6 STP Settings .................................................................................................. 63
6.4 COM Port Configuration ........................................................................................ 64
6.4.1 TCP Server for Link Mode ............................................................................. 64
6.4.2 TCP Client for Link Mode ............................................................................... 64
6.4.3 UDP Link Mode .............................................................................................. 65
iv
Page 5

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
6.4.4 Serial Settings ................................................................................................ 65
6.5 Alert Settings .......................................................................................................... 66
6.5.1 Configuring E-mail ......................................................................................... 66
6.5.2 Configuring Alert Event .................................................................................. 67
6.6 System Configuration ............................................................................................ 68
6.6.1 Link State ....................................................................................................... 68
6.6.2 Time Settings ................................................................................................. 69
6.6.3 Security Settings ............................................................................................ 69
6.7 Restoring Factory Default ..................................................................................... 70
6.8 Restart System ....................................................................................................... 70
7 Link Modes and Applications ............................................................... 71
7.1 Link Mode Configuration ....................................................................................... 71
7.1.1 TCP Server Mode .......................................................................................... 72
7.1.2 TCP Client Mode ............................................................................................ 75
7.1.3 UDP Mode ..................................................................................................... 77
7.2 Link Mode Applications ......................................................................................... 79
7.2.1 TCP Server Application: Enable Virtual COM................................................ 79
7.2.2 TCP Server Application: Enable RFC 2217 ................................................... 80
7.2.3 TCP Client Application: Enable Virtual COM ................................................. 80
7.2.4 TCP Client Application: Enable RFC 2217 .................................................... 81
7.2.5 TCP Server Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection
Master ...................................................................................................................... 81
7.2.6 TCP Client Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection
Slave 82
7.2.7 TCP Server Application: Enable Reverse Telnet ........................................... 83
7.2.8 UDP Application: Multi-Point Pair Connection ............................................... 84
7.2.9 TCP Server Application: Multiple TCP Connections ...................................... 86
7.2.10 TCP Server Application: Multi-Point TCP Pair Connections .......................... 87
8 VCOM Installation & Troubleshooting ................................................. 88
8.1 Enabling VCOM ...................................................................................................... 88
v
Page 6

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
8.1.1 VCOM driver setup ........................................................................................ 90
8.1.2 Limitations ...................................................................................................... 90
8.1.3 Installation ...................................................................................................... 91
8.1.4 Uninstalling .................................................................................................... 91
8.2 Enabling Virtual COM............................................................................................. 91
8.2.1 Enable VCOM in Serial device servers .......................................................... 91
8.2.2 Running Serial/IP in Windows ....................................................................... 92
8.2.3 Configuring VCOM Ports ............................................................................... 95
8.2.4 Exceptions ..................................................................................................... 96
8.3 Using Serial/IP Port Monitor ................................................................................ 103
8.3.1 Opening the Port Monitor ............................................................................. 103
8.3.2 The Activity Panel ........................................................................................ 103
8.3.3 The Trace Panel .......................................................................................... 104
8.3.4 Serial/IP Advanced Settings ........................................................................ 104
8.3.5 Using Serial/IP with a Proxy Server ............................................................. 106
9 Specifications ...................................................................................... 107
9.1 Hardware ............................................................................................................... 107
9.2 Software ................................................................................................................ 108
9.3 Pin Assignments .................................................................................................. 108
9.3.1 Serial and RJ-45 Connectors ....................................................................... 108
9.3.2 Serial and Female DB9 Connectors ............................................................ 109
9.3.3 Serial and Male DB9 Connectors ................................................................ 109
9.3.4 RJ-45 to Female DB9 Connection ............................................................... 110
9.3.1 RJ-45 to Male DB9 Connection ................................................................... 110
9.4 LED Indicators ....................................................................................................... 111
9.5 Buzzer ..................................................................................................................... 111
10 Upgrade System Firmware ................................................................. 112
10.1 Upgrade Procedure ............................................................................................... 112
11 Warranty ............................................................................................... 113
vi
Page 7

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
vii
Page 8

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
1 Preface
Purpose of the Manual
This manual supports you during the installation and configuring of the SE5408A/SE5416A
Series only, as well as it explains some technical options available with the mentioned product.
As such, it contains some advanced network management knowledge, instructions, examples,
guidelines and general theories designed to help users manage this device and its
corresponding software; a background in general theory is a must when reading it. Please
refer to the Glossary for technical terms and abbreviations.
Who Should Use This User Manual
This manual is to be used by qualified network personnel or support technicians who are
familiar with network operations; it might be useful for system programmers or network
planners as well. This manual also provides helpful and handy information for first time users.
For any related problems please contact your local distributor, should they be unable to assist
you, please redirect your inquiries to www.atop.com.tw or www.atop-tech.com .
Supported Platform
This manual is designed for the SE5408A/SE5416A Series and that model only.
Warranty Period
We provide a 5 year limited warranty for SE5408A/SE5416A Series.
Federal Communications Commission Statement
FCC - This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
8
Page 9

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference
at his own expense.
CE Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take appropriate measures.
9
Page 10

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
2 Introduction
2.1 Product Overview
Many industrial and Commercial devices equipped with slow serial communication
ports—RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422—are limited by transmission distance of 15 m.
Examples of these devices are PLC controllers, card readers, display signs, security controls,
CNC controller, etc. ATOP Technologies has overcome this limit with our new family of
SE5416A Series Serial Device Servers. SE5416A Series is designed to transmit data between
one-or-more serial devices and one-or-more TCP/IP devices through Ethernet or the optional
modem, and hence enhance the accessibility of the serial device through the ubiquitous
TCP/IP based Ethernet.
10
Page 11
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
2.2 Features
Dual 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet for redundancy with full duplex auto negotiation
Support RAW TCP Server/ TCP Client / UDP / Virtual COM / Tunneling Modes
Configuration: Built-in Web Server /Serial Console/ Telnet / Windows-based Utility
Monitor, manage and control industrial field devices remotely
Caution
Beginning from here there will be extreme caution exercised.
Never install or work on electrical or cabling during periods of lighting activity. Never
connect or disconnect power when hazardous gases are present.
WARNING: Disconnect the power and allow to cool 5 minutes before touching.
11
Page 12
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Model
Description
SE5408A
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, AC Inlet, US Plug, Rack Mount
SE5408A-DC
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, DC TB3, Rack Mount
SE5408A-S5
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, AC Inlet, US Plug, Rack Mount
SE5408A-S5-DC
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, DC TB3, Rack Mount
SE5408A-EU
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, AC Inlet, EU Plug, Rack Mount
SE5408A-EU-S5
8-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, AC Inlet, EU Plug, Rack Mount
SE5416A
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, AC Inlet, US Plug, Rack Mount
SE5416A-DC
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, DC TB3, Rack Mount
SE5416A-S5
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, AC Inlet, US Plug, Rack Mount
SE5416A-S5-DC
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, DC TB3, Rack Mount
SE5416A-EU
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-232, AC Inlet, EU Plug, Rack Mount
SE5416A-EU-S5
16-Port Industrial Serial Device Server, RS-422/485, AC Inlet, EU Plug, Rack Mount
3.1 Model Comparison
3 Getting Started
12
Page 13

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Item
Quantity
Description
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
1
Industrial Serial Device Server
RJ-45 to Male DB9 cable
1
Converts RJ-45 serial port to standard DB9
AC Power Cord
1
US or EU models only
Terminal Block
1
Lockable 3-pin Terminal Block for DC
models only
Foot Rubbers
4
Attach to the bottom of the device so it will
stand solidly on a surface
Rack Mount Kit
1
Mounting kit to mount the device on the 19”
Rack
Installation Guide + Warranty Card
1
CD (Utilities)
1
Inside you will find:
User’s Manual
Installation Guide
Serial Manager© Utility
3.2 Inside the Package
Inside the product purchased you will find the following items:
Note: Please notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged
in any form upon delivery. If your sales representative is unable to satisfy your enquiries,
please contact us directly.
13
Page 14
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
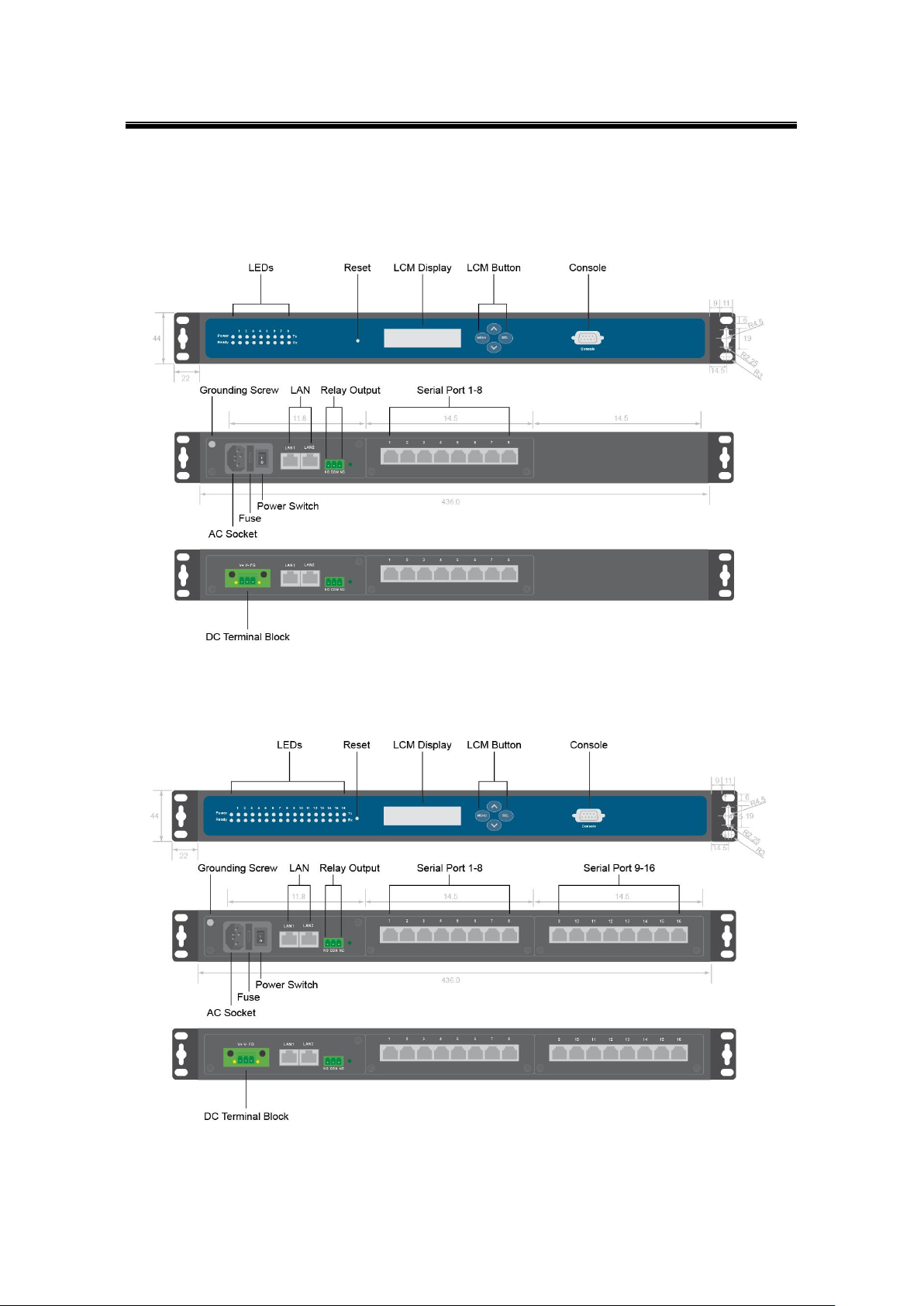
3.3 Panel Layout and Dimensions
Front and Rear Panels (SE5408A):
Front and Rear Panels (SE5416A):
Figure 3.1
Figure 3.2
14
Page 15
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
3.4 First Time Installation
Before installing the device, please adhere to all safety procedures described below, Atop will
not be held liable for any damages to property or personal injuries resulting from the
installation or overall use of the device. Do not attempt to manipulate the product in any
way if unsure of the steps described here, in such cases please contact your dealer
immediately.
1. Prepare the necessary cables, power cord, LAN cable, serial cable, etc.; do not connect
the unit yet.
2. Proceed then to plug the power source to the unit.
3. Place the device in the desired location and connect it to the LAN via an Ethernet cable
with an RJ45 connector.
4. Connect your computer to the LAN network.
Note: Remember to please consult your Hardware Installation Guide when attempting an
installation. Also, please follow all safe procedures when doing so.
15
Page 16
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
3.5 User Interface Overview
The SE5416A Series is designed as a device capable of transmitting data between Serial and
Ethernet; its user interface is designed intuitively for ease of use to suit the customer needs.
The web configuration appears as follows, Figure 3.3. The device can be configured using our
Serial Manager utility also, for more information, refer to Serial Manager’s manual.
Figure 3.3
On the left side, a menu-tree appears with all the modes and options available; while on the
right side of your screen the contents of each mode/option will be displayed in a graphical state.
For more information on each selection please refer to each option’s Section throughout the
manual. It is also worth noting that as a first step to view your device’s overall settings, you
should use Serial Manager© (the utility provided in the CD). There will be however, some
buttons which will be present during almost each section.
16
Page 17
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Parameters
Default Values
LAN 1
IP Address
10.0.50.100
Gateway
10.0.0.254
Subnet Mask
255.255.0.0
LAN 2
IP Address
192.168.1.1
Gateway
192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0
User Name
admin
Password
null (leave it blank)
COM
RS-232 (RS-422 if RS-232 is unavailable), 9600, None, 8,1,No Flow
Control
COM Link Mode
Mode: RAW, Type: TCP Server, Listen port 4660, Filter=0.0.0.0
3.6 Factory Default Settings
Upon arrival, the device will be set as follows:
17
Page 18

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Buttons
Function
Open Main Menu or go back one level
higher
Scroll up
Scroll down
Confirm the selection. When working
with IP addresses, pressing <SEL>
means moving to the next digit
4 LCM Configuration
There is an LCM (Liquid Crustal Monitor) installed on the front panel of the device that can be
used to display device information and perform basic configurations. The table below
illustrates its buttons and corresponding functions.
4.1 Welcome Screen
When the device boots up, the LCM will display LAN1. If you scroll down, it will display LAN2
information. The format is:
LAN1: Link down
10.0.50.100 ▼
4.2 Main Menu Structure
Press the <Menu> Key to enter the main menu. Press <Scroll Down> to go to the next layer or
option. Press <Scroll Up> to go to the back one layer or option.
18
Page 19
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
1.Overview
1.Model name
Display Model name
2.Kernel ver.
Display kernel version
3. AP ver.
Display AP version
4.Lan 1
1.Lan status
Display LAN1 status
2.MAC
Display MAC address of
LAN1
5.Lan 2
1.Lan status
Display LAN2 status
2.MAC
Display MAC address of
LAN2
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
2.Network set
1.Lan 1
1.IP config
1.Static IP
Change to Static IP mode
2.DHCP
Chang to DHCP mode
2.IP address
Display/Change LAN1 IP
3.Net mask
Display/Change Net mask
4.Gateway
Display/Change the
Gateway IP
2.Lan 2
1.IP config
1.Static IP
Change to Static IP mode
2.DHCP
Chang to DHCP mode
2.IP address
Display/Change LAN2 IP
3.Net mask
Display/Change Net mask
4.Gateway
Display/Change Gateway
IP
3.DNS server1
Display/ Change DNS
Server 1 IP address
4.DNS server2
Display/ Change DNS
Server 2 IP address
4.2.1 Overview
4.2.2 Network Settings
19
Page 20
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
3.Serial set
1.Select port
Select a COM Port to
configure
2.Parameter
set
1.Baud Rate
1. 300
Display/Change baud rate
2. 600
3. 1200
4. 2400
5. 4800
6. 9600
7. 19200
8. 38400
9. 57600
10. 115200
11. 230400
12. 460800
13. 921600
2.Parity
1. None
Display/Change Parity
2. Odd
3. Even
4. Mark
5.Space
3.Data bits
1. 5 bits
Display/Change Data bit
2. 6 bits
3. 7 bits
4. 8 bits
4.Stop bits
1. 1 bits
Display/Change Stop bit
2. 2 bits
4.2.3 Serial Settings
20
Page 21

