Asus S6Fm Service Manual 06-v1.2

SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
T
Chapter
Software Specifications
Get to know more about theS6Fm series Notebook with a detailed look at
the software specifications.
he information contained in the chapter can be quite useful when you are troubleshooting the
system’s hardware. Each item has its individual usage for you to understand the software side of
the notebook’s architecture.
6-1

SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
1. Introduction
This BIOS specification describes the major features of key components and system BIOS, the usage of
general purpose input/output (GPIO) pins of south bridge (SB) and embedded controller (EC), the
hardware IRQ routing and resource allocation, setup menu, system power management mechani sm,
system security policy, and so on.
The system BIOS is designed to comply with all industry standards, specifications , and design guides of
PC/AT system including:
z PC 2001 System Design Guide, Version 1.0
z Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification, Revision 1.0b & 2.0
z Simple Boot Flag Specification, Revision 2.0
z PCI BIOS Specification, Revision 2.0
z Plug and Play BIOS Specification, Version 1.0A
z Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) Specification
z System Management BIOS (SMBIOS, i.e. DMI) Reference Specification, Versio n 2.3
z System Management Bus BIOS Interface Specificatio n, Revision 1.0
z BIOS Boot Specification
z Multiprocessor Specification, Revision 1.4
z Universal Serial Bus Specification, Revision 1.1 & 2.0
z Universal Host Controller Design Guide
z Universal Serial Bus PC Legacy Compatibility S pecification
z Enhanced Host Controller Interface Specification for Universal Serial Bus, Revision 1.0
z PCI Express Base Specification, Revisio n 1.0
z PCI Local Bus Specification, Revisio n 2.3
z PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification
This specification is one of the porting guides of system BIOS for engineers and is for internal use only.
Anyone who needs the information of system BIOS could also refer to it. Any question about this
specification, please feedback to Nicole_Pei@asus.com.tw
6-2
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
1. Hardware Overview
1.1. Key Components
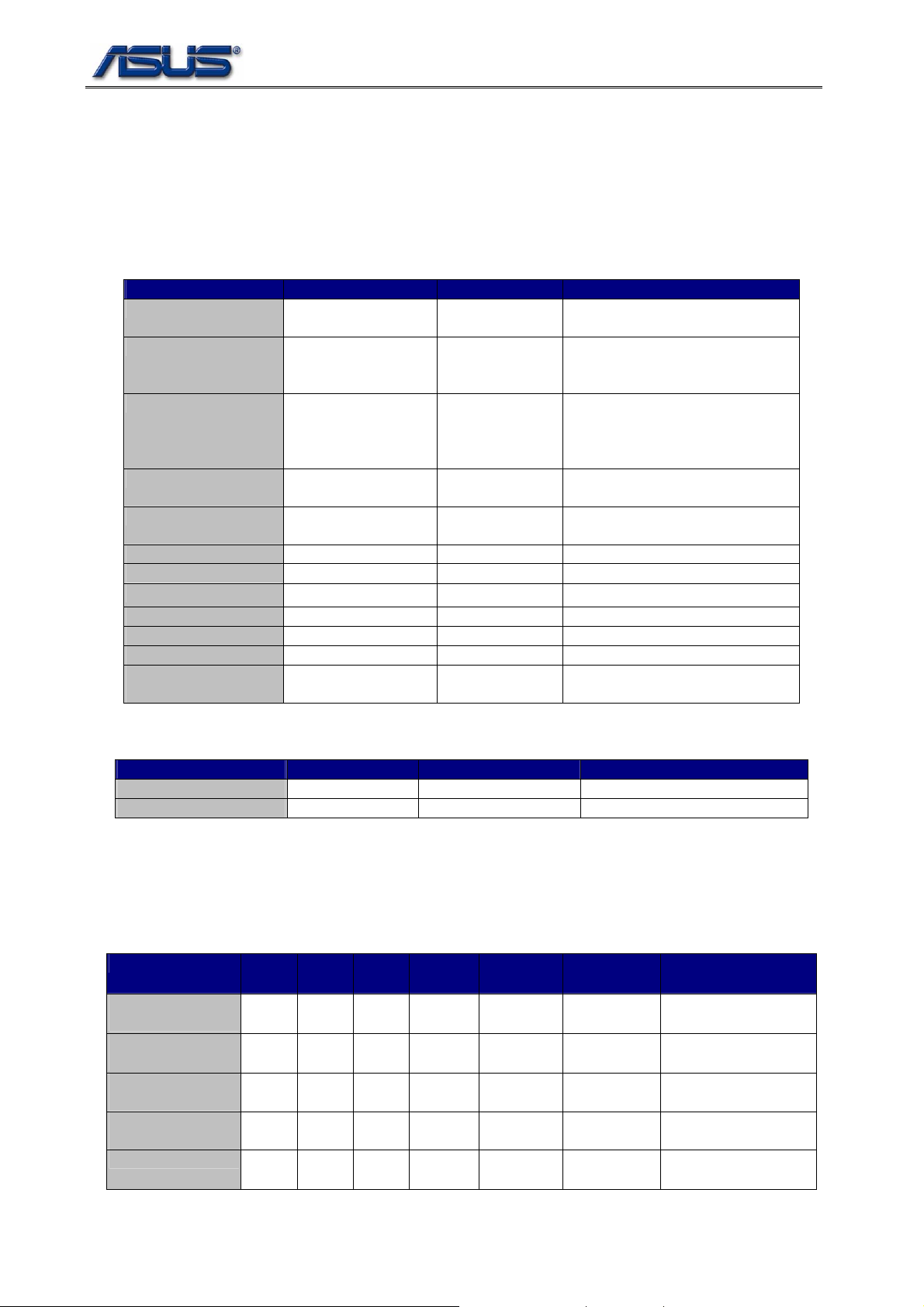
The onboard key components and optional mini-PCI modules are listed at table 2-1 and 2-2.
