Atlas Copco XAHS 37 DD, XAHS 70 DD7, XAS 90 DD7, XAS 57 DD, XAS 110 DD7 Instruction Manual
...
Instruction Manual for Portable Compressors
English
XAHS 37 DD - XAHS 70 DD7
XAS 47 DD - XAS 90 DD7
XAS 57 DD - XAS 110 DD7
Engine Deutz
D2011L02

Instruction Manual
for Portable Compressors
XAHS 37 DD - XAHS 70 DD7
XAS 47 DD - XAS 90 DD7
XAS 57 DD - XAS 110 DD7
Printed matter N°
2954 2140 02
07/2007
ATLAS COPCO - PORTABLE AIR DIVISION
www.atlascopco.com

4
Instruction Manual
Warranty and Liability Limitation
Use only authorized parts.
Any damage or malfunction caused by the use of unauthorized parts is not
covered by Warranty or Product Liability.
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for any damage arising for
modifications, additions or conversions made without the manufacturer's approval
in writing.
While every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is
correct, Atlas Copco does not assume responsibility for possible errors.
Copyright 2007, Atlas Copco Airpower n.v., Antwerp, Belgium.
Any unauthorized use or copying of the contents or any part thereof is prohibited.
This applies in particular to trademarks, model denominations, part numbers and
drawings.

5
Instruction Manual
Follow the instructions in this booklet and we guarantee you years
of troublefree operation. Please read the following instructions
carefully before starting to use your machine.
Always keep the manual available near the machine.
In all correspondence always mention the compressor type and
serial number, shown on the data plate.
The company reserves the right to make changes without prior
notice.
CONTENTS PAGE
1 Safety precautions for portable compressors
(with generator) .......................................................................7
1.1 Introduction.................................................................7
1.2 General safety precautions..........................................7
1.3 Safety during transport and installation ......................8
1.4 Safety during use and operation..................................9
1.5 Safety during maintenance and repair............... ... .....10
1.6 Tool applications safety .................................. ..........10
1.7 Specific safety precautions..................... ...................11
2 Leading particulars ...............................................................12
2.1 Description of safety pictograms
used in this manual....................................................12
2.2 General description ...................................................12
2.3 Markings and information labels.............. ... ..............14
2.4 Main Parts .................................................................15
2.5 Air flow .....................................................................17
2.6 Oil system..................................................................17
2.7 Continuous regulating system...................................17
2.8 Electrical system ....... ............................. ...................18
2.8.1 Circuit diagram (standard) .......... ..............................1 8
2.8.2 Circuit diagram XAS 47 DDG - XAS 90 DD7G
(Generator DDG 110V without automatic
control system)..........................................................20
2.8.3 Circuit diagram XAS 47 DDG - XAS 90 DD7G
(Generator DDG 110V with automatic
control system)..........................................................22
2.8.4 Circuit diagram XAS 47 DDG - XAS 90 DD7G
(Generator DDG IT 230/400V without automatic
control system)..........................................................24
2.8.5 Circuit diagram XAS 47 DDG - XAS 90 DD7G
(Generator DDG IT 230/400V with automatic
control system)..........................................................26
2.8.6 Circuit diagram XAS 47 DDG - XAS 90 DD7G
(Generator DDG IT 230V, 6 kVA)...........................28
2.8.7 Circuit diagram cold start (all types).........................30
2.8.8 Circuit diagram refinary equipment (all types).........31
CALIFORNIA
Proposition 65 Warning
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its
constituents are known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects,
and other reproductive harm.

6
Instruction Manual
CONTENTS PAGE
3 Operating instructions.......................................................... 32
3.1 Parking, towing and lifting instructions.................... 32
3.1.1 Parking instructions .......................... ........................ 32
3.1.2 Towing instructions ........................ .......................... 33
3.1.3 Spillage-Free instruction................. .......................... 33
3.1.4 Height adjustment (with adjustable towbar)............. 33
3.1.5 Lifting instructions.................................................... 34
3.1.6 Anti-Frost Device (option)........................................ 34
3.2 Starting/Stopping......................................................34
3.2.1 Before starting........................................................... 34
3.2.2 Starting procedure (with cold start; option).............. 35
3.2.3 Starting procedure (without cold start)..................... 36
3.2.4 During operation....................................................... 37
3.2.5 Stopping procedure................................................... 37
3.2.6 Fault situations and protective devices:.................... 37
3.3 Function of generator (option).......... ... ..................... 38
3.3.1 Function of generator DDG 110V without
automatic control system -
Functional description........ ............................. .......... 38
3.3.2 Function of generator DDG 110V with
automatic control system (option) -
Functional description........ ............................. .......... 39
3.3.3 Function of generator DDG 230/400V and
230V - 3ph without automatic control system -
Functional description........ ............................. .......... 40
3.3.4 Function of generator DDG 230/400V and
230V - 3ph with automatic control system
(option) - Functional description .............................. 41
4 Maintenance........................................................................... 42
4.1 Use of service paks .................................. ................. 42
4.2 Preventive maintenance schedule
for the compressor ................. ... ............................ .... 42
4.3 Lubrication oils.. ............................. .......................... 43
4.4 Oil level check .......................................................... 43
4.4.1 Check engine oil level............................................... 43
4.4.2 Check compressor oil level....................................... 44
4.5 Oil and oil filter change ............................................ 44
4.5.1 Engine oil and oil filter change................................. 44
4.5.2 Compressor oil and oil filter change......................... 44
4.6 Cleaning coolers ........................................ ............... 45
4.7 Cleaning fuel tank..................................................... 45
4.8 Cleaning hardhat............................... ... ..................... 45
4.9 Battery care.. ............................. ............................ .... 45
4.9.1 Electrolyte................................................................. 45
4.9.2 Activating a dry-charged battery .............................. 46
4.9.3 Recharging a battery ................................................. 46
4.9.4 Battery maintenance ... .............................................. 46
4.10 Changing tyres.......................................................... 46
CONTENTS PAGE
4.11 Storage ...................................................................... 46
4.12 Service paks .............................................................. 46
4.13 Service kits........................... ..................................... 46
4.14 Compressor element overhaul .................................. 46
4.15 Liability..................................................................... 46
5 Adjustments and servicing procedures.............................. 47
5.1 Adjustment of the continuous regulating system...... 47
5.2 Air filter engine/compressor ..................................... 48
5.2.1 Main parts ................................................................. 48
5.2.2 Recommendations..................................................... 48
5.2.3 Cleaning the dust trap ............................ ................... 48
5.2.4 Replacing the air filter element....................... .. ........ 48
5.3 Air receiver ............................................................... 48
5.4 Safety valve............................................................... 48
5.5 Fuel system ............................ ............................. ...... 49
5.6 Brake (= option) adjustment ..................................... 49
5.6.1 Brake shoe adjustment.............................................. 49
5.6.2 Test procedure of brake cable adjustment ................ 50
5.6.3 Brake cable adjustment............................................. 50
5.7 Drive Belt.................................................................. 50
6 Problem solving..................................................................... 51
6.1 Alternator precautions............................................... 51
7 Available options................................................................... 53
8 Technical specifications........................................................ 54
8.1 Torque values............................................................ 54
8.1.1 For general applications............................................ 54
8.1.2 For important assemblies.......................................... 54
8.2 Settings of shutdown switches and safety valves .....54
8.3 Compressor/Engine specifications............................ 55
8.4 Conversion list of SI units into British units.............61
9 Data plate ............................................................................... 62

7
Instruction Manual
1. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR PORTABLE COMPRESSORS (WITH GENERATOR)
To be read attentively and acted accordingly before towing, lifting, operating, performing maintenance or repairing the unit
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The policy of Atlas Copco is to provide the users of their equipment with
safe, reliable and efficient products. Factors taken into account are among
others:
- the intended and predictable future use of the products, and the
environments in which they are expected to operate,
- applicable rules, codes and regulations,
- the expected useful product life, assuming proper service and
maintenance,
- providing the manual with up-to-date information.
Before handling any product, take time to read the relevant instruction
manual. Besides giving detailed operating instructions, it also gives specific
information about safety, preventive maintenance, etc.
Keep the manual always at the unit location, easy accessible to the operating
personnel.
See also the safety precautions of the engine and possible other equipment,
which are separately sent along or are mentioned on the equipment or parts
of the unit.
These safety precautions are general and some statements will therefore not
always apply to a particular unit.
Only people that have the right skills should be allowed to operate, adjust,
perform maintenance or repair on Atlas Copco equipment. It is the
responsibility of management to appoint operators with the appropriate
training and skill for each category of job.
Skill level 1: Operator
An operator is trained in all aspects of operating the unit with the pushbuttons, and is trained to know the safety aspects.
Skill level 2: Mechanical technician
A mechanical technician is trained to operate the unit the same as the
operator. In addition, the mechanical technician is also trained to perform
maintenance and repair, as described in the instruction manual, and is
allowed to change settings of the control and safety system. A mechanical
technician does not work on live electrical components.
