Page 1
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/ATMEL
Features
• 80C51 Core Architecture
• 256 Bytes of On-chip RAM
• 2048 Bytes of On-chip ERAM
• 64K Bytes of On-chip Flash Memory
– Data Retention: 10 Years at 85°C
– Read/Write Cycle: 100K
• 2K Bytes of On-chip Flash for Bootloader
• 2K Bytes of On-chip EEPROM
Read/Write Cycle: 100K
• Integrated Power Monitor (POR: PFD) To Supervise Internal Power Supply
• 14-sources 4-level Interrupts
• Three 16-bit Timers/Counters
• Full Duplex UART Compatible 80C51
• High-speed Architecture
– In Standard Mode:
40 MHz (Vcc 3V to 5.5V, both Internal and external code execution)
60 MHz (Vcc 4.5V to 5.5V and Internal Code execution only)
– In X2 mode (6 Clocks/machine cycle)
20 MHz (Vcc 3V to 5.5V, both Internal and external code execution)
30 MHz (Vcc 4.5V to 5.5V and Internal Code execution only)
• Five Ports: 32 + 4 Digital I/O Lines
• Five-channel 16-bit PCA with
– PWM (8-bit)
– High-speed Output
– Timer and Edge Capture
• Double Data Pointer
• 21-bit WatchDog Timer (7 Programmable Bits)
• A 10-bit Resolution Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) with 8 Multiplexed Inputs
• SPI Interface, (PLCC52 and VPFP64 packages only)
• Full CAN Controller
– Fully Compliant with CAN Rev 2.0A and 2.0B
– Optimized Structure for Communication Management (Via SFR)
– 15 Independent Message Objects
– Each Message Object Programmable on Transmission or Reception
– Individual Tag and Mask Filters up to 29-bit Identifier/Channel
– 8-byte Cyclic Data Register (FIFO)/Message Object
– 16-bit Status and Control Register/Message Object
– 16-bit Time-Stamping Register/Message Object
– CAN Specification 2.0 Part A or 2.0 Part B Programmable for Each Message
Object
– Access to Message Object Control and Data Registers Via SFR
– Programmable Reception Buffer Length Up To 15 Message Objects
– Priority Management of Reception of Hits on Several Message Objects at the
Same Time (Basic CAN Feature)
– Priority Management for Transmission
– Message Object Overrun Interrupt
– Supports
– Time Triggered Communication
– Autobaud and Listening Mode
– Programmable Automatic Reply Mode
– 1-Mbit/s Maximum Transfer Rate at 8 MHz
– Readable Error Counters
– Programmable Link to On-chip Timer for Time Stamping and Network
Synchronization
– Independent Baud Rate Prescaler
– Data, Remote, Error and Overload Frame Handling
1. At BRP = 1 sampling point will be fixed.
(1)
Crystal Frequency in X2 Mode
Enhanced 8-bit
MCU with CAN
Controller and
Flash Memory
AT89C51CC03
Rev. 4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 2
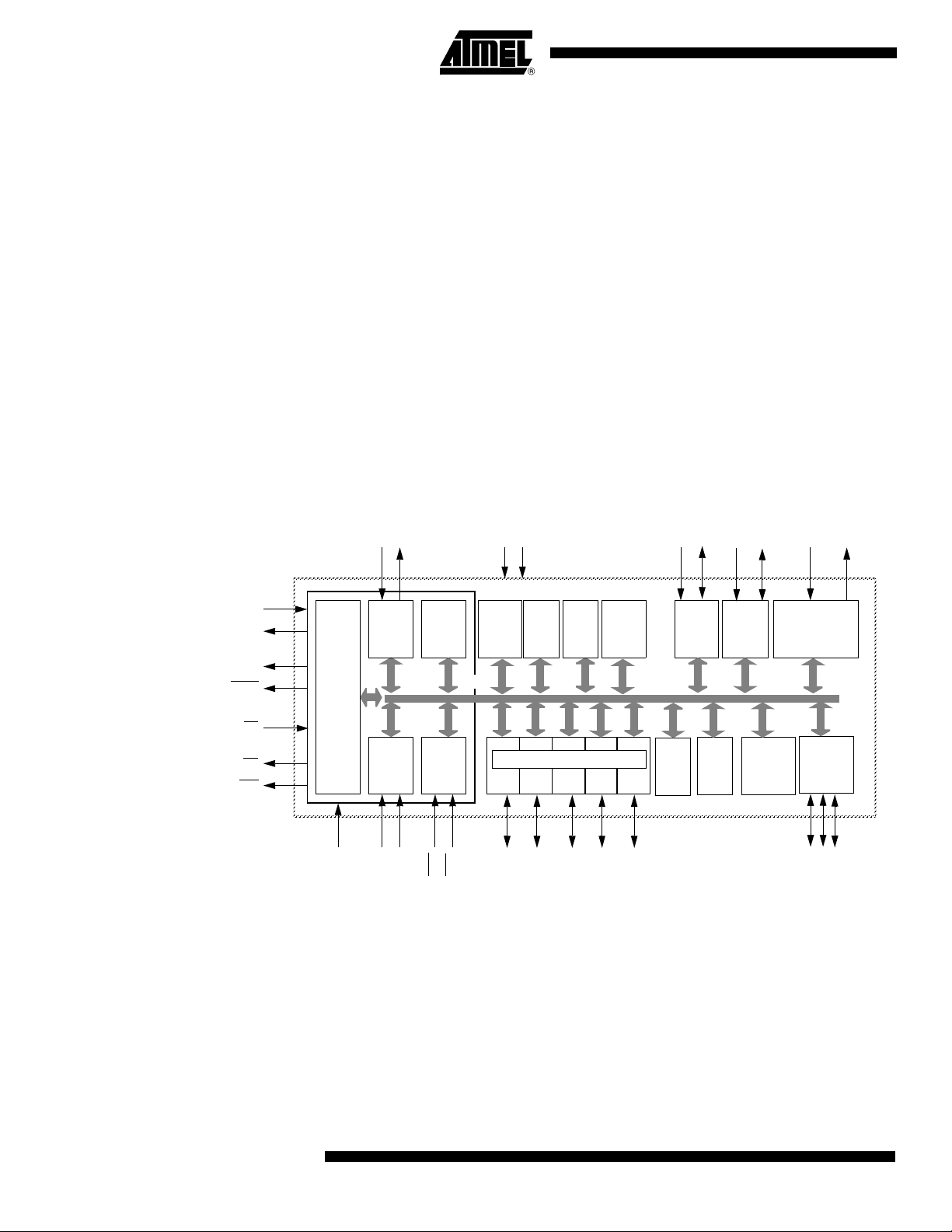
AT89C51CC03
•
Timer 0
INT
RAM
256x8
T0
T1
RxD
TxD
WR
RD
EA
PSEN
ALE
XTAL2
XTAL1
UART
CPU
Timer 1
INT1
Ctrl
INT0
C51
CORE
Port 0P0Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Parallel I/O Ports and Ext. Bus
P1(1)
P2
P3
ERAM
2048
IB-bus
PCA
RESET
Watch
Dog
PCA
ECI
Vss
Vcc
Timer2
T2EX
T2
Port 4
P4(2)
Emul
Unit
10 bit
ADC
Flash
64k x
8
Boot
loader
2kx8
EE
PROM
2kx8
CAN
CONTROLLER
TxDC
RxDC
SPI
Interface
MOSI
SCK
MISO
On-chip Emulation Logic (Enhanced Hook System)
•
Power Saving Modes
– Idle Mode
– Power-down Mode
•
Power Supply: 3 volts to 5.5 volts
•
Temperature Range: Industrial (-40° to +85°C), Automotive (-40°C to +125°C)
•
Packages: VQFP44, PLCC44, VQFP64, PLCC52
Description
Block Diagram
The AT89C51CC03 is a member of the family of 8-bit microcontrollers dedicated to CAN
network applications.
In X2 mode a maximum external clock rate of 20 MHz reaches a 300 ns cycle time.
Besides the full CAN controller AT89C51CC03 provides 64K Bytes of Flash memory
including In-System Programming (ISP), 2K Bytes Boot Flash Memory, 2K Bytes
EEPROM and 2048 byte ERAM.
Primary attenti o n i s pai d to th e red u ction of the electro- magnetic emission o f
AT89C51CC03.
2
Notes: 1. 8 analog Inputs/8 Digital I/O
2. 5-Bit I/O Port
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 3
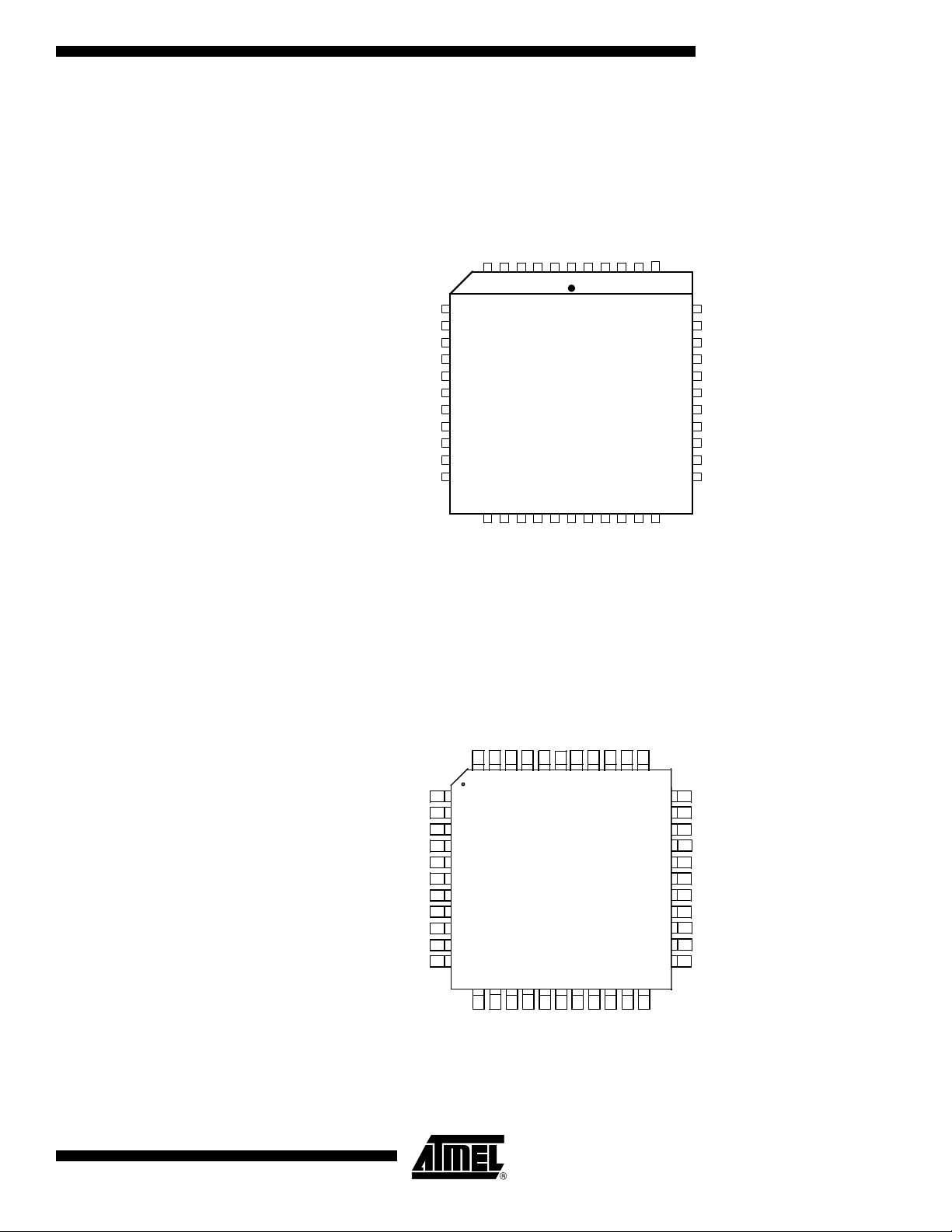
Pin Configuration
PLCC44
P1.3/AN3/CEX0
P1.2/AN2/ECI
P1.1/AN1/T2EX
P1.0/AN 0/T2
VAREF
VAGND
RESET
VSS
VCC
XTAL1
XTAL2
P3.7/RD
P4.0/ TxDC
P4.1/RxDC
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P3.6/WR
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
29
30
31
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
17
16
15
1819202122232425262728
65432
4443424140
ALE
PSEN
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P0.5/AD5
P0.2/AD2
P0.3/AD3
P0.4/AD4
P0.1/AD1
P0.0/AD0
P2.0/A8
P1.4/AN4/CEX1
P1.5/AN5/CEX2
P1.6/AN6/CEX3
P1.7/AN7/CEX4
EA
P3.0/RxD
P3.1/TxD
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
1
43 42 41 40 3944
38 37 36 35 34
12 13 17161514 201918 21 22
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
VQFP44
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
P1.4/AN4/CEX1
P1.5/AN5/CEX2
P1.6/AN6/CEX3
P1.7/AN7/CEX4
EA
P3.0/RxD
P3.1/TxD
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
ALE
PSEN
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P0.5/AD5
P0.2 /AD2
P0.3 /AD3
P0.4 /AD4
P0.1 /AD1
P0.0 /AD0
P2.0/A8
P1.3/AN3/CEX0
P1.2/AN2/ECI
P1.1/AN1/T2EX
P1.0/AN 0/T2
VAREF
VAGND
RESET
VSS
VCC
XTAL1
XTAL2
P3.7/RD
P4.0/TxDC
P4.1/RxDC
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P3.6/WR
AT89C51CC03
4182N–CAN–03/08
3
Page 4
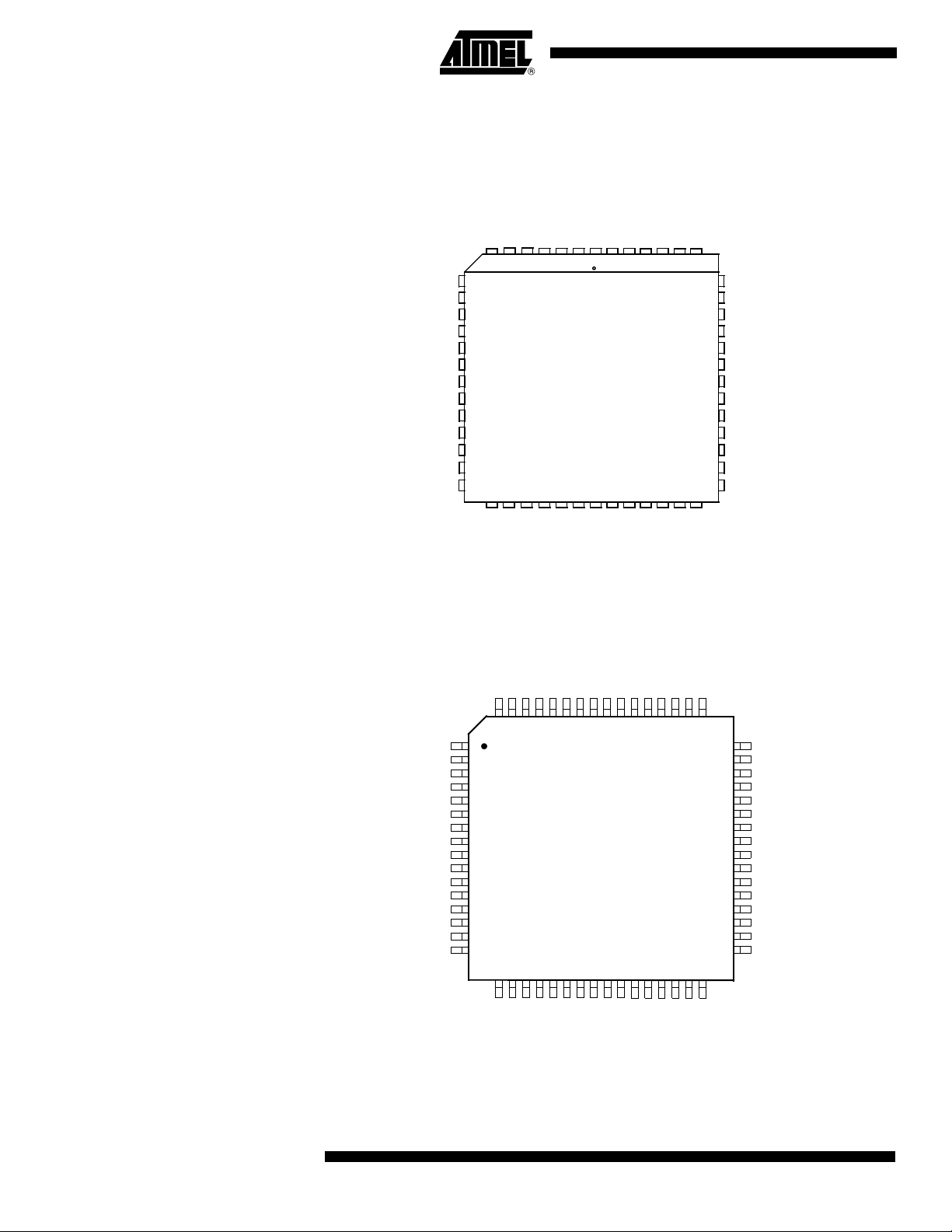
AT89C51CC03
21 22 26252423 292827 30 31
5 4 3 2 1 6
52 51 50 49 48
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
PLCC52
7 47
19
20
32 33
34
35
P1.3/AN3/CEX0
P1.2/AN2/ECI
P1.1/AN1/T2EX
P1.0/AN 0/T2
VAREF
VAGND
RESET
VSS
VCC
XTAL1
XTAL2
TESTI
P1.4/AN4/CEX1
P1.5/AN5/CEX2
P1.6/AN6/CEX3
P1.7/AN7/CEX4
EA
P3.0/RxD
P3.1/TxD
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1/SS
P4.3/SCK
ALE
PSEN
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P0.5/AD5
P0.2 /AD2
P0.3 /AD3
P0.4 /AD4
P0.1 /AD1
P0.0 /AD0
P2.0/A8
P4.4/MOSI
P3.7/RD
P4.0/TxDC
P4.1/RxDC
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P3.6/WR
P4.2/MISO
NC
NC
NC
TESTI must be connected to VSS
VCC
5453525150
49
VQFP64
P1.3/AN3/CEX0
P1.2/AN2/ECI
P1.1/AN1/T2EX
P1.0/AN0/T2
VAREF
VAGND
RESET
VSS
VSS
VSS
P3.7/RD
P4.0/TxDC
P4.1/RxDC
P2.7/A15
P2.6/A14
NCNCNC
NC
P3.6/WR
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
39
40
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
9
171819202122232425
26
646362616059585756
55
NC
ALE
PSEN
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
NC
P0.5/AD5
NC
NC
P0.4/AD4
P1.4/AN4/CEX1
NC
P1.5/AN5/CEX2
P1.6/AN6/CEX3
P1.7/AN7/CEX4
NC
EA
NC
NC
P3.0/RxD
11
12
13
16
15
14
P4.3/SCK
P3.1/TxD
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1/SS
38
37
36
33
34
35
P0.1/AD1
P0.2/AD2
P0.3/AD3
P4.4/MOSI
P0.0/AD0
P2.0/A8
P2.5/A13
P2.4/A12
P2.3/A11
P2.2/A10
P2.1/A9
P4.2/MISO
2728293031
32
TESTI
VCC
VCC
XTAL1
XTAL2
VCC
TESTI must be connected to VSS
4
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 5
Pin Name Type Description
VSS GND Circuit ground
TESTI I Must be connected to VSS
VCC Supply Voltage
VAREF Reference Voltage for ADC
VAGND Reference Ground for ADC
P0.0:7 I/O Port 0:
Is an 8-bit open drain bi-directional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1’s written to them float, and in this state can be used as
high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order address and data bus during accesses to external Program
and Data Memory. In this application it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1’s.
Port 0 also outputs the code Bytes during program validation. External pull-ups are required during program verification.
AT89C51CC03
P1.0:7 I/O Port 1:
Is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 1 pins can be used for digital input/output or as analog inputs for
the Analog Digital Converter (ADC). Port 1 pins that have 1’s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up transistors
and can be used as inputs in this state. As inputs, Port 1 pins that are being pulled low externally will be the source of current
(IIL, see section "Electrical Characteristic") because of the internal pull-ups. Port 1 pins are assigned to be used as analog
inputs via the ADCCF register (in this case the internal pull-ups are disconnected).
As a secondary digital function, port 1 contains the Timer 2 external trigger and clock input; the PCA external clock input and
the PCA module I/O.
P1.0/AN0/T2
Analog input channel 0,
External clock input for Timer/counter2.
P1.1/AN1/T2EX
Analog input channel 1,
Trigger input for Timer/counter2.
P1.2/AN2/ECI
Analog input channel 2,
PCA external clock input.
P1.3/AN3/CEX0
Analog input channel 3,
PCA module 0 Entry of input/PWM output.
P1.4/AN4/CEX1
Analog input channel 4,
PCA module 1 Entry of input/PWM output.
P1.5/AN5/CEX2
Analog input channel 5,
PCA module 2 Entry of input/PWM output.
P1.6/AN6/CEX3
Analog input channel 6,
PCA module 3 Entry of input/PWM output.
P1.7/AN7/CEX4
Analog input channel 7,
PCA module 4 Entry ot input/PWM output.
Port 1 receives the low-order address byte during EPROM programming and program verification.
It can drive CMOS inputs without external pull-ups.
P2.0:7 I/O Port 2:
4182N–CAN–03/08
Is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1’s written to them are pulled high by the internal
pull-ups and can be used as inputs in this state. As inputs, Port 2 pins that are being pulled low externally will be a source of
current (IIL, see section "Electrical Characteristic") because of the internal pull-ups. Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during accesses to the external Program Memory and during accesses to external Data Memory that uses 16-bit addresses
(MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1’s. During accesses to external Data
Memory that use 8 bit addresses (MOVX @Ri), Port 2 transmits the contents of the P2 special function register.
It also receives high-order addresses and control signals during program validation.
It can drive CMOS inputs without external pull-ups.
5
Page 6
AT89C51CC03
Pin Name Type Description
P3.0:7 I/O Port 3:
Is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1’s written to them are pulled high by the internal
pull-up transistors and can be used as inputs in this state. As inputs, Port 3 pins that are being pulled low externally will be a
source of current (IIL, see section "Electrical Characteristic") because of the internal pull-ups.
The output latch corresponding to a secondary function must be programmed to one for that function to operate (except for
TxD and WR). The secondary functions are assigned to the pins of port 3 as follows:
P3.0/RxD:
Receiver data input (asynchronous) or data input/output (synchronous) of the serial interface
P3.1/TxD:
Transmitter data output (asynchronous) or clock output (synchronous) of the serial interface
P3.2/INT0:
External interrupt 0 input/timer 0 gate control input
P3.3/INT1:
External interrupt 1 input/timer 1 gate control input
P3.4/T0:
Timer 0 counter input
P3.5/T1/SS:
Timer 1 counter input
SPI Slave Select
P3.6/WR:
External Data Memory write strobe; latches the data byte from port 0 into the external data memory
P3.7/RD:
External Data Memory read strobe; Enables the external data memory.
It can drive CMOS inputs without external pull-ups.
P4.0:4 I/O Port 4:
Is an 2-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 4 pins that have 1’s written to them are pulled high by the internal
pull-ups and can be used as inputs in this state. As inputs, Port 4 pins that are being pulled low externally will be a source of
current (IIL, on the datasheet) because of the internal pull-up transistor.
The output latch corresponding to a secondary function RxDC must be programmed to one for that function to operate. The
secondary functions are assigned to the two pins of port 4 as follows:
P4.0/TxDC:
Transmitter output of CAN controller
P4.1/RxDC:
Receiver input of CAN controller.
P4.2/MISO:
Master Input Slave Output of SPI controller
P4.3/SCK:
Serial Clock of SPI controller
P4.4/MOSI:
Master Ouput Slave Input of SPI controller
It can drive CMOS inputs without external pull-ups.
6
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 7
Pin Name Type Description
Reset:
RESET I/O
ALE O
PSEN O
EA I
XTAL1 I
A high level on this pin during two machine cycles while the oscillator is running resets the device. An internal pull-down
resistor to VSS permits power-on reset using only an external capacitor to VCC.
ALE:
An Address Latch Enable output for latching the low byte of the address during accesses to the external memory. The ALE is
activated every 1/6 oscillator periods (1/3 in X2 mode) except during an external data memory access. When instructions are
executed from an internal Flash (EA = 1), ALE generation can be disabled by the software.
PSEN:
The Program Store Enable output is a control signal that enables the external program memory of the bus during external
fetch operations. It is activated twice each machine cycle during fetches from the external program memory. However, when
executing from of the external program memory two activations of PSEN are skipped during each access to the external Data
memory. The PSEN is not activated for internal fetches.
EA:
When External Access is held at the high level, instructions are fetched from the internal Flash. When held at the low level,
AT89C51CC03 fetches all instructions from the external program memory
XTAL1:
Input of the inverting oscillator amplifier and input of the internal clock generator circuits.
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should be driven, while XTAL2 is left unconnected. To operate
above a frequency of 16 MHz, a duty cycle of 50% should be maintained.
AT89C51CC03
.
XTAL2 O
XTAL2:
Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
I/O Configurations
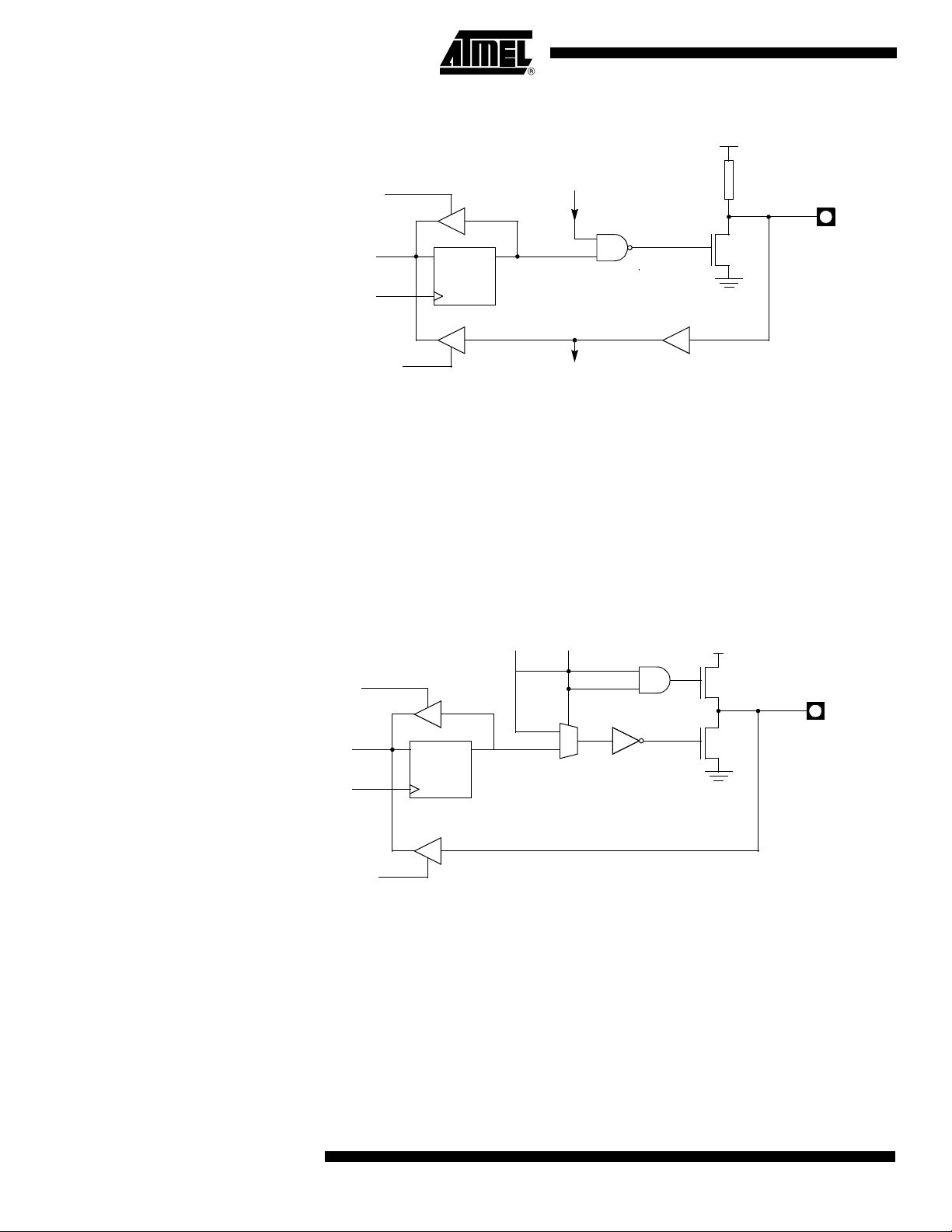
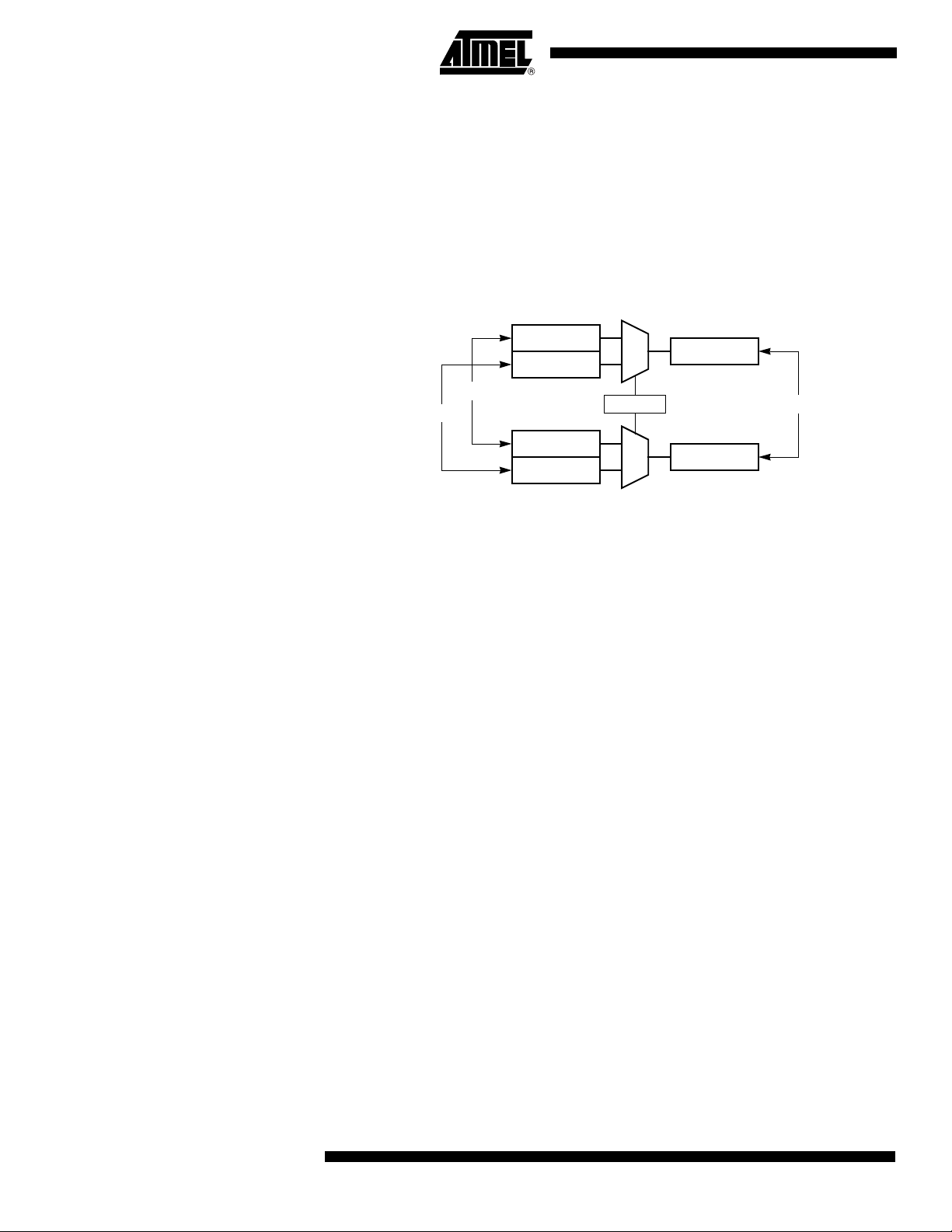
Port 1, Port 3 and Port 4
Each Port SFR operates via type-D latches, as illustrated in Figure 1 for Ports 3 and 4. A
CPU "write to latch" signal initiates transfer of internal bus data into the type-D latch. A
CPU "read latch" signal transfers the latched Q output onto the internal bus. Similarly, a
"read pin" signal transfers the logical level of the Port pin. Some Port data instructions
activate the "read latch" signal while others activate the "read pin" signal. Latch instructi ons are referr e d to a s Re a d-Modif y -Write inst ructions . E ach I/O line may be
independently programmed as input or output.
Figure 1 shows the structure of Ports 1 and 3, which have internal pull-ups. An external
source can pull the pin low. Each Port pin can be configured either for general-purpose
I/O or for its alternate input output function.
To use a pin for general-purpose output, set or clear the corresponding bit in the Px register (x = 1,3 or 4). To use a pin for general-purpose input, set the bit in the Px register.
This turns off the output FET drive.
To configure a pin for its alternate function, set the bit in the Px register. When the latch
is set, the "alternate output function" signal controls the output level (see Figure 1). The
operation of Ports 1, 3 and 4 is discussed further in the "quasi-Bidirectional Port Operation" section.
4182N–CAN–03/08
7
Page 8
AT89C51CC03
Figure 1. Port 1, Port 3 and Port 4 Structure
D
CL
QP1.X
LATCH
INTERNAL
WRITE
TO
LATCH
READ
PIN
READ
LATCH
P1.x
P3.X
P4.X
ALTERNATE
OUTPUT
FUNCTION
VCC
INTERNAL
PULL-UP (1)
ALTERNATE
INPUT
FUNCTION
P3.x
P4.x
BUS
D
Q
P0.X
LATCH
INTERNAL
WRITE
TO
LATCH
READ
PIN
READ
LATCH
0
1
P0.x (1)
ADDRESS LOW/
DATA
CONTROL
VDD
BUS
(2)
Note: The internal pull-up can be disabled on P1 when analog function is selected.
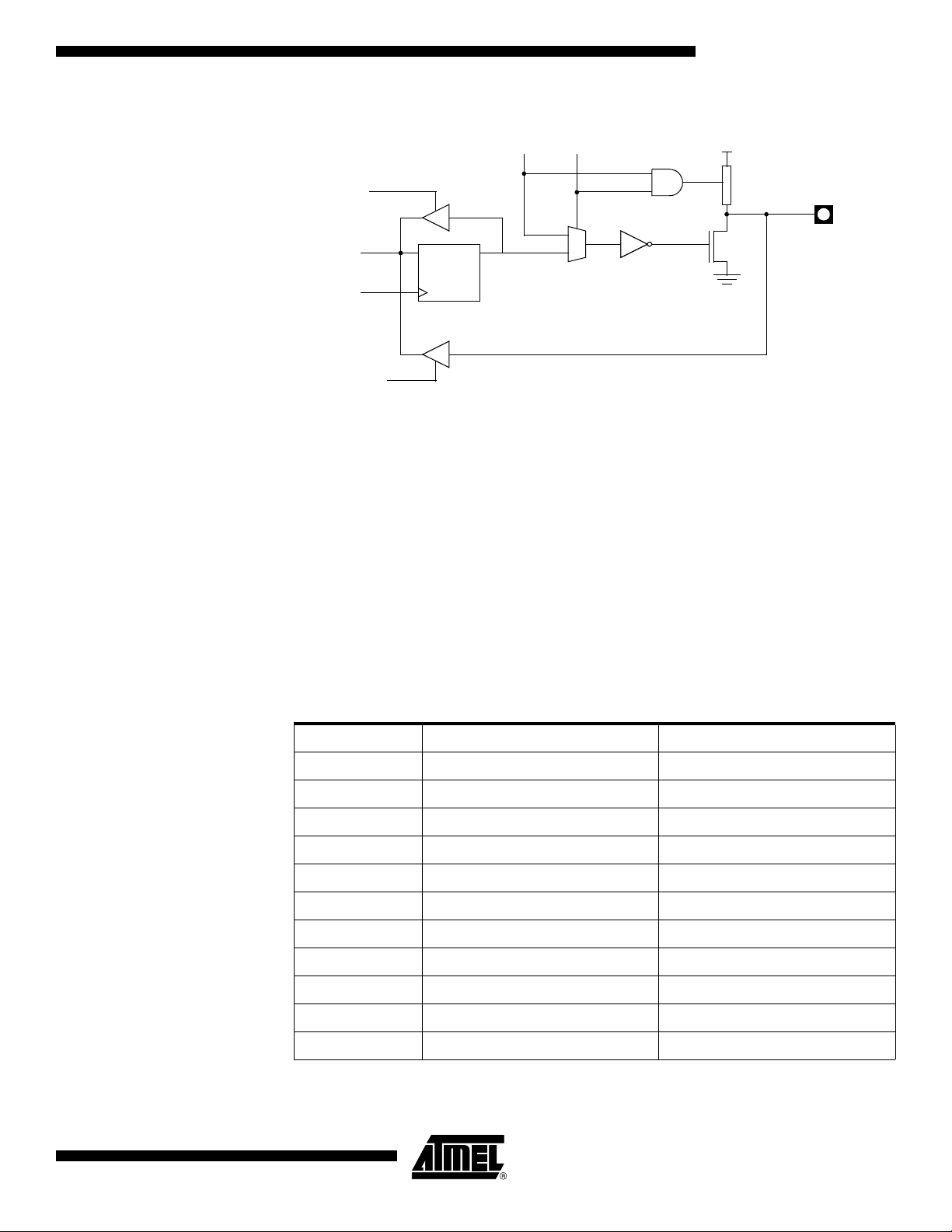
Port 0 and Port 2
8
Ports 0 and 2 are used for general-purpose I/O or as the external address/data bus. Port
0, shown in Figure 3, differs from the other Ports in not having internal pull-ups. Figure 3
shows the structure of Port 2. An external source can pull a Port 2 pin low.
To use a pin for general-purpose output, set or clear the corresponding bit in the Px register (x = 0 or 2). To use a pin for general-purpose input, set the bit in the Px register to
turn off the output driver FET.
Figure 2. Port 0 Structure
Notes: 1. Port 0 is precluded from use as general-purpose I/O Ports when used as
address/data bus drivers.
2. Port 0 internal strong pull-ups assist the logic-one output for memory bus cycles only.
