Page 1

R
INT
V
+
–
V
+
–
Battery 2302/2306
R
OUT
2302
2306, 2306-PJ
• Ultrafast response to transient
load currents
• Choice of single- or dual-
channel supplies
• Optimized for development
and testing of battery-powered
devices
• Variable output resistance
for simulating battery response
(U.S. Patent No. 6,204,647)
• Pulse peak, average, and
baseline current measurements
• 100nA DC current sensitivity
• Current step measure function
• Sink up to 3A
• Open sense lead detection
• Built-in digital voltmeter
SERVICES AVAILABLE
2302-3Y-EW 1-year factory warranty extended to 3 years
from date of shipment
2306-3Y-EW 1-year factory warranty extended to 3 years
from date of shipment
2306-PJ-3Y-EW 1-year factory warranty extended to 3 years
from date of shipment
C/2302-3Y-ISO 3 (ISO-17025 accredited) calibrations within 3
years of purchase for Model 2302*
C/2306-3Y-ISO 3 (ISO-17025 accredited) calibrations within 3
years of purchase for Models 2306, 2306-P*
*Not available in all countries
Battery Simulator
Battery/Charger Simulators
The single-channel Model 2302 Battery
Simulator and dual-channel Model 2306 Battery/
Charger Simulator were designed specifically for
development and test applications of portable,
battery-operated products, such as cellular and
cordless telephones, mobile radios, and pagers.
These precision power supplies have ultrafast
transient response so they can have output
characteristics identical to actual batteries.
These supplies employ a unique variable output
resistance so the voltage output can emulate a
battery’s response (U.S. Patent No. 6,204,647).
They provide stable voltage outputs, even when
a device-under-test (DUT) makes the rapid transition from the standby (low current) state to the
RF transmission (high current) state. In addition,
they can monitor DUT power consumption by
meas uring both DC currents and pulse load currents. The Model 2302’s and the Model 2306’s
battery-simulator channel can be programmed
to operate like a discharged rechargeable battery, sinking current from a separate charger or from the
Model 2306’s charger- simulator channel.
Maximize Test Throughput with Accurate Battery Simulation
The battery-output channels of the Models 2302 and 2306 are designed to simulate the output
response of a battery. This capability, combined with their fast transient response, makes it possible
to power the device during testing in exactly the
same way as a battery will power the device
during actual use. The output resistance of the
Model 2302’s and the Model 2306’s battery channel can be programmed (with 10mΩ resolution)
over the range from 0Ω to 1Ω so that the output resistance can be set to the same level as the
output resistance of the battery that powers the
device. See Figure 1.
Portable wireless devices make great demands
on their battery power sources. The battery must
source load currents that can jump virtually
instantaneously from a standby current level
(100–300mA) to a full-power RF transmission
current level (1–3A). In other words, the load
current on the battery can increase rapidly by
a factor of 700–1000%. As a result, the battery
voltage drops by an amount equal to the value
of the current change multiplied by the battery’s
internal resistance. The Models 2302 and 2306
power supplies enable test systems to duplicate
this voltage drop by programming their output
resistance to be equivalent to that of the battery
that will power the device. This allows wireless device manufacturers to test their products
under the same power conditions that they will
encounter in actual use. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 1. Simplified schematic of a battery
and the 2302/2306.
ACCESSORIES AVAILABLE
CABLES
7007-1 Shielded IEEE-488 Cable, 1m (3.3 f t)
7007-2 Shielded IEEE-488 Cable, 2m (6.6 f t)
SC-182 Low-Inductance Coax ial Cable (42nH/f t)
RACK MOUNT KITS
4288-1 Single Fi xed Rack Mount Kit
4288-2 Dual Fi xed Rack Mount Kit
IEEE-488 INTERFACES
KPCI- 488LPA IEEE- 488 Interface/Control ler for the PCI Bus
KPXI-488 IEEE- 488 Interface Board for the PXI Bus
KUSB- 488A IEEE- 488 USB-to- GPIB Interface Adapter
Fast transient response power supplies
1.888.KEITHLEY
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
Page 2
High current level
Trigger level
Average current level
High
Time
Low current level
Low Time
Average Time
(out to 60s with long integration)
2302
Battery Simulator
2306, 2306-PJ
Ordering Information
2302 Battery Simulator
2306 Dual-Channel Battery/
2306-PJ Dual-Channel Battery/
Accessories Supplied
User and service manuals,
CS-846 output connectors
mating terminal
Conventional Power Supplies
and Wireless Device Testing
During production testing, supplying
power to a device that undergoes large,
instantaneous load current changes can be
extremely difficult. Changes like this force
a conventional power supply’s output voltage to fall instantaneously. When the power
supply’s control circuitry senses the error
Fast transient response power supplies
condition (the difference in voltage between
the programmed level and the actual
level), it attempts to correct or restore the
voltage to the programmed level. During
this time, the voltage will fall or droop
substantially, with the amount of the droop
depending on the size of the load current
change. The recovery time depends on the
transient response of the power supply’s
control loop. Conventional power supplies
have transient voltage drops of >1V when
confronted with load current changes of
up to 1000%, and take up to a millisecond
to recover to the programmed voltage. For
portable devices such as cellular phones
that operate at full power for only short
intervals, the full power event is over before
the conventional power supply can recover.
