Page 1

MODEL 6034
BATTERY TESTER
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
This manual contains important safety and operating instructions for battery tester Model 6034. You may need to refer to these instructions at a later
date.
CAUTION: The electrolyte in automotive batteries is sulfuric acid, which is capable of causing severe damage to skin, eyes, and clothing. When
contact with battery acid occurs, proceed as follows:
a) Eyes: Force open and flood with cool running water at least for 10 minutes, then see a doctor. Never use eyes drops or other medication before
seeing a doctor.
b) Skin: Remove contaminated clothing and flood skin for at least 10 minutes with clear, cool water.
While batteries are being charged or tested, an explosive gas mixture forms inside each cell. Some of this gas escape through the vent holes in the filler
caps and may remain around the battery in an explosive condition. Sparks or flames igniting this gas mixture will burn back through the vent hole and
explode inside the battery cell. Such an explosion is dangerous not only because of its own force, but also because of the acid electrolyte which would
spray onto anything in the vicinity.
TO PREVENT EXPLOSIONS:
a) Use well ventilated areas for charging and testing batteries.
b) Add distilled water in each cell until battery acid reaches level specified by battery manufacture. This helps purge excessive gas from cells. Do not
over-fill. For a battery without cell caps, carefully follow manufacturer’s instructions.
c) Allow no smoking, sparks or open flames near batteries being charged, tested or batteries recently charged and to be tested.
WARNING - RISK OF EXPLOSIVE GASES.
a) Working in vicinity of lead-acid battery is dangerous. Batteries generate explosive gases during normal battery operation. For this reason, it is of
utmost importance to read this manual and follow the instructions exactly each time you use this battery tester.
b) To reduce the risk of battery explosions, follow these instructions and those published by battery manufacturer and manufacturer of any equipment
you intend to used in the vicinity of battery. Review cautionary marking on these products and on the engine.
c) Do not break live electrical circuits at the terminals of batteries because a spark may occur at that point causing an explosion. Always turn the
battery tester OFF before connecting or disconnecting the clamps from the battery terminals.
PERSONAL PRECAUTIONS:
a) Wear complete protection and avoid touching eyes while working near battery.
b) For acid contact on skin or clothing, remove clothing and wash skin immediately with soap and water. For acid in eye, immediately flood eye with
running cold water for at least 10 minutes and obtain medical attention immediately. Never use eye drops or other medication before seeing a
doctor.
c) NEVER smoke or allow a spark or flame in the vicinity of battery or engine.
d) Be extra cautious to reduce risk of dropping a metal tool onto a battery. The tool may spark or short-circuit the battery or other electrical parts which
may cause an explosion.
e) Remove personal metal items such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, and watches when working with a lead-acid battery. A lead-acid battery can
produce a short-circuit current high enough to instantly weld a ring or the like to metal, and cause severe burn.
f) Spilled acid: Neutralize with a solution of baking soda (1 pound per gallon of cold water) or household ammonia (1 pint per gallon of cold water)
PREPARING TO TEST
a) When necessary to remove battery from vehicle for testing, always remove ground terminal first. Make sure all accessories in the vehicle are
turned off, so as not to cause an arc.
b) Clean battery terminals. Be careful to keep corrosion from coming in contact with eyes.
c) Determine the cold cranking amps (CCA) rating of battery by referring to car owner’s manual or label on battery.
TESTER LOCATION
a) Locate tester as far away from battery as DC cables permit.
b) Never allow battery acid to drip on tester or other items when handling a hydrometer, reading specific gravity or filling a battery.
c) Do not set a battery on top of the tester.
d) Position cables to reduce risk of danger by hood, door or moving engine parts.
e) Stay clear of fan blades, belts, pulleys, and other parts that can cause personal injuries.
f) Do not block air passage through the tester.
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1
Page 2
CONNECTIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
a) Connect and disconnect DC output clamps only after the LOAD CONTROL knob is counter-clockwise (CCW.) as far as possible. (Don’t force
knob).
b) When attaching clamps to battery posts, twist or rock clamp back and forth several times to make a good connection. This tends to prevent the
clamps from slipping off of the terminals and helps reduce risk of sparking.
