
®
ABLELink
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
User’s Manual
Version 1.3
Updated on June 8, 2010.
TEL: 886-3-5508137
FAX: 886-3-5508131
http://www.atop.com.tw

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Important Announcement
The information contained in this document is the property of Atop Technologies, Inc. and is supplied for
the sole purpose of operation and maintenance of products of Atop Technologies, Inc. No part of this
publication is to be used for any other purposes, and it is not to be reproduced, copied, disclosed,
transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language, in any form,
by any means, in whole or in part, without the prior explicit written consent of Atop Technologies, Inc.
Published by
Atop Technologies, Inc.
2F, No. 146, Sec. 1, Tung-Hsing Rd.
Jubei, Hsinchu 30261
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-3-5508137
Fax: 886-3-5508131
www.atop.com.tw
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
All other product names referenced herein are registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Copyright © 2007 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved
I

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
FCC WARNING
Class B for this product
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This product complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This product complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
model should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
IEEE 802.11b/g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to channels 1 through 11.
UL NOTICE FOR POWER SUPPLIER
All the series of SW5002 products are intended to be supplied by a Listed Power Unit marked with “LPS”,
“Limited Power Source” or “Class 2” and output rate 9~48VDC, 1.0A minimum. Or, use the recommended
power supply in “Optional Accessories”.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- II -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Contents
1.1. OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................................................................1
1.2. FEATURES........................................................................................................................................................1
2.1. PACKAGING INCLUDE......................................................................................................................................2
2.2. ORDERING INFORMATION ................................................................................................................................2
2.3. INTERFACES ....................................................................................................................................................2
2.4. INSTALLATION PROCEDURES ...........................................................................................................................3
3.1. DEFAULT SETTINGS.........................................................................................................................................4
3.2. IP ASSIGNMENT...............................................................................................................................................5
3.2.1. Configure IP by SerialManager Utility......................................................................................5
3.2.2. Configure IP by web interface..................................................................................................6
3.2.3. Configure IP by Telnet utility ....................................................................................................6
3.2.4. Auto IP with DHCP...................................................................................................................6
3.3. TCP/IP PORT NUMBER....................................................................................................................................6
4.1. TCP & UDP PROTOCOLS ................................................................................................................................7
4.1.1. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)......................................................................................7
4.1.2. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)...............................................................................................7
4.2. CONNECTIVITY TOPOLOGY .............................................................................................................................7
4.2.1. Virtual COM Mode...................................................................................................................8
4.2.2. Tunneling Mode.......................................................................................................................9
5.1. LOGIN TO SYSTEM.........................................................................................................................................12
5.2. GENERAL INFORMATION ...............................................................................................................................12
5.3. NETWORK CONFIGURATIONS ........................................................................................................................15
5.3.1. LAN Settings..........................................................................................................................17
5.3.2. WLAN Settings ......................................................................................................................17
5.3.3. DNS Settings.........................................................................................................................17
5.3.4. SNMP Settings.......................................................................................................................18
5.4. WIRELESS CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................................... 18
5.4.1. Wireless Detail Settings.........................................................................................................19
5.4.2. Sample Wireless Application Cases......................................................................................20
5.5. COM PORT CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................................22
5.5.1. Link Mode Settings................................................................................................................23
5.5.2. TCP Server Mode..................................................................................................................23
5.5.3. TCP Client Mode....................................................................................................................24
5.5.4. UDP Mode.............................................................................................................................25
5.5.5. Serial Settings........................................................................................................................25
5.5.6. Advanced Settings.................................................................................................................27
5.6. CONFIGURE SYSTEM .....................................................................................................................................28
5.6.1. Configure Time by NTP Service............................................................................................29
5.6.2. WLAN Region........................................................................................................................29
5.6.3. Security (change the Password)............................................................................................30
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- III -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
5.6.4.
Restoring Factory Default Configurations..............................................................................30
5.6.5. Restart System ......................................................................................................................31
6.1. GENERAL INFORMATION ...............................................................................................................................33
6.2. NETWORKING CONFIGURATION.....................................................................................................................34
6.2.1. LAN Settings..........................................................................................................................35
6.2.2. DNS Settings.........................................................................................................................35
6.2.3. SNMP Settings.......................................................................................................................36
6.3. WIRELESS CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................................... 36
6.3.1. Wireless IP, Netmask, Gateway and IP mode Settings.........................................................37
6.3.2. Configure Region...................................................................................................................37
6.3.3. Site Survey ............................................................................................................................38
6.3.4. Manual Wireless Settings......................................................................................................39
6.3.5. Configure Ad-Hoc Mode ........................................................................................................39
6.3.6. Configure Infrastructure Mode...............................................................................................41
6.4. COM PORT CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................................43
6.4.1. TCP Server Mode for Link Mode...........................................................................................44
6.4.2. TCP Client for Link Mode.......................................................................................................45
6.4.3. UDP for Link Mode ................................................................................................................45
6.4.4. Serial Settings........................................................................................................................46
6.5. SECURITY CONFIGURATION...........................................................................................................................47
6.5.1. Change the Password ...........................................................................................................48
APPENDIX A. USING VIRTUAL COM............................................................................................................49
A.1. PRE-INST ALLATION REQUIREMENTS..............................................................................................................49
A.2. APPL YING T O THE SW5002........................................................................................................................... 49
A.3. VIRTUAL COM COMMUNICATION.................................................................................................................50
APPENDIX B. CONFIGURATION UTILITY..................................................................................................54
B.1. SERIALMANAGER UTILITY INTRODUCTION ...................................................................................................54
B.2. INTERFACE....................................................................................................................................................54
B.3. FUNCTIONS ...................................................................................................................................................54
APPENDIX C. UPGRADING SYSTEM SOFTWARE....................................................................................70
C.1. SYSTEM UPGRADING PROCEDURES...............................................................................................................70
C.2. CRITICAL ISSUES IN UPGRADING PROCESS....................................................................................................71
APPENDIX D. SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................... 72
D.1. HARDWARE SPECIFICATIONS .........................................................................................................................72
D.2. SOFTWARE SPECIFICATIONS ..........................................................................................................................73
D.3. PIN ASSIGNMENTS.........................................................................................................................................73
D.4. BEEP & LED STATUS ....................................................................................................................................74
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- IV -

User manual Version 1.1
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server is a gateway between wireless LAN or Ethernet (TCP/IP) and
RS-232/RS-485 communications. It allows almost any serial devices to be connected to a new or
existing wireless network. The information transmitted by Serial Server is transparent to both host
computers (IP network over wireless LAN or Ethernet) and devices (RS-232/RS-485). Data from the
wireless LAN or Ethernet (TCP/IP) is transmitted to the designated RS-232/RS-485 port and data
from RS-232/RS-485 port is transmitted to the Wireless or Ethernet (TCP/IP) transparently.
In the computer integration manufacturing or industrial automation area, Wireless Serial Server is
used for field devices to direct connect to network. Terminal Server (main control program run in
SW5002) transforms whatever data received from RS-232/RS-485 to TCP/UDP port then connects
devices to the IP network via a single application program or multiple application programs.
Many control devices provide the ability to communicate with hosts through RS-232/RS-485 however
RS-232/RS-485 serial communication has its limitations. For instance, it is hard to transfer data
through a long distance. With SW5002, it is possible to communicate with a remote device in the
Intranet environment or even in the Internet and thus, increases the communication distance
dramatically.
Flexible configuration options enable this unit to be setup remotely over IP network by Telnet, web
browser, or Window utility. Packed in a rugged DIN Rail mountable case and 9~48V DC power input
range, SW5002 is ideal for almost any industrial and manufacturing automation.
1.2. Features
Dual-port DIN-Rail mounting module.
Metal housing with IP50 standard.
15KV ESD protection for serial ports
IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps wireless network connectivity
Support UDP, TCP server and client protocols for Virtual COM mode and pair connection
Selectable RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 serial mode by software
Configurable via console, telnet, built-in web server and Windows-based utilities
Standard 2.4GHz High-gain antenna
Upgradeable firmware via network
Copyright © 2006 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved
1

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
2. Getting Started
2.1. Packaging Include
Atop Wireless Serial Server x 1
5 pins Terminal Block for Serial Connector (TB model only) x 2
3 pins Terminal Block for Power Connector (TB model only) x 1
4 dBi Antenna x 1
Wall mount kits x 2
Atop Wireless Serial Server quick start guide x 1
Product CD containing configuration utility x 1
NOTE: Notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged.
2.2. Ordering information
SW5002-WgN1(DB)
SW5002-WgN1(TB)
SW5002-WgN1Sis(TB)
Optional Accessories
12VDC-1.25A(US)
12VDC-1.25A(EU)
HG055
2-ports wireless serial server with D-Sub 9pin serial connector
2-ports wireless serial server with Terminal Block serial connector
2-ports RS-422/485 photo Isolated wireless serial server with terminal
block serial Connector
AC100~240V US plug / DC12V 3 pin Terminal block for TB model
AC100~240V US plug / DC12V DC-jack for DB model
AC100~240V EU plug / DC12V, 3 pin Terminal block for TB model
AC100~240V EU plug / DC12V DC-jack for DB model
5.5dBi antenna, SMA (R) Female connector with 180cm cable
2.3. Interfaces
The SW5002 interfaces is shown by Fig 1.
Antenna Connector
Wireless Status
LEDs
Serial Status
LED
System/WLAN
status LED
10/100M
Ethernet port
Reset
button
DB Model (9 pin D-Sub Connectors) TB Model (5pin Terminal Block Connectors)
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
D-sub 9-pin
Connector
D-sub 9-pin
Connector
DC-Jack
for Power
Fig 1. SW5002 Interfaces
- 2 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
2.4. Installation Procedures
Prepare necessary cables, DC power adapter and RS-232/RS-485 connector.
Place SW5002 under the access point signal coverage area, or connect SW5002 to Ethernet
cable with RJ45 connector.
