Page 1

RX3042H
User's Manual
Revision 0.8
May 12, 2005
Page 2

2
Page 3

i
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ............................................................1
1.1 Features ....................................................................1
1.2 System Requirements ...............................................1
1.3 Using this Document .................................................2
1.3.1 Notational conventions ............................................... 2
1.3.2 Typographical conventions .........................................
2
1.3.3 Special messages ...................................................... 2
2 Getting to Know RX3042H ....................................3
2.1 Parts List ...................................................................3
2.2 Hardware Features ....................................................3
2.3 Software Features .....................................................3
2.3.1 NAT Features ............................................................. 3
2.3.2 Firewall Features ........................................................ 4
2.3.2.1 Stateful Packet Inspection .................................. 4
2.3.2.2 Packet Filtering – ACL (Access Control List) ......
4
2.3.2.3 Defense against DoS Attacks .............................
5
2.3.2.4 Application Level Gateway (ALG) .......................
6
2.3.2.5 Log ...................................................................... 6
2.4 Finding Your Way Around ..........................................7
2.4.1 Front Panel ................................................................. 7
2.4.2 Rear Panel ................................................................. 8
2.4.3 Bottom View ...............................................................
9
2.5 Placement Options ....................................................9
2.5.1 Desktop Placement .................................................... 9
2.5.2 Wall Mount Instructions: .............................................
9
3 Quick Start Guide ................................................ 11
Page 4

ii
3.1 Part 1 — Connecting the Hardware ........................11
3.1.1 Step 1. Connect an ADSL or a cable modem ............11
3.1.2 Step 2. Connect computers or a Network ................ 12
3.1.3 Step 3. Attach the AC adapter ..................................
12
3.1.4 Step 4. Power on RX3042H, the ADSL or cable
modem and power up your computers .................... 12
3.2 Part 2 — Configuring Your Computers ....................13
3.2.1 Before you begin ...................................................... 13
3.2.2 Windows® XP PCs: ..................................................
13
3.2.3 Windows® 2000 PCs: ............................................. 14
3.2.4 Windows® 95, 98, and ME PCs ............................... 15
3.2.5 Windows® NT 4.0 workstations: ..............................
16
3.2.6 Assigning static IP addresses to your PCs ...............
17
3.3 Part 3 — Quick Configuration of the RX3042H .......19
3.3.1 Setting Up the RX3042H .......................................... 19
3.3.2 Testing Your Setup ...................................................
21
3.3.3 Default Router Settings ............................................ 21
4 Using the Configuration Manager ...................... 23
4.1 Log into the Configuration Manager ........................23
4.2 Functional Layout ....................................................24
4.2.1 Menu Navigation ...................................................... 25
4.2.2 Commonly Used Buttons and Icons ......................... 25
4.3 Overview of System Configuration ..........................26
5 Router Setup ........................................................27
5.1 LAN Configuration ...................................................27
5.1.1 LAN IP Address ........................................................ 27
5.1.2 LAN Configuration Parameters ................................
27
5.1.3 Configuring the LAN IP Address ...............................
28
5.2 WAN/DMZ Configuration .........................................29
Page 5

iii
5.2.1 WAN Connection Mode ............................................ 29
5.2.2 PPPoE ...................................................................... 30
5.2.2.1 WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters ...........
31
5.2.2.2 Configuring PPPoE for WAN ............................
32
5.2.3 PPPoE Unnumbered ................................................ 33
5.2.3.1 WAN PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration
Parameters ....................................................... 34
5.2.3.2 Configuring PPPoE Unnumbered for WAN ......
35
5.2.4 Dynamic IP ............................................................... 36
5.2.4.1 Configuring Dynamic IP for WAN ......................
36
5.2.5 Static IP .................................................................... 37
5.2.5.1 WAN or DMZ Static IP Configuration Parameters 37
5.2.5.2 Configuring Static IP for WAN or DMZ ..............
38
5.2.6 PPTP ........................................................................ 39
5.2.6.1 WAN PPTP Configuration Parameters .............
39
5.2.6.2 Configuring PPTP for WAN ...............................
41
5.3 WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up ..................41
5.3.1 WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up Configuration
Parameters .............................................................. 42
5.3.2 Setting Up WAN Load Balancing ............................
43
5.3.3 Setting Up WAN Line Back Up .................................
44
6 DHCP Server Configuration ................................45
6.1 DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) ..................45
6.1.1 What is DHCP? ........................................................ 45
6.1.2 Why use DHCP? ...................................................... 45
6.1.3 Configuring DHCP Server ........................................
46
6.1.4 Viewing Current DHCP Address Assignments .........
48
6.1.5 Fixed DHCP Lease ...................................................
48
6.1.5.1 Access Fixed DHCP Configuration Page –
(Advanced ->DHCP Server
) ............................. 48
Page 6

iv
6.1.5.2 Add a Fixed DHCP Lease ................................. 49
6.1.5.3 Delete a Fixed DHCP Lease .............................
49
6.1.5.4 Viewing Fixed DHCP Lease Table ....................
49
6.2 DNS .........................................................................50
6.2.1 About DNS .............................................................. 50
6.2.2 Assigning DNS Addresses .......................................
50
6.2.3 Configuring DNS Relay ............................................
51
7 Routing .................................................................53
7.1 Overview of IP Routes .............................................53
7.1.1 Do I need to define static routes? ............................ 53
7.2 Dynamic Routing using RIP (Routing Information
Protocol) ..................................................................54
7.2.1 RIP Configuration Parameters ................................. 54
7.2.2 Configuring RIP ........................................................
55
7.3 Static Route .............................................................56
7.3.1 Static Route Configuration Parameters .................... 56
7.3.2 Adding Static Routes ................................................
57
7.3.3 Deleting Static Routes .............................................. 58
7.3.4 Viewing the Static Routing Table ..............................
58
8 Configuring DDNS ...............................................59
8.1 DDNS Configuration Parameters ............................60
8.2 Configuring HTTP DDNS Client ..............................
60
9 Configuring Firewall and NAT ............................63
9.1 Firewall Overview ....................................................63
9.1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection ........................................ 63
9.1.2 DoS (Denial of Service) Protection .......................... 64
9.1.3 Firewall and Access Control List (ACL) ....................
64
9.1.3.1 Priority Order of ACL Rule ................................
64
9.1.3.2 Tracking Connection State ................................
64
Page 7

v
9.1.4 Default ACL Rules .................................................... 64
9.2 NAT Overview ..........................................................65
9.2.1 NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation) or PAT
(Port Address Translation)
......................................... 65
9.2.2 Reverse NAPT / Virtual Server .................................
67
9.3 Firewall Settings – (Firewall/NAT ->Settings) ..........67
9.3.1 Firewall Options ....................................................... 67
9.3.2 DoS Configuration ....................................................
67
9.3.2.1 DoS Protection Configuration Parameters ........
68
9.3.2.2 Configuring DoS Settings .................................
70
9.4 ACL Rule Configuration Parameters .......................70
9.4.1 ACL Rule Configuration Parameters ........................ 70
9.5 Configuring ACL Rules – (Firewall ->ACL) ..............74
9.5.1 Add an ACL Rule ...................................................... 75
9.5.2 Modify an ACL Rule ..................................................
76
9.5.3 Delete an ACL Rule ..................................................
77
9.5.4 Display ACL Rules ....................................................
77
9.6 Configuring Self-Access ACL Rules –(Firewall/NAT
->Self-Access ACL) .................................................77
9.6.1 Add a Self-Access Rule ............................................ 78
9.6.2 Modify a Self-Access Rule ....................................... 79
9.6.3 Delete a Self-Access Rule ....................................... 79
9.6.4 View Configured Self-Access Rules .........................
80
9.7 Configure Virtual Server ..........................................80
9.7.1 Virtual Server Configuration Parameters .................. 80
9.7.2 Virtual Server Example 1 – Web Server ...................
83
9.7.3 Virtual Server Example 2 – FTP Server ...................
85
9.8 Configure Special Application ..................................85
9.8.1 Special Application Configuration Parameters ......... 86
Page 8

vi
9.8.2 Special Application Example .................................... 87
10 System Management ......................................... 89
10.1 Configure System Services ...................................89
10.2 Login Password and System Settings ...................90
10.2.1 Changing Password ............................................... 90
10.2.2 Configure System Settings .....................................
91
10.3 Viewing System Information ..................................91
10.4 Setup Date and Time .............................................
92
10.4.1 View the System Date and Time ............................ 93
10.5 SNMP Setup ..........................................................94
10.5.1 SNMP Configuration Parameters ........................... 94
10.5.2 Configuring SNMP ..................................................
94
10.6 Log Setup ...............................................................95
10.6.1 Setting Up Remote Logging Using a Syslog Server .. 95
10.6.2 View the System Log ..............................................
96
10.7 System Configuration Management ......................95
10.7.1 Restore System Configuration to Factory Default
Settings .................................................................. 96
10.7.2 Backup System Configuration ................................
98
10.7.3 Restore System Configuration ...............................
99
10.8 Firmware Upgrade ...............................................101
10.9 Restart System ....................................................103
10.10 Logout Configuration Manager ...........................
104
11 IP Addresses, Network Masks, and Subnets 105
11.1 IP Addresses ........................................................105
11.1.1 Structure of an IP address .................................... 105
11.2 Network classes ..................................................106
11.3 Subnet masks ......................................................
107
Page 9

vii
12 Troubleshooting ..............................................109
12.1 Diagnosing Problem using IP Utilities ................. 111
12.1.1 ping .......................................................................111
12.1.2 nslookup ................................................................112
13 Index ................................................................. 115
List of Figures
Figure 2.1 Front Panel LEDs .......................................................... 7
Figure 2.2 Rear Panel Connectors ................................................. 8
Figure 3.1 Overview of Hardware Connections ............................ 12
Figure 3.2 Login Screen ............................................................... 19
Figure 3.3 System Status Page .................................................... 20
Figure 4.1 Configuration Manager Login Screen .........................
24
Figure 4.2 Typical Configuration Manager Page ..........................
25
Figure 4.3 System Status Page .................................................... 26
Figure 5.1 Network Setup Configuration – LAN Configuration .....
28
Figure 5.2 Network Setup Configuration Page – WAN Configura-
tion .............................................................................. 30
Figure 5.3 WAN – PPPoE Configuration ......................................
30
Figure 5.4 WAN – PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration ................
33
Figure 5.5 WAN – Dynamic IP (DHCP client) Configuration ........
36
Figure 5.6 WAN – Static IP Configuration ....................................
37
Figure 5.7 WAN – PPTP Configuration ........................................
40
Figure 5.8 Load Balancing Configuration .....................................
43
Figure 6.1 DHCP Server Configuration Page ...............................
46
Figure 6.2 DHCP Lease Table ......................................................
48
Figure 6.3 Fixed DHCP Lease Configuration Page ......................
49
Page 10

viii
Figure 7.1 RIP Configuration Page .............................................. 54
Figure 7.2 Static Route Configuration Page ................................
56
Figure 7.3 Static Route Configuration .........................................
57
Figure 7.4 Sample Routing Table ................................................
58
Figure 8.1 Network Diagram for HTTP DDNS ..............................
59
Figure 8.2 HTTP DDNS Configuration Page ................................
60
Figure 9.1 NAPT – Map Any Internal PCs to a Single Global IP
Address .......................................................................
66
Figure 9.2 Reverse NAPT – Relayed Incoming Packets to the
Internal Host Base on the Protocol, Port Number or
IP Address ...................................................................
66
Figure 9.3 Firewall General Configuration Page ..........................
70
Figure 9.4 ACL Configuration Page ..............................................
75
Figure 9.5 ACL Configuration Example ........................................
76
Figure 9.6 Sample ACL List Table ................................................
76
Figure 9.7 Self-Access ACL Configuration Page ..........................
78
Figure 9.8 Self-Access ACL Configuration Example ....................
79
Figure 9.9 Virtual Server Configuration Page ...............................
80
Figure 9.10 Virtual Server Deployment Topology .........................
83
Figure 9.11 Virtual Server Example 1 – Web Server ....................
84
Figure 9.12 Adding a New Service ...............................................
84
Figure 9.13 Virtual Server Example 2 – FTP Server ....................
85
Figure 9.14 Special Application Configuration Page ....................
87
Figure 10.1 System Services Configuration Page ........................
89
Figure 10.2 System Administration Configuration Page ...............
90
Figure 10.3 System Information Page .......................................... 92
Figure 10.4 Time Zone Configuration Page .................................
93
Figure 10.5 SNMP Configuration Page ........................................
95
Figure 10.6 Syslog Server Configuration .....................................
95
Figure 10.7 Sample Log ............................................................... 96
Page 11

ix
RX3042H User's Manual
Introduction
Figure 10.8 Factory Reset Page .................................................. 97
Figure 10.9 Factory Reset Confirmation ......................................
97
Figure 10.10 Factory Reset Count Down Timer ...........................
97
Figure 10.11 Backup System Configuration Page ........................
98
Figure 10.12 Restore System Configuration Page .......................
99
Figure 10.13 Selecting System Configuration from the File Manager
.................................................................................100
Figure 10.14 System Configuration Restoration Confirmation ...
100
Figure 10.15 System Reboot Counter Timer ..............................
101
Figure 10.16 Firmware Upgrade Page ....................................... 101
Figure 10.17 Selecting Firmware from the File Manager ........... 102
Figure 10.18 Firmware Upgrade Confirmation ...........................
102
Figure 10.19 Firmware Upgrade Progress ................................. 102
Figure 10.20 System Reboot Count Down Timer for Firmware
Upgrade ................................................................. 103
Figure 10.21 Restart System Page ............................................ 104
Figure 10.22 Configuration Manager Logout Page ....................
104
Figure 10.23 Confirmation for Closing Browser (IE) ...................
104
Figure 12.1 Using the ping Utility ................................................111
Figure 12.2 Using the nslookup Utility .........................................113
List of Tables
Table 2.1 DoS Attacks .................................................................... 5
Table 2.2 Front Panel Label and LEDs ...........................................
7
Table 2.3 Rear Panel Labels and LEDs .........................................
8
Table 3.1 LED Indicators ..............................................................
13
Table 3.2 Default Settings Summary ............................................
21
Table 4.1 Description of Commonly Used Buttons and Icons ......
25
Page 12

x
Introduction
RX3042H User's Manual
Table 5.1 LAN Configuration Parameters ..................................... 28
Table 5.2 WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters .......................
31
Table 5.3 WAN PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration Parameters .
34
Table 5.4 WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters .....................
37
Table 5.5 WAN PPTP Configuration Parameters .........................
39
Table 5.6 WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up Configuration
Parameters ................................................................... 42
Table 6.1 DHCP Configuration Parameters ..................................
47
Table 6.2 Fixed DHCP Lease Configuration Parameters .............
49
Table 7.1 Static Route Configuration Parameters ........................
54
Table 7.2 Static Route Configuration Parameters ........................
56
Table 8.1 DDNS Configuration Parameters ..................................
60
Table 9.1 Firewall Options Parameters ........................................
67
Table 9.2 DoS Attack Definition ....................................................
68
Table 9.3 ACL Rule Configuration Parameters .............................
71
Table 9.4 Service Configuration Parameters ................................
73
Table 9.5 Virtual Server Configuration Parameters ......................
81
Table 9.6 Port Numbers for Popular Applications .........................
82
Table 9.7 Special Application Configuration Parameters ..............
86
Table 9.8 Port Numbers for Popular Applications .........................
86
Table 10.1 SNMP Configuration Parameters ................................
94
Table 11.1 IP Address Structure .................................................
106
Page 13