Table 1-1 Key Component List
Item Vendor Part’s Name Features
CPU Intel Yonah
Merom
North Bridge Intel 945-GM Support 533,667Hz processor
South Bridge Intel ICH7-M NEW: Support Azalia Interface.
VGA Intel 945-GM PCI Express graphic chip.
USB Intel ICH7-M Support USB SPEC. 1.0, 1.1 &
LAN Realtek RTL-8111B Support 10/100/1000Mb/s.
IEEE1394 Ricoh R5C832
Azalia Audio codec Realtek ALC660 Ver.D Support 7.1 audio channels.
Clock Gen. ICS ICS954310 Provide clock to system.
Thermal ANALOG DEVICES ADT7473 Control fan and thermal trip.
Azalia Modem codec Motorola ML3054 Function like as MC97 modem.
Embedded
Controller
Mitsubishi M38857 Keyboard, mouse, brightness and
Geyserville III Speed-Step
Thermal Monitor 2
NEW: Support DDR & DDR2
SDRAM
NEW: Support SATA interface.
NEW: Support 6 PCI Express root
ports.
2.0.
EC SCI control.
Table 1-2 Optional Component List
Item Vendor Part’s Name Revision
Wireless LAN Intel 3945ABG\4965AGN
1.2. Bus Number Allocation
The bus number allocation for PCI-to-PCI and PCI Express Graphic bridges are listed at table 2-3.
Table 1-3 Bus Number Allocation
Device Bus# Dev# Fun# Primary
Bus#
PCI-to-PCI
Bridge
PCI Express Root
Port 0
PCI Express Root
Port 1
PCI Express Root
Port 2
I.G.D.* Bridge 0 2 0 0 0 0 PCI Express Graphic
*: I.G.D. – PCI Express Graphic
0 30 0 0 5 5 1394
0 28 0 0 1 1 LAN
0 28 1 0 2 2 Wireless LAN
0 28 2 0 3 4 New Card
Secondary