Connect SW5002 serial port to serial device, make sure the connector and wiring of RS-232 or
RS-485 is correct.
Plug in SW5002 to DC-9-48V power source (with DC-jack or 3-pin terminal bock connector),
buzzer will beep and the RUN LED will blink if SW5002 functions normally. For LED Status sees
Appendix D4
Use SerialManager configuration utility on the product CD to check the status of SW5002. If it starts up
successfully, User shall find the IP and MAC address of SW5002. User can change IP address, gateway IP
address and subnet mask networking parameters of SW5002 according to user networking configurations.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 3 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
3. Software Setup
Now the SW5002 hardware is installed and power is on, network IP configuration will be set in this
section.
3.1. Default Settings
The SW5002 has two IP addresses one for Ethernet interface and another one for wireless network
interface. These default settings are shown from under information
Default IP addresses
Interface Device IP Subnet mask Gateway IP
LAN port 10.0.0.50.100 255.255.0.0 10.0.0.254
WLAN Port 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.254
The other default settings of SW5002 are shown in the following table
Property Default Value
Ethernet Port
IP Address 10.0.50.100
Gateway 10.0.0.254
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
WLAN Port
IP Address 192.168.1.100
Gateway 192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Security
User Name
Password
Serial
COM 9600/None/ 8/1,No flow control, packet delimiter disabled
Link Mode TCP Server, Listen port 4660/4661,No Filter, Virtual COM disabled
SNMP
SysName of SNMP Name
SysLocation of SNMP Location
Admin
Null (Leave it blank)
SysContact of SNMP Contact
Table 1. Default settings of the SW5002 device
NOTE: Press reset button for 5 seconds then release the button to restart SW5002 to the default
settings.
Waring: Please avoid setting LAN and WLAN IP address in the same subnet, that may make
unexpect networking problem.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 4 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
3.2. IP Assignment
3.2.1. Configure IP by SerialManager Utility
Use SerialManager configuration utility that comes with product CD or diskette to configure the network
parameters. For more details, please refer to Appendix B1.
Find new device and IP assignment
Use SerialManager Utility for finding new device IP address, get device’s current IP from table
list
Re-assigned IP, network mask and gateway if need with SerialManager Utility.
User can configure User ID, Password and Host Name with SerialManager Utility.
Fig 2. IP settings for SerialManager Utility tool
Note: All settings were NOT changed if user ID or password was incorrect.
If there is more than one device using the same IP address in same Subnet. User has to correct mapping
between MAC address & IP address by ARP commands.
ARP commands
ARP (address resolution protocol) commands can be used to assign a static IP address on SW5002 using
its hardware MAC (media access control) address. The MAC address"0060E9-xxxxxx" is printed on the rear
side of SW5002. The following figure shows how to use ARP command on MS-DOS command prompt
window.
Example: Set IP 10.0.50.101 to MAC address 00-60-E9-00-79-F8.
Fig 3. Map IP address to MAC address by ARP Command
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 5 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Note: ARP commands can only be used to set a static IP address of SW5002
- arp –a command show the current mapping IP and MAC addresses.
- arp –s “IP address” “MAC address” map the IP address to specify MAC address.
3.2.2. Configure IP by web interface
Use common Web browser, ex. Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox, to configure the network
parameters of SW5002.
Open web browser, type in the IP address (default IP: 10.0.50.100) of SW5002 to be configured.
Default user name is admin and default password is null (leave it blank).
Configure IP settings from web Network links page then click “Save Configuration” to save
settings.
Click on ”Restart” button to make the change effective.
Please refer to contents of Web Configuration section
.
for more details.
3.2.3. Configure IP by Telnet utility
Use common Telnet utility, ex. Microsoft Hyper-terminal, to configure the network parameters of SW5002.
Run command telnet “IP address” to telnet to SW5002 . Default IP address is 10.0.50.100 and
default password is null (leave it blank).
Configure IP settings from network settings menu, and restart system after saved settings.
Please refer to Telnet Configuration
section for more details.
3.2.4. Auto IP with DHCP
DHCP server will automatically supply an IP address gateway address, and subnet mask to SW5002. By
default, the DHCP client function on SW5002 is disabled, user can activate the DHCP functions by the
following steps
Execute SerialManager Utility
Click on the IP address (of SW5002)
Click “Config” to pop-up the static IP Dialog Window
Check on ”Auto IP”
Click “Config Now” (The SW5002 will restart and obtain the IP from the DHCP server
automatically)
3.3. TCP/IP Port Number
Default Port numbers of SW5002 is 4660 (1st port) & 4661 (2nd Port) and it is associated with the serial port
COM1 and COM2 respectively. After the application program connected to the TCP port 4660 (or 4661) on
the SW5002, data of user’s application program are transmitted transparently to SW5002 and vice versa.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 6 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
4. Application Connectivity
SW5002 provides Tunneling and Virtual COM operation mode. The SW5002 is designed to transmit data
between one-or-more serial devices to/from one-or-more TCP/IP devices through wireless or wire Ethernet,
so SW5002 can enhance the accessibility of the serial device through the ubiquitous TCP/IP based
Ethernet. The connection distance limit is overcome by SW5002. Examples of these devices are PLC
controllers, card readers, display signs, security controls, CNC controller, etc.
4.1. TCP & UDP Protocols
SW5002 can be operated in two most common protocols TCP and UDP.
4.1.1. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
TCP provides a connection and a byte oriented data stream with control parameters such as flow control,
multiple ports option, and order delivery notification. Once the connection is established, data can be
transmitted in both directions. TCP guarantees data is transmitted from one node to the other node(s) in
orderly. The protocol also distinguishes the transmitted data for different applications (such as a Web server
or an Email server) on the same computer.
For redundant or dual-network connectivity purposes, SW5002 offers two TCP operation Modes so
users may choose for their specific application, TCP Server Mode and TCP Client Mode.
4.1.2. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a faster datagram delivery protocol. User can configure SW5002 to work in the UDP mode. UDP is
connectionless protocol and can transmit multicast data to/from a serial device to one/multiple host
computer. Because UDP is the connectionless protocol, UDP does not guarantee the reliability and orderly
data streams like TCP protocol. Datagram may arrive out of order or lose without notice. But the advantage
of UDP is the speed. UDP is faster and hence more attractive in time-sensitive applications.
4.2. Connectivity Topology
SW5002 is also equipped with Tunneling and Virtual COM operation modes. It is designed to transmit
data to/from multiple serial devices and from/to multiple TCP/IP devices on Ethernet, so it can enhance the
accessibility of the serial devices immensely. Fig 4. is the example of SW5002 connection topology.
Fig 4. Typical Topology of SW5002 Connection
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 7 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
4.2.1. Virtual COM Mode
The Virtual COM software emulates a serial port with Internet or LAN topology. In the Virtual COM Mode,
COM port data (RS232) is encapsulated to Ethernet data format. By creating a virtual COM port on a PC,
the Virtual COM driver redirects communications from the virtual COM port to the destination IP address
(and the designated port number) by encapsulated COM data into IP data. Fig 5. illustrates a Virtual COM
connection diagram.
Fig 5. TCP Connection in Virtual COM Mode
TCP Server in Virtual COM Mode
SW5002 can be configured in the TCP server mode (PC as a client) with a unique IP and Port number, and
SW5002 waits passively for the PC to establish a connection to. After the connection is established, PC can
communicate to serial devices through SW5002.
Configure SW5002 to be TCP server
Using one of the three configuration methods (Telnet, Web, and console), User can configure SW5002 to be
as TCP Server as following.
Disabled the IP filter (default)
Set the port number (default port is 4660 for COM1, 4661 for COM2).
If IP filter is enabled, only the assigned source IP is allowed to be connected to SW5002.
Fig 6. TCP Server in Virtual COM Mode
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 8 -
User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
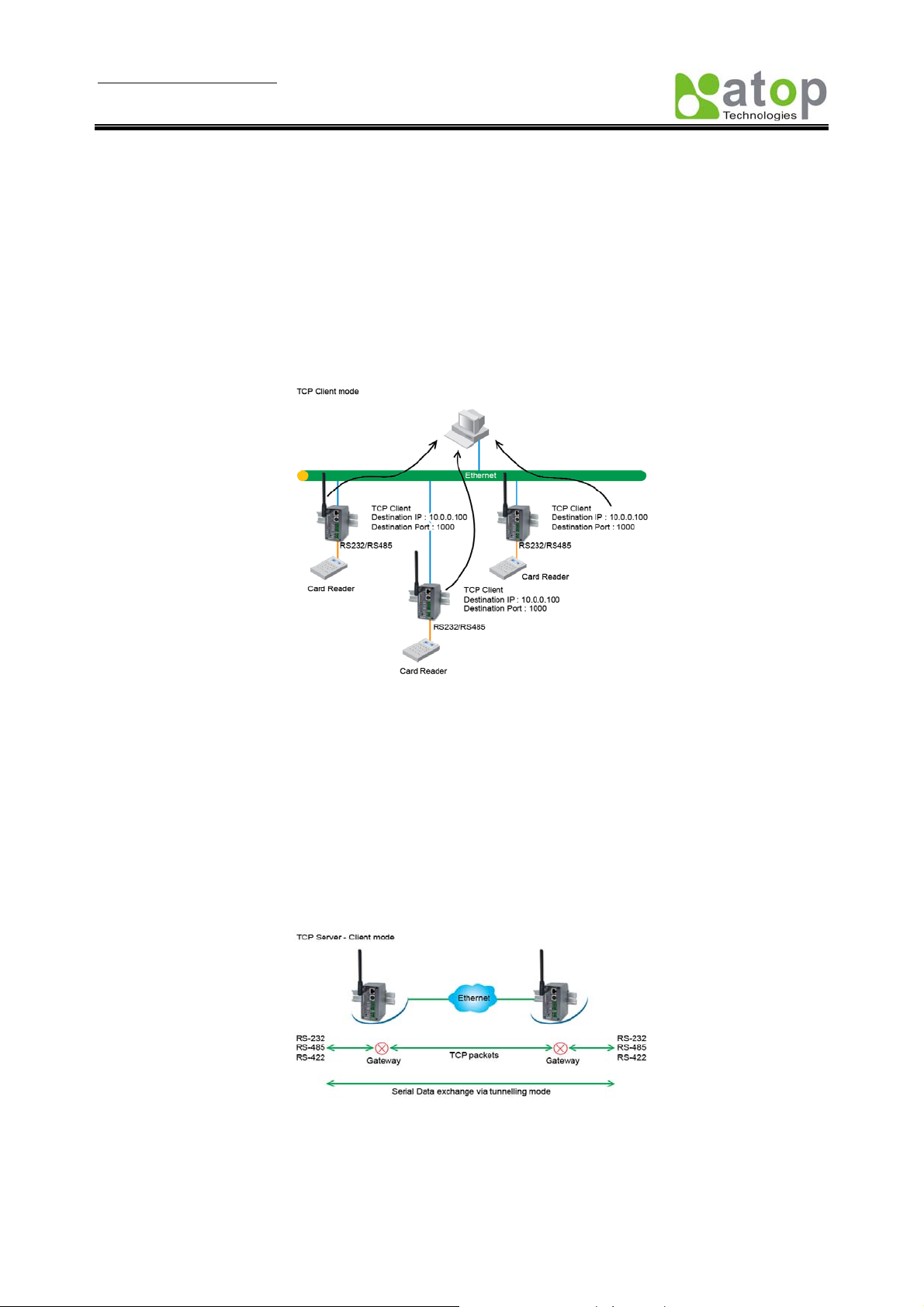
TCP Client in Virtual COM Mode
SW5002 can be configured to be TCP Client mode (PC as a server) to establish a TCP connection to an
application server on PC, or the Remote Control Host. Once the connection is established, PC or Remote
Control Host can exchange data with several serial devices at the same time through SW5002.
