Page 1

PR-DLSW
User Guide
Motherboard
Page 2

Checklist
E1089
First Edition
October 2002
Copyright © 2002 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
language in any form or by any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser for
backup purposes, without the express written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC.
(“ASUS”).
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modified or
altered, unless such repair, modification of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2)
the serial number of the product is defaced or missing.
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE
OR DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT OR
ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR PRODUCT.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED
FOR INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT ANY TIME
WITHOUT NOTICE, AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS.
ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS OR
INACCURACIES THAT MAY APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS
AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered
trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or
explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
ii
Page 3

Contents
FCC/CDC statements.....................................................................vi
Safety information ......................................................................... vii
About this guide............................................................................ viii
How this guide is organized ................................................ viii
Conventions used in this guide .............................................ix
Where to find more information .............................................ix
ASUS contact information ...............................................................x
PR-DLSW specifications summary ................................................xi
Chapter 1: Product introduction
1.1 Welcome! ........................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Package contents............................................................... 1-1
1.3 Special features.................................................................. 1-2
1.3.1 Product highlights .................................................. 1-2
1.3.2 Value-added solutions............................................ 1-4
1.4 Motherboard overview........................................................ 1-6
1.4.1 Major components ................................................. 1-6
1.4.2 Core specifications ................................................ 1-8
Features
Chapter 2: Hardware information
2.1 Motherboard installation ..................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Placement direction ............................................... 2-1
2.1.2 Screw holes ........................................................... 2-1
2.2 Motherboard layout ............................................................ 2-2
2.3 Before you proceed ............................................................ 2-3
2.4 Central Processing Unit (CPU)........................................... 2-4
2.4.1 Overview ................................................................ 2-4
2.4.2 Installing the CPU .................................................. 2-5
2.4.3 Installing the CPU heatsink and fan....................... 2-6
2.5 System memory ................................................................. 2-8
2.5.1 Overview ................................................................ 2-8
2.5.2 Memory Configurations.......................................... 2-9
2.5.3 Installing a DIMM ................................................. 2-10
2.5.4 Removing a DIMM ............................................... 2-10
iii
Page 4

Safeguards
Contents
2.6 Expansion slots .................................................................2-11
2.6.1 Installing an expansion card .................................2-11
2.6.2 Configuring an expansion card .............................2-11
2.6.3 PCI slots .............................................................. 2-13
2.7 Switches and jumper ........................................................ 2-14
2.7.1 Switches .............................................................. 2-14
2.7.2 Jumper ................................................................. 2-14
2.8 Connectors ....................................................................... 2-17
Chapter 3: Powering up
3.1 Starting up for the first time ................................................ 3-1
3.2 Powering off the computer ................................................. 3-2
Chapter 4: BIOS setup
4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS .................................... 4-1
4.1.1 Creating a bootable disk ........................................ 4-1
4.1.2 Updating the BIOS ................................................. 4-3
4.2 BIOS Setup program .......................................................... 4-5
4.2.1 BIOS menu bar ...................................................... 4-6
4.2.2 Legend bar............................................................. 4-6
4.3 Main Menu.......................................................................... 4-8
4.3.1 Primary and Secondary Master/Slave ................. 4-10
4.3.2 Keyboard Features .............................................. 4-14
4.4 Advanced Menu ............................................................... 4-15
4.4.1 Chip Configuration ............................................... 4-17
4.4.2 I/O Device Configuration...................................... 4-18
4.4.3 PCI Configuration ................................................ 4-20
4.5 Power Menu ..................................................................... 4-22
4.5.1 Power Up Control ................................................ 4-24
4.5.2 Hardware Monitor ................................................ 4-26
4.6 Boot Menu ........................................................................ 4-27
4.7 Server Menu..................................................................... 4-29
4.8 Exit Menu ......................................................................... 4-30
iv
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 5: OS Installation
5.1 Microsoft® Windows® NT Server 4.0................................... 5-1
5.1.1 LSI® SCSI Driver Installation................................. 5-1
5.1.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation................ 5-4
5.1.3 C-Media Audio Device Driver Installation .............. 5-8
5.2 Microsoft
5.2.1 LSI® SCSI Driver Installation.................................. 5-9
5.2.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ............... 5-12
5.2.3 C-Media Audio Device Driver Installation ............ 5-15
5.2.4 Enabling ATA100 Feature in Windows® 2000 ..... 5-17
5.2.5 Enabling AGP Bridge Driver in
5.3 Microsoft
5.3.1 LSI SCSI Driver and Intel 82551QM LAN Driver
5.3.2 C-Media Audio Device Driver Installation ............ 5-19
5.4 Novell
5.4.1 LSI® SCSI Driver Installation................................ 5-20
5.4.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ............... 5-22
®
Windows® 2000 Server ..................................... 5-9
Windows® 2000................................................... 5-17
®
Windows® XP Professional.............................. 5-18
Installation............................................................ 5-18
®
NetWare® Server.................................................. 5-20
5.5 SUN Solaris 7 Server ....................................................... 5-24
®
5.5.1 LSI
SCSI Driver Installation................................ 5-24
5.5.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ............... 5-29
5.6 SCO Open Server 5.0.x ................................................... 5-30
5.6.1 LSI
®
SCSI Driver Installation................................ 5-30
5.6.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ............... 5-33
5.7 SCO UnixWare Server ..................................................... 5-34
®
5.7.1 LSI
SCSI Driver Installation................................ 5-34
5.7.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ............... 5-37
5.8 Linux RedHat 7.x.............................................................. 5-38
5.8.1 LSI SCSI Driver Installation ................................. 5-38
5.8.2 Intel 82551QM LAN Driver Installation ................ 5-38
5.8.3 C-Media Audio Device Driver Installation ............ 5-38
v
Page 6

FCC/CDC statements
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
manufacturer’s instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The use of shielded cables for connection of the monitor to the
graphics card is required to assure compliance with FCC regulations.
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to
operate this equipment.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise
emissions from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference
Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
This class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
vi
Page 7

Safety information
Electrical safety
• To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect the power cable from
the electrical outlet before relocating the system.
• When adding or removing devices to or from the system, ensure that
the power cables for the devices are unplugged before the signal
cables are connected. If possible, disconnect all power cables from the
existing system before you add a device.
• Before connecting or removing signal cables from the motherboard,
ensure that all power cables are unplugged.
• Seek professional assistance before using an adpater or extension
cord. These devices could interrupt the grounding circuit.
• Make sure that your power supply is set to the correct voltage in your
area. If you are not sure about the voltage of the electrical outlet you
are using, contact your local power company.
• If the power supply is broken, do not try to fix it by yourself. Contact a
qualified service technician or your retailer.
Operation safety
• Before installing the product and adding devices on it, carefully read all
the documentation that came with the package.
• Before using the product, make sure all cables are correctly connected
and the power cables are not damaged. If you detect any damage,
contact your dealer immediately.
• To avoid short circuits, keep paper clips, screws, and staples away from
connectors, slots, sockets and circuitry.
• Avoid dust, humidity, and temperature extremes. Do not place the
product in any area where it may become wet.
• Place the product on a stable surface.
• If you encounter technical problems with the product, contact a
qualified service technician or your retailer.
vii
Page 8

About this guide
This user guide contains the information you need when installing the
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard.
How this guide is organized
This manual contains the following parts:
• Chapter 1: Product introduction
This chapter describes the features of the PR-DLSW motherboard. It
includes brief descriptions of the special attributes of the motherboard
and the new technology it supports.
• Chapter 2: Hardware information
This chapter lists the hardware setup procedures that you have to
perform when installing system components. It includes description of
the switches, jumpers, and connectors on the motherboard.
• Chapter 3: Powering up
This chapter describes the power up sequence and gives information
on the BIOS beep codes.
• Chapter 4: BIOS setup
This chapter tells how to change system settings through the BIOS
Setup menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS parameters are also
provided.
• Chapter 5: OS Installation
This chapter tells how to install SCSI, LAN, and audio drivers for
various operating systems.
viii
Page 9

Conventions used in this guide
To make sure that you perform certain tasks properly, take note of the
following symbols used throughout this manual.
WARNING: Information to prevent injury to yourself when trying
to complete a task.
CAUTION: Information to prevent damage to the components
when trying to complete a task.
IMPORTANT: Information that you MUST follow to complete a
task.
NOTE: Tips and additional information to aid in completing a task.
Where to find more information
Refer to the following sources for additional information and for product
and software updates.
1. ASUS Websites
The ASUS websites worldwide provide updated information on ASUS
hardware and software products. The ASUS websites are listed in the
ASUS Contact Information on page x.
2. Optional Documentation
Your product package may include optional documentation, such as
warranty flyers, that may have been added by your dealer. These
documents are not part of the standard package.
ix
Page 10

ASUS contact information
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (Asia-Pacific)
Address: 150 Li-Te Road, Peitou, Taipei, Taiwan 112
General Tel: +886-2-2894-3447
General Fax: +886-2-2894-3449
General Email: info@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
MB/Others (Tel): +886-2-2890-7121 (English)
Notebook (Tel): +886-2-2890-7122 (English)
Desktop/Server (Tel): +886-2-2890-7123 (English)
Support Fax: +886-2-2890-7698
Support Email: tsd@asus.com.tw
Web Site: www.asus.com.tw
Newsgroup: cscnews.asus.com.tw
ASUS COMPUTER INTERNATIONAL (America)
Address: 6737 Mowry Avenue, Mowry Business Center,
Building 2, Newark, CA 94560, USA
General Fax: +1-510-608-4555
General Email: tmd1@asus.com
Technical Support
Support Fax: +1-510-608-4555
General Support: +1-502-933-8713
Web Site: www.asus.com
Support Email: tsd@asus.com
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH (Europe)
Address: Harkortstr. 25, 40880 Ratingen, BRD, Germany
General Fax: +49-2102-442066
General Email: sales@asuscom.de (for marketing requests only)
Technical Support
Support Hotline: MB/Others: +49-2102-9599-0
Notebook (Tel): +49-2102-9599-10
Support Fax: +49-2102-9599-11
Support (Email): www.asuscom.de/de/support (for online support)
Web Site: www.asuscom.de
x
Page 11
PR-DLSW specifications summary
CPU
Chipsets
Front Side Bus (FSB)
Memory
Onboard LAN
Onboard SCSI
Onboard audio
Expansion slots
Support for Intel® Xeon™ processor
On-die 256KB/512KB L2 cache
RCC Grand Champion Work Station (GCWS)
- Champion Memory and I/O Controller (CMIC-WS)
- Champion I/O Bridge 2X (CIOBX2)
- Champion I/O Bridge Graphics (CIOBG)
RCC Champion South Bridge 5.0 (CSB5)
400 MHz
6 x 184-pin DDR DIMM sockets
Supports PC2100/PC1600 registered ECC DDR DIMMs
Supports up to 12GB system memory using 2GB DIMMs
Intel® 82551QM Fast Ethernet controller
LSI® 53C1010R PCI SCSI controller
C-Media CMI8738/PCI-SX 4-channel audio controller
1 x AGP Pro 4x slot
4 x PCI 64-bit/133MHz 3V (PCI-X1 to PCI-X4)
1 x PCI 64-bit/66MHz 3V (PCI-X5)
1 x PCI 32-bit/33MHz 5V (PCI6)
Rear panel I/O
Internal connectors
BIOS features
1 x Parallel port
2 x Serial ports
1 x PS/2 keyboard port
1 x PS/2 mouse port
2 x USB 1.1 ports
1 x RJ-45 port (with LED)
Line In/Line Out/Microphone ports
2 x 68-pin Ultra-160 SCSI connectors
2 x ATA/100 IDE connectors
1 x Floppy disk connector
1 x USB 1.1 connector for two additional USB ports
CD/AUX/Modem audio connectors
CPU/Power/Chassis fan connectors
24-pin, 8-pin SSI power connectors
IDE LED/Power LED connectors
20-pin Front panel connector
Chassis intrusion, SMBus, WOL, and WOR connectors
4Mb Flash ROM, Award BIOS with ACPI, DMI, Green, PnP
features, and Enhanced Server BIOS features
(continued on the next page)
xi
Page 12

PR-DLSW specifications summary
Form Factor
Support CD contents
* Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Extended ATX form factor: 12 in x 13 in (30.5 cm x 33 cm)
Device drivers
Utilities
Contact information
xii
Page 13
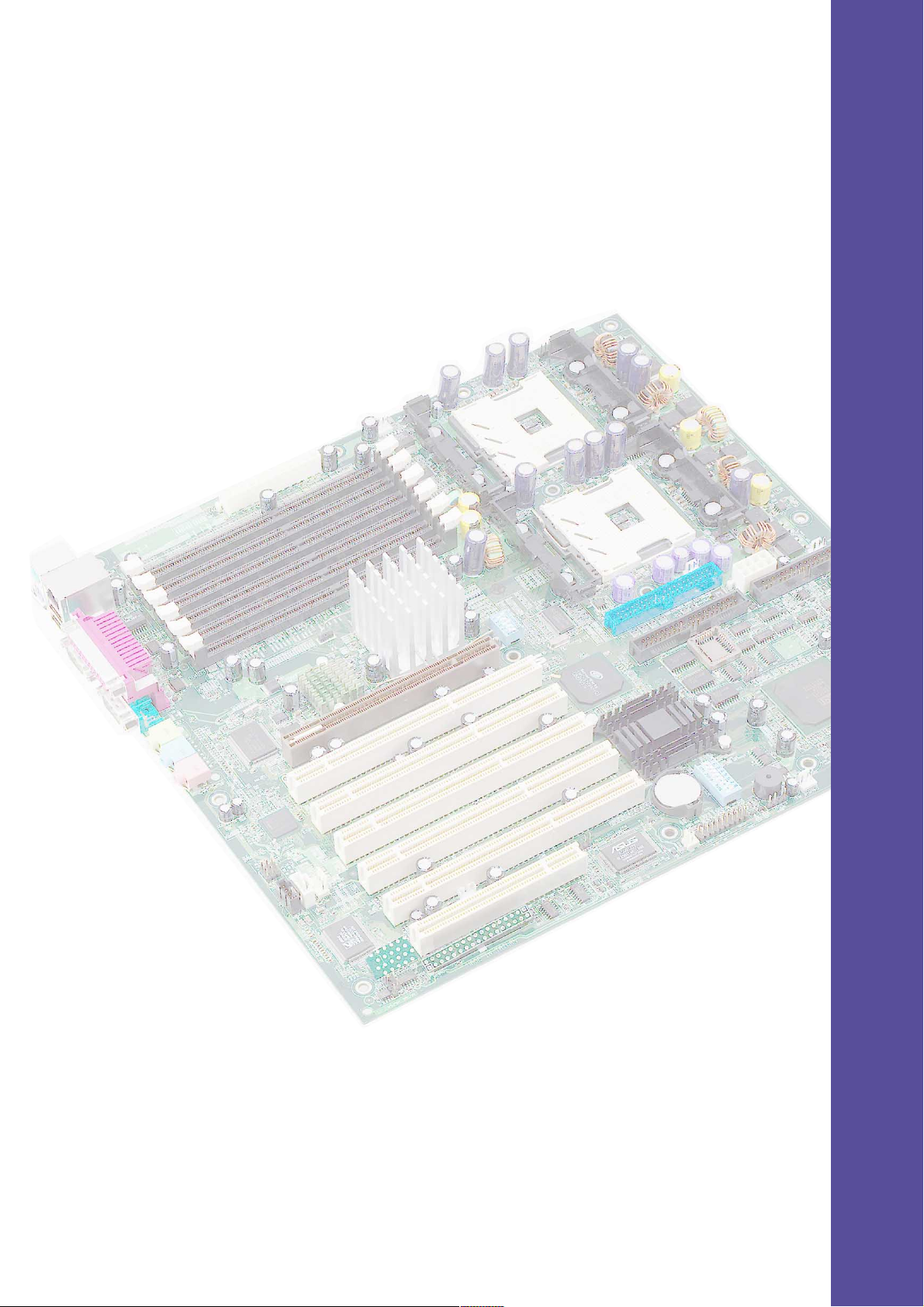
Chapter 1
This chapter describes the features of the
PR-DLSW motherboard. It includes brief
explanations of the special attributes of the
motherboard and the new technology it
supports.
Product introduction
Page 14