1
RX3042H User's Manual
Introduction
Chapter 1 Introduction
Congratulations on becoming the owner of RX3042H. Your LAN
(local area network) will now be able to access the Internet using
your high-speed broadband connection such as those with ADSL or
cable modem.
This User's Manual will show you how to set up the RX3042H,
and how to customize its configuration to get the most out of this
product.
1.1 Features
• LAN: 4-port Fast Ethernet switch
• WAN: Dual 10/100Base-T Ethernet ports to provide Internet
acc
ess for all computers on your LAN
• Firewall, and NAT (Network Address Translation) functions to
provide secure Internet access for you
r LAN
• Automatic network address assignment through DHCP Server
Services including IP route, DNS and DDNS configuration
• Configuration program accessible via a web browser, such as
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or newer.
• User configuration dual-WAN or WAN plus DMZ support
• USB storage support (to be supported with firmware upgrade)
1.2 System Requirements
In order to use the RX3042H for Internet access, you must have the
following:
•
ADSL or cable modem and the corresponding service up and
running, with at least one public Internet address assigned to
your WAN
• One or more computers each containing an Ethernet 10Base-T
or 100Base-T or 1000Base-T network interface card (NIC)
•
(Optional) An Ethernet hub/switch, if you want to connect the
router to more than four computers on an Ethernet network.
Page 14

2
Introduction
RX3042H User's Manual
• For system configuration using the web-based GUI: a web
browser such as Internet Explorer 6.0 or newer.
1.3 Using this Document
1.3.1 Notational conventions
• Acronyms are defined the first time they appear in the text.
• For brevity, RX3042H is sometimes referred to as the “router”
or the ”gateway”.
• The terms LAN and network are used interchangeably to refer
to a group of Ethernet-connected computers at one site.
• Sequence of mouse actions is denoted by the “->” character.
For instance,
System -> Network Setup
means click the
System menu
and then click the
Network Setup
submenu.
1.3.2 Typographical conventions
•
Boldface
type text is used for items you select from menus
and drop-down lists, and text strings you type when prompted
by the program.
1.3.3 Special messages
This document uses the following icons to call your attention to
specific instructions or explanations.
Note: Provides clarification or non-essential
information on the current topic.
Definition: Explains terms or acronyms that may be
unfamiliar to many readers. These terms are also
included in the Glossary.
Warning: Provides messages of high importance,
including messages relating to personal safety or
system integrity.
Page 15
RX3042H User's Manual
Getting to Know RX3042H
3
Chapter 2 Getting to Know RX3042H
2.1 Parts List
In addition to this document, RX3042H should come with the following:
• The system unit
• AC adapter
• Ethernet cable (“straight-through” type)
2.2 Hardware Features
LAN
• 4-port Fast Ethernet switch
• Auto speed negotiation
WAN
• Dual 10/100M Ethernet ports
• Auto MDI/MDIX
2.3 Software Features
2.3.1 NAT Features
RX3042H provides NAT to share a single high-speed Internet
connection and to save the cost of multiple connections required
for the hosts on the LAN segments connected to it. This feature
conceals network address and prevents them from becoming
public. It maps unregistered IP address of hosts connected to the
LAN with valid ones for Internet access. RX3042H also provides
reverse NAT capability, which enables users to host vario us
services such as e-mail servers, web servers, etc. The NAT rules
drive the translation mechanism. The following types of NAT are
supported by RX3042H.
• NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)– Also called IP
Masqueradi ng or ENAT (Enhanced NAT). Maps many internal
hosts to only one globally valid IP address. The mapping usually
Page 16

Getting to Know RX3042H
RX3042H User's Manual
4
contains a pool of network ports to be used for translation.
Every packet is translated with the globally valid IP address;
the port number is translated with a free pool from the pool of
network ports.
• Reverse NAPT – Also called inbound mapping, port mapping,or
virtual server. Any packet coming to the router can be relayed
to an internal host based on the protocol, port number and/or
IP Address specified in the rule. This is useful when multiple
services are hosted on different internal hosts.
2.3.2 Firewall Features
The firewall as implemented in RX3042H provides the following
features to protect your network from being attacked and to prevent
your network from being used as the springboard for attacks.
• Stateful Packet Inspection
• Packet Filtering (ACL)
• Defense against Denial of Service Attacks
• Log
2.3.2.1 Stateful Packet Inspection
The RX3042H Firewall uses “stateful packet inspection” that
extracts state-related information required for the security decision
from the packet and maintains this information for evaluating
subsequent connection attempts. It has awareness of application
and creates dynamic sessions that allow dynamic connections so
that no ports need to be opened other than the required ones. This
provides a solution which is highly secure and that offers scalability
and extensibility.
2.3.2.2 Packet Filtering – ACL (Access Control List)
ACL rule is one of the basic building blocks for network security.
Firewall monitors each individual packet, decodes the header
information of inbound and outbound traffic and then either blocks
the packet from passing or allows it to pass based on the contents
of the source address, destination address, source port, destination
port, and protocol defined in the ACL rules.
Page 17
RX3042H User's Manual
Getting to Know RX3042H
5
ACL is a very appropriate measure for providing isolation of one
subnet from another. It can be used as the first line of defense in
the network to block inbound packets of specific types from ever
reaching the protected network.
The RX3042H Firewallʼs ACL methodology supports:
• Filtering based on destination and source IP address, port
number and protocol
• Use of the wild card for composing filter rules
• Filter Rule priorities
2.3.2.3 Defense against DoS Attacks
The RX3042H Firewall has an Attack Defense Engine that protects
internal networks from known types of Internet attacks. It provides
automatic protection from Denial of Service (DoS) attacks such
as SYN flooding, IP smurfing, LAND, Ping of Death and all reassembly attacks. For example, the RX3042H Firewall provides
protection from “WinNuke”, a widely used program to remotely
crash unprotected Windows systems in the Internet. The RX3042H
Firewall also provides protection from a variety of common Internet
attacks such as IP Spoofing, Ping of Death, Land Attack, and
Reassembly attacks.
The type of attack protections provided by the RX3042H is listed in
Table 2.1.
Table 2.1. DoS Attacks
Type of Attack Name of Attacks
Re-assembly Attacks Bonk, Boink, Teardrop ( New Tear),
Overdrop, Opntear, Syndrop, Jolt, IP
fragmentation overlap.
ICMP Attacks Ping of Death, Smurf, Twinge
Flooders Logging only for ICMP Flooder, UDP
Flooder, SYN Flooder
Port Scans Logging only for TCP SYN Scan,
At ta cking packe ts d ropped: TCP
XMAS Scan, TCP Null Scan, TCP
Stealth Scan
Protection with PF Rules Echo-Chargen, Ascend Kill
Miscellaneous Attacks IP Spoofing, LAND, Targa, Winnuke
Page 18

Getting to Know RX3042H
RX3042H User's Manual
6
2.3.2.4 Application Level Gateway (ALG)
Applications such as FTP open connections dynamically based
on the respective application parameter. To go through the firewall
on the RX3042H, packets pertaining to an application, require a
corresponding allow rule. In the absence of such rules, the packets
will be dropped by the RX3042H Firewall. As it is not feasible to
create policies for numerous applications dynamically (at the same
time without compromising security), intelligence in the form of
Application Level Gateways (ALG), is built to parse packets for
applications and open dynamic associations. The RX3042H NAT
provides a number of ALGs for popular applications such as FTP,
and Netmeeting.
2.3.2.5 Log
Events in the network, that could be attempts to affect its security,
are recorded in the RX3042H system log file. The log maintains a
minimum log details such as, time of packet arrival, description of
action taken by Firewall and reason for action.
Page 19
RX3042H User's Manual
Getting to Know RX3042H
7
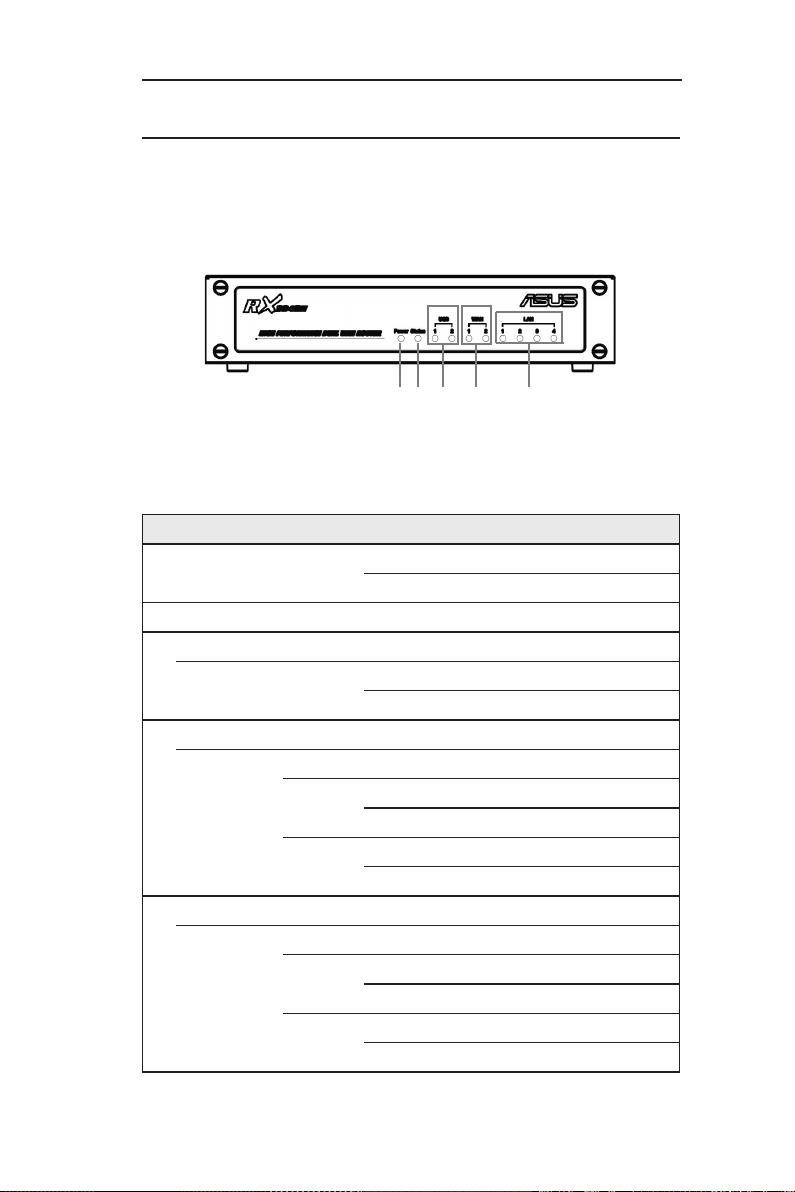
Table 2.2 Front Panel Label and LEDs
LED Label Color Status
Indication
1 Power Green
ON RX3042H is powered on.
OFF RX3042H is powered off.
2 Status Green
3
USB Identifies the USB port.
1-2 Green
OFF USB device is not detected.
ON USB device is detected.
4
WAN Identifies the WAN port.
1-2
OFF No link is detected.
Green
ON 100Mbps link is detected.
Blinking 100Mbps activity is detected.
Amber
ON 10Mbps link is detected.
Blinking 10Mbps activity is detected.
5
LAN Identifies the LAN port.
1-4
OFF No link is detected.
Green
ON 100Mbps link is detected.
Blinking 100Mbps activity is detected.
Amber
ON 10Mbps link is detected.
Blinking 10Mbps activity is detected.
2.4 Finding Your Way Around
2.4.1 Front Panel
The front panel contains LED indicators that show the status of the unit.
Figure 2.1 Front Panel Label and LEDs
1
2
3
4
5
Page 20
Getting to Know RX3042H
RX3042H User's Manual
8
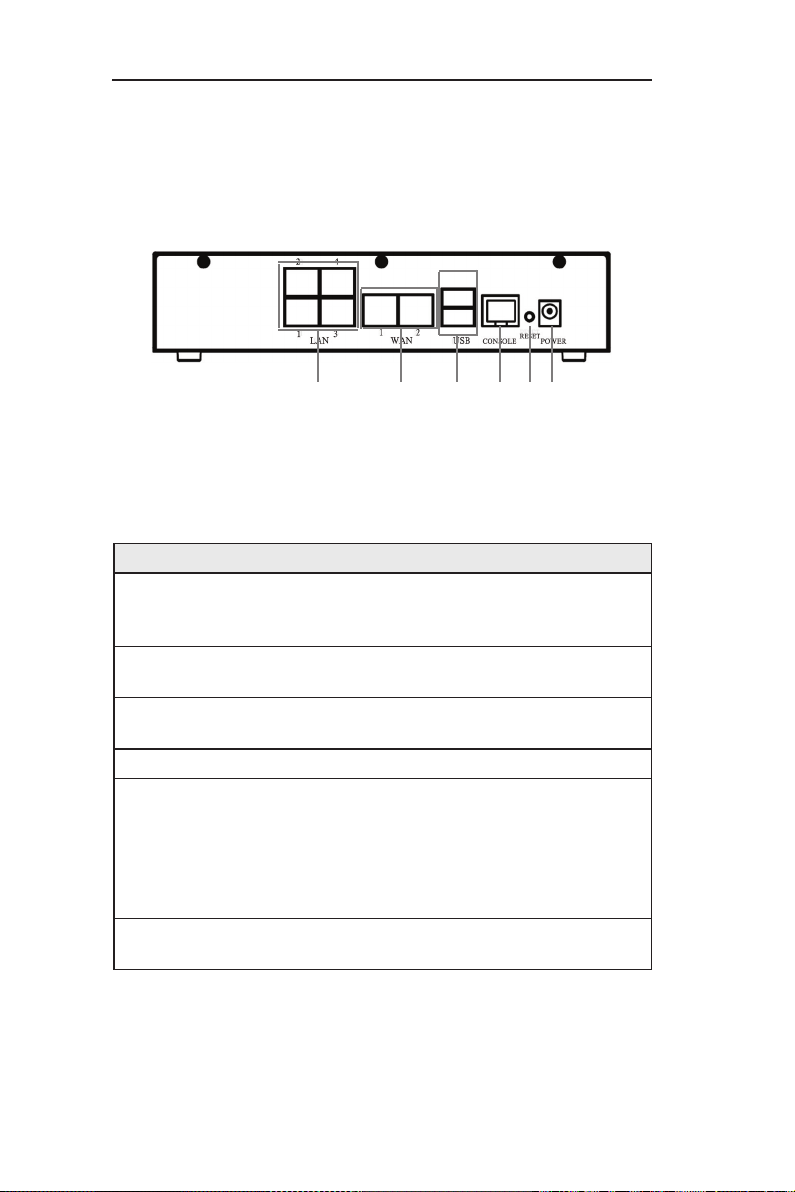
Table 2.3 Rear Panel Labels and LEDs
Label Indication
6 1--4
LAN Ports: connect to your PC's Ethernet
port, or to the uplink port on your LAN's
hub/switch, using the Ethernet cable.
7
Dual WAN or
WAN + DMZ
WAN ports:Connect to your WAN device,
such as ADSL or cable modem.
8 USB
USB Ports: connect to USB 1.1 OR 2.0
devices
9 Console
10 RESET
Reset Button:
1. Reboot the device
2. Reset the system configuration to
factory defaults if pressed for more than 5
seconds.
11
POWER
Power Input Jack: Connect to the supplied
AC adapter.
2.4.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel contains the ports for the unitʼs data and power
connections.
Figure 2.2 Rear Panel Labels and Connectors
6 7 8 9 10 11
Page 21
RX3042H User's Manual
Getting to Know RX3042H
9
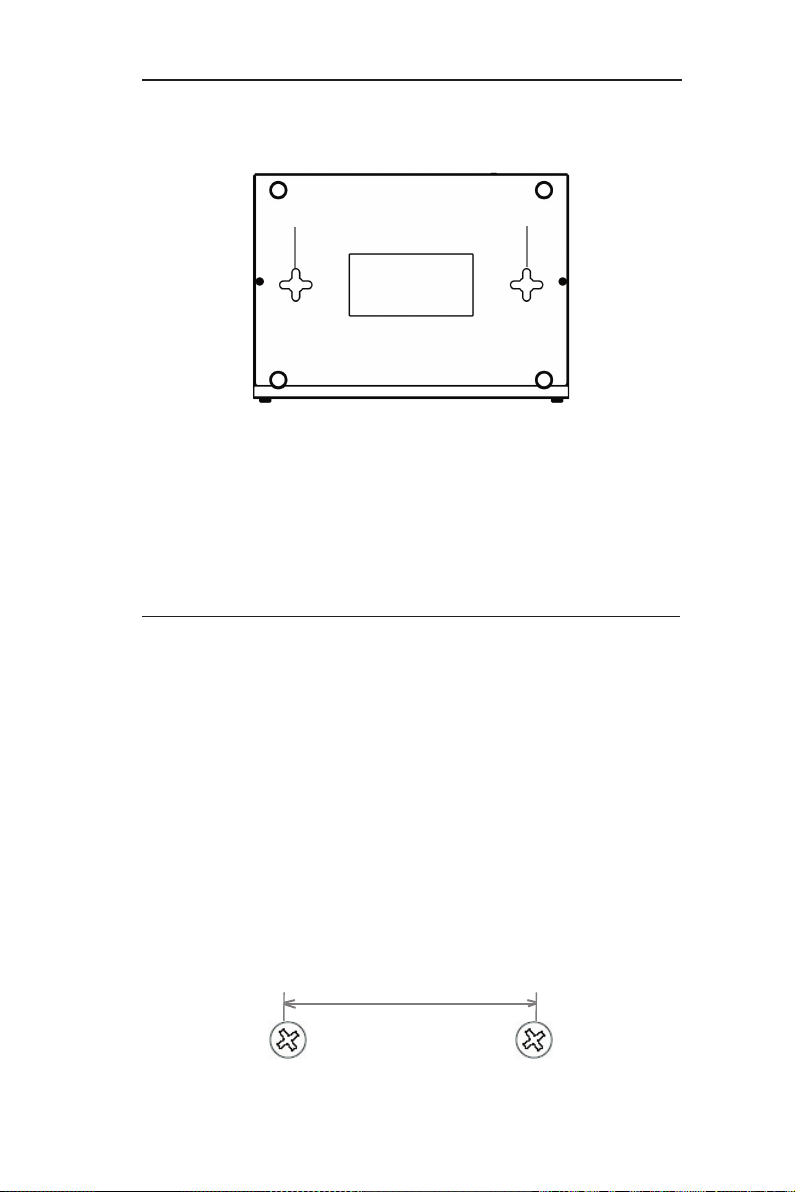
2.4.3 Bottom View
12.Wall Mount Slots: You may use these slots to hang RX3042H
on the wall to save space. Depend in g on your particular
requirement by taking into account the location of the power
outlet, power cord length, Ethernet cable length and etc., you
can hang RX3042H in 4 different orientations: front panel up,
rear panel up, left side up or right side up.
2.5 Placement Options
Depending on your environment, you may choose one of the three
supported placement options for RX3042H – desktop placement,
magnet mount and wall mount.
2.5.1 Desktop Placement
You may place RX3042H on any flat surface. The space-saving
design of RX3042H occupies only a small area on your desk.
2.5.2 Wall Mount Instructions:
1. Attach two screws on the wall, separated by 150mm, and make
sure that the two screws are leveled.
12 12
150mm
Page 22
Getting to Know RX3042H
RX3042H User's Manual
10
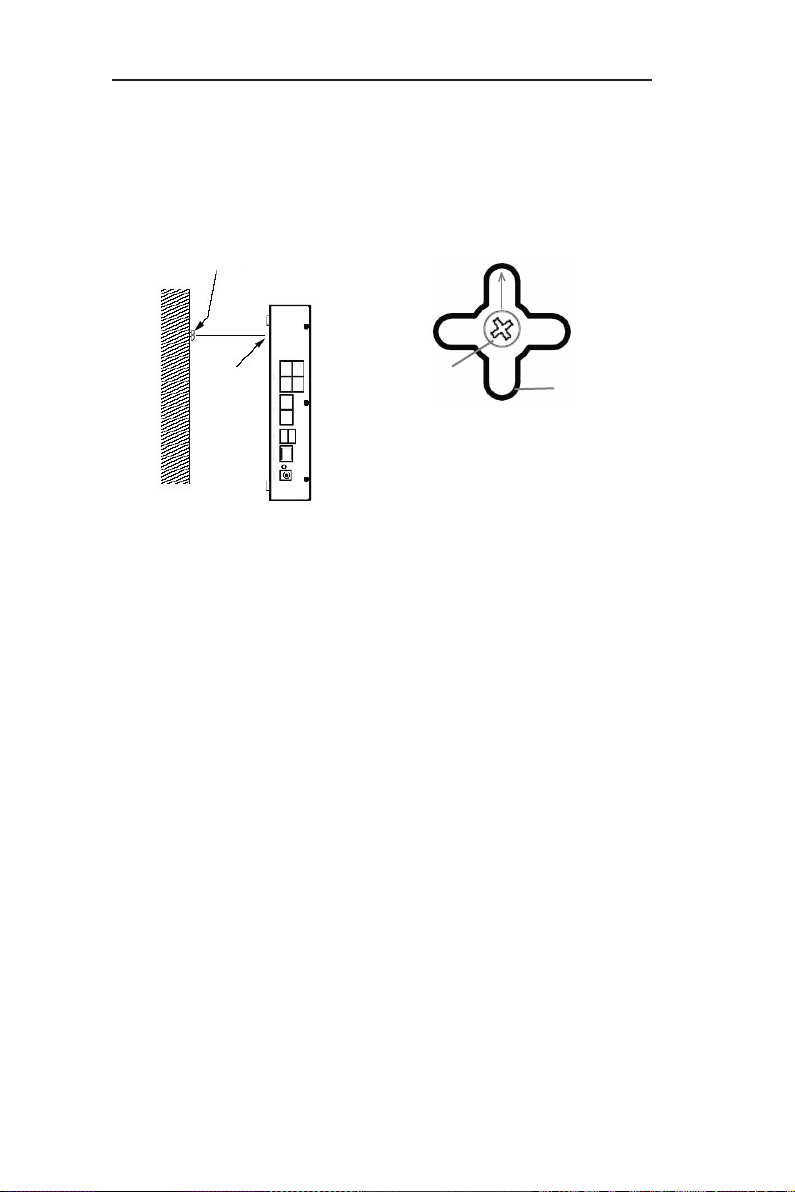
2. Line up the wall mount slots with the screws and maneuver
RX3042H so that both screws are inserted into the wall mount
slots as indicated in the following figures. The wall mount design
supports 4 different orientations: rear side up, rear side down,
rear side to the left and rear side to the right.
Screw
Wall
mount
slot
Line up the wall amount slot with
both screws.
Mane uv er t he rou te r so that
b o t h sc r e w s a r e in se r t e d
into the wall mount slots and
th en slow ly pu sh the router
dow n ward as s h own in the
above figure.
Wall
mount
slot
Screw
Page 23

RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
11
3 Quick Start Guide
This Quick Start Guide provides basic instructions for connecting
the RX3042H to a computer or a network and to the Internet.
• Part 1 provides instructions to set up the hardware.
• Part 2 describes how to configure Internet properties on your
computer(s).
• Pa rt 3 shows you how to configure basic settings on the
RX3042H to get your LAN connected to the Internet.
After setting up and configuring the device, you can follow the
instructions on page 15 to verify that it is working properly.
This Quick Start Guide assumes that you have already established
ADSL or cable modem service with your Internet service provider
(ISP). These instructions provide a basic configuration that should
be compatible with your home or small office network setup. Refer
to the subsequent chapters for additional configuration instructions.
3.1 Part 1 — Connecting the Hardware
In Part 1, you connect the device to an ADSL or a cable modem
(which in turn is connected to a phone jack or a cable outlet), the
power outlet, and your computer or network.
Warning: Before you begin, turn the power off for all
devices. These include your computer(s), your LAN
hub/ switch (if applicable), and the RX3042H.
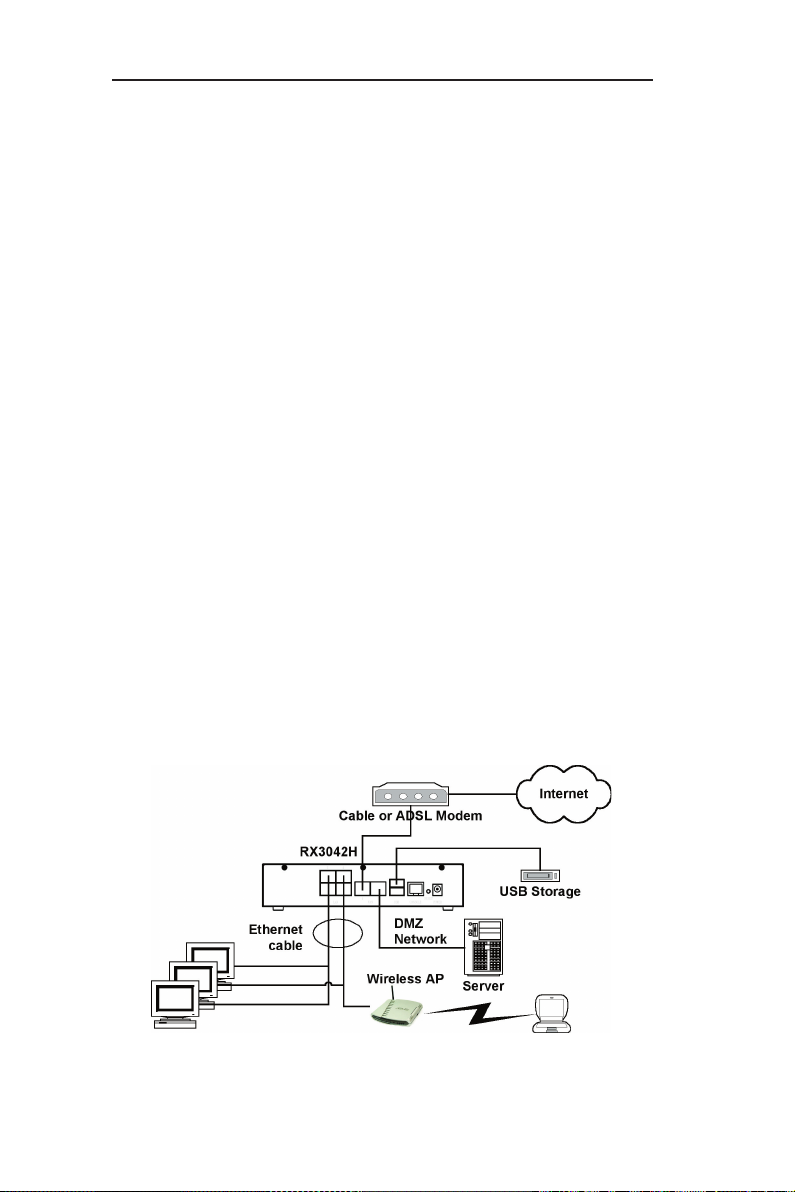
Figure 3.1 illustrates the hardware connections. Please follow the
steps that follow for specific instructions.
3.1.1 Step 1. Connect an ADSL or a cable modem
For the RX3042H: Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the
port labeled WAN on the rear panel of the device. Connect the
other end to the Ethernet port on the ADSL or cable modem.
Page 24
Quick Start Guide
RX3042H User's Manual
12
3.1.2 Step 2. Connect computers or a Network.
If your LAN h as no more than 4 computers, you can use an
Ethernet cable to connect computers directly to the built-in switch
on the device. Note that you should attach one end of the Ethernet
cable to any of the port labeled 1 – 4 on the rear panel of the router
and connect the other end to the Ethernet port of a computer.
If your LAN has more than 4 computers, you can attach one end
of an Ethernet cable to a hub or a switch (probably an uplink port;
please refer to the hub or switch documentations for instructions)
and the other to the Ethernet switch port (labeled 1 – 4) on the
RX3042H.
Note that either the crossover or straight-through Ethernet cable
can be used to connect the built-in switch and computers, hubs or
switches as the built-in switch is smart enough to make connections
with either type of cables.
3.1.3 Step 3. Attach the AC adapter.
Attach the AC adapter to the POWER input jack on the back of the
device and plug in the adapter to a wall outlet or a power strip.
3.1.4 Step 4. Power on RX3042H, the ADSL or cable
modem and power up your computers
Plug the AC adapter to the power input jack of RX3042H. Turn on
your ADSL or cable modem. Turn on and boot up your computer(s)
and/or any LAN devices such as wireless AP, hubs or switches.
Figure 3.1 Overview of Hardware Connections
Page 25
RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
13
You should verify that the LEDs are illuminated as indicated in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 LED Indicators
This LED: ...should be:
POWER Solid green to indicate that the device is turned
on. If this light is not on, check if the AC adapter is
attached to the RX3042H and if it is plugged into a
power source.
LAN LEDs Soli d gre en t o i n dica t e t hat th e dev ice ca n
communicate with your LAN or flashing when the
device is sending or receiving data to/from your
LAN computer(s).
WAN Sol i d g r een to ind icat e tha t the devic e ha s
successfully established a connection with your ISP
or flashing when the device is sending or receiving
data to/from the Internet.
If the LEDs illuminate as expected, the RX3042H is working properly.
3.2 Part 2 — Configuring Your Computers
Part 2 of the Quick Start Guide provides instructions for configuring the
network settings on your computers to work with the RX3042H.
3.2.1 Before you begin
By default, the RX3042H automatically assigns all required network
settings (e.g. IP address, DNS server IP address, default gateway
IP address) to your PCs. You need only to configure your PCs to
accept the network settings provided by the RX3042H.
Note: In some cases, you may want to configure
network settings manually to some or all of your
computers rather than allow the RX3042H to do so.
See “Assigning static IP addresses to your PCs” in
page 13 for instructions.
• If you have connected your PC via Ethernet to the RX3042H,
follow the instructions that correspond to the operating
system installed on your PC.
3.2.2 Windows® XP PCs:
Page 26

Quick Start Guide
RX3042H User's Manual
14
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <
Start
> button, and then click
Control Panel.
2. Double-click the
Network
Connections icon.
3. In the LAN or High-Speed Internet window, right-click on icon
corresponding to your network interface card (NIC) and select
Properties
. (Often this icon is labeled Local Area Connection).
The Local Area Connection dialog box displays with a list of
currently installed network items.
4. Ensure that the check box to the left of the item labeled Internet
Protocol TCP/IP is checked, and click <
Properties
> button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click
the radio button labeled
Obtain an IP address automatically
.
Also click the radio button labeled
Obtain DNS server address
automatically
.
6. Click <
OK
> button twice to confirm your changes, and close the
Control Panel.
3.2.3 Windows® 2000 PCs:
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
1.In the Windows task bar, click the <
Start
> button, point to
Settings, and then click
Control Panel
.
2. Double-click the
Network and Dial-up Connections
icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the
Local Area Connection
icon, and then select
Properties
.
The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box displays
a list of currently installed network components. If the list
includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then the protocol has
already been enabled. Skip to step 10.
4. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not display as an installed
component, click <
Install
> button.
5. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select
Protocol, and then click <
Add
> button.
6. Select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
in the Network Protocols list,
Page 27

RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
15
and then click <OK> button.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 2000
installation CD or other media. Follow the instructions to install
the files.
7. If prompted, click <
OK
> button to restart your computer with the
new settings.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP addresses assigned by
the RX3042H:
8. In the Control Panel, double-click the
Network and Dial-up
Connections
icon.
9. In Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the
Local Area Connection
icon, and then select
Properties
.
10.In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
, and then click <
Properties
>
button.
11.In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the
radio button labeled
Obtain an IP address automatically
. Also
click the radio button labeled
Obtain DNS server address
automatically
.
12.Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and
then close the Control Panel.
3.2.4 Windows® 95, 98, and ME PCs
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <
Start
> button, point to
Settings
, and then click
Control Panel
.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
In the Network dialog box, look for an entry started with “
TCP/
IP ->
” and the name of your network adapter, and then click
<
Properties
> button. You may have to scroll down the list to
find this entry. If the list includes such an entry, then the TCP/
IP protocol has already been enabled. Skip to step 8.
3. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not display as an installed
component, click <
Add
> button.
4. In the Select Network Component Type dialog box, select
Page 28