Configuring SW5002 to be TCP client
User can configure SW5002 to be as TCP Client for example, from Fig. 7. PC, as a server, has IP address
10.0.0.100 and listening on port 1000. Each SW5002, connected with serial device, configured as TCP
client mode with destination IP address 10.0.0.100 and the destination port 1000, and the IP filter is
disabled (by default).
Fig 7. TCP Client in Virtual COM Mode
4.2.2. Tunneling Mode
Tunneling Mode is used for multiple serial devices to “talk” among one another through SW5002’s through
wireless LAN or wired Ethernet. This mode is particularly useful when two or more serial devices are far
away. This mode can be used to extend the normal serial communication distance of 15 m to 100 m or
longer.
One SW5002 can be configured to be the TCP Server Mode with serial device connected and also another
SW5002 is configured as TCP client with serial device connected. After the connection is established, both
serial devices can exchange data to each other transparently. For example, User can implement SW5002
tunneling mode for Master /Slave mode PLCs or between other serial devices.
Fig 8. TCP Link in Tunneling mode
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 9 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Configuring SW5002 to Tunneling Mode
Using one of three configuration methods (Telnet, Web, or Console), user can configure SW5002 to TCP
Server mode with a desired IP address and port, and with other SW5002 is configured as TCP Clients
mode with Server IP and port as destination IP and port respectively.
Note: TCP client has to assign the destination IP and the destination port corresponding to TCP
server’s IP and listening port (example: TCP 4660 port).
Fig 9. TCP Tunneling Mode
UDP
In UDP mode, User may exchange Multicast data from one SW5002 with multiple SW5002s, Vice versa is
also true.
Fig 10. UDP Link in Tunneling mode
Configure SW5002 in UDP Mode
Use one of the three configuration methods (Telnet, Web, and console). User can configure SW5002 to
UDP mode. In UDP mode, SW5002 can be configured to communicate to more than one node
(Multicasting). Note that the Multicast IP address is limited by the Class of IP address and subnet mask. As
an example, for a network of Class C of subnet 192.168.1.X and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the
maximum Multicast IP address to be configured is four destinations IP’s.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 10 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 11. Multi-UDP Link in Tunneling Mode
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 11 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
5. Configure SW5002 by web interface
User has to assign IP address to SW5002 before working on web configuration operations. Please refer to
section 3.2
for more detail.
5.1. Login to System
Open one of the web browsers, ex. Microsoft IE or Firefox etc. Enter the IP address of SW5002 on the URL.
Example: http://10.0.50.100 or http://user-device-IP
The following authentication screen shall appear. Enter user name and password then click on “OK”. The
default user name is admin and password is null (leave it blank).
Fig 12. Authorization request for system security
The overview screen shall appear (Fig. 13).
5.2. General Information
This system overview window gives the general information on SW5002, included Network, and Serial
information.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 12 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 13. Overview for system information by Web Interface
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 13 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Device Information
SW5002’s system information includes model name、 Device Name、 Kernel version and AP version.
The information is read only and is attributed from another setting page or system status
Fig 14. Device Information from Overview web page
Networking information
Networking information fields are displayed both ‘LAN & Wireless LAN (WLAN) Information. The
information provided LAN MAC address, LAN IP address, WLAN MAC address, WLAN IP address and
WLAN status
Fig 15. Network Information from Overview web page
Serial Information
SW5002 COM1 (COM2) information includes UART mode, link mode, baud rate, parity, data bits, stop
bits, flow control and link status. The COM1 (COM2) information is read only and is attributed from Serial
settings of COM1 or COM2 Port of SW5002.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 14 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 16. Serial Information from Overview web page
5.3. Network Configurations
There are four items allowed to change on Network page, included LAN, WLAN, DNS and SNMP
Information.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 15 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 17. Network information by Web page
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 16 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
5.3.1. LAN Settings
Operation: [Network] Æ [LAN Setting]
Click on the “Network” link and the following screen shall appear. Fill in IP information on TCP/IP field.
Alternatively, click on DHCP to automatically obtain IP address, gateway and subnet mask information.
Fig 18. LAN Setting from Network web page
5.3.2. WLAN Settings
Operation: [Network] Æ [WLAN Settings]
Click on the “Network” link Mode and the following screen shall appear. Fill in WLAN IP information on
WLAN settings fields. Alternatively, User may activate DHCP client function by checking on “Obtain an IP
automatically” field to automatically obtain IP address, gateway and subnet mask from DHCP server.
Fig 19. WLAN Setting from Network web page
5.3.3. DNS Settings
Operation: [Network] Æ [DNS Settings]
Click on the “Network” link and the following screen shall appear. Fill in DNS information on DNS
Settings field. Alternatively, User can configure DNS by checking on “Obtain an IP automatically” field in
LAN Settings or WLAN Settings fields to automatically obtain DNS from DHCP server.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 17 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 20. DNS Setting from Network web page
5.3.4. SNMP Settings
Operation: [Network] Æ [SNMP Settings]
Click on the “Network” link and the following screen shall appear. Check on “Enabling Settings” field. Fill
in desired SysName、 SysLocation、 SysContact information on SNMP Settings fields. The changes of
SNMP Settings will take effect only after the SW5002 restarted.
Fig 21. SNMP Setting from Network web page
5.4. Wireless Configuration
There are three fields of information on Wireless Configuration page which are Default, Current and
Site-Survey Information. Click on “Wireless” link and the following screen shall appear.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 18 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 22. Wireless information by Web page
There are 3 buttons can be operated on Wireless page
Rescan: Click on the “Rescan” button, and SW5002 will start site-survey procedures, then on the
site-survey list will display the access points founded.
Select: On the site-survey list, click on radio button to attach the access point you wanted
User defined: Users can also define information for wireless parameters by themselves.
5.4.1. Wireless Detail Settings
User can configure wireless LAN parameters through web pages. Pop-up windows page will be shown for
advanced wireless settings if “select” or “user define” button was clicked (FIG. 23). For example, User can
configure SSID, wireless topology, Wireless Band Mode, TxRate, Channel, Authentication, and
Encryption of the access point that SW5002 want to connect to.
The advanced wireless settings also include roaming threshold. User can configure roaming signal
threshold for the SW5002. SW5002 will change to the stronger wireless signal access point, if the original
access point’s signal is less than roaming threshold.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 19 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 23. Pop-up Windows for Wireless Detail settings
5.4.2. Sample Wireless Application Cases
Below are some screen shot examples of wireless detail settings for different wireless security schemes.
Attach access point without Authorization
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: open
Encryption: None
Fig 24. Open Authorization and no Encryption
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 20 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Attach access point with WEP
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: share
Encryption: WEP
WEP Key1~4: Hexadecimal or ASCII / 64 or 128bit / <WEP Key>
Fig 25. Share Authorization and WEP Encryption
Note1: Enter 5 ASCII value or 10 Hexadecimal digit if select WEP64 encryption.
Note2: Enter 13 ASCII value or 26 Hexadecimal digit if select WEP128 encryption
Attach access point with WPA-PSK
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: WPA-PSK
Encryption: TKIP or AES
WPA-PSK: 8~ 63 Characters
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 21 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 26. WPA-PSK Authorization and TKIP Encryption
5.5. COM Port Configuration
Here User can configure Serial parameters, include alias, baud rate, parity, data bit and type of flow control
defined by user.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 22 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 27. COM port Information Web Page
5.5.1. Link Mode Settings
Click on the “Serial” link and the Fig. 27 screen will appear.
Fill in Serial parameter information on Serial Settings field
Click on “Save Configuration” button to save the changes.
5.5.2. TCP Server Mode
TCP Server mode is default Link mode of Serial Settings, and it can wait for connecting requirement from
remote host PC which running “serial-to IP” utility or setting SW5002s in tunneling mode. User has to
configure listening port to allow client establish connection to this server. Default port number of SW5002 is
4660.