Chapter summary
1.1 Welcome! ........................................................ 1-1
1.2 Package contents .......................................... 1-1
1.3 Special features ............................................. 1-2
1.4 Motherboard overview................................... 1-6
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Page 15

1.1 Welcome!
Thank you for buying the ASUS® PR-DLSW motherboard!
The ASUS
latest technologies making it another standout in the long line of ASUS
quality server motherboards!
The PR-DLSW incorporates dual Intel
package coupled with the ServerWorks® Grand Champion Work Station
(GCWS) SystemSet to deliver a reliable and high performance dualprocessor server platform.
Before you start installing the motherboard, and hardware devices on it,
check the items in your package with the list below.
PR-DLSW motherboard delivers a host of new features and
®
Xeon™ processors in 603/604-pin
1.2 Package contents
Check your PR-DLSW package for the following items.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Extended ATX form factor: 12 in x 13 in (30.5 cm x 33 cm)
ASUS PR-DLSW support CD
I/O shield
80-conductor ribbon cable for UltraDMA100/66/33 IDE drives
68-pin LVD SCSI cable for Ultra 160 SCSI devices
Ribbon cable for a 3.5-inch floppy drive
Bag of extra jumper caps
PR-DLSW User Guide
LSI SCSI Controller User’s Manual
If any of the above items is damaged or missing, contact your retailer.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
1-1
Page 16

1.3 Special features
1.3.1 Product highlights
Latest processor technology
The PR-DLSW motherboard supports the Intel
604-pin surface mount ZIF sockets. The processor features the Intel
NetBurst™ micro-architecture that includes hyper-pipelined technology, a
rapid execution engine, a 400MHz system bus, and an execution trace cache
to offer a significant increase in performance. See page 2-4 for more
information.
®
Xeon processor via dual
®
DDR memory support
Employing the Double Data Rate (DDR) memory technology, the PRDLSW motherboard supports up to 12GB of system memory using
PC2100/1600 registered ECC DDR DIMMs. The ultra-fast 200MHz
memory bus doubles the speed of the PC100 SDRAM to deliver the
required bandwidth for the latest 3D graphics, multimedia, and Internet
applications. See page 2-10.
Dual-channel Ultra-160 SCSI
The LSI® 53C1010R 64-bit/66MHz PCI SCSI controller is onboard to
support dual-channel Ultra-160 SCSI connectors that provide high-speed
data transfer interfaces.
Advanced 64-bit PCI-X slots
The 64-bit/133MHz PCI-X slots onboard maximizes I/O bandwidth for the
next generation 64-bit PCI-X cards that support 133MHz bus. The PCI-X
specification 1.0a allows full peer-to-peer transactions between PCI buses
and provides options for intelligent I/O and server management cards.
AGP Pro 4X slot
The motherboard comes with an Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) Pro 4X
slot for 3.3V/1.5V AGP cards. The slot supports 1X, 2X, or 4X mode bus to
support high performance 3D graphics applications.
Onboard LAN
The motherboard comes with the Intel® 82551QM Fast Ethernet controller
to fully support 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet networking.
1-2
Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 17

Onboard audio
The C-Media CMI8738/PCI-SX audio controller is onboard to provide
HTRF-based 3D positional audio (C3DX™) 4-channel audio output.
ATA/100 IDE support
The dual-channel bus master IDE connectors comply with the ATA/100
protocol and supports ATA/100, Multi-Word DMA Mode2, PIO modes 3 & 4
IDE devices such as ATAPI IDE CD-ROM, CD-R/RW, ZIP, and LS-120
drives.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
1-3
Page 18

1.3.2 Value-added solutions
Temperature, fan, and voltage monitoring
The CPU temperature is monitored by the ASUS ASIC to prevent
overheating and damage. The system fan rotations per minute (RPM) is
monitored for timely failure detection. The system voltage levels are
monitored to ensure stable supply of current for critical components.
Dual function power switch
While the system is ON, pressing the power switch for less than 4 seconds
puts the system to sleep mode or to soft-off mode, depending on the BIOS
setting. Pressing the power switch for more than 4 seconds lets the
system enter the soft-off mode regardless of the BIOS setting.
Wake-Up support
The motherboard includes Wake-On-LAN, Wake-On-Ring, and BIOS
Wake-Up features.
ACPI ready
The Advanced Configuration power Interface (ACPI) provides more energy
saving features for operating systems that support OS Direct Power
Management (OSPM).
Concurrent PCI
This feature allows multiple PCI transfers from PCI master buses to the
memory and processor.
Chassis intrusion detection
With this feature, the chassis intrusion circuitry logs “chassis-open” events
into the system BIOS. The onboard battery supports the chassis intrusion
detection feature even when the normal power is removed.
Smart BIOS
The 4Mbit firmware gives an easy-to-use interface that provides more
control and protection to the motherboard. The BIOS has a boot block
write protection and HD/SCSI/MO/ZIP/CD/Floppy boot selection, and is
Year 2000 certified.
1-4
Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 19

Compliance
Both the BIOS and the hardware levels of the motherboard meet the
stringent requirements for SDG 2.0 certification. The new SDG 2.0
requirements for systems and components are based on the following
high-level goals: support for Plug-and-Play compatibility and power
management for configuring and managing all system components, 32-bit
device drivers, and installation procedures for Windows NT/2000/XP.
Color-coded connectors and descriptive icons make identification easy as
required by the PC ‘99 specification.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
1-5
Page 20
1.4 Motherboard overview
Before you install the PR-DLSW motherboard, familiarize yourself with its
physical configuration and available features to facilitate the motherboard
installation and future upgrades. A sufficient knowledge of the motherboard
specifications will also help you avoid mistakes that may damage the
board and its components.
1.4.1 Major components
The following are the major components of the PR-DLSW motherboard as
pointed out in the picture on page 1-7.
1. DDR DIMM sockets
®
2. ServerWorks
Bridge Graphics (CIOBG)
3. ATX power connector
4. ServerWorks
WS North Bridge (CMIC-WS)
5. DIP switches (5-switch)
6. IDE connectors
7. 604-pin CPU sockets
8. 8-pin 12V SSI power connector
9. Floppy disk connector
10. Ultra-160 SCSI connectors
®
11. LSI
12. Flash ROM
13. DIP switches (8-switch)
14. ServerWorks
15. ServerWorks
53C1010R SCSI controller
Bridge (CIOBX2)
Bridge (CSB5)
Champion I/O
®
Grand Champion
®
Champion I/O
®
Champion South
16. ASUS ASIC
17. Audio controller
18. PCI-X slots (PCI-X1 to PCI-X5)
PCI slot (PCI6)
19. Intel
20. AGP Pro 4X slot
21. LPC super I/O controller
22. PS/2 mouse port
23. RJ-45 port
24. Parallel port
25. Microphone port
26. Line In port
27. Line Out port
28. Serial ports
29. USB ports 1 and 2
30. Keyboard port
®
82551QM Fast Ethernet
controller
1-6
See page 1-8 for the specifications of each component. Refer to
Chapter 2 for detailed information on the components.
Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 21
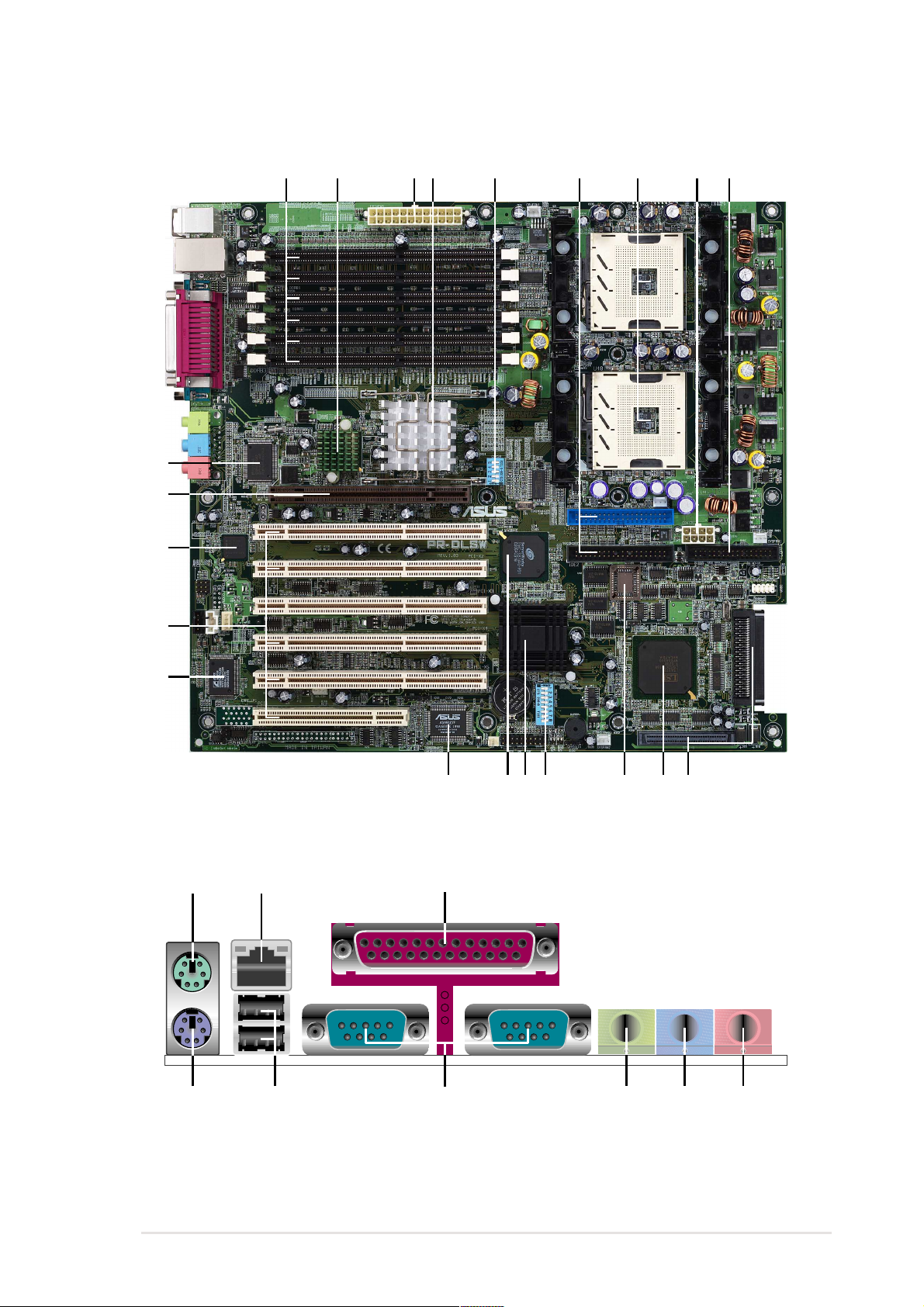
21
20
19
1 2 3 7 8
4 6
5
9
18
17
22
16 13
23 24
15
10
111214
30
2829
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
27 26 25
1-7
Page 22

1.4.2 Core specifications
1
DDR DIMM sockets. These six 184-pin DIMM sockets support up
to 12GB system memory using registered ECC PC2100/1600 DDR
DIMMs.
2
ServerWorks
®
Champion I/O Bridge Graphics (CIOBG). The
CIOBG is an integrated I/O bridge that provides high performance
data flow path between the Inter Module Bus (IMB) and the
Graphics Controller sub-system.
3
ATX power connector. This 24/20-pin connector is for an ATX
power supply.
4
ServerWorks
®
Grand Champion WS north bridge (CMIC-WS).
The Champion Memory and I/O Controller WS (CMIC-WS) acts as
the host bridge of the Grand Champion Work Station (GCWS)
SystemSet. The CMIC-WS device interfaces directly to the
processor bus, and integrates the functions of the main memory
controller and the Inter Module Bus (IMB) interface unit. The
processor interface supports a 400MHz Front Side Bus (FSB)
providing a 3.2GB/s bandwidth, 2-way interleaved 3.2GB/s memory
bandwidth with up to 12GB registered ECC PC2100/1600 DDR
DIMMs, and two high speed IMBs plus one thin IMB to connect to
the south bridge CSB5.
5
DIP switches (5-switch). This 5-switch Dual Inline Package (DIP)
allows you to set the CPU external frequency.
6
IDE connectors. These dual-channel bus master IDE connectors
support up to four Ultra DMA/100/66, PIO Modes 3 & 4 IDE
devices. Both the primary (blue) and secondary (black) connectors
are slotted to prevent incorrect insertion of the IDE ribbon cable.
7
604-pin CPU sockets. A 604-pin surface mount, Zero Insertion
Force (ZIF) socket for the Intel
®
Xeon™ processor with 256KB/
512KB L2 cache and a 400 MHz system bus that allows up to
3.2GB/s data transfer rate. These sockets also support Intel Xeon
CPUs with Hyper-Threading Technology feature.
8
8-pin 12V SSI power connector. This 8-pin connector is for an
ATX power supply.
9
Floppy disk connector. This connector accommodates the
provided ribbon cable for the floppy disk drive. One side of the
connector is slotted to prevent incorrect insertion of the floppy disk
cable.
1-8
Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 23

