ASME Unified Inch Screw User Manual

ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
[Revision of ASME B1.1-2003 (R2018)]
Unified Inch Screw
Threads (UN, UNR, and
UNJ Thread Forms)
AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD

ASME B1.1-2019
Two Park Avenue • New York, NY • 10016 USA
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
[Revision of ASME B1.1-2003 (R2018)]
Unified Inch Screw
Threads (UN, UNR, and
UNJ Thread Forms)
AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
x

Date of Issuance: June 30, 2020
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
The next edition of this Standard is scheduled for publication in 2024. This Standard will become effective 1 year afterthe Dateof
Issuance.
Periodically certain actions of the ASME B1 Committee may be published as Cases. Cases are published on the ASME website
under the B1 Committee Page at http://go.asme.org/B1committee as they are issued.
Errata to codes and standards may be posted on the ASME website under the Committee Pages to provide corrections to
incorrectly published items, or to correct typographical or grammatical errors in codes and standards. Such errata shall be used
on the date posted.
The B1 Committee Page can be found at http://go.asme.org/B1committee. There is an option available to automatically receive
an e-mail notification when errata are posted to a particular code or standard. This option can be found on the appropriate
Committee Page after selecting “Errata” in the “Publication Information” section.
ASME is the registered trademark of The American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
This code or standard was developed under procedures accredited as meeting the criteria for American National Standards. The Standards
Committee that approved the code or standard was balanced to assure that individuals from competent and concerned interests have had an
opportunity to participate. The proposed code or standard was made available for public review and comment that provides an opportunity
for additional public input from industry, academia, regulatory agencies, and the public-at-large.
ASME does not “approve,” “rate,” or endorse any item, construction, proprietary device, or activity.
ASME does not take any position with respect to the validity of any patient rights asserted in connection with any items mentioned in this
document, and does not undertake to insure anyone utilizing a standard against liability for infringement of any applicable letters patent, nor
assume any such liability. Users of a code or standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the
risk of infringement of such rights, is entirely their own responsibility.
Participation by federal agency representative(s) or person(s) affiliated with industry is not to be interpreted as government or industry
endorsement of this code or standard.
ASME accepts responsibility for only those interpretations of this document issued in accordance with the established ASME procedures
and policies, which precludes the issuance of interpretations by individuals.
No part of this document may be reproduced in any form,
in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of the publisher.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Two Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990
Copyright ©2020 by
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS
All Rights Reserved
Printed in U.S.A.

CONTENTS
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Foreword . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . v
Committee Roster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Correspondence With the B1 Committee . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 Screw Thread Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3 Screw Thread Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
4 Screw Thread Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
5 Screw Thread Allowance and Tolerance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
6 Screw Thread Designation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
7 Dimensional Accommodation of Coating or Plating for 60-Deg Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
8 Limits of Size for Standard (UN, UNR, and UNJ) and Special (UNS, UNRS, and UNJS) Series of
Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
9 Thread Form Tolerances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
10 Formulas and Nomenclature for Thread Form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
11 Tables of Basic Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Nonmandatory Appendices
A Terminology and Identification of Unified Inch Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
B Thread Strength Design Formulas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
C Unified Inch Screw Threads — Metric Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
D Special Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
E Changes to ASME B1.1-1989, Tables 3A and 3B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
F Special Lengths of Engagement Specifications and Designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Figures
1 Illustration of Assembly Interference of UNJ-3A Thread and UN-3B Thread in the Maximum
Material Condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Basic Profile for UN and UNR Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3 Basic Profile for UNJ Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
4 Root Radius of UNJ External Thread . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
5 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread
Series UN, Classes 1A, 2A, 1B, and 2B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
6 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UN,
Classes 3A and 3B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
7 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread
Series UNR, Classes 1A and 2A, and Series UN, Classes 1B and 2B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
8 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UNR,
Class 3A and Series UN, Class 3B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
9 External UNJ Thread Design Profile and Tolerances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
iii

10 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread
D
3
LE
P
2
3
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Series UNJ, Classes 2A and 2B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
11 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UNJ,
Classes 3A and 3B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
12 Internal UNJ Thread Design Profile and Tolerances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
13 Basic Method of Designating Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
14 Ratio of Pitch Diameter Change to Thickness of Coating on 60-deg Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
15 Effect of Electrodeposited Coating on 60-deg External Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
16 Application of General Thread Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
A-1 Identification of 60-deg Inch Screw Threads Within the Scope of the ASME B1 Committee . . . 148
Tables
1 Standard Series Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2B Limits of Size for Standard Series Internal Threads (UN and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3 Allowable Variations in Lead and Equivalent Change in Functional Diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
4 Increments in Pitch Diameter Tolerance — Class 2A
(PD Tolerance = 0.0015
+ 0.0015
+ 0.015
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
100
5 Basic Profile and Constants for Calculation Formulas of Thread Dimensions, in. . . . . . . . . . . . 102
6 Basic Dimensions for Coarse-Thread Series (UNC, UNRC, and UNJC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
7 Basic Dimensions for Fine-Thread Series (UNF, UNRF, and UNJF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
8 Basic Dimensions for Extra-Fine-Thread Series (UNEF, UNREF, and UNJEF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
9 Basic Dimensions for 4-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
10 Basic Dimensions for 6-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
11 Basic Dimensions for 8-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
12 Basic Dimensions for 12-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
13 Basic Dimensions for 16-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
14 Basic Dimensions for 20-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
15 Basic Dimensions for 28-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
16 Basic Dimensions for 32-Thread Series (UN, UNR, and UNJ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
17A Outline Guide for Determining Limits of Size of External Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
17B Outline Guide for Determining Limits of Size of Internal Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
18A Examples of External Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
18B Examples of Internal Screw Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
19 Allowable Variation in 30-deg Basic Half Angle of External and Internal Screw Threads . . . . . 145
20 Nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
A-1 Identification of 60-deg Inch Screw Threads Within the Scope of the ASME B1 Committee . . . 149
D-1 Limits of Size for Selected Combinations of UNS/UNRS Series Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
E-1 Limits of Size for Standard Series Internal and External Threads as Listed in Table 3A of ASME B1.1-
1989 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
E-2 Limits as Listed in Table D-1 (Formerly 3B) Prior to ASME B1.1-2003 Edition . . . . . . . . . . . 174
iv

FOREWORD
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
ASME B1.1, Unified Inch Screw Threads, is an integrated system of threads for fastening purposes in mechanisms and
structures. Its outstanding characteristic is its general interchangeability of threads, achieved through the standardization of thread form, diameter-pitch combinations, and limits of size.
This Standardis the outgrowth of and supersedes previous editions that were published as ASME B1-1924, ASME B1.11935, ASME B1.1-1949, ASME B1.1-1960, ASME B1.1-1974, ASME B1.1-1982, ASME B1.1-1989, and ASME B1.1-2003.
The achievements represented by ASME B1.1 in development, standardization, and unification are the result of the
cooperation and coordination of many organizations, including The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME),
SAE International (formerly Society of Automotive Engineers), National Institute of Science and Technology (formerly
National Bureau of Standards), Committee B1, the former National Screw Thread Commission, the former Interdepartmental Screw Thread Committee, British Standards Institution, CSA Group (formerly Canadian Standards Association),
and American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
This Standard has its basis in the work done more than a century ago by William Sellers in the United States and Sir
Joseph Whitworth in Great Britain. Through the intervening years, there have been many developments and revisions,
culminating in the Unified Thread Standard approved and adopted for use by all inch-using countries.
The unification of screwthread standards meets the needfor interchangeability among the billions of fasteners made in
different countries and used in the complex equipment of modern technology. Unification is equally important for the
international trade in mechanisms of all kinds and the servicing of transportation equipment that moves from country to
country. Unification is therefore not only highly advantageous but also essential.
Complete unification of certain thread series and six tolerance classes in sizes
1
∕4in. and larger was achieved with the
signing of an accord in Washington, D. C. on November 18, 1948. Since that time, unification has extended to smaller sizes.
Developed by Technical Committee No. 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the unified inch
standard that was adopted as ISO 5864 is parallel to the ISO metric screw thread system. Both systems have a common
basic profile. The standard was subject to Quadripartite Standardization Agreement (QSTAG) 247 in the ABCA Army
Standardization Program of America, Britain, Canada, and Australia.
Throughout this history, special attention has been given to the practical aspects of thread standardization, and many
details of ASME B1.1 result from studies and tests based on real-world use. For example, users communicated the need for
free assembly in high-production industries and the desirability of providing for threads that require a coating. The
tolerance classes 2A and 2B were developed to meet these two major requirements as well as to provide a general
standard for externally and internally threaded fasteners. Thread symbols and nomenclature are now consistent with
ASME B1.7. Thread acceptability now follows ASME B1.3.
In 1992, ASME B1.30 implemented eight-place decimal and rounding rules that are mandatory for all new editions and
future revisions of ASME B1 documents. To comply with this decision, the 2003 edition, ASME B1.1-2003
(a) revised some of the values in Table 2 and created Table E-1 of Nonmandatory Appendix E, which identifies and lists
the revised dimensions from Table 2 in the ASME B1.1-1989 edition. The majority of the dimensional changes are within
±0.0001 in. As stated in para. 8.2.1, the values in this former Table 2, now Tables 2A and 2B, and Table E-1 should be
considered acceptable until a future revision of this Standard makes the values in Tables 2A and 2B the only acceptable
values.
(b) moved Table 3B, which provides calculated values for various UNS (unified specials), to Nonmandatory Appendix
D. The ASME B1 Committee strongly urges users to adopt the standard thread sizes in Tables 2A and 2B instead of those
listed in Table D-1.
(c) moved Tables 31 through 40, which include some values that differ from those derived by use of the formulas in
paras. 5 and 8, to Nonmandatory Appendix D and renamed these Tables D-2 through D-11. (All future special threads
should be based on calculations only.)
(d) eliminated all references to thread engagement from this Standard. Past changes in the thread form designation of
the “basic” thread height from 0.7500H to 0.62500H confused the calculation of percent of thread engagement.
(e) included the definition of “functional diameter” and added the term to Table 2 in the same column as “pitch
diameter,” since both characteristics have the same limits of size.
(f) explained in greater depth the effects of coating on threads (see section 7).
v

Changes to this 2019 edition include the splitting of ASME B1.1-2003 Table 2, which contained values for both internal
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
and external threads for UN and UNR only, into two tables, Table 2A: Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads
(UN, UNR, and UNJ), and Table 2B: Limits of Size for Standard Series Internal Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ). The metric
translation of this Standardwas removed, as were TablesD-2 through D-11 (formerly Tables31 through 40 in ASMEB1.1-
1989).
Finally, the UNJ thread profile, formerly defined in ASME B1.15, was added to this Standard. Following the U.S. Depart-
ment of Defense (DoD) approval of SAE AS8879C-2003, ASME B1 Subcommittee 15 recognized it would become the
standard used by the aerospace industry for this thread form. As a result, Subcommittee 15 recommended that the
technical information from ASME B1.15 be included in ASME B1.1 for non-aerospace applications.
The UNJ thread form havingthe enlarged root radius in the external thread was introduced to minimize size and weight
in parts for applications requiring high-fatigue strength under high working-stress levels, as in aerospace applications. It
is also appropriate for designs in commercial products where stresses are critical. To meet these requirements, the UNJ
external thread root radius is designed to be between 0.15011107P and 0.18042196P and the minor diameter of the
mating internal thread is increased to ensure the necessary clearance.
This Standard includes Classes 2A and 2B UNJ screw threads. Either Class 2A or Class 3A UNJ threads are appropriate for
commercial applications commensurate with the fatigue and stress levels required.
The UNJ thread form is the UN thread form modified to 0.562500H, which allows the 0.18042196P maximum root
radius in the external thread. The first known U.S. standard of similar thread form was SAE AS-82, published in March
1942, which describes a modified American National thread form to 75% h basic thread depth and specifies 0.10800P to
0.1800P root radius in the external thread. This thread was symbolized NR, National Round, and was developed for
aircraft engine applications.
Tension fatigue testing of aircraft fasteners in 1942 demonstratedthe importance of the external thread root contour in
the fatigue life of a screw thread rolled after heat treatment. Fatigue testing isolated the elements of good external thread
root design. The root should be radiused, not sharp. Theoretically, it should be a continuous circular arc, blending
smoothly with the thread flanks. The radius should be as large as possible within the allowable design form. The
root contour should also be smooth throughout and free of any imperfections, tool marks, or other minor notches.
Recognizing the need for improved 160,000 psi tensile strength bolts, the DoD published MIL-B-7838A, the bolt
procurement specification for aircraft applications based on the unified thread form of 0.62500H, in April 1952,
thus acknowledging a larger external root radius requires a shallower internal thread depth to clear the flank tangency
point.
The root radius of the external thread was increased to 0.15011107P minimum and 0.18042196P maximum for the
180,000 psi and higher tensile strength bolts. This external thread form was developed in 1955 by the aerospace fastener
industry and was known as the “Hi R” thread form.
Through coordinated effort with the SAE E-25 Engine and Propeller Standard Utility Parts Committee and the Aero-
space Industries Association National Aerospace Standards Committee (NASC), the DoD developed and published in
September 1960 the thread specification MIL-S-8879, which features the “Hi R” thread root radius in the external thread
and the internal thread modified to 0.562500H basic. In aircraft gas turbine engines, the high-temperature threaded
fasteners exhibited better elevated temperature performance using MIL-S-8879 UNJ thread root radius, as the stressrupture life of bolts was greatly improved.
The UNJ thread form has been adopted by the aerospace industry as the all-purpose thread standard, except for
electrical hardware and thread sizes 0.1380 and smaller, which may use the UN thread form.
The UNJ profile as defined in this Standard is similar to SAE AS8879C-2003 (superseding MIL-S-8879C) and equivalent
to ISO 3161:1977 for thread Classes 3A and 3B. British Standards Institution BS 4084:1978, including Amendment 1, is
technically identical to ISO 3161:1977, except for Appendix A, which provides information for a 20-UNJ constant pitch
series for diameters through 3 in.
ASME B1.1-2019 was approved by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) on August 26, 2019.
vi