Max Connections (default=1):
This option is used if you need to receive data from different hosts simultaneously. When set to 1, only a
single host may open the TCP connection to the serial port. When set to 2 or greater, up to the specified
number of hosts may open this port at the same time.
ATTENTION
When Max. Connections is greater than 1, the Serial server device will apply multi connection application
(i.e., 4 hosts are allowed access to the port at the same time). When using a multi connection application,
all hosts connected to the port must use identical serial settings. If one of the hosts opens the COM port
with different serial settings, data will not be transmitted properly
Request and response Mode
This option determines how the port will proceed if multiple hosts are connected and one or more of the
hosts stop responding when the port is transmitting data. If you select Reply to requester only, the port will
keep other hosts’ request data in the buffer and continue data transmission to the request host only. If you
select Reply to all, the port will transmit reply data to all connected hosts.
Transparent Mode
The port will allow the other hosts and continue data transmission to all hosts. This mode does not take
“Response Interval Timeout” into consideration.
IP filtering function is a simple ACL (Access Control List). It can be disabled by setting FILTER_IP to
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 23 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
“0.0.0.0”.
User can configure one or group IP for source IP. If IP filter is enabled, only source IP assigned can be
connected to SW5001.
Fig 28. TCP Server in Link mode
Note: Enable Virtual COM mode if the remote site PC’s “Serial to IP” tool is installed
5.5.3. TCP Client Mode
User may enter destination IP & port (default: 4660) to establish connection of counter-pair (remote) host
(For example, another SW5002, or PC for data-collection). SW5002 can support two destination hosts
simultaneously.
Fig 29. TCP Client in Link mode
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 24 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
5.5.4. UDP Mode
SW5002 can be configured in a UDP mode to establish connection using Unicast or Multicast data from
the serial device to one or multiple host computers. Vice versa is also true. For example, the original
RS-422/ RS485 bus can be transferred and extended connected distance by SW5002s.
The destination IP is assigned by single IP or group IPs, The configuration is limited by the Local Listening
Port. For example, on SW5002 listening port is 4660 which receive data sending from the host computers.
SW5002 can support up to 4-group IPs for UDP connection, if users needed.
Fig 30. UDP protocol in Link mode
Note: In this phase, UDP mode does not support Virtual COM mode.
5.5.5. Serial Settings
This filed can be configured with serial parameters for SW5002. Here User can configure Serial parameters,
include UART Mode, baud rate, parity, data bit and type of flow control.
Configure UART Mode: RS-232 or RS-485 or RS-422
Baud rate: 1200/2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200
Parity: None or Odd or Even or Mark or Space
Data bits: 7 or 8
Stop bits: 1 or 2
Flow control: None or Xon/Xoff or Hardware (RTS/CTS).
Fig 31-1. Serial Communication Settings from Web Page
Note: The isolation, SW5002-WgN1Sis (TB), only support max 230Kbps baud rate.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 25 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 26 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
5.5.6. Advanced Settings
Fig 31-2. Advanced Settings from Web Page
Time out for receiving TCP data (Default: Disabled): This field specifies how long the serial device
server will wait for a response to “keep alive” packets before closing the TCP connection. The serial device
server checks connection status by sending periodic “keep alive” packets. If the remote host does not
respond to the packet within the time specified in this field, the serial device server will force the existing
TCP connection to close. If this setting is set to 0, the TCP connection will remain open even if there is no
response to the “keep alive” packets.
Character send interval (Default: Disabled)
This parameter defines how large a gap in character communication the serial device server will allow
before packing the serial data in its internal buffer for network transmission.
Serial to Network Packet Delimiter
Packet delimiter is a way of packing data in a serial communication. It is designed to keep packets in track.
Serial device server provides three patterns in parameter setting: (1) packet delimiter by (1) Interval
timeout, (2) Max Byte and (3) Character pattern.
1. By Time – The device will transmit the data when set time interval has reached and no more
data comes in.
2. By Max Bytes – The device will transmit the data when the data queue has reached the set
size.
3. By Character - The device will transmit the data when it sees the set character.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 27 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
If one or more of the delimiters are selected, data would be transmitted when any of the conditions are met.
ATTENTION
Packet delimiter by Interval timeout,
This parameter defines how large a gap in serial communication the serial device server will allow
before packing the serial data in its internal buffer for network transmission.
The optional “Internal timeout” transmit time depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baud rate. For example, assume that the serial port is set to 1200
bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed to send a character is
10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is (10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s)) × 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set the “Interval timeout” to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must be greater
than or equal to 10 ms. If it is necessary to send a series of characters in the same packet, the serial device
will need to send that series of characters within the specified transmit time, and the total length of data
must be less than or equal to the serial device server internal UART buffer size (4K per port).
Network to Serial Packet Delimiter
Network to Serial Packet Delimiter is used less often compared to Serial to Network Delimiter because
Ethernet has better speeds. Packet delimiter is a way of packing data in a serial communication. It is
designed to keep packets in track. Serial device server provides three patterns in parameter setting: (1)
packet delimiter by (1) Interval timeout, (2) Max Byte and (3) Character pattern.
1. By Time – The device will transmit the data when set time interval has reached and no more
data comes in.
2. By Max Bytes – The device will transmit the data when the data queue has reached the set
size.
3. By Character - The device will transmit the data when it sees the set character
If one or more of the delimiters are selected, data would be transmitted when any of the conditions are met.
Response interval timeout (Default: 1000ms):
This option only work in Request & Response Mode. When TCP data is received (request) and passed to
Serial side, the device will wait for the set time before transferring another TCP data if the Serial side did not
receive any data (response).
Keep serial buffer data before TCP connection is Established (Default: Disable):
If “Enable” is selected, the device will store received data in buffer and sent them out when
connection is establish. Otherwise, data will be discarded when “Disable” is selected.
5.6. Configure System
There are five subsystems for system settings, included Time, WLAN Region, Security, Set to default
and Restart.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 28 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 32. Subsystem menu of system settings Web Interface
5.6.1. Configure Time by NTP Service
Operation: SystemÆTime
User can set date and time manually by fill in “Set Date and Time manually” field. User can also configure
NTP Server to obtain Network time automatically.
Fig 33. Time service settings from System web page
5.6.2. WLAN Region
Operation: System->WLAN Region
Click on the “WLAN Region” link and the following screen shall appear (Fig. 34).
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 29 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 34. Time service settings from System web page
Select the country from drop-down list box to country that user wants to implement the SW5002. This
selection will be effected to the bands of channel of SW5002 wireless mode. For example, the normal
system level channel configurations for deployments are channels 1, 6 and 11 for FCC countries and 1, 5, 9
and 13 for European Union countries
5.6.3. Security (change the Password)
Operation: System->Security
Click on the “Security” link and the following screen shall appear (Fig. 35).
Enter the old password on “Old Password” field then enter the new password on “New Password” and the
“Verified Password” fields, and then click on “Save Configuration” to update the password. The maximum
is 8 characters.
Fig 35. Change password from System Security Page
Note: User may press the default reset key to reset password to the default value(blank)
5.6.4. Restoring Factory Default Configurations
Operation: SystemÆ Set to Default
User can click on “set to default and restart” button to restore SW5002’s settings to factory default
(Fig. 36).
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 30 -
User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 36. Set all parameters to factory default by Web Interface
5.6.5. Restart System
Operation: SystemÆ Restart
The changes of networking parameters will take effect only after the SW5002 is restarted. User can
restart the SW5002 manually by click on Restart button on the restart menu web page (Fig 37).
Fig 37. Restart system by Web
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 31 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6. Telnet Configuration
User can also use Telnet utility to change SW5002 configuration settings.
Open Ms-DOS command prompt window or other telnet tools
Enter the “IP address” of the SW5002 (For example, Telnet 10.0.50.100). The system then
prompts for username and password, the default username is “admin” and the default password
is null (blank).
Fig 38. Login into System by Telnet
Then the following main menu shall appear
Fig 39. Overview information by telnet
If the SW5002 does not receive any command within 1 minute, Telnet will be terminated
automatically.
The changes of networking parameters will take effect only after the SW5002 is restarted.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 32 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.1. General Information
Operation: [Main]Æ[1 Overview]
Select “1” from “Input choice (0~6) and enter:” to enter “overview page.
This system overview window gives the general information on Ethernet & WLAN IP, MAC address,
SNMP information, kernel and AP version, and the connection status of the SW5002 (Fig. 39).
The following overview information shall appear.
Device Information:
Model Name: SW5002’s Model
Device Name: [Allows for changes in SNMP settings]
Kernel Version: [Read Only, Generated by system]
AP Version: [Read Only, Generated by system]
Ethernet Information:
MAC: [Read Only]
IP: [Allows for changes in Network Page]
WLAN Information:
MAC: [Read Only]
IP: [Allows for changes in Auto IP of Network Page]
Connected: [SSID name, if Wireless SW5002 is connected]
Fig 40. System Information from Overview
DNS Information:
DNS1: [IP address of 1
DNS2: [IP address of 2
st
DNS Server, Allows for changes in Auto IP of Networking Page]
nd
DNS Server, Allows for changes in Auto IP of Networking Page]
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 33 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
SNMP Information:
SNMP Status: Enable [or Disable, Allows for changes in Networking Page]
SysName: [Allows for changes in Networking Page]
SysLocation: [Allows for changes in Networking Page]
SysContact: Allows for changes in Networking Page]
Serial Information:
UART mode RS485/RS232/RS422
Link Mode: TCP Server [or TCP Client/UDP Mode, Allows for changes in Serial Page]
Baud rate: 115200 [or 1200/2400/4800/9600...Allows for changes in Serial Page]
Parity: None [or Even/Odd/Space/Mark...Allows for changes in Serial Page]
Data bits: 8 [or 7 (bits).Allows for changes in Serial Page]
Stop bits 1 bit or 2 bits
Flow Control None, Xon/Xoff, RTS/CTS
6.2. Networking Configuration
Operation: [Main]Æ[2 Networking]:
Select “2” on “Input choice (0~6) and enter:” to enter Networking settings page.
