Page 1

www.acg
-
id.com
rfid@acg
-
id.com
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader
Document No.: 1508-USM-01-0-02
Firmware: Version 1.0
User Manual
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH
Am Klingenweg 6A
65396 Walluf
Germany
Phone +49 (0) 6123 791 0
Fax +49 (0) 6123 791 199
Document Nr.: QSI-040902-OM-1-a-UserManual Dual ISO Module, V2.0
Page 2

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Edition Three - June 2006
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH (ACG) reserves the right to make changes to
its products or services or to discontinue any product or service at any time without
notice. ACG provides customer assistance in various technical areas, but does not
have full access to data concerning the use and applications of customer's products.
Therefore, ACG assumes no liability and is not responsible for customer applications
or product or software design or performance relating to systems or applications
incorporating ACG products. In addition, ACG assumes no liability and is not
responsible for infringement of patents and/or any other intellectual or industrial
property rights of third parties, which may result from assistance provided by ACG.
ACG products are not designed, intended, authorized or warranted to be suitable for
life support applications or any other life critical applications that could involve potential risk of death, personal injury or severe property or environmental damage.
With the edition of this document, all previous editions become void. Indications
made in this manual may be changed without previous notice.
Composition of the information in this manual has been done to the best of our
knowledge. ACG does not guarantee the correctness and completeness of the
details given in this manual and may not be held liable for damages ensuing from
incorrect or incomplete information. Since, despite all our efforts, errors may not be
completely avoided, we are always grateful for your useful tips.
The installation instructions given in this manual are based on advantageous
boundary conditions. ACG does not give any guarantee promise for perfect function
in cross environments.
The ACG logo is a registered trademark of ACG Identification Technologies GmbH.
The mifare
®
logo is a registered trademark of Philips Electronic N.V.
All other products mentioned in this document might be brands or brand names of
the different suppliers.
Copyright
©
2006 ACG Identification Technologies GmbH (ACG)
This document may be downloaded onto a computer, stored and duplicated as necessary to support the use of the related ACG products. Any other type of duplication,
circulation or storage on data carriers in any manner not authorized by ACG
represents a violation of the applicable copyright laws and shall be prosecuted.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 1
Page 3

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Safety Instructions / Warning - Read before start-up!
• The device may only be used for the intended purpose designed by for the
manufacturer. The operation manual should be conveniently kept available at
all times for each user.
• Unauthorized changes and the use of spare parts and additional devices that
have not been sold or recommended by the manufacturer may cause fire,
electric shocks or injuries. Such unauthorized measures shall exclude any
liability by the manufacturer.
• The liability-prescriptions of the manufacturer in the issue valid at the time of
purchase are valid for the device. The manufacturer shall not be held legally
responsible for inaccuracies, errors, or omissions in the manual or
automatically set parameters for a device or for an incorrect application of a
device.
• Repairs may be executed by the manufacturer only.
• Only qualified personnel should carry out installation, operation, and
maintenance procedures.
• Use of the device and its installation must be in accordance with national legal
requirements and local electrical codes.
• When working on devices the valid safety regulations must be observed.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 2
Page 4

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Preface
Read This First
About This Guide
This manual describes the ACG HF Multi ISO Reader Module. Its goal is to describe
the reader, how it works, how to integrate it and how to use it.
If You Need Assistance
Our application center is located in Europe to provide direct support. For more
information, please contact your nearest ACG Sales Center. The contact addresses
can be found on our home page:
http://www.acg-id.com
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 3
Page 5

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Table of contents
1 Scope.............................................................................................11
2 Extended Documentation.............................................................11
3 Definitions and Abbreviations .....................................................12
3.1 Definitions .................................................................................................. 12
3.1.1 Anti-collision loop................................................................................ 12
3.1.2 Hex notation........................................................................................ 12
3.1.3 ASCII notation..................................................................................... 12
3.2 Abbreviations.............................................................................................. 13
4 Supported tags..............................................................................15
5 The mifare® Transponder Family.................................................17
5.1 mifare
5.1.1 Sector 0 / Block 0................................................................................ 17
5.1.2 Blocks 3, 7, 11, 15, …......................................................................... 18
5.2 State Diagram ............................................................................................ 19
5.3 mifare
5.4 mifare
5.5 mifare
5.6 mifare
5.6.1 Memory organization........................................................................... 21
5.6.2 State diagram of DESFire ................................................................... 22
5.6.2.1 Activate PICC............................................................................... 23
5.6.2.2 Select application......................................................................... 23
5.6.2.3 Login to application...................................................................... 23
5.6.2.4 Select file ..................................................................................... 23
5.6.2.5 Change file................................................................................... 23
5.6.2.6 Commit / Abort transaction........................................................... 23
5.7 my-d™ IC (SLE 55Rxx).............................................................................. 24
®
Standard........................................................................................ 17
®
Ultralight ........................................................................................ 20
®
4k................................................................................................... 20
®
ProX............................................................................................... 20
®
DESFire......................................................................................... 21
6 ISO 14443 Type B..........................................................................25
6.1 SR176........................................................................................................ 25
6.1.1 Memory organization........................................................................... 25
6.1.2 Serial number UID............................................................................... 25
6.1.3 Lock byte............................................................................................. 26
6.1.4 Chip ID................................................................................................ 26
6.2 SRIX4K ...................................................................................................... 26
6.2.1 Memory organization........................................................................... 26
6.2.2 Lock block........................................................................................... 26
7 ISO 15693.......................................................................................27
7.1 Coding of UID............................................................................................. 27
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 4
Page 6

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
7.2 Memory organization.................................................................................. 28
7.3 my-d™ IC (SRF55VxxP)............................................................................ 29
7.3.1 UID...................................................................................................... 29
7.3.2 Security Bit.......................................................................................... 29
7.4 EM 4135..................................................................................................... 30
8 ICODE ............................................................................................31
8.1 Memory organization.................................................................................. 31
8.2 Serial number............................................................................................. 31
8.3 Write access condition ............................................................................... 31
8.4 Special function (EAS), AFI........................................................................ 32
8.5 User data.................................................................................................... 32
9 ICODE EPC....................................................................................33
9.1 Memory organization.................................................................................. 33
9.2 Serial number............................................................................................. 33
9.3 Read Block................................................................................................. 33
9.4 Write Block................................................................................................. 33
10
ICODE UID..................................................................................34
10.1 Memory organization.................................................................................. 34
10.2 Read Block................................................................................................. 34
10.3 Write Block................................................................................................. 34
11
Hardware ....................................................................................35
11.1 Dimensions................................................................................................. 35
11.1.1 Pin out of J1........................................................................................ 36
11.1.2 Electrical characteristics of J1 PINs.................................................... 37
11.1.3 Pin out of J2........................................................................................ 38
11.1.4 Electrical characteristics of J2 PINs.................................................... 39
11.1.5 External Connections.......................................................................... 40
11.1.5.1 Power Supply............................................................................... 40
11.1.5.2 Antenna........................................................................................ 41
11.1.5.3 Serial Interface............................................................................. 41
11.1.5.4 Function Control LEDs................................................................. 42
12
Software......................................................................................43
12.1 ASCII Protocol............................................................................................ 43
12.2 Binary Protocol........................................................................................... 43
12.2.1 STX..................................................................................................... 44
12.2.2 Station ID ............................................................................................ 44
12.2.3 Length................................................................................................. 44
12.2.4 Flags................................................................................................... 44
12.2.5 Data .................................................................................................... 44
12.2.6 Block Check Character (BCC)............................................................. 45
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 5
Page 7

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.2.7 ETX..................................................................................................... 45
12.2.8 Remarks.............................................................................................. 45
12.2.9 Examples: ........................................................................................... 45
12.3 Register Set................................................................................................ 46
12.3.1 EEPROM memory organization.......................................................... 47
12.3.2 Unique device ID (00h – 04h).............................................................. 47
12.3.3 Station ID (0Ah)................................................................................... 48
12.3.4 Protocol configuration (0Bh)................................................................ 48
12.3.4.1 Auto start (default 1) .................................................................... 48
12.3.4.2 Protocol (default 0)....................................................................... 48
12.3.4.3 Multitag (default 0)....................................................................... 48
12.3.4.4 New Serial Mode (default 0)......................................................... 48
12.3.4.5 LED (default 0)............................................................................. 48
12.3.4.6 Single Shot (default 0) ................................................................. 49
12.3.4.7 Extended Protocol (default 1)....................................................... 49
12.3.4.8 Extend ID (default 0).................................................................... 50
12.3.5 BAUD, Baud rate control register (0Ch).............................................. 51
12.3.5.1 CF Card Version.......................................................................... 52
12.3.6 Command Guard Time (0Dh).............................................................. 52
12.3.7 OPMODE, operating mode register (0Eh)........................................... 53
12.3.8 Single Shot Time-out (0Fh)................................................................. 53
12.3.9 Protocol configuration 2 (13h)............................................................. 53
12.3.9.1 Disable multi-tag reset (default 0)................................................ 53
12.3.9.2 Disable start-up message (default 0) ........................................... 54
12.3.9.3 Enable binary frame v2 (default 0)............................................... 54
12.3.9.4 Noisy Environment (default 0)...................................................... 54
12.3.9.5 Reset Recovery Time Multiplier (default 0).................................. 54
12.3.9.6 Enable ISO14443 B Anti-collision (default 0)............................... 54
12.3.9.7 Disable ISO 14443-4 Error Handling (default 0)........................... 54
12.3.10 Reset Off Time (14h)....................................................................... 54
12.3.11 Reset Recovery Time (15h)............................................................. 55
12.3.12 Application Family Identifier (16h) ................................................... 55
12.3.13 Selection Time-out ISO 14443A (17h)............................................. 55
12.3.14 Selection Time-out ISO 14443B (18h)............................................. 55
12.3.15 Selection Time-out SR176 (19h) ..................................................... 55
12.3.16 Selection Time-out ISO 15693 (1Ah)............................................... 55
12.3.17 Protocol configuration 3 (1Bh)......................................................... 56
12.3.17.1 Disable automatic ISO 14443-4 timeouts (default 0)................... 56
12.3.17.2 Page read (default 0)................................................................... 56
12.3.17.3 ReqA Extended ID (default 0)...................................................... 56
12.3.18 User data (80h - EFh)...................................................................... 56
12.4 Instruction Set ............................................................................................ 57
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 6
Page 8

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.1 Common Commands Overview .......................................................... 58
12.4.2 Error Codes......................................................................................... 60
12.4.3 Common commands........................................................................... 61
12.4.3.1 Test Continuous Read / Check KTT Upload Status..................... 61
12.4.3.2 Continuous Read......................................................................... 61
12.4.3.2.1 Multitag continuous read mode............................................... 62
12.4.3.2.2 Auto start ................................................................................ 62
12.4.3.2.3 Noisy Environment.................................................................. 62
12.4.3.2.4 Binary mode............................................................................ 62
12.4.3.2.5 Simple access control applications......................................... 62
12.4.3.3 Set LED........................................................................................ 63
12.4.3.4 DES encryption / decryption of data............................................. 64
12.4.3.5 Get ID........................................................................................... 65
12.4.3.5.1 Time slotted answer................................................................ 66
12.4.3.5.2 Binary Protocol Version 2 ....................................................... 67
12.4.3.6 High speed select ........................................................................ 67
12.4.3.6.1 Answer from 0xh and 1xh....................................................... 69
12.4.3.6.2 Answer from 2xh and 3xh....................................................... 69
12.4.3.6.3 Select a single tag................................................................... 69
12.4.3.6.4 Extended ID............................................................................ 69
12.4.3.6.5 Multiple tags............................................................................ 70
12.4.3.6.6 RATS Guard Time SFGT........................................................ 70
12.4.3.7 Lock block.................................................................................... 70
12.4.3.7.1 Operation mode failure 'O'...................................................... 70
12.4.3.7.2 Apply settings ......................................................................... 71
12.4.3.8 Multi-Tag Selection / List.............................................................. 71
12.4.3.8.1 Multi-tag list............................................................................. 71
12.4.3.8.2 Reading distance.................................................................... 72
12.4.3.8.3 Multi-tag select........................................................................ 72
12.4.3.8.4 Multi-tag reset......................................................................... 72
12.4.3.8.5 Maximum number of tags ....................................................... 72
12.4.3.9 Include tag type............................................................................ 73
12.4.3.10 Exclude tag type.......................................................................... 74
12.4.3.11 Set tag type................................................................................. 75
12.4.3.12 Set Configuration Flags............................................................... 76
12.4.3.12.1 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 77
12.4.3.13 Set Configuration Register.......................................................... 78
12.4.3.13.1 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 79
12.4.3.14 Antenna power on/off.................................................................. 80
12.4.3.14.1 Power off............................................................................... 80
12.4.3.14.2 Power on............................................................................... 80
12.4.3.15 Read/Write user port ................................................................... 81
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 7
Page 9

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.15.1 Read port.............................................................................. 81
12.4.3.15.2 Write port.............................................................................. 82
12.4.3.16 Quiet............................................................................................ 83
12.4.3.16.1 ISO 14443 Type A................................................................ 84
12.4.3.16.2 ISO 14443 Type B................................................................ 84
12.4.3.16.3 SR176................................................................................... 84
12.4.3.17 Resend Last Answer................................................................... 84
12.4.3.18 Read block.................................................................................. 85
12.4.3.18.1 Read failure 'F'...................................................................... 85
12.4.3.18.2 No tag in field 'N'................................................................... 85
12.4.3.18.3 Operation mode failure 'O'.................................................... 85
12.4.3.18.4 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 86
12.4.3.19 Read reader EEPROM................................................................ 86
12.4.3.19.1 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 86
12.4.3.20 Select.......................................................................................... 87
12.4.3.20.1 Select a single tag................................................................. 87
12.4.3.20.2 Extended ID.......................................................................... 87
12.4.3.20.3 Multiple tags.......................................................................... 87
12.4.3.21 Get Version................................................................................. 88
12.4.3.22 Write block................................................................................... 89
12.4.3.22.1 Write failure 'F'...................................................................... 89
12.4.3.22.2 No tag error 'N'...................................................................... 89
12.4.3.22.3 Operation mode failure 'O'.................................................... 89
12.4.3.22.4 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 90
12.4.3.23 Write EEPROM ........................................................................... 90
12.4.3.23.1 Out of range failure 'R'.......................................................... 90
12.4.3.24 Reset........................................................................................... 91
12.4.3.24.1 Disable Start-up Message..................................................... 91
12.4.3.24.2 Reset Timing......................................................................... 91
12.4.3.25 Field Reset.................................................................................. 92
12.4.4 ISO 14443 Type A (mifare
12.4.4.1 Increment value block (credit)...................................................... 93
12.4.4.1.1 No value block 'I'..................................................................... 93
12.4.4.1.2 Increment failure 'F'................................................................. 93
12.4.4.1.3 No tag error 'N'........................................................................ 94
12.4.4.1.4 Operation mode failure 'O'...................................................... 94
12.4.4.2 Decrement value block (debit) ..................................................... 94
12.4.4.2.1 No value block 'I'..................................................................... 94
12.4.4.2.2 Decrement failure 'F'............................................................... 95
12.4.4.2.3 No tag error 'N'........................................................................ 95
12.4.4.2.4 Operation mode failure 'O'...................................................... 95
12.4.4.3 Copy value block (backup)........................................................... 95
®
) only commands...................................... 93
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 8
Page 10

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.3.1 Target block............................................................................ 96
12.4.4.3.2 No value block 'I'..................................................................... 96
12.4.4.3.3 Copy failure 'F'........................................................................ 96
12.4.4.3.4 No tag error 'N'........................................................................ 96
12.4.4.3.5 Operation mode failure 'O'...................................................... 96
12.4.4.4 Login (authenticate tag) ............................................................... 97
12.4.4.4.1 No tag error 'N'........................................................................ 98
12.4.4.4.2 Operation mode failure 'O'...................................................... 98
12.4.4.4.3 Out of range failure 'R'............................................................ 98
12.4.4.4.4 <CR>...................................................................................... 99
12.4.4.4.5 Login with key data from EEPROM ........................................ 99
12.4.4.4.6 Usage of key A, key B............................................................. 99
12.4.4.5 Read value block ....................................................................... 100
12.4.4.5.1 No value block 'I'................................................................... 100
12.4.4.5.2 No tag error 'N'...................................................................... 100
12.4.4.5.3 General failure 'F'.................................................................. 100
12.4.4.5.4 Operation mode failure 'O'.................................................... 100
12.4.4.6 Write value block........................................................................ 101
12.4.4.6.1 Invalid value 'I' ...................................................................... 101
12.4.4.6.2 Write failure 'F'...................................................................... 101
12.4.4.6.3 No tag error 'N'...................................................................... 101
12.4.4.6.4 Operation mode failure 'O'.................................................... 102
12.4.4.6.5 Writing values....................................................................... 102
12.4.5 Key Management.............................................................................. 103
12.4.5.1 Authenticate to reader................................................................ 103
12.4.5.2 Get Key Access Rights .............................................................. 106
12.4.5.3 Get key status............................................................................ 107
12.4.5.4 Reset key table.......................................................................... 108
12.4.5.5 Update key access rights........................................................... 109
12.4.5.6 Change key type........................................................................ 110
12.4.5.7 Update key................................................................................. 111
12.4.6 my-d™ secure................................................................................... 113
12.4.6.1 Abort KTT upload....................................................................... 113
12.4.6.2 Authenticate to sector ................................................................ 113
12.4.6.3 Issue transponder key................................................................ 115
12.4.6.4 Prepare for KTT......................................................................... 116
12.4.6.5 my-d™ command....................................................................... 119
13
Frequently Asked Questions...................................................121
13.1 Getting Started......................................................................................... 121
13.2 How should the Multi ISO Reader be personalized?................................ 121
13.3 What type of mifare
13.4 How safe is mifare
®
card should I use?.................................................. 122
®
Standard for cashless payment?.............................. 122
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 9
Page 11