ASME B1 COMMITTEE
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Standardization and Unification of Screw Threads
(The following is the roster of the Committee at the time of approval of this Standard.)
STANDARDS COMMITTEE OFFICERS
A. L. Barrows, Chair
STANDARDS COMMITTEE PERSONNEL
D. S. George, Vice Chair
D. Papert, Secretary
A. L. Barrows, Swanson Tool Manufacturing, Inc.
K. Bly, Vermont Thread Gage
L. Borowski, Greenslade & Co., Inc.
H. J. Cox, Frank Cox Metrology, Ltd.
G. A. Cuccio, Capitol Manufacturing Co.
R. Dodge, Pennoyer Dodge Co.
D. Everett, National Institute of Standards and Technology
J. O. Gehret III, Gehret Gage, LLC
D. S. George, Michigan Metal Coating
J. R. Gervasi, Kerr Lakeside, Inc.
P. Holahan, Fastenal Co.
L. C. Johnson, Johnson Gage Co.
D. D. Katz, Precision Fittings
D. R. Maisch, PMC Lone Star
SUBCOMMITTEE 1 — UNIFIED SCREW THREADS
A. L. Barrows, Chair, Swanson Tool Manufacturing, Inc.
D. Miskinis, Vice Chair, Consultant
K. Bly, Vermont Thread Gage
L. Borowski, Greenslade & Co., Inc.
R. Dodge, Pennoyer Dodge Co.
D. S. George, Michigan Metal Coating
J. R. Gervasi, Kerr Lakeside, Inc.
P. Holahan, Fastenal Co.
L. C. Johnson, Johnson Gage Co.
P. Larouche, Johnson Gage Co.
M. Oliver, M. Oliver Consulting
D. Miskinis, Consultant
D. Papert, The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
J. R. Popovic, Cleveland Specialty Inspection Services, Inc.
M. W. Rose, Glastonbury Southern Gage
P. Larouche, Alternate, Johnson Gage Co.
R. J. Hukari, Contributing Member, SPS Technologies
R. P. Knittel, Contributing Member, Consultant
D. R. Oas, Contributing Member, Seaway Bolt & Specials Corp.
E. Schwartz, Contributing Member, Consultant
B. F. Sheffler, Contributing Member, Consultant
D. Skierski, Contributing Member, Sterling Gage & Calibration, LLC
R. D. Strong, Contributing Member, Lear Corp.
C. J. Wilson, Contributing Member, Consultant
S. Brahimi, Contributing Member, Industrial Fasteners Institute
M. Cox, Contributing Member, Consultant
R. J. Hukari, Contributing Member, SPS Technologies
J. C. Jennings, Contributing Member, Naval Surface Warfare Center,
Philadelphia Division
X. Li, Contributing Member, China Productivity Center for Machinery
Industry
E. Schwartz, Contributing Member, Consultant
B. F. Sheffler, Contributing Member, Consultant
R. D. Strong, Contributing Member, Lear Corp.
C. J. Wilson, Contributing Member, Consultant
vii

CORRESPONDENCE WITH THE B1 COMMITTEE
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
General. ASME Standards are developed and maintained with the intent to represent the consensus of concerned
interests. As such, users of this Standard may interact with the Committee by requesting interpretations, proposing
revisions or a case, and attending Committee meetings. Correspondence should be addressed to:
Secretary, B1 Standards Committee
Proposing Revisions. Revisions are made periodically to the Standard to incorporate changes that appear necessary
or desirable, as demonstrated by the experience gained from the application of the Standard. Approved revisions will be
published periodically.
This Standard is always open for comment, and the Committee welcomes proposals for revisions to this Standard. Such
proposals should be as specific as possible, citing the paragraph number(s), the proposed wording, and a detailed
description of the reasons for the proposal, including any pertinent documentation.
Proposing a Case. Cases may be issued to provide alternative rules when justified, to permit early implementation of
an approved revision when the need is urgent, or to provide rules not covered by existing provisions. Cases are effective
immediately upon ASME approval and shall be posted on the ASME Committee web page.
Requests for Cases shall provide a Statement of Need and Background Information. The request should identify the
Standard and the paragraph, figure, or table number(s), and be written as a Question and Reply in the same format as
existing Cases. Requests for Cases should also indicate the applicable edition(s) of the Standard to which the proposed
Case applies.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Two Park Avenue
New York, NY 10016-5990
http://go.asme.org/Inquiry
Attending Committee Meetings. The B1 Standards Committee regularly holds meetings and/or telephone confer-
ences that are open to the public. Persons wishing to attend any meeting and/or telephone conference should contact the
Secretary of the B1 Standards Committee. Future Committee meeting dates and locations can be found on the Committee
Page at http://go.asme.org/B1committee.
viii

ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
UNIFIED INCH SCREW THREADS (UN,
UNR, AND UNJ THREAD FORMS)
1 GENERAL
1.1 Scope
This Standard specifies the thread form, series, class,
allowance, tolerance, and designation for unified screw
threads. (In order to emphasize that unified screw
threads are based on inch modules, they may be
denoted unified inch screw threads.) Several variations
in thread form have been developed for unified
threads; however, this Standard covers only UN, UNR,
and UNJ thread forms.
The metric translation of this Standard that was in the
2003 edition has been removed (see Nonmandatory
Appendix C). Nonmandatory Appendices D through F
contain information that is supplementary to the sections
of this Standard.
1.2 Unified Screw Thread Standards
The standards for unified screw threads published in
this Standard are in agreement with formal standards
of the International Organization for Standardization
(ISO) for diameter-pitch combinations, designations,
and tolerances for 60-deg triangular form inch screw
threads. The unified screw thread symbols UN, UNC,
UNF, and UNEF were derived by the addition of the
letter “U”preceding the thread symbols used for American
National screw threads N, NC, NF, and NEF.
Unified screw threads have their origin in an accord
signed in Washington, D.C. on November 18, 1948 by
representatives of standardizing bodies of Canada, the
United Kingdom, and the United States and have subsequently superseded American National screw threads.
1.3 Thread Forms
UN applies to both internal and external threads. UNR
applies only to external threads; the difference between
UN and UNR threads, in addition to designation, is that a
flat or rounded root contour due to tool wear is specified
for UN threads, while only a defined rounded root contour
is specified for UNR threads. Basic thread height is
0.54126588P.
The UNJ screw thread is designed for use on highly
stressed applications requiring high-fatigue strength.
For aerospace applications, only Classes 3A and 3B
should be used. Basic thread height is only
0.48713929P to permit a root radius larger than that
of the UN and UNR forms.
1.4 Interchangeability
1.4.1 UN and UNR. Unified (UN/UNR) and its prede-
cessor American National (N) screw threads have
substantially the same thread form, and threads of
both standards having the same diameter and pitch
are mechanically interchangeable. The principal differences between these standards relate to the application
of allowances, the variation of tolerances with size, differences in the amounts of pitch diameter tolerances for
external and internal threads, and differences in thread
designations. Unified inch and ISO metric screw
threads are not mechanically interchangeable.
1.4.2 UNJ. UN and UNJ threads are interchangeable
with the exception of UNJ-3A external threads, which
at maximum material condition will not assemble with
a UN internal thread of any class at maximum material
condition (see Figure 1).
1.5 Designations
Unified thread sizes (specific combinations of diameter
and pitch shown in Table 1) are identified by the letter
combination “UN” in the thread symbol. In the unified
standards, the pitch diameter tolerances for external
threads differ from those for internal threads; for this
reason the letter “A” is used in the thread symbol to
denote an external thread and the letter “B,” an internal
thread. Where the letters “U,” “A,” or “B” do not appear in
the thread designation, the threads conform to the
outdated American National screw threads. Details
regarding thread designations are given in section 6.
1.6 References
The following is a list of publications referenced in this
Standard. Unless otherwise specified, the latest edition
shall apply. The following documents form a part of
this Standard to the extent specified herein.
ASME B1.2, Gages and Gaging for Unified Inch Screw
Threads
ASME B1.3, Screw Thread Gaging Systems for Accept-
ability: Inch and Metric Screw Threads
1
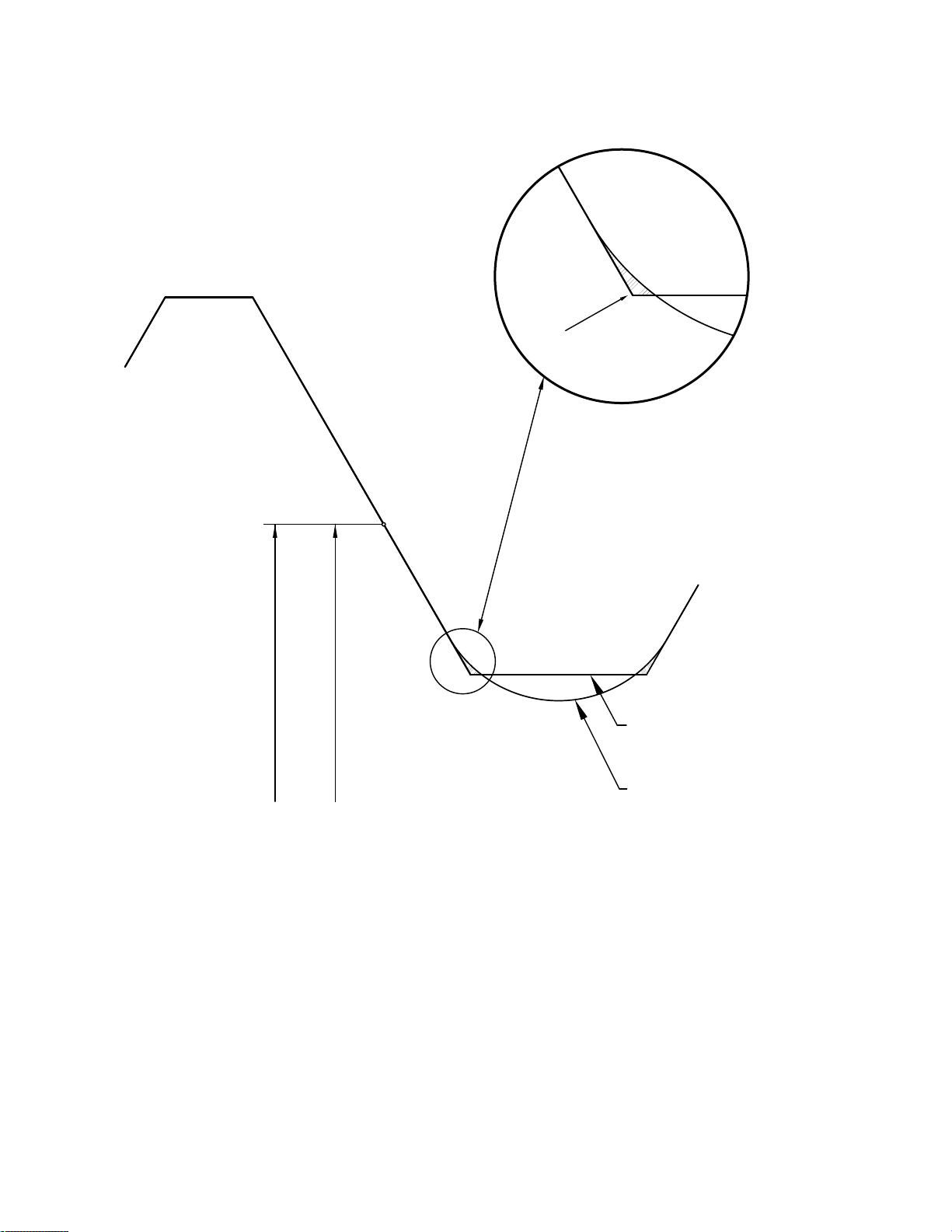
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Maximum minor diameter of
UNJ-3A external thread
Minimum minor diameter of
UN-3B internal thread
Interference
Detail
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Figure 1 Illustration of Assembly Interference of UNJ-3A Thread and UN-3B Thread in the Maximum Material Condition
ASME B1.7, Screw Threads: Nomenclature, Definitions,
and Letter Symbols
ASME B1.30, Screw Threads: Standard Practice for Calcu-
lating and Rounding Dimensions
ASME B47.1, Gage Blanks
ASME B94.11M, Twist Drills
ASME Y14.5, Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Publisher: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
(ASME), Two Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990
(www.asme.org)
ISO 68, General Purpose Screw Threads — Basic Profile
Publisher: International Organization for Standardization
(ISO), Central Secretariat, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, Case
Postale 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland
(www.iso.org)
1.7 Acceptability
Acceptability of product threads shall be in accordance
with ASME B1.3. Gages and gaging shall be in accordance
with ASME B1.2.
1.8 Reference Temperature
The reference temperature is 68°F for dimensions
defined by this system.
2
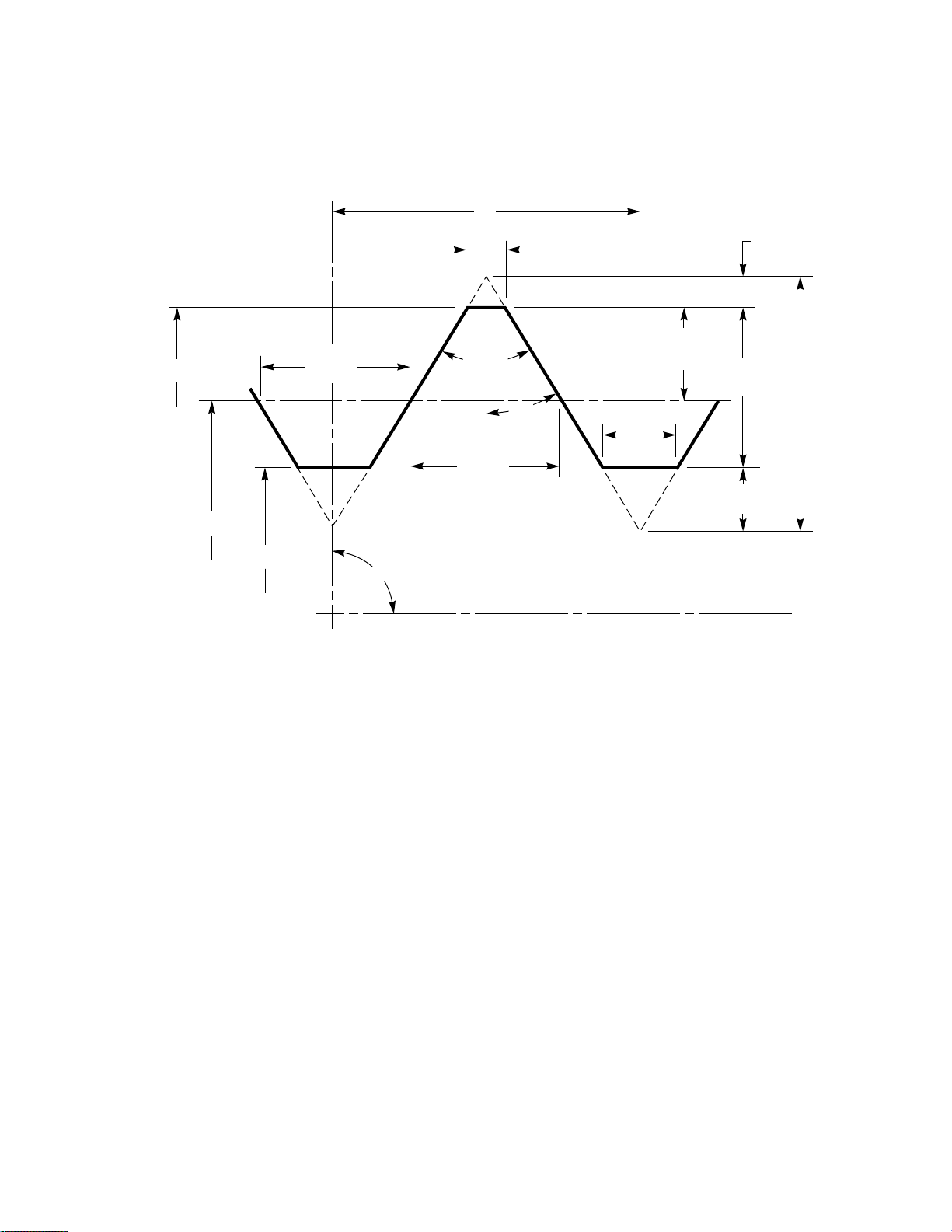
0.86602540P
(H)
P
60 deg
30
deg
90 deg
Axis of screw thread
D bsc, d bsc
D2 bsc, d2 bsc
D1 bsc, d1 bsc
0.125P
0.10825318P
(0.125H )
0.32475953P
(0.375H )
0.54126588P
(0.625H )
0.21650635P
(0.25H )
0.250P
0.500P
0.500P
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Figure 2 Basic Profile for UN and UNR Screw Threads
1.9 Units of Measure
All dimensions in this Standard, including all tables, are
in inches unless otherwise specified.
1.10 Federal Government Use
When this Standard is approved by the Department of
Defense and federal agencies and is incorporated into
FED-STD-H28/2, Screw-Thread Standards for Federal
Services, para. 2, the use of this Standard by the
federal government will be subject to all the requirements
and limitations of FED-STD-H28/2.
2 SCREW THREAD PROFILE
2.1 Scope
The basic profile and design profiles are defined in this
Section and are the basis of all thread dimensions given in
this Standard.
2.2 Basic Profile
2.2.1 UN and UNR. The basic profile for UN screw
threads is identical to that for UNR screw threads and
is shown in Figure 2. Profile applies to an axial plane.
For reference, the basic profile for UN and UNR screw
threads is identical to that for ISO metric screw threads
shown in ISO 68.
2.2.2 UNJ. The basic profile for UNJ screw threads is
shown in Figure 3. It is the theoretical profile corresponding to the basic dimensions of the thread major
diameter, pitch diameter, and minor diameter. This
profile includes a 0.15011107P to 0.18042196P radius
at the root of the external thread as shown in Figure
4. This also requires that the minor diameter of the
external and internal threads be larger than the UN
and UNR thread forms to accommodate the external
thread maximum root radius. It is similar to but not
the same as the profile for UN and UNR.
2.3 Design Profiles
ditions for external and internal threads with no allowance and are derived from the basic profile. The design
profiles of both external and internal screw threads
The design profiles define the maximum material con-
vary from the basic profile.
3
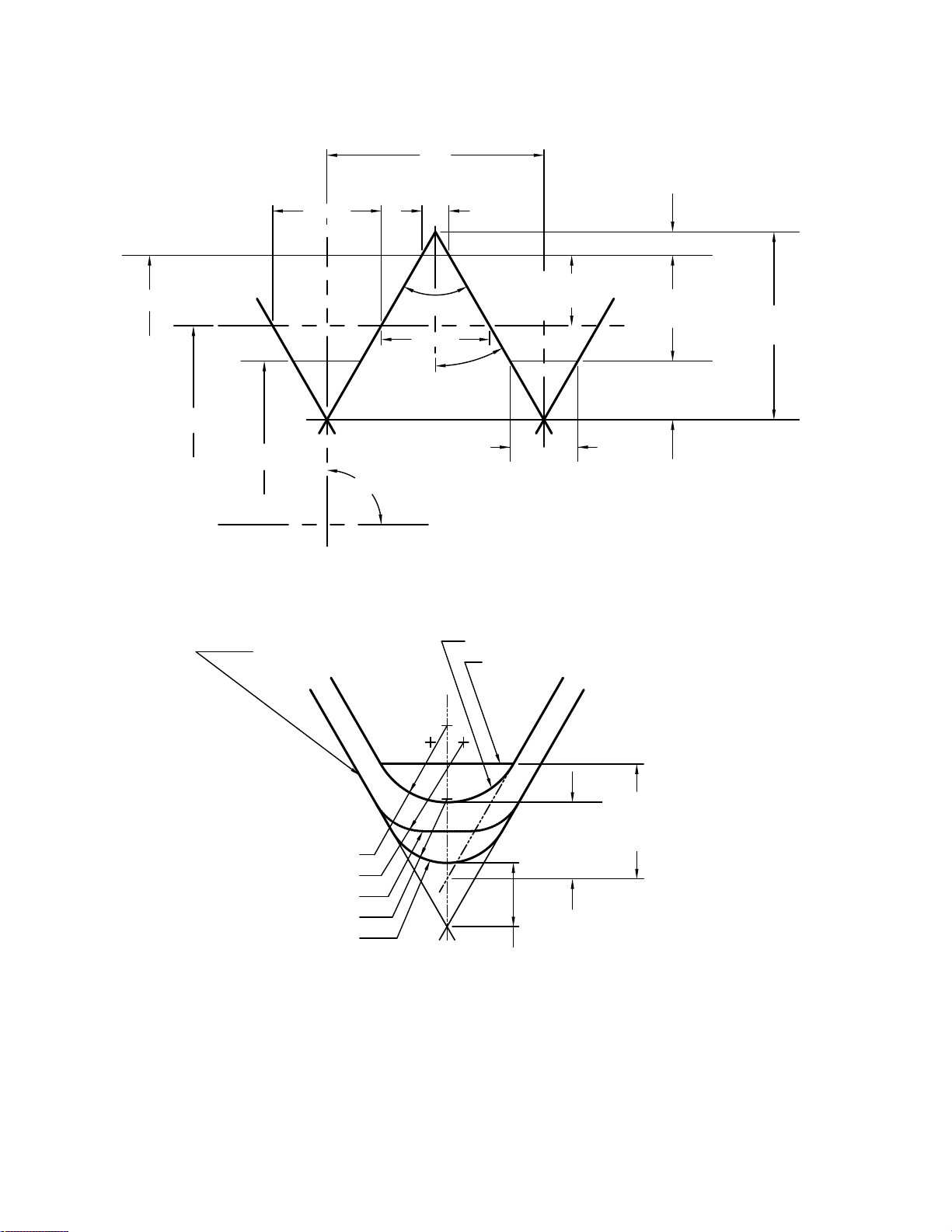
0.12500P0.500P
P
60
deg
30
deg
0.500P
Axis of thread
90 deg
0.312500P
0.32475953P
(0.3750H)
0.10825318P
(0.1250H)
0.48713929P
(0.5625H)
0.27063294P
(0.3125H)
0.86602540P
(H)
D bsc, d bsc
D bsc, d bsc
2
2
D bsc, d bsc
1
1
Basic UNJ profile
Basic limit profile
Minimum material limit
0.27063294P
(0.3125H)
[Note (4)]
0.18042196P
(0.2083H)
[Note (3)]
0.15011107P
(0.1733H)
[Note (2)]
r max. = 0.18042196P
Lower limit profile
[Note (1)]
(X)
r min. = 0.15011107P
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Figure 3 Basic Profile for UNJ Screw Threads
NOTES:
(1) Optional profile comprised of two circular arcs (X) tangential to the flanks and flat at the root.
(2) Minimum truncation.
(3) Maximum truncation.
(4) Tangent flank radii (minor diameter).
Figure 4 Root Radius of UNJ External Thread
4

ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
2.3.1 Design Profiles of External Threads
2.3.1.1 UN and UNR. The design profiles of external
UN and UNR screw threads are included in Figures 5
through 8. A flat root contour is specified for UN
threads; however, it is permissible to provide for some
threading tool crest wear. Therefore, a rounded root
contour cleared beyond the 0.2500P flat width of the
basic profile is optional. The rounded root also reduces
the rate of threading tool crest wear and improves
is necessary to provide for some threading tool crest
wear resulting in a profile that may be flat or partially
or fully rounded; therefore, the root of the design
profile is rounded and cleared beyond the 0.12500P
flat width of the basic profile. No root radius is specified.
2.4 Formulas and Nomenclature
The formulas and nomenclature pertaining to the basic
profile and the design profiles are given in section 10.
fatigue strength over that of a flat root thread.
(a) At the least material condition (LMC), the root form
3 SCREW THREAD SERIES
of the UNR external thread shall be a full root radius of not
less than 0.10825318P. At maximum material condition
(MMC), the root form of the UNR external thread may be
one of the following types:
(1) a full root radius of not more than 0.14433757P,
which makes the point of tangency between the radius and
the flanks at a point 0.54126588P below the basic major
diameter (the equivalent of a 0.2500P width of flat).
(2) a “rounded form” consisting of a combination of
flats and radii not less than 0.10825318P, as shown in
Figures 7 and 8. When the root is the rounded form,
the radii may exceed 0.14433757P so long as the point
of tangency between the radii and the flanks is no less
than 0.54126588P below the basic major diameter (the
equivalent of a 0.2500P width of flat).
(b) The design profiles of external UN and UNR screw
threads have flat crests. However, in practice, product
thread crests may be flat, partially rounded, or fully
rounded. A rounded crest tangent at a 0.12500P flat is
shown as an option in Figures 5 through 8.
2.3.1.2 UNJ. The design profile of the external UNJ
screw thread specifies that the actual root of the
thread shall lie within the root radius tolerance zone
3.1 Thread Series Definition
Thread series are groups of diameter-pitch combinations distinguished from each other by the number of
threads per inch applied to a series of specific diameters.
There are two general series classifications: standard and
special.
3.1.1 Standard Series. The standard series consists of
three series with graded pitches (coarse, fine, and extra
fine) and eight series with constant pitches (4, 6, 8, 12, 16,
20, 28, and 32 threads per inch). The standard series is
shown in Table 1.Limits of size are shown in Tables 2A and
2B and discussed in section 8.
3.1.2 Special Series. The special series consists of all
threads with diameter-pitch combinations that are not
included in the standard series. When allowances and
tolerances of special series threads are derived from
unified formulation as shown in section 5, the threads
are designated UNS, UNJS, or UNRS. If allowance and tolerance are not derived from unified formulation, the threads
are designated “SPL 60-deg Form.” (See para. 6.1 and
Figure 13 for details of designation.)
shown in Figures 4 and 9. The limit dimensions of the
root radius, r, are shown in Figures 10 and 11 and
their values are specified in Table 2A. The profile shall
be a continuous smoothly blended non-reversing
curve, no part of which shall have a radius of less than
0.15011107P and which is tangent to the thread flanks
at not less than 0.48713929P basic thread depth. The
profile may comprise tangent flank circular arcs that
are tangent to the flanks and a flat at the minor diameter
provided that the minor diameter, d
, is within the zone
3
3.2 Order of Selection
Wherever possible, selection should be made from
Table 1, preference being given to the coarse- and
fine-thread series. As second choice, if the threads in
the standard series in Table 1 do not meet the requirements of the design, special thread sizes should be selected
from Table E-1 and their limits calculated using the
formulas in section 8. The limits in Table D-1 are for reference only and are not recommended for new applications.
established in Figures 10 and 11. Unless otherwise specified, the runout or incomplete UNJ threads on externally
threaded parts shall be no less than 1 pitch nor more than 2
pitches in length. The threads shall runout onto the shank
without any abrupt change in cross-sectional area. The
root radius shall be no less than the minimum radius
of the full thread section.
2.3.2 Design Profile of Internal Threads. The design
profiles of the internal UN and UNJ screw threads are
included in Figures 2, 5 through 8, and 10 through 12
3.3 Coarse-Thread Series Applications
The coarse-thread series (UNC, UNRC, or UNJC) is
generally used for the bulk production of screws, bolts,
and nuts. It is commonly used in materials such as cast
iron, aluminum, magnesium, brass, bronze, and plastic,
because the coarse-thread series provides more resistance to internal thread stripping than the fine- or
extra-fine-thread series. The coarse-thread series is
advantageous where rapid assembly or disassembly is
(there is no internal UNR screw thread). In practice, it
5
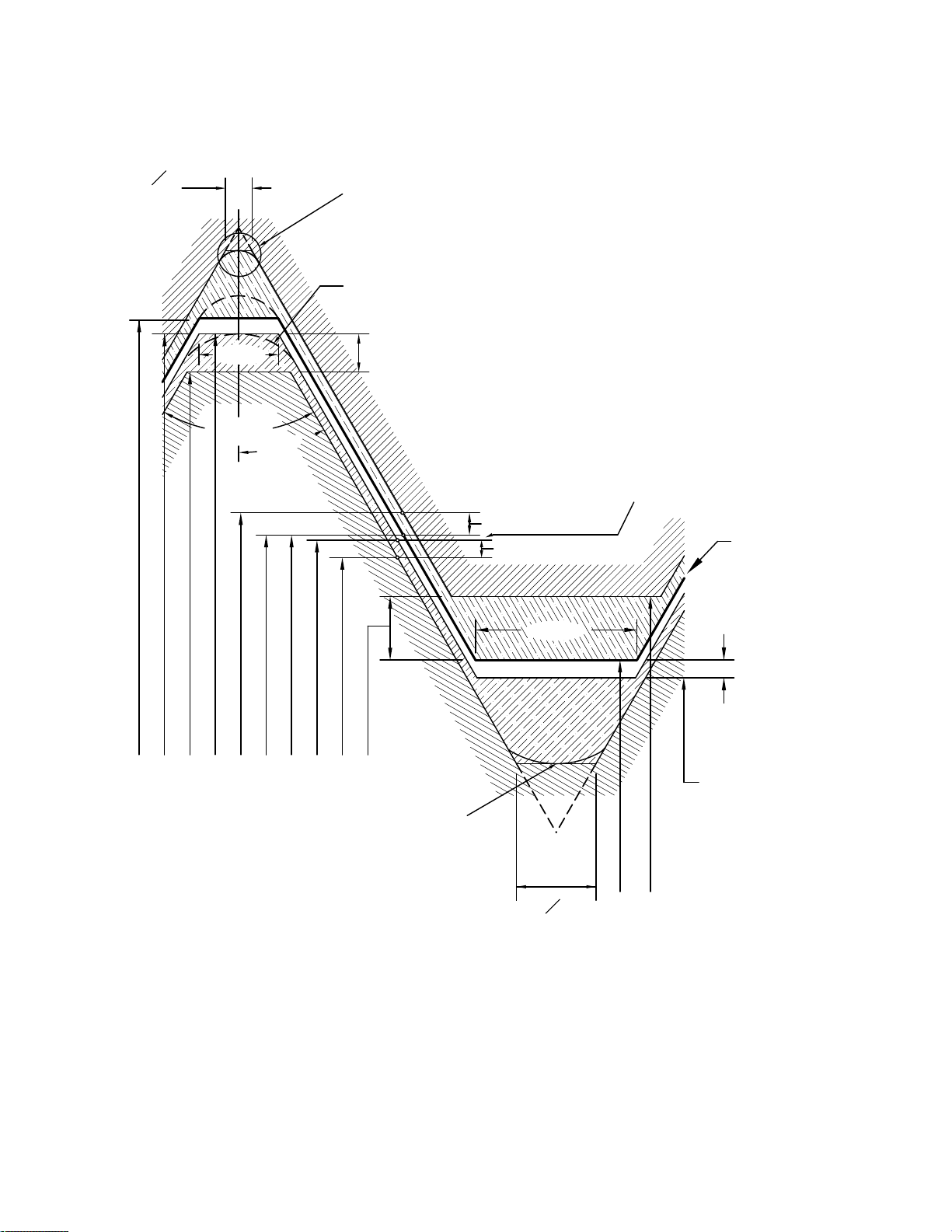
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
½ allowance (external)
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Basic pitch diameter
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
Internal Thread
In practice, roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
(see para. 2.3.2)
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
Minimum major diameter of external
Basic major diameter
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
External Thread
UN note: external root may be flat
or rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(a)]
½ allowance
(external only)
Basic
form
½ tolerance on major
diameter of external
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
0.12500P
½ tolerance on minor
diameter of internal
0.2500P
Maximum minor
diameter of internal
Minimum minor
diameter of internal
UN (maximum) minor
diameter of external
(minimum reference)
(minimum reference)
P
24
P
8
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
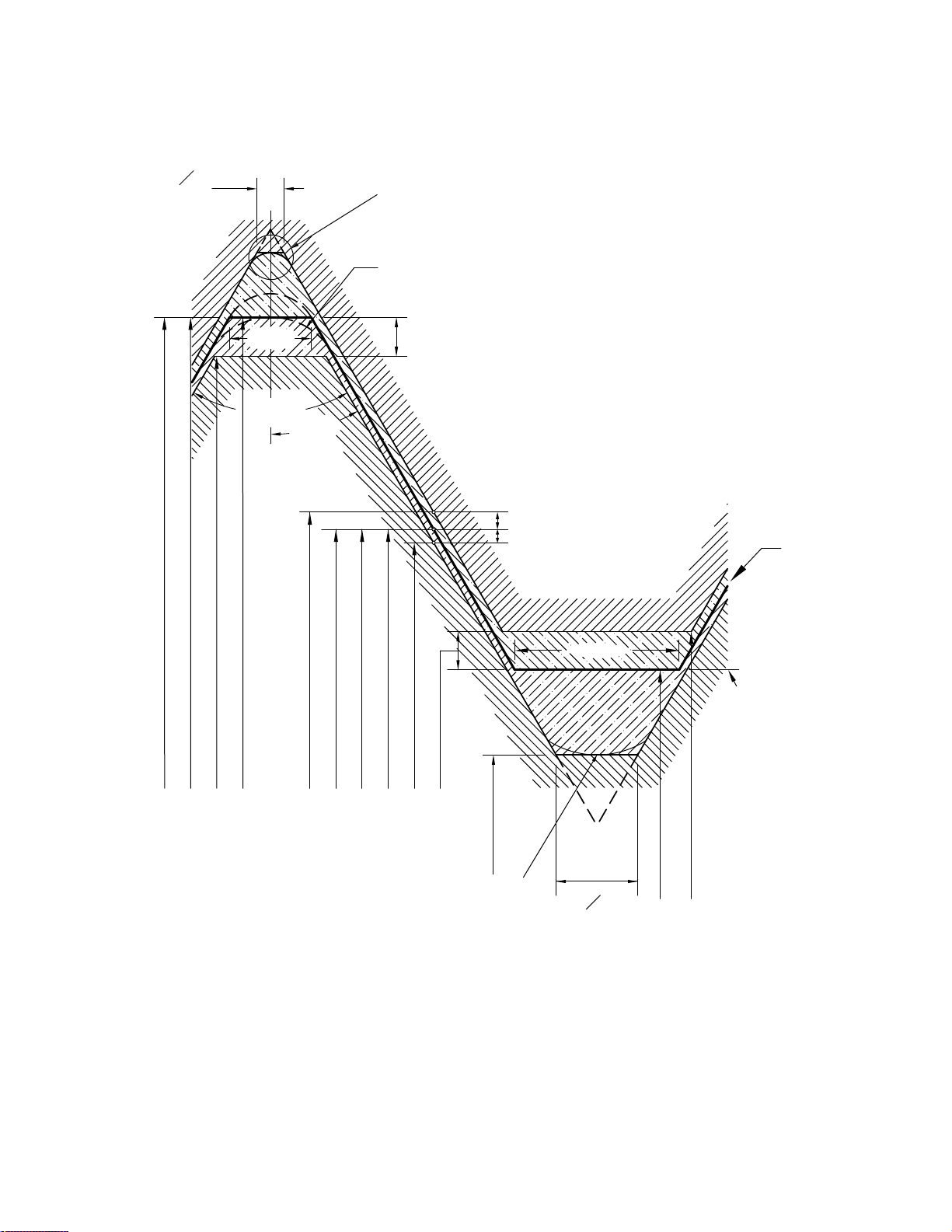
Figure 5 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UN,
Classes 1A, 2A, 1B, and 2B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
6
Internal Thread
External Thread
0.12500P
½ tolerance on major diameter of external
Basic
form
Basic major diameter of external and internal
Minimum major diameter of external
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Basic pitch diameter of external and internal
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
½ tolerance on minor
diameter of internal
Minimum minor
diameter of external
UN (maximum) minor
diameter of external
Maximum minor
diameter of internal
Minimum minor
diameter of internal
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
0.2500P
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
UN note: external root may be flat
or rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(a)]
In practice, roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
(see para. 2.3.2)
(minimum reference)
(minimum reference)
P
24
P
8
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
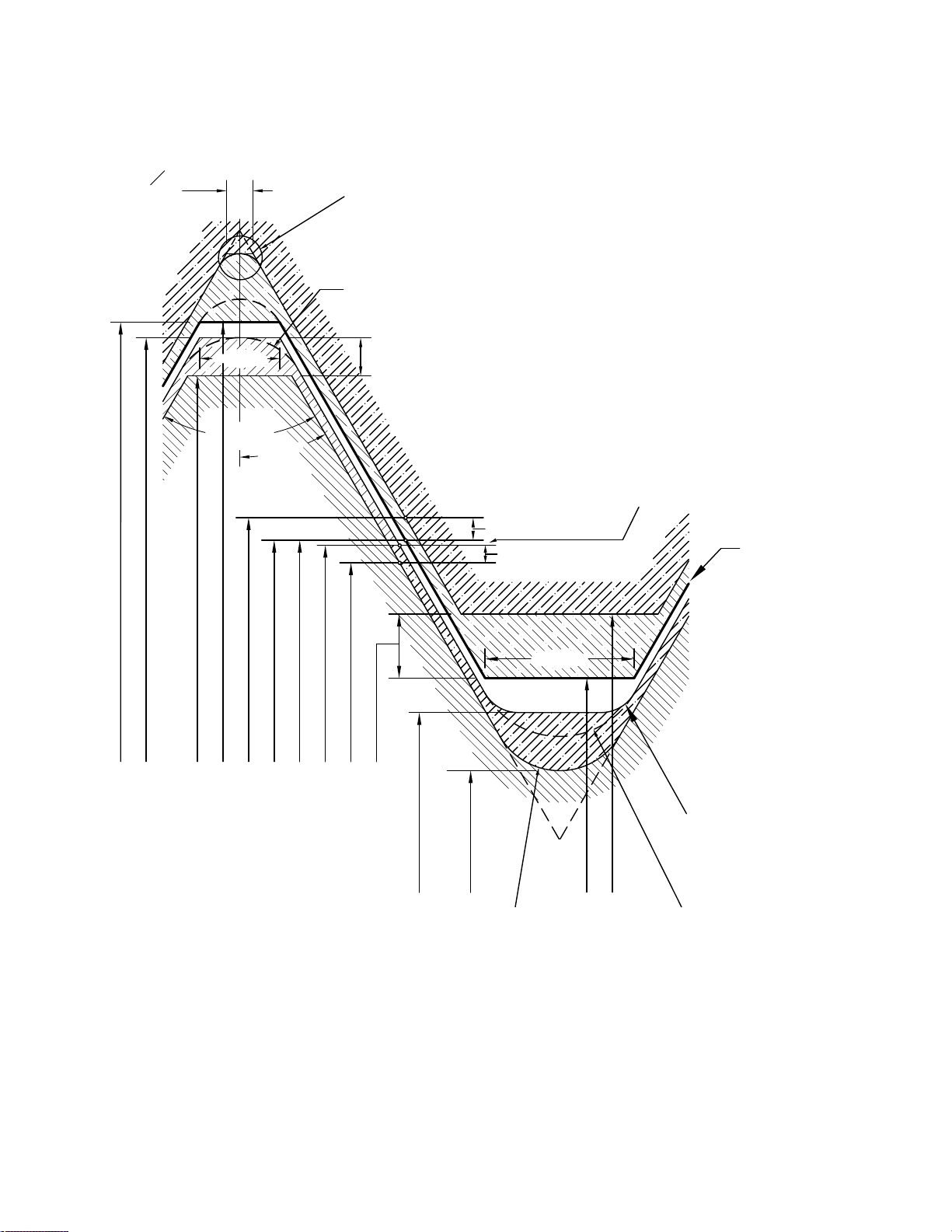
Figure 6 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UN,