Skill level 3: Electrical technician
An electrical technician is trained and has the same qualifications as both the
operator and the mechanical technician. In addition, the electrical technician
may carry out electrical repairs within the various enclosures of the unit.
This includes work on live electrical components.
Skill level 4: Specialist from the manufacturer
This is a skilled specialist sent by the manufacturer or its agent to perform
complex repairs or modifications to the equipment.
In general it is recommended that not more than two people operate the unit,
more operators could lead to unsafe operating conditions. Take necessary
steps to keep unauthorized persons away from the unit and eliminate all
possible sources of danger at the unit.
When handling, operating, overhauling and/or performing maintenance or
repair on Atlas Copco equipment, the mechanics are expected to use safe
engineering practices and to observe all relevant local safety requirements
and ordinances. The following list is a reminder of special safety directives
and precautions mainly applicable to Atlas Copco equipment.
These safety precautions apply to machinery processing or consuming air.
Processing of any other gas requires additional safety precautions typical to
the application and are not included herein.
Neglecting the safety precautions may endanger people as well as
environment and machinery:
- endanger people due to electrical, mechanical or chemical influences,
- endanger the environment due to leakage of oil, solvents or other
substances,
- endanger the machinery due to function failures.
All responsibility for any damage or injury resulting from neglecting these
precautions or by non-observance of ordinary caution and due care required
in handling, operating, maintenance or repair, also if not expressly
mentioned in this instruction manual, is disclaimed by Atlas Copco.
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for any damage arising from
the use of non-original parts and for modifications, additions or conversions
made without the manufacturer’s approval in writing.
If any statement in this manual does not comply with local legislation, the
stricter of the two shall be applied.
Statements in these safety precautions should not be interpreted as
suggestions, recommendations or inducements that it should be used in
violation of any applicable laws or regulations.
1.2 GENERAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1 The owner is responsible for maintaining the unit in a safe operating
condition. Unit parts and accessories must be replaced if missing or
unsuitable for safe operation.
2 The supervisor, or the responsible person, shall at all times make sure
that all instructions regarding machinery and equipment operation and
maintenance are strictly followed and that the machines with all
accessories and safety devices, as well as the consuming devices, are in
good repair, free of abnormal wear or abuse, and are not tampered with.
3 Wheneve r there is an indication or any suspicion that an internal part of
a machine is overheated, the machine shall be stopped but no inspec tion
covers shall be opened before sufficient cooling time has elapsed; this to
avoid the risk of spontaneous ignition of oil vapour when air is admitted.
4 N ormal ratings (pressures, temperatures, speeds, etc.) shall be durably
marked.
5 Operate the unit only for the intended purpose and within its rated limits
(pressure, temperature, speeds, etc.).
6 The machinery and equipment shall be kept clean, i.e. as free as possible
from oil, dust or other deposits.
7 To prevent an increase in working temperature, inspect and clean heat
transfer surfaces (cooler fins, intercoolers, water jackets, etc.) regularly.
See the maintenance schedule.
8 All regula ting and safety devices shall be maintained with due care to
ensure that they function properly. They may not be put out of action.
9 Care shall be taken to avoid damage to safety valves and other pressure-
relief devices, especially to avoid plugging by paint, oil coke or dirt
accumulation, which could interfere with the functioning of the device.
10 Pressure and temperature gauges shall be checked regularly with regard
to their accuracy. They shall be replaced whenever outside acceptable
tolerances.
11 Safety devices shall be tested as described in the maintenance schedule
of the instruction manual to determine that they are in good operating
condition.
12 Mind the markings and information labels on the unit.
13 In the event the safety labels are damaged or destroyed, they must be
replaced to ensure operator safety.
14 Keep the work area neet. Lack of order will increase the risk of
accidents.
15 When working on the unit, wear safety clothing. Depending on the kind
of activities these are: safety glasses, ear protection, safety helmet
(including visor), safety gloves, protective clothing, safety shoes. Do not
wear the hair long and loose (protect long hair with a hairnet), or wear
loose clothing or jewelry.

8
Instruction Manual
16 Take precautions against fire. Handle fuel, oil and anti-freeze with care
because they are inflammable substances. Do not smoke or approach
with naked flame when handling such substances. Keep a fireextinguisher in the vicinity.
17a Portable compressors with generator (with earthing pin):
Earth the generator as well as the load properly.
17b Portable compressors with generator IT:
Note: This generator is built to supply a sheer alternating current IT
network.
Earth the load properly.
1.3 SAFETY DURING TRANSPORT AND
INSTALLATION
To lift a unit, all loose or pivoting parts, e.g. doors and towbar, shall first be
securely fastened.
Do not attach cables, chains or ropes directly to the lifting eye; apply a crane
hook or lifting shackle meeting local safety regulations. Never allow sharp
bends in lifting cables, chains or ropes.
Helicopter lifting is not allowed.
It is strictly forbidden to dwell or stay in the risk zone under a lifted load.
Never lift the unit over people or residential areas. Lifting acceleration and
retardation shall be kept within safe limits.
1 Before towing the unit:
- ascertain that the pressure vessel(s) is (are) depressurized,
- check the towbar, the brake system and the towing eye. Also check
the coupling of the towing vehicle,
- check the towing and brake capability of the towing vehicle,
- check that the towbar, jockey wheel or stand leg is safely locked in
the raised position,
- ascertain that the towing eye can swivel freely on the hook,
- check that the wheels are secure and that the tyres are in good
condition and inflated correctly,
- connect the signalisation cable, check all lights and connect the
pneumatic brake couplers,
- attach the safety break-away cable or safety chain to the towing
vehicle,
- remove wheel chocks, if applied, and disengage the parking brake.
2 To tow a unit use a towing vehicle of ample capacity. Refer to the
documentation of the towing vehicle.
3 If the unit is to be backed up by the towing vehicle, disengage the
overrun brake mechanism (if it is not an automatic mechanism).
4 Neve r exceed the maximum towing speed of the unit (mind the local
regulations).
5 Place the unit on level ground and apply the parking brake before
disconnecting the unit from the towing vehicle. Unclip the safety breakaway cable or safety chain. If the unit has no parking brake or joc key
wheel, immobilize the unit by placing chocks in front of and/or behind
the wheels. When the towbar can be positioned vertically, the locking
device must be applied and kept in good order.
6 To lift heavy parts, a hoist of ample capacity, tested and approved
according to local safety regulations, shall be used.
7 Lifting hooks, eyes, shackles, etc., shall never be bent and shall only
have stress in line with their design load axis. The capacity of a lifting
device diminishes when the lifting force is applied at an angle to its load
axis.
8 For maximum safety and efficiency of the lifting apparatus all lifting
members shall be applied as near to perpendicular as possible. If
required, a lifting beam shall be applied between hoist and load.
9 Never leave a load hanging on a hoist.
10 A hoist has to be installed in such a way that the object will be lifted
perpendicular. If that is not possible, the necessary precautions must be
taken to prevent load-swinging, e.g. by using two hoists, each at
approximately the same angle not exceeding 30° from the vertical.
11 Locate the unit away from walls. Take all precautions to ensure that hot
air exhausted from the engine and driven machine cooling systems
cannot be recirculated. If such hot air is taken in by the engine or driven
machine cooling fan, this may cause overheating of the unit; if taken in
for combustion, the engine power will be reduced.
12 The electrical connections shall correspond to local codes. The
machines shall be earthed and protected against short circuits by fuses or
circuit breakers.
13 Never connect the generator outlets to an installation which is also
connected to a public mains.
14 Before connecting a load, switch off the corresponding circuit breaker,
and check whether frequency, voltage, current and power factor comply
with the ratings of the generator.

9
Instruction Manual
1.4 SAFETY DURING USE AND OPERATION
1 When the unit has to operate in a fire-hazardous environment, each
engine exhaust has to be provided with a spark arrestor to trap
incendiary sparks.
2 The exhaust contains carbon monoxide which is a lethal gas. When the
unit is used in a confined space, conduct the engine exhaust to the
outside atmosphere by a pipe of sufficient diameter; do this in such a
way that no extra back pressure is created for the engine. If necessary,
install an extractor. Observe any existing local regulations. Make sure
that the unit has sufficient air intake for operation. If necessary, install
extra air intake ducts.
3 When operating in a dust-laden atmosphere, place the unit so that dust is
not carried towards it by the wind. Operation in clean surroundings
considerably extends the intervals for cleaning the air intake filters and
the cores of the coolers.
4 Close the compressor air outlet valve before connecting or
disconnecting a hose. Ascertain that a hose is f u lly depressurized before
disconnecting it. Before blowing compressed air through a hose or air
line, ensure that the open end is held securely, so that it cannot whip and
cause injury.
5 The air line end connected to the outlet valve must be safeguarded with
a safety cable, attached next to the valve.
6 No external force may be exerted on the air outlet valves, e.g. by pulling
on hoses or by installing auxiliary equipment directly to a valve, e.g. a
water separator, a lubricator, etc. Do not step on the air outlet valves.
