Page 1

COMPACT ROUTER
ADSL
A02-RA110
USER’S MANUAL
A02-RA110 _ME01
Page 2

Page 3

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
INDEX
CHAPTER 1: GETTING TO KNOW THE ADSL ROUTER 1
1.1 Introducing the Compact Router ADSL 1
1.2 Package Contents 1
1.3 Features of the Compact Router ADSL 2
1.4 Applications for the ADSL Router 4
1.4.1 Internet Access 4
CHAPTER 2: USING COMPACT ROUTER ADSL 6
2.1 Cautions for using the Compact Router ADSL 6
2.2 The Front Panel LEDs 6
2.3 The Rear Ports 7
2.4 Cabling 8
CHAPTER 3: INTRODUCING THE WEB CONFIGURATOR 9
3.1 Web Configurator Overview 9
3.2 Configuring PC in Windows 10
3.2.1 For Windows 95/98/ME 10
3.2.2 For Windows NT4.0 10
3.2.3 For Windows 2000 10
3.2.4 For Windows XP 11
3.3 Factory Default Settings 14
3.3.1 Username and Password 14
3.3.2 LAN and WAN Port Addresses 14
3.4 Information from the ISP 14
3.5 Accessing the ADSL Router Web Configurator 15
3.6 Navigating the Compact Router ADSL Web Configurator 16
3.7 Configuring Password 17
3.8 Resetting the ADSL Router 18
3.8.1 Using The Reset Button 18
CHAPTER 4: WIZARD SETUP 19
4.1 Wizard Setup Introduction 19
Page 4

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
4.2 Encapsulation 19
4.2.1 ENET ENCAP 19
4.2.2 PPP over Ethernet 19
4.2.3 PPPoA 19
4.2.4 RFC 1483 20
4.3 Multiplexing 20
4.3.1 VC-based Multiplexing 20
4.3.2 LLC-based Multiplexing 20
4.4 VPI and VCI 20
4.5 Wizard Setup Configuration: First Screen 20
4.6 IP Address and Subnet Mask 22
4.7 IP Address Assignment 22
4.7.1 IP Assignment with PPPoA or PPPoE Encapsulation 23
4.7.2 IP Assignment with RFC 1483 Encapsulation 23
4.7.3 IP Assignment with ENET ENCAP Encapsulation 23
4.7.4 Private IP Addresses 23
4.8 Nailed-Up Connection (PPP) 23
4.9 NAT 24
4.10 Wizard Setup Configuration: Second Screen 24
4.10.1 PPPoE 24
4.10.2 RFC 1483 25
4.10.3 ENET ENCAP 27
4.10.4 PPPoA 28
4.11 DHCP Setup 30
4.11.1 IP Pool Setup 30
4.12 Wizard Setup Configuration: Third Screen 30
4.13 Wizard Setup Configuration: Connection Tests 33
4.14 Test Your Internet Connection 33
CHAPTER 5: LAN SETUP 34
5.1 LAN Overview 34
5.1.1 LANs, WANs and the ADSL Router 34
5.2 DNS Server Address 35
5.3 DNS Server Address Assignment 35
5.4 LAN TCP/IP 36
5.4.1 Factory LAN Defaults 36
5.4.2 IP Address and Subnet Mask 36
5.4.3 RIP Setup 36
5.4.4 Multicast 37
5.5 Configuring LAN 38
Page 5

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 6: WAN SETUP 40
6.1 WAN Overview 40
6.2 PPPoE Encapsulation 40
6.3 PPTP Encapsulation 40
6.4 Traffic Shaping 41
6.5 Configuring WAN Setup 42
CHAPTER 7: NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION (NAT) 46
7.1 NAT Overview 46
7.1.1 NAT Definitions 46
7.1.2 What NAT Does 47
7.1.3 How NAT Works 47
7.1.4 NAT Application 48
7.1.5 NAT Mapping Types 49
7.2 SUA (Single User Account) Versus NAT 49
7.3 SUA Server 50
7.3.1 Port Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers 50
7.3.2 Configuring Servers Behind SUA (Example) 51
7.4 Selecting the NAT Mode 52
7.5 Configuring SUA Server 53
7.6 Configuring Address Mapping 54
7.7 Editing an Address Mapping Rule 56
CHAPTER 8: SECURITY 58
CHAPTER 9: DYNAMIC DNS SETUP 59
9.1 Dynamic DNS 59
9.1.1 DYNDNS Wildcard 59
9.2 Configuring Dynamic DNS 59
CHAPTER 10: TIME AND DATE SETUP 61
10.1 Configuring Time Zone 61
CHAPTER 11: REMOTE MANAGEMENT CONFIGURATION 64
11.1 Remote Management Overview 64
11.1.1 Remote Management Limitations 64
11.1.2 Remote Management and NAT 64
Page 6

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
11.1.3 System Timeout 65
11.2 Telnet 65
11.3 FTP 65
11.4 Web 65
11.5 Configuring Remote Management 65
CHAPTER 12: MAINTENANCE 67
12.1 Maintenance Overview 67
12.2 System Status Screen 67
12.2.1 System Statistics 69
12.3 DHCP Table Screen 70
12.4 Diagnostic Screens 71
12.4.1 Diagnostic General Screen 71
12.4.2 Diagnostic DSL Line Screen 72
12.5 Firmware Screen 74
APPENDIX A: TROUBLESHOOTING 76
A.1 Using LEDs to Diagnose Problems 76
A.1.1 Power LED 76
A.1.2 LAN LED 76
A.1.3 DSL LED 76
A.2 Telnet 77
A.3 Web Configurator 77
A.4 Login Username and Password 78
A.5 LAN Interface 79
A.6 WAN Interface 79
A.7 Internet Access 80
A.8 Remote Management 80
A.9 Remote Node Connection 81
APPENDIX B: TECHNICAL FEATURES 82
APPENDIX C:SUPPORT 83
A02-RA110_ME01 (V1.0 July 2004)
Page 7

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Page 8

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Copyright
The Atlantis Land logo is a registered trademark of Atlantis Land SpA. All other
names mentioned mat be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
owners. Subject to change without notice. No liability for technical errors and/or
omissions.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause
radio interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the regulations for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with this user’s guide, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
Page 9

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
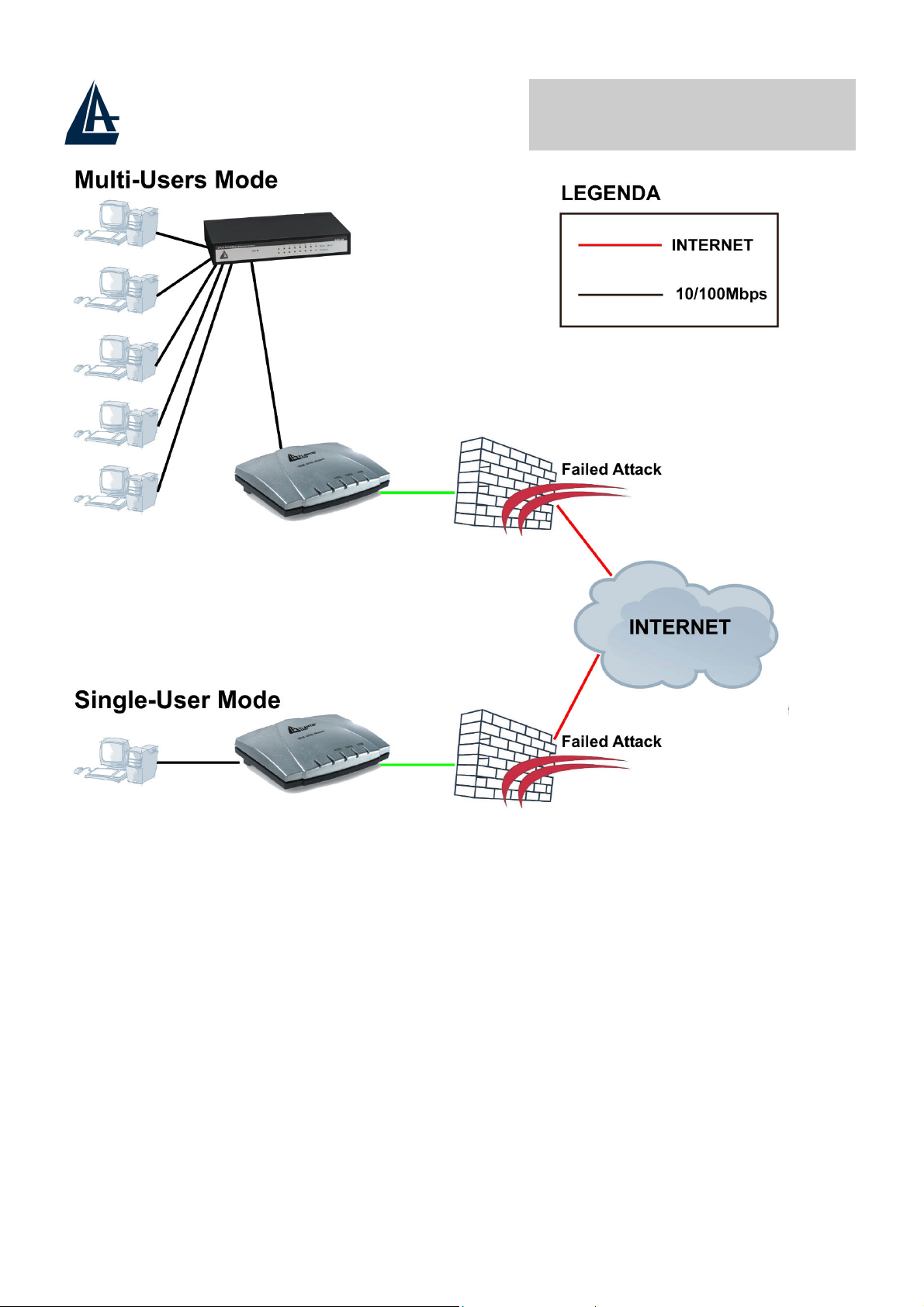
CHAPTER 1: Getting to Know the ADSL Router
This chapter describes the key features and applications of ADSL Router.
1.1 Introducing the Compact Router ADSL
Broadband Sharing and IP sharing
The Compact Router ADSL supports 1 port 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiating Fast
Ethernet for connection to your PC or LAN and downstream (with built-in ADSL
modem) rate up to 8Mbps. Power by NAT technology, dozens of network users
can surf on the Internet and share the ADSL connection simultaneously by using
one ISP account and one single IP address.
Easy Configuration and Management
Support web based GUI and Telnet for configuration and management.
The web browser-based Graphical User Interface provides easy management
and is totally independent of the operating system platform you use.
Also supports remote management (Web and telnet) capability for remote user to
configure and manage this product. It incorporates besides a client Dynamic
DNS.
1.2 Package Contents
•
Compact Router ADSL
•
One CD-ROM containing the online manual
•
One Quick Start Guide
•
One RJ-11 ADSL/telephone cable
•
One CAT-5 LAN cable
• One AC-DC power adapter (9VDC, 1A)
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
A02-RA110 Pag. 1
Page 10

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
1.3 Features of the Compact Router ADSL
The following sections describe the features of the ADSL Router.
High Speed Internet Access: The ADSL Router can support downstream
transmission rates of up to 8Mbps and upstream transmission rates of 832 Kbps.
PPPoE Support (RFC2516): PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)
emulates a dial-up connection. It allows your ISP to use their existing network
configuration with newer broadband technologies such as ADSL. The PPPoE
driver on the ADSL Router is transparent to the computers on the LAN, which see
only Ethernet and are not aware of PPPoE thus saving you from having to
manage PPPoE clients on individual computers.
Network Address Translation (NAT): Network Address Translation (NAT) allows
the translation of an Internet protocol address used within one network (for
example a private IP address used in a local network) to a different IP address
known within another network (for example a public IP address used on the
Internet).
10/100M Auto-negotiation Ethernet/Fast Ethernet Interface: This autonegotiation feature allows the ADSL Router to detect the speed of incoming
transmissions and adjust appropriately without manual intervention. It allows data
transfer of either 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode
depending on your Ethernet network.
Dynamic DNS Support: With Dynamic DNS support, you can have a static
hostname alias for a dynamic IP address, allowing the host to be more easily
accessible from various locations on the Internet. You must register for this
service with a Dynamic DNS client.
Multiple PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuits) Support
The ADSL Router supports up to 8 PVC’s.
ADSL Standards: Full-Rate (ANSI T1.413, Issue 2; G.dmt (G.992.1) with line rate
support of up to 8 Mbps downstream and 832 Kbps upstream. G.lite (G.992.2)
with line rate support of up to 1.5Mbps downstream and 512Kbps upstream.
Supports Multi-Mode standard (ANSI T1.413, Issue 2; G.dmt (G.992.1); G.994.1
and G.996.1 (for ISDN only); G.991.1;G.lite (G992.2)).Supports OAM F4/F5 loopback, AIS and RDI OAM cells.ATM Forum UNI 3.1/4.0 PVC.Supports up to 8
PVCs (UBR, CBR, VBR).Multiple Protocols over AAL5 (RFC 1483).PPP over
AAL5 (RFC 2364).PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516).
A02-RA110 Pag. 2
Page 11

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
DHCP Support: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows individual
clients (computers) to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a centralized
DHCP server. The ADSL Router has built-in DHCP server capability enabled by
default. It can assign IP addresses, an IP default gateway and DNS servers to
DHCP clients. The ADSL Router can now also act as a surrogate DHCP server
(DHCP Relay) where it relays IP address assignment from the actual real DHCP
server to the clients.
IP Alias: IP Alias allows you to partition a physical network into logical networks
over the same Ethernet interface. The ADSL Router supports three logical LAN
interfaces via its single physical Ethernet interface with the ADSL Router itself as
the gateway for each LAN network.
IP Policy Routing (IPPR): Traditionally, routing is based on the destination
address only and the router takes the shortest path to forward a packet. IP Policy
Routing (IPPR) provides a mechanism to override the default routing behavior
and alter the packet forwarding based on the policy defined by the network
administrator.
Protocol Support: PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) link layer protocol.PPP over
PAP (RFC 1334).PPP over CHAP (RFC 1994).RIP I/RIP II.IGMP Proxy,ICMP
support,MIB II support (RFC 1213),PPPoE feature,PPPoE idle time out,PPPoE
dial on demand.
Networking Compatibility: The ADSL Router is compatible with major ADSL
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) providers.
Multiplexing:
Encapsulation: The ADSL Router series supports PPPoA (RFC 2364 - PPP over
ATM Adaptation Layer 5), RFC 1483 encapsulation over ATM, MAC encapsulated
routing (ENET Encapsulation) as well as PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516).
Network Management: Embedded Web Configurator,CLI (Command Line
Interpreter),SNMP manageable,DHCP Server/Client,Built-in Diagnostic Tools.
Syslog, TFTP/FTP server, firmware upgrade and configuration backup/support
supported.
Diagnostics Capabilities: The ADSL Router can perform self-diagnostic tests.
These tests check the integrity of the following circuitry:
The ADSL Router supports VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing.
A02-RA110 Pag. 3
Page 12