Bus#
Subordinate
Bus#
Onboard Devices On
Secondary Bus
Controller
6-3
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
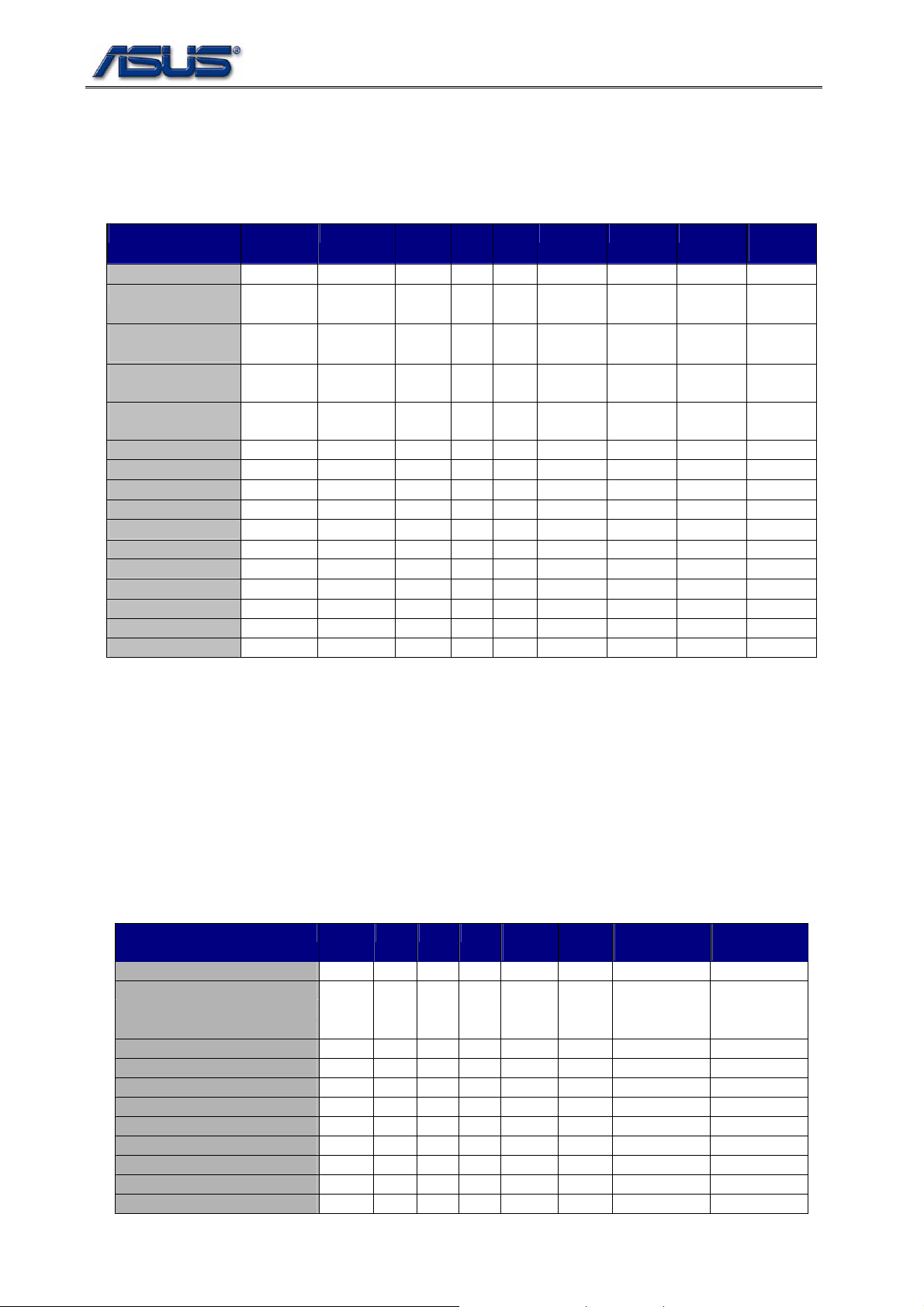
1.3. IRQ Routing of PCI Devices
The IRQ routing of onboard PCI chipsets and mini-PCI slot are shown at table 2-4.
Table 1-4 IRQ Routing of Onboard PCI Chipsets and mini-PCI Slot
Device Vendor IDSEL Bus# Dev# Fun# INTA INTB INTC INTD
I.G.D. VGA Intel AD16 0 2 0 PIRQA
Azalia Controller Intel * 0 27 0 PIRQF
PCI Express Root
Intel * 0 28 0 PIRQA
port 0
PCI Express Root
Intel * 0 28 1 PIRQB
port 1
PCI Express Root
Intel 0 28 2 PIRQC
port 2
USB #0 Intel * 0 29 0 PIRQH
USB #1 Intel * 0 29 1 PIRQD
USB #2 Intel * 0 29 2 PIRQC
USB #3 Intel * 0 29 3 PIRQG
EHCI Intel * 0 29 7 PIRQH
IDE #0 (PATA) Intel * 0 31 1 PIRQC**
1394 Ricoh AD16 5 3 0 PIRQF
SD Card Ricoh AD16 5 3 1 PIRQB
MMC Ricoh AD16 5 3 2 PIRQE
Memory Stick Ricoh AD16 5 3 3 PIRQE
xD-Picture card Ricoh AD16 5 3 4 PIRQE
*: Chipset Internal Routing
**: Chipset Internal Routing at NATIVE mode
IRQs Available for PIRQA~PIRQH on PIC-Enabled O.S. are:
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11
IRQs Available for PIRQA~PIRQH on APIC-Enabled O.S. are:
PIRQA – 16, PIRQB – 17, PIRQC – 18, PIRQD – 19
PIRQE – 20, PIRQF – 21, PIRQG – 22, PIRQH – 23
1.4. PCI Device IDs
The vendor/device and sub-system/sub-vendor IDs of onboard PCI devices are listed at table 2-5.