10
11
Ultra-160 SCSI connectors. These dual-channel 68-pin Ultra-160
SCSI connectors support up to 30 SCSI devices, and data transfers
of 160Mbps.
®
LSI
SCSI controller. The LSI 53C1010R SCSI controller supports
up to 30 SCSI devices through the onboard dual-channel SCSI
connectors.
12
13
14
15
Flash ROM. This 4Mb firmware contains the programmable BIOS
program.
DIP switches (8-switch). This 8-switch Dual Inline Package (DIP)
allows you to select the CPU frequency multiple.
ServerWorks
®
Champion I/O Bridge 2X (CIOBX2). The
Champion I/O Bridge 2X (CIOBX2) provides a high performance
data flow path between the IMB and the I/O subsystem, which
supports multiple PCI-X interfaces that allows large, efficient, and
flexible I/O configurations. The CIOBX2 supports a 64-bit PCI-X I/O
bus that complies with PCI 2.2 specification.
ServerWorks
®
Champion south bridge (CSB5). The Champion
South Bridge (CSB5) primarily acts as a PCI to Low Pin Count
(LPC) bridge, but also supports several integrated functions
including dual-channel ATA/100 IDE controller, 4-port USB 1.1
interface, ACPI power management and detection, XIO-APIC, and
legacy functions 8237DMA, 8259APIC, and 8254 timer.
16
17
18
19
20
ASUS ASIC. This chip performs multiple system functions that
include hardware and system voltage monitoring, IRQ routing,
among others.
Audio controller. This C-Media 4-channel PCI audio chip supports
legacy audio and HRTF 3D positional audio functions.
PCI-X/PCI slots. Four 64-bit/133MHz PCI-X slots and one 64-bit/
66MHz PCI slot, and a 32-bit/33MHz PCI expansion slot support
bus master PCI-X/PCI cards.
®
Intel
82551QM Fast Ethernet controller. This LAN controller fully
supports 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX networking protocols.
AGP Pro 4X slot. This Accelerated Graphics (AGP) Pro 4X slot is
for 3.3V/1.5V AGP cards that support 1X, 2X, or 4X bus modes.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
1-9
Page 24
21
LPC super I/O controller. This Low Pin Count (LPC) interface
provides the commonly used Super I/O functionality. The chipset
supports UART compatible serial ports, one parallel port with EPP
and ECP capabilities, a floppy drive, and PS/2 keyboard and
mouse.
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
PS/2 mouse port. This green 6-pin connector is for a PS/2 mouse.
RJ-45 port. This port allows connection to a Local Area Network
(LAN) through a network hub.
Parallel port. This 25-pin port connects a parallel printer, a
scanner, or other devices.
Microphone port. This Mic (pink) port connects a microphone. In a
4-channel mode, the function of this jack becomes Rear Speaker
Out.
Line In port. This Line In (light blue) port connects a tape player or
other audio sources. In a 4-channel mode, the function of this jack
becomes Bass/Center .
Line Out port. This Line Out (lime) port connects a headphone or a
speaker . In a 4-channel mode, the function of this jack becomes
Front Speaker Out.
Serial ports. These 9-pin COM1/COM2 ports are for pointing
devices or other serial devices.
29
30
USB 1.1 ports. These two 4-pin Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
are available for connecting USB devices.
PS/2 keyboard port. This purple 6-pin connector is for a PS/2
keyboard.
1-10
Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 25
Chapter 2
This chapter describes the hardware setup
procedures that you have to perform when
installing system components. It includes
details on the switch/jumper settings and
connector locations on the motherboard.
Hardware information
Page 26

Chapter summary
2.1 Motherboard installation ............................... 2-1
2.2 Motherboard layout ....................................... 2-2
2.3 Before you proceed ....................................... 2-3
2.4 Central Processing Unit (CPU) ..................... 2-4
2.5 System memory ............................................. 2-8
2.6 Expansion slots ............................................2-11
2.7 Switches and jumpers ................................. 2-14
2.8 Connectors ................................................... 2-17
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Page 27
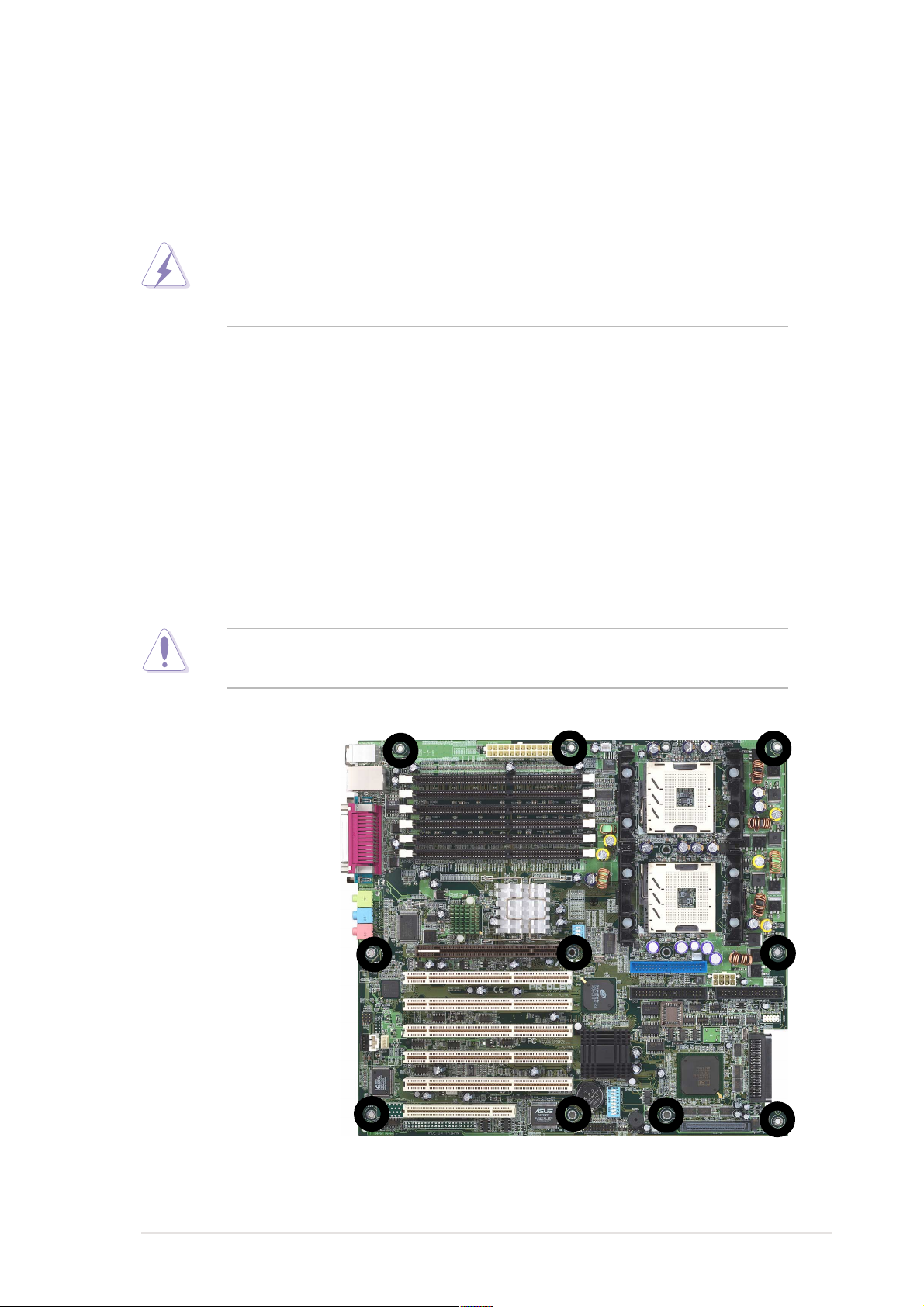
2.1 Motherboard installation
Before you install the motherboard, study the configuration of your chassis
to ensure that the motherboard fits into it. The PR-DLSW uses the
extended ATX form factor that measures 12 in x 13 in (30.5 cm x 33cm).
Make sure to unplug the power cord before installing or removing the
motherboard. Failure to do so may cause you physical injury and
damage motherboard components.
2.1.1 Placement direction
When installing the motherboard, make sure that you place it into the
chassis in the correct orientation. The edge with external ports goes to the
rear part of the chassis as indicated in the image below.
2.1.2 Screw holes
Place 11 screws into the holes indicated by circles to secure the
motherboard to the chassis.
Do not overtighten the screws! Doing so may damage the
motherboard.
Place this side towards
the rear of the chassis
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-1
Page 28
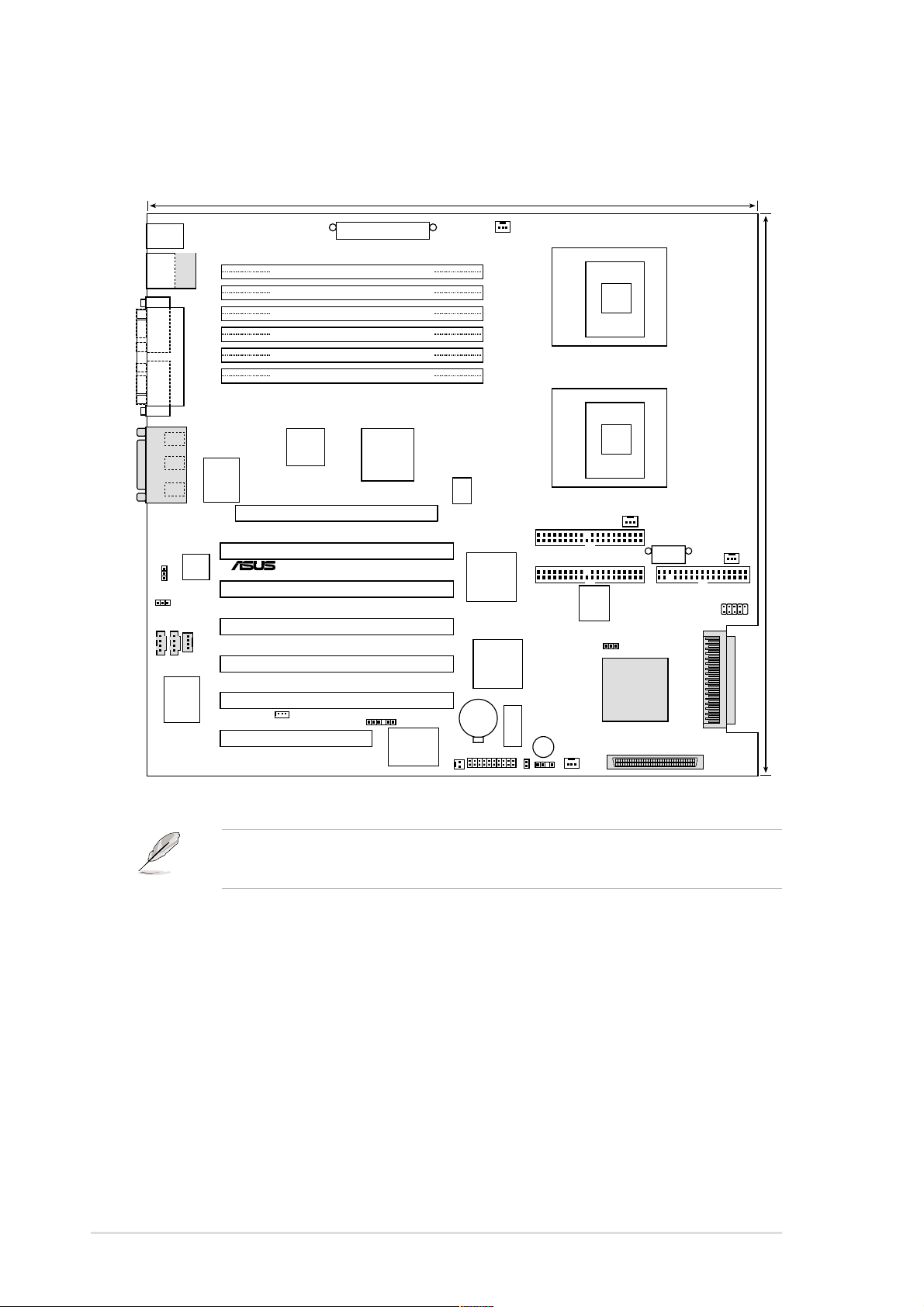
2.2 Motherboard layout
33cm (13in)
PS/2KBMS
T: Mouse
B: Keyboard
USB2.0
Top:
T:USB1
RJ-45
B:USB2
COM1
PARALLEL PORT
COM2
Line
Out
Line
In
Mic
In
GAME_AUDIO
Intel
82551
Ethernet
LAN_SW
AUDIO_EN
CD1
AUX
C-Media
CMI8738 6CH
DDR DIMMA1 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
DDR DIMMB1 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
DDR DIMMA2 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
DDR DIMMB2 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
DDR DIMMA3 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
DDR DIMMB3 (72 bit, 184-pin module)
I/O
Super
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGPPRO)
PCI-X1 (64-bit, 133MHz 3V)
Fast
®
PCI-X2 (64-bit, 133MHz 3V)
PCI-X3 (64-bit, 133MHz 3V)
MODEM
PCI-X4 (64-bit, 133MHz 3V)
PCI-X5 (64-bit, 66MHz 3V)
Audio Controller
PCI6 (32-bit, 33MHz 5V)
CIOBG
WOL_CON
EATXPWR
ServerWorks
CMIC-WS
North Bridge
PR-DLSW
with Hardware
SMB
ASUS
ASIC
Monitor
CPUFAN1
mPGA 604
®
mPGA 604
CLKSW
CMOS Power
WOR
ServerWorks
RCC CSB5
South Bridge
ServerWorks
CIOB-X2
I/O Bridge
CR2032 3V
Lithium Cell
PANEL
®
®
BUZZER
CONFIG_SW
IDELED
CHASSIS
IDE1
IDE2
SYSFAN2
CPUFAN2
4Mbit
Flash
BIOS
SCSI_EN
®
LSI 53C1010R
SCSI
Controller
34 1
CON12V
SCSI-A
3568
30.5cm (12in)
SYSFAN1
FLOPPY
USB2
SCSI-B
2-2
The SCSI features are optional. These components are grayed out in
the above motherboard layout.
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 29
2.3 Before you proceed
Take note of the following precautions before you install motherboard
components or change any motherboard settings.
1. Unplug the power cord from the wall socket before touching any
component.
2. Use a grounded wrist strap or touch a safely grounded object or to
a metal object, such as the power supply case, before handling
components to avoid damaging them due to static electricity.
3. Hold components by the edges to avoid touching the ICs on them.
4. Whenever you uninstall any component, place it on a grounded
antistatic pad or in the bag that came with the component.
5. Before you install or remove any component, ensure that the
ATX power supply is switched off or the power cord is
detached from the power supply. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to the motherboard, peripherals, and/or
components.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-3
Page 30
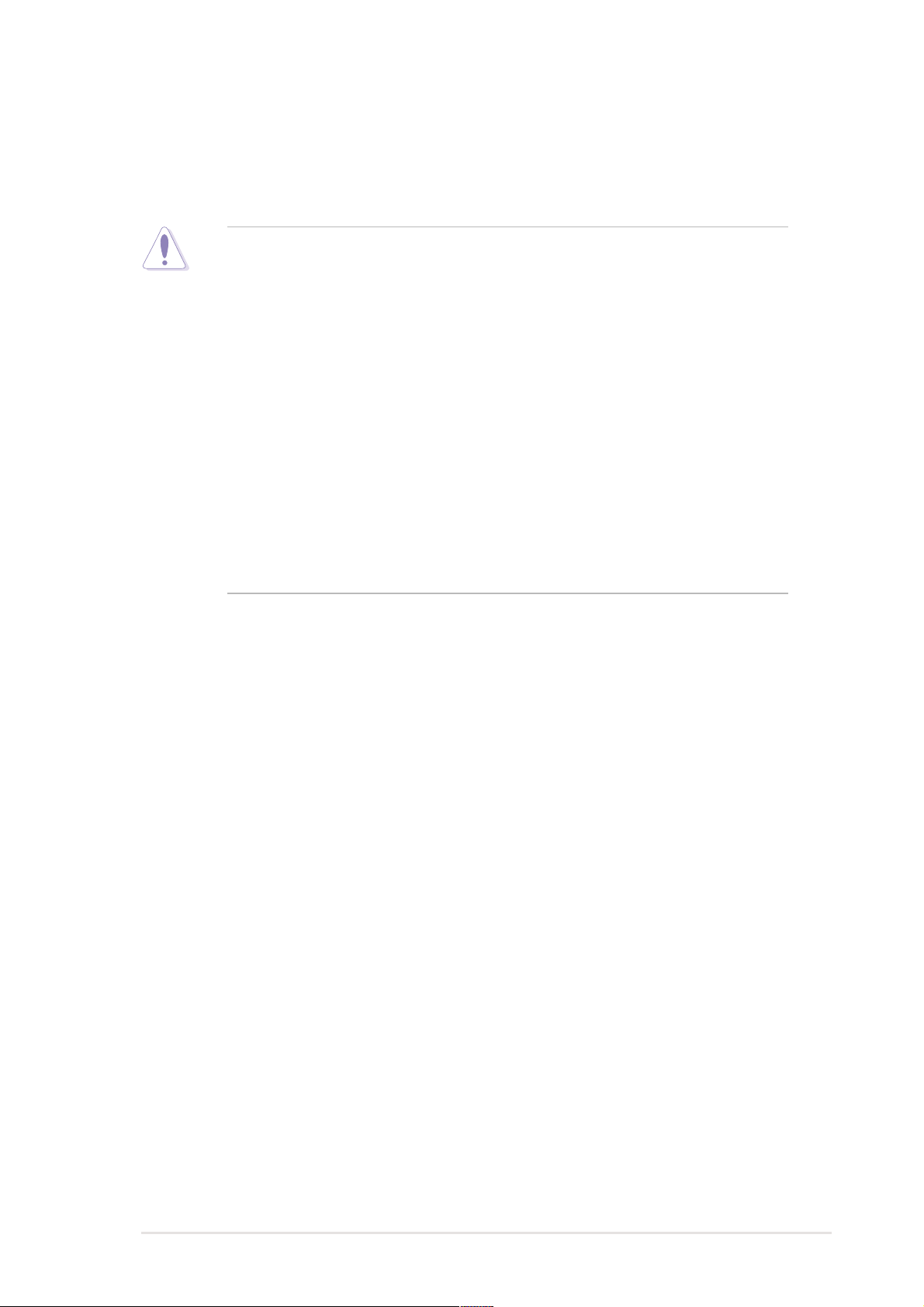
2.4 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
2.4.1 Overview
The motherboard comes with dual surface mount 604-pin Zero Insertion
Force (ZIF) sockets. The sockets are designed for the Intel Processor in
the 603/604-pin package with 512KB L2 cache. The processor includes
the Intel® NetBurst™ micro-architecture that features the hyper-pipelined
technology, rapid execution engine, 400MHz system bus, and execution
trace cache. Together, these attributes improve system performance by
allowing higher core frequencies, faster execution of integer instructions,
and data transfer rate of up to 3.2GB/s.
You may install Intel
®
Xeon™ CPUs that support Hyper-Threading
Technology. For more information on Hyper-Threading Technology, visit
www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
Intel® Xeon™
®
PR-DLSW
Gold Mark
PR-DLSW Socket 604
Note in the illustration that the CPU has a gold triangular mark on one
corner. This mark indicates the processor Pin 1 that should match a
specific corner of the CPU socket.
Incorrect installation of the CPU into the socket may bend the pins and
severely damage the CPU!
2-4
The motherboard supports either one or two CPUs. If you are installing
only one CPU, you MUST install it in CPU socket 1.
CPU Socket 1
(outer socket)
CPU Socket 2
(inner socket)
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 31