Quick Start Guide
RX3042H User's Manual
16
Protocol, and then click <
Add
> button.
5. Select Microsoft in the Manufacturers list box, and then click
TCP/IP in the Network Protocols list, box and then click <
OK
>
button.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows 95, 98
or Me installation CD or other media. Follow the instructions to
install the files.
6. If prompted, click <OK> button to restart your computer with the
new settings.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP information assigned by
the RX3042H:
7. In the Control Panel, double-click the Network icon.
8. In the Network dialog box, select an entry started with “
TCP/
IP ->
” and the name of your network adapter, and then click
<
Properties
> button.
9. In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the radio button
labeled
Obtain an IP address automatically
.
10 .In the TCP/I P Properti es di alog box , click the “
De fault
Gateway
” tab. Enter
192.168.1.1
(the default LAN port IP
address of the RX3042H) in the “
New gateway
” address field
and click <
Add
> button to add the default gateway entry.
11. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes,
and then close the Control Panel.
12. If prompted to restart your computer, click <OK> button to do
so with the new settings.
3.2.5 Windows® NT 4.0 workstations:
First, check for the IP protocol and, if necessary, install it:
1. In the Windows NT task bar, click the <
Start
> button, point to
Settings
, and then click
Control Panel
.
2. In the Control Panel window, double click the
Network
icon.
3. In the Network dialog box, click the
Protocols
tab.
The Protocols tab displays a list of currently installed network
Page 29

RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
17
protocols. If the list includes TCP/IP Protocol, then the protocol
has already been enabled. Skip to step 9.
4. If TCP/IP does not display as an installed component, click
<
Add
> button.
5. In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, select TCP/IP, and
then click <OK> button.
You may be prompted to install files from your Windows NT
installation CD or other media. Follow the instructions to install
the files.
After all files are installed, a window displays to inform you that
a TCP/IP service called DHCP can be set up to dynamically
assign IP information.
6. Click <
Yes
> button to continue, and then click <OK> button if
prompted to restart your computer.
Next, configure the PCs to accept IP addresses assigned by
the RX3042H:
7. Open the
Control Panel
window, and then double-click the
Network
icon.
8. In the Network dialog box, click the
Protocols
tab.
9. In the Protocols tab, select
TCP/IP
, and then click <
Properties
>
button.
10.In the Microsoft TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the radio
button labeled
Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server
.
11. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes,
and then close the Control Panel.
3.2.6 Assigning static IP addresses to your PCs
In some cases, you may want to assign IP addresses to some or all
of your PCs directly (often called “statically”), rather than allowing
the RX3042H to assign them. This option may be desirable (but not
required) if:
• You have obtained one or more public IP addresses that
you want to always associate with specific computers (for
example, if you are using a computer as a public web
Page 30
Quick Start Guide
RX3042H User's Manual
18
server).
• You maintain different subnets on your LAN.
However, during the first time configuration of your RX3042H, you
must assign an IP address in the 192.168.1.0 network for your
PC, say 192.168.1.2, in order to establish connection between the
RX3042H and your PC as the default LAN IP on RX3042H is preconfigured as 192.168.1.1. Enter 255.255.255.0 for the subnet
mask and 192.168.1.1 for the default gateway. These settings may
be changed later to reflect your true network environment.
On each PC to which you want to assign static information, follow
the instructions on pages 11 through 12 relating only to checking
for and/or installing the IP protocol. Once it is installed, continue to
follow the instructions for displaying each of the Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) properties. Instead of enabling dynamic assignment of the
IP addresses for the computer, DNS server, and default gateway,
click the radio buttons that enable you to enter the information
manually.
Note: Your PCs must have IP addresses that place
them in the same subnet as the RX3042Hʼs LAN
port. If you manually assign IP information to all your
LAN PCs, you can follow the instructions in Chapter
5 to change the LAN port IP address accordingly.
3.3 Part 3 — Quick Configuration of the RX3042H
In Part 3, you log into the Configuration Manager on the RX3042H
and configure basic settings for your router. Your ISP should
provide you with the necessary information to complete this step.
Note the intent here is to quickly get the RX3042H up and running,
instructions are concise. You may refer to corresponding chapters
for more details.
3.3.1 Setting Up the RX3042H
Follow these instructions to setup the RX3042H:
12.Before accessing the Configuration Manager in RX3042H, make
sure that the HTTP proxy setting is disabled in your browser. In
IE, click “Tools” -> “Internet Options...” -> “Connections” tab ->
“LAN settings...” and then uncheck “Use proxy server for your
LAN ...”
Page 31

RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
19
13.On any PC connected to one of the four LAN ports on the
RX3042H, open your Web browser, and type the following URL
in the address/location box, and press <Enter>:
http://192.168.1.1
This is the predefined IP address for the LAN port on the RX3042H.
A login screen displays, as shown in Figure 3.2.
Figure 3.2 Login Screen
If you have problem connecting to the RX3042H, you may want to
check if your PC is configured to accept IP address assignment
from the RX3042H. Another method is to set the IP address of
your PC to any IP address in the 192.168.1.0 network, such as
192.168.1.2.
14.Enter your username and password, and then click "OK" to
enter the Configuration Manager. The first time you log into this
program, use these defaults:
Default Username: admin
Default Password: admin
You can change the password at any time (see
section 10.2 Login Password and System Settings on
page 66).
The System Information page displays each time you log into the
Configuration Manager (shown in Figure 3.3).
Page 32

Quick Start Guide
RX3042H User's Manual
20
15. Follow the instructions described in Chapter 5 “Router Setup” to
set up the LAN and WAN settings for RX3042H.
After completing the basic configuration for RX3042H, read the
following section to determine if you can access the Internet.
3.3.2 Testing Your Setup
At this point, the RX3042H should enable any computers on your
LAN to use the RX3042Hʼs ADSL or cable modem connection to
access the Internet.
To test the Internet connection, open your web browser, and type
the URL of any external website (such as
http://www.asus.com
).
The LED labeled WAN should be blinking rapidly and may appear
solid as the device connects to the site. You should also be able to
browse the web site through your web browser.
Figure 3.3 System Status Page
Page 33

RX3042H User's Manual
Quick Start Guide
21
If the LEDs do not illuminate as expected or the web page does not
display, see Appendix 12 for troubleshooting suggestions.
3.3.3 Default Router Settings
In addition t o handling the DSL connection t o your ISP, the
RX3042H can provide a variety of services to your network. The
device is pre-configured with default settings for use with a typical
home or small office network.
Table 3.2 lists some of the most important default settings; these
and other features are described fully in the subsequent chapters.
If you are familiar with network configuration settings, review the
settings in Table 3.2 to verify that they meet the needs of your
network. Follow the instructions to change them if necessary. If
you are unfamiliar with these settings, try using the device without
modification, or contact your ISP for assistance.
Before you modifying any settings, review Chapter 4 for general
information about accessing and using the Configuration Manager
program. We strongly recommend that you contact your ISP prior to
changing the default configuration.
Table 3.2 Default Settings Summary
Option Default
Setting
Explanation/Instruction
DHCP
(Dynamic Host
Configuration
Protocol)
DHCP server
enabled with
the following
pool of
addresses:
192.168.1.100
through
192.168.1.200
The RX3042H maintains a
pool of private IP addresses for
dynamic assignment to your LAN
computers. To use this service,
you must have set up your
computers to accept IP information
dynamically, as described in Part
2 of the Quick Start Guide. See
section 6.1 for an explanation of
the DHCP service.
LAN Port IP
Address
Static IP
address:
192.168.1.1
subnet mask:
255.255.255.0
This is the IP address of the
LAN port on the RX3042H. The
LAN port connects the device to
your Ethernet network. Typically,
you will not need to change this
address. See section 5.1 LAN
Configuration LAN IP Address
for instructions.
Page 34

Page 35

RX3042H User's Manual
Using the Configuration Manager
23
4 Using the Configuration Manager
The RX 3042 H i ncl udes a pr ein sta l led pro gra m c alle d t he
Configuration Manager, which provides an interface to the software
installed on the device. It enables you to configure the device
settings to meet the needs of your network. You access it through
your web browser from any PC connected to the RX3042H via the
LAN or the WAN ports.
Thi s chapt e r d e s crib e s t h e g e n eral gu ides for u s ing th e
Configuration Manager.
4.1 Log into the Configuration Manager
Th e Confi gurat ion Man ager progr am is p reins talle d on th e
RX3042H. To access the program, you need the following:
• A computer connected to the LAN or WAN port on the RX3042H
as described in the Quick Start Guide chapter.
• A web browser installed on the computer. The program is
designed to work best with Microsoft Internet Explorer® 6.0 or
later.
You may access the program from any computer connected to the
RX3042H via the LAN or WAN ports. However, the instructions
provided here are for computers connected via the LAN ports.
1. From a LAN computer, open yo ur web browser, type the
following in the web address (or location) box, and press
<Enter>:
http://192.168.1.1
This is the pred ef ined IP address for the LAN p ort on the
RX3042H. A login screen displays, as shown in Figure 4.1.
Page 36

Using the Configuration Manager
RX3042H User's Manual
24
Figure 4.1 Configuration Manager Login Screen
2. Enter your username and password, and then click .
The first time you log into the program, use these defaults:
Default Username: admin
Default Password: admin
Note: You can change the password at any time (see
section 10.2 Login Password and System Settings on
page 66).
The System Information page displays every time you log into the
Configuration Manager (shown in Figure 4.3 on page 20).
4.2 Functional Layout
Typical Typical Configuration page consists of several elements
– banner, menu, menu navigation tips, configuration, and on-line
help. You can click on any menu item to expand/contract any menu
groups or to access a specific configuration page. The configuration
pane is where you interact with the Configuration Manager to
configure the settings for RX3042H. Menu navigation tips show how
the current configuration can be accessed via the menus.
Page 37

RX3042H User's Manual
Using the Confi guration Manager
25
Figure 4.2 Typical Confi guration Manager Page
4.2.1 Menu Navigation
• To expand a group of related menus, double click the menu or the icon:
• To contract a group of related menus, double click the menu or the icon:
• To open a specifi c confi guration page, double click the menu or the icon:
4.2.2 Commonly Used Buttons and Icons
The following buttons or icons are used throughout the application.
The following table describes the function for each button or icon.
Table 4.1 Description of Commonly Used Bottons and Icons
Button Function
Stores any changes you have made on the current page.
Adds the existing confi guration to the system, e.g. a
static route or a fi rewall ACL rule and etc.
Modifi es the existing confi guration in the system, e.g.
a static route or a fi rewall ACL rule and etc.
Redisplays the current page with updated statistics
or settings.
Selects the item for editing.
Deletes the selected item.
Page 38

Using the Configuration Manager
RX3042H User's Manual
26
4.3 Overview of System Configuration
To view the overall system configuration, log into the Configuration
Manager, or click the Status menu if you have already logged on.
Figure 4.3 shows sample information available in the System Status
page.
Figure 4.3 System Status Page
Page 39

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
27
5 Router Setup
This chapter describes how to configure the basic settings for your
router so that the computers on your LAN can communicate with
each other and have access to the Internet. Network setup consists
of LAN and WAN configurations.
5.1 LAN Configuration
5.1.1 LAN IP Address
If you are using RX3042H with multiple PCs on your LAN, you
must co nnect your LAN to the Ethernet ports on the built-i n
Ethernet switch. You must assign a unique IP address to each
device residing on your LAN. The LAN IP address that identifies
the RX3042H as a node on your network must be in the same
subnet as the PCs on your LAN. The default LAN IP address for the
RX3042H is 192.168.1.1.
Definition: A network node can be thought of as any
interface where a device connects to the network,
such as the RX3042Hʼs LAN port and the network
interface cards on your PCs. See Appendix 11 for an
explanation of subnets.
You can change the default IP address to reflect the true IP address
that you want to use with your network.
5.1.2 LAN Configuration Parameters
Table 5.1 describes the configuration parameters available for LAN
IP configuration.
Page 40

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
28
Table 5.1 LAN Configuration Parameters
Settings Description
Host Name For identification only.
IP Address The LAN IP address of the RX3042H. This IP
address is used by your computers to identify
the RX3042Hʼs LAN port. Note that the public IP
address assigned to you by your ISP is not your
LAN IP address. The public IP address identifies
the WAN port on the RX3042H to the Internet.
Subnet Mask The LAN subnet mask identifies which parts of
the LAN IP Address refer to your network as a
whole and which parts refer specifically to nodes
on the network. Your device is preconfigured with
a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
5.1.3 Configuring the LAN IP Address
Follow these steps to change the default LAN IP address.
1. Open the Connection configuration page, as shown in Figure 5.1
by clicking the
Router Setup -> Connection
menu.
Figure 5.1 Network Setup Configuration- LAN Configuration
2. (Optional) Enter the host name for RX3042H. Note that host
name is used for identification only and is not used for any other
purpose.
3. Enter the LAN IP address and subnet mask for the RX3042H in
the space provided.
4. Proceed to the WAN Configuration section for instructions on
setting up the WAN port if you have not yet done so.
Page 41

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
29
5. Click "
Apply
" to save the settings. If you were using an Ethernet
connection for the current session, and changed the IP address
or subnet mask, the connection will be terminated.
6. You will see the following message displayed as shown below.
7. You will be prompted to log back into the Configuration Manager
once the timer elapses.
5.2 WAN/DMZ Configuration
This section describes how to configure WAN/DMZ settings for the
WAN interface on the RX3042H that communicates with your ISP.
Youʼll learn to configure IP address, DHCP and DNS server for your
WAN in this section.
DMZ (short for demilitarized zone) is a host or a small network that
sits between a trusted internal network, such as a corporate private
LAN, and an untrusted external network, such as the Internet.
Typically, the DMZ contains devices accessible to the Internet
traffic, such as Web servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers
and DNS servers. The DMZ contains no corporate confidential
information. In the event that the DMZ is compromised, no other
company information will be exposed.
Note: Only static IP connection mode is supported for DMZ.
5.2.1 WAN Connection Mode
Five modes of WAN connection are supported by the RX3042H –
static IP, dynamic IP, PPPoE (multi-session), PPPoE unnumbered,
and PPTP. You may select one of the WAN connection modes
required by your ISP from the Connection Mode drop-down list in
Network Setup Configuration page as shown in Figure 5.2.
Page 42

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
30
Figure 5.2 Network Setup Configuration Page-WAN Configuration
5.2.2 PPPoE
PPPoE connection is most often used by ADSL service providers.
Figure 5.3. WAN – PPPoE Configuration
Page 43

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
31
5.2.2.1 WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters
Table 5.2 describes the configuration parameters available for
PPPoE connection mode.
Table 5.2. WAN PPPoE Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Link Select a port to configure. Available options are
WAN1, WAN2 or DMZ.
Connection
Mode
Select PPPoE from the connection mode drop-down list.
PPPoE
Session
Select the PPPoE session ID for this PPPoE
session. Note that only two simultaneous PPPoE
sessions are supported.
Enable Check or uncheck this box to activate or de-activate
this PPPoE session.
User
Name and
Password
Enter the username and password you use to log into
your ISP. (Note: this is different from the information you
used to log into Configuration Manager.)
Service
Name
Enter the service name provided by your ISP. Service
name is optional but may be required by some ISP.
AC Name Enter the access concentrator name provided by
your ISP. Access concentrator name is optional but
may be required by some ISPs.
IP Address If your ISP allows you to always obtain the same IP
address for your WAN, enter it here.
Primary /
Secondary
DNS
Server
IP address of the primary and/or secondary DNS
are optional as PPPoE will automatically detect the
DNS IP addresses configured at your ISP. However,
if there are other DNS servers you would rather use,
enter the IP addresses here.
MTU You may specify the maximum size of the transmitted
packet. For PPPoE, the range of MTU is from 546 to
1492. The default value is 1492.
Disconnect
after idle
(min.)
Enter the inactivity timeout period at which you want
to disconnect the Internet connection when there
is no traffic. A value of 0 means no activity time
out. Note that SNTP service may interfere with this
function if there are activities from the service.
Page 44

