Page 1

Internet Security
Router
User’s Manual
Revision 1.1
Oct. 30, 2003
Page 2

Copyright Information
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form or by any means, except
documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission of
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS
DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS
OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF
ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT
OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR PRODUCT.
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modified or altered, unless such
repair, modification of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2) the serial number of the product is
defaced or missing.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or
copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or explanation and to the owners’
benefit, without intent to infringe.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR
INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND
SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY
OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MAY APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL,
INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 2003 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction...............................................1
1.1 Features..................................................................................................................1
1.2 System Requirements............................................................................................1
1.3 Using this Document..............................................................................................1
1.3.1 Notational conventions................................................................................1
1.3.2 Typographical conventions.........................................................................1
1.3.3 Special messages........................................................................................1
2 Getting to Know the Internet Security
Router.......................................................3
2.1 Parts List.................................................................................................................3
2.2 Front Panel..............................................................................................................3
2.3 Rear Panel..............................................................................................................3
2.4 Major Features........................................................................................................4
2.4.1 Firewall Features.........................................................................................4
2.4.1.1 Address Sharing and Management...............................................4
2.4.1.1 ACL (Access Control List)..............................................................5
2.4.1.2 Stateful Packet Inspection..............................................................5
2.4.1.3 Defense against DoS Attacks........................................................5
2.4.1.4 Application Command Filtering......................................................6
2.4.1.5 Application Level Gateway (ALG)..................................................6
2.4.1.6 URL Filtering....................................................................................6
2.4.1.7 Log and Alerts.................................................................................6
2.4.1.8 Remote Access...............................................................................7
2.4.2 VPN...............................................................................................................7
3 Quick Start Guide.....................................9
3.1 Part 1 — Connecting the Hardware......................................................................9
3.1.1 Step 1. Connect an ADSL or a cable modem...........................................9
3.1.2 Step 2. Connect computers or a LAN........................................................9
3.1.3 Step 3. Attach the power adapter...............................................................9
iii
Page 4

3.1.4 Step 4. Turn on the Internet Security Router, the ADSL or cable modem
and power up your computers..................................................................10
3.2 Part 2 — Configuring Your Computers...............................................................11
3.2.1 Before you begin........................................................................................11
3.2.2 Windows® XP PCs:...................................................................................11
3.2.3 Windows® 2000 PCs:...............................................................................11
3.2.4 Windows® 95, 98, and Me PCs...............................................................12
3.2.5 Windows® NT 4.0 workstations:...............................................................12
3.2.6 Assigning static IP addresses to your PCs..............................................13
3.3 Part 3 — Quick Configuration of the Internet Security Router..........................14
3.3.1 Buttons Used in Setup Wizard..................................................................14
3.3.2 Setting Up the Internet Security Router....................................................14
3.3.3 Testing Your Setup....................................................................................20
3.3.4 Default Router Settings.............................................................................20
4 Getting Started with the Configuration
Manager.................................................21
4.1 Log into Configuration Manager..........................................................................21
4.2 Functional Layout.................................................................................................22
4.2.1 Setup Menu Navigation Tips.....................................................................22
4.2.2 Commonly Used Buttons and Icons.........................................................22
4.3 The Home Page of Configuration Manager.......................................................23
4.4 Overview of System Configuration......................................................................23
5 Configuring LAN Settings......................25
5.1 LAN IP Address....................................................................................................25
5.1.1 LAN IP Configuration Parameters............................................................25
5.1.2 Configuring the LAN IP Address...............................................................25
5.2 DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol).............................................................26
5.2.1 What is DHCP?..........................................................................................26
5.2.2 Why use DHCP?........................................................................................27
5.2.3 Configuring DHCP Server.........................................................................27
5.2.4 Viewing Current DHCP Address Assignments........................................28
iv
5.3 DNS.......................................................................................................................29
5.3.1 About DNS.................................................................................................29
Page 5

5.3.2 Assigning DNS Addresses........................................................................29
5.3.3 Configuring DNS Relay.............................................................................29
5.4 Viewing LAN Statistics.........................................................................................30
6 Configuring WAN Settings.....................31
6.1 WAN Connection Mode.......................................................................................31
6.2 PPPoE...................................................................................................................31
6.2.1 WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters..................................................31
6.2.2 Configuring PPPoE for WAN....................................................................32
6.3 Dynamic IP............................................................................................................32
6.3.1 WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Parameters...........................................32
6.3.2 Configuring Dynamic IP for WAN.............................................................33
6.4 Static IP.................................................................................................................34
6.4.1 WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters................................................34
6.4.2 Configuring Static IP for WAN...................................................................34
6.5 Viewing WAN Statistics........................................................................................35
7 Configuring Routes................................37
7.1 Overview of IP Routes.........................................................................................37
7.1.1 Do I need to define IP routes?..................................................................37
7.2 Dynamic Routing using RIP (Routing Information Protocol).............................38
7.2.1 Enabling/Disabling RIP..............................................................................38
7.3 Static Routing........................................................................................................38
7.3.1 Static Route Configuration Parameters....................................................38
7.3.2 Adding Static Routes.................................................................................38
7.3.3 Deleting Static Routes...............................................................................38
7.3.4 Viewing the Static Routing Table..............................................................39
8 Configuring DDNS..................................41
8.1 DDNS Configuration Parameters........................................................................42
8.2 Access DDNS Configuration Page.....................................................................43
8.3 Configuring RFC-2136 DDNS Client..................................................................43
8.4 Configuring HTTP DDNS Client..........................................................................44
v
Page 6

9 Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings.........45
9.1 Firewall Overview.................................................................................................45
9.1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection.........................................................................45
9.1.2 DoS (Denial of Service) Protection...........................................................45
9.1.3 Firewall and Access Control List (ACL)....................................................45
9.1.3.1 Priority Order of ACL Rule............................................................45
9.1.3.2 Tracking Connection State...........................................................46
9.1.4 Default ACL Rules.....................................................................................46
9.2 NAT Overview.......................................................................................................46
9.2.1 Static (One to One) NAT...........................................................................46
9.2.2 Dynamic NAT.............................................................................................47
9.2.3 NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation) or PAT (Port Address
Translation).................................................................................................48
9.2.4 Reverse Static NAT...................................................................................49
9.2.5 Reverse NAPT / Virtual Server.................................................................49
9.3 Configuring Inbound ACL Rules..........................................................................49
9.3.1 Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters.........................................49
9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è Inbound
ACL)............................................................................................................52
9.3.3 Add Inbound ACL Rules............................................................................52
9.3.4 Modify Inbound ACL Rules.......................................................................53
9.3.5 Delete Inbound ACL Rules.......................................................................53
9.3.6 Display Inbound ACL Rules......................................................................53
9.4 Configuring Outbound ACL Rules.......................................................................53
9.4.1 Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters......................................54
9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è
Outbound ACL)..........................................................................................56
9.4.3 Add an Outbound ACL Rule.....................................................................57
9.4.4 Modify Outbound ACL Rules....................................................................57
9.4.5 Delete Outbound ACL Rules....................................................................58
9.4.6 Display Outbound ACL Rules...................................................................58
9.5 Configuring URL Filters........................................................................................58
9.5.1 URL Filter Configuration Parameters.......................................................58
9.5.2 Access URL Filter Configuration Page – (Firewall è URL Filter)..........58
9.5.3 Add an URL Filter Rule..............................................................................59
vi
9.5.4 Modify an URL Filter Rule.........................................................................59
Page 7

9.5.5 Delete an URL Filter Rule.........................................................................59
9.5.6 View Configured URL Filter Rules............................................................59
9.5.7 URL Filter Rule Example...........................................................................59
9.6 Configuring Advanced Firewall Features – (Firewall è Advanced).................60
9.6.1 Configuring Self Access Rules.................................................................60
9.6.1.1 Self Access Configuration Parameters........................................61
9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è
Advanced è Self Access)............................................................61
9.6.1.3 Add a Self Access Rule................................................................61
9.6.1.4 Modify a Self Access Rule............................................................62
9.6.1.5 Delete a Self Access Rule............................................................62
9.6.1.6 View Configured Self Access Rules............................................62
9.6.2 Configuring Service List.............................................................................62
9.6.2.1 Service List Configuration Parameters........................................63
9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration Page – (Firewall è Advanced
è Service).....................................................................................63
9.6.2.3 Add a Service................................................................................63
9.6.2.4 Modify a Service............................................................................64
9.6.2.5 Delete a Service............................................................................64
9.6.2.6 View Configured Services............................................................64
9.6.3 Configuring DoS Settings..........................................................................64
9.6.3.1 DoS Protection Configuration Parameters..................................64
9.6.3.2 Access DoS Configuration Page – (Firewall è Advanced è
DoS)...............................................................................................66
9.6.3.3 Configuring DoS Settings.............................................................66
9.7 Firewall Policy List – (Firewall è Policy List).....................................................66
9.7.1 Configuring Application Filter....................................................................67
9.7.1.1 Application Filter Configuration Parameters................................67
9.7.1.2 Access Application Filter Configuration Page – (Firewall è
Policy List è Application Filter)....................................................68
9.7.1.3 Add an Application Filter...............................................................69
9.7.1.3.1 FTP Example: Add a FTP Filter Rule to Block FTP DELETE
Command......................................................................................69
9.7.1.3.2 HTTP Example: Add a HTTP Filter Rule to Block JAVA Applets
and Java Archives.........................................................................71
9.7.1.4 Modify an Application Filter..........................................................72
9.7.1.5 Delete an Application Filter...........................................................73
9.7.2 Configuring IP Pool....................................................................................73
9.7.2.1 IP Pool Configuration Parameters...............................................73
vii
Page 8

9.7.2.2 Access IP Pool Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è
IP Pool)..........................................................................................74
9.7.2.3 Add an IP Pool..............................................................................74
9.7.2.4 Modify an IP Pool..........................................................................74
9.7.2.5 Delete an IP Pool..........................................................................75
9.7.2.6 IP Pool Example............................................................................75
9.7.3 Configuring NAT Pool................................................................................76
9.7.3.1 NAT Pool Configuration Parameters...........................................76
9.7.3.2 Access NAT Pool Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List
è NAT Pool).................................................................................77
9.7.3.3 Add a NAT Pool.............................................................................78
9.7.3.4 Modify a NAT Pool........................................................................78
9.7.3.5 Delete a NAT Pool........................................................................78
9.7.3.6 NAT Pool Example........................................................................78
9.7.4 Configuring Time Range...........................................................................80
9.7.4.1 Time Range Configuration Parameters.......................................80
9.7.4.2 Access Time Range Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy
List è Time Range)......................................................................81
9.7.4.3 Add a Time Range........................................................................81
9.7.4.4 Modify a Time Range....................................................................81
9.7.4.5 Delete a Time Range....................................................................82
9.7.4.6 Delete a Schedule in a Time Range............................................82
9.7.4.7 Time Range Example...................................................................82
9.8 Firewall Statistics – Firewall è Statistics...........................................................83
10 Configuring VPN....................................85
10.1 Default Parameters..............................................................................................85
10.2 VPN Tunnel Configuration Parameters..............................................................87
10.3 Establish VPN Connection Using Automatic Keying.........................................90
10.3.1 Add a Rule for VPN Connection Using Pre-shared Key.........................91
10.3.2 Modify VPN Rules......................................................................................92
10.3.3 Delete VPN Rules......................................................................................92
10.3.4 Display VPN Rules....................................................................................92
10.4 Establish VPN Connection Using Manual Keys.................................................93
viii
10.4.1 Add a Rule for VPN Connection Using Manual Key...............................93
10.4.2 Modify VPN Rules......................................................................................94
10.4.3 Delete VPN Rules......................................................................................94
Page 9

10.4.4 Display VPN Rules....................................................................................94
10.5 VPN Statistics.......................................................................................................95
10.6 VPN Connection Examples.................................................................................96
10.6.1 Intranet Scenario – firewall + VPN and no NAT for VPN traffic..............96
10.6.1.1 Configure Rules on Internet Security Router 1 (ISR1)...............97
10.6.1.2 Configure Rules on Internet Security Router 2 (ISR2)...............98
10.6.1.3 Establish Tunnel and Verify........................................................100
10.6.2 Extranet Scenario – firewall + static NAT + VPN for VPN traffic..........100
10.6.2.1 Setup the Internet Security Routers...........................................101
10.6.2.2 Configure VPN Rules on ISR1...................................................102
10.6.2.3 Configure VPN Rules on ISR2...................................................104
10.6.2.4 Establish Tunnel and Verify........................................................107
11 Configuring Remote Access................109
11.1 Remote Access..................................................................................................109
11.2 Manage User Groups and Users......................................................................109
11.2.1 User Group Configuration Parameters...................................................109
11.2.2 Access User Group Configuration Page – (Remote Access è User
Group).......................................................................................................110
11.2.3 Add a User Group and/or a User............................................................110
11.2.4 Modify a User Group or a User...............................................................111
11.2.5 Delete a User Group or a User...............................................................111
11.2.6 User Group and Users Configuration Example.....................................112
11.3 Configure Group ACL Rules..............................................................................112
11.3.1 Group ACL Specific Configuration Parameters.....................................112
11.3.2 Access Group ACL Configuration Page – (Remote Access è Group
ACL)..........................................................................................................113
11.3.3 Add/Modify/Delete Group ACL Rules.....................................................113
11.4 Remote User Login Process.............................................................................113
11.5 Configure Firewall for Remote Access.............................................................115
11.6 Virtual IP Address Configuration for Remote Access VPN.............................116
11.6.1 Access VPN Virtual IP Configuration Page – (Remote Access è VPN
Virtual IP)..................................................................................................116
11.6.2 Assign VPN Virtual IP Address for Remote Access Users...................116
11.6.3 Change Virtual IP Assignments for Remote Access Users..................117
11.6.4 Delete Virtual IP Address for Remote Access Users............................117
11.7 Configure VPN for Remote Access..................................................................118
ix
Page 10

11.7.1 Main Mode Remote Access....................................................................118
11.7.2 Aggressive Mode Remote Access.........................................................120
12 System Management...........................123
12.1 Configure System Services...............................................................................123
12.2 Change the Login Password.............................................................................124
12.3 Modify System Information................................................................................124
12.4 Setup Date and Time.........................................................................................125
12.4.1 View the System Date and Time............................................................126
12.5 System Configuration Management.................................................................126
12.5.1 Reset System Configuration...................................................................126
12.5.2 Backup System Configuration................................................................127
12.5.3 Restore System Configuration................................................................127
12.6 Upgrade Firmware..............................................................................................128
12.7 Reset the Internet Security Router....................................................................129
12.8 Logout Configuration Manager..........................................................................130
13 ALG Configuration................................131
14 IP Addresses, Network Masks, and
Subnets................................................135
14.1 IP Addresses......................................................................................................135
14.1.1 Structure of an IP address.......................................................................135
14.2 Network classes.................................................................................................135
14.3 Subnet masks.....................................................................................................136
15 Troubleshooting....................................139
15.1 Diagnosing Problem using IP Utilities...............................................................140
15.1.1 ping...........................................................................................................140
15.1.2 nslookup...................................................................................................141
16 Glossary...............................................143
x
Page 11

17 Index.....................................................149
List of Figures
Figure 2.1. Front Panel LEDs.....................................................................................................................................3
Figure 2.2. Rear Panel Connections..........................................................................................................................3
Figure 3.1. Overview of Hardware Connections.....................................................................................................10
Figure 3.2. Login Screen...........................................................................................................................................14
Figure 3.3. Setup Wizard Home Page.....................................................................................................................15
Figure 3.4. Setup Wizard – Password Configuration Page....................................................................................15
Figure 3.5. Setup Wizard – System Identity Configuration Page..........................................................................16
Figure 3.6. Setup Wizard – Date/Time Configuration Page...................................................................................16
Figure 3.7. Setup Wizard – LAN IP Configuration Page........................................................................................17
Figure 3.8. Setup Wizard – DHCP Server Configuration Page.............................................................................17
Figure 3.9. Setup Wizard – WAN PPPoE Configuration Page..............................................................................18
Figure 3.10. Setup Wizard – WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Page.....................................................................18
Figure 3.11. Setup Wizard – WAN Static IP Configuration Page..........................................................................19
Figure 4.1. Configuration Manager Login Screen...................................................................................................21
Figure 4.2. Typical Configuration Manager Page...................................................................................................22
Figure 4.3. Setup Wizard Home Page.....................................................................................................................23
Figure 4.4. System Information Page......................................................................................................................24
Figure 5.1. LAN IP Address Configuration Page....................................................................................................26
Figure 5.2. DHCP Configuration Page....................................................................................................................27
Figure 5.3. LAN Statistics Page...............................................................................................................................30
Figure 6.1. WAN PPPoE Configuration Page.........................................................................................................31
Figure 6.2. WAN Dynamic IP (DHCP client) Configuration Page..........................................................................33
Figure 6.3. WAN Static IP Configuration Page.......................................................................................................34
Figure 6.4. WAN Statistics Page..............................................................................................................................35
Figure 7.1. Routing Configuration Page.................................................................................................................37
Figure 8.1. Network Diagram for RFC-2136 DDNS...............................................................................................41
Figure 8.2. Network Diagram for HTTP DDNS.......................................................................................................42
Figure 8.3. RFC-2136 DDNS Configuration Page..................................................................................................43
Figure 8.4. HTTP DDNS Configuration Page.........................................................................................................44
Figure 9.1 Static NAT – Mapping Four Private IP Addresses to Four Globally Valid IP Addresses...................47
Figure 9.2 Dynamic NAT – Four Private IP addresses Mapped to Three Valid IP Addresses...........................47
Figure 9.3 Dynamic NAT – PC-A can get an NAT association after PC-B is disconnected................................47
xi
Page 12