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.Flow control
1. None
Display/Change Flow
control mode
2. Xon/Xoff
3. Hardware
6.Delimiter
1.Net to serial
1.Disable
Disable UART Delimiter
2.Enable
1.Timer: Change UART
delimiter to timer mode
and set its time
2.Char: Change UART
delimiter to character
mode and set the
character
2.Serial to net
1.Disable
Disable UART Delimiter
2.Enable
1.Timer: Change UART
delimiter to timer mode
and set its time
2.Char: Change UART
delimiter to character
mode and set the
character
7.UART
mode
1. 232
Display/Change UART
mode to RS232
2. 422
Display/Change UART
mode to RS422
3. 485
Display/Change UART
mode to RS485
8.Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply serial settings to all
serial ports
3.Link mode
Display/Change Link
mode
1.TCP server
1.Virtual
COM
1.Disable
Display/Change Virtual
COM mode
2.Enable
21
Page 22
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
2.Local port
Display/Change Local
listening port
3.Max
connect
Display/Change
maximum client
connection (1~4)
4.IP Filter
1.Disable
Display/Change IP Filter
function and the IP
address
2.Enable
5. Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
2.TCP client
1.Dest IP 1
Display/Change
Destination IP 1
2.Dest port 1
Display/Change
Destination port 1
3.Destination
2
1.Disable
Disable destination 2
2.Enable
Display/Change
Destination IP 2 and
Destination port 2
4. Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
3.UDP
1.Local port
Display/Change Local
listening port
2.Dest IP1
Display/Change
Destination IP 1
3.Dest port 1
Display/Change
Destination Port 1
4.Destination
[2-8]
1.Disable
Disable Destination [2-8]
2.Enable
Display/Change
Destination IP [2-8] and
Destination port [2-8]
22
Page 23
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
b.Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
4.Server state
1.Console
1.Web
console
1.Disable
Disable Web console
2.Enable
Enable Web console
2.Telnet
console
1.Disable
Disable Telnet console
2.Enable
Enable Telnet console
2.Pwd protect
1.LCM
console
1.No
Disable LCM console
password protection
2.Yes
Enable and change the
password
2.Reset
button
1.No
Disable the Reset button
password protection
2.Yes
Enable and change the
password on Reset button
3.Ping
1.Lan 1
Use "ping" command to
check specific IP address
for LAN1
2.Lan 2
Use "ping" command to
check specific IP address
for LAN2
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
5.Restart
1.No
Cancel Restart command
2.Yes
Restart immediately
4.2.4 Server State
4.2.5 Restart
23
Page 24
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 5.1
5 Web Configuration
5.1 Administrator Login
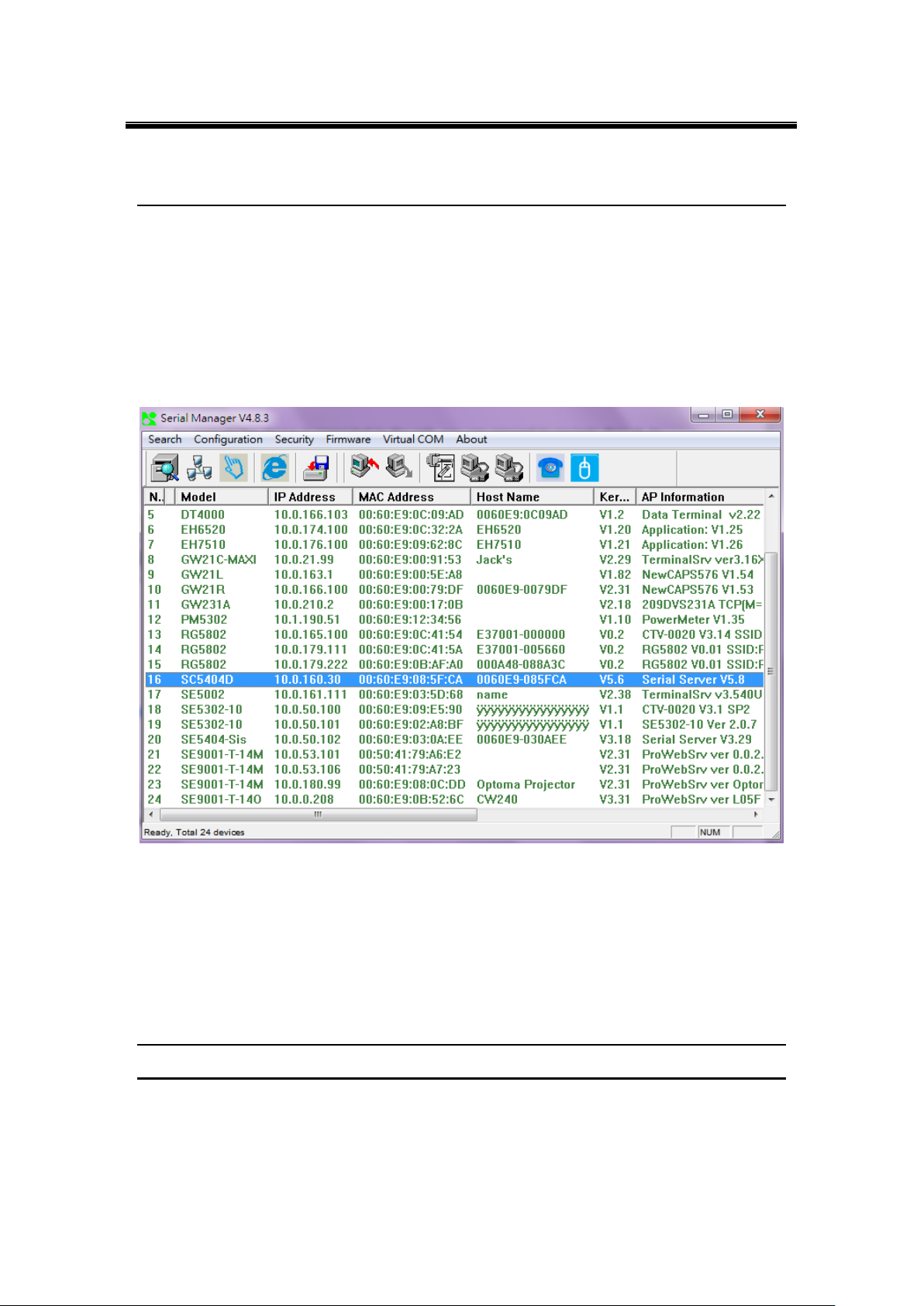
As soon as the device is connected on the LAN, the user can proceed to navigate through its
configuration using Serial Manager© (utility that comes in the CD); as noted in Figure 5.1
below, important information such as the IP, MAC address, etc. is going to be displayed.
To access the device’s Web UI click on the Config by browser icon, the web browser will
open and prompt you to enter username and password (see Factory Default Settings for more
information), proceed then to click “OK” or press Enter. Alternatively, enter the IP address of
the device in the URL bar of the browser.
Note: Be sure your PC Is located in the same network sub-net as SE5416A Series.
24
Page 25

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
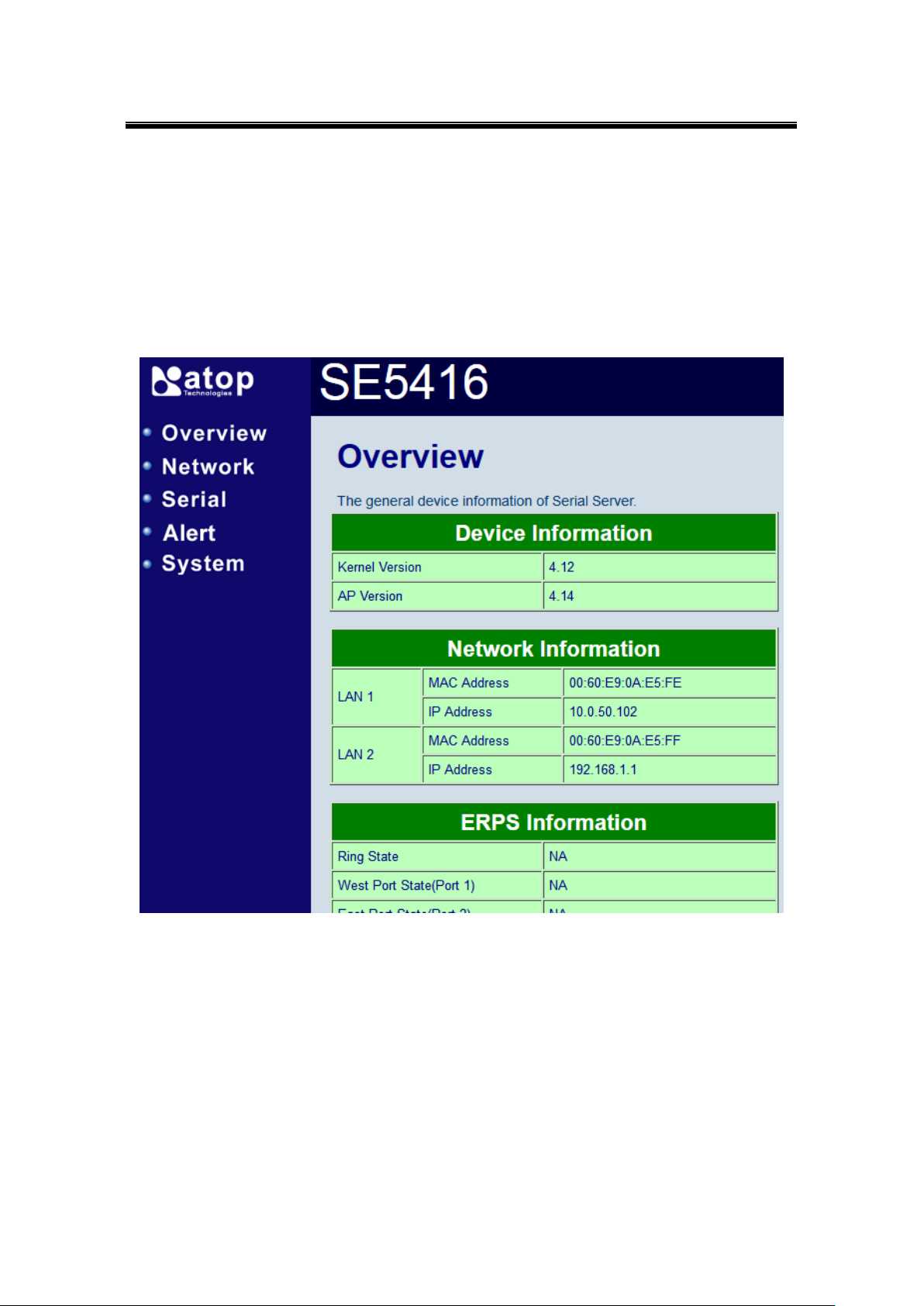
5.2 Overview
This section gives a general status information on Device, network, ERPS and STP.
Figure 5.2
Device Information, displays system Kernel and AP versions.
Figure 5.3
25
Page 26

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Networking Information, displays both ‘LAN1 and LAN 2’sinformation on the overview page.
The information provided with networking settings.
Note: If the device is in the bridge mode, Bridge information will be shown instead.
Figure 5.4
ERPS Information, displays Ring and Port status.
Figure 5.5
26
Page 27
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
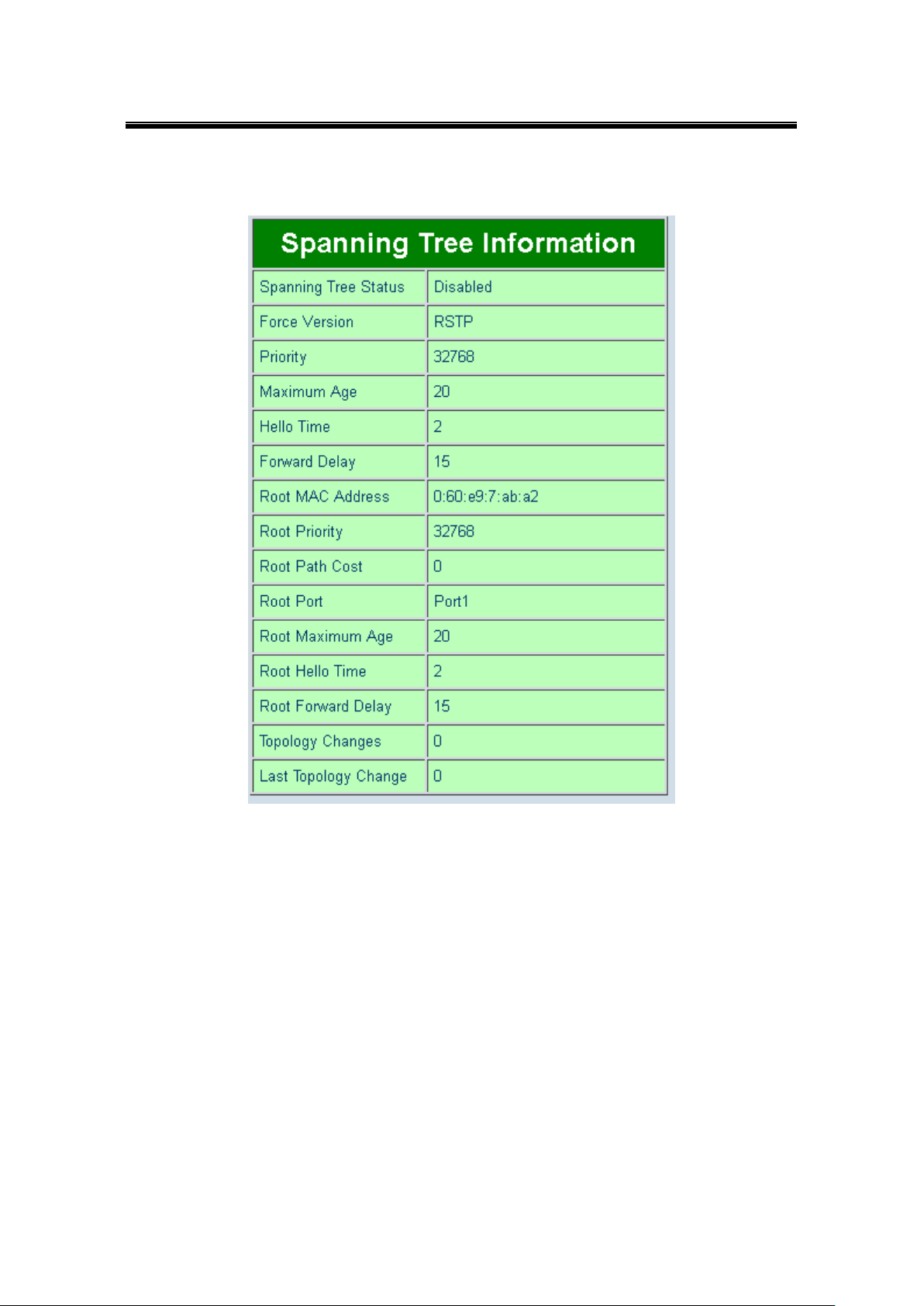
Spanning Tree Information, STP and STP Port Information display the current STP settings
and status.
Figure 5.6
27
Page 28