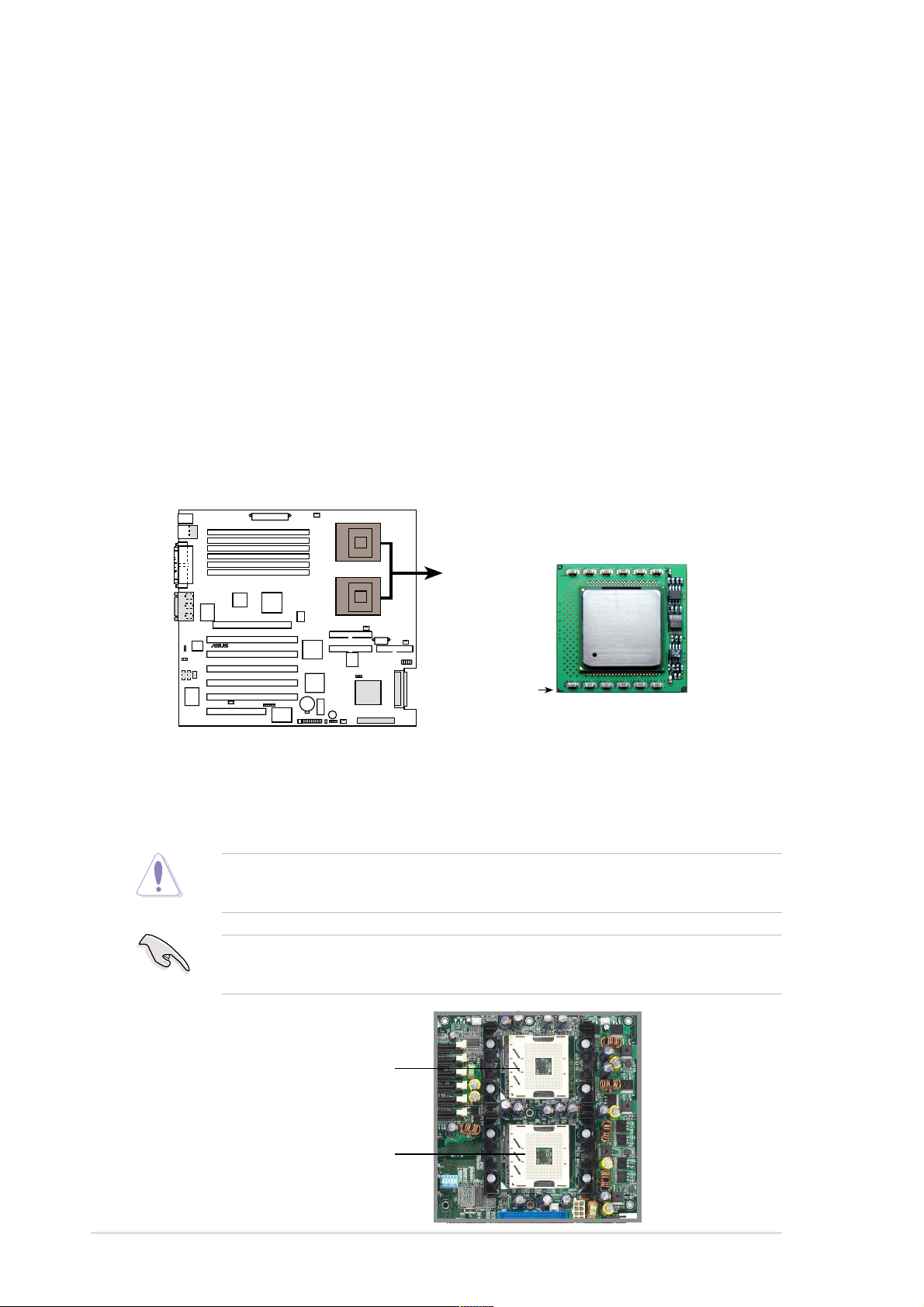
2.4.2 Installing the CPU
If you are installing two CPUs, install in the CPU socket 2 first.
Follow these steps to install a CPU.
1. Locate the 604-pin ZIF sockets on
the motherboard. Unlock the
socket by pressing the lever
sideways, then lift it up to at least
115° angle.
Make sure that the socket
lever is lifted up to at least
115° angle, otherwise the CPU
does not fit in completely.
2. Position the CPU above the
socket as shown.
3. Carefully insert the CPU into the
socket until it fits in place.
Marked Corner
The CPU fits only in one
correct orientation. DO NOT
force the CPU into the socket
to prevent bending the pins
and damaging the CPU!
4. When the CPU is in place, press it
firmly on the socket while you
push down the socket lever to
secure the CPU. The lever clicks
on the side tab to indicate that it is
locked.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-5
Page 32

2.4.3 Installing the CPU heatsink and fan
The Intel
®
Xeon™ processors require specially designed heatsink and fan
assembly to ensure optimum thermal condition and performance.
Follow these steps to install the CPU heatsink and fan.
1. Place the heatsink and fan
assembly on top of the installed
CPU, making sure that it fits in
place.
2. Hook one end of the retention
bracket into the protruding tab on
the corner of the plastic retention
base. (The retention base comes
installed with the motherboard.)
2-6
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 33

3. Use a small flat screw driver to
attach the other end of the
bracket, while firmly holding down
the heatsink and fan assembly.
The middle hook of the bracket
snaps in place if you properly
attached the two ends.
4. As shown, the middle hook of the
bracket snaps in place if you
properly attached the two ends.
5. Do steps 2 to 4 to install the other
bracket.
6. When the heatsink and fan
assembly is in place, connect the
fan cable to the fan connector on
the motherboard labeled
CPUFAN1 (for the CPU on socket
1) and CPUFAN2 (for the CPU on
socket 2).
Don’t forget to connect the
CPU fan cable. Hardware
monitoring problems may
occur if you fail to plug the
cable.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-7
Page 34

2.5 System memory
2.5.1 Overview
The motherboard comes with six Double Data Rate (DDR) Dual Inline
Memory Module (DIMM) sockets. These sockets support up to 12GB
system memory using 184-pin registered PC2100/1600 DIMMs with Serial
Presence Detect (SPD) and Error Check and Correction (ECC).
80 Pins104 Pins
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW 184-Pin DDR DIMM Sockets
A DDR DIMM is keyed with a notch so that it fits in only one direction.
DO NOT force a DIMM into a socket to avoid damaging the DIMM.
The DDR SDRAM technology evolved from the mainstream PC66, PC100,
PC133 memory known as Single Data Rate (SDR) SDRAM. DDR memory
however, has the ability to perform two data operations in one clock cycle,
thus providing twice the throughput of SDR memory. For example, a
200MHz DDR DIMM will support a 100MHz memory bus, and a 266MHz
DDR DIMM will support a 133MHz memory bus.
DDR Data Transfer Rate DDR Base Frequency
266MHz 133MHz
200MHz 100MHz
A DDR DIMM has the same physical dimensions as an SDR DIMM, but it
has a 184-pin footprint compared to the 168-pin of the SDR DIMM. Also, a
DDR DIMM is single notched while an SDR DIMM is double notched.
Therefore, a DDR DIMM is not backward compatible with SDR, and should
be installed only in a socket specially designed for DDR DIMMs.
2-8
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 35

2.5.2 Memory Configurations
The motherboard supports system memory of up to 12GB in a two-way
interleaved configuration. As a rule, this configuration requires that you
install identical DDR DIMMs (exactly the same type and size) in pairs. For
example, if you installed a 512MB module into DDRA1, you must install
the same type of 512MB module into DDRB1. The same rule applies to
pairs DDRA2/DDRB2 and DDRA3/DDRB3.
The only exception to the above rule allows you to install one DIMM into
DDRA1 socket (the socket closest to the ATX power connector). Installing
a single DIMM into any other socket would not work.
The following table lists the DIMM socket pairs and the memory modules
that you can install.
Memory configuration table
DIMM Socket 184-pin ECC DDR DIMM Total Memory
DDRA1 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
DDRB1 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
DDRA2 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
DDRB2 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
DDRA3 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
DDRB3 SDRAM 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 2GB x1
Total System Memory (Max. 12GB)
The system chipset only supports PC2100/1600 registered ECC
DIMMs. Make sure to use only the specified DIMM types for stable
system operation.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-9
Page 36

2.5.3 Installing a DIMM
Make sure to unplug the power supply before adding or removing
DIMMs or other system components. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to both the motherboard and the components.
Follow these steps to install a DIMM.
1. Unlock a DIMM socket by pressing
the retaining clips outward.
2. Align a DIMM on the socket such
that the notch on the DIMM
matches the break on the socket.
Unlocked Retaining Clip
3. Firmly insert the DIMM into the
socket until the retaining clips
snap back in place and the DIMM
is properly seated.
Locked Retaining Clip
2.5.4 Removing a DIMM
Follow these steps to remove a DIMM.
1. Simultaneously press the retaining
clips outward to unlock the DIMM.
2. Remove the DIMM from the
socket.
Support the DIMM lightly with
your fingers when pressing
the retaining clips. The DIMM
might get damaged when it
flips out with extra force.
2-10
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 37

2.6 Expansion slots
In the future, you may need to install expansion cards. The following subsections describe the slots and the expansion cards that they support.
Make sure to unplug the power cord before adding or removing
expansion cards. Failure to do so may cause you physical injury and
damage motherboard components.
2.6.1 Installing an expansion card
Follow these steps to install an expansion card.
1. Before installing the expansion card, read the documentation that
came with it and make the necessary hardware settings for the card.
2. Remove the system unit cover (if your motherboard is already installed
in a chassis).
3. Remove the bracket opposite the slot that you intend to use. Keep the
screw for later use.
4. Align the card connector with the slot and press firmly until the card is
completely seated on the slot.
5. Secure the card to the chassis with the screw you removed earlier.
6. Replace the system cover.
2.6.2 Configuring an expansion card
After installing the expansion card, configure the it by adjusting the
software settings.
1. Turn on the system and change the necessary BIOS settings, if any.
See Chapter 4 for information on BIOS setup.
2. Assign an IRQ to the card. Refer to the tables on the next page.
3. Install the software drivers for the expansion card.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-11
Page 38