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
13.5 Using a mifare® card ................................................................................ 124
13.6 Using a DESFire card............................................................................... 125
13.6.1 Create a plain standard data file ....................................................... 125
13.6.2 Use a plain standard data file............................................................ 125
13.6.3 Create a value file............................................................................. 126
13.6.4 Use a DES secured value file............................................................ 127
13.7 Using NFC................................................................................................ 128
14
References ...............................................................................129
15
Appendix A: SAM.....................................................................130
16
Appendix B:..............................................................................131
16.1 Compact Serial Plug & Play Module (RDHC-020xN0-02) ........................ 131
16.1.1 Features............................................................................................ 132
16.1.2 Dimensions ....................................................................................... 133
16.1.3 Pin Out.............................................................................................. 135
16.1.3.1 Pin Out of J3.............................................................................. 135
16.1.3.2 Electrical characteristics of J3 PINs in RS232 Configuration..... 136
16.1.3.3 Electrical characteristics of J3 PINs in RS422 Configuration..... 137
16.1.3.4 Electrical characteristics of J3 PINs in RS485 Configuration..... 138
16.1.3.5 Pin Out of J4.............................................................................. 139
16.1.3.6 Electrical characteristics of J4 PINs........................................... 139
16.2 Short Range Plug & Play Module (RDHS-0204N0-02)............................. 140
16.2.1 Features............................................................................................ 141
16.2.2 Dimensions ....................................................................................... 142
16.2.2.1 Pin Out of J5.............................................................................. 145
16.2.2.2 Electrical characteristics of J5 PINs........................................... 145
16.3 Short Range USB Desktop Reader (RDHS-0204D0-02).......................... 146
16.3.1 Features............................................................................................ 147
16.4 Plug-In Reader (RDHP-0206P0-02)......................................................... 148
16.4.1 Features............................................................................................ 149
17
Appendix C: Timings...............................................................150
18
Appendix D: Release Notes.....................................................152
18.1 Version History......................................................................................... 152
18.1.1 MultiISO 1.0 ...................................................................................... 152
18.2 Revision history........................................................................................ 153
19
Appendix E: Approvals / Certificates .....................................154
19.1 CE Declaration......................................................................................... 154
19.2 FCC Declaration....................................................................................... 155
19.3 RoHS Compliance.................................................................................... 156
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 10
Page 12

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
1 Scope
The ACG HF Multi ISO Reader Module supports a broad range of tags compliant
with ISO 14443 type A and B standards, including SR176 tags, tags which belong to
the Philips mifare
command structure allows the device to communicate with tags that use an operating
system. The read/write unit supports ISO 14443-4 layer with automatic chaining, 256
byte buffer and frame length, extended time framing and up to 848kBaud
transmission rates over the air interface.
Additionally this unit implements a DES cipher which enables to use mifare
tags. These tags are designed for use in high security algorithms.
A SAM interface is also available.
Major applications are:
®
family, ISO 15693 tags, ISO 18000-3, EPC and UID tags. An open
®
DESFire
• Access control, identification using high security cards
• Ticketing using standard mifare
• Data storage
• Multi-applications using operating systems
®
cards
2 Extended Documentation
Please note that all confidential material is excluded from this documentation.
You can obtain the extended documentation containing the confidential information
after signing a NDA.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 11
Page 13

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
3 Definitions and Abbreviations
3.1 Definitions
3.1.1 Anti-collision loop
An algorithm used to identify and handle a dialogue between a reader and one or
more tags in its antenna field.
3.1.2 Hex notation
A hexadecimal value is marked with the suffix ‘h’, i.e. A1h has the value A1
hexadecimal.
3.1.3 ASCII notation
ASCII characters are listed within apostrophes, i.e. ‘x’ means a single x.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 12
Page 14
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
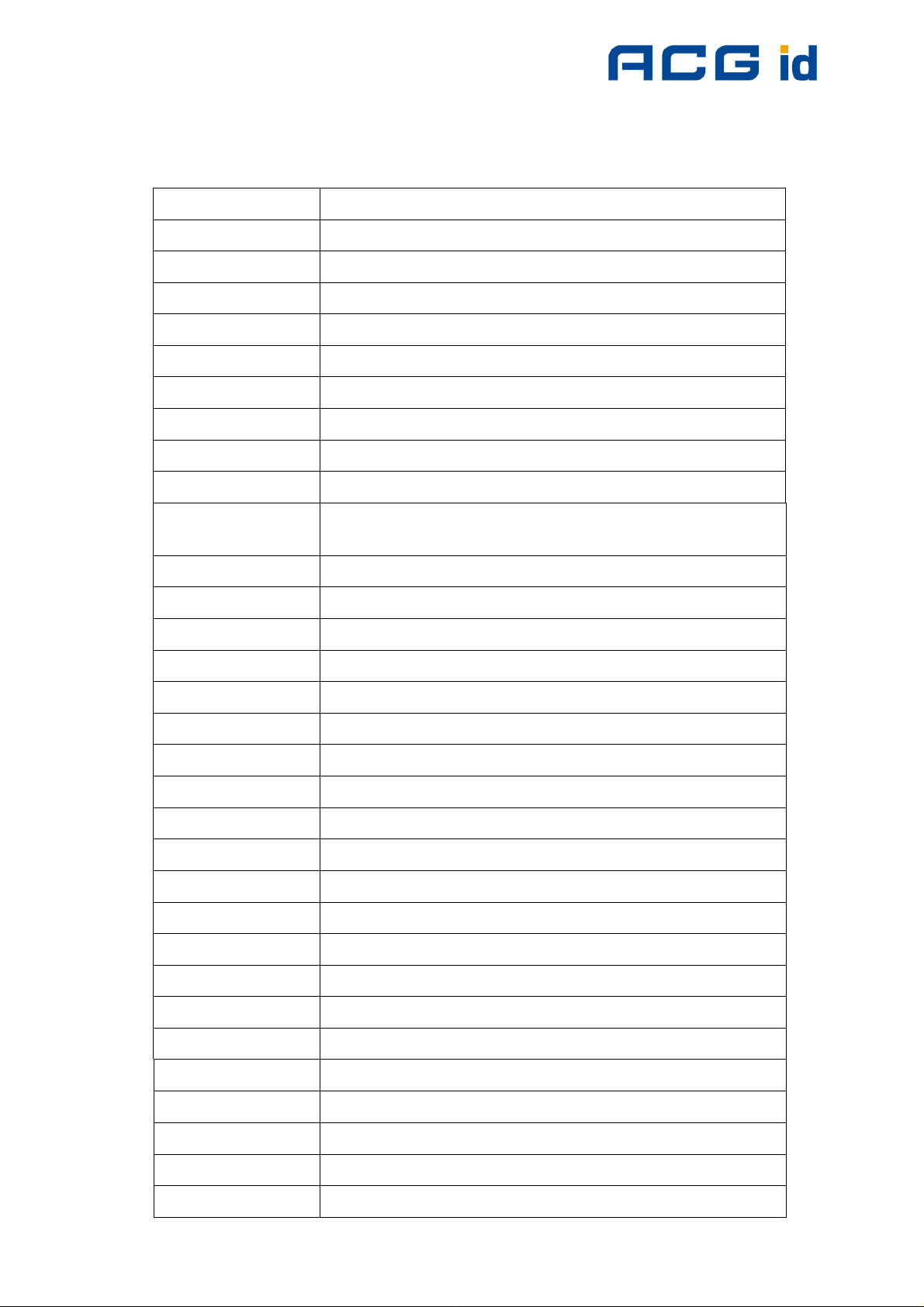
3.2 Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
AID Application ID
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ATR Answer to Reset
ATS Answer to Select
AFI Application Family Identifier
block For the mifare® Standard one block contains 16 bytes
CBC Cipher Block Chaining
CID Card Identifier (logical card address, ISO 14443-4)
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DES Data Encryption Standard, for more details about DES
refer to [3].
DSFID Data storage format identifier
EDC Error Detection Code
EGT Extra Guard Time
EOF End of Frame
ETU Elementary time unit
Hex / xxh Value in Hexadecimal notation
I-block Information block
KTT Key Transfer Transponder
LSB Least Significant Bit or Byte
MSB Most Significant Bit or Byte
NAD Node Address (ISO 14443-4)
OSI Open System Interconnection
OTP One time programmable
PCB Protocol Control Byte (ISO 14443-4)
PCON Protocol Configuration byte of the reader
PPS Protocol and Parameter Selection
RATS Request for Answer to Select
R-block Receive ready block
REQA Request ISO Type A
REQB Request ISO Type B
RFU Reserved for Future Use
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 13
Page 15
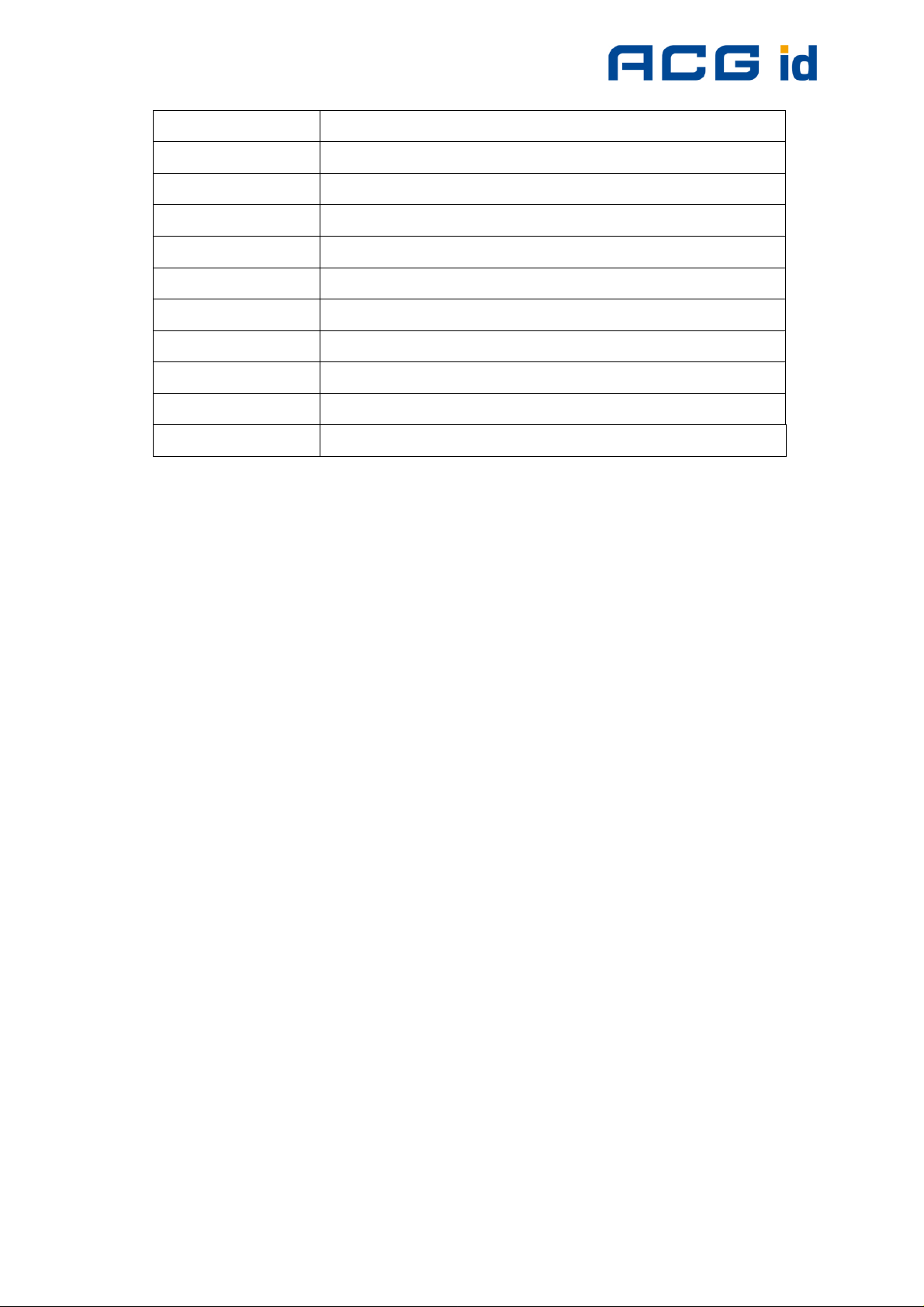
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Abbreviation Description
S-block Supervisory block
Sector For the mifare® Standard one sector contains 4 blocks
SID Station ID
SFGT Guard time after RATS
SN Serial Number of a tag (a 32 bit number)
SOF Start of frame
TDES Triple DES
Value block 32 bit data block format. Used in ticketing application
<CR> Carriage return (0Dh)
<LF> Line feed (0Ah)
Figure 3-1: Abbreviations
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 14
Page 16
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 15
command
√
1
Performance varies
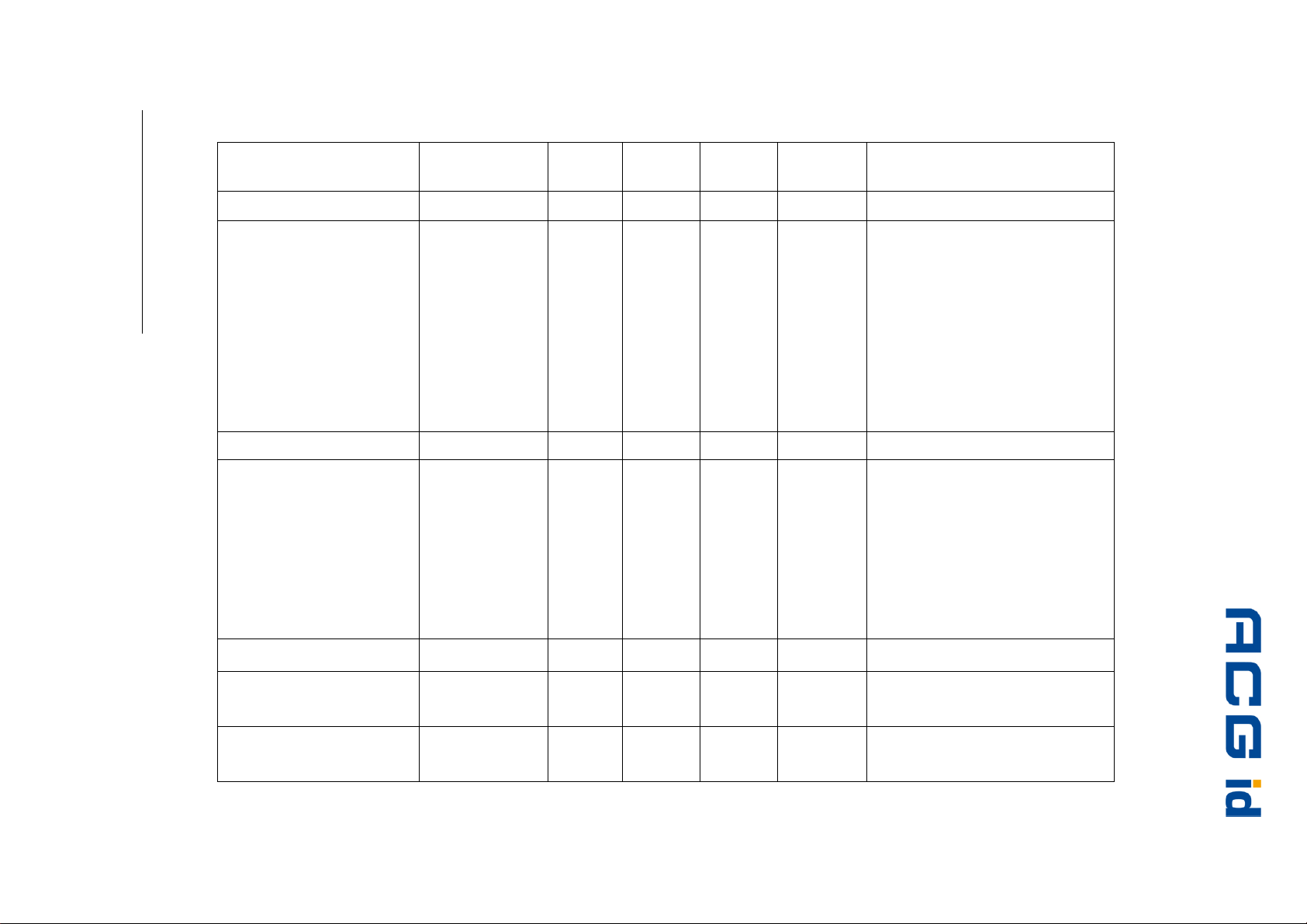
4 Supported tags
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Transfer
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Comments
encryption included
encryption not included
encryption included
works only with ‘t’ command
extended setup needed
ISO 14443 A
mifare
mifare
Figure 4-1: Supported labels (Part 1)
mifare
®
mifare
®
mifare
®
Standard
®
4k
Ultralight
®
ProX
DESFire
SLE66CLX320P
SLE 55R04 / 08
Smart MX
Jewel Tag
ISO 14443 B
SLE6666CL160S
SR176
SLIX 4K
ASK GTML2 ISO
ASK GTML
Sharp B
TOSMART P0032/64
Manufacturer
Philips
Philips
Philips
Philips
Philips
Infineon
Infineon
Philips
Innovision
Infineon
STM
STM
ASK
ASK
Sharp
Toshiba
Serial
number
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
-
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Read
block
√
√
√
√
-
-
-
-
-
-
√
√
-
-
-
-
Write
block
√
√
√
√
-
-
-
-
-
-
√
√
-
-
-
-
Dual Interface
ISO 14443 A compliant
1
(
)
ISO 14443 B
compliant(
1
)
various
various
√
√
-
-
-
-
√
√
Page 17
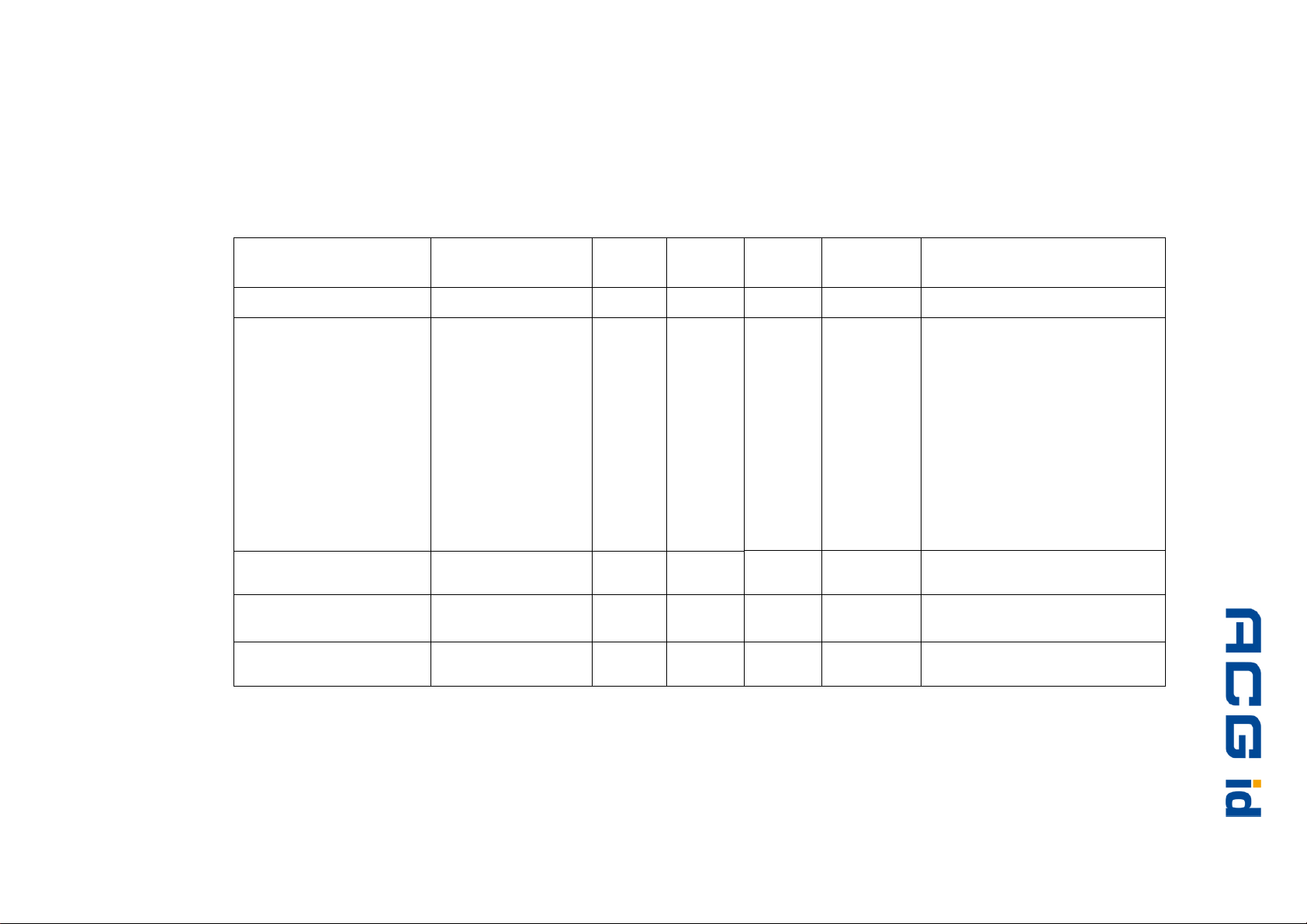
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 16
√
√
√
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Figure 4-2: Supported labels (Part 2)
ISO 15693
EM 4135
ICODE® SLI
LRI12
LRI64
LRI512
SRF55VxxP
SRF55VxxS
Tag-it™ HF-I Standard
Tag-it™ HF-I Pro
TempSense
ICODE®
ICODE® EPC
ICODE® UID
Manufacturer
EM Microelec.
Philips
STM
STM
STM
Infineon
Infineon
TI
TI
KSW
Philips
Philips
Philips
Serial
number
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
-
√
√
√
√
Read
block
√
√
√
√
√
√
-
√
-
√
√
√
√
Write
block
√
√
√
√
√
√
-
√
-
√
√
√
√
Transfer
command
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Comments
with 10% modulation index
encryption included
only in addressed mode
temperature logging
Page 18
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
5 The mifare® Transponder Family
The mifare
compliant to the ISO 14443 standard.
5.1 mifare® Standard
The mifare® Standard card consists of 16 sectors. A sector includes four blocks of 16
bytes each.
®
transponder family consists of various 13.56 MHz transponder ICs, all
mifare
Sector 0 (Block: 0...3) Block 8: Data or value (16 bytes)
Sector 1 (Block: 4...7) Block 9: Data or value (16 bytes)
Sector 2 (Block 8...11) Block 10: Data or value (16 bytes)
...
Sector 15 (Block 60...63)
®
Standard Sector 2
Block 11: Access Conditions (4
bytes), Key A, Key B (16 bytes)
Figure 5-1: mifare® Standard: sector diagram
5.1.1 Sector 0 / Block 0
Block 0 is read only.
Serial Number (4 bytes) Check byte (1 byte) Manufacturer data (11 bytes)
Figure 5-2: mifare® Standard: sector 0 / block 0
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 17
Page 19