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
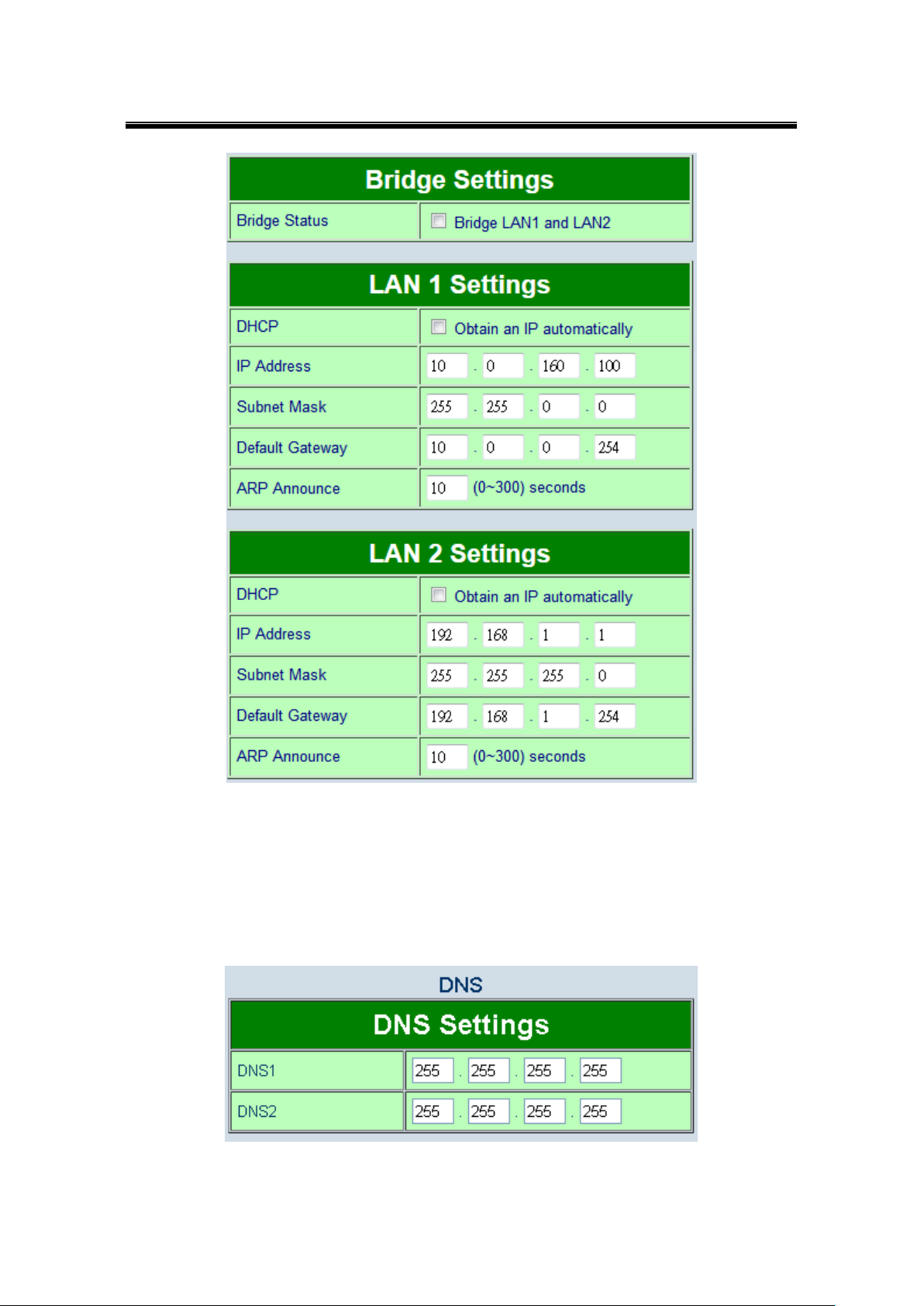
5.3 Network Configuration
Figure 5.7
Click on the “Network” link to open network settings.
LAN / Bridge Settings, when the bridge function is enabled, LAN1 and LAN2 will use
the same IP address for redundancy. Therefore, LAN1 Settings will become Bridge
Settings and LAN2 Settings will be disabled. When the bridge function is disabled, you
can LAN1 and LAN2 can be in different subnets. Fill in Bridge / LAN settings accordingly.
Alternatively, you may activate DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) client
function by checking on “Obtain an IP automatically” field to obtain IP address, gateway
and subnet mask, and DNS from a DHCP server automatically.
28
Page 29
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 5.8
DNS Settings, Fill in DNS (Domain Name System) information in order to have an
external DNS server resolve domain name into IP address. This is crucial if the NTP and
SMTP services use domain names instead of IP addresses. A DNS server will be
retrieved from the DHCP server automatically if DHCP is enabled.
Figure 5.9
29
Page 30

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
SNMP Settings, The SNMP function is disabled by default. To enable this function check
on “Enable SNMP” option. Basic SNMP configurations such as Read/Write Community,
SysName (System Name), SysLocation (System Location), and SysContact (System
Contact) are supported. In addition, you can send SNMP Trap events to a SNMP Trap
server by entering its IP address. The changes will become effective immediately after a
successful save.
Figure 5.10
ERPS Settings, A typical ring topology provides multipoint connectivity economically, but
the network traffic will loop inside the ring without a proper protection mechanism.
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) is a protocol for Ethernet layer ring networks.
ERPS provides highly reliable and stable protection in the ring topology while not forming
network loops that could potentially affect the network operation. In a the Ring topology,
each Ring Node is connected to an adjacent Ring Node participating in the same Ring
using two independent links (i.e. two ways). Loops can be avoided by guaranteeing that
traffic may flow on all but one of the ring links at any given time. This particular link is
called Ring Protection Link (RPL). A control message called R-APS coordinates the
activities of switching on/off the RPL. Under normal conditions, this link is blocked by the
Owner Node, which is referred as the blocking state. In case of a network failure, the RPL
Owner node will be responsible to unblock the RPL to allow it to be used for forwarding,
hence called the protection state. Therefore, the RPL becomes the backup link when a
link failure occurs. The following table describes the functions of different ERPS settings.
30
Page 31

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Label
Description
ERPS
Choose whether to enable ERPS or not.
RAPSD VLAN
Specifies the ring’s R-APS VLAN ID. VLAN ID ranges from 1 to 4094, every
ring should have its own ID.
PRL Owner
Enable to set this device as the RPL Owner.
RPL Port
Select the RPL Port when the device is an Owner.
WTR Timer
Set the wait-to-restore (WTR) time of the ring in minutes, ranges from 0 to 12
minutes.
Holdoff Timer
Set the holdoff time for the ring, it ranges from 0 to 10000 milliseconds.
Guard Timer
Set the ring’s guard time, ranges from 0 to 2000 milliseconds.
MEL
Sets the ring’s maintenance entity group level, ranges from 0 to 7.
Figure 5.11
STP Settings, Standard Spanning Tree specified by IEEE supported. The Spanning
Tree Protocol (STP) provides function to prevent switching loops and ensuring broadcast
radiation. A switching loop occurs in network when there are multiple connections
between two network devices. The loop will create broadcast radiation: accumulation of
broadcast and multicast traffic on a network. As broadcasts and multicasts are forwarded
31
Page 32

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Label
Description
Spanning Tree
Choose whether to enable or disable Spanning tree.
Force Version
Select STP or RSTP.
Priority
Configures the bridge priority in the range of 0 ~ 61440. The switch with lower bridge priority
has more chance to become a root bridge.
Maximum Age
If a device is not the root and it does not receive a hello message in within the “Maximum Age”,
it will reconfigure itself as a root, ranges from 6 to 40 seconds.
Hello Time
The amount of time that the root should wait before sending hello messages again, ranges
from 1 to 10 seconds.
Forward Delay
Configures the amount of time the device should wait before checking to see if it should change
from the learning state to the forwarding state. Lesser delay time means that the state will
change more quickly, ranges from 4 to 30 seconds.
Port Path Cost
Configures the port path cost in the range of 1~200000000. This value will affect the
combination path cost. The lowest combination path cost will be the best path to the Root
Bridge
Port Priority
Configures the port priority in the range of 0~240. The port with the lowest priority value has the
best route to the root bridge.
Port P2P
Selects P2P (point to point) connection type:
Force No: Force Port P2P link false.
Force Yes: Force Port P2P link to true.
Auto: Set Port P2P link to auto detection.
Port Edge
Choose whether the port is an edge connection.
by bridges/switches to every port, the bridges/switches will repeatedly rebroadcast the
broadcast messages, and this can flood the network. STP creates a spanning tree and
disables those redundant links that are on the same level of the tree, which leaves only a
single active path between any two nodes. This function avoids flooding and increases
network efficiency. RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) are also supported. It is an
evolution of the STP. It has a slightly changed topology, which helps to provide a much
faster spanning tree convergence. The following table explains each STP option’s usage.
32
Page 33

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 5.12
33
Page 34

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.4 Serial
Click on the “Serial” link to open its submenu and COM1 settings.
Figure 5.13
34
Page 35

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.4.1 COM Configuration
This section will only focus on the serial settings (Figure 5.15). Details on connectivity
protocols and their settings (Figure 5.14) are given in Link Modes and Applications.
Figure 5.14
35
Page 36

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 5.15
Match these settings with your serial device:
UART Mode, Select between RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485. Note that RS-485 refers to
2-Wire RS-485 and RS-422 is compatible with 4-Wire RS-485.
Baud Rate, Select one of the baudrates from the dropdown box.
Parity/Data Bits/Stop Bits, Configure them accordingly.
Flow Control, Choose between No Flow Control, RTS/CTS (Hardware Flow Control),
and Xon/Xoff (Software Flow Control). If Xon/Xoff is selected, Xon and Xoff characters
are changeable. Defaults are 0x11 for Xon and 0x13 for Xoff. If the connecting program
or serial device would like to receive the Xon/Xoff signals also, enable “Permit Xon/Xoff
Character Pass Through”. Enable “Xon/Xoff Special Control” to allow
synchronization between Xon/Xoff states and DSR/DTR signals.
Note: Check “Apply to all serial ports” to execute these settings through all serial ports.
36
Page 37

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.4.2 COM Configuration: Advanced Settings
Click on the “Advanced Settings” button to open the dialog (Figure 5.16).
Figure 5.16
TCP
TCP Timeout, Specify the value in “TCP Timeout” to force SE5416A Series actively
close a TCP connection after some specific inactivity time (no packets). The default value
for it is 3600 seconds. Disabling this option means SE5416A Series would never actively
close an established connection.
Delimiters
Serial to Network Packet Delimiter, Packet delimiter is a way of packing data in the
serial communication. It is designed to keep packets in track. SE5416A Series provides
three types of delimiter: Time Delimiter, Maximum Bytes and Character Delimiter. Note
that the following delimiters (Interval, Max Byte and Character) are programmed in the
OR logic. Meaning that if any of the three conditions were met, SE5416A Series would
37
Page 38

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Attention
Interval Timeout Manual Calculation
The optimal “Interval timeout” depends on the application, but it must be at least larger
than one character interval within the specified baud rate. For example, assuming that
the serial port is set to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity. In this case, the
total number of bits needed to send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to
transfer one character is (10 (bits)/1200 (bits/s))*1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set the “Interval timeout” to be larger than 8.3 ms. Rounding 8.3
ms to the next integer would get you 9 ms.
transmit the serial data in its buffer over the network.
Interval timeout, SE5416A Series will transmit the serial data in its buffer when the
specified time interval has reached and no more serial data comes in. The default
value is calculated automatically based on the baud rate. If the automatic value
results in chopped data, the timeout could be increased manually by switching to
“Manual setting” and specifying a larger value. If the bytes do not reach certain
length condition, the bytes could be discard to avoid devices connect on the TCP
side running into issues. To do this, enable “Discard Byte”, then select the
condition (>, <, =, !=) you want and the length desired.
Max Byte, SE5416A Series will transmit the serial data in its buffer when the
specified length has reached. Enable this option if you would like SE5416A Series
to queue the data until it reaches a specific length. This option is disabled by
default.
Character, SE5416A Series will transmit the serial data in its buffer when it sees
the incoming data include the specified character (in HEX format). This field allows
one or two characters. If character delimiter is set to 0x0d, SE5416A Series will
push out its serial buffer when it sees 0x0d (carriage return) in the serial data. This
option is disabled by default.
Network to Serial Packet Delimiter, Same as the delimiters above, but controls data
flow in the opposite direction. It will store data from the network interface in the queue
and send it over to the serial interface until one of the delimiter conditions is met.
Character Send Interval, This option specifies the time gap between each character.
When set to two seconds, SE5416A Series will split the data in the queue and only
transmit one character (byte) every two seconds; this option is disabled by default.
Response Interval Timeout, This option only affects the Request & Response Mode
38
Page 39

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
and has no effect on the Transparent Mode. When TCP data is received (request) and
passed to Serial side, the device will wait for the set time before transferring another TCP
data if the Serial side did not receive any data (response).
Serial
Serial FIFO, By default, SE5416A Series has its FIFO function enabled to optimize its
serial performance. In some applications (particularly when the flow control is enabled), it
may deem necessary to disable the FIFO function to minimize the amount of data that is
transmitted through the serial interface after a flow off event is triggered to reduce the
possibility of overloading the buffer inside the serial device. Please note that disabling
this option on baud rates higher than 115200bps would reduce the data integrity
noticeably.
Serial Buffer, By default, SE5416A Series will empty its serial buffer when a new TCP
connection is established. This means that the TCP application will not receive buffered
serial data during a TCP link breakage. To keep the serial data when there is no TCP
connection and send out the buffered serial data immediately after a TCP connection is
established, disable this option.
39
Page 40

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.5 Alert Settings
Click on the “Alert” link to open its submenu and E-mail settings.
Figure 5.17
5.5.1 Email Settings
In case the device raises an alert and/or warning message, it will send an email to the
administrator’s mailbox. Email Settings allows you to set up the device to be able to send an
email. To set up the email sending, you need to put a “Sender” email address which will be
the “From” on the email. Then, you fill in “Receiver” email address to which the email is sent.
You can send the email to several recipients using Semicolon (;) to separate each email
address. Next step is to set the Email Server. First, you fill in the IP address of a Mail Server
in your local network. If the Mail Server needs a user authentication, you need to enable
“SMTP server authentication required”, and fill in Username and Password. Please
contact your network administrator for Mail Server IP address and the Username and
Password,
Note: You can click on the “Send test Mail” button to verify your mail settings.
Figure 5.18
40
Page 41
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Attention
It is also important to setup Default Gateway and DNS Servers in the Network
Settings properly, so your SE5416A Series can lookup DNS names and route the
mails to the proper default gateway.
Figure 5.19
5.5.2 Alert Event
Events could be triggered in different ways. Including Cold Star, Warm Start, Authentication
Failure, IP Change, Password Change, and Link Down. SE5416A Series supports three
different types of event alerts, which are E-mail, SNMP Trap, and Relay.
Figure 5.20
41
Page 42

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.6 System Configuration
Click on the “System” link to open its submenu and this will lead you to the Link State.
Figure 5.21
5.6.1 Link State
Link State displays the information of each connection for all serial ports for debugging
purposes. It also displays the byte count of each serial port’s Transmit (Tx) and Receive (Rx)
data.
Figure 5.22
42
Page 43

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.6.2 Log Settings
The Syslog function is turned on by default and cannot be turned off. It is used to log system
events and report to an external Syslog server if necessary. Also, Transmitted data could be
logged for recording or debugging purposes. The logs could be reported to an external Syslog
server as well.
Figure 5.23
System Log Settings
Enable Log Event to Flash, this would write log events to the local flash, otherwise the
logs would be cleared when the device restarts because they are stored in the RAM by
default.
Log Level, 3 (We only allow logging at this level).
Enable Syslog Server, enabling this option would allow you to send Syslog events to a
remote Syslog server.
Syslog Server IP, please specify the remote Syslog Serve IP.
Syslog Server Service Port, please specify the remote Syslog Server Port.
43
Page 44
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
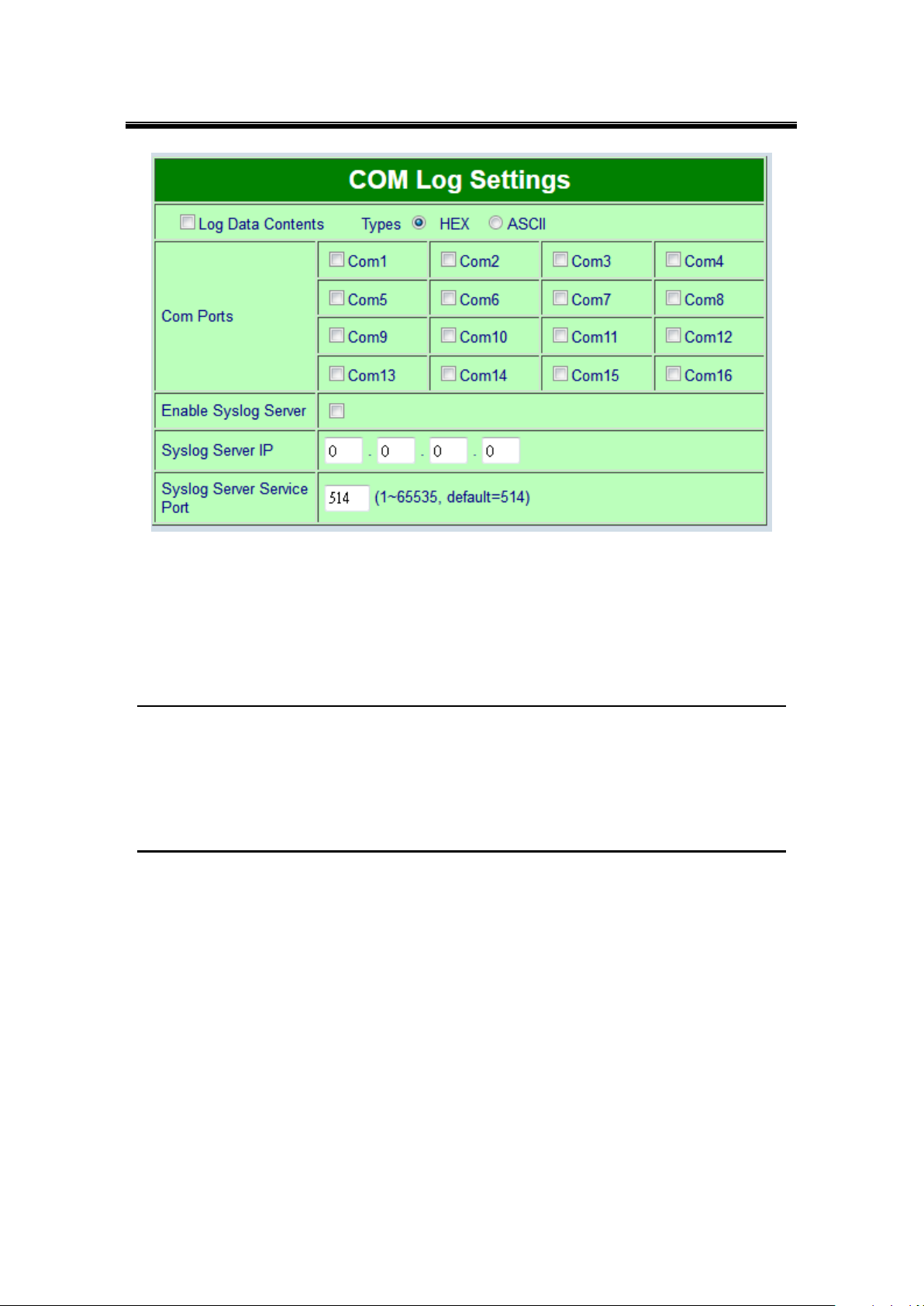
COM Log Settings
Figure 5.24
Log Data Contents, if enabled, the COM logging function will log the content (raw bytes)
of data that is being transmitted and received. If disabled, COM logging function will only
log data length to reduce system load.
Note: SE5416A Series can store up to 1500 lines internally. A request or a response will
consist of one line, data longer than 512 bytes will go into another line. You can retrieve the
logs by using a FTP Client. FTP login is the same as the WebUI. They are locates in
/var/log/logcomxx (xx is the port number). When the reserved space is full, new logs will
replace old logs. We strongly recommend sending COM logs to a remote Syslog server.
Data Log Types, Hex or ASCII.
COM x, choose which port to log.
Enable Syslog Server, enabling this option will allow you to send COM logs to a remote
Syslog server. You can send COM logs to the same Syslog server used previously for
logging events.
Syslog Server IP, please specify the remote Syslog Server IP.
Syslog Server Service Port, please specify the remote Syslog Server Port.
44
Page 45