Standard Interrupt Assignments
IRQ Priority Standard Function
0 1 System Timer
1 2 Keyboard Controller
2 N/A Programmable Interrupt
3* 11 Communications Port (COM2)
4* 12 Communications Port (COM1)
5* 13 Sound Card (sometimes LPT2)
6 14 Floppy Disk Controller
7* 15 Printer Port (LPT1)
8 3 System CMOS/Real Time Clock
9* 4 ACPI Mode when used
10* 5 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
11* 6 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
12* 7 PS/2 Compatible Mouse Port
13 8 Numeric Data Processor
14* 9 Primary IDE Channel
15* 10 Secondary IDE Channel
* These IRQs are usually available for ISA or PCI devices.
IRQ assignments for this motherboard
PCI INTA PCI INTB PCI INTC PCI INTD
PCI slot 1 1 12 13 14
PCI slot 2 4 15 16 17
PCI slot 3 5 18 19 20
PCI slot 4 8 21 22 23
PCI slot 5 9 24 25 26
PCI slot 6 10 27 28 29
AGP Pro slot 11 0 — —
Onboard 82551QM controller 2 — — —
Onboard SCSI controller 6 7 — —
When using PCI cards on shared slots, ensure that the drivers support
“Share IRQ” or that the cards do not need IRQ assignments.
Otherwise, conflicts will arise between the two PCI groups, making the
system unstable and the card inoperable.
2-12
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 39

2.6.3 PCI slots
This motherboard implements the PCI-X (Peripheral Component Interconnect
Extended) bus technology to support up to 133MHz data transfers, or about
1.06GB/s. This bus technology is primarily designed for servers to increase
the performance of high bandwidth devices such as Ultra3 SCSI. PCI-X is
backward compatible with the earlier PCI bus technology making it possible to
install PCI and PCI-X cards at the same time, but the bus speed will be that of
the slowest card. The following figure shows the five PCI-X slots and one PCI
slot on the motherboard.
PCI-X1
PCI-X2
PCI-X3
PCI-X4
PCI-X5
PCI6
PCI-X slots (PCI X1 to X5)
The motherboard comes with the LSI® 53C1010R SCSI controller . The
following table shows the varying bus speeds for the PCI-X slots according to
the PCI-X specification 1.0a.
Number of
cards installed PCI-X1 to PCI-X4 * PCI-X5
1 64-bit/133MHz PCI-X 64-bit/66MHz PCI
2 64-bit/100MHz PCI-X
3 or 4 64-bit/66MHz PCI-X
*
Plugging in a card into one of the slots allow for 133MHz bus speed. Plugging in two
cards reduces the bus speeds to 100MHz for both cards. Plugging in three or four
cards allows for 66MHz for all the cards.
PCI slot (PCI6)
PCI6 is a 32-bit/33MHz 5V PCI slot.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-13
Page 40

2.6.4 AGP PRO slot
This motherboard has an Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) PRO slot that
supports AGP cards. Note the notches on the card golden fingers to
ensure that they fit the AGP slot on your motherboard.
The AGP PRO slot comes with a warning label and a safety tab.
Remove the label and tab ONLY if you are installing an AGP PRO
card. Use a pointed object, such as a pen tip, to dislodge the tab.
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP )
2-14
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 41

2.7 Switches and jumper
2.7.1 Switches
The following figure shows the location and default settings of the DIP
switches on the motherboard.
Keep the default settings for stable system operation.
CLKSW
ON
ON
®
PR-DLSW
CONFIG_SW
ON
12345678
1.Frequency Selection
2.Frequency Selection
3.Frequency Selection
12345
4.Frequency Selection
5.Reserved(Must On)
OFF
1. Reserved
2. Reserved
3. Reserved
PR-DLSW DIP Switches
OFF ON
4. Reserved
5. Frequency Multiple
6. Frequency Multiple
7. Frequency Multiple
8. Frequency Multiple
1. CPU external frequency selection (CLKSW Switches 1-5)
This option tells the clock generator what frequency to send the CPU.
This allows the selection of the CPU’s external frequency (or Bus
Clock). The BUS Clock multiplied by the Frequency Multiple equals the
CPU’s internal frequency (the advertised CPU speed).
CLKSW
®
PR-DLSW
ON
CPU 100MHz
PR-DLSW CPU
External Frequency Selection
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
12345
2-15
Page 42

2. CPU Core:Bus frequency multiple (CONFIG_SW Switches 5-8)
This option sets the frequency multiple between the CPU internal and
external frequencies. This must be set in conjunction with the CPU Bus
Frequency.
CONFIG_SW
®
PR-DLSW
12345678
ON
12345678
11.0x
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
12.0x
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
13.0x
ON
12345678
ON
PR-DLSW CPU Frequency
Multiple Selection
14.0x
15.0x
16.0x
20.0x
2.7.2 Jumper
SCSI setting (2-pin SCSI_EN)
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the onboard SCSI feature.
Keep the jumper open if you wish to install SCSI devices. Place a cap
on the jumper to disable the onboard SCSI controller.
2-16
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW SCSI Setting
SCSI_EN
2132
Enable Disable
(Default)
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 43

2.8 Connectors
This section describes and illustrates the internal connectors on the
motherboard.
Always connect ribbon cables with the red stripe to Pin 1 on the
connectors. Pin 1 is usually on the side closest to the power connector
on hard drives and CD-ROM drives, but may be on the opposite side
on floppy disk drives.
1. Hard disk activity LED (2-pin IDE_LED)
This connector supplies power to the hard disk activity LED. The read
or write activities of any device connected to the primary or secondary
IDE connector cause this LED to light up.
IDELED
®
PR-DLSW
TIP: If the case-mounted LED does not
light, try reversing the 2-pin plug.
PR-DLSW IDE Activity LED
2. Floppy disk drive connector (34-1 pin FLOPPY)
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon cable. After
connecting one end to the motherboard, connect the other end to the
floppy drive. (Pin 5 is removed to prevent incorrect insertion when
using ribbon cables with pin 5 plug).
FLOPPY
®
PR-DLSW
PIN 1
NOTE: Orient the red markings on
the floppy ribbon cable to PIN 1.
PR-DLSW Floppy Disk Drive Connector
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-17
Page 44

3. IDE connectors (40-1 pin IDE1, IDE2)
This connector supports the provided UltraDMA/100/66 IDE hard disk
ribbon cable. Connect the cable’s blue connector to the primary
(recommended) or secondary IDE connector, then connect the gray
connector to the UltraDMA/100/66 slave device (hard disk drive) and
the black connector to the UltraDMA/100/66 master device. It is
recommended that you connect non-UltraDMA/100/66 devices to the
secondary IDE connector. If you install two hard disks, you must
configure the second drive as a slave device by setting its jumper
accordingly. Refer to the hard disk documentation for the jumper
settings. BIOS supports specific device bootup. If you have more than
two UltraDMA/100/66 devices, purchase another UltraDMA/100/66
cable. You may configure two hard disks to be both master devices
with two ribbon cables – one for the primary IDE connector and
another for the secondary IDE connector.
1. Pin 20 on each IDE connector is removed to match the covered
hole on the UltraDMA cable connector. This prevents incorrect
orientation when you connect the cables.
2. The hole near the blue connector on the UltraDMA/100/66 cable is
intentional.
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW IDE Connectors
For UltraDMA/100/66 IDE devices, use an 80-conductor IDE cable.
The UltraDMA/66 cable included in the motherboard package also
supports UltraDMA/100.
IDE1
PIN 1
IDE2
PIN 1
NOTE: Orient the red markings
(usually zigzag) on the IDE
ribbon cable to PIN 1.
2-18
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 45

4. Chassis alarm lead (4-1 pin CHASSIS)
This lead is for a chassis designed with intrusion detection feature.
This requires an external detection mechanism such as a chassis
intrusion sensor or microswitch. When you remove any chassis
component, the sensor triggers and sends a high-level signal to this
lead to record a chassis intrusion event.
By default, the pins labeled “Chassis Signal” and “Ground” are shorted
with a jumper cap. If you wish to use the chassis intrusion detection
feature, remove the jumper cap from the pins.
®
PR-DLSW
Chassis Signal
+5Volt
Ground
(Power Supply Stand By)
CHASSIS
PR-DLSW Chassis Open Alarm Lead
5. SMBus connector (6-1 pin SMB)
This connector allows you to connect SMBus (System Management
Bus) devices. Devices communicate with an SMBus host and/or other
SMBus devices using the SMBus interface. SMBus is a specific
implementation of an I
2
C bus, a multi-device bus that allows multiple
chips to connect to the same bus and enable each one to act as a
master by initiating data transfer.
SMB
®
PR-DLSW
Ground
+5V
SMBDATA
PR-DLSW SMBus Connectors
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
SMBCLK
FLOATING
1
2-19
Page 46

6. ATX power connectors (24/20-pin EATXPWR, 8-pin CON12V)
These connectors connect to an ATX 12V power supply. The plugs
from the power supply are designed to fit these connectors in only one
orientation. Find the proper orientation and push down firmly until the
connectors completely fit.
In addition to the 24/20-pin EATXPWR connector, this motherboard
requires that you connect the 8-pin +12V power plug to the CON12V
connector to provide sufficient power to the CPU.
Make sure that your ATX 12V power supply can provide 20A on the
+12V lead and at least 1A on the +5-volt standby lead (+5VSB). The
minimum recommended wattage is 300W for a fully configured system.
The system may become unstable and may experience difficulty
powering up if the power supply is inadequate.
20-pin
24-pin Power Connector
EATXPWR
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW ATX Power Connector
CON12V
+12 Volts
+3 Volts
Ground
+5 Volts
4-pin
Ground
Power OK
+12 Volts
+5V Standby
-5 Volts
+5 Volts
Ground
+5 Volts
For Power Supply
with 20-pin+4-pin
Power Connector
12V
12V
12V
GND
GND
GND
+5 Volts
Ground
Ground
Ground
12V
8-pin
GND
Ground
+5 Volts
Ground
PSON#
+3 Volts
-12 Volts
+3 Volts
+3 Volts
1
2-20
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 47

7. CPU, Chassis, and Power Fan Connectors
(3-pin CPUFAN1, CPUFAN2, SYSFAN1, SYSFAN2, SYSFAN3)
The fan connectors support cooling fans of 350mA~740mA (8.88W
max.) or a total of 1A~2.22A (26.64W max.) at +12V. Connect the fan
cables to the fan connectors on the motherboard, making sure that the
black wire of each cable matches the ground pin of the connector.
Do not forget to connect the fan cables to the fan connectors. Lack of
sufficient air flow within the system may damage the motherboard
components. These are not jumpers! DO NOT place jumper caps on
the fan connectors!
CPUFAN1
CPUFAN2
SYSFAN1
®
PR-DLSW
SYSFAN2
GND
+12V
Rotation
GND
+12V
Rotation
N.C.
GND
+12V
PR-DLSW 12-Volt Cooling Fan Power
8. USB header (10-1 pin USB2)
If the USB ports on the rear panel are inadequate, a USB header is
available for additional USB ports. The USB header complies with USB
1.1 specification that supports up to 12 Mbps connection speed.
®
PR-DLSW
USB2
PR-DLSW USB Header
USB Power
USBP2–
USBP2+
GND
15
6
NC
GND
USBP3–
USBP3+
USB Power
10
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-21
Page 48

9. Two 68-pin Ultra160 SCSI Connectors (CHA-WIDE, CHB-WIDE)
This motherboard has two 68-Pin Ultra160 SCSI connectors; one for
each of the two channels. Each channel can support a maximum of 15
devices as specified by Ultra160 standards.
SCSI-A
68-Pin Ultra160/
Ultra2-Wide SCSI Connector
®
PR-DLSW
SCSI-B
68-Pin Ultra160/
Ultra2-Wide SCSI Connector
34 1
3568
35
1
6834
PR-DLSW Onboard SCSI Connectors
SCSI Connection Notes
This motherboard has two 68-Pin Ultra160 SCSI connectors; one for each
of the two channels.
The onboard SCSI chipset incorporates an advanced multimode I/O cell
that supports both single-ended (SE), Ultra2, and Ultra160 devices. With
Ultra160 devices, the SCSI bus platform performs at full Ultra160 speeds
(up to 160MB/s) and extended cabling 12m (or 25m in a point-to-point
configuration). When an SE device is attached, the bus defaults to an SE
speed and 1.5m cable length.
Connect SCSI devices as shown. Each channel should have only one
type of SCSI standard (e.g. Ultra160, Ultra2, Ultra-Wide). Mixing SCSI
devices on the same channel decreases performance of the slower
device.
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW SCSI Connection Example
2-22
68-pin Internal SCSI Cable (Twisted-Pair Ribbon)
Internal SCSI Devices (up to 15 devices)
68-pin Internal SCSI Cable (Twisted-Pair Ribbon)
Internal SCSI Devices (up to 15 devices)
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Channel B
68-pin Female
Terminator
Channel A
68-pin Female
Terminator
Page 49

10.Wake-On-LAN Connector (3-pin WOL_CON)
This connector supports a LAN card with a Wake-On-LAN output. The
connector powers up the system when a wakeup packet or signal is
received through the LAN card.
WOL_CON
Ground
®
PR-DLSW
IMPORTANT: Requires an ATX power
supply with at least 720mA +5 volt
standby power
+5 Volt StandbyPME
PR-DLSW Wake-On-LAN Connector
11. Wake-On-Ring Connector (2-pin WOR)
This connector connects to internal modem cards with a Wake-OnRing output. The connector wakes up the system when a ringup packet
or signal is received through the internal modem card.
For external modems, Wake-On-Ring is detected through the COM
port.
®
PR-DLSW
WOR
Ring#
Ground
PR-DLSW Wake-On-Ring Connector
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-23
Page 50

12.Internal audio connectors (4-pin CD, AUX, MODEM)
These connectors allow you to receive stereo audio input from sound
sources such as a CD-ROM, TV tuner, or MPEG card. The MODEM
connector allows the onboard audio to interface with a voice modem
card with a similar connector. It also allows the sharing of mono_in
(such as a phone) and a mono_out (such as a speaker) between the
audio and a voice modem card.
CD1 (Black)
Left Audio Channel
Right Audio Channel
®
PR-DLSW
Ground
Ground
Modem-In
Modem-Out
Ground
Ground
AUX (White)
MODEM
PR-DLSW Internal Audio Connectors
13.System panel connector (20-pin PANEL)
This connector accommodates several system front panel functions.
PLED
Keylock
MLED
Ground
Speaker
Connector
Ground
Speaker
Ground
+5V
20
10
PWR
Reset
Ground
Ground
Reset SW
ATX Power
Switch*
®
PR-DLSW
PR-DLSW System Panel Connectors
Keyboard Lock
Power LED
+5 V
11
1
+5 V
Message LED
2-24
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 51