For example, a cellular phone designed to
the GSM cellular phone standard transmits
and receives information in 576µs pulses. If
the power supply used to test these types of
phones cannot recover quickly enough, the
performance of the phone during testing
will be compromised by the power supply.
If the power supply voltage drops below the
threshold of the phone’s low battery detection circuitry for long enough, then the
phone will turn off during testing, giving a
false indication of a failed device.
1.888.KEITHLEY
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
www.keithley.com
Charger Simulator
Charger Simulator
with 500mA Range
(U.S. only)
Battery/Charger Simulators
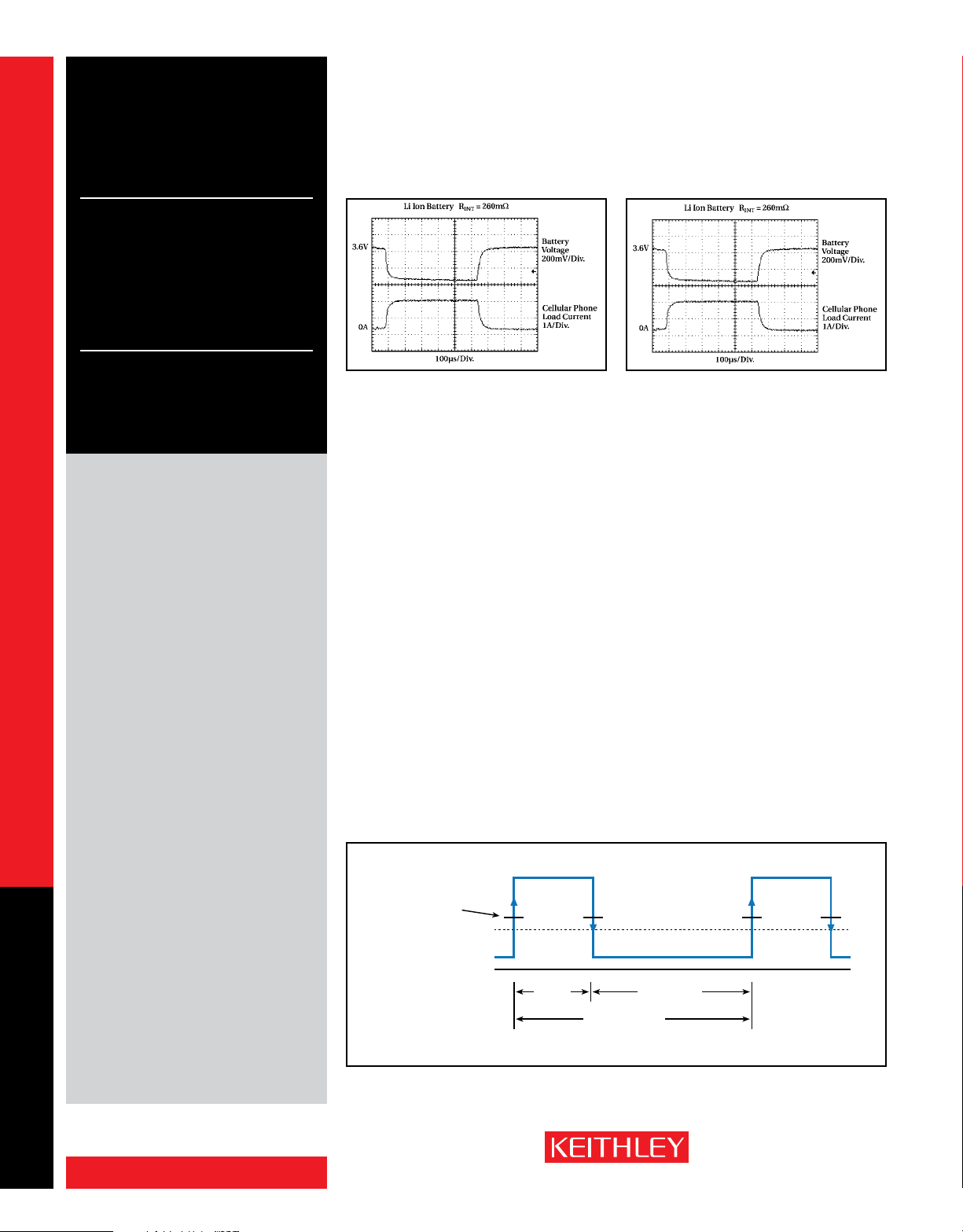
Figure 2. Comparison of the voltage outputs of a lithium-ion battery (with an internal resistance of
260mΩ) and the Model 2306’s battery channel (programmed with an output resistance of 260mΩ )
when powering a cellular telephone as it makes the transition from standby mode to transmit mode.