Table 1-5 Vendor/Device & Sub-System/Sub-Vendor IDs
Device Vendor Bus Dev. Fun. Vendor
Host Bridge Intel 0 0 0 8086 27A0 1043 12A7
VGA
VGA#1
LPC Intel 0 31 0 8086 27B9 8086 27B9
SATA IDE Intel 0 31 1 8086 27DF 1043 12A7
PCI EXPRESS Root Port Intel 0 28 0 8086 27D0 n/a n/a
USB0 Intel 0 29 0 8086 27C8 1043 12A7
USB1 Intel 0 29 1 8086 27C9 1043 12A7
USB2 Intel 0 29 2 8086 27CA 1043 12A7
USB3 Intel 0 29 3 8086 27CB 1043 12A7
EHCI Intel 0 29 7 8086 27CC 1043 12A7
Azalia controller Intel 0 27 0 8086 27D8 1043 1339
Intel
Intel 0 0
2 2 0 1 8086
8086
6-4
ID
Device
ID
27A2
27A6
Sub-Vendor
ID
1043
1043
Sub-System
ID
1252
1252
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
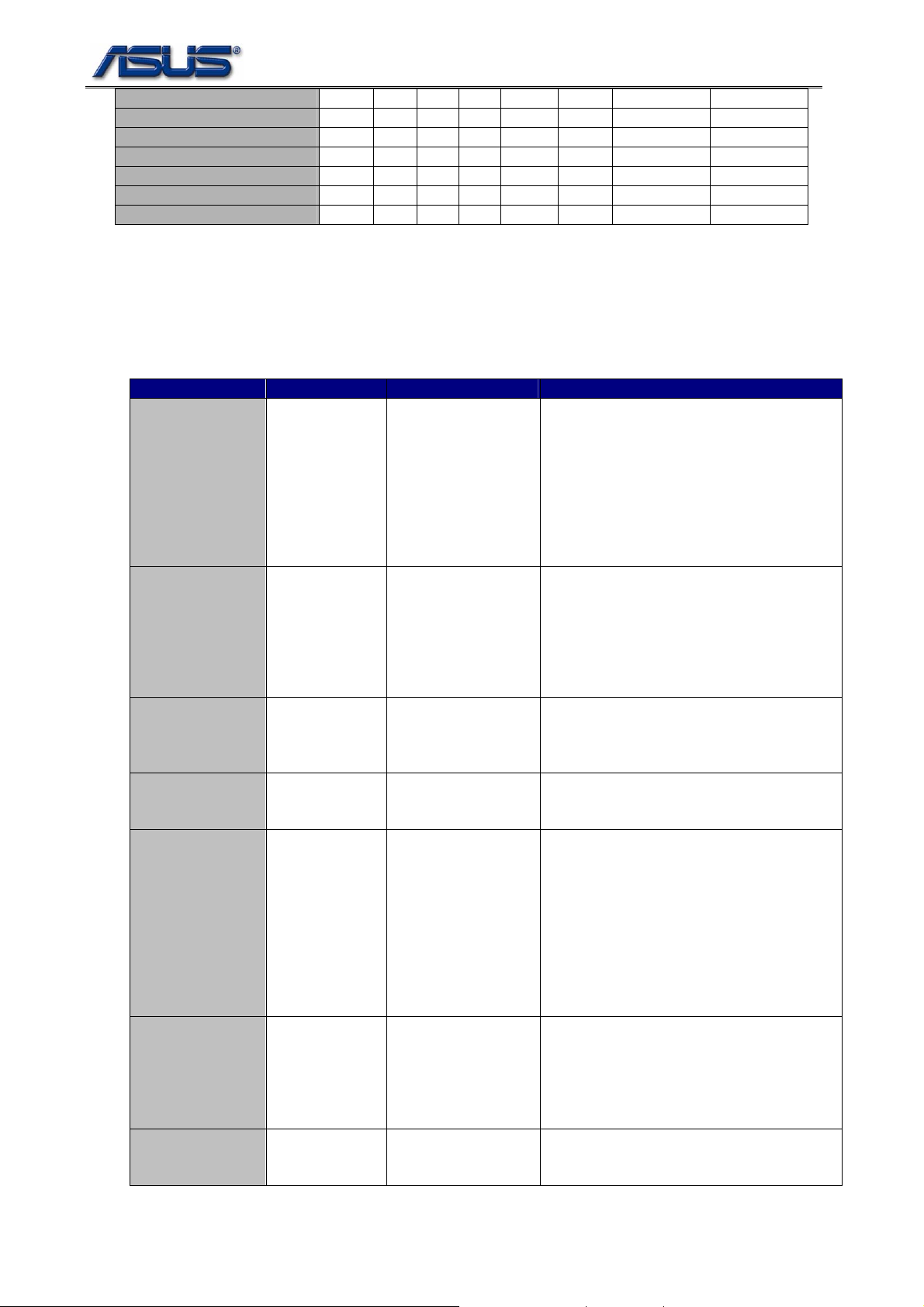
LAN Realtek 1 0 0 10EC 8168 1043 11F5
Wireless Intel 2 0 0 8086 4222 8086 1001
IEEE 1394 Ricoh 5 3 0 1180 0832 1043 12A7
SD Ricoh 5 3 1 1180 0822 1043 12A7
MMC Ricoh 5 3 2 1180 0843 1043 12A7
Memory Stick Ricoh 5 3 3 1180 0592 1043 12A7
xD-Picture card Ricoh 5 3 4 1180 0852 1043 12A7
1.5. Chipset Strapping
The strapping signals are used for static configuration. Table 2-6 an d 2-7 show the strapping pins’ driven
states of SB and EC for the system.