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
FLASH memory
ADSL circuitry
RAM
LAN port
Filters: The ADSL Router 's packet filtering functions allows added network
security and management.
Ease of Installation: The ADSL Router is designed for quick, intuitive and easy
installation.
Compact Housing: The ADSL Router 's all new compact and ventilated housing
minimizes space requirements making it easy to position anywhere in your busy
office.
1.4 Applications for the ADSL Router
Here are some example uses for which the ADSL Router is well suited.
1.4.1 Internet Access
The ADSL Router is the ideal high-speed Internet access solution. The Compact
Router ADSL Router supports the TCP/IP protocol, which the Internet uses
exclusively. It is compatible with all major ADSL DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line
Access Multiplexer) providers. A DSLAM is a rack of ADSL line cards with data
multiplexed into a backbone network interface/connection (for example, T1, OC3,
DS3, ATM or Frame Relay). Think of it as the equivalent of a modem rack for
ADSL.
A02-RA110 Pag. 4
Page 13
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
A02-RA110 Pag. 5
Page 14
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 2: Using Compact Router ADSL
This chapter describes how to access and navigate the web configurator.
2.1 Cautions for using the Compact Router ADSL
Do not place the Compact Router ADSL under high humidity and high
temperature.
Do not use the same power source for Compact Router ADSL with other
equipment.
Do not open or repair the case yourself. If the Compact Router ADSL is too
hot, turn off the power immediately and have a qualified serviceman repair it.
Place the Compact Router ADSL on a stable surface.
Only use the power adapter that comes with the package.
Do NOT upgrade firmware on any Atlantis Land product over a wireless
connection. Failure of the device may result. Use only hard-wired network
connections.
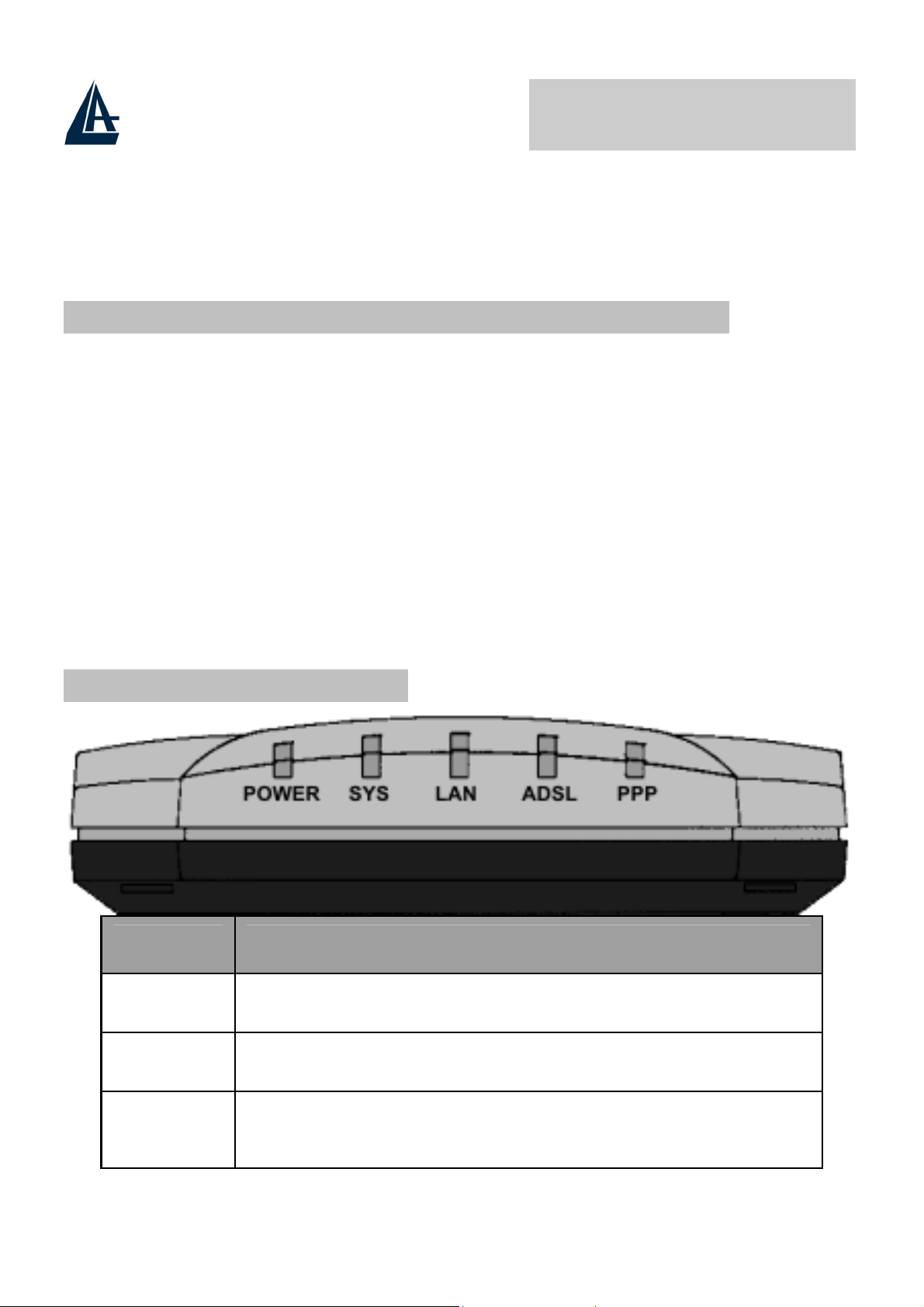
2.2 The Front Panel LEDs
LED MEANING
POWER
SYS
LAN
Lit when power ON
Lit when system is ready
Lit when connected to Ethernet device
Green for 100Mbps; Orange for 10Mbps
Blinking when data transmit/received
A02-RA110 Pag. 6
Page 15
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
ADSL
PPP
Lit when successfully connected to an ADSL DSLAM
Lit when there is a PPPoA/PPPoE connection
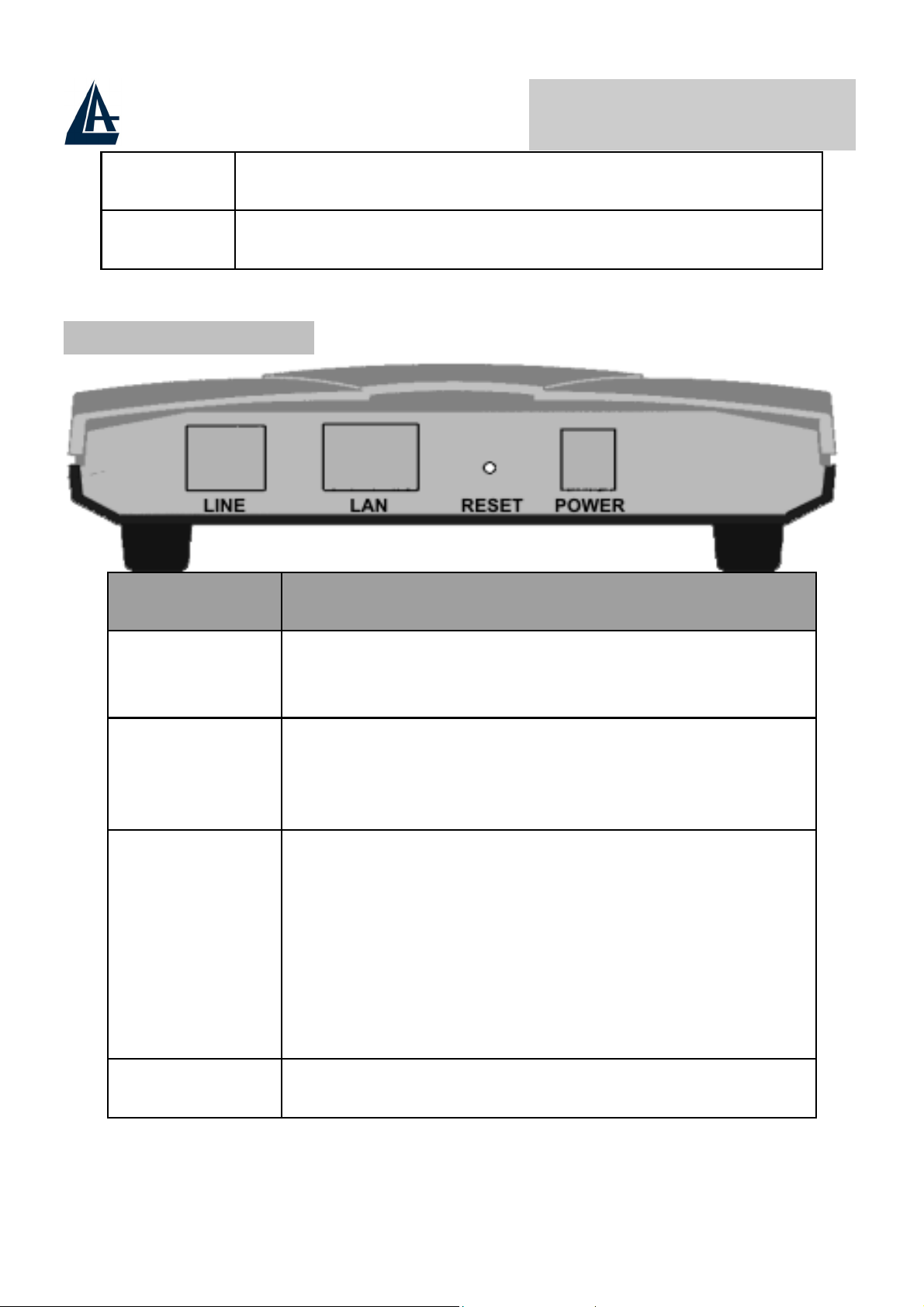
2.3 The Rear Ports
PORT MEANING
LINE (RJ11)
LAN
(RJ-45)
RESET
POWER (jack)
Connect the supplied RJ-11 cable to this port when
connecting to the ADSL/telephone network.
Connect an UTP Ethernet cable to one of the four
LAN ports when connecting to a PC or an
office/home network of 10Mbps or 100Mbps.
After the device has turned on, press it to reset the
device or restore to factory default settings. The
operation is as below:
0-3 seconds: reset the device
3-5 seconds: no action
6 seconds or above:
settings (this is used when you can not login to the
router, e.g. forgot the password)
Connect the supplied power adapter to this jack.
restore to factory default
A02-RA110 Pag. 7
Page 16

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
2.4 Cabling
The most common problem is bad cabling or ADSL line. Make sure that all
connected devices are turned on. On the front of the product is a bank of LEDs.
As a first check, verify that the LAN Link and ADSL line LEDs are lit and SYS is
blanking. If they are not, verify that you are using the proper cables.
A02-RA110 Pag. 8
Page 17

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 3: Introducing the Web Configurator
This chapter describes how to access and navigate the web configurator.
3.1 Web Configurator Overview
The embedded web configurator allows you to manage the Compact Router
ADSL from anywhere through a browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or
Netscape Navigator. Use Internet Explorer 6.0 and later or Netscape Navigator
7.0 and later versions with JavaScript enabled. It is recommended that you set
your screen resolution to 1024 by 768 pixels.
This section describes the configuration required by LAN-attached PCs that
communicate with the Compact Router ADSL, either to configure the device or for
network access. These PCs must have an Ethernet interface installed properly, be
connected to the ADSL Router either directly or through an external Switch, and
have TCP/IP installed and configured to obtain an IP address through a DHCP
server or a fixed IP address that must be in the same subnet of the Compact
Router ADSL. The default IP address of the Compact Router ADSL is
192.168.1.254 and subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. The best and easy way is to
configure the PC to get an IP address from the ADSL Router. Also make sure you
have UNINSTALLED any kind of software firewall that can cause problems while
accessing the 192.168.1.254 IP address of the router.
Please follow the steps below for PC’s network environment installation. First of
all, please check your PC’s network components. The TCP/IP protocol stack and
Ethernet network adapter must be installed. If not, please refer to MS Windows
related manuals.
Any TCP/IP capable workstation can be used to communicate
with or through the Compact Router ADSL. To configure other
types of workstations, please consult the manufacturer’s
documentation.
A02-RA110 Pag. 9
Page 18