Fig 41. Networking Settings by Telnet
Note: Press “0” key to return to the previous menu
This section allows for changes in IP address, subnet mask, gateway IP address and SNMP information.
Please note that setting changes will not take effect until the SW5002 is restarted.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 34 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.2.1. LAN Settings
Operation: [Main]Æ[2 Networking]Æ[1 LAN Settings]
Select “1” from “Input choice (0~3) and enter on Networking page:” to enter LAN Settings page. The
MAC address, IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and IP mode information will be shown
(Fig. 42). User also can set IP, Netmask, Gateway, and IP mode of LAN interfaces by enter the
corresponding menus and values. For example, enter 1 for setting the IP address on LAN interface.
Fig 42. LAN Settings by Telnet
6.2.2. DNS Settings
Operation: [Main]Æ[2 Networking]Æ[2 DNS Settings]
Select “2” from “Input choice (0~3) and enter on Networking page:” to enter DNS Settings page.
Fill in the DNS information DNS1 or DNS2 or both according to user DNS server (Fig. 43).
Fig 43. DNS Settings by Telnet
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 35 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.2.3. SNMP Settings
Operation: [Main]Æ[2 Networking]Æ[3 SNMP Settings]
Select “3” from “Input choice (0~3) and enter on Networking page:” to enter SNMP Settings page. User
can enable/disable SNMP, and set network identification information on SNMP Settings page. The
changes will not become effective until SW5002 is restarted
SW5002 basically supports get/set SNMP parameters, these are SysName (System Name), SysLocation
(System Location) and SysContact (System Contact). These fields will response and supply basic system
information from standard SNMP query. User can set the SNMP system parameters by enter the
corresponding menus and values. For example, enter 2 for changing the SysName then enter the desired
name.
Fig 44. SNMP Settings by Telnet
6.3. Wireless Configuration
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Settings]
Select “3” from “Input choice (0~6) and enter:” the following screen shall appear (Fig. 45).
User can configure wireless IP, Netmask, Gateway, IP mode, and Region by enter the corresponding
menu and corresponding values.
Fig 45. Configure Wireless Settings by Telnet
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 36 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.3.1. Wireless IP, Netmask, Gateway and IP mode Settings
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Settings]Æ [1 IP]/[2 Netmask]/ [3 Gateway]/[4 IP Mode]
User can configure SW5002 Wireless IP/Netmask/Gateway by enter 1/2/3 at Wireless Settings page and
enter the desired IP/Netmask/Gateway address.
User can also configure wireless IP mode by enter 4 at Wireless Settings page and enter 1 for static IP
address or enter 2 for DHCP mode (Fig. 47).
Fig 46. Configure Wireless Networking by Telnet
Fig 47. Configure Wireless IP mode by Telnet
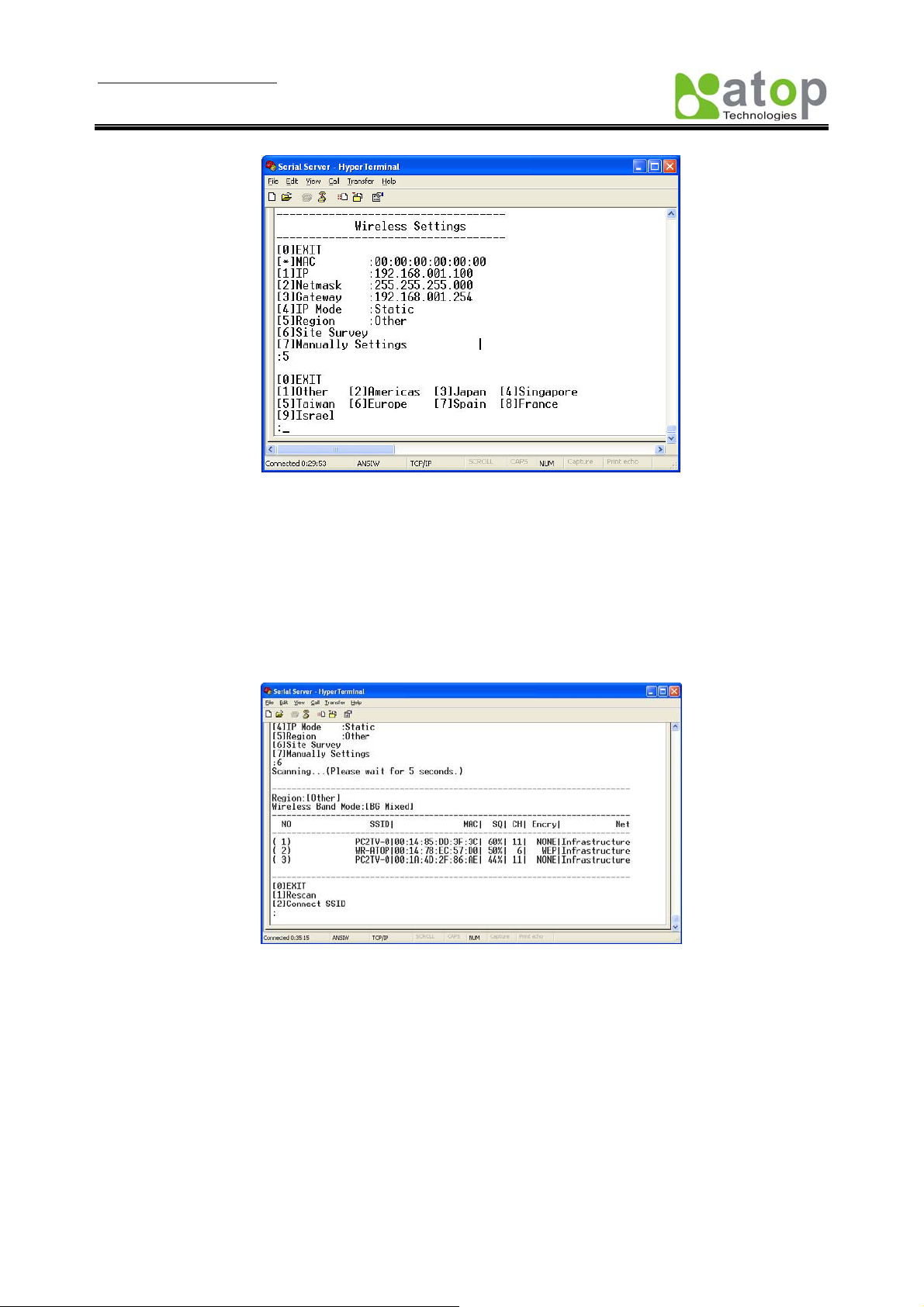
6.3.2. Configure Region
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [5 Region]
WLAN Region is the geography area that user want to implement the SW5002. Because the wireless
channel implement the frequency band differently in a different regions. User can configure the WLAN
Region by enter 5 at Wireless Settings page and enter the menu according to user’s region.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 37 -
User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 48. Wireless Region by Telnet
6.3.3. Site Survey
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [6 Site Survey]
Site survey function can support to auto-assignment wireless parameters, and attached to access point
selected automatically. After user do the site survey the result of all access points nearby will be displayed
(Fig.49). Then user can select the access point that user want SW5002 to be connected to by enter the
number of access point (Fig. 50).
Fig 49. Wireless AP List from Site Survey
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 38 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 50. Connected to AP from Site list
6.3.4. Manual Wireless Settings
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [7 Manually Settings]
User can manually configure SW5002 wireless configurations by enter 7 at the Wireless Settings page.
Then user can set any wireless parameters by enter the menu corresponding to that parameters. Wireless
parameters are shown in Fig. 51 below.
Fig 51. Configure Wireless LAN by Manual
6.3.5. Configure Ad-Hoc Mode
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [7 Manually Settings] Æ [2 Topology]
Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS), the most basic type of IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN, is commonly
referred to as an ad-hoc network. An IBSS may consist of as few as two stations. Unlike infrastructure mode,
all stations are capable of communicating directly with each other without access point.
User can configure Wireless SW5002 to be Ad-Hoc mode, by manually configure the wireless network
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 39 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
topology as shown in Fig.52 below.
Fig 52. Configure Ad-Hoc mode by Telnet
User can select wireless link by none or WEP encryption in Ad-hoc mode and these encryptions can
support applications from customer’s requirements.
Configure Wireless for WEP
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [7 Manually Settings] Æ [8 Encryption Type]
For security reason, Wireless SW5002 can configure to use WEP key of 40 bits or 128 bits, or advance
WPA-PSK to securely communicate in the wireless network. WEP key manually configure via telnet screen
is shown as Fig. 53 below.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 40 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 53. Configure WEP 64 bits Settings in Ad-Hoc mode with open key
Note1: Enter 5 ASCII value or 10 Hexadecimal digit if select WEP64 encryption.
Note2: Enter 13 ASCII value or 26 Hexadecimal digit if select WEP128 encryption
6.3.6. Configure Infrastructure Mode
Operation: [Main] Æ [3 Wireless Setting] Æ [7 Manually Settings] Æ [2 Topology]
The 802.11 infrastructure networking framework is the framework which devices communicated with each
other have to connect to an Access Point (AP) first before connect to the other devices.
Wireless SW5002 supports different type of authorizations in infrastructure modes; include Open system,
shared encryption with WEP64/128, WPA-PSK, from wireless encryption features.
The Figures below are some screen shot schemes for different authorized modes.
Settings with open authorization and none encryption
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: open
Encryption: None
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 41 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 54. Wireless: Open authorization and none encryption
Configure share authorization with WEP encryption
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: shared
Encryption: WEP
Fig 55. Wireless: Share authorization and WEP encryption
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 42 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Configure wireless network via access point with WPA-PSK
Topology: Infrastructure
Channel: Auto-assignment from Access point
Authentication: WPA-PSK
Encryption: TKIP or AES
WPA-PSK: 8~ 63 Characters
Fig 56. Wireless: WPA-PSK authorization and TKIP encryption
6.4. COM Port Configuration
User can configure serial parameters, include COM1(COM2) operation mode, port parameters, enable
or disable serial buffer’s data and packet delimiter.