Except for these bus cycles, the pull-up FET is off, Port 0 outputs are open-drain.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 9
AT89C51CC03
D
Q
P2.X
LATCH
INTERNAL
WRITE
TO
LATCH
READ
PIN
READ
LATCH
0
1
P2.x (1)
ADDRESS HIGH/
CONTROL
BUS
VDD
INTERNAL
PULL-UP (2)
Figure 3. Port 2 Structure
Notes: 1. Port 2 is precluded from use as general-purpose I/O Ports when as address/data bus
drivers.
2. Port 2 internal strong pull-ups FET (P1 in FiGURE) assist the logic-one output for
memory bus cycle.
Read-Modify-Write Instructions
When Port 0 and Port 2 are used for an external memory cycle, an internal control signal
switches the output-driver input from the latch output to the internal address/data line.
Some instructions read the latch data rather than the pin data. The latch based instructions read the data, modify the data and then rewrite the latch. These are called "ReadModify-Write" instructions. Below is a complete list of these special instructions (see
Table ). When the destination operand is a Port or a Port bit, these instructions read the
latch rather than the pin:
Instruction Description Example
ANL logical AND ANL P1, A
ORL logical OR ORL P2, A
XRL logical EX-OR XRL P3, A
JBC jump if bit = 1 and clear bit JBC P1.1, LABEL
CPL complement bit CPL P3.0
INC increment INC P2
DEC decrement DEC P2
It is not obvious the last three instructions in this list are Read-Modify-Write instructions.
DJNZ decrement and jump if not zero DJNZ P3, LABEL
MOV Px.y, C move carry bit to bit y of Port x MOV P1.5, C
CLR Px.y clear bit y of Port x CLR P2.4
SET Px.y set bit y of Port x SET P3.3
These instructions read the port (all 8 bits), modify the specifically addressed bit and
4182N–CAN–03/08
9
Page 10
AT89C51CC03
write the new byte back to the latch. These Read-Modify-Write instructions are directed
READ PIN
INPUT DATA
P1.x
OUTPUT DATA
2 Osc. PERIODS
n
p1(1)
p2
p3
VCCVCCVCC
P2.x
P3.x
P4.x
to the latch rather than the pin in order to avoid possible misinterpretation of voltage
(and therefore, logic) levels at the pin. For example, a Port bit used to drive the base of
an external bipolar transistor can not rise above the transistor’s base-emitter junction
voltage (a value lower than VIL). With a logic one written to the bit, attempts by the CPU
to read the Port at the pin are misinterpreted as logic zero. A read of the latch rather
than the pins returns the correct logic-one value.
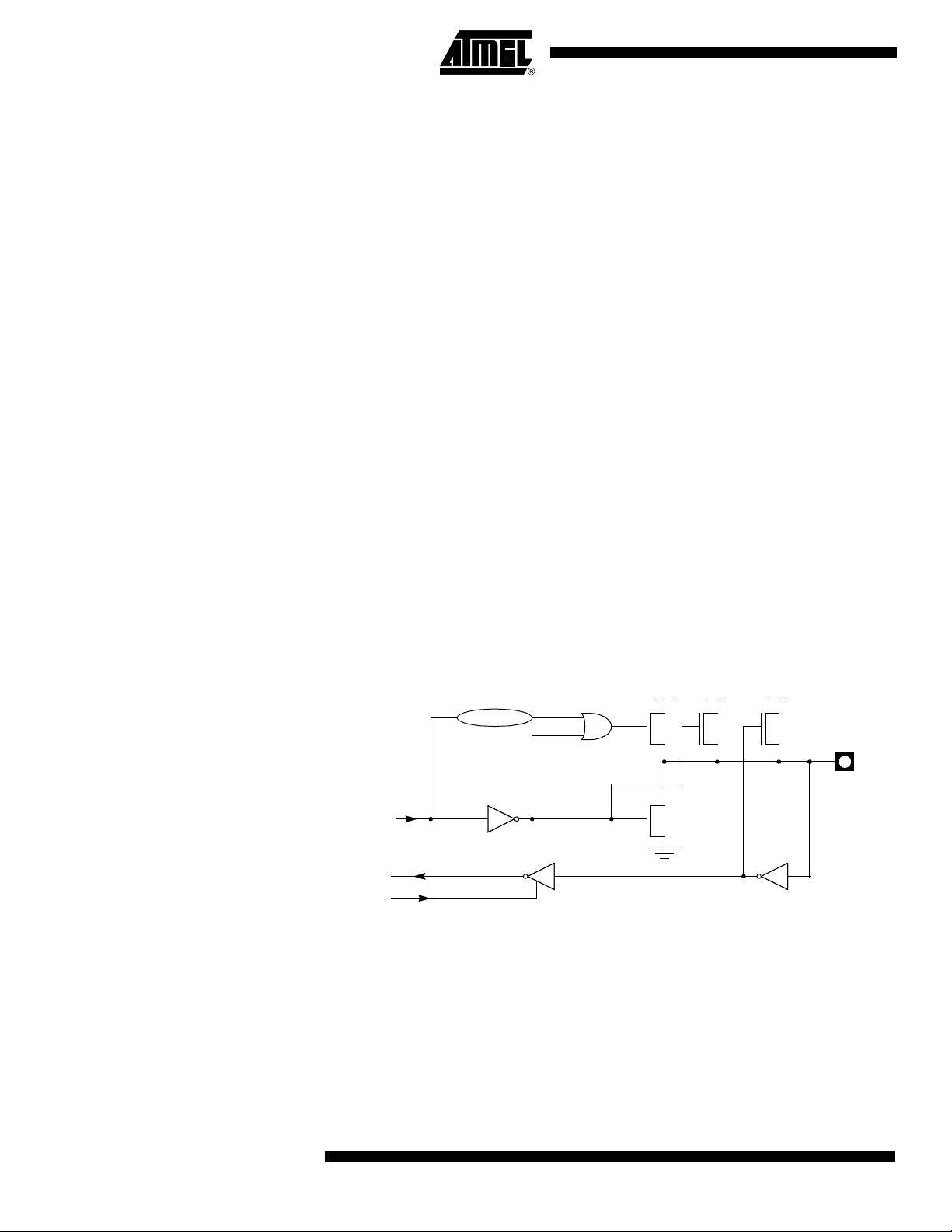
Quasi-Bidirectional Port Operation
Port 1, Port 2, Port 3 and Port 4 have fixed internal pull-ups and are referred to as
"quasi-bidirectional" Ports. When configured as an input, the pin impedance appears as
logic one and sources current in response to an external logic zero condition. Port 0 is a
"true bidirectional" pin. The pins float when configured as input. Resets write logic one to
all Port latches. If logical zero is subsequently written to a Port latch, it can be returned
to input conditions by a logical one written to the latch.
Note: Port latch values change near the end of Read-Modify-Write instruction cycles. Output
buffers (and therefore the pin state) update early in the instruction after Read-ModifyWrite instruction cycle.
Logical zero-to-one transitions in Port 1, Port 2, Port 3 and Port 4 use an additional pullup (p1) to aid this logic transition (see Figure 4.). This increases switch speed. This
extra pull-up sources 100 times normal internal circuit current during 2 oscillator clock
periods. The internal pull-ups are field-effect transistors rather than linear resistors. Pullups consist of three p-channel FET (pFET) devices. A pFET is on when the gate senses
logical zero and off when the gate senses logical one. pFET #1 is turned on for two
oscillator periods immediately after a zero-to-one transition in the Port latch. A logical
one at the Port pin turns on pFET #3 (a weak pull-up) through the inverter. This inverter
and pFET pair form a latch to drive logical one. pFET #2 is a very weak pull-up switched
on whenever the associated nFET is switched off. This is traditional CMOS switch convention. Current strengths are 1/10 that of pFET #3.
Figure 4. Internal Pull-Up Configurations
10
Note: Port 2 p1 assists the logic-one output for memory bus cycles.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 11
AT89C51CC03
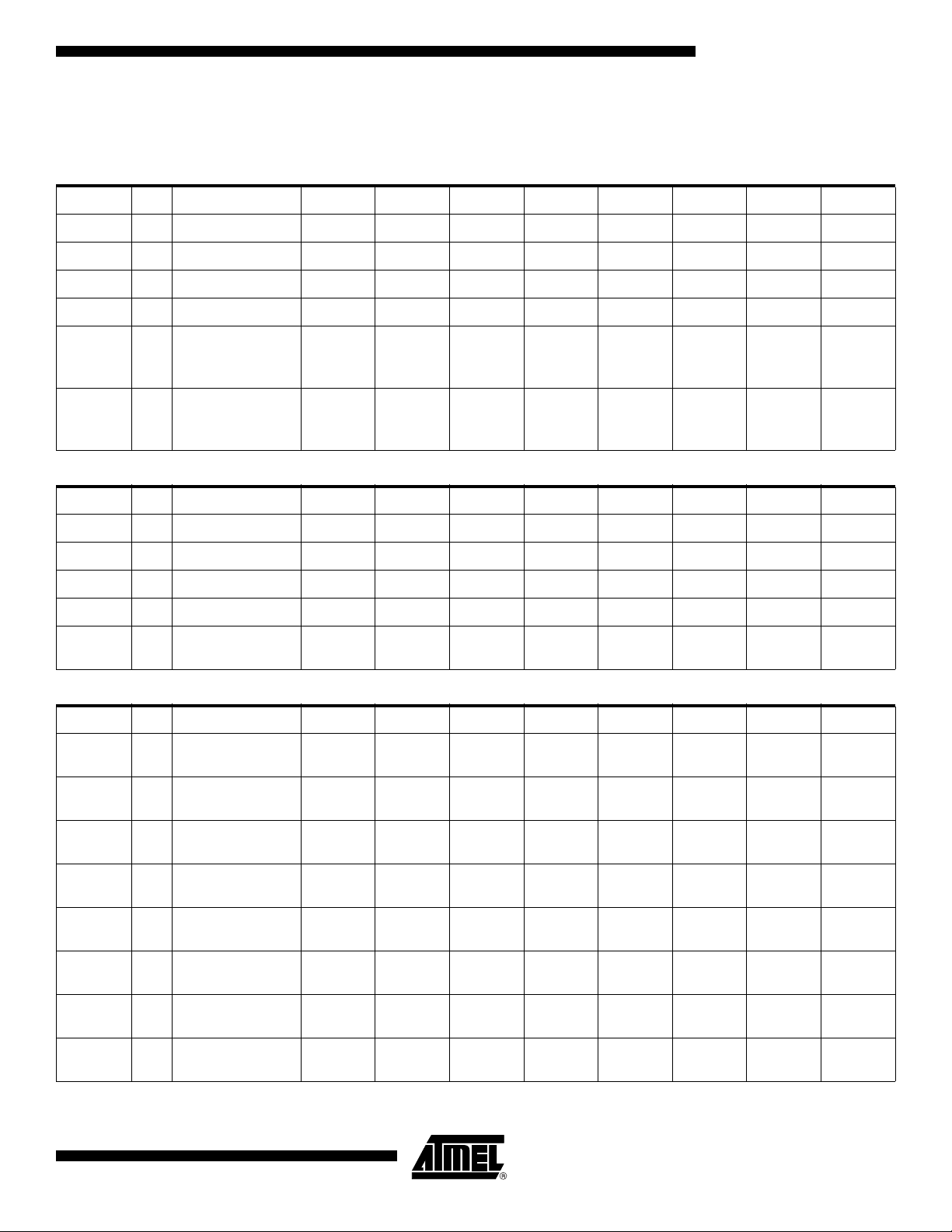
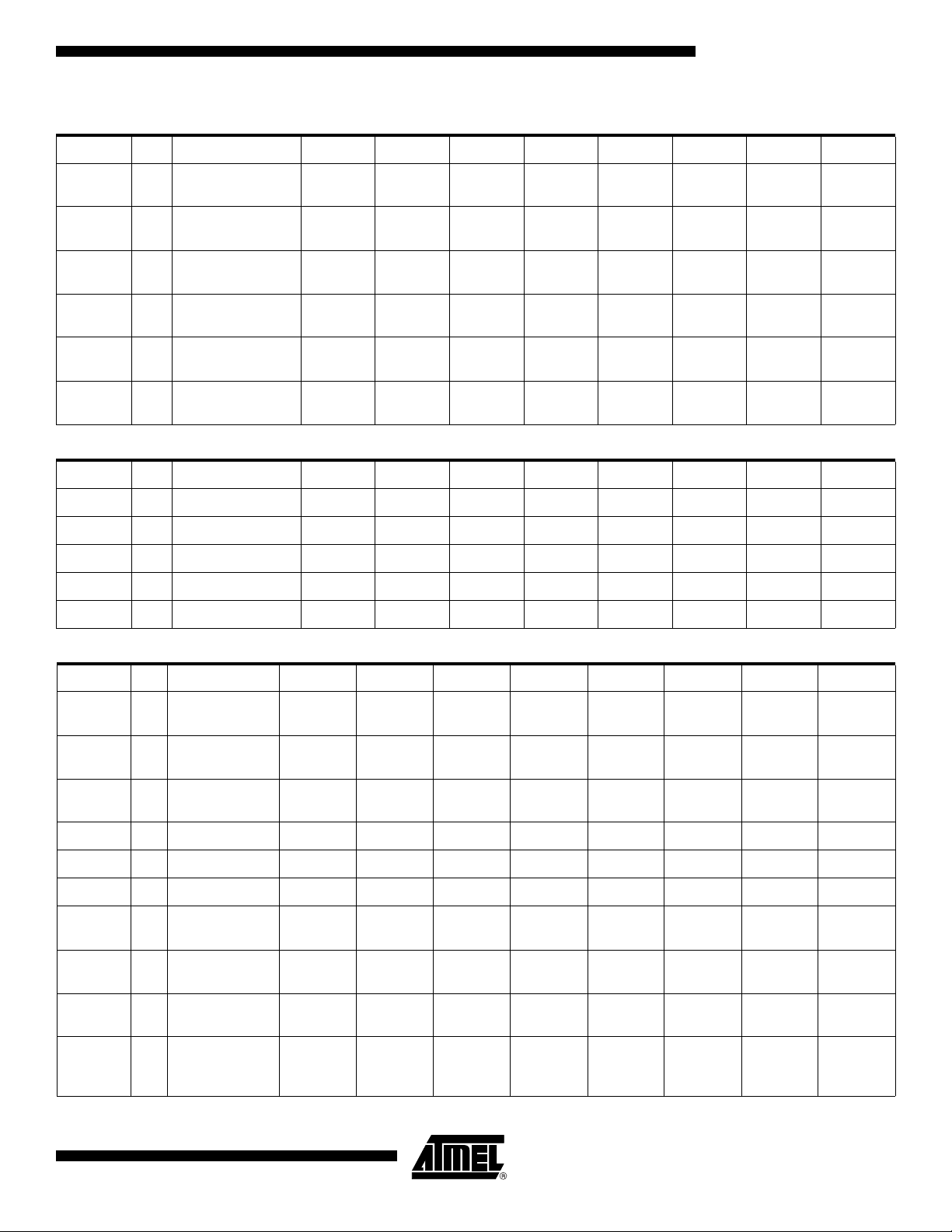
SFR Mapping
The Special Function Registers (SFRs) of the AT89C51CC03 fall into the following
categories:
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ACC E0h Accumulator – – – – – – – –
B F0h B Register – – – – – – – –
PSW D0h Program Status Word CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P
SP 81h Stack Pointer – – – – – – – –
Data Pointer Low
DPL 82h
DPH 83h
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
P0 80h Port 0 – – – – – – – –
P1 90h Port 1 – – – – – – – –
byte
LSB of DPTR
Data Pointer High
byte
MSB of DPTR
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
P2 A0h Port 2 – – – – – – – –
P3 B0h Port 3 – – – – – – – –
P4 C0h Port 4 (x5) – – –
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TH0 8Ch
TL0 8Ah
TH1 8Dh
TL1 8Bh
TH2 CDh
TL2 CCh
TCON 88h
Timer/Counter 0 High
byte
Timer/Counter 0 Low
byte
Timer/Counter 1 High
byte
Timer/Counter 1 Low
byte
Timer/Counter 2 High
byte
Timer/Counter 2 Low
byte
Timer/Counter 0 and
1 control
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
P4.4 /
MOSI
P4.3 /
SCK
P4.2 /
MISO
P4.1 /
RxDC
P4.0 /
TxDC
TMOD 89h
4182N–CAN–03/08
Timer/Counter 0 and
1 Modes
GATE1 C/T1# M11 M01 GATE0 C/T0# M10 M00
11
Page 12
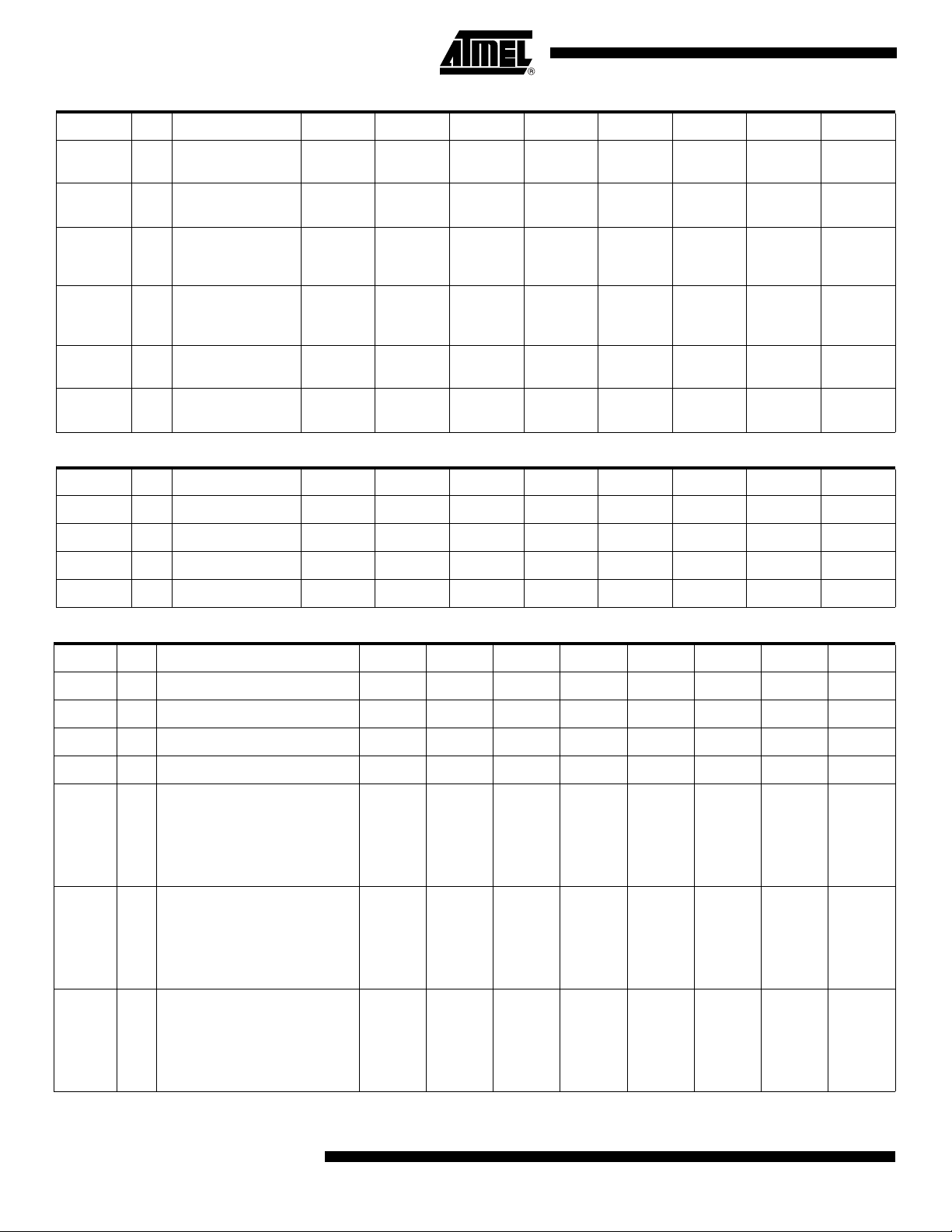
AT89C51CC03
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
T2CON C8h
T2MOD C9h
RCAP2H CBh
RCAP2L CAh
WDTRST A6h
WDTPRG A7h
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SCON 98h Serial Control FE/SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
SBUF 99h Serial Data Buffer – – – – – – – –
SADEN B9h Slave Address Mask – – – – – – – –
SADDR A9h Slave Address – – – – – – – –
Timer/Counter 2
control
Timer/Counter 2
Mode
Timer/Counter 2
Reload/Capture High
byte
Timer/Counter 2
Reload/Capture Low
byte
WatchDog Timer
Reset
WatchDog Timer
Program
TF2 EXF2 RCLK TCLK EXEN2 TR2 C/T2# CP/RL2#
– – – – – – T2OE DCEN
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – –
– – – – – S2 S1 S0
Mnemonic
CCON D8h PCA Timer/Counter Control CF CR – CCF4 CCF3 CCF2 CCF1 CCF0
CMOD D9h PCA Timer/Counter Mode CIDL WDTE – – – CPS1 CPS0 ECF
CL E9h PCA Timer/Counter Low byte – – – – – – – –
CH F9h PCA Timer/Counter High byte – – – – – – – –
CCAPM0
CCAPM1
CCAPM2
CCAPM3
CCAPM4
CCAP0H
CCAP1H
CCAP2H
CCAP3H
CCAP4H
CCAP0L
CCAP1L
CCAP2L
CCAP3L
CCAP4L
Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DAh
PCA Timer/Counter Mode 0
DBh
PCA Timer/Counter Mode 1
DCh
PCA Timer/Counter Mode 2
DDh
PCA Timer/Counter Mode 3
DEh
PCA Timer/Counter Mode 4
FAh
PCA Compare Capture Module 0 H
FBh
PCA Compare Capture Module 1 H
FCh
PCA Compare Capture Module 2 H
FDh
PCA Compare Capture Module 3 H
FEh
PCA Compare Capture Module 4 H
EAh
PCA Compare Capture Module 0 L
EBh
PCA Compare Capture Module 1 L
ECh
PCA Compare Capture Module 2 L
EDh
PCA Compare Capture Module 3 L
EEh
PCA Compare Capture Module 4 L
CCAP0H7
CCAP1H7
CCAP2H7
CCAP3H7
CCAP4H7
CCAP0L7
CCAP1L7
CCAP2L7
CCAP3L7
CCAP4L7
–
ECOM0
ECOM1
ECOM2
ECOM3
ECOM4
CCAP0H6
CCAP1H6
CCAP2H6
CCAP3H6
CCAP4H6
CCAP0L6
CCAP1L6
CCAP2L6
CCAP3L6
CCAP4L6
CAPP0
CAPP1
CAPP2
CAPP3
CAPP4
CCAP0H5
CCAP1H5
CCAP2H5
CCAP3H5
CCAP4H5
CCAP0L5
CCAP1L5
CCAP2L5
CCAP3L5
CCAP4L5
CAPN0
CAPN1
CAPN2
CAPN3
CAPN4
CCAP0H4
CCAP1H4
CCAP2H4
CCAP3H4
CCAP4H4
CCAP0L4
CCAP1L4
CCAP2L4
CCAP3L4
CCAP4L4
MAT0
MAT1
MAT2
MAT3
MAT4
CCAP0H3
CCAP1H3
CCAP2H3
CCAP3H3
CCAP4H3
CCAP0L3
CCAP1L3
CCAP2L3
CCAP3L3
CCAP4L3
TOG0
TOG1
TOG2
TOG3
TOG4
CCAP0H2
CCAP1H2
CCAP2H2
CCAP3H2
CCAP4H2
CCAP0L2
CCAP1L2
CCAP2L2
CCAP3L2
CCAP4L2
PWM0
PWM1
PWM2
PWM3
PWM4
CCAP0H1
CCAP1H1
CCAP2H1
CCAP3H1
CCAP4H1
CCAP0L1
CCAP1L1
CCAP2L1
CCAP3L1
CCAP4L1
ECCF0
ECCF1
ECCF2
ECCF3
ECCF4
CCAP0H0
CCAP1H0
CCAP2H0
CCAP3H0
CCAP4H0
CCAP0L0
CCAP1L0
CCAP2L0
CCAP3L0
CCAP4L0
12
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 13
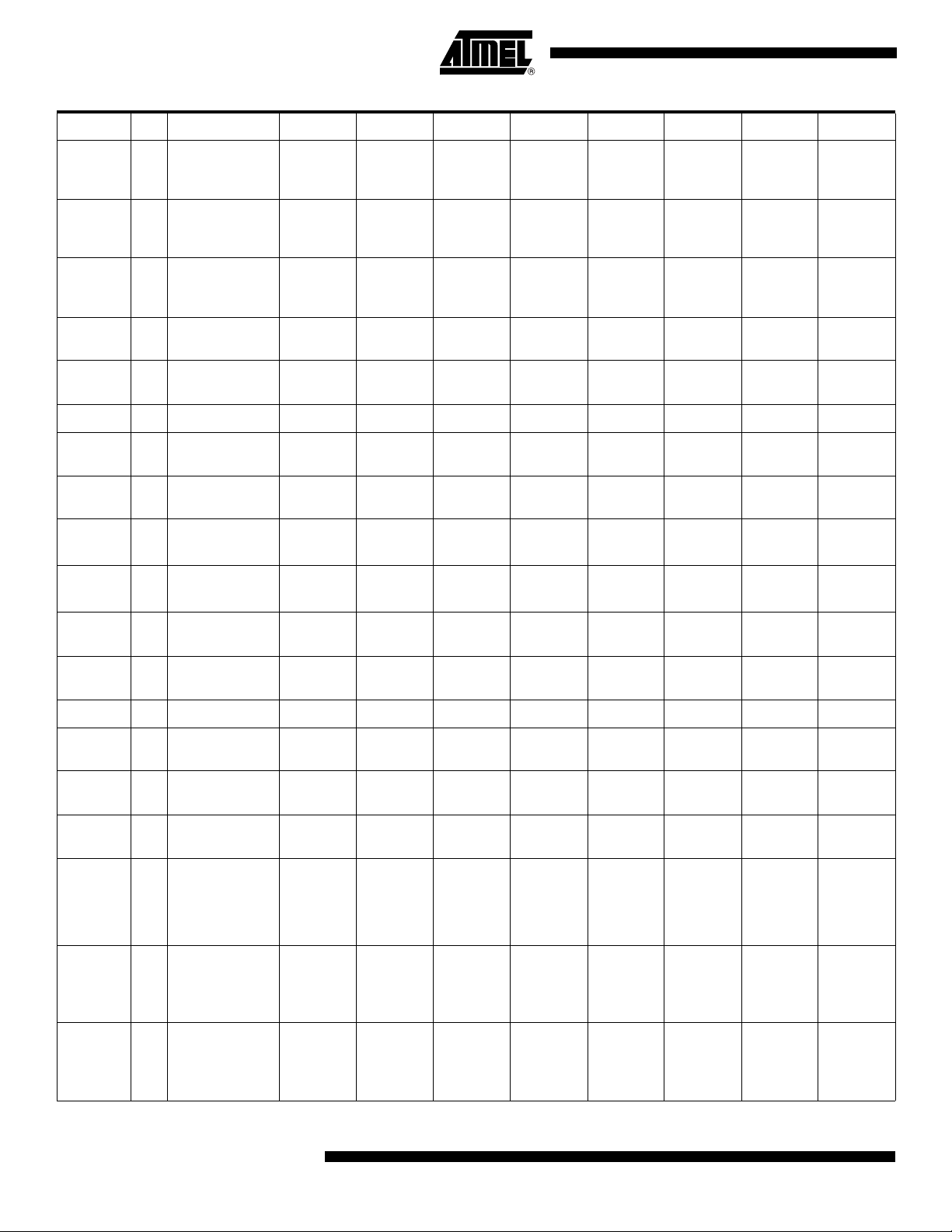
AT89C51CC03
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
IEN0 A8h
IEN1 E8h
IPL0 B8h
IPH0 B7h
IPL1 F8h
IPH1 F7h
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ADCON F3h ADC Control – PSIDLE ADEN ADEOC ADSST SCH2 SCH1 SCH0
ADCF F6h ADC Configuration CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 CH0
ADCLK F2h ADC Clock – – – PRS4 PRS3 PRS2 PRS1 PRS0
ADDH F5h ADC Data High byte ADAT9 ADAT8 ADAT7 ADAT6 ADAT5 ADAT4 ADAT3 ADAT2
ADDL F4h ADC Data Low byte – – – – – – ADAT1 ADAT0
Interrupt Enable
Control 0
Interrupt Enable
Control 1
Interrupt Priority
Control Low 0
Interrupt Priority
Control High 0
Interrupt Priority
Control Low 1
Interrupt Priority
Control High1
EA EC ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0
– – – – ESPI ETIM EADC ECAN
– PPC PT2 PS PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0
– PPCH PT2H PSH PT1H PX1H PT0H PX0H
– – – – SPIL POVRL PADCL PCANL
– – – – SPIH POVRH PADCH PCANH
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CANGCON ABh
CANGSTA AAh
CANGIT 9Bh
CANBT1 B4h CAN Bit Timing 1 – BRP5 BRP4 BRP3 BRP2 BRP1 BRP0 –
CANBT2 B5h CAN Bit Timing 2 – SJW1 SJW0 – PRS2 PRS1 PRS0 –
CANBT3 B6h CAN Bit Timing 3 – PHS22 PHS21 PHS20 PHS12 PHS11 PHS10 SMP
CANEN1 CEh
CANEN2 CFh
CANGIE C1h
CANIE1 C2h
CAN General
Control
CAN General
Status
CAN General
Interrupt
CAN Enable
Channel byte 1
CAN Enable
Channel byte 2
CAN General
Interrupt Enable
CAN Interrupt
Enable Channel
byte 1
ABRQ OVRQ TTC SYNCTTC
– OVFG – TBSY RBSY ENFG BOFF ERRP
CANIT – OVRTIM OVRBUF SERG CERG FERG AERG
– ENCH14 ENCH13 ENCH12 ENCH11 ENCH10 ENCH9 ENCH8
ENCH7 ENCH6 ENCH5 ENCH4 ENCH3 ENCH2 ENCH1 ENCH0
– – ENRX ENTX ENERCH ENBUF ENERG –
– IECH14 IECH13 IECH12 IECH11 IECH10 IECH9 IECH8
AUT–
BAUD
TEST ENA GRES
4182N–CAN–03/08
13
Page 14
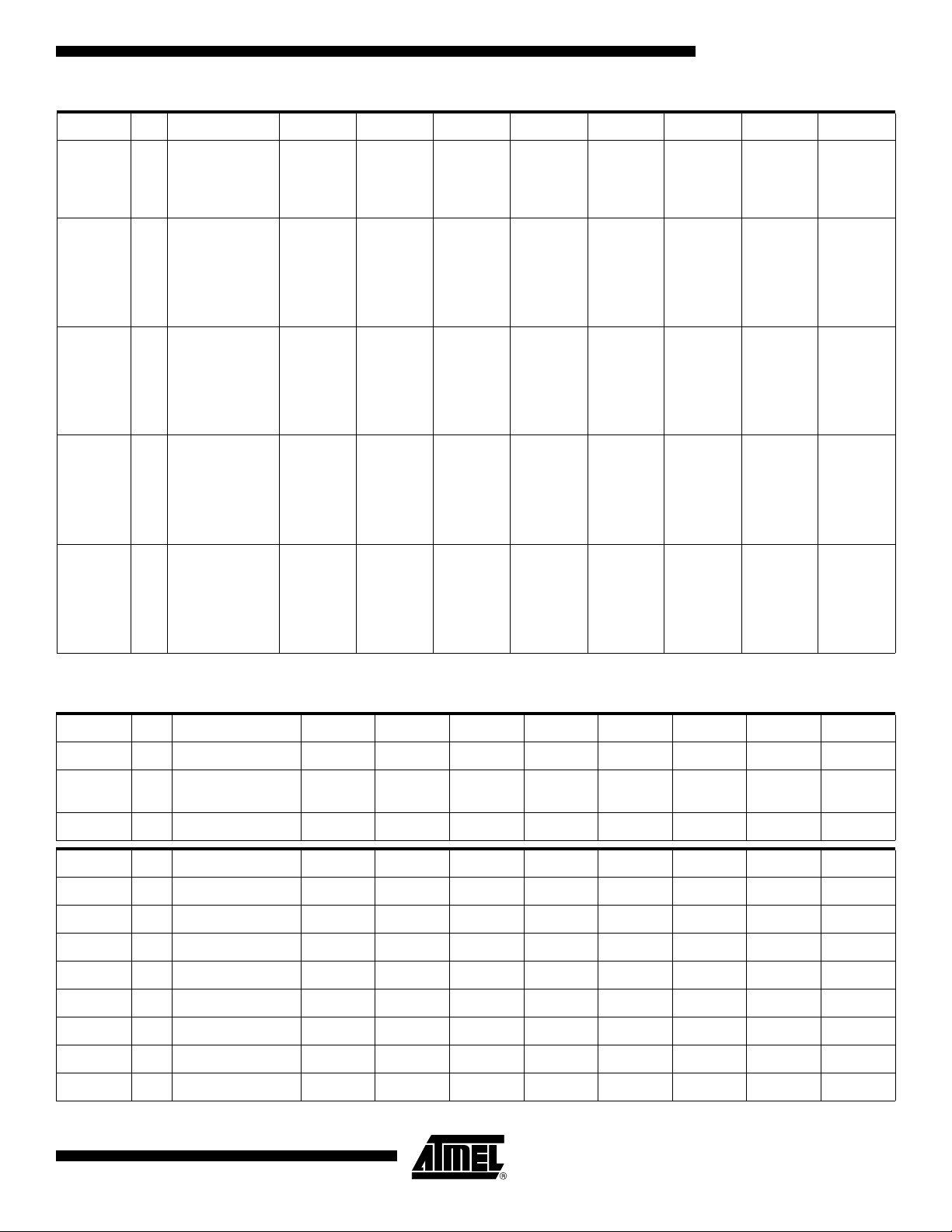
AT89C51CC03
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CAN Interrupt
CANIE2 C3h
Enable Channel
byte 2
IECH7 IECH6 IECH5 IECH4 IECH3 IECH2 IECH1 IECH0
CANSIT1 BAh
CANSIT2 BBh
CANTCON A1h
CANTIMH ADh CAN Timer high
CANTIML ACh CAN Timer low CANTIM 7 CANTIM 6 CANTIM 5 CANTIM 4 CANTIM 3 CANTIM 2 CANTIM 1 CANTIM 0
CANSTMP
H
CANSTMP
L
CANTTCH A5h
CANTTCL A4h
CANTEC 9Ch
CAN Status
Interrupt Channel
byte1
CAN Status
Interrupt Channel
byte2
CAN Timer
Control
CAN Timer Stamp
AFh
high
CAN Timer Stamp
AEh
low
CAN Timer TTC
high
CAN Timer TTC
low
CAN Transmit
Error Counter
– SIT14 SIT13 SIT12 SIT11 SIT10 SIT9 SIT8
SIT7 SIT6 SIT5 SIT4 SIT3 SIT2 SIT1 SIT0
TPRESC 7 TPRESC 6 TPRESC 5 TPRESC 4 TPRESC 3 TPRESC 2 TPRESC 1 TPRESC 0
CANTIM 15CANTIM 14CANTIM 13CANTIM 12CANTIM 11CANTIM
TIMSTMP 15TIMSTMP 14TIMSTMP 13TIMSTMP 12TIMSTMP 11TIMSTMP 10TIMSTMP 9TIMSTMP
TIMSTMP7
TIMTTC 15 TIMTTC 14 TIMTTC 13 TIMTTC 12 TIMTTC 11 TIMTTC 10
TIMTTC7TIMTTC
TEC7 TEC6 TEC5 TEC4 TEC3 TEC2 TEC1 TEC0
TIMSTMP 6TIMSTMP 5TIMSTMP 4TIMSTMP 3TIMSTMP 2TIMSTMP 1TIMSTMP
TIMTTC5TIMTTC
6
4
TIMTTC
3
10
TIMTTC
2
CANTIM 9 CANTIM 8
8
0
TIMTTC
9
TIMTTC
1
TIMTTC
8
TIMTTC
0
CANREC 9Dh
CANPAGE B1h CAN Page CHNB3 CHNB2 CHNB1 CHNB0 AINC INDX2 INDX1 INDX0
CANSTCH B2h
CANCONC
H
CANMSG A3h
CANIDT1 BCh
CANIDT2 BDh
CANIDT3 BEh
CAN Receive
Error Counter
CAN Status
Channel
CAN Control
B3h
Channel
CAN Message
Data
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 1(Part A)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 1(PartB)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 2 (PartA)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 2 (PartB)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 3(PartA)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 3(PartB)
REC7 REC6 REC5 REC4 REC3 REC2 REC1 REC0
DLCW TXOK RXOK BERR SERR CERR FERR AERR
CONCH1 CONCH0 RPLV IDE DLC3 DLC2 DLC1 DLC0
MSG7 MSG6 MSG5 MSG4 MSG3 MSG2 MSG1 MSG0
IDT10 IDT9 IDT8 IDT7 IDT6 IDT5 IDT4 IDT3
IDT28 IDT27 IDT26 IDT25 IDT24 IDT23 IDT22 IDT21
IDT2
IDT20
–
IDT12
IDT1
IDT19
–
IDT11
IDT0
IDT18
–
IDT10
–
IDT17
–
IDT9
–
IDT16
–
IDT8
–
IDT15
–
IDT7
–
IDT14
–
IDT6
–
IDT13
–
IDT5
14
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 15
AT89C51CC03
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CANIDT4 BFh
CANIDM1 C4h
CANIDM2 C5h
CANIDM3 C6h
CANIDM4 C7h
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 4(PartA)
CAN Identifier Tag
byte 4(PartB)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
1(PartA)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
1(PartB)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
2(PartA)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
2(PartB)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
3(PartA)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
3(PartB)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
4(PartA)
CAN Identifier
Mask byte
4(PartB)
–
IDT4
IDMSK10
IDMSK28
IDMSK2
IDMSK20
–
IDMSK12–IDMSK11–IDMSK10–IDMSK9
–
IDMSK4–IDMSK3–IDMSK2–IDMSK1
–
IDT3
IDMSK9
IDMSK27
IDMSK1
IDMSK19
–
IDT2
IDMSK8
IDMSK26
IDMSK0
IDMSK18–IDMSK17–IDMSK16–IDMSK15–IDMSK14–IDMSK13
–
IDT1
IDMSK7
IDMSK25
–
RTRTAG
IDT0
IDMSK6
IDMSK24
–
IDMSK8–IDMSK7–IDMSK6
–
IDMSK0
IDMSK5
IDMSK23
RTRMSK – IDEMSK
–
RB1TAG
IDMSK4
IDMSK22
RB0TAF
IDMSK3
IDMSK21
–
IDMSK5
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SPCON D4h SPI Control SPR2 SPEN SSDIS MSTR CPOL CPHA SPR1 SPR0
SPSCR D5h
SPDAT D6h SPI Data - - - - - - - -
Mnemonic Add Name 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
PCON 87h Power Control SMOD1 SMOD0 – POF GF1 GF0 PD IDL
AUXR 8Eh Auxiliary Register 0 DPU VPFDP M0 XRS2 XRS1 XRS0 EXTRAM A0
AUXR1 A2h Auxiliary Register 1 – – ENBOOT – GF3 0 – DPS
CKCON0 8Fh Clock Control 0 CANX2 WDX2 PCAX2 SIX2 T2X2 T1X2 T0X2 X2
CKCON1 9Fh Clock Control 1 - - - - - - - SPIX2
FCON D1h Flash Control FPL3 FPL2 FPL1 FPL0 FPS FMOD1 FMOD0 FBUSY
EECON D2h EEPROM Contol EEPL3 EEPL2 EEPL1 EEPL0 – – EEE EEBUSY
FSTA D3 Flash Status - - - - - - SEQERR FLOAD
4182N–CAN–03/08
SPI Status and
Control
SPIF - OVR MODF SPTE UARTM SPTEIE MOFIE
15
Page 16
AT89C51CC03
Table 1. SFR Mapping
(2)
0/8
1/9 2/A 3/B 4/C 5/D 6/E 7/F
F8h
F0h
E8h
E0h
D8h
D0h
C8h
C0h
B8h
B0h
A8h
IPL1
xxxx x000
B
0000 0000
IEN1
xxxx x000
ACC
0000 0000
CCON
0000 0000
PSW
0000 0000
T2CON
0000 0000
P4
xxx1 1111
IPL0
x000 0000
P3
1111 1111
IEN0
0000 0000
CH
0000 0000
CL
0000 0000
CMOD
00xx x000
FCON
0000 0000
T2MOD
xxxx xx00
CANGIE
xx00 000x
SADEN
0000 0000
CANPAGE
0000 0000
SADDR
0000 0000
CCAP0H
0000 0000
ADCLK
xxx0 0000
CCAP0L
0000 0000
CCAPM0
x000 0000
EECON
xxxx xx00
RCAP2L
0000 0000
CANIE1
x000 0000
CANSIT1
0000 0000
CANSTCH
xxxx xxxx
CANGSTA
x0x0 0000
CCAP1H
0000 0000
ADCON
x000 0000
CCAP1L
0000 0000
CCAPM1
x000 0000
FSTA
xxxx xx00
RCAP2H
0000 0000
CANIE2
0000 0000
CANSIT2
0000 0000
CANCONCH
xxxx xxxx
CANGCON
0000 0x00
CCAP2H
0000 0000
ADDL
0000 0000
CCAP2L
0000 0000
CCAPM2
x000 0000
SPCON
0001 0100
TL2
0000 0000
CANIDM1
xxxx xxxx
CANIDT1
xxxx xxxx
CANBT1
xxxx xxxx
CANTIML
0000 0000
CCAP3H
0000 0000
ADDH
0000 0000
CCAP3L
0000 0000
CCAPM3
x000 0000
SPSCR
0000 0000
TH2
0000 0000
CANIDM2
xxxx xxxx
CANIDT2
xxxx xxxx
CANBT2
xxxx xxxx
CANTIMH
0000 0000
CCAP4H
0000 0000
ADCF
0000 0000
CCAP4L
0000 0000
CCAPM4
x000 0000
SPDAT
xxxx xxxx
CANEN1
x000 0000
CANIDM3
xxxx xxxx
CANIDT3
xxxx xxxx
CANBT3
xxxx xxxx
CANSTMPL
0000 0000
IPH1
xxxx x000
CANEN2
0000 0000
CANIDM4
xxxx xxxx
CANIDT4
xxxx xxxx
IPH0
x000 0000
CANSTMPH
0000 0000
FFh
F7h
EFh
E7h
DFh
D7h
CFh
C7h
BFh
B7h
AFh
A0h
98h
90h
88h
80h
P2
1111 1111
SCON
0000 0000
P1
1111 1111
TCON
0000 0000
P0
1111 1111
(2)
0/8
CANTCON
0000 0000
SBUF
0000 0000
TMOD
0000 0000
SP
0000 0111
1/9 2/A 3/B 4/C 5/D 6/E 7/F
AUXR1
xxxx 00x0
TL0
0000 0000
DPL
0000 0000
Reserved
Note: 1. Do not read or write Reserved Registers
2. These registers are bit–addressable.
Sixteen addresses in the SFR space are both byte–addressable and bit–addressable. The bit–addressable SFR’s are those
whose address ends in 0 and 8. The bit addresses, in this area, are 0x80 through to 0xFF.
CANMSG
xxxx xxxx
CANGIT
0x00 0000
TL1
0000 0000
DPH
0000 0000
CANTTCL
0000 0000
CANTEC
0000 0000
TH0
0000 0000
CANTTCH
0000 0000
CANREC
0000 0000
TH1
0000 0000
WDTRST
1111 1111
AUXR
x001 0100
WDTPRG
xxxx x000
CKCON1
xxxx xxx0
CKCON0
0000 0000
PCON
00x1 0000
A7h
9Fh
97h
8Fh
87h
16
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 17