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
5.1.2 Blocks 3, 7, 11, 15, …
Transport keys are set on delivery:
Key A (6 bytes) Access Conditions (4 bytes) Key B (6 bytes)
Figure 5-3: mifare® Standard: block 3, 7, 11, 15, …
Key A
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 (Infineon) or FF FF FF FF FF FF (new Philips cards)
Key B
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 (Infineon) or FF FF FF FF FF FF (new Philips cards)
Access Conditions
FF 07 80 xx (key A is used to read or write; key A itself is not readable; key B is data
only). For further information refer to the mifare
®
card manual.
Remarks
Enabled keys are always read as 00 00 00 00 00 00
Using key B as a data area will cause a security gap, due to the fact that it is
necessary to rewrite key A and the access conditions at each write process. It is not
recommended to use key B as a data storage area.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 18
Page 20
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
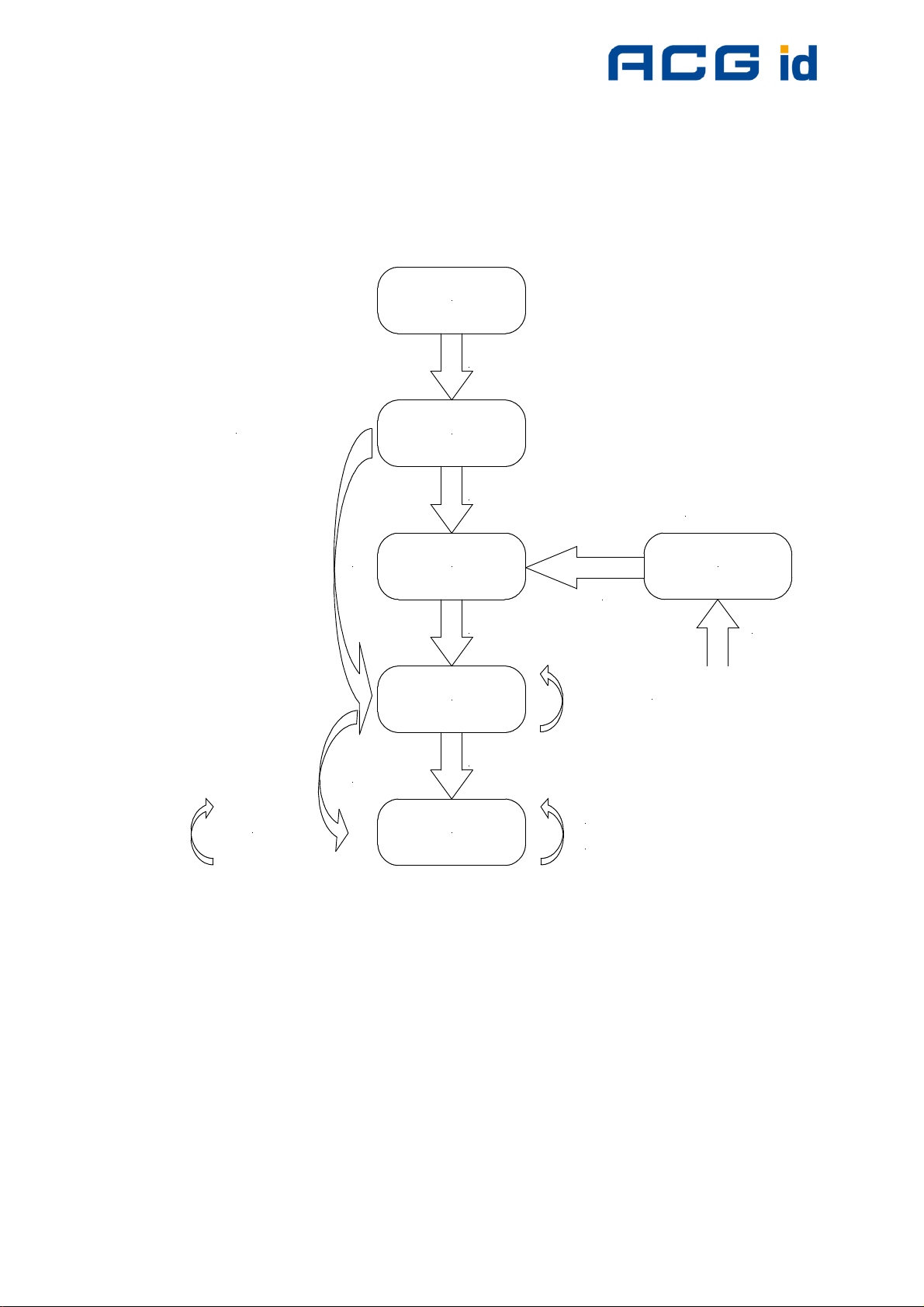
5.2 State Diagram
All mifare
®
cards use the following state diagram.
Power Off
Reset
Reader Instruction Set
read/write/...
Idle
Ready
Select
Active
Log In
Authenticated
REQA
Wake Up
Select
Anticollision Loop
Authenticate
ISO 14443 Commands
Halt
Halt
Tag interfacing
commands
Figure 5-4: State diagram
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 19
Page 21
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
5.3 mifare® Ultralight
mifare® Ultralight cards have no encryption included. They only support plain text
data transmission.
mifare
bytes per sector. Only the 4 least significant bytes are valid when using mifare
Ultralight.
Ensure that the other bytes match with the tag content when using the write
command; otherwise the read back will fail.
®
Ultralight only supports 4 bytes per sector, but the command set uses 16
®
5.4 mifare® 4k
mifare® 4k cards have an increased memory. Beginning from sector 32 (20h), sectors
have 16 blocks. Due to compatibility reasons, the sector indices have changed
according to the following table. The login sector has to be used to access the
corresponding sector on the card.
Sector Block Login sector
00h 00h – 03h 00h
01h 04h – 07h 01h
… … …
1Fh 7Ch – 7Fh 1Fh
20h 80h – 8Fh 20h
21h 90h – 9Fh 24h
22h A0h – AFh 28h
23h B0h – BFh 2Ch
24h C0h – CFh 30h
25h D0h – DFh 34h
26h E0h – EFh 38h
27h F0h – FFh 3Ch
Figure 5-5: mifare® 4k sector index table
5.5 mifare® ProX
mifare® ProX tags have an operating system onboard. Data organization depends on
the operating system installed on the card. These cards can include additional
functionalities such as DES or a proprietary encipher algorithm.
Before accessing the operating system, the card must be selected. Customized
commands are issued using the transfer command.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 20
Page 22
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
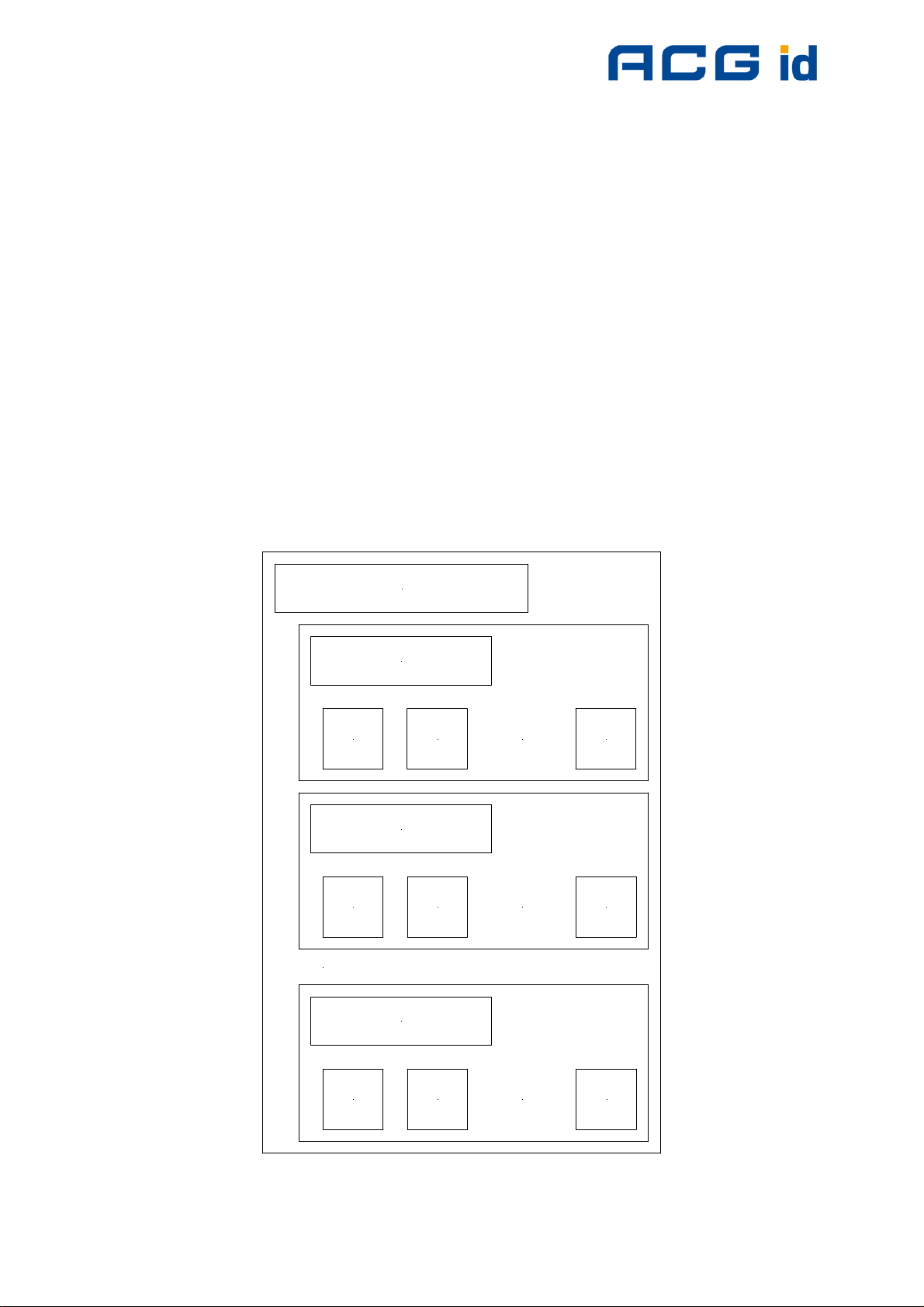
5.6 mifare® DESFire
This tag supports additional security algorithms (DES, Triple-DES, MAC) for security
sensitive applications.
DESFire tags are addressed using a specific command set (see DESFire command
set).
5.6.1 Memory organization
The memory of a DESFire card can be personalized to specific requirements. The
card can be seen as data storage device like a hard disk in a PC. The memory is
divided into a maximum of 28 different applications (directories) with 16 files each. An
application has up to 14 keys. Depending on keys and access conditions a file can
be accessed in four different ways. Plain data is never secured. Data is secured
using a MAC, single DES or triple DES enciphers.
The following figure describes the memory organization of a DESFire card.
DESFire card (Application 0)
Application 1
File
ID 1
File
ID 2
...
File
ID n
Application 2
File
ID 1
File
ID 2
...
File
ID n
...
Application n
File
ID 1
Figure 5-6: DESFire memory organization
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 21
File
ID 2
...
File
ID n
Page 23
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
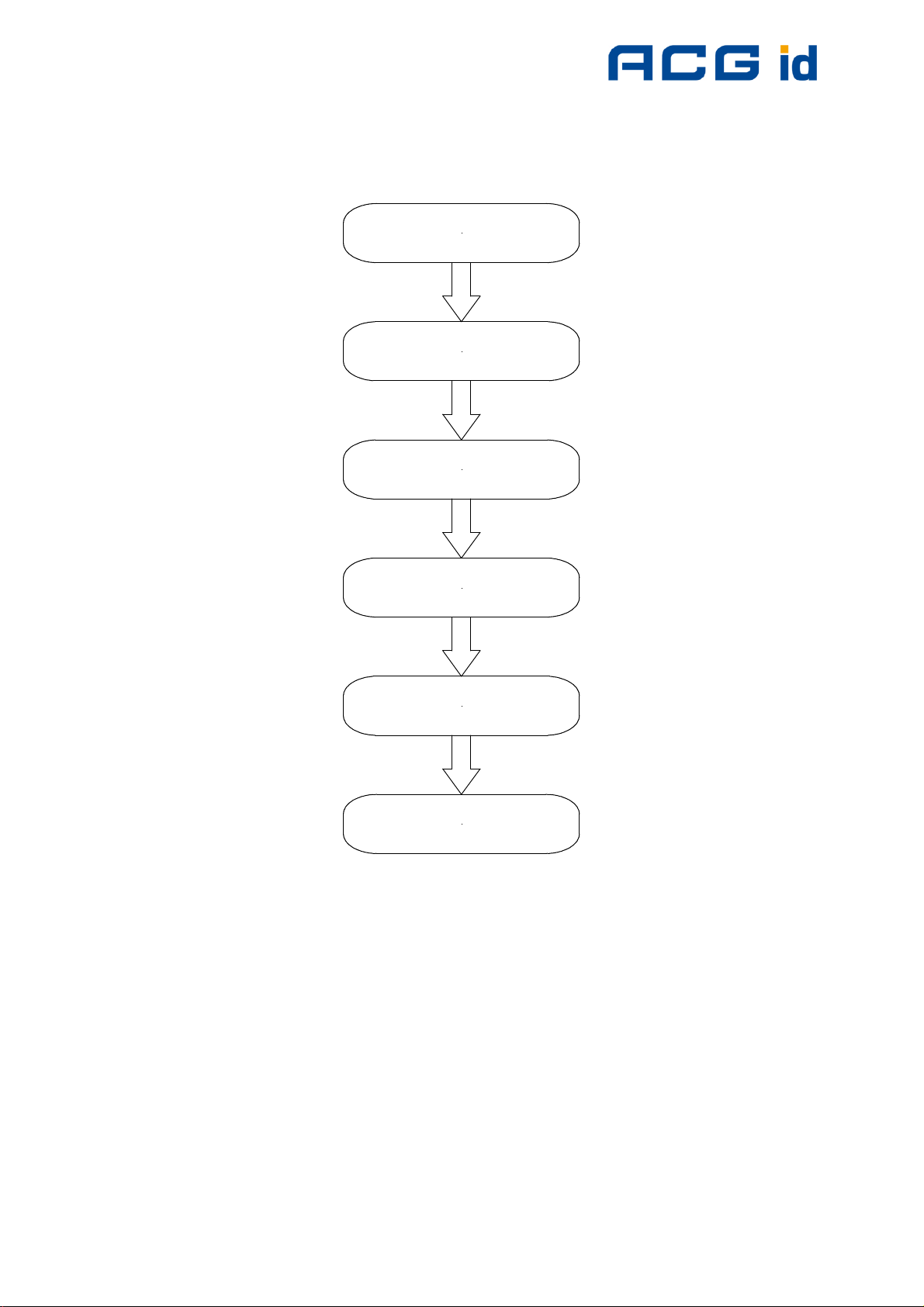
5.6.2 State diagram of DESFire
Activate DESFire card
Select Application
Login to Application
Select File with ID
Change File
Commit / Abort Transaction
Figure 5-7: DESFire state diagram
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 22
Page 24