Figure 9.4 NAPT – Map Any Internal PCs to a Single Global IP Address............................................................48
Figure 9.5 Reverse Static NAT – Map a Global IP Address to An Internal PC....................................................48
Figure 9.6 Reverse NAPT – Relayed Incoming Packets to the Internal Host Base on the Protocol, Port
Number or IP Address......................................................................................................................................48
Figure 9.7. Inbound ACL Configuration Page.........................................................................................................49
Figure 9.8. Inbound ACL configuration example....................................................................................................52
Figure 9.9. Outbound ACL Configuration Page......................................................................................................54
Figure 9.10. Outbound ACL Configuration Example..............................................................................................57
Figure 9.11. URL Filter Configuration Page............................................................................................................59
Figure 9.12. URL Filter Rule Example.....................................................................................................................60
Figure 9.13. Self Access Rule Configuration Page.................................................................................................61
Figure 9.14. Service List Configuration Page..........................................................................................................63
Figure 9.15. DoS Configuration Page......................................................................................................................66
Figure 9.16. Application Filter Configuration Page.................................................................................................69
Figure 9.17 Network Diagram for FTP Filter Example – Blocking FTP Delete Command..................................69
Figure 9.18. FTP Filter Example – Configuring FTP Filter Rule............................................................................70
Figure 9.19 FTP Filter Example – Firewall Configuration Assistant......................................................................70
Figure 9.20 FTP Filter Example – Add an FTP Filter to Deny FTP Delete Command........................................70
Figure 9.21. FTP Filter Example – Associate FTP Filter Rule to an ACL Rule....................................................71
Figure 9.22. HTTP Filter Example – Configuring HTTP Filter Rule.......................................................................71
Figure 9.23. HTTP Filter Example – Associate HTTP Filter Rule to an ACL Rule...............................................72
Figure 9.24. Modify an Application Filter.................................................................................................................73
Figure 9.25 IP Pool Configuration Page..................................................................................................................74
Figure 9.26. Network Diagram for IP Pool Configuration.......................................................................................75
Figure 9.27. IP Pool Example – Add Two IP Pools – MISgroup1 and MISgroup2..............................................76
Figure 9.28. IP Pool Example – Deny QUAKE-II Connection for MISgroup1......................................................76
Figure 9.29. NAT Pool configuration page..............................................................................................................77
Figure 9.30. Network Diagram for NAT Pool Example...........................................................................................79
Figure 9.31. NAT Pool Example – Create a Static NAT Pool................................................................................79
Figure 9.32. NAT Pool Example – Associate a NAT Pool to an ACL Rule...........................................................80
Figure 9.33. Time Range Configuration Page........................................................................................................81
Figure 9.34. Time Range Example – Create a Time Range..................................................................................82
Figure 9.35. Time Range Example – Deny FTP Access for MISgroup1 During OfficeHours.............................82
Figure 9.36. Firewall active connections statistics..................................................................................................83
Figure 10.1. VPN Tunnel Configuration Page – Pre-shared Key Mode...............................................................91
Figure 10.2. VPN Tunnel Configuration Page – Manual Key Mode......................................................................93
Figure 10.3. VPN Statistics Page.............................................................................................................................96
xii
Page 13

Figure 10.4. Typical Intranet Network Diagram......................................................................................................97
Figure 10.5. Intranet VPN Policy Configuration on ISR1........................................................................................98
Figure 10.6. Intranet VPN Policy Configuration on ISR2........................................................................................99
Figure 10.7. Typical Extranet Network Diagram...................................................................................................101
Figure 10.8. Extranet Example –VPN Policy Configuration on ISR1..................................................................102
Figure 10.9. Extranet Example – Outgoing NAT Pool Configuration on ISR1...................................................103
Figure 10.10. Extranet Example – Incoming NAT Pool Configuration on ISR1.................................................103
Figure 10.11. Extranet Example – Outbound ACL Rule on ISR1........................................................................104
Figure 10.12. Extranet Example – Inbound ACL Rule on ISR1...........................................................................104
Figure 10.13. Extranet Example –VPN Policy Configuration on ISR2................................................................105
Figure 10.14. Extranet Example – Outgoing NAT Pool Configuration on ISR2.................................................105
Figure 10.15. Extranet Example – Incoming NAT Pool Configuration on ISR2.................................................106
Figure 10.16. Extranet Example – Outbound ACL Rule on ISR2........................................................................106
Figure 10.17. Extranet Example – Inbound ACL Rule on ISR2...........................................................................107
Figure 11.1. User Group Configuration Page........................................................................................................110
Figure 11.2. User Group and Users Configuration Example...............................................................................112
Figure 11.3. Goup ACL Configuration Page.........................................................................................................113
Figure 11.4. Login Console.....................................................................................................................................114
Figure 11.5. Login Status Screen...........................................................................................................................114
Figure 11.6. Network Diagram for Inbound Remote Access...............................................................................114
Figure 11.7. User and User Group Configuration Example.................................................................................115
Figure 11.8. Group ACL Configuration Example..................................................................................................115
Figure 11.9. VPN Virtual IP Configuration Page...................................................................................................116
Figure 11.10. Network Diagram for VPN Remote Access...................................................................................117
Figure 11.11. Main Mode Remote Access Example – Create a User Group and Add Two Users into the Group
..........................................................................................................................................................................118
Figure 11.12. Main Mode Remote Access Example – Configure the Virtual IP address..................................119
Figure 11.13. Main Mode Remote Access Example – Remote VPN Connection Setup for “RoadWarrior”
Group................................................................................................................................................................119
Figure 11.14. Aggressive Mode Remote Access Example – Create a User Group and Add Two Users into the
Group................................................................................................................................................................120
Figure 11.15. Aggressive Mode Remote Access Example – Configure the Virtual IP address........................120
Figure 11.16. Aggressive Mode Remote Access Example – Remote VPN Connection Setup for “RoadWarrior”
Group................................................................................................................................................................121
Figure 12.1. System Services Configuration Page...............................................................................................123
Figure 12.2. Password Configuration Page..........................................................................................................124
Figure 12.3. System Information Configuration Page...........................................................................................125
Figure 12.4. Date and Time Configuration Page..................................................................................................125
xiii
Page 14

Figure 12.5. Default Setting Configuration Page..................................................................................................126
Figure 12.6. Backup System Configuration Page.................................................................................................127
Figure 12.7. Restore System Configuration Page................................................................................................128
Figure 12.8. Windows File Browser.......................................................................................................................128
Figure 12.9. Firmware Upgrade Page...................................................................................................................129
Figure 12.10. Configuration Manager Reset Page...............................................................................................129
Figure 12.11. Configuration Manager Logout Page.............................................................................................130
Figure 12.12. Confirmation for Closing Browser (IE)............................................................................................130
Figure 15.1. Using the ping Utility..........................................................................................................................141
Figure 15.2. Using the nslookup Utility..................................................................................................................142
List of Tables
Table 2.1. Front Panel Label and LEDs....................................................................................................................3
Table 2.2. Rear Panel Labels and LEDs...................................................................................................................4
Table 2.3. DoS Attacks...............................................................................................................................................5
Table 2.4. VPN Features of the Internet Security Router.........................................................................................7
Table 3.1. LED Indicators.........................................................................................................................................10
Table 3.2. Default Settings Summary......................................................................................................................20
Table 4.1. Description of Commonly Used Buttons and Icons..............................................................................22
Table 5.1. LAN IP Configuration Parameters..........................................................................................................25
Table 5.2. DHCP Configuration Parameters...........................................................................................................28
Table 5.3. DHCP Address Assignment...................................................................................................................28
Table 6.1. WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters...............................................................................................32
Table 6.2. WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Parameters........................................................................................32
Table 6.3. WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters..............................................................................................34
Table 7.1. Static Route Configuration Parameters.................................................................................................38
Table 8.1. DDNS Configuration Parameters...........................................................................................................42
Table 9.1. Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters.......................................................................................49
Table 9.2. Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters....................................................................................54
Table 9.3. URL Filter Configuration Parameters.....................................................................................................58
Table 9.4. Self Access Configuration Parameters..................................................................................................61
Table 9.5. Service List configuration parameters....................................................................................................63
Table 9.6. DoS Protection Configuration Parameters............................................................................................64
Table 9.7. Application Filter Configuration Parameters..........................................................................................67
Table 9.8. IP Pool Configuration Parameters..........................................................................................................73
Table 9.9. NAT Pool Configuration Parameters......................................................................................................76
xiv
Page 15

Table 9.10. Time Range Configuration Parameters...............................................................................................80
Table 10.1. Default Connections in the Internet Security Router...........................................................................85
Table 10.2. Pre-configured IKE proposals in the Internet Security Router...........................................................85
Table 10.3. Pre-configured IPSec proposals in the Internet Security Router.......................................................86
Table 10.4. VPNTtunnel Configuration Parameter.................................................................................................87
Table 10.5. VPN Statistics........................................................................................................................................95
Table 10.6. Outbound Un-translated Firewall Rule for VPN Packets on ISR1.....................................................98
Table 10.7. Inbound Un-translated Firewall Rule for VPN Packets on ISR1........................................................98
Table 10.8. Outbound Un-translated Firewall Rule for VPN Packets on ISR1.....................................................99
Table 10.9. Inbound Un-translated Firewall Rule for VPN Packets on ISR1......................................................100
Table 11.1. User Group Configuration Parameters..............................................................................................109
Table 11.2. Group ACL Specific Configuration Parameters................................................................................112
Table 13.1. Supported ALG....................................................................................................................................131
Table 14.1. IP Address structure............................................................................................................................135
xv
Page 16

Page 17
Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 1. Introduction
1 Introduction
Congratulations on becoming the owner of the Internet Security Router. Your LAN (local area network) will
now be able to access the Internet using your high-speed broadband connection such as those with ADSL or
cable modem.
This User Manual will show you how to set up the Internet Security Router, and how to customize its
configuration to get the most out of this product.
1.1 Features
„ 10/100Base-T Ethernet router to provide Internet connectivity to all computers on your LAN
„ Firewall, NAT (Network Address Translation), and IPSec VPN functions to provide secure Internet
access for your LAN
„ Automatic network address assignment through DHCP Server
„ Services including IP route, DNS and DDNS configuration, RIP, and IP performance monitoring
„ Configuration program accessible via a web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5,
Netscape 7.0.2 or later.
1.2 System Requirements
In order to use the Internet Security Router for Internet access, you must have the following:
„ ADSL or cable modem and the corresponding service up and running, with at least one public Internet
address assigned to your WAN
„ One or more computers each containing an Ethernet 10Base-T/100Base-T network interface card
(NIC)
„ (Optional) An Ethernet hub/switch, if you are connecting the device to more than four computers on an
Ethernet network.
„ For system configuration using the supplied web-based program: a web browser such as Internet
Explorer v5.5 or later.
1.3 Using this Document
1.3.1 Notational conventions
„ Acronyms are defined the first time they appear in text and in the glossary (Appendix 16).
„ For brevity, the Internet Security Router is sometimes referred to as “the router.”
„ The terms LAN and network are used interchangeably to refer to a group of Ethernet-connected
computers at one site.
1.3.2 Typographical conventions
„ Italics are used to identify terms that are defined in the glossary (Chapter 16).
„ Boldface type text is used for items you select from menus and drop-down lists, and text strings you
type when prompted by the program.
1.3.3 Special messages
This document uses the following icons to call your attention to specific instructions or explanations.
Page 18

Chapter 1. Introduction Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Note
topic.
Explains terms or acronyms that may be unfamiliar to many
Provides clarification or non-essential information on the current
Definition
readers. These terms are also included in the Glossary.
Provides messages of high importance, including messages
relating to personal safety or system integrity.
WARNING
2
Page 19

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 2. Getting to Know the Internet Security Router
2 Getting to Know the Internet Security Router
2.1 Parts List
In addition to this document, your Internet Security Router should come with the following:
„ The Internet Security Router
„ Power adapter
„ Ethernet cable (“straight -through” type)
„ Optional console port cable (RJ-45)
2.2 Front Panel
The front panel contains LED indicators that show the status of the unit.
Figure 2.1. Front Panel LEDs
Table 2.1. Front Panel Label and LEDs
Label Color Function
POWER green On: Unit is powered on
Off: Unit is powered off
ALARM green (For factory testing only)
WAN green On: WAN link established and active
Flashing: Data is transmitted via WAN connection
Off: No WAN link
LAN1 –
LAN4
green On: LAN link is established
Flashing: Data is transmitted via LAN connection
Off: No LAN link
2.3 Rear Panel
The rear panel contains the ports for the unit's data and power connections.
Figure 2.2. Rear Panel Connections
3
Page 20

Chapter 2. Getting to Know the Internet Security Router Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Table 2.2. Rear Panel Labels and LEDs
Label Function
POWER Connects to the supplied power adapter
Reset Resets the device
CONSOLE RJ-45 serial port for console management
WAN Connects to your WAN device, such as ADSL or
P1 – P4 Connects the device to your PC's Ethernet port,
Switches the unit on and off
cable modem.
or to the uplink port on your LAN's hub/switch,
using the cable provided
2.4 Major Features
2.4.1 Firewall Features
The Firewall as implemented in the Internet Security Router provides the following features to protect your
network from being attacked and to prevent your network from being used as the springboard for attacks.
„ Address Sharing and Management
„ Packet Filtering
„ Stateful Packet Inspection
„ Defense against Denial of Service Attacks
„ Application Content Filtering
„ Log and Alert
„ Remote Access
„ Keyword based URL Filtering
2.4.1.1 Address Sharing and Management
The Internet Security Router Firewall provides NAT to share a single high-speed Internet connection and to
save the cost of multiple connections required for the hosts on the LAN segments connected to the Internet
Security Router. This feature conceals network address and prevents them from becoming public. It maps
unregistered IP addresses of hosts connected to the LAN with valid ones for Internet access. The Internet
Security Router Firewall also provides reverse NAT capability, which enables SOHO users to host various
services such as e-mail servers, web servers, etc. The NAT rules drive the translation mechanism at the NAT
router. The following types of NAT are supported by the Internet Security Router.
„ Static NAT – Maps an internal host address to a globally valid Internet address (one-to-one). All
packets are directly translated with the information contained in the map.
„ Dynamic NAT – Maps an internal host address dynamically to a globally valid Internet address (m-to-
n). The map usually contains a pool of internal IP addresses (m) and a pool of globally valid Internet IP
addresses (n) with m usually greater than n. Each internal IP address is mapped to one external IP
address on a first come first serve basis.
„ NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation) – Also called IP Masquerading. Maps many internal
hosts to only one globally valid Internet address. The map usually contains a pool of network ports to
be used for translation. Every packet is translated with the globally valid Internet address; the port
number is translated with a free pool from the pool of network ports.
4
Page 21

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Internet Security Router
„ Reverse Static – This is inbound mapping that maps a globally valid Internet address to an internal
host address. All packets coming to that external address are relayed to the internal address. This is
useful when hosting services in an internal machine.
„ Reverse NAPT – Also called inbound mapping, port mapping, and virtual server. Any packet coming
to the router can be relayed to the internal host based on the protocol, port number or IP Address
specified in the rule. This is useful when multiple services are hosted on different internal machines.
Note
For a complete listing of all NAT ALGs supported, refer to
Appendix A “ALG Configuration” on.
2.4.1.1 ACL (Access Control List)
ACL rule is one of the basic building blocks for network security. Firewall monitors each individual packet,
decodes the header information of inbound and outbound traffic and then either blocks the packet from
passing or allows it to pass based on the contents of the source address, destination address, source port,
destination port, protocol and other criterion, e.g. application filter, time ranges, defined in the ACL rules.
ACL is a very appropriate measure for providing isolation of one subnet from another. It can be used as the
first line of defense in the network to block inbound packets of specific types from ever reaching the protected
network.
The Internet Security Router Firewall’s ACL methodology supports:
„ Filtering based on destination and source IP address, port number and protocol
„ Use of the wild card for composing filter rules
„ Filter Rule priorities
„ Time based filters
„ Application specific filters
„ User group based filters for remote access
2.4.1.2 Stateful Packet Inspection
The Internet Security Router Firewall uses “stateful packet inspection” that extracts state-related information
required for the security decision from the packet and maintains this information for evaluating subsequent
connection attempts. It has awareness of application and creates dynamic sessions that allow dynamic
connections so that no ports need to be opened other than the required ones. This provides a solution which is
highly secure and that offers scalability and extensibility.
2.4.1.3 Defense against DoS Attacks
The Internet Security Router Firewall has an Attack Defense Engine that protects internal networks from
known types of Internet attacks. It provides automatic protection from Denial of Service (DoS) attacks such as
SYN flooding, IP smurfing, LAND, Ping of Death and all re-assembly attacks. It can drop ICMP redirects and
IP loose/strict source routing packets. For example, the Internet Security Router Firewall provides protection
from “WinNuke”, a widely used program to remotely crash unprotected Windows systems in the Internet. The
Internet Security Router Firewall also provides protection from a variety of common Internet attacks such as IP
Spoofing, Ping of Death, Land Attack, Reassembly and SYN flooding.
The type of attack protections provided by the Internet Security Router are listed in Table 2.3.
Table 2.3. DoS Attacks
Type of Attack Name of Attacks
Re-assembly attacks
ICMP Attacks Ping of Death, Smurf, Twinge
Flooders
5
Bonk, Boink, Teardrop (New Tear),
Overdrop, Opentear, Syndrop, Jolt
Page 22

Chapter 2. Getting to Know the Internet Security Router Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Flooder
Port Scans
TCP Attacks
Protection with PF Rules Echo-Chargen, Ascend Kill
Miscellaneous Attacks
TCP XMAS Scan, TCP Null Scan
TCP SYN Scan, TCP Stealth Scan
TCP sequence number prediction, TCP
out-of sequence attacks
IP Spoofing, LAND, Targa, Tentacle
MIME Flood, Winnuke, FTP Bounce, IP
unaligned time stamp attack
2.4.1.4 Application Command Filtering
The Internet Security Router Firewall allows network administrators to block, monitor, and report on network
users access to non-business and objectionable content. This high-performance content access control results
in increased productivity, lower bandwidth usage and reduced legal liability.
The Internet Security Router Firewall has the ability to handle active content filtering on certain application
protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP and RPC.
„ HTTP – You can define HTTP extension based filtering schemes for blocking
„ ActiveX
„ Java Archive
„ Java Applets
„ Microsoft Archives
„ URLs based on file extensions.
„ FTP – allows you to define and enforce the file transfer policy for the site or group of users
„ SMTP – allows you to filter operations such as VRFY, EXPN, etc. which reveal excess information
about the recipient.
„ RPC – allows you to filter programs based on the assigned RPC program numbers.
2.4.1.5 Application Level Gateway (ALG)
Applications such as FTP, games etc., open connections dynamically based on the respective application
parameter. To go through the firewall on the Internet Security Router, packets pertaining to an application,
require a corresponding allow rule. In the absence of such rules, the packets will be dropped by the Internet
Security Router Firewall. As it is not feasible to create policies for numerous applications dynamically (at the
same time without compromising security), intelligence in the form of Application Level Gateways (ALG), is
built to parse packets for applications and open dynamic associations. The Internet Security Router Firewall
provides a number of ALGs for popular applications such as FTP, H.323, RTSP, Microsoft Games, SIP, etc.
2.4.1.6 URL Filtering
A set of keywords that should not appear in the URL (Uniform Resource Locator, e.g. www.yahoo.com) can be
defined. Any URL containing one or more of these keywords will be blocked. This is a policy independent
feature i.e. it cannot be associated to ACL rules. This feature can be independently enabled or disabled, but
works only if firewall is enabled.
2.4.1.7 Log and Alerts
Events in the network, that could be attempts to affect its security, are recorded in the Internet Security Router
System log file. Event details are recorded in WELF (WebTrends Enhanced Log Format ) format so that
statistical tools can be used to generate custom reports. The Internet Security Router Firewall can also forward
Syslog information to a Syslog server on a private network.
The Internet Security Router Firewall supports:
6
Page 23