AT89C51CC03
Clock
Description
The AT89C51CC03 core needs only 6 clock periods per machine cycle. This feature,
called”X2”, provides the following advantages:
• Divides frequency crystals by 2 (cheaper crystals) while keeping the same CPU
power.
• Saves power consumption while keeping the same CPU power (oscillator power
saving).
• Saves power consumption by dividing dynamic operating frequency by 2 in
operating and idle modes.
• Increases CPU power by 2 while keeping the same crystal frequency.
In order to keep the original C51 compatibility, a divider-by-2 is inserted between the
XTAL1 signal and the main clock input of the core (phase generator). This divider may
be disabled by the software.
An extra feature is available to start after Reset in the X2 mode. This feature can be
enabled by a bit X2B in the Hardware Security Byte. This bit is described in the section
"In-System Programming".
The X2 bit in the CKCON register (see Table 2) allows switching from 12 clock cycles
per instruction to 6 clock cycles and vice versa. At reset, the standard speed is activated
(STD mode).
Setting this bit activates the X2 feature (X2 mode) for the CPU Clock only (see Figure
5.).
The Timers 0, 1 and 2, Uart, PCA, WatchDog or CAN switch in X2 mode only if the corresponding bit is cleared in the CKCON register.
The clock for the whole circuit and peripheral is first divided by two before being used by
the CPU core and peripherals. This allows any cyclic ratio to be accepted on the XTAL1
input. In X2 mode, as this divider is bypassed, the signals on XTAL1 must have a cyclic
ratio between 40 to 60%. Figure 5. shows the clock generation block diagram. The X2
bit is validated on the XTAL1÷2 rising edge to avoid glitches when switching from the X2
to the STD mode. Figure 6 shows the mode switching waveforms.
4182N–CAN–03/08
17
Page 18
AT89C51CC03
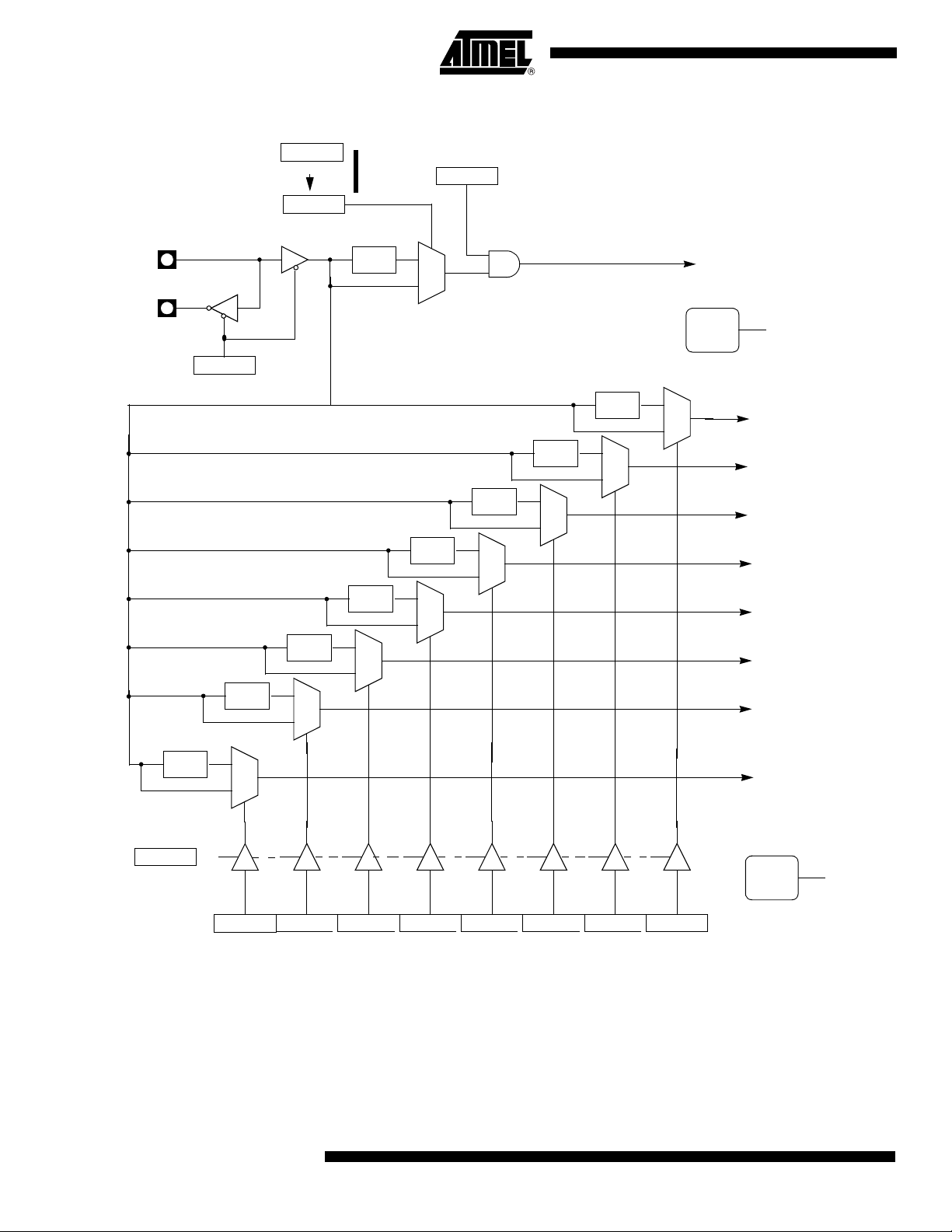
Figure 5. Clock CPU Generation Diagram
XTAL1
XTAL2
PD
PCON.1
CPU Core
1
0
÷
2
PERIPH
CLOCK
Clock
Peripheral
CPU
CLOCK
CPU Core Clock Symbol
X2
CKCON.0
X2B
Hardware byte
CANX2
CKCON0.7
WDX2
CKCON0.6
PCAX2
CKCON0.5
SIX2
CKCON0.4
T2X2
CKCON0.3
T1X2
CKCON0.2
T0X2
CKCON0.1
IDL
PCON.0
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
1
0
÷
2
X2
CKCON.0
FCan Clock
FWd Clock
FPca Clock
FUart Clock
FT2 Clock
FT1 Clock
FT0 Clock
and ADC
On RESET
1
0
÷
2
FSPIClock
SPIX2
CKCON1.0
Clock Symbol
18
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 19
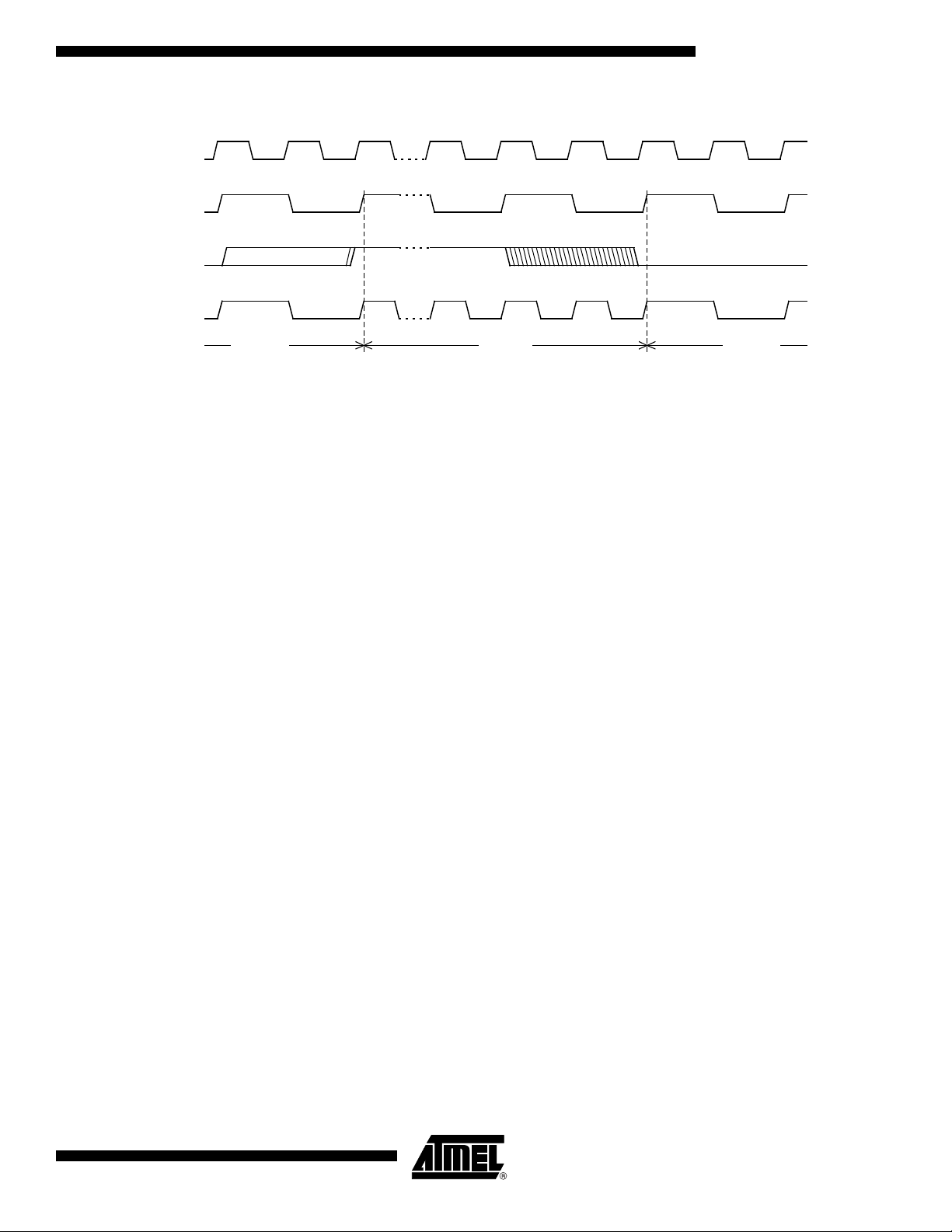
AT89C51CC03
XTAL1/2
XTAL1
CPU clock
X2 bit
X2 ModeSTD Mode STD Mode
Figure 6. Mode Switching Waveforms
Note: In order to prevent any incorrect operation while operating in the X2 mode, users must be aware that all peripherals using the
clock frequency as a time reference (UART, timers...) will have their time reference divided by two. For example a free running
timer generating an interrupt every 20 ms will then generate an interrupt every 10 ms. A UART with a 4800 baud rate will have
a 9600 baud rate.
4182N–CAN–03/08
19
Page 20
AT89C51CC03
Registers
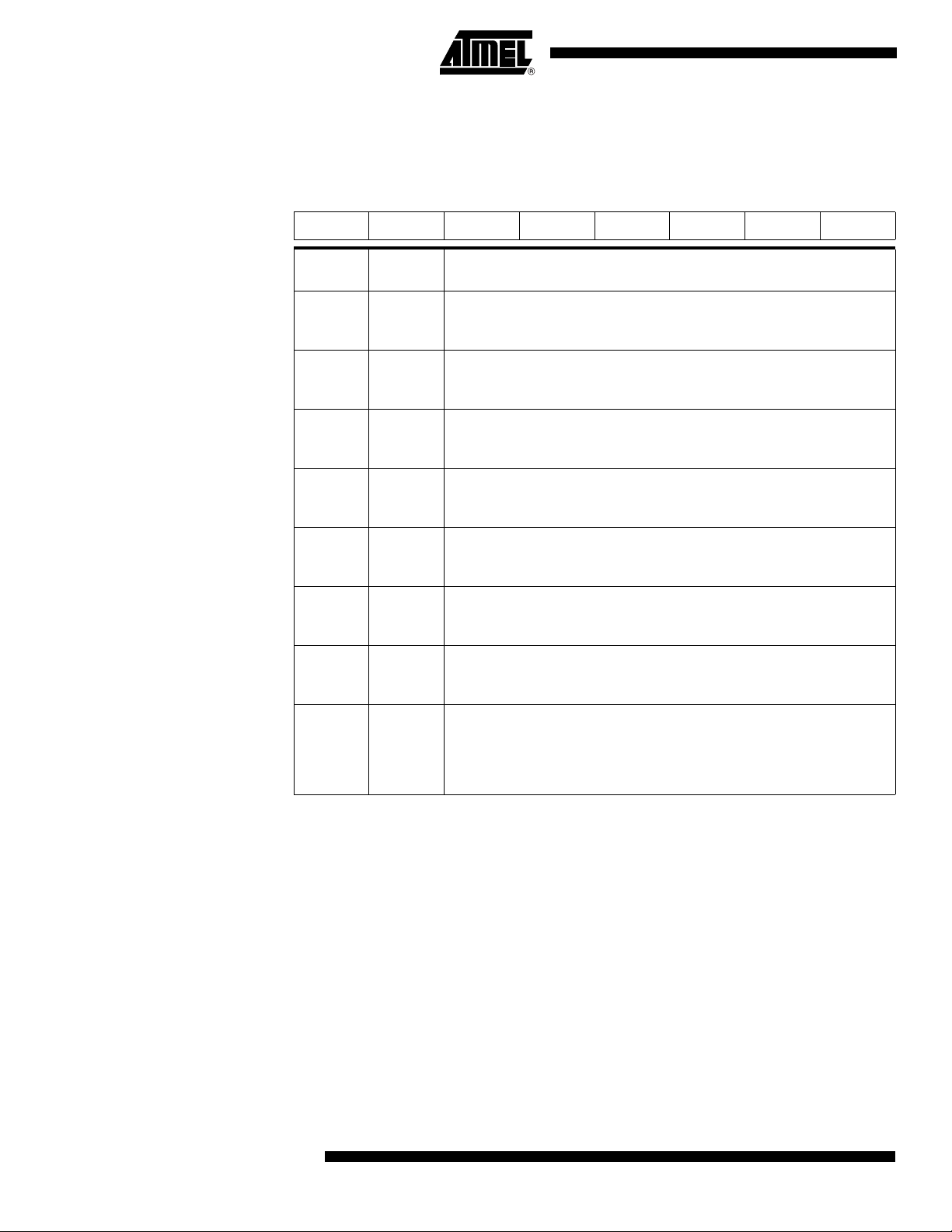
Table 2. CKCON0 Register
CKCON0 (S:8Fh)
Clock Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CANX2 WDX2 PCAX2 SIX2 T2X2 T1X2 T0X2 X2
Bit
Number
7 CANX2
6 WDX2
5 PCAX2
4 SIX2
3 T2X2
2 T1X2
1 T0X2
Bit
Mnemonic Description
CAN clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
WatchDog clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Programmable Counter Array clock
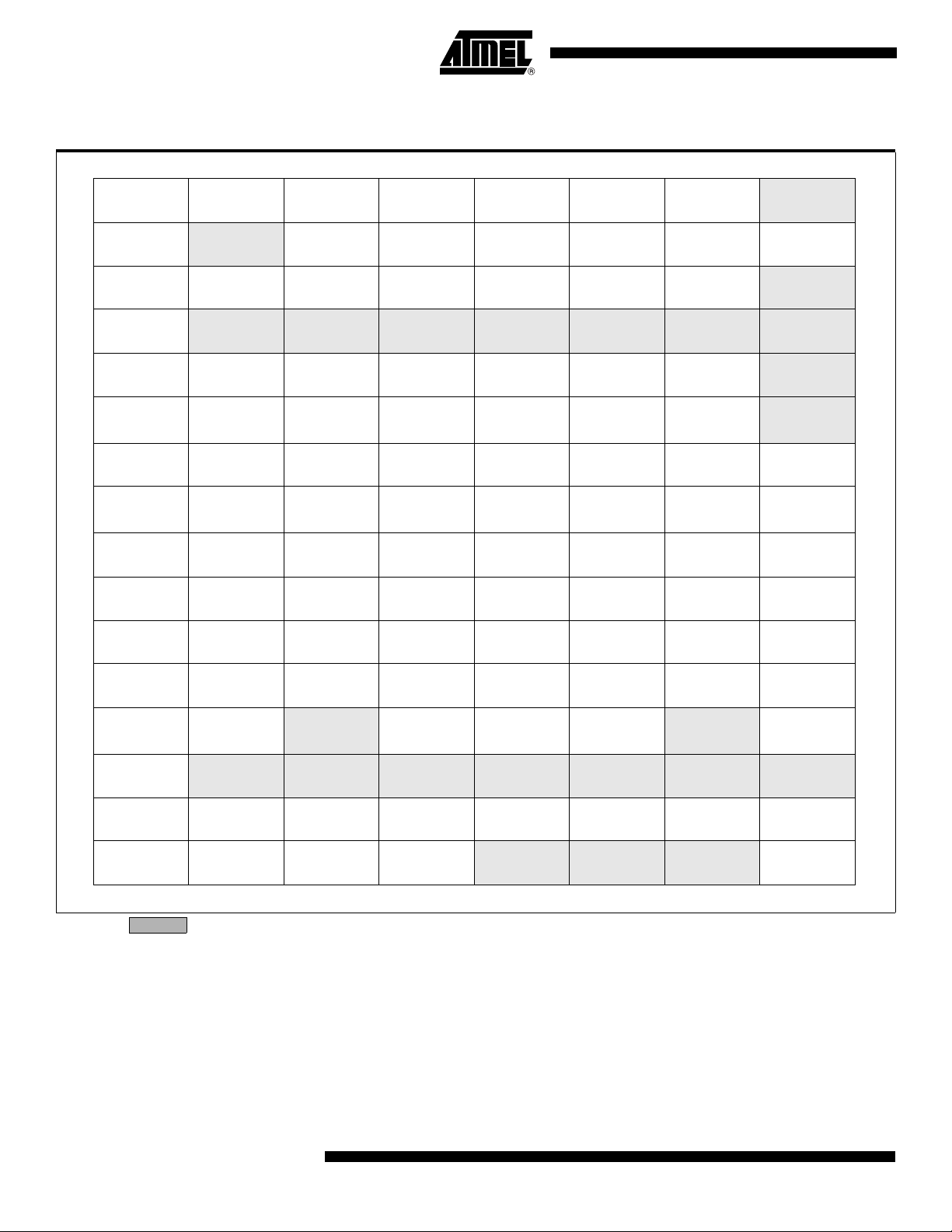
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Enhanced UART clock (MODE 0 and 2)
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Timer2 clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Timer1 clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Timer0 clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
20
CPU clock
0 X2
Clear to select 12 clock periods per machine cycle (STD mode) for CPU and all
the peripherals.
Set to select 6 clock periods per machine cycle (X2 mode) and to enable the
individual peripherals "X2"bits.
Note: 1. This control bit is validated when the CPU clock bit X2 is set; when X2 is low, this bit
has no effect.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 21
AT89C51CC03
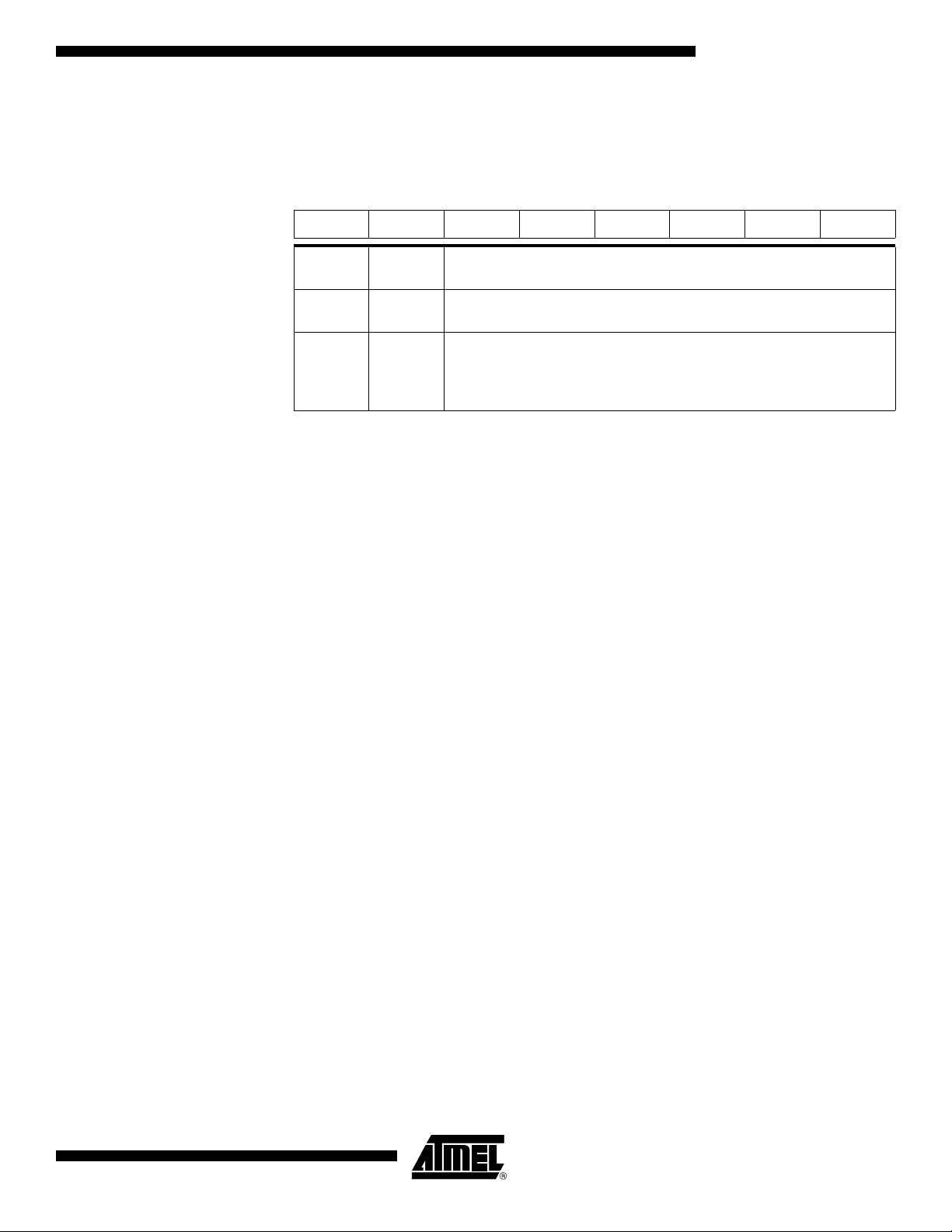
Table 3. CKCON1 Register
CKCON1 (S:9Fh)
Clock Control Register 1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SPIX2
Bit
Number
7-1 -
0 SPIX2
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from these bits is indeterminate. Do not set these bits.
SPI clock
Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
Set to select 12 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle.
(1)
Note: 1. This control bit is validated when the CPU clock bit X2 is set; when X2 is low, this bit
has no effect.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
4182N–CAN–03/08
21
Page 22
AT89C51CC03
Data Memory
Upper
128 Bytes
Internal RAM
Lower
128 Bytes
Internal RAM
Special
Function
Registers
80h
80h
00h
FFh
FFh
direct addressing
addressing
7Fh
direct or indirect
indirect addressing
256 up to 2048 Bytes
00h
64K Bytes
External XRAM
0000h
FFFFh
Internal ERAM
EXTRAM = 0
EXTRAM = 1
FFh or 7FFh
Internal
External
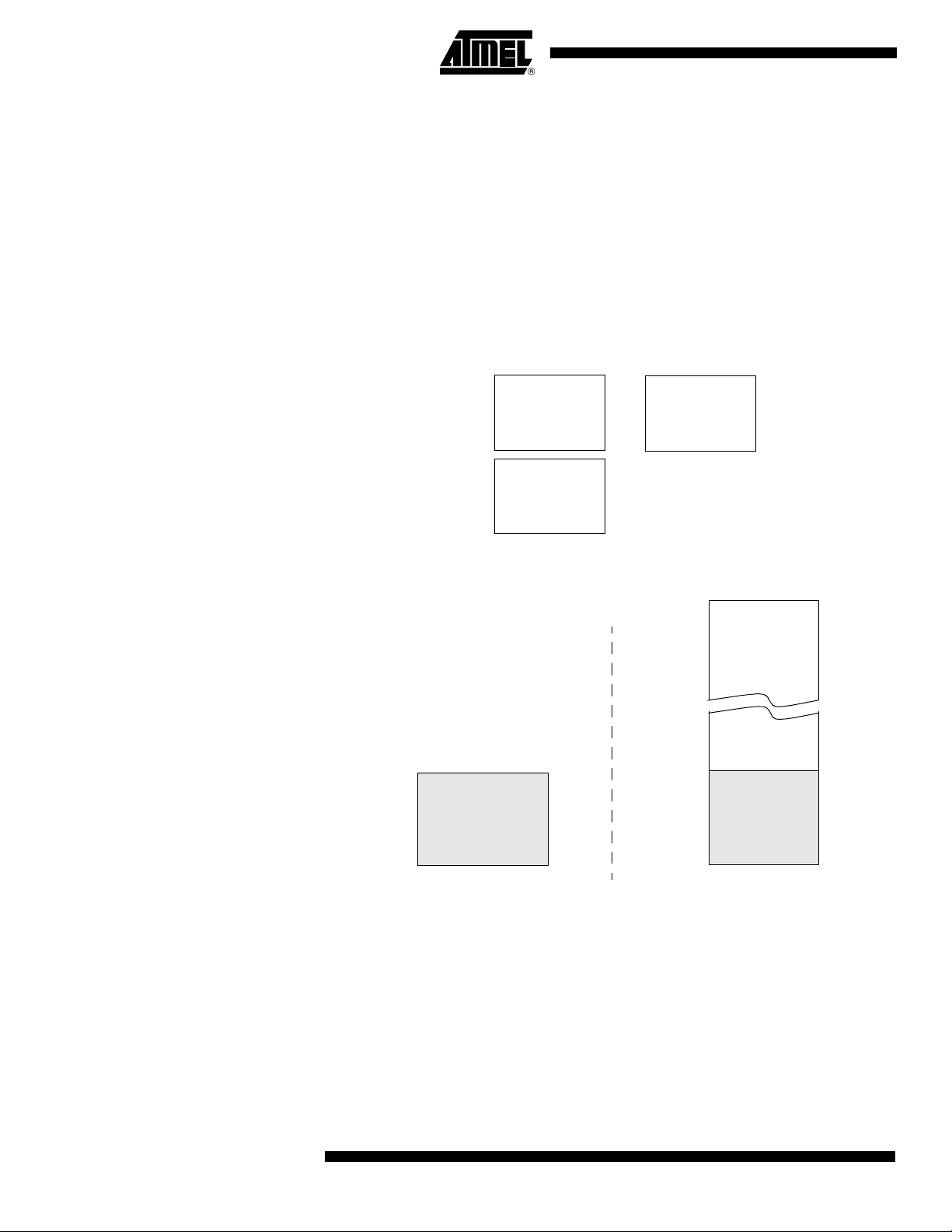
The AT89C51CC03 provides data memory access in two different spaces:
1. The internal space mapped in three separate segments:
• the lower 128 Bytes RAM segment.
• the upper 128 Bytes RAM segment.
• the expanded 2048 Bytes RAM segment (ERAM).
2. The external space.
A fourth internal segment is available but dedicated to Special Function Registers,
SFRs, (addresses 80h to
FFh
) accessible by direct addressing mode.
Figure 8 shows the internal and external data memory spaces organization.
Figure 7. Internal Memory - RAM
Figure 8. Internal and External Data Memory Organization ERAM-XRAM
22
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 23
AT89C51CC03
Bit-Addressable Space
4 Banks of
8 Registers
R0-R7
30h
7Fh
(Bit Addresses 0-7Fh)
20h
2Fh
18h
1Fh
10h
17h
08h
0Fh
00h
07h
Internal Space
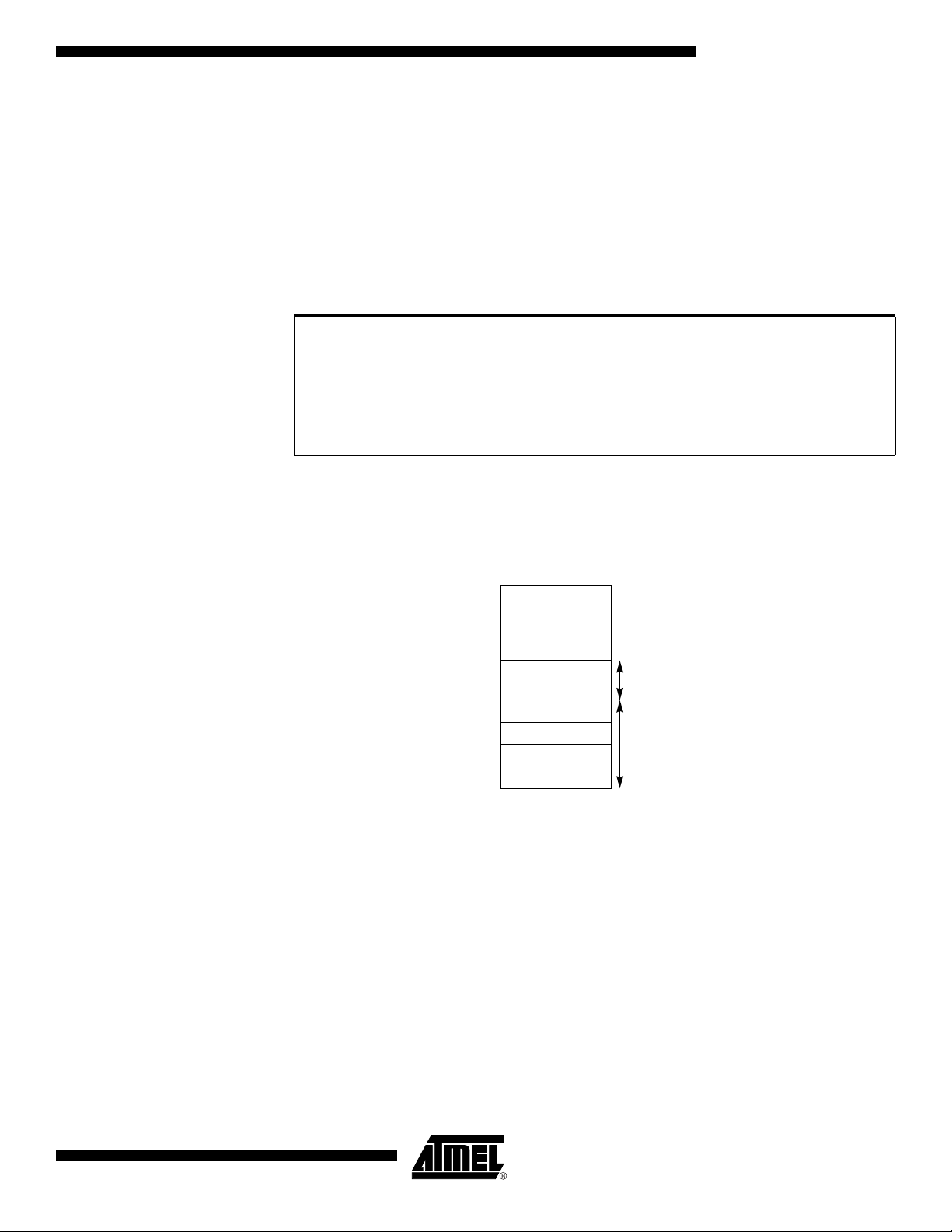
Lower 128 Bytes RAM The lower 128 Bytes of RAM (see Figure 8) are accessible from address 00h to 7Fh
using direct or indirect addressing modes. The lowest 32 Bytes are grouped into 4
banks of 8 registers (R0 to R7). Two bits RS0 and RS1 in PSW register (see Figure 6)
select which bank is in use according to Table 4. This allows more efficient use of code
space, since register instructions are shorter than instructions that use direct addressing, and can be used for context switching in interrupt service routines.
Table 4. Register Bank Selection
RS1 RS0 Description
0 0 Register bank 0 from 00h to 07h
0 1 Register bank 0 from 08h to 0Fh
1 0 Register bank 0 from 10h to 17h
1 1 Register bank 0 from 18h to 1Fh
The next 16 Bytes above the register banks form a block of bit-addressable memory
space. The C51 instruction set includes a wide selection of single-bit instructions, and
the 128 bits in this area can be directly addressed by these instructions. The bit
addresses in this area are 00h to 7Fh.
Figure 9. Lower 128 Bytes Internal RAM Organization
Upper 128 Bytes RAM The upper 128 Bytes of RAM are accessible from address 80h to FFh using only indirect
addressing mode.
Expanded RAM The on-chip 2048 Bytes of expanded RAM (ERAM) are accessible from address 0000h
to 07FFh using indirect addressing mode through MOVX instructions. In this address
range, the bit EXTRAM in AUXR register is used to select the ERAM (default) or the
XRAM. As shown in Figure 8 when EXTRAM = 0, the ERAM is selected and when
EXTRAM = 1, the XRAM is selected.
The size of ERAM can be configured by XRS2-0 bit in AUXR register (default size is
2048 Bytes).
4182N–CAN–03/08
Note: Lower 128 Bytes RAM, Upper 128 Bytes RAM, and expanded RAM are made of volatile
memory cells. This means that the RAM content is indeterminate after power-up and
must then be initialized properly.
23
Page 24
AT89C51CC03
External Space
RAM
PERIPHERAL
AT89C51CC03
P2
P0
AD7:0
A15:8
A7:0
A15:8
D7:0
A7:0
ALE
WR
OERD#
WR#
Latch
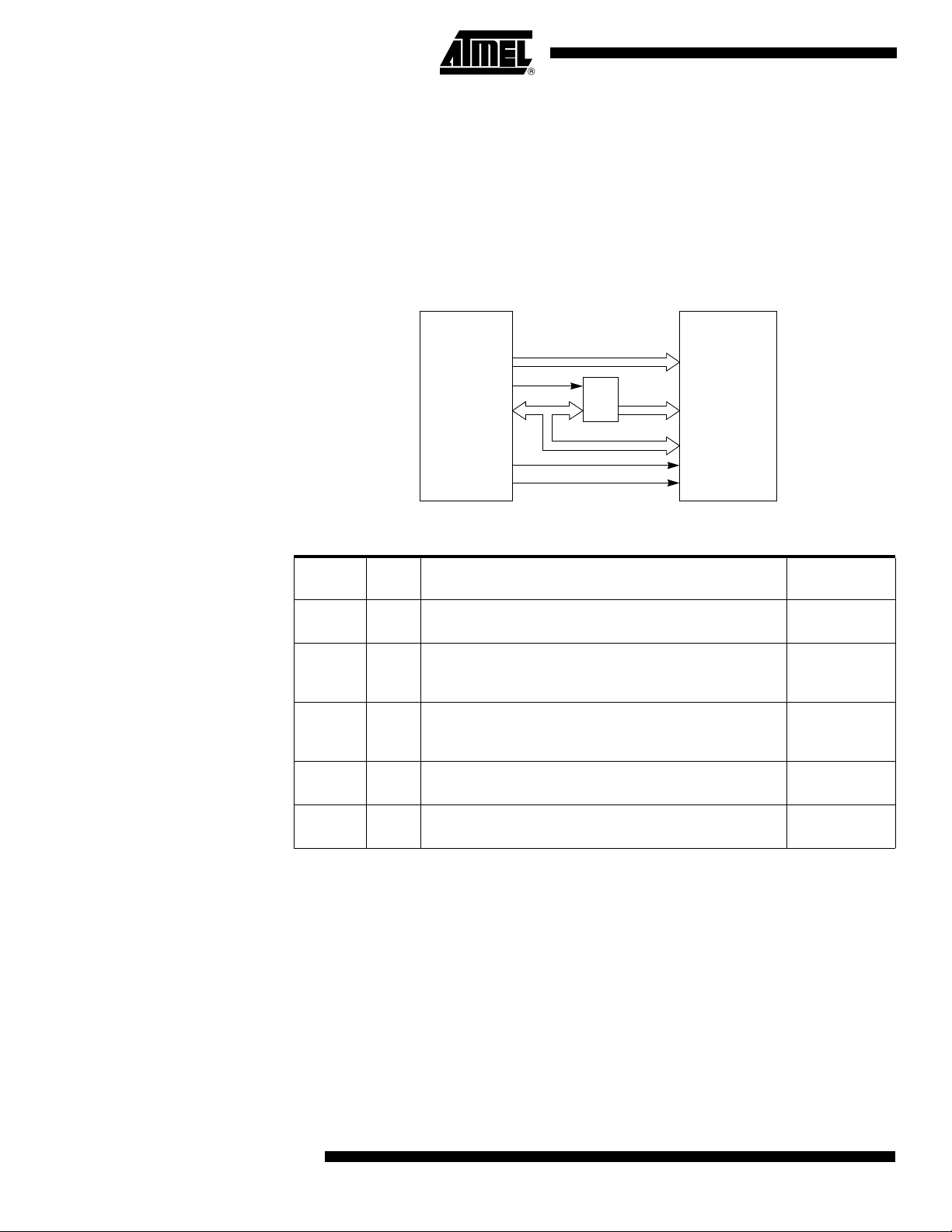
Memory Interface The external memory interface comprises the external bus (port 0 and port 2) as well as
the bus control signals (RD#, WR#, and ALE).
Figure 10 shows the structure of the external address bus. P0 carries address A7:0
while P2 carries address A15:8. Data D7:0 is multiplexed with A7:0 on P0. Table 5
describes the external memory interface signals.
Figure 10. External Data Memory Interface Structure
Table 5. External Data Memory Interface Signals
Signal
Name Type Description
A15:8 O
AD7:0 I/O
ALE O
RD# O
WR# O
Address Lines
Upper address lines for the external bus.
Address/Data Lines
Multiplexed lower address lines and data for the external
memory.
Address Latch Enable
ALE signals indicates that valid address information are available
on lines AD7:0.
Read
Read signal output to external data memory.
Write
Write signal output to external memory.
Alternative
Function
P2.7:0
P0.7:0
-
P3.7
P3.6
External Bus Cycles This section describes the bus cycles the AT89C51CC03 executes to read (see
Figure 11), and write data (see Figure 12) in the external data memory.
External memory cycle takes 6 CPU clock periods. This is equivalent to 12 oscillator
clock period in standard mode or 6 oscillator clock periods in X2 mode. For further information on X2 mode.
Slow peripherals can be accessed by stretching the read and write cycles. This is done
using the M0 bit in AUXR register. Setting this bit changes the width of the RD# and
WR# signals from 3 to 15 CPU clock periods.
For simplicity, the accompanying figures depict the bus cycle waveforms in idealized
form and do not provide precise timing information. For bus cycle timing parameters
refer to the Section “AC Characteristics” of the AT89C51CC03 datasheet.
24
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 25
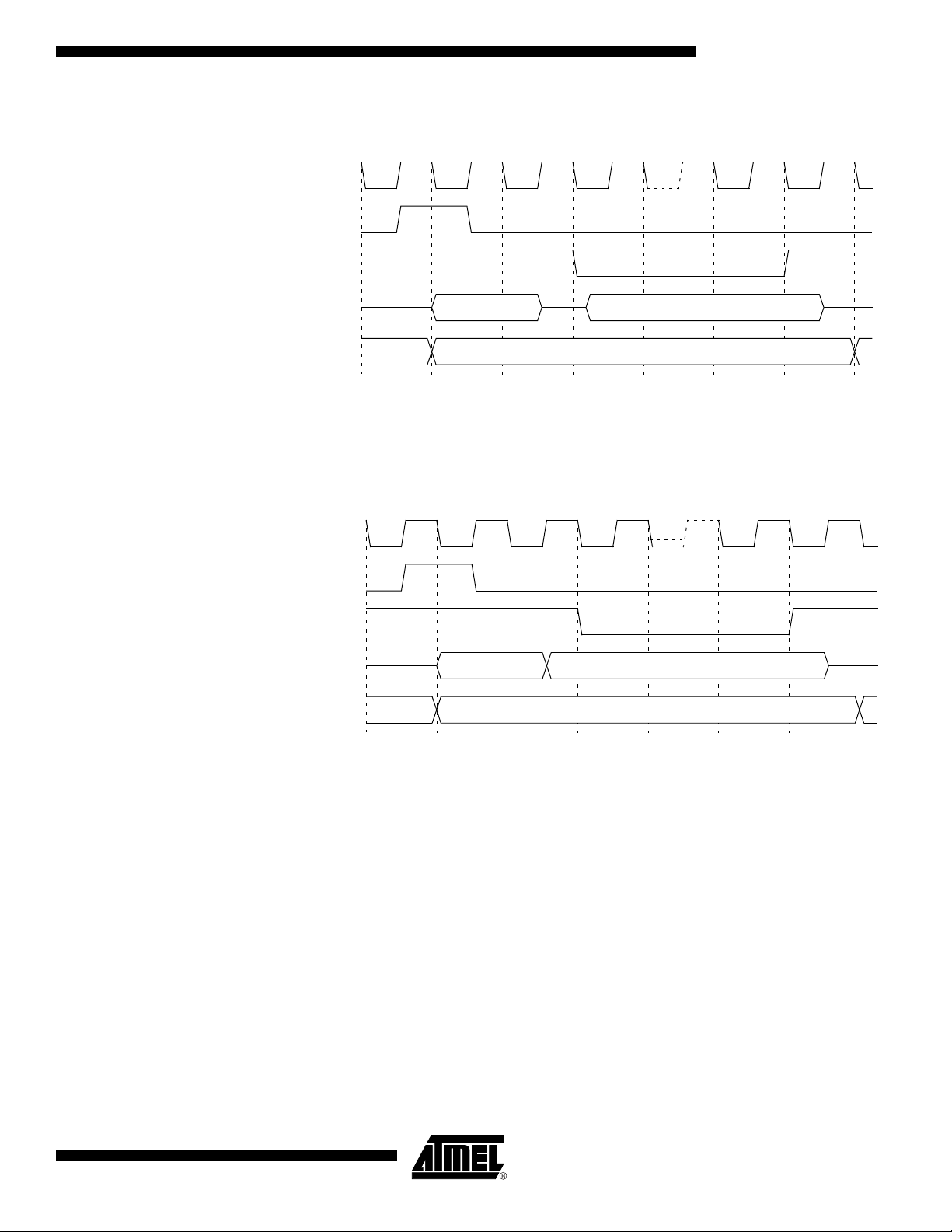
AT89C51CC03
ALE
P0
P2
RD#1
DPL or Ri D7:0
DPH or P22
P2
CPU Clock
ALE
P0
P2
WR#1
DPL or Ri D7:0
P2
CPU Clock
DPH or P22
Figure 11. External Data Read Waveforms
Notes: 1. RD# signal may be stretched using M0 bit in AUXR register.
2. When executing MOVX @Ri instruction, P2 outputs SFR content.
Figure 12. External Data Write Waveforms
4182N–CAN–03/08
Notes: 1. WR# signal may be stretched using M0 bit in AUXR register.
2. When executing MOVX @Ri instruction, P2 outputs SFR content.
25
Page 26
AT89C51CC03
Dual Data Pointer
0
1
DPH0
DPH1
DPL0
0
1
DPS
AUXR1.0
DPH
DPL
DPL1
DPTR
DPTR0
DPTR1
Description The AT89C51CC03 implements a second data pointer for speeding up code execution
and reducing code size in case of intensive usage of external memory accesses.
DPTR 0 and DPTR 1 are seen by the CPU as DPTR and are accessed using the SFR
addresses 83h and 84h that are the DPH and DPL addresses. The DPS bit in AUXR1
register (see Figure 8) is used to select whether DPTR is the data pointer 0 or the data
pointer 1 (see Figure 13).
Figure 13. Dual Data Pointer Implementation
Application Software can take advantage of the additional data pointers to both increase speed and
reduce code size, for example, block operations (copy, compare…) are well served by
using one data pointer as a “source” pointer and the other one as a “destination” pointer.
Hereafter is an example of block move implementation using the two pointers and coded
in assembler. The latest C compiler takes also advantage of this feature by providing
enhanced algorithm libraries.
26
The INC instruction is a short (2 Bytes) and fast (6 machine cycle) way to manipulate the
DPS bit in the AUXR1 register. However, note that the INC instruction does not directly
force the DPS bit to a particular state, but simply toggles it. In simple routines, such as
the block move example, only the fact that DPS is toggled in the proper sequence matters, not its actual value. In other words, the block move routine works the same whether
DPS is '0' or '1' on entry.
; ASCII block move using dual data pointers
; Modifies DPTR0, DPTR1, A and PSW
; Ends when encountering NULL character
; Note: DPS exits opposite to the entry state unless an extra INC AUXR1 is added
AUXR1EQU0A2h
move:movDPTR,#SOURCE ; address of SOURCE
incAUXR1 ; switch data pointers
movDPTR,#DEST ; address of DEST
mv_loop:incAUXR1; switch data pointers
movxA,@DPTR; get a byte from SOURCE
incDPTR; increment SOURCE address
incAUXR1; switch data pointers
movx@DPTR,A; write the byte to DEST
incDPTR; increment DEST address
jnzmv_loop; check for NULL terminator
end_move:
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 27
AT89C51CC03
Registers
Table 6. PSW Register
PSW (S:8Eh)
Program Status Word Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P
Bit
Number
7 CY
6 AC
5 F0
4-3 RS1:0
2 OV
1 F1
0 P
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Carry Flag
Carry out from bit 1 of ALU operands.
Auxiliary Carry Flag
Carry out from bit 1 of addition operands.
User Definable Flag 0.
Register Bank Select Bits
Refer to Table 4 for bits description.
Overflow Flag
Overflow set by arithmetic operations.
User Definable Flag 1
Parity Bit
Set when ACC contains an odd number of 1’s.
Cleared when ACC contains an even number of 1’s.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Table 7. AUXR Register
AUXR (S:8Eh)
Auxiliary Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - M0 XRS2 XRS1 XRS0 EXTRAM A0
Bit
Number
7-6 -
5 M0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from these bits are indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Stretch MOVX control:
the RD/ and the WR/ pulse length is increased according to the value of M0.
M0 Pulse length in clock period
0 6
1 30
4182N–CAN–03/08
27
Page 28
AT89C51CC03
Bit
Number
4-2 XRS1-0
1 EXTRAM
0 A0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
ERAM size:
Accessible size of the ERAM
XRS 2:0 ERAM size
000 256 Bytes
001 512 Bytes
010 768 Bytes
011 1024 Bytes
100 1792 Bytes
101 2048 Bytes (default configuration after reset)
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
Internal/External RAM (00h - FFh)
access using MOVX @ Ri/@ DPTR
0 - Internal ERAM access using MOVX @ Ri/@ DPTR.
1 - External data memory access.
Disable/Enable ALE)
0 - ALE is emitted at a constant rate of 1/6 the oscillator frequency (or 1/3 if X2
mode is used)
1 - ALE is active only during a MOVX or MOVC instruction.
Reset Value = X001 0100b
Not bit addressable
Table 8. AUXR1 Register
AUXR1 (S:A2h)
Auxiliary Control Register 1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - ENBOOT - GF3 0 - DPS
Bit
Number
7-6 -
5 ENBOOT
4 -
3 GF3
2 0
1 -
0 DPS
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from these bits is indeterminate. Do not set these bits.
Enable Boot Flash
Set this bit for map the boot Flash between F800h -FFFFh
Clear this bit for disable boot Flash.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
General-purpose Flag 3
Always Zero
This bit is stuck to logic 0 to allow INC AUXR1 instruction without affecting GF3
flag.
Reserved for Data Pointer Extension.
Data Pointer Select Bit
Set to select second dual data pointer: DPTR1.
Clear to select first dual data pointer: DPTR0.
28
Reset Value = XXXX 00X0b
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 29
AT89C51CC03
VCC
Power On Reset
Power Fail Detect
Voltage Regulator
XTAL1
(1)
CPU core
Memories
Peripherals
Regulated
Supply
RST pin
Hardware
Watchdog
PCA
Watchdog
Internal Reset
Power Monitor
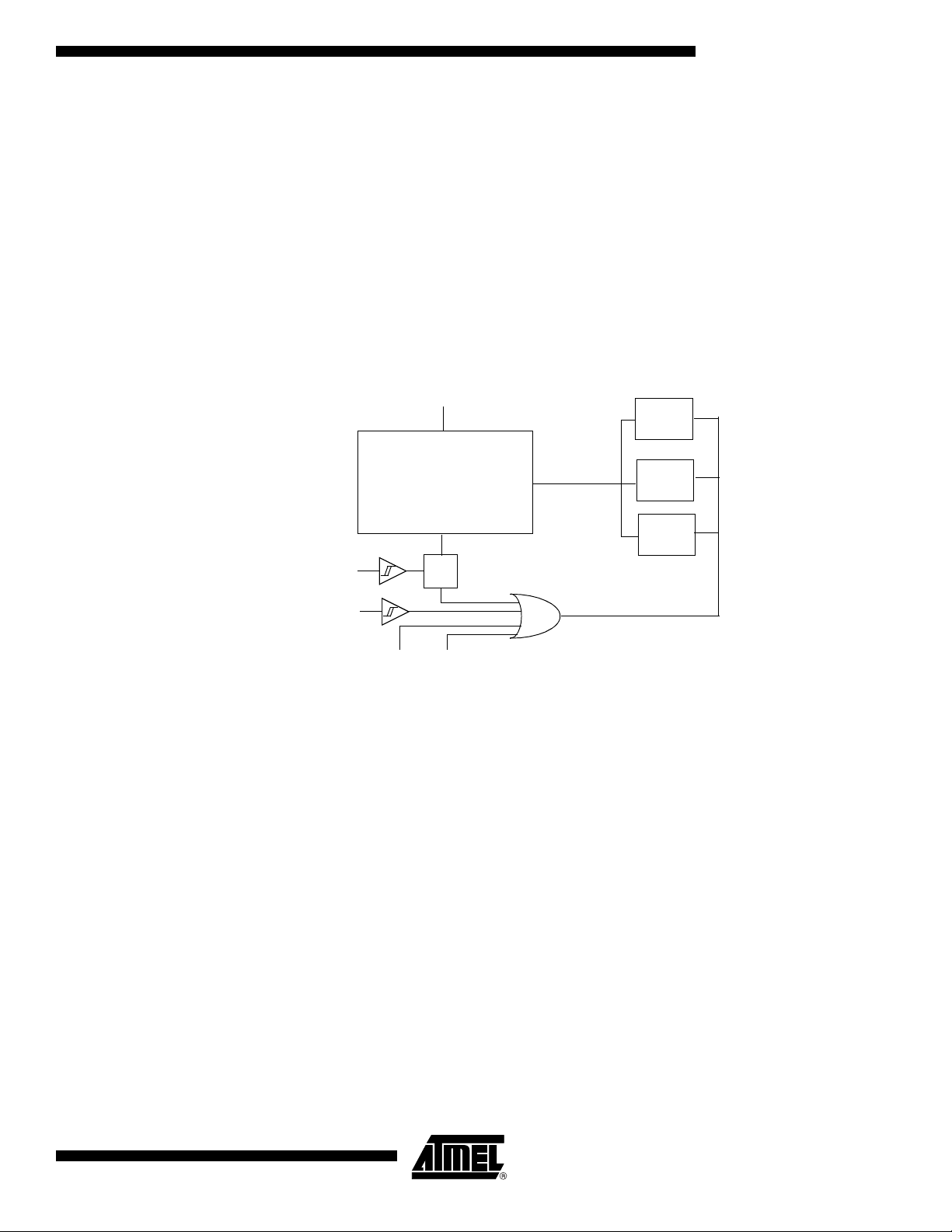
The POR/PFD function monitors the internal power-supply of the CPU core memories
and the peripherals, and if needed, suspends their activity when the internal power supply falls below a safety threshold. This is achieved by applying an internal reset to them.
By ge n e rating t h e R e s e t the Power Monitor insures a c o r r e ct st a r t up when
AT89C51CC03 is powered up.
Description
In order to startup and maintain the microcontroller in correct operating mode, VCC has
to be stabilized in the VCC operating range and the oscillator has to be stabilized with a
nominal amplitude compatible with logic level VIH/VIL.
These parameters are controlled during the three phases: power-up, normal operation
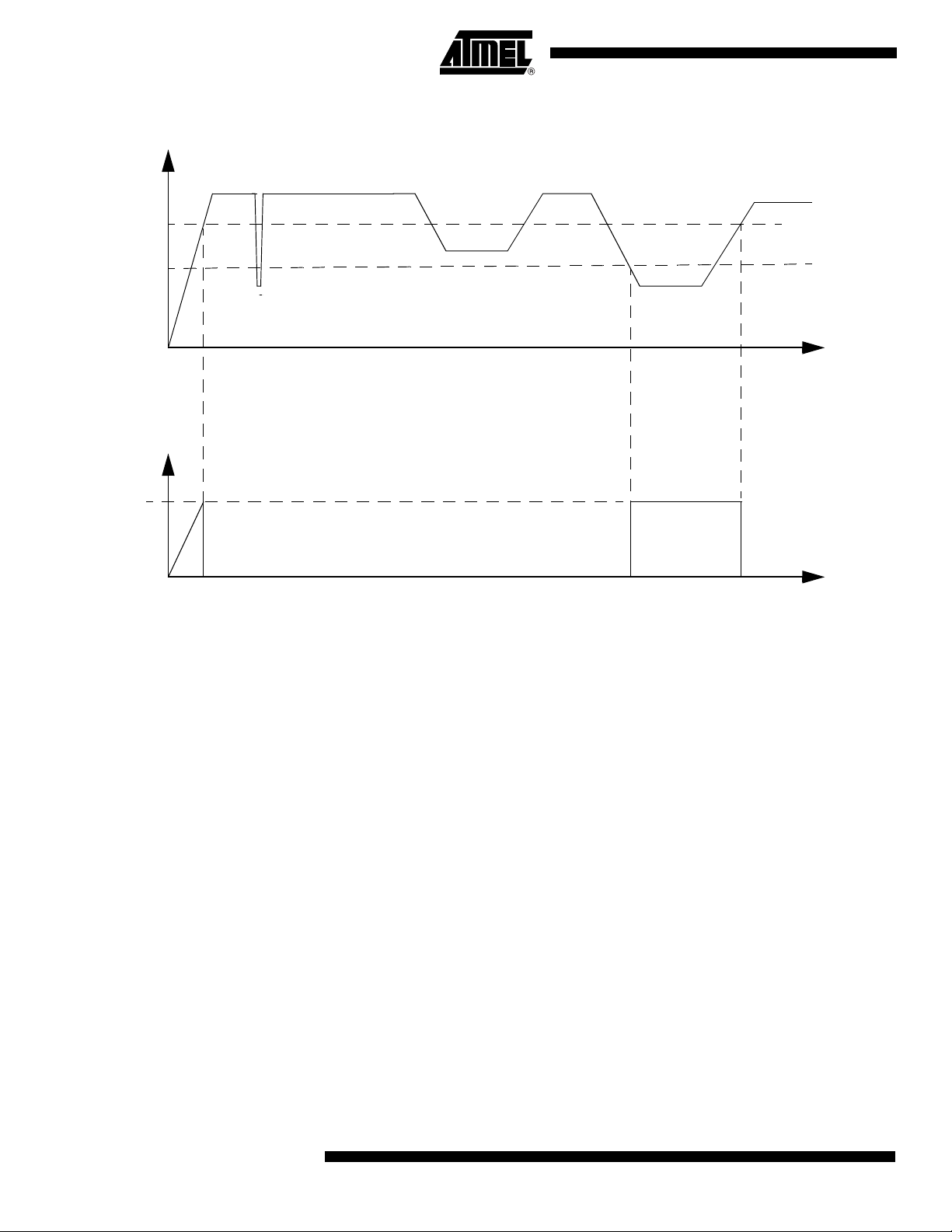
and power going down. See Figure 14.
Figure 14. Power Monitor Block Diagram
Note: 1. Once XTAL1 high and low levels reach above and below VIH/VIL a 1024 clock period
delay will extend the reset coming from the Power Fail Detect. If the power falls below
the Power Fail Detect thresthold level, the reset will be applied immediately.
The Voltage regulator generates a regulated internal supply for the CPU core the memories and the peripherals. Spikes on the external Vcc are smoothed by the voltage
regulator.
The Power fail detect monitor the supply generated by the voltage regulator and generate a reset if this supply falls below a safety threshold as illustrated in the Figure 15.
4182N–CAN–03/08
29
Page 30
AT89C51CC03
Figure 15. Power Fail Detect
Vcc
t
Reset
Vcc
When the power is applied, the Power Monitor immediately asserts a reset. Once the
internal supply after the voltage regulator reach a safety level, the power monitor then
looks at the XTAL clock input. The internal reset will remain asserted until the Xtal1 levels are above and below VIH and VIL. Further more. An internal counter will count 1024
clock periods before the reset is de-asserted.
If the internal power supply falls below a safety level, a reset is immediately asserted.
.
30
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 31