Table 1-6 ICH7 Strapping Pin States
Pin Name Usage Strapping State Function
GNT3# Top-Block Swap
Override
SPKR No Reboot High The signal has a weak internal pull-down. If
INTVRMEN Integrated
VccSus1_5
VRM Enable /
Disable
GPIO25 Reserved Low This signal has a weak internal pull-up.
GNT[5]#/GPIO17#,
GNT4#/GPIO48
Boot BIOS
Destination
Selection
ACZ_SDOUT XOR Chain
Entrance / PCI
Express Port
Config bit1.
ACZ_SYNC PCI Express
Port Config bit 1
Low The signal has a weak internal pull-up. If
the signal is sampled low, this indi cates that
the system is strapped to the “top-block
swap” mode (ICH7 inverts A16 for all cycles
readable via the Top Swap bit (Chipset
Config Registers: Offset 3414:bit 0).Note
that software will not be able to clear the
Top-Swap bit until the system is rebooted
without GNT3# being pulled down
the signal sampled high, this indicates that
the system is strapped to the “No Reboot”
mode (ICH7 will disable the TCO Timer
system reboot feature). The status of this
strap is readable via the NO REBOOT bit
(Chipset Config registers: Offset 3410:bit5)
Low Enable integrated VccSus1_5 VRM when
sampled high
NOTE: This signal should not be pulled
high.
11b This field determines the destination of
accesses to the BIOS memory range.