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Internet Security Router
, Aggressive Mode, Quick
„ Alerts sent to the administrator via e-mail.
„ Maintains at a minimum, log details such as, time of packet arrival, description of action taken by
Firewall and reason for action.
„ Supports the UNIX Syslog format.
„ Sends log report e-mails as scheduled by the network administrator or by default when the log file is
full.
„ All the messages are sent in the WELF format.
„ ICMP logging to show code and type.
2.4.1.8 Remote Access
The Internet Security Router Firewall allows the network administrator to segregate the user community into
Access Policies per group. A user can log in using the login page (Refer to “User Login Process ” on page 67).
After a user is authenticated successfully, the Internet Security Router Firewall dynamically activates the usergroup’s set of access policies.
These policies will subsequently be enforced until the user logs out of the session or until inactivity timeout
period has lapsed.
2.4.2 VPN
The introduction of broadband Internet access at an affordable price has attracted a large number of users to
use the Internet for business. Large-scale use of a very open public network such as, the Internet comes with a
lot of advantages and associated risks. These risks include the lack of confidentiality of data being sent and the
authenticity of the identities of the parties involved in the exchange of data. The VPN supported in the Internet
Security Router is intended to resolve these issues at an affordable price.
The VPN supported by the Internet Security Router is IPSec compliant. Packets sent via VPN are encrypted to
maintain privacy. The encrypted packets are then tunneled through a public network. As a result, tunnel
participants enjoy the same security features and facilities that are available only to members of private
networks at a reduced cost.
The following table lists the VPN features supported by the Internet Security Router:
Table 2.4. VPN Features of the Internet Security Router
Features
Transport Mode for Client-Client Connectivity
Tunnel Mode for Network-Network Connectivity
IP Fragmentation and Reassembly
IPSec Support
Hardware Encryption Algorithm DES, 3DES
Hardware Authentication Algorithm MD5, SHA-1
Transforms ESP, AH
Key Management IKE (Pre-shared key), Manual
Mode configuration for IKE
Main Mode
Mode
„ Site-to-Site VPN connection – Site-to-Site VPN connection is an alternative WAN infrastructure that is
7
used to connect branch offices, home offices, or business partners’ sites to all or portions of a
company’s network.
Page 24

Chapter 2. Getting to Know the Internet Security Router Internet Security Router User’s Manual
„ Remote Access VPN – Corporations use VPN to establish secure, end-to-end private network
connections over a public networking infrastructure. VPN have become the logical solution for remote
access connectivity. Deploying a remote access VPN enables corporations to reduce communications
expenses by leveraging the local dial-up infrastructure of Internet Service Providers. At the same time,
VPNs allow mobile workers, telecommuters and day extenders to take advantage of broadband
connectivity.
8
Page 25
Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
3 Quick Start Guide
This Quick Start Guide provides basic instructions for connecting the Internet Security Router to a computer or
a LAN and to the Internet.
„ Part 1 provides instructions to set up the hardware.
„ Part 2 describes how to configure Internet properties on your computer(s).
„ Part 3 shows you how to configure basic settings on the Internet Security Router to get your LAN
connected to the Internet.
After setting up and configuring the device, you can follow the instructions on page 20 to verify that it is working
properly.
This Quick Start Guide assumes that you have already established ADSL or cable modem service with your
Internet service provider (ISP). These instructions provide a basic configuration that should be compatible with
your home or small office network setup. Refer to the subsequent chapters for additional configuration
instructions.
3.1 Part 1 — Connecting the Hardware
In Part 1, you connect the device to an ADSL or a cable modem (which in turn is connected to a phone jack or
a cable outlet), the power outlet, and your computer or network.
Before you begin, turn the power off for all devices. These
include your computer(s), your LAN hub/switch (if applicable),
WARNING
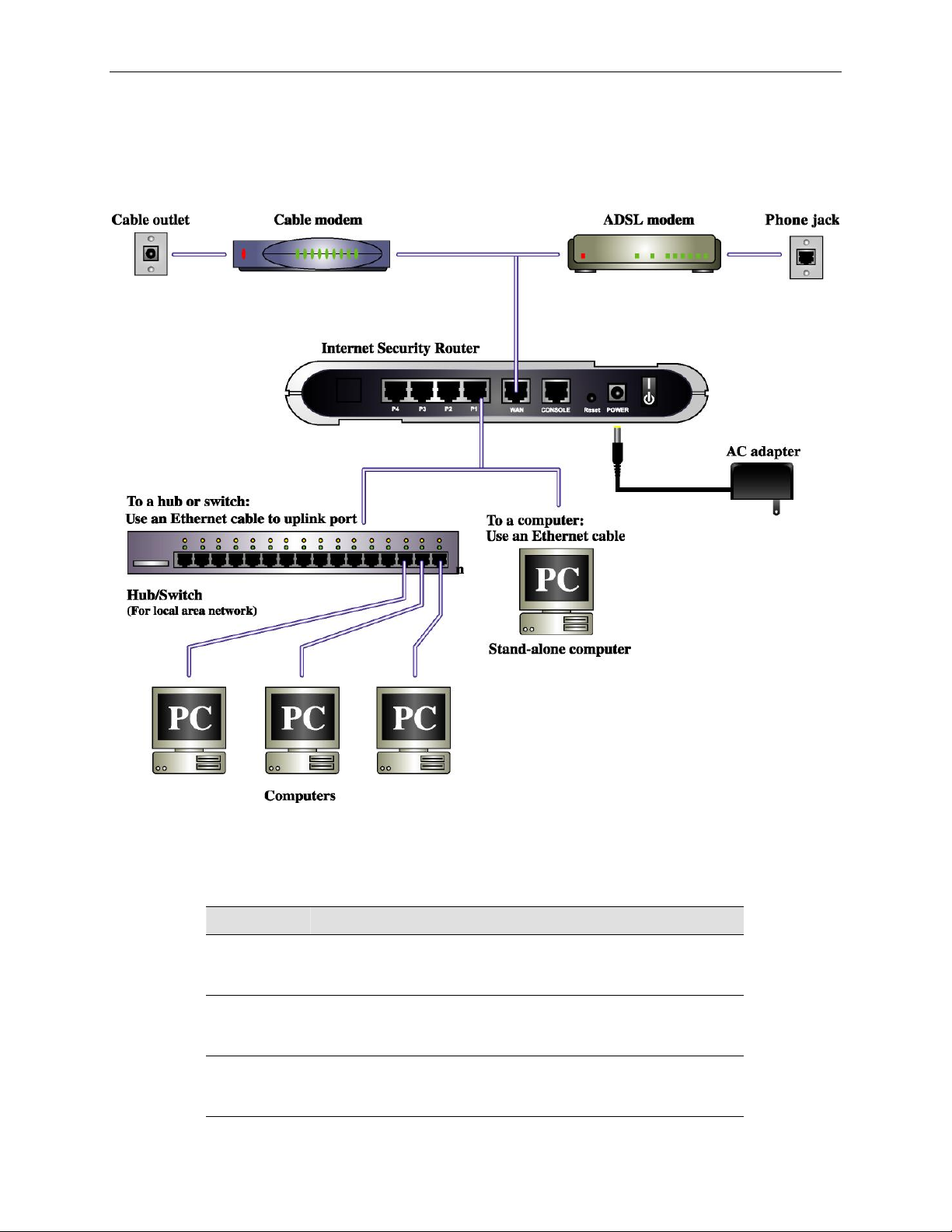
Figure 3.1 illustrates the hardware connections. Please follow the steps that follow for specific instructions.
and the Internet Security Router.
3.1.1 Step 1. Connect an ADSL or a cable modem.
For the Internet Security Router: Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the port labeled WAN on the rear
panel of the device. Connect the other end to the Ethernet port on the ADSL or cable modem.
3.1.2 Step 2. Connect computers or a LAN.
If your LAN has no more than 4 computers, you can use an Ethernet cable to connect computers directly to
the built-in switch on the device. Note that you should attach one end of the Ethernet cable to any of the port
labeled LAN1 – LAN4 on the rear panel of the device and connect the other end to the Ethernet port of a
computer.
If your LAN has more than 4 computers, you can attach one end of an Ethernet cable to a hub or a switch
(probably an uplink port; please refer to the hub or switch documentations for instructions) and the other to the
Ethernet switch port (labeled LAN1 – LAN4) on the Internet Security Router.
Note that either the crossover or straight-through Ethernet cable can be used to connect the built-in switch and
computers, hubs or switches as the built-in switch is smart enough to make connections with either type of
cables.
3.1.3 Step 3. Attach the power adapter.
Connect the AC power adapter to the POWER connector on the back of the device and plug in the adapter to
a wall outlet or a power strip.
9
Page 26
Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
3.1.4 Step 4. Turn on the Internet Security Router, the ADSL or cable modem and power up your computers.
Press the Power switch on the rear panel of the Internet Security Router to the ON position. Turn on your
ADSL or cable modem. Turn on and boot up your computer(s) and any LAN devices such as hubs or switches.
Figure 3.1. Overview of Hardware Connections
You should verify that the LEDs are illuminated as indicated in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1. LED Indicators
This LED: ...should be:
POWER Solid green to indicate that the device is turned on. If this light
is not on, check if the power adapter is attached to the Internet
Security Router and if it is plugged into a power source.
LAN1 –
LAN4
Solid green to indicate that the device can communicate with
your LAN or flashing when the device is sending or receiving
data from your LAN computer.
WAN Solid green to indicate that the device has successfully
established a connection with your ISP or flashing when the
device is sending or receiving data from the Internet.
10
Page 27

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
If the LEDs illuminate as expected, the Internet Security Router hardware is working properly.
3.2 Part 2 — Configuring Your Computers
Part 2 of the Quick Start Guide provides instructions for configuring the Internet settings on your computers to
work with the Internet Security Router.
3.2.1 Before you begin
By default, the Internet Security Router automatically assigns all required Internet settings to your PCs. You
need only to configure the PCs to accept the information when it is assigned.
In some cases, you may want to configure network settings
manually to some or all of your computers rather than allow the
Note
„ If you have connected your PC via Ethernet to the Internet Security Router, follow the instructions that
correspond to the operating system installed on your PC.
Internet Security Router to do so. See “Assigning static IP
addresses to your PCs” in page 13 for instructions.
3.2.2 Windows[CT6]® XP PCs:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <Start> button, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network Connections icon.
3. In the LAN or High-Speed Internet window, right-click on icon corresponding to your network
interface card (NIC) and select Properties. (Often this icon is labeled Local Area Connection).
The Local Area Connection dialog box displays with a list of currently installed network items.
4. Ensure that the check box to the left of the item labeled Internet Protocol TCP/IP is checked, and
click <Properties> button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Obtain an
IP address automatically. Also click the radio button labeled Obtain DNS server address
automatically.
6. Click <OK> button twice to confirm your changes, and close the Control Panel.
3.2.3 Windows® 2000 PCs:
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <Start> button, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the Local Area Connection icon,
and then select Properties.
The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box displays a list of currently installed network
components. If the list includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then the protocol has already been
enabled. Skip to step 10.
4. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not display as an installed component, click <Install> button.
5. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select Protocol, and then click <Add> button.
6. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Network Protocols list, and then click <OK> button.
11
Page 28

Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 2000 installation CD or other media. Follow
the instructions to install the files.
7. If prompted, click <OK> button to restart your computer with the new settings.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP addresses assigned by the Internet Security Router:
8. In the Control Panel, double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
9. In Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the Local Area Connection icon, and
then select Properties.
10. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then
click <Properties> button.
11. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Obtain an
IP address automatically. Also click the radio button labeled Obtain DNS server address
automatically.
12. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the Control Panel.
3.2.4 Windows® 95, 98, and Me PCs
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <Start> button, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
In the Network dialog box, look for an entry started w/ “TCP/IP ->” and the name of your network
adapter, and then click <Properties> button. You may have to scroll down the list to find this entry.
If the list includes such an entry, then the TCP/IP protocol has already been enabled. Skip to step 8.
3. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not display as an installed component, click <Add> button.
4. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select Protocol, and then click <Add> button.
5. Select Microsoft in the Manufacturers list box, and then click TCP/IP in the Network Protocols list,
box and then click <OK> button.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 95, 98 or Me installation CD or other media.
Follow the instructions to install the files.
6. If prompted, click <OK> button to restart your computer with the new settings.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP information assigned by the Internet Security Router:
7. In the Control Panel, double-click the Network icon.
8. In the Network dialog box, select an entry started with “TCP/IP ->” and the name of your network
adapter, and then click <Properties> button.
9. In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Obtain an IP address
automatically.
10. In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the “Default Gateway” tab. Enter 192.168.1.1 (the
default LAN port IP address of the Internet Security Router) in the “New gateway” address field
and click <Add> button to add the default gateway entry.
11. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the Control Panel.
12. If prompted to restart your computer, click <OK> button to do so with the new settings.
3.2.5 Windows® NT 4.0 workstations:
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
12
Page 29

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
1. In the Windows NT task bar, click the <Start> button, point to Settings, and then click Control
Panel.
2. In the Control Panel window, double click the Network icon.
3. In the Network dialog box, click the Protocols tab.
The Protocols tab displays a list of currently installed network protocols. If the list includes TCP/IP
Protocol, then the protocol has already been enabled. Skip to step 9.
4. If TCP/IP does not display as an installed component, click <Add> button.
5. In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, select TCP/IP, and then click <OK> button.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows NT installation CD or other media. Follow
the instructions to install the files.
After all files are installed, a window displays to inform you that a TCP/IP service called DHCP can
be set up to dynamically assign IP information.
6. Click <Yes> button to continue, and then click <OK> button if prompted to restart your computer.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP addresses assigned by the Internet Security Router:
7. Open the Control Panel window, and then double-click the Network icon.
8. In the Network dialog box, click the Protocols tab.
9. In the Protocols tab, select TCP/IP, and then click <Properties> button.
10. In the Microsoft TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Obtain an IP
address from a DHCP server.
11. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the Control Panel.
3.2.6 Assigning static IP addresses to your PCs
In some cases, you may want to assign IP addresses to some or all of your PCs directly (often called
“statically”), rather than allowing the Internet Security Router to assign them. This option may be desirable (but
not required) if:
„ You have obtained one or more public IP addresses that you want to always associate with specific
computers (for example, if you are using a computer as a public web server).
„ You maintain different subnets on your LAN.
However, during the first time configuration of your Internet Security Router, you must assign an IP address in
the 192.168.1.0 network for your PC, say 192.168.1.2, in order to establish connection between the Internet
Security Router and your PC as the default LAN IP on Internet Security Router is pre-configured as
192.168.1.1. Enter 255.255.255.0 for the subnet mask and 192.168.1.1 for the default gateway. These settings
may be changed later to reflect your true network environment.
On each PC to which you want to assign static information, follow the instructions on pages 11 through 13
relating only to checking for and/or installing the IP protocol. Once it is installed, continue to follow the
instructions for displaying each of the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) properties. Instead of enabling dynamic
assignment of the IP addresses for the computer, DNS server, and default gateway, click the radio buttons that
enable you to enter the information manually.
Your PCs must have IP addresses that place them in the same
subnet as the Internet Security Router’s LAN port. If you manually
assign IP information to all your LAN PCs, you can follow the
Note
instructions in Chapter 5 to change the LAN port IP address
accordingly.
13
Page 30
Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
3.3 Part 3 — Quick Configuration of the Internet Security Router
In Part 3, you log into the Configuration Manager on the Internet Security Router and configure basic settings
for your Internet connection. Your ISP should provide you with the necessary information to complete this step.
Note the intent here is to quickly get the Internet Security Router up and running, instructions are concise. You
may refer to corresponding chapters for more details.
3.3.1 Buttons Used in Setup Wizard
The Internet Security Router provides a preinstalled software program called Configuration Manager that
enables you to configure the Internet Security Router via your Web browser. The settings that you are most
likely to need to change before using the device are grouped onto sequence of Configuration pages guided by
Setup Wizard. The following table shows the buttons that you’ll encounter in Setup Wizard.
Button Function
Click this button to save the information and proceed to the next
configuration page.
Click this button to go back to the previous configuration page.
3.3.2 Setting Up the Internet Security Router
Follow these instructions to setup the Internet Security Router:
1. Before accessing the Configuration Manager in the Internet Security Router, make sure that the
HTTP proxy setting is disabled in your browser. In IE, click “Tools” è “Internet Options…” è
“Connections” tab è “LAN settings…” and then uncheck “Use proxy server for your LAN …”
2. On any PC connected to one of the four LAN ports on the Internet Security Router, open your
Web browser, and type the following URL in the address/location box, and press <Enter>:
http://192.168.1.1
This is the predefined IP address for the LAN port on the Internet Security Router.
A login screen displays, as shown in Figure 3.2.
14
Figure 3.2. Login Screen
If you have problem connecting to the Internet Security Router, you may want to check if your PC is
configured to accept IP address assignment from the Internet Security Router. Another method is to
set the IP address of your PC to any IP address in the 192.168.1.0 network, such as 192.168.1.2.
Page 31

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
3. Enter your user name and password, and then click to enter the Configuration
Manager. The first time you log into this program, use these defaults:
Default User Name:
Default Password:
admin
admin
You can change the password at any time (see section 12.2
Note
Change the Login Password on page 124).
The Setup Wizard home page displays each time you log into the Configuration Manager (shown in
Figure 3.3 on page 15).
Figure 3.3. Setup Wizard Home Page
Figure 3.4. Setup Wizard – Password Configuration Page
4. Click on the button to enter the password configuration page as shown in Figure 3.4.
Change the password in the spaces provided if desired. Otherwise, proceed to the next
configuration page by clicking on the button.
When changing passwords, make sure you enter the existing login password in the Login Password
field, make any changes for the passwords and click the button to save the changes.
15
Page 32

Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Time Zone
list
5. Now we are at the System Information setup page; enter the requested information in the spaces
provided and click the button to save the changes. Otherwise, proceed to the next
configuration page by clicking on the button.
Figure 3.5. Setup Wizard – System Identity Configuration Page
drop-down
Figure 3.6. Setup Wizard – Date/Time Configuration Page
6. Set the time zone for the Internet Security Router by selecting your time zone from the Time Zone
drop-down list. Click to save the settings and then click on the button to go to
the next configuration page.
There is no real time clock inside the Internet Security Router. The system date and time are
maintained by the external network time server. There is no need to set the date and time here unless
you don’t have access to a time server and you want the Internet Security Router to maintain its own
time.
7. It is recommended that you keep the default LAN IP settings at this point until after you have
completed the rest of the configurations and confirm that your Internet connection is working.
Click on the button to proceed to the next configuration page.
16
Page 33

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
Figure 3.7. Setup Wizard – LAN IP Configuration Page
Figure 3.8. Setup Wizard – DHCP Server Configuration Page
8. It is recommended that you keep the default settings for DHCP server until after you have
completed the rest of the configurations and confirm that your Internet connection is working.
Click on the button to proceed to the next configuration page.
9. Now we are at the last page of the Setup Wizard, which is to configure the WAN settings for the
Internet Security Router. Depending on the connection mode required for your ISP, you can
select from the following three connection modes from the Connection Mode drop-down list (see
Figure 3.9): PPPoE, Dynamic and Static.
17
Page 34

Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Connection
do
wn list
Connection
down list
Mode drop-
Figure 3.9. Setup Wizard – WAN PPPoE Configuration Page
Mode drop-
Figure 3.10. Setup Wizard – WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Page
a) PPPoE Connection Mode (see Figure 3.9)
• You don’t need to enter primary/secondary DNS IP addresses as PPPoE is able to
automatically obtain this information for you from your ISP. However, if you prefer to use
your favorite DNS servers, you may enter them in the space provided.
18
Page 35

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide
Connection
down list
• Host name is optional. You may leave it empty if your ISP did not provide such
information.
• Enter the user name and password provided by your ISP.
• Click on button to save the PPPoE settings.
b) Dynamic IP Connection Mode (see Figure 3.10)
• You don’t need to enter primary/secondary DNS IP addresses as DHCP client is able to
automatically obtain this information for you from your ISP. However, if you prefer to use
your favorite DNS servers, you may enter them in the space provided.
• Host name is optional. You may leave it empty if your ISP did not provide such
information.
• If you had previously registered a specific MAC address with your ISP for Internet
connections, enter the registered MAC address here and make sure you check the MAC
cloning check box.
• Click on button to save the dynamic IP settings.
Mode drop-
Figure 3.11. Setup Wizard – WAN Static IP Configuration Page
c) Static IP Connection Mode
• Enter WAN IP address in the IP Address field. This information should be provided by
your ISP.
• Enter Subnet Mask for the WAN. This information should be provided by your ISP.
Typically, it is 255.255.255.0.
• Enter gateway address provided by your ISP in the space provided.
19
Page 36

Chapter 3. Quick Start Guide Internet Security Router User’s Manual
• Enter at lease the primary DNS IP address provided by your ISP. Secondary DNS IP
address is optional. Enter it in the space provided if you have such information from your
ISP.
• Click to save the static IP settings
You have now completed customizing basic configuration settings. Read the following section to determine if
you have access to the Internet.
3.3.3 Testing Your Setup
At this point, the Internet Security Router should enable any computer on your LAN to use the Internet Security
Router’s ADSL or cable modem connection to access the Internet.
To test the Internet connection, open your web browser, and type the URL of any external website (such as
http://www.asus.com). The LED labeled WAN should be blinking rapidly and may appear solid as the device
connects to the site. You should also be able to browse the web site through your web browser.
If the LEDs do not illuminate as expected or the web page does not display, see Appendix 15 for
troubleshooting suggestions.
3.3.4 Default Router Settings
In addition to handling the DSL connection to your ISP, the Internet Security Router can provide a variety of
services to your network. The device is pre-configured with default settings for use with a typical home or small
office network.
Table 3.2 lists some of the most important default settings; these and other features are described fully in the
subsequent chapters. If you are familiar with network configuration settings, review the settings in Table 3.2 to
verify that they meet the needs of your network. Follow the instructions to change them if necessary. If you are
unfamiliar with these settings, try using the device without modification, or contact your ISP for assistance.
Before you modifying any settings, review Chapter 4 for general information about accessing and using the
Configuration Manager program. We strongly recommend that you contact your ISP prior to changing the
default configuration.
Table 3.2. Default Settings Summary
Option Default Setting Explanation/Instructions
DHCP (Dynamic
Host
Configuration
Protocol)
LAN Port IP
Address
DHCP server enabled with the
following pool of addresses:
192.168.1.10 through 192.168.1.108
Static IP address: 192.168.1.1
subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
The Internet Security Router maintains a
pool of private IP addresses for dynamic
assignment to your LAN computers. To
use this service, you must have set up
your computers to accept IP information
dynamically, as described in Part 2 of the
Quick Start Guide. See section 5.2 for an
explanation of the DHCP service.
This is the IP address of the LAN port on
the Internet Security Router. The LAN port
connects the device to your Ethernet
network. Typically, you will not need to
change this address. See section 5.1 LAN
IP Address for instructions.
20
Page 37

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 4. Getting Started with the Configuration Manager
4 Getting Started with the Configuration
Manager[CT9]
The Internet Security Router includes a preinstalled program called the Configuration Manager, which provides
an interface to the software installed on the device. It enables you to configure the device settings to meet the
needs of your network. You access it through your web browser from any PC connected to the Internet
Security Router via the LAN or WAN ports.
This chapter describes the general guides for using the Configuration Manager.
4.1 Log into Configuration Manager
The Configuration Manager program is preinstalled on the Internet Security Router. To access the program,
you need the following:
„ A computer connected to the LAN or WAN port on the Internet Security Router as described in the
Quick Start Guide chapter.
„ A web browser installed on the computer. The program is designed to work best with Microsoft
Internet Explorer® 5.5, Netscape 7.0.2 or later.
You may access the program from any computer connected to the Internet Security Router via the LAN or
WAN ports. However, the instructions provided here are for computers connected via the LAN ports.
1. From a LAN computer, open your web browser, type the following in the web address (or location)
box, and press <Enter>:
http://192.168.1.1
This is the predefined IP address for the LAN port on the Internet Security Router. A login screen
displays, as shown in Figure 4.1.
Figure 4.1. Configuration Manager Login Screen
2. Enter your user name and password, and then click .
The first time you log into the program, use these defaults:
Default User Name:
Default Password:
21
admin
admin
Page 38

Chapter 4. Getting Started with the Configuration Manager Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Configuration Frame
You can change the password at any time (see section 12.2
Note
The Setup Wizard page displays each time you log into the program (shown in Figure 4.3 on page
23).
Change the Login Password on page 124).
4.2 Functional Layout
Typical Configuration Manager page consists of two separate frames. The left frame, as shown in Figure 4.2,
contains all the menus available for device configuration. Menus are indicated by file icons, , and related
menus are grouped into categories, such as LAN, WAN and etc., and indicated by folder icons, or ,
depending on whether the group of menus are expanded or not. You can click on any of these to display a
specific configuration page.
Setup Menu Frame
Figure 4.2. Typical Configuration Manager Page
A separate page displays in the right-hand-side frame for each menu. For example, the configuration page
displayed in Figure 4.2 is intended for DHCP configuration.
4.2.1 Setup Menu Navigation Tips
„ To expand a group of related menus: click on the + sign next to the corresponding file folder icon, .
„ To contract a group of related menus: click on the – sign next to the “opened” file folder icon, .
„ To open a specific configuration page, click on the file icons, , next to the desired menu item.
4.2.2 Commonly Used Buttons and Icons
The following buttons or icons are used throughout the application. The following table describes the function
for each button or icon.
Table 4.1. Description of Commonly Used Buttons and Icons
22
Button/Icon
Stores any changes you have made on the current page.
Function
Page 39

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 4. Getting Started with the Configuration Manager
Button/Icon
Adds the existing configuration to the system, e.g. a static route
or a firewall ACL rule and etc.
Modifies the existing configuration in the system, e.g. a static
route or a firewall ACL rule and etc.
Deletes the selected item, e.g. a static route or a firewall ACL rule
and etc.
Launches the online help for the current topic in a separate
browser window. Help is available from any main topic page.
Redisplays the current page with updated statistics or settings.
Selects the item for editing.
Deletes the selected item.
Function
4.3 The Home Page of Configuration Manager
The Setup Wizard home page displays when you first access the Configuration Manager.
Figure 4.3. Setup Wizard Home Page
4.4 Overview of System Configuration
To view the overall system configuration, log into Configuration Manager as administrator, and then click the
System Info menu. Figure 4.4 shows the information available in the System Info page.
23
Page 40

Chapter 4. Getting Started with the Configuration Manager Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Figure 4.4. System Information Page
24
Page 41

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings
5 Configuring LAN Settings
This chapter describes how to configure LAN properties for the LAN interface on the Internet Security Router
that communicates with your LAN computers. You’ll learn to configure IP address, DHCP and DNS server for
your LAN in this chapter.
5.1 LAN IP Address
If you are using the Internet Security Router with multiple PCs on your LAN, you must connect the LAN via the
Ethernet ports on the built-in Ethernet switch. You must assign a unique IP address to each device residing on
your LAN. The LAN IP address identifies the Internet Security Router as a node on your network; that is, its IP
address must be in the same subnet as the PCs on your LAN. The default LAN IP for the Internet Security
Router is 192.168.1.1.
A network node can be thought of as any interface where a
device connects to the network, such as the Internet Security
Definition
Router’s LAN port and the network interface cards on your PCs.
See Appendix 13 for an explanation of subnets.
You can change the default to reflect the set of IP addresses that you want to use with your network.
The Internet Security Router itself can function as a DHCP server
for your LAN computers, as described in section 5.2.3 Configuring
Note
DHCP Server, but not for its own LAN port.
5.1.1 LAN IP Configuration Parameters
Table 5.1describes the configuration parameters available for LAN IP configuration.
Table 5.1. LAN IP Configuration Parameters
Setting
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Description
The LAN IP address of the Internet Security Router. This IP is used by your
computers to identify the Internet Security Router’s LAN port. Note that the
public IP address assigned to you by your ISP is not your LAN IP address.
The public IP address identifies the WAN port on the Internet Security Router
to the Internet.
The LAN subnet mask identifies which parts of the LAN IP Address refer to
your network as a whole and which parts refer specifically to nodes on the
network. Your device is preconfigured with a default subnet mask of
255.255.255.0.
5.1.2 Configuring the LAN IP Address
Follow these steps to change the default LAN IP address.
1. Log into Configuration Manager as administrator, and then click the LAN menu.
When the submenus of LAN Configuration displays, click IP submenu to display the IP Address
configuration page as shown in Figure 5.1.
25
Page 42

Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Figure 5.1. LAN IP Address Configuration Page
2. Enter a LAN IP address and subnet mask for the Internet Security Router in the space provided.
3. Click. to save the LAN IP address.
If you were using an Ethernet connection for the current session, and changed the IP address, the
connection will be terminated.
4. Reconfigure your PCs, if necessary, so that their IP addresses place them in the same subnet as
the new IP address of the LAN port. See the Quick Start Guide chapter, “Part 2 — Configuring
Your Computers,” for instructions.
5. Log into Configuration Manager by typing the new IP address in your Web browser’s
address/location box.
5.2 DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol)
5.2.1 What is DHCP?
DHCP is a protocol that enables network administrators to centrally manage the assignment and distribution of
IP information to computers on a network.
When you enable DHCP on a network, you allow a device — such as the Internet Security Router — to assign
temporary IP addresses to your computers whenever they connect to your network. The assigning device is
called a DHCP server, and the receiving device is a DHCP client.
If you followed the Quick Start Guide instructions, you either
configured each LAN PC with an IP address, or you specified that
it will receive IP information dynamically (automatically). If you
Note
chose to have the information assigned dynamically, then you
configured your PCs as DHCP clients that will accept IP
addresses assigned from a DCHP server such as the Internet
Security Router.
The DHCP server draws from a defined pool of IP addresses and “leases” them for a specified amount of time
to your computers when they request an Internet session. It monitors, collects, and redistributes the addresses
as needed.
26
Page 43

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings
On a DHCP-enabled network, the IP information is assigned dynamically rather than statically. A DHCP client
can be assigned a different address from the pool each time it reconnects to the network.
5.2.2 Why use DHCP?
DHCP allows you to manage and distribute IP addresses throughout your network from the Internet Security
Router. Without DHCP, you would have to configure each computer separately with IP address and related
information. DHCP is commonly used with large networks and those that are frequently expanded or otherwise
updated.
5.2.3 Configuring DHCP Server
By default, the Internet Security Router is configured as a DHCP
server on the LAN side, with a predefined IP address pool of
Note
First, you must configure your PCs to accept DHCP information assigned by a DHCP server:
1. Log into Configuration Manager as administrator, click the LAN menu, and then click the DHCP
submenu. The DHCP Configuration page displays as shown in Figure 5.2:
192.168.1.10 through 192.168.1.42 (subnet mask
255.255.255.0). To change this range of addresses, follow the
procedures described in this section.
Figure 5.2. DHCP Configuration Page
2. Enter the information for the IP Address Pool (Begin/End Address), Subnet Mask, Lease Time
and Default Gateway IP Address, fields; others, such as Primary/Secondary DNS Server IP
Address and Primary/Secondary WINS Server IP Address are optional. However, it is
recommended that you enter the primary DNS server IP address in the space provided. You may
27
Page 44

Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
enter the LAN IP or your ISP’s DNS IP in the primary DNS Server IP Address field. Table 5.2
describes the DHCP configuration parameters in detail.
Table 5.2. DHCP Configuration Parameters
Field Description
IP Address Pool
Begin/End
Subnet Mask
Lease Time
Default Gateway IP
Address
Primary/Secondary
DNS Server IP
Address
Primary/Secondary
WINS Server IP
Address (optional)
Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the DHCP address pool.
Enter the subnet mask to be used for the DHCP address pool.
The amount of time the assigned address will be used by a device connected
on the LAN.
The address of the default gateway for computers that receive IP addresses
from this pool. The default gateway is the device that the DHCP client
computers first contacted to communicate with the Internet. Typically, it is the
Internet Security Router’s LAN port IP address.
The IP address of the Domain Name System server to be used by computers
that receive IP addresses from this pool. The DNS server translates common
Internet names that you type into your web browser into their equivalent
numeric IP addresses. Typically, the server(s) are located with your ISP.
However, you may enter LAN IP address of the Internet Security Router as it
will serve as DNS proxy for the LAN computers and forward the DNS request
from the LAN to DNS servers and relay the results back to the LAN
computers. Note that both the primary and secondary DNS servers are
optional.
The IP address of the WINS servers to be used by computers that receive IP
addresses from the DHCP IP address pool. You don’t need to enter this
information unless your network has WINS servers.
3. Click to save the DHCP server configurations.
5.2.4 Viewing Current DHCP Address Assignments
When the Internet Security Router functions as a DHCP server for your LAN, it keeps a record of any
addresses it has leased to your computers. To view a table of all current IP address assignments, just go to the
DHCP Server Configuration page. A page displays similar to that shown in Figure 5.2; the bottom half of the
same page shows the existing DHCP address assignments.
The DHCP Server Address Table lists any IP addresses that are currently leased to LAN devices. For each
leased address, the table lists the following information:
Table 5.3. DHCP Address Assignment
Field Description
MAC Address
Assigned IP Address
IP Address Expired
on
A hardware ID of the device that leases an IP address from the DHCP server.
The address that has been leased from the pool.
The time when the leased address is to be terminated.
28
Page 45

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings
5.3 DNS
5.3.1 About DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) servers map the user-friendly domain names that users type into their Web
browsers (e.g., "yahoo.com") to the equivalent numerical IP addresses that are used for Internet routing.
When a PC user types a domain name into a browser, the PC must first send a request to a DNS server to
obtain the equivalent IP address. The DNS server will attempt to look up the domain name in its own database,
and will communicate with higher-level DNS servers when the name cannot be found locally. When the
address is found, it is sent back to the requesting PC and is referenced in IP packets for the remainder of the
communication.
5.3.2 Assigning DNS Addresses
Multiple DNS addresses are useful to provide alternatives when one of the servers is down or is encountering
heavy traffic. ISPs typically provide primary and secondary DNS addresses, and may provide additional
addresses. Your LAN PCs learn these DNS addresses in one of the following ways:
„ Statically: If your ISP provides you with their DNS server addresses, you can assign them to each PC
by modifying the PCs' IP properties.
„ Dynamically from a DHCP pool: You can configure the DHCP Server the Internet Security Router
and create an address pool that specify the DNS addresses to be distributed to the PCs. Refer to the
section Configuring DHCP Server on page 27 for instructions on creating DHCP address pools.
In either case, you can specify the actual addresses of the ISP's DNS servers (on the PC or in the DHCP pool),
or you can specify the address of the LAN port on the Internet Security Router (e.g., 192.168.1.1). When you
specify the LAN port IP address, the device performs DNS relay, as described in the following section.
Note
If you specify the actual DNS addresses on the PCs or in the
DHCP pool, the DNS relay feature is not used.
5.3.3 Configuring DNS Relay
When you specify the device's LAN port IP address as the DNS address, then the Internet Security Router
automatically performs “DNS relay”; i.e., because the device itself is not a DNS server, it forwards domain
name lookup requests from the LAN PCs to a DNS server at the ISP. It then relays the DNS server’s response
to the PC.
When performing DNS relay, the Internet Security Router must maintain the IP addresses of the DNS servers
it contacts. It can learn these addresses in either or both of the following ways:
„ Learned through PPPoE or Dynamic IP Connection: If the Internet Security Router uses a PPPoE
(see section 6.2.2 Configuring PPPoE for WAN) or Dynamic IP (see section 6.3.2 Configuring
Dynamic IP for WAN) connection to the ISP, the primary and secondary DNS addresses can be
learned via the PPPoE protocol. Using this option provides the advantage that you will not need to
reconfigure the PCs or the Internet Security Router if the ISP changes their DNS addresses.
„ Configured on the Internet Security Router: You can also specify the ISP's DNS addresses in the
WAN Configuration page as shown in Figure 6.1. WAN PPPoE Configuration Page, Figure 6.2. WAN
Dynamic IP (DHCP client) Configuration Page, or Figure 6.3. WAN Static IP Configuration Page.
Follow these steps to configure DNS relay:
1. Enter LAN IP in the DNS Server IP Address field in DHCP configuration page as shown in Figure
5.2.
29
Page 46