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
5.6.2.1 Activate PICC
Before accessing a DESFire card, the card must be selected. A DESFire card has a
7 byte UID. After activation, the card is powered up and ready to accept a DESFire
command. Application 0 is selected automatically.
5.6.2.2 Select application
To jump into another application, the application has to be selected. An application
can be seen as a directory, which contains up to 16 files. The size of the application
depends on the stored files.
5.6.2.3 Login to application
Specific access rights can be set for each application. Login to an application allows
changing the organization of the application. Login to a file opens a secured file for
access. A file can be accessed in four different ways: without any security or secured
with MAC, single DES or triple DES.
5.6.2.4 Select file
Before accessing a file, the file must be selected
5.6.2.5 Change file
A selected file can be changed according its access rights. If a file is secured, a login
is required before changes can be made.
5.6.2.6 Commit / Abort transaction
Value files, backup files, linear record files and cyclic record files only adapt their
values after the commit transaction command is given. Several files can be changed
within an application at the same time. The abort transactions command annuls all
changes within an application. Power loss will cancel all modifications too.
For more details about application settings and access rights refer to [2].
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 23
Page 25
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
5.7 my-d™ IC (SLE 55Rxx)
my-d™ ICs are specific ICs from Infineon. These labels show a different memory
organization. Two different modes of tags are supported: plain and secure mode.
Memory Size of SLE Rxx-family
Type User Memory Administration
Memory
SLE 55R01 128 Bytes 32 Bytes 16
SLE 55R02 256 Bytes 64 Bytes 32
SLE 55R04 616 Bytes 154 Bytes 77
SLE 55R08 1024 Bytes 256 Bytes 128
SLE 55R16 2048 Bytes 512 Bytes 256
Address
Byte number within a page
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
FFh User data
… …
7Fh User data
… …
4Ch User data
Number of pages
… …
1Fh User data
… …
0Fh User data
… …
04h User data
03h
02h
01h
00h
Serial number (UID)
Figure 5-8: SLE 55Rxx memory organization
SLE 55R02
SLE 55R01
SLE 55R04
SLE 55R08
SLE 55R16
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 24
Page 26
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
6 ISO 14443 Type B
ISO 14443 type B cards are supported.
6.1 SR176
The SR176 label contains only 30 bytes of data organized in two bytes per page.
6.1.1 Memory organization
Block
address
0Fh Lock byte RFU Chip ID
0Eh User data
… …
04h User data
03h Serial number
02h Serial number
01h Serial number
00h Serial number
Byte 1 Byte 0
Figure 6-1: SR176 memory organization
6.1.2 Serial number UID
The UID is stored in the first 4 pages. Page 00h contains the LSB of the UID.
Page 03h Page 02h Page 01h Page 00h
Byte 1h Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 0
Figure 6-2: SR176 Serial number
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 25
Page 27
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
6.1.3 Lock byte
The lock byte defines the write access condition of a pair of pages. Each bit can only
be set once. This procedure is irreversible. This byte is implemented as an OTP.
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Page 08h
Page 0Fh
Page 0Eh
Page 0Ch
Page 0Dh
Page 0Ah
Page 0Bh
Figure 6-3: Lock byte
Page 09h
Page 06h
Page 07h
Page 04h
Page 05h
Page 02h
Page 03h
Page 00h
Page 01h
6.1.4 Chip ID
The Chip ID is defined in the low nibble of page 0Fh. It is manufacturer set and is
used internally to select and separate single tags.
6.2 SRIX4K
The SRIX4K label contains 512 bytes of data organized into four-byte pages.
6.2.1 Memory organization
Block
address
FFh OTP Lock Reg ST Reserved ST Reserved Fixed Chip ID
7Fh User data
… …
07h User data
06h 32 bits binary counter
05h 32 bits binary counter
04h 32 bits Boolean Area
Byte 3 Byte 2 Byte 1 Byte 0
03h 32 bits Boolean Area
02h 32 bits Boolean Area
01h 32 bits Boolean Area
00h 32 bits Boolean Area
Figure 6-4: SRIX4K memory organization
6.2.2 Lock block
Locking of blocks is not supported with this tag.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 26
Page 28
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
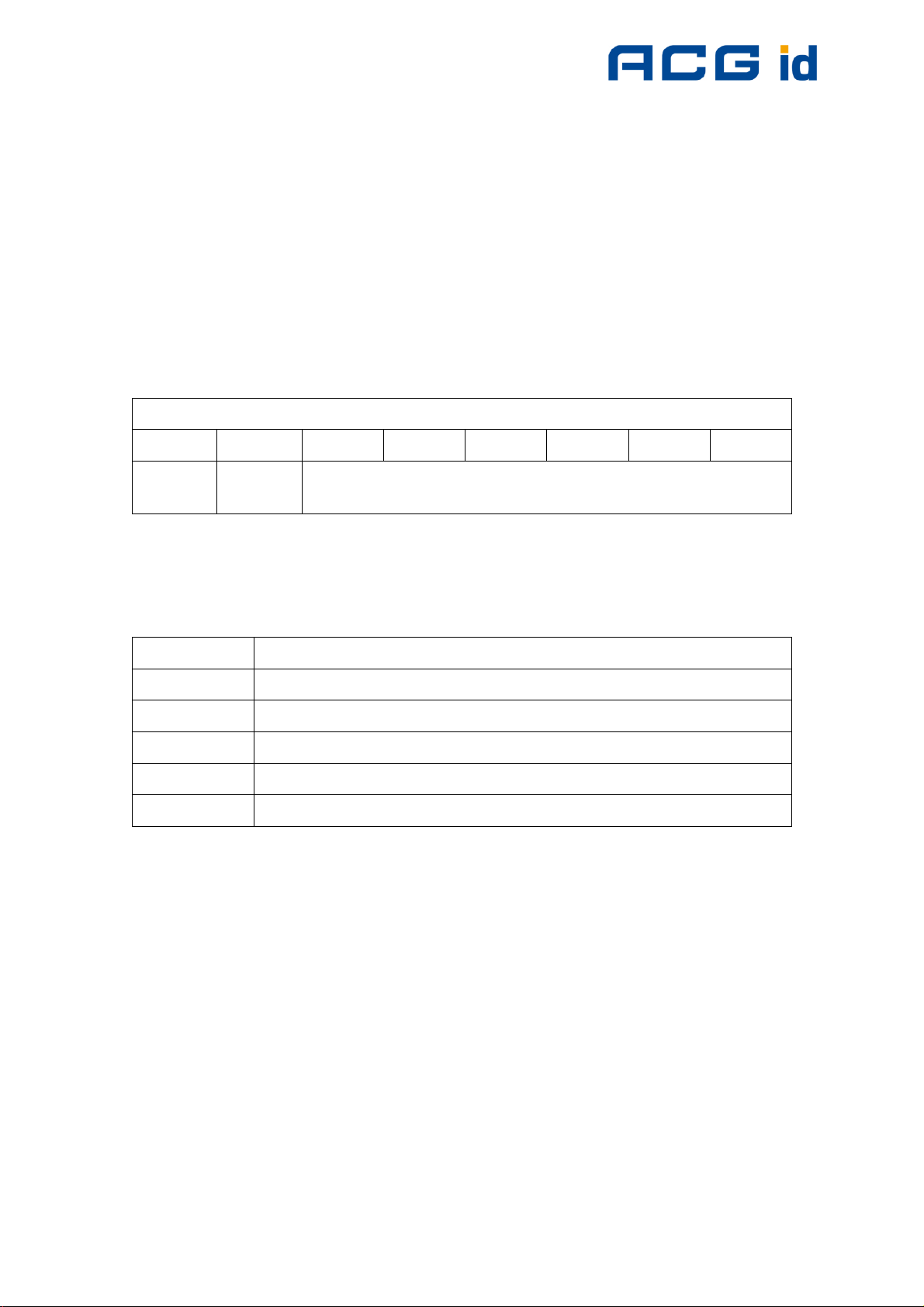
7 ISO 15693
The reader can communicate with ISO15693 tags. An anti-collision is needed if
multiple instances of tags are in the same antenna field. The reader detects each
type of ISO15693 labels and handles them individually
7.1 Coding of UID
The UID of a tag is defined in ISO/IEC 15693-3. All tags compliant to ISO15693
support the specified format. The UID is factory programmed and cannot be
changed. The UID is needed for the anti-collision sequence to separate several tags
in the same antenna field.
Byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
E0h MFR
Code
The MFR Code is listed in ISO/IEC 7816-6:1996/Amd.1: 2000(E). Following
manufacturer are tested with our reader
MFR-Code Company
02h ST Microelectronics
04h Philips Semiconductors
05h Infineon Technologies AG
07h Texas Instrument
16h EM Microelectronic-Marin SA
Serial number
Figure 7-1: Coding of ISO 15693 UID
Figure 7-2: Manufacturer codes
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 27
Page 29
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
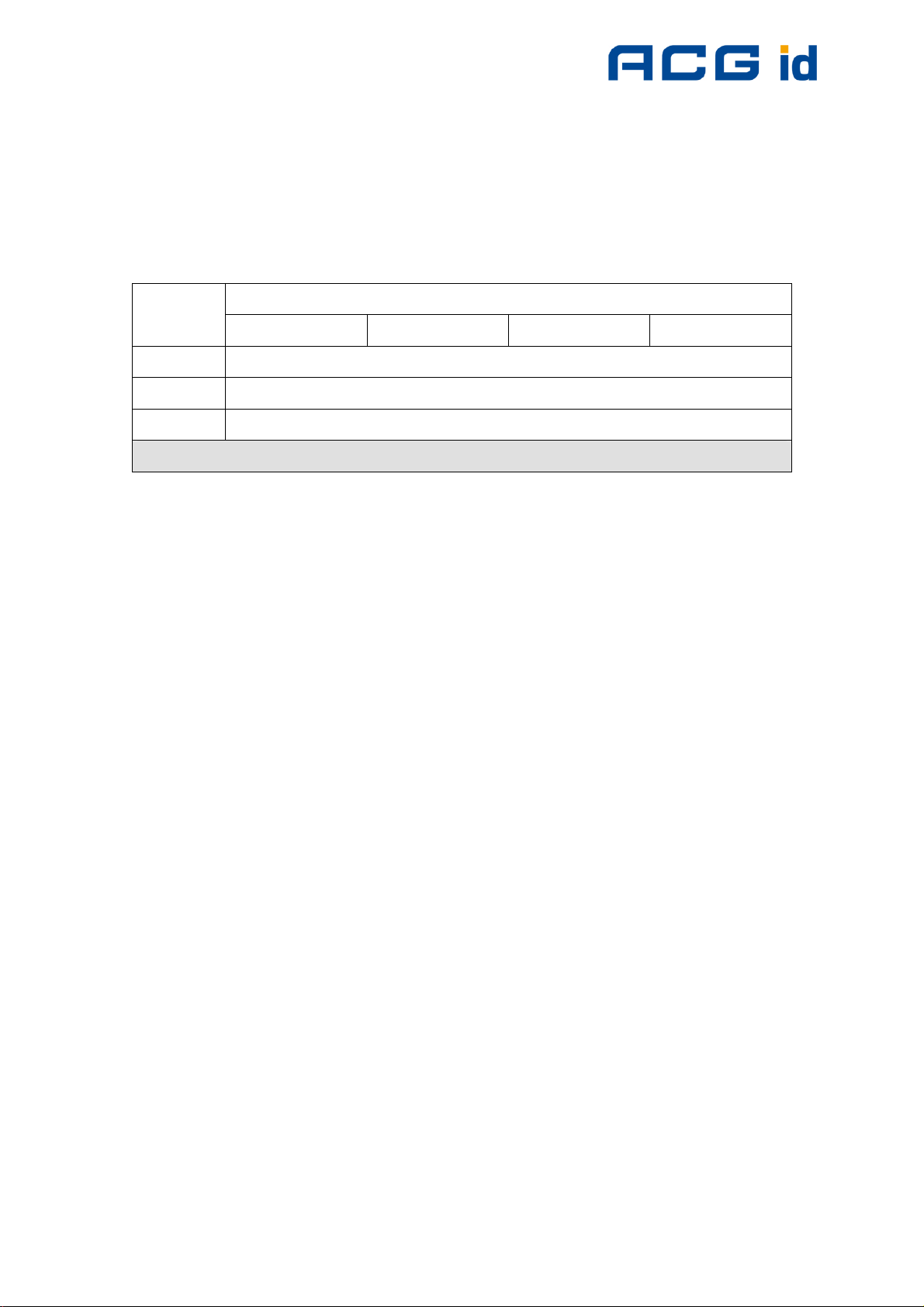
7.2 Memory organization
An ISO15693 tag is separated into two blocks. An administrative block which
contains the UID, AFI, DSFID and the lock page state. The user block is free for
custom use. The chip manufacturer defines the amount of bytes and number of
pages of each tag. As default four bytes are used for several tags.
Page
address
3Fh User data
… …
00h User data
Byte
0 1 2 3
Administrative block
Figure 7-3: Memory organization of ISO 15693
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 28
Page 30
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
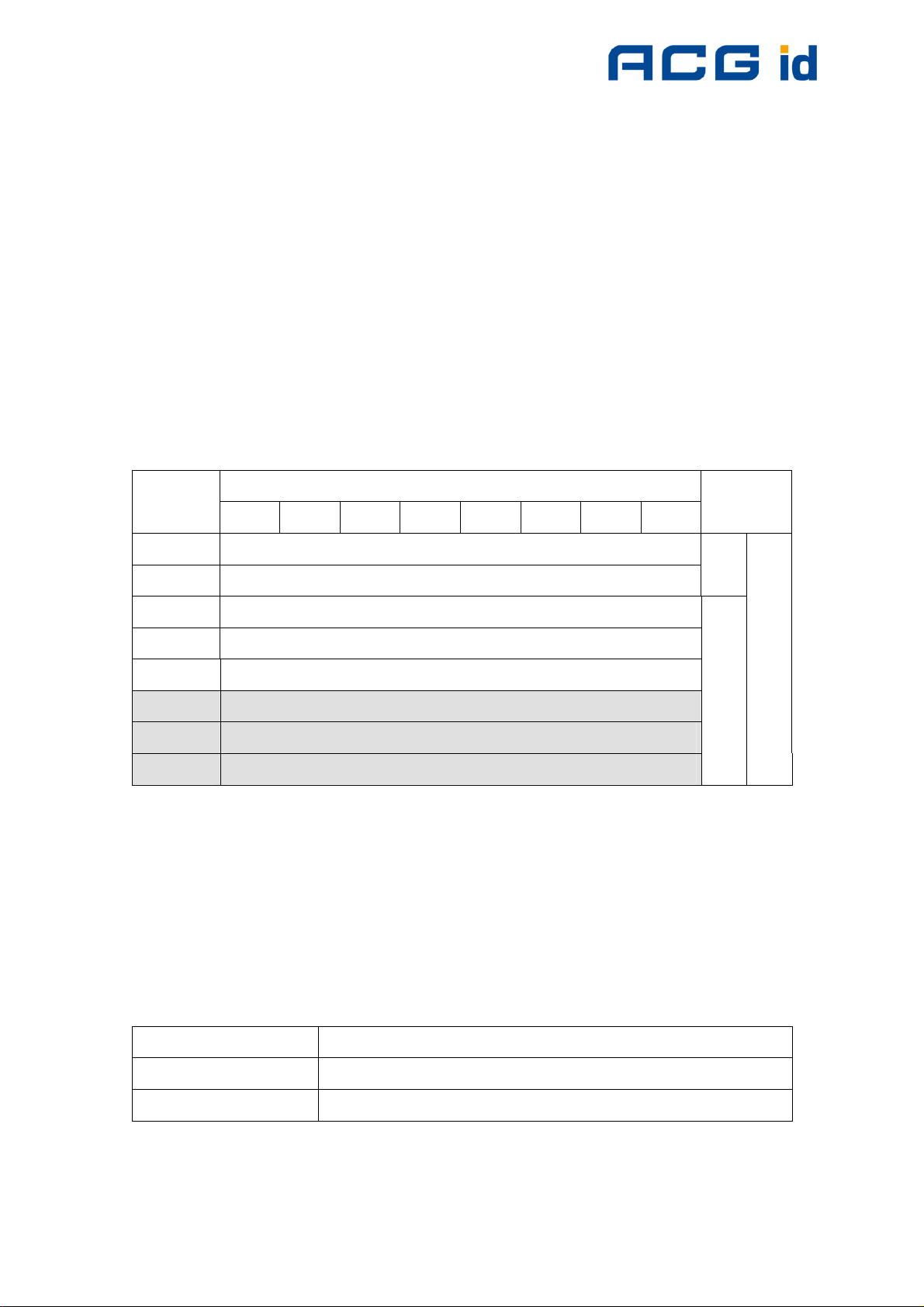
7.3 my-d™ IC (SRF55VxxP)
my-d™ ICs are specific ICs from Infineon. These labels show a different memory
organization. Two different modes of tags are supported: plain and secure mode.
Two different cards with 320 bytes or 1k bytes EEPROM memory are available. The
EEPROM memory is divided into pages.
Each tag is split into two parts: The administrative blocks (00h, 01h, 02h) and the
user area. Administrative pages are read only and cannot be changed. User data is
free for use. Additionally user data pages can be locked. This procedure is
irreversible.
The EEPROM of SRF55V10P is organized in 128 pages addressed 00h to 7Fh. The
EEPROM of SRF55V02P consists of 32 pages addressed 00h to 1Fh.
Address
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
7Fh User data
… …
1Fh User data
… …
03h User data
02h
01h
00h
Figure 7-4: SRF55VxxP memory organization
Byte number within a page
Serial number (UID)
7.3.1 UID
The UID of SRF55Vxx labels starts with 60h or E0h.
7.3.2 Security Bit
SRF55V10P
SRF55V02P
Bit 45 of the UID defines the secure mode of the SRF55Vxx. If set the tag supports
security algorithm.
Bit 45 Description
1 Tag supports crypto security mechanism
0 Chip supports plain mode only
Figure 7-5: Security bit
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 29
Page 31