Fig 57. Select COM Port from Serial Settings by Telnet
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 43 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 58. The COM1 Setting page
6.4.1. TCP Server Mode for Link Mode
Operation: [Main] Æ [4 Serial Settings] Æ [1 Link mode] Æ [1 TCP Server]
TCP Server mode is default setting for Link mode of serial settings of SW5002, and it can be configured to
wait for the host computers to establish a connection with the serial device through SW5002. SW5002
needs to be configure the listening port to waiting for host connection, Default Port number of SW5002 is
4660 (4661) and it is associated with the serial port COM1 (COM2). After the connection is established,
data can flow in both directions. SW5002 can wait for connection requested from remote PC which installed
“serial-to IP” tool or counter-pair SW5002 in tunneling mode. After the application program being
connected to the TCP port 4660 (4661) on the SW5002, data of user application program are transmitted
transparently to serial devices through SW5002 and vice versa.
User enters 1 at COM1 (COM2) Settings page and enters 1 for the TCP Server mode. To enable the remote
client which install “serial-to IP” to connect to SW5002, user has to enable the Virtual COM and Set up the
designated port number.
IP filtering menu is a simple ACL (Access Control List). It can be disabled by setting FILTER_IP to
“0.0.0.0”. User can configure one or group IPs for source IP in IP filtering. If IP filtering is enabled, only
source IP assigned can connect to SW5002.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 44 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Note: Enable Virtual COM mode if the remote site PC’s “Serial to IP” tool is installed.
Fig 59. TCP Server mode in link mode
6.4.2. TCP Client for Link Mode
Operation: [Main] Æ [4 Serial Settings] Æ [1 Link mode] Æ [2 TCP Client]
User can configure SW5002 to work in TCP Client mode. On destination IP & port (default:
COM1:4660/COM2:4661), Enter the desired destination IP and port (Server IP and port) that SW5002 want
to connect to (For example, another SW5002, or PC for data-collection). The SW5002 can support two
destination host computers simultaneously. Fig. 60 is the TCP Client page.
Fig 60. TCP Client mode in link mode
6.4.3. UDP for Link Mode
Operation: [Main] Æ [4 Serial Settings] Æ [1 Link mode] Æ [3 UDP]
SW5002 can be configured to work in UDP mode to establish connection using Unicast or Multicast
protocol. Data can be transmitted from one or multiple serial devices to/from one or multiple host PCs and
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 45 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
vice versa. For example, the original RS-422/ RS485 bus data is transferred over the extended connected
distance by SW5002s, The destination IP is assigned by single IP or group IPs, The configuration is limited
by the Local Listening Port, default 4660 and 4661 on the COM1 and COM2 of SW5002.
SW5002 can support up to 4-group IPs for UDP connection, if users needed.
Fig 61. UDP mode in link mode
Note: In this phase, UDP mode does not support Virtual COM mode.
6.4.4. Serial Settings
Operation:
[Main] Æ [4 Serial Settings] Æ [2 Baud rate]/ [3 Parity]/[4 Data bits]/ [5 Stop bits]/ [6 Flow control]
User can configure baud rate、data bits, parity、stop bit and type of flow control.
Fig 62. Serial Settings by Telnet
Note: The isolation one, SW5002-WgN1Sis (TB), only supported max 230Kbps baud rate.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 46 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.5. Security Configuration
Operation: [Main] Æ [5 Security]
User can change password of SW5002 with this menu.
Fig 65. Security settings by Telnet
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 47 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
6.5.1. Change the Password
Operation: [Main] Æ [5 Security]Æ [1 Change Password]
Enter desired password on “New password” fields.
Fig 66. Changing the Password by Telnet
Note: User may press the reset key on the product to reset to default password(blank).
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 48 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Appendix A. Using Virtual COM
Virtual COM driver mode for windows converts COM port data (RS232) to IP data to control the RS-232C
port on a SW5002 over the IP network. By creating Virtual COM ports on the PC, Virtual COM redirects the
communications from the Virtual COM ports to an IP address and port number on a SW5002 which
connected to the serial devices. The following figure is Virtual COM connection diagram.
Physical COM1
Physical COM2
(Virtual COM Port)
(Virtual COM Port)
(Virtual COM Port)
(Virtual COM Port)
COM256
(Virtual COM Port)
PC
COM3
COM4
COM5
COM6
:
:
HUB
TCP/IP Network
SW5002-WgN1
Fig 67. Setup of a Virtual COM driver
Serial Line
Serial Device 1
Serial Line
Serial Device 2
Serial Line
Serial Device 3
Serial Line
Serial Device 4
A.1. Pre-installation Requirements
Please check the operating system on your PC complied with the following requirements:
Processor: Intel-compatible, Pentium class
Operation system: Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows NT 4.0 SP5 or
later, Windows Me, Windows 98, Windows 95, Microsoft NT/2000 Terminal Server, Citrix Meta
Frame
Windows Installer 2.0
Network: Microsoft TCP/IP networking software
A.2. Applying to the SW5002
Limitation
Virtual COM driver provides user to select up to 256 COM ports as Virtual COM ports in a SerialManager
Utility PC. User can select them from a list of COM ports, which is from COM1 up to COM256.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 49 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Installation
Make sure you have turned off all anti-virus software before beginning the installation. Run Vcom.exe
program included in the CD to install Virtual COM for your operating system.
In the end of the installation, please select one or two COM ports to become the Virtual COM ports.
Uninstalling
From Windows Start menu, select Setting\ Control Panel\ Add/Remove Programs.
Select Serial IP for in the list of installed software.
Click the Add/Remove button to remove the program, or From Windows Start menu select
Programs, Serial IP click Uninstall Serial IP to remove the program.
A.3. Virtual COM Communication
Enable Virtual COM on SW5002 by web interface
From web browser access to SW5002 by typing its IP address, click on “Serial” link to access Serial page,
on the top half of the page click on “TCP Server” and enable Virtual COM by putting a check in front of the
“Enable” checkbox, then type in the local port number in the “Local Port” field as indicated in the following
screen.
Fig 68. Enable Virtual COM Mode by Web page
Enable Virtual COM on SW5002 by Telnet
User may also enable Virtual COM through telnet by setting Serial as a TCP server, and enter the local port
number for Serial, then enable virtual COM as shown in the following procedure:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 50 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Login SW5002 via Telnet
Fig 69. Login into SW5002 by Telnet or Console
Select serial setting for TCP server/Client, and enabling Virtual COM mode
Fig 70. Enable Virtual COM mode by Telnet
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 51 -
User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
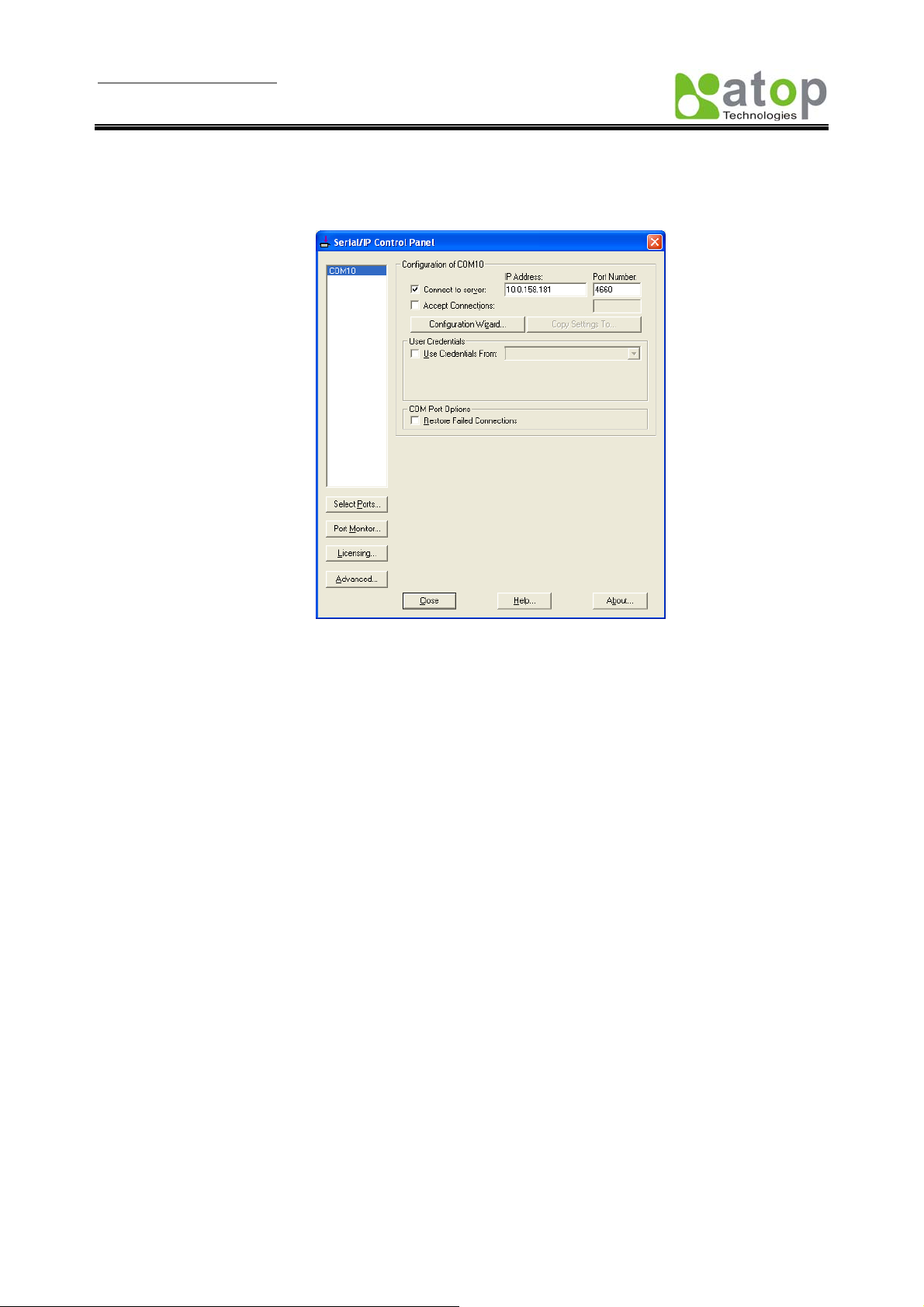
Running Serial to IP for program on PC
On Window Start Menu, go to\program\Serial/IP\Control panel\, The “Serial to IP for Control Panel”
window shall appear. Then select the serial port.