NOTE: Either when receiving the unit new or when the unit has been sitting around awhile. The carbon stacks in the unit will collect moisture from the
air and will need to be evaporated out. To do this, the unit will need to be pre-loaded, by turning the knob to a 100 amps and holding the knob for 5 to 10
seconds and releasing the knob (Do this on a good battery that you are not testing). This releases any water that might be in the carbon stacks and
prevents the carbons from cracking during normal operation. Note: If a lot of water or steam come out of the unit, do this a few more times to get most of
the moisture out.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
DUTY CYCLE: It is difficult to specify a duty cycle on a carbon pile load tester. It will vary greatly with ambient temperature, length of test and load
current on battery. To insure long life it is recommended to let the carbon pile cool (about 10 minutes) between battery test. For maximum life, it is
recommended that the carbon pile never be heated until it is red hot. This can be easily seen by looking in the unit when running a test. A red glow will
indicate the carbon discs are so hot that the binders that hold the carbon granules together are burning and deteriorating. This will lead to a deterioration
of the carbon discs, which will be exhibited by the surfaces of the disc turning soft and powdery.
1. Visually inspect batteries for obvious damage. Do not test a battery if posts are loose, case is cracked or fluid level is below the top of the plates.
With “maintenance free” batteries, see manufacturer’s instructions for checking water level. Do not test a frozen battery.
2. Be sure Voltmeter and Ammeter pointers are zeroed. Zero meters by adjusting screw on face of meter until meter points to zero.
3. See connection precautions before connecting or disconnecting clamp prior to test.
4. Connect RED clamp to POSITIVE (POS, +, P) battery post and BLACK clamp to NEGATIVE (NEG, -, N) battery post.
5. DETERMINE STATE OF CHARGE OF BATTERY
a) Adjust LOAD CONTROL knob clockwise (CW) to 100 amps for 3 seconds. Adjust LOAD CONTROL knob counter-clockwise until the ammeter
reads zero. Read Voltmeter.
b) Results:
1. Pointer is in green zone on the "STATE OF CHARGE" scale, proceed to LOAD TEST.
2. Pointer to left of green zone on the "STATE OF CHARGE" scale, battery is too low to test. Recharge & repeat procedure.
c) Pointer in "STATE OF CHARGE" scale green zone indicates a battery that is at least 75% charged.
6. LOAD TEST
Note: During heating caused by a load test, the carbon pile may emit steam and odors that have been absorbed by the carbon discs, this is normal.