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
7.4 EM 4135
The EM4135 is an ISO15693 compliant label of EM Microelectronic-Marin SA. It has
eight bytes per page as the same as the my-d™ label. It only supports 36 pages. The
administrative area holds the information of the access condition and the UID.
Address
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
23h User data
… …
00h User data
Figure 7-6: Memory organization of EM 4135
Administrative area
Page
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 30
Page 32

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Special
function
Write
access
Serial
number
Serial
number
User
data
User
data
8 ICODE
ICODE® IC data is stored in a non-volatile EEPROM. Its capacity is 512 bits
organized in 16 blocks consisting 4 bytes each (1 block = 32 bits). First 3 blocks
contain administrative data.
8.1 Memory organization
Page
address
0Fh User data
… …
05h User data
04h Family code identifier / User data
03h Special function (EAS) / User data
02h
01h
00h
Byte
0 1 2 3
Write access condition
Serial number
Serial number
Figure 8-1: ICODE® memory organization
8.2 Serial number
The serial number of a label is defined at the manufacturer process. It is stored on
page 00h and page 01h. LSB is stored first.
8.3 Write access condition
Page 02h contains the write access condition for each page. Each page can be set to
read only (bits are set to 0). This procedure is irreversible. Locking page 2 no further
changed of the access condition can be done. Always two bits must be change at the
same time. This register is implemented as OTP.
Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB LSB
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 B A 9 8 F E D C
…
…
…
…
…
…
…
…
…
…
Figure 8-2: Write access condition bytes
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 31
Page 33

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
8.4 Special function (EAS), AFI
Special Functions (EAS) and Family Code/Application Identifier are additional
features. For more information refer to the ICODE® manual.
8.5 User data
All other blocks are free for use and can be changed according the state of the write
access conditions.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 32
Page 34

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
9 ICODE EPC
ICODE EPC labels data is stored in a OTP memory. Its capacity is 136 bits
organized in 17 blocks consisting of 1 bytes each. All MSB of the different fields
(EPC, CRC16, Destroy Code) are located at the lowest block address.
9.1 Memory organization
Page
address
14h – 16h Destroy Code
12h – 13h CRC 16
00h – 11h EPC
Figure 9-1: ICODE EPC memory organization
Byte
9.2 Serial number
The serial number of a label is defined within the EPC blocks.
9.3 Read Block
It is not possible to read a block with the read block 'rb' command.
9.4 Write Block
It is possible to write the EPC data (12 bytes) with the write block 'wb' command
using block address 00h.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 33
Page 35

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
10 ICODE UID
The memory has a capacity of 192 bits and is organized in 24 blocks, consisting of 1
byte each. All MSB of the different fields (UD, UD CRC, CRC16, Destroy Code) are
located at the lowest block address.
10.1 Memory organization
Page address
21h – 23h OTP Destroy Code
19h - 20h OTP CRC16
14h – 18h RO UID
12h – 13h R/W UD CRC16
00h – 11h R/W User data (UD)
Access Condition Description
Figure 10-1: ICODE UID memory organization
10.2 Read Block
It is possible to read the user data (12 bytes) with the read block 'rb' command using
block address 00h.
10.3 Write Block
It is possible to write the UD data (12 bytes) with the write block 'wb' command using
block address 00h.
Additionally it is possible to write the destroy code (3 bytes) with the write block 'wb'
command using block address 01h.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 34
Page 36

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11 Hardware
11.1 Dimensions
All dimensions listed in mm
J1
25,40 mm
1,27 mm
1
30,48 mm
29,21 mm
1,27 mm
20
J2
10
11
2,54 mm
Top View
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 35
Page 37

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.1 Pin out of J1
PIN PIN No. Description
ARX 1 Antenna RX
ATX1 2 Antenna TX1
VDD 3 Supply Voltage
GND 4 Ground
ATX2 5 Antenna TX2
TGND 6 Antenna Ground
SAM CLK 7 SAM clock
SAM IO 8 SAM IO
SAM
RESET
RTS 10 Request to Send
9 SAM Reset
Figure 11-1: Pin out of jumper 1
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 36
Page 38

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.2 Electrical characteristics of J1 PINs
PIN PIN No. Min Typ. Max. Description
ARX 1 1.1V 4.4V Antenna RX
ATX1 2 13,56 MHz
34 V
PP
VDD 3
+4.5V +5.0V +5.5V Supply Voltage
13.56MHz
100 mA
PP
50VPP
Antenna TX1
32mA 150mA 250mA Supply Current (without
SAM)
GND 4 GND Ground
ATX2 5 13,56 MHz
34 V
PP
13.56MHz
100 mA
PP
50VPP
Antenna TX2
TGND 6 GND Antenna Ground
SAM CLK 7
TTL
SAM clock
25mA
3,39MHz
SAM IO 8 TTL 25 mA IO for SAM Input and
SAM Output
SAM RESET 9 TTL 25 mA SAM Reset
RTS 10 TTL 25 mA Request to Send
Figure 11-2: Electrical characteristics of pins
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 37
Page 39

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.3 Pin out of J2
PIN PIN Nr Description
VDD 20 Supply Voltage
GND 19 Ground
LEDg 18 LED green (reading LED)
LEDr 17 LED red
EN 16 Enable reader, open or logic high
MCLR 15 Master clear
USER 14 User Port
DIR 13 Direction of RS 485
TX 12 TX to PC
RX 11 RX from PC
Figure 11-3: Pin out of jumper 2
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 38
Page 40

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.4 Electrical characteristics of J2 PINs
PIN PIN No.
RX 11 USART-
Min Typ. Max. Description
25 mA RX to PC
1
TTL
To RS232, RS485 or RS422
device driver
TX 12 USART-
1
TTL
25 mA TX to PC
To RS232, RS485 or RS422
device driver
DIR 13 TTL 25 mA Direction of RS 485
Logic High = Reader to Host
Logic Low = Host to Reader
USER 14 TTL2 25 mA User Port
MCLR
15 TTL3 Master clear
Leave unconnected.
Low will reset the register
and the key management to
default values.
EN 16 ST4 25 mA Enable reader
logic low will disable the
reader
Open or logic high
LEDr 17
VDD
min
@ 25mA
VDD
typ
@ 11mA
VDD
max
@ 0 mA
LED red
Output Voltage
11mA 25mA External Resistor
min. 200 Ω
LEDg 18
1.4V
@ 11mA
VDD
@ 0mA
LED green (reading LED)
with 330 Ω (internal serial)
resistor
11mA 15mA
GND 19 GND Ground
VDD 20 +4.5V +5.0V +5.5V Supply Voltage
IDD 32 mA 150 mA 250 mA Supply Current (Without
SAM)
Figure 11-4: Electrical characteristics of pins
1
Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
2
TTL buffer output / input
3
Voltage spikes below GND at the MCLR/VDD pin, including currents greater than 80mA, may cause
latch-up. Thus, a series resistor of 50-100Ω should be used when applying a "low" level to the
MCLR/V
4
Schmitt trigger buffer input
, rather than pulling this pin directly to GND.
DD
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 39
Page 41
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
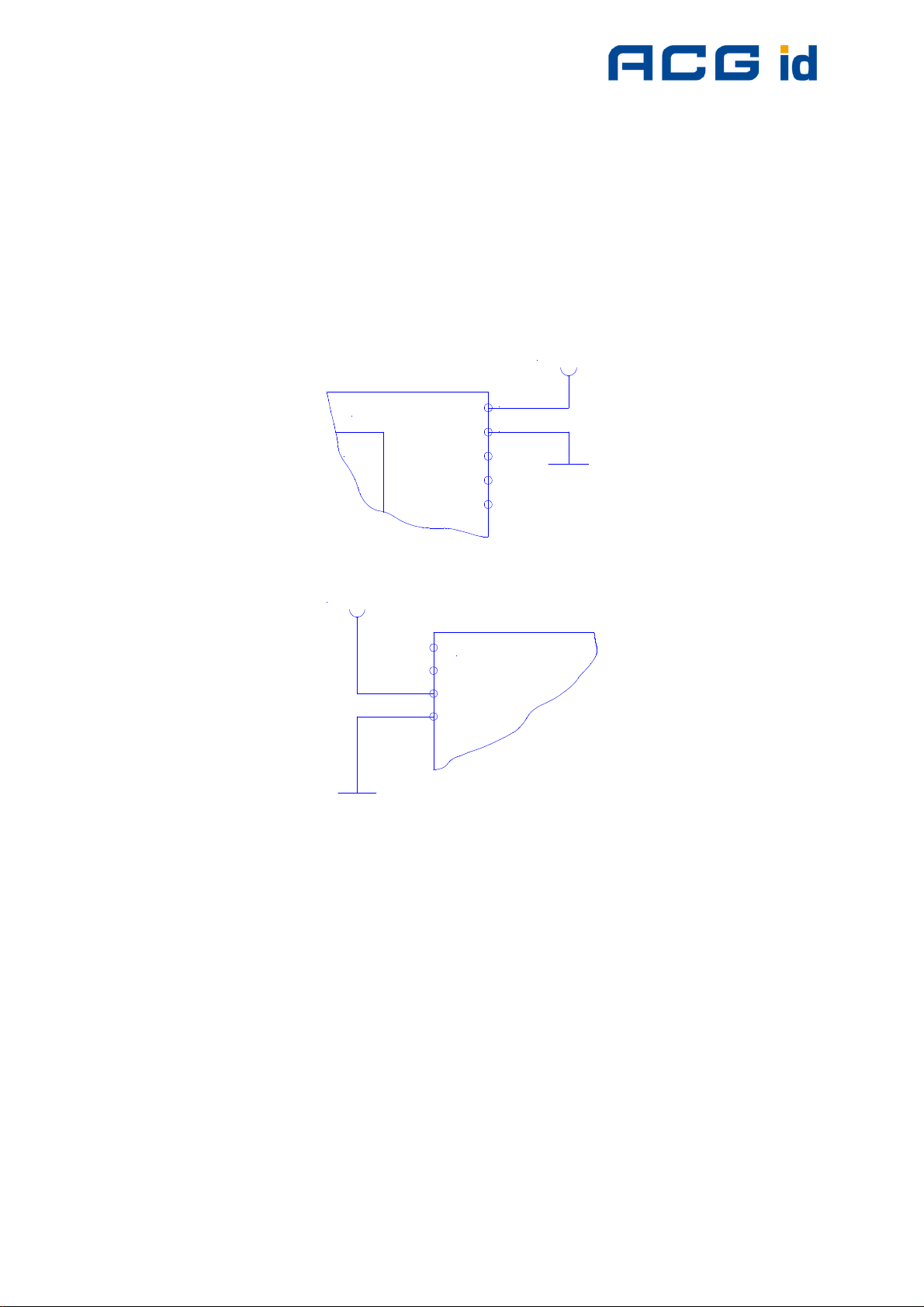
11.1.5 External Connections
11.1.5.1 Power Supply
If the supply voltage and any noise modulated on the supply voltage remains within
the specified limits, no further filtering is required. In some cases it is recommended
to use additional filtering for the power supply line. Insufficient power line filtering
could cause unexpected or irregular performance drops.
Option 1
+5V DC
OEM Board
20
19
uC
Option 2
+5V DC
OEM Board
3
4
The board can be connected as shown above. Both alternatives are possible and can
be used as they fit best into the layout of the carrier board. The two VCC PINs and
the two GND PINs are connected internally.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 40
Page 42