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.6.3 System Log
Display the current syslog stored in the device.
Figure 5.25
Click on “Last Page” to go to the last page. Click on “Show All Event” to show all events in one
page. Click on “Clear All Event” to clear the events stored in the device.
5.6.4 COM Log
You can select from the COMx dropdown box to display logs from different COM ports. The
first three lines were set to show the logging of data length and the last two lines were set to
show data content in Hexadecimal.
Figure 5.26
Click on “Last Page” to go to the last page. Click on “Show All Event” to show all events in one
page. Click on “Clear All Event” to clear the events stored in the device.
45
Page 46

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Attention
It is also important to setup Default Gateway and DNS Servers in the Network
Settings properly, so your SE5416A Series can lookup DNS names and find
the external NTP Server.
5.6.5 Time Settings
Date and time can be set manually, or using Network Time Protocol (NTP) to automatically
synchronizes with a Time Server. For auto-synching select NTP in the Time Setting field,
proceeding then to fill the IP address or host name for it. If a hostname is entered, the DNS
server must be configured properly; a Time Zone can be selected as well.
In case that you are located in a region where Daylight Saving Time (DST) is being used,
enable this option and setup the start and end date when DST will become effective. Also enter
the time that DST offsets (usually one hour).
46
Page 47

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 5.27
5.6.6 Security Configuration
Figure 5.28
Change Password
Enter the old password in the “Old Password” field; enter the new password in the “New
Password” and the “Verified Password” fields, and then click on “Save Configuration” to
update the password.
Note: You can press the reset button on the device to reset the password to its default value
(blank), in case it is forgotten. This will however, erase all the data/settings previously in the
device so remember to always save it.
Figure 5.29
Security
You can disable certain access methods to reduce the risk of system intrusion. This includes
the Web UI, Telnet console, LCM, and the Reset Button.
Web Console – Disable to prevent the Web UI from being accessed.
Telnet Console – Disable to prevent the Telnet console from be accessed.
LCM Password Protect – LCM will prompt for a password before the device can be
configured through the LCM when it is protected. Press the “Up” and “Down” buttons next to
47
Page 48

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
the LCM to select the characters one by one.
Reset Button Protect – Resetting the device back to the defaults becomes impossible when
the reset button is protected.
5.6.7 Import/Export
Once all the configurations are set and the device is working properly, you may want to back
up your configuration. Backup can be used when the new firmware is uploaded and it is reset
to a factory default settings, it is done to prevent accidental loading of incompatible old settings.
The backup file could also be used to efficiently deploy multiple SE5416A Series of similar
settings by uploading these settings to the devices.
To backup your configuration, click “Export Configuration”, and a pop-up dialog is prompted
for saving the backup file on your computer. It is important NOT to modify the saved
configuration file by any editor. Any modification to the file may corrupt the file, and it
may not be used for restore. Please contact our authorized distributors for more information
on this subject.
To restore the configuration backup, click “Browse” to locate the backup file, and then click
“Import Configuration” to upload the configuration backup file to the device. Once, the
backup file is successfully uploaded; the device will restart, the time needed for this process
may vary on the equipment used.
Figure 5.30
48
Page 49
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.6.8 Set to Default
Click on “Set to Default and Restart” button to restore the device’s settings to Factory Default
Settings.
Figure 5.31
5.6.9 Restart
Click on the “Restart” button to restart the device. The web page will refresh after the device
complete the reboot.
Figure 5.32
49
Page 50

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Baud rate
115200bps
Parity
None
Data bits
8 bits
Stop bit
1 bit
Flow Control
None
6 CLI Configuration
6.1 Accessing the CLI
SE5416A Series can be configured by CLI (Command-Line Interface). There are two ways to
access the CLI. Both methods will lead to the same CLI, i.e., a command line interface that
allows you to modify most settings in your device.
6.1.1 Serial Console
The console interface follows standard RS-232 specification, find pin assignments in Section
9.3.2. The interface can be accessed with the following settings:
6.1.2 Telnet Console
Please be aware that Windows Vista / Windows 7 or higher do not have Telnet client installed
by default, to install Microsoft Telnet client on these systems:
1. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
2. On the Control Panel Home page, click Programs.
3. In the Programs and Features section, click Turn Windows features on or off.
4. If the User Account Control dialog box appears, confirm that the action it displays is
what you want, and then click Continue.
5. In the Windows Features list, select Telnet Client, and then click OK, Figure 6.1.
50
Page 51

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 6.1
6.2 General Information
Open the command line interface (console terminal) and telnet to the device using its IP
address. The default username is “admin” and password is empty (blank). A main menu
should appear, Figure 6.2.
Figure 6.2
Note:
1. SE5416A Series will automatically close the telnet connection after three minute of inactivity.
51
Page 52

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Buttons
Function
Open Main Menu or go back one level
higher
Scroll up
Scroll down
Confirm the selection. When working
with IP addresses, pressing <SEL>
means moving to the next digit
2. Press the “ESC” key to return to the previous menu.
3. Some changes to the device would take effect only after the device is restarted.
4. Detailed explanations are embedded in the LCM Configuration
There is an LCM (Liquid Crustal Monitor) installed on the front panel of the device that can be
used to display device information and perform basic configurations. The table below
illustrates its buttons and corresponding functions.
6.3 Welcome Screen
When the device boots up, the LCM will display LAN1. If you scroll down, it will display LAN2
information. The format is:
LAN1: Link down
10.0.50.100 ▼
6.4 Main Menu Structure
Press the <Menu> Key to enter the main menu. Press <Scroll Down> to go to the next layer or
option. Press <Scroll Up> to go to the back one layer or option.
52
Page 53
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
1.Overview
1.Model name
Display Model name
2.Kernel ver.
Display kernel version
3. AP ver.
Display AP version
4.Lan 1
1.Lan status
Display LAN1 status
2.MAC
Display MAC address of
LAN1
5.Lan 2
1.Lan status
Display LAN2 status
2.MAC
Display MAC address of
LAN2
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
2.Network set
1.Lan 1
1.IP config
1.Static IP
Change to Static IP mode
2.DHCP
Chang to DHCP mode
2.IP address
Display/Change LAN1 IP
3.Net mask
Display/Change Net mask
4.Gateway
Display/Change the
Gateway IP
2.Lan 2
1.IP config
1.Static IP
Change to Static IP mode
2.DHCP
Chang to DHCP mode
2.IP address
Display/Change LAN2 IP
3.Net mask
Display/Change Net mask
4.Gateway
Display/Change Gateway
IP
3.DNS server1
Display/ Change DNS
Server 1 IP address
4.DNS server2
Display/ Change DNS
Server 2 IP address
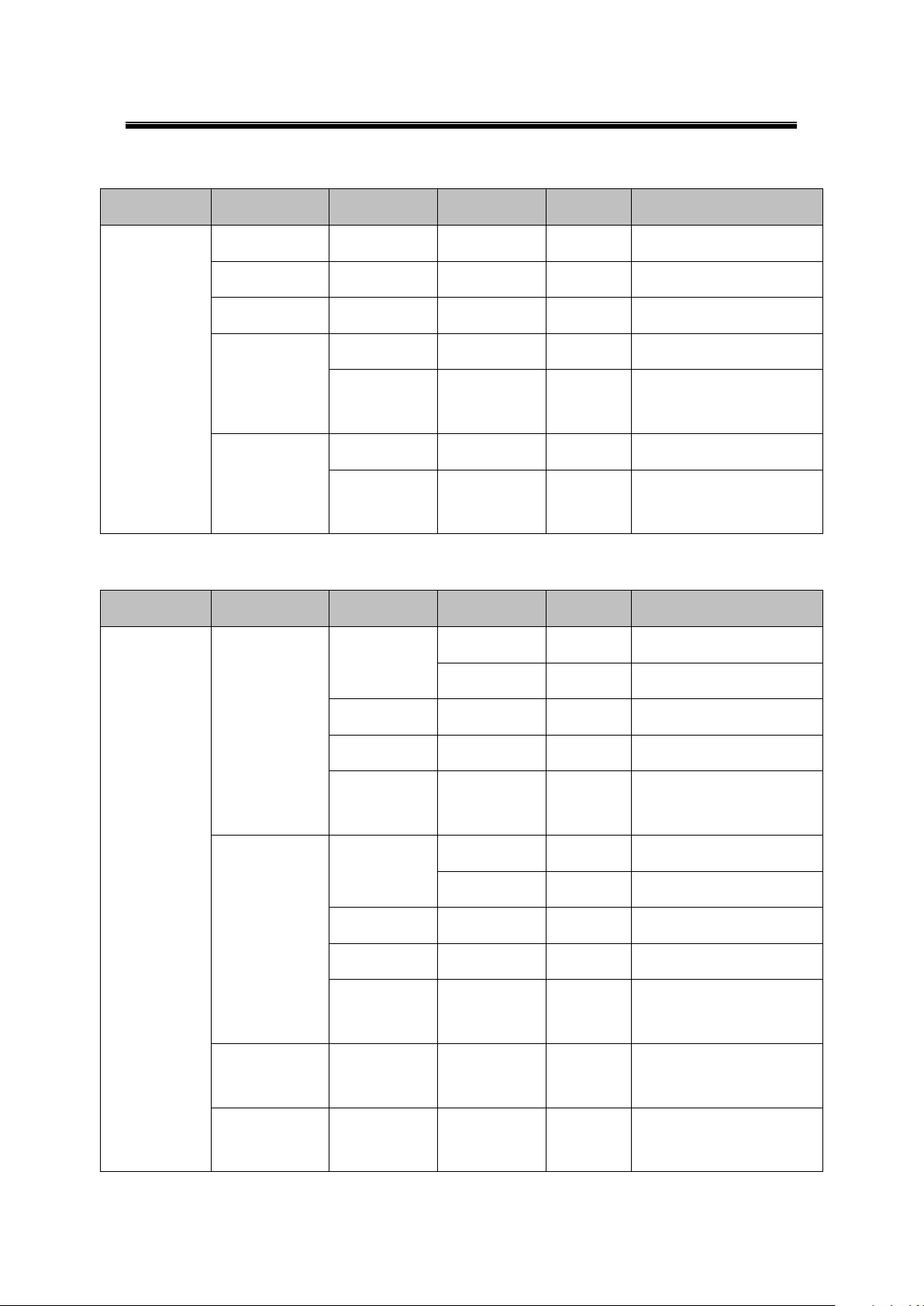
6.4.1 Overview
6.4.2 Network Settings
53
Page 54
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
3.Serial set
1.Select port
Select a COM Port to
configure
2.Parameter
set
1.Baud Rate
1. 300
Display/Change baud rate
2. 600
3. 1200
4. 2400
5. 4800
6. 9600
7. 19200
8. 38400
9. 57600
10. 115200
11. 230400
12. 460800
13. 921600
2.Parity
1. None
Display/Change Parity
2. Odd
3. Even
4. Mark
5.Space
3.Data bits
1. 5 bits
Display/Change Data bit
2. 6 bits
3. 7 bits
4. 8 bits
4.Stop bits
1. 1 bits
Display/Change Stop bit
2. 2 bits
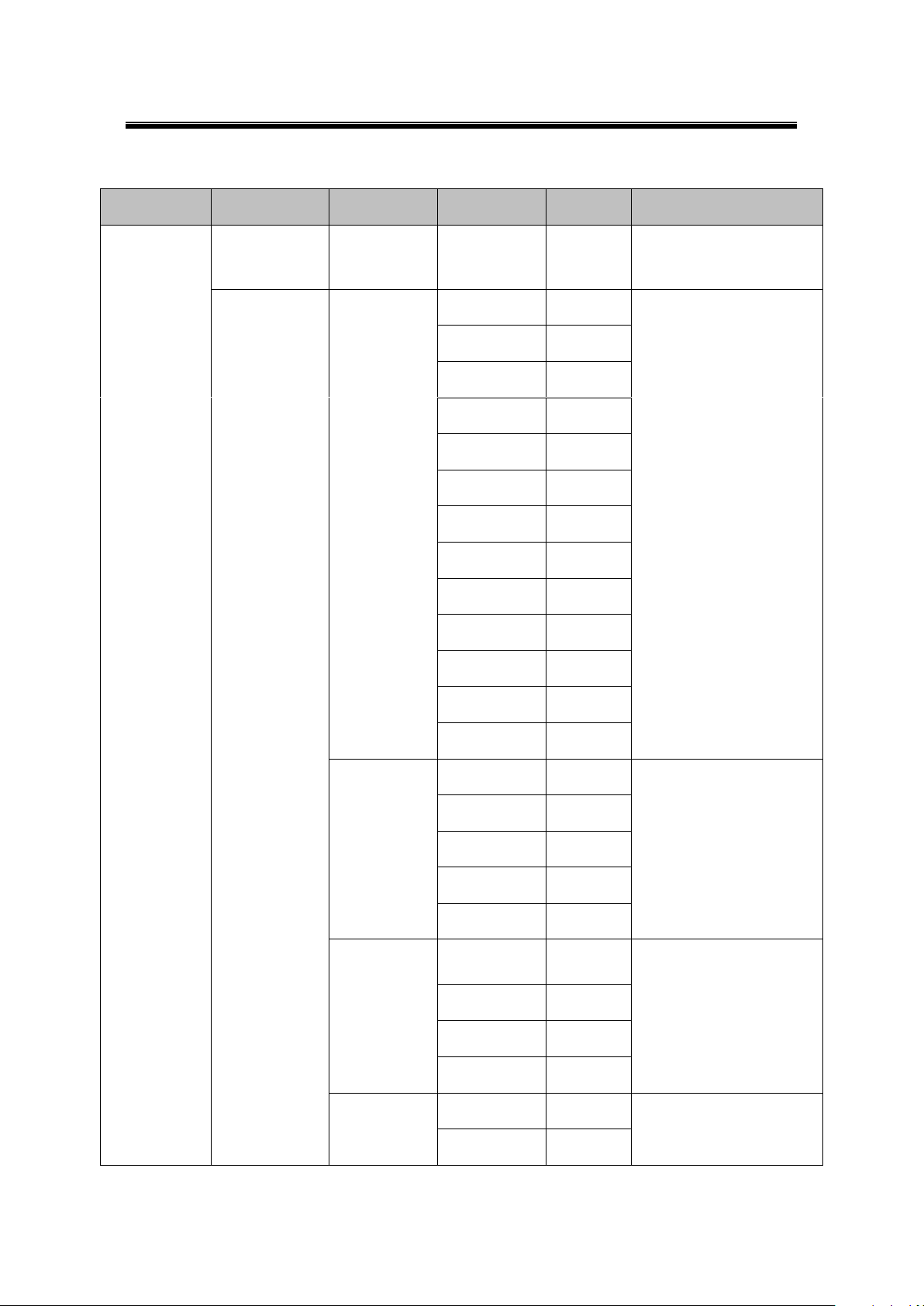
6.4.3 Serial Settings
54
Page 55
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
5.Flow control
1. None
Display/Change Flow
control mode
2. Xon/Xoff
3. Hardware
6.Delimiter
1.Net to serial
1.Disable
Disable UART Delimiter
2.Enable
1.Timer: Change UART
delimiter to timer mode
and set its time
2.Char: Change UART
delimiter to character
mode and set the
character
2.Serial to net
1.Disable
Disable UART Delimiter
2.Enable
1.Timer: Change UART
delimiter to timer mode
and set its time
2.Char: Change UART
delimiter to character
mode and set the
character
7.UART
mode
1. 232
Display/Change UART
mode to RS232
2. 422
Display/Change UART
mode to RS422
3. 485
Display/Change UART
mode to RS485
8.Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply serial settings to all
serial ports
3.Link mode
Display/Change Link
mode
1.TCP server
1.Virtual
COM
1.Disable
Display/Change Virtual
COM mode
2.Enable
55
Page 56