7 Never move a unit when external lines or hoses are connected to the
outlet valves, to avoid damage to valves, manifold and hoses.
8 Do not use compressed air from any type of compressor, without taking
extra measures, for breathing purposes as this may result in injury or
death. For breathing air quality, the compressed air must be adequately
purified according to local legislation and standards. Breathing air must
always be supplied at stable, suitable pressure.
9 Distribution pipework and air hoses must be of correct diameter and
suitable for the working pressure. Never use frayed, damaged or
deteriorated hoses. Replace hoses and flexibles before the lifetime
expires. Use only the correct type and size of hose end fittings and
connections.
10 If the compressor is to be used for sand-blasting or will be connected to
a common compressed-air system, fit an appropriate non-return valve
(check valve) between compressor outlet and the connected sandblasting or compressed-air system. Observe the right mounting position/
direction.
11 Before removing the oil filler plug, ensure that the pressure is released
by opening an air outlet valve.
12 Never remove a filler cap of the cooling water system of a hot engine.
Wait until the engine has sufficiently cooled down.
13 Never refill fuel while the unit is running, unless otherwise stated in the
Atlas Copco Instruction Book (AIB). Keep fuel away from hot parts
such as air outlet pipes or the engine exhaust. Do not smoke when
fuelling. When fuelling from an automatic pump, an earthing cable
should be connected to the unit to discharge static electricity. Never spill
nor leave oil, fuel, coolant or cleansing agent in or around the unit.
14 All doors shall be shut during operation so as not to disturb the cooling
air flow inside the bodywork and/or render the silencing less effective.
A door should be kept open for a short period only e.g. for inspection or
adjustment.
15 Periodically carry out maintenance works according to the maintenance
schedule.
16 Stationary housing guards are provided on all rotating or reciprocating
parts not otherwise protected and which may be hazardous to personnel.
Machinery shall never be put into operation, when such guards have
been removed, before the guards are securely reinstalled.
17 Noise, even at reasonable levels, can cause irritation and disturbance
which, over a long period of time, may cause severe injuries to the
nervous system of human beings.
When the sound pressure level, at any point where personnel normally
has to attend, is:
below 70 dB(A): no action needs to be taken,
above 70 dB(A): noise-protective devices should be provided for
people continuously being present in the room,
below 85 dB(A): no action needs to be taken for occasional visitors
staying a limited time only,
above 85 dB(A): room to be classified as a noise-hazardous area and
an obvious warning shall be placed permanently at
each entrance to alert people entering the room, for
even relatively short times, about the need to wear
ear protectors,
above 95 dB(A): the warning(s) at the entrance(s) shall be completed
with the recommendation that also occasional
visitors shall wear ear protectors,
above 105 dB(A): special ear protectors that are adequate for this noise
level and the spectral composition of the noise shall
be provided and a special warning to that effect shall
be placed at each entrance.
18 Insulation or safety guards of parts the temperature of which can be in
excess of 80 °C (175 °F) and which may be accidentally touched by
personnel shall not be removed before the parts have cooled to room
temperature.
19 Never operate the unit in surroundings where there is a possibility of
taking in flammable or toxic fumes.
20 If the working process produces fumes, dust or vibration hazards, etc.,
take the necessary steps to eliminate the risk of personnel injury.
21 When using compressed air or inert gas to clean down equipment, do so
with caution and use the appropriate protection, at least safety glasses,
for the operator as well as for any bystander. Do not apply compressed
air or inert gas to your skin or direct an air or gas stream at people.
Never use it to clean dirt from your clothes.
22 When washing parts in or with a cle aning solvent, provide the required
ventilation and use appropriate protection such as a breathing filter,
safety glasses, rubber apron and gloves, etc.
23 Safety shoes should be compulsory in any workshop and if there is a
risk, however small, of falling objects, wearing of a safety helmet should
be included.
24 If there is a risk of inhaling hazardous gases, fumes or dust, the
respiratory organs must be protected and depending on the nature of the
hazard, so must the eyes and skin.
25 Remember that where there is visible dust, the finer, invisible particles
will almost certainly be present too; but the fact that no dust can be seen
is not a reliable indication that dangerous, invisible dust is not present in
the air.
26 Never operate the unit at pressures or speeds below or in excess of its
limits as indicated in the technical specifications.
27 Never operate the generator in excess of its limits as indicated in the
technical specifications and avoid long no-load sequences.
28 Never operate the generator in a humid atmosphere. Excessive moisture
causes worsening of the generator insulation.
29 Do not open electrical cabinets, cubicles or other equipment while
voltage is supplied. If such cannot be avoided, e.g. for measurements,
tests or adjustments, have the action carried out by a qualified electrician
only, with appropriate tools, and ascertain that the required bodily
protection against electrical hazards is applied.
30 Never touch the power terminals during operation of the machine.
31 Whenever an abnormal condition arises, e.g. excessive vibration, noise,
odour, etc., switch the circuit breakers to OFF and stop the engine.
Correct the faulty condition before restarting.
32 Check the electric cables regularly. Damaged cables and insufficient
lightening of connections may cause electric shocks. Whenever
damaged wires or dangerous conditions are observed, switch the circuit
breakers to OFF and stop the engine. Replace the damaged wires or
correct the dangerous condition before restarting. Make sure that all
electric connections are securely tightened.

10
Instruction Manual
33 Do not use aerosol types of starting aids such as ether. Such use could
result in an explosion and personal injury.
34 Avoid overloading the generator. The generator is provided with circuit
breakers for overload protection. When a breaker has tripped, reduce the
concerned load before restarting.
35 If the generator is used as stand-by for the mains supply, it must not be
operated without control system which automatically disconnects the
generator from the mains when the mains supply is restored.
36 Never remove the cover of the output terminals during operation. Before
connecting or disconnecting wires, switch off the load and the circuit
breakers, stop the machine and make sure that the machine cannot be
started inadvertently or there is any residual voltage on the power
circuit.
37 Running the generator at low load for long periods will reduce the
lifetime of the engine.
1.5 SAFETY DURING MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
Maintenance, overhaul and repair work shall only be carried out by
adequately trained personnel; if required, under supervision of someone
qualified for the job.
1 Use only the correct tools for maintenance and repair work, and only
tools which are in good condition.
2 Parts shall only be replaced by genuine Atlas Copco replacement parts.
3 All maintenance work, other than routine attention, shall only be
undertaken when the unit is stopped. Steps shall be taken to prevent
inadvertent starting. In addition, a warning sign bearing a legend such as
”work in progress; do not start” shall be attached to the starting
equipment.
On engine-driven units the battery shall be disconnected and removed or
the terminals covered by insulating caps.
On electrically driven units the main switch shall be locked in open
position and the fuses shall be taken out. A warning sign bearing a
legend such as ”work in progress; do not supply voltage” shall be
attached to the fuse box or main switch.
4 Before dismantling any pressurized component, the compressor or
equipment shall be effectively isolated from all sources of pressure and
the entire system shall be relieved of pressure. Do not rely on non-retur n
valves (check valves) to isolate pressure systems. In addition, a warning
sign bearing a legend such as ”work in progress; do not open” shall be
attached to each of the outlet valves.
5 Prior to stripping an engine or other machine or undertaking major
overhaul on it, prevent all movable parts from rolling over or moving.
6 Make sure that no tools, loose parts or rags are left in or on the machine.
Never leave rags or loose clothing near the engine air intake.
7 Never use flammable solvents for cleaning (fire-risk).
8 Take safety precautions against toxic vapours of cleaning liquids.
9 Never use machine parts as a climbing aid.
10 Observe scrupulous cleanliness during maintenance and repair. Keep
away dirt, cover the parts and exposed openings with a clean cloth,
paper or tape.
11 Never weld on or perform any operation involving heat near the fuel or
oil systems. Fuel and oil tanks must be completely purged, e.g. by
steam-cleaning, before carrying out such operations. Never weld on, or
in any way modify, pressure vessels. Disconnect the alternator cables
during arc welding on the unit.
12 Support the towbar and the axle(s) securely if working underneath the
unit or when removing a wheel. Do not rely on jacks.
13 Do not remove any of, or tamper with, the sound-damping material.
Keep the material free of dirt and liquids such as fuel, oil and cleansing
agents. If any sound-damping material is damaged, replace it to prevent
the sound pressure level from increasing.
14 Use only lubricating oils and greases recommended or approved by
Atlas Copco or the machine manufacturer. Ascertain that the selected
lubricants comply with all applicable safety regulations, especially with
regard to explosion or fire-risk and the possibility of decomposition or
generation of hazardous gases. Never mix synthetic with mineral oil.
15 Protect the engine, alternator, air intake filter, electrical and regulating
components, etc., to prevent moisture ingress, e.g. when steam-cleaning.
16 When performing any operation involving heat, flames or sparks on a
machine, the surrounding components shall first be screened with nonflammable material.