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.5.2 Antenna
The typical antenna tuning and matching network is shown below. The external
antenna has to have the right inductance and a certain resistor and capacitor
combination for an optimized frequency tuning and antenna matching.
L ANT
C5
C3
C4
R1
C1
C2
1
2
5
6
OEM Board
More details about the antenna design are available in the ACGid antenna design
guide manual. This document can be downloaded from
www.acg-id.com
Please refer also to the specific application notes for the Philips reader IC (mifare
.
®
&
I-Code, Micore Reader IC family Directly Matched Antenna Design).
11.1.5.3 Serial Interface
The OEM Board can be connected directly with a micro controller. Alternatively the
OEM Board also can be connected to most serial interface types by using the right
interface converter circuit. In order to optimize the communication quality the specific
application note of the interface converter circuit needs to be taken into
consideration.
Interface
Converter
Circuit
Host Interface
OEM Board
12
11
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 41
Page 43

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
11.1.5.4 Function Control LEDs
Two external LEDs can be connected to the OEM Board. There are two alternatives
possible.
Option 1
OEM Board
uC
330 Ohm
18
17
Option 2
OEM Board
uC
330 Ohm
18
17
330 Ohm
In both cases the LED supply voltage levels are TTL levels.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 42
Page 44

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12 Software
By default, data is transmitted at 9600, n, 8, 1, no handshaking. Two protocol modes
are supported. The protocol mode is configured in the reader EEPROM. As factory
default, the ASCII protocol is used.
12.1 ASCII Protocol
This protocol is designed for easy handling. The commands are issued using a
terminal program. Data is transmitted as ASCII hexadecimal that can be displayed on
any terminal program (i.e. HyperTerminal).
Command Data
Variable length Variable length
Figure 12-1: ASCII protocol frame
12.2 Binary Protocol
This protocol is designed for industrial applications with synchronization and frame
checking. An addressing byte for party line (master/slave, multi-drop) is also
included.
The protocol usually requires a device driver. Data is transmitted in binary mode. The
reader uses an internal binary watchdog timer to ensure correct framing.
STX Station ID
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte Variable length 1 byte 1 byte
The binary frame version 2 is only sent to the host. It is implemented to give
extended information to the host.
Version 2 must be enabled in the Protocol configuration 2 register.
STX Station ID Length
Length Data BCC ETX
Figure 12-2: Binary Frame Version 1
Flags Data BCC ETX
1 byte
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 43
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte Variable length 1 byte 1 byte
Figure 12-3: Binary Frame Version 2
Page 45
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.2.1 STX
Start of transmission (02h)
12.2.2 Station ID
Unique ID of the station
00h: reserved for the bus master. Readers send response to this device ID.
FFh: Broadcast message. All devices will execute the command and send their
response.
12.2.3 Length
Length defines the length of the data block, including the flag byte, if binary protocol
version 2 is activated.
If length is set to zero, 256 data bytes are transmitted. The reader module only can
send 256 data bytes, but cannot receive commands with 256 bytes.
12.2.4 Flags
The flag byte gives additional information to the host.
Bit 3 – Bit 7 Bit 1 – Bit 2 Bit 0
RFU Leading Character Info Error State
Error State
If cleared, the command was processed successfully.
If Error State is set, an error occurred.
Leading Character Info
Bit 1 & 2 defines how to interpret the data in the binary frame.
Bit 2 Bit 1 Description
0 0 No leading character available, all values are hexadecimal.
0 1 The data contains one leading character.
1 0 All data bytes are characters.
1 1 RFU
12.2.5 Data
This part contains the command and the data. The command values are the same as
in ASCII protocol mode (‘x’, ‘s’, …) whereas data is transmitted in binary mode.
The length of the command block depends on the instruction.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 44
Page 46

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.2.6 Block Check Character (BCC)
The BCC is used to detect transmission errors. The BCC is calculated XOR-ing each
byte of the transmission frame excluding the STX/BCC and ETX characters. The
flags are part of the data.
0 N
DataCommandXORXORDataCommandXORLengthXORStatIDBCC =
12.2.7 ETX
End of transmission. (03h)
12.2.8 Remarks
If the reader device receives an invalid instruction frame (i.e. wrong BCC) or the
requested station ID does not match the internal ID of the reader, the command is
not executed. The reader waits for the next valid frame.
)/(...)/()()(
The automatic binary time-out (see protocol configuration register) is used to detect
incomplete binary frames.
12.2.9 Examples:
02h 64h 01h 78h 1Dh 03h
STX Station ID Length ‘x’ BCC ETX
This instruction frame will reset the reader module with the station ID 64h.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 45
Page 47

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3 Register Set
The reader has several system flags used for customization purposes. The flags are
stored in its non-volatile EEPROM. The reader accepts changes to these settings
only during the start-up phase. Clearing all RFU bits is recommended in order to
guarantee compatibility with future releases.
The reader can store up to 32 authentication keys internally to login standard mifare®
cards. An additional 32 keys can be stored for DESFire authentication. All keys are
read only and cannot be accessed via the interface lines.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 46
Page 48

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.1 EEPROM memory organization
Register Description
00h … 04h Unique device ID; read only
05h … 09h Administrative data; read only
0Ah Station ID
0Bh Protocol configuration
0Ch Baud rate
0Dh Command Guard Time
0Eh Operation Mode
0Fh Single shot time-out value
10h Internal use / Do not change
11h Internal use / Do not change
12h Internal use / Do not change
13h Protocol configuration 2
14h Reset Off Time
15h Reset Recovery Time
16h Application Family Identifier
17h ISO 14443A Selection Time-out
18h ISO 14443B Selection Time-out
19h SR176 Selection Time-out
1Ah ISO 15693 Selection Time-out
1Bh Protocol configuration 3
1Ch Page Start
1Dh Internal use / Do not change
1Eh Internal use / Do not change
1Fh Page number
20h - 7Fh RFU
80h … EFh User data
Figure 12-4: EEPROM memory
12.3.2 Unique device ID (00h – 04h)
The unique device ID identifies a reader module. It is factory programmed and
cannot be changed.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 47
Page 49

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.3 Station ID (0Ah)
The station ID is used in binary mode to address a device in party line set up. The
station ID can range from 01h to FEh and can be set freely. The value 00h is
reserved for the bus master. All readers send their response to this device.
The broadcast message (FFh) forces all readers to response to the command.
Default value is 01h.
12.3.4 Protocol configuration (0Bh)
The protocol configuration register (PCON) specifies general behavior of the reader
device.
Default value is 41h.
Protocol configuration register
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Extend-
ed ID
12.3.4.1 Auto start (default 1)
If set, the reader device will start up in continuous read mode automatically.
This is only valid in ASCII mode.
12.3.4.2 Protocol (default 0)
If Protocol is set to ‘1’, then the reader uses binary protocol mode. Refer to binary
protocol for further information on the binary protocol format.
Default setting = ASCII protocol (0).
12.3.4.3 Multitag (default 0)
The Multitag flag will enable multi-tag recognition in continuous read mode. All tags
are detected and displayed. Due to the more complex search algorithm, the
continuous read command decreases its detection speed.
Extend-
ed
Protocol
Single-
shot
Figure 12-5: Protocol configuration register
LED
New
serial
mode
Multitag
Protocol
Auto-
start
12.3.4.4 New Serial Mode (default 0)
If New Serial Mode is set to ‘1’, new serial mode is enabled. The leading character
‘M’ is added to the serial number of ISO 14443 type A tags, a leading 'Z' character is
added to ISO 14443 type B tags and a leading 'S' character for SR176 tags.
12.3.4.5 LED (default 0)
If set the reader suppresses any LED activity. The user manages the state of the
LEDs.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 48
Page 50

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.4.6 Single Shot (default 0)
If Single Shot is set, the reader displays the serial number of a tag in continuous read
mode once within a specified time-out. The time-out is defined at EEPROM register
0Fh.
The delay time can be adjusted stepwise in 100ms steps. 00h indicates no delay and
FFh indicates infinite delay.
12.3.4.7 Extended Protocol (default 1)
If Extended Protocol is set, the transfer data telegram command supports ISO144434 and automatically process the WTX and chaining for smaller frames.
If sending ISO 14443-3 commands this flag has to be switched off.
The transfer data telegram command is only supported in normal mode, not in
transmit / receive mode.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 49
Page 51

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.4.8 Extend ID (default 0)
If Extended ID is set, the reader extends the serial number of tags with additional
bytes.
ISO 14443 A tags (5/8/11 bytes transmitted)
Tag type Serial number
1 byte 4 / 7 / 10 bytes
Figure 12-6: ISO 14443 A Extended Serial number
The tag type byte indicates the type of cascade level.
Tag type Description
00h Cascade level 1 transponder
01h Cascade level 2 transponder
02h Cascade level 3 transponder
Figure 12-7: ISO 14443 A tag type
ISO 14443 B tags (12 bytes transmitted)
Serial number Application data Protocol info CID
4 bytes 4 bytes 3 bytes 1 byte
Figure 12-8: ISO 14443 B Extended Serial number
For detailed description of Application Data, Protocol Info and CID, refer to the ISO
14443 documentation [1].
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 50
Page 52

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.5 BAUD, Baud rate control register (0Ch)
The baud rate register defines the communication speed of the reader device.
Default value is 00h.
Baud rate register
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU BS2 BS1 BS0
Figure 12-9: Baud rate register
This register defines the baud rate of the device.
BS2 BS1 BS0 Baud rate
0 0 0 9600 baud (default)
0 0 1 19200 baud
0 1 0 38400 baud
0 1 1 57600 baud
1 0 0 115200 baud
1 0 1 230400 baud (depends on the used interface
chip)
1 1 0 460800 baud (depends on the used interface
chip)
Figure 12-10: Baud rate settings
With the high baud rates (230400 and 460800 baud), proper operation depends on
the interface chip used. Please note that some of the interface chips available do not
support these high baud rates.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 51
Page 53

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
The following table describes the exact baud rates used by the reader.
Baud rate Exact baud rate Difference
9600 baud 9603 baud 0.03 %
19200 baud 19207 baud 0.04 %
38400 baud 38305 baud -0.25 %
57600 baud 57458 baud -0.25 %
115200 baud 114915 baud -0.25 %
230400 baud 233793 baud 1.47 %
460800 baud 452000 baud -1.91 %
Figure 12-11: Exact baud rates
The following table describes the communication settings
Description
8 data bits
No parity bit
1 stop bit
No flow control
Figure 12-12: Communication settings
12.3.5.1 CF Card Version
The Baud rate of the CF Card version is limited to 115200 baud. 230400 and 460800
are not supported.
12.3.6 Command Guard Time (0Dh)
The Command Guard Time is used to ensure that commands are not sent to fast
consecutively. Following commands are sent after the guard time is elapsed. One
time slice is around 37,8us. The longest timeout value is 9,6ms (FFh).
The default value is 20h (1,2ms).
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 52
Page 54

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.7 OPMODE, operating mode register (0Eh)
The operation mode register defines which tag types the reader supports. This
register enables fast tag recognition because only defined tag types are requested.
Operation mode register
Bit 7
(MSB)
RFU
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(LSB)
UID
ICODE
Figure 12-13: Operation mode register
EPC
ICODE
ISO 15693
ICODE
SR176
ISO
14443B
ISO
14443A
12.3.8 Single Shot Time-out (0Fh)
The time-out value defines the delay time between two responses of the reader. It
only has effect in continuous read mode. To enable the time-out, the single shot flag
has to be set. See the protocol configuration register above. One time-out slice is
around 100ms. Exact timing depends on the protocol used.
Value 00h indicates no delay time.
Default value is 0Ah (1 second).
12.3.9 Protocol configuration 2 (13h)
The protocol configuration register 2 (PCON2) further specifies the general behavior
of the reader device.
Default value is 00h.
Protocol configuration 2 register
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Disable
ISO
14443 -4
Error
Handling
12.3.9.1 Disable multi-tag reset (default 0)
If set, the reader does not reset before the multi-tag list and multi-select command
have been performed.
Enable
ISO
14443B
Anti-
collision
Figure 12-14: Protocol configuration register
Reset
Recovery Time
Multiplier
Noisy
Environ-
ment
Enable
binary
frame
v2
Disable
start-up
message
Disable
multi-
tag
reset
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 53
Page 55

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.9.2 Disable start-up message (default 0)
If Disable start-up message is set, the reader suppresses the start-up message in
ASCII mode. This flag is ignored in binary protocol mode.
12.3.9.3 Enable binary frame v2 (default 0)
If Enable binary frame v2 is set, the reader sends version 2 binary frames.
The get station ID command always sends version 1 binary frames!
12.3.9.4 Noisy Environment (default 0)
If Noisy Environment is set, the continuous read mode can only be aborted with the '.'
character. When working in a noisy environment, the probability for a reception of an
arbitrary/stochastic signal is quite high. This implies a high probability of an
unintentional command execution. To reduce this probability, only one character (out
of 255) is chosen (‘.’) to be interpreted as the continuous read stop command.
12.3.9.5 Reset Recovery Time Multiplier (default 0)
Multiplies the Reset Recovery Time, including the recovery time of the field reset
command.
Reset Recovery Time Multiplier Reset Recovery Time
0 1x
1 2x
2 3x
3 4x
Figure 12-15: Reset Recovery Time Multiplier
12.3.9.6 Enable ISO14443 B Anti-collision (default 0)
If set, the anti-collision algorithm for ISO 14443 B tags is enabled.
12.3.9.7 Disable ISO 14443-4 Error Handling (default 0)
If Disable ISO 14443-4 Error Handling is set, ISO14443-4 Error Handling is disabled.
The error handling always uses the TMR time-out.
12.3.10 Reset Off Time (14h)
The Reset Off Time register represents the field off time in ms.
This register is used for the select, continuous read and multi-tag commands.
Default value is 0Ah.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 54
Page 56

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.11 Reset Recovery Time (15h)
The Reset Recovery Time register represents the recovery time in ms after the field
is turned on.
This register is used for the select, continuous read and multi-tag commands.
Default value is 25h.
12.3.12 Application Family Identifier (16h)
The AFI (Application Family Identifier) is only supported for ISO14443B and
ISO15693 tags. If the set value is different from 00h, the AFI is used. Only
transponders with an identical AFI will answer to the reader.
Default value is 00h.
12.3.13 Selection Time-out ISO 14443A (17h)
The Selection Time-out represents the reader card communication time-out for the
select, high speed select, continuous read, multilist, multiselect and mifare
command with ISO 14443A tags. Use low values for a better reaction time between
the card and the reader. One time slice is around 300us.
The default value is 10h.
®
login
12.3.14 Selection Time-out ISO 14443B (18h)
The Selection Time-out represents the reader card communication time-out for the
select, high speed select, continuous read, multilist and multiselect commands with
ISO 14443B tags. For a better reaction time, use low values. One time slice is around
300µs.
The default value is 50h.
12.3.15 Selection Time-out SR176 (19h)
The Selection Time-out represents the reader card communication time-out for the
select, continuous read, multilist and multiselect command with SR176 tags. For a
better reaction time, use low values. One time slice is around 300µs.
The default value is 10h.
12.3.16 Selection Time-out ISO 15693 (1Ah)
The Selection Time-out represents the reader card communication time-out for the
select, high speed select, continuous read, multilist, multiselect and mifare® login
command with ISO 15693 tags. Use low values for a better reaction time between
the card and the reader. One time slice is around 300us.
The default value is 20h.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 55
Page 57