Reset
Power
Monitor
Hardware
Watchdog
PCA
Watchdog
RST
Internal Reset
RST
R
RST
VSS
To internal reset
RST
VDD
+
b. Power-on Reseta. RST input circuitry
AT89C51CC03
Introduction
Reset Input
The reset sources are : Power Management, Hardware Watchdog, PCA Watchdog and
Reset input.
Figure 16. Reset Schematic
The Reset input can be used to force a reset pulse longer than the internal reset controlled by the Power Monitor. RST input has a pull-down resistor allowing power-on
reset by simply connecting an external capacitor to VCC as shown in Figure 17. Resistor
value and input characteristics are discussed in the Section “DC Characteristics” of the
AT89C51CC03 datasheet. The status of the Port pins during reset is detailed in Table 9.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Figure 17. Reset Circuitry and Power-On Reset
31
Page 32

AT89C51CC03
Reset Output
RST
VDD
+
VSS
VDD
RST
1K
To other
on-board
circuitry
AT89C51CC03
As detailed in Section “Watchdog Timer”, page 81, the WDT generates a 96-clock
period pulse on the RST pin. In order to properly propagate this pulse to the rest of the
application in case of external capacitor or power-supply supervisor circuit, a 1 kΩ resistor must be added as shown Figure 18.
Figure 18. Recommended Reset Output Schematic
32
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 33