17 Never use a light source with open flame for inspecting the interior of a
machine.
18 When repair has been completed, the machine shall be barred over at
least one revolution for reciprocating machines, several revolutions for
rotary ones to ensure that there is no mechanical interference within the
machine or driver. Check the direction of rotation of electric motors
when starting up the machine initially and after any alteration to the
electrical connection(s) or switch gear, to check that the oil pump and
the fan function properly.
19 Maintenance and repair work should be recorded in an operator’s
logbook for all machinery. Frequency and nature of repairs can reveal
unsafe conditions.
20 When hot parts have to be handled, e.g. shrink fitting, special heat-
resistant gloves shall be used and, if required, other body protection
shall be applied.
21 When using cartridge type breathing filter equipment, ascertain that the
correct type of cartridge is used and that its useful service life is not
surpassed.
22 Make sure that oil, solvents and other substances likely to pollute the
environment are properly disposed of.
23 Before clearing the unit for use after maintenance or overhaul, check
that operating pressures, temperatures and speeds are correct and that
the control and shutdown devices function correctly. Submit the
generator to a testrun, check that the AC power performance is correct.
1.6 TOOL APPLICATIONS SAFETY
Apply the proper tool for each job. With the knowledge of correct tool use
and knowing the limitations of tools, along with some common sense, many
accidents can be prevented.
Special service tools are available for specific jobs and should be used when
recommended. The use of these tools will save time and prevent damage to
parts.

11
Instruction Manual
1.7 SPECIFIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Batteries
When servicing batteries, always wear protecting clothing and glasses.
1 The electrolyte in batteries is a sulphuric acid solution which is fatal if it
hits your eyes, and which can cause burns if it contacts your skin.
Therefore, be careful when handling batteries, e.g. when checking the
charge condition.
2 Install a sign prohibiting fire, open flame and smoki ng at the post where
batteries are being charged.
3 When batteries are being charged, an explosive gas mixture forms in the
cells and might escape through the vent holes in the plugs.
Thus an explosive atmosphere may form around the battery if
ventilation is poor, and can remain in and around the battery for several
hours after it has been charged. Therefore:
- never smoke near batteries being, or hav i ng recently been, charged,
- never break live circuits at battery terminals, because a spark usually
occurs.
4 When connecting an auxiliary battery (AB) in parallel to the unit battery
(CB) with booster cables: connect the + pole of AB to the + pole of CB,
then connect the - pole of CB to the mass of the unit. Disconnect in the
reverse order.
Pressure vessels
(according to directive 87/404/EEC annex II § 2)
Maintenance/installation requirements:
1 The vessel can be used as pressure vessel or as separator and is designed
to hold compressed air for the following application:
- pressure vessel for compressor,
-medium AIR/OIL,
and operates as detailed on the data plate of the vessel:
- the maximum working pressure ps in bar,
- the maximum working temperature Tmax in °C,
- the minimum working temperature Tmin in °C,
- the capacity of the vessel V in l.
2 The pressure vessel is only to be used for the applications as specified
above and in accordance with the technical specifications. Safety
reasons prohibit any other applications.
3 National legislation requirement s with respect to re-inspection must be
complied with.
4 No welding or heat treatment of any kind is permitted to those vessel
walls which are exposed to pressure.
5 The vessel is provided and may only be used with the required safety
equipment such as manometer, overpressure control devices, safety
valve, etc.
6 Draining of condensate shall be performed regularly when vessel is in
use.
7 Installation, design and connections should not be changed.
8 Bolts of cover and flanges may not be used for extra fixation.
Safety valves
All adjustments or repairs are to be done by an authorized representative of
the valve supplier (see maintenance schedule 4.2).
12
Instruction Manual
2. LEADING PARTICULARS
2.1 DESCRIPTION OF SAFETY PICTOGRAMS USED IN THIS MANUAL
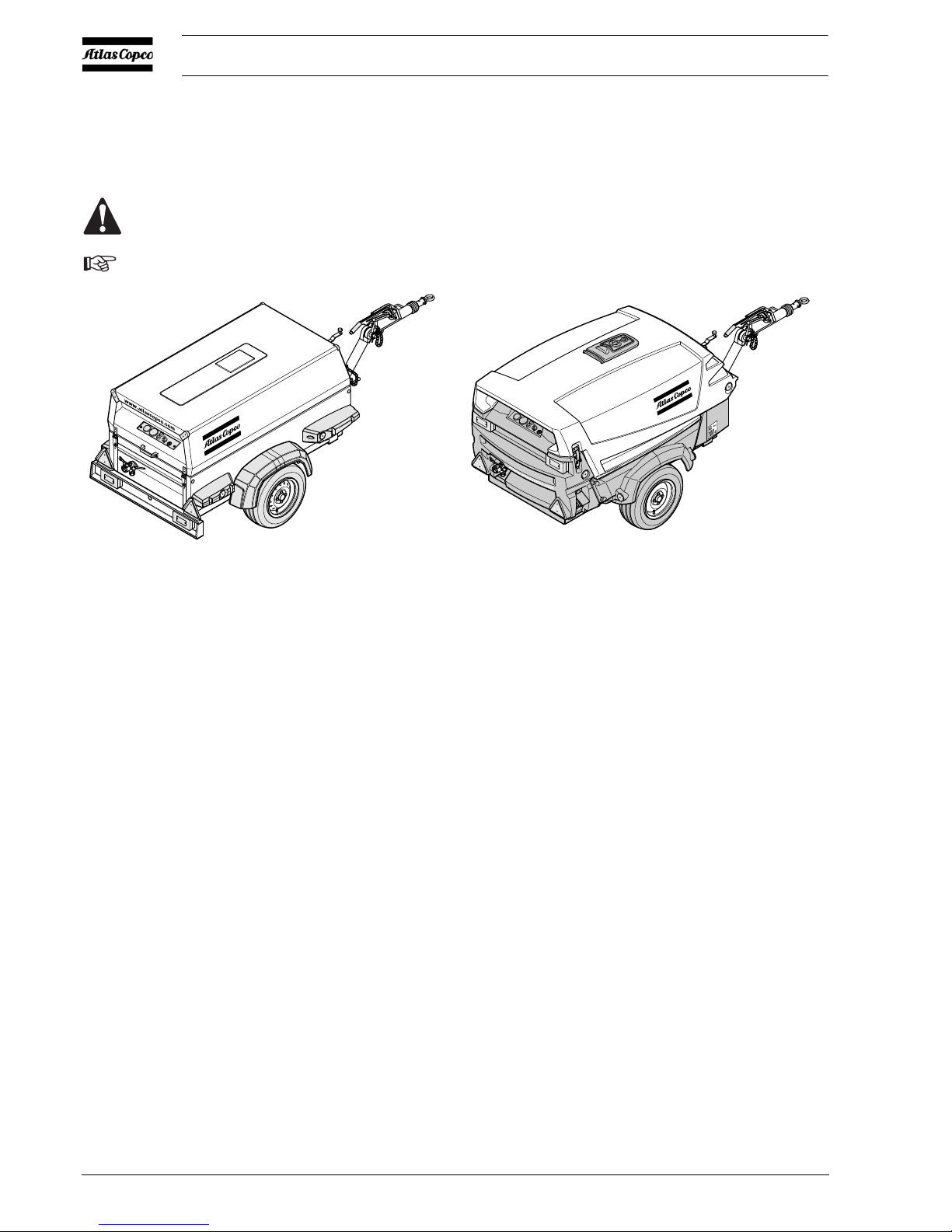
Fig. 2.1.a General view metal canopy
2.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The compressors type XAHS 37 DD - XAHS 70 DD7,
XAS 47 DD - XAS 90 DD7 and XAS 57 DD - XAS 110 DD7 are
silenced, single-stage, oil-injected screw compressors, built for a
nominal effective working pressure, ranging from 7 bar up to 12 bar
(see chapter 8, technical specifications).
The compressor is available with metal or PE canopy (HardHat).
–Engine
The compressor is driven by an oil-cooled diesel engine.
The engine’s power is transmitted to the compressor through a
heavy-duty drive belt.
– Compressor element
The compressor casing houses two screw-type rotors, mounted on
ball and roller bearings. The male rotor, driven by the engine, drives
the female rotor. The element delivers pulsation-free air.
Injected oil is used for sealing, cooling and lubricating purposes.
– Compressor oil system
The oil is boosted by air pressure. The system has no oil pump.
The oil is removed from the air, in the air/oil vessel at first by
centrifugal force, secondly through the oil separator element.
The vessel is provided with an oil level indicator.
Fig. 2.1.b General view HardHat
This symbol draws your attention to dangerous
situations. The operation concerned may endanger
persons and cause injuries.
This symbol is followed by supplementary information.

13
Instruction Manual
– Regulation
The compressor is provided with a continuous regulating system and
a blow-down valve which is integrated in the unloader assembly . The
valve is closed during operation by outlet pressure of the compressor
element and opens by air receiver pressure when the compressor is
stopped.