In response to large load changes, the Model
2302 and the battery channel of the Model 2306
have transient voltage droops of less than 100mV
and transient recovery times of less than 60µs,
even when the test leads between the power
supply and the DUT are long. This fast transient
response, combined with the supplies’ variable output resistance, allows engineers to test
their portable products under the most realistic
operating conditions and eliminate false failures
due to conventional power supplies with slow
response times. (See the sidebar titled “Conventional Power Supplies and Wireless Device
Testing.”) These supplies also eliminate the large
stabilizing capacitors needed at the DUT to compensate for the large droop that occurs when
testing with conventional power supplies. By
varying the output resistance, which can be done
while the output is turned on, test engineers can
simulate the operation of different battery types,
as well as batteries nearing the end of their
useful lives.
The Models 2302 and 2306 ensure maximum
production throughput when testing portable
Figure 3. Built-in pulse current measurement functions allow test engineers to measure peak,
average, and baseline load currents.
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
devices by minimizing false failures, minimizing
the number of test setups by performing multiple tests with the same power supply, and minimizing test fixture complexity by eliminating the
need for voltage-stabilizing capacitors.
Measure Load Currents for
Power Consumption Verification
or Analysis
As manufacturers of portable devices strive to
extend their products’ battery life, measuring
load currents accurately has become increasingly
essential in both design and production test in
order to ensure the product meets its demanding
specifications. Comprehensive testing of these
devices requires measuring peak currents, average currents, and baseline currents in various
operation modes. When testing these devices,
these measurements are complicated by the pulsating nature of load currents, such as the transmit and receive load currents of digital cellular
phones. The Models 2302 and 2306 can measure
the peak and average currents of pulses as short
as 60µs and as long as 833ms. (See Figure 3.)
Page 3
I
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
5
I
6
I
7
I
8
Trigger Levels
Load Currents
R
+
–
Battery Channel Charger Channel
V
battery
V
charger
> V
battery
Battery
Terminals
Charger
Terminals
+
–
II
DVM
+
–
+
–
V
OUT
V
IN
–5V to +30V DC
RI Sense
R
OUT
+
–
2302
Battery Simulator
2306, 2306-PJ
Battery/Charger Simulators
Measure Long-Period Waveform Currents
For pulse trains with periods longer than 850ms, the Models 2302 and
2306 offer a unique, long integration current measurement mode. This
mode can provide an average measurement of a current waveform from
850ms up to 60 seconds long.
Measure Low Currents Accurately
The Models 2302 and 2306 are based on Keithley’s expertise in low current
measurement technologies, so they’re well-suited for making fast, accurate
measurements of sleep and standby mode currents. With 100nA resolution
and 0.2% basic accuracy, they provide the precision needed to monitor the
low sleep mode currents of both today’s battery-operated products and
tomorrow’s.