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
2.Local port
Display/Change Local
listening port
3.Max
connect
Display/Change
maximum client
connection (1~4)
4.IP Filter
1.Disable
Display/Change IP Filter
function and the IP
address
2.Enable
5. Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
2.TCP client
1.Dest IP 1
Display/Change
Destination IP 1
2.Dest port 1
Display/Change
Destination port 1
3.Destination
2
1.Disable
Disable destination 2
2.Enable
Display/Change
Destination IP 2 and
Destination port 2
4. Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
3.UDP
1.Local port
Display/Change Local
listening port
2.Dest IP1
Display/Change
Destination IP 1
3.Dest port 1
Display/Change
Destination Port 1
4.Destination
[2-8]
1.Disable
Disable Destination [2-8]
2.Enable
Display/Change
Destination IP [2-8] and
Destination port [2-8]
56
Page 57

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
b.Apply to all
1.No
2.Yes
Apply Link mode Settings
to all serial ports
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
4.Server state
1.Console
1.Web
console
1.Disable
Disable Web console
2.Enable
Enable Web console
2.Telnet
console
1.Disable
Disable Telnet console
2.Enable
Enable Telnet console
2.Pwd protect
1.LCM
console
1.No
Disable LCM console
password protection
2.Yes
Enable and change the
password
2.Reset
button
1.No
Disable the Reset button
password protection
2.Yes
Enable and change the
password on Reset button
3.Ping
1.Lan 1
Use "ping" command to
check specific IP address
for LAN1
2.Lan 2
Use "ping" command to
check specific IP address
for LAN2
1st layer
2nd layer
3rd layer
4th layer
5th layer
Descriptions
5.Restart
1.No
Cancel Restart command
2.Yes
Restart immediately
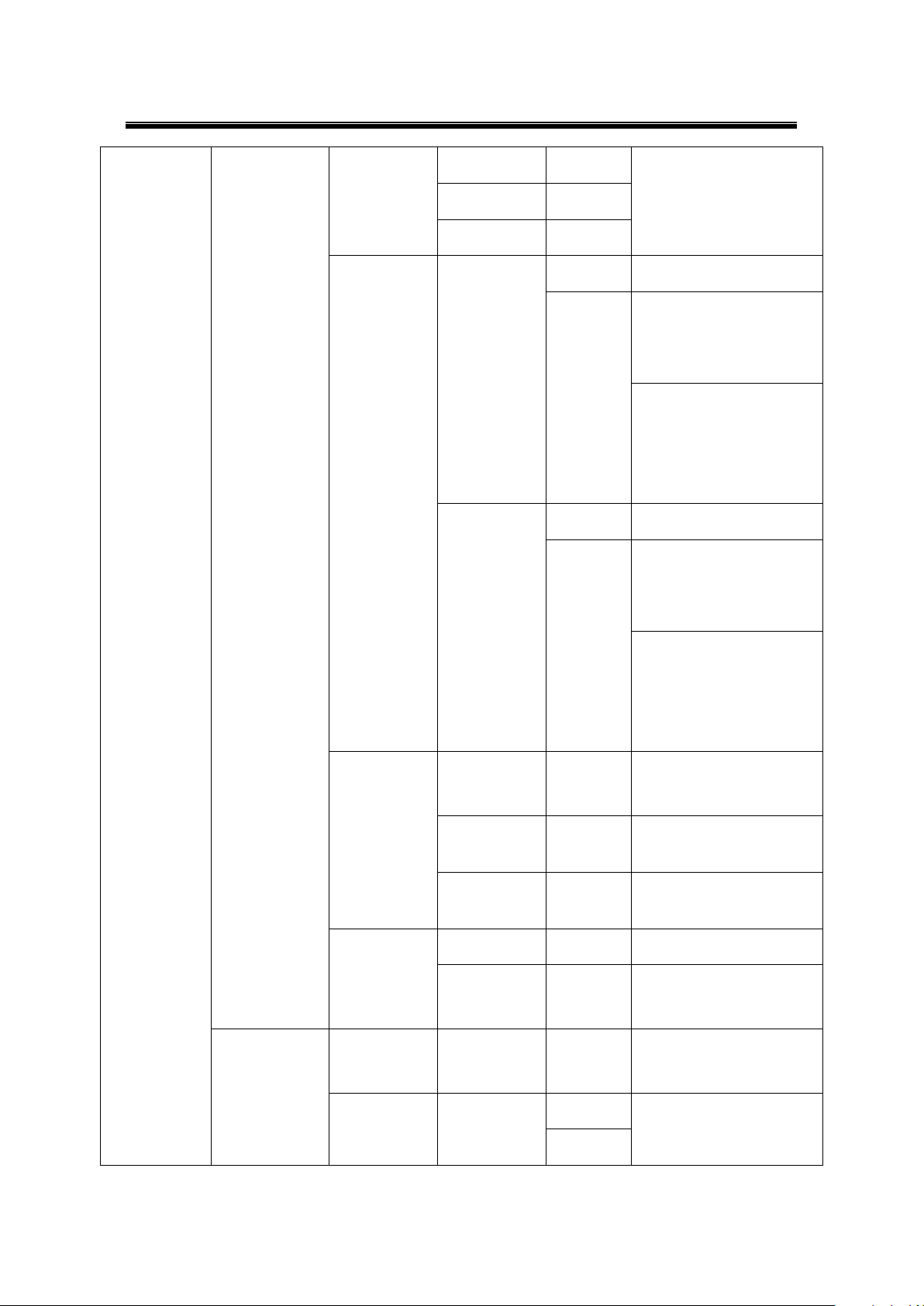
6.4.4 Server State
6.4.5 Restart
Web Configuration chapter; please refer to the respective sections.
57
Page 58

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
This system overview window gives the general information on Ethernet, MAC address, kernel
and AP version, ERPS, and STP status.
Operation: Main → [1]Overview
Figure 6.3
58
Page 59

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
6.5 Networking Configuration
This section allows you to change IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and SNMP information.
Please note that the new settings will not take effect until the device is restarted.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking
Figure 6.4
6.5.1 LAN 1 / LAN 2 Settings
Enter “LAN settings” and you will see a menu to configure the DHCP, IP address, subnet mask,
and gateway of that LAN.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [1]LAN 1 Settings;
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [2]LAN 2 Settings
Figure 6.5
59
Page 60

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Note: It is not possible to configure LAN1 or LAN2 when bridge mode is enabled. Please go to
the Bridge Settings instead.
6.5.2 DNS Settings
You can configure the DNS1 or DNS2 Server IP Address manually. Alternatively, if you enable
the DHCP option in “LAN 1 Settings”, SE5416A Series will retrieve the DNS server address
from the DHCP server automatically.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [3]DNS Settings
Figure 6.6
6.5.3 SNMP Settings
SE5416A Series allows the user to Enable or Disable the SNMP function. The changes will
become effective immediately. Basic SNMP configurations such as Read/Write Community,
SysName (System Name), SysLocation (System Location), SysContact (System Contact),
and SNMP Trap Server IP are supported.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [5]SNMP Settings
60
Page 61

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 6.7
6.5.4 Bridge Settings
SE5416A Series has a bridge mode that can be enabled. When the bridge mode is enabled,
LAN1 and LAN2 would be merged to create one single Ethernet interfaces. When one of the
physical LAN port fails, SE5416A Series would automatically use the other LAN port.
Configure network settings of the bridge here.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [6]Bridge Settings
Figure 6.8
6.5.5 ERPS Settings
SE5416A Series supports the ERPS function, a standard ring protocol. The options in this
menu allows you to definite ERPS status, RAPS VLAN, RPL owner, RPL port, WTR timer,
holdoff timer, guard timer, and MEL.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [7]Bridge Settings
61
Page 62

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 6.9
Note: It is not possible to enable ERPS when Bridge is disabled.
62
Page 63

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
6.5.6 STP Settings
STP function in SE5416A Series can be enabled or disabled. Once enabled, you can set STP
version, priority, maximum age, hello time, forward delay, port path cost, port priority, port P2P,
and port Edge.
Operation: Main → [2]Networking → [8]STP Settings
Figure 6.10
Note: It is not possible to enable STP when Bridge is disabled.
63
Page 64
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
6.6 COM Port Configuration
SE5416A Series allows you to configure the parameters of the COM port including COM Link
mode and COM port parameters. First enter the number of the COM port that you want to
configure.
Figure 6.11
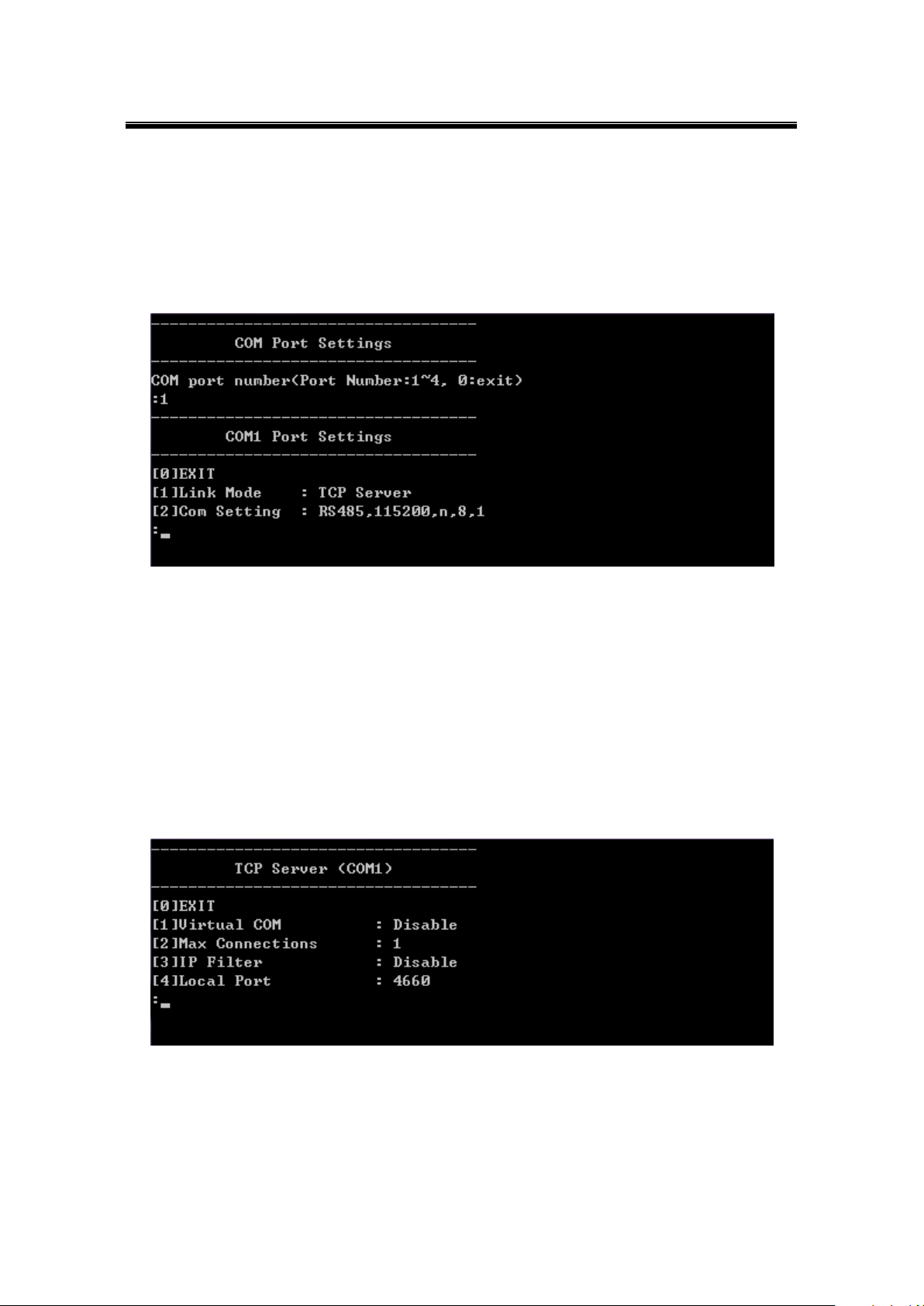
6.6.1 TCP Server for Link Mode
TCP Server mode is the default Link Mode for SE5416A Series. A TCP Client is required to
connect to this TCP Server. You will need to configure Virtual COM, Max Connections, IP
Filter, and Local Port settings.
Operation: Main [6]COM Port Setting[1-4]Select Port[1]Link Mode[1]TCP Server
Figure 6.12
6.6.2 TCP Client for Link Mode
SE5416A Series’ Link Mode can be configured as a TCP Client. In this case, SE5416A Series
will connect to a TCP Server. You will need to configure the settings for Destination IP 1 and 2
64
Page 65

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
(if enabled).
Operation: Main [6]COM Port Setting[1-4]Select Port[1]Link Mode[2]TCP Client
Figure 6.13
6.6.3 UDP Link Mode
SE5416A Series’ Link Mode can be configured to utilize UDP. Note that UDP is a
connection-less protocol, so data delivery is not guaranteed. You will need to configure the
settings of Destination IPs. The Destination IP field supports input of IP range and up to eight
Destination IPs are supported.
Operation: Main [6]COM Port Setting[1-4]Select Port[1]Link Mode[3]UDP
Figure 6.14
6.6.4 Serial Settings
Here you can configure Uart mode, baud rate, parity, data bit, stop bit, and flow control.
65
Page 66

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Operation: Main [6]COM Port Setting[1-4]Select Port[2]Com Settings
Figure 6.15
6.7 Alert Settings
There are two sub-menu settings included inside the Alert Settings, which are E-mail Settings
and Alert Event.
Figure 6.16
6.7.1 Configuring E-mail
When an alert event triggered, SE5416A Series can send that event through email. Here you
can configure Sender’s Email Address, Receiver’s Email Address (up to 5), Mail Server,
and Require Authentication.
Operation: Main [7]Alert Settings[1]E-mail Settings
66
Page 67

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 6.17
6.7.2 Configuring Alert Event
Choose the Alert events that SE5416A Series should trigger and the method it should use to
notify that event (Email, Trap, or Relay). Available events are Cold Start, Warm Start,
Authentication Failure, IP Address Change, Password Change, and Link Down.
Operation: Main [7]Alert Settings[2]Alert Event
Figure 6.18
67
Page 68

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
6.8 System Configuration
There are three sub-menus included inside the System Settings, which are Link State, Time,
and Security.
Operation: Main [8]System
Figure 6.19
6.8.1 Link State
Link State information of each COM port will be displayed.
Operation: Main [8]System[1]Link State
68
Page 69