Chapter 5. Configuring LAN Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
2. Configure the LAN PCs to use the IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server on the Internet
Security Router, or enter the Internet Security Router's LAN IP address as their DNS server
address manually for each PC on your LAN.
DNS addresses that are assigned to LAN PCs prior to enabling
DNS relay will remain in effect until the PC is rebooted. DNS relay
will only take effect when a PC's DNS address is the LAN IP
address.
Note
Similarly, if after enabling DNS relay, you specify a DNS address
(other than the LAN IP address) in a DHCP pool or statically on a
PC, then that address will be used instead of the DNS relay
address.
5.4 Viewing LAN Statistics
You can view statistics of your LAN traffic on the Internet Security Router. You will not typically need to view
this data, but you may find it helpful when working with your ISP to diagnose network and Internet data
transmission problems.
To view LAN IP statistics, click Statistics on the LAN submenu. Figure 5.3 shows the LAN Statistics page:
Figure 5.3. LAN Statistics Page
To display the updated statistics since you opened the page, click .
30
Page 47

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 6. Configuring WAN Settings
Connection
down list
6 Configuring WAN Settings
This chapter describes how to configure WAN settings for the WAN interface on the Internet Security Router
that communicates with your ISP. You’ll learn to configure IP address, DHCP and DNS server for your WAN in
this chapter.
6.1 WAN Connection Mode
Three modes of WAN connection are supported by the Internet Security Router – PPPoE, dynamic IP and
static IP. You may select one of the WAN connection modes required by your ISP from the Connection Mode
drop-down list in WAN Configuration page as shown in Figure 6.1.
Mode drop-
Figure 6.1. WAN PPPoE Configuration Page
6.2 PPPoE
6.2.1 WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters
Table 6.1describes the configuration parameters available for PPPoE connection mode.
31
Page 48

Chapter 6. Configuring WAN Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Table 6.1. WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Host Name
Host name is optional but may be required by some ISP.
User Name and
Password
Primary/ Secondary
DNS
Connection Options
Dial-On-Demand
Keep Alive
Enter the username and password you use to log into your ISP. (Note: this is
different from the information you used to log into Configuration Manager.)
IP address of the primary and/or secondary DNS are optional as PPPoE will
automatically detect the DNS IP addresses configured at your ISP. However,
if there are other DNS servers you would rather use, enter the IP addresses
in the spaces provided.
The default setting for this option is “Disable”. You can also select either Dial-
On-Demand or Keep-Alive if desired.
Enter the inactivity timeout period at which you want to disconnect the Internet
connection when there is no traffic. The minimum value of inactivity timeout is
30 seconds. RIP and SNTP services may interfere with this function if there
are activities from these two services. Make sure that the update interval
setting of the system date and time (in the System Management / Date/Time
Setup configuration page – see 12.4 Setup Date and Time for details) is
greater than the inactivity timeout value.
Enable this option if you wish to keep your Internet connection active, even
when there is no traffic. Enter the value for the “Echo Interval” at which you
want the Internet Security Router to send out some data periodically to your
ISP. The default value of “Echo Interval” is 60 second.
6.2.2 Configuring PPPoE for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure PPPoE settings:
1. Select PPPoE from the Connection Mode drop-down list as shown in Figure 6.1.
2. (Optional) Enter host name in the space provided if required by your ISP.
3. If you are connecting to the Internet using PPPoE, you probably only have to enter User Name
and Password in the PPPoE Configuration page as shown in Figure 6.1 unless you want to use
your preferred DNS servers.
4. (Optional) Enter the IP addresses for the primary and secondary DNS servers if you want to use
your preferred DNS servers; otherwise, skip this step.
5. Choose a connection option and enter appropriate setting if desired. The default setting is
“Disable”.
6. Click to save the PPPoE settings when you are done with the configuration. You’ll see a
summary of the WAN configuration at the bottom half of the configuration page. Note that if the
default gateway address is not shown immediately, click on the WAN menu to open the WAN
configuration page again.
6.3 Dynamic IP
6.3.1 WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Parameters
Table 6.2 describes the configuration parameters available for dynamic IP connection mode.
Table 6.2. WAN Dynamic IP Configuration Parameters
32
Page 49

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 6. Configuring WAN Settings
Connection
down list
Field Description
Host Name
Host name is optional but may be required by some ISP.
Primary/ Secondary
DNS
IP address of the primary and/or secondary DNS are optional as DHCP client
will automatically obtain the DNS IP addresses configured at your ISP.
However, if there are other DNS servers you would rather use, enter the IP
addresses in the spaces provided.
MAC Cloning
The default is to use the MAC address of the WAN interface. However, if you
had registered a MAC address previously with your ISP, you may need to
enter that MAC address here.
6.3.2 Configuring Dynamic IP for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure dynamic IP settings:
1. Select Dynamic from the Connection Mode drop-down list as shown in Figure 6.2.
2. (Optional) Enter host name in the space provided if required by your ISP.
3. (Optional) Enter the IP addresses for the primary and secondary DNS servers if you want to use
your preferred DNS servers; otherwise, skip this step.
4. If you had previously registered a specific MAC address with your ISP for Internet access, enter
the registered MAC address here and make sure you check the MAC cloning check box.
5. Click to save the Dynamic IP settings when you are done with the configuration. You’ll
see a summary of the WAN configuration at the bottom half of the configuration page. Note that if
the default gateway address is not shown immediately, click on the WAN menu to open the WAN
configuration page again.
Mode drop-
Figure 6.2. WAN Dynamic IP (DHCP client) Configuration Page
33
Page 50

Chapter 6. Configuring WAN Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Connection
down list
6.4 Static IP
6.4.1 WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters
Table 6.3 describes the configuration parameters available for static IP connection mode.
Table 6.3. WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
IP Address
WAN IP address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask
Gateway Address
Primary/ Secondary
DNS
WAN subnet mask provided by your ISP. Typically, it is set as 255.255.255.0.
Gateway IP address provided by your ISP. It must be in the same subnet as
the WAN on the Internet Security Router.
You must at least enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. Secondary
DNS is optional
6.4.2 Configuring Static IP for WAN
Mode drop-
Figure 6.3. WAN Static IP Configuration Page
Follow the instructions below to configure static IP settings:
1. Select Static from the Connection Mode drop-down list as shown in Figure 6.3.
2. Enter WAN IP address in the IP Address field. This information should be provided by your ISP.
3. Enter Subnet Mask for the WAN. This information should be provided by your ISP. Typically, it is
255.255.255.0.
4. Enter gateway address provided by your ISP in the space provided.
34
Page 51

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 6. Configuring WAN Settings
5. Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. This information should be provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS server is optional.
6. Click to save the static IP settings when you are done with the configuration. You’ll see a
summary of the WAN configuration at the bottom half of the configuration page.
6.5 Viewing WAN Statistics
You can view statistics of your WAN traffic. You will not typically need to view this data, but you may find it
helpful when working with your ISP to diagnose network and Internet data transmission problems.
To view WAN IP statistics, click Statistics on the WAN submenu. Figure 6.4 shows the LAN Statistics page:
Figure 6.4. WAN Statistics Page
To see the updated statistics since you opened the page, simply click .
35
Page 52

Page 53

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 7. Configuring Routes
7 Configuring Routes
You can use Configuration Manager to define specific routes for your Internet and network data
communication. This chapter describes basic routing concepts and provides instructions for creating routes.
Note that most users do not need to define routes.
7.1 Overview of IP Routes
The essential challenge of a router is: when it receives data intended for a particular destination, which next
device should it send that data to? When you define IP routes, you provide the rules that the Internet Security
Router uses to make these decisions.
7.1.1 Do I need to define IP routes?
Most users do not need to define IP routes. On a typical small home or office LAN, the existing routes that set
up the default gateways for your LAN computers and for the Internet Security Router provide the most
appropriate path for all your Internet traffic.
„ On your LAN computers, a default gateway directs all Internet traffic to the LAN port on the Internet
Security Router. Your LAN computers know their default gateway either because you assigned it to
them when you modified their TCP/IP properties, or because you configured them to receive the
information dynamically from a server whenever they access the Internet. (Each of these processes is
described in the Quick Start Guide instructions, Part 2.)
„ On the Internet Security Router itself, a default gateway is defined to direct all outbound Internet traffic
to a router at your ISP. This default gateway is assigned automatically by your ISP whenever the
device negotiates an Internet connection. (The process for adding a default route is described in
section 7.3.2 Adding Static Routes.)
You may need to define routes if your home setup includes two or more networks or subnets, if you connect to
two or more ISP services, or if you connect to a remote corporate LAN.
Figure 7.1. Routing Configuration Page
37
Page 54

Chapter 7. Configuring Routes Internet Security Router User’s Manual
7.2 Dynamic Routing using RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
RIP enables routing information exchange between routers; thus, routes are updated automatically without
human intervention. It is recommended that you enable RIP in the System Services Configuration Page as
shown in Figure 12.1.
7.2.1 Enabling/Disabling RIP
Follow these instructions to enable or disable RIP:
1. In the System Services Configuration page (as shown in Figure 12.1), click the “Enable” or
“Disable” radio button depending on whether you want to enable or disable RIP.
2. Click to enable or disable RIP.
7.3 Static Routing
7.3.1 Static Route Configuration Parameters
The following table defines the available configuration parameters for static routing configuration.
Table 7.1. Static Route Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Destination IP
Address
Destination Netmask
Gateway IP Address
Specifies the IP address of the destination computer or an entire destination
network. It can also be specified as all zeros to indicate that this route should
be used for all destinations for which no other route is defined (this is the
route that creates the default gateway). Note that destination IP must be a
network ID. The default route uses a destination IP of 0.0.0.0. Refer to
Appendix 13 for an explanation of network ID.
Indicates which parts of the destination address refer to the network and
which parts refer to a computer on the network. Refer to Appendix 13, for an
explanation of network masks. The default route uses a netmask of 0.0.0.0.
Gateway IP address
7.3.2 Adding Static Routes
Follow these instructions to add a static route to the routing table.
1. In the Static Routes Configuration page (as shown in Figure 7.1), enter static routes information
such as destination IP address, destination netmask and gateway IP address in the
corresponding fields.
For a description of these fields, refer to Table 7.1. Static Route Configuration Parameters.
To create a route that defines the default gateway for your LAN, enter 0.0.0.0 in both the Destination
IP Address and Destination Netmask fields.
2. Click to add a new route.
7.3.3 Deleting Static Routes
Follow these instructions to delete a static route from the routing table.
1. In the Static Routes Configuration page (as shown in Figure 7.1), select the route from the
service drop-down list or click on the icon of the route to be deleted in the Static Routing
Table.
38
Page 55

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 7. Configuring Routes
2. Click to delete the selected route.
Do not remove the route for default gateway unless you know
what you are doing. Removing the default route will render the
WARNING
Internet unreachable.
7.3.4 Viewing the Static Routing Table
All IP-enabled computers and routers maintain a table of IP addresses that are commonly accessed by their
users. For each of these destination IP addresses, the table lists the IP address of the first hop the data should
take. This table is known as the device’s routing table.
To view the Internet Security Router’s routing table, click the Routing menu. The Static Routing Table displays
at the bottom half of the Static Routing Configuration page, as shown in Figure 7.1:
The Static Routing Table displays a row for each existing route containing the IP address of the destination
network, subnet mask of destination network and the IP of the gateway that forwards the traffic. Theis table
shows only user-added routes.
39
Page 56

Page 57

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 8. Configuring DDNS
8 Configuring DDNS
Dynamic DNS is a service that allows computers to use the same domain name, even when the IP address
changes from time to time (during reboot or when the ISP's DHCP server resets IP leases). Internet Security
Router connects to a Dynamic DNS service whenever the WAN IP address changes. It supports setting up the
web services such as Web server, FTP server using a domain name instead of the IP address. Dynamic DNS
supports the DDNS clients with the following features:
„ Update DNS records (addition) when an external interface comes up
„ Force DNS update
Dynamic DNS supports two modes, namely RFC-2136 DDNS Client and HTTP DDNS Client.
RFC-2136 DDNS Client
domain.com
sl1000.domain.com
ISR
Windows 2000
DNS Server
Figure 8.1. Network Diagram for RFC-2136 DDNS
Any interface status change to an external interface sends a DDNS update to the DNS server. When
connection to Primary DNS server fails, the Internet Security Router updates the Secondary DNS server.
When a DNS update is forced by the administrator, update is sent to the server for all active external interfaces.
HTTP Dynamic DNS Client
HTTP DDNS client uses the mechanism provided by the popular DDNS service providers for updating the
DNS records dynamically. In this case, the service provider updates DNS records in the DNS. Internet Security
Router uses HTTP to trigger this update.
The Internet Security Router supports HTTP DDNS update with the following service providers:
„ www.dyndns.org
„ www.zoneedit.com
„ www.dns-tokyo.jp
41
Page 58

Chapter 8. Configuring DDNS Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Internet
(DynDNS, TokyoDNS)
DynDNS
sl1000.homeunix.com
ISR
TokyoDNS
sl1000.dns-tokyo.jp
HTTP DDNS Server
Figure 8.2. Network Diagram for HTTP DDNS
Whenever IP address of the configured DDNS interface changes, DDNS update is sent to the specified DDNS
service provider. Internet Security Router should be configured with the DDNS username and password that
are obtained from the DDNS service provider.
8.1 DDNS Configuration Parameters
Table 8.1 describes the configuration parameters available for DDNS service.
Table 8.1. DDNS Configuration Parameters
Field Description
DDNS State
Enable Click on this radio button to enable the DDNS Service
Disable Click on this radio button to disable the DDNS Service
DDNS Type – select a DDNS service type: HTTP or RFC-2136 DDNS
HTTP DDNS Click this radio button if HTTP DDNS is desired.
RFC-2136 DDNS Click this radio button if RFC-2136 DDNS is desired.
DNS Zone Name
Enter the registered domain name provided by your ISP into this field. (Note: The host name of Internet
Security Router has to be configured in the System Information Setup page properly. For example, If the
host name of your Internet Security Router is “host1” and the DNS Zone Name is “yourdomain.com”, The
fully qualify domain name (FQDN) is “host1.yourdomain.com”.)
RFC-2136 DDNS Specific Settings
Primary/Secondary DNS Server [For RFC-2136 DDNS only]
Enter the IP addresses of the Primary and secondary DNS Servers in these fields. The IP addresses of
the primary and secondary DNS servers are inherited from the settings in the WAN configuration page.
Unless you want to change these settings for WAN, leave them as they are.
42
Page 59

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 8. Configuring DDNS
Field Description
HTTP DDNS Specific Settings
DDNS Service [For HTTP DDNS only]
dyndns Please visit http://www.dyndns.org for more details.
zoneedit Please visit http://www.zoneedit.com for more details.
dyn-tokyo Please visit http://www.dns-tokyo.jp for more details.
DDNS Username [For HTTP DDNS only]
Enter the username provided by your DDNS service provider in this field.
DDNS Password [For HTTP DDNS only]
Enter the password provided by your DDNS service provider in this field.
8.2 Access DDNS Configuration Page
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, and then click the DDNS menu. The DDNS Configuration page
displays, as shown in Figure 8.3.
Note that when you open the DDNS Configuration page, a list of existing DDNS configuration is displayed at
the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 8.3.
8.3 Configuring RFC-2136 DDNS Client
Figure 8.3. RFC-2136 DDNS Configuration Page
Follow these instructions to configure the RFC-2136 DDNS:
1. First you need to ask your system administrator to turn on the DNS dynamic update functionality
on your DNS server. If you are running Windows 2000/XP/2003 DNS server, Please refer to the
Microsoft Knowledge Base article “Q317590: Configure DNS Dynamic Update in Windows 2000”,
for details.
2. Make sure that you have a host name configured for the Internet Security Router; otherwise, go
to the System Information Configuration page (System Management è System Identity) to
configure one.
3. Open the DDNS Configuration page (see section 8.2 Access DDNS Configuration Page).
43
Page 60

Chapter 8. Configuring DDNS Internet Security Router User’s Manual
4. In the DDNS Configuration page, select “Enable” for the DDNS State and “RFC-2136 DDNS” for
the DDNS Type. The RFC-2136 DDNS Configuration page is then displayed as shown in Figure
8.3.
5. Enter the domain name in the DNS Zone Name field.
6. There is no need to change the settings for the primary and secondary DNS servers as they are
inherited from the settings in the WAN configuration page. Unless you want to change these
settings for WAN, leave them as they are.
7. Click on button to send a DNS update request to the DNS server(s) as specified in the
Primary DNS and Secondary DNS fields. Note that DNS update request will also be sent to the
DNS Server automatically whenever the WAN port status is changed.
8.4 Configuring HTTP DDNS Client
Figure 8.4. HTTP DDNS Configuration Page
Follow these instructions to configure the HTTP DDNS:
1. First, you should have already registered a domain name to the DDNS service provider. If you
have not done so, please visit www.dns-tokyo.jp or www.dyndns.org for more details.
2. Make sure that you have a host name configured for the Internet Security Router; otherwise, go
to the System Information Configuration page (System Management è System Identity) to
configure one.
3. Open the DDNS Configuration page (see section 8.2 Access DDNS Configuration Page).
4. In the DDNS Configuration page, select “Enable” for the DDNS State and “HTTP DDNS” for the
DDNS Type. The HTTP DDNS Configuration is then displayed as shown in Figure 8.4.
5. Enter the domain name in the DNS Zone Name field.
6. Select a DDNS service from the DDNS Service drop-down list.
7. Enter the username and password provided by your DDNS service providers.
8. Click on button to send a DNS update request to your DDNS service provider. Note that
DNS update request will also be sent to your DDNS Service provider automatically whenever the
WAN port status is changed.
44
Page 61