Signals have weak internal pull-ups. Also
controllable via Boot BIOS Destination bit
(Chipset Config Registers: Of fset 3410h: bit
11:10)
(GNT5# is MSB)
01-SPI
10-PCI
11-LPC
Internal pull low Allow entrance to XOR Chain testing when
TP3 pulled low at rising edge of PWROK.
When TP3 not pulled low at rising edge of
PWROK, sets bit 1 of PRC.PC (Chipset
Config Registers :Offset 0224h).
This signal has a weak internal pull-down.
Internal pull low This signal has a weak internal pull-down.
Set bit 0 of PRC.PC (Chipset Config
Registers :Offset 0224h).
6-5
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
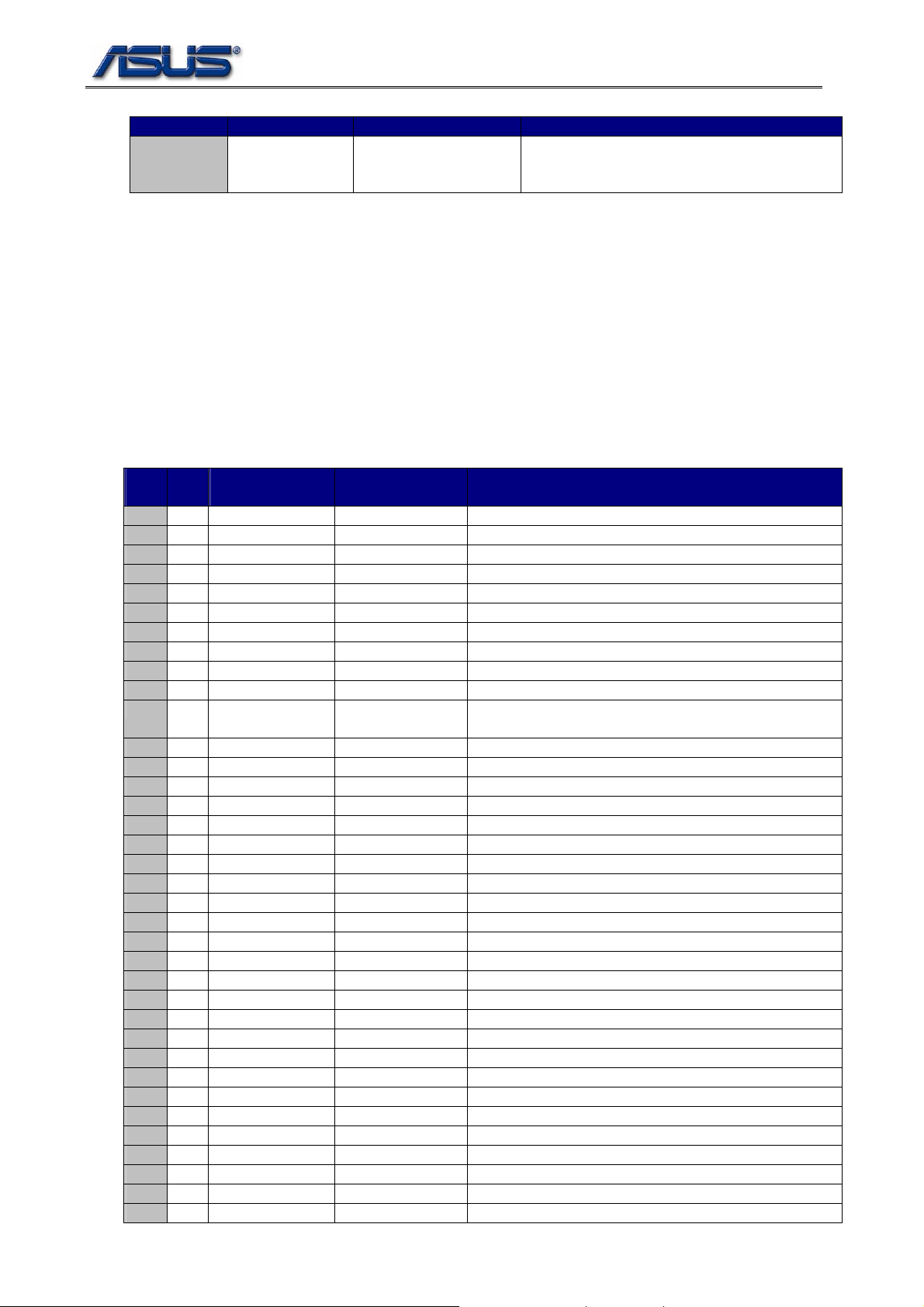
Table 1-7 M38857 Strapping Pin States
Pin Name Usage Strapping State Function
P2.1 Enable/Disable
Power Button
Override feature
Low Disable P5.4 Power button input function
1.6. Multiplex Pin Assignment and GPIO Pin Definition
The GPIO pin assignment of south bridge (SB) and embedded controller (EC) are shown at table 2-8 and
2-9. Some of multiplex GPIO pins should be initialized by system BIOS as general purpose input or
output pins. The “#” symbol at the end of the signal name indicates that the active (or asserted) state
occurs when the signal is at a low voltage level, i.e. low active.