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
32
Setting Description
Connect on
Demand
Click on the Enable or Disable radio button to enable
or disable this option.
Status On: PPPoE connection is active.
Off: No PPPoE connection is active.
Connecting: RX3042H is trying to connect to your
ISP using PPPoE connection mode.
Manual
Disconnect/
Connect
Click the Disconnect or Connect button to disconnect
or connect using the PPPoE connection mode.
5.2.2.2 Configuring PPPoE for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure PPPoE settings:
1. Open the Network Setup configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup -> Connection
menu.
2. Select which WAN port (WAN1/WAN2) to configure for PPPoE
connection mode.
3. Select
PPPoE
from the WAN Connection Mode drop-down list
as shown in Figure 5.3.
4. Select
PPPoE session ID
from the PPPoE session ID dropdown list. Currently, two sessions are supported for each WAN
port.
5. Enter the service name if required by your ISP.
6. (Optional) Enter the service name and/or AC name if required by
your ISP.
7. (Optional) If your ISP allows you to always obtain the same IP
address for your WAN, enter it in the IP Address field; otherwise,
skip this step.
8. (Optional) Enter the IP ad dresses for the primary and/or
secondary DNS servers if you want to use your preferred DNS
servers; otherwise, skip this step.
9. (Opt ional) Change the MTU value if ne cessary. If you do
not know what value to enter, leave it as is. For dynamic IP
Page 45

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
33
Figure 5.4. WAN – PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration
connection mode, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1492. The
default value is 1492.
10.Enter appropriate connection settings for “
Disconnect after
Idle (min)
” and “
Connect on Demand
”.
11.Click "
Apply
" to save the settings.
5.2.3 PPPoE Unnumbered
Some of the ADSL service providers may offer PPPoE unnumbered
service. Choose this connection mode if your ISP provides such
service.
Page 46

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
34
5.2.3.1 WAN PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration Parameters
Table 5.3 describes the configuration parameters available for
PPPoE Unnumbered connection mode.
Table 5.3. WAN PPPoE Unnumbered Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Link Select a port to configure. Available options are
WAN1, WAN2 or DMZ.
Connection
Mode
Select PPPoE Unnumbered from the connection
mode drop-down list. Traditionally, each network
interface must have a unique IP address. However,
an unnumbered interface does not have to have a
unique IP address. This means that when this option
is selected, the WAN and the LAN use the same IP
address. Network resources are therefore conserved
because fewer network IP addresses are used and
routing table is smaller.
Enable NAPT Check or uncheck this box to enable NAPT for
this connection.
User Name
and Password
Enter the username and password you use to log into
your ISP. (Note: this is different from the information
you used to log into Configuration Manager.)
Service Name Enter the service name provided by your ISP. Service
name is optional but may be required by some ISPs.
AC Name Enter the access concentrator name provided by
your ISP. Access concentrator name is optional
but may be required by some ISPs.
IP Address Enter a static IP address here for the PPPoE
unnumbered connection. This IP address must be
provided by your service provider.
Unnumbered
Network
Address
Enter the network address provided by your ISP.
Primary /
Secondary
DNS Server
IP address of the primary and/or secondary DNS
are optional as PPPoE will automatically detect
the DNS IP addresses configured at your ISP.
However, if there are other DNS servers you
would rather use, enter the IP addresses here.
Page 47

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
35
Setting Description
MTU You may specify the maximum size of the
transmitted packet. For PPPoE, the range of MTU
is from 546 to 1492. The default value is 1492.
Disconnect
after Idle
(min.)
Enter the inactivity timeout period at which you
want to disconnect the Internet connection when
there is no traffic. A value of 0 means no activity
time out. Note that SNTP service may interfere
with this function if there are activities from the
service.
Connect on
Demand
Click on the Enable or Disable radio button to
enable or disable this option.
Status On: PPPoE unnumbered connection is active.
Off: No PPPoE unnumbered connection is active.
Connecting: RX3042H is trying to connect to your
ISP using PPPoE unnumbered connection mode.
Manual
Disconnect/
Connect
Click the Disconnect or Connect button to
disconnect or connect using the PPPoE
unnumbered connection mode.
5.2.3.2 Configuring PPPoE Unnumbered for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure PPPoE unnumbered
settings:
1. Open the Network Setup configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup -> Connection
menu.
2. Select which WAN port (WAN1/WAN2) to configure for PPPoE
unnumbered connection mode.
3. Select
PPPoE Unnumbered
from the WAN Connection Mode
drop-down list as shown in Figure 5.4.
4. Check
NAPT
box if NAT is to be used for this connection.
5. Enter user name and password provided by your ISP
6. (Optional) Enter the service name and/or AC name if required by
your ISP.
7. Enter the IP address, unnumbered network address, and
unnumbered netmask provided by your ISP.
8. (Optional) Enter the IP ad dresses for the p ri ma ry and/or
Page 48

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
36
Figure 5.5. WAN – Dynamic IP (DHCP client) Configuration
5.2.4.1 Configuring Dynamic IP for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure dynamic IP settings:
1. Open the
Network Setup
configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup -> Connection
menu.
2. Select which WAN port (WAN1/WAN2) to configure for
dynamic connection mode.
3. Select
Dynamic
from the Connection Mode drop-down list as
shown in Figure 5.5. Note that the IP addresses for the primary
and/or the secondary DNS servers are automatically assigned
secondary DNS servers if you want to use your preferred DNS
servers; otherwise, skip this step.
9. (Opt ional) Change the MTU value if ne cessary. If you do
not know what value to enter, leave it as is. For dynamic IP
connection mode, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1492. The
default value is 1492.
10.Enter appropriate connection settings for
Disconnect after Idle
(min)
and
Connect on Demand
.
11.Click
Apply
to save the settings.
5.2.4 Dynamic IP
Dynamic IP is most often used by the cable modem service
providers.
Page 49

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
37
by the DHCP server of your ISP.
4. (Opt ional) Change the MTU value if ne cessary. If you do
not know what value to enter, leave it as is. For dynamic IP
connection mode, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1500. The
default value is 1500.
5. Click
Apply
"to save the settings.
5.2.5 Static IP
Figure 5.6. WAN – Static IP Configuration
5.2.5.1 WAN or DMZ Static IP Configuration Parameters
Table 5.4 describes the configuration parameters available for static
IP connection mode.
Table 5.4. WAN Static IP Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Link
Select a port to configure. Available options are
WAN1/WAN2 or WAN/DMZ.
Connection
Mode
Select Static from the connection mode dropdown list.
IP Address
WAN IP address provided by your ISP. For
DMZ mode, typically, it is a private IP address.
Page 50

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
38
Setting Description
Subnet Mask
WAN subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Typically, it is set as 255.255.255.0.
Gateway
Address
Gateway IP address provided by your ISP. It
must be in the same subnet as the WAN on the
RX3042H.
Primary/
Secondary DNS
Server
You must at least enter the IP address of the
primary DNS server. Secondary DNS server is
optional
MTU
You may specify the maximum size of the
transmitted packet. For static IP connection, the
range of MTU is from 546 to 1500. The default
value is 1500.
5.2.5.2 Configuring Static IP for WAN or DMZ
Follow the instructions below to configure static IP settings:
1. Open the
Network Setup
configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup -> Connection
menu.
2. Select which WAN port (WAN1/WAN2) or DMZ port to configure
for static connection mode.
3. Select
Static
from the Connection Mode drop-down list as
shown in Figure 5.6.
4. Enter WAN IP address in the IP Address field. This information
should be provided by your ISP.
5. Enter Subnet Mask for the WAN. This information should be
provided by your ISP. Typically, it is 255.255.255.0.
6. Enter gateway address provided by your ISP in the space
provided.
7. Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server. This information
should be provided by your ISP. Secondary and third DNS
servers are optional.
8. (Opt ional) Change the MTU value if ne cessary. If you do
not know what value to enter, leave it as is. For dynamic IP
connection mode, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1500. The
default value is 1500.
Page 51

RX3042H User's Manual
Router Setup
39
9. Click
Apply
to save the settings
5.2.6 PPTP
Some of the service providers require user to login using PPTP
connection.
5.2.6.1 WAN PPTP Configuration Parameters
Table 5.5 describes the configuration parameters available for
PPTP connection mode.
Table 5.5. WAN PPTP Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Link
Select a port to configure. Available options are WAN1,
WAN2 or DMZ.
Connection
Mode
Select PPTP from the connection mode drop-down list.
WAN
Interface IP
Select how WAN IP address is to be configured – static
(manually set the IP address) o r dynamic (obtained
automatically from the DHCP server).
Static
Choose this connection mode if the WAN IP is a fixed IP
provided by your ISP.
IP Address
Enter the WAN IP address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask
Enter the subnet mask for the WAN IP provided by your ISP.
Gateway
Address
Enter the gateway IP address for the WAN provided by your
ISP.
Dynamic
(DHCP)
Select this connection mode if your WAN IP address is
obtained automatically from your ISPʼs DHCP server.
User
Name and
Password
Enter the username and password you use to log into your
ISP. (Note: this is different from the information you used to
log into Configuration Manager.)
Server IP
Address
Enter the PPTP server IP address provided by your ISP.
MTU
You may specify the maximum size of the transmitted packet.
For PPTP, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1460. The default
value is 1460.
MPPE
MPPE stands for Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption
protocol. Check this box, if the packet is to be encrypted w/
this protocol.
Page 52

Router Setup
RX3042H User's Manual
40
Setting Description
Connect on
Demand
Click on the Enable or Disable radio button to enable or
disable this option.
Disconnect
after Idle
(min)
Enter the inactivity timeout period at which you want to
disconnect the Internet connection when there is no traffic. A
value of 0 means no activity time out. Note that SNTP service
may interfere with this function if there are activities from the
service.
Status
On: PPTP connection is active.
Off: No PPTP connection is active.
Connecting: RX3042H is trying to connect to your ISP using
PPTP connection mode.
Manual
Disconnect/
Connect
Click the Disconnect or Connect button to disconnect or
connect using the PPTP connection mode.
Figure 5.7. WAN – PPTP Configuration
Page 53

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Configuration
41
5.2.6.2 Configuring PPTP for WAN
Follow the instructions below to configure PPTP settings:
1. Open the Network Setup configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup ->Connection
menu.
2. Select which WAN port (WAN1/WAN2) to configure for PPTP
connection mode.
3. Select
PPTP
from the
WAN Connection Mode
drop-down list
as shown in Figure 5.7.
4. Select how WAN IP is to be obtained – static or dynamic. If
your ISP provides a fixed IP address, select
Static
in the WAN
Interface IP drop-down list. Consult with your ISP if you have no
idea.
5. Enter IP address, subnet mask and gateway IP address for your
WAN if your WAN IP is to be set manually.
6. Enter user name and password provided by your ISP.
7. Enter PPTP server IP address provided by your ISP.
8. (Optional) Change the MTU value if necessary. If you do not
know what value to enter, leave it as is. For PPTP connection
mode, the range of MTU is from 546 to 1460. The default value
is 1460.
9. Check MPPE box if the packet is to be encrypted with this
protocol.
10.Enter appropriate connection settings for
Disconnect after Idle
(min)
and
Connect on Demand
.
11.Click
Apply
to save the settings.
5.3 WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up
RX3042H supports load balancing and line back up on the WAN
connection. This function is available only when “Dual-WAN” is
selected in the Router Connection configuration page (accessible
by clicking the Router Setup ->Connection menu).
WAN load balancing distributes communication activities across
the two WANs on RX3042H based on the preconfigured bandwidth
Page 54

DHCP Server Configuration
RX3042H User's Manual
42
requirement on the WANs. Another feature supported is fail-over
for the WAN ports. If one of the WAN links is down, RX3042H will
direct the traffic destined for the downed WAN port to the still active
WAN port.
The line back up function is another feature supported to ensure
uninterrupted Internet access. When the primary WAN link is down,
the Internet access is automatically switched to the backup WAN
link.
5.3.1 WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up
Configuration Parameters
Table 5.6 describes the configuration parameters available for WAN
load balancing and line back up.
Table 5.6. WAN Load Balancing and Line Back Up
Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Load Balance
Select one of the three available options:
Disable: disable both the WAN load balancing and line
back up functionalities.
Auto Mode: select this option if load balancing is desired.
The algorithm used for the load balancing is weighted
round robin.
Line Backup: select this option if line backup is needed. In
the existing implementation, the primary link is always set
to WAN1 and the backup link is always set to WAN2.
WAN1/WAN2
Bandwidth
Enter the ratio of the traffic amount that you want to
distribute between the WANs. The number should be
between 0 to 100%. For example, 80% for WAN1 and 20%
for WAN2 means 80% of the traffic is directed to WAN1
and 20% of the traffic is directed to WAN2.
Connectivity
Check
Click Enable or Disable radio button to enable or disable
this feature. Connectivity check is used to monitor the
link status for the WAN ports. If this option is disabled,
RX3042H will not perform fail-over; this means that if
one of the WAN links is down, the traffic directed to the
downed link will not be re-directed to the active link. It is
recommended that you keep this option enabled. However,
if the gateway or the specific network device that will be
checked for connectivity does not respond to ping, you
Page 55

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Configuration
43
Setting Description
Connectivity
Check (Cont.)
will need to disable this feature. Otherwise, RX3042H will
make incorrect judgment regarding the WAN link status
and thus affect the behavior of the load balancing or line
back up.
Connectivity
Check Interval
The interval that RX3042H will check for the WAN link
status. The allowable value is 1 to 60 seconds.
Connectivity
Check IP
Address
(WAN1)
Enter the IP address of the specific network device that
the traffic will pass through. This field is optional. Normally,
you donʼt need to provide any IP address here, unless you
know the traffic must pass a specific network device.
Connectivity
Check IP
Address
(WAN2)
Enter the IP address of the specific network device that
the traffic will pass through. This field is optional. Normally,
you donʼt need to provide any IP address here, unless you
know the traffic must pass a specific network device.
5.3.2 Setting Up WAN Load Balancing and Line
Back Up
Figure 5.8. Load Balancing Configuration
Page 56

DHCP Server Configuration
RX3042H User's Manual
44
Follow the instructions below to set up WAN load balancing:
1. Open the Load Balancing configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup ->Load Balance
menu.
2. Select
Auto Mode
in the Load Balance field.
3. Enter the ratio of the traffic amount that you want to distribute
between the two WANs. The allowable value is from 0 to 100%.
The sum of the two numbers is 100%.
4. Select whether you need to enable or disable connectivity
check. If this option is enabled, please also enter the following:
a) Enter the connectivity check interval.
b) (Optional) Enter the connectivity check IP address for WAN1
and/or WAN2.
5. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
5.3.3 Setting Up WAN Line Back Up
Follow the instructions below to set up line backup:
1. Open the Load Balancing configuration page by clicking the
Router Setup ->Load Balance
menu.
2. Select “
Line Backup
” in the Load Balance field.
3. Select whether you need to enable or disable connectivity
check. If this option is enabled, please also enter the following:
a) Enter the connectivity check interval.
b) (Optional) Enter the connectivity check IP address for WAN1
and/or WAN2.
4. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
Page 57