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
9 Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
The Internet Security Router provides built-in firewall/NAT functions, enabling you to protect the system
against denial of service (DoS) attacks and other types of malicious accesses to your LAN while providing
Internet access sharing at the same time. You can also specify how to monitor attempted attacks, and who
should be automatically notified.
This chapter describes how to create/modify/delete ACL (Access Control List) rules to control the data passing
through your network. You will use firewall configuration pages to:
„ Create, modify, delete and view inbound/outbound ACL rules.
„ Create, modify and delete pre-defined services, IP pools, NAT pools, application filters and time
ranges to be used in inbound/outbound ACL configurations.
„ View firewall statistics.
Note: When you define an ACL rule, you instruct the Internet Security Router to examine each data packet it
receives to determine whether it meets criteria set forth in the rule. The criteria can include the network or
internet protocol it is carrying, the direction in which it is traveling (for example, from the LAN to the Internet or
vice versa), the IP address of the sending computer, the destination IP address, and other characteristics of
the packet data.
If the packet matches the criteria established in a rule, the packet can either be accepted (forwarded towards
its destination), or denied (discarded), depending on the action specified in the rule.
9.1 Firewall Overview
9.1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection
The stateful packet inspection engine in the Internet Security Router maintains a state table that is used to
keep track of connection states of all the packets passing through the firewall. The firewall will open a “hole” to
allow the packet to pass through if the state of the packet that belongs to an already established connection
matches the state maintained by the stateful packet inspection engine. Otherwise, the packet will be dropped.
This “hole” will be closed when the connection session terminates. No configuration is required for stateful
packet inspection; it is enabled by default when the firewall is enabled. Please refer to section 12.1 Configure
System Services to enable or disable firewall service on the Internet Security Router.
9.1.2 DoS (Denial of Service) Protection
Both DoS protection and stateful packet inspection provide first line of defense for your network. No
configuration is required for both protections on your network as long as firewall is enabled for the Internet
Security Router. By default, the firewall is enabled at the factory. Please refer to section 12.1 Configure System
Services to enable or disable firewall service on the Internet Security Router.
9.1.3 Firewall and Access Control List (ACL)
9.1.3.1 Priority Order of ACL Rule
All ACL rules have a rule ID assigned – the smaller the rule ID, the higher the priority. Firewall monitors the
traffic by extracting header information from the packet and then either drops or forwards the packet by looking
for a match in the ACL rule table based on the header information. Note that the ACL rule checking starts from
the rule with the smallest rule ID until a match is found or all the ACL rules are examined. If no match is found,
the packet is dropped; otherwise, the packet is either dropped or forwarded based on the action defined in the
matched ACL rule.
45
Page 62

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
9.1.3.2 Tracking Connection State
The stateful inspection engine in the firewall keeps track of the state, or progress, of a network connection. By
storing information about each connection in a state table, Internet Security Router is able to quickly determine
if a packet passing through the firewall belongs to an already established connection. If it does, it is passed
through the firewall without going through ACL rule evaluation.
For example, an ACL rule allows outbound ICMP packet from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.2.1. When 192.168.1.1
send an ICMP echo request (i.e. a ping packet) to 192.168.2.1, 192.168.2.1 will send an ICMP echo reply to
192.168.1.1. In the Internet Security Router, you don’t need to create another inbound ACL rule because
stateful packet inspection engine will remember the connection state and allows the ICMP echo reply to pass
through the firewall
9.1.4 Default ACL Rules
The Internet Security Router supports three types of default access rules:
„ Inbound Access Rules: for controlling incoming access to computers on your LAN.
„ Outbound Access Rules: for controlling outbound access to external networks for hosts on your LAN.
„ Self Access Rules: for controlling access to the Internet Security Router itself.
Default Inbound Access Rules
No default inbound access rule is configured. That is, all traffic from external hosts to the internal hosts is
denied.
Default Outbound Access Rules
The default outbound access rule allows all the traffic originated from your LAN to be forwarded to the external
network using NAT.
It is not necessary to remove the default ACL rule from the ACL
rule table! It is better to create higher priority ACL rules to override
WARNING
the default rule.
9.2 NAT Overview
Network Address Translation allows use of a single device, such as the Internet Security Router, to act as an
agent between the Internet (public network) and a local (private) network. This means that a NAT IP address
can represent an entire group of computers to any entity outside a network. Network Address Translation (NAT)
is a mechanism for conserving registered IP addresses in large networks and simplifying IP addressing
management tasks. Because of the translation of IP addresses, NAT also conceals true network address from
privy eyes and provide a certain degree security to the local network.
The NAT modes supported are static NAT, dynamic NAT, NAPT, reverse static NAT and reverse NAPT.
9.2.1 Static (One to One) NAT
Static NAT maps an internal host address to a globally valid Internet address (one-to-one). The IP address in
each packet is directly translated with a globally valid IP contained in the mapping. Figure 9.1 illustrates the IP
address mapping relationship between the four private IP addresses and the four globally valid IP addresses.
Note that this mapping is static, i.e. the mapping will not change over time until this mapping is manually
changed by the administrator. This means that a host will always use the same global valid IP address for all
its outgoing traffic.
46
Page 63

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Figure 9.1 Static NAT – Mapping Four Private IP Addresses to Four Globally Valid IP Addresses
9.2.2 Dynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT maps an internal host dynamically to a globally valid Internet address (m-to-n). The mapping
usually contains a pool of internal IP addresses (m) and a pool of globally valid Internet IP addresses (n) with
m usually greater than n. Each internal IP address is mapped to one external IP address on a first come first
serve basis. Figure 9.2 shows that PC B, C and D are mapped to a globally valid IP address respectively,
while PC A does not map to any globally valid IP address. If PC A wants to go to the Internet, PC A must wait
until a global valid IP address is available. For example, in Figure 9.3, PC B must disconnect from the Internet
first to allow PC A to access Internet.
Figure 9.2 Dynamic NAT – Four Private IP
addresses Mapped to Three Valid IP Addresses
Figure 9.3 Dynamic NAT – PC-A can get an NAT
association after PC-B is disconnected
47
Page 64

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
9.2.3 NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation) or PAT (Port Address Translation)
Also called IP Masquerading, this feature maps many internal hosts to one globally valid Internet address. The
mapping contains a pool of network ports to be used for translation. Every packet is translated with the globally
valid Internet address and the port number is translated with an un-used port from the pool of network ports.
Figure 9.4 shows that all the hosts on the local network gain access to the Internet by mapping to only one
globally valid IP address and different port numbers from a free pool of network ports.
Figure 9.4 NAPT – Map Any Internal PCs to a Single Global IP Address
Figure 9.5 Reverse Static NAT – Map a Global
IP Address to An Internal PC
Figure 9.6 Reverse NAPT – Relayed Incoming
Packets to the Internal Host Base on the
Protocol, Port Number or IP Address
48
Page 65

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
9.2.4 Reverse Static NAT
Reverse static NAT maps a globally valid IP address to an internal host address for the inbound traffic. All
packets coming to that globally valid IP address are relayed to the Internal address. This is useful when
hosting services in an internal machine. Figure 9.5 shows that four globally valid IP addresses are mapped to
four hosts on the internal network and each can be used to host some services for inbound traffic, e.g. FTP
server.
9.2.5 Reverse NAPT / Virtual Server
Reverse NAPT is also called inbound mapping, port mapping, or virtual server. Any packet coming to the
Internet Security Router can be relayed to the internal host based on the protocol, port number and/or IP
address specified in the ACL rule. This is useful when multiple services are hosted on different internal
machines. Figure 9.6 shows that web server (TCP/80) is hosted on PC A, telnet server (TCP/23) on PC B,
DNS server (UDP/53) on PC C and FTP server (TCP/21) on PC D. This means that the inbound traffic of
these four services will be directed to respective host hosting these services.
9.3 Configuring Inbound ACL Rules
By creating ACL rules in Inbound ACL configuration page as shown in Figure 9.7, you can control (allow or
deny) incoming access to computers on your LAN.
Options in this configuration page allow you to:
„ Add a rule, and set parameters for it
„ Modify an existing rule
„ Delete an existing rule
„ View configured ACL rules
Figure 9.7. Inbound ACL Configuration Page
9.3.1 Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Table 9.1 describes the configuration parameters available for firewall inbound ACL rule.
Table 9.1. Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Field Description
49
Page 66

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Field Description
ID
Add New Click on this option to add a new 'basic' Firewall rule.
Rule Number Select a rule from the drop-down list, to modify its attributes.
Action
Allow
Select this button to configure the rule as an allow rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will allow matching packets to pass
through.
Deny
Select this button to configure the rule as a deny rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will not allow matching packets to
pass through.
Mave to
This option allows you to set a priority for this rule. The Internet Security Router Firewall acts on
packets based on the priority of the rules. Set a priority by specifying a number for its position in the
list of rules:
1 (First) This number marks the highest priority.
Other numbers Select other numbers to indicate the priority you wish to assign to the rule.
Source IP
This option allows you to set the source network to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down
list to select one of the following options:
Any This option allows you to apply this rule to all the computers in the source
network, such as those on the Internet.
IP Address This option allows you to specify an IP address on which this rule will be
applied.
IP Address Specify the appropriate network address
Subnet This option allows you to include all the computers that are connected in an
IP subnet. When this option is selected, the following fields become
available for entry:
Address Enter the appropriate IP address.
Mask Enter the corresponding subnet mask.
Range This option allows you to include a range of IP addresses for applying this
rule. The following fields become available for entry when this option is
selected:
Begin Enter the starting IP address of the range
End Enter the ending IP address of the range
IP Pool This option allows you to associate a pre-configured IP pool with this rule.
The available IP pool can be selected from the IP pool drop-down list.
Destination IP
This option allows you to set the destination network to which this rule should apply. Use the dropdown list to select one of the following options:
Any This option allows you to apply this rule to all the computers in the local
network.
50
Page 67

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Field Description
IP Address, Subnet,
Range and IP Pool
Select any of these options and enter details as described in the Source IP
section above.
Source Port
This option allows you to set the source port to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down list to
select one of the following options:
Any Select this option if you want this rule to apply to all applications with an
arbitrary source port number.
Single This option allows you to apply this rule to an application with a specific
source port number.
Port Number Enter the source port number
Range Select this option if you want this rule to apply to applications with this port
range. The following fields become available for entry when this option is
selected.
Begin Enter the starting port number of the range
End Enter the ending port number of the range
Destination Port
This option allows you to set the destination port to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down
list to select one of the following options:
Any Select this option if you want this rule to apply to all applications with an
arbitrary destination port number.
Single, Range
Select any of these and enter details as described in the Source Port
section above.
Service This option allows you to select any of the pre-configured services
(selectable from the drop-down list) instead of the destination port. The
following are examples of services:
BATTLE-NET, PC-ANYWHERE, FINGER, DIABLO-II, L2TP, H323GK,
CUSEEME, MSN-ZONE, ILS, ICQ_2002, ICQ_2000, MSN, AOL, RPC,
RTSP7070, RTSP554, QUAKE, N2P, PPTP, MSG2, MSG1, IRC, IKE,
H323, IMAP4, HTTPS, DNS, SNMP, NNTP, POP3, SMTP, HTTP, FTP,
TELNET.
Note: service is a combination of protocol and port number. They appear
here after you add them in the “Firewall Service” configuration page.
Protocol
This option allows you to select protocol type from a drop-down list. Available settings are All, TCP,
UDP, ICMP, AH and ESP. Note that if you select “service” for the destination port, this option will not
be available.
NAT
This option allows you to select the type of NAT for the inbound traffic.
None Select this option if you don’t intend to use NAT in this inbound ACL rule.
IP Address Select this option to specify the IP address of the computer (usually a server
in your LAN) that you want the incoming traffic to be directed. Note this
option is called reverse NAPT or virtual server.
NAT Pool Select this option to associate a pre-configured NAT pool to the rule. Note
51
Page 68

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Field Description
associate with an inbound ACL rule.
Time Ranges
Select a pre-configured time range during which the rule is active. Select “Always” to make the rule
active at all times.
Application Filtering
This option allows you to select pre-configured FTP, HTTP, RPC and/or SMTP application filters
from the drop-down list.
Log
Click on the “Enable” or “Disable ” radio button to enable or disable logging for this ACL rule.
VPN
Click on the “Enable” radio button if you want the traffic to go through VPN; otherwise, click on the
“Disable” radio button.
9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è Inbound ACL)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, and then click the Inbound ACL submenu.
The Firewall Inbound ACL Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.7.
Note that when you open the Inbound ACL Configuration page, a list of existing ACL rules is also displayed at
the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.8.
Figure 9.8. Inbound ACL configuration example
9.3.3 Add Inbound ACL Rules
To add an inbound ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Select “Add New” from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Set desired action (Allow or Deny) from the “Action” drop-down list.
52
Page 69

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
4. Make changes to any or all of the following fields: source/destination IP, source/destination port,
protocol, port mapping, time ranges, application filtering, log, and VPN. Please see Table 9.1 for
explanation of these fields.
5. Assign a priority for this rule by selecting a number from the “Move to” drop-down list. Note that
the number indicates the priority of the rule with 1 being the highest. Higher priority rules will be
examined prior to the lower priority rules by the firewall.
6. Click on the button to create the new ACL rule. The new ACL rule will then be displayed in
the inbound access control list table at the bottom half of the Inbound ACL Configuration page.
Figure 9.8 illustrates how to create a rule to allow inbound HTTP (i.e. web server) service. This rule allows
inbound HTTP traffic to be directed to the host w/ IP address 192.168.1.28.
9.3.4 Modify Inbound ACL Rules
To modify an inbound ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the rule to be modified in the inbound ACL table or select the rule number
from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: action, source/destination IP,
source/destination port, protocol, port mapping, time ranges, application filtering, log, and VPN.
Please see Table 9.1 for explanation of these fields.
4. Click on the button to modify this ACL rule. The new settings for this ACL rule will then be
displayed in the inbound access control list table at the bottom half of the Inbound ACL
Configuration page.
9.3.5 Delete Inbound ACL Rules
To delete an inbound ACL rule, click on the in front of the rule to be deleted follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the rule to be deleted in the inbound ACL table or select the rule number
from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete this ACL rule. Note that the ACL rule deleted will be
removed from the ACL rule table located at the bottom half of the same configuration page.
9.3.6 Display Inbound ACL Rules
To see existing inbound ACL rules, just open the Inbound ACL Rule Configuration page as described in
section 9.3.2 Access Inbound ACL Rule Configuration Page.
9.4 Configuring Outbound ACL Rules
By creating ACL rules in outbound ACL configuration page as shown in Figure 9.9, you can control (allow or
deny) Internet or external network access for computers on your LAN.
Options in this configuration page allow you to:
„ Add a rule, and set parameters for it
„ Modify an existing rule
„ Delete an existing rule
„ View configured ACL rules
53
Page 70

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Figure 9.9. Outbound ACL Configuration Page
9.4.1 Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Table 9.2 describes the configuration parameters available for firewall outbound ACL rule.
Table 9.2. Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Field Description
ID
Add New Click on this option to add a new 'basic' Firewall rule.
Rule Number Select a rule from the drop-down list, to modify its attributes.
Action
Allow
Deny
Mave to
This option allows you to set a priority for this rule. The Internet Security Router Firewall acts on
packets based on the priority of the rules. Set a priority by specifying a number for its position in the
list of rules:
1 (First) This number marks the highest priority.
Select this button to configure the rule as an allow rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will allow matching packets to pass
through.
Select this button to configure the rule as a deny rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will not allow matching packets to
pass through.
Other numbers Select other numbers to indicate the priority you wish to assign to the rule.
Source IP
This option allows you to set the source network to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down
list to select one of the following options:
Any
54
Page 71

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Field Description
network.
IP Address This option allows you to specify an IP address on which this rule will be
applied.
IP Address Specify the appropriate network address
Subnet This option allows you to include all the computers that are connected in an
IP subnet. When this option is selected, the following fields become
available for entry:
Address Enter the appropriate IP address.
Mask Enter the corresponding subnet mask.
Range This option allows you to include a range of IP addresses for applying this
rule. The following fields become available for entry when this option is
selected:
Begin Enter the starting IP address of the range
End Enter the ending IP address of the range
IP Pool This option allows you to associate a pre-configured IP pool with this rule.
The available IP pool can be selected from the IP pool drop-down list.
Destination IP
This option allows you to set the destination network to which this rule should apply. Use the dropdown list to select one of the following options:
Any This option allows you to apply this rule to all the computers in the
destination network, such as those on the Internet.
IP Address, Subnet,
Range and IP Pool
Select any of these and enter details as described in the Source IP section
above.
Source Port
This option allows you to set the source port to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down list to
select one of the following options:
Any Select this option if you want this rule to apply to all applications with an
arbitrary source port number.
Single This option allows you to apply this rule to an application with a specific
source port number.
Port Number Enter the source port number
Range Select this option if you want this rule to apply to applications with this port
range. The following fields become available for entry when this option is
selected.
Begin Enter the starting port number of the range
End Enter the ending port number of the range
Destination Port
This option allows you to set the destination port to which this rule should apply. Use the drop-down
list to select one of the following options:
Any Select this option if you want this rule to apply to all applications with an
arbitrary destination port number.
55
Page 72

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Field Description
Single, Range
Service This option allows you to select any of the pre-configured services
Protocol
This option allows you to select protocol type from a drop-down list. Available settings are All, TCP,
UDP, ICMP, AH and ESP. Note that if you select “service” for the destination port, this option will not
be available.
NAT
This option allows you to select the type of NAT for the outbound traffic.
None Select this option if you don’t intend to use NAT in this outbound ACL rule.
IP Address Select this option to specify the IP address that you want the outbound
Select any of these and enter details as described in the Source Port
section above.
(selectable from the drop-down list) instead of the destination port. The
following are examples of services:
BATTLE-NET, PC-ANYWHERE, FINGER, DIABLO-II, L2TP, H323GK,
CUSEEME, MSN-ZONE, ILS, ICQ_2002, ICQ_2000, MSN, AOL, RPC,
RTSP7070, RTSP554, QUAKE, N2P, PPTP, MSG2, MSG1, IRC, IKE,
H323, IMAP4, HTTPS, DNS, SNMP, NNTP, POP3, SMTP, HTTP, FTP,
TELNET.
Note: service is a combination of protocol and port number. They appear
here after you add them in the “Firewall Service” configuration page.
traffic to use. Note this option is called NAPT or overload.
NAT Pool Select this option to associate a pre-configured NAT pool to the rule. Note
that only static, dynamic and overload NAT pool can be used to associate
with an outbound ACL rule.
Interface Select this option to use the WAN interface IP address for the outbound
traffic. Note that WAN IP must be configured prior to selecting this option.
Time Ranges
Select a pre-configured time range during which the rule is active. Select “Always” to make the rule
active at all times.
Application Filtering
This option allows you to select pre-configured FTP, HTTP, RPC and/or SMTP application filters
from the drop-down list.
Log
Click on the “Enable” or “Disable” radio button to enable or disable logging for this ACL rule.
VPN
Click on the “Enable” radio button if you want the traffic to go through VPN; otherwise, click on the
“Disable” radio button.
9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è Outbound
ACL)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, and then click the Outbound ACL
submenu. The Firewall Outbound ACL Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.9.
Note that when you open the Outbound ACL Configuration page, a list of existing ACL rules is also displayed
at the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.9.
56
Page 73