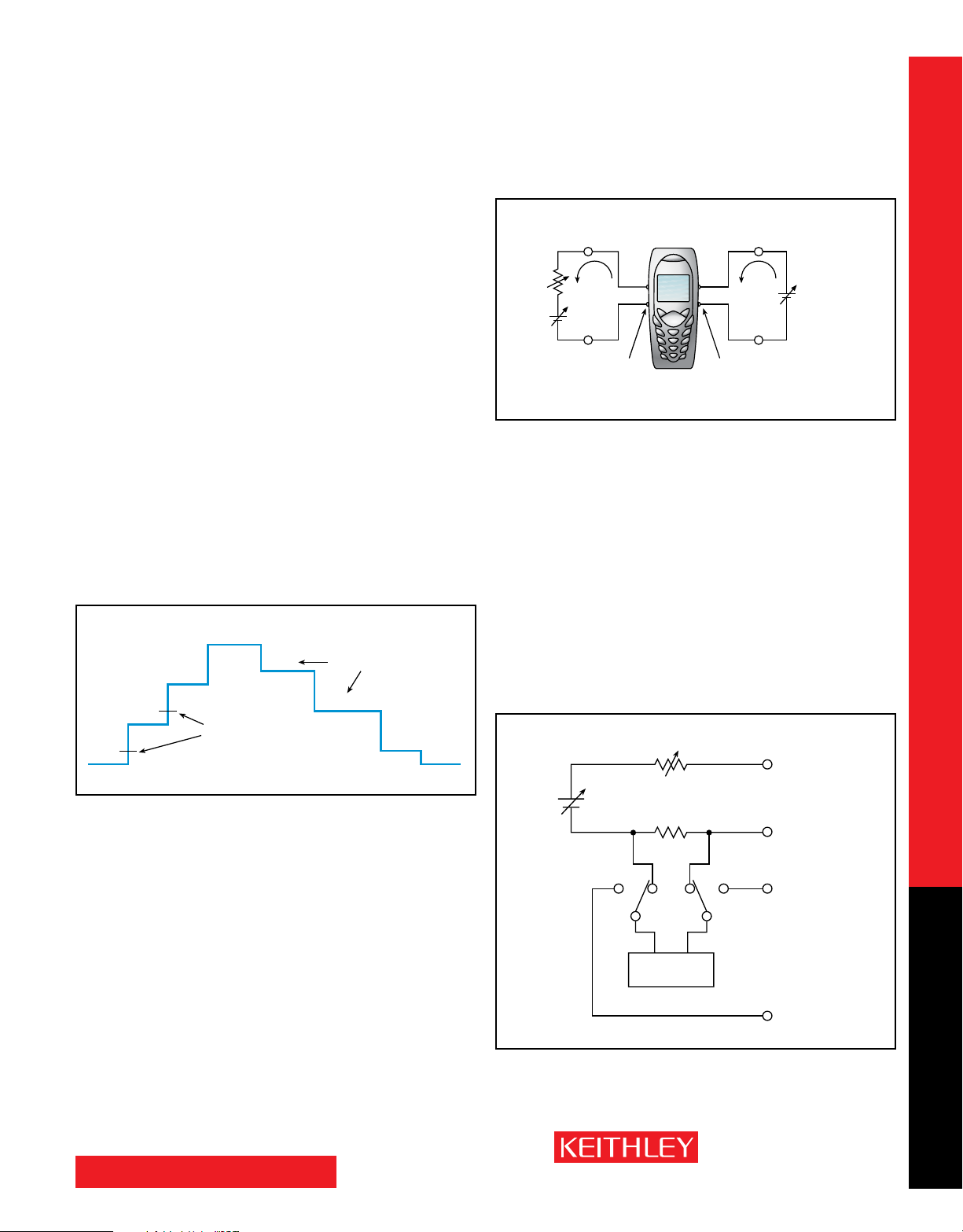
Verify Load Currents in All Operating States
The Models 2302 and 2306 employ a unique pulse current step function
for measuring the load current at each level of a device’s operational
states. (See Figure 4.) For example, if a cellular phone is ramped up and
down through as many as 20 discrete power consumption states, the
Models 2302 and 2306 can measure the load currents in synchronization
with the current steps. This capability allows a test engineer to verify
performance at each operational state and simultaneously acquire power
consumption information. The fast current measure capability is another
way the Models 2302 and 2306 power supplies save test time and production costs.
Figure 5. For charger control circuit testing applications, the Model
2306 and 2306-PJ can provide the functions of both a charger-simulating source and a discharged battery simulator.
the output voltage does not change from the programmed level, which
could cause production devices to be improperly calibrated, the user can
set high and low limits around the desired voltage level.
Independent Digital Voltmeter Inputs
Many programmable power supplies offer output readback capabilities, but
the Model 2302 and 2306 also offer DVM inputs. Both instruments allow
measuring signals from –5V to +30V DC anywhere in the test system with
the same rated accuracy as the voltage readback. The Model 2306 has two
sets of DVM inputs; the Model 2302 has one. The DVMs and the power
sources can operate simultaneously. For many applications, these built-in
DVMs eliminate the expense and space required to add a separate voltage
measurement instrument.
Fast transient response power supplies
Figure 4. These power supplies can obtain a load current profile
synchronized to the transitions of a DUT as it is stepped through its
operating states.
Simulate a Discharged Battery for Charger Testing
The Models 2302 and 2306 can sink up to 3A continuously, just like
an electronic load. This allows these supplies to simulate a discharged
rechargeable battery for use in testing the performance of battery chargers
or battery charger control circuitry.
The Model 2306 Battery/Charger Simulator combines the functionality of
both the charging current source (the charger channel) and the current
sinking to simulate the recharging of a discharged battery (the battery
channel) in a single enclosure. (See Figure 5.)
Open-Sense Lead Detection
The Model 2302 and 2306 have an automatic open–sense lead detection
capability, which indicates if there is a broken remote sense lead or an
open connection from a remote sense lead to the test fixture. To ensure
1.888.KEITHLEY
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
Figure 6. Model 2302 and Model 2306 Battery Channel Block Diagram.