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Configuration
45
6 DHCP Server Configuration
6.1 DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol)
6.1.1 What is DHCP?
DHCP is a protocol that enables network administrators to centrally
manage the assignment and distribution of IP information to
computers on a network.
When you enable DHCP on a network, you allow a device — such
as the RX3042H — to assign temporary IP addresses to your
computers whenever they connect to your network. The assigning
device is called a DHCP server, and the receiving device is a DHCP
client.
Note: If you followed the Quick Start Guide instructions,
you either configured each LAN PC with an IP address,
or you specified that it will receive IP information
dynamically (automatically). If you chose to have the
information assigned dynamically, then you configured
your PCs as DHCP clients that will accept IP addresses
assigned from a DCHP server such as the RX3042H.
The DHCP server draws from a defined pool of IP addresses and
“leases” them for a specified amount of time to your computers
when they request an Internet session. It monitors, collects, and
redistributes the addresses as needed.
On a DHCP-enabled network, the IP information is assigned
dynamically rather than statically. A DHCP client can be assigned
a different address from the pool each time it reconnects to the
network.
6.1.2 Why use DHCP?
DHCP allows you to manage and distribute IP addresses throughout
your network from the RX3042H. Without DHCP, you would have
to configure each computer separately with IP address and related
information. DHCP is commonly used with large networks and
those that are frequently expanded or otherwise updated.
Page 58

DHCP Server Configuration
RX3042H User's Manual
46
6.1.3 Configuring DHCP Server
Note: By default, the RX3042H is configured as a
DHCP server on the LAN side, with a predefined IP
address pool of 192.168.1.100 through 192.168.1.149
(subnet mask 255.255.255.0). To change this range
of addresses, follow the procedures described in this
section.
First, you must configure your PCs to accept DHCP information
assigned by a DHCP server:
1. Open the DHCP Server Configuration page, shown in Figure 6.1,
by clicking Advanced -> DHCP Server menu.
Figure 6.1. DHCP Server Configuration Page
2. Enter the information for the IP Address Pool (Begin/End
Address), Subnet Mask, Lease Time and Default Gateway IP
Address, fields; others, such as Primary/Secondary DNS Server
IP Address and Primary/Secondary WINS Server IP Address are
optional. However, it is recommended that you enter the primary
DNS server IP address in the space provided. You may enter
the LAN IP or your ISPʼs DNS IP in the primary DNS Server
IP Address field. Table 6.1 describes the DHCP configuration
parameters in detail.
Page 59

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Configuration
47
Table 6.1. DHCP Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Enable Check or uncheck this box to enable or disable
DHCP server service for your LAN.
IP Address
Pool Begin/
End
Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the
DHCP address pool.
Lease Time The amount of time in seconds the assigned
address will be used by a device connected on the
LAN.
Default
Gateway IP
Address
The address of the default gateway for computers
that receive IP addresses from this pool. The
default gateway is the device that the DHCP client
computers first contacted to communicate with the
Internet. Typically, it is the RX3042Hʼs LAN port IP
address.
Primary/
Secondary
DNS Server
IP Address
The IP address of the Domain Name System server
to be used by computers that receive IP addresses
from this pool. The DNS server translates common
Internet names that you type into your web browser
into their equivalent numeric IP addresses. Typically,
the server(s) are located with your ISP. However,
you may enter LAN IP address of the RX3042H as
it will serve as DNS proxy for the LAN computers
and forward the DNS request from the LAN to
DNS servers and relay the results back to the
LAN computers. Note that both the primary and
secondary DNS servers are optional.
Primary/
Secondary
WINS Server
IP Address
(optional)
The IP address of the WINS servers to be used
by computers that receive IP addresses from the
DHCP IP address pool. You donʼt need to enter
this information unless your network has WINS
servers.
3. Click
Apply
to save the DHCP server configurations.
Page 60

DHCP Server Configuration
RX3042H User's Manual
48
6.1.4 Viewing Current DHCP Address Assignments
When the RX3042H functions as a DHCP server for your LAN, it
keeps a record of any addresses it has leased to your computers.
To view a table of all current IP address assignments, just open
the DHCP Server Configuration page and click on the link “Current
DHCP Lease Table” located at the bottom of the configuration page.
A page displays similar to that shown in Figure 6.2.
The DHCP lease table lists any IP addresses leased and the
corresponding MAC addresses.
Figure 6.2. DHCP Lease Table
6.1.5 Fixed DHCP Lease
Fixed DHCP lease is used in situation when a fixed DHCP address
is desired for a host that gets IP from the DHCP server. First, you
should configure your PCs to accept DHCP information assigned
by a DHCP server:
6.1.5.1
Access Fixed DHCP Configuration Page – (Advanced
->DHCP Server)
Open the Fixed DHCP Lease configuration page, as shown in
Figure 6.3, by clicking Advanced ->DHCP Server menu.
Note that when you open the Fixed DHCP Lease configuration
page, a list of existing lease is also displayed at the bottom half of
the configuration page such as those shown in Figure 6.3.
Page 61

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Confi guration
49
Figure 6.3. Fixed DHCP Lease Confi guration Page
6.1.5.2 Add a Fixed DHCP Lease
To add a fi xed DHCP lease, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Fixed DHCP Lease confi guration page, as shown in
Figure 6.3, by clicking Advanced ->DHCP Server menu.
2. Enter the MAC address and the desired IP address of the host
requiring a fi xed IP address. Table 6.2 describes the fi xed DHCP
lease confi guration parameters in detail.
Table 6.2. Fixed DHCP Lease Confi guration Parameters
Field Description
Fixed DHCP Lease
MAC
A hardware ID of the device that needs a fi xed
IP address from the DHCP server.
Fixed DHCP Lease
IP
The IP address leased from the DHCP server.
Note that it is recommended that this IP
address be outside of the DHCP IP pool.
3. Click on the
Add
button to add the new fi xed DHCP lease entry.
6.1.5.3 Delete a Fixed DHCP Lease
To delete a fixed DHCP lease, click on the in front of the
specifi c fi xed DHCP lease to be deleted.
6.1.5.4 Viewing Fixed DHCP Lease Table
To see existing inbound fixed DHCP lease, just open the Fixed
Page 62

DHCP Server Configuration
RX3042H User's Manual
50
DHCP Lease configuration page by clicking Advanced ->DHCP
Server menu
6.2 DNS
6.2.1 About DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) servers map the user-friendly domain
names that users type into their Web browsers (e.g., “yahoo.com”)
to the equivalent numerical IP addresses that are used for Internet
routing.
When a PC user types a domain name into a browser, the PC must
first send a request to a DNS server to obtain the equivalent IP
address. The DNS server will attempt to look up the domain name
in its own database, and will communicate with higher-level DNS
servers when the name cannot be found locally. When the address
is found, it is sent back to the requesting PC and is referenced in IP
packets for the remainder of the communication.
6.2.2 Assigning DNS Addresses
Multiple DNS addresses are useful to provide alternatives when
one of the servers is down or is encountering heavy traffic. ISPs
typically provide primary and secondary DNS addresses, and may
provide additional addresses. Your LAN PCs learn these DNS
addresses in one of the following ways:
• Statically: If your ISP provides you with their DNS server
addresses, you can assign them to each PC by modifying the
PCsʼ IP properties.
• Dynamically from a DHCP Server: You can configure the DNS
addresses in the DHCP server in the RX3042H and allow the
DHCP server to distribute the DNS addresses to the PCs. Refer
to the section 6.1.3 “Configuring DHCP Server” for instructions
on configuring DHCP server.
In either case, you can specify the actual addresses of the ISPʼs
DNS servers (on the PC or in the DHCP Server configuration page),
or you can specify the address of the LAN port on the RX3042H
(e.g., 192.168.1.1). When you specify the LAN port IP address, the
device performs DNS relay, as described in the following section.
Page 63

RX3042H User's Manual
DHCP Server Configuration
51
Note: If you specify the actual DNS addresses on the
PCs or in the DHCP pool, the DNS relay feature is not
used.
6.2.3 Configuring DNS Relay
When you specify the deviceʼs LAN port IP address as the DNS
address, then the Internet Security Router automatically performs
“DNS relay”; i.e., because the device itself is not a DNS server, it
forwards domain name lookup requests from the LAN PCs to a
DNS server at the ISP. It then relays the DNS serverʼs response to
the PC.
When performing DNS relay, the RX3042H must maintain the
IP addresses of the DNS servers it contacts. It can learn these
addresses in either or both of the following ways:
• Learned through PPPoE or Dynamic IP Connection: If the
RX3042H uses a PPPoE (see section 5.2.2 PPPoE or 5.2.3
PP PoE U nnumb ere d) or Dynami c IP (se e sec tion 5.2.4
Dynamic IP) connection to the ISP, the primary and secondary
DNS addresses can be learned via the PPPoE protocol. Using
this option provides the advantage that you will not need to
reconfigure the PCs or the RX3042H if the ISP changes their
DNS addresses.
• Configured on the RX3042H: You can also specify the ISPʼs
DNS addresses in the WAN configuration page as shown in
Figure 5.3, Figure 5.4 or Figure 5.5 or Figure 5.6.
Follow these steps to configure DNS relay:
1. Enter LAN IP in the DNS Server IP Address field in DHCP
configuration page as shown in Figure 6.1.
2. Configure the LAN PCs to use the IP addresses assigned by
the DHCP server on the Internet Security Router, or enter the
Internet Security Routerʼs LAN IP address as their DNS server
address manually for each PC on your LAN.
Note: DNS addresses that are assigned to LAN PCs
prior to enabling DNS relay will remain in effect until
the PC is rebooted. DNS relay will only take effect
when a PCʼs DNS address is the LAN IP address.
Similarly, if after enabling DNS relay, you specify a
Page 64

Routing
RX3042H User's Manual
52
DNS address (other than the LAN IP address) in a
DHCP pool or statically on a PC, then that address
will be used instead of the DNS relay address.
Page 65

RX3042H User's Manual
Routing
53
7 Routing
You can use Configuration Manager to define specific routes
for your Internet and network data communication. This chapter
describes basic routing concepts and provides instructions for
creating static routes. Note that most users do not need to define
static routes.
7.1 Overview of IP Routes
The essential challenge of a router is: when it receives data
intended for a particular destination, which next device should it
send that data to? When you define IP routes, you provide the rules
that the RX3042H uses to make these decisions.
7.1.1 Do I need to define static routes?
Most users do not need to define static routes. On a typical small
home or office network, the existing routes that set up the default
gateways for your LAN computers and for the RX3042H provide the
most appropriate path for all your Internet traffic.
• On your LAN computers, a default gateway directs all Internet
traffic to the LAN port on the RX3042H. Your LAN computers
know their default gateway either because you assigned it to
them when you modified their TCP/IP properties, or because
you configured them to receive the information dynamically from
a server whenever they access the Internet. (Each of these
processes is described in the Quick Start Guide instructions,
Part 2.)
• On the RX3042H itself, a default gateway is defined to direct
all outbound Internet traffic to a router at your ISP. This default
gateway is assigned automatically by your ISP whenever the
device negotiates an Internet connection. (The process for
adding a default route is described in section 7.3.2 Adding Static
Routes.)
You may need to define static routes if your home setup includes
two or more networks or subnets, if you connect to two or more ISP
services, or if you connect to a remote corporate LAN.
Page 66

Routing
RX3042H User's Manual
54
7.2 Dynamic Routing using RIP (Routing
Information Protocol)
RIP enables routing information exchange between routers; thus,
routes are updated automatically without human intervention.
It is recommended that you enable RIP in the System Services
Configuration Page as shown in Figure 10.1.
Figure 7.1. RIP Configuration Page
7.2.1 RIP Configuration Parameters
The following table defines the available configuration parameters
for static routing configuration.
Table 7.1. Static Route Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Interface
Select an interface through which the routing
information is exchanged. Available options are
LAN, WAN1, WAN2, PPPoE1, PPPoE2, PPPoE3
and PPPoE4.
RIP
Click the “Enable” or “Disable” radio button to
enable or disable “RIP” for the interface selected.
Note that you must enable RIP service first in the
Management / System Services configuration
page first.
Page 67

RX3042H User's Manual
Routing
55
Field Description
Passive Mode
Enable this mode if RIP configured for this interface
will only receive routing information from other
routers and not send routing information to other
routers. Disable this mode if you want this interface
to send and receive routing information to/from
other routers.
RIP Version
(Send)
Select the RIP version for sending the routing
information. Three options are available: Version 1.
Version 2 and Both.
RIP Version
(Receive)
Select the RIP version for receiving the routing
information. Three options are available: Version 1.
Version 2 and Both.
Authentication
Click on “Enable” or “Disable” radio button to
enable/disable authentication for exchanging
the routing information. Note that all the routers
exchanging routing information must use the
same authentication key.
Authentication
Mode
Select RIP authentication mode from the drop
down list. Two modes are supported - Clear Text
and MD5.
Authentication
Key
Enter the authentication key shared by all the
routers exchanging the routing information.
7.2.2 Configuring RIP
Follow these instructions to enable or disable RIP:
1. In the
System Servic es Configuration
page (as shown
in Figure 10.1), click t he
Enable
or
Disable
radio button
depending on whether you want to enable or disable RIP.
2. Select an interface from the drop-down list for routing information
exchange.
3. Click the
Enable
radio button to enable RIP for the particular
interface selected.
4. Decide whether the RIP is operated in passive mode or not by
clicking the
Enable
or
Disable
radio button.
5. Choose RIP version for sending and receiving the routing
Page 68

Routing
RX3042H User's Manual
56
information. Available options are Version 1, Version 2 and Both.
6. Choose whether authentication is required by clicking the
Enable
or
Disable
radio button.
7. (Optional) If authentication is enable, you must also select
authentication mode and the desired authentication key.
8. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
7.3 Static Route
Figure 7.2. Static Route Configuration Page
7.3.1 Static Route Configuration Parameters
The following table defines the available configuration parameters
for static routing configuration.
Table 7.2. Static Route Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Destination
Address
Specifies the IP address of the destination computer or
an entire destination network. It can also be specified
as all zeros to indicate that this route should be used for
all destinations for which no other route is defined (this
is the route that creates the default gateway). Note that
destination IP must be a network ID. The default route uses
a destination IP of 0.0.0.0. Refer to Appendix 11 for an
explanation of network ID.
Page 69

RX3042H User's Manual
Routing
57
Field Description
Subnet
Mask
Indicates which parts of the destination address refer to the
network and which parts refer to a computer on the network.
Refer to Appendix 11, for an explanation of network masks.
The default route uses a 0.0.0.0 for subnet mask.
Gateway
Gateway IP address
Interface
Available option include AUTO, Eth0 (LAN), Eth1 (WAN),
PPPoE:0 (unnumbered), PPPoE:1 (1st PPPoE session),
PPPoE:2 (2nd PPPoE session). These options are
selectable from the drop-down list. If AUTO is selected, the
router will automatically assign an interface to route the
packets based on the gateway IP address.
7.3.2 Adding Static Routes
Figure 7.3. Static Route Configuration
Follow these instructions to add a static route to the routing table.
1. Open the
Static Route
configuration page by clicking the
Advanced ->Static Route
menu.
2. Enter static routes information such as destination IP address,
destination subnet mask, gateway IP address and the interface
in the corresponding fields.
For a description of these fields, refer to Table 7.2. Static
Route Configuration Parameters.
To create a route that defines the default gateway for your
LAN, enter 0.0.0.0 in both the Destination IP Address and
Subnet Mask fields.
3. Click
Add
to add a new route.
Page 70

Routing
RX3042H User's Manual
58
7.3.3 Deleting Static Routes
Figure 7.4. Sample Routing Table
Follow these instructions to delete a static route from the routing
table.
1. Open the Static Route conf iguration pa ge by clicking the
Advanced ->Static Route
menu.
2. Click on the
icon of the route to be deleted in the Routing
Table.
WARNING Do not remove the route for default
ga teway unl ess you kno w what yo u are doing.
Removing the default route will render the Internet
unreachable.
7.3.4 Viewing the Static Routing Table
All I P-enabled computers and routers maintain a ta ble of IP
addresses that are commonly accessed by their users. For each of
these destination IP addresses, the table lists the IP address of the
fi rst hop the data should take. This table is known as the deviceʼs
routing table.
To view the RX3042Hʼs routing table, click the
Advanced ->Static
Route
menu. The Routing Table displays at the upper half of the
Static Route Confi guration page, as shown in Figure 7.2:
The Routing Table displays a row for each existing route containing
th e IP a ddres s of the destinat ion net work, s ubnet mas k of
destination network and the IP of the gateway that forwards the
traffi c.
Page 71