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.3.17 Protocol configuration 3 (1Bh)
The protocol configuration register 3 (PCON3) further specifies the general behavior
of the reader device.
Default value is 00h.
Protocol configuration 3 register
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ReqA
RFU
12.3.17.1 Disable automatic ISO 14443-4 timeouts (default 0)
If Disable automatic ISO 14443-4 timeouts is set the automatic ISO 14443-4 timeouts
are disabled. The timeouts specified with TMR registers are used.
12.3.17.2 Page read (default 0)
If set the continuous read mode retrieves the content of the tag instead of the serial
number. The register Page Start (1Ch) defines the start block and the Page Number
(1Fh) defines the number of blocks to be read.
12.3.17.3 ReqA Extended ID (default 0)
Extended
ID
Figure 12-16: Protocol configuration register
Internal use / do not
change
Page
Read
RFU
Disable
automatic
ISO 14443-4
timeouts
If set the Extended ID information for ISO14443 A tags replaces the cascade level
information (1 byte) with Request A answer (2 bytes).
12.3.18 User data (80h - EFh)
These registers are for free use.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 56
Page 58

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4 Instruction Set
Following table describes all the commands of the reader device. Each command
returns an answer to the host. Exceptions are mentioned explicitly. The green LED
acknowledges a successfully executed command. The red LED indicates an error.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 57
Page 59

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.1 Common Commands Overview
Command Description
'!' Test continuous read / Check KTT upload status
'c' Continuous read
'.' Abort continuous read, refer to continuous read
'dg' / 'dn' / 'dr' Set LED
'ds' DES encryption / decryption of data
'f' DESFire command set
'g' Get ID
'h' High speed select
'k' Lock block
'm' MultiTag select / tag list
'o+a' / 'o+b' / 'o+d' /
'o+e' / 'o+i' / 'o+s' /
'o+v'
'o-a' / 'o-b' / 'o-d' /
'o-e' / 'o-i' / 'o-s' /
'o-v'
'oa' / 'ob' / 'od' / 'oe' /
'oi' / 'ot' / 'os' / 'ov'
'of' Set configuration flags
'og' Set configuration register
'poff' / 'pon' Antenna power off/on
'pr' / 'pw' Read / write user port
'q' Quiet
'ra' Resend last answer
'rp' Read EEPROM register
'r' / 'rb' Read block
Include tag type
Exclude tag type
Set tag type
's' Select
'v' Get version
'w' / 'wb' Write block
'wp' Write EEPROM register
Figure 12-17: Command overview (Part 1)
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 58
Page 60

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Command Description
'x' Reset
'y' Field reset
ISO 14443 Type A (mifare®) only commands
'+' Increment value block (credit)
'-' Decrement value block (debit)
'=' Copy value block (backup)
'l' Login (authenticate tag)
'rv' Read value block
'wv' Write value block
Key Management
'ar' Authenticate to reader
'ia' Get key access rights
'it' Get key status
'rt' Reset key table
'ua' Update key access rights
'uc' Change key type
'uk' Update key
my-d™ secure commands
'!' Check KTT upload status / Test continuous read
'*' Abort KTT upload
'as' Authenticate to sector
'ik' Issue transponder key
'ut' Prepare for KTT
'z' my-d™ command
Figure 12-18: Command overview (Part 2)
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 59
Page 61

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.2 Error Codes
Following figure shows an overview of all error messages of the reader device.
Error Code Description
‘?’ Unknown command
'C' Collision or CRC/MAC Error
‘F’ General failure
‘I’
‘N’ No tag in the field
'O' Operation mode failure or file not selected
‘R’ Command parameter out of range
'X' Authentication failed
Invalid value format, specified block does not match the value
format
Figure 12-19: Error codes
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 60
Page 62

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3 Common commands
12.4.3.1 Test Continuous Read / Check KTT Upload Status
This command tests the state of the continuous read command and the state of the
Prepare for KTT 'ut' command.
The test continuous read command is only valid in ASCII mode.
Command
Command Data
'!' None
Answer
Answer Description
'!' Continuous read mode is active.
00h Keys from KTT successfully uploaded
01h Error during key upload detected, upload aborted
02h No KTT found, other tag was detected
FFh Prepare for KTT is in awareness mode
'F' Continuous read and Prepare for KTT is not active.
no response Key uploading is in progress
12.4.3.2 Continuous Read
The reader device reads and displays serial numbers continuously while one or more
tags remain in the field. This command stops if any character is sent to the reader
module. The reader module returns the character ‘S’ (53h).
The reader supports different tag types at the same time. To increase the reading
performance switch to a single tag mode. If more than one tag of the same type
should be detected at the same time, the Multitag flag must be activated. The
response data length depends on the tag type.
Command
Command Data
'c' None
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 61
Page 63

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Answer
Answer Description
Data Serial number (n bytes)
'N' Error: No Tag in the field (only binary protocol)
12.4.3.2.1 Multitag continuous read mode
If the Multitag flag is set in the Protocol Configuration (PCON) register the reader
reads multiple tags continuously.
12.4.3.2.2 Auto start
The continuous read mode is started automatically in ASCII mode. The auto start flag
must be set in the PCON register.
12.4.3.2.3 Noisy Environment
If the Noisy Environment flag is set, the continuous read mode can only be aborted
with the '.' character.
This is only valid in ASCII mode.
12.4.3.2.4 Binary mode
This command is fully supported in binary protocol mode except the test continuous
read command and the noisy environment flag.
Do not use this command on bus system environment in binary mode, because the
continuous read mode will take possession of the bus system.
12.4.3.2.5 Simple access control applications
Serial numbers are always sent plain. Data encryption is activated after a successful
login.
For simple access control applications the use read-only blocks for the identification
of the tag is recommended.
Reading any block (even the manufacturer block) of the transponder will increase
your security.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 62
Page 64

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.3 Set LED
This command controls the LED activity. If the LED flag is set, the automatic LED
function is switched off. The user can set the state of the LED manually.
Command
Command Data
'dg' None
'dr' None
'dn' None
Answer
Answer Description
'DG'
String of LED state
'DR'
'DN'
Example
Command Answer Description
'dg' DG Switch on LED green, LED red off
'dr' DR Switch on LED red, LED green off
'dn' DN Switch off both LEDs
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 63
Page 65

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.4 DES encryption / decryption of data
This command returns 8 bytes of encrypted / decrypted data.
Command
Command Data
'ds' Options (1 byte)
Key (8/16 bytes) / Key Number (1 byte)
Data (8 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data Encrypted / Decrypted data (8 bytes)
Option byte
Option byte
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
RFU RFU RFU RFU RFU Encode
Key
Length
Key
Index
Key Index
If the Key Index is set, the command only needs the key number (1 byte) instead of
the key (8/16 bytes).
The key number corresponds to the key number used in the key management.
Key Length
If the Key Length is set, the command uses the TDES algorithm with 16-byte key.
If cleared, the command uses the DES algorithm with 8-byte key.
If key index is used the key length flag is valid.
Encode
Setting this flag encodes the data.
Clearing this flag decodes the data.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 64
Page 66

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.5 Get ID
This command returns the station ID of the reader device. The answer is time slotted
to enable the detection of all devices in party line mode.
The station ID has only effect in binary mode.
Command
Command Data
'g' None
Answer
Answer Description
Data Station ID of the reader device (1 byte)
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 65
Page 67

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Baudrate
12.4.3.5.1 Time slotted answer
In party line mode, more than one reader can be used simultaneously. The time
slotted answer allows separating in time the answers from all connected devices. The
station ID is used to determine the correct time slot.
The reader supports up to 254 unique time slots. The following formula calculates the
duration of one time slot (only one baud rate is supported per party line):
0
][
sT =
10
6*
Figure 12-20: Time slot formula
The following figure shows the timing diagram of time slotted answers.
Timeslot 0 1 2 3 4 5 … 252 253 254
HOST
0
'g'
1
→
2
3
T
T
4
5
T
T
252
253
T
T
T
T
Reader (01)
←
01
Reader (03)
←
03
T
254
Reader (04)
←
04
Reader (254)
←
254
Figure 12-21: Timing diagram of time slotted answers
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 66
Page 68

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.5.2 Binary Protocol Version 2
This command never sends version 2 binary frames.
12.4.3.6 High speed select
This command selects a card in the antenna field (according to the selection criteria)
or prepares a multiselect command, switches to high baud rates and enables 256byte frames. If execution is successful, the command returns the UID of the selected
card and the used baud rate. The reader automatically detects the maximum frame
size of the card. The reader also tries to communicate to the transponder with the
specified baud rate. If no communication is possible, the reader will automatically
decrease the speed to the next lower value.
This command can also force the reader to the communication speed and frame size
of the tag to the specified values. This is only needed if the high speed select is done
manually with the transfer command.
Command
Command Data
‘h’ Option byte (1 byte)
00h … select a single card with 106kBaud
02h … select a single card with 212kBaud
04h … select a single card with 424kBaud
08h … select a single card with 848kBaud
10h … prepare next multiselect for 106kbaud
12h … prepare next multiselect for 212kbaud
14h … prepare next multiselect for 424kbaud
18h … prepare next multiselect for 848kbaud
20h … forces reader to 106kBaud
22h … forces reader to 212kBaud
24h … forces reader to 424kBaud
28h … forces reader to 848kBaud
30h – 38h … force tag frame size
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 67
Page 69

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Answer
Answer Description
Data (n bytes)
+ frame size
and baud rate
(1byte)
'F' Error: General failure
‘N’ Error: No Tag in the field
Examples
High speed select
Command Description
Serial number + frame size used and baud rate
h08 1234567890ABCD84
Select the card with UID 1234567890SABCD.
The card supports a 256-byte frame size and 424kBaud on the
air interface.
High speed multiselect
Command Description
h18
m1234567890ABCD<CR>
Prepare next multiselect for 848kBd
1234567890ABCD84
Select the card with UID 1234567890SABCD.
The card supports a 256-byte frame size and
424kBaud on the air interface.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 68
Page 70

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.6.1 Answer from 0xh and 1xh
The lower nibble contains the baud rate used for the air interface.
Baud Rate Description
x0 106kBaud
x2 212kBaud
x4 424kBaud
x8 848kBaud
Figure 12-22: Baud Rate values
The higher nibble contains the frame size used for the air interface.
Frame Size Description
0x 16 Bytes
1x 24 Bytes
2x 32 Bytes
3x 40 Bytes
4x 48 Bytes
5x 64 Bytes
6x 96 Bytes
7x 128 Bytes
8x 256 Bytes
Figure 12-23: Frame Size
12.4.3.6.2 Answer from 2xh and 3xh
The option byte is returned as the answer.
12.4.3.6.3 Select a single tag
No previous continuous read is required. The command executes an automatic field
reset.
12.4.3.6.4 Extended ID
See above for more information on Extended ID.
The RATS answer is inserted between the serial number and baud rate / frame size
byte for ISO14443 A tags.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 69
Page 71

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.6.5 Multiple tags
This command with parameter 1xh prepares the next multiselect command as a highspeed select. Any other command will disable the preparation.
12.4.3.6.6 RATS Guard Time SFGT
A high-speed select with parameters 0xh and 1xh automatically waits the SFGT
guard time received from the tag before sending the PPS command.
12.4.3.7 Lock block
This command locks a block permanently. Only SR176 and ISO 15693 tags are
supported.
Command
Command Data
'k' Block address (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
data 'K' + page address
'F' Error: Lock failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure (only SR176 and ISO 15693
tags are supported)
'X' Error: Block already locked
Example
Command Description
k05 K05
Lock block 05.
12.4.3.7.1 Operation mode failure 'O'
The presented tag is not a SR176 or a ISO 15693 tag.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 70
Page 72

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.7.2 Apply settings
After locking a block permanently, the tag needs to be selected for the settings to
apply.
12.4.3.8 Multi-Tag Selection / List
This command detects several tags at the same time. It replaces the fast select
command ('s') in multiple tag surroundings. The Multi-Tag List command lists all tags
with their serial numbers. Use the Multi-Tag Select command to select a single tag.
Each tag has to be selected separately.
Command
Command Data
'm' Serial number (n bytes)
<CR> (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data serial number
'N' Error: No Tag in the field
Example
Command Description
m<CR> 04E9E700000000 first card
34030F07
02
second card
number of detected tags
m04E9E700000000<CR> Select card with its serial number
12.4.3.8.1 Multi-tag list
Sending a <CR> as the first parameter, the reader returns a list of all tags present in
the antenna field. In the end the total number of tags detected is returned.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 71
Page 73

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.8.2 Reading distance
Each card needs a specific amount of power. The reader always provides the same
power level. Therefore, the reading distance will decrease if more tags are present.
Basically, the reading distance depends on the tag, the antenna and the tuning of the
antenna.
12.4.3.8.3 Multi-tag select
Using the serial number with <CR> as parameter, the corresponding tag will be
selected. High-level interactions can be performed addressing only this card. All
other tags remain silent.
12.4.3.8.4 Multi-tag reset
The antenna field reset can be deactivated with the Protocol configuration 2 register.
By suppressing the antenna field reset, it is possible to detect only new tags in the
antenna field.
12.4.3.8.5 Maximum number of tags
The maximum number of tags in the antenna field is limited to 64 and by the physical
characteristics of the antenna.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 72
Page 74

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.9 Include tag type
This command includes a specific tag type to those addressed by the reader device.
Command
Command Data
‘o+’ Tag type (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
'O+' + tag type (1 byte) Command code + String of tag type
Tag type character
Refer to Set tag type.
Example
Command Description
o+a Include ISO14443-A to the tag types addressed
by the reader device.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 73
Page 75

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.10 Exclude tag type
This command excludes a specific tag type from being addressed by the reader
device.
Command
Command Data
‘o-’ Tag type (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
'O-' + tag type (1 byte) Command code + String of tag type
Tag type character
Refer to Set tag type.
Example
Command Description
o-a Exclude ISO14443-A from the tag types
addressed by the reader device.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 74
Page 76

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.11 Set tag type
This command sets up the reader for a specific tag type. The continuous read
function will speed up because only this type of tag is addressed. After a reset, the
reader starts as defined in its start-up configuration.
Command
Command Data
'o' ISO type (1 byte)
'a' … ISO 14443 Type A
'b' … ISO 14443 Type B
'd' … ICODE UID
'e' … ICODE EPC
'i' … ICODE
's' … SR176
't' … activate all tags
'v' ... ISO 15693
Answer
Answer Description
'OA'
String of tag type
'OB'
'OD'
'OE'
'OI'
'OS'
'OT'
'OV'
Example
Command Description
oa Sets the reader device to address ISO14443-A type tags.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 75
Page 77

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.12 Set Configuration Flags
This command allows setting some configuration flags just in time; no reset is
needed. The values are not stored in the EEPROM; therefore the changed values
are not available after a reset.
Command
Command Data
of flag type (1 byte)
data (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data (1 byte) Current state of changed flag.
'R' Error: Out of range
Example
Command Description
of0101 Answer: 01
Enables the New Serial Mode flag.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 76
Page 78

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Flag Types
The following table shows the Flag Type with its corresponding flag from the
specified Protocol Configuration Register.
Flag
Type
00h Multitag 1 00 / 01
01h New Serial Mode 1 00 / 01
02h LED 1 00 / 01
03h Single Shot 1 00 / 01
04h Extended Protocol 1 00 / 01
05h Extended ID 1 00 / 01
Corresponding Flag Protocol
Configuration
Register
Valid
values
06h Disable Multitag Reset 2 00 / 01
07h Noisy Environment 2 00 / 01
08h Reset Recovery Time
2 00 … 03
Multiplier
09h Enable ISO14443 B Anti-
2 00 / 01
collision
0Ah Disable ISO14443-4 Error
2 00 / 01
Handling
0Bh Disable automatic
3 00 / 01
ISO14443-4 timeouts
0Dh Page Read 3 00 / 01
11h ReqA Extended ID 3 00 / 01
Figure 12-24: Flag Type with corresponding flag
12.4.3.12.1 Out of range failure 'R'
The entered flag type is out of range.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 77
Page 79