• System Power LED Lead (3-1 pin PLED)
This 3-1 pin connector connects to the system power LED. The LED
lights up when you turn on the system power, and blinks when the
system is in sleep mode.
• System Message LED Lead (2-pin MLED)
This 2-pin connector is for the system message LED that indicates
receipt of messages from a fax/modem. The normal status for this LED
is OFF, when there is no incoming data signal. The LED blinks when
data is received. The system message LED feature requires an ACPI
OS and driver support.
• System Warning Speaker Lead (4-pin SPEAKER)
This 4-pin connector is for a chassis-mounted speaker.
• ATX Power Switch / Soft-Off Switch Lead (2-pin PWR)
This connector connects a switch that controls the system power.
Pressing the power switch turns the system between ON and SLEEP,
or ON and SOFT OFF, depending on the BIOS or OS settings.
Pressing the power switch while in the ON mode for more than 4
seconds turns the system OFF.
• Reset Switch Lead (2-pin RESET)
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset switch for
rebooting the system without turning off the system power.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
2-25
Page 52

2-26
Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 53

Chapter 3
This chapter describes the power up
sequence and gives information on the
BIOS beep codes.
Powering up
Page 54

Chapter summary
3.1 Starting up for the first time.......................... 3-1
3.2 Powering off the computer ........................... 3-2
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Page 55

3.1 Starting up for the first time
1. After making all the connections, replace the system case cover.
2. Be sure that all switches are off.
3. Connect the power cord to the power connector at the back of the system
chassis.
4. Connect the power cord to a power outlet that is equipped with a surge
protector.
5. Turn on the devices in the following order:
a. Monitor
b. External SCSI devices (starting with the last device on the chain)
c. System power (if you are using an ATX power supply , you need to
switch on the power supply as well as press the ATX power switch on
the front of the chassis).
6. After applying power, the power LED on the system front panel case lights
up. For ATX power supplies, the system LED lights up when you press the
ATX power switch. If your monitor complies with “green” standards or if it
has a “power standby” feature, the monitor LED may light up or switch
between orange and green after the system LED turns on. The system
then runs the power-on tests. While the tests are running, the BIOS beeps
or additional messages appear on the screen. If you do not see anything
within 30 seconds from the time you turned on the power , the system may
have failed a power-on test. Check the jumper settings and connections or
call your retailer for assistance.
Award BIOS Beep Codes
Beep Meaning
One short beep when No error during POST
displaying logo
Long beeps in an endless loop No DRAM installed or detected
One long beep followed by Video card not found or video card
three short beeps memory bad
High frequency beeps when CPU overheated;
system is working System running at a lower frequency
7. At power on, hold down <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup. Follow the
instructions in Chapter 4.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
3-1
Page 56

3.2 Powering off the computer
You must first exit the operating system and shut down the system before
switching off the power. For ATX power supplies, you can press the ATX
power switch after exiting or shutting down the operating system. If you
use Windows 2000/XP, click the Start button, click Shut Down, then click
the OK button to shut down the computer. The power supply should turn
off after Windows shuts down.
The message “You can now safely turn off your computer” does not
appear when shutting down with ATX power supplies.
3-2
Chapter 3: Powering up
Page 57

Chapter 4
This chapter tells how to change system
settings through the BIOS Setup menus.
Detailed descriptions of the BIOS
parameters are also provided.
BIOS setup
Page 58

Chapter summary
4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS .............. 4-1
4.2 BIOS Setup program...................................... 4-5
4.3 Main Menu ...................................................... 4-8
4.4 Advanced Menu ........................................... 4-15
4.5 Power Menu.................................................. 4-22
4.6 Boot Menu .................................................... 4-27
4.7 Server Menu ................................................. 4-29
4.8 Exit Menu ...................................................... 4-30
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Page 59

4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS
4.1.1 Creating a bootable disk
AFLASH.EXE is a Flash Memory Writer utility that updates the BIOS by
uploading a new BIOS file to the programmable flash ROM on the
motherboard. This file works only in DOS mode. To determine the BIOS
version of your motherboard, check the last four numbers of the code
displayed on the upper left-hand corner of your screen during bootup.
Larger numbers represent a newer BIOS file.
1. Type FORMAT A:/S at the DOS prompt to create a bootable system
disk. DO NOT copy AUTOEXEC.BAT and CONFIG.SYS to the disk.
2. Type COPY D:\AFLASH\AFLASH.EXE A:\ (assuming D is your
CD-ROM drive) to copy AFLASH.EXE to the boot disk you created.
AFLASH works only in DOS mode. It does not work in the DOS prompt
within Windows, and does not work with certain memory drivers that
may be loaded when you boot from the hard drive. It is recommended
that you reboot using a floppy disk.
3. Reboot the computer from the floppy disk.
BIOS setup must specify “Floppy” as the first item in the boot
sequence.
4. In DOS mode, type A:\AFLASH <Enter> to run AFLASH.
If the word “unknown” appears after Flash Memory:, the memory chip
is either not programmable or is not supported by the ACPI BIOS and
therefore, cannot be programmed by the Flash Memory Writer utility.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-1
Page 60

5. Select 1. Save Current BIOS to File from the Main menu and press
<Enter>. The Save Current BIOS To File screen appears.
6. Type a filename and the path, for example, A:\XXX-XX.XXX, then
press <Enter>.
4-2
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 61

4.1.2 Updating the BIOS
Update the BIOS only if you have problems with the motherboard and
you are sure that the new BIOS revision will solve your problems.
Careless updating may result to more problems with the motherboard!
1. Download an updated ASUS BIOS file from the Internet (WWW or
FTP) (see ASUS CONTACT INFORMATION on page x for details) and
save to the boot floppy disk you created earlier.
2. Boot from the floppy disk.
3. At the “A:\” prompt, type AFLASH and then press <Enter>.
4. At the Main Menu, type 2 then press <Enter>. The Update BIOS
Including Boot Block and ESCD screen appears.
5. Type the filename of your new BIOS and the path, for example,
A:\XXX-XX.XXX, then press <Enter>.
To cancel this operation, press <Enter>.
6. When prompted to confirm the BIOS update, press Y to start the
update.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-3
Page 62

7. The utility starts to program the new BIOS information into the Flash
ROM. The boot block is updated automatically only when necessary.
This minimizes the possibility of boot problems in case of update
failures. When the programming is done, the message
Successfully”
appears.
“Flashed
8. Follow the onscreen instructions to continue.
4-4
If you encounter problems while updating the new BIOS, DO NOT turn
off the system because this may cause boot problems. Just repeat the
process, and if the problem persists, load the original BIOS file you
saved to the boot disk. If the Flash Memory Writer utility is not able to
successfully update a complete BIOS file, the system may not boot. If
this happens, call the ASUS service center for support.
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 63

4.2 BIOS Setup program
This motherboard supports a programmable Flash ROM that you can
update using the provided utility described in section
updating your BIOS.”
Use the BIOS Setup program when you are installing a motherboard,
reconfiguring your system, or prompted to “Run Setup”. This section
explains how to configure your system using this utility.
Even if you are not prompted to use the Setup program, you may want to
change the configuration of your computer in the future. For example, you
may want to enable the security password feature or make changes to the
power management settings. This requires you to reconfigure your system
using the BIOS Setup program so that the computer can recognize these
changes and record them in the CMOS RAM of the Flash ROM.
The Flash ROM on the motherboard stores the Setup utility. When you
start up the computer, the system provides you with the opportunity to run
this program. Press <Delete> during the Power-On Self Test (POST) to
enter the Setup utility, otherwise, POST continues with its test routines.
“
4.1 Managing and
If you wish to enter Setup after POST, restart the system by pressing
<Ctrl> + <Alt> + <Delete>, or by pressing the reset button on the system
chassis. You can also restart by turning the system off and then back on.
Do this last option only if the first two failed.
The Setup program is designed to make it as easy to use as possible. It is
a menu-driven program, which means you can scroll through the various
sub-menus and make your selections among the predetermined choices.
Because the BIOS software is constantly being updated, the following
BIOS setup screens and descriptions are for reference purposes only,
and may not exactly match what you see on your screen.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-5
Page 64

4.2.1 BIOS menu bar
The top of the screen has a menu bar with the following selections:
MAIN Use this menu to make changes to the basic system
configuration.
ADVANCED Use this menu to enable and make changes to the
advanced features.
POWER Use this menu to configure power management features.
BOOT Use this menu to configure the default system device used
to locate and load the Operating System.
SERVER Use this menu to set server-related items
EXIT Use this menu to exit the current menu or to exit the Setup
program.
To access the menu bar items, press the right or left arrow key on the
keyboard until the desired item is highlighted.
4.2.2 Legend bar
At the bottom of the Setup screen is a legend bar . The keys in the legend bar
allow you to navigate through the various setup menus. The following table
lists the keys found in the legend bar with their corresponding functions.
Navigation Key(s) Function Description
<F1> or <Alt + H> Displays the General Help screen from any-
where in the BIOS Setup
<Esc> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main
menu from a sub-menu
Left or Right arrow Selects the menu item to the left or right
Up or Down arrow Moves the highlight up or down between fields
- (minus key) Scrolls backward through the values for the
highlighted field
+ (plus key) or spacebar Scrolls forward through the values for the high-
lighted field
<Enter> Brings up a selection menu for the highlighted
field
<Home> or <PgUp> Moves the cursor to the first field
<End> or <PgDn> Moves the cursor to the last field
<F5> Resets the current screen to its Setup Defaults
<F10> Saves changes and exits Setup
4-6
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 65

General help
In addition to the Item Specific Help window, the BIOS setup program also
provides a General Help screen. You may launch this screen from any
menu by simply pressing <F1> or the <Alt> + <H> combination. The
General Help screen lists the legend keys and their corresponding
functions.
Saving changes and exiting the Setup program
See “4.8 Exit Menu” for detailed information on saving changes and exiting
the setup program.
Scroll bar
When a scroll bar appears to the right of a help window, it indicates that
there is more information to be displayed that will not fit in the window. Use
<PgUp> and <PgDn> or the up and down arrow keys to scroll through the
entire help document. Press <Home> to display the first page, press
<End> to go to the last page. To exit the help window, press <Enter> or
<Esc>.
Sub-menu
Note that a right pointer symbol (as shown on the
left) appears to the left of certain fields. This pointer
indicates that you can display a sub-menu from this
field. A sub-menu contains additional options for a
field parameter. To display a sub-menu, move the
highlight to the field and press <Enter>. The submenu appears. Use the legend keys to enter values
and move from field to field within a sub-menu as
you would within a menu. Use the <Esc> key to
return to the main menu.
Take some time to familiarize yourself with the legend keys and their
corresponding functions. Practice navigating through the various menus
and sub-menus. If you accidentally make unwanted changes to any of the
fields, use the set default hot key <F5> to load the Setup default values.
While moving around through the Setup program, note that explanations
appear in the Item Specific Help window located to the right of each menu.
This window displays the help text for the currently highlighted field.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-7
Page 66

4.3 Main Menu
When you enter the Setup program, the following screen appears.
System Time [XX:XX:XX]
Sets the system to the time that you specify (usually the current time). The
format is hour, minute, second. Valid values for hour, minute and second
are Hour: (00 to 23), Minute: (00 to 59), Second: (00 to 59). Use the <Tab>
or <Shift> + <Tab> keys to move between the hour, minute, and second
fields.
System Date [XX/XX/XXXX]
Sets the system to the date that you specify (usually the current date). The
format is month, day, year. Valid values for month, day, and year are
Month: (1 to 12), Day: (1 to 31), Year: (up to 2099). Use the <Tab> or
<Shift> + <Tab> keys to move between the month, day, and year fields.
Legacy Diskette A [1.44M, 3.5 in.]
Sets the type of floppy drive installed. Configuration options: [None] [360K,
5.25 in.] [1.2M , 5.25 in.] [720K , 3.5 in.] [1.44M, 3.5 in.] [2.88M, 3.5 in.]
Floppy 3 Mode Support [Disabled]
This is required to support older Japanese floppy drives. The Floppy 3
Mode feature allows reading and writing of 1.2MB (as opposed to 1.44MB)
on a 3.5-inch diskette. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-8
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 67

Supervisor Password [Disabled] / User Password [Disabled]
These fields allow you to set passwords. To set a password, highlight the
appropriate field and press <Enter>. Type in a password then press
<Enter>. You can type up to eight alphanumeric characters. Symbols and
other characters are ignored. To confirm the password, type the password
again and press <Enter>. The password is now set to [Enabled]. This
password allows full access to the BIOS Setup menus. To clear the
password, highlight this field and press <Enter>. The same dialog box as
above appears. Press <Enter>. The password is set to [Disabled].
A note about passwords
The BIOS Setup program allows you to specify passwords in the Main
menu. The passwords control access to the BIOS during system
startup. Passwords are not case sensitive, meaning, passwords typed
in either uppercase or lowercase letters are accepted. The BIOS Setup
program allows you to specify two different passwords: a Supervisor
password and a User password. If you did not set a Supervisor
password, anyone can access the BIOS Setup program. If you did, the
Supervisor password is required to enter the BIOS Setup program and
to gain full access to the configuration fields.
Forgot the password?
If you forget your password, you can clear it by erasing the CMOS
Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM. The RAM data containing the password
information is powered by the onboard button cell battery. See section
“2.7 Switches and jumpers” for information on how to erase the RTC
RAM.
Halt On [All Errors]
This field specifies the types of errors that will cause the system to halt.
Configuration options: [All Errors] [No Error] [All but Keyboard] [All but
Disk] [All but Disk/Keyboard]
Installed Memory [XXX MB]
This field automatically displays the amount of conventional memory
detected by the system during the boot process.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-9
Page 68

4.3.1 Primary and Secondary Master/Slave
Type [Auto]
Select [Auto] to automatically detect an IDE hard disk drive. If automatic
detection is successful, Setup automatically fills in the correct values for
the remaining fields on this sub-menu. If automatic detection fails, this may
be because the hard disk drive is too old or too new. If the hard disk was
already formatted on an older system, Setup may detect incorrect
parameters. In these cases, select [User Type HDD] to manually enter the
IDE hard disk drive parameters. Refer to the next section for details.
Before attempting to configure a hard disk drive, make sure you have
the correct configuration information supplied by the drive
manufacturer. Incorrect settings may cause the system to fail to
recognize the installed hard disk.
4-10
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 69

[User Type HDD]
Manually enter the number of cylinders, heads and sectors per track for
the drive. Refer to the drive documentation or on the drive label for this
information.
After entering the IDE hard disk drive information into BIOS, use a disk
utility, such as FDISK, to partition and format new IDE hard disk drives.
This is necessary so that you can write or read data from the hard disk.
Make sure to set the partition of the Primary IDE hard disk drives to
active.
If no drive is installed or if you are removing a drive and not replacing it,
select [None].
Other options for the Type field are:
[CD-ROM] - for IDE CD-ROM drives
[LS-120] - for LS-120 compatible floppy disk drives
[ZIP] - for ZIP-compatible disk drives
[MO] - for IDE magneto optical disk drives
[Other A TAPI Device] - for IDE devices not listed here
After making your selections on this sub-menu, press the <Esc> key to
return to the Main menu. When the Main menu appears, the hard disk
drive field displays the size for the hard disk drive that you configured.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-11
Page 70