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
3.2 Configuring PC in Windows
3.2.1 For Windows 95/98/ME
1.
Go to
Network and choose the Configuration tab.
2. Select TCP / IP -> NE2000 Compatible, or the name of any Network
Interface Card (NIC) in your PC.
Start / Settings / Control Panel
. In the Control Panel, double-click on
3. Click Properties.
4.
Select the
automatically
5.
Then select the
6. Select the Disable DNS radio button and click “OK” to finish the
configuration.
IP Address
radio button.
DNS Configuration
tab. In this page, click the
tab.
Obtain an IP address
3.2.2 For Windows NT4.0
1. Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network
2. Select TCP/IP Protocol and click Properties.
3.
Select the
“OK”.
and choose the
Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server
Protocols
tab.
radio button and click
3.2.3 For Windows 2000
1. Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network and Dial-up Connections
2. Double-click LAN Area Connection.
A02-RA110 Pag. 10
.
Page 19
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
3. In the LAN Area Connection Status window, click Properties.
4.
Select
5. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically and the Obtain DNS server
address automatically
6.
Click
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
radio buttons.
“OK”
to finish the configuration.
and click
Properties
.
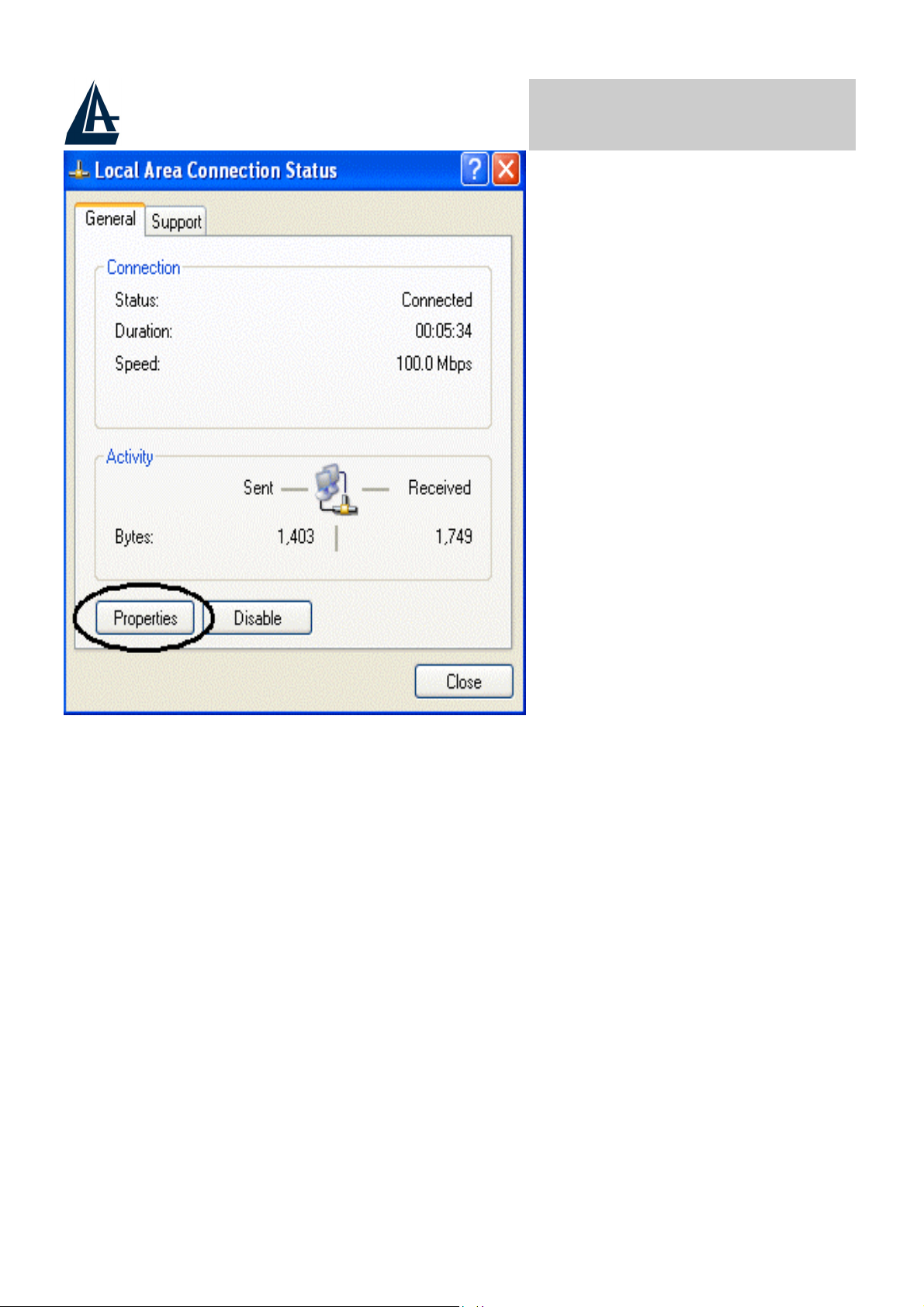
3.2.4 For Windows XP
1. Go to Start / Control Panel (in Classic View). In the Control Panel, double-
Network Connections.
Local Area Connection
click on
2.
Double-click
3.
In the
LAN Area Connection Status
A02-RA110 Pag. 11
window, click
Properties
.
Page 20
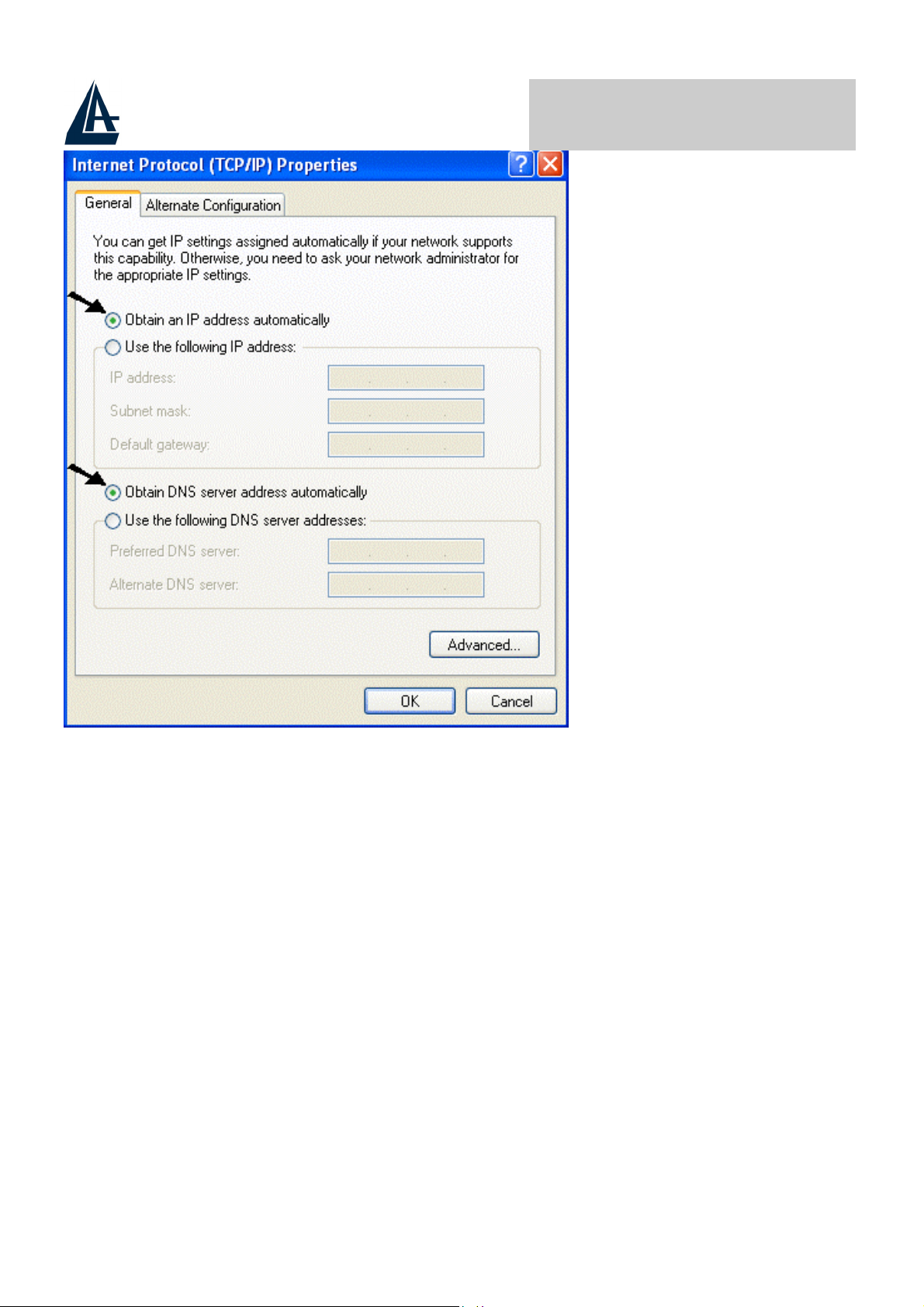
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
4.
Select
5.
Select the
address automatically
6. Click “OK” to finish the configuration.
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Obtain an IP address automatically
radio buttons
and click
Properties
and the
.
Obtain DNS server
A02-RA110 Pag. 12
Page 21
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
A02-RA110 Pag. 13
Page 22

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
3.3 Factory Default Settings
Before configurating this ADSL Router, you need to know the following default
settings.
•
Username:
•
Password : atlantis
•
IP Address : 192.168.1.254
•
Subnet Mask :
•
DHCP server is enabled.
• WAN=Routing, PPPoA, VC-Mux, VPI=8, VCI=35
admin
255.255.255.0
3.3.1 Username and Password
The default username and password are
If you ever forget the password to log in, you may press the RESET
button (6 seconds or above) to restore the factory default settings..
admin
and
atlantis
respectively.
3.3.2 LAN and WAN Port Addresses
The parameters of LAN and WAN ports are pre-set in the factory. The default
values are shown below.
LAN Port WAN Port
IP Address 192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP From 192.168.1.100 to
192.168.1.199
Mode=Routing
Encapsulation=PPPoA
Multiplex=VC
VPI=8
VCI=35
3.4 Information from the ISP
Before configuring this device, you have to check with your ISP (Internet Service
Provider) what kind of service is provided such as PPPoE, PPPoA, RFC1483,
IpoA.
A02-RA110 Pag. 14
Page 23
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Gather the information as illustrated in the following table and keep it for
reference.
PPPoE VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based
multiplexing, Username, Password,
Service Name, and Domain Name
System (DNS) IP address (it can be
automatically assigned from ISP or be
set fixed).
PPPoA
RFC1483 Bridge VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based
RFC1483 Routed
IPoA VPI/VCI, IP address, Subnet mask,
VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based
multiplexing, Username, Password, and
Domain Name System (DNS) IP
address (it can be automatically
assigned from ISP or be set fixed).
multiplexing and configure this product
into BRIDGE Mode.
VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based
multiplexing, IP address, Subnet mask,
Gateway address, and Domain Name
System (DNS) IP address (it is fixed IP
address).
Gateway address, and Domain Name
System (DNS) IP address (it is fixed IP
address).
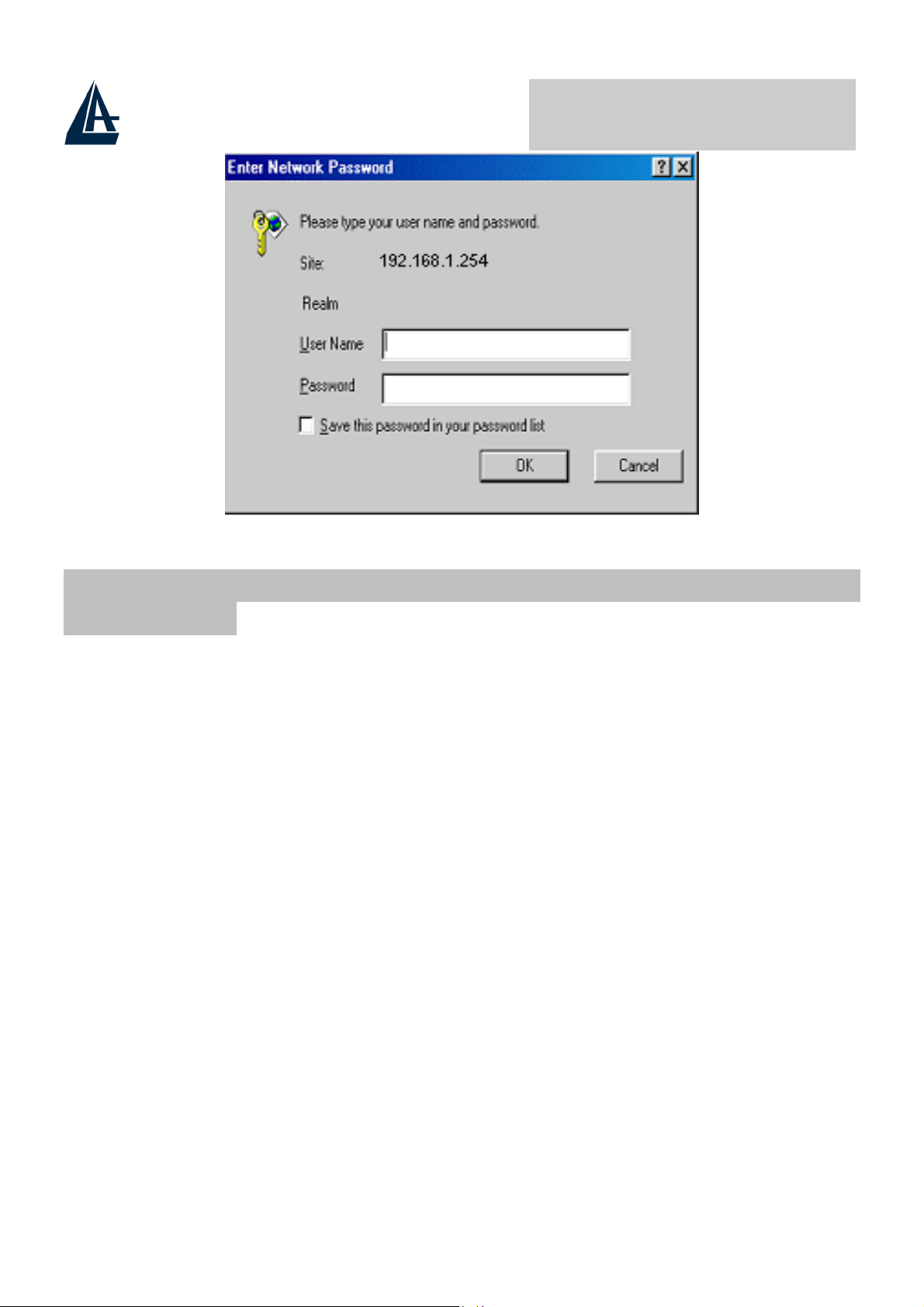
3.5 Accessing the ADSL Router Web Configurator
Step 1. Launch your web browser.
Step 2. Type "192.168.1.254" as the URL.
Step 3. An Enter Network Password window displays. Enter the user name
admin
(“
” is the default), password (“
atlantis
A02-RA110 Pag. 15
” default) and click OK.
Page 24
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Step 4. You should now see the Site Map screen.
3.6 Navigating the Compact Router ADSL Web
Configurator
The following summarizes how to navigate the web configurator from the Site
Map screen. Screens vary slightly for different ADSL Router models.
Select a language from the Language drop-down list box.
Click Wizard Setup to begin a series of screens to configure the ADSL Router
for the first time.
Click a link under Advanced Setup to configure advanced ADSL Router
features.
Click a link under Maintenance to see the ADSL Router performance
statistics, upload firmware and back up, restore or upload a configuration file.
Click SITE MAP to go to the Site Map screen.
Click Logout in the navigation panel when you have finished a ADSL Router
management session.
A02-RA110 Pag. 16
Page 25