59
RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring DDNS
8 Configuring DDNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a service that allows computers to use the
same domain name, even when the IP address changes from time
to time (during reboot or when the ISPʼs DHCP server resets IP
leases). RX3042H connects to a DDNS service provider whenever
the WAN IP address changes. It supports setting up the web
services such as Web server, FTP server using a domain name
instead of the IP address. DDNS supports the DDNS clients with
the following features:
• Update DNS records (addition) when an external interface
comes up
• Force DNS update
HTTP DDNS Client
HTTP DDNS client uses the mechanism provided by the popular
DDNS service providers for updating the DNS records dynamically.
In this case, the service provider updates DNS records in the DNS.
RX3042H uses HTTP to trigger this update. RX3042H supports
HTTP DDNS update with the following service provider:
• www.dyndns.org
Figure 8.1. Network Diagram for HTTP DDNS
Whenever IP address of the configured DDNS interface changes,
DDNS update is sent to the specified DDNS service provider.
RX3042H should be configured with the DDNS username and
password that are obtained from your DDNS service provider.
Page 72

60
Configuring DDNS
RX3042H User's Manual
8.1 DDNS Configuration Parameters
Table 8.1 describes the configuration parameters available for
DDNS service.
Table 8.1. DDNS Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Interface
Select the interface that the DDNS service is to be used.
Status
Shows the state of DDNS.
Enable
DDNS
Check this box to enable DDNS service; otherwise, keep the
box unchecked.
Domain
Name
Enter the registered domain name into this field. For example,
If the host name of your RX3042H is “host1” and the domain
name is “yourdomain.com”, The fully qualify domain name
(FQDN) is “host1.yourdomain.com”.
Username
Enter the username provided by your DDNS service provider
in this field.
Password
Enter the password provided by your DDNS service provider
in this field.
8.2 Configuring HTTP DDNS Client
Figure 8.2. HTTP DDNS Configuration Page
Page 73

61
RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring DDNS
Follow these instructions to configure the HTTP DDNS:
1. First, you should have already registered a domain name to the
DDNS service provider, dyndns. If you have not done so, please
visit www.dyndns.org for more details.
2. Open the DDNS configuration page by clicking
Advanced ->
DDNS Service
menu.
3. Select the interface that the DDNS service is to be used.
4. Check
Enable DDNS
checkbox to enable the DDNS service.
5. Enter the registered domain name in the
Domain Name
field.
6. Enter the username and password provided by your DDNS
service provider.
7. Click on
Apply
button to send a DNS update request to your
DDNS service provider. Note that DNS update request will also
be sent to your DDNS service provider automatically whenever
the WAN port status is changed.
Page 74

Page 75

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
63
9 Configuring Firewall and NAT
The RX3042H provides built-in firewall/NAT functions, enabling
you to protect the system against denial of service (DoS) attacks
and other types of malicious accesses to your LAN while providing
Internet access sharing at the same time. You can also specify how
to monitor attempted attacks, and who should be automatically
notified.
This chapter describes how to create/modify/delete ACL (Access
Control List) rules to control the data passing through your network.
You will use firewall configuration pages to:
• Configure firewall global and DoS settings
• Create, modify, delete and view ACL rules.
Note
: When you define an ACL rule, you instruct the RX3042H to
examine each data packet it receives to determine whether it meets
criteria set forth in the rule. The criteria can include the network or
internet protocol it is carrying, the direction in which it is traveling (for
example, from the LAN to the Internet or vice versa), the IP address
of the sending computer, the destination IP address, and other
characteristics of the packet data.
If the packet matches the criteria established in a rule, the packet
can either be accepted (forwarded towards its destination), or
denied (discarded), depending on the action specified in the rule.
9.1 Firewall Overview
9.1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection
The stateful packet inspection engine in the RX3042H maintains a
state table that is used to keep track of connection states of all the
packets passing through the firewall. The firewall will open a “hole”
to allow the packet to pass through if the state of the packet that
belongs to an already established connection matches the state
maintained by the stateful packet inspection engine. Otherwise,
the packet will be dropped. This “hole” will be closed when the
connection session terminates. No configuration is required for
stateful packet inspection; it is enabled by default when the firewall
is enabled. Please refer to section 9.3.1 “Firewall ” to enable or
disable firewall service on the RX3042H.
Page 76

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
64
9.1.2 DoS (Denial of Service) Protection
Both DoS protection and stateful packet inspection provide first line
of defense for your network. No configuration is required for both
protections on your network as long as firewall is enabled for the
RX3042H. By default, the firewall is enabled at the factory. Please
refer to section 9.3.1 “Firewall ” to enable or disable firewall service
on the RX3042H.
9.1.3 Firewall and Access Control List (ACL)
9.1.3.1 Priority Order of ACL Rule
All ACL rules have a rule ID assigned – the smaller the rule ID, the
higher the priority. Firewall monitors the traffic by extracting header
information from the packet and then either drops or forwards the
packet by looking for a match in the ACL rule table based on the
header information. Note that the ACL rule checking starts from the
rule with the smallest rule ID until a match is found or all the ACL
rules are examined. If no match is found, the packet is dropped;
otherwise, the packet is either dropped or forwarded based on the
action defined in the matched ACL rule.
9.1.3.2 Tracking Connection State
The stateful packet inspection engine in the firewall keeps track
of the state, or progress, of a network connection. By storing
information about each connection in a state table, RX3042H is
able to quickly determine if a packet passing through the firewall
belongs to an already established connection. If it does, it is passed
through the firewall without going through ACL rule evaluation.
For example, an ACL rule allows outbound ICMP packet from
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.2.1. When 192.168.1.1 send an ICMP echo
request (i.e. a ping packet) to 192.168.2.1, 192.168.2.1 will send an
ICMP echo reply to 192.168.1.1. In the RX3042H, you donʼt need to
create another inbound ACL rule because stateful packet inspection
engine will remember the connection state and allows the ICMP
echo reply to pass through the firewall
9.1.4 Default ACL Rules
The RX3042H supports two types of access rules:
Page 77

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
65
• ACL Rules: for controlling all access to the computers on the
LAN and DMZ and for controlling access to external networks
for hosts on the LAN and DMZ.
• Self-Access Rules: for controlling access to the RX3042H itself.
Default Access Rules
• All traffic from external hosts to the hosts on the LAN and DMZ is
denied.
• All traffic originated from the LAN is forwarded to the external
network using NAT.
WARNING: It is not necessary to remove the default
ACL rule from the ACL rule table! It is better to create
higher priority ACL rules to override the default rule.
9.2 NAT Overview
Network Address Translation allows use of a single device, such
as the RX3042H, to act as an agent between the Internet (public
network) and a local (private) network. This means that a NAT
IP address can represent an entire group of computers to any
entity outside a network. Network Address Translation (NAT) is
a mechanism for conserving registered IP addresses in large
networks and simplifying IP addressing management tasks.
Because of the translation of IP addresses, NAT also conceals
true network address from privy eyes and provide a certain degree
security to the local network.
The NAT modes supported are static NAT, dynamic NAT, NAPT,
reverse static NAT and reverse NAPT.
9.2.1 NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)
or PAT (Port Address Translation)
Also called IP Masquerading, this feature maps many internal hosts
to one globally valid Internet address. The mapping contains a pool
of network ports to be used for translation. Every packet is translated
with the globally valid Internet address and the port number is
translated with an un-used port from the pool of network ports.
Figure 9.1 shows that all the hosts on the local network gain access
to the Internet by mapping to only one globally valid IP address and
different port numbers from a free pool of network ports.
Page 78

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
66
Figure 9.1 NAPT – Map Any Internal PCs to a Single Global IP Address
Figure 9.2 Reverse NAPT – Relayed Incoming Packets to the
Internal Host Base on the Protocol, Port Number or IP Address
Page 79

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
67
9.2.2 Reverse NAPT / Virtual Server
Reverse NAPT is also called inbound mapping, port mapping, or
virtual server. Any packet coming to the RX3042H can be relayed
to the internal host based on the protocol, port number and/or IP
address specified in the ACL rule. This is useful when multiple
services are hosted on different internal hosts. Figure 9.2shows that
web server (TCP/80) is hosted on PC A, telnet server (TCP/23) on
PC B, DNS server (UDP/53) on PC C and FTP server (TCP/21) on
PC D. This means that the inbound traffic of these four services will
be directed to respective host hosting these services.
9.3 Firewall Settings – (Firewall/NAT ->Settings)
9.3.1 Firewall Options
Table 9.1 lists the firewall options parameters.
Table 9.1. Firewall Options Parameters
Field Description
DoS Check
Check or uncheck this box to enable or disable DoS
check. When DoS check is disabled, the following
functionalities are disabled:
• Stateful packet inspection
• Skip all DoS attack check
Default NAT
Log Port Probing
Connection attempt to closed ports will be logged if
this option is enabled.
Stealth Mode
If enabled, RX3042H will not respond to remote peerʼs
attempt to connect to the closed TCP/UDP ports.
To configure firewall settings, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the
Firewall Settings
configuration page as shown in
Figure 9.3 by clicking on
Firewall/NAT ->Settings
menu.
2. Check or uncheck individual check box for each firewall option.
3. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
9.3.2 DoS Configuration
Page 80

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
68
The RX3042H has an Attack Defense Engine that protects internal
networks from Denial of Service (DoS ) attacks such as SYN
flooding, IP smurfing, LAND, Ping of Death and all re-assembly
attacks. It can drop ICMP redirects and IP loose/strict source
routing packets. For example, a security device with the RX3042H
Firewall provides protection from “WinNuke”, a widely used program
to remotely crash unprotected Windows systems in the Internet.
The RX3042H Firewall also provides protection from a variety
of common Internet attacks such as IP Spoofing, Ping of Death,
Land Attack, and Reassembly attacks. For a complete list of DoS
protection provided by the RX3042H, please see Table 2.1.
9.3.2.1 DoS Protection Configuration Parameters
Table 9.2 provides explanation for each type of DoS attacks. You
may check or uncheck the check box to enable or disable the
protection for each type DoS attacks.
Table 9.2. DoS Attack Definition
Field Description
IP Source Route
Intruder uses “source routing” in order to break into the
target system.
IP Spoofing
Spoofing is the creation of TCP/IP packets using
somebody elseʼs IP address. IP spoofing is an integral
part of many network attacks that do not need to see
responses.
Land
Attacker sends out packets to the system with the
same source and destination IP address being that of
the target system and causes the target system trying
to resolve an infinite series of connections to itself. This
can cause the target system to slow down drastically.
Ping of Death
An attacker sends out larger than 64KB packets to
cause certain operating system to crash.
Smurf
An attacker issues ICMP echo requests to some
broadcast addresses. Each datagram has a spoofed
IP source address to be that of a real target-host. Most
of the addressed hosts will respond with an ICMP
echo reply, but not to the real initiating host, instead all
replies carry the IP address of the previously spoofed
host as their current destination and cause the victim
host or network to slow down drastically.
Page 81

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
69
Field Description
SYN/ ICMP/ UDP
Flooding
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable the
logging for SYN/ICMP/UDP flooding attacks. These
attacks involve sending lots of TCP SYN/ICMP/UDP
to a host in a very short period. RX3042H will not drop
the flooding packets to avoid affecting the normal
traffic.
TCP XMAS/
NULL/ FIN Scan
A hacker may be scanning your system by sending
these specially formatted packets to see what services
are available. Sometimes this is done in preparation for
a future attack, or sometimes it is done to see if your
system might have a service, which is susceptible to
attack.
XMAS scan:
A TCP packet has been seen with a
sequence number of zero and the FIN, URG, and
PUSH bits are all set.
NULL scan:
A TCP packet has been seen with a
sequence number of zero and all control bits are set to
zero.
FIN scan:
A hacker is scanning the target system
using a “stealth” method. The goal of the hacker is to
find out if they can connect to the system without really
connecting using the “FIN” scanning. It attempts to
close a non-existent connection on the server. Either
way, it is an error, but systems sometimes respond
with different error results depending upon whether the
desired service is available or not.
Re-assembly
In the teardrop attack, the attackerʼs IP puts a
confusing offset value in the second or later fragment.
If the receiving operating system does not have a plan
for this situation, it can cause the system to crash.
WinNUKE
Check or un-check this option to enable or disable
protection against Winnuke attacks. Some older
versions of the Microsoft Windows OS are vulnerable
to this attack. If the computers in the LAN are not
updated with recent versions/patches, you are advised
to enable this protection by checking this check box.
Page 82

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
70
9.3.2.2 Configuring DoS Settings
To configure DoS settings, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Firewall General configuration page as shown in
Figure 9.3 by clicking on Firewall ->Security menu.
2. Check or uncheck individual check box for each type DoS
protection.
3. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
Figure 9.3. Firewall General Configuration Page
9.4 ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
9.4.1 ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Table 9.3 describes the configuration parameters firewall inbound,
outbound and self-access ACL rules.
Page 83

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
71
Table 9.3. ACL Rule Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Filter Direction
– choose the available option from the drop-down
list to configure the ACL.
For dual-WAN configuration, two options are available – LAN ->WAN and
WAN ->LAN.
For WAN + DMZ configuration, six options are available – LAN ->WAN,
WAN ->LAN, LAN ->DMZ, DMZ->LAN, WAN ->DMZ and DMZ ->WAN.
ID
Add New
Click on this option to add a new ACL rule.
Rule Number
Select a rule from the drop-down list, to modify its
settings.
Move to
This option allows you to set a priority for this rule. The RX3042H Firewall
acts on packets based on the priority of the rules. Set a priority by specifying
a number for its position in the list of rules:
1 (First)
This number marks the highest priority.
Other
numbers
Select other numbers to indicate the priority you wish to
assign to the rule.
Log
Click on the “Enable” or “Disable” radio button to enable or disable logging for
this ACL rule.
Action
Allow
Select this button to configure the rule as an allow rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will allow matching
packets to pass through.
Deny
Select this button to configure the rule as a deny rule.
This rule when bound to the Firewall will not allow
matching packets to pass through.
Route to
– keep the setting to “AUTO” unless packets are routed to specific interface.
Available options include AUTO, eth1 (WAN1), eth2 (WAN2), PPP1 (WAN1unnumbered), PPP1 (WAN2-unnumbered), PPP3 (WAN1-PPPoE1), PPP4
(WAN1-PPPoE2), PPP5 (WAN2-PPPoE1), PPP6 (WAN2-PPPoE2). If WAN
interface is set to DMZ mode, only AUTO, eth1, PPP1/3/4 are available.
These options are selectable from the drop-down list. If AUTO is selected,
the router will route the packets based on the information in the routing
table.
Page 84

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
72
Field Description
NAT
None
Select this option if you donʼt intend to use NAT in this
ACL rule.
IP Address
Select this option to specify the IP address of the you
want the outgoing traffic to use as the source IP address.
Note this option is called.
Auto
RX3042H automatically uses the IP address of the
interface that the traffic is to be forwarded as the source
IP address. It is recommended that you select this option
if NAT is to be used for out going traffic
Source
This option allows you to set the source network to which this rule
should apply. Use the drop-down list to select one of the following
options:
Any
This option allows you to apply this rule to all the
computers in the source network, such as those on the
Internet for the inbound traffic or all the computers in the
local network for outbound traffic.
IP Address
This option allows you to specify an IP address on which
this rule will be applied.
IP Address
Specify the appropriate network address
Subnet
This option allows you to include all the computers that
are connected in an IP subnet. When this option is
selected, the following fields become available:
Field Description
Address
Enter the appropriate IP address.
Mask
Enter the corresponding subnet mask.
MAC Address
This option allows you to specify a MAC address on
which this rule will be applied.
MAC
Enter the desired MAC address.
Destination
This option allows you to set the destination network to which
this rule should apply. Use the drop-down list to select one of the
following options:
Any
This option allows you to apply this rule to all the
computers in the local network for inbound traffic or any
computer in the Internet for outbound traffic.
Page 85