Power Management
AT89C51CC03
Introduction
Two power reduction modes are implemented in the AT89C51CC03. The Idle mode and
the Power-Down mode. These modes are detailed in the following sections. In addition
to these power reduction modes, the clocks of the core and peripherals can be dynamically divided by 2 using the X2 mode detailed in Section “Clock”, page 17.
Idle Mode
Idle mode is a power reduction mode that reduces the power consumption. In this mode,
program execution halts. Idle mode freezes the clock to the CPU at known states while
the peripherals continue to be clocked. The CPU status before entering Idle mode is
preserved, i.e., the program counter and program status word register retain their data
for the duration of Idle mode. The contents of the
SFRs
and RAM are also retained. The
status of the Port pins during Idle mode is detailed in Table 9.
Entering Idle Mode To enter Idle mode, set the IDL bit in PCON register (see Table 10). The AT89C51CC03
enters Idle mode upon execution of the instruction that sets IDL bit. The instruction that
sets IDL bit is the last instruction executed.
Note: If IDL bit and PD bit are set simultaneously, the AT89C51CC03 enters Power-Down
mode. Then it does not go in Idle mode when exiting Power-Down mode.
Exiting Idle Mode There are two ways to exit Idle mode:
1. Generate an enabled interrupt.
– Hardware clears IDL bit in PCON register which restores the clock to the
CPU. Execution resumes with the interrupt service routine. Upon completion
of the interrupt service routine, program execution resumes with the
instruction immediately following the instruction that activated Idle mode.
The general purpose flags (GF1 and GF0 in PCON register) may be used to
indicate whether an interrupt occurred during normal operation or during Idle
mode. When Idle mode is exited by an interrupt, the interrupt service routine
may examine GF1 and GF0.
2. Generate a reset.
– A logic high on the RST pin clears IDL bit in PCON register directly and
asynchronously. This restores the clock to the CPU. Program execution
momentarily resumes with the instruction immediately following the
instruction that activated the Idle mode and may continue for a number of
clock cycles before the internal reset algorithm takes control. Reset
initializes the AT89C51CC03 and vectors the CPU to address C:0000h.
Power-Down Mode
4182N–CAN–03/08
Note: During the time that execution resumes, the internal RAM cannot be accessed; however,
it is possible for the Port pins to be accessed. To avoid unexpected outputs at the Port
pins, the instruction immediately following the instruction that activated Idle mode should
not write to a Port pin or to the external RAM.
The Power-Down mode places the AT89C51CC03 in a very low power state. PowerDown mode stops the oscillator, freezes all clock at known states. The CPU status prior
to entering Power-Down mode is preserved, i.e., the program counter, program status
word register retain their data for the duration of Power-Down mode. In addition, the
SFR
and RAM contents are preserved. The status of the Port pins during Power-Down mode
is detailed in Table 9.
Note: VCC may be reduced to as low as V
power dissipation. Take care, however, that VDD is not reduced until Power-Down mode
is invoked.
during Power-Down mode to further reduce
RET
33
Page 34

AT89C51CC03
Entering Power-Down Mode To enter Power-Down mode, set PD bit in PCON register. The AT89C51CC03 enters
INT1:0#
OSC
Power-down phase Oscillator restart phase Active phaseActive phase
the Power-Down mode upon execution of the instruction that sets PD bit. The instruction
that sets PD bit is the last instruction executed.
Exiting Power-Down Mode
Note: If VCC was reduced during the Power-Down mode, do not exit Power-Down mode until
VCC is restored to the normal operating level.
There are two ways to exit the Power-Down mode:
1. Generate an enabled external interrupt.
– The AT89C51CC03 provides capability to exit from Power-Down using
INT0#, INT1#.
Hardware clears PD bit in PCON register which starts the oscillator and
restores the clocks to the CPU and peripherals. Using INTx# input,
execution resumes when the input is released (see Figure 19). Execution
resumes with the interrupt service routine. Upon completion of the interrupt
service routine, program execution resumes with the instruction immediately
following the instruction that activated Power-Down mode.
Note: The external interrupt used to exit Power-Down mode must be configured as level sensi-
tive (INT0# and INT1#) and must be assigned the highest priority. In addition, the
duration of the interrupt must be long enough to allow the oscillator to stabilize. The execution will only resume when the interrupt is deasserted.
Note: Exit from power-down by external interrupt does not affect the
content.
SFRs
nor the internal RAM
Figure 19. Power-Down Exit Waveform Using INT1:0#
2. Generate a reset.
– A logic high on the RST pin clears PD bit in PCON register directly and
asynchronously. This starts the oscillator and restores the clock to the CPU
and peripherals. Program execution momentarily resumes with the
instruction immediately following the instruction that activated Power-Down
mode and may continue for a number of clock cycles before the internal
reset algorithm takes control. Reset initializes the AT89C51CC03 and
vectors the CPU to address 0000h.
Note: During the time that execution resumes, the internal RAM cannot be accessed; however,
it is possible for the Port pins to be accessed. To avoid unexpected outputs at the Port
pins, the instruction immediately following the instruction that activated the Power-Down
mode should not write to a Port pin or to the external RAM.
Note: Exit from power-down by reset redefines all the
RAM content.
SFRs
, but does not affect the internal
34
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 35

AT89C51CC03
Table 9. Pin Conditions in Special Operating Modes
Mode Port 0 Port 1 Port 2 Port 3 Port 4 ALE PSEN#
Reset Floating High High High High High High
Idle
(internal
code)
Idle
(external
code)
Power-
Down(inter
nal code)
Power-
Down
(external
code)
Data Data Data Data Data High High
Floating Data Data Data Data High High
Data Data Data Data Data Low Low
Floating Data Data Data Data Low Low
4182N–CAN–03/08
35
Page 36

AT89C51CC03
Registers
Table 10. PCON Register
PCON (S87:h) Power configuration Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - GF1 GF0 PD IDL
Bit
Number
7-4 -
3 GF1
2 GF0
1 PD
0 IDL
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from these bits is indeterminate. Do not set these bits.
General Purpose flag 1
One use is to indicate whether an interrupt occurred during normal operation or
during Idle mode.
General Purpose flag 0
One use is to indicate whether an interrupt occurred during normal operation or
during Idle mode.
Power-Down Mode bit
Cleared by hardware when an interrupt or reset occurs.
Set to activate the Power-Down mode.
If IDL and PD are both set, PD takes precedence.
Idle Mode bit
Cleared by hardware when an interrupt or reset occurs.
Set to activate the Idle mode.
If IDL and PD are both set, PD takes precedence.
Reset Value= XXXX 0000b
36
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 37

AT89C51CC03
EEPROM Data Memory
Write Data in the Column Latches
The 2-Kbyte on-chip EEPROM memory block is located at addresses 0000h to 07FFh of
the XRAM/ERAM memory space and is selected by setting control bits in the EECON
register. A read in the EEPROM memory is done with a MOVX instruction.
A physical write in the EEPROM memory is done in two steps: write data in the column
latches and transfer of all data latches into an EEPROM memory row (programming).
The number of data written on the page may vary from 1 up to 128 Bytes (the page
size). When programming, only the data written in the column latch is programmed and
a ninth bit is used to obtain this feature. This provides the capability to program the
whole memory by Bytes, by page or by a number of Bytes in a page. Indeed, each ninth
bit is set when the writing the corresponding byte in a row and all these ninth bits are
reset after the writing of the complete EEPROM row.
Data is written by byte to the column latches as for an external RAM memory. Out of the
11 address bits of the data pointer, the 4 MSBs are used for page selection (row) and 7
are used for byte selection. Between two EEPROM programming sessions, all the
addresses in the column latches must stay on the same page, meaning that the 4 MSB
must no be changed.
The following procedure is used to write to the column latches:
• Save and disable interrupt.
• Set bit EEE of EECON register
• Load DPTR with the address to write
• Store A register with the data to be written
• Execute a MOVX @DPTR, A
• If needed loop the three last instructions until the end of a 128 Bytes page
• Restore interrupt.
Note: The last page address used when loading the column latch is the one used to select the
page programming address.
Programming
Read Data
4182N–CAN–03/08
The EEPROM programming consists of the following actions:
• writing one or more Bytes of one page in the column latches. Normally, all Bytes
must belong to the same page; if not, the first page address will be latched and the
others discarded.
• launching programming by writing the control sequence (50h followed by A0h) to the
EECON register.
• EEBUSY flag in EECON is then set by hardware to indicate that programming is in
progress and that the EEPROM segment is not available for reading.
• The end of programming is indicated by a hardware clear of the EEBUSY flag.
Note: The sequence 5xh and Axh must be executed without instructions between then other-
wise the programming is aborted.
The following procedure is used to read the data stored in the EEPROM memory:
• Save and disable interrupt
• Set bit EEE of EECON register
• Load DPTR with the address to read
• Execute a MOVX A, @DPTR
• Restore interrupt
37
Page 38

AT89C51CC03
Examples
;*F*************************************************************************;* NAME: api_rd_eeprom_byte
;* DPTR contain address to read.
;* Acc contain the reading value
;* NOTE: before execute this function, be sure the EEPROM is not BUSY
;***************************************************************************
api_rd_eeprom_byte:
MOV EECON, #02h; map EEPROM in XRAM space
MOVX A, @DPTR
MOV EECON, #00h; unmap EEPROM
ret
;*F*************************************************************************
;* NAME: api_ld_eeprom_cl
;* DPTR contain address to load
;* Acc contain value to load
;* NOTE: in this example we load only 1 byte, but it is possible upto
;* 128 Bytes.
;* before execute this function, be sure the EEPROM is not BUSY
;***************************************************************************
api_ld_eeprom_cl:
MOV EECON, #02h ; map EEPROM in XRAM space
MOVX @DPTR, A
MOVEECON, #00h; unmap EEPROM
ret
;*F*************************************************************************
;* NAME: api_wr_eeprom
;* NOTE: before execute this function, be sure the EEPROM is not BUSY
;***************************************************************************
api_wr_eeprom:
MOV EECON, #050h
MOV EECON, #0A0h
ret
38
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 39

AT89C51CC03
Registers
Table 11. EECON Register
EECON (S:0D2h)
EEPROM Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
EEPL3 EEPL2 EEPL1 EEPL0 - - EEE EEBUSY
Bit
Bit Number
7-4 EEPL3-0
3 -
2 -
1 EEE
0 EEBUSY
Mnemonic Description
Programming Launch command bits
Write 5Xh followed by AXh to EEPL to launch the programming.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Enable EEPROM Space bit
Set to map the EEPROM space during MOVX instructions (Write in the column
latches)
Clear to map the XRAM space during MOVX.
Programming Busy flag
Set by hardware when programming is in progress.
Cleared by hardware when programming is done.
Can not be set or cleared by software.
Reset Value = XXXX XX00b
Not bit addressable
4182N–CAN–03/08
39
Page 40

AT89C51CC03
Program/Code
0000h
64K Bytes
FFFFh
internal
0000h
FFFFh
Flash
64K Bytes
external
memory
EA = 0
EA = 1
Memory
The AT89C51CC03 implement 64K Bytes of on-chip program/code memory. Figure 20
shows the partitioning of internal and external program/code memory spaces depending
on the product.
The Flash memory increases EPROM and ROM functionality by in-circuit electrical erasure and programming. Thanks to the internal charge pump, the high voltage needed for
programming or erasing Flash cells is generated on-chip using the standard VDD voltage. Thus, the Flash Memory can be programmed using only one voltage and allows InSystem Programming commonly known as ISP. Hardware programming mode is also
available using specific programming tool.
Figure 20. Program/Code Memory Organization
40
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 41

AT89C51CC03
Flash
EPROM
AT89C51CC0
P2
P0
AD7:0
A15:8
A7:0
A15:8
D7:0
A7:0
ALE
Latch
OEPSEN#
External Code Memory Access
Memory Interface The external memory interface comprises the external bus (port 0 and port 2) as well as
the bus control signals (PSEN#, and ALE).
Figure 21 shows the structure of the external address bus. P0 carries address A7:0
while P2 carries address A15:8. Data D7:0 is multiplexed with A7:0 on P0. Table 21
describes the external memory interface signals.
Figure 21. External Code Memory Interface Structure
Table 12. External Code Memory Interface Signals
Signal
Name Type Description
A15:8 O
AD7:0 I/O
ALE O
PSEN# O
Address Lines
Upper address lines for the external bus.
Address/Data Lines
Multiplexed lower address lines and data for the external memory.
Address Latch Enable
ALE signals indicates that valid address information are available on lines
AD7:0.
Program Store Enable Output
This signal is active low during external code fetch or external code read
(MOVC instruction).
Alternate
Function
P2.7:0
P0.7:0
-
-
External Bus Cycles This section describes the bus cycles the AT89C51CC03 executes to fetch code (see
Figure 22) in the external program/code memory.
External memory cycle takes 6 CPU clock periods. This is equivalent to 12 oscillator
clock period in standard mode or 6 oscillator clock periods in X2 mode. For further information on X2 mode see section “Clock “.
For simplicity, the accompanying figure depicts the bus cycle waveforms in idealized
form and do not provide precise timing information.
For bus cycling parameters refer to the ‘AC-DC parameters’ section.
4182N–CAN–03/08
41
Page 42
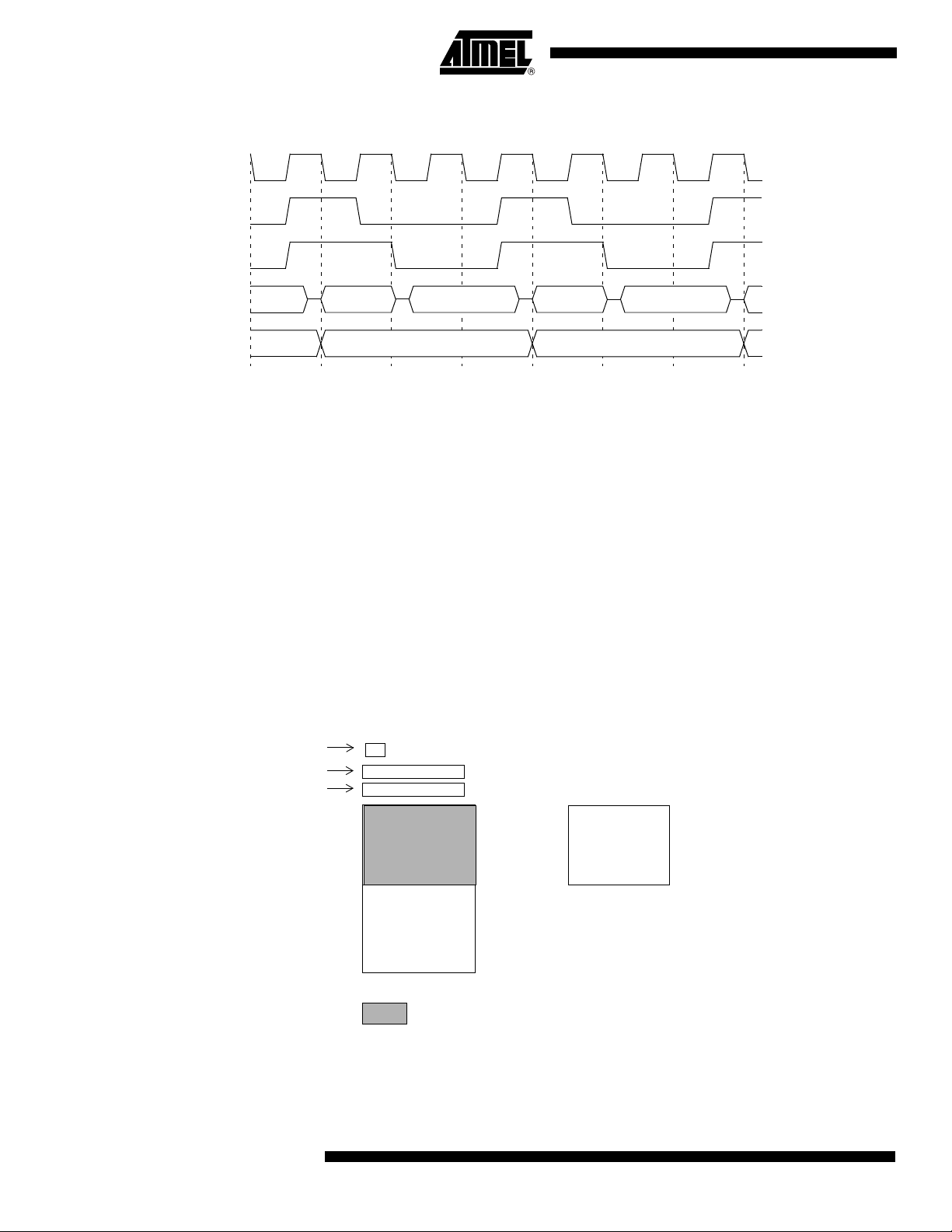
AT89C51CC03
Figure 22. External Code Fetch Waveforms
ALE
P0
P2
PSEN#
PCL
PCHPCH
PCLD7:0 D7:0
PCH
D7:0
CPU Clock
FFFFh
64K Bytes
FM0
0000h
Hardware Security (1 byte)
Column Latches (128 Bytes)
Extra Row (128 Bytes)
2K Bytes
Flash memory
FM1
boot space
FFFFh
F800h
FM1 mapped between FFFFh and
F800h when bit ENBOOT is set in
AUXR1 register
F800h
Memory space not accessible
Flash Memory Architecture
AT89C51CC03 features two on-chip Flash memories:
• Flash memory FM0:
containing 64K Bytes of program memory (user space) organized into 128 byte
pages,
• Flash memory FM1:
2K Bytes for boot loader and Application Programming Interfaces (API).
The FM0 can be program by both parallel programming and Serial In-System Programming (ISP) whereas FM1 supports only parallel programming by programmers. The ISP
mode is detailed in the "In-System Programming" section.
All Read/Write access operations on Flash Memory by user application are managed by
a set of API described in the "In-System Programming" section.
The bit ENBOOT in AUXR1 register is used to map FM1 from F800h to FFFFh. Figure
23 and F i gure 24 show the Flash memory configu ra tion with ENBO O T=1 and
ENBOOT=0.
Figure 23. Flash Memory Architecture with ENBOOT=1 (boot mode)
42
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 43

Figure 24. Flash Memory Architecture with ENBOOT=0 (user modemode)
FFFFh
64K Bytes
FM0
0000h
Hardware Security (1 byte)
Column Latches (128 Bytes)
Extra Row (128 Bytes)
2K Bytes
Flash memory
FM1
boot space
FFFFh
F800h
FM1 mapped between FFFFh and
F800h when bit ENBOOT is set in
AUXR1 register
F800h
Memory space not accessible
AT89C51CC03
4182N–CAN–03/08
43
Page 44

AT89C51CC03
FM0 Memory Architecture The Flash memory is made up of 4 blocks (see Figure 23):
• The memory array (user space) 64K Bytes
• The Extra Row
• The Hardware security bits
• The column latch registers
User Space This space is composed of a 64K Bytes Flash memory organized in 512 pages of 128
Bytes. It contains the user’s application code.
Extra Row (XRow) This row is a part of FM0 and has a size of 128 Bytes. The extra row may contain infor-
mation for boot loader usage.
Hardware security Byte (HSB) The Hardware security Byte space is a part of FM0 and has a size of 1 byte.
The 4 MSB can be read/written by software (from FM0 and , the 4 LSB can only be read
by software and written by hardware in parallel mode.
H Hardware Security Byte (HSB)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
X2 BLJB - - - LB2 LB1 LB0
Bit
Number
7 X2
6 BLJB
5 -
4 -
3 -
2-0 LB2-0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
X2 Mode
Programmed (=’0’) to force X2 mode (6 clocks per instruction) after reset
Unprogrammed to force X1 mode, Standard Mode, afetr reset (Default)
Boot Loader Jump Bit
When unprogrammed (=’1’), at the next reset :
-ENBOOT=0 (see code space memory configuration)
-Start address is 0000h (PC=0000h)
When programmed (=’0’)at the nex reset:
-ENBOOT=1 (see code space memory configuration)
-Start address is F800h (PC=F800h)
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
General Memory Lock Bits (only programmable by programmer tools)
Section “Flash Protection from Parallel Programming”, page 53
Column Latches The column latches, also part of FM0, have a size of full page (128 Bytes).
The column latches are the entrance buffers of the three previous memory locations
(user array, XROW and Hardware security byte). The column latches are write only and
can be accessed only from FM1 (boot mode) and from external memory
Cross Flash Memory Access
Description
44
The FM0 memory can be program only from FM1. Programming FM0 from FM0 or from
external memory is impossible.
The FM1 memory can be program only by parallel programming.
The Table show all software Flash access allowed.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 45

Cross Flash Memory Access
AT89C51CC03
Action
Read ok -
Load column latch ok -
Write - -
Read ok ok
Load column latch ok -
Write ok -
Read (a) -
Load column latch - -
Write - -
(user Flash)
(boot Flash)
Code executing from
FM0
FM1
External
memory
EA = 0
(a) Depend upon general lock bit configuration.
FM0
(user Flash)
FM1
(boot Flash)
4182N–CAN–03/08
45
Page 46

AT89C51CC03
Overview of FM0 Operations
Flash Registers (SFR)
FCON Register
The CPU interfaces to the flash memory through the FCON register, AUXR1 register
and FSTA register.
These registers are used to map the column latches, HSB, extra row and EEDATA in
the working data or code space.
Table 13. FCON Register
FCON Register (S:D1h)
Flash Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FPL3 FPL2 FPL1 FPL0 FPS FMOD1 FMOD0 FBUSY
Bit
Number
7-4 FPL3:0
3 FPS
2-1 FMOD1:0
0 FBUSY
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Programming Launch Command Bits
Write 5Xh followed by AXh to launch the programming according to FMOD1:0.
(see Table 16.)
Flash Map Program Space
When this bit is set:
The MOVX @DPTR, A instruction writes in the columns latches space
When this bit is cleared:
The MOVX @DPTR, A instruction writes in the regular XDATA memory space
Flash Mode
See Table 16.
Flash Busy
Set by hardware when programming is in progress.
Clear by hardware when programming is done.
Can not be changed by software.
Reset Value= 0000 0000b
46
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 47

FSTA Register
AT89C51CC03
Table 14. FSTA Register
FSTA Register (S:D3h)
Flash Status Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SEQERR FLOAD
Bit
Number
7-2
1 SEQERR
0 FLOAD
Bit
Mnemonic Description
unusesd
Flash activation sequence error
Set by hardware when the flash activation sequence(MOV FCON 5X and MOV
FCON AX )is not correct (See Error Repport Section)
Clear by software or clear by hardware if the last activation sequence was
correct (previous error are canceled)
Flash Colums latch loaded
Set by hardware when the first data is loaded in the column latches.
Clear by hardware when the activation sequence suceed (flash write sucess, or
reset column latch success)
Reset Value= 0000 0000b
Mapping of the Memory Space By default, the user space is accessed by MOVC A, @DPTR instruction for read only.
The column latches space is made accessible by setting the FPS bit in FCON register.
Writing is possible from 0000h to FFFFh, address bits 6 to 0 are used to select an
address within a page while bits 15 to 7 are used to select the programming address of
the page.
Setting FPS bit takes precedence on the EXTRAM bit in AUXR register.
The other memory spaces (user, extra row, hardware security) are made accessible in
the code segment by programming bits FMOD0 and FMOD1 in FCON register in accordance with Table 15. A MOVC instruction is then used for reading these spaces.
Table 15. FM0 Blocks Select Bits
FMOD1 FMOD0 FM0 Adressable space
0 0 User (0000h-FFFFh)
0 1 Extra Row(FF80h-FFFFh)
1 0 Hardware Security Byte (0000h)
1 1 Column latches reset (note1)
Notes: 1. The column latches reset is a new option introduced in the AT89C51CC03, and is not
available in T89C51CC01/2
Launching Programming FPL3:0 bits in FCON register are used to secure the launch of programming. A specific
sequence must be written in these bits to unlock the write protection and to launch the
programming. This sequence is 5xh followed by Axh. Table 16 summarizes the memory
spaces to program according to FMOD1:0 bits.
47
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 48

AT89C51CC03
Table 16. Programming Spaces
Write to FCON
5 X 0 0 No action
OperationFPL3:0 FPS FMOD1 FMOD0
Write the column latches in user
space
Write the column latches in extra row
space
User
Extra Row
Hardware
Security
Byte
Reset
Columns
Latches
A X 0 0
5 X 0 1 No action
A X 0 1
5 X 1 0 No action
A X 1 0 Write the fuse bits space
5 X 1 1 No action
A X 1 1 Reset the column latches
Notes: 1. The sequence 5xh and Axh must be executing without instructions between them
otherwise the programming is not executed (see Flash Status Register)
2. The sequence 5xh and Axh must be executed with the same FMOD0 FMOD1
configuration.
3. Interrupts that may occur during programming time must be disabled to avoid any
spurious exit of the programming mode.
Status of the Flash Memory The bit FBUSY in FCON register is used to indicate the status of programming.
FBUSY is set when programming is in progress.
The flash programming process is launched the second machine cycle following the
sequence 5xh and Axh in FCON. Thus the FBUSY flag should be read by sofware not
during the insctruction after the 5xh, Axh sequence but the the second instruction after
the 5xh, Axh sequence in FCON (See next example). FBUSY is cleared when the programming is completed.
;*F*************************************************************************
;* NAME: launch_prog
;;***************************************************************************
launch_prog:
MOV FCON, #050h
MOV FCON #0A0h ; Flash Write Sequence
NOP ;Required time before reading busy flag
wait_busy:
MOV A,FCON
JB ACC.0,wait_busy
RET
Selecting FM1 The bit ENBOOT in AUXR1 register is used to map FM1 from F800h to FFFFh.
Loading the Column Latches Any number of data from 1-byte to 128 Bytes can be loaded in the column latches. This
provides the capability to program the whole memory by byte, by page or by any number
of Bytes in a page. Data written in the column latches do not have to be in consecutive
48
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 49

AT89C51CC03
order. The page address of the last address loaded in the column latches will be used
for the whole page.
When programming is launched, an automatic erase of the locations loaded in the column latches is first performed, then programming is effectively done. Thus no page or
block erase is needed and only the loaded data are programmed in the corresponding
page
Notes: 1. : If no bytes are written in the column latches the SEQERR bit in the FSTA register
will be set.
2. When a flash write sequence is in progress (FBUSY is set) a write sequence to the
column latches will be ignored and the content of the column latches at the time of
the launch write sequence will be preserved.
3. MOVX @DPTR, A instruction must be used to load the column latches. Never use
MOVX @Ri, A instructions.
4. When a programming sequence is launched, Flash bytes corresponding to activated
bytes in the column latches are first erased then the bytes in the column latches are
copied into the Flash bytes. Flash bytes corresponding to bytes in the column latches
not activated (not loaded during the load column latches sequence) will not be erased
and written.
The following procedure is used to load the column latches and is summarized in
Figure 25:
• Save and Disable interrupt and map the column latch space by setting FPS bit.
• Load the DPTR with the address to load.
• Load Accumulator register with the data to load.
• Execute the MOVX @DPTR, A instruction.
• If needed loop the three last instructions until the page is completely loaded.
• unmap the column latch.
• Restore Interrupt
4182N–CAN–03/08
49
Page 50

AT89C51CC03
Figure 25. Column Latches Loading Procedure
Column Latches
Loading
Data Load
DPTR = Address
ACC = Data
Exec: MOVX @DPTR, A
Last Byte
to load?
Column Latches Mapping
FCON = 08h (FPS=1)
Data memory Mapping
FCON = 00h (FPS = 0)
Save and Disable IT
EA = 0
Restore IT
Note: The last page address used when loading the column latch is the one used to select the
page programming address.
Programming the Flash Spaces
User The following procedure is used to program the User space and is summarized in
Figure 26:
• Load up to one page of data in the column latches from address 0000h to FFFFh.
• Save and Disable the interrupts.
• Launch the programming by writing the data sequence 50h followed by A0h in
FCON register (only from FM1).
The end of the programming indicated by the FBUSY flag cleared.
• Restore the interrupts.
Extra Row The following procedure is used to program the Extra Row space and is summarized in
Figure 26:
• Load data in the column latches from address FF80h to FFFFh.
• Save and Disable the interrupts.
• Launch the programming by writing the data sequence 52h followed by A2h in
FCON register (only from FM1).
The end of the programming indicated by the FBUSY flag cleared.
• Restore the interrupts.
50
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 51

Figure 26. Flash and Extra Row Programming Procedure
Flash Spaces
Programming
Save and Disable IT
EA = 0
Launch Programming
FCON = 5xh
FCON = Axh
End Programming
Restore IT
Column Latches Loading
see Figure 25
FBusy
Cleared?
Clear Mode
FCON = 00h
AT89C51CC03
Hardware Security Byte
The following procedure is used to program the Hardware
Security
Byte space
and is summarized in Figure 27:
• Set FPS and map Hardware byte (FCON = 0x0C)
• Save and disable the interrupts.
• Load DPTR at address 0000h.
• Load Accumulator register with the data to load.
• Execute the MOVX @DPTR, A instruction.
• Launch the programming by writing the data sequence 54h followed by A4h in
FCON register (only from FM1).
The end of the programming indicated by the FBusy flag cleared.
• Restore the interrupts.
4182N–CAN–03/08
51
Page 52

AT89C51CC03
Figure 27. Hardware Programming Procedure
Flash Spaces
Programming
Save and Disable IT
EA = 0
Launch Programming
FCON = 54h
FCON = A4h
End Programming
RestoreIT
FBusy
Cleared?
Clear Mode
FCON = 00h
Data Load
DPTR = 00h
ACC = Data
Exec: MOVX @DPTR, A
FCON = 0Ch
Save and Disable IT
EA = 0
End Loading
Restore IT
Reset the Column Latches
Error Reports
Flash Programming Sequence
Errors
An automatic reset of the column latches is performed after a successful Flash
write sequence. User can also reset the column latches manually, for instance
to reload the column latches before writing the Flash. The following procedure is
summarized below.
• Save and disable the interrupts.
• Launch the reset by writing the data sequence 56h followed by A6h in FCON
register (only from FM1).
• Restore the interrupts.
When a wrong sequence is detected, the SEQERR bit in FSTA register is set. Possible
wrong sequence are :
• MOV FCON, 5xh instruction not immediately followed by a MOV FCON, Ax
instruction.
• A write Flash sequence is launched while no data were loaded in the column latches
The SEQERR bit can be cleared
• By software
• By hardware when a correct programming sequence is completed
When multiple pages are written into the Flash, the user should check FSTA for errors
after each write page sequences, not only at the end of the multiple write pages.
52
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 53

AT89C51CC03
Flash Spaces Reading
Flash Spaces Mapping
FCON= 00000xx0b
Data Read
DPTR= Address
ACC= 0
Exec: MOVC A, @A+DPTR
Clear Mode
FCON = 00h
Power Down Request Before entering in Power Down (Set bit PD in PCON register) the user should check that
no write sequence is in progress (check BUSY=0), then check that the column latches
are reset (FLOAD=0 in FSTA register. Launch a reset column latches to clear FLOAD if
necessary.
Reading the Flash Spaces
User The following procedure is used to read the User space:
• Read one byte in Accumulator by executing MOVC A,@A+DPTR with
A+DPTR=read@.
Note: FCON is supposed to be reset when not needed.
Extra Row The following procedure is used to read the Extra Row space and is summarized in
Figure 28:
• Map the Extra Row space by writing 02h in FCON register.
• Read one byte in Accumulator by executing MOVC A,@A+DPTR with A = 0 and
DPTR = FF80h to FFFFh.
• Clear FCON to unmap the Extra Row.
Hardware Security Byte
The following procedure is used to read the Hardware
Security
space and is
summarized in Figure 28:
• Map the Hardware Security space by writing 04h in FCON register.
• Read the byte in Accumulator by executing MOVC A,@A+DPTR with A = 0 and
DPTR = 0000h.
Figure 28. Clear FCON to unmap the Hardware Security Byte.Reading Procedure
Flash Protection from Parallel
Programming
4182N–CAN–03/08
The three lock bits in Hardware Security Byte (see "In-System Programming" section)
are programmed according to Table 17 provide different level of protection for the onchip code and data located in FM0 and FM1.
The only way to write this bits are the parallel mode. They are set by default to level 4
53
Page 54
AT89C51CC03
Table 17. Program Lock Bit
Program Lock Bits
Security
level
1 U U U No program lock features enabled.
2 P U U
3 U P U
4 U U P Same as 3, also external execution is disabled
LB0 LB1 LB2
Protection Description
MOVC instruction executed from external program memory are
disabled from fetching code bytes from internal memory, EA is sampled
and latched on reset, and further parallel programming of the Flash is
disabled.
ISP and software programming with API are still allowed.
Writing EEprom Data from external parallel programmer is disabled but
still allowed from internal code execution.
Same as 2, also verify through parallel programming interface is
disabled.
Writing And Reading EEPROM Data from external parallel programmer
is disabled but still allowed from internal code execution..
Program Lock bits
U: unprogrammed
P: programmed
WARNING: Security level 2 and 3 should only be programmed after Flash and Core
verification.
54
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 55