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 6.20
6.8.2 Time Settings
You can configure the system time manually or let SE5416A Series retrieve time information
from a NTP server. The changed will take effect immediately after the settings are saved.
Operation: Main [8]System[2]Time
Figure 6.21
6.8.3 Security Settings
You can change the system password here. Moreover, you can block different access method
to prevent system intrusion.
Operation: Main[8]System[3]Security
Figure 6.22
Note: Please be aware not to disable options [2-4] all together because further configuration
would be not possible.
69
Page 70
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
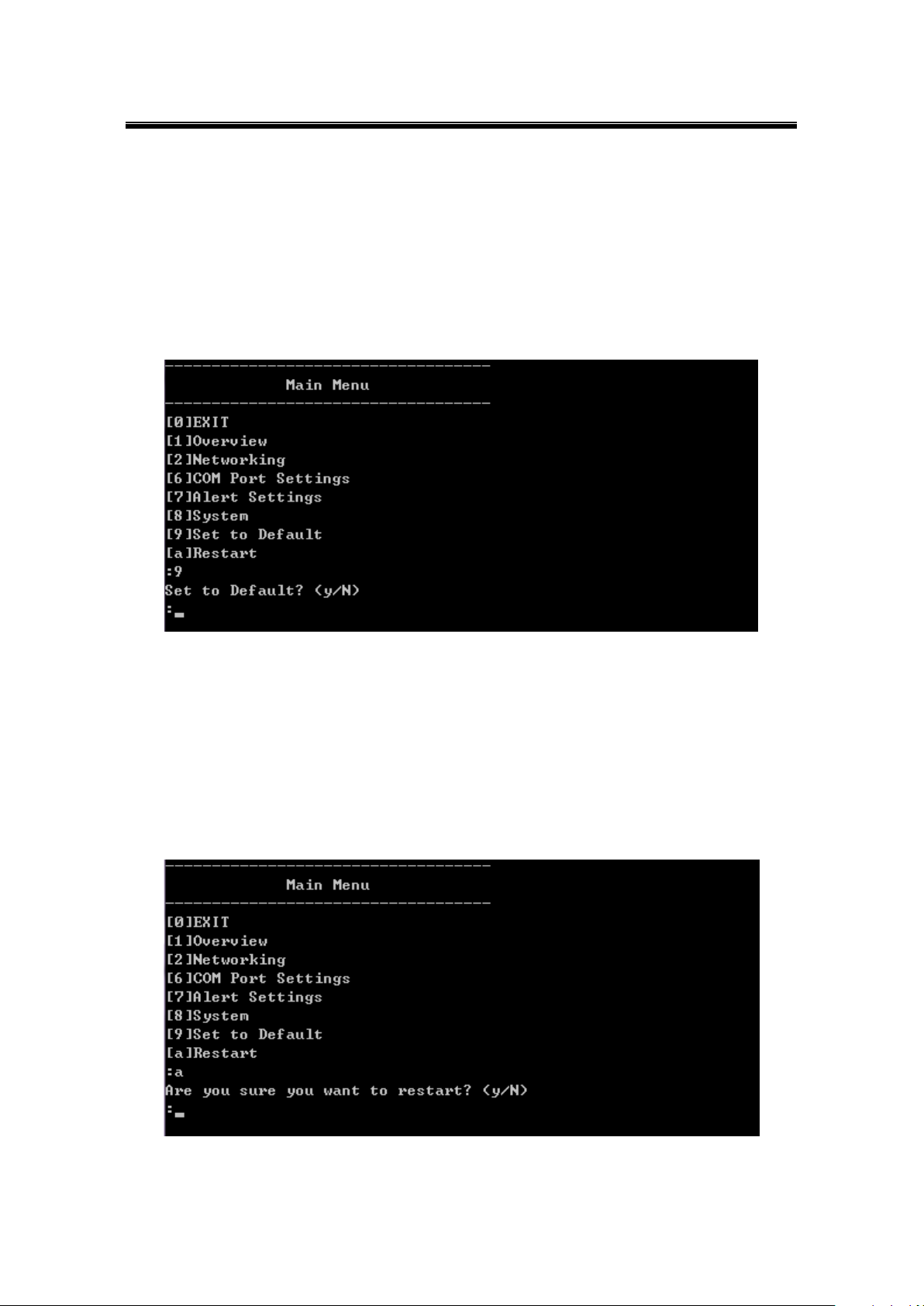
6.9 Restoring Factory Default
Choose and confirm this option to reset SE5416A Series back to its default settings. The
device would restart automatically to apply the default settings.
Operation: Main [9]Set to Default
Figure 6.23
6.10 Restart System
Choose and confirm this option to restart SE5416A Series.
Operation: main → [a]Restart
Figure 6.24
70
Page 71

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Modes
Supports
TCP
Server
RAW
VCOM
Reverse Telnet
Client
VCOM
UDP
Connectionless protocol
7 Link Modes and Applications
7.1 Link Mode Configuration
SE5416A Series supports different Link Modes, which are TCP Server, TCP Client, and UDP.
Under the three Link Modes, TCP Server can support RAW, Virtual COM, or Reverse Telnet
applications. TCP Client can support Virtual COM application. In the upcoming sections, we
will discuss how to setup different Link Modes properly.
71
Page 72
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
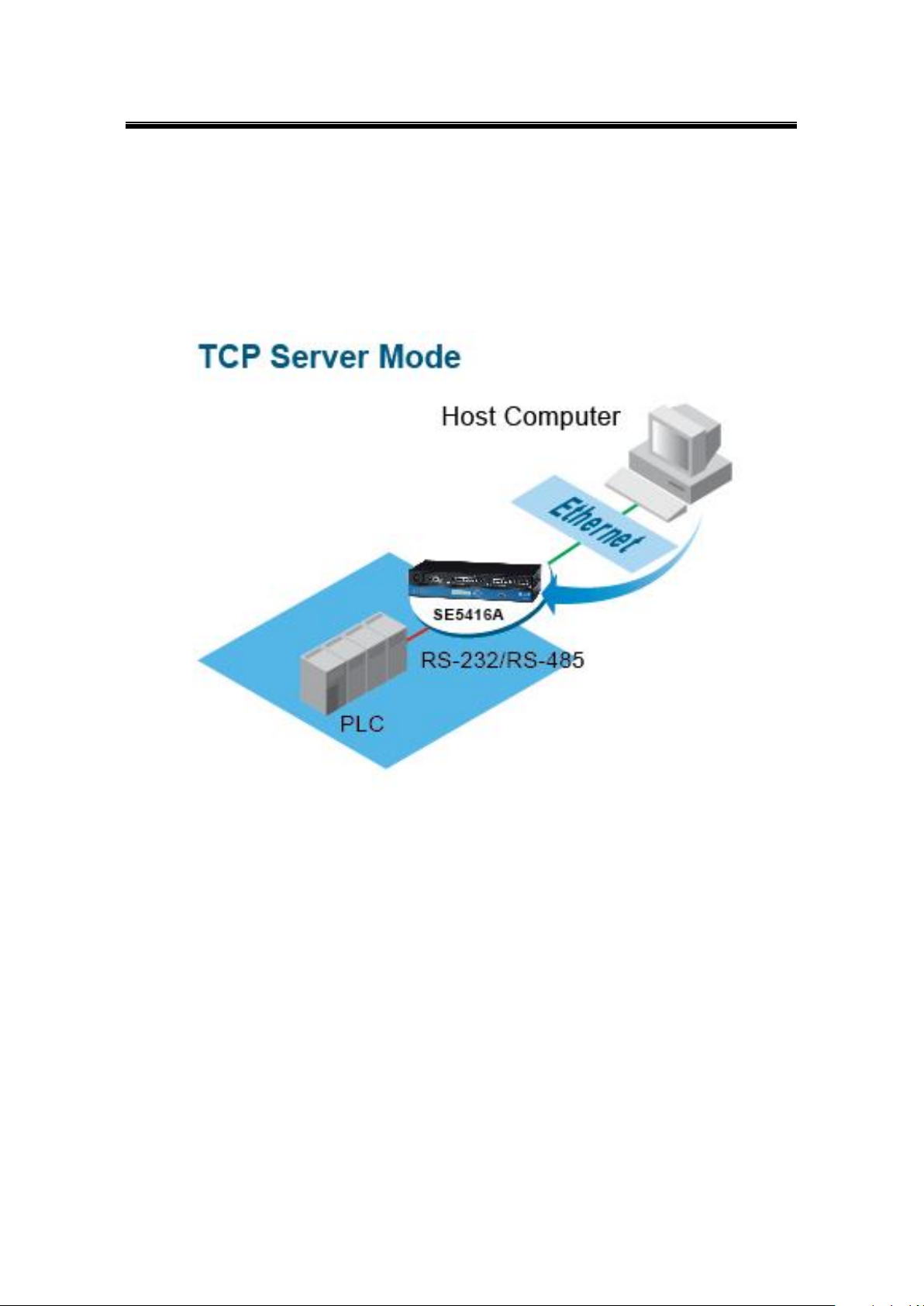
7.1.1 TCP Server Mode
SE5416A Series can be configured as a TCP server in a TCP/IP Network to listen for an
incoming TCP client connection to a serial device. After the connection is established between
the serial device server and the host computer, data can be transmitted in both directions; this
also applies whenever the VCOM is running on server mode. Please be reminded that this is
the device’s default link mode.
Figure 7.1
SE5416A Series defaults in TCP Server mode, there are additional connection settings that
can be configured, Figure 7.2. By selecting the TCP Server mode, a TCP Client program
should be prepared to connect to SE5416A Series.
72
Page 73

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.2
For setting as a TCP Server, please follow these steps.
Click on the COMX link under Serial on the left hand side.
Select TCP Server in the Link Modes; TCP Server is the default link mode. Also in this
section you will find the following options.
Mode, there are 3 different communication modes here:
RAW, there is no protocol on this mode, meaning the data is passed
transparently.
Virtual COM, the Virtual COM protocol is enabled on the device to
communicate with a virtualized port from the client. It is possible to create a
Virtual COM port on Windows/Linux in order to communicate with the device
as a Client.
Reverse Telnet, used to connect the device and another serial device
(usually a Terminal Server) with a Telnet program. Telnet programs in
Windows / Linux usually require special handshaking to get the outputs and
formatting show properly. The SE5416A Series will interact with those special
commands (CR/LF commands) once Reverse Telnet is enabled.
Enter the Local Port, this option specifies the port number that the server should listen to;
it is used by the client to connect to the server. Default local port is 4660.
Go to Response Behavior for more information on this setting. For serial settings, go to
73
Page 74

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Sec. 5.4.1. For Advanced settings, go to Sec. 5.4.2.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
Other important variables to consider are:
IP Filter, enables the Source IP option below to block an IP address from accessing the
COM port.
Source IP, specifies the device’s Source IP which will be transmitting data to our Server.
In other words, our Server will only allow data from this IP to flow (hence its own name
implies Source IP); only one source is allowed.
Maximum Connection, the number of devices/clients (max. of 4 clients), to be served is
set in this section.
Response Behavior, in which we will have as options:
Request & Response Mode, it determines how the device will proceed when it
receives requests from connected hosts. Under this mode, the port will hold requests
from all other connected hosts until the serial device replies or the Response Interval
timeout takes into effect to discard it; however, unrequested data sent from the serial
device would be forwarded to all connected hosts.
Reply to requester only, the port will reply to the connected host who
requested the data only.
Reply to all, a reply is sent to all connected hosts.
Transparent mode, the port will forward requests from all connected hosts to the
serial device immediately and reply to all connected hosts once it receives data from
the serial device.
Note: LINK1 is associated with COM1; LINK2 is associated with COM2, and so on.
74
Page 75

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
7.1.2 TCP Client Mode
SE5416A Series can be configured as a TCP client in TCP/IP Network to establish a
connection with a TCP server in the host computer. After the connection is established, data
can be transmitted between a serial device and a host computer in both directions; this also
applies to Virtual COM running in the client mode.
Figure 7.3
By selecting the TCP Client mode, it means that a TCP Server program should be prepared to
connect to SE5416A Series; Figure 7.4 shows all the settings provided for the TCP Client.
75
Page 76

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.4
For setting as a TCP Client, please follow these steps.
Click on the COMX port under Serial on the left hand side.
Select TCP Client in the Link modes.
Only two communication modes are available here: RAW and Virtual COM which
definitions are the same as above in Mode.
Enter the preferred Destination IP and Port. This should match the IP settings of the
TCP Server program.
Enable and enter Destination IP 2 and Port 2 if necessary. Two different servers can be
set here (for redundancy), the second server has to be enabled by ticking the box.
Go to Response Behavior for more information on this setting. For serial settings, go to
Sec. 5.4.1. For Advanced settings, go to Sec. 5.4.2.
Scroll to the bottom and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the changes.
76
Page 77

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
7.1.3 UDP Mode
UDP is a faster but connectionless network protocol; it does not guarantee the delivery of
network datagram. The SE5416A Series can be configured to transfer data using unicast or
multicast UDP from the serial device to one or multiple host computers, data can be
transmitted between serial device and host computer in both directions.
There is no server or client concept on this protocol, they are called peers or nodes. So here
you only need to specify the Local Port that we should listen to and specify the Destination
IPs of the remote UDP nodes.
Figure 7.5
SE5416A Series also supports connectionless UDP protocol compared to the
connection-oriented TCP protocol. Please be aware that even though UDP provides better
efficiency in terms of response time and resource usage, it does not guarantee data delivery. It
is recommended to utilize UDP only with cyclic polling protocols where each request is
repeated and independent, such as Modbus Protocol; Figure 7.6 shows the UDP settings.
77
Page 78
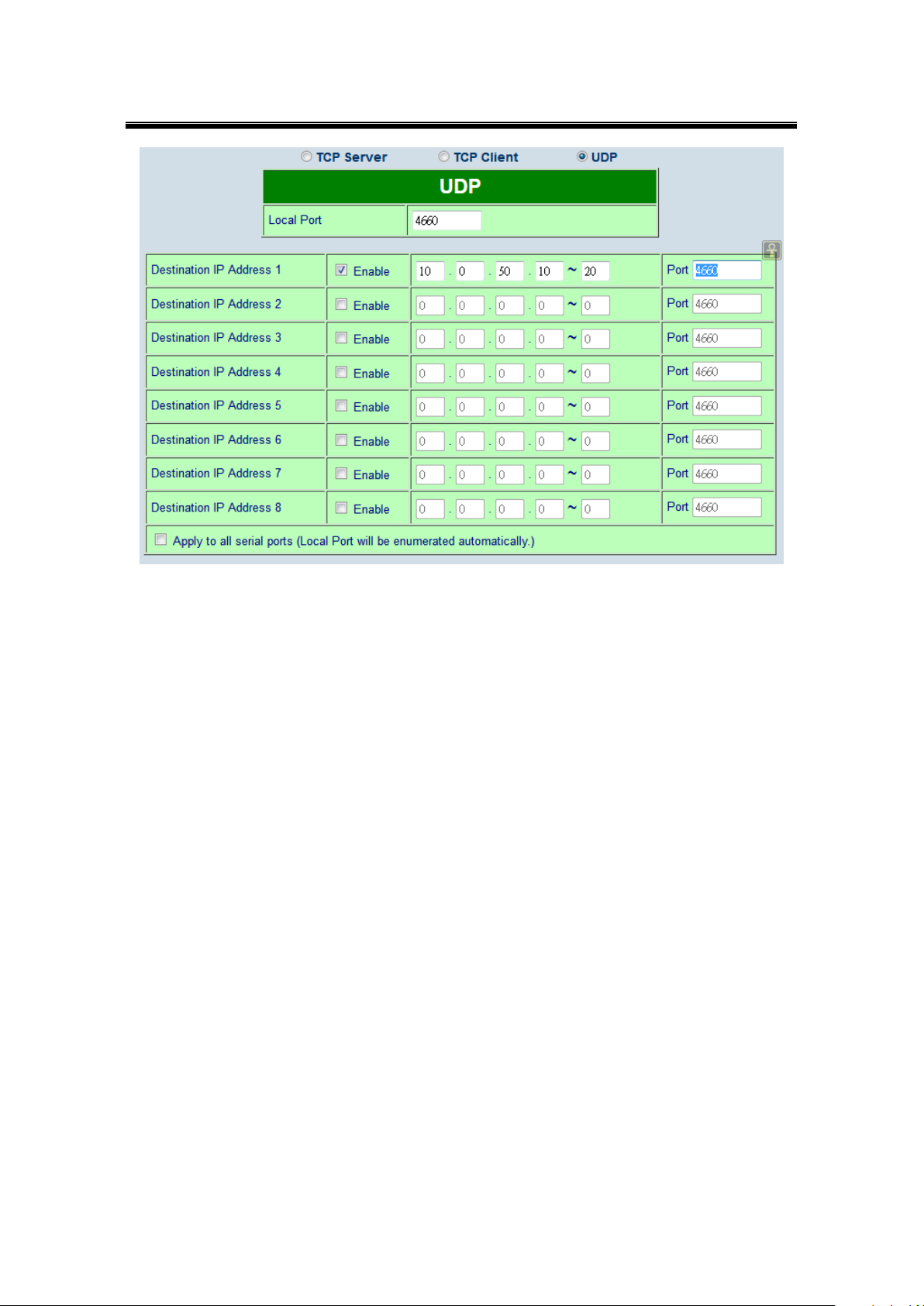
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.6
Click on the COMX port under Serial on the left hand side.
Select UDP in the Link modes.
Destination IP and Port: Specify the Begin and End IP here. Four groups of range IPs
are allowed. This is the IP address of the UDP program and the Port it is listening to.
Note that the maximum number of UDP nodes that SE5416A Series can handle would
highly depend on the traffic load. We have tested that SE5416A Series can handle up to
100 UDP nodes (baud rate 9600 bps, request interval 100ms, and data length 30bytes).
Enter the Local Listening Port. This is the port that SE5416A Series should listen to.
Match this setting in the UDP program (usually called destination port in the UDP
program).
For serial settings, go to Sec. 5.4.1. For Advanced settings, go to Sec. 5.4.2.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
78
Page 79