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.13 Set Configuration Register
This command allows setting some configuration registers just in time; no reset is
needed. The values are not stored in the EEPROM; therefore the changed values
are not available after a reset.
Command
Command Data
og Register type (1 byte)
data (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data (1 byte) Current state of changed register.
'R' Error: Out of range
Example
Command Description
og0450 Answer: 50
Sets the Reset Recovery Time to 50h.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 78
Page 80
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Register Types
The following table shows the Register Type with its corresponding register.
Register Type Corresponding Register
00h Single shot time-out value
01h Internal use / Do not change
02h Internal use / Do not change
03h Reset Off Time
04h Reset Recovery Time
05h ISO 14443A Selection Time-out
06h ISO 14443B Selection Time-out
07h SR176 Selection Time-out
08h AFI
0Ch Page Read Start
0Dh Page Read Number
0Eh Command Guard Time
Figure 12-25: Register Type with corresponding register
12.4.3.13.1 Out of range failure 'R'
The entered register type is out of range.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 79
Page 81
ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.14 Antenna power on/off
This command controls the antenna power. It can be used to decrease the power
consumption of the reader.
Command
Command Data
'pon' Switch reader on
'poff' Put reader in standby mode
Answer
Answer Description
'P' Positive acknowledge
Example
Command Description
poff Put reader in standby mode
12.4.3.14.1 Power off
The reader enters standby mode. Power consumption is decreased. All tags in the
antenna field are powered off and reset. Standby mode is only entered manually.
To switch off the whole unit, pin 16 (Enable) has to be set to logic low.
12.4.3.14.2 Power on
The reader leaves standby mode and is ready for the next command. Sending a tag
command (i.e. select, continuous read) the reader is powered up.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 80
Page 82

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.15 Read/Write user port
This command sets or reads the state of the user port (pin 14) of the OEM reader
device. The port is set either as output or as input.
Command
Command Data
'pr' None
'pw' State of user port (1 Byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data State of user port (1 Byte)
'C' Error: Error correction fails
'F' Error: Transmission Error / No answer received
Example
Command Description
pr Reads user port
pw01 Sets user port state to high
12.4.3.15.1 Read port
The port read command returns the current state of the USER port.
Port state Description
00h USER port is low
01h USER port is high
Figure 12-26: Read USER port return values
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 81
Page 83

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.15.2 Write port
If user port is used as an output, a 1k
Otherwise the reader device can be damaged.
Port state Description
00h Sets USER port to low
01h Sets USER port to high
02h – 7Fh RFU
80h - FFh Sends a serial data frame and checks the received frame
Figure 12-27: Write User port settings
Sending a Data Frame
If the highest bit (MSB) is set in the State of the User Port, the command sends a
serial data frame out the USER port.
The frame includes a start bit, 8 data bits, parity bit and a stop bit.
Ω
resistor has to be integrated into the wire.
Transmit
Frame
Low Start bit
Description
Low RFU
Data Bit 6 State of the User Port Bit 6
Data Bit 5 State of the User Port Bit 5
Data Bit 4 State of the User Port Bit 4
Data Bit 3 State of the User Port Bit 3
Data Bit 2 State of the User Port Bit 2
Data Bit 1 State of the User Port Bit 1
Data Bit 0 State of the User Port Bit 0
Parity Bit Even Parity Bit
High Stop Bit
Figure 12-28: Sending Serial Data Frame
After 2ms Guard Time the answer should be received on the User Port otherwise an
error is returned.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 82
Page 84

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Receive
Frame
Low Start bit
Error Bit If set, an error was detected.
Data Bit 6 State of the User Port Bit 6
Data Bit 5 State of the User Port Bit 5
Data Bit 4 State of the User Port Bit 4
Data Bit 3 State of the User Port Bit 3
Data Bit 2 State of the User Port Bit 2
Data Bit 1 State of the User Port Bit 1
Data Bit 0 State of the User Port Bit 0
Description
Parity Bit Even Parity Bit
High Stop Bit
Figure 12-29: Receiving Serial Data Frame
If the Error bit is set or the Parity Bit is not correct, the Write User Port command
returns an error code.
12.4.3.16 Quiet
This command sets a selected tag into halt state. Only ISO14443 A+B and SR176
tags are supported.
Command
Command Data
'q' None
Answer
Answer Description
'Q' Halt state successfully set.
'N' Error: No Tag in the field
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 83
Page 85

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.16.1 ISO 14443 Type A
With ISO14443 Type A tags, the Quiet command always answers with 'Q' because
the halt command does not send any acknowledge.
12.4.3.16.2 ISO 14443 Type B
Some ISO14443 Type B tags do not support this command or do not respond. ‘Quiet’
is an ISO 14443-4 command, so it will work only if the ‘Deselect’ command is
supported by the corresponding transponder.
12.4.3.16.3 SR176
With SR176 tags the Quiet command always answer with 'Q' because the completion
command does not send any acknowledge.
12.4.3.17 Resend Last Answer
This command resends the last answer from the internal serial buffer of the reader.
Command
Command Data
'ra' Resend last answer
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 84
Page 86

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.18 Read block
This command reads a data block on a card. The size of the returned data depends
on the tag used. The block address range depends on the tag as well.
Command
Command Data
'r' Block address (1 byte), valid range 00h – 40h
'rb' Block address (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data data block (depends on tag type)
'F' Error: read failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
'R' Error: Out of range
Example
Command Description
rb05 Reads block 05.
12.4.3.18.1 Read failure 'F'
This error is returned if either the reader receives bad data or the block address
exceeds the block address range of the sector.
12.4.3.18.2 No tag in field 'N'
The tag does not respond. There is either no tag present or addressed.
12.4.3.18.3 Operation mode failure 'O'
The presented tag is not ISO14443 type A, SR 176, ICode, ICode-UID and ISO
15693 compliant.
For ISO 14443 type A only mifare
®
tags are supported.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 85
Page 87

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.18.4 Out of range failure 'R'
The block address of the 'r' command is higher than 40h.
The block address of the 'r' command conflicts with other commands, therefore the
block address has to be limited to 40h.
Use the 'rb' command instead.
12.4.3.19 Read reader EEPROM
This command reads the internal reader EEPROM. It contains all start-up parameters
and the device ID. Changes in the start-up settings will only go into effect after a
reset of the device.
Command
Command Data
'rp' EEPROM address (1 byte) 00h … EFh
Answer
Answer Description
Data EEPROM data (1 byte)
'R' Error: Out of range failure
Example
Command Description
rp0B Reads protocol configuration register.
12.4.3.19.1 Out of range failure 'R'
The entered EEPROM address is not valid.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 86
Page 88

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.20 Select
This command selects a single card in the antenna field. It can only be used in single
tag mode. If successfully executed, the command returns the UID of the selected
card. The reader detects the length of the UID automatically.
Command
Command Data
's' None
Answer
Answer Description
Data serial number
'N' Error: No Tag in the field
Example
Command Description
s 1234567890ABCD
Select the card with UID 1234567890SABCD.
12.4.3.20.1 Select a single tag
No previous continuous read is required. The command executes an automatic field
reset.
12.4.3.20.2 Extended ID
See above for more information on Extended ID.
12.4.3.20.3 Multiple tags
This command is designed for fast access of a single tag in the field. If multiple cards
are used the 'm' instruction has to be used instead.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 87
Page 89

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.21 Get Version
This command returns the current version of the reader module.
Command
Command Data
'v' None
Answer
Answer Description
'MultiISO 1.0' + <CR> + <LF> ASCII Mode
02 00 0C 4D 75 6C 74 69 49 53 4F 20 31
2E 30 1F 03
Example
Command Description
v ‘MultiISO 1.0’
Version of the reader module
Binary Mode
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 88
Page 90

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.22 Write block
This command writes data to a block. A read is done automatically after every write
to ensure correct writing.
Command
Command Data
'w' Block address (1 byte), valid range 00h – 40h
Data (n bytes)
'wb' Block address (1 byte)
Data (n bytes)
Answer
Answer Description
Data Data block (depends on tag type)
'F' Error: Write failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
'R' Error: Out of range
Example
Command Description
wb0511223344 Writes data 11223344 on block 05.
12.4.3.22.1 Write failure 'F'
This error is displayed if bad transmission conditions are given. If the block address
exceeds the physical number of blocks of a tag, this error is shown.
12.4.3.22.2 No tag error 'N'
This error is returned if no tag is present or the card does not respond.
12.4.3.22.3 Operation mode failure 'O'
The presented tag is not ISO14443 type A, SR 176, ICode, ICode-UID and ISO
15693 compliant.
For ISO 14443 type A only mifare
®
tags are supported.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 89
Page 91

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.22.4 Out of range failure 'R'
The block address of the 'w' command is higher than 40h.
The block address of the 'w' command conflicts with other commands, therefore the
block address has to be limited to 40h.
Use the 'wb' command instead.
12.4.3.23 Write EEPROM
Writes to the internal reader EEPROM. It contains all start-up parameters and the
device ID. Changes to the start-up settings will only go into effect after a reset of the
device.
Command
Command Data
'wp' Address (1 byte), valid range 0Ah - EFh
Data (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data EEPROM data (1 byte)
'F' Error: Read after write failure
'R' Error: Out of range failure
Example
Command Description
wp0A01 Set EEPROM address 0A (Station ID) to 01h
12.4.3.23.1 Out of range failure 'R'
The entered address exceeds the address range.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 90
Page 92

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.24 Reset
This command executes a power on (software) reset. New configuration settings will
be loaded. It resets all tags in the antenna field.
Command
Command Data
'x' None
Answer
Answer Description
MultiISO 1.0' + <CR> +
ASCII Mode
<LF>
None Binary Mode
12.4.3.24.1 Disable Start-up Message
If the start-up message is disabled in the protocol configuration register 2, the ASCII
mode does not respond with the version of the reader.
12.4.3.24.2 Reset Timing
The power up timing depends on environmental conditions such as voltage ramp up.
For handheld devices the timing can vary based on the charge state of the battery.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 91
Page 93

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.3.25 Field Reset
The field reset switches off the antenna field for the specified duration. All tags need
a certain amount of time to initialize before a command can be processed. The
second byte specifies the field recovery time.
Command
Command Data
'y' Off time in milliseconds (1 byte)
Field recovery time in milliseconds (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
'Y' After the field reset the reader sends back a ‘Y’ to
acknowledge the command.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 92
Page 94

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4 ISO 14443 Type A (mifare®) only commands
12.4.4.1 Increment value block (credit)
Increments a value block with a defined value. A read is done automatically after a
write to verify data integrity. The command fails if the source block is not in value
block format. A previous login is needed to access a block.
Command
Command Data
'+' Block (1 byte)
Value (4 bytes)
Answer
Answer Description
Data Value (4 bytes)
'I' Error: value block failure
'F' Error: increment failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
Example
Command Description
+0400000001 Adds 1 to value block 4
+0500000100 Adds 256 to value block 5
12.4.4.1.1 No value block 'I'
Specified block does not match the value format. The value block is corrupted. A
backup block can be used to restore the correct value.
12.4.4.1.2 Increment failure 'F'
This indicates a general failure during the increment procedure or an inability to read
after the write process.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 93
Page 95

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.1.3 No tag error 'N'
The reader does not detect a response from the tag. There is either no tag present or
the tag does not respond to the request.
12.4.4.1.4 Operation mode failure 'O'
The tag is not ISO14443 type A compliant.
12.4.4.2 Decrement value block (debit)
Decrements a value block with a defined value. A read is done automatically after the
write to verify data integrity. The command fails if the source block is not in value
block format. A previous login is needed to access a block.
Command
Command Data
'-' Block (1 byte)
Value (4 bytes)
Answer
Answer Description
Data Value (4 bytes)
'I' Error: value block failure
'F' Error: decrement failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
Example
Command Description
-0400000001 Subtract 1 to value block 4
-0500000100 Subtract 256 to value block 5
12.4.4.2.1 No value block 'I'
Specified block does not match the value format. The value block is corrupted. A
backup block can be used to restore the correct value.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 94
Page 96

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.2.2 Decrement failure 'F'
This indicates a general failure during the decrement procedure or an inability to read
after the write process.
12.4.4.2.3 No tag error 'N'
The reader does not detect a response from the tag. There is either no tag present or
the tag does not respond to the request.
12.4.4.2.4 Operation mode failure 'O'
The tag is not ISO14443 type A compliant.
12.4.4.3 Copy value block (backup)
Copies a value block to another block of the same sector. A read is done
automatically after the write to ensure data integrity. Used for backup and error
recovery. A previous login is needed to access a block.
Command
Command Data
'=' Source block (1 byte)
Target block (1 byte)
Answer
Answer Description
Data New value of target block (4 bytes).
'I' Error: value block failure
'F' Error: copy failure
'N' Error: No tag in field
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
Example
Command Description
=0405 Copy value block 4 to block 5
=0506 Copy value block 5 to block 6
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 95
Page 97

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.3.1 Target block
The target block does not need to be a valid value block. If the source block is not in
value format, the command fails.
12.4.4.3.2 No value block 'I'
Source value block is not in a valid value block. The value block is corrupted. A
backup block can be used to restore the correct value.
12.4.4.3.3 Copy failure 'F'
This indicates a general failure during the copy procedure or an inability to read after
the write process.
12.4.4.3.4 No tag error 'N'
The reader does not detect a response of the tag. There is either no tag present or
the tag does not respond to the request.
12.4.4.3.5 Operation mode failure 'O'
The tag is not ISO14443 type A compliant.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 96
Page 98

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.4 Login (authenticate tag)
Performs an authentication in order to access one sector of a mifare
sector can be accessed at a time.
Command
Command Data
'l' Sector (1 byte), valid range 00h - 3Fh
Key type (1 byte)
AAh authenticate with key type A
FFh authenticate with key type A, transport key
FFFFFFFFFFFFh
BBh authenticate with key type B
10h … 2Fh authenticate with key type A using stored
key (00h … 1Fh)
30h … 4Fh authenticate with key type B using stored
key (00h … 1Fh)
Key (6 bytes) / <CR> (1 byte), optional
By transmitting <CR> instead of the keydata
authentication is done with manufacturer’s transport
keys (A0A1A2A3A4A5h, B0B1B2B3B4B5h,
FFFFFFFFFFFFh).
®
card. Only one
Answer
Answer Description
data Login status (1 byte)
'L' Login success
'F' Error: General failure
'N' Error: No tag
'O' Error: Operation mode failure
'R' Error: Out of range
'X' Error: Authentication failed
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 97
Page 99

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
Example
Command Description
l02AA<CR> Authenticate for sector 2, using the transport key A
(A0A1A2A3A4A5h, key type A)
l3FBB<CR> Authenticate for sector 63, using the transport
key 2 (B0B1B2B3B4B5h, key type B)
l04FF<CR> Authenticate for sector 4, using the transport key 3
(FFFFFFFFFFFFh, key type A)
l0FAAFFFFFFFFFFFF Authenticate for sector 15, using key
FFFFFFFFFFFFh, key type A
l0E14 Authenticate for sector 14, using EEPROM key 4,
key type A
l0530 Authenticate for sector 5, using EEPROM key 0,
key type B
l0732 Authenticate for sector 7, using EEPROM key 2,
key type B
l0110 Authenticate for sector 1, using EEPROM key 0,
key type A
l0ABBFF12FFFFFF35 Authenticate for sector 10, using key
FF12FFFFFF35h, key type B
12.4.4.4.1 No tag error 'N'
The reader does not detect a response from the tag. There is either no tag present or
the tag does not respond to the request.
12.4.4.4.2 Operation mode failure 'O'
The tag is not ISO14443 type A compliant.
12.4.4.4.3 Out of range failure 'R'
The entered key type or the sector is out of range.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 98
Page 100

ACG HF Multi ISO RFID Reader V1.0
12.4.4.4.4 <CR>
Three transport keys are implemented to access cards quickly.
By transmitting <CR> instead of the key, the reader module uses the transport keys
for the login procedure.
Command Description
LxxAA<CR> Authenticate for sector xx, using the transport key 1
(A0A1A2A3A4A5h, key type A)
LxxBB<CR> Authenticate for sector xx, using the transport key 2
(B0B1B2B3B4B5h, key type B)
LxxFF<CR> Authenticate for sector xx, using the transport key 3
(FFFFFFFFFFFFh, key type A)
12.4.4.4.5 Login with key data from EEPROM
Each key stored in the reader EEPROM can be used as type A or type B key. To use
a key as type A, the value 10h must be added to the key index. 30h must be added
to use a key as type B.
12.4.4.4.6 Usage of key A, key B
mifare
®
cards support two different crypto keys for each sector. Each key is 32 bits
long and is stored in the sector trailer (last block of the sector) on the card. It is
possible to set different access rights for each key.
ACG Identification Technologies GmbH 99
 Loading...
Loading...