a) Adjust “LOAD CONTROL” knob to the one-half of the battery’s cold cranking amperage (CCA) rating using DC AMPS meter as a reference. Hold
this reading. During this 15 seconds interval the amperage will probably change due to resistance changes in the cables, carbons and the battery.
Readjust the "LOAD CONTROL" knob during this 15 seconds interval to maintain the amperage value required. At the end of 15 seconds and with
the load on, read the battery voltage on the "BATTERY TEST" scale. TURN THE LOAD CONTROL KNOB COUNTER-CLOCKWISE AS FAR AS
POSSIBLE. (OFF) Alarm will sound after 15 seconds.
b) The voltage reading obtained from the battery changes in relation to the temperature of the battery and also in relation to the amperage being
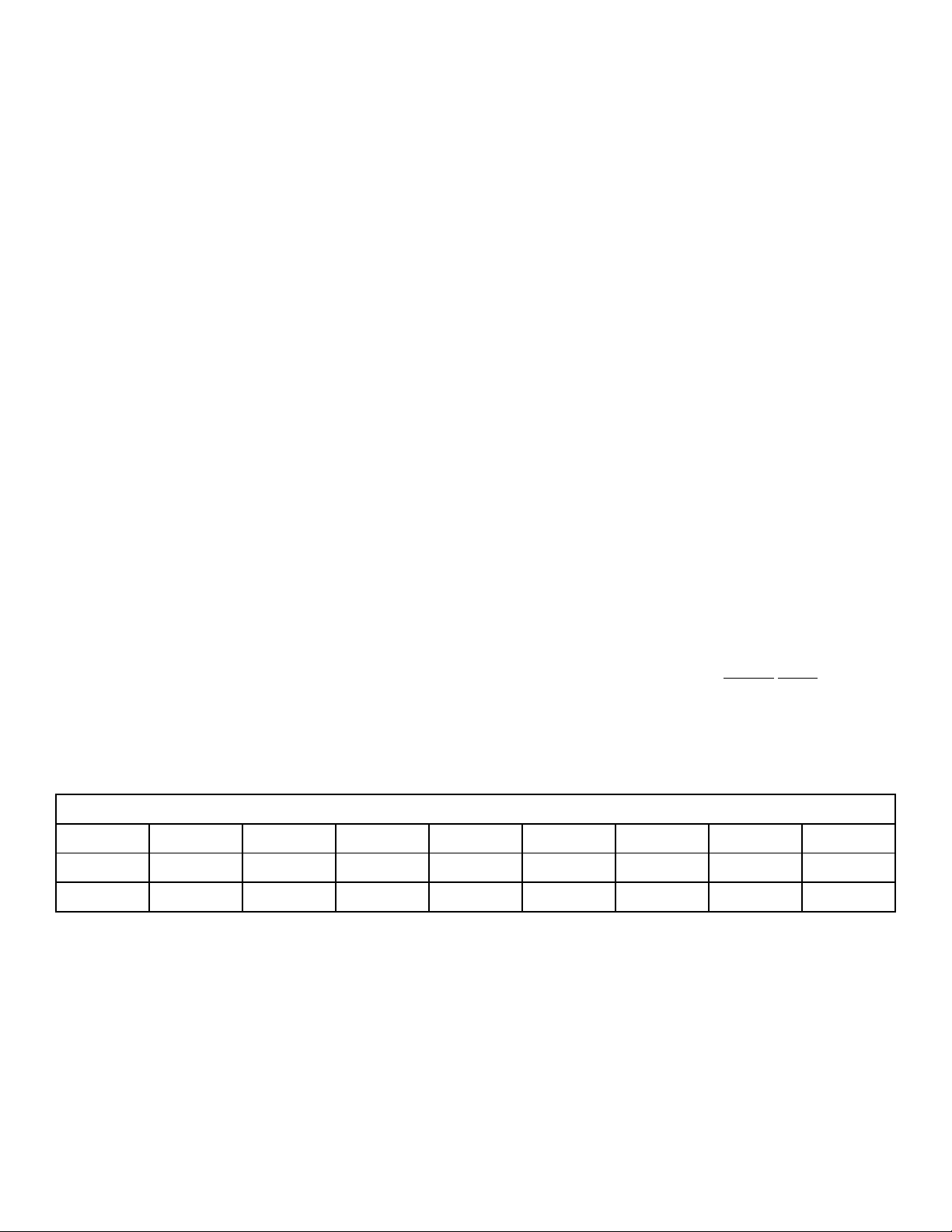
drawn from the battery. The “Battery Temperature Compensation” given here and on the side of the tester gives the minimum
be obtained for the test procedure given. i.e.: The outside temperature is 60 degrees F. From chart note that the minimum volts for a good battery
is 9.5 at 60 degrees F. When at the end of the 15 second test you find that the battery’s voltage is equal to or greater than 9.5, the battery is good.
When the voltage is 9.4 or less the battery is defective.
When a six-volt battery is to be tested, simply divide the minimum volts of the chart by two to obtain the voltage reference to be used.
When smoke is emitted from any cell of the battery, the battery is defective regardless of the test indications
°C
°F
MIN. VOLTS
7. STRESS TEST:
a) To determine if a battery is adequate for an application, a stress test may be applied to a battery. Determine the maximum current draw, minimum
acceptable voltage, and maximum cranking time of the vehicle in which the battery is to be installed.
b) Run a load test at the determined current and time and check that the battery voltage is above the minimum required.
21↑
70↑
9.6
BATTERY TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION 15 SECOND LOAD TEST
16
60
9.5
10
50
9.4
4
40
9.3
-1
30
9.1
-7
20
8.9
voltage that should
-12
10
8.7
-18
0
8.5
APPLICATION DATA:
ALTERNATOR TEST: Be sure that the battery in the car tests good. Start engine with tester connected to the battery. The charging voltage of the
alternator should allow the pointer to fall in the green zone on the alternator test (ALT. & REG. TEST) scale. If the pointer is in the red zone to the left of
the green zone, the voltage is too low to fully charge the battery. If the pointer is in the red zone to the right of the green zone, the voltage is too high
and may damage the battery. NOTE: In very cold weather, the alternator may read above 14.8 VDC. Check owner’s service manual.