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
3.7 Configuring Password
It is highly recommended that you change the password for accessing the ADSL
Router. To change the ADSL Router’ password, click Advanced Setup and then
Password. The screen appears as shown.
A02-RA110 Pag. 17
Page 26

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Old Password Type the default password or the existing password you use
to access the system in this field.
New Password Type the new password in this field.
Retype to Confirm Type the new password again in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ADSL Router.
Cancel
Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
3.8 Resetting the ADSL Router
If you forget your password or cannot access the Compact Router ADSL, you will
need to reload the factory-default configuration file or use the RESET button the
back of the ADSL Router. Uploading this configuration file replaces the current
configuration file with the factory-default configuration file.
3.8.1 Using The Reset Button
Step 1. Make sure the SYS LED is on (not blinking).
Step 2. Press the RESET button for five seconds, and then release it. When the
SYS LED begins to blink, the defaults have been restored and the ADSL Router
restarts.
A02-RA110 Pag. 18
Page 27

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Chapter 4: Wizard Setup
This chapter provides information on the Wizard Setup screens in the web
configurator.
4.1 Wizard Setup Introduction
Use the Wizard Setup screens to configure your system for Internet access
settings and fill in the fields with the information in the Internet Account
Information table of the Compact Guide or Read Me First. Your ISP may have
already configured some of the fields in the wizard screens for you.
4.2 Encapsulation
Be sure to use the encapsulation method required by your ISP. The ADSL Router
supports the following methods.
4.2.1 ENET ENCAP
The MAC Encapsulated Routing Link Protocol (ENET ENCAP) is only
implemented with the IP network protocol. IP packets are routed between the
Ethernet interface and the WAN interface and then formatted so that they can be
understood in a bridged environment. For instance, it encapsulates routed
Ethernet frames into bridged ATM cells. ENET ENCAP requires that you specify a
gateway IP address in the Ethernet Encapsulation Gateway field in the second
wizard screen. You can get this information from your ISP.
4.2.2 PPP over Ethernet
PPPoE provides access control and billing functionality in a manner similar to
dial-up services using PPP. The ADSL Router bridges a PPP session over
Ethernet (PPP over Ethernet, RFC 2516) from your computer to an ATM PVC
(Permanent Virtual Circuit) which connects to ADSL Access Concentrator where
the PPP session terminates. One PVC can support any number of PPP sessions
from your LAN. For more information on PPPoE, see the appendix.
4.2.3 PPPoA
PPPoA stands for Point to Point Protocol over ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5). It
provides access control and billing functionality in a manner similar to dial-up
services using PPP. The ADSL Router encapsulates the PPP session based on
A02-RA110 Pag. 19
Page 28

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
RFC1483 and sends it through an ATM PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit) to the
Internet Service Provider's (ISP) DSLAM (digital access multiplexer). Please refer
to RFC 2364 for more information on PPPoA. Refer to RFC 1661 for more
information on PPP.
4.2.4 RFC 1483
RFC 1483 describes two methods for Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM
Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5). The first method allows multiplexing of multiple
protocols over a single ATM virtual circuit (LLC-based multiplexing) and the
second method assumes that each protocol is carried over a separate ATM virtual
circuit (VC-based multiplexing). Please refer to the RFC for more detailed
information.
4.3 Multiplexing
There are two conventions to identify what protocols the virtual circuit (VC) is
carrying. Be sure to use the multiplexing method required by your ISP.
4.3.1 VC-based Multiplexing
In this case, by prior mutual agreement, each protocol is assigned to a specific
virtual circuit; for example, VC1 carries IP, etc. VC-based multiplexing may be
dominant in environments where dynamic creation of large numbers of ATM VCs
is fast and economical.
4.3.2 LLC-based Multiplexing
In this case one VC carries multiple protocols with protocol identifying information
being contained in each packet header. Despite the extra bandwidth and
processing overhead, this method may be advantageous if it is not practical to
have a separate VC for each carried protocol, for example, if charging heavily
depends on the number of simultaneous VCs.
4.4 VPI and VCI
Be sure to use the correct Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and Virtual Channel
Identifier (VCI) numbers assigned to you. The valid range for the VPI is 0 to 255
and for the VCI is 32 to 65535 (0 to 31 is reserved for local management of ATM
traffic). Please see the appendix for more information.
4.5 Wizard Setup Configuration: First Screen
In the SITE MAP screen click Wizard Setup to display the first wizard screen.
A02-RA110 Pag. 20
Page 29

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Mode
Encapsulation Select the encapsulation type your ISP uses from the
Multiplex
Virtual Circuit ID
VPI
VCI
From the Mode drop-down list box, select Routing (default) if
your ISP allows multiple computers to share an Internet
account. Otherwise select Bridge.
Encapsulation drop-down list box. Choices vary depending on
what you select in the Mode field.
If you select Bridge in the Mode field, select either PPPoA or
RFC 1483.
If you select Routing in the Mode field, select PPPoA, RFC
1483, ENET ENCAP or PPPoE.
Select the multiplexing method used by your ISP from the
Multiplex drop-down list box either VC-based or LLC-based.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) and VCI (Virtual Channel
Identifier) define a virtual circuit. Refer to
Enter the VPI assigned to you. This field may already be
configured.
Enter the VCI assigned to you. This field may already be
A02-RA110 Pag. 21
Page 30

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
configured.
Next Click this button to go to the next wizard screen. The next
wizard screen you see depends on what protocol you chose
above. Click on the protocol link to see the next wizard screen
for that protocol.
4.6 IP Address and Subnet Mask
Similar to the way houses on a street share a common street name, so too do
computers on a LAN share one common network number.
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If
the ISP or your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP
addresses, follow their instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet
mask.
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you
have a single user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address
when the connection is established. If this is the case, it is recommended that you
select a network number from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.0 and you must enable
the Network Address Translation (NAT) feature of the ADSL Router. The Internet
Assigned Number Authority (IANA) reserved this block of addresses specifically
for private use; please do not use any other number unless you are told
otherwise. Let's say you select 192.168.1.0 as the network number; which covers
254 individual addresses, from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 (zero and 255 are
reserved). In other words, the first three numbers specify the network number
while the last number identifies an individual computer on that network.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address that is easy to
remember, for instance, 192.168.1.254, for the ADSL Router, but make sure that
no other device on your network is using that IP address.The subnet mask
specifies the network number portion of an IP address. The ADSL Router will
compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP address that you
entered. You don't need to change the subnet mask computed by the ADSL
Router unless you are instructed to do otherwise.
4.7 IP Address Assignment
A static IP is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP is not fixed; the ISP
assigns you a different one each time. The Single User Account feature can be
enabled or disabled if you have either a dynamic or static IP. However the
encapsulation method assigned influences your choices for IP address and ENET
ENCAP Gateway.
A02-RA110 Pag. 22
Page 31

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
4.7.1 IP Assignment with PPPoA or PPPoE Encapsulation
If you have a dynamic IP, then the IP Address and ENET ENCAP Gateway fields
are not applicable (N/A). If you have a static IP, then you only need to fill in the IP
Address field and not the ENET ENCAP Gateway field.
4.7.2 IP Assignment with RFC 1483 Encapsulation
In this case the IP Address Assignment must be static with the same requirements
for the IP Address and ENET ENCAP Gateway fields as stated above.
4.7.3 IP Assignment with ENET ENCAP Encapsulation
In this case you can have either a static or dynamic IP. For a static IP you must fill
in all the IP Address and ENET ENCAP Gateway fields as supplied by your ISP.
However for a dynamic IP, the ADSL Router acts as a DHCP client on the WAN
port and so the IP Address and ENET ENCAP Gateway fields are not applicable
(N/A) as the DHCP server assigns them to the ADSL Router.
4.7.4 Private IP Addresses
Every machine on the Internet must have a unique address. If your networks are
isolated from the Internet, for example, only between your two branch offices, you
can assign any IP addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the Internet
Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP
addresses specifically for private networks:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255; 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255; 192.168.0.0 -
192.168.255.255
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP or it can be assigned
from a private network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet
access is through an ISP, the ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for
your local networks. On the other hand, if you are part of a much larger
organization, you should consult your network administrator for the appropriate IP
addresses.
4.8 Nailed-Up Connection (PPP)
A nailed-up connection is a dial-up line where the connection is always up
regardless of traffic demand. The ADSL Router does two things when you specify
a nailed-up connection. The first is that idle timeout is disabled. The second is that
the ADSL Router will try to bring up the connection when turned on and whenever
the connection is down. A nailed-up connection can be very expensive for obvious
reasons.
A02-RA110 Pag. 23
Page 32

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Do not specify a nailed-up connection unless your telephone company offers flatrate service or you need a constant connection and the cost is of no concern.
4.9 NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP
address of a host in a packet, for example, the source address of an outgoing
packet, used within one network to a different IP address known within another
network.
4.10 Wizard Setup Configuration: Second Screen
The second wizard screen varies depending on what mode and encapsulation
type you use. All screens shown are with routing mode. Configure the fields and
click Next to continue.
4.10.1 PPPoE
Select PPPoE from the Encapsulation drop-down list box in the first wizard screen
to display the screen as shown.
A02-RA110 Pag. 24
Page 33

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Service Name
User Name Configure User Name and Password fields for PPPoA and
Password
IP Address
Connection
Network
Address
Translation
Back
Next
Type the name of your PPPoE service here.
PPPoE encapsulation only. Enter the user name exactly as your
ISP assigned. If assigned a name in the form user@domain
where domain identifies a service name, then enter both
components exactly as given.
Enter the password associated with the user name above.
A static IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A
dynamic IP address is not fixed; the ISP assigns you a different
one each time you connect to the Internet. The Single User
Account feature can be used with either a dynamic or static IP
address.
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if you have a
dynamic IP address; otherwise select Static IP Address and type
your ISP assigned IP address in the IP Address text box below.
Select Connect on Demand when you don't want the connection
up all the time and specify an idle time-out (in seconds) in the
Max. Idle Timeout field. The default setting selects Connection
on Demand with 0 as the idle time-out, which means the
Internet session will Select Nailed-Up Connection when you
want your connection up all the time. The ADSL Router will try to
bring up the connection automatically if it is disconnected.
Select None, SUA Only or Full Feature from the drop-sown list
box. Refer to the NAT chapter for more details.
Click Back to go back to the first wizard screen.
Click Next to continue to the next wizard screen.
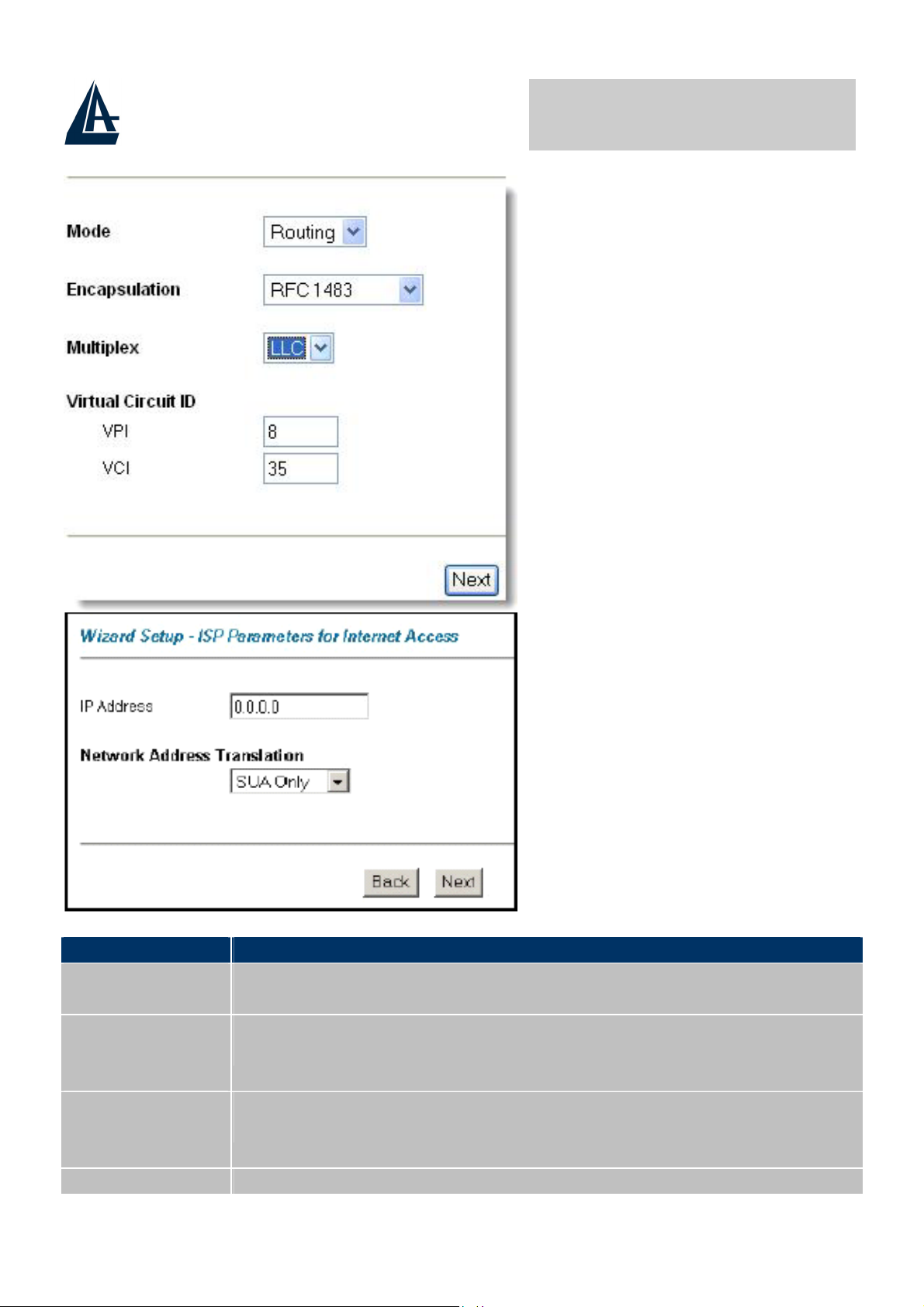
4.10.2 RFC 1483
Select RFC 1483 from the Encapsulation drop-down list box in the first wizard
screen to display the screen as shown.
This configuration is valid in case of a subscription with a static IP and active NAT
(SUA) (for the managing of the public class turn to the CD handbook). Make sure
that the parameters are, in case of
specifically shown by the ISP.
RFC1483
A02-RA110 Pag. 25
, the ones in the picture, if not
Page 34
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
IP Address
Network
Address
Translation
Network
Address
Translation
LABEL
This field is available if you select Routing in the Mode field.
Type your ISP assigned IP address in this field.
Select None, SUA Only or Full Feature from the drop-sown list
box. Refer to the NAT chapter for more details.
Select None, SUA Only or Full Feature from the drop-sown list
box. Refer to the NAT chapter for more details.
DESCRIPTION
A02-RA110 Pag. 26
Page 35