The Model 2306 charger channel is identical except it does not have
the variable output resistance.
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 4

2302
Battery Simulator
2306, 2306-PJ
Battery/Charger Simulators
Big Functionality in a Small Package
For high volume production environments where floor and test rack space
are at a premium, the Model 2306 packs two power supplies into one
half-rack enclosure. In addition to power control, both the Model 2302
and 2306 provide extensive measurement capabilities in the same halfrack case. The front panel of each unit displays the user’s choice of either
the output voltage and output current, the average, peak, and baseline
pulse current levels, long integration currents, or DC DVM meas urements.
A minimum of front panel buttons ensures that operation is simple and
straight-forward.
For additional control requirements, the Models 2302 and 2306 each have
four digital relay control outputs and a 5V DC output to power a relay coil.
GENERAL
ISOLATION (l ow–ea rth): 22V DC max. For Models 2306 and 2306-PJ, do not exceed 60V DC
between any t wo terminals of eit her connector.
PROGRAMMING: IEEE-488.2 (SCPI).
USER-DEFINABLE POWER-UP STATES: 5 (4 for Model 2306-PJ).
REA R PANEL CONNECTORS: Two (one for Model 2302) 8-position quick disconnect termi-
nal block for output (4), sense (2), and DVM (2).
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT (outside 23°C ±5°C): Derate accuracy specification by (0.1 ×
specification)/°C.
OPERATING TEMPER ATURE: 0° to 50°C (Derate to 70%). 0° to 35°C (Full power).
STORAGE TEMPERATURE: –20° to 70°C.
HU MIDI TY: <80% @ 35°C non-condensing.
DISPLAY T YPE: 2-line × 16-character VFD.
REMOTE DISPLAY/KE YPAD OPTION: Disables standard front panel.
DIMENSIONS: 89mm high × 213mm wide × 411mm deep (3
NE T W EIGH T: 3.2kg (7.1 lbs).
SHIPPING WEIGHT: 5.4kg (12 lbs).
INPUT POWER: 100–120V AC/220–240V AC, 50 or 60Hz (auto detected at power-up).
POWER CONSUMPTION: 150VA max.
EMC: 2302, 2306: Conforms w ith European Union Directive 89/336/EEC, EN 55011, EN
50082-1, EN 61000-3-2 and 61000 -3-3, FCC part 15 class B. 2306-PJ: Conforms with
European Union Directive 89/336/EEC.
SAFETY: 2302, 2306: Conforms with European Union Directive 73/23/EEC, EN 61010-1.
2306-PJ: Conforms with European Union Directive 73/23/EEC.
1
⁄2 in × 83⁄8 in × 163⁄16 in).
Fast transient response power supplies
Figure 7. Model 2306 Rear Panel showing 8-position power output
connectors, RJ-45 remote display connector, DB-9 relay output connector, IEEE-488 connector, and power input socket.
1.888.KEITHLEY
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 5

2302
Battery Simulator
2306, 2306-PJ
Battery/Charger Simulators
Output #1 (Battery)
DC VOLTAGE OUTPUT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE: 0 to +15V DC.
OUTPUT ACCURACY: ±(0.05% + 3mV).
PROGRAMMING RESOLUTION: 1 mV.
REA DBACK ACCU RACY
REA DBACK R ESOLUTION: 1mV.
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETTLING TI ME: 5ms to within stated accuracy.
LOAD R EGULATION: 0.01% + 2mV.
LINE REGUL ATION: 0.5mV.
2
STABILITY
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
TRANSIENT RESPONSE: High Bandwidth Low Bandwidth
Transient Recovery Time
Transient Voltage Drop <75mV3 or <100mV4 <250mV3 or <400mV
REMOTE SENSE: 1V max. drop in each lead. Add 2mV to the voltage load regulation specification for
: 0.01% + 0.5mV.
each 1V change in the negative output lead due to load current change. Remote sense required.
Integrity of connection continually monitored. If compromised, output will turn off automatically
once settable window (±0 to ±8V) around normal voltage exceeded.
VARIABLE OUTPUT IMPEDANCE
RANGE: 0 to 1.00Ω in 0.01Ω steps. Value can be changed with output on.
DC CURRENT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
OUTPUT CURRENT (2302):
0–4V: 5A max.
= 60W/(V
>4V: I
MAX
CONTINUOUS AVERAGE OUTPUT CURRENT (2306, 2306-PJ):
Channel #2 (Charger) OFF:
I = 50W/(V
Channel #2 (Charger) ON:
I = (50W – Power consumed by channel #2)/(V
The power consumed by channel #2 is calculated as:
Channel #2 sourcing current:
Power consumed = (V
Channel #2 sinking current:
Power consumed = 5 × (sink current)
Peak currents can be a maximum of 5A provided the average current is w ithin the above limits.