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
7.2 Link Mode Applications
7.2.1 TCP Server Application: Enable Virtual COM
SE5416A Series will encapsulate control packets on top of the real data when Virtual COM is
enabled. This will allow the Virtual COM port in the Windows/Linux system to access SE5416A
Series’ COM ports. The benefit of using Virtual COM is that rewriting an existing COM program
to read IP packets is unnecessary. In other words, it is possible to use an ordinary serial (COM)
program. The conversion/virtualization of IP to COM is all done in the system driver
transparently. Figure 7.7 shows SE5416A Series in TCP Server mode with Virtual COM
enabled.
Figure 7.7
Follow Sec 7.1.1 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Server mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Virtual COM” to enabled
Virtual COM application in SE5416A Series.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
Configure Virtual COM in the Operating System. For Windows, refer to Chapter 8. For
Linux, refer to a separate manual included in the Linux driver zip file. Remember
SE5416A Series’ IP address and Local Port here in order to enter this information in
79
Page 80

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Serial/IP Virtual COM’s Control Panel later.
7.2.2 TCP Server Application: Enable RFC 2217
The underlying protocol of Virtual COM is based on RFC 2217, the Telnet COM Control Option.
Therefore, it is possible to use RFC 2217 with SE5416A Series in the TCP Server mode. To do
so, refer to Sec 7.2.1 to enable Virtual COM, so that SE5416A Series becomes aware of the
commands. Note that there is no need to configure Virtual COM on the Operating System
because Virtual COM ports would not be used.
7.2.3 TCP Client Application: Enable Virtual COM
It is also possible to run VCOM in TCP Client mode. It is usually easier to use Virtual COM in
the Client mode if SE5416A Series uses dynamic IP (DHCP) because setting a static IP
address in Virtual COM’s Control Panel in the Operating System is not possible.
Figure 7.8
Follow Sec. 7.1.2 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Client mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Virtual COM” to enabled
80
Page 81

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Virtual COM application in SE5416A Series.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
Configure Virtual COM in the Operating System. For Windows, refer to Chapter 8. For
Linux, refer to a separate manual included in the Linux driver zip file. Remember the
Destination Port here in order to enter this information in Serial/IP Virtual COM’s Control
Panel later.
7.2.4 TCP Client Application: Enable RFC 2217
The underlying protocol of Virtual COM is based on RFC 2217, the Telnet COM Control Option.
Therefore, it is possible to use RFC 2217 with SE5416A Series in the TCP Client mode. To do
so, refer to Sec. 7.2.3 to enable Virtual COM, so that SE5416A Series becomes aware of the
commands. Note that there is no need to configure Virtual COM on the Operating System
because Virtual COM ports would not be used.
7.2.5 TCP Server Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection Master
Pair Connection is useful when pairing up two serial devices over the Ethernet or when it is
impossible to install Virtual COM in the serial device. Pair connection does require two
SE5416A Series to work in pair, one would be the Pair Connection Master and the other would
be the Pair Connection Slave.
81
Page 82

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.9
Follow Sec. 7.2.1 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Server mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Virtual COM” to enabled
Virtual COM application in SE5416A Series.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
Remember Pair Connection Master’s IP address here in order to enter this information in
the Slave later.
Proceed to the Sec. 7.2.6 to configure a Slave to connect to this Master.
7.2.6 TCP Client Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection Slave
A Pair Connection Slave, is shown in Figure 7.10; it is necessary to pair up with a Pair
Connection Master. Please setup a Pair Connection Master first before proceeding.
82
Page 83
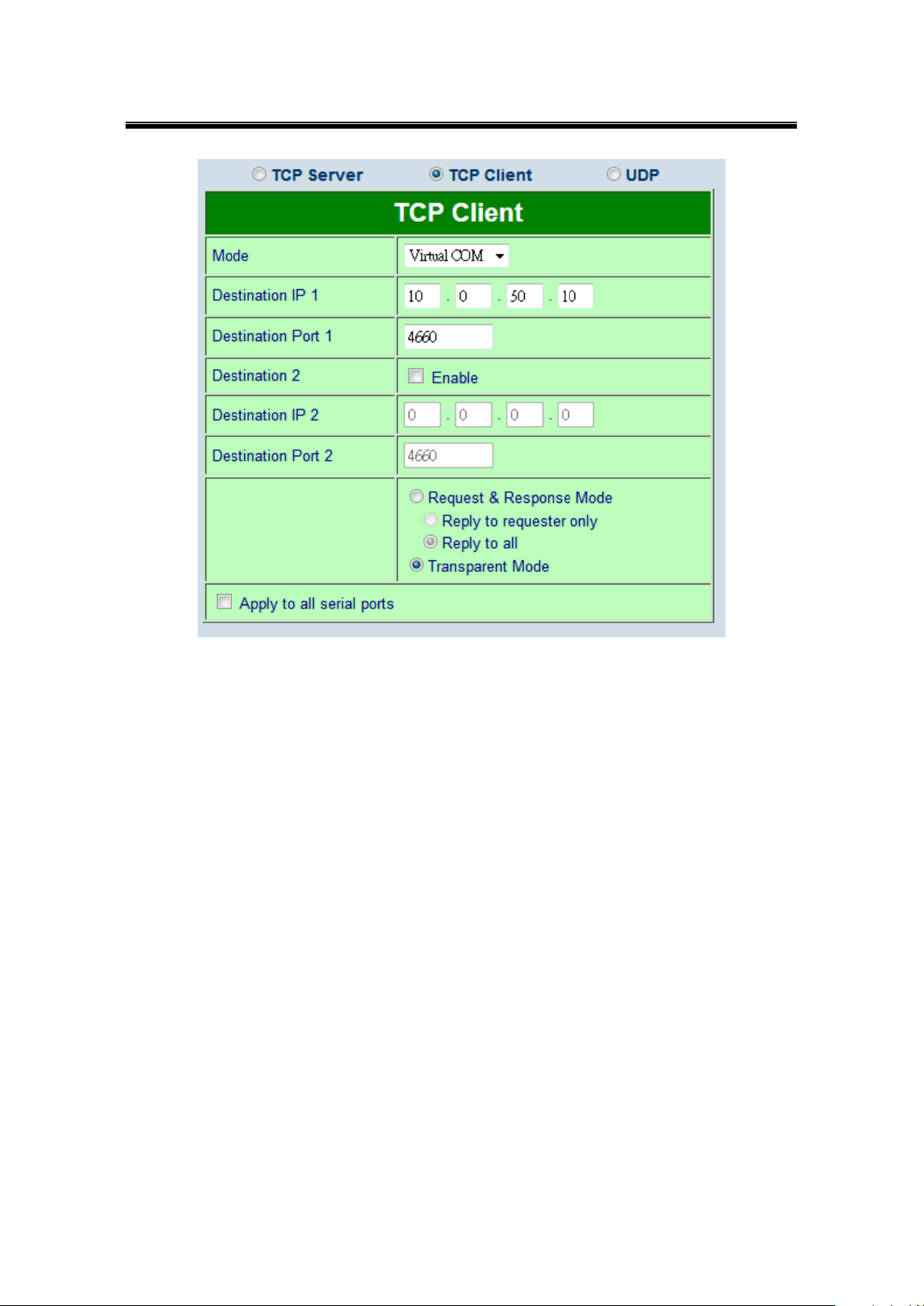
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.10
Follow Sec. 7.1.2 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Client mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Virtual COM” to enabled
Virtual COM application in SE5416A Series.
Match the Destination IP with the settings of Pair Connection Master’s IP that was setup
previously.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
7.2.7 TCP Server Application: Enable Reverse Telnet
Reverse Telnet is useful if a telnet program is used to connect to SE5416A Series and the
serial interface of the SE5416A Series is connected to a Terminal Server. Telnet programs in
Windows/Linux require special handshaking to get the outputs and formatting show properly.
SE5416A Series will interact with those special commands (CR/LF commands) if Reverse
Telnet is enabled.
83
Page 84
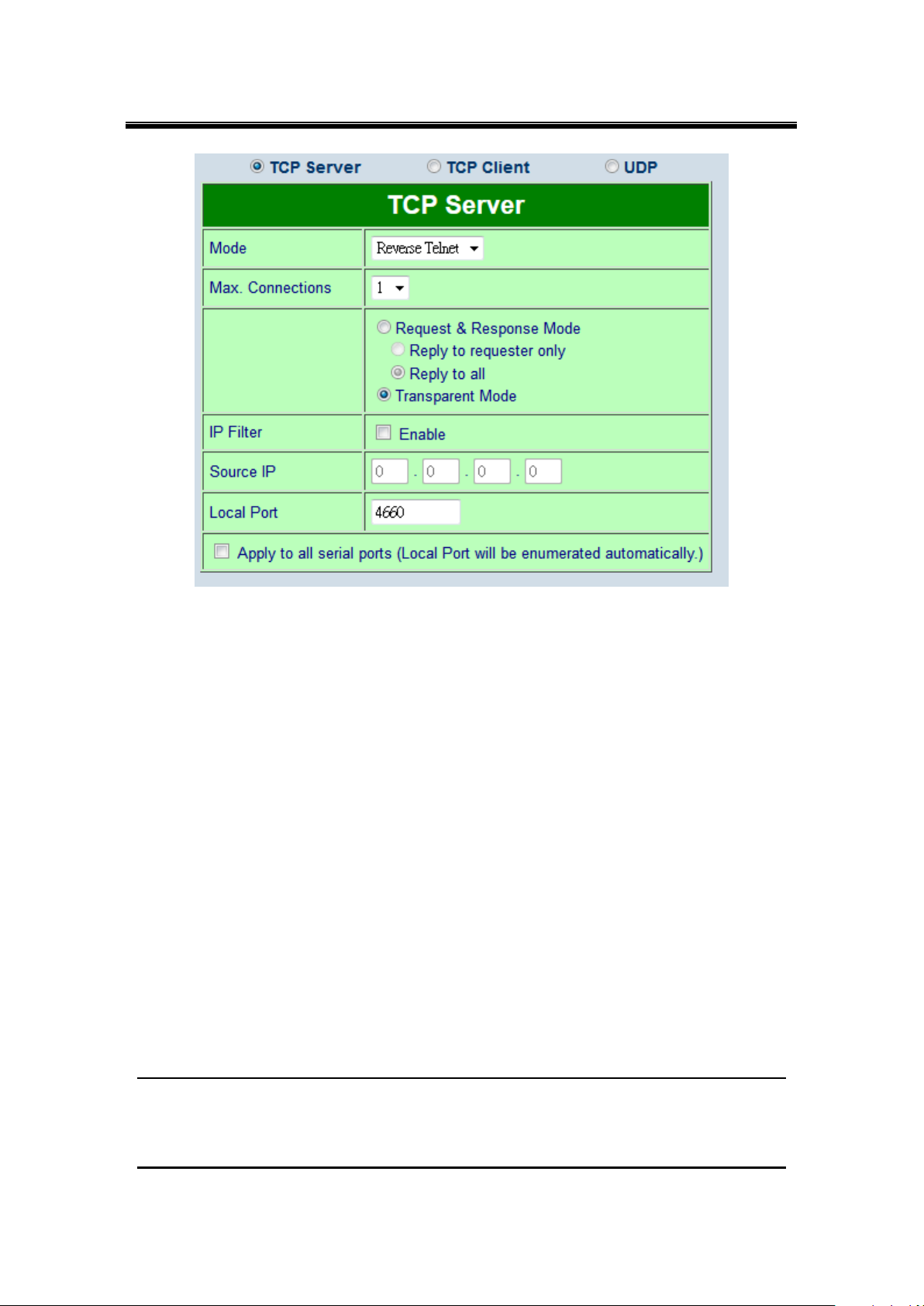
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 7.11
Follow Sec. 7.2.1 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Server mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Reverse Telnet” to enabled
Reverse Telnet application in SE5416A Series.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
7.2.8 UDP Application: Multi-Point Pair Connection
It is also possible to setup pair connection in UDP mode to have more than one Pair
Connection Master or Slave to communicate to each other. For example, it is possible to setup
one Modbus Master and six Modbus Slaves in UDP, Figure 7.12. Note again that UDP does
not guarantee data delivery and only data would be transmitted over Ethernet; other serial
pings are not transmitted. If RS-232 along with flow control, it is recommended to use
Multi-Point Pair Connection in TCP, see Sec. 7.2.10.
Note: the destination IP and Port of the Slaves need to be equal to the Master’s IP and Port.
Local Listening Port for the Slaves need to be equal to the Master’s Destination Port, see table
below for an example.
84
Page 85

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
IP Address
Link Mode
Local Listening Port
Destination IP
Destination Port
SE5416A Master COM1
10.0.50.100
UDP
5000
10.0.50.200~10.0.50.202
5000
SE5416A Master COM1
10.0.50.100
UDP
5001
10.0.50.200~10.0.50.201
5000
SE5416A Master COM1
10.0.50.100
UDP
5002
10.0.50.200
5000
SE5416A Slave 1 COM1
10.0.50.200
UDP
5000
10.0.50.100
5000
SE5416A Slave 1 COM2
10.0.50.200
UDP
5001
10.0.50.100
5001
SE5416A Slave 1 COM3
10.0.50.200
UDP
5002
10.0.50.100
5002
SE5416A Slave 2 COM1
10.0.50.201
UDP
5000
10.0.50.100
5000
SE5416A Slave 2 COM2
10.0.50.201
UDP
5001
10.0.50.100
5001
SE5416A Slave 3 COM1
10.0.50.202
UDP
5000
10.0.50.100
5000
Figure 7.12
85
Page 86

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
7.2.9 TCP Server Application: Multiple TCP Connections
The Multi-Connection option will allow up to a maximum of four TCP Client connections. Note
that it is also possible to use this multi-connection feature in conjunction with other TCP Server
applications, such as Virtual COM, Pair Connection, and Reverse Telnet. For example,
enabling multi-connection along with Pair Connection will result in Multi-Point Pair Connection
in TCP mode (Sec. 7.2.10). For more information on Response behaviors please go to
(Response Behavior).
Figure 7.13
86
Page 87

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
IP Address
Link Mode
Application
Local Listening
Port
Destination
IP
Destination Port
SE5416A Master COM1
10.0.50.100
TCP Server
Pair Connection Master
4660 - -
SE5416A Slave 1 COM1
10.0.50.200
TCP Client
Pair Connection Slave
-
10.0.50.100
4660
SE5416A Slave 1 COM2
10.0.50.200
TCP Client
Pair Connection Slave
-
10.0.50.100
4660
SE5416A Slave 2 COM3
10.0.50.200
TCP Client
Pair Connection Slave
-
10.0.50.100
4660
SE5416A Slave 3 COM1
10.0.50.201
TCP Client
Pair Connection Slave
-
10.0.50.100
4660
7.2.10 TCP Server Application: Multi-Point TCP Pair Connections
The difference between Multi-Point TCP Pair Connection and Multi-Point UDP Pair Connection
is that the TCP implementation would also exchange flow control pins for RS-232. However,
the TCP Server is limited to a maximum of four connections. If there are four serial devices and
they don’t use flow control pins with RS-232 or RS-485, it is possible to setup pair connection
in UDP mode, Sec. 7.2.8. After multi-connection is enabled in the WebUI, refer to the following
table to setup Pair Connection as in Figure 7.14.
Figure 7.14
87
Page 88