When the air consumption increases, the air receiver pressure will
decrease and vice versa.
This receiver pressure variation is sensed by the regulating valve
which, by means of control air to the unloader and engine speed
regulator, matches the air output to the air consumption. The air
receiver pressure is maintained between the pre-selected working
pressure and the corresponding unloading pressure.
– Cooling system
Engine and compressor are provided with an oil cooler.
The cooling air is generated by a fan, driven by the engine.
– Safety devices
A thermal shut-down switch protects the compressor against
overheating. The air receiver is provided with a safety valve.
The engine is equipped with low oil pressure and high oil
temperature shut-down switches.
– Frame and axle
The compressor/engine unit is supported by rubber buffers in a
spillage-free frame. The standard unit has a none adjustable towbar
with support leg and one of the following towing eyes AC, DIN, ball,
ITA, GB or NATO.
As an option the unit can be equipped with an adjustable towbar, a
jockey wheel and/or overrun parking brake (for options see chapter
7).
The braking system consists of an integrated parking brake and
overrunbrake. When driving backwards the overrunbrake is not
engaged automatically.
– Bodywork
The bodywork has openings at the shaped front and rear end for the
intake and outlet of cooling air and a hood for maintenance and
service operations. The bodywork is internally lined with soundabsorbing material.
–Lifting eye
A lifting eye is accessible when the small door at the top of the unit
is unlocked.
– Control panel
The control panel grouping the air pressure gauge, control switch
etc., is placed in the center at the rear end.
– Data plate
The compressor is furnished with a data plate showing the product
code, the unit number and the working pressure (see chapter 9).
– Serial number
The serial number is located on the right-hand front side of the
frame.
– Generator (option for XAS 47 DD - XAS 90 DD7)
The built-in generator is driven by a multi V -belt drive. The generated
current can be drawn via 3 sockets (see chapter 8, Technical
Specifications).
The compressor and the generator of the XAS 47 DDG XAS 90 DD7G / DDG IT may be used simultaneously.
As an option the generator can be equipped with an automatic control
system to save fuel when no electric power is used.
14
Instruction Manual
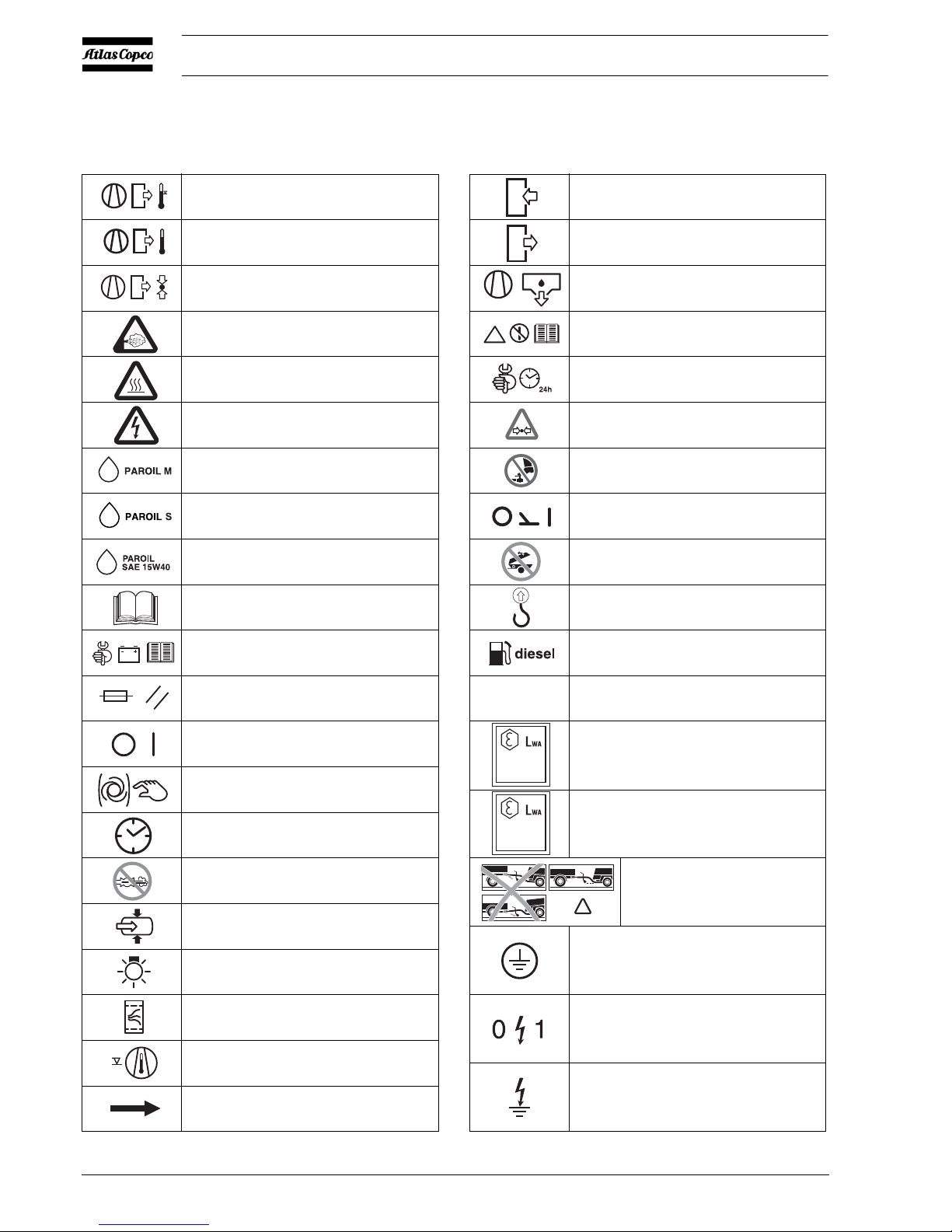
2.3 MARKINGS AND INFORMATION LABELS
Compressor outlet temperat ure too high.
Compressor outlet temperature.
Compressor outlet pressure.
Dangerous outlet.
Danger, heat flat.
Electrocution hazard.
Atlas Copco mineral compressor oil.
Atlas Copco synthetic compressor oil.
Atlas Copco mineral engine oil.
Manual.
Read the instruction manual
before working on the battery.
Reset fuse.
On / off button.
Manual override switch.
Hours, time.
Prohibition to open air valves without conn e cted h os es.
Compressor loaded.
Runlamp.
Airfilter.
Compressor temperature too high.
Rotation direction.
Inlet.
Outlet.
Compressor oil drain.
Read the instruction manual before starting.
Service every 24 hours.
Warning!
Part under pressure.
Do not stand on outlet valves.
Start-Stop indication of switch.
Do not run the motor with open doors.
Lifting permitted.
Use diesel fuel only.
Tyre pressure.
Sound power level in accordance with
Directive 2000/14/EC (expressed in dB (A)).
Sound power level in accordance with
Directive 2000/14/EC (expressed in dB (A)).
Horizontal towbar position required
in case of coupling.
Earthing connections.
Generator
Insulation fault.