CONTINUOUS AVERAGE SINK CURRENT:
Channel #2 (Charger) OFF:
0–5V: 3A max.
5–15V: Derate 0.2A per volt above 5V. Compliance setting controls sinking.
Channel #2 (Charger) ON:
Available current = (50W – Power consumed by channel #2)/5; 3A max. (0–5V).
Derate 0.2A per volt above 5V.
SOURCE COMPLIANCE ACCURACY: ±(0.16% + 5mA)
PROGRAMMED SOURCE COMPLIANCE RESOLUTION: 1.25mA.
READBACK ACCURACY
5mA Range: ±(0.2% + 1µA) (2302 and 2306).
500mA Range: ±(0.2% + 20µA) (2306-PJ only).
READBACK RESOLUTION: 5A Range: 100µA.
5mA Range: 0.1µA (2302 and 2306).
500mA Range: 10µA (2306-PJ only).
LOAD REGULATION: 0.01% + 1mA.
LINE REGULATION: 0.5mA.
4
STABILITY
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
: 0.01% + 50µA.
1
: ±(0.05% + 3mV).
7
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
13
<40µs3 or <60µs4 <80µs3 or <100µs
+6) (not intended to be operated in parallel).
OUT
channel 1 + 6V); 5A max.
SET
channel 2 + 6V) × (current supplied)
SET
1
: 5A Range: ±(0.2% + 200µA).
7
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
, in 0.01PLC steps.
channel 1 + 6V); 5A max.
SET
5
.
, in 0.01PLC steps.
4
4
PULSE CURRENT MEASUREMENT OPERATION
TRIGGER LEV EL:
5A CURRENT R ANGE
5A Range: 5mA to 5A, in 5mA steps.
1A Range: 1mA to 1A , in 1mA steps.
100mA R ange: 0.1mA to 100m A, in 100µA steps.
500mA CURRENT R ANGE (2306-PJ)
500mA Range: 0.5mA to 500mA, in 0.5mA steps.
100mA R ange: 0.1mA to 100m A, in 100µA steps.
10mA Ra nge: 100µA to 10mA , in 100µA steps.
TRIGGER DELAY: 0 to 100ms, in 10µs steps.
INTERNAL TRIGGER DELAY: 15µs.
HIGH/LOW/AVERAGE MODE:
Measurement Aperture Settings: 33.3µs to 833ms, in 33.3µs steps.
Average Readings: 1 to 100.
PULSE CURRENT MEASUREMENT ACCURACY
Aperture
<100 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 2 mA 0.2% + 90 µA + 2 mA
100 µs – 200 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 1.5 mA 0.2% + 90 µA + 1.5 mA
200 µs – 500 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 1 mA 0.2% + 90 µA + 1 mA
500 µs – <1 PLC 0.2% + 600 µA + 0.8 mA 0.2% + 60 µA + 0.8 mA
12
1 PLC
>1 PLC 0.2% + 400 µA + 100 µA 0.2% + 40 µA + 100 µA
5A Range 500mA Range (2306-PJ)
0.2% + 400 µA + 0 mA 0.2% + 40 µA + 0 mA
11
(2 Years, 23°C ±5°C):
±(% reading + offset + rms noise
Accuracy
10
)
BURST MODE CURRENT MEASUREMENT
MEASUREMENT APERTURE: 33.3µs.
CONVERSION RATE: 3650/second, typical.
INTERNAL TRIGGER DELAY: 15µs.
NUMBER OF SAMPLES: 1 to 5000.
TRANSFER SAMPLES ACROSS IEEE BUS IN BINARY MODE: 4800 bytes/s, typical.
LONG INTEGRATION MODE CURRENT MEASUREMENT
2302, 2306: Available on 5A range only.
2306-PJ: Available on 5A and 500mA current ranges.
MEASUREMENT TIME
6
: 850ms (840ms) to 60 seconds in 1ms steps.
DIGITAL VOLTMETER INPUT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE: –5 to +30V DC.
INPUT IMPEDANCE: 2MΩ typical.
MAXIMUM VOLTAGE (either input terminal) WITH RESPECT TO OUTPUT LOW: –5V, +30V.
READING ACCURACY
READING RESOLUTION: 1mV.
CONNECTOR: HI and LO input pair part of Output #1’s terminal block.
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
1
: ±(0.05% + 3mV).
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
7
, in 0.01PLC steps.
Model 2302, 2306, 2306-PJ specifications
1.888.KEITHLEY
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 6

2302
Battery Simulator
2306, 2306-PJ
Battery/Charger Simulators
OUTPUT #2 (CHARGER)
DC VOLTAGE OUTPUT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE: 0 to +15V DC.