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
9.4.3 Add an Outbound ACL Rule
To add an outbound ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Select “Add New” from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Set desired action (Allow or Deny) from the “Action” drop-down list.
4. Make changes to any or all of the following fields: source/destination IP, source/destination port,
protocol, NAT, time ranges, application filtering, log, and VPN. Please see Table 9.2 for
explanation of these fields.
5. Assign a priority for this rule by selecting a number from the “Move to” drop-down list. Note that
the number indicates the priority of the rule with 1 being the highest. Higher priority rules will be
examined prior to the lower priority rules by the firewall.
6. Click on the button to create the new ACL rule. The new ACL rule will then be displayed in
the outbound access control list table at the bottom half of the Outbound ACL Configuration page.
Figure 9.10 illustrates how to create a rule to allow outbound HTTP traffic. This rule allows outbound HTTP
traffic to be directed to any host on the external network for a host in your LAN w/ IP address 192.168.1.15.
Figure 9.10. Outbound ACL Configuration Example
9.4.4 Modify Outbound ACL Rules
To modify an outbound ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the rule to be modified in the outbound ACL table or select the rule
number from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: action, source/destination IP,
source/destination port, protocol, NAT, time ranges, application filtering, log, and VPN. Please
see Table 9.2 for explanation of these fields.
57
Page 74

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
4. Click on the button to modify this ACL rule. The new settings for this ACL rule will then
be displayed in the outbound access control list table at the bottom half of the Outbound ACL
Configuration page.
9.4.5 Delete Outbound ACL Rules
To delete an outbound ACL rule, just click on the in front of the rule to be deleted or follow the instructions
below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page (see section 9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the rule to be deleted in the outbound ACL table or select the rule number
from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete this ACL rule. Note that the ACL rule deleted will be
removed from the ACL rule table located at the bottom half of the same configuration page.
9.4.6 Display Outbound ACL Rules
To see existing outbound ACL rules, just open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration page as described in
section 9.4.2 Access Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page.
9.5 Configuring URL Filters
Keyword based URL (Uniform Resource Locator, e.g. www.yahoo.com) filtering allows you to define one or
more keywords that should not appear in URL’s. Any URL containing one or more of these keywords will be
blocked. This is a policy independent feature i.e. it cannot be associated to ACL rules. This feature can be
independently enabled/disabled, but works only if firewall is enabled.
9.5.1 URL Filter Configuration Parameters
Table 9.3 describes the configuration parameters available for an URL filter rule.
Table 9.3. URL Filter Configuration Parameters
Field Description
URL Filter State
Proxy Server Port
ID
Add New Click on this option to add a new URL filter rule.
Rule Number Select a rule from the drop-down list to modify its attributes.
Keyword
Click on “Enable” or “Disable” radio button to enable or disable URL filtering.
Enter the proxy server (web server) port number configured for your web
browser. Note that the proxy server port change requires you to disable and
enable the firewall to take effect.
Define a keyword that should not appear in the URL.
9.5.2 Access URL Filter Configuration Page – (Firewall è URL Filter)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, and then click the URL Filter submenu.
The Firewall URL Filter Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.11.
Note that when you open the URL Filter Configuration page, a list of existing URL filter rules is also displayed
at the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.11.
58
Page 75

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Figure 9.11. URL Filter Configuration Page
9.5.3 Add an URL Filter Rule
To add an URL Filter, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the URL Configuration page (see section 9.5.2 Access URL Filter Configuration Page).
2. Select “Add New” from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Enter a keyword to the Keyword field.
4. Click on the button to create the URL Filter rule. The new rule will then be displayed in the
URL Filter Configuration Summary table.
9.5.4 Modify an URL Filter Rule
To modify an URL Filter rule, you must first delete the existing URL filter rule (see Section 9.5.5) and then add
a new one (see Section 9.5.3 Add an URL Filter Rule).
9.5.5 Delete an URL Filter Rule
To delete an URL Filter rule, just click on the in front of the rule to be deleted or follow the instructions below:
1. Open the URL Configuration page (see section 9.5.2 Access URL Filter Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the rule to be deleted in the URL Filter Configuration Summary table or
select the rule number from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete this rule.
9.5.6 View Configured URL Filter Rules
To see existing URL filter rules, just open the URL Filter Configuration page as described in section 9.5.2
Access URL Filter Configuration Page.
9.5.7 URL Filter Rule Example
Figure 9.12 shows an URL filter rule example. It demonstrates
„ How to add the keyword “abcnews ”. Any URL containing this keyword will be blocked.
„ Set the proxy web server port number to 80 (you may use a different port number for your proxy
server). This means that this URL filter rule will be applied over the proxy server port 80 in case a
59
Page 76

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
proxy web server is used. If you don’t use a proxy server for your browser, this setting will be ignored.
Note that you must disable and then enable the firewall for this change to take effect. Please refer to
section 12.1 Configure System Services on details of enabling and disabling firewall services.
Figure 9.12. URL Filter Rule Example
9.6 Configuring Advanced Firewall Features – (Firewall è Advanced)
This option sequence brings up the screen with the following sub-options for setting advanced firewall features:
„ Self Access – This option allows you to configure rules for controlling packets targeting the Internet
Security Router itself.
„ Services – Use this option to configure services (applications using specified port numbers). Each
service record contains the name of service record, the IP protocol value and its corresponding port
number.
„ DoS – Use this option to configure DoS – Denial of Service – parameters. This option lists the default
set of DoS attacks against which the Internet Security Router firewall provides protection.
The following sections describe usage of these options
9.6.1 Configuring Self Access Rules
Self Access rules control access to the Internet Security Router itself. You may use Self Access Rule
Configuration page, as illustrated in Figure 9.13, to:
„ Add a Self Access rule, and set basic parameters for it
„ Modify an existing Self Access rule
„ Delete an existing Self Access rule
„ View existing Self Access rules
60
Page 77

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Figure 9.13. Self Access Rule Configuration Page
9.6.1.1 Self Access Configuration Parameters
Table 9.4 describes the configuration parameters available in the Self Access configuration page.
Table 9.4. Self Access Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Protocol
Port
Direction
Select the direction from which the traffic will be allowed.
From LAN Select Enable or Disable to allow or deny traffic from the LAN (internal
From WAN Select Enable or Disable to allow or deny traffic from WAN (external
Select protocol from drop down list - TCP/ UDP/ICMP
Enter the Port Number.
network) to the Internet Security Router.
network) to the Internet Security Router.
9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule Configuration Page – (Firewall è Advanced è Self
Access)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Advanced submenu and then
click the Self Access submenu. The Firewall Self Access Rule Configuration page displays, as shown in
Figure 9.13.
Note that when you open the Self Access Configuration page, a list of existing Self Access rules is also
displayed at the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.13.
9.6.1.3 Add a Self Access Rule
To add a Self Access rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Self Access Rule Configuration page (see section 9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule
Configuration Page).
61
Page 78

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
2. Select “Add New” from the Self Access rule drop-down list.
3. Select a protocol from the Protocol drop-down list. If you select TCP or UDP protocol, you will
need to enter port number as well.
4. Click on the button to create the new Self Access rule. The new rule will then be displayed
in the Self Access Rule list table at the bottom half of the Self Access Rule Configuration page.
Example
Figure 9.13 displays the screen with entries to:
„ Add a new Self Access rule to:
• Allow TCP port 80 traffic (i.e. HTTP traffic) from the LAN and deny the HTTP traffic from the WAN
port (i.e. from the external network) to the Internet Security Router.
9.6.1.4 Modify a Self Access Rule
To modify a Self Access rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Self Access Rule Configuration page (see section 9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the Self Access rule to be modified in the Self Access rule table or select
the Self Access rule from the Self Access rule drop-down list.
3. You may then disable or enable the traffic from LAN or WAN or both. Note that port number
cannot be changed if TCP or UCP protocol is selected. To modify the port number, you must first
delete the existing Self Access rule and add a new rule instead.
4. Click on the button to save the changes. The new settings for this Self Access rule will
then be displayed in the Self Access rule table located at the bottom half of the Self Access Rule
Configuration page.
9.6.1.5 Delete a Self Access Rule
To delete a Self Access rule, click on the icon of the rule to be deleted or follow the instruction below:
1. Open the Self Access Rule Configuration page (see section 9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule
Configuration Page).
2. Click on the icon of the Self Access rule to be deleted in the Self Access rule table or select
the Self Access rule from the Self Access rule drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete the rule. Note that the rule deleted will be removed from the
Self Access rule table located at the bottom half of the same configuration page.
9.6.1.6 View Configured Self Access Rules
To see existing Self Access Rules, just open the Self Access Rule Configuration page as described in section
9.6.1.2 Access Self Access Rule Configuration Page.
9.6.2 Configuring Service List
Services are a combination of Protocol and Port number. It is used in inbound and outbound ACL rule
configuration. You may use Service Configuration Page to:
„ Add a service, and set parameters for it
„ Modify an existing service
„ Delete an existing service
„ View configured services
Figure 9.14 shows the Firewall Service List Configuration page. The configured services are listed at the
bottom half of the same page.
62
Page 79

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Service drop
-
down list
Edit icon
Figure 9.14. Service List Configuration Page
9.6.2.1 Service List Configuration Parameters
Table 9.5 describes the available configuration parameters for firewall service list.
Table 9.5. Service List configuration parameters
Field Description
Service Name
Protocol
Port
Enter the name of the Service to be added. Note that only alphanumeric
characters are allowed in a name.
Enter the type of protocol the service uses.
Enter the port number that is set for this service.
9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration Page – (Firewall è Advanced è Service)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Advanced submenu and then
click the Service submenu. The Service List Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.14.
Note that when you open the Service List Configuration page, a list of existing configured services is also
displayed at the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.14.
9.6.2.3 Add a Service
To add a service, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Service List Configuration Page (see section 9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration
Page).
2. Select “Add New” from the service drop-down list.
3. Enter a desired name, preferably a meaningful name that signifies the nature of the service, in the
“Service Name” field. Note that only alphanumeric characters are allowed in a name.
4. Make changes to any or all of the following fields: public port and protocol. Please see Table 9.5
for explanation of these fields.
63
Page 80

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
5. Click on the button to create the new service. The new service will then be displayed in
the service list table at the bottom half of the Service Configuration page.
9.6.2.4 Modify a Service
To modify a service, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Service List Configuration Page (see section 9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration
Page).
2. Select the service from the service drop-down list or click on the icon of the service to be
modified in the service list table.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: service name, public port and protocol.
Please see Table 9.5 for explanation of these fields.
4. Click on the button to modify this service. The new settings for this service will then be
displayed in the service list table at the bottom half of the Service Configuration page.
9.6.2.5 Delete a Service
To delete a service, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Service List Configuration Page (see section 9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration
Page).
2. Select the service from the service drop-down list or click on the icon of the service to be
modified in the service list table.
3. Click on the button to delete this service. Note that the service deleted will be removed
from the service list table located at the bottom half of the same configuration page.
9.6.2.6 View Configured Services
To see a list of existing services, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Service List Configuration Page (see section 9.6.2.2 Access Service List Configuration
Page).
2. The service list table located at the bottom half of the Service Configuration page shows all the
configured services.
9.6.3 Configuring DoS Settings
The Internet Security Router has a proprietary Attack Defense Engine that protects internal networks from
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks such as SYN flooding, IP smurfing, LAND, Ping of Death and all re-assembly
attacks. It can drop ICMP redirects and IP loose/strict source routing packets. For example, a security device
with the Internet Security Router Firewall provides protection from “WinNuke”, a widely used program to
remotely crash unprotected Windows systems in the Internet. The Internet Security Router Firewall also
provides protection from a variety of common Internet attacks such as IP Spoofing, Ping of Death, Land Attack,
Reassembly and SYN flooding. For a complete list of DoS protection provided by the Internet Security Router,
please see Table 2.3.
9.6.3.1 DoS Protection Configuration Parameters
Table 9.6 describes the configuration parameters available for DoS Protection.
Table 9.6. DoS Protection Configuration Parameters
Field Description
SYN Flooding
64
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against SYN
Flood attacks. This attack involves sending connection requests to a server,
Page 81

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Field Description
to get into a "stuck state" where they cannot accept connections from
legitimate users. ("SYN" is short for "SYNchronize"; this is the first step in
opening an Internet connection). You can select this box if you wish to
protect the network from TCP SYN flooding. By default, SYN Flood
protection is enabled.
Winnuke
MIME Flood
FTP Bounce
IP Unaligned Time
Stamp
Sequence Number
Prediction Check
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against
Winnuke attacks. Some older versions of the Microsoft Windows OS are
vulnerable to this attack. If the computers in the LAN are not updated with
recent versions/patches, you are advised to enable this protection by
checking this check box.
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against MIME
attacks. You can select this box to protect the mail server in your network
against MIME flooding.
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against FTP
bounce attack. In its simplest terms, the attack is based on the misuse of the
PORT command in the FTP protocol. An attacker can establish a
connection between the FTP server machine and an arbitrary port on
another system. This connection may be used to bypass access controls
that would otherwise apply.
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against
unaligned IP time stamp attack. Certain operating systems will crash if they
receive a frame with the IP timestamp option that isn't aligned on a 32-bit
boundary.
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against TCP
sequence number prediction attacks. For TCP packets, sequence number is
used to guard against accidental receipt of unintended data and malicious
use by the attackers if the ISN (Initial Sequence Number) is generated
randomly. Forged packets w/ valid sequence numbers can be used to gain
trust from the receiving host. Attackers can then gain access to the
compromised system. Note that this attack affects only the TCP packets
originated or terminated at the Internet Security Router.
Sequence Number
Out of Range Check
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against TCP
out of range sequence number attacks. An attacker can send a TCP packet
to cause an intrusion detection system (IDS) to become unsynchronized
with the data in a connection. Subsequent frames sent in that connection
may then be ignored by the IDS. This may indicate an unsuccessful attempt
to hijack a TCP session.
ICMP Verbose
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable protection against ICMP
error message attacks. ICMP messages can be used to flood your network
w/ undesired traffic. By default, this option is enabled.
Maximum IP
Fragment Count
Enter the maximum number of fragments the Firewall should allow for every
IP packet. This option is required if your connection to the ISP is through
PPPoE. This data is used during transmission or reception of IP fragments.
When large sized packets are sent via the Internet Security Router, the
packets are chopped into fragments as large as MTU (Maximum
Transmission Unit). By default, this number is set to 45. If MTU of the
interface is 1500 (default for Ethernet), then there can be a maximum of 45
fragments per IP packet. If the MTU is less, then there can be more number
of fragments and this number should be increased.
65
Page 82

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Field Description
Minimum IP
Fragment Size
Enter the Minimum size of IP fragments to be allowed through Firewall. This
limit will not be enforced on the last fragment of the packet. If the Internet
traffic is such that it generates many small sized fragments, this value can
be decreased. This can be found if there are lots of packet loss, degradation
in speed and if the following log message is generated very often:”fragment
of size less than configured minimum fragment size detected”.
9.6.3.2 Access DoS Configuration Page – (Firewall è Advanced è DoS)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Advanced submenu and then
click the DoS submenu. The DoS Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.15.
Note that when you open the DoS Configuration page, a list of supported DoS protection is also displayed at
the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.15. Note that most of these
protections are enabled by default when firewall is enabled.
9.6.3.3 Configuring DoS Settings
By default, most DoS protection against all supported attack types are enabled. Figure 9.15 shows the default
configuration for DoS settings. You may check or un-check individual type of attack defense to disable or
enable protection against that specific type of attack.
Figure 9.15. DoS Configuration Page
9.7 Firewall Policy List – (Firewall è Policy List)
Firewall policy list provides a convenient way to manage firewall ACL rules (inbound/outbound ACL rules, and
group ACL rules).
„ Application Filters – This option allows you to configure Command Filters for FTP, HTTP, RPC and
SMTP applications. Configure filters here before attaching them to policies.
„ IP Pools – This option allows you to configure logical names for IP Pools and set appropriate IP
addresses. Each record contains the name of the IP record and the types of IP address (single IP
address or a range of IP address or a subnet address).
66
Page 83

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
„ NAT Pools – This option allows you to configure NAT Pools that will ensure mapping of the internal IP
address to public IP address. Configure NAT Pools here before attaching them to policies.
„ Time Ranges – This option allows you to configure time-windows for user-access to the networks
across the Internet Security Router.
9.7.1 Configuring Application Filter
Application filter allows network administrator to block, monitor, and report on network users’ access to non-
business and objectionable content. This high-performance content access control results in increased
productivity, lower bandwidth usage and reduced legal liability.
The Internet Security Router has the ability to handle active content filtering on certain application protocols
such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP and RPC.
„ HTTP – You can define HTTP extension based filtering schemes for blocking
ActiveX – *.ocx
Java Archive – *.jar
Java Applets – *.class
Microsoft Archives – *.msar
Other URLs based on file extensions.
„ FTP – allows you to define and enforce the file transfer policy for the site or group of users
„ SMTP – allows you to filter operations such as VRFY, EXPN, etc. which reveal excess information
about the recipient.
„ RPC – allows you to filter programs based on the assigned RPC program numbers.
9.7.1.1 Application Filter Configuration Parameters
Table 9.7 describes the configuration parameters available for application filter.
Table 9.7. Application Filter Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Filter Type
Filter Name
Protocol
Port
Log
This option includes buttons to enable and disable logging for this Application Filter.
Enable Select this option to enable logging for this application filter.
Disable Select this option to disable logging for this application filter.
Action
Allow Select this option to configure the rule as an “allow” rule. This rule when
Deny Select this option to configure the rule as a “deny” rule. This rule when
Filter Commands
This section allows you to enter a command for the respective application. The list of supported
commands per application is as follows:
Select the type of filter: FTP, HTTP, RPC and SMTP.
Enter a name for the filter.
Select the protocol that Application Filter uses (TCP/UDP).
Enter the port number that the Application Filter uses.
bound to the Firewall will allow matching packets to pass through.
bound to the Firewall will not allow matching packets to pass through.
FTP Commands
67
Add the following command to an FTP filter to:
Page 84