Fig 71. Detail setting from Serial/IP
On the right of the panel is a sample for COM 4 settings. On the left is the list of the COM ports that have
been selected (on Select Ports window) for use by the Virtual COM Redirector. Change the list by clicking
the Select Ports button.
Each COM port has its own settings. When click on a COM port, the Control Panel changes to reflect that
the selected port.
Note: COM port changes become effective immediately.
Configure Virtual COM Ports
Serial/IP COM port can be changed as follows:
Select a COM port on the list.
On IP Address of Server, enter SW5002 IP address.
On Port Number, enter the TCP port number of the SW5002.
On Server Credentials, the default is No Login Required. If the SW5002 does require login by
the Virtual COM Redirector, the Virtual COM Redirector must provide a username and/or
password every time an application tries to access the SW5002.
Click the Configuration Wizard button and then click the Start button that shall appear on the
wizard window. This step verifies that the Virtual COM Redirector communicates with the SW5002.
If Log display does not show errors, click Use Settings, return to the Control Panel
Settings on the Connection Protocol must match the TCP/IP protocol supported by the
SW5002. The Configuration Wizard is capable of determining the correct settings.
On COM Port Options, the settings must match the COM port behavior expected by the PC
application. The Configuration Wizard will recommend such settings.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 52 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Fig 72. Configuration Wizard from Serial to IP tool
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 53 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Appendix B. Configuration Utility
B.1. SerialManager utility Introduction
SerialManager utility, developed by ATOP, is a special tool for device management and configuration, and
can realize the daily management on various ATOP network devices for address search, device positioning,
parameter configuring, firmware downloading and so on.
B.2. Interface
The operating interface of the SerialManager utility shown as below:
Main menu Device details
Status bar
B.3. Functions
B3.1 Device Search
This function is applied to search devices in the network. The user can use four ways to search devices.
They are search by broadcast, search by special IP addresses, search by special MAC addresses and
rescanning devices by using the current search way. The user can select his required search way by
clicking the Search option on the main menu, shown as below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 54 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Or, select by clicking a button on the toolbar, as below:
Broadcast
Search
Rescan
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 55 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.1.1 Broadcast Search
Once Broadcast Search is selected, a box will pop up as below:
The user may type in or select different broadcast address based on his/her own requirement.
B3.1.2 Search by IP address
Once Search by IP Address is selected, an interface will pop up as below:
Here user may have two options: Select an IP address to search or Search device in the range of IP
address.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 56 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.1.3 Search by MAC Address
If Search by MAC Address is selected, another box will pop up as below:
Here the user may search in two ways: Search a MAC address to search or Search devices in the
range of MAC address
B3.1.4 Rescan
Once the user click the Rescan button on the toolbar, the SerialManager utility shall re-search devices by
using the current search way.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 57 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.2 Firmware
This function is applied to downloading a firmware into a selected device.
Upgrade from disk
Upgrade from disk
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 58 -

User manual Version 1.3
r
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
The user can enter the window for downloading by firstly clicking a designated network device, and then
selecting the submenu option Upgrade from disk in the main menu option Firmware, or directly clicking
the button Upgrade from disk. And then the user can select and download the required firmware from the
disk, as shown in the figure below:
The user can also select several same devices at one time, and realize the firmware updating for them by
selecting Apply for all selected devices have same model.
Download Paramete
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 59 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
In addition for some devices with JFFS2 file system supported, the user can download the related
parameter data into the device that supports the JFFS2 file system through a submenu Download
Parameter. See details as the figure below:
Note: Some of old firmware version did not support SerialManual firmware upgrade function. Please refer to
appendix "Upgrading System Software “for detail.
B3.3 Security
This function is applied to the security protection for the network devices, so as to supply some necessary
protection to a device for configuration modifying, configuration leading-in and leading-out, and some other
important functions. Here three functions are mainly supplied, including: Login, Logout and Change
Password, shown as the figure below:
Login Logout
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 60 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.3.1 Login
This function is applied to the login to any network device, as some important devices can only be operated
after a successful login, shown as the figure below:
The user can also select several devices at one time, and log in them at the same time by selecting Apply
for all selected devices.
B3.3.2 Logout
This function is applied to the logout from any network device, as the user should always carry out a logout
after he/she has finished the operating action to any important device, shown as the figure below:
The user can also select several devices at one time, and log out them at the same time by selecting Apply
for all selected devices.
B3.3.3 Change Password
This function is applied to modifying the password for logging in any network device, but can only be
realized after a successful log-in, shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 61 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
The user can also select several devices at one time, and modify their pins at the same time by selecting
Apply for all selected devices.
B3.4 Configuration
This function is applied to the configuring, import and export of work parameters for any network device,
and here are mainly supplied with: ‘Network …’, ‘COM Port…’, ‘Locate’, ‘Reset’, ‘Erase Flash’, ‘Import
Setting…’, ‘Export Setting…’, ‘Virtual COM…’, ‘Config by IE’ and ‘Options’, and some other application
functions. The user can carry out a configuration operating through menu or by clicking the corresponded
button on the toolbar, shown as the figure below:
Locate
Network … COM
Port …
Import
Setting
Export
Setting …
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 62 -
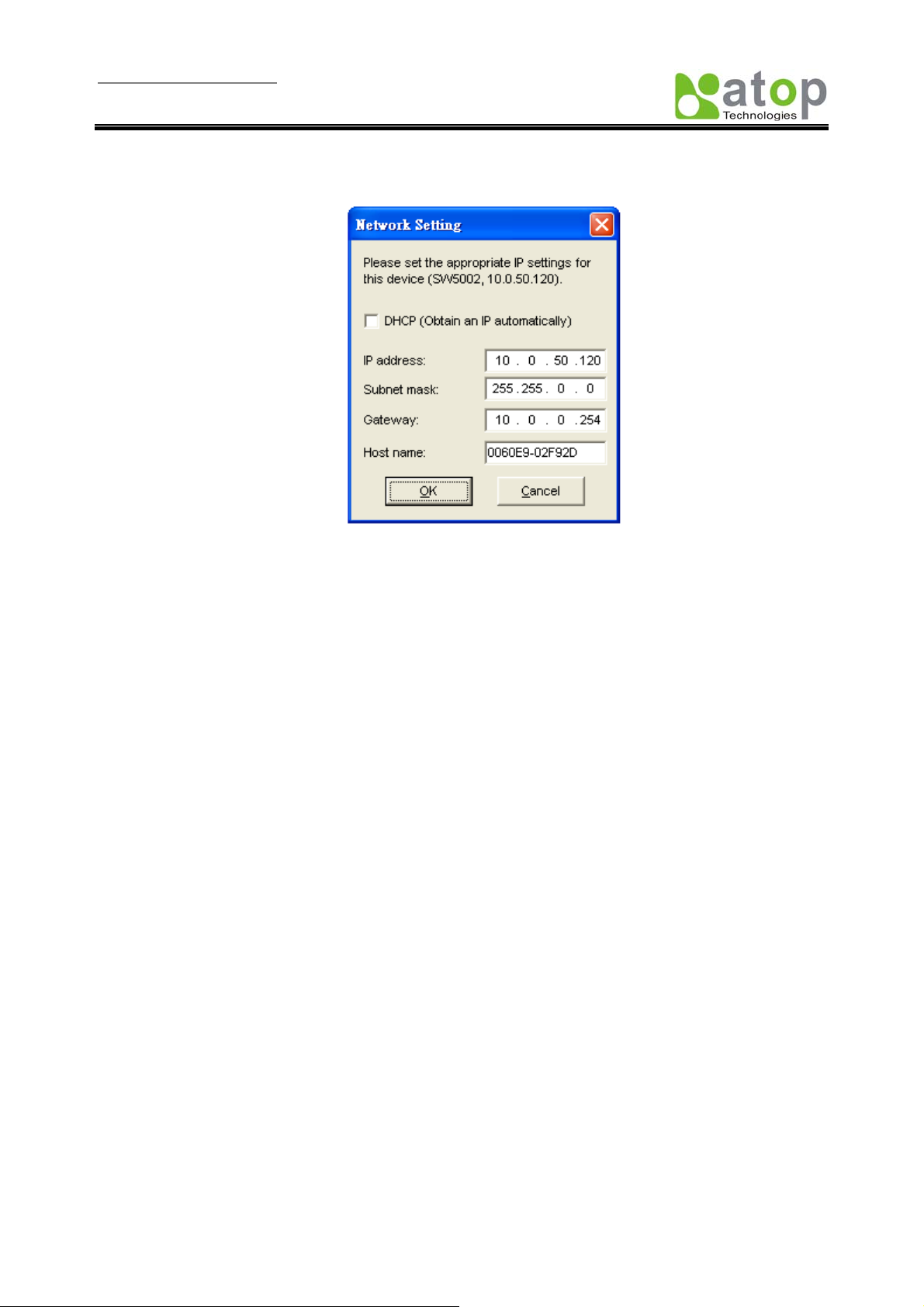
User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.4.1 Network …
The user can modify the IP address of any selected device, shown as the figure below:
B3.4.2 COM Port …
ATOP has developed various network products, and some of the ATOP devices are specially supplied to
some serial-port servers, while this function is applied to the configuration of COM port parameters.