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Back Click Back to go back to the first wizard screen.
Next Click Next to continue to the next wizard screen.
4.10.3 ENET ENCAP
Select ENET ENCAP from the Encapsulation drop-down list box in the first wizard
screen to display the screen as shown.
In case of
Multiplex=LLC
RFC1577(IpoA)
.
choose
Encapsulation=ENET ENCAP
and
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
IP Address
A static IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A
dynamic IP address is not fixed; the ISP assigns you a
A02-RA110 Pag. 27
Page 36

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
different one each time you connect to the Internet. The Single
User Account feature can be used with either a dynamic or
static IP address.
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if you have a
dynamic IP address; otherwise select Static IP Address and
type your ISP assigned IP address in the IP Address text box
below.
Subnet Mask
ENET ENCAP
Gateway
Network
Address
Translation
Back Click Back to go back to the first wizard screen.
Next Click Next to continue to the next wizard screen.
Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
Refer to the IP Subnetting appendix to calculate a subnet
mask If you are implementing subnetting.
You must specify a gateway IP address (supplied by your ISP)
when you use ENET ENCAP in the Encapsulation field in the
previous screen.
Select None, SUA Only or Full Feature from the drop-sown list
box. Refer to the NAT chapter for more details.
4.10.4 PPPoA
Select PPPoA from the Encapsulation drop-down list box in the first wizard screen
to display the screen as shown.
A02-RA110 Pag. 28
Page 37

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
y
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
User Name
Password Enter the password associated with the user name above.
IP Address
Enter the user name exactly as your ISP assigned. If assigned
a name in the form user@domain where domain identifies a
service name, then enter both components exactly as given.
This option is available if you select Routing in the Mode field.
A static IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A
dynamic IP address is not fixed; the ISP assigns you a
different one each time you connect to the Internet. The Single
User Account feature can be used with either a dynamic or
static IP address. Click Obtain an IP Address Automatically if
ou have a dynamic IP address; otherwise click Static IP
A02-RA110 Pag. 29
Page 38

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Address and type your ISP assigned IP address in the IP
Address text box below
Connection Select Connect on Demand when you don't want the
connection up all the time and specify an idle time-out (in
seconds) in the Max. Idle Timeout field. The default setting
selects Connection on Demand with 0 as the idle time-out,
which means the Internet session will not timeout
Select Nailed-Up Connection when you want your connection
up all the time. The ADSL Router will try to bring up the
connection automatically if it is disconnected.
Network
Address
Translation
Back
Next Click Next to continue to the next wizard screen.
This option is available if you select Routing in the Mode field.
Select None, SUA Only or Full Feature from the drop-sown list
box. Refer to the NAT chapter for more details.
Click Back to go back to the first wizard screen.
4.11 DHCP Setup
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows
individual clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can
configure the ADSL Router as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a
server, the ADSL Router provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If you
turn DHCP service off, you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else
the computer must be manually configured.
4.11.1 IP Pool Setup
The ADSL Router is pre-configured with a pool of 32 IP addresses starting from
192.168.1.33 to 192.168.1.64 for the client machines. This leaves 31 IP
addresses, 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.32 (excluding the ADSL Router itself which
has a default IP of 192.168.1.254) for other server machines, for example, server
for mail, FTP, telnet, web, etc., that you may have.
4.12 Wizard Setup Configuration: Third Screen
Verify the settings in the screen shown next. To change the LAN information on
the ADSL Router, click Change LAN Configurations. Otherwise click Save
Settings to save the configuration and skip to section 3.13.
A02-RA110 Pag. 30
Page 39

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
If you want to change the ADSL Router LAN settings, click Change LAN
Configuration to display the screen as shown next.
A02-RA110 Pag. 31
Page 40

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAN IP Address
LAN Subnet
Mask
DHCP Server From the DHCP Server drop-down list box, select On to
Client IP Pool
Starting
Address
Size of Client IP
Pool
Primary DNS
Server
Enter the IP address of the ADSL Router in dotted decimal
notation, for example, 192.168.1.254 (factory default).
Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
DHCP
allow the ADSL Router to assign IP addresses, an IP default
gateway and DNS servers to computer systems that support
the DHCP client. Select Off to disable DHCP server.
When DHCP server is used, set the following items:
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in
the IP address pool.
This field specifies the size or count of the IP address pool.
Enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers. The DNS
servers are passed to the
A02-RA110 Pag. 32
Page 41

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
DHCP clients along with the IP address and the subnet
mask.
Secondary DNS
Server
Back
Finish
As above.
Click Back to go back to the first wizard screen.
Click Finish to save the settings and proceed to the next
wizard screen.
4.13 Wizard Setup Configuration: Connection Tests
The ADSL Router automatically tests the connection to the computer(s)
connected to the LAN ports. To test the connection from the ADSL Router to the
ISP, click Start Diagnose. Otherwise click Return to Main Menu to go back to the
Site Map screen.
4.14 Test Your Internet Connection
Launch your web browser and navigate to www.atlantis-land.com.com. Internet
access is just the beginning. Refer to the rest of this User’s Guide for more
detailed information on the complete range of ADSL Router features. If you
cannot access the Internet, open the web configurator again to confirm that the
Internet settings you configured in the Wizard Setup are correct.
A02-RA110 Pag. 33
Page 42

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 5: LAN Setup
This chapter describes how to configure LAN settings.
5.1 LAN Overview
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many
computers are attached. A LAN is a computer network limited to the immediate
area, usually the same building or floor of a building.
The LAN screens can help you configure a LAN DHCP server and manage IP
addresses.
5.1.1 LANs, WANs and the ADSL Router
The actual physical connection determines whether the ADSL Router ports are
LAN or WAN ports. There are two separate IP networks, one inside, the LAN
network; the other outside: the WAN network as shown next:
A02-RA110 Pag. 34
Page 43

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
5.2 DNS Server Address
DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding
IP address and vice versa, for example, the IP address of www.atlantis-land.com
is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you
must know the IP address of a machine before you can access it. The DNS server
addresses that you enter in the DHCP setup are passed to the client machines
along with the assigned IP address and subnet mask.
There are two ways that an ISP disseminates the DNS server addresses. The first
is for an ISP to tell a customer the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of
an information sheet, when s/he signs up. If your ISP gives you the DNS server
addresses, enter them in the DNS Server fields in DHCP Setup, otherwise, leave
them blank.
Some ISP’s choose to pass the DNS servers using the DNS server extensions of
PPP IPCP (IP Control Protocol) after the connection is up. If your ISP did not give
you explicit DNS servers, chances are the DNS servers are conveyed through
IPCP negotiation. The ADSL Router supports the IPCP DNS server extensions
through the DNS proxy feature.
If the Primary and Secondary DNS Server fields in DHCP Setup are not specified,
for instance, left as 0.0.0.0, the ADSL Router tells the DHCP clients that it itself is
the DNS server. When a computer sends a DNS query to the ADSL Router, the
ADSL Router forwards the query to the real DNS server learned through IPCP
and relays the response back to the computer.
Please note that DNS proxy works only when the ISP uses the IPCP DNS server
extensions. It does not mean you can leave the DNS servers out of the DHCP
setup under all circumstances. If your ISP gives you explicit DNS servers, make
sure that you enter their IP addresses in the DHCP Setup menu. This way, the
ADSL Router can pass the DNS servers to the computers and the computers can
query the DNS server directly without the ADSL Router’s intervention.
5.3 DNS Server Address Assignment
Use DNS (Domain Name System) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without
it, you must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it.
There are two ways that an ISP disseminates the DNS server addresses.
1. The ISP tells you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an
information sheet, when you sign up. If your ISP gives you DNS server
addresses, enter them in the DNS Server fields in DHCP Setup.
2. Leave the DNS Server fields in DHCP Setup blank (for example 0.0.0.0). The
ADSL Router acts as a DNS proxy when this field is blank.
A02-RA110 Pag. 35
Page 44

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
5.4 LAN TCP/IP
The ADSL Router has built-in DHCP server capability that assigns IP addresses
and DNS servers to systems that support DHCP client capability.
5.4.1 Factory LAN Defaults
The LAN parameters of the ADSL Router are preset in the factory with the
following values:
IP address of 192.168.1.254 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
DHCP server enabled with 100 client IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.100.
These parameters should work for the majority of installations. If your ISP gives
you explicit DNS server address(es), read the embedded web configurator help
regarding what fields need to be configured.
5.4.2 IP Address and Subnet Mask
Refer to the IP Address and Subnet Mask section in the Wizard Setup chapter for
this information.
5.4.3 RIP Setup
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing
information with other routers. The RIP Direction field controls the sending and
receiving of RIP packets. When set to:
1. Both - the ADSL Router will broadcast its routing table periodically and
incorporate the RIP information that it receives.
2. In Only - the ADSL Router will not send any RIP packets but will accept all RIP
packets received.
3. Out Only - the ADSL Router will send out RIP packets but will not accept any
RIP packets received.
4. None - the ADSL Router will not send any RIP packets and will ignore any RIP
packets received.
The Version field controls the format and the broadcasting method of the RIP
packets that the ADSL Router sends (it recognizes both formats when receiving).
RIP-1 is universally supported; but RIP-2 carries more information. RIP-1 is
probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an unusual network
topology.
Both RIP-2B and RIP-2M sends the routing data in RIP-2 format; the difference
being that RIP-2B uses subnet broadcasting while RIP-2M uses multicasting.
A02-RA110 Pag. 36
Page 45

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
5.4.4 Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1
sender - 1 recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network).
Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of hosts on the network - not everybody
and not just 1.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to
establish membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data.
IGMP version 2 (RFC 2236) is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but
IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If you would like to read more detailed
information about interoperability between IGMP version 2 and version 1, please
see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is used to identify host
groups and can be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The address
224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group and is used by IP multicast computers.
The address 224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is assigned to the
permanent group of all IP hosts (including gateways). All hosts must join the
224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP. The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned
to the multicast routers group.
The ADSL Router supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2
(IGMP-v2). At start up, the ADSL Router queries all directly connected networks to
gather group membership. After that, the ADSL Router periodically updates this
information. IP multicasting can be enabled/disabled on the ADSL Router LAN
and/or WAN interfaces in the web configurator (LAN; WAN). Select None to
disable IP multicasting on these interfaces.
A02-RA110 Pag. 37
Page 46

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
5.5 Configuring LAN
Click LAN to open the following screen.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
DHCP If set to Server, the ADSL Router can assign IP addresses, an
IP default gateway and DNS servers to Windows 95, Windows
NT and other systems that support the DHCP client.
If set to None, the DHCP server will be disabled.
If set to Relay, the ADSL Router acts as a surrogate DHCP
server and relays DHCP requests and responses between the
remote server and the clients. Enter the IP address of the
actual, remote DHCP server in the Remote DHCP Server field
A02-RA110 Pag. 38
Page 47

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
in this case.
When DHCP is used, the following items need to be set:
LAN Subnet
Mask
Client IP Pool
Starting
Address
Size of Client IP
Pool
Primary DNS
Server
Secondary DNS
Server
Remote DHCP
Server
IP Address
IP Subnet Mask
RIP Direction Select the RIP direction from None, Both, In Only and Out
RIP Version
Multicast
Apply
Cancel Click this button to reset the fields in this screen.
Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the
IP address pool.
This field specifies the size or count of the IP address pool.
Enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers. The DNS servers
are passed to the
DHCP clients along with the IP address and the subnet mask.
As above.
If Relay is selected in the DHCP field above then enter the IP
address of the actual remote DHCP server here.
TCP/IP
Enter the IP address of the ADSL Router in dotted decimal
notation, for example, 192.168.1.254 (factory default).
Type the subnet mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
Only.
Select the RIP version from RIP-1, RIP-2B and RIP-2M.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a session-layer
protocol used to establish membership in a multicast group.
The ADSL Router supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1)
and IGMP-v2. Select None to disable it.
Click this button to save these settings back to the ADSL
Router.
A02-RA110 Pag. 39
Page 48

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 6: WAN Setup
This chapter describes how to configure WAN settings.
6.1 WAN Overview
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is an outside connection to another network or the
Internet.
See the Wizard Setup chapter for more information on the fields in the WAN
screens.
6.2 PPPoE Encapsulation
The ADSL Router supports PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet).
PPPoE is an IETF Draft standard (RFC 2516) specifying how a personal
computer (PC) interacts with a broadband modem (DSL, cable, wireless, etc.)
connection. The PPPoE option is for a dial-up connection using PPPoE.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that
works with existing access control systems (for example Radius). PPPoE
provides a login and authentication method that the existing Microsoft Dial-Up
Networking software can activate, and therefore requires no new learning or
procedures for Windows users.
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple
network services, a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables
the service provider to easily create and offer new IP services for individuals.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both you and the ISP or carrier,
as it requires no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer
site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the ADSL Router (rather than individual
computers), the computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed,
since the ADSL Router does that part of the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the
LANs’ computers will have access.
6.3 PPTP Encapsulation
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables
secure transfer of data from a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual
Private Network (VPN) using TCP/IP-based networks.
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol and virtual private networking over
public networks, such as the Internet.
A02-RA110 Pag. 40
Page 49