2.7 bar / 39 psi
98
10 0
0 = OFF
1 = ON
15
Instruction Manual
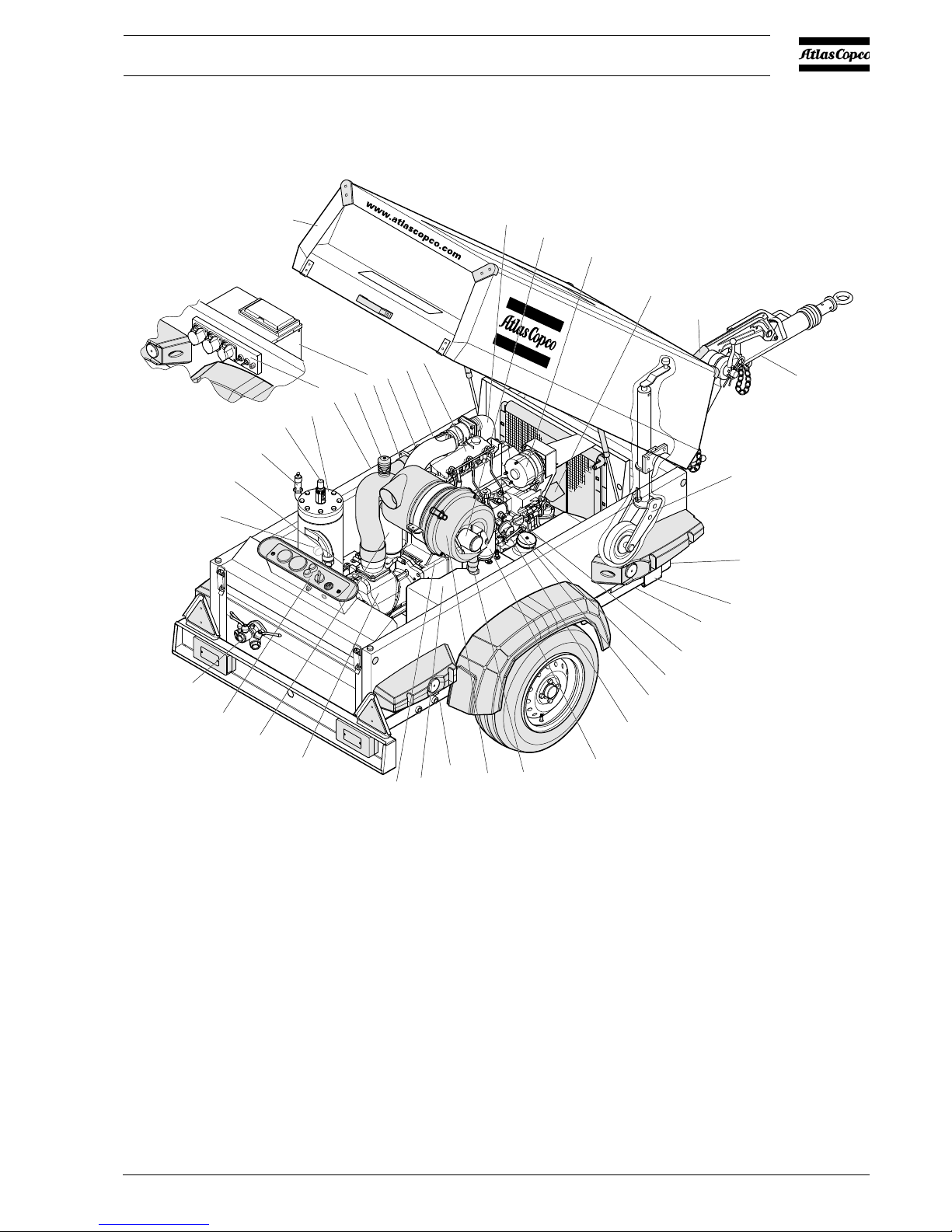
2.4 MAIN PARTS
Fig. 2.2 Main parts with some options
AAlternator DPFTDrain Plug Fuel Tank H Hood
AF Air Filter DS
E
Engine Oil Level Dipstick JW Jockey wheel
AFD Anti-Frost Device (option) E Engine OF
CE
Oil Filter (compressor element)
AOV Air outlet valves EP Exhaust Pipe OF
E
Oil Filter (engine)
AR Air Receiver F Fan OLG Oil Level Gauge (compressor element)
BH Brake Handle FC
1
Filler Cap (engine oil) RV Regulating Valve
CE Compressor Element FC
2
Filler Cap (fuel tank) S Starting Motor
CP Control Panel (compressor) FF Fuel Filter SN Serial Number
CP
G
Control Panel (generator), (option) FP Filler Plug (compressor oil) SV Safety Valve
D Data plate FT Fuel Tank TB Towbar
DB Drive Belt FU Fuel Pump VI Vacuum Indicator
DP
EC
Drain Plug Engine Oil Cooler G Generator (option) VV Vacuator Valve
SV
A
VI
AR
RV
FP
G
OLG
AOV
CP
DB
AF
VV
FF
FU
CE
F
EP
FT
D
SN
1
FC
2
FC
EC
DP
E
DS
E
OF
CE
OF
JW
BH
TB
H
FT
DP
G
CP
S
E
AFD
16
Instruction Manual
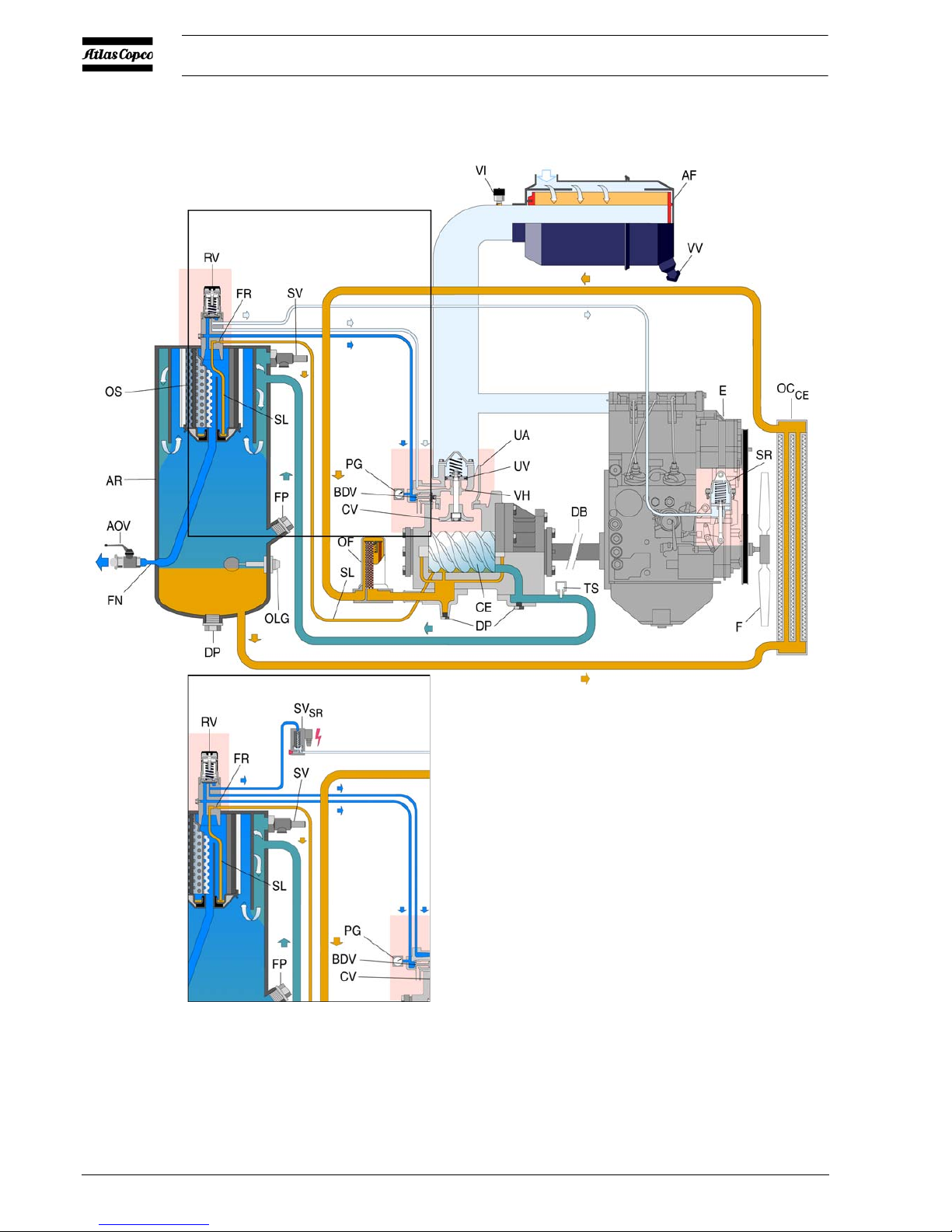
COMPRESSOR REGULATING SYSTEM
Fig. 2.3
With generator
Without generator
AF Air Filter
AR Air Receiver
AOV Air Outlet Valves
BDV Blow Down Valve
CE Compressor Element
CV Check Valve
DB Drive Belt
DP Drain Plug
E Engine
FFan
FN Flow Nozzle
FP Filler Plug
FR Flow Restrictor
OC
CE
Oil Cooler
(compressor element)
OF Oil Filter
OLG Oil Level Gauge
OS Oil Separator
PG Pressure Gauge
RV Regulating Valve
SL Scavenge Line
SR Speed Regulator
SV Safety Valve
SV
SR
Solenoid Valve
(Speed regulator)
TS Temperature Switch
UA Unloader Assembly
UV Unloader Valve
VH Vent Hole
VI Vacuum Indicator
VV Vacuator Valve

17
Instruction Manual
2.5 AIR FLOW (SEE FIG. 2.3)
The system comprises:
AF Air filter
AR/OS Air receiver/oil separator
CE Compressor element
UA/UV Unloader assembly with unloader valve
BDV Blow-down valve
FN Flow nozzle
Air drawn through the airfilter (AF) into the compressor element
(CE) is compressed. At the element outlet, compressed air and oil
pass into the air receiver/oil separator (AR/OS).
The check valve (CV) prevents blow-back of compressed air when
the compressor is stopped. In the air receiver/oil separator (AR/OS),
most of the oil is removed from the air/oil mixture; the remaining oil
is removed by the separator element.
The oil collects in the receiver and on the bottom of the separator
element.
The air leaves the receiver via a flow nozzle (FN) which prevents the
receiver pressure from dropping below the minimum working
pressure (specified in section 8.3), even when the air outlet valves
are open. This ensures adequate oil injection and prevents oil
consumption.
A temperature switch (TS) and a working pressure gauge (PG) are
comprised in the system.
A blow-down valve (BDV) is fitted in the unloader assembly to
automatically depressurise the air receiver (AR) when the
compressor is stopped.