Table 1-8 ICH7 GPIO Definition
GPIO
I/O
Pin
Type
0* I BM_BUSY# PM_BMBUSY# Native Function
1 N/A REQ5# NOT USED N/A
2 N/A PIRQE# NOT USED N/A
3 N/A PIRQF# NOT USED N/A
4 N/A PIRQG# NOT USED N/A
5 N/A PIRQH# NOT USED N/A
6 O None Back_OFF# Turn on/off LCD’s backlight
7 I None WIRELESS_SW# Turn Off WIRELESS
8 I None EXTSMI#_3A EC’s SMI event
9 I None SATA_DET# SATA_DET#
10 I None CHG_FULL_OC Battery charge full indicator (HIGH – full, LOW –
11 N/A SMBALERT# NOT USED N/A
12 I None KB_SCI# EC’s SCI event
13 I None MEM_ID0 MEM_ID0
14 I None MEM_ID1 MEM_ID1
15 O None 802_LED_EN# Turn on/off WLAN LED
16* O DPRSLPVR PM_DPRSLPVR Native Function
17 N/A GNT5# NOT USED N/A
18* O STP_PCI# STP_PCI# Native Function
19 I SATA1GP PANEL_ID1 PANEL_ID1
20* O STP_CPU# STP_CPU# Native Function
21 N/A SATA0GP NOT USED N/A
22 N/A REQ4# NOT USED N/A
23 N/A LDRQ1# NOT USED N/A
24 I None MEM_667/533# Tell from DDR2 533 and 667
25 O None CB_SD# Resume/suspend 1394 controller
26 O EL_RSVD OP_SD# Turn On/Off speaker.
27 N/A EL_STATE0 WLAN_ON# Turn On/Off Wireless
28 I EL_STATE1 MEM_667/533# MEM_667/533#
29 N/A OC#5 NOT USED N/A
30 N/A OC#6 NOT USED N/A
31 N/A OC#7 NOT USED N/A
32* N/A CLKRUN# PM_CLKRUN# Native Function
33 O AZ_DOCK_EN# BT_ON/OFF# Turn On/Off Bluetooth
34 O AZ_DOCK_RST# FWH_WP# Protect/Unprotect EEPROM(Default value: High)
35 N/A SATACLKREQ# NOT USED N/A
Multiplex
W/ Pin
Usage Description
charging)
6-6
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
36 O SATA2GP BT_LED_EN# Enable BlueTooth LED
37 I SATA3GP PCB_ID0 1st PCB ID pin
38 I None PCB_ID1 2nd PCB ID pin
39 I None MEM_ID2 MEM_ID2
40** N/A N/A N/A N/A
41** N/A N/A N/A N/A
42** N/A N/A N/A N/A
43** N/A N/A N/A N/A
44** N/A N/A N/A N/A
45** N/A N/A N/A N/A
46** N/A N/A N/A N/A
47** N/A N/A N/A N/A
48 N/A GNT4# NOT USED N/A
49* O CPUPWRGD CPUPWRGD Native Function
*: Not implemented as GPIO but native function pin.
**: Not implemented.
Table 1-9 M38857 GPIO Definition
Pin I/O
Usage Description
Type
2.0 O KBCRSM Connected to power button for triggering power button press and release
events.
2.1 N/A NOT USED
2.2 O BAT_LEARN This pin is used for battery learning (refresh). Set it low for charging a
battery or batteries and high for discharging a battery or batteries.
2.3 O MSK_LEARN Clear status of INSTANT_FUN#
2.4 O SET_PCIRSTNS# Set PCI reset
2.5 O CAP_LED# CAP Lock Indicator.
2.6 O NUM_LED# Number Lock Indicator
2.7 O SCR_LED# Scroll Lock Indicator
4.0 O KBC_EXTSMI Any system management interrupt will be issued through this pin. It will
notify the system that some events happened.
4.1 N/A NOT USED
4.2 N/A NOT USED
4.3 O BT_ON/OFF# Turn On/Off Bluetooth
4.4 O KBCPURST_3Q CPU reset signal from KBC
4.5 O KBC_GA20 A20 is gated by this pin from KBC.
4.6 O KBCSCI_3Q SCI pin to notify system of runtime or wake up events from KBC.
4.7 I PM_CLKRUN# Standard PCI clock run protocol
5.0 I BAT_LL OW# _OC Battery Low event
5.1 N/A NOT USED
5.2 N/A NOT USED
5.3 N/A NOT USED
5.4 I LID_KBC# LID switch event
5.5 I BAT_IN_OC# Low level indicates that battery is existed.
5.6 O FF_INT HD Protection IC
5.7 O ADJ_BL Adjust LCD brightness
6.0 I PP_TPM PP_TPM
6.1 I CPPE_#_DET It indicates that New Card is plug-in
6.2 O RST#_NEWCARD Reset New Card about 0.5sec(Optional)
6.3 O CPPE__EN Give power to SB PCIE
6.4 I ACIN_OC# High level indicates that AC adapter is existed.
6.5 I BAT_SAVING# Read VID’s voltage
6.6 N/A NOT USED
6.7 N/A NOT USED
7.6 I/O SMD_BAT Monitor/ Control battery.
7.7 I/O SMC_BAT Monitor/ Control battery.
6-7
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
1.7. System Management Bus Connections
The system has three independent system management bus (SMB us) interfaces on SB and EC chip set s,
respectively. The devices connected to these 3 host interfaces are shown at table 2-10 and 2-11.
Table 1-10 SMBus Connections on South Bridge
Device Address Usage
1st DIMM Module 1010000xb* Read DRAM timing and configuration stored on “Serial
Presence Detect” (SPD) device of a DIMM module for
determining memory size and optimum timing.
Clock Generator 1101001xb Disable unused clock source and enable spread
spectrum.
Thermal Monitor 1001100xb Set thermal trip and automatic fan on points; Provide
current temperature
*: Where x=1 – READ, x=0 – WRITE.
Table 1-11 SMBus Connections on Embedded Controller
Device Address Usage
Smart Battery 0001011xb Access gas gauge for getting design/remaining
capacity, charging/discharging state, etc.