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
6.4 Traffic Shaping
Traffic Shaping is an agreement between the carrier and the subscriber to
regulate the average rate and “burstiness” or fluctuation of data transmission over
an ATM network. This agreement helps eliminate congestion, which is important
for transmission of real time data such as audio and video connections.
Peak Cell Rate (PCR) is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
This parameter may be lower (but not higher) than the maximum line speed. 1
ATM cell is 53 bytes (424 bits), so a maximum speed of 832 Kbps gives a
maximum PCR of 1962 cells/sec. This rate is not guaranteed because it is
dependent on the line speed.
Sustained Cell Rate (SCR) is the mean cell rate of a bursty, on-off traffic source
that can be sent at the peak rate, and a parameter for burst-type traffic. SCR may
not be greater than the PCR; the system default is 0 cells/sec.
Maximum Burst Size (MBS) is the maximum number of cells that can be sent at
the PCR. After MBS is reached, cell rates fall below SCR until cell rate averages
to the SCR again. At this time, more cells (up to the MBS) can be sent at the PCR
again.The following figure illustrates the relationship between PCR, SCR and
MBS.
A02-RA110 Pag. 41
Page 50

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
6.5 Configuring WAN Setup
To change the ADSL Router’s WAN remote node settings, click WAN. The screen
differs by the encapsulation.
A02-RA110 Pag. 42
Page 51

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Name Enter the name of your Internet Service Provider, e.g.,
MyISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Mode
Encapsulation Select the method of encapsulation used by your ISP from
Multiplex
Virtual Circuit ID VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) and VCI (Virtual Channel
VPI
VCI
ATM QoS Type Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed (always-
Cell Rate Cell rate configuration often helps eliminate traffic congestion
Peak Cell Rate
Sustain Cell
Rate
Maximum Burst
Select Routing (default) from the drop-down list box if your
ISP allows multiple computers to share an Internet account.
Otherwise select Bridge.
the drop-down list box.
Choices vary depending on the mode you select in the Mode
field.
If you select Bridge in the Mode field, select either PPPoA or
RFC 1483.
If you select Routing in the Mode field, select PPPoA, RFC
1483, ENET ENCAP or PPPoE.
Select the method of multiplexing used by your ISP from the
drop-down list. Choices are VC or LLC.
Identifier) define a virtual circuit. Refer to the appendix for
more information.
The valid range for the VPI is 0 to 255. Enter the VPI
assigned to you.
The valid range for the VCI is 32 to 65535 (0 to 31 is
reserved for local management of ATM traffic). Enter the VCI
assigned to you.
on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR
(Unspecified Bit Rate) for applications that are non-time
sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable Bit Rate) for
bursty traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
VBR is not available on all models.
that slows transmission of real time data such as audio and
video connections.
Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM
cell) to find the Peak Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum
rate at which the sender can send cells. Type the PCR here.
The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (longterm) that can be transmitted. Type the SCR, which must be
less than the PCR.
Maximum Burst Size (MBS) refers to the maximum number
A02-RA110 Pag. 43
Page 52

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
A
Size of cells that can be sent at the peak rate. Type the MBS,
which is less than 65535.
Login
Information
Service Name
User Name
Password
Connection
(PPPoA and
PPPoE
encapsulation
only)
Nailed-Up
Connection
Connect on
Demand
Max Idle
Timeout
Subnet Mask
(ENET ENCAP
encapsulation
only)
ENET ENCAP
Gateway (ENET
ENCAP
encapsulation
only)
(PPPoA and PPPoE encapsulation only)
(PPPoE only) Type the name of your PPPoE service here.
Enter the user name exactly as your ISP assigned. If
assigned a name in the form user@domain where domain
identifies a service name, then enter both components
exactly as given.
static IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A
dynamic IP address is not fixed; the ISP assigns you a
different one each time you connect to the Internet. The
Single User Account feature can be used with either a
dynamic or static IP address.
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if you have a
dynamic IP address; otherwise select Static IP Address and
type your ISP assigned IP address in the IP Address field
below.
The schedule rule(s) have priority over your Connection
settings.
Select Nailed-Up Connection when you want your
connection up all the time. The ADSL Router will try to bring
up the connection automatically if it is disconnected.
Select Connect on Demand when you don't want the
connection up all the time and specify an idle time-out in the
Max Idle Timeout field.
Specify an idle time-out in the Max Idle Timeout field when
you select Connect on Demand. The default setting is 0,
which means the Internet session will not timeout.
Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
Refer to the Subnetting appendix in the to calculate a subnet
mask If you are implementing subnetting.
You must specify a gateway IP address (supplied by your
ISP) when you select ENET ENCAP in the Encapsulation
field.
A02-RA110 Pag. 44
Page 53

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
A02-RA110 Pag. 45
Page 54

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 7: Network Address Translation
(NAT)
This chapter discusses how to configure NAT on the ADSL Router.
7.1 NAT Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP
address of a host in a packet, for example, the source address of an outgoing
packet, used within one network to a different IP address known within another
network.
7.1.1 NAT Definitions
Inside/outside denotes where a host is located relative to the ADSL Router, for
example, the computers of your subscribers are the inside hosts, while the web
servers on the Internet are the outside hosts.
Global/local denotes the IP address of a host in a packet as the packet traverses
a router, for example, the local address refers to the IP address of a host when
the packet is in the local network, while the global address refers to the IP
address of the host when the same packet is traveling in the WAN side.
Note that inside/outside refers to the location of a host, while global/local refers to
the IP address of a host used in a packet. Thus, an inside local address (ILA) is
the IP address of an inside host in a packet when the packet is still in the local
network, while an inside global address (IGA) is the IP address of the same inside
host when the packet is on the WAN side. The following table summarizes this
information.
Item Description
Inside
This refers to the host on the LAN.
Outside
Local This refers to the packet address (source or destination) as the packet
Global
This refers to the host on the WAN.
travels on the LAN.
This refers to the packet address (source or destination) as the packet
travels on the WAN.
A02-RA110 Pag. 46
Page 55

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.1.2 What NAT Does
In the simplest form, NAT changes the source IP address in a packet received
from a subscriber (the inside local address) to another (the inside global address)
before forwarding the packet to the WAN side. When the response comes back,
NAT translates the destination address (the inside global address) back to the
inside local address before forwarding it to the original inside host. Note that the
IP address (either local or global) of an outside host is never changed.
The global IP addresses for the inside hosts can be either static or dynamically
assigned by the ISP. In addition, you can designate servers, for example, a web
server and a telnet server, on your local network and make them accessible to the
outside world. With no servers defined, the ADSL Router filters out all incoming
inquiries, thus preventing intruders from probing your network. For more
information on IP address translation, refer to RFC 1631, The IP Network Address
Translator (NAT).
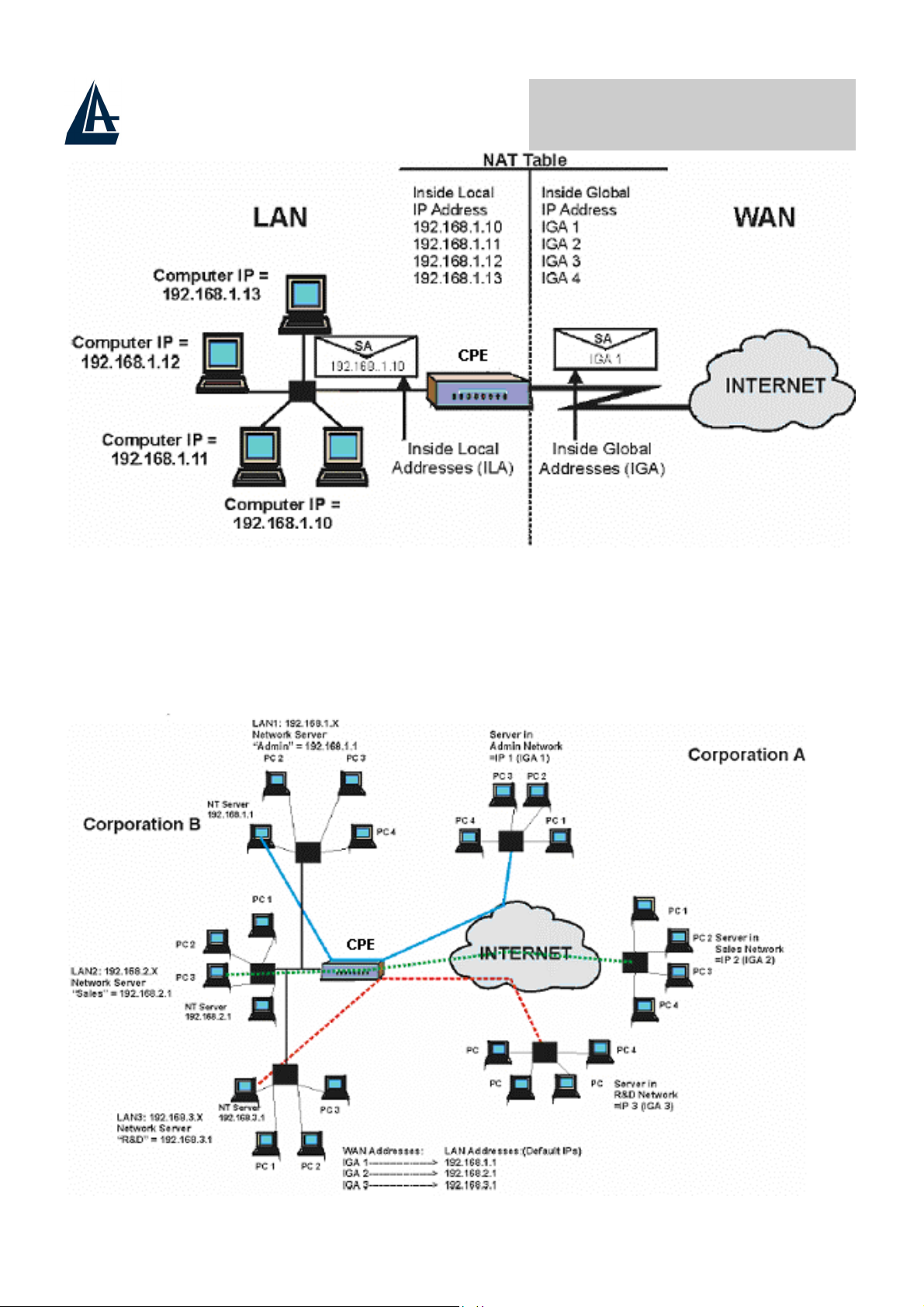
7.1.3 How NAT Works
Each packet has two addresses – a source address and a destination address.
For outgoing packets, the ILA (Inside Local Address) is the source address on the
LAN, and the IGA (Inside Global Address) is the source address on the WAN. For
incoming packets, the ILA is the destination address on the LAN, and the IGA is
the destination address on the WAN. NAT maps private (local) IP addresses to
globally unique ones required for communication with hosts on other networks. It
replaces the original IP source address (and TCP or UDP source port numbers for
Many-to-One and Many-to-Many Overload NAT mapping) in each packet and
then forwards it to the Internet. The ADSL Router keeps track of the original
addresses and port numbers so incoming reply packets can have their original
values restored. The following figure illustrates this.
A02-RA110 Pag. 47
Page 56
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.1.4 NAT Application
The following figure illustrates a possible NAT application, where three inside
LANs (logical LANs using IP Alias) behind the ADSL Router can communicate
with three distinct WAN networks. More examples follow at the end of this
chapter.
A02-RA110 Pag. 48
Page 57

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.1.5 NAT Mapping Types
NAT supports five types of IP/port mapping. They are:
1. One to One: In One-to-One mode, the ADSL Router maps one local IP address
to one global IP address.
2. Many to One: In Many-to-One mode, the ADSL Router maps multiple local IP
addresses to one global IP address.
3. Many to Many Overload: In Many-to-Many Overload mode, the ADSL Router
maps the multiple local IP addresses to shared global IP addresses.
4. Many-to-Many No Overload: In Many-to-Many No Overload mode, the ADSL
Router maps each local IP address to a unique global IP address.
5. Server: This type allows you to specify inside servers of different services
behind the NAT to be accessible to the outside world.
The following table summarizes these types.
Type IP Mapping
One-to-One ILA1 IGA1
Many-to-One (SUA/PAT) ILA1 IGA1
ILA2 IGA1
…
Many-to-Many Overload ILA1 IGA1
ILA2 IGA2
ILA3 IGA1
ILA4 IGA2
…
Many-to-Many No Overload ILA1 IGA1
ILA2 IGA2
ILA3 IGA3
…
Server Server 1 IP IGA1
Server 2 IP IGA1
Server 3 IP IGA1
7.2 SUA (Single User Account) Versus NAT
SUA (Single User Account) is a implementation of a subset of NAT that supports
two types of mapping, Many-to-One and Server. The ADSL Router also supports
Full Feature NAT to map multiple global IP addresses to multiple private LAN IP
addresses of clients or servers using mapping types as outlined in
A02-RA110 Pag. 49
Page 58

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.3 SUA Server
A SUA server set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for example,
web or FTP, that you can make visible to the outside world even though SUA
makes your whole inside network appear as a single computer to the outside
world.
You may enter a single port number or a range of port numbers to be forwarded,
and the local IP address of the desired server. The port number identifies a
service; for example, web service is on port 80 and FTP on port 21. In some
cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can support more than
one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might be better to specify
a range of port numbers. You can allocate a server IP address that corresponds to
a port or a range of ports.
Many residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server
processes (such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may
periodically check for servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any
active services at your location. If you are unsure, refer to your ISP.
Default Server IP Address
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server IP
address. A default server receives packets from ports that are not specified in this
screen.
7.3.1 Port Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers
A NAT server set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for example,
web or FTP, that you can make accessible to the outside world even though NAT
makes your whole inside network appear as a single machine to the outside
world.
Use the SUA Server page to forward incoming service requests to the server(s)
on your local network. You may enter a single port number or a range of port
numbers to be forwarded, and the local IP address of the desired server. The port
number identifies a service; for example, web service is on port 80 and FTP on
port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can
support more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might
be better to specify a range of port numbers.
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A
service request that does not have a server explicitly designated for it is
forwarded to the default server. If the default is not defined, the service request is
simply discarded.
The most often used port numbers are shown in the following table. Please refer
to RFC 1700 for further information about port numbers.
A02-RA110 Pag. 50
Page 59