2.6 OIL SYSTEM (SEE FIG. 2.3)
The system comprises:
AR/OS Air receiver/oil separator
OC
CE
Oil cooler
OF Oil filter
The lower part of the air receiver (AR) serves as oil tank.
Air pressure forces the oil from the air receiver/oil separator (AR/
OS) through the oil cooler (OC
CE
) and oil filter (OF) to the
compressor element (CE).
The compressor element has an oil gallery in the bottom of its casing.
The oil for rotor lubrication, cooling and sealing is injected through
holes in the gallery .
Lubrication of the bearings is ensured by oil injected into the bearing
housings.
The injected oil, mixed with the compressed air, leaves the
compressor element and re-enters the air receiver, where it is
separated from the air as described in section 2.5. The oil that
collects in the bottom of the oil separator element is returned to the
system through a scavenging line (SL), which is provided with a
flow restrictor (FR).
The oil filter by-pass valve opens when the pressure drop over the
filter is above normal because of a clogged filter. The oil then bypasses the filter without being filtered. For this reason, the oil filter
must be replaced at regular intervals (see section 4.2).
When cold start equipment is installed; a thermostatic valve wil l
bypass the compressor oil (oil will not pass through oil cooler
OC
CE
), until the working temperature is reached.
2.7 CONTINUOUS REGULATING SYSTEM
(
SEE FIG. 2.3)
The system comprises:
R V Regulating valve
UA Unloader assembly
SR Speed regulator
The compressor is provided with a continuous regulating system.
This system is provided with a blow-down valve which is integrated
in the unloader assembly (UA). The valve is closed during operation
by outlet pressure of the compressor element and opens by air
receiver pressure when the compressor is stopped.
When the air consumption increases, the air receiver pressure will
decrease and vice versa. This receiver pressure variation is sensed by
the regulating valve which, by means of control air to the unloader,
matches the air output to the air consumption. The air receiver
pressure is maintained between the pre-selected working pressure
and the corresponding unloading pressure.
When starting the compressor, the unloader valve (UV) is kept open
by spring force, the engine runs at maximum speed. The compressor
element (CE) takes in air and pressure builds up in the receiver (AR).
The air output is controlled from maximum output (100%) to no
output (0%) by:
1. Speed control of the engine between maximum load speed and
unloading speed (the output of a screw compressor is
proportional to the rotating speed).
2. Air inlet throttling.
If the air consumption is equal to or exceeds the maximum air output,
the engine speed is held at maximum load speed and the unloading
valve is fully open.
If the air consumption is less than the maximum air output, the
regulating valve supplies control air to unloader valve (UV) to
reduce the air output and holds air receiver pressure between the
normal working pressure and the corresponding unloading pressure
of approx. 1.5 bar above the normal working pressure.
When the air consumption is resumed, the unloader valve (UV)
gradually opens the air intake and the speed regulator (SR) increases
the engine speed.
The construction of the regulating valve (RV) is such that any
increase (decrease) of the air receiver pressure above the pre-set
valve opening pressure results in a proportional increase (decrease)
of the control pressure to the unloading valve and the speed
regulator.
Part of the control air is vented to the atmosphere, and any
condensate discharged, through the vent holes (VH).
Generator
When the generator is switched on, the solenoid valve (SV
SR
) via the
speed regulator (SR) controls the engine and allows it to reach
maximum speed (the normal control system is switched off).
18
Instruction Manual
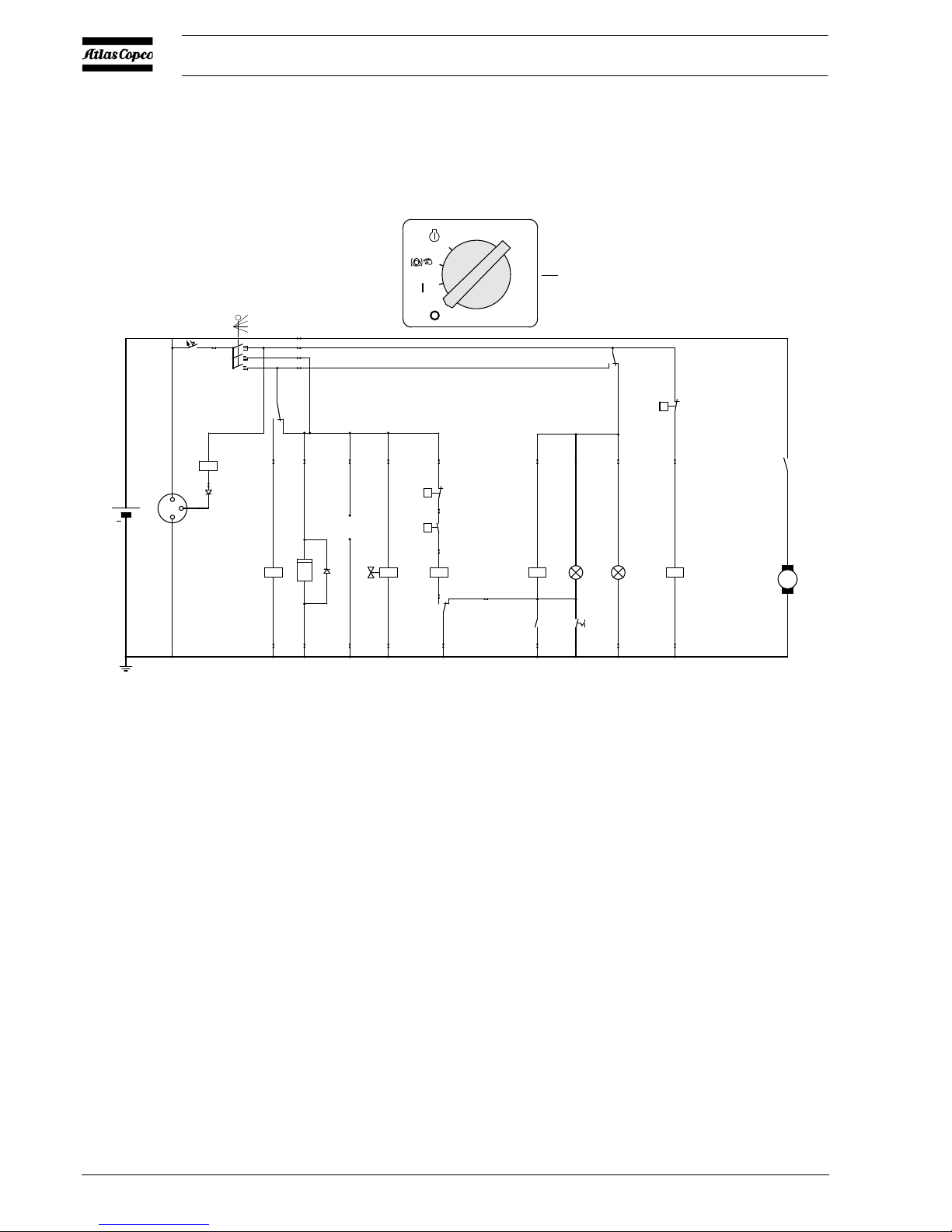
2.8 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
2.8.1 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM (STANDARD)
The compressor is equipped with a negative earthed system.
Fig. 2.4 Circuit diagram (No. 9822 0797 01)
F1 Circuit Breaker (10 A) M1 Starter Motor
G1 Alternator P1 Hourmeter
G2 Battery S1 Contact Switch (Off-On-Override-start)
H1 Temperature Alarm Lamp S2 Temperature Switch Engine
H2 General Alarm Lamp S3 Oil Pressure Switch Engine
K0 Starter Solenoid (part of M1) S4 Lamptest Switch
K1 Shut-down Relay S5 Temperature Switch Compressor
K2 Blocking Relay Y1 Fuel Solenoid Valve
K3 Override Start Relay V1 Diode
K4 Start Relay V2 Diode
S1
3
2
1
0
q
q
21
20
6
8
7
9
24
25
28
29
3
5
4
21
8«
7«
1«
2«
12
14
4«
3«
26
27
12«
34
35
9´,10´,11´
p
12V DC
5«
Tem p
K1
General
alarm
(Lamp tester)
13«
15«
14«
11
10
13
11999
15
14
Auxiliary
33338
18
1615
4
3
2
1
3
2
1
0
32
33
31
30
5
10A
2322
19
17
6
7
6«
D-
D+
B+
+
M
M1
K0
S2
S3
G2
G1
K4
F1
S1
K4
K3
S5
K1H2H1K2
S4
K2
1212
V1
h
12121212121212
K3Y1
P1
K0
V2
10
13
19
Instruction Manual
Fig. 2.5 Location of relais K1-K4
Operation of the electric circuit in detail
Start switch S1 position 1:
Line 2 on 12V contact K3 closed (13-11), lamp H2 is on. K4
excites contact K4 (18-15). Thermocontact element S5 normally
closed, K1 excites contact K1 (1-4).