OUTPUT ACCURACY: ±(0.05% + 10mV).
PROGRAMMING RESOLUTION: 10mV.
READBACK ACCURACY
READBACK RESOLUTION: 1mV.
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETTLING TIME: 5ms to within stated accuracy.
LOAD REGULATION: 0.01% + 2mV.
LINE REGULATION: 0.5mV.
2
STABILITY
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
TRANSIENT RESPONSE: High Bandwidth Low Bandwidth
Transient Recovery Time
Transient Voltage Drop <120mV3 or <150mV4 <160mV3 or <200mV
REMOTE SENSE: 1V max. drop in each lead. Add 2mV to the voltage load regulation specification for
Side Text
: 0.01% + 0.5mV.
each 1V change in the negative output lead due to load current change. Remote sense required.
Integrity of connection continually monitored. If compromised, output will turn off automatically
once settable window (±0 to ±8V) around normal voltage exceeded.
DC CURRENT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
CONTINUOUS AVERAGE OUTPUT CURRENT:
Channel #1 (Battery) OFF:
I = 50W/(V
Channel #1 (Battery) ON:
I = (50W – Power consumed by channel #1)/(V
Model 2302, 2306, 2306-PJ specifications
The power consumed by channel #1 is calculated as:
Channel #1 sourcing current:
Power consumed = (V
Channel #1 sinking current:
Power consumed = 5 × (sink current)
Peak currents can be a maximum of 5A provided the average current is w ithin the above limits.
CONTINUOUS AVERAGE SINK CURRENT:
Channel #1 (Battery) OFF:
0–5V: 3A max.
5–15V: Derate 0.2A per volt above 5V. Compliance setting controls sinking.
Channel #1 (Battery) ON:
Available current = (50W – Power consumed by channel #1)/5; 3A max. (0–5V).
Derate 0.2A per volt above 5V.
SOURCE COMPLIANCE ACCURACY: ±(0.16% + 5mA)
PROGRAMMED SOURCE COMPLIANCE RESOLUTION: 1.25mA.
READBACK ACCURACY
5mA Range: ±(0.2% + 1µA).
READBACK RESOLUTION: 5A Range: 100µA.
5mA Range: 0.1µA.
LOAD REGULATION: 0.01% + 1mA.
LINE REGULATION: 0.5mA.
4
STABILITY
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
: 0.01% + 50µA.
1
: ±(0.05% + 3mV).
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
13
<50µs3 or <80µs4 <60µs3 or <100µs
channel 2 + 6V); 5A max.
SET
channel 1 + 6V) × (current supplied)
SET
1
: 5A Range: ±(0.2% + 200µA).
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
7
, in 0.01PLC steps.
channel 2 + 6V); 5A max.
SET
5
.
7
, in 0.01PLC steps.
PULSE CURRENT MEASUREMENT OPERATION
TRIGGER LEVEL: 5mA to 5A, in 5mA steps.
TRIGGER DELAY: 0 to 100ms, in 10µs steps.
INTERNAL TRIGGER DELAY: 15µs.
HIGH/LOW/AVERAGE MODE:
Measurement Aperture Settings: 33.3µs to 833ms, in 33.3µs steps.
Average Readings: 1 to 100.
PULSE CURRENT MEASUREMENT ACCURACY
Aperture
<100 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 2 mA
100 µs – 200 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 1.5 mA
200 µs – 500 µs 0.2% + 900 µA + 1 mA
500 µs – <1 PLC 0.2% + 600 µA + 0.8 mA
12
4
4
1 PLC
>1 PLC 0.2% + 400 µA + 100 µA
±(% reading + offset + rms noise10)
11
(2 Years, 23°C ±5°C):
Accuracy
0.2% + 400 µA + 0 mA
BURST MODE CURRENT MEASUREMENT
MEASUREMENT APERTURE: 33.3µs.
CONVERSION RATE: 2040/second, typical.
INTERNAL TRIGGER DELAY: 15µs.
NUMBER OF SAMPLES: 1 to 5000.
TRANSFER SAMPLES ACROSS IEEE BUS IN BINARY MODE: 4800 bytes/s, typical.
LONG INTEGRATION MODE CURRENT MEASUREMENT
MEASUREMENT TIME6: 850ms (840ms) to 60 seconds in 1ms steps.
DIGITAL VOLTMETER INPUT (2 Years, 23°C ± 5°C)
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE: –5 to +30V DC.
INPUT IMPEDANCE: 2MΩ typical.
MAXIMUM VOLTAGE (either input terminal) WITH RESPECT TO OUTPUT LOW: –5V, +30V.
READING ACCURACY
READING RESOLUTION: 1mV.
CONNECTOR: HI and LO input pair part of Output #2’s terminal block.