Translation Method [LBA]
Select the hard disk drive type in this field. When Logical Block Addressing
(LBA) is enabled, the 28-bit addressing of the hard drive is used without
regard for cylinders, heads, or sectors. Note that LBA Mode is necessary
for drives with more than 504MB storage capacity. Configuration options:
[LBA] [LARGE] [Normal] [Match Partition Table] [Manual]
Cylinders
This field configures the number of cylinders. Refer to the drive
documentation to determine the correct value. To make changes to this
field, set the Type field to [User Type HDD] and the Translation Method
field to [Manual].
Head
This field configures the number of read/write heads. Refer to the drive
documentation to determine the correct value. To make changes to this
field, set the Type field to [User Type HDD] and the Translation Method
field to [Manual].
Sector
This field configures the number of sectors per track. Refer to the drive
documentation to determine the correct value. To make changes to this
field, set the Type field to [User Type HDD] and the Translation Method
field to [Manual].
CHS Capacity
This field shows the drive’s maximum CHS capacity as calculated by the
BIOS based on the drive information you entered.
Maximum LBA Capacity
This field shows the drive’s maximum LBA capacity as calculated by the
BIOS based on the drive information you entered.
Multi-Sector Transfers [Maximum]
This option automatically sets the number of sectors per block to the
highest number that the drive supports. Note that when this field is
automatically configured, the set value may not always be the fastest
value for the drive. You may also manually configure this field. Refer to the
documentation that came with the hard drive to determine the optimum
value and set it manually. To make changes to this field, set the Type field
to [User Type HDD]. Configuration options: [Disabled] [2 Sectors] [4
Sectors] [8 Sectors] [16 Sectors] [32 Sectors] [Maximum]
4-12
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 71

SMART Monitoring [Disabled]
This field allows you to enable or disable the S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring,
Analysis and Reporting Technology) system that utilizes internal hard disk
drive monitoring technology. This parameter is normally disabled because
the resources used in the SMART monitoring feature may decrease
system performance. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PIO Mode [4]
This option lets you set a PIO (Programmed Input/Output) mode for the
IDE device. Modes 0 through 4 provide successive increase in
performance. Configuration options: [0] [1] [2] [3] [4]
Ultra DMA Mode [Disabled]
Ultra DMA capability allows improved transfer speeds and data integrity for
compatible IDE devices. Set to [Disabled] to suppress Ultra DMA
capability. To make changes to this field, set the Type field to [User Type
HDD]. Configuration options: [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [Disabled]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-13
Page 72

4.3.2 Keyboard Features
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
This field enables users to activate the Number Lock function upon system
boot. Configuration options: [Off] [On]
Keyboard Auto-Repeat Rate [6/Sec]
This controls the speed at which the system registers repeated keystrokes.
Options range from 6 to 30 characters per second. Configuration options:
[6/Sec] [8/Sec] [10/Sec] [12/Sec] [15/Sec] [20/Sec] [24/Sec] [30/Sec]
Keyboard Auto-Repeat Delay [1/4 Sec]
This field sets the time interval for displaying the first and second
characters. Configuration options: [1/4 Sec] [1/2 Sec] [3/4 Sec] [1 Sec]
4-14
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 73

4.4 Advanced Menu
CPU Speed [Manual]
This field displays the auto-detected CPU speed.
CPU Level 1 Cache, CPU Level 2 Cache [Enabled]
These fields allow you to choose from the default [Enabled] or choose
[Disabled] to turn on or off the CPU Level 1 and Level 2 built-in cache.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Hyper-Threading Technology [Enabled]
This item allows you to enable or disable support for Hyper-Threading
Technology enabled processors which contain multiple logical processors
per physical processor package. Configuration options: [Disabled]
[Enabled]
BIOS Update [Enabled]
This field functions as an update loader integrated into the BIOS to supply
the processor with the required data. When set to [Enabled], the BIOS
loads the update on all processors during system bootup. Configuration
options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PS/2 Mouse Function Control [Auto]
The default setting [Auto] allows the system to detect a PS/2 mouse at
startup. If a mouse is detected, the BIOS assigns IRQ12 to the PS/2
mouse. Otherwise, IRQ12 can be used for expansion cards. When you set
this field to [Enabled], BIOS reserves IRQ12, whether or not a PS/2 mouse
is detected at startup. Configuration options: [Enabled] [Auto]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-15
Page 74

OS/2 Onboard Memory > 64M [Disabled]
When using OS/2 operating systems with installed DRAM of greater than
64MB, you need to set this option to [Enabled]. Otherwise, leave to the
default setting [Disabled]. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
USB Legacy Support [Auto]
This motherboard supports Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices. The
default of [Auto] allows the system to detect a USB device at startup. If
detected, the USB controller legacy mode is enabled. If not detected, the
USB controller legacy mode is disabled.
When you set this field to [Disabled], the USB controller legacy mode is
disabled whether or not you are using a USB device. Configuration
options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
4-16
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 75

4.4.1 Chip Configuration
Graphics Aperture Size [64MB]
This feature allows you to select the size of mapped memory for AGP
graphic data. Configuration options: [32MB] [64MB] [128MB] [256MB]
Video Memory Cache Mode [UC]
USWC (uncacheable, speculative write combining) is a new cache
technology for the video memory of the processor. It can greatly improve
the display speed by caching the display data. You must set this to UC
(uncacheable) if your display card cannot support this feature; otherwise
your system may not boot. Configuration options: [UC] [USWC]
Onboard PCI IDE [Both]
You can select to enable the primary IDE channel, both the primary and
secondary channels, or disable both channels. Configuration options:
[Both] [Primary] [Disabled]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-17
Page 76

4.4.2 I/O Device Configuration
Floppy Disk Access Control [R/W]
When set to [Read Only], this parameter protects files from being copied to
floppy disks by allowing reads from, but not writes to, the floppy disk drive.
The default setting [R/W] allows both reads and writes. Configuration
options: [R/W] [Read Only]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8H/IRQ4]
Onboard Serial Port 2 [2F8H/IRQ3]
These fields allow you to set the addresses for the onboard serial
connectors. Serial Port 1 and Serial Port 2 must have different addresses.
Configuration options: [3F8H/IRQ4] [2F8H/IRQ3] [3E8H/IRQ4] [2E8H/
IRQ10] [Disabled]
Onboard Parallel Port [378H/IRQ7]
This field allows you to set the address of the onboard parallel port
connector . If you disable this field, the Parallel Port Mode and ECP DMA
Select configurations are not available. Configuration options: [Disabled]
[378H/IRQ7] [278H/IRQ5]
4-18
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 77

Parallel Port Mode [ECP+EPP]
This field allows you to set the operation mode of the parallel port.
[Normal] allows normal-speed operation but in one direction only; [EPP]
allows bidirectional parallel port operation; [ECP] allows the parallel port to
operate in bidirectional DMA mode; [ECP+EPP] allows normal speed
operation in a two-way mode. Configuration options: [Normal] [EPP] [ECP]
[ECP+EPP]
ECP DMA Select [3]
This field allows you to configure the parallel port DMA channel for the
selected ECP mode. This selection is available only if you select [ECP] or
[ECP+EPP] in Parallel Port Mode above. Configuration options: [1] [3]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-19
Page 78

4.4.3 PCI Configuration
Slot 1, Slot 2, Slot 3, Slot 4, Slot 5, Slot 6 IRQ [Auto]
These fields set how IRQ use is determined for each PCI slot. The
default setting for each field is [Auto], which utilizes auto-routing to
determine IRQ use. Configuration options: [Auto] [NA] [3] [4] [5] [7] [9]
[10] [11] [12] [14] [15]
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop [Disabled]
Some non-standard VGA cards, like graphics accelerators or MPEG video
cards, may not show colors properly. Setting this field to [Enabled] corrects
this problem. If you are using standard VGA cards, leave this field to the
default setting [Disabled]. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PCI Latency Timer [32]
Leave on default setting for best performance vs. stability.
Sparse PCI Host Bus [3 BUS]
This field allows you to reserve the bus number for the PCI slots.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [2 BUS] [3 BUS] [4 BUS]
4-20
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 79

Onboard SCSI BIOS [Auto]
[Auto] allows the motherboard BIOS to detect whether you have a Adaptec
SCSI controller. If the SCSI controller is detected, the SCSI BIOS will be
enabled. If no SCSI controller is detected, the onboard SCSI BIOS will be
disabled.
Setting to [Disabled] deactivates the onboard SCSI BIOS so that the
BIOS on an add-on SCSI card can be used . If your SCSI card does not
have a BIOS, the SCSI card will not function. Configuration options: [Auto]
[Disabled]
ONB SCSI BIOS First [No]
This field allows giving priority to the onboard SCSI BIOS for SCSI
functions over other SCSI controllers. Configuration options: [No] [Yes]
ONB Primary SCSI Term [Enabled]
ONB Secondary SCSI Term [Enabled]
This field allows you to enable or disable the onboard termination for the
primary and secondary SCSI channels. Configuration options: [Enabled]
[Disabled]
Primary VGA BIOS First [PCI VGA Card]
This field allows you to select the primary graphics card. Configuration
options: [PCI VGA Card] [AGP VGA Card]
USB Function [Enabled]
Set this field to [Enabled] if you want to use Universal Serial Bus devices.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Onboard LAN Boot ROM [Disabled]
When set to [Enabled], this field allows the system to boot from the
network using the onboard LAN controller boot ROM. Configuration
options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-21
Page 80

4.5 Power Menu
The Power menu allows you to reduce power consumption. This feature
turns off the video display and shuts down the hard disk after a period of
inactivity.
Power Management [User Defined]
This field allows you to activate or deactivate the automatic power saving
features. When set to [Disabled], the power management features do not
function regardless of the other settings on this menu. The [User Defined]
option allows you to set the period of inactivity before the system enters
suspend mode. Refer to “Suspend Mode” item.
When set to [Max Saving], system power is conserved to its greatest
amount. This setting automatically puts the system into suspend mode
after a brief period of system inactivity. [Min Saving] allows the least power
saving as the system enters suspend mode only after a long period of
inactivity. Configuration options: [User Defined] [Disabled] [Min Saving]
[Max Saving]
You should install the Advanced Power Management (APM) utility to
keep the system time updated even when the computer enters
suspend mode. In Windows 3.x and Windows 95, you need to install
Windows with the APM feature. In Windows 98 or later, APM is
automatically installed as indicated by a battery and power cord icon
labeled “Power Management” in the Control Panel. Select the item
“Advanced” in the Power Management Properties dialog box.
4-22
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 81

Video Off Option [Suspend -> Off ]
This field determines when to activate the video off feature for monitor
power management. Configuration options: [Always On] [Suspend -> Off]
Video Off Method [DPMS OFF]
This field defines the video off features. The Display Power Management
System (DPMS) feature allows the BIOS to control the video display card if
it supports the DPMS feature. [Blank Screen] only blanks the screen. Use
this for monitors without power management or “green” features.
Even if installed, your screen saver does not display when you select
[Blank Screen] for the above field.
[V/H SYNC+Blank] blanks the screen and turns off vertical and horizontal
scanning. Configuration options: [Blank Screen] [V/H SYNC+Blank]
[DPMS Standby] [DPMS Suspend] [DPMS OFF] [DPMS Reduce ON]
HDD Power Down [Disabled]
Shuts down any IDE hard disk drives in the system after a period of
inactivity as set in this user-configurable field. This feature does not affect
SCSI hard drives. Configuration options: [Disabled] [1 Min] [2 Min] [3
Min]...[15 Min]
Suspend Mode [Disabled]
Sets the time period before the system goes into suspend mode.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [1~2 Min] [2~3 Min] [4~5 min] [8~9 Min]
[20 Min] [30 Min] [40 Min] [1 Hour]
PWR Button < 4 Secs [Soft Off]
When set to [Soft off], the ATX switch can be used as a normal system
power-off button when pressed for less than 4 seconds. [Suspend] allows
the button to have a dual function where pressing less than 4 seconds
puts the system in sleep mode. Regardless of the setting, holding the ATX
switch for more than 4 seconds powers off the system. Configuration
options: [Soft off] [Suspend]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-23
Page 82

4.5.1 Power Up Control
AC PWR Loss Restart [Disabled]
This allows you to set whether or not to reboot the system after power
interruptions. [Disabled] leaves your system off. [Previous State] sets the
system back to the state it was before the power interruption.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Previous State]
Wake/Power Up On Ext. Modem [Disabled]
This allows either settings of [Enabled] or [Disabled] for powering up the
computer when the external modem receives a call while the computer is
in Soft-off mode. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The computer cannot receive or transmit data until the computer and
applications are fully running. Thus, connection cannot be made on the
first try. Turning an external modem off and then back on while the
computer is off causes an initialization string that turns the system
power on.
Onboard LAN Power Up [Disabled]
Power Up on PCI Card [Disabled]
These fields allow you to boot your computer from another computer by
sending a wake-up frame or signal to the LAN device, or the PCI modem
card if present. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-24
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 83

Power On By PS/2 Keyboard [Disabled]
This parameter allows you to use specific keys on the keyboard to turn on
the system. This feature requires an ATX power supply that provides at
least 1A on the +5VSB lead. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Space Bar]
[Ctrl-Esc] [Power Key]
Automatic Power Up [Disabled]
This allows an unattended or automatic system power up. You may
configure your system to power up at a certain time of the day by selecting
[Everyday] or at a certain time and day by selecting [By Date].
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Everyday] [By Date]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-25
Page 84

4.5.2 Hardware Monitor
MB Temperature [xxxC/xxxF]
CPU1 Temperature [xxxC/xxxF]
CPU2 Temperature [xxxC/xxxF]
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the MB (motherboard) and
CPU temperatures. Set to [Ignore] only if necessary.
CPU1 Fan Speed [xxxxRPM]
CPU2 Fan Speed [xxxxRPM]
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the CPU fan speeds in
rotations per minute (RPM). The presence of the fans is automatically
detected.
VCORE Voltage, 3.3V Voltage, 5V Voltage, 12V Voltage
, 3VSB
Voltage
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the voltage output by the
onboard voltage regulators.
If any of the monitored items is out of range, the following error
message appears: “Hardware Monitor found an error. Enter Power
setup menu for details”. You will then be prompted to “Press F1 to
continue or DEL to enter SETUP”.
4-26
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 85