Note: This function can be realized only after a successful login, shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 63 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
The user can also select several devices at one time, and carry out the configuration for them at the same
time by selecting Apply for all selected same model devices
Note:
1. COM tags: generated automatically according to the COM port number of the device. If a device has 4
COM port, there will be 4 tags: respectively COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, and the like.
2. Connecting mode: it means the connecting mode between the serial-port server and other network
devices. Each COM corresponds to a connecting mode through which the transferring data will not be
interfered by that in another connection. The user can set each corresponded connecting mode and the
working parameter by clicking the button "Option", shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 64 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
TCP Server mode TCP Client mode
UDP mode
3. COM port property: it mainly represents the working parameter of the serial port setting, including:
serial-port working type, baud rate, data bit, stop bit, parity bit, data packet delimiter and flow control,
etc.
B3.4.3 Locate
The user can apply this function to locate a device when he knows it’s IP address, but doesn’t know its
position. If a device is selected, the device will appear with singing by which the user can locate the device
through the submenu option Locate or clicking the Locate button on the toolbar.
B3.4.4 Reset
The device should be restarted after a successful modification of parameter configuration. And the user can
carry out a restart through the submenu option Reset.
B3.4.5 Erase Flash
Some devices are supplied to the user with a certain capacity of Flash memory to save the user's data. And
the user can erase the Flash through the submenu option Erase Flash or clicking the Erase Flash button
on the toolbar when the memory capacity is to be used up or the history data are unnecessary to be saved.
B3.4.6 Import Setting …
If a network has a large number of devices which are used for a same purpose, it would be very
complicated to carry out the parameter configuration for each of the devices in the network one by one,
while the user can import the parameter information of a standard parameter file directly into all the devices
of the network through the submenu option Import setting … or clicking the Import setting … button on
the toolbar, thus the work procedures can be largely reduced, shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 65 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
The user can also select several devices at one time, and lead the parameter information of a standard
parameter file into all the selected devices by selecting Apply for all selected devices have same model.
B3.4.7 Export Setting…
If a network has a large number of devices which are used for a same purpose, it would be very
complicated to carry out the parameter configuration for each of the devices in the network one by one,
while the user can save the parameter information of a standard device into a parameter file through the
submenu option Export setting… or clicking the Export setting… button on the toolbar, thus the
parameter information can be led in over again from this parameter file when the user is to carry out a
configuration for any other device, shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 66 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
The user can also select several devices at one time, and save the parameter information of these selected
devices into a designated parameter file by selecting "Save all the selected devices".
B3.4.8 Virtual COM
Some devices are supplied with the function of virtual serial port, and the user can carry out any related
setting through the submenu option "Virtual COM", shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 67 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.4.9 Configure by IE
Some devices are supplied with build-in Web servers, and the user can carry out any parameter setting
directly through the submenu option Config by IE, shown as the figure below:
B3.4.10 Option
The option is mainly applied to setting some common work rules of SerialManager utility, such as: search
for the time interval of a network device, or whether to display any device indication and so on, shown as
the figure below:
3.5 View
The user can select a display mode of the network device according to his/her own requirement through the
menu option "View", such as: display in sequence of device module name, or display in sequence of IP
address and so on, shown as the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 68 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
B3.6 Help
This function is mainly applied to displaying some help information of the SerialManager utility, shown as
the figure below:
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 69 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Appendix C. Upgrading System Software
Updated version of firmware can be downloaded from www.atop.com.tw.
C.1. System Upgrading Procedures
Follow the upgrading procedures below for the latest firmware.
Make sure the PC and SW5002 on the same network. Use command “ping” or “SerialManager”
utility program to verify their availability
Edit “dll.bat ” to fit the system requirements, Be sure to save all modifications
Run dll.bat ,or type command and parameters by linux_dl_v2.exe, the following screen shall
appear:
linux_dl_v2.exe zImage.bin 10.0.152.100 (device’s IP is 10.0.152.100)
Tips : “linux_dl_v2.exe” is the upgraded executing file(can find on setup cd) and zImage.bin is the
name of the firmware file; xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of SW5002.
Fig 81. Start firmware upgrade perceudre for SW5002
SW5002 shall automatically perform the download at first phase, and restart after downloaded
process at secondary phase
Fig 82. Connected & downloading process for SW5002’s Upgrade
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 70 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
C.2. Critical Issues in Upgrading Process
If the upgrading is successful, SW5002 shall re-program the flash memory, and the buzzer will beep before
restarting. It takes around 5 seconds to complete the re-programming. If an error occurs during the
process, SW5002 will clear the corresponding memories, and the system will remain the same as the
one before the upgrading process.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 71 -

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Appendix D. Specifications
D.1. Hardware Specifications
System
CPU 150MHz RISC with MMU support
Memory Flash: 8MB, 2MB for Bootloader /
SDRAM: 16MBytes.
Interface Mini-PCI Slot (for Wireless Module)
Watchdog Hardware Watchdog Reset
Debug Port CPU Build in Com.
Wireless LAN
Protocols Compliance for IEEE802.11b/g
Modulation Type: CCK, DQPSK, DBPSK, OFDM (11g)
Topologies Infrastructure, Ad-Hoc
Security WEP 64-bit/128-bit data encryption
WPA Compatible (TKIP/AES Encryption)
RF Performance Tx Power 11b: 14dBm / 11g: 13 dBm
Rx Sensitivity: -66 dBm @ 54 Mbps, -80 dBm @ 11Mbps
Transmission Rate: 54 Mbps (max.) with auto fallback
Transmission distance: Up to 300 meters (@12 Mbps, in open areas)
Mobile for Fast Roaming
Interfaces Reverse SMA Connector for Antenna
Network
Protocol 10/100M Auto-Negotiation Fast Ethernet
Interface RJ-45 Connector with 2LEDs
Protection: Built-in 1.5 KV magnetic isolation
Application Configuration with Telnet Protocol
Serial
Protocols Support RS232/485/422 & Software Selection
Interface Terminal Block Connector –TB model (with 12KV ESD)
D-sub 9-pin Connector –DB Model (with 12KV ESD)
Parameters Baud Rate: 1200~921Kbps
Parity Check: None/Odd/Even/Mark/Space
Data Length: 7/8 Bit
Stop Bit: 1/2
Flow Control: None/ Software: Xon/Xoff / Hardware: RTS/CTS
Power
Input DC 9V-48V
Consumption 4.5 W max @Tx Mode
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 72 -

User manual Version 1.3
P
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Mechanical
Dimensions HxWxD: 90mm x 45mm x 75mm
Casing Metal Housing for IP50 Standard
Environmental
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
Regulatory Approvals
EMC FCC/CE
Safety UL
Warranty 5 Years
0 to 65°C (32 to 140°F), 5 to 95% RH
-20 to 85°C (-4 to 185°F), 5 to 95%RH
D.2. Software Specifications
Software
Protocol ICMP, IP, TCP, UDP, DHCP Client, Telnet, DNS, SNMP, HTTP, SMTP, SNT
Utility Virtual COM Utilities for Windows 98/2000/XP/2003/Vista
Configure Utilities: Supported for Windows 98/2000/NT/XP/2003/Vista
Configuration Web browser
Telnet Console
Windows utility
Buffer Size TCP receiving buffer size = 8K bytes
TCP transmitting buffer size = 16K bytes
RS-232/RS-485 receiving buffer size = 4K bytes
RS-232/RS-485 transmitting buffer size = 4K bytes
D.3. Pin Assignments
DB9 male connector pin assignments for Serial
DB9
Pin#
1
2
RS-232
DCD
RXD T+
RS-485 RS-422
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 73 -
TXD Data+ R+
DTR
SG (Signal Ground)
DSR
RTS Data- R-
CTS T-
RI

User manual Version 1.3
*
5
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
Terminal block pin assignments for Serial and Power
5-pin for serial connections
SG
RTS/R-
TxD/R+
CTS/T-
RS-232 RS-485 RS-422
GND GND GND
RTS Data- R-
TxD Data+ R+
3-pin for Power input
FG
Vin-
Vin+
CTS T-
RxD/T+
Note: RS-485 2 or 4 pins assignments of DB9 connector are different from those of Mini DIN
connector.
RxD T+
D.4. Beep & LED Status
Startup status
Message
^==^========^^^ (5sec) Startup OK and AP firmware is enabled
Buzzer indication: “ ^ “ : Beep twice “ = “ : Beep off
Description
FG
GND
9~48V
Wireless Signal Strength status
The BSS quality can be detected by LED indicator on SW5002. On running time, pressed default key and
then released, one of the specified actions below shall be done that depend on the released time after you
heard how many beeps. BSS quality is indicated by count of LEDs as shown below.
RSSI LEDs Message:
○ Off ● On ☼ blinking
Operations
Connecting
Connected
Status
Search AP (sequentially blinking) ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼
Connected AP/ Get assigned IP ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼ ☼
Not matched SSID ☼
Not available IP ☼ ☼
Signal Strength is less 20%
Bad Signal Strength (20%)
Poor Signal Strength (40%)
Fair Signal Strength (60%)
Good Signal Strength (80%)
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 LED
●
● ●
● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ●
Excellent Signal Strength (100%)
Note: The lowest LED is indicated for STATUS at SW5002’s front plate.
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 74 -
● ● ● ● ● ●

User manual Version 1.3
SW5002 Wireless Serial Server
WLAN LED Message
Message
LED Off
LED blinking
No data is transmitting on Ethernet
Data is transmitting on Ethernet
COM Port LED Message
Message Description
LED off
LED on blinking state
No data is transmitting on COM port
Data is transmitting on COM port
RUN LED Message
Message
LED blinking (rate: 0.5Sec) AP firmware is running
Description
Description
Copyright © 2010 Atop Technologies, Inc.
All rights reserved. Designed in Taiwan
- 75 -
 Loading...
Loading...