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Services Port Number
ECHO 7
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) 21
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) 25
DNS (Domain Name System) 53
Finger 79
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer protocol or WWW, Web) 80
POP3 (Post Office Protocol) 110
NNTP (Network News Transport Protocol) 119
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) 161
SNMP trap 162
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) 1723
7.3.2 Configuring Servers Behind SUA (Example)
Let's say you want to assign ports 22-25 to one server, port 80 to another and
assign a default server IP address of 192.168.1.35 as shown in the next figure.
A02-RA110 Pag. 51
Page 60

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.4 Selecting the NAT Mode
Click NAT to open the following screen.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
None Select this radio button to disable NAT.
SUA Only Select this radio button if you have just one public WAN IP
address for your ADSL Router. The ADSL Router uses
Address Mapping Set 1 in the NAT - Edit SUA/NAT Server Set
screen.
Edit Details Click this link to go to the NAT - Edit SUA/NAT Server Set
screen.
Full Feature Select this radio button if you have multiple public WAN IP
addresses for the ADSL Router.
Edit Details Click this link to go to the NAT - Address Mapping Rules
screen.
Apply
Click Apply to save your configuration.
A02-RA110 Pag. 52
Page 61

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
7.5 Configuring SUA Server
Click NAT, Select SUA Only and click Edit Details to open the following screen.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Start Port No.
Enter a port number in this field.
To forward only one port, enter the port number again in the
End Port No. field.
To forward a series of ports, enter the start port number here
A02-RA110 Pag. 53
Page 62

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
and the end port number in the End Port No. field.
End Port No. Enter a port number in this field.
To forward only one port, enter the port number again in the
Start Port No. field above and then enter it again in this field.
To forward a series of ports, enter the last port number in a
series that begins with the port number in the Start Port No.
field above.
IP Address
Save
Cancel
Enter your server IP address in this field.
Click Save to save your changes back to the ADSL Router.
Click Cancel to return to the previous configuration.
7.6 Configuring Address Mapping
Ordering your rules is important because the ADSL Router applies the rules in the
order that you specify. When a rule matches the current packet, the ADSL Router
takes the corresponding action and the remaining rules are ignored. If there are
any empty rules before your new configured rule, your configured rule will be
pushed up by that number of empty rules. For example, if you have already
configured rules 1 to 6 in your current set and now you configure rule number 9.
In the set summary screen, the new rule will be rule 7, not 9. Now if you delete
rule 4, rules 5 to 7 will be pushed up by 1 rule, so old rules 5, 6 and 7 become
new rules 4, 5 and 6.
To change the ADSL Router’s address mapping settings, click NAT, Select Full
Feature and click Edit Details to open the following screen.
A02-RA110 Pag. 54
Page 63

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Local Start IP This is the starting Inside Local IP Address (ILA). Local IP
addresses are N/A for Server port mapping.
Local End IP
Global Start IP
Global End IP
Type 1-1: One-to-one mode maps one local IP address to one
This is the end Inside Local IP Address (ILA). If your rule is for
all local IP addresses, then enter 0.0.0.0 as the Local Start IP
address and 255.255.255.255 as the Local End IP address.
This field is N/A for One-to-one and Server mapping types.
This is the starting Inside Global IP Address (IGA). Enter
0.0.0.0 here if you have a dynamic IP address from your ISP.
You can only do this for Many-to-One and Server mapping
types.
This is the ending Inside Global IP Address (IGA). This field is
N/A for One-to-one, Many-to-One and Server mapping types.
global IP address. Note that port numbers do not change for
the One-to-one NAT mapping type.
M-1: Many-to-One mode maps multiple local IP addresses to
one global IP address.
A02-RA110 Pag. 55
Page 64

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
M-M Ov (Overload): Many-to-Many Overload mode maps
multiple local IP addresses to shared global IP addresses.
MM No (No Overload): Many-to-Many No Overload mode
maps each local IP address to unique global IP addresses.
Server: This type allows you to specify inside servers of
different services behind the NAT to be accessible to the
outside world.
Back
Click Back to return to the NAT Mode screen.
7.7 Editing an Address Mapping Rule
To edit an address mapping rule, click the rule’s link in the NAT Address Mapping
Rules screen to display the screen shown next.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Type Choose the port mapping type from one of the following.
1. One-to-One: One-to-One mode maps one local IP address
A02-RA110 Pag. 56
Page 65

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
to one global IP address. Note that port numbers do not
change for One-to-one NAT mapping type.
2. Many-to-One: Many-to-One mode maps multiple local IP
addresses to one global IP address.
3. Many-to-Many Overload: Many-to-Many Overload mode
maps multiple local IP addresses to shared global IP
addresses.
4. Many-to-Many No Overload: Many-to-Many No Overload
mode maps each local IP address to unique global IP
addresses.
5. Server: This type allows you to specify inside servers of
different services behind the NAT to be accessible to the
outside world.
Local Start IP
Local End IP
Global Start IP This is the starting Inside Global IP Address (IGA). Enter
Global End IP This is the ending Inside Global IP Address (IGA). This field
Server Mapping
Set
Edit Details Click this link to go to the NAT - Edit SUA/NAT Server Set
Apply
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previously saved settings.
Delete Click Delete to exit this screen without saving
This is the starting Inside Local IP Address (ILA). Local IP
addresses are N/A for Server port mapping.
This is the end Inside Local IP Address (ILA). If your rule is
for all local IP addresses, then enter 0.0.0.0 as the Local
Start IP address and 255.255.255.255 as the Local End IP
address.
This field is N/A for One-to-one and Server mapping types.
0.0.0.0 here if you have a dynamic IP address from your ISP.
is N/A for One-to-one, Many-to-One and Server mapping
types.
Only available when Type is set to Server.
Select a number from 1 to 10 from the drop-down menu to
choose a server set from the NAT - Address Mapping Rules
screen.
screen to edit a server set that you have selected in the
Server Mapping Set field.
Click Apply to save your changes back to the ADSL Router.
A02-RA110 Pag. 57
Page 66

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 8: Security
Thanks to the Security function the Compact Router ADSL is able to prevent the
intrusions from the WAN (Internet). You can deny the access to high risk services
such as Telnet, FTP and HTTP. Click on “Security” link in the Site Map screen to
open the following interface.
Selecting on of the services in the table the access to the associated port from the
WAN will come closed.
A02-RA110 Pag. 58
Page 67

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 9: Dynamic DNS Setup
This chapter discusses how to configure the ADSL Router to use Dynamic DNS.
9.1 Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS allows you to update your current dynamic IP address with one or
many dynamic DNS services so that anyone can contact you (in NetMeeting, CUSeeMe, etc.). You can also access your FTP server or Web site on your own
computer using a DNS-like address (for instance myhost.dhs.org, where myhost
is a name of your choice) that will never change instead of using an IP address
that changes each time you reconnect. Your friends or relatives will always be
able to call you even if they don't know your IP address.
First of all, you need to have registered a dynamic DNS account with
www.dyndns.org. This is for people with a dynamic IP from their ISP or DHCP
server that would still like to have a DNS name. The Dynamic DNS service
provider will give you a password or key.
9.1.1 DYNDNS Wildcard
Enabling the wildcard feature for your host causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be
aliased to the same IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful if
you want to be able to use, for example, www.yourhost.dyndns.org and still reach
your hostname.
9.2 Configuring Dynamic DNS
To change the ADSL Router’s DDNS, click Dynamic DNS. The screen appears as
shown.
A02-RA110 Pag. 59
Page 68

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Active
Service Provider
Host Name Type the domain name assigned to the ADSL Router by your
E-mail Address
User
Password Type the password assigned to you.
Enable Wildcard Select this check box to enable DYNDNS Wildcard.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ADSL Router.
Cancel
Select this check box to use dynamic DNS.
Select the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
Dynamic DNS provider.
Type your e-mail address.
Type your user name.
Click Cancel to return to the previously saved settings.
A02-RA110 Pag. 60
Page 69

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 10: Time and Date Setup
Use this screen to configure the ADSL Router’s time and date settings. This
chapter is not available on all models.
10.1 Configuring Time Zone
To change the ADSL Router’s time and date, click Time Zone. The screen
appears as shown. Use this screen to configure the ADSL Router’s time based on
your local time zone.
A02-RA110 Pag. 61
Page 70

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Time Server
Use Time Server
when Bootup
Time Server IP
Address
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your location. This will set the time
Daylight Savings Select this option if you use daylight savings time. Daylight
Start Date Enter the month and day that your daylight-savings time
End Date
Calibrate system
clock with Time
Server now
Current Date This field displays the date of the ADSL Router.
Select the time service protocol that your time server sends
when you turn on the ADSL Router. Not all time servers
support all protocols, so you may have to check with your
ISP/network administrator or use trial and error to find a
protocol that works.
The main difference between them is the format.
Daytime (RFC 867) format is day/month/year/time zone of
the server.
Time (RFC 868) format displays a 4-byte integer giving the
total number of seconds since 1970/1/1 at 0:0:0.
The default, NTP (RFC 1305), is similar to Time (RFC 868).
Select None to enter the time and date manually.
Enter the IP address of your time server. Check with your
ISP/network administrator if you are unsure of this
information.
difference between your time zone and Greenwich Mean
Time (GMT).
saving is a period from late spring to early fall when many
countries set their clocks ahead of normal local time by one
hour to give more daytime light in the evening.
starts on if you selected Daylight Savings.
Enter the month and day that your daylight-savings time
ends on if you selected Daylight Savings.
Click this button to have the ADSL Router use the time
server (that you configured above) to set its internal system
clock.
Please wait for up to 60 seconds while the ADSL Router
locates the time server. If the ADSL Router cannot find the
time server, please check the time server protocol and its IP
address. If the IP address was entered correctly, try pinging
it for example to test the connection.
Date
Each time you reload this page, the ADSL Router
synchronizes the time with the time server.
A02-RA110 Pag. 62
Page 71

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
New Date (yyyymm-dd)
Time
Current Time This field displays the time of the ADSL Router.
New Time
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ADSL Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previously saved settings.
This field displays the last updated date from the time
server.
When you select None in the Use Time Server when Bootup
field, enter the new date in this field and then click Apply.
Each time you reload this page, the ADSL Router
synchronizes the time with the time server.
This field displays the last updated time from the time server.
When you select None in the Use Time Server when Bootup
field, enter the new time in this field and then click Apply.
A02-RA110 Pag. 63
Page 72

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
CHAPTER 11: Remote Management
Configuration
This chapter provides information on configuring remote management. Remote
management is not available on all models
11.1 Remote Management Overview
Remote management allows you to determine which services/protocols can
access which ADSL Router interface (if any) from which computers.
You may manage the ADSL Router from a remote location via:
Internet (WAN only) ALL (LAN and WAN)
LAN only Neither (Disable)
To disable remote management of a service, select Disable in the corresponding
Server Access field.
11.1.1 Remote Management Limitations
Remote management over LAN or WAN will not work when:
A filter is applied to block a Telnet, FTP or Web service.
You have disabled that service in one of the remote management screens.
The IP address in the Secured Client IP field does not match the client IP
address. If it does not
There is an console session running.
There is already another remote management session of the same type (web,
FTP or Telnet) running. You may only have one remote management session
of the same type running at one time.
There is a web remote management session running with a Telnet session. A
Telnet session will be disconnected if you begin a web session; it will not
begin if there already is a web session.
11.1.2 Remote Management and NAT
When NAT is enabled:
Use the ADSL Router’s WAN IP address when configuring from the WAN.
Use the ADSL Router’s LAN IP address when configuring from the LAN.
A02-RA110 Pag. 64
Page 73

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
11.1.3 System Timeout
There is a system timeout of five minutes (three hundred seconds) for either the
console port or telnet/web/FTP connections. The ADSL Router automatically logs
you out if you do nothing in this timeout period, except when sys stdio has been
changed on the command line.
11.2 Telnet
You can configure the ADSL Router for remote Telnet access as shown next.
11.3 FTP
You can upload and download ADSL Router firmware and configuration files using
FTP. To use this feature, your computer must have an FTP client.
11.4 Web
You can use the ADSL Router’s embedded web configurator for configuration and
file management. See the online help for details.
11.5 Configuring Remote Management
Click Remote Management to open the following screen.
A02-RA110 Pag. 65
Page 74

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Server Type Each of these labels denotes a service that you may use to
remotely manage the ADSL Router.
Access Status Select the access interface. Choices are All, LAN Only, WAN
Only and Disable.
Port
Secured Client IP
Apply Click Apply to save your settings back to the ADSL Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
This field shows the port number for the remote
management service. You may change the port number for a
service in this field, but you must use the same port umber
to use that service for remote management.
The default 0.0.0.0 allows any client to use this service to
remotely manage the ADSL Router. Type an IP address to
restrict access to a client with a matching IP address.
A02-RA110 Pag. 66
Page 75

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Chapter 12: Maintenance
This chapter displays system information such as Atlantis Land firmware, port IP
addresses and port traffic statistics.
12.1 Maintenance Overview
Use the maintenance screens to view system information, upload new firmware,
manage configuration and restart the ADSL Router.
12.2 System Status Screen
Click System Status to open the following screen, where you can use to monitor
the ADSL Router. Note that these fields are READ-ONLY and are meant to be
used for diagnostic purposes.
A02-RA110 Pag. 67
Page 76