Operation Cross Memory Access
Space addressable in read and write are:
• RAM
• ERAM (Expanded RAM access by movx)
• XRAM (eXternal RAM)
• EEPROM DATA
• FM0 ( user flash )
• Hardware byte
• XROW
• Boot Flash
• Flash Column latch
The table below provide the different kind of memory which can be accessed from different code location.
Table 18. Cross Memory Access
AT89C51CC03
Action RAM
boot FLASH
FM0
External memory
EA = 0
or Code Roll Over
Read OK OK OK OK -
Write - OK
Read OK OK OK OK -
Write - OK (idle) OK
Read - - OK - -
Write - - OK
Note: 1. RWW: Read While Write
XRAM
ERAM Boot FLASH FM0 E² Data
(1)
OK
(1)
(1)
(1)
Hardware
Byte XROW
(1)
OK
- OK
- -
OK
(1)
4182N–CAN–03/08
55
Page 56

AT89C51CC03
Sharing Instructions
Table 19. Instructions shared
XRAM
Action RAM
Read MOV MOVX MOVX MOVC MOVC MOVC MOVC
Write MOV MOVX MOVX - by cl by cl by cl
ERAM
EEPROM
DATA
Boot
FLASH FM0
Hardware
Byte XROW
Note: by cl : using Column Latch
Table 20. Read MOVX A, @DPTR
EEE bit in
EECON
Register
0 0 X X OK
0 1 X X OK
1 0 X X OK
1 1 X X OK
FPS in
FCON Register ENBOOT EA
XRAM
ERAM
EEPROM
DATA
Table 21. Write MOVX @DPTR,A
EEE bit in
EECON
Register
FPS bit in
FCON Register ENBOOT EA
XRAM
ERAM
EEPROM
Data
Flash
Column
Latch
Flash
Column
Latch
0 0 X X OK
0 1 X
1 0 X X OK
1 1 X
1 OK
0 OK
1 OK
0 OK
56
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 57

Table 22. Read MOVC A, @DPTR
AT89C51CC03
Code Execution
From FM0
From FM1
(ENBOOT =1
FCON Register
ENBOOT DPTR FM1 FM0 XROW
0 0000h to FFFFh OK
0 0 X
0 1 X X
1 0 X X X OK
1 1 X
0
0 0
1
0 1 X
1
0 000h to FFFFh OK
1
1
0 X NA
1 X OK
0 X NA
1
0 NA
0000h to F7FF OK
F800h to FFFFh Do not use this configuration
0000 to 007Fh
(1)
See
0000h to F7FF OK
F800h to FFFFh Do not use this configuration
0000h to F7FF OK
F800h to FFFFh OK
0000h to 007h
(2)
See
OK
OK
Hardware
Byte
External
CodeFMOD1 FMOD0 FPS
External code :
EA=0 or Code
Roll Over
1 0 X
1 1 X
X 0 X X X OK
1
0 NA
1
0 NA
X
OK
000h to FFFFh
OK
1. For DPTR higher than 007Fh only lowest 7 bits are decoded, thus the behavior is the same as for addresses from 0000h to
007Fh
2. For DPTR higher than 007Fh only lowest 7 bits are decoded, thus the behavior is the same as for addresses from 0000h to
007Fh
4182N–CAN–03/08
57
Page 58
AT89C51CC03
In-System
F800h
FFFFh
64K Bytes
Flash memory
2K Bytes IAP
bootloader
FM0
FM1
Custom
Boot Loader
[SBV]00h
FFFFh
FM1 mapped between F800h and FFFFh
when API called
0000h
Programming (ISP)
With the implementation of the User Space (FM0) and the Boot Space (FM1) in Flash
technology the AT89C51CC03 allows the system engineer the development of applications with a very high level of flexibility. This flexibility is based on the possibility to alter
the customer program at any stages of a product’s life:
• Before assembly the 1st personalization of the product by programming in the FM0
and if needed also a customized Boot loader in the FM1.
Atmel provide also a standard Boot loader by default UART or CAN.
• After assembling on the PCB in its final embedded position by serial mode via the
CAN bus or UART.
This In-System Programming (ISP) allows code modification over the total lifetime of the
product.
Besides the default Boot loader Atmel provide to the customer also all the needed Application-Programming-Interfaces (API) which are needed for the ISP. The API are located
also in the Boot memory.
This allow the customer to have a full use of the 64-Kbyte user memory.
Flash Programming and Erasure
There are three methods of programming the Flash memory:
• The Atmel bootloader located in FM1 is activated by the application. Low level API
routines (located in FM1)will be used to program FM0. The interface used for serial
downloading to FM0 is the UART or the CAN. API can be called also by the user’s
bootloader located in FM0 at [SBV]00h.
• A further method exists in activating the Atmel boot loader by hardware activation.
• The FM0 can be programmed also by the parallel mode using a programmer.
Figure 29. Flash Memory Mapping
Boot Process
Software Boot Process
Example
58
Many algorithms can be used for the software boot process. Before describing them,
The description of the different flags and Bytes is given below:
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 59

AT89C51CC03
Boot Loader Jump Bit (BLJB):
- This bit indicates if on RESET the user wants to jump to this application at address
@0000h on FM0 or execute the boot loader at address @F800h on FM1.
- BLJB = 0 on parts delivered with bootloader programmed.
- To read or modify this bit, the APIs are used.
Boot Vector Address (SBV):
- This byte contains the MSB of the user boot loader address in FM0.
- The default value of SBV is FCh (no user boot loader in FM0).
- To read or modify this byte, the APIs are used.
Extra Byte (EB) and Boot Status Byte (BSB):
- These Bytes are reserved for customer use.
- To read or modify these Bytes, the APIs are used.
Hardware Boot Process At the falling edge of RESET, the bit ENBOOT in AUXR1 register is initialized with the
value of Boot Loader Jump Bit (BLJB).
Further at the falling edge of RESET if the following conditions (called Hardware condition) are detected:
• PSEN low,
• EA high,
• ALE high (or not connected).
– After Hardware Condition the FCON register is initialized with the value 00h
and the PC is initialized with F800h (FM1).
The Hardware condition makes the bootloader to be executed, whatever BLJB value is.
If no hardware condition is detected, the FCON register is initialized with the value F0h.
Check of the BLJB value.
• If bit BLJB = 1:
User application in FM0 will be started at @0000h (standard reset).
• If bit BLJB = 0:
Boot loader will be started at @F800h in FM1.
Note: 1. As PSEN is an output port in normal operating mode (running user applications or
bootloader applications) after reset it is recommended to release PSEN after the falling edge of Reset is signaled.
The hardware conditions are sampled at reset signal Falling Edge, thus they can be
released at any time when reset input is low.
2. To ensure correct microcontroller startup, the PSEN pin should not be tied to ground
during power-on.
4182N–CAN–03/08
59
Page 60
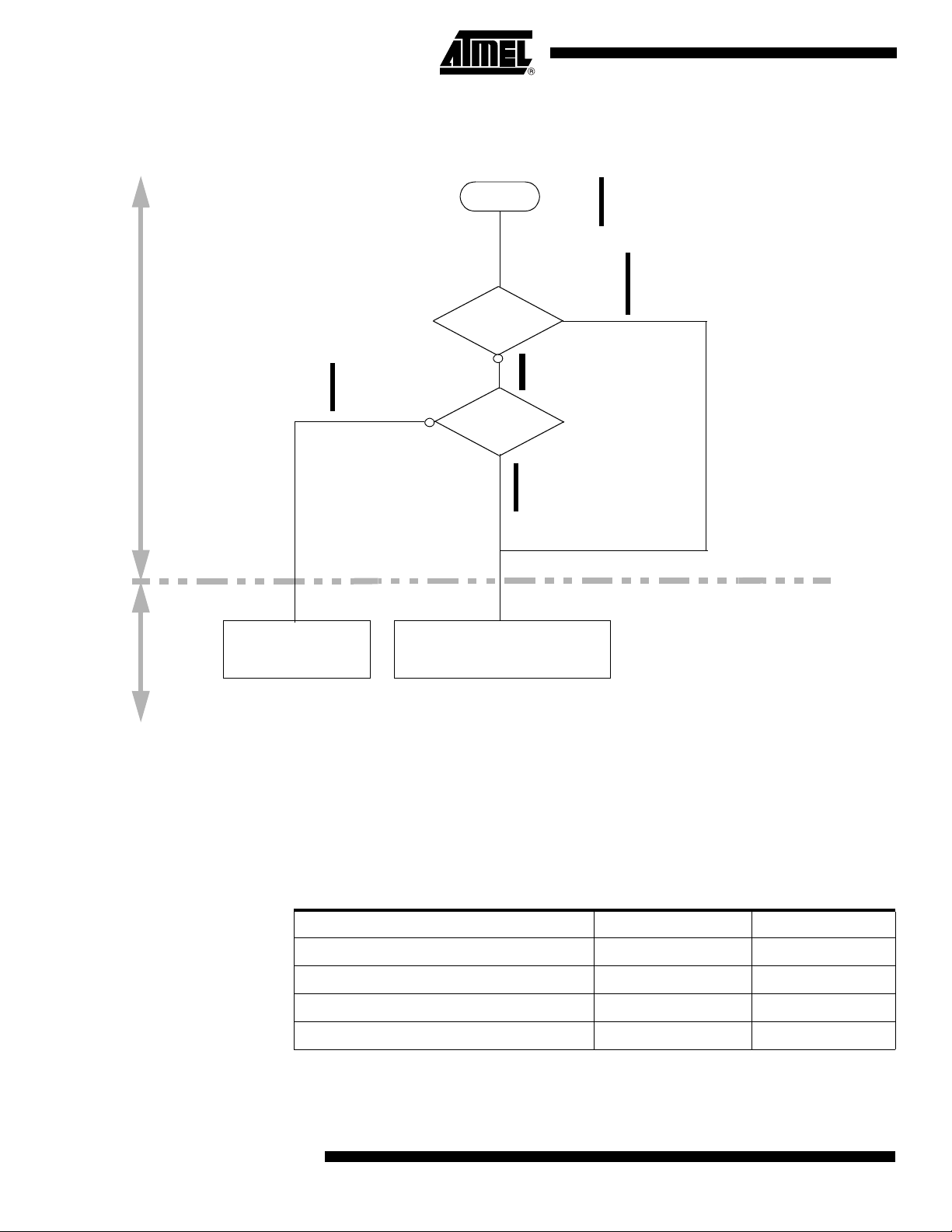
AT89C51CC03
Figure 30. Hardware Boot Process Algorithm
RESET
Hardware
condition?
BLJB = = 0
?
bit ENBOOT in AUXR1 register
is initialized with BLJB.
Hardware
Software
ENBOOT = 1
PC = F800h
ENBOOT = 1
PC = F800h
FCON = 00h
FCON = F0h
Boot Loader
in FM1
ENBOOT = 0
PC = 0000h
Yes
Yes
No
No
Application
in FM0
Application Programming Interface
XROW Bytes
Several Application Program Interface (API) calls are available for use by an application
program to permit selective erasing and programming of Flash pages. All calls are made
by functions.
All these APIs are describe in an documentation: "In-System Programing: Flash Library
for AT89C51CC03" available on the Atmel web site.
Table 23. XROW Mapping
Description Default Value Address
Copy of the Manufacturer Code 58h 30h
Copy of the Device ID#1: Family code D7h 31h
Copy of the Device ID#2: Memories size and type FFh 60h
Copy of the Device ID#3: Name and Revision FEh 61h
60
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 61

AT89C51CC03
Hardware Security Byte
Table 24. Hardware Security Byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
X2B BLJB - - - LB2 LB1 LB0
Bit
Number
7 X2B
6 BLJB
5-3 -
2-0 LB2:0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
X2 Bit
Set this bit to start in standard mode
Clear this bit to start in X2 mode.
Boot Loader JumpBit
- 1: To start the user’s application on next RESET (@0000h) located in FM0,
- 0: To start the boot loader(@F800h) located in FM1.
Reserved
The value read from these bits are indeterminate.
Lock Bits
After erasing the chip in parallel mode, the default value is : FFh
The erasing in ISP mode (from bootloader) does not modify this byte.
Notes: 1. Only the 4 MSB bits can be accessed by software.
2. The 4 LSB bits can only be accessed by parallel mode.
4182N–CAN–03/08
61
Page 62
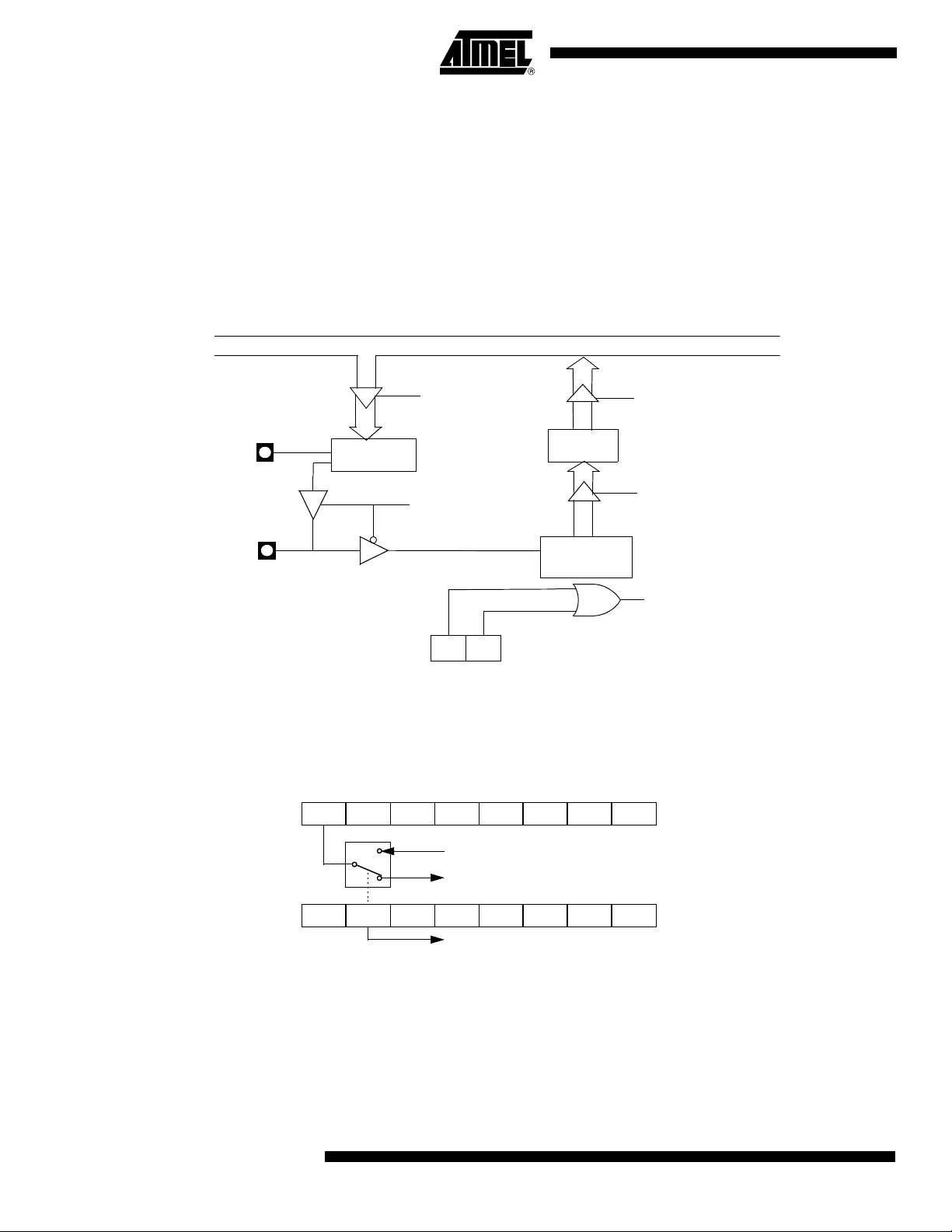
AT89C51CC03
Serial I/O Port
Write SBUF
RI
TI
SBUF
Transmitter
SBUF
Receiver
IB Bus
Mode 0 Transmit
Receive
Shift register
Load SBUF
Read SBUF
SCON reg
Interrupt Request
Serial Port
TXD
RXD
RITIRB8TB8RENSM2SM1SM0/FE
IDLPDGF0GF1POF-SMOD0SMOD
To UART framing error control
SM0 to UART mode control
Set FE bit if stop bit is 0 (framing error)
The AT89C51CC03 I/O serial port is compatible with the I/O serial port in the 80C52.
It provides both synchronous and asynchronous communication modes. It operates as a
Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART) in three full-duplex modes
(Modes 1, 2 and 3). Asynchronous transmission and reception can occur simultaneously
and at different baud rates
Serial I/O port includes the following enhancements:
• Framing error detection
• Automatic address recognition
Figure 31. Serial I/O Port Block Diagram
Framing Error Detection
Figure 32. Framing Error Block Diagram
62
Framing bit error detection is provided for the three asynchronous modes. To enable the
framing bit error detection feature, set SMOD0 bit in PCON register.
When this feature is enabled, the receiver checks each incoming data frame for a valid
stop bit. An invalid stop bit may result from noise on the serial lines or from simultaneous
transmission by two CPUs. If a valid stop bit is not found, the Framing Error bit (FE) in
SCON register bit is set.
The software may examine the FE bit after each reception to check for data errors.
Once set, only software or a reset clears the FE bit. Subsequently received frames with
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 63
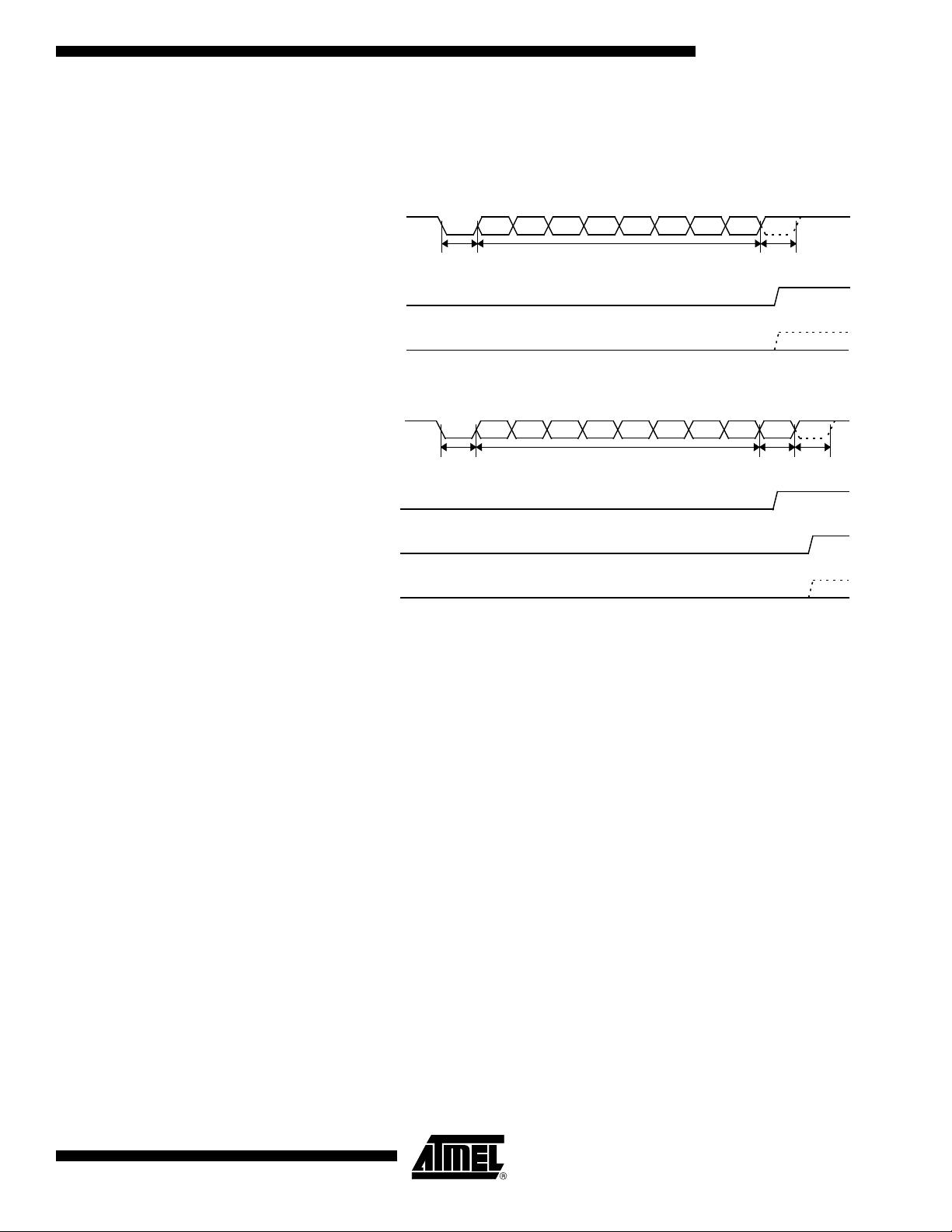
AT89C51CC03
Data byte
RI
SMOD0=X
Stop
bit
Start
bit
RXD
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
FE
SMOD0=1
RI
SMOD0=0
Data byte Ninth
bit
Stop
bit
Start
bit
RXD
D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
RI
SMOD0=1
FE
SMOD0=1
valid stop bits cannot clear the FE bit. When the FE feature is enabled, RI rises on the
stop bit instead of the last data bit (See Figure 33. and Figure 34.).
Figure 33. UART Timing in Mode 1
Figure 34. UART Timing in Modes 2 and 3
Automatic Address Recognition
4182N–CAN–03/08
The automatic address recognition feature is enabled when the multiprocessor communication feature is enabled (SM2 bit in SCON register is set).
Implemented in the hardware, automatic address recognition enhances the multiprocessor communication feature by allowing the serial port to examine the address of each
incoming command frame. Only when the serial port recognizes its own address will the
receiver set the RI bit in the SCON register to generate an interrupt. This ensures that
the CPU is not interrupted by command frames addressed to other devices.
If necessary, you can enable the automatic address recognition feature in mode 1. In
this configuration, the stop bit takes the place of the ninth data bit. Bit RI is set only when
the received command frame address matches the device’s address and is terminated
by a valid stop bit.
To support automatic address recognition, a device is identified by a given address and
a broadcast address.
Note: The multiprocessor communication and automatic address recognition features cannot
be enabled in mode 0 (i.e. setting SM2 bit in SCON register in mode 0 has no effect).
63
Page 64

AT89C51CC03
Given Address
Each device has an individual address that is specified in the SADDR register; the
SADEN register is a mask byte that contains don’t-care bits (defined by zeros) to form
the device’s given address. The don’t-care bits provide the flexibility to address one or
more slaves at a time. The following example illustrates how a given address is formed.
To address a device by its individual address, the SADEN mask byte must be 1111
1111b.
For example:
SADDR0101 0110b
SADEN1111 1100b
Given0101 01XXb
Here is an example of how to use given addresses to address different slaves:
Slave A:SADDR1111 0001b
SADEN1111 1010b
Given1111 0X0Xb
Slave B:SADDR1111 0011b
SADEN1111 1001b
Given1111 0XX1b
Slave C:SADDR1111 0011b
SADEN1111 1101b
Given1111 00X1b
The SADEN byte is selected so that each slave may be addressed separately.
For slave A, bit 0 (the LSB) is a don’t-care bit; for slaves B and C, bit 0 is a 1. To communicate with slave A only, the master must send an address where bit 0 is clear (e.g.
1111 0000b).
For slave A, bit 1 is a 0; for slaves B and C, bit 1 is a don’t care bit. To communicate with
slaves A and B, but not slave C, the master must send an address with bits 0 and 1 both
set (e.g. 1111 0011b).
To communicate with slaves A, B and C, the master must send an address with bit 0 set,
bit 1 clear, and bit 2 clear (e.g. 1111 0001b).
Broadcast Address
64
A broadcast address is formed from the logical OR of the SADDR and SADEN registers
with zeros defined as don’t-care bits, e.g.:
SADDR0101 0110b
SADEN1111 1100b
SADDR OR SADEN1111 111Xb
The use of don’t-care bits provides flexibility in defining the broadcast address, however
in most applications, a broadcast address is FFh. The following is an example of using
broadcast addresses:
Slave A:SADDR1111 0001b
SADEN1111 1010b
Given1111 1X11b,
Slave B:SADDR1111 0011b
SADEN1111 1001b
Given1111 1X11B,
Slave C:SADDR=1111 0010b
SADEN1111 1101b
Given1111 1111b
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 65
AT89C51CC03
For slaves A and B, bit 2 is a don’t care bit; for slave C, bit 2 is set. To communicate with
all of the slaves, the master must send an address FFh. To communicate with slaves A
and B, but not slave C, the master can send and address FBh.
Registers
Table 25. SCON Register
SCON (S:98h)
Serial Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
FE/SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
Bit
Number
7 FE
6 SM1
5 SM2
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Framing Error bit (SMOD0=1
Clear to reset the error state, not cleared by a valid stop bit.
Set by hardware when an invalid stop bit is detected.
SM0
Serial port Mode bit 0 (SMOD0=0)
Refer to SM1 for serial port mode selection.
Serial port Mode bit 1
SM0 SM1 Mode Baud Rate
0 0 Shift Register F
0 1 8-bit UART Variable
1 0 9-bit UART F
1 1 9-bit UART Variable
Serial port Mode 2 bit/Multiprocessor Communication Enable bit
Clear to disable multiprocessor communication feature.
Set to enable multiprocessor communication feature in mode 2 and 3.
)
XTAL
XTAL
/12 (or F
/64 or F
/6 in mode X2)
XTAL
/32
XTAL
4 REN
3 TB8
2 RB8
1 TI
0 RI
Reception Enable bit
Clear to disable serial reception.
Set to enable serial reception.
Transmitter Bit 8/Ninth bit to transmit in modes 2 and 3
Clear to transmit a logic 0 in the 9th bit.
Set to transmit a logic 1 in the 9th bit.
Receiver Bit 8/Ninth bit received in modes 2 and 3
Cleared by hardware if 9th bit received is a logic 0.
Set by hardware if 9th bit received is a logic 1.
Transmit Interrupt flag
Clear to acknowledge interrupt.
Set by hardware at the end of the 8th bit time in mode 0 or at the beginning of the
stop bit in the other modes.
Receive Interrupt flag
Clear to acknowledge interrupt.
Set by hardware at the end of the 8th bit time in mode 0, see Figure 33. and
Figure 34. in the other modes.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Bit addressable
4182N–CAN–03/08
65
Page 66

AT89C51CC03
Table 26. SADEN Register
SADEN (S:B9h)
Slave Address Mask Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7-0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Mask Data for Slave Individual Address
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
Table 27. SADDR Register
SADDR (S:A9h)
Slave Address Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7-0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Slave Individual Address
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
Table 28. SBUF Register
66
SBUF (S:99h)
Serial Data Buffer
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7-0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Data sent/received by Serial I/O Port
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 67

AT89C51CC03
Table 29. PCON Register
PCON (S:87h)
Power Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SMOD1 SMOD0 – POF GF1 GF0 PD IDL
Bit
Number
7 SMOD1
6 SMOD0
5 -
4 POF
3 GF1
2 GF0
1 PD
0 IDL
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Serial port Mode bit 1
Set to select double baud rate in mode 1, 2 or 3.
Serial port Mode bit 0
Clear to select SM0 bit in SCON register.
Set to select FE bit in SCON register.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Power-Off Flag
Clear to recognize next reset type.
Set by hardware when VCC rises from 0 to its nominal voltage. Can also be set
by software.
General-purpose Flag
Cleared by user for general-purpose usage.
Set by user for general-purpose usage.
General-purpose Flag
Cleared by user for general-purpose usage.
Set by user for general-purpose usage.
Power-Down mode bit
Cleared by hardware when reset occurs.
Set to enter power-down mode.
Idle mode bit
Clear by hardware when interrupt or reset occurs.
Set to enter idle mode.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Reset Value = 00X1 0000b
Not bit addressable
67
Page 68

AT89C51CC03
Timers/Counters
The AT89C51CC03 implements two general-purpose, 16-bit Timers/Counters. Such are
identified as Timer 0 and Timer 1, and can be independently configured to operate in a
variety of modes as a Timer or an event Counter. When operating as a Timer, the
Timer/Counter runs for a programmed length of time, then issues an interrupt request.
When operating as a Counter, the Timer/Counter counts negative transitions on an
external pin. After a preset number of counts, the Counter issues an interrupt request.
The various operating modes of each Timer/Counter are described in the following
sections.
Timer/Counter Operations
A basic operation is Timer registers THx and TLx (x = 0, 1) connected in cascade to
form a 16-bit Timer. Setting the run control bit (TRx) in TCON register (see Figure 30)
turns the Timer on by allowing the selected input to increment TLx. When TLx overflows
it increments THx; when THx overflows it sets the Timer overflow flag (TFx) in TCON
register. Setting the TRx does not clear the THx and TLx Timer registers. Timer registers can be accessed to obtain the current count or to enter preset values. They can be
read at any time but TRx bit must be cleared to preset their values, otherwise the behavior of the Timer/Counter is unpredictable.
The C/Tx# control bit selects Timer operation or Counter operation by selecting the
divided-down peripheral clock or external pin Tx as the source for the counted signal.
TRx bit must be cleared when changing the mode of operation, otherwise the behavior
of the Timer/Counter is unpredictable.
For Timer operation (C/Tx# = 0), the Timer register counts the divided-down peripheral
clock. The Timer register is incremented once every peripheral cycle (6 peripheral clock
periods). The Timer clock rate is F
/6, i.e. F
PER
/12 in standard mode or F
OSC
OSC
/6 in X2
mode.
For Counter operation (C/Tx# = 1), the Timer register counts the negative transitions on
the Tx external input pin. The external input is sampled every peripheral cycles. When
the sample is high in one cycle and low in the next one, the Counter is incremented.
Since it takes 2 cycles (12 peripheral clock periods) to recognize a negative transition,
the maximum count rate is F
/12, i.e. F
PER
/24 in standard mode or F
OSC
/12 in X2
OSC
mode. There are no restrictions on the duty cycle of the external input signal, but to
ensure that a given level is sampled at least once before it changes, it should be held for
at least one full peripheral cycle.
Timer 0
68
Timer 0 functions as either a Timer or event Counter in four modes of operation.
Figure 35 to Figure 38 show the logical configuration of each mode.
Timer 0 is controlled by the four lower bits of TMOD register (see Figure 31) and bits 0,
1, 4 and 5 of TCON register (see Figure 30). TMOD register selects the method of Timer
gating (GATE0), Timer or Counter operation (T/C0#) and mode of operation (M10 and
M00). TCON register provides Timer 0 control functions: overflow flag (TF0), run control
bit (TR0), interrupt flag (IE0) and interrupt type control bit (IT0).
For normal Timer operation (GATE0 = 0), setting TR0 allows TL0 to be incremented by
the selected input. Setting GATE0 and TR0 allows external pin INT0# to control Timer
operation.
Timer 0 overflow (count rolls over from all 1s to all 0s) sets TF0 flag generating an interrupt request.
It is important to stop Timer/Counter before changing mode.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 69

AT89C51CC03
FTx
CLOCK
TRx
TCON reg
TFx
TCON reg
0
1
GATEx
TMOD reg
÷
6
Overflow
Timer x
Interrupt
Request
C/Tx#
TMOD reg
TLx
(5 bits)
THx
(8 bits)
INTx#
Tx
See the “Clock” section
TRx
TCON reg
TFx
TCON reg
0
1
GATEx
TMOD reg
Overflow
Timer x
Interrupt
Request
C/Tx#
TMOD reg
TLx
(8 bits)
THx
(8 bits)
INTx#
Tx
FTx
CLOCK
÷
6
See the “Clock” section
Mode 0 (13-bit Timer) Mode 0 configures Timer 0 as an 13-bit Timer which is set up as an 8-bit Timer (TH0
register) with a modulo 32 prescaler implemented with the lower five bits of TL0 register
(see Figure 35). The upper three bits of TL0 register are indeterminate and should be
ignored. Prescaler overflow increments TH0 register.
Figure 35. Timer/Counter x (x = 0 or 1) in Mode 0
Mode 1 (16-bit Timer) Mode 1 configures Timer 0 as a 16-bit Timer with TH0 and TL0 registers connected in
cascade (see Figure 36). The selected input increments TL0 register.
Figure 36. Timer/Counter x (x = 0 or 1) in Mode 1
4182N–CAN–03/08
69
Page 70

AT89C51CC03
Mode 2 (8-bit Timer with Auto-
TRx
TCON reg
TFx
TCON reg
0
1
GATEx
TMOD reg
Overflow
Timer x
Interrupt
Request
C/Tx#
TMOD reg
TLx
(8 bits)
THx
(8 bits)
INTx#
Tx
FTx
CLOCK
÷
6
See the “Clock” section
TR0
TCON.4
TF0
TCON.5
INT0#
0
1
GATE0
TMOD.3
Overflow
Timer 0
Interrupt
Request
C/T0#
TMOD.2
TL0
(8 bits)
TR1
TCON.6
TH0
(8 bits)
TF1
TCON.7
Overflow
Timer 1
Interrupt
Request
T0
FTx
CLOCK
÷
6
FTx
CLOCK
÷
6
See the “Clock” section
Reload)
Mode 2 configures Timer 0 as an 8-bit Timer (TL0 register) that automatically reloads
from TH0 register (see Figure 37). TL0 overflow sets TF0 flag in TCON register and
reloads TL0 with the contents of TH0, which is preset by software. When the interrupt
request is serviced, hardware clears TF0. The reload leaves TH0 unchanged. The next
reload value may be changed at any time by writing it to TH0 register.
Figure 37. Timer/Counter x (x = 0 or 1) in Mode 2
Mode 3 (Two 8-bit Timers) Mode 3 configures Timer 0 such that registers TL0 and TH0 operate as separate 8-bit
Timers (see Figure 38). This mode is provided for applications requiring an additional 8bit Timer or Counter. TL0 uses the Timer 0 control bits C/T0# and GATE0 in TMOD register, and TR0 and TF0 in TCON register in the normal manner. TH0 is locked into a
Timer function (counting F
/6) and takes over use of the Timer 1 interrupt (TF1) and
PER
run control (TR1) bits. Thus, operation of Timer 1 is restricted when Timer 0 is in mode
3.
Figure 38. Timer/Counter 0 in Mode 3: Two 8-bit Counters
70
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 71