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
8 VCOM Installation & Troubleshooting
8.1 Enabling VCOM
SE5416A Series will encapsulate control packets on top of the real data when Virtual COM is
enabled. This will allow the Virtual COM port in the Windows/Linux system to access SE5416A
Series’ COM ports. Remember that VCOM can only be enabled on TCP Server Mode or TCP
Client, Figure 8.1.
Figure 8.1
88
Page 89

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.2
Virtual COM allows remote access of serial devices over TCP/IP networks through Serial/IP
Virtual COM ports that work like local native COM ports; Figure 8.3 is a Virtual COM
connection diagram.
89
Page 90

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.3
8.1.1 VCOM driver setup
System Requirements
Windows 7/2008/Vista/2003/XP/2000/NT4/9x (32-bit or 64-bit version automatically
installs)
Native and virtual platforms, including Virtual Server and VMware
Linux, also available but first you might need to download a separate package called
Virtual COM driver for Linux (TTYredirector) available for download on Atop website or
in the product CD. The zipped package includes a binary file for installation and a manual
for Linux systems.
8.1.2 Limitations
The Virtual COM driver allows up to 256 Virtual COM ports in a single PC. Selecting in the
range from COM1 to COM4096 is allowed. Note that COM ports already occupied by the
system or other devices will not be available.
90
Page 91
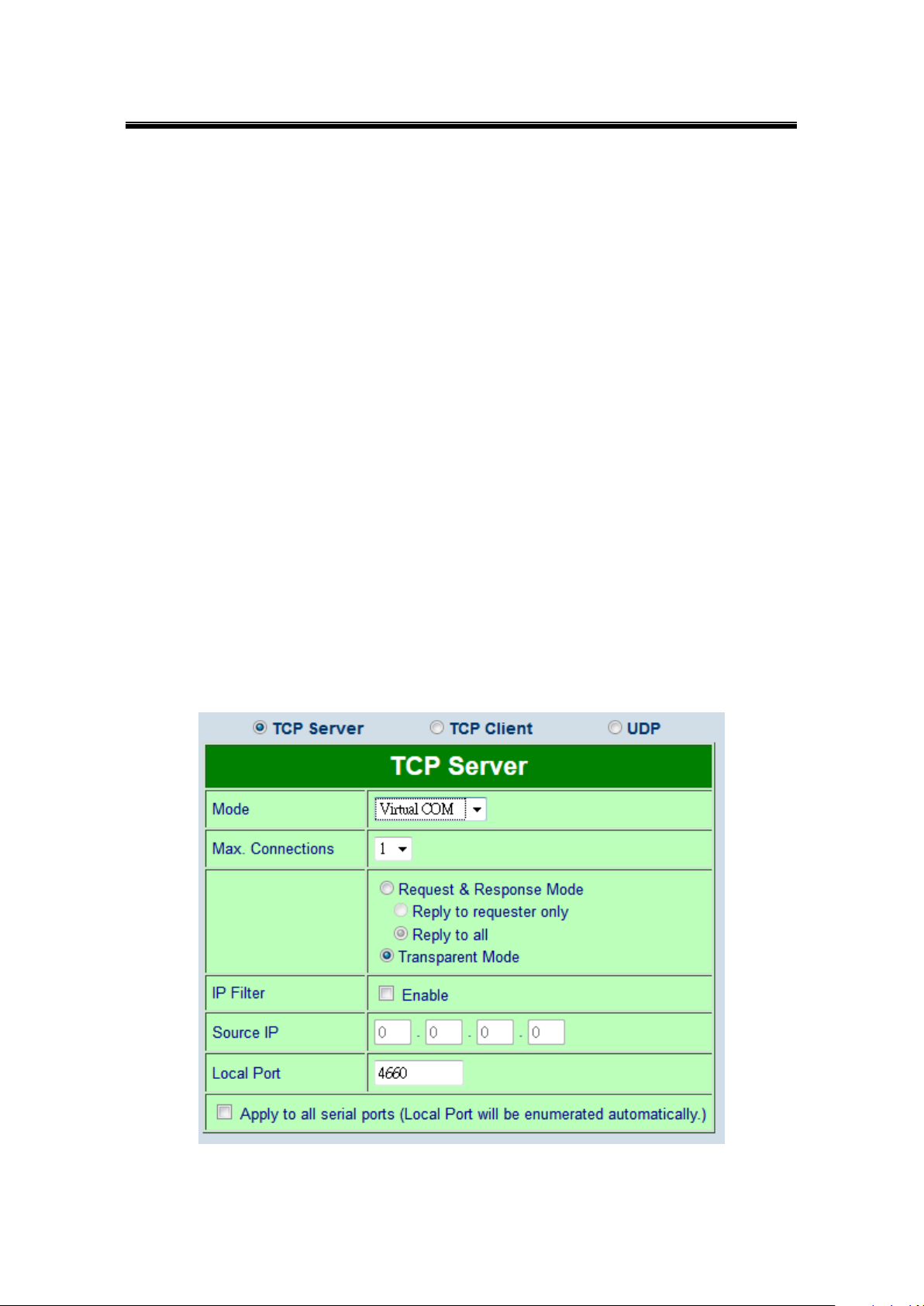
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
8.1.3 Installation
Run the Virtual COM setup file included in the CD or download a copy from our website to
install the Virtual COM driver for the operating system. Turn off your anti-virus software and try
again if installation fails. At the end of the installation, please select at least one Virtual COM
port from the Serial/IP Control Panel.
8.1.4 Uninstalling
From Windows Start Menu select Control Panel, Add/Remove Programs.
Select Serial/IP Version x.x.x in the list of installed software.
Click the Remove button to remove the program.
8.2 Enabling Virtual COM
8.2.1 Enable VCOM in Serial device servers
Enable Virtual COM in our serial device servers by logging into our WebUI. It is located under
COM configuration. Figure 8.4 show how to enable Virtual COM in SE5416A Series. For a
detailed Link Mode configuration with Virtual COM, please refer to Sec. 7.2.1.
Figure 8.4
91
Page 92

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
8.2.2 Running Serial/IP in Windows
Find Serial/IP Control Panel from:
Start → All Programs → Serial/IP → Control Panel
In the Windows Control Panel, open the Serial/IP applet.
In the Windows notification area, Figure 8.5; right click in the Serial/IP tray icon and
click on Configure to open the Control Panel.
Figure 8.5
If no Virtual COM port is selected, a dialog will pop up and asks to select at least one port as
the Virtual COM port before proceeding, Figure 8.6.
92
Page 93

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.6
After at least one Virtual COM port is selected, the Control Panel will show, Figure 8.7.
93
Page 94

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.7
The left hand side of the Control Panel shows the list of selected Virtual COM ports. Click on
Select Ports to add or remove Virtual COM ports from the list. The right hand side of the
Control Panel shows the configurations of the selected Virtual COM port marked in blue. Each
Virtual COM port can have its own settings.
Note: The changes to Virtual COM ports apply immediately, so there is no need to save the
settings manually. However, if the Virtual COM port is already in use, it is necessary to close
the Virtual COM port and open it after the TCP connection closes completely in order for the
changes to take effect.
94
Page 95

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
8.2.3 Configuring VCOM Ports
If the serial device server is running in TCP Server mode (recommended), a Serial/IP
should be the TCP Client connecting to the serial device server. Enable Connect to
Server and enter the IP Address of the serial device server with the Port Number
specified. The Port Number here is the Local Listening Port for the serial device server.
If the serial device server is running in TCP Client mode, Serial/IP should be the TCP
Server waiting for a serial device server to connect it. Enable Accept Connections and
enter the Port Number. The Port Number here is the Destination Port of the serial
device server. Do not enable Connect to Server and Accept Connections together.
Figure 8.8
Enable Restore Failed Connections to force Virtual COM to automatically restore failed
connections with the serial device server in the case of unstable network connections.
To test the Virtual COM connection, click the Configuration Wizard button and then click
Start button in the pop up window, Figure 8.9. If the test passes, all checks should be in
green. To apply the changes in the Configuration Wizard window to the Control Panel,
95
Page 96

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
click on Use Settings. Click on Copy to copy the results to the system clipboard.
To transfer the settings between Virtual COM ports, click on the Copy Settings To button.
Figure 8.9
8.2.4 Exceptions
96
Page 97

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.10
If the exclamation mark begins with Warning: timeout trying x.x.x.x as in Figure 8.10,
recheck the VCOM IP and Port configuration or the PC’s network configuration.
97
Page 98
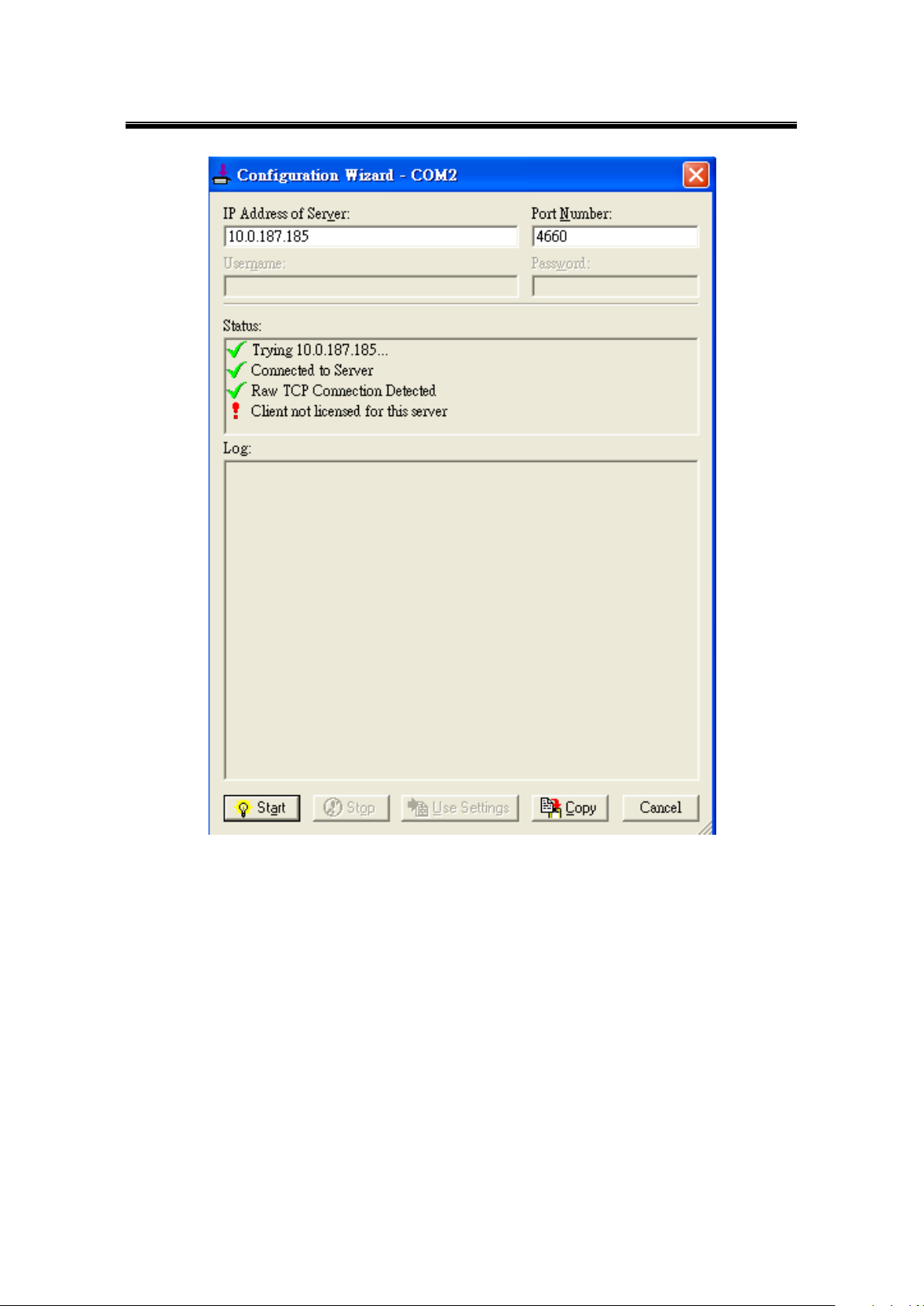
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.11
If there is a check with Raw Connection Detected and an exclamation mark with Client not
licensed for this server, Figure 8.11, enable VCOM in the serial device server.
98
Page 99

Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.12
If there is a check with Telnet Protocol Detected and an exclamation mark with Client not
licensed for this server as in Figure 8.12, this means that there is a licensing issue between
the serial device server and Serial/IP. Please contact Atop technical support to obtain the
correct VCOM software.
99
Page 100
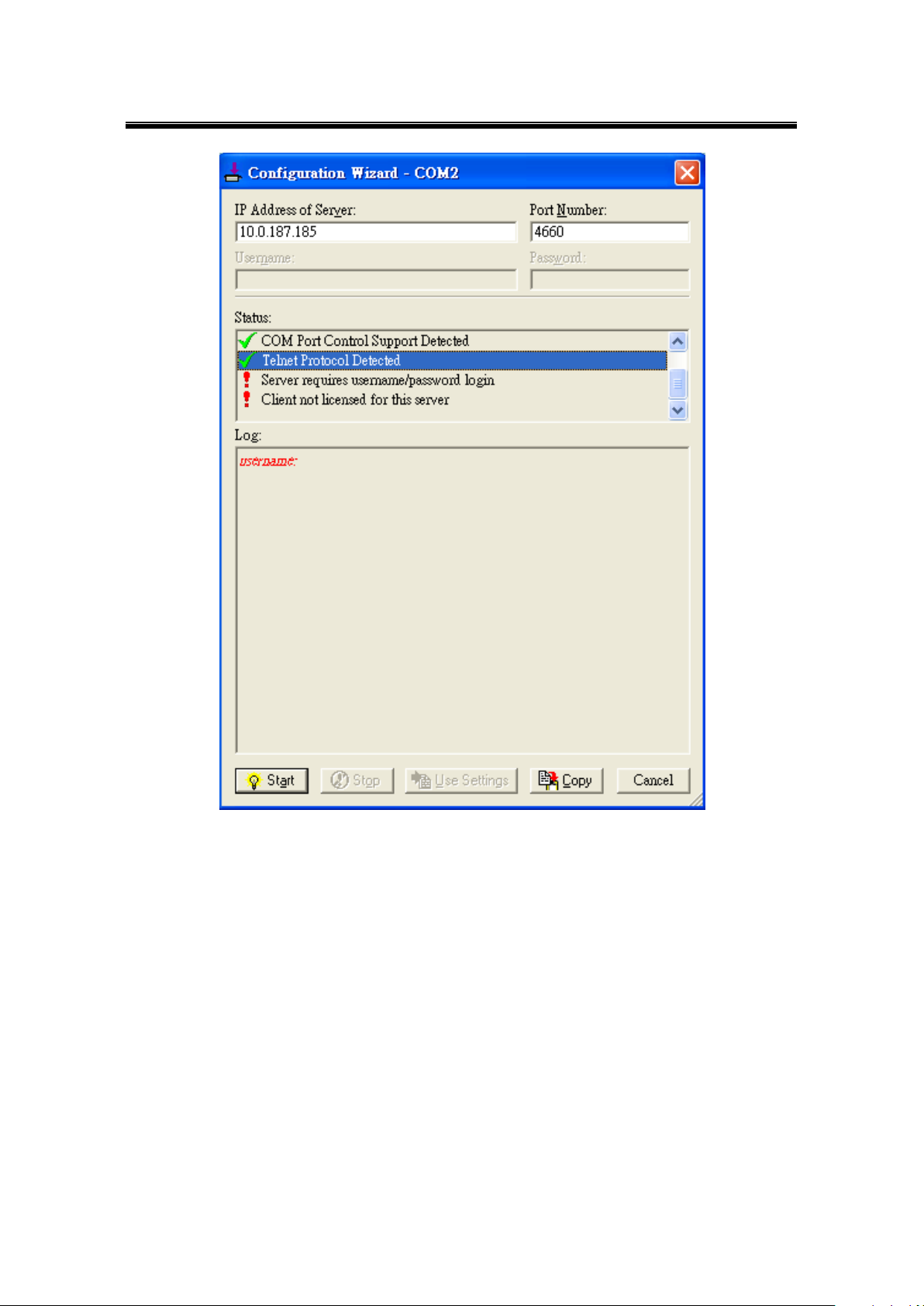
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
Figure 8.13
If the exclamation mark begins with Server requires username/password login Figure 8.13
It means VCOM Authentication in the serial device server is enabled, but credentials in the
Serial/IP are not enabled.
100
 Loading...
Loading...