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
System Status
System Name This is the name of the ADSL Router. It is for identification
purposes.
RAS F/W Version
DSL FW Version This is the DSL firmware version associated with the ADSL
Standard
WAN Information
IP Address This is the WAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This is the WAN port IP subnet mask.
Default Gateway This is the IP address of the default gateway, if applicable.
VPI/VCI
LAN Information
MAC Address
IP Address This is the LAN port IP address.
IP Subnet Mask
DHCP
DHCP Start IP
DHCP Pool Size This is the number of IP addresses in the IP address pool.
Show Statistics
This is the firmware version and the date created.
Router.
This is the standard that the ADSL Router is using.
This is the Virtual Path Identifier and Virtual Channel
Identifier that you entered in the first Wizard screen.
This is the MAC (Media Access Control) or Ethernet address
unique to the ADSL Router.
This is the LAN port IP subnet mask.
This is the WAN port DHCP role - Server, Relay (not all
ADSL Router models) or None.
This is the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP
address pool.
Click Show Statistics to see router performance statistics
such as number of
packets sent and number of packets received for each port.
A02-RA110 Pag. 68
Page 77

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
12.2.1 System Statistics
Click Show Statistics in the System Status screen to open the following screen.
Read-only information here includes port status and packet specific statistics. Also
provided are "system up time" and "poll interval(s)". The Poll Interval(s) field is
configurable.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
System up Time This is the elapsed time the system has been up.
CPU Load
WAN Port
Statistics
Link Status
Transfer Rate This is the transfer rate in kbps.
Upstream Speed This is the upstream speed of the ADSL Router.
Downstream
Speed
This field specifies the percentage of CPU utilization.
This is the WAN port.
This is the status of your WAN link.
This is the downstream speed of the ADSL Router.
A02-RA110 Pag. 69
Page 78

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
Node-Link This field displays the remote node index number and link
type. Link types are PPPoA, ENET, RFC 1483 and PPPoE.
LAN Port
Statistics
Interface
Status
TxPkts
RxPkts This field displays the number of packets received on this
Errors This field displays the number of error packets on this port.
Tx B/s
Rx B/s This field displays the number of bytes received in the last
Up Time This field displays the elapsed time this port has been up.
Collisions
Poll Interval(s)
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in
Stop
This is the LAN port.
This field displays the type of port.
For the WAN port, this displays the port speed and duplex
setting if you're using Ethernet encapsulation and down (line
is down), idle (line (ppp) idle), dial (starting to trigger a call)
and drop (dropping a call) if you're using PPPoE
encapsulation.
For a LAN port, this shows the port speed and duplex
setting.
This field displays the number of packets transmitted on this
port.
port.
This field displays the number of bytes transmitted in the last
second.
second.
This is the number of collisions on this port.
Type the time interval for the browser to refresh system
statistics.
the Poll Interval field above.
Click this button to halt the refreshing of the system
statistics.
12.3 DHCP Table Screen
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows
individual clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can
configure the ADSL Router as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a
server, the ADSL Router provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If set to
None, DHCP service will be disabled and you must have another DHCP server on
your LAN, or else the computer must be manually configured.
Click MAINTENANCE, and then the DHCP Table tab. Read-only information here
relates to your DHCP status. The DHCP table shows current DHCP client
information (including IP Address, Host Name and MAC Address) of all network
A02-RA110 Pag. 70
Page 79

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
clients using the DHCP server.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Host Name
IP Address
MAC Address This field displays the MAC (Media Access Control) address
This is the name of the host computer.
This field displays the IP address relative to the Host Name
field.
of the computer with the displayed host name.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC address. The
MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six
pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example,
00:AA:BB:00:00:02.
12.4 Diagnostic Screens
These read-only screens display information to help you identify problems with
the ADSL Router. Click Diagnostic to display the following screen.
12.4.1 Diagnostic General Screen
Click Diagnostic and then General to open the screen shown next.
A02-RA110 Pag. 71
Page 80

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
TCP/IP Address Type the IP address of a computer that you want to ping in
order to test a connection.
Ping Click this button to ping the IP address that you entered.
Reset System
Back
Click this button to reboot the ADSL Router. A warning dialog
box is then displayed asking you if you're sure you want to
reboot the system. Click OK to proceed.
Click this button to go back to the main Diagnostic screen.
12.4.2 Diagnostic DSL Line Screen
Click Diagnostic and then DSL Line to open the screen shown next.
A02-RA110 Pag. 72
Page 81

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
Reset ADSL Line Click this button to reinitialize the ADSL line. The large text
box above then displays the progress and results of this
operation, for example:
"Start to reset ADSL
Loading ADSL modem F/W...
Reset ADSL Line Successfully!"
ATM Status Click this button to view ATM status.
ATM Loopback
Test
Click this button to start the ATM loopback test. Make sure
you have configured at least one PVC with proper VPIs/VCIs
before you begin this test. The ADSL Router sends an OAM
F5 packet to the DSLAM/ATM switch and then returns it
(loops it back) to the ADSL Router.
The ATM loopback test is useful for troubleshooting
A02-RA110 Pag. 73
Page 82

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
problems with the DSLAM and ATM network.
Upstream Noise
Margin
Downstream
Noise Margin
Back
Click this button to display the upstream noise margin.
Click this button to display the downstream noise margin.
Click this button to go back to the main Diagnostic screen.
12.5 Firmware Screen
Find firmware at www.atlantis-land.com in a file that (usually) uses the system
model name with a "*.bin" extension, e.g., " ADSL Router.bin". The upload
process uses FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and may take up to two minutes. After
a successful upload, the system will reboot. Click Firmware to open the following
screen. Follow the instructions in this screen to upload firmware to the ADSL
Router.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Label Description
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field
or click Browse ... to find it.
Browse... Click Browse... to find the .bin file you want to upload.
Remember that you must decompress compressed (.zip)
A02-RA110 Pag. 74
Page 83
COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
files before you can upload them.
Upload Click Upload to begin the upload process. This process may
take up to two minutes.
Reset Click this button to clear all user-entered configuration
information and return the ADSL Router to its factory
defaults. Refer to the Resetting the ADSL Router section.
After you see the Firmware Upload in Process screen, wait two minutes before
logging into the ADSL Router again.The ADSL Router automatically restarts in this
time causing a temporary network disconnect. In some operating systems, you
may see the following icon on your desktop.
After two minutes, log in again and check your new firmware version in the
System Status screen. If the upload was not successful, the following screen will
appear. Click Back to go back to the Firmware screen.
A02-RA110 Pag. 75
Page 84

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
APPENDIX A: Troubleshooting
This chapter covers potential problems and the corresponding remedies.
A.1 Using LEDs to Diagnose Problems
The LEDs are useful aides for finding possible problem causes.
A.1.1 Power LED
The PWR LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure that the ADSL Router’s power adaptor is connected
to the ADSL Router and plugged in to an appropriate power
source. Use only the supplied power adaptor.
2
3 Turn the ADSL Router off and on.
4
Check that the ADSL Router and the power source are both
turned on and the ADSL Router is receiving sufficient power.
If the error persists, you may have a hardware problem. In this
case, you should contact your vendor.
A.1.2 LAN LED
The LAN LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2 Check for faulty Ethernet cables.
3
4
Check the Ethernet cable connections between the ADSL Router
and the computer or hub.
Make sure your computer’s Ethernet card is working properly.
If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact your local
distributor for assistance.
A.1.3 DSL LED
The DSL LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
Check the telephone wire and connections between the ADSL
Router DSL port and the wall jack.
A02-RA110 Pag. 76
Page 85

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
2 Make sure that the telephone company has checked your phone
line and set it up for DSL service.
3 Reset your ADSL line to reinitialize your link to the DSLAM. For
details, refer to the Maintenance chapter (web configurator) or
the System Information and Diagnosis chapter.
4 If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact your local
distributor for assistance.
A.2 Telnet
I cannot telnet into the ADSL Router.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the LAN port and the other Ethernet connections.
2
3 Ping the ADSL Router from your computer.
4
5
Make sure you are using the correct IP address of the ADSL
Router. Check the IP address of the ADSL Router.
If you cannot ping the ADSL Router, check the IP addresses of
the ADSL Router and your computer. Make sure your computer
is set to get a dynamic IP address; or if you want to use a static
IP address on your computer, make sure that it is on the same
subnet as the ADSL Router.
Make sure you entered the correct password. The default
password is “admin”.
If you have forgot your username or password, refer to Section
A.5.
If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact the distributor.
A.3 Web Configurator
I cannot access the web configurator.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2 Make sure that there is not an console session running.
3
Make sure you are using the correct IP address of the ADSL
Router. Check the IP address of the ADSL Router.
Check that you have enabled web service access. If you have
configured a secured client IP address, your computer’s IP
address must match it. Refer to the chapter on remote
management for details.
A02-RA110 Pag. 77
Page 86

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
p
4 For WAN access, you must configure remote management to
allow server access from the Wan (or all).
5 Your computer’s and the ADSL Router’s IP addresses must be
on the same subnet for LAN access.
6
7 Remove any filters in LAN or WAN that block web service.
8
The web configurator does not display properly.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure you are using Internet Explorer 5.0 and later
2 Delete the temporary web files and log in again.
If you changed the ADSL Router’s LAN IP address, then enter
the new one as the URL.
See also Section A.9.
versions.
In Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then click
the Delete Files ... button.
When a Delete Files window displays, select Delete all offline
content and click OK. (Steps may vary depending on the version
of your Internet browser.)
A.4 Login Username and Password
I forgot my login username and/or password.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2
3
4
If you have changed the password and have now forgotten it,
you will need to upload the default configuration file. This will
erase all custom configurations and restore all of the factory
defaults including the password.
Press the RESET button for five seconds, and then release it.
When the SYS LED begins to blink, the defaults have been
restored and the ADSL Router restarts. Or refer to the Resetting
the ADSL Router section for uploading a configuration file via
console port.
The default username is “admin”. The default password is
“atlantis”. The Password and Username fields are casesensitive. Make sure that you enter the correct password and
username using the proper casing.
It is highly recommended to change the default username and
assword. Make sure you store the username and password in a
A02-RA110 Pag. 78
Page 87

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
save place.
A.5 LAN Interface
I cannot access the ADSL Router from the LAN or ping any computer on the LAN.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the Ethernet LEDs on the front panel. A LAN LED should
be on if the port is connected to a computer or hub. If the
10M/100M LEDs on the front panel are both off, refer to Section
A.1.2.
2
Make sure that the IP address and the subnet mask of the ADSL
Router and your computer(s) are on the same subnet.
A.6 WAN Interface
Initialization of the ADSL connection failed.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2 Check that your VPI, VCI, type of encapsulation and type of
3
I cannot get a WAN IP address from the ISP.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 The ISP provides the WAN IP address after authenticating you.
2 The username and password apply to PPPoE and PPoA
Check the cable connections between the ADSL port and the
wall jack. The DSL LED on the front panel of the ADSL Router
should be on.
multiplexing settings are the same as what you collected from
your telephone company and ISP.
Restart the ADSL Router. If you still have problems, you may
need to verify your VPI, VCI, type of encapsulation and type of
multiplexing settings with the telephone company and ISP.
Authentication may be through the user name and password,
the MAC address or the host name.
encapsulation only. Make sure that you have entered the correct
Service Type, User Name and Password (be sure to use the
correct casing).
A02-RA110 Pag. 79
Page 88

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
A.7 Internet Access
I cannot access the Internet.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2 If the DSL LED is off, refer to Section A.1.3.
3
4
5
Internet connection disconnects.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the schedule rules.
2 If you use PPPoA or PPPoE encapsulation, check the idle time-
3
Make sure the ADSL Router is turned on and connected to the
network.
Verify your WAN settings.
Make sure you entered the correct user name and password.
For wireless stations, check that both the ADSL Router and
wireless station(s) are using the same ESSID, channel and WEP
keys (if WEP encryption is activated).
out setting.
Contact your ISP.
A.8 Remote Management
I cannot remotely manage the ADSL Router from the LAN or WAN.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Refer to the Remote Management Limitations section in the
Firmware and Configuration File Management chapter for
scenarios when remote management may not be possible.
2
3
4
Use the ADSL Router’s WAN IP address when configuring from
the WAN.
Use the ADSL Router’s LAN IP address when configuring from
the LAN.
Refer to Section A.6 for instructions on checking your LAN
connection.
Refer to Section A.7 for instructions on checking your WAN
connection.
See also the Section A.4.
A02-RA110 Pag. 80
Page 89

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
A.9 Remote Node Connection
I cannot connect to a remote node or ISP.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1
2 Verify your login name and password for the remote node.
3
Check WAN screen to verify that the username and password
are entered properly.
If these steps fail, you may need to verify your login and
password with your ISP.
A02-RA110 Pag. 81
Page 90

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
APPENDIX B: Technical Features
Protocols IP, NAT, ARP, ICMP, DHCP(server and client),
RIP1/2 , SNTP client, UPnP, Telnet server
LAN port 1 10/100 Base-T port on
WAN port RJ-11 (1 port ADSL)
External buttons Reset
LED Indicators
Standard ADSL
Compliance
Protocols ADSL RFC2364(PPPoA), RFC2516(PPPoE), RFC1577 e
ATM ATM AAL2/AAL5 and ATM service class : CBR,
Firewall
VPN
Input Power
Power Consumption < 9watts
Agency and Regulatory CE
Dimensions 135x 90 x 42 mm
Weight
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Operating Humidity 5-95% non-condensing
Power, System, Lan, ADSL and PPP
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2, ITU-T G.992.1(Full Rate
DMT), ITU-T G.992.2 (Lite DMT), ITU-T G.994.1
(Multimode)
RFC1483
UBR, VBR-rt, VBR, ATM Forum UNI 3.0, 3.1 and
4.0
Static Packet Filtering and NAT
Pass Through
9V DC @ 1A
<190g
0° to 40°C
-10° to 70°C
A02-RA110 Pag. 82
Page 91

COMPACT ROUTER ADSL
APPENDIX C:Support
If you have any problems with the Router ADSL, please consult this manual.
If you continue to have problems you should contact the dealer where you bought
this ADSL Router. If you have any other questions you can contact the Atlantis
Land company directly at the following address:
Atlantis Land SpA
Viale De Gasperi, 122
20017 Mazzo di Rho(MI)
Tel: +39. 02.93906085, +39. 02.93907634(help desk)
Fax: +39. 02.93906161
Email: info@atlantis-land.com
WWW: http://www.atlantis-land.com
or tecnici@atlantis-land.com
A02-RA110 Pag. 83
 Loading...
Loading...