AT89C51CC03
Timer 1
Timer 1 is identical to Timer 0 excepted for Mode 3 which is a hold-count mode. The following comments help to understand the differences:
• Timer 1 functions as either a Timer or event Counter in three modes of operation.
Figure 35 to Figure 37 show the logical configuration for modes 0, 1, and 2. Timer
1’s mode 3 is a hold-count mode.
• Timer 1 is controlled by the four high-order bits of TMOD register (see Figure 31)
and bits 2, 3, 6 and 7 of TCON register (see Figure 30). TMOD register selects the
method of Timer gating (GATE1), Timer or Counter operation (C/T1#) and mode of
operation (M11 and M01). TCON register provides Timer 1 control functions:
overflow flag (TF1), run control bit (TR1), interrupt flag (IE1) and interrupt type
control bit (IT1).
• Timer 1 can serve as the Baud Rate Generator for the Serial Port. Mode 2 is best
suited for this purpose.
• For normal Timer operation (GATE1 = 0), setting TR1 allows TL1 to be incremented
by the selected input. Setting GATE1 and TR1 allows external pin INT1# to control
Timer operation.
• Timer 1 overflow (count rolls over from all 1s to all 0s) sets the TF1 flag generating
an interrupt request.
• When Timer 0 is in mode 3, it uses Timer 1’s overflow flag (TF1) and run control bit
(TR1). For this situation, use Timer 1 only for applications that do not require an
interrupt (such as a Baud Rate Generator for the Serial Port) and switch Timer 1 in
and out of mode 3 to turn it off and on.
• It is important to stop Timer/Counter before changing mode.
Mode 0 (13-bit Timer) Mode 0 configures Timer 1 as a 13-bit Timer, which is set up as an 8-bit Timer (TH1 reg-
ister) with a modulo-32 prescaler implemented with the lower 5 bits of the TL1 register
(see Figure 35). The upper 3 bits of TL1 register are ignored. Prescaler overflow increments TH1 register.
Mode 1 (16-bit Timer) Mode 1 configures Timer 1 as a 16-bit Timer with TH1 and TL1 registers connected in
cascade (see Figure 36). The selected input increments TL1 register.
Mode 2 (8-bit Timer with AutoReload)
Mode 3 (Halt) Placing Timer 1 in mode 3 causes it to halt and hold its count. This can be used to halt
Mode 2 configures Timer 1 as an 8-bit Timer (TL1 register) with automatic reload from
TH1 register on overflow (see Figure 37). TL1 overflow sets TF1 flag in TCON register
and reloads TL1 with the contents of TH1, which is preset by software. The reload
leaves TH1 unchanged.
Timer 1 when TR1 run control bit is not available i.e. when Timer 0 is in mode 3.
4182N–CAN–03/08
71
Page 72

AT89C51CC03
Interrupt
TF0
TCON.5
ET0
IEN0.1
Timer 0
Interrupt Request
TF1
TCON.7
ET1
IEN0.3
Timer 1
Interrupt Request
Each Timer handles one interrupt source that is the timer overflow flag TF0 or TF1. This
flag is set every time an overflow occurs. Flags are cleared when vectoring to the Timer
interrupt routine. Interrupts are enabled by setting
ETx
bit in IEN0 register. This assumes
interrupts are globally enabled by setting EA bit in IEN0 register.
Figure 39. Timer Interrupt System
Registers
Table 30. TCON Register
TCON (S:88h)
Timer/Counter Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
Bit
Number
7 TF1
6 TR1
5 TF0
4 TR0
3 IE1
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Timer 1 Overflow Flag
Cleared by hardware when processor vectors to interrupt routine.
Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow, when Timer 1 register overflows.
Timer 1 Run Control Bit
Clear to turn off Timer/Counter 1.
Set to turn on Timer/Counter 1.
Timer 0 Overflow Flag
Cleared by hardware when processor vectors to interrupt routine.
Set by hardware on Timer/Counter overflow, when Timer 0 register overflows.
Timer 0 Run Control Bit
Clear to turn off Timer/Counter 0.
Set to turn on Timer/Counter 0.
Interrupt 1 Edge Flag
Cleared by hardware when interrupt is processed if edge-triggered (see IT1).
Set by hardware when external interrupt is detected on INT1# pin.
72
2 IT1
1 IE0
0 IT0
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Interrupt 1 Type Control Bit
Clear to select low level active (level triggered) for external interrupt 1 (INT1#).
Set to select falling edge active (edge triggered) for external interrupt 1.
Interrupt 0 Edge Flag
Cleared by hardware when interrupt is processed if edge-triggered (see IT0).
Set by hardware when external interrupt is detected on INT0# pin.
Interrupt 0 Type Control Bit
Clear to select low level active (level triggered) for external interrupt 0 (INT0#).
Set to select falling edge active (edge triggered) for external interrupt 0.
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 73

AT89C51CC03
Table 31. TMOD Register
TMOD (S:89h)
Timer/Counter Mode Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
GATE1 C/T1# M11 M01 GATE0 C/T0# M10 M00
Bit
Number
7 GATE1
6 C/T1#
5 M11
4 M01
3 GATE0
2 C/T0#
1 M10
0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Timer 1 Gating Control Bit
Clear to enable Timer 1 whenever TR1 bit is set.
Set to enable Timer 1 only while INT1# pin is high and TR1 bit is set.
Timer 1 Counter/Timer Select Bit
Clear for Timer operation: Timer 1 counts the divided-down system clock.
Set for Counter operation: Timer 1 counts negative transitions on external pin T1.
Timer 1 Mode Select Bits
M11 M01 Operating mode
0 0 Mode 0: 8-bit Timer/Counter (TH1) with 5-bit prescaler (TL1).
0 1 Mode 1: 16-bit Timer/Counter.
1 0 Mode 2: 8-bit auto-reload Timer/Counter (TL1)
1 1 Mode 3: Timer 1 halted. Retains count
Timer 0 Gating Control Bit
Clear to enable Timer 0 whenever TR0 bit is set.
Set to enable Timer/Counter 0 only while INT0# pin is high and TR0 bit is set.
Timer 0 Counter/Timer Select Bit
Clear for Timer operation: Timer 0 counts the divided-down system clock.
Set for Counter operation: Timer 0 counts negative transitions on external pin T0.
Timer 0 Mode Select Bit
M10 M00 Operating mode
0 0 Mode 0: 8-bit Timer/Counter (TH0) with 5-bit prescaler (TL0).
0 1 Mode 1: 16-bit Timer/Counter.
M00
1 0 Mode 2: 8-bit auto-reload Timer/Counter (TL0)
1 1 Mode 3: TL0 is an 8-bit Timer/Counter
TH0 is an 8-bit Timer using Timer 1’s TR0 and TF0 bits.
(1)
(2)
4182N–CAN–03/08
1. Reloaded from TH1 at overflow.
2. Reloaded from TH0 at overflow.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
73
Page 74

AT89C51CC03
Table 32. TH0 Register
TH0 (S:8Ch)
Timer 0 High Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7:0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
High Byte of Timer 0.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Table 33. TL0 Register
TL0 (S:8Ah)
Timer 0 Low Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7:0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Low Byte of Timer 0.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Table 34. TH1 Register
TH1 (S:8Dh)
Timer 1 High Byte Register
74
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7:0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
High Byte of Timer 1.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 75

AT89C51CC03
Table 35. TL1 Register
TL1 (S:8Bh)
Timer 1 Low Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7:0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Low Byte of Timer 1.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
4182N–CAN–03/08
75
Page 76

AT89C51CC03
Timer 2
(DOWN COUNTING RELOAD VALUE)
TF2
T2
EXF2
TH2
(8-bit)
TL2
(
8-bit)
RCAP2H
(8-bit)
RCAP2L
(8-bit)
FFh
(8-bit)
FFh
(
8-bit)
TOGGLE
(UP COUNTING RELOAD VALUE)
TIMER 2
INTERRUPT
:6
T2CONreg
T2CONreg
T2EX:
1=UP
2=DOWN
0
1
CT/2
T2CON.1
TR2
T2CON.2
FT2
CLOCK
see section “Clock”
The AT89C51CC03 timer 2 is compatible with timer 2 in the 80C52.
It is a 16-bit timer/counter: the count is maintained by two eight-bit timer registers, TH2
and TL2 that are cascade- connected. It is controlled by T2CON register (See Table )
and T2MOD register (See Table 38). Timer 2 operation is similar to Timer 0 and Timer
1. C/T2 selects F
/6 (timer operation) or external pin T2 (counter operation) as
T2 clock
timer clock. Setting TR2 allows TL2 to be incremented by the selected input.
Timer 2 includes the following enhancements:
• Auto-reload mode (up or down counter)
• Programmable clock-output
Auto-Reload Mode
The auto-reload mode configures timer 2 as a 16-bit timer or event counter with automatic reload. This feature is controlled by the DCEN bit in T2MOD register (See
Table 38). Setting the DCEN bit enables timer 2 to count up or down as shown in
Figure 40. In this mode the T2EX pin controls the counting direction.
When T2EX is high, timer 2 counts up. Timer overflow occurs at FFFFh which sets the
TF2 flag and generates an interrupt request. The overflow also causes the 16-bit value
in RCAP2H and RCAP2L registers to be loaded into the timer registers TH2 and TL2.
When T2EX is low, timer 2 counts down. Timer underflow occurs when the count in the
timer registers TH2 and TL2 equals the value stored in RCAP2H and RCAP2L registers.
The underflow sets TF2 flag and reloads FFFFh into the timer registers.
The EXF2 bit toggles when timer 2 overflow or underflow, depending on the direction of
the count. EXF2 does not generate an interrupt. This bit can be used to provide 17-bit
resolution.
Figure 40. Auto-Reload Mode Up/Down Counter
76
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 77
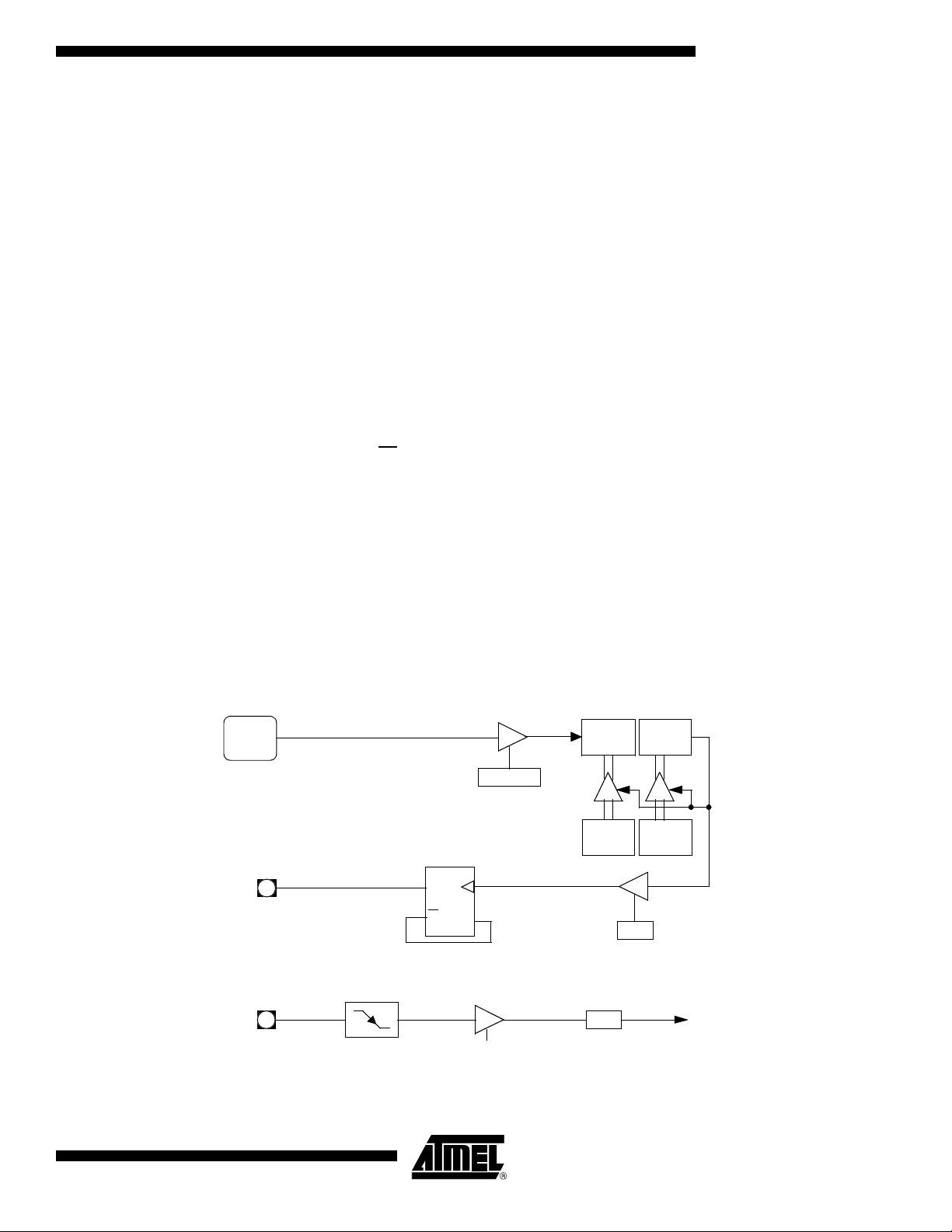
AT89C51CC03
Clo ck OutFre q uency–
FT 2 c lock
4 65536 RCAP2H– RC A P 2L⁄( )×
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
=
EXEN2
EXF2
OVERFLOW
T2EX
TH2
(8-bit)
TL2
(8-bit)
TIMER 2
RCAP2H
(8-bit)
RCAP2L
(8-bit)
T2OE
T2CON reg
T2CON reg
T2MOD reg
INTERRUPT
TR2
T2CON.2
FT2
CLOCK
T2
Q D
Toggle
Q
Programmable ClockOutput
In clock-out mode, timer 2 operates as a 50%-duty-cycle, programmable clock generator (See Figure 41). The input clock increments TL2 at frequency F
/2. The timer
OSC
repeatedly counts to overflow from a loaded value. At overflow, the contents of RCAP2H
and RCAP2L registers are loaded into TH2 and TL2. In this mode, timer 2 overflows do
not generate interrupts. The formula gives the clock-out frequency depending on the
system oscillator frequency and the value in the RCAP2H and RCAP2L registers:
For a 16 MHz system clock in x1 mode, timer 2 has a programmable frequency range of
61 Hz (F
OSC
16)
/2
to 4 MHz (F
/4). The generated clock signal is brought out to T2 pin
OSC
(P1.0).
Timer 2 is programmed for the clock-out mode as follows:
• Set T2OE bit in T2MOD register.
• Clear C/T2 bit in T2CON register.
• Determine the 16-bit reload value from the formula and enter it in RCAP2H/RCAP2L
registers.
• Enter a 16-bit initial value in timer registers TH2/TL2. It can be the same as the
reload value or different depending on the application.
• To start the timer, set TR2 run control bit in T2CON register.
Figure 41. Clock-Out Mode
It is possible to use timer 2 as a baud rate generator and a clock generator simultane o usly. For t his configuratio n, th e ba u d rat e s an d cloc k fre q u e ncies are not
independent since both functions use the values in the RCAP2H and RCAP2L registers.
4182N–CAN–03/08
77
Page 78

AT89C51CC03
Registers
Table 36. T2CON Register
T2CON (S:C8h)
Timer 2 Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TF2 EXF2 RCLK TCLK EXEN2 TR2 C/T2# CP/RL2#
Bit
Number
7 TF2
6 EXF2
5 RCLK
4 TCLK
3 EXEN2
2 TR2
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Timer 2 Overflow Flag
TF2 is not set if RCLK=1 or TCLK = 1.
Must be cleared by software.
Set by hardware on timer 2 overflow.
Timer 2 External Flag
Set when a capture or a reload is caused by a negative transition on T2EX pin if
EXEN2=1.
Set to cause the CPU to vector to timer 2 interrupt routine when timer 2 interrupt
is enabled.
Must be cleared by software.
Receive Clock bit
Clear to use timer 1 overflow as receive clock for serial port in mode 1 or 3.
Set to use timer 2 overflow as receive clock for serial port in mode 1 or 3.
Transmit Clock bit
Clear to use timer 1 overflow as transmit clock for serial port in mode 1 or 3.
Set to use timer 2 overflow as transmit clock for serial port in mode 1 or 3.
Timer 2 External Enable bit
Clear to ignore events on T2EX pin for timer 2 operation.
Set to cause a capture or reload when a negative transition on T2EX pin is
detected, if timer 2 is not used to clock the serial port.
Timer 2 Run Control bit
Clear to turn off timer 2.
Set to turn on timer 2.
78
1 C/T2#
0 CP/RL2#
Timer/Counter 2 Select bit
Clear for timer operation (input from internal clock system: F
Set for counter operation (input from T2 input pin).
Timer 2 Capture/Reload bit
If RCLK=1 or TCLK=1, CP/RL2# is ignored and timer is forced to auto-reload on
timer 2 overflow.
Clear to auto-reload on timer 2 overflows or negative transitions on T2EX pin if
EXEN2=1.
Set to capture on negative transitions on T2EX pin if EXEN2=1.
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Bit addressable
).
OSC
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 79
AT89C51CC03
Table 37. T2MOD Register
T2MOD (S:C9h)
Timer 2 Mode Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - T2OE DCEN
Bit
Number
7 -
6 -
5 -
4 -
3 -
2 -
1 T2OE
0 DCEN
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Timer 2 Output Enable bit
Clear to program P1.0/T2 as clock input or I/O port.
Set to program P1.0/T2 as clock output.
Down Counter Enable bit
Clear to disable timer 2 as up/down counter.
Set to enable timer 2 as up/down counter.
Reset Value = XXXX XX00b
Not bit addressable
4182N–CAN–03/08
Table 38. TH2 Register
TH2 (S:CDh)
Timer 2 High Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - - -
Bit
Number
7-0 High Byte of Timer 2.
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
79
Page 80
AT89C51CC03
Table 39. TL2 Register
TL2 (S:CCh)
Timer 2 Low Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - - -
Bit
Number
7-0 Low Byte of Timer 2.
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
Table 40. RCAP2H Register
RCAP2H (S:CBh)
Timer 2 Reload/Capture High Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - - -
Bit
Number
7-0 High Byte of Timer 2 Reload/Capture.
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
Table 41. RCAP2L Register
80
RCAP2L (S:CAH)
T
IMER
2 REload/Capture Low Byte Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - - -
Bit
Number
7-0 Low Byte of Timer 2 Reload/Capture.
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reset Value = 0000 0000b
Not bit addressable
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 81

AT89C51CC03
WDTPRG
Watchdog Timer
Figure 42. Watchdog Timer
AT89C51CC03 contains a powerful programmable hardware Watchdog Timer (WDT)
that automatically resets the chip if it software fails to reset the WDT before the selected
time interval has elapsed. It permits large Time-Out ranking from 16ms to 2s @Fosc =
12MHz in X1 mode.
This WDT consists of a 14-bit counter plus a 7-bit programmable counter, a Watchdog
Timer reset register (WDTRST) and a Watchdog Timer programming (WDTPRG) register. When exiting reset, the WDT is -by default- disable.
To enable the WDT, the user has to write the sequence 1EH and E1H into WDTRST
register no instruction in between. When the Watchdog Timer is enabled, it will increment every machine cycle while the oscillator is running and there is no way to disable
the WDT except through reset (either hardware reset or WDT overflow reset). When
WDT overflows, it will generate an output RESET pulse at the RST pin. The RESET
pulse duration is 96xT
, where T
OSC
OSC
=1/F
. To make the best use of the WDT, it
OSC
should be serviced in those sections of code that will periodically be executed within the
time required to prevent a WDT reset
Note: When the Watchdog is enable it is impossible to change its period.
Fwd Clock
RESET
-
Decoder
WR
WDTRST
Enable
14-bit COUNTER
-
-
-
-
2
0
1
Control
7-bit COUNTER
Outputs
RESET
4182N–CAN–03/08
81
Page 82
AT89C51CC03
Watchdog Programming
FT i me Out
F
osc
6 2×
WD X2X2∧
2142
Sv a lue
×( )
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
=–
The three lower bits (S0, S1, S2) located into WDTPRG register permit to program the
WDT duration.
Table 42. Machine Cycle Count
S2 S1 S0 Machine Cycle Count
0 0 0 214
0 0 1 215
0 1 0 2
0 1 1 217
1 0 0 218
1 0 1 219
1 1 0 220
1 1 1 221
16
To compute WD Time-Out, the following formula is applied:
Note: Svalue represents the decimal value of (S2 S1 S0)
The following table outlines the time-out value for Fosc
= 12 MHz in X1 mode
XTAL
Table 43. Time-Out Computation
S2 S1 S0 Fosc = 12 MHz Fosc = 16 MHz Fosc = 20 MHz
0 0 0 16.38 ms 12.28 ms 9.82 ms
0 0 1 32.77 ms 24.57 ms 19.66 ms
0 1 0 65.54 ms 49.14 ms 39.32 ms
0 1 1 131.07 ms 98.28 ms 78.64 ms
1 0 0 262.14 ms 196.56 ms 157.28 ms
1 0 1 524.29 ms 393.12 ms 314.56 ms
1 1 0 1.05 s 786.24 ms 629.12 ms
1 1 1 2.10 s 1.57 s 1.25 s
82
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 83

AT89C51CC03
Watchdog Timer During Power-down Mode and Idle
In Power-down mode the oscillator stops, which means the WDT also stops. While in
Power-down mode, the user does not need to service the WDT. There are 2 methods of
exiting Power-down mode: by a hardware reset or via a level activated external interrupt
which is enabled prior to entering Power-down mode. When Power-down is exited with
hardware reset, the Watchdog is disabled. Exiting Power-down with an interrupt is significantly different. The interrupt shall be held low long enough for the oscillator to
stabilize. When the interrupt is brought high, the interrupt is serviced. To prevent the
WDT from resetting the device while the interrupt pin is held low, the WDT is not started
until the interrupt is pulled high. It is suggested that the WDT be reset during the interrupt service for the interrupt used to exit Power-down.
To ensure that the WDT does not overflow within a few states of exiting powerdown, it is
best to reset the WDT just before entering powerdown.
In the Idle mode, the oscillator continues to run. To prevent the WDT from resetting
AT89C51CC03 while in Idle mode, the user should always set up a timer that will periodically exit Idle, service the WDT, and re-enter Idle mode.
Register Table 44. WDTPRG Register
WDTPRG (S:A7h)
Watchdog Timer Duration Programming Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – S2 S1 S0
Bit
Number
7 -
6 -
5 -
4 -
3 -
2 S2
1 S1
0 S0
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Reserved
The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit.
Watchdog Timer Duration selection bit 2
Work in conjunction with bit 1 and bit 0.
Watchdog Timer Duration selection bit 1
Work in conjunction with bit 2 and bit 0.
Watchdog Timer Duration selection bit 0
Work in conjunction with bit 1 and bit 2.
Reset Value = XXXX X000b
4182N–CAN–03/08
83
Page 84

AT89C51CC03
Table 45. WDTRST Register
WDTRST (S:A6h Write only)
Watchdog Timer Enable Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
– – – – – – – –
Bit
Number
7 - Watchdog Control Value
Bit
Mnemonic Description
Reset Value = 1111 1111b
Note: The WDRST register is used to reset/enable the WDT by writing 1EH then E1H in
sequence without instruction between these two sequences.
84
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 85
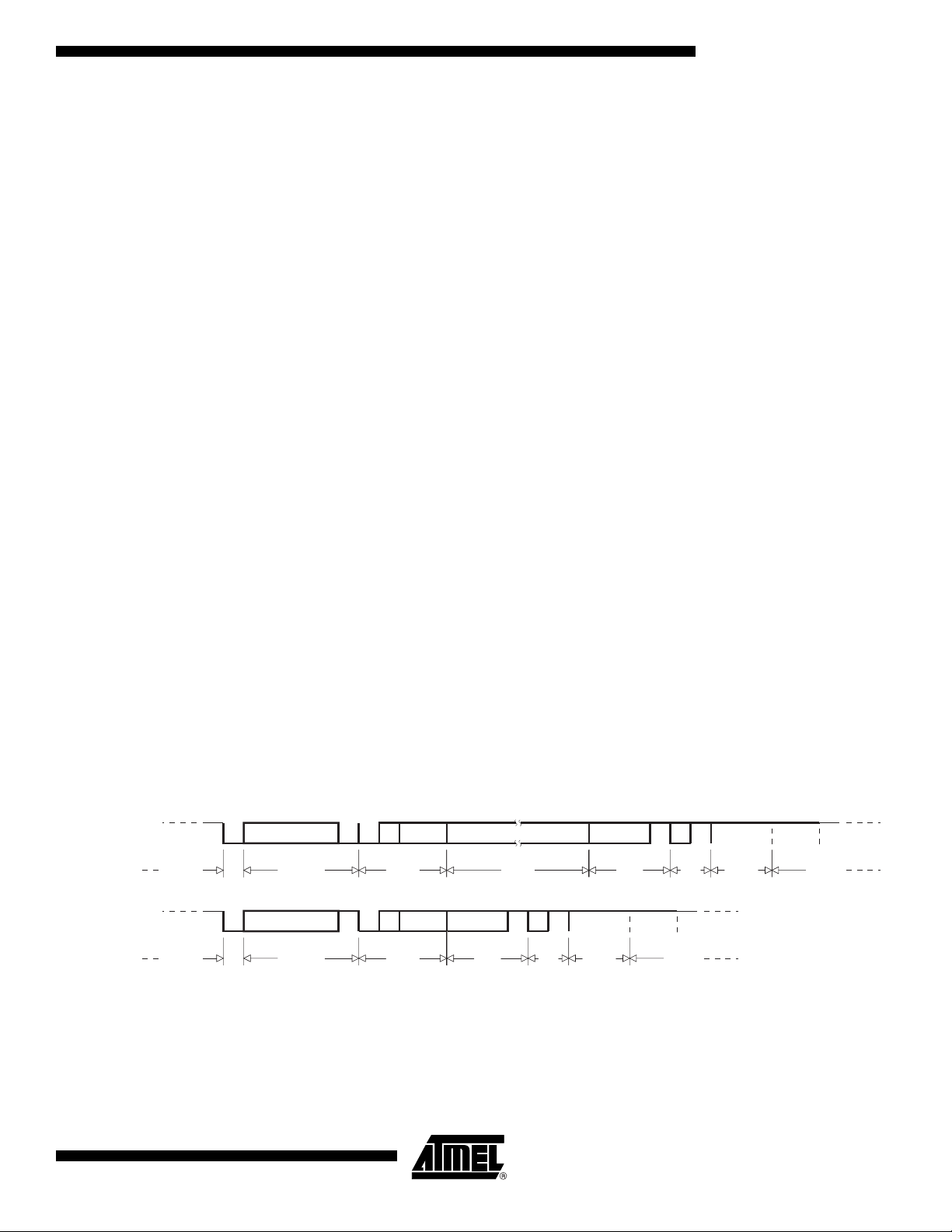
AT89C51CC03
11-bit identifier
ID10..0
Interframe
Space
4-bit DLC
DLC4..0
CRC
del.
ACK
del.
15-bit CRC
0 - 8 bytes
SOF
SOF
RTR
IDE r0
ACK
7 bits
Intermission
3 bits
Bus Idle Bus Idle
(Indefinite)
Arbitration
Field
Data
Field
Data Frame
Control
Field
End of
Frame
CRC
Field
ACK
Field
Interframe
Space
11-bit identifier
ID10..0
Interframe
Space
4-bit DLC
DLC4..0
CRC
del.
ACK
del.
15-bit CRC
SOF
SOF
RTR
IDE r0
ACK
7 bits
Intermission
3 bits
Bus Idle Bus Idle
(Indefinite)
Arbitration
Field
Remote Frame
Control
Field
End of
Frame
CRC
Field
ACK
Field
Interframe
Space
CAN Controller
The CAN Controller provides all the features required to implement the serial communication protocol CAN as defined by BOSCH GmbH. The CAN specification as referred to
by ISO/11898 (2.0A and 2.0B) for high speed and ISO/11519-2 for low speed. The CAN
Controller is able to handle all types of frames (Data, Remote, Error and Overload) and
achieves a bitrate of 1-Mbit/sec at 8 MHz1 Crystal frequency in X2 mode.
Note: 1. At BRP = 1 sampling point will be fixed.
CAN Protocol
The CAN protocol is an international standard defined in the ISO 11898 for high speed
and ISO 11519-2 for low speed.
Principles CAN is based on a broadcast communication mechanism. This broadcast communica-
tion is achieved by using a message oriented transmission protocol. These messages
are identified by using a message identifier. Such a message identifier has to be unique
within the whole network and it defines not only the content but also the priority of the
message.
The priority at which a message is transmitted compared to another less urgent message is specified by the identifier of each message. The priorities are laid down during
system design in the form of corresponding binary values and cannot be changed
dynamically. The identifier with the lowest binary number has the highest priority.
Bus access conflicts are resolved by bit-wise arbitration on the identifiers involved by
each node observing the bus level bit for bit. This happens in accordance with the "wired
and" mechanism, by which the dominant state overwrites the recessive state. The competition for bus allocation is lost by all nodes with recessive transmission and dominant
observation. All the "losers" automatically become receivers of the message with the
highest priority and do not re-attempt transmission until the bus is available again.
Message Formats The CAN protocol supports two message frame formats, the only essential difference
being in the length of the identifier. The CAN standard frame, also known as CAN 2.0 A,
supports a length of 11 bits for the identifier, and the CAN extended frame, also known
as CAN 2.0 B, supports a length of 29 bits for the identifier.
Can Standard Frame
Figure 43. CAN Standard Frames
A message in the CAN standard frame format begins with the "Start Of Frame (SOF)",
this is followed by the "Arbitration field" which consist of the identifier and the "Remote
Transmission Request (RTR)" bit used to distinguish between the data frame and the
data request frame called remote frame. The following "Control field" contains the "IDentifier Extension (IDE)" bit and the "Data Length Code (DLC)" used to indicate the
4182N–CAN–03/08
85
Page 86

AT89C51CC03
CAN Extended Frame
11-bit base identifier
IDT28..18
Interframe
Space
CRC
del.
ACK
del.
15-bit CRC
0 - 8 bytes
SOF
SOF
SRR
IDE
ACK
7 bits
Intermission
3 bits
Bus Idle Bus Idle
(Indefinite)
Arb itrat ion
Field
Arb itrat ion
Field
Data
Field
Data Frame
Control
Field
Control
Field
End of
Frame
CRC
Field
ACK
Field
Interframe
Space
11-bit base identifier
IDT28..18
18-bit identifier extension
ID17..0
18-bit identifier extension
ID17..0
Interframe
Space
4-bit DLC
DLC4..0
CRC
del.
ACK
del.
15-bit CRC
SOF
SOF
SRR
IDE r0
4-bit DLC
DLC4..0
RTR
RTR
r0r1
r1
ACK
7 bits
Intermission
3 bits
Bus Idle Bus Idle
(Indefinite)
Remote Frame
End of
Frame
CRC
Field
ACK
Field
Interframe
Space
Figure 44. CAN Extended Frames
number of following data bytes in the "Data field". In a remote frame, the DLC contains
the number of requested data bytes. The "Data field" that follows can hold up to 8 data
bytes. The frame integrity is guaranteed by the following "Cyclic Redundant Check
(CRC)" sum. The "ACKnowledge (ACK) field" compromises the ACK slot and the ACK
delimiter. The bit in the ACK slot is sent as a recessive bit and is overwritten as a dominant bit by the receivers which have at this time received the data correctly. Correct
messages are acknowledged by the receivers regardless of the result of the acceptance
test. The end of the message is indicated by "End Of Frame (EOF)". The "Intermission
Frame Space (IFS)" is the minimum number of bits separating consecutive messages. If
there is no following bus access by any node, the bus remains idle.
A message in the CAN extended frame format is likely the same as a message in CAN
standard frame format. The difference is the length of the identifier used. The identifier is
made up of the existing 11-bit identifier (base identifier) and an 18-bit extension (identifier extension). The distinction between CAN standard frame format and CAN extended
frame format is made by using the IDE bit which is transmitted as dominant in case of a
frame in CAN standard frame format, and transmitted as recessive in the other case.
Format Co-existence As the two formats have to co-exist on one bus, it is laid down which message has
higher priority on the bus in the case of bus access collision with different formats and
the same identifier / base identifier: The message in CAN standard frame format always
has priority over the message in extended format.
There are three different types of CAN modules available:
– 2.0A - Considers 29 bit ID as an error
– 2.0B Passive - Ignores 29 bit ID messages
– 2.0B Active - Handles both 11 and 29 bit ID Messages
Bit Timing To ensure correct sampling up to the last bit, a CAN node needs to re-synchronize
throughout the entire frame. This is done at the beginning of each message with the falling edge SOF and on each recessive to dominant edge.
Bit Construction One CAN bit time is specified as four non-overlapping time segments. Each segment is
constructed from an integer multiple of the Time Quantum. The Time Quantum or TQ is
the smallest discrete timing resolution used by a CAN node.
86
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 87

AT89C51CC03
Time Quantum
(producer)
Nominal CAN Bit Time
Segments
(producer)
SYNC_SEG
PROP_SEG PHASE_SEG_1 PHASE_SEG_2
propagation
delay
Segments
(consumer)
SYNC_SEG PROP_SEG PHASE_SEG_1 PHASE_SEG_2
Sample Point
Transmission Point
(producer)
CAN Frame
(producer)
Figure 45. CAN Bit Construction
Synchronization Segment The first segment is used to synchronize the various bus nodes.
On transmission, at the start of this segment, the current bit level is output. If there is a
bit state change between the previous bit and the current bit, then the bus state change
is expected to occur within this segment by the receiving nodes.
Propagation Time Segment This segment is used to compensate for signal delays across the network.
Phase Segment 1 Phase Segment 1 is used to compensate for edge phase errors.
Sample Point The sample point is the point of time at which the bus level is read and interpreted as the
Phase Segment 2 This segment is also used to compensate for edge phase errors.
Information Processing Time It is the time required for the logic to determine the bit level of a sampled bit.
Bit Lengthening As a result of resynchronization, Phase Segment 1 may be lengthened or Phase Seg-
4182N–CAN–03/08
This is necessary to compensate for signal propagation delays on the bus line and
through the transceivers of the bus nodes.
This segment may be lengthened during resynchronization.
value of the respective bit. Its location is at the end of Phase Segment 1 (between the
two Phase Segments).
This segment may be shortened during resynchronization, but the length has to be at
least as long as the information processing time and may not be more than the length of
Phase Segment 1.
The Information processing Time begins at the sample point, is measured in TQ and is
fixed at 2 TQ for the Atmel CAN. Since Phase Segment 2 also begins at the sample
point and is the last segment in the bit time, Phase Segment 2 minimum shall not be
less than the Information processing Time.
ment 2 may be shortened to compensate for oscillator tolerances. If, for example, the
transmitter oscillator is slower than the receiver oscillator, the next falling edge used for
resynchronization may be delayed. So Phase Segment 1 is lengthened in order to
adjust the sample point and the end of the bit time.
87
Page 88