4.6 Boot Menu
The motherboard BIOS supports the BIOS Boot Specification (BBS)
version 1.01. BBS is an intelligent mechanism that provides flexible ways
to set boot sequence for Initial Program Load (IPL) devices such as
CD-ROMs, network remote boot ROM, and SCSI or RAID controllers on
PnP cards.
The IPL devices are classified into three categories:
1. BIOS Aware IPL Devices (BAID)
2. PnP devices, includes Boot Connection Vector (BCV) and Bootstrap
Entry Vector (BEV) devices
3. Legacy devices
1st Boot : (BAID) [<0> Floppy]
This field allows you to select a BIOS Aware IPL Devices (BAID) to boot
from. A BAID is any device that can boot on an operating system but
requires a specific BIOS code for support. Bootable FDDs, ATA HDD,
ATAPI CD-ROM, ATA ZIP, and ATA MO drives are classified as BAID. The
drives present in the system will appear as options for this field.
2nd Boot : (BCV) [None]
This field allows you to select a Boot Connection Vector (BCV) device to
boot from. BCV devices include SCSI controllers or SCSI cards, RAID
cards, and other devices on add-on cards with option ROM that hooks INT
13 to BIOS. The BCV devices present in the system will appear as options
for this field. The field shows [None] if no BCV device is installed.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-27
Page 86

3rd Boot : (BEV) [<0> Intel Corporation]
This field allows you to select a Bootstrap Entry Vector (BCV) device to
boot from. BEV devices include network controllers or cards. The BEV
devices present in the system will appear as options for this field. For this
motherboard, the following options are present onboard:
[<0> Intel Corporation IBA 4.0.22 Slo (LAN A)]
[<1> Intel Corporation IBA 4.0.22 Slo (LAN B)]
4th Boot : (Legacy) [Disabled]
This field reserves the boot sequence selection only to legacy devices
including FDD, HDD, CD-ROM, SCSI, and LAN. This mode does not allow
booting from a boot device on an add-on card or controller. If you wish to
assign a device as a 1st Boot device for a specific application, you must
set that legacy device at the 1st Boot sequence.
For this motherboard, the following options are present onboard:
[Disabled] [Floppy] [HDD] [CD-ROM] [LAN Option ROM] [SCSI]
Plug & Play O/S [No]
This field allows you to use a Plug-and-Play (PnP) operating system to
configure the PCI bus slots instead of using the BIOS. When [Yes] is
selected, interrupts may be reassigned by the OS. If you installed a nonPnP OS or if you want to prevent reassigning of interrupt settings, keep
the default setting [No]. Configuration options: [No] [Yes]
Reset Configuration Data [No]
The Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) contain information
about non-PnP devices. It also holds the complete record of how the
system was configured the last time it was booted. Select [Yes] if you want
to clear these data during the Power-On-Self-Test (POST). Configuration
options: [No] [Yes]
MPS 1.4 Support [Enabled]
This field allows you to enable or disable the MultiProcessor Specification
1.4 support. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Quick Power On Self Test [Enabled]
This field speeds up the Power-On-Self Test (POST) routine by skipping
retesting a second, third, and fourth time. Configuration options: [Disabled]
[Enabled]
Boot Up Floppy Seek [Enabled]
When enabled, the BIOS will seek the floppy disk drive to determine
whether the drive has 40 or 80 tracks. Configuration options: [Disabled]
[Enabled]
4-28
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 87

4.7 Server Menu
DRAM Hot Spare [Disabled]
This field allows you to allocate rows of SDRAM for hot spare.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [1 row] [2 rows] [3 rows]
Remote Console [Disabled]
This field allows the text mode VGA display to be sent out to VT100
terminal through COM1. This function is effective at BIOS POST and DOS
environment. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [POST Only]
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-29
Page 88

4.8 Exit Menu
When you have made all of your selections from the various menus in the
Setup program, save your changes and exit Setup. Select Exit from the
menu bar to display the following menu.
Pressing <Esc> does not immediately exit this menu. Select one of the
options from this menu or <F10> from the legend bar to exit.
Exit Saving Changes
Once you are finished making your selections, choose this option from the
Exit menu to ensure the values you selected are saved to the CMOS RAM.
The CMOS RAM is sustained by an onboard backup battery and stays on
even when the PC is turned off. When you select this option, a
confirmation window appears. Select [Yes] to save changes and exit.
If you attempt to exit the Setup program without saving your changes,
the program prompts you with a message asking if you want to save
your changes before exiting. Pressing <Enter> saves the changes
while exiting.
Exit Discarding Changes
Select this option only if you do not want to save the changes that you
made to the Setup program. If you made changes to fields other than
system date, system time, and password, the BIOS asks for a confirmation
before exiting.
4-30
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 89

Load Setup Defaults
This option allows you to load the default values for each of the
parameters on the Setup menus. When you select this option or if you
press <F5>, a confirmation window appears. Select [Yes] to load default
values. Select Exit Saving Changes or make other changes before saving
the values to the non-volatile RAM.
Discard Changes
This option allows you to discard the selections you made and restore the
previously saved values. After selecting this option, a confirmation
appears. Select [Yes] to discard any changes and load the previously
saved values.
Save Changes
This option saves your selections without exiting the Setup program. You
can then return to other menus and make further changes. After you select
this option, a confirmation window appears. Select [Yes] to save any
changes to the non-volatile RAM.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
4-31
Page 90

4-32
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup
Page 91

Chapter 5
This chapter tells how to install SCSI, LAN,
and audio drivers for various operating
systems.
OS Installation
Page 92

Chapter summary
5.1 Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0 ................ 5-1
5.2 Microsoft Windows 2000 Server................... 5-9
5.3 Microsoft Windows XP Professional.......... 5-18
5.4 Novell NetWare Server................................. 5-20
5.5 SUN Solaris 7 Server ................................... 5-24
5.6 SCO Open Server 5.0.x................................ 5-30
5.7 SCO UnixWare Server.................................. 5-34
5.8 Linux RedHat 7.x.......................................... 5-38
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard
Page 93

5.1 Microsoft® Windows® NT Server 4.0
5.1.1 LSI® SCSI Driver Installation
Windows NT 4.0 do not have drivers for the new SCSI controllers, you
must load the driver manually prior to Windows NT 4.0 installation.
A. Preparing an LSI Driver Disk
The drivers are located on the ASUS Driver Support CD at:
\Drivers\Sdms\Drivers\WINNT
Copy all the files and subdirectory under the WINNT subdirectory to the
root directory of a clean floppy disk. Use this LSI driver disk during
installation, or use the self-extracting image files for Windows NT drivers.
The LSI_U3.SYS executable driver is in ASUS Driver Support CD at:
\Drivers\Sdms\Diskimag\NT40.exe
B. New System Installation
This procedure installs the LSI_U3.SYS driver onto a Windows NT system.
Use this procedure when installing Windows NT onto an unused SCSI
drive. Windows NT automatically adds the driver to the registry and copies
the driver to the appropriate directory. There are two methods to install the
Windows NT system. One is installed by booting from NT CD Disc; the
other is by booting from NT three installation floppy disks.
B1. CD-ROM Installation
1. Start the Windows NT installation by booting from the Windows NT
CD-ROM. The system BIOS must support booting from a CD-ROM.
LSI BIOS settings may need to be changed to allow CD-ROM booting
when using SCSI-interface CD-ROM drive.
2. When the screen displays “Windows NT Setup”, immediately press
the F6 key. This must be done or else the new driver installed from
the LSI driver disk will not be recognized.
Even if you did not press F6, you are still allowed to load additional
drivers later in the installation process. However, any drivers loaded
during Windows NT Setup are not immediately recognized and no
devices controlled by that driver are available during Windows NT
Setup.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
5-1
Page 94

3. When prompted for the manufacturer-supplied hardware support disk,
insert the appropriate LSI driver disk containing the Windows NT
driver required to support your LSI adapter(s) and press Enter. The
driver files are distributed with ASUS Driver Support CD and are
created from above “Preparing a LSI Driver disk” Section.
4. Depending on the driver being installed, “Symbios Ultra3 PCI SCSI
Driver” is shown highlighted. Press Enter to proceed.
5. Windows NT should now recognize the miniport driver(s) and the
SCSI hardware. Press Enter to continue. As for the onboard LAN and
VGA, please refer to the later sections for network and graphics
driver installation.
B2. Boot Floppy Disk Installation
1. Start the Windows NT installation by booting from the Microsoft Setup
floppy disk.
2. Press Enter when the Welcome to Setup screen appears. The
Windows NT Workstation Setup window appears next.
3. Press S to skip automatic detection and perform a manual selection.
A screen displays the message “Setup has recognized the following
mass storage devices in your computer...”.
4. With floppy disk 2, there is an initial setup screen that prompts you to
continue by pressing Enter.
5. Press S to skip mass storage device detection. If you pressed Enter,
the installation program scans for SCSI adapters and finds the LSI
PCI driver 53C1010R, which is an older version of the
SYMC8XX.SYS driver. Let installation continue and change the drive
when the installation is completed. To change the driver, see
“C. Existing System Installation.”
6. When a screen displays the SCSI adapters found, select S to
configure additional SCSI adapters.
7. Move the highlight bar to Other and press Enter.
8. When prompted for the manufacturer-supplied hardware support disk,
insert the appropriate LSI driver disk containing the Windows NT
driver required to support your LSI adapter(s) and press Enter. The
driver files are distributed with ASUS Driver Support CD and are
created from the previous section for “Preparing a LSI Driver disk”.
5-2
Chapter 5: OS Installation
Page 95

9. Depending on the driver being installed, Symbios Ultra3 PCI SCSI
Driver is shown highlighted. Press Enter to proceed.
10. The Windows NT Workstation Setup window reappears. If using an
IDE CD-ROM Drive for installation, press S to load additional drives.
Another window appears. Scroll up and select: IDE CD-ROM (ATAPI
1.2/PCI IDE Controller. Press Enter. (-or-) If you have completed
configuring additional SCSI adapters, press Enter.
11. Windows NT should now recognize the miniport driver and the SCSI
hardware. Press Enter to continue. At this point, simply follow the
Microsoft Windows NT installation procedure. As for the onboard LAN
and VGA, please refer to the later sections for network and graphics
driver installation.
C. Existing System Installation
1. Boot Windows NT system and log on as Administrator.
2. Click on the Start button. Select Settings—>Control Panel.
3. Double click on SCSI Adapters icon.
4. Click the Drivers tab. If the old NCRSDMS.SYS, NCRC810.SYS,
NCRC8XX.SYS, or SYMC810.SYS drivers are listed, select the
driver(s) and choose Remove before adding the new driver. If the
driver name of the driver you are installing SYM_HI.SYS or
LSI_U3.SYS is listed, remove it before adding the new driver. Select
OK when the Remove Driver message prompts: “Are you sure you
want to remove this driver?” Click OK.
5. Click Add. A list of installed adapters will appear.
6. Click the Have Disk button.
7. When prompted, insert the appropriate LSI driver disk containing the
Windows NT driver required to support your LSI adapter(s). The path
to copy manufacturer’s files is: A:\WINNT\MINIPORT and select OK.
8. Depending on the driver being installed, Symbios Ultra3 PCI SCSI
Driver is shown highlighted on the Install Driver menu. If it is not
highlighted, select it. Choose OK.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
5-3
Page 96

9. For the path to the OEM SCSI Adapter files, A:\WINNT\MINIPORT
should be displayed. Select Continue. Then remove the floppy disk
from your A: drive.
10. The System Settings Change message displays: “You must restart
your computer before the new settings take effect. Do you want to
restart your computer now?” Click on the Yes button to restart and
reboot Windows NT. If you choose Cancel, remember that you must
restart before the new driver loads.
11. Rebooting loads your new miniport driver(s).
5.1.2 Intel® 82551QM LAN Driver Installation
A. Preparing the Intel 82551QM LAN Driver Disk
Windows NT 4.0 does not have the drivers for the Intel 82551QM LAN
controller. Before installing Windows NT 4.0, copy the LAN drivers from
the PR-DLSW support CD into a floppy disk.
Prepare one blank formatted high density floppy disk before
proceeding.
1. Insert the PR-DLSW support CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Run the
\Drivers\LAN\MAKEDISK
3. Insert the floppy disk into the floppy disk drive when prompted.
4. Proceed to the next section to install the LAN drivers from the driver
disk that you created.
dcreat.exe utility from the following path:
5-4
Chapter 5: OS Installation
Page 97

B. New System Installation
1. When the Installing Windows NT Networking screen appears, press
Next to display the following screen.
2. Check the
3. On the screen that appears, click the button
Wired to the Network box, then click Next.
Select from list... to
dispaly the following.
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
5-5
Page 98

4. Insert the LAN driver disk that you created, then click Have Disk...
5. Type A:\ in the dialog box that appears, then click OK. The following
screen lists the Intel LAN adapters that you can install.
6. Select
Intel(R) PRO/100 Family Adapter, then click OK. Follow the
succeeding screen instructions.
7. When done, the following screen appears showing the
PRO/100 Family Adapter
in the list.
Intel(R)
8. Click
Select from list..., then click Have Disk...
9. Type A:\ in the dialog box, then click OK.
10. In the following screen, select
Intel(R) PRO/1000 Family Adapter, then
click OK. Follow the succeeding screen instructions.
5-6
Chapter 5: OS Installation
Page 99

11. When done, the following screen appears showing the Intel(R)
PRO/1000 Family Adapter
in the list.
12. Click
Next and follow any other screen instructions to complete the
installation.
C. Existing System Installation
1. Double-click the Network icon in the Control Panel.
2. Select the
4. Do not select an adapter from the list. Instead, insert the LAN driver
disk that you created from the PR-DLSW support CD.
Refer to the section
Disk”
if you have not yet created the LAN driver disk.
5. Follow steps 4 to 12 in the section
install the required LAN drivers.
Adapter tab, then click Add. A list of adapters appears.
“A. Preparing the Intel 82551QM LAN Driver
“B. New System Installation”
to
ASUS PR-DLSW motherboard user guide
5-7
Page 100

5.1.3 C-Media Audio Device Driver Installation
It is recommended that you install Windows NT 4.0 before installing the
device driver for the C-Media CMI8738/PCI-SX audio controller. Do not
install any other audio device drivers if you install the C-Media driver.
To install the audio device driver:
1. Click
Control Panel.
2. From the Control Panel, double-click
Start from your Windows task bar. Highlight Settings, then select
Multimedia to display the
Multimedia Properties window. Click the Devices tab, then click Add.
3. Select
Unlisted or Updated Driver from the List of Drivers.
4. Specify the drive path where the NT drivers are located. For example,
D:\NT40\DRV.
5. Select
C-Media CMI8738, then click OK.
6. Select the proper I/O value, then click OK.
7. Restart the computer when prompted.
After successfully installing the PCI audio drivers, you may install the
Windows applications.
To install the Windows applications:
1. Click Start from your Windows task bar, and select Run.
2. Type in the drive path where the Windows NT applications are
located. For example, D:\NT40\APP\SETUP.EXE.
3. Click OK to start the installation procedure. Follow the screen
instructions to complete the installation.
4. When done installing all the applications, shut down and restart the
system.
5-8
Chapter 5: OS Installation
 Loading...
Loading...