MEASUREMENT TIME CHOICES: 0.01 to 10PLC
AVERAGE READINGS: 1 to 10.
REA DING TIME
AC LINE LEA KAGE CURRENT: 450µ A @ 110VAC, typ.; 60 0µA @ 220V, typ.
RELAY CONTROL PORT: 4- channel, each capable of 100m A sink, 24V max. Total port sink capac-
ity (all 4 combined) is 250mA max. Accepts DB-9 male plug.
1 PLC = 1.00.
2 Following 15 mi nute warm-up, t he change in o utput over 8 hours under ambient t emperature, constant load,
and li ne operating conditio ns.
3 Remote sense, at output termi nals, 0.5A to 5A t ypical.
4 Remote sense, with 4.5m (15 ft) of 16 gaug e (1.31mm
test env ironment, 1.5A load change (0.15A to 1.65A).
5 Minimum cu rrent in const ant current mode is 6mA .
6 60Hz (50Hz).
7 PLC = Power Lin e Cycle. 1PLC = 16.7ms for 60Hz operat ion, 20ms for 50 Hz operation.
8 Display off.
9 Speed includes measurement a nd binary d ata transf er out of GPIB.
10 Typical values, peak-t o-peak nois e equals 6 ti mes rms noise .
11 Based on settled sig nal: 100µs pul se trigger d elay.
12 Als o applies to oth er aperture s that are in teger multiples of 1PLC.
13 Recover y to withi n 20mV of previous level.
1
: ±(0.05% + 3mV).
1, 8, 9
: 31ms, typical.
7
, in 0.01PLC steps.
2
) wire and 1Ω resist ance in each le ad to simulate typical
1.888.KEITHLEY
1.888.KEITHLEY
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
www.keithley.com
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
(U.S. only)
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 7

1.888.KEITHLEY
www.keithley.com
(U.S. only)
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 8

All Keithley trademar ks and t rade names are the property of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All other trademark s and trade names are the pro perty of their respective companie s.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. ■ 28775 AURORA ROAD ■ CLEVELAND, OHIO 44139-1891 ■ 440-248-0400 ■ Fax: 440-248-6168 ■ 1-888-KEITHLEY ■ www.keithley.com
BELGIUM
Sint-Pieters-Leeuw
Ph: 02-3630040
Fax: 02-3630064
info@keithley.nl
www.keithley.nl
CHINA
Beijing
Ph : 8610 - 82 255010
Fax: 8610-82255018
china@keithley.com
www.keithley.com.cn
FINLAND
Espoo
Ph: 358-40-7600-880
Fax: 44-118-929-7509
finland@keithley.com
www.keithley.com
FRANCE
Saint-Aubin
Ph: 01-64532020
Fa x: 01- 60117726
info@keithley.fr
www.keithley.fr
GERMANY
Germering
Ph: 089-84930740
Fax: 089-84930734
info@keithley.de
www.keithley.de
INDIA
Bangalore
Ph: 080-26771071, -72, -73
Fax: 080-26771076
support_india@keithley.com
www.keithley.com
ITALY
Peschiera Borromeo (Mi)
Ph: 02-5538421
Fax: 02-55384228
info@keithley.it
www.keithley.it
JAPAN
Tok yo
Ph: 81-3-5733-7555
Fax: 81-3-5733-7556
info.jp@keithley.com
www.keithley.jp
SWEDEN
Stenungsund
Ph: 08-50904600
Fax: 08-6552610
sweden@keithley.com
www.keithley.com
KOREA
Seoul
Ph: 82-2-574-7778
Fax: 82-2-574-7838
keithley@keithley.co.kr
www.keithley.co.kr
SWITZERLAND
Zürich
Ph: 044-8219444
Fax: 044-8203081
info@keithley.ch
www.keithley.ch
MALAYSIA
Penang
Ph: 60-4-643-9679
Fax: 60-4-643-3794
chan_patrick@keithley.com
www.keithley.com
TAIWAN
Hsinchu
Ph: 886-3-572-9077
Fax: 886-3-572-9031
info_tw@keithley.com
www.keithley.com.tw
NETHERLANDS
Gorinchem
Ph: 0183-635333
Fax: 0183-630821
info@keithley.nl
www.keithley.nl
UNITED KINGDOM
Theale
Ph: 0118-9297500
Fax: 0118-9297519
info@keithley.co.uk
www.keithley.co.uk
SINGAPORE
Singapore
Ph: 65-6747-9077
Fax: 65-6747-2991
koh_william@keithley.com
www.keithley.com.sg
SPECIALIZED POWER SUPPLIES
© Copyright 2009 Keithley Instruments, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. No. 2118 60909.2KCG
30%
 Loading...
Loading...