AT89C51CC03
Bit Shortening If, on the other hand, the transmitter oscillator is faster than the receiver one, the next
node A
TXCAN
node B
TXCAN
ID10 ID9 ID8 ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
SOF
SOF
RTRIDE
CAN bus
- - - - - - - - -
Arbitration lost
Node A loses the bus
Node B wins the bus
falling edge used for resynchronization may be too early. So Phase Segment 2 in bit N
is shortened in order to adjust the sample point for bit N+1 and the end of the bit time
Synchronization Jump Width The limit to the amount of lengthening or shortening of the Phase Segments is set by the
Resynchronization Jump Width.
This segment may not be longer than Phase Segment 2.
Programming the Sample Point Programming of the sample point allows "tuning" of the characteristics to suit the bus.
Early sampling allows more Time Quanta in the Phase Segment 2 so the Synchronization Jump Width can be programmed to its maximum. This maximum capacity to
shorten or lengthen the bit time decreases the sensitivity to node oscillator tolerances,
so that lower cost oscillators such as ceramic resonators may be used.
Late sampling allows more Time Quanta in the Propagation Time Segment which allows
a poorer bus topology and maximum bus length.
Arbitration
Figure 46. Bus Arbitration
The CAN protocol handles bus accesses according to the concept called “Carrier Sense
Multiple Access with Arbitration on Message Priority”.
During transmission, arbitration on the CAN bus can be lost to a competing device with
a higher priority CAN Identifier. This arbitration concept avoids collisions of messages
whose transmission was started by more than one node simultaneously and makes sure
the most important message is sent first without time loss.
The bus access conflict is resolved during the arbitration field mostly over the identifier
value. If a data frame and a remote frame with the same identifier are initiated at the
same time, the data frame prevails over the remote frame (c.f. RTR bit).
Errors The CAN protocol signals any errors immediately as they occur. Three error detection
mechanisms are implemented at the message level and two at the bit level:
Error at Message Level • Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
The CRC safeguards the information in the frame by adding redundant check bits at
the transmission end. At the receiver these bits are re-computed and tested against
the received bits. If they do not agree there has been a CRC error.
• Frame Check
This mechanism verifies the structure of the transmitted frame by checking the bit
88
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 89

AT89C51CC03
fields against the fixed format and the frame size. Errors detected by frame checks
are designated "format errors".
• ACK Errors
As already mentioned frames received are acknowledged by all receivers through
positive acknowledgement. If no acknowledgement is received by the transmitter of
the message an ACK error is indicated.
Error at Bit Level • Monitoring
The ability of the transmitter to detect errors is based on the monitoring of bus
signals. Each node which transmits also observes the bus level and thus detects
differences between the bit sent and the bit received. This permits reliable detection
of global errors and errors local to the transmitter.
• Bit Stuffing
The coding of the individual bits is tested at bit level. The bit representation used by
CAN is "Non Return to Zero (NRZ)" coding, which guarantees maximum efficiency
in bit coding. The synchronization edges are generated by means of bit stuffing.
Error Signalling If one or more errors are discovered by at least one node using the above mechanisms,
the current transmission is aborted by sending an "error flag". This prevents other nodes
accepting the message and thus ensures the consistency of data throughout the network. After transmission of an erroneous message that has been aborted, the sender
automatically re-attempts transmission.
CAN Controller Description
The CAN Controller accesses are made through SFR.
Several operations are possible by SFR:
• arithmetic and logic operations, transfers and program control (SFR is accessible by
direct addressing).
• 15 independent message objects are implemented, a pagination system manages
their accesses.
Any message object can be programmed in a reception buffer block (even non-consecutive buffers). For the reception of defined messages one or several receiver message
objects can be masked without participating in the buffer feature. An IT is generated
when the buffer is full. The frames following the buffer-full interrupt will not be taken into
account until at least one of the buffer message objects is re-enabled in reception.
Higher priority of a message object for reception or transmission is given to the lower
message object number.
The programmable 16-bit Timer (CANTIMER) is used to stamp each received and sent
message in the CANSTMP register. This timer starts counting as soon as the CAN controller is enabled by the ENA bit in the CANGCON register.
The Time Trigger Communication (TTC) protocol is supported by the AT89C51CC03.
4182N–CAN–03/08
89
Page 90

AT89C51CC03
Figure 47. CAN Controller Block Diagram
Bit
Stuffing /Destuffing
Cyclic
Redundancy Check
Receive Transmit
Error
Counter
Rec/Tec
Bit
Timing
Logic
Page
Register
DPR(Mailbox + Registers)
Priority
Encoder
µC-Core Interface
Core
Control
Interface
Bus
TxDC
RxDC
CAN Controller Mailbox and Registers Organization
The pagination allows management of the 321 registers including 300(15x20) Bytes of
mailbox via 34 SFR’s.
All actions on the message object window SFRs apply to the corresponding message
object registers pointed by the message object number find in the Page message object
register (CANPAGE) as illustrate in Figure 48.
90
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 91

Figure 48. CAN Controller Memory Organization
Ch.14 - ID Tag - 1
Ch.14 - ID Tag - 2
Ch.14 - ID Tag - 4
Ch.14 - ID Tag - 3
Ch.14 - ID Mask - 1
Ch.14 - ID Mask - 2
Ch.14 - ID Mask - 4
Ch.14 - ID Mask - 3
Ch.14 - Message Data - byte 0
General Control
General Status
Bit Timing - 1
Bit Timing - 2
Bit Timing - 3
Enable Interrupt
Enable Interrupt message object - 1
Page message object
message object Status
message object Control and DLC
Message Data
ID Tag - 1
ID Tag - 2
ID Tag - 4
ID Tag - 3
ID Mask - 1
ID Mask - 2
ID Mask - 4
ID Mask - 3
message object 0 - Status
message object 0 - Control and DLC
Ch.0 - ID Tag - 1
Ch.0 - ID Tag - 2
Ch.0 - ID Tag - 4
Ch.0 - ID Tag - 3
Ch.0 - Message Data - byte 0
message object 14 - Status
message object 14 - Control and DLC
Enable Interrupt message object - 2
Status Interrupt message object - 1
Status Interrupt message object - 2
(message object n umber)(Data offset)
SFR’s On-chip CAN Controller registers
15 message objec ts
8 Bytes
TimStmp High
TimStmp Low
Ch.0 - ID Mask- 1
Ch.0 - ID Mask- 2
Ch.0 - ID Mask - 4
Ch.0 - ID Mask- 3
CANTimer High
CANTimer Low
TimTTC High
TimTTC Low
TEC counter
REC counter
Timer Control
Enable message object - 1
Enable message object - 2
message object Window SFRs
Ch.0 TimStmp High
Ch.0 TimStmp Low
Ch.14 TimStmp High
Ch.14 TimStmp Low
General Interrupt
AT89C51CC03
4182N–CAN–03/08
91
Page 92

AT89C51CC03
Working on Message Objects The Page message object register (CANPAGE) is used to select one of the 15 message
objects. Then, message object Control (CANCONCH) and message object Status
(CANSTCH) are available for this selected message object number in the corresponding
SFRs. A single register (CANMSG) is used for the message. The mailbox pointer is
managed by the Page message object register with an auto-incrementation at the end of
each access. The range of this counter is 8.
Note that the maibox is a pure RAM, dedicated to one message object, without overlap.
In most cases, it is not necessary to transfer the received message into the standard
memory. The message to be transmitted can be built directly in the maibox. Most calculations or tests can be executed in the mailbox area which provide quicker access.
CAN Controller Management
In order to enable the CAN Controller correctly the following registers have to be
initialized:
• General Control (CANGCON),
• Bit Timing (CANBT 1, 2 and 3),
• And for each page of 15 message objects
– message object Control (CANCONCH),
– message object Status (CANSTCH).
During operation, the CAN Enable message object registers 1 and 2 (CANEN 1 and 2)
gives a fast overview of the message objects availability.
The CAN messages can be handled by interrupt or polling modes.
A message object can be configured as follows:
• Transmit message object,
• Receive message object,
• Receive buffer message object.
• Disable
This configuration is made in the CONCH1:2 field of the CANCONCH register (see
Table 46).
When a message object is configured, the corresponding ENCH bit of CANEN 1 and 2
register is set.
92
Table 46. Configuration for CONCH1:2
CONCH 1 CONCH 2 Type of Message Object
0 0 Disable
0 1 Transmitter
1 0 Receiver
1 1 Receiver buffer
When a Transmitter or Receiver action of a message object is completed, the corresponding ENCH bit of the CANEN 1 and 2 register is cleared. In order to re-enable the
message object, it is necessary to re-write the configuration in CANCONCH register.
Non-consecutive message objects can be used for all three types of message objects
(Transmitter, Receiver and Receiver buffer),
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 93
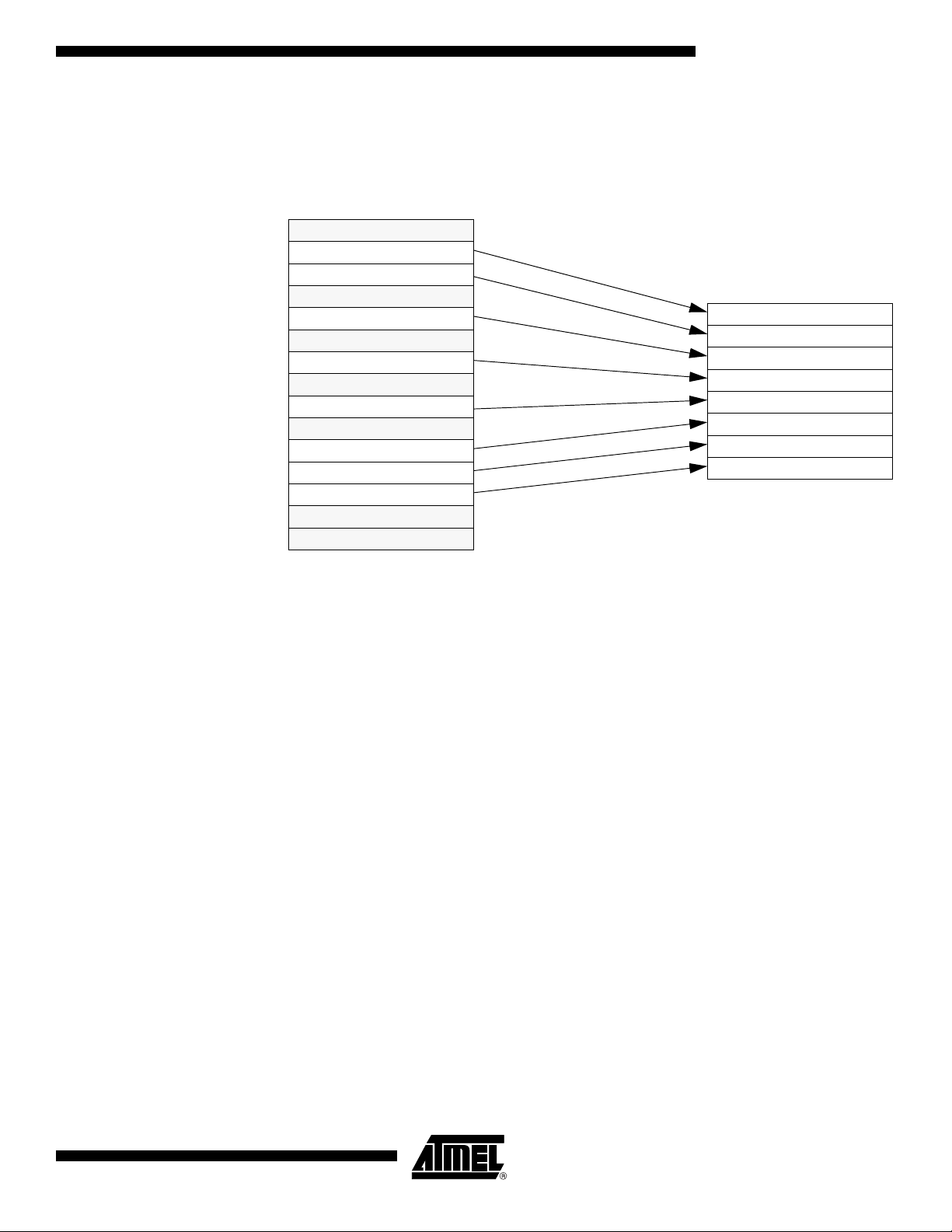
AT89C51CC03
message object 0
message object 1
message object 2
message object 3
message object 4
message object 5
message object 6
message object 7
message object 8
message object 9
message object 10
message object 11
message object 12
message object 13
Block buffer
buffer 0
buffer 1
buffer 2
buffer 3
buffer 4
buffer 5
buffer 6
buffer 7
message object 14
Buffer Mode Any message object can be used to define one buffer, including non-consecutive mes-
sage objects, and with no limitation in number of message objects used up to 15.
Each message object of the buffer must be initialized CONCH2 = 1 and CONCH1 = 1;
Figure 49. Buffer mode
4182N–CAN–03/08
The same acceptance filter must be defined for each message objects of the buffer.
When there is no mask on the identifier or the IDE, all messages are accepted.
A received frame will always be stored in the lowest free message object.
When the flag Rxok is set on one of the buffer message objects, this message object
can then be read by the application. This flag must then be cleared by the software and
the message object re-enabled in buffer reception in order to free the message object.
The OVRBUF flag in the CANGIT register is set when the buffer is full. This flag can
generate an interrupt.
The frames following the buffer-full interrupt will not stored and no status will be overwritten in the CANSTCH registers involved in the buffer until at least one of the buffer
message objects is re-enabled in reception.
This flag must be cleared by the software in order to acknowledge the interrupt.
93
Page 94

AT89C51CC03
IT CAN Management
SIT i
i=0
i=14
OVRIT
ENRX
CANGIE.5
ENTX
CANGIE.4
ENERCH
CANGIE.3
ENBUF
CANGIE.2
ECAN
IEN1.0
RXOK i
CANSTCH.5
TXOK i
CANSTCH.6
BERR i
CANSTCH.4
SERR i
CANSTCH.3
FERR i
CANSTCH.1
CERR i
CANSTCH.2
AERR i
CANSTCH.0
EICH i
CANIE1/2
OVRTIM
CANGIT.5
CANIT
CANGIT.7
OVRBUF
CANGIT.4
FERG
CANGIT.1
AERG
CANGIT.0
SERG
CANGIT.3
CERG
CANGIT.2
ENERG
CANGIE.1
ETIM
IEN1.2
SIT i
CANSIT1/2
The different interrupts are:
• Transmission interrupt,
• Reception interrupt,
• Interrupt on error (bit error, stuff error, crc error, form error, acknowledge error),
• Interrupt when Buffer receive is full,
• Interrupt on overrun of CAN Timer.
Figure 50. CAN Controller Interrupt Structure
94
To enable a transmission interrupt:
• Enable General CAN IT in the interrupt system register,
• Enable interrupt by message object, EICHi,
• Enable transmission interrupt, ENTX.
To enable a reception interrupt:
• Enable General CAN IT in the interrupt system register,
• Enable interrupt by message object, EICHi,
• Enable reception interrupt, ENRX.
To enable an interrupt on message object error:
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 95

AT89C51CC03
• Enable General CAN IT in the interrupt system register,
• Enable interrupt by message object, EICHi,
• Enable interrupt on error, ENERCH.
To enable an interrupt on general error:
• Enable General CAN IT in the interrupt system register,
• Enable interrupt on error, ENERG.
To enable an interrupt on Buffer-full condition:
• Enable General CAN IT in the interrupt system register,
• Enable interrupt on Buffer full, ENBUF.
To enable an interrupt when Timer overruns:
• Enable Overrun IT in the interrupt system register.
When an interrupt occurs, the corresponding message object bit is set in the SIT
register.
To acknowledge an interrupt, the corresponding CANSTCH bits (RXOK, TXOK,...) or
CANGIT bits (OVRTIM, OVRBUF,...), must be cleared by the software application.
When the CAN node is in transmission and detects a Form Error in its frame, a bit Error
will also be raised. Consequently, two consecutive interrupts can occur, both due to the
same error.
When a message object error occurs and is set in CANSTCH register, no general error
are set in CANGIE register.
4182N–CAN–03/08
95
Page 96
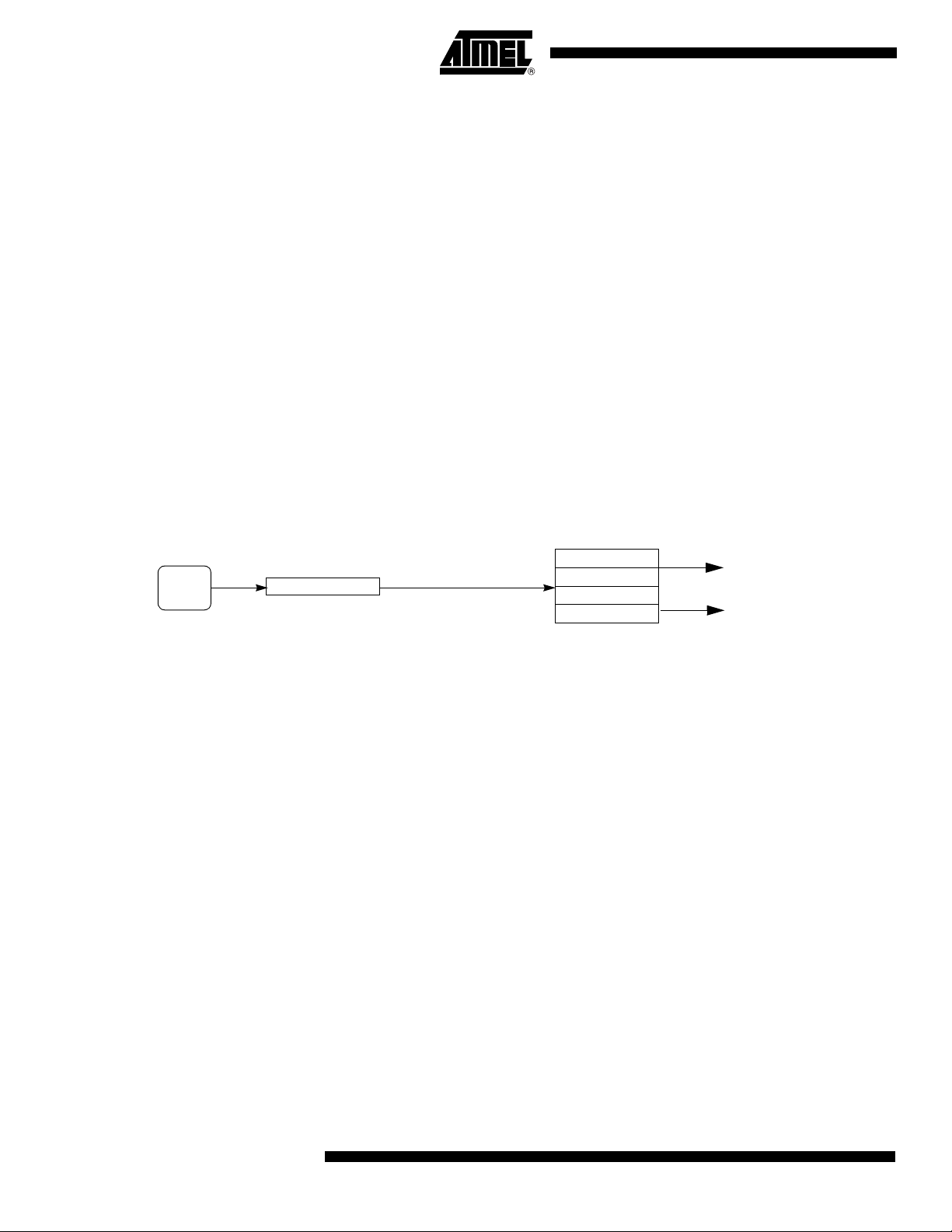
AT89C51CC03
Bit Timing and Baud Rate
FCAN
CLOCK
Prescaler BRP
PRS 3-bit length
PHS1 3-bit length
PHS2 3-bit length
SJW 2-bit length
Bit Timing
System clock Tscl
Time Quantum
Sample point
Transmission point
FSM’s (Finite State Machine) of the CAN channel need to be synchronous to the time
quantum. So, the input clock for bit timing is the clock used into CAN channel FSM’s.
Field and segment abbreviations:
• BRP: Baud Rate Prescaler.
• TQ: Time Quantum (output of Baud Rate Prescaler).
• SYNS: SYNchronization Segment is 1 TQ long.
• PRS: PRopagation time Segment is programmable to be 1, 2, ..., 8 TQ long.
• PHS1: PHase Segment 1 is programmable to be 1, 2, ..., 8 TQ long.
• PHS2: PHase Segment 2 is programmable to be superior or equal to the
INFORMATION PROCESSING TIME and inferior or equal to TPSH1.
• INFORMATION PROCESSING TIME is 2 TQ.
• SJW: (Re) Synchronization Jump Width is programmable to be minimum of PHS1
and 4.
The total number of TQ in a bit time has to be programmed at least from 8 to 25.
Figure 51. Sample And Transmission Point
The baud rate selection is made by Tbit calculation:
Tbit = Tsyns + Tprs + Tphs1 + Tphs2
1. Tsyns = Tscl = (BRP[5..0]+ 1)/Fcan = 1TQ.
2. Tprs = (1 to 8) * Tscl = (PRS[2..0]+ 1) * Tscl
3. Tphs1 = (1 to 8) * Tscl = (PHS1[2..0]+ 1) * Tscl
4. Tphs2 = (1 to 8) * Tscl = (PHS2[2..0]+ 1) * Tscl
Tphs2 = Max of (Tphs1 and 2TQ)
5. Tsjw = (1 to 4) * Tscl = (SJW[1..0]+ 1) * Tscl
The total number of Tscl (Time Quanta) in a bit time must be comprised between 8 to
25.
96
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 97

Figure 52. General Structure of a Bit Period
Bit Rate Prescaler
oscillator
1/ Fcan
Tscl
system clock
one nominal bit
Tsyns (*)
Tprs
Sample Point
(*) Synchronization Segment: SYNS
Tbit
Tsyns = 1xTscl (fixed)
data
Tbit Ts yns Tprs Tphs 1 Tphs2+ + +=
Tbit calculation:
Transmission Point
Tphs1 + Tsjw (3)
Tphs2 - Tsjw (4)
(1) Phase error ≤ 0
(2) Phase error ≥ 0
(3) Phase error > 0
(4) Phase error < 0
Tphs2 (2)
Tphs1 (1)
AT89C51CC03
example of bit timing determination for CAN baudrate of 500kbit/s:
Fosc = 12 MHz in X1 mode => FCAN = 6 MHz
Verify that the CAN baud rate you want is an integer division of FCAN clock.
FCAN/CAN baudrate = 6 MHz/500 kHz = 12
The time quanta TQ must be comprised between 8 and 25: TQ = 12 and
Define the various timing parameters: Tbit = Tsyns + Tprs + Tphs1 + Tphs2 = 12TQ
Tsyns = 1TQ and Tsjw =1TQ =>
If we chose a sample point at 66.6% => Tphs2 = 4TQ =>
Tbit = 12 = 4 + 1 + Tphs1 + Tprs, let us choose Tprs = 3 Tphs1 = 4
PHS1 = 3
BRP = 0 so CANBT1 = 00h
SJW = 0 and PRS = 2 so CANBT2 = 04h
PHS2 = 3 and PHS1 = 3 so CANBT3 = 36h
and
PRS = 2
SJW = 0
PHS2 = 3
BRP = 0
4182N–CAN–03/08
97
Page 98
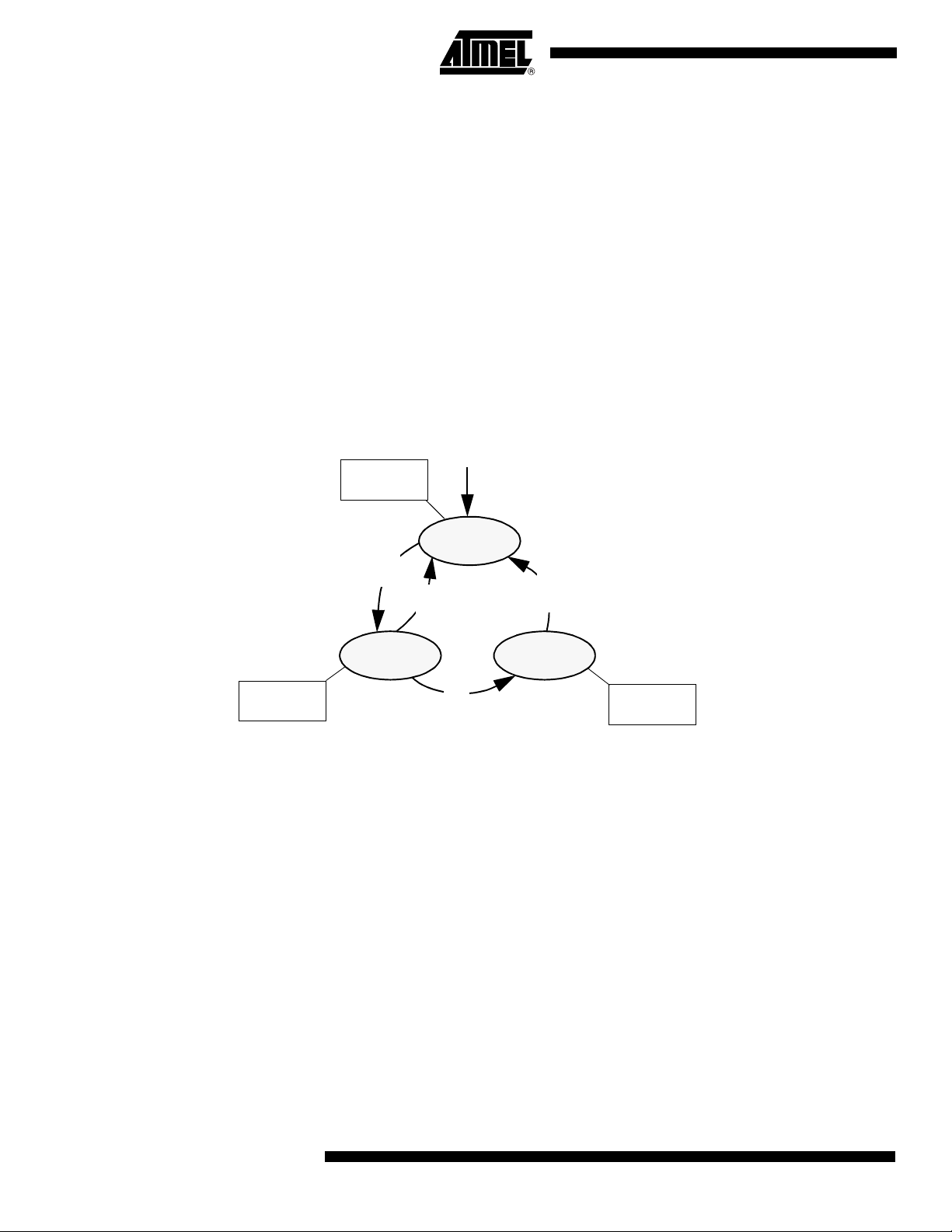
AT89C51CC03
Fault Confinement
TEC>255
Error
Active
Error
Passive
Bus
Off
Init.
TEC<127
and
REC<127
TEC>127
or
REC>127
128 occurrences
of
11 consecutive
recessive
bit
TEC: Transmit Error Counter
REC: Receive Error Counter
ERRP = 0
BOFF = 0
ERRP = 0
BOFF = 1
ERRP = 1
BOFF = 0
With respect to fault confinement, a unit may be in one of the three following status:
• error active
• error passive
• bus off
An error active unit takes part in bus communication and can send an active error frame
when the CAN macro detects an error.
An error passive unit cannot send an active error frame. It takes part in bus communication, but whe n an er ror is detec ted, a passive error fr ame is sent. Also, afte r a
transmission, an error passive unit will wait before initiating further transmission.
A bus off unit is not allowed to have any influence on the bus.
For fault confinement, two error counters (TEC and REC) are implemented.
See CAN Specification for details on Fault confinement.
Figure 53. Line Error Mode
98
4182N–CAN–03/08
Page 99
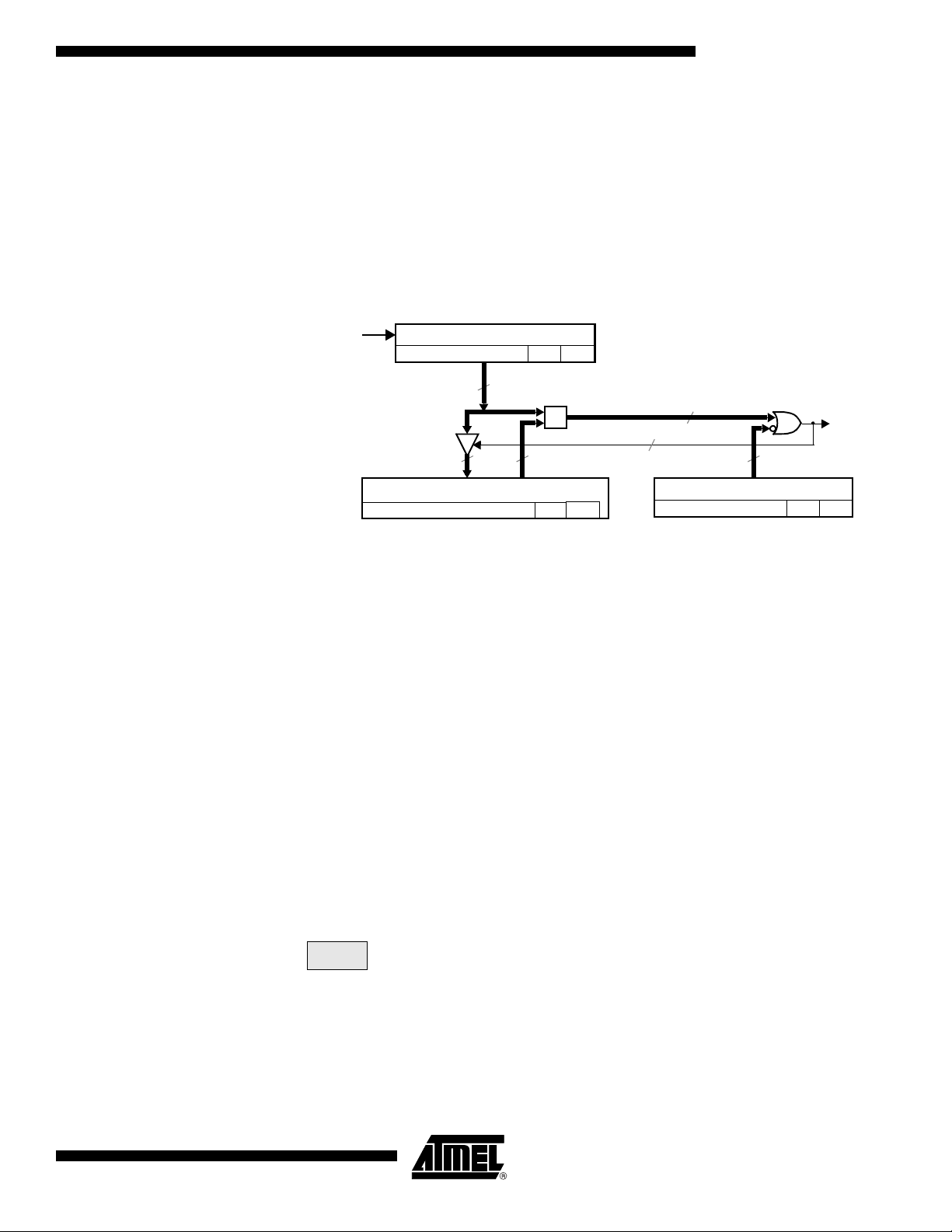
AT89C51CC03
13/32
=
13/32
RxDC
13/32
Write
13/32
1
Hit
13/32
ID MSK Registers (Ch i)
ID and RB RTR IDE
Rx Shift Register (internal)
ID and RB RTR IDE
Enable
(Ch i)
ID TAG Registers (Ch i) and CanConch
ID and RB RTR
IDE
Acceptance Filter
Upon a reception hit (i.e., a good comparison between the ID+RTR+RB+IDE received
and an ID+RTR+RB+IDE specified while taking the comparison mask into account) the
ID+RTR+RB+IDE received are written over the ID TAG Registers.
ID => IDT0-29
RTR => RTRTAG
RB => RB0-1TAG
IDE => IDE in CANCONCH register
Figure 54. Acceptance filter block diagram
example:
To accept only ID = 318h in part A.
ID MSK = 111 1111 1111 b
ID TAG = 011 0001 1000 b
4182N–CAN–03/08
CAN SFRs
99
Page 100

AT89C51CC03
Data and Remote Frame
u uu uu
0 1 x 0 0
u uu uu
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
0 1 x 0 0
c uc uu
0 0 x 1 0
u cc uu
0 0 x 0 1
D
A
T
A
F
R
A
M
E
Node A Node B
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
message object in reception
message object disabled
message object in
message object disabled
transmission
u uu uu
1 1 x 0 0
c uu uc
0 1 x 1 0
u
c
c uu
0 0 x 0 1
R
E
M
O
T
E
F
R
A
M
E
D
A
T
A
F
R
A
M
E
u uu uu
1 1 1 0 0
u uu cc
0 1 0 0 0
c uc cu
0 0 0 1 0
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
(
i
m
m
e
d
i
a
t
e
)
message object in reception
message object in transmission
message object disabled
message object in
message object in
reception by CAN by CAN controller
transmission
controller
message object disabled
u uu uu
1 1 x 0 0
u uu uu
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
1 1 0 0 0
c uu uc
0 1 x 1 0
u cc uu
1 0 0 0 1
R
E
M
O
T
E
F
R
A
M
E
E
N
C
H
R
T
R
R
P
L
V
T
X
O
K
R
X
O
K
u uu uu
0 1 x 0 0
c uc uu
0 0 x 1 0
u cc uc
0 0 x 0 1
D
A
T
A
F
R
A
M
E
(
d
e
f
e
r
r
e
d
)
u
: modified by user
i
c
: modified by CAN
i
message object in reception
message object in transmission by user
message object disabled
message object disabled
message object in
message object in
message object disabled
reception by user
transmission
Description of the different steps for:
• Data Frame
• Remote Frame, With Automatic Reply,
• Remote Frame
100
4182N–CAN–03/08
 Loading...
Loading...