Use of lamp test:
Start switch S1 position 1 press lamp test S4, across K3 and line
9 lamp H1 and relay K2 are excited. After releasing lamp test
button S4, lamp H1 remains on, S4 taken over by contact K2.
Start switch S1 position 2:
Line 3 on 12V (overwrite function) hourmeter P1 and fuel
solenoid Y1 excited. Thermocontact engine S2 normally closed,
oil pressure contact S3 open.
Start switch S1 position 3:
Start relay K0 is excited and starter motor is running, engine
builds up oil pressure and oil pressure contact S3 closes. K3
excited and contact K3 changes over to (13-10). Relay K2 no
longer excited, contact K2 opens, lamp H1 goes out. Alternator
also commences supplying voltage and K4 is no longer excited
and contact K4 changes over to (18-16). Lamp H2 goes out, one
can release start switch S1 and it returns to position 1. Exciting
the safety devices occurs no longer across line 3 but across line 2
to line 4 and this way to line 3.
Engine is running normally:
Oil pressure contact S3 opens, K3 no longer excited. K3 changes
over (13-11), engine cuts out because fuel solenoid Y1 no longer
excited and lamp H2 goes on simultaneously.
Thermocontact S2 opens, K3 no longer excited. K3 changes over
(13-11), engine cuts out because fuel solenoid Y1 no longer
excited and lamp H2 goes on simultaneously.
Thermocontact S5 opens, K1 no longer excited. Contact K1
changes over (4-2). K3 no longer excited. K3 changes over (13-
11), engine cuts out because fuel solenoid Y1 no longer excited
and lamp H2 and H1 go on simultaneously. Take-over relay K2
is excited simultaneously with H1 and contact K2 cl oses (8-6).
Thermocontact S5 cools off and closes, K1 excited again and
contact K1 changes over (4-1). However, lamp H1 remains on
across line 9 and contact K2 (6-8).
A fault in the alternator part causes terminal D+ to go to 0V and
K4 to be excited. Contact K4 changes over to (18-15), engine
cuts out because fuel solenoid Y1 no longer excited and lamp H2
goes on simultaneously.
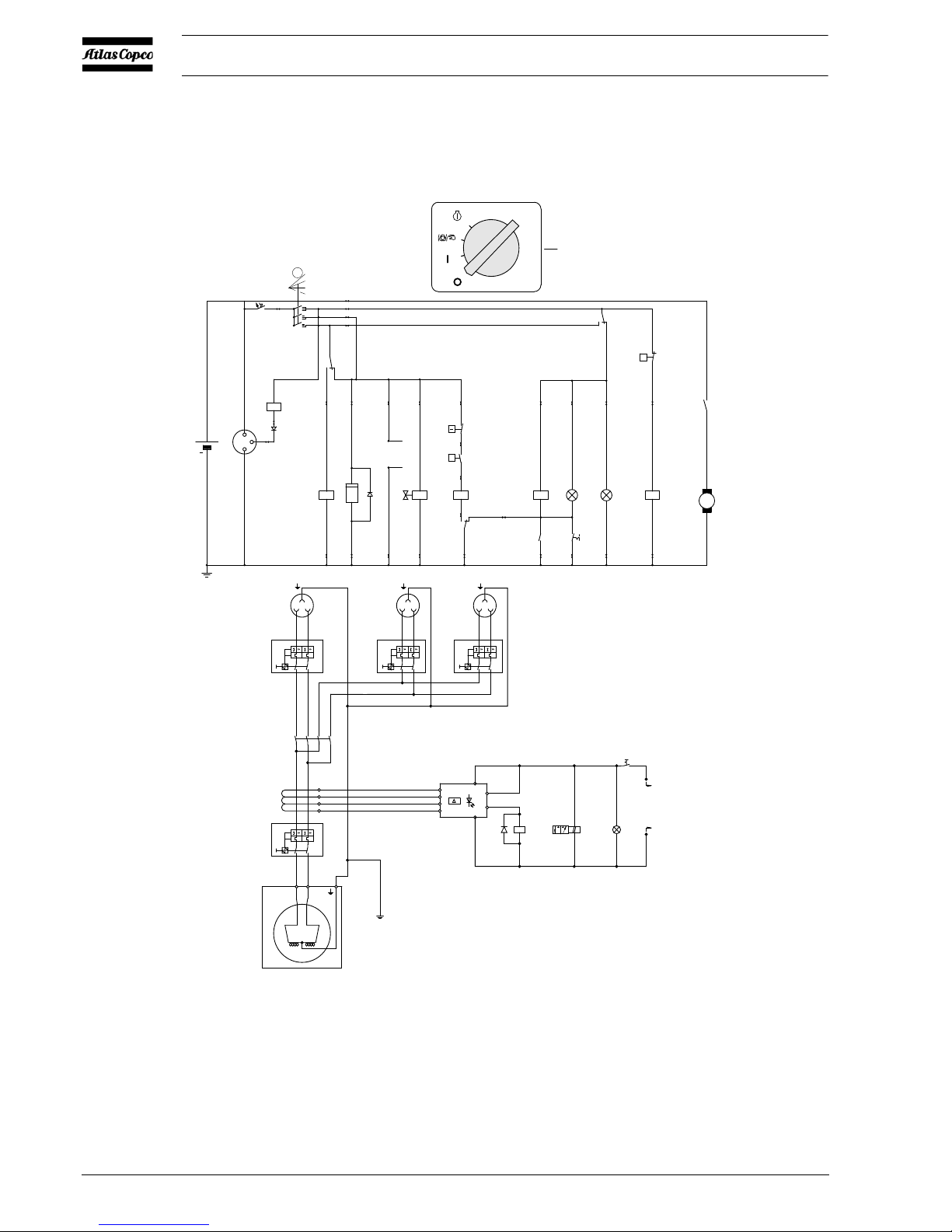
20
Instruction Manual
2.8.2 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM XAS 47 DDG XAS 90 DD7G (G
ENERATOR DDG 110V
WITHOUT AUTOMATIC CONTROL SYSTEM)
(Not on HardHat)
The compressor is equipped with a negative earthed system.
10
12 12 12 12 12 12 12
V2
h
V1
12
12
K2
S4
K2
H1
H2
K1
S5
K3
K4
S1
F1
K4
G1
G2
K0
P1
Y1
K3
S3
S2
K0
M1
M
+
B+
D+
D-
6'
7
6
17
19
22 23
10A
5
30
31
33
32
1
2
3
4
15
16
18
83 3 3 3
35
34
12'
27
26
3'
4'
14
12
2'
1'
7'
8'
15
12
4
99 9 11
13
10
11
14'
15'
13'
5
3
29
28
25
24
9
7
8
62021
(Lamp tester)
General
alarm
K1
Temp
5'
12V DC
0
p
9',10',11'
0
1
2
3
13
Auxiliary
To Circuit diagram
9822 1055 27
S1
3
2
1
0
X3
3L1
3L2
L2L1
16A
e54
c0c0
X2
L2L1
16A
H3
A1
A2
K5
52
51
S7
P
B
R
Y2
K5
123
4
V
W
V1
W1
1L1
1L2
2L1
2L2
50A
Q1
b3
G
G3
VW
14
12
3
13
b6 b6
12
b6
b3
To Circuit diagram
9822 0797 01
b6
b3
13
12
12
b3
13
35
34
e54
c0c0
e54
e0e0
f0f0
f0f0
e0e0
e0e0
e0e0
e54
567
8
X1
L2L1
32A
32A
Q2
16A
Q3
16A
Q4
13
b3
L1
L2
b6
12
b3
I n
30mA
40msec
4
5
6
7
10
11
1
3
N13
D1
e0
e0
1
2
3
4
T13
EARTHING PIN
Fig. 2.6 Circuit diagram (No. 9822 0797 01 + No. 9822 1055 27)
For location of relais K1, K2, K3, K4, see paragraph 2.8.1
D1 Diode
F1 Circuit Breaker (10A)
G1 Alternator
G2 Battery
G3 Generator
H1 Temperature Alarm Lamp
H2 General Alarm Lamp
H3 Lamp (Power ON)
K0 Starter Solenoid (part of M1)
K1 Shut-down Relay
K2 Blocking Relay
K3 Override Start Relay
K4 Start Relay
K5 Contactor
M1 Starter Motor
N13 Earth fa ul tc urrent relay
P1 Hourmeter
Q1 Main circuit breaker 2-pole
Q2 Circuit breaker 2-pole
Q3 Circuit breaker 2-pole
Q4 Circuit breaker 2-pole
S1 Contact Sw itch (Off-On-
Override-start)
S2 Temperature Switch Engine
S3 Oil Pressure Switch Engine
S4 Lamptest Switch
S5 Temperature Switch
Compressor
S7 Switch (Generator-compressor)
T13 Current transformer for N13
V1 Diode
V2 Diode
X1 Socket outlet
X2 Socket outlet
X3 Socket outlet
Y1 Fuel solenoid Valve
Y2 Solenoid valve (Generator
action)
 Loading...
Loading...