STARTER CURRENT TEST: Connect tester to battery. Be sure battery is fully charged. Ground the ignition, by removing the coil cable from the
distributor cap. Ground the cable to the block with a jumper wire to prevent arcing of high- voltage spark that could cause a fire, someone getting
shocked, or damage to the ignition system. (On GM car with HEI ignition, simply disconnect the small lead connected to the BAT. terminal on the
2
Page 3

distributor.) Turn ignition switch on and allow starter to run for 5 seconds. Read the voltage on the VOLT scale while cranking. With car circuit off and
with the tester connected to the battery terminals, adjust LOAD CONTROL knob to give VOLTMETER reading the same as measured while cranking
engine. Read Amps on ammeter and the reading is the starting current of the car.
VOLTMETER: The tester may be used as a voltmeter to troubleshoot electrical problems on any 6 or 12 volt vehicle. Read voltages on volt scale.
NOTE: A static charge may build-up on the meter face, causing the needle to be off zero. For the meter to read correctly, this charge must be
neutralized. Spray “Static Guard” or equivalent on the meter or wipe with a cloth dampened with soap and water.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Associated Equipment Corporation warrants that for 90 days from the date of original retail purchase, that if the product shall prove to be defective in
workmanship or materials, the Company will repair the product at no charge for parts and labor. If, after reasonable efforts by the Company, the product
is determined not repairable, The Company will, at its option, refund the original purchase price or supply a replacement unit.
THE TERMS OF THE ASSOCIATED EQUIPMENT CORPORATION LIMITED WARRANTY CONSTITUTE THE BUYER'S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE
REMEDY. THIS IS THE ONLY EXPRESS LIMITED WARRANTY ASSOCIATED WITH THE PRODUCT AND THE COMPANY NEITHER ASSUMES
NOR AUTHORIZES ANYONE TO ASSUME OR MAKE ANY OTHER EXPRESS WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCT OTHER THAN
THIS EXPRESS LIMITED WARRANTY. ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
LIMITED TO A PERIOD OF 90 DAYS. AFTER 90 DAYS FROM DATE OF PURCHASE, ALL RISK OF LOSS FROM WHATEVER REASON SHALL BE
PUT UPON THE PURCHASER.
THE COMPANY IS NOT AND SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOSS, CLAIM, INJURY OR DAMAGE, TO ANY PERSON OR PROPERTY, OR LOST
PROFITS OR OTHER SIMILAR LOSS OR DAMAGE, WHICH MAY ARISE, DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, RESULT OR BE CLAIMED TO HAVE
RESULTED FROM A DEFECT IN MATERIALS OR WORKMANSHIP OF THE PRODUCT. THE COMPANY'S LIABILITY, IF ANY, SHALL NEVER
EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE OF THIS PRODUCT REGARDLESS OF WHETHER LIABILITY IS PREDICTED UPON BREACH OF WARRANTY
(EXPRESS OR IMPLIED), NEGLIGENCE, STRICT TORT OR ANY OTHER THEORY.
This warranty extends to each person who acquires lawful ownership within 90 days of the original retail purchase, but is void if the product has been
abused, altered, misused or improperly packaged and damaged when returned for repair.
This warranty applies to the product only and does not apply to any accessory items included with the product or product parts which are subject to wear
from usage, including, but not limited to, clamps and cables; the replacement or repair of these items shall be at the expense of the owner.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of consequential or incidental damages, so the above exclusion and limitation may not apply to you.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
TO OBTAIN SERVICES UNDER THIS WARRANTY
DO NOT RETURN THE BATTERY TESTER TO THE STORE WHERE PURCHASED.
For answers to questions regarding warranty service, out of warranty service or product use call the phone number listed below.
Mail your battery tester prepaid (all postage, transportation and freight charges to and from the factory are the responsibility of the customer) with the
sales receipt (or other proof of purchase date), also include your name, mailing address, name of the store where the product was purchased and the
daytime phone number you can be reached to:
ASSOCIATED EQUIPMENT CORPORATION
5043 Farlin Avenue St. Louis, MO. 63115
(314) 385-5178
3
Page 4

Rev. 03/05 027-0793
4
 Loading...
Loading...