1.8. Display Data Channels (DDC) and GMBus
The VGA con troller sup ports display data channels (DDC) on LCD, CRT, and SDVO interfaces as well as
SMBus on SDVO. Thus, the VGA BIOS and driver could determine the resolution and timing of a display
device by reading its EDID data. The system BIOS do esn’t h ave to provide callb ack function f or reporting
LCD type.
Table 1-12 DDC and GMBus Connections on VGA Controller
Device Address Usage
LCD Panel Access EDID data for determining the resolution and
timing of the display device
CRT Monitor Ditto.
1.9. LED Indicators
The colors and states of system LED indicators are described at tab le below.
Table 1-13 Colors and States of LED Indicators
LED State Color Indication
Power Steady On Blue System power is supplied
Power Flashing Blue blinking S3 (suspend to RAM) state
Battery-Charging Steady On Orange Charge a battery or batteries
Battery Low Power Flashing Orange blinking Battery capacity is below 10%
Hard Disk Flashing White Access a hard drive
CAPS Lock Steady On White CAPS Lock enable/ disable
WLAN Steady On Blue Wlan on/off
Bluetooth Steady On White Bluetooth on/off
1.10. General Purpose Events of South Bridge
The general-purpose inputs of the south bridge could trigger SCI, SMI, and/or wake-up events. These
inputs come from LID switch, EC, USB, LAN, modem, and audio interfaces. Table 2-14 lists the
general-purpose event (GPE) connections.
6-8
SOFTWARE PECIFICATION
Table 1-14 GPE Connections on SB
ACPI Mode Legacy Mode Source GPE#
SCI SMI Wake SCI SMI Wake**
Thermal (THRM#) 0 V V
Battery Low (PIC) 20h V V
EC’s SCI Pin (P46) 22h V V
EC’s SMI Pin (P40) 1Eh V V
LAN’s PME* 0bh V
Ring Indication (RI#) 08h V
Modem CODEC 05h V
Audio CODEC 05h V
USB0 03h V
USB1 04h V
USB2 0Ch V
USB3 0Eh V
EHCI 0Dh V
*: PME – Power Management Event
**: Because the chipset doesn’t support S1 state and the BIOS do not support S3 state for none ACPI
O.S., either, it actually has no sleep state at legacy mode.
1.11. Events of Embedded Controller
The internal keys and general-purpose input pins are the SCI, SMI, and WKI event sources of the
embedded controller (EC). The event sources of this system are shown at t able below.
Table 1-15 SCI, SMI, and WKI Events of Embedded Controller
Trigger Pin Source Notification
Code (Hex.)
Fn+F1 (FHK1) 0Ah SCI SMI Simulate a sleep button.
Fn+F2 (FHK2) 0Bh SCI SMI Switch BT on/off.(canceled)
Fn+F3 (FHK3) 0Ch SCI X Invoke E-mail
Fn+F4 (FHK4) 0Dh SCI X Invoke Intenet
Fn+F5 (FHK5) 0Eh SCI SMI Decrease LCD brightness.
Fn+F6 (FHK6) 0Fh SCI SMI Increase LCD brightness.
Fn+F7 (FHK7) 10h SCI SMI Turn off LCD backlight.
Fn+F8 (FHK8) 1 1h SCI SMI Toggle display devices.
Fn=F9 (FHK9) 12h SCI X Switch Touchpad on/off
Fn+F10 (FHK10) 13h SCI SMI Turn audio volume on/off.
Fn+F11 (FHK11) 14h SCI SMI Decrease audio volume.
Fn+F12 (FHK12) 15h SCI SMI Increase audio volume.
Fn+C (FHK14) 69h SCI X Invoke Splendid
Fn+ Sp ace (FHK19) 6Eh SCI X Incoke Power4Gear
Fn+ T (FHK20) 6Fh SCI X Invoke Power4Phone
M_MODE (P65) 35h SCI X Invoke a designated
Fn+ESC (FHK13) 68h SMI SMI Break into debugger.
AC_IN (P64) 34h SCI SMI Notify if the AC power is
BAT_IN# (P55) 2Fh SCI SMI Notify if a battery is plugged
Any Key being pressed at
suspend state
NOTE: The WKI (KBCRSM) pin is connected to power button switch. So, it looks like a power button is
being pressed when typing any key of internal keyboard.
28h WKI WKI Wake up a system from sle ep
ACPI Mode Legacy Mode
(Color Enhance)
application program.
supplied or cut off.
in or removed
state.
6-9
Function
 Loading...
Loading...