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Field Description
CWD Allow or deny of change directory.
LIST Allow or deny of Listing of files/directory.
MKD Allow or deny of Creating a directory.
NLST Allow Short listing of directory contents.
PASV Allow initiation of a passive data connection.
PORT Allow or deny Port Number to participate in an active data connection.
RETR Allow or deny getting a file from the FTP server.
RMD Allow Removing a directory.
RNFR Allow Rename from.
RNTO Allow Rename to.
DELE Allow Deletion of a file.
SITE Allow Site parameters (Specific services provided by the FTP server).
STOR Allow or deny of putting a file to the FTP server.
SMTP Commands
Add the following command to an SMTP filter to:
MAIL Allow or deny initiating a mail transaction.
RCPT Allow or deny identifying an individual recipient of the mail data.
DATA Allow or deny mail data.
VRFY Allow or deny verifying the existence of the user.
EXPN Allow or deny identification for a mailing list.
TURN Allow or deny the switching roles of the client and server, to send mail in the
reverse direction.
SEND Allow or deny initiating a mail transaction.
HTTP (Deny
Add the following command to an HTTP filter to:
Following Files)
Java Applet Deny all *.class files.
Java-archive Deny all *.jar files.
MS Archive Deny all *.msar files.
ActiveX Deny all *.ocx files.
RPC Numbers
RPC numbers Add this command to an RPC filter to allow or deny RPC program numbers.
9.7.1.2 Access Application Filter Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è
Application Filter)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Policy List submenu and then
click the Application Filter submenu. The Application Filter Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure
9.16.
Note that when you open the Application Filter Configuration page, a list of existing application filter rules is
also displayed at the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.16.
68
Page 85

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Figure 9.16. Application Filter Configuration Page
9.7.1.3 Add an Application Filter
The application filter configuration is best explained with a few examples. Note that the configuration for RPC
and SMTP is similar to that for FTP and will not be presented here.
9.7.1.3.1 FTP Example: Add a FTP Filter Rule to Block FTP DELETE Command
10.64.2.0
Outside FW
ISR
Inside FW
FTP Server
10.64.2.254
Private Network 192.168.1.0/24
Figure 9.17 Network Diagram for FTP Filter Example – Blocking FTP Delete Command
1. Open the Application Filer Rule Configuration page (Firewall è Policy List è Application Filter)
69
Page 86

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Filter Type drop
-
down list
FTP Command drop
-
down list
Filter Rule drop
-
down list
Figure 9.18. FTP Filter Example – Configuring FTP Filter Rule
2. Select FTP from the Filter Type drop-down list.
3. Select “Add New Filter” from the Filter Rule drop-down list.
4. Enter a name for this rule – in this example, FTPRule1.
5. Change the port number if necessary. However, it is recommended that you keep the “Default”
setting.
6. Choose to enable to disable the logging option. The default setting is to keep the logging for this
rule disabled.
7. Click on the first FTP commands field, a Firewall Configuration Assistant page is displayed.
Figure 9.19 FTP Filter Example – Firewall Configuration Assistant
8. Select the desired FTP command from the FTP Command drop-down list and then click on the
button. The selected FTP command will be added into the selected Deny FTP
Commands field.
Figure 9.20 FTP Filter Example – Add an FTP Filter to Deny FTP Delete Command
70
9. Repeat step 8 if more commands are to be added; otherwise, proceed to the next step.
10. Click on button to create this FTP application filter rule.
Page 87

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
FTP filter drop
-
down list
Filter Type drop
-
down list
Filter Rule dro
p
-
Figure 9.21. FTP Filter Example – Associate FTP Filter Rule to an ACL Rule
11. Associate the newly added FTP application filter rule to a firewall ACL rule (inbound, outbound or
group ACL) by selecting a FTP filter from the FTP filter drop-down list (see Figure 9.21) and then
click on or button to save the settings.
9.7.1.3.2 HTTP Example: Add a HTTP Filter Rule to Block JAVA Applets and Java Archives
1. Open the Application Filer Rule Configuration page (Firewall è Policy List è Application Filter)
down list
Figure 9.22. HTTP Filter Example – Configuring HTTP Filter Rule
2. Select HTTP from the Filter Type drop-down list.
3. Select “Add New Filter” from the Filter Rule drop-down list.
4. Enter a name for this rule – in this example, HTTPrule1.
5. Change the port number if necessary. However, it is recommended that you keep the “Default”
setting.
6. Choose to enable to disable the logging option. The default setting is to keep the logging for this
rule disabled.
71
Page 88

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
HTTP filter drop
-
down list
7. Check the web application files to block – in this example, Java Applets and Java Archives
8. Enter additional web application files to block. Enter the file extension in the “Deny Following
Files” fields if desired. Figure 9.22 shows that flash files (file extension is *.swf) are to be blocked
in addition to Java applet and archive files.
9. Click on button to create this HTTP application filter rule.
10. Associate the newly created HTTP application filter rule to a firewall ACL rule (inbound, outbound
or group ACL) by selecting a HTTP filter from the HTTP filter drop-down list (see Figure 9.23) and
then click on or button to save the settings.
Figure 9.23. HTTP Filter Example – Associate HTTP Filter Rule to an ACL Rule
9.7.1.4 Modify an Application Filter
To modify an IP Pool, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Application Filter Configuration page (see section 9.7.1.2Access Application Filter
Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Application Filter)).
2. Select the application filter to modify. Click on the icon of the application filter to be modified in
the Application Filter List table or select the filter type from the Filter Type drop-down list and then
select the filter rule from the Filter Rule drop-down.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: Port number, logging option, etc.
4. Click on the button to save the new settings. The new settings for this application filter
will then be displayed in the Application Filter List table.
72
Page 89

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Filter Type drop
-
down list
Filter Rule drop
-
down list
Figure 9.24. Modify an Application Filter
9.7.1.5 Delete an Application Filter
To delete an Application Filter, click on the icon of the filter to be deleted or follow the instruction below:
1. Open the Application Filter Configuration page (see section 9.7.1.2Access Application Filter
Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Application Filter)).
2. Select the application filter to delete. Click on the icon of the application filter to be deleted in
the Application Filter List table or select the filter type from the Filter Type drop-down list and then
select the filter rule from the Filter Rule drop-down.
3. Click on the button to delete this filter.
9.7.2 Configuring IP Pool
9.7.2.1 IP Pool Configuration Parameters
Table 9.8 describes the configuration parameters available for an IP pool.
Table 9.8. IP Pool Configuration Parameters
Field Description
IP Pool Name
IP Pool Type
IP Range This option allows you to configure the range of IP addresses.
Start IP Enter the starting IP address of the range.
Enter the name of the local IP
Select the type of IP Pool.
End IP Enter the ending IP address of the range.
Subnet This option allows you to include all the computers that are connected in an
IP subnet.
Subnet Address Enter the appropriate IP address.
Subnet Mask Enter the corresponding mask.
IP Address This option allows you to configure single IP address.
73
Page 90

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
IP Pool drop
-
down list
IP Pool Type drop
-
down list
Field Description
IP Address Enter the IP Address.
9.7.2.2 Access IP Pool Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è IP Pool)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Policy List submenu and then
click the IP Pool submenu. The IP Pool Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.25.
Note that when you open the IP Pool Configuration page, a list of existing IP pools is also displayed at the
bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.25.
Figure 9.25 IP Pool Configuration Page
9.7.2.3 Add an IP Pool
To add an IP Pool, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the IP Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.2.2 Access IP Pool Configuration Page –
(Firewall è Policy List è IP Pool)).
2. Select “Add New Pool” from the IP Pool drop-down list.
3. Enter a pool name into the Name field.
4. Select a pool type from the IP Pool Type drop-down list.
5. If “IP Range” pool type is selected, enter start IP address and end IP address. If “Subnet” pool
type is selected, enter subnet address and subnet mask. If “IP Address” pool type is selected,
enter an IP adderss.
6. Click on the button to create the new IP Pool. The new IP Pool will then be displayed in
the IP Pool list table.
9.7.2.4 Modify an IP Pool
To modify an IP Pool, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the IP Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.2.2 Access IP Pool Configuration Page –
(Firewall è Policy List è IP Pool)).
74
Page 91

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
2. Click on the icon of the IP pool to be modified in the IP Pool List table or select the IP pool
from the IP Pool drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: Pool name, Pool type and IP address.
4. Click on the button to save the new settings. The new settings for this pool will then be
displayed in the IP Pool list table.
9.7.2.5 Delete an IP Pool
To delete an IP Pool, click on the icon of the IP pool to be deleted or follow the instruction below:
1. Open the IP Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.2.2 Access IP Pool Configuration Page –
(Firewall è Policy List è IP Pool)).
2. Click on the icon of the IP pool to be deleted in the IP Pool List table or select the IP pool from
the IP Pool drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete this IP pool.
9.7.2.6 IP Pool Example
Internet
Outside FW
ISR
Inside FW
192.168.1.10
Figure 9.26. Network Diagram for IP Pool Configuration
1. Open the IP Pool Configuration page to create two IP groups – see Figure 9.27.
192.168.1.11192.168.1.12
MISgroup1
MISgroup2
75
Page 92

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Source IP Type drop
-
down list
IP Pool drop
-
down list
Figure 9.27. IP Pool Example – Add Two IP Pools – MISgroup1 and MISgroup2
2. Associate an IP pool to firewall ACL rules – inbound, outbound or group ACL by selecting “IP
Pool” from the Source IP Type drop-down list and then choose an IP pool from the IP pool dropdown list. In this example, IP pool is used to associate to source IP; however, it can be used to
associate to destination IP as well. As shown in Figure 9.28, MISgroup1 is not allow to play
networked game, Quake-II at all times.
9.7.3 Configuring NAT Pool
9.7.3.1 NAT Pool Configuration Parameters
Table 9.9 describes the configuration parameters available for a NAT pool.
Field Description
NAT Pool Name
NAT Pool Type
76
Figure 9.28. IP Pool Example – Deny QUAKE-II Connection for MISgroup1
Table 9.9. NAT Pool Configuration Parameters
Enter a name for the NAT Pool.
Select the type of NAT Pool and make appropriate IP Address entries.
Page 93

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
NAT Pool drop
-
down list
NAT Pool Type drop
-
down
Field Description
Static
Select this type of NAT to set a one-to-one Mapping between the Internal Address and the
External Address.
LAN IP range For the Internal Address
Start IP Enter the starting IP address.
End IP Enter the ending IP address.
Internet IP Range For the External Address
Start IP Enter the starting IP address.
End IP Enter the ending IP address.
Dynamic
Select this type of NAT to map a set of internal (corporate) machines to a set of public IP
addresses. Make entries for the LAN IP Range and the Internet IP Range as described above.
Overload
Select this type of NAT to use a single public IP address to connect multiple internal (corporate
LAN) machines to external (Internet) network.
NAT IP Address Enter NAT IP address, for the overload.
Interface
Select this type of NAT to specify the Dynamic Interface whose IP address should be used for
subjecting traffic to NAT.
9.7.3.2 Access NAT Pool Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è NAT Pool)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Policy List submenu and then
click the NAT Pool submenu. The NAT Pool Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.29.
Note that when you open the NAT Pool Configuration page, a list of existing NAT pools is also displayed at the
bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.29.
77
Figure 9.29. NAT Pool configuration page
Page 94

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
9.7.3.3 Add a NAT Pool
To add a NAT Pool, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the NAT Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.3.2 Access NAT Pool Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è NAT Pool)).
2. Select “Add New Pool” from the NAT Pool drop-down list.
3. Enter a pool name into the Name field.
4. Select a pool type from the Type drop-down list.
5. If “Static” or “Dynamic” pool type is selected, enter the original IP addresses (start IP Address,
and end IP Address), and mapped IP addresses (start NAT IP Address and end NAT IP Address).
If “Overload” pool type is selected, enter the NAT IP address. If you want to use the IP address
assigned for the WAN port as the NAT IP address, select the Interface pool type.
6. Click on the button to create the new NAT pool. The new NAT pool will then be displayed
in the NAT Pool List table.
9.7.3.4 Modify a NAT Pool
To modify a NAT Pool, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the NAT Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.3.2 Access NAT Pool Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è NAT Pool)).
2. Click on the icon of the NAT pool to be modified in the NAT Pool List table or select the NAT
pool from the NAT Pool drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: Pool name, Pool type and IP address.
4. Click on the button to save the new settings. The new settings for this pool will then be
displayed in the NAT Pool List table.
9.7.3.5 Delete a NAT Pool
To delete a NAT Pool, click on the icon of the NAT pool to be deleted or follow the instruction below:
1. Open the NAT Pool Configuration page (see section 9.7.3.2 Access NAT Pool Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è NAT Pool)).
2. Click on the icon of the NAT pool to be deleted in the NAT Pool List table or select the NAT
pool from the NAT Pool drop-down list.
3. Click on the button to delete this NAT pool.
9.7.3.6 NAT Pool Example
Figure 9.30 shows the network diagram for this NAT pool example.
78
Page 95

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
10.64.2.0/24
Static NAT Pool
10.64.2.1
10.64.2.2
10.64.2.3
WAN Port
10.64.2.254
ISR
LAN Port
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.11
Figure 9.30. Network Diagram for NAT Pool Example
1. Create a NAT pool for static NAT – see Figure 9.31.
192.168.1.12192.168.1.13
Figure 9.31. NAT Pool Example – Create a Static NAT Pool
2. Associate the NAT pool to an outbound ACL rule by selecting “NAT Pool” from the NAT type
drop-down list and then choose an existing NAT pool from the NAT pool drop-down list.
79
Page 96

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
NAT typ
e drop
-
down list
NAT pool drop
-
down list
Figure 9.32. NAT Pool Example – Associate a NAT Pool to an ACL Rule
9.7.4 Configuring Time Range
With this option you can configure access time range records for eventual association with ACL rules. ACL
rules associated with a time range record will be active only during the scheduled period. If the ACL rule
denies HTTP access during 10:00hrs to 18:00hrs, then before 10:00hrs and after 18:00hrs the HTTP traffic will
be permitted to pass through. One time range record can contain up to three time periods. For example:
Office hours on weekdays (Mon-Fri) can have the following periods:
„ Pre-lunch period between 9:00 and 13:00 Hrs
„ Post-lunch period between 14:00 and 18:30 Hrs
Office hours on weekends (Saturday-Sunday) can have the following periods:
„ 9:00 to 12:00 Hrs
Such varying time periods can be configured into a single time range record. Access rules can be activated
based on these time periods.
9.7.4.1 Time Range Configuration Parameters
Table 9.10 describes the configuration parameters available for a time range.
Table 9.10. Time Range Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Time Range drop-
down list
Time Range Name
Select "Add New Time Range" to add a new time range or select an existing
time range from the drop-down list.
Enter a name for the Time Range.
Schedule drop-down
list
Days of Week
Time (hh:mm)
80
Select "Add New Schedule" to add a new schedule or select an existing
schedule from the drop-down list.
Set the days for the schedule.
Set the time windows for the schedule in hh:mm format.
Page 97

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
Time Range drop
-
down list
Schedule drop
-
down list
9.7.4.2 Access Time Range Configuration Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Time Range)
Log into Configuration Manager as admin, click the Firewall menu, click the Policy List submenu and then
click the Time Range submenu. The Time Range Configuration page displays, as shown in Figure 9.33.
Note that when you open the Time Range Configuration page, a list of existing time ranges is also displayed at
the bottom half of the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 9.33.
Figure 9.33. Time Range Configuration Page
9.7.4.3 Add a Time Range
To add a Time Range, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Time Range Configuration page (see section 9.7.4.2 Access Time Range Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Time Range)).
2. Select “Add New Time Range” from the Time Range drop-down list.
3. Enter a name into the Time Range Name field.
4. Select “Add New Schedule” from the Schedule drop-down list.
5. Select Days of Week. For example, from Sunday to Saturday.
6. Enter day hours, For example, from 08:00 to 18:00.
7. Click on the button to create the new schedule.
9.7.4.4 Modify a Time Range
To modify a Time Range, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Time Range Configuration page (see section 9.7.4.2 Access Time Range Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Time Range)).
2. Click on the icon of the Time Range to be modified in the Time Range list table or select the
Time Range from the Time Range drop-down list.
3. Select the Schedule from the schedule drop-down list.
4. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: Days of week and hours.
81
Page 98

Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings Internet Security Router User’s Manual
Time Range drop
-
down list
5. Click on the button to save the new settings.
9.7.4.5 Delete a Time Range
To delete a Time Range, click on the icon of the Time Range to be deleted.
9.7.4.6 Delete a Schedule in a Time Range
To delete a schedule in a Time Range, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Time Range Configuration page (see section 9.7.4.2 Access Time Range Configuration
Page – (Firewall è Policy List è Time Range)).
2. Click on the icon of the Time Range to be deleted in the Time Range list table or select the
Time Range from the Time Range drop-down list.
3. Select the Schedule from the drop-down list.
4. Click on the button to delete this schedule.
9.7.4.7 Time Range Example
1. Create a time range – see Figure 9.31.
Figure 9.34. Time Range Example – Create a Time Range
2. Associate the time range to an outbound ACL rule by selecting an existing time range from the
Time Range drop-down list. Figure 9.35 shows that MISgroup1 is denied FTP access during
office hours.
Figure 9.35. Time Range Example – Deny FTP Access for MISgroup1 During OfficeHours
82
Page 99

Internet Security Router User’s Manual Chapter 9. Configuring Firewall/NAT Settings
9.8 Firewall Statistics – Firewall è Statistics
The Firewall Statistics page displays details regarding the active connections. Figure 9.36 shows a sample
firewall statistics for active connections. To see an updated statistics, click on button.
Figure 9.36. Firewall active connections statistics
83
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...