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
73
IP Address,
Subnet
Select any of these options a nd en ter details as
described in the Source IP section above.
Service
Select a service, from the drop-down list, to which this rule
should apply. If the desired service is not listed, click on the
Edit button to create a new service.
Time
Select a time slot during which this rule should apply.
Enable
Check this box if you want to activate the ACL rule at the
time specified.
Date and Time
Chck the desired dates and time for this ACL rule.
Table 9.4. Service Configuration Parameters
Field Description
Service Name
Enter a distinctive name identifying the new service.
Protocol
Select a protocol type from the drop-down list. Available options are All,
TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP, AH ESP and TCP/UDP.
Port Range
This option allows you to set the destination port to which this rule should
apply. Use the drop-down list to select one of the following options:
Any
Select this option if you want this rule to apply to all
applications with an arbitrary source port number.
Single
This option allows you to apply this rule to an application
with a specific source port number.
Port Number
Enter the source port number
Range
Select this option if you want this rule to apply to
applications with this port range. The following fields
become available for entry when this option is selected.
Start Port
Enter the starting port number of the range
End Port
Enter the ending port number of the range
Page 86

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
74
Field Description
This option allows you to select the ICMP message type for the service. The
supported ICMP message types are:
• Any (default)
• 0: Echo reply
• 1: Type 1
• 2: Type 2
• 3: Dst unreach: destination unreachable
• 4: Src quench: source quench
• 5: Redirect
• 6: Type 6
• 7: Type 7
• 8: Echo req:
• 9: Router advertisement
• 10: Router solicitation
• 11: Time exceed: time exceeded
• 12: Parameter problem
• 13: Timestamp request
• 14: Timestamp reply
• 15: Info request: information request
• 16: Info reply: information reply
• 17: Addr mask req: address mask request
• 18: Addr mask reply: address mask reply
9.5 Configuring ACL Rules – (Firewall ->ACL)
By creating ACL rules in the ACL configuration page as shown in
Figure 9.4, you can perform access control (allow or deny) to both
the trusted and un-trusted networks.
Options in this configuration page allow you to:
• Add a rule, and set parameters for it
• Modify an existing rule
• Delete an existing rule
• View configured ACL rules
Page 87

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
75
Figure 9.4. ACL Configuration Page
9.5.1 Add an ACL Rule
To add an ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the ACL Rule configuration page, as shown in Figure 9.4,
by clicking
Firewall ->ACL
menu.
2. Select an option from the “Filter Direction” drop-down list. For
example, if you want to create an ACL to filter traffic originated from
LAN and destined to WAN, then choose
LAN ->WAN
option.
3. Select
Add New
from the “ID” drop-down list.
4. Set desired action (Allow or Deny) from the
Action
drop-down list.
5. Select from the
Route To
drop-down list if you intend to direct
the traffic to a specific interface. Choose AUTO if you want to
have RX3042H route the traffic automatically.
6. Choose NAT type and enter the required information for the
selected NAT type.
7. Make changes to any or all of the following fields: source/
destination IP, service, time and log. Please see Table 9.3 for
Page 88

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
76
Figure 9.5. ACL Configuration Example
explanation of these fields.
8. Assign a priority for this rule by selecting a number from the
Move to
drop-down list. Note that the number indicates the
priority of the rule with 1 being the highest. Higher priority rules
will be examined prior to the lower priority rules by the firewall.
9. Click on the
Add
button to create the new ACL rule. The new
ACL rule will then be displayed in the inbound access control list
table at the bottom half of the Inbound ACL Configuration page.
Figure 9.5 illustrates how to create a rule to deny outbound HTTP
traffic originated from the host w/ IP address 192.168.1.129.
Figure 9.6. Sample ACL List Table
Page 89

RX3042H User's Manual
Confi guring Firewall
77
9.5.2 Modify an ACL Rule
To modify an inbound ACL rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Outbound ACL Rule Configuration Page by clicking
Firewall/NAT ->ACL
menu.
2. Click on the
icon of the rule to be modifi ed in the inbound
ACL table or select the rule number from the
ID
drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fi elds: action,
source/destination IP, service, time and log. Please see Table 9.3
for explanation of these fi elds.
4. Click on the
Modify
button to modify this ACL rule. The new
settings for this ACL rule will then be displayed in the inbound
access control list table at the bottom half of the Inbound ACL
Confi guration page.
9.5.3 Delete an ACL Rule
To delete an inbound ACL rule, click on the in front of the rule to
be deleted.
9.5.4 Display ACL Rules
To see existing ACL rules, just open the ACL Rule Configuration
page by clicking
Firewall/NAT ->ACL
menu and then select a traffi c
direction from the T
raffi c Direction
drop-down list.
9.6 Confi guring Self-Access ACL Rules
–(Firewall/NAT ->Self-Access ACL)
Self-Access rules control access to/from the RX3042H itself. You
may use Self-Access Rule Configuration page, as illustrated in
Figure 9.7, to:
• Add a Self-Access rule
• Modify an existing Self-Access rule
• Delete an existing Self-Access rule
• View existing Self-Access rules
Page 90

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
78
9.6.1 Add a Self-Access Rule
To add a Self-Access rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Self-Access Rule Configuration page by clicking
Firewall/NAT ->Self-Access ACL
menu.
2. Select “
Add New
” from the “ID” drop-down list.
3. Set desired action (Allow or Deny) from the “
Action
” drop-down list.
4. Assign a priority for this rule by selecting a number from the
“
Move to
” drop-down list. Note that the number indicates the
priority of the rule with 1 being the highest. Higher priority rules
will be examined prior to the lower priority rules by the firewall.
5. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields:
source/destination IP, service, time and log. Please see Table 9.3
for explanation of these fields.
6. Cl ick on the "
Add
" button to create the ne w Self-Access
rule. The new rule will then be displayed in the Existing SelfAccess ACL list table at the bottom half of the Self-Access ACL
configuration page.
Figure 9.7. Self-Access ACL Configuration Page
Page 91

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
79
Figure 9.8. Self-Access ACL Configuration Example
9.6.2 Modify a Self-Access Rule
To modify a Self-Access rule, follow the instructions below:
1. Open the Self-Access ACL configuration page by clicking
Firewall/NAT ->Self-Access ACL
menu.
2. Click on the icon of the Self-Access rule to be modified in the
Existing Self-Access ACL
table or select the Self-Access ACL
from the ID drop-down list.
3. Make desired changes to any or all of the following fields: action,
source/destination IP, service, time and log. Please see Table 9.3
for explanation of these fields.
4. Click on the "
Modifiy
" button to save the changes. The new
settings for this Self-Access rule will then be displayed in the
Existing Self-Access ACL table located at the bottom half of the
Self-Access ACL configuration page.
9.6.3 Delete a Self-Access Rule
To delete a Self-Access rule, click on the icon of the rule to be
deleted.
Example
Figure 9.8 shows a sample self-access ACL configuration to allow
HTTP traffic from any one to RX3042H.
Page 92

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
80
9.7 Configure Virtual Server
Virtual server allows you to configure up to ten public servers, such
as a Web, E-mail, FTP server and etc. accessible by external users
of the Internet. Each service is provided by a dedicated server
configured with a fixed IP Address. Although the internal service
addresses are not directly accessible to the external users the
router is able to identify the service requested by the service port
number and redirects the request to the appropriate internal server.
Note: RX3042H supports only one server of any
particular type at a time.
9.6.4 View Configured Self-Access Rules
To see existing Self-Access Rules, just open the Self-Access ACL
configuration page by clicking
Firewall/NAT ->Self-Access ACL
menu.
Figure 9.9. Virtual Server Configuration Page
9.7.1 Virtual Server Configuration Parameters
Table 9.5 describes the configuration parameters available for
Page 93

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
81
virtual server configuration.
Table 9.5. Virtual Server Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
ID
Add New
Click on this option to add a new virtual server.
Number
Select the ID of a virtual server from the drop-down list to
modify its settings.
Move to
This option allows you to set a priority for virtual server rule check. NAT
does the IP and/or port mapping based on the priority of the rules. Set a
priority by specifying a number for its position in the list of rules
1 (First)
This number marks the highest priority.
Other
numbers
Select other numbers to indicate the priority you wish to
assign to the rule.
Destination IP
This option allows you to set the destination network to which this rule
should apply. Use the drop-down list to select one of the following options:
Any
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the virtual server if the virtual
server has a known public IP address.
Interface
Use the IP address of the selected interface as the
destination IP address. Available options are:
eth1 (WAN1)
eth2 (WAN2)
ppp1 (WAN1 – unnumbered)
ppp2 (WAN2 – unnumbered)
ppp3 (WAN1 – PPPoE 1)
ppp4 (WAN1 – PPPoE 2)
ppp5 (WAN2 – PPPoE 1)
ppp6 (WAN2 – PPPoE 2)
Service
Select a service, from the drop-down list, to which this rule
should apply. If the desired service is not listed, click on
the
Edit
button to create a new service.
Redirect IP
Enter the IP address of the computer (usually a server in
your LAN) that you want the incoming traffic to be directed.
For example, if IP address of the web server on your LAN
is 192.168.1.28, please enter 192.168.1.28 here.
Page 94

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
82
Setting Description
Redirect
Service
Select a service, from the drop-down list, to which this rule
should apply. If the desired service is not listed, click on
the "
Edit
" button to create a new service.
Bypass ACL
Check this option if you do not want firewall to perform
access control on this virtual server. This means that
the virtual server allows anyone to access the service
provided. If you want to control who has access to this
virtual server, un-check this option and create a proper
ACL rule to control access to the virtual server.
Table 9.6. Port Numbers for Popular Applications
Application Service Port Numbers
AOE II (Server) 2300-2400
AUTH 113
Baldurs Gate II 2300-2400
Battle Isle 3004-3004
Counter Strike 27005-27015
Cu See Me 7648-7648, 56800, 24032
Diablo II 4000-4000
DNS UDP 53-53
FTP TCP 21-21
FTP TCP 20(ALG)-21
GOPHER TCP 70-70
HTTP TCP 80-80
THHP8080 TCP 8080-80880
HTTPS TCP 443-443
I-phone 5.0 TCP/UDP 22555-22555
ISAKMP UDP 500-500
mirc 66011-700
MSN Messenger 1863 ALG
Need for Speed 5 9400-9400
Netmeeting Audio TCPP 1731-1731
Netmeeting Call TCP 1720-1720
Netmeeting Conference UDP 495000-49700
Netmeeting File Transfer TCP 1503--1503
Page 95

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
83
Application Service Port Numbers
Netmeeting or VoIP
1503-1503, 1720(ALG)
NEWS TCP 119-119
PC Anywhere TCP 5631
PC Anywhere TCP 5631, UDP 5632
POP3 TCP 110-110
Powwow Chat 13233-13233
Red Alert II 1234-1237
SMTP TCP 25-25
Sudden Strike 2300-2400
TELNET TCP 23-23
Win VNC UDP 5800-5800
9.7.2 Virtual Server Example 1 – Web Server
Figure 9.10 illustrates the network topology for the web server
deployment. This web server provides HTTP service using TCP
port 8080.
Figure 9.10. Virtual Server Deployment Topology
Following describes the procedure to setup the web server as
illustrated in Figure 9.10.
1. Open the Virtual Server configuration page, as shown in Figure
9.9, by clicking the
Firewall/NAT ->Virtual Server
menu.
2. Select destination IP type and service type as shown in Figure
9.11.
Page 96

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
84
Figure 9.11. Virtual Server Example 1 – Web Server
3. Enter the IP address of the web server, which is 192.168.1.28,
in
Redirect IP
field.
4. Since the web server is not using the standard TCP port, which
is 80, for providing the http service, a new service type must
be created for http service using TCP port 80. Click on the
Edit
button on the redirect service field to create a new service type.
In the popped up Service configuration page, enter the service
name, protocol and port number as shown in Figure 9.12 and
then click on the
Add to list
to create the new service type,
HTTP_8080. Finally, click the
Save & Exit
button to save the
new service.
Figure 9.12. Adding a New Service
Page 97

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
85
5. Select the service, HTTP_8080, from the Redirect Service dropdown list.
6. Click
Add
to save the virtual server settings.
9.7.3 Virtual Server Example 2 – FTP Server
Figure 9.10 illustrates the network topology for the FTP server
deployment. This FTP server provides FTP service using standard
FTP port.
Following describes the procedure to setup the FTP server as
illustrated in Figure 9.10.
1. Open the Virtual Server configuration page, as shown in Figure
9.9, by clicking the
Firewall/NAT ->Virtual Server
menu.
2. Enter the needed information as shown in Figure 9.13.
3. Click
Add
to save the virtual server settings.
Figure 9.13. Virtual Server Example 2 – FTP Server
9.8 Configure Special Application
Some applications use multiple TCP/UDP ports to transmit data.
Due to NAT, these applications cannot work with the router. Special
Application setting allows some of these applications to work
properly.
Page 98

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
86
Note: Only one PC can use one particular special
application at a time..
9.8.1 Special Application Configuration Parameters
Table 9.7 describes the configuration parameters available for
virtual server configuration.
Table 9.7. Special Application Configuration Parameters
Setting Description
Enabled
Check this box to activate the policy.
Trigger Protocol
Select the protocol type from the drop-down list. The
available options are TCP, UDP and TCP/UDP.
Outgoing
(Trigger) Port
The port range this application uses when it sends
outbound packets. The outgoing port numbers act
as the trigger. When the router detects the outgoing
packets with these port numbers, it will allow the
corresponding inbound packets with the incoming port
numbers specified in the
Incoming Port Range
field to
pass through the router. For a list of port numbers used
by some popular applications, please refer to Table 9.8
Incoming
Protocol
The protocol that the corresponding inbound packet
used. The available options are TCP, UDP and TCP/
UDP.
Incoming Port
The port range that the corresponding inbound packet
used. For a list of port numbers used by some popular
applications, please refer to Table 9.8. Note that port
range is indicated by a pair of numbers w/ a dash
separating the numbers, e.g. 100-200. Multiple port
ranges is separated by a comma, e.g. 100-200, 700-800.
Comment
You may enter a description for the application here, e.g.
a name identifying the application.
Table 9.8. Port Numbers for Popular Applications
Application Outgoing Port
Number
Incoming Port Range
Battle.net 6112 6112
DialPad 7175 51200, 51201, 51210
Page 99

RX3042H User's Manual
Configuring Firewall
87
Application Outgoing Port
Number
Incoming Port Range
ICU II 2019 2000-2038, 2050-2051,
2069, 2085, 3010-3030
MSN Gaming Zone 47624 2300-2400, 28800-29000
PC to Phone 12053 12120, 12122, 150-24220
Quick Time 4
554 6970-6999
wowcall 8000 4000-4020
Yahoo Messenger
5050 5000-5101
9.8.2 Special Application Example
Figure 9.14. Special Application Configuration Page
Following describes the procedure to setup a special application for
MSN Gaming Zone.
1. Open the Special Application configuration page, as shown in
Figure 9.14, by clicking the
Firewall/NAT ->Special Application
menu.
2. Check
Enabled
checkbox.
3. Select
TCP/UDP
from the trigger protocol drop-down list. If you
are not sure whether the application uses TCP or UDP protocol,
you may select TCP/UDP in this field.
4. Enter outgoing port range, in this case: 47624 ~ 47624.
Page 100

Configuring Firewall
RX3042H User's Manual
88
5. Select
TCP/UDP
from the incoming protocol drop-down list.
If you are not sure whether the application uses TCP or UDP
protocol, you may select TCP/UDP in this field.
6. Enter incom in g po rt r an ge, in thi s cas e: 230 0-2400 and
28800-29000
7. In the
Comment
field, enter the name identifying this application,
which is MSN Gaming Zone in this instance.
8. Click
Apply
to save the settings.
 Loading...
Loading...