Classes 3A and 3B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
7
External Thread
UNR note: external root is defined as a
continuous rounded contour with a radius
not less than 0.10825318P
Maximum minor
diameter of external
Minimum minor
diameter of external
Minimum minor
diameter of internal
Maximum minor
diameter of internal
Basic
form
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
½ allowance (external)
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Basic pitch diameter
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
½ tolerance on minor
diameter of internal
In practice, roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
(see para. 2.3.2)
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
Internal Thread
½ tolerance on major
diameter of external
Basic major diameter
Min
imum major diameter of external
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
0.2500P
0.12500P
UNR theoretical
maximum full root radius
is 0.14433757P
Maximum UNR root form
[see para. 2.3.1.1(a)]
(minimum reference)
P
24
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
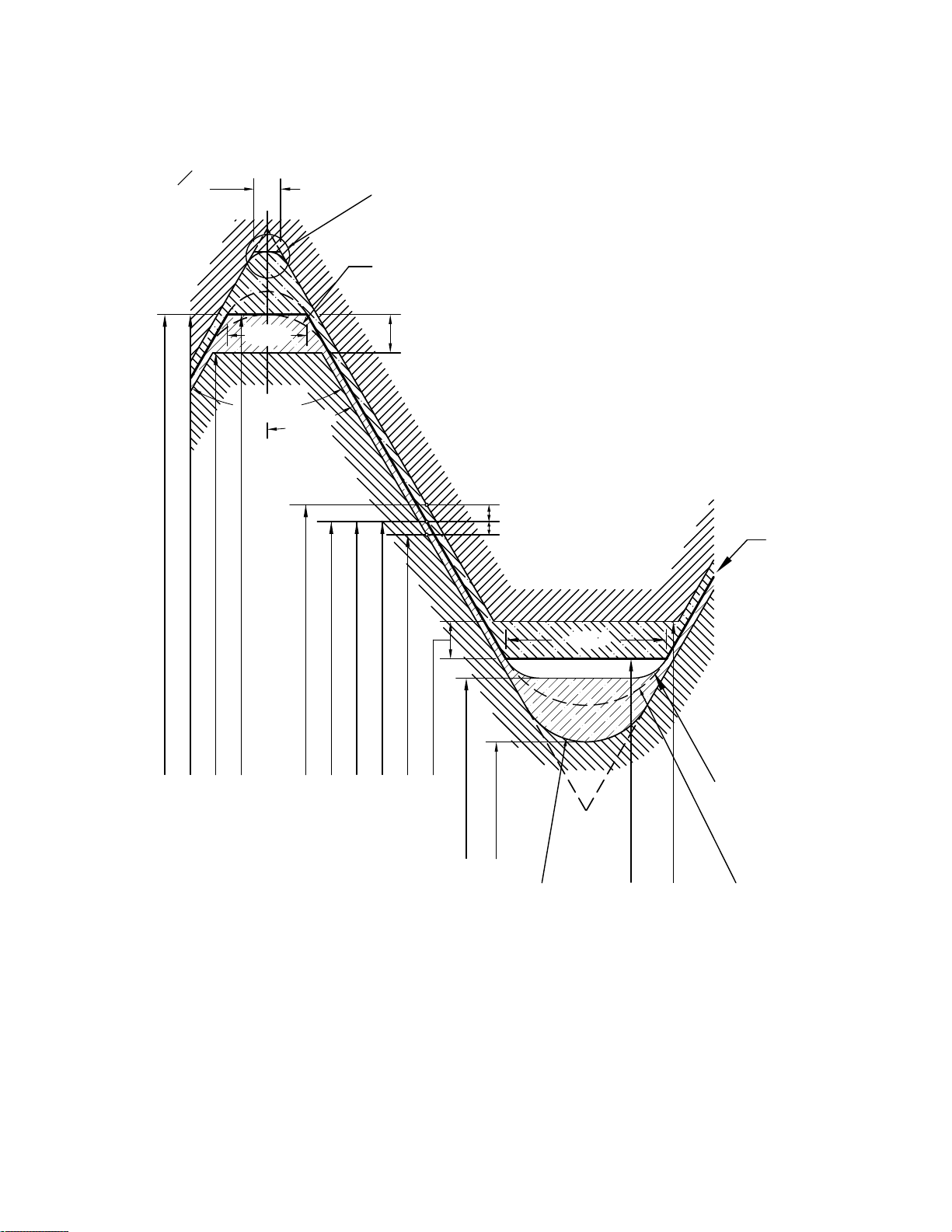
Figure 7 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series
UNR, Classes 1A and 2A, and Series UN, Classes 1B and 2B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
8
Internal Thread
External Thread
0.12500P
Basic
form
Basic major diameter of external and internal
Minimum major diameter of external
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Basic pitch diameter of external and internal
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
Minimum minor
diameter of external
Maximum minor
diameter of internal
Minimum minor
diameter of internal
0.2500P
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
UNR note: external root is defined as a
continuous rounded contour with a radius
not less than 0.10825318P
½ tolerance on minor
diameter of internal
½ tolerance on major diameter of external
In practice, roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
(see para. 2.3.2)
Maximum minor
diameter of external
UNR theoretical
maximum full root radius
is 0.14433757P
Maximum UNR root form
[see para. 2.3.1.1(a)]
(minimum reference)
P
24
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
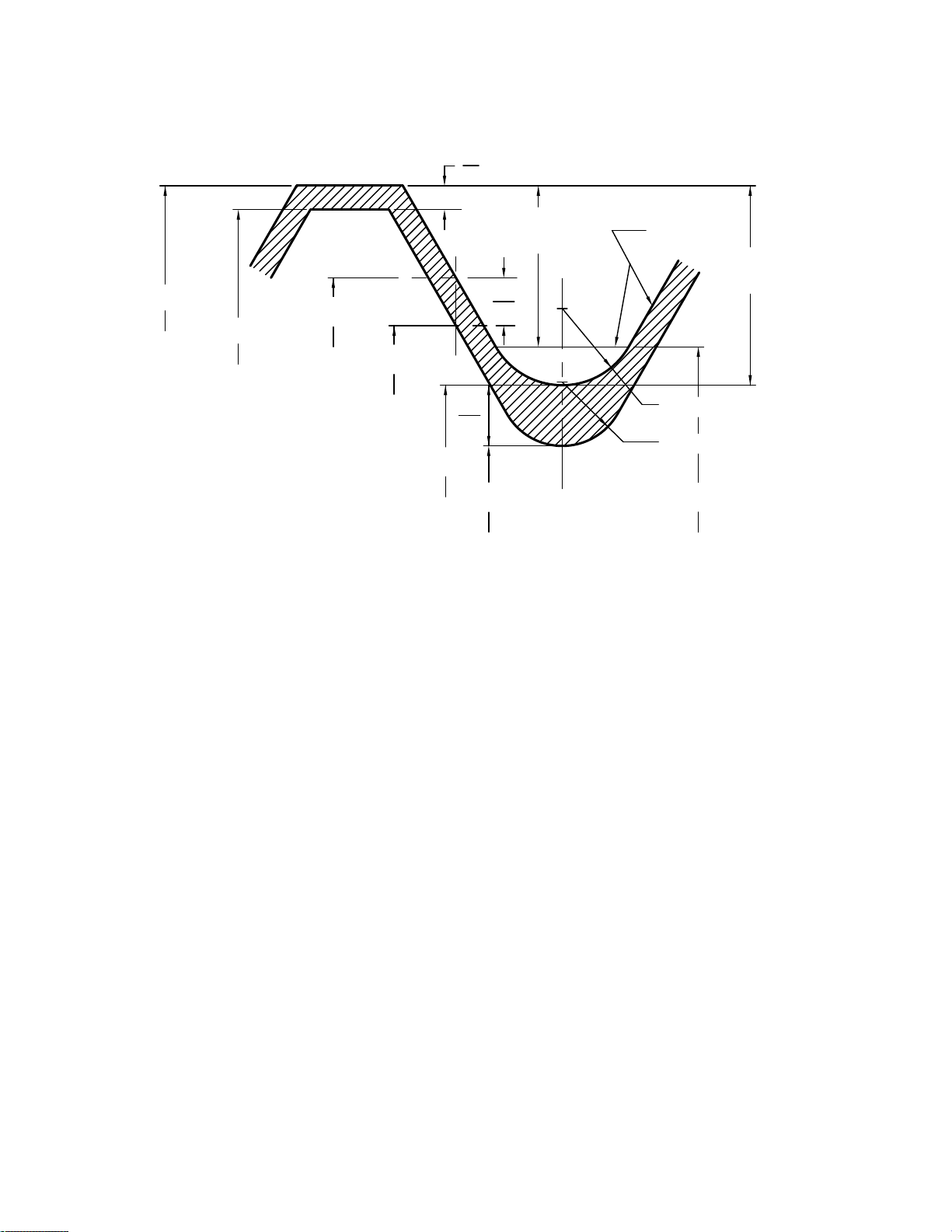
Figure 8 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UNR, Class 3A
and Series UN, Class 3B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
9
d bsc
1
r max. = 0.18042196P
r min. = 0.15011107P
Td
3
2
d min.
3
d max.
3
d min.
2
d max. = d bsc
2
2
d max. = d bsc
Td
2
Td
2
2
Basic profile
2
d min.
0.48713929P
(0.5625H)
0.57735027P
(0.6667H)
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
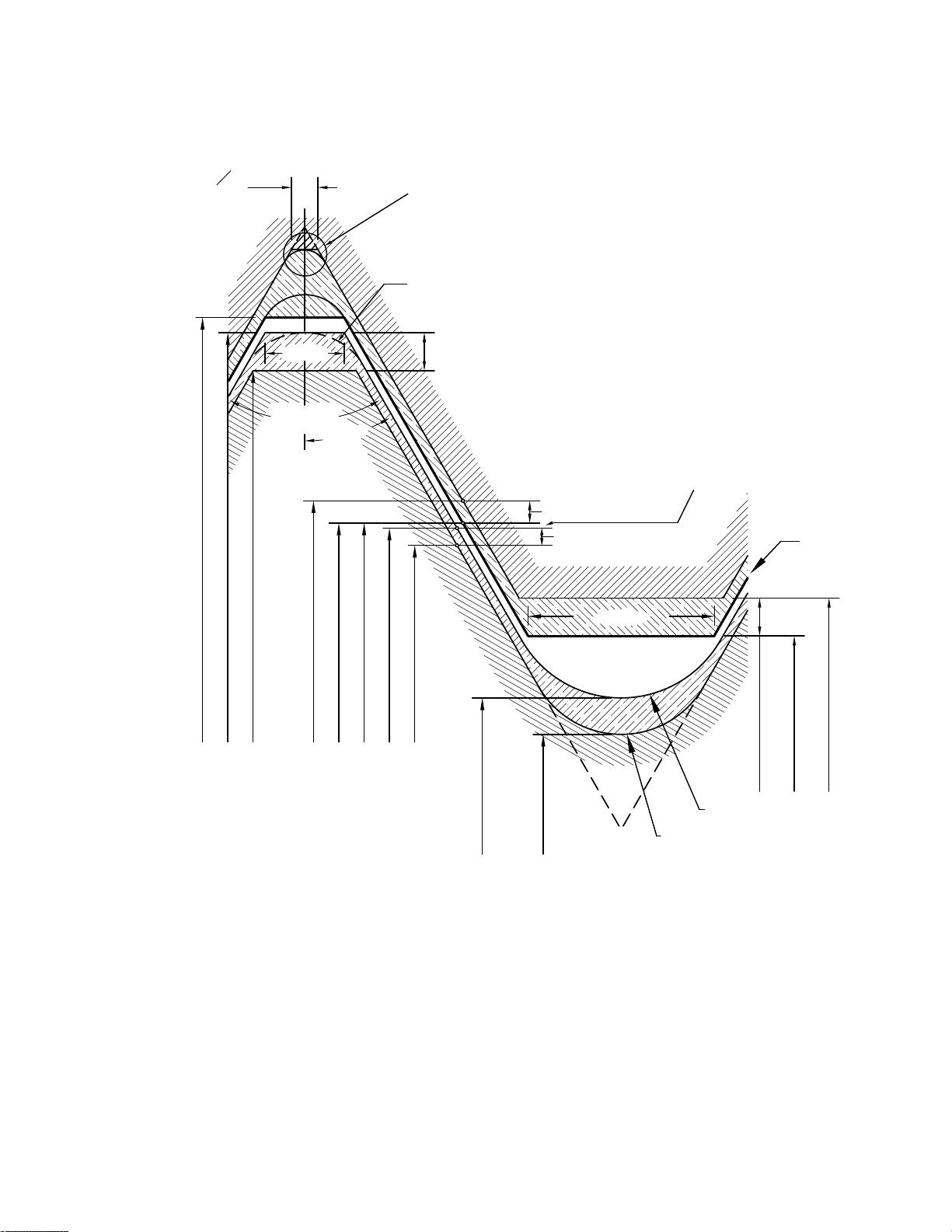
Figure 9 External UNJ Thread Design Profile and Tolerances
GENERAL NOTE: Rounded crest is optional (see para. 7.1.2.2).
required, or if corrosion or damage from nicks due to
handling or use is likely.
3.4 Fine-Thread Series Applications
The fine-thread series (UNF, UNRF, or UNJF) is
commonly used for bolts and nuts in high-strength applications. This series has less thread depth and a larger
minor diameter than the coarse-thread series. Consequently, thinner walls are permitted for internal
threads and more strength is available to external
threads than for coarse-thread series of the same
nominal size. In order to prevent internal thread stripping,
a longer length of engagement is required for fine-thread
series than for coarse-thread series for thread materials of
the same strength levels. However, for both fine- and
coarse-thread series, length of engagement in tapped
holes must be selected to meet strength requirements.
This also allows for finer adjustment in cases such as a
slotted nut and cotter pin assembly.
3.5 Extra-Fine-Thread Series Applications
The extra-fine-thread series (UNEF, UNREF, or UNJEF)
is used particularly for equipment and threaded parts that
require fine adjustment, such as bearing retaining nuts,
adjusting screws, etc., and for thin-wall tubing and thin
nuts.
3.6 Constant-Pitch-Thread Series Applications
The various constant-pitch series (UN, UNR, or UNJ)
with 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 28, and 32 threads per inch
(see Table 1) offers a comprehensive range of
diameter-pitch combinations for those purposes where
the threads in the coarse-, fine-, and extra-fine-thread
series do not meet the particular requirements of the
design. The primary sizes of the 8-UN, 12-UN, and 16UN series shown in Table 1 are the most commonly used.
Whenever a thread in a constant-pitch series also
appears in the UNC, UNF, or UNEF series, the symbols
and tolerances for limits of size of those standard
series are applicable.
3.6.1 8-Thread Series. The 8-thread series (8-UN) is a
uniform-pitch series used for large diameters or as a
compromise between coarse- and fine-thread series.
Although originally intended for high-pressure-joint
bolts and nuts, it is now widely used as a substitute
for the coarse-thread series for diameters larger than
1 in.
is a uniform-pitch series for large diameters requiring
threads of medium-fine pitch. Although originally
intended for boiler practice, it is now used as a continuation of the fine-thread series for diameters larger than
1
1
10
3.6.2 12-Thread Series. The 12-thread series (12-UN)
∕2in.
r max.
0.18042196P
r min.
0.15011107P
½ minor diameter tolerance
of internal thread
Minimum minor diameter
of internal thread
Maximum minor diameter
of internal thread
Basic
form
Maximum minor
diameter of external
Minimum minor
diameter of external
External Thread
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
½ allowance (external)
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
Minimum major diameter of external
0.12500P
0.312500P
½ tolerance on major diameter of external
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
In practice roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
(see para. 2.3.2)
Basic pitch diameter of internal
Internal Thread
(minimum reference)
P
24
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Figure 10 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances, Allowance, and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series
UNJ, Classes 2A and 2B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
11
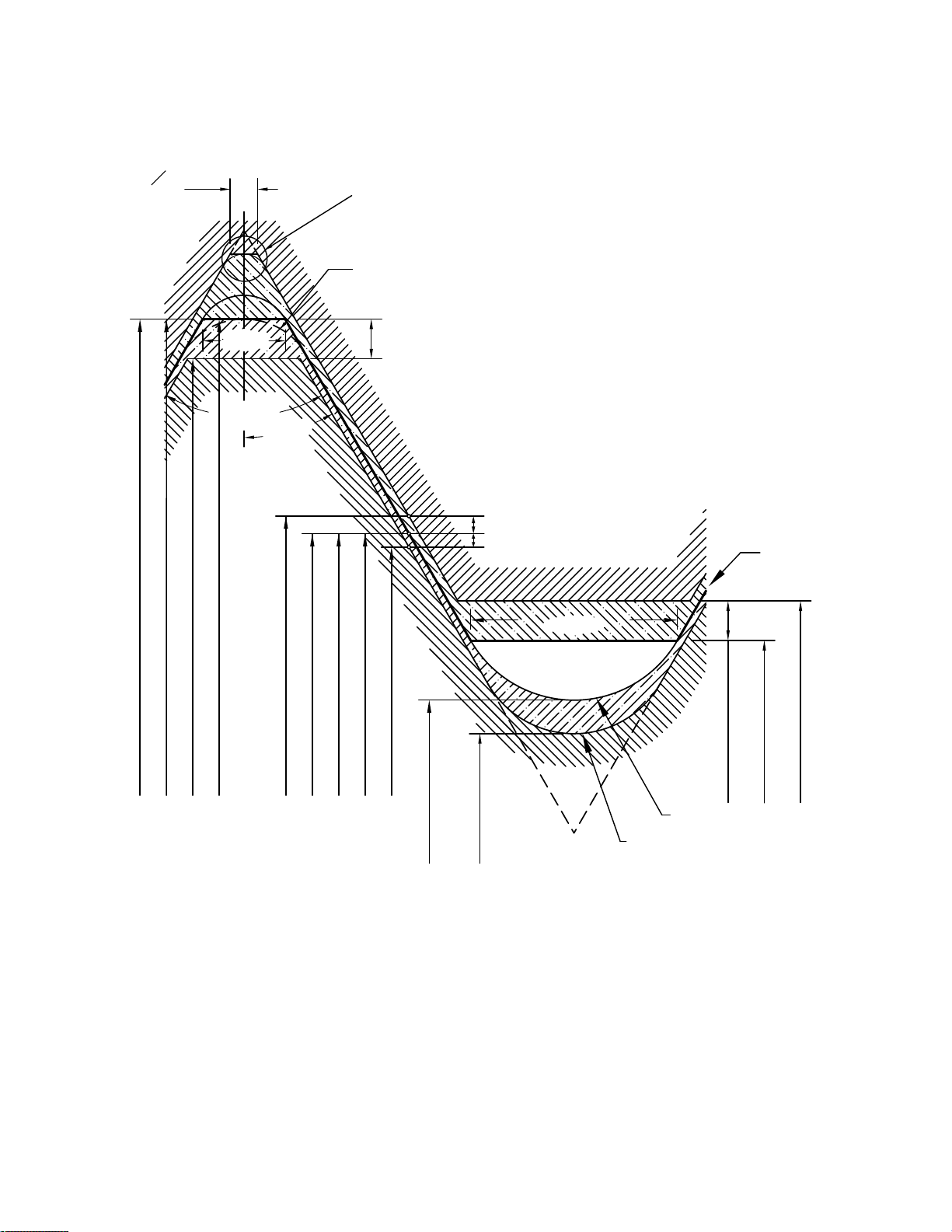
Internal Thread
External Thread
Basic
form
Basic major diameter of external and internal
Minimum major diameter of external
Maximum major diameter of external
Minimum major diameter of internal
Maximum pitch diameter of internal
Minimum pitch diameter of internal
Basic pitch diameter of external and internal
Maximum pitch diameter of external
Minimum pitch diameter of external
½ PD tolerance on internal
½ PD tolerance on external
Minimum minor
diameter of external
½ minor diameter tolerance
of internal thread
Minimum minor diameter
of internal thread
Maximum minor diameter
of internal thread
0.312500P
0.12500P
Maximum minor
diameter of external
In practice, crests may be partially
or fully rounded [see para. 2.3.1.1(b)]
½ tolerance on major diameter of external
In practice roots of internal threads
may be flat or partially or fully rounded
[see para. 2.3.2]
r max.
0.18042196P
r min.
0.15011107P
(minimum reference)
P
24
60 deg
3
0
d
e
g
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Figure 11 Disposition of Diametral Tolerances and Crest Clearance for Unified Inch Screw Thread Series UNJ,
Classes 3A and 3B
GENERAL NOTE: Lead and angle tolerances are defined in section 9.
12

ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 1 Standard Series Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ)
Threads/in.
Nominal
Size, in.
Basic
Major
Primary Secondary
Diameter
0 … 0.0600 … 80 … … … … … … … … … 0
… 1 0.0730 64 72 … … … … … … … … … 1
2 … 0.0860 56 64 … … … … … … … … … 2
… 3 0.0990 48 56 … … … … … … … … … 3
4 … 0.1120 40 48 … … … … … … … … … 4
5 … 0.1250 40 44 … … … … … … … … … 5
6 … 0.1380 32 40 … … … … … … … … UNC 6
8 … 0.1640 32 36 … … … … … … … … UNC 8
10 … 0.1900 24 32 … … … … … … … … UNF 10
… 12 0.2160 24 28 32 … … … … … … UNF UNEF 12
Series With Graded
Pitches Series With Constant Pitches
Extra
Coarse
UNC
Fine
Fine
UNF
UNEF 4–UN 6–UN 8–UN 12–UN 16–UN 20–UN 28–UN 32–UN
Nominal
Size, in.
1
∕
4
5
∕
16
3
∕
8
7
∕
16
1
∕
2
9
∕
16
5
∕
8
…
3
∕
4
…
7
∕
8
…
… 0.2500 20 28 32 … … … … … UNC UNF UNEF
… 0.3125 18 24 32 … … … … … 20 28 UNEF
… 0.3750 16 24 32 … … … … UNC 20 28 UNEF
… 0.4375 14 20 28 … … … … 16 UNF UNEF 32
… 0.5000 13 20 28 … … … … 16 UNF UNEF 32
… 0.5625 12 I8 24 … … … UNC 16 20 28 32
… 0.6250 11 18 24 … … … 12 16 20 28 32
11
∕
16
0.6875 … … 24 … … … 12 16 20 28 32
0.7500 10 16 20 … … … 12 UNF UNEF 28 32
13
∕
16
0.8125 … … 20 … … … 12 16 UNEF 28 32
… 0.8750 9 14 20 … … … 12 16 UNEF 28 32
15
∕
16
0.9375 … … 20 … … … 12 16 UNEF 28 32
1 … 1.0000 8 12 20 … … UNC UNF 16 UNEF 28 32 1
1
… 1
11∕
8
… 13∕
11∕
4
… 15∕
13∕
8
… 17∕
11∕
2
… 19∕
15∕
8
… 111∕
13∕
4
∕
16
… 1.1250 7 12 18 … … 8 UNF 16 20 28 … 11∕
16
… 1.2500 7 12 18 … … 8 UNF 16 20 28 … 11∕
16
… 1.3750 6 12 18 ... UNC 8 UNF 16 20 28 ... 13∕
16
… 1.5000 6 12 18 … UNC 8 UNF 16 20 28 … 11∕
16
… 1.6250 … … 18 … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 15∕
… 1.7500 5 … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 13∕
1.0625 … … 18 … … 8 12 16 20 28 … 11∕
1.1875 … … 18 … … 8 12 16 20 28 … 13∕
1.3125 … … 18 … … 8 12 16 20 28 … 15∕
1.4375 … … 18 … 6 8 12 16 20 28 … 17∕
1.5625 … … 18 … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 19∕
1.6875 … … 18 … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 111∕
16
1
∕
4
5
∕
16
3
∕
8
7
∕
16
1
∕
2
9
∕
16
5
∕
8
11
∕
16
3
∕
4
13
∕
16
7
∕
8
15
∕
16
16
8
16
4
16
8
16
2
16
8
16
4
… 113∕
17∕
8
… 115∕
… 1.8750 … … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 17∕
1.8125 … … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 113∕
16
1.9375 … … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 115∕
16
2 … 2.0000 41∕
… 2
1
∕
2.1250 … … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 21∕
8
… … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 2
2
13
16
8
16
8
ASME B1.1-2019
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 1 Standard Series Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Threads/in.
Nominal
Size, in.
Basic
Major
Primary Secondary
1
2
∕
4
… 23∕
21∕
2
… 25∕
23∕
4
… 27∕
Diameter
… 2.2500 41∕
2.3750 … … … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 23∕
8
… 2.5000 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 20 … … 21∕
2.6250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 20 … … 25∕
8
… 2.7500 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 20 … … 23∕
2.8750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 20 … … 27∕
8
3 … 3.0000 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 20 … … 3
… 3
31∕
4
… 33∕
1
∕
3.1250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 31∕
8
… 3.2500 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 … … … 31∕
3.3750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 33∕
8
Series With Graded
Pitches Series With Constant Pitches
Extra
Coarse
UNC
Fine
Fine
UNF
UNEF 4–UN 6–UN 8–UN 12–UN 16–UN 20–UN 28–UN 32–UN
… … … 6 8 12 16 20 … … 21∕
2
Nominal
Size, in.
4
8
2
8
4
8
8
4
8
31∕
2
… 35∕
33∕
4
… 37∕
… 3.5000 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 … … … 31∕
3.6250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 35∕
8
… 3.7500 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 … … … 33∕
3.8750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 37∕
8
2
8
4
8
4 … 4.0000 4 … … UNC 6 8 12 16 ... ... ... 4
… 4
41∕
4
… 43∕
41∕
2
… 45∕
43∕
4
… 47∕
1
∕
4.1250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 41∕
8
… 4.2500 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 41∕
4.3750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 43∕
8
… 4.5000 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 41∕
4.6250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 45∕
8
… 4.7500 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 43∕
4.8750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 47∕
8
8
4
8
2
8
4
8
5 … 5.0000 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 5
1
∕
… 5
51∕
4
… 53∕
51∕
2
… 55∕
53∕
4
… 57∕
… 5.2500 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 51∕
… 5.5000 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 51∕
… 5.7500 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 53∕
5.1250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 51∕
8
5.3750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 53∕
8
5.6250 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 55∕
8
5.8750 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 57∕
8
8
4
8
2
8
4
8
6 … 6.0000 … … … 4 6 8 12 16 … … … 6
GENERAL NOTE: Series designation shown indicates the UN thread form; however, the UNJ thread form may be specified by substituting
applicable symbol in place of UN in all designations for both internal and external use and the UNR thread form may be specified by substituting
applicable symbol in place of UN in all designations for external use only.
14

Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
d
, and
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
0 – 80 or 0.0600 – 80 UNF 2A 0.0005 0.0595 0.0563 ... 0.0514 0.0496 0.001762 0.0460 0.0415 0.0446 ... 0.0018 0.0014 0.0451 0.0425 0.0023 0.0019
80 3A 0.0000 0.0600 0.0568 … 0.0519 0.0506 0.0013 0.0465 0.0425 0.0451 … 0.0018 0.0014 0.0456 0.0435 0.0023 0.0019
(8) 1 – 64 or 0.0730 – 64 UNC 2A 0.0006 0.0724 0.0686 ... 0.0623 0.0603 0.001970 0.0555 0.0502 0.0538 … 0.0023 0.0017 0.0544 0.0515 0.0028 0.0023
(8) 64 3A 0.0000 0.0730 0.0692 ... 0.0629 0.0614 0.0015 0.0561 0.0513 0.0544 … 0.0023 0.0017 0.0550 0.0526 0.0028 0.0023
(8) 1 – 72 or 0.0730 – 72 UNF 2A 0.0006 0.0724 0.0689 ... 0.0634 0.0615 0.001899 0.0574 0.0525 0.0559 … 0.0020 0.0015 0.0564 0.0536 0.0025 0.0021
(8) 72 3A 0.0000 0.0730 0.0695 ... 0.0640 0.0626 0.0014 0.0580 0.0536 0.0565 … 0.0020 0.0015 0.0570 0.0547 0.0025 0.0021
2 – 56 or 0.0860 – 56 UNC 2A 0.0006 0.0854 0.0813 ... 0.0738 0.0717 0.002127 0.0661 0.0601 0.0641 … 0.0026 0.0019 0.0648 0.0616 0.0032 0.0027
56 3A 0.0000 0.0860 0.0819 ... 0.0744 0.0728 0.0016 0.0667 0.0612 0.0647 … 0.0026 0.0019 0.0654 0.0627 0.0032 0.0027
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019
15
(8) 2 – 64 or 0.0860 – 64 UNF 2A 0.0006 0.0854 0.0816 ... 0.0753 0.0733 0.002040 0.0685 0.0632 0.0668 … 0.0023 0.0017 0.0674 0.0645 0.0028 0.0023
(8) 64 3A 0.0000 0.0860 0.0822 ... 0.0759 0.0744 0.0015 0.0691 0.0643 0.0674 … 0.0023 0.0017 0.0680 0.0656 0.0028 0.0023
3 – 48 or 0.0990 – 48 UNC 2A 0.0007 0.0983 0.0938 ... 0.0848 0.0825 0.002302 0.0757 0.0690 0.0735 … 0.0030 0.0023 0.0743 0.0707 0.0038 0.0031
48 3A 0.0000 0.0990 0.0945 ... 0.0855 0.0838 0.0017 0.0764 0.0703 0.0742 … 0.0030 0.0023 0.0750 0.0720 0.0038 0.0031
3 – 56 or 0.0990 – 56 UNF 2A 0.0007 0.0983 0.0942 ... 0.0867 0.0845 0.002191 0.0790 0.0729 0.0770 … 0.0026 0.0019 0.0777 0.0744 0.0032 0.0027
56 3A 0.0000 0.0990 0.0949 ... 0.0874 0.0858 0.0016 0.0797 0.0742 0.0777 … 0.0026 0.0019 0.0784 0.0757 0.0032 0.0027
4 – 40 or 0.1120 – 40 UNC 2A 0.0008 0.1112 0.1061 ... 0.095 0.0925 0.002507 0.0841 0.0763 0.0814 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.0824 0.0784 0.0045 0.0038
40 3A 0.0000 0.1120 0.1069 ... 0.0958 0.0939 0.0019 0.0849 0.0777 0.0822 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.0832 0.0798 0.0045 0.0038
4 – 48 or 0.1120 – 48 UNF 2A 0.0007 0.1113 0.1068 ... 0.0978 0.0954 0.002361 0.0887 0.0819 0.0865 … 0.0030 0.0023 0.0873 0.0836 0.0038 0.0031
48 3A 0.0000 0.1120 0.1075 ... 0.0985 0.0967 0.0018 0.0894 0.0832 0.0872 … 0.0030 0.0023 0.0880 0.0849 0.0038 0.0031
5 – 40 or 0.1250 – 40 UNC 2A 0.0008 0.1242 0.1191 ... 0.1080 0.1054 0.002562 0.0971 0.0892 0.0944 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.0954 0.0913 0.0045 0.0038
40 3A 0.0000 0.1250 0.1199 ... 0.1088 0.1069 0.0019 0.0979 0.0907 0.0952 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.0962 0.0928 0.0045 0.0038
5 – 44 or 0.1250 – 44 UNF 2A 0.0007 0.1243 0.1195 ... 0.1095 0.1070 0.002484 0.0997 0.0922 0.0972 … 0.0033 0.0025 0.0980 0.0941 0.0041 0.0034
44 3A 0.0000 0.1250 0.1202 ... 0.1102 0.1083 0.0019 0.1004 0.0935 0.0979 … 0.0033 0.0025 0.0987 0.0954 0.0041 0.0034
6 – 32 or 0.1380 – 32 UNC 2A 0.0008 0.1372 0.1312 ... 0.1169 0.1141 0.002820 0.1034 0.0938 0.1000 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1011 0.0964 0.0056 0.0047
(8) 32 3A 0.0000 0.1380 0.1320 ... 0.1177 0.1156 0.0021 0.1042 0.0953 0.1008 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1019 0.0979 0.0056 0.0047
6 – 40 or 0.1380 – 40 UNF 2A 0.0008 0.1372 0.1321 ... 0.1210 0.1184 0.002614 0.1101 0.1022 0.1074 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.1084 0.1043 0.0045 0.0038
40 3A 0.0000 0.1380 0.1329 ... 0.1218 0.1198 0.0020 0.1109 0.1036 0.1082 … 0.0036 0.0027 0.1092 0.1057 0.0045 0.0038
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
, and
d
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
8 – 32 or 0.1640 – 32 UNC 2A 0.0009 0.1631 0.1571 ... 0.1428 0.1399 0.002916 0.1293 0.1196 0.1259 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1270 0.1222 0.0056 0.0047
(8) 32 3A 0.0000 0.1640 0.1580 ... 0.1437 0.1415 0.0022 0.1302 0.1212 0.1268 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1279 0.1238 0.0056 0.0047
8 – 36 or 0.1640 – 36 UNF 2A 0.0008 0.1632 0.1577 ... 0.1452 0.1424 0.002804 0.1331 0.1244 0.1301 … 0.0040 0.0030 0.1312 0.1267 0.0050 0.0042
36 3A 0.0000 0.1640 0.1585 ... 0.1460 0.1439 0.0021 0.1339 0.1259 0.1309 … 0.0040 0.0030 0.1320 0.1282 0.0050 0.0042
(8) 10 – 24 or 0.1900 – 24 UNC 2A 0.0010 0.1890 0.1818 ... 0.1619 0.1586 0.003319 0.1439 0.1315 0.1394 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.1409 0.1350 0.0075 0.0063
24 3A 0.0000 0.190 0.1828 ... 0.1629 0.1604 0.0025 0.1449 0.1333 0.1404 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.1419 0.1368 0.0075 0.0063
10 – 32 or 0.1900 – 32 UNF 2A 0.0009 0.1891 0.1831 ... 0.1688 0.1658 0.003004 0.1553 0.1455 0.1519 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1530 0.1481 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.1900 0.1840 ... 0.1697 0.1674 0.0023 0.1562 0.1471 0.1528 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1539 0.1497 0.0056 0.0047
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019
16
12 – 24 or 0.2160 – 24 UNC 2A 0.0010 0.2150 0.2078 ... 0.1879 0.1845 0.003400 0.1699 0.1574 0.1654 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.1669 0.1609 0.0075 0.0063
24 3A 0.0000 0.2160 0.2088 ... 0.1889 0.1863 0.0026 0.1709 0.1592 0.1664 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.1679 0.1627 0.0075 0.0063
12 – 28 or 0.2160 – 28 UNF 2A 0.0010 0.2150 0.2085 ... 0.1918 0.1886 0.003224 0.1763 0.1654 0.1725 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.1738 0.1684 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.2160 0.2095 ... 0.1928 0.1904 0.0024 0.1773 0.1672 0.1735 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.1748 0.1702 0.0064 0.0054
(8) 12 – 32 or 0.2160 – 32 UNEF 2A 0.0010 0.2150 0.2090 ... 0.1947 0.1915 0.003183 0.1812 0.1712 0.1778 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1789 0.1738 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.2160 0.2100 ... 0.1957 0.1933 0.0024 0.1822 0.1730 0.1788 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.1799 0.1756 0.0056 0.0047
1
∕4– 20 or 0.2500 – 20 UNC 1A 0.0011 0.2489 0.2367 ... 0.2164 0.2108 0.0056 0.1948 0.1783 0.1894 … 0.0072 0.0054 ... ... ... ...
20 2A 0.0011 0.2489 0.2408 0.2367 0.2164 0.2127 0.003731 0.1948 0.1802 0.1894 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.1911 0.1844 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.2500 0.2419 ... 0.2175 0.2147 0.0028 0.1959 0.1822 0.1905 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.1922 0.1864 0.009 0.0075
1
∕4– 28 or 0.2500 – 28 UNF 1A 0.0010 0.2490 0.2392 ... 0.2258 0.2208 0.0050 0.2103 0.1976 0.2065 … 0.0052 0.0039 ... ... ... ...
28 2A 0.0010 0.2490 0.2425 ... 0.2258 0.2225 0.003322 0.2103 0.1993 0.2065 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.2078 0.2023 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.2500 0.2435 ... 0.2268 0.2243 0.0025 0.2113 0.2011 0.2075 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.2088 0.2041 0.0064 0.0054
1
∕4– 32 or 0.2500 – 32 UNEF 2A 0.0010 0.2490 0.2430 ... 0.2287 0.2255 0.003228 0.2152 0.2052 0.2118 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.2129 0.2078 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.2500 0.2440 ... 0.2297 0.2273 0.0024 0.2162 0.2070 0.2128 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.2139 0.2096 0.0056 0.0047
5
∕16– 18 or 0.3125 – 18 UNC 1A 0.0012 0.3113 0.2982 ... 0.2752 0.2691 0.0061 0.2512 0.2330 0.2451 … 0.0080 0.0060 ... ... ... ...
18 2A 0.0012 0.3113 0.3026 0.2982 0.2752 0.2712 0.004041 0.2512 0.2351 0.2451 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.2471 0.2398 0.0100 0.0083
18 3A 0.0000 0.3125 0.3038 ... 0.2764 0.2734 0.0030 0.2524 0.2373 0.2463 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.2483 0.2420 0.0100 0.0083
5
(8)
∕16– 20 or 0.3125 – 20 UN 2A 0.0012 0.3113 0.3032 ... 0.2788 0.2747 0.004060 0.2572 0.2422 0.2518 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.2535 0.2464 0.0090 0.0075
(8) 20 3A 0.0000 0.3125 0.3044 ... 0.2800 0.2770 0.0030 0.2584 0.2445 0.2530 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.2547 0.2487 0.0090 0.0075

Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
17
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
d
, and
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
5
∕16– 24 or 0.3125 – 24 UNF 1A 0.0011 0.3114 0.3006 ... 0.2843 0.2788 0.0055 0.2663 0.2517 0.2618 … 0.0060 0.0045 ... ... ... ...
24 2A 0.0011 0.3114 0.3042 ... 0.2843 0.2806 0.003660 0.2663 0.2535 0.2618 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.2633 0.2570 0.0075 0.0063
24 3A 0.0000 0.3125 0.3053 ... 0.2854 0.2827 0.0027 0.2674 0.2556 0.2629 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.2644 0.2591 0.0075 0.0063
5
(8)
∕16– 28 or 0.3125 – 28 UN 2A 0.00100 0.3115 0.3050 ... 0.2883 0.2848 0.003495 0.2728 0.2616 0.2690 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.2703 0.2646 0.0064 0.0054
(8) 28 3A 0.0000 0.3125 0.3060 ... 0.2893 0.2867 0.0026 0.2738 0.2635 0.2700 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.2713 0.2665 0.0064 0.0054
5
(8)
∕16– 32 or 0.3125 – 32 UNEF 2A 0.0010 0.3115 0.3055 ... 0.2912 0.2879 0.003301 0.2777 0.2676 0.2743 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.2754 0.2702 0.0056 0.0047
(8) 32 3A 0.0000 0.3125 0.3065 ... 0.2922 0.2897 0.0025 0.2787 0.2694 0.2753 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.2764 0.2720 0.0056 0.0047
3
∕8– 16 or 0.3750 – 16 UNC 1A 0.0013 0.3737 0.3595 ... 0.3331 0.3266 0.0065 0.3060 0.2860 0.2993 … 0.0090 0.0068 ... ... ... ...
16 2A 0.0013 0.3737 0.3643 0.3595 0.3331 0.3287 0.004363 0.3060 0.2881 0.2993 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.3015 0.2933 0.0113 0.0094
16 3A 0.0000 0.3750 0.3656 ... 0.3344 0.3311 0.0033 0.3073 0.2905 0.3006 … 0.009 0.0068 0.3028 0.2957 0.0113 0.0094
3
∕8– 20 or 0.3750 – 20 UN 2A 0.0012 0.3738 0.3657 ... 0.3413 0.3372 0.004124 0.3197 0.3047 0.3143 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.3160 0.3089 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.3750 0.3669 ... 0.3425 0.3394 0.0031 0.3209 0.3069 0.3155 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.3172 0.3111 0.0090 0.0075
3
∕8– 24 or 0.3750 – 24 UNF 1A 0.0011 0.3739 0.3631 ... 0.3468 0.3411 0.0057 0.3288 0.3140 0.3243 … 0.0060 0.0045 ... ... ... ...
24 2A 0.0011 0.3739 0.3667 ... 0.3468 0.3430 0.003804 0.3288 0.3159 0.3243 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.3258 0.3194 0.0075 0.0063
24 3A 0.0000 0.3750 0.3678 ... 0.3479 0.3450 0.0029 0.3299 0.3179 0.3254 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.3269 0.3214 0.0075 0.0063
3
∕8– 28 or 0.3750 – 28 UN 2A 0.0011 0.3739 0.3674 ... 0.3507 0.3471 0.003559 0.3352 0.3239 0.3314 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.3327 0.3269 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.3750 0.3685 ... 0.3518 0.3491 0.0027 0.3363 0.3259 0.3325 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.3338 0.3289 0.0064 0.0054
3
∕8– 32 or 0.3750 – 32 UNEF 2A 0.0010 0.3740 0.3680 ... 0.3537 0.3503 0.003365 0.3402 0.3300 0.3368 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.3379 0.3326 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.3750 0.3690 ... 0.3547 0.3522 0.0025 0.3412 0.3319 0.3378 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.3389 0.3345 0.0056 0.0047
7
∕16– 14 or 0.4375 – 14 UNC 1A 0.0014 0.4361 0.4206 ... 0.3897 0.3826 0.0071 0.3588 0.3362 0.3510 … 0.0103 0.0077 ... ... ... ...
14 2A 0.0014 0.4361 0.4258 0.4206 0.3897 0.3850 0.004713 0.3588 0.3386 0.3510 … 0.0103 0.0077 0.3536 0.3446 0.0129 0.0107
14 3A 0.0000 0.4375 0.4272 ... 0.3911 0.3876 0.0035 0.3602 0.3412 0.3524 … 0.0103 0.0077 0.3550 0.3472 0.0129 0.0107
7
(8)
∕16– 16 or 0.4375 – 16 UN 2A 0.0014 0.4361 0.4267 ... 0.3955 0.3909 0.004626 0.3684 0.3503 0.3617 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.3639 0.3555 0.0113 0.0094
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.4375 0.4281 ... 0.3969 0.3934 0.0035 0.3698 0.3528 0.3631 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.3653 0.3580 0.0113 0.0094
7
(8)
∕16– 20 or 0.4375 – 20 UNF 1A 0.0013 0.4362 0.4240 ... 0.4037 0.3974 0.0063 0.3821 0.3649 0.3767 … 0.0072 0.0054 ... ... ... ...
20 2A 0.0013 0.4362 0.4281 ... 0.4037 0.3995 0.004167 0.3821 0.3670 0.3767 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.3784 0.3712 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.4375 0.4294 ... 0.4050 0.4019 0.0031 0.3834 0.3694 0.3780 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.3797 0.3736 0.0090 0.0075
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019
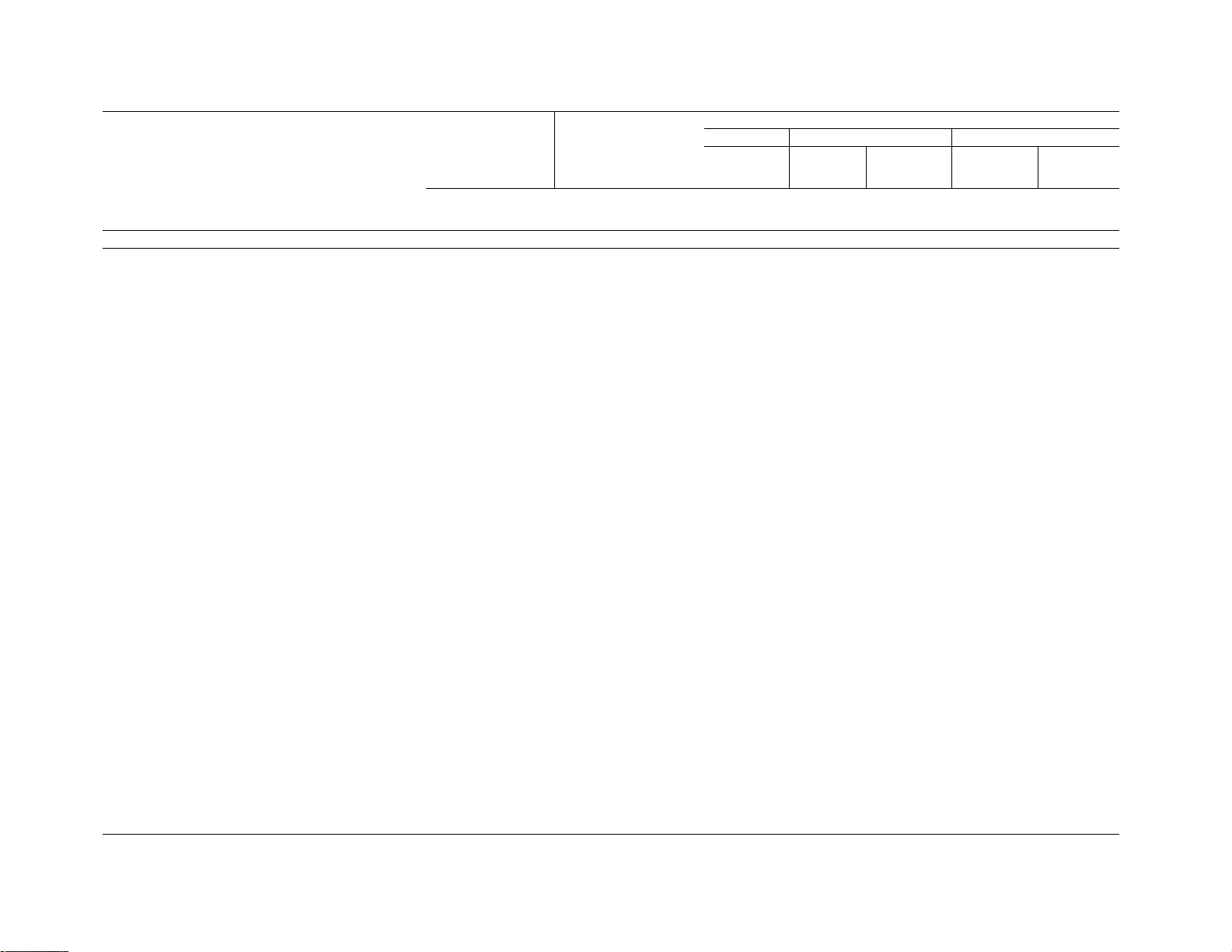
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
18
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
, and
d
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
7
(8)
∕16– 28 or 0.4375 – 28 UNEF 2A 0.0011 0.4364 0.4299 ... 0.4132 0.4096 0.003616 0.3977 0.3864 0.3939 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.3952 0.3894 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.4375 0.4310 ... 0.4143 0.4116 0.0027 0.3988 0.3884 0.3950 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.3963 0.3914 0.0064 0.0054
7
(8)
∕16– 32 or 0.4375 – 32 UN 2A 0.0010 0.4365 0.4305 ... 0.4162 0.4128 0.003422 0.4027 0.3925 0.3993 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.4004 0.3951 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.4375 0.4315 ... 0.4172 0.4146 0.0026 0.4037 0.3943 0.4003 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.4014 0.3969 0.0056 0.0047
1
∕2– 13 or 0.5000 – 13 UNC 1A 0.0015 0.4985 0.4822 ... 0.4485 0.4411 0.0074 0.4152 0.3911 0.4069 … 0.0111 0.0083 ... ... ... ...
13 2A 0.0015 0.4985 0.4876 0.4822 0.4485 0.4435 0.004965 0.4152 0.3935 0.4069 … 0.0111 0.0083 0.4096 0.4000 0.0139 0.0115
13 3A 0.0000 0.5000 0.4891 ... 0.4500 0.4463 0.0037 0.4167 0.3963 0.4084 … 0.0111 0.0083 0.4111 0.4028 0.0139 0.0115
1
∕2– 16 or 0.5000 – 16 UN 2A 0.0014 0.4986 0.4892 ... 0.4580 0.4533 0.004678 0.4309 0.4127 0.4242 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.4264 0.4179 0.0113 0.0094
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.5000 0.4906 ... 0.4594 0.4559 0.0035 0.4323 0.4153 0.4256 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.4278 0.4205 0.0113 0.0094
1
∕2– 20 or 0.5000 – 20 UNF 1A 0.0013 0.4987 0.4865 ... 0.4662 0.4598 0.0064 0.4446 0.4273 0.4392 … 0.0072 0.0054 ... ... ... ...
20 2A 0.0013 0.4987 0.4906 ... 0.4662 0.4619 0.004288 0.4446 0.4294 0.4392 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.4409 0.4336 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.5000 0.4919 ... 0.4675 0.4643 0.0032 0.4459 0.4318 0.4405 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.4422 0.4360 0.0090 0.0075
1
∕2– 28 or 0.5000 – 28 UNEF 2A 0.0011 0.4989 0.4924 ... 0.4757 0.4720 0.003668 0.4602 0.4488 0.4564 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.4577 0.4518 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.5000 0.4935 ... 0.4768 0.4740 0.0028 0.4613 0.4508 0.4575 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.4588 0.4538 0.0064 0.0054
1
∕2– 32 or 0.5000 – 32 UN 2A 0.0010 0.4990 0.4930 ... 0.4787 0.4752 0.003474 0.4652 0.4549 0.4618 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.4629 0.4575 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.5000 0.4940 ... 0.4797 0.4771 0.0026 0.4662 0.4568 0.4628 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.4639 0.4594 0.0056 0.0047
9
∕16– 12 or 0.5625 – 12 UNC 1A 0.0016 0.5609 0.5437 ... 0.5068 0.4990 0.0078 0.4707 0.4449 0.4617 … 0.0120 0.0090 ... ... ... ...
12 2A 0.0016 0.5609 0.5495 0.5437 0.5068 0.5016 0.005225 0.4707 0.4475 0.4617 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.4647 0.4545 0.0150 0.0125
12 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5511 ... 0.5084 0.5045 0.0039 0.4723 0.4504 0.4633 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.4663 0.4574 0.0150 0.0125
9
∕16– 16 or 0.5625 – 16 UN 2A 0.0014 0.5611 0.5517 ... 0.5205 0.5158 0.004725 0.4934 0.4752 0.4867 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.4889 0.4804 0.0113 0.0094
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5531 ... 0.5219 0.5184 0.0035 0.4948 0.4778 0.4881 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.4903 0.4830 0.0113 0.0094
9
∕16– 18 or 0.5625 – 18 UNF 1A 0.0014 0.5611 0.5480 ... 0.5250 0.5182 0.0068 0.5010 0.4821 0.4949 … 0.0080 0.0060 ... ... ... ...
18 2A 0.0014 0.5611 0.5524 ... 0.5250 0.5205 0.004547 0.501 0.4844 0.4949 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.4969 0.4891 0.0100 0.0083
18 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5538 ... 0.5264 0.5230 0.0034 0.5024 0.4869 0.4963 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.4983 0.4916 0.0100 0.0083
9
(8)
∕16– 20 or 0.5625 – 20 UN 2A 0.0013 0.5612 0.5531 ... 0.5287 0.5244 0.004280 0.5071 0.4919 0.5017 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.5034 0.4961 0.0090 0.0075
(8) 20 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5544 ... 0.5300 0.5268 0.0032 0.5084 0.4943 0.5030 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.5047 0.4985 0.0090 0.0075
9
∕16– 24 or 0.5625 – 24 UNEF 2A 0.0012 0.5613 0.5541 ... 0.5342 0.5302 0.003960 0.5162 0.5031 0.5117 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.5132 0.5066 0.0075 0.0063
(8)
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019

Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
19
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
d
, and
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
(8) 24 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5553 ... 0.5354 0.5324 0.0030 0.5174 0.5053 0.5129 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.5144 0.5088 0.0075 0.0063
9
∕16– 28 or 0.5625 – 28 UN 2A 0.0011 0.5614 0.5549 ... 0.5382 0.5345 0.003715 0.5227 0.5113 0.5189 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.5202 0.5143 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5560 ... 0.5393 0.5365 0.0028 0.5238 0.5133 0.5200 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.5213 0.5163 0.0064 0.0054
9
∕16– 32 or 0.5625 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.5614 0.5554 ... 0.5411 0.5376 0.003521 0.5276 0.5173 0.5242 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.5253 0.5199 0.0056 0.0047
(8)
32 3A 0.0000 0.5625 0.5565 ... 0.5422 0.5396 0.0026 0.5287 0.5193 0.5253 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.5264 0.5219 0.0056 0.0047
5
(8)
∕8– 11 or 0.625 – 11 UNC 1A 0.0017 0.6233 0.6051 ... 0.5643 0.5560 0.0083 0.5249 0.4970 0.5150 … 0.0131 0.0098 ... ... ... ...
(8) 11 2A 0.0017 0.6233 0.6112 0.6052 0.5643 0.5588 0.005501 0.5249 0.4998 0.5150 … 0.0131 0.0098 0.5184 0.5074 0.0164 0.0136
11 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6129 ... 0.5660 0.5619 0.0041 0.5266 0.5029 0.5167 … 0.0131 0.0098 0.5201 0.5105 0.0164 0.0136
5
∕8– 12 or 0.625 – 12 UN 2A 0.0016 0.6234 0.6120 ... 0.5693 0.5639 0.005443 0.5332 0.5098 0.5242 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.5272 0.5168 0.0150 0.0125
12 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6136 ... 0.5709 0.5668 0.0041 0.5348 0.5127 0.5258 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.5288 0.5197 0.0150 0.0125
5
∕8– 16 or 0.6250 – 16 UN 2A 0.0014 0.6236 0.6142 ... 0.5830 0.5782 0.004769 0.5559 0.5376 0.5492 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.5514 0.5428 0.0113 0.0094
16 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6156 ... 0.5844 0.5808 0.0036 0.5573 0.5402 0.5506 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.5528 0.5454 0.0113 0.0094
5
∕8– 18 or 0.6250 – 18 UNF 1A 0.0014 0.6236 0.6105 ... 0.5875 0.5805 0.0070 0.5635 0.5444 0.5574 … 0.0080 0.0060 ... ... ... ...
18 2A 0.0014 0.6236 0.6149 ... 0.5875 0.5828 0.004652 0.5635 0.5467 0.5574 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.5594 0.5514 0.0100 0.0083
18 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6163 ... 0.5889 0.5854 0.0035 0.5649 0.5493 0.5588 … 0.0080 0.0060 0.5608 0.5540 0.0100 0.0083
5
∕8– 20 or 0.6250 – 20 UN 2A 0.0013 0.6237 0.6156 ... 0.5912 0.5869 0.004324 0.5696 0.5544 0.5642 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.5659 0.5586 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6169 ... 0.5925 0.5893 0.0032 0.5709 0.5568 0.5655 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.5672 0.5610 0.0090 0.0075
5
∕8– 24 or 0.6250 – 24 UNEF 2A 0.0012 0.6238 0.6166 ... 0.5967 0.5927 0.004004 0.5787 0.5656 0.5742 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.5757 0.5691 0.0075 0.0063
24 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6178 ... 0.5979 0.5949 0.0030 0.5799 0.5678 0.5754 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.5769 0.5713 0.0075 0.0063
5
∕8– 28 or 0.6250 – 28 UN 2A 0.0011 0.6239 0.6174 ... 0.6007 0.5969 0.003759 0.5852 0.5737 0.5814 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.5827 0.5767 0.0064 0.0054
28 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6185 ... 0.6018 0.5990 0.0028 0.5863 0.5758 0.5825 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.5838 0.5788 0.0064 0.0054
5
∕8– 32 or 0.6250 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.6239 0.6179 ... 0.6036 0.6000 0.003565 0.5901 0.5797 0.5867 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.5878 0.5823 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.6250 0.6190 ... 0.6047 0.6020 0.0027 0.5912 0.5817 0.5878 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.5889 0.5843 0.0056 0.0047
11
(8)
∕16– 12 or 0.6875 – 12 UN 2A 0.0016 0.6859 0.6745 ... 0.6318 0.6263 0.005485 0.5957 0.5722 0.5867 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.5897 0.5792 0.0150 0.0125
12 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6761 ... 0.6334 0.6293 0.0041 0.5973 0.5752 0.5883 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.5913 0.5822 0.0150 0.0125
11
∕16– 16 or 0.6875 – 16 UN 2A 0.0014 0.6861 0.6767 ... 0.6455 0.6407 0.004811 0.6184 0.6001 0.6117 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.6139 0.6053 0.0113 0.0094
(8)
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019
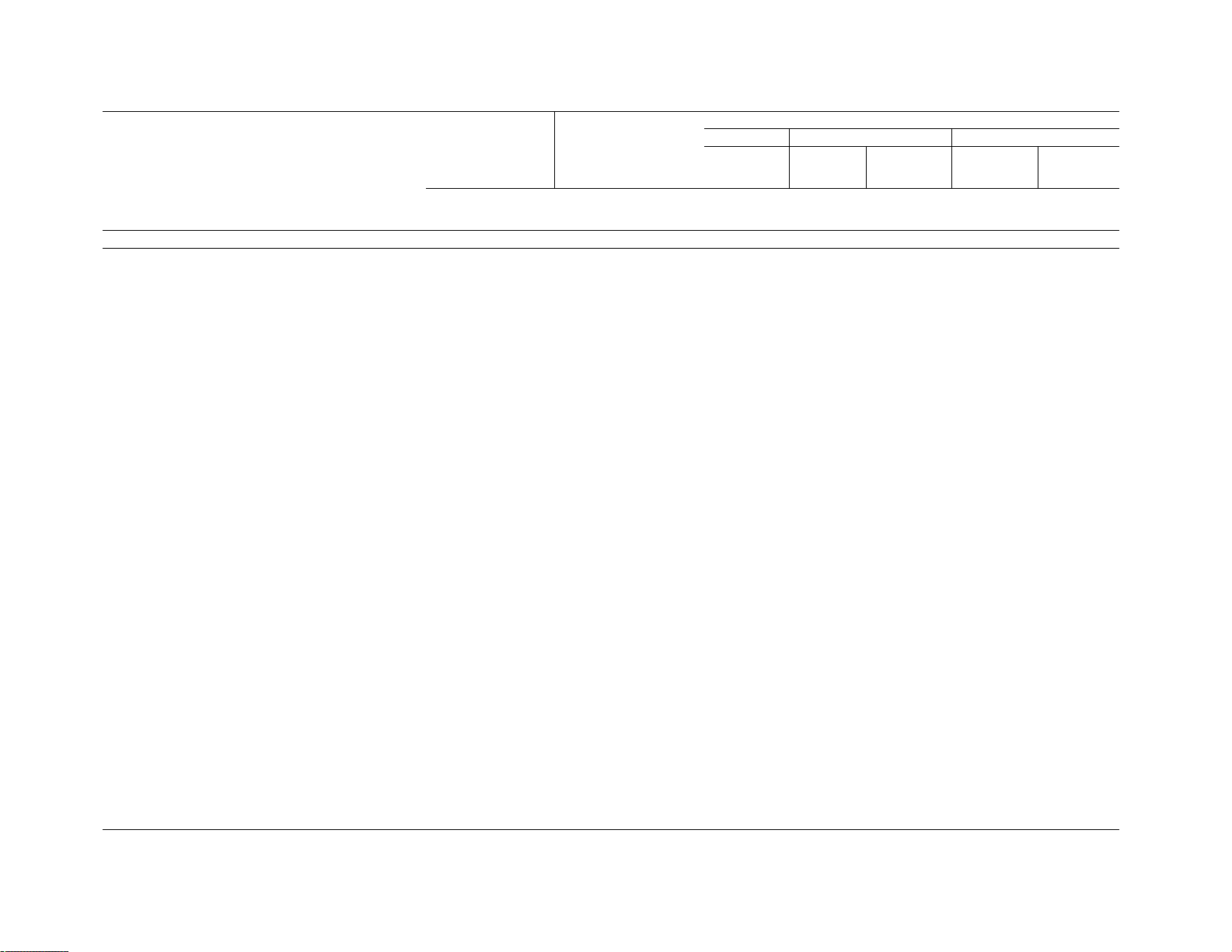
Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
20
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
, and
d
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
16 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6781 ... 0.6469 0.6433 0.0036 0.6198 0.6027 0.6131 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.6153 0.6079 0.0113 0.0094
11
(8)
∕16– 20 or 0.6875 – 20 UN 2A 0.0013 0.6862 0.6781 ... 0.6537 0.6493 0.004366 0.6321 0.6168 0.6267 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.6284 0.6210 0.0090 0.0075
(8) 20 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6794 ... 0.6550 0.6517 0.0033 0.6334 0.6192 0.6280 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.6297 0.6234 0.0090 0.0075
11
∕16– 24 or 0.6875 – 24 UNEF 2A 0.0012 0.6863 0.6791 ... 0.6592 0.6552 0.004046 0.6412 0.6281 0.6367 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.6382 0.6316 0.0075 0.0063
(8)
24 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6803 ... 0.6604 0.6574 0.0030 0.6424 0.6303 0.6379 … 0.0060 0.0045 0.6394 0.6338 0.0075 0.0063
11
∕16– 28 or 0.6875 – 28 UN 2A 0.0011 0.6864 0.6799 ... 0.6632 0.6594 0.003801 0.6477 0.6362 0.6439 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.6452 0.6392 0.0064 0.0054
(8) 28 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6810 ... 0.6643 0.6614 0.0029 0.6488 0.6382 0.6450 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.6463 0.6412 0.0064 0.0054
11
(8)
∕16– 32 or 0.6875 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.6864 0.6804 ... 0.6661 0.6625 0.003607 0.6526 0.6422 0.6492 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.6503 0.6448 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.6875 0.6815 ... 0.6672 0.6645 0.0027 0.6537 0.6442 0.6503 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.6514 0.6468 0.0056 0.0047
3
∕4– 10 or 0.7500 – 10 UNC 1A 0.0018 0.7482 0.7288 ... 0.6832 0.6744 0.0088 0.6399 0.6094 0.6291 … 0.0144 0.0108 ... ... ... ...
10 2A 0.0018 0.7482 0.7353 0.7288 0.6832 0.6773 0.005894 0.6399 0.6123 0.6291 … 0.0144 0.0108 0.6327 0.6207 0.0180 0.0150
10 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7371 ... 0.6850 0.6806 0.0044 0.6417 0.6156 0.6309 … 0.0144 0.0108 0.6345 0.6240 0.0180 0.0150
3
∕4– 12 or 0.7500 – 12 UN 2A 0.0017 0.7483 0.7369 ... 0.6942 0.6887 0.005524 0.6581 0.6346 0.6491 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.6521 0.6416 0.0150 0.0125
12 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7386 ... 0.6959 0.6918 0.0041 0.6598 0.6377 0.6508 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.6538 0.6447 0.0150 0.0125
3
∕4– 16 or 0.7500 – 16 UNF 1A 0.0015 0.7485 0.7343 ... 0.7079 0.7004 0.0075 0.6808 0.6598 0.6741 … 0.0090 0.0068 ... ... ... ...
16 2A 0.0015 0.7485 0.7391 ... 0.7079 0.7029 0.005024 0.6808 0.6623 0.6741 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.6763 0.6675 0.0113 0.0094
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7406 ... 0.7094 0.7056 0.0038 0.6823 0.6650 0.6756 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.6778 0.6702 0.0113 0.0094
3
∕4– 20 or 0.7500 – 20 UNEF 2A 0.0013 0.7487 0.7406 ... 0.7162 0.7118 0.004405 0.6946 0.6793 0.6892 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.6909 0.6835 0.0090 0.0075
20 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7419 ... 0.7175 0.7142 0.0033 0.6959 0.6817 0.6905 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.6922 0.6859 0.0090 0.0075
3
∕4– 28 or 0.7500 – 28 UN 2A 0.0012 0.7488 0.7423 ... 0.7256 0.7218 0.003840 0.7101 0.6986 0.7063 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.7076 0.7016 0.0064 0.0054
(8) 28 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7435 ... 0.7268 0.7239 0.0029 0.7113 0.7007 0.7075 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.7088 0.7037 0.0064 0.0054
3
∕4– 32 or 0.7500 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.7489 0.7429 ... 0.7286 0.7250 0.003646 0.7151 0.7047 0.7117 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.7128 0.7073 0.0056 0.0047
32 3A 0.0000 0.7500 0.7440 ... 0.7297 0.7270 0.0027 0.7162 0.7067 0.7128 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.7139 0.7093 0.0056 0.0047
13
∕16– 12 or 0.8125 – 12 UN 2A 0.0017 0.8108 0.7994 ... 0.7567 0.7511 0.005561 0.7206 0.6970 0.7116 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.7146 0.7040 0.0150 0.0125
(8)
(8) 12 3A 0.0000 0.8125 0.8011 ... 0.7584 0.7542 0.0042 0.7223 0.7001 0.7133 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.7163 0.7071 0.0150 0.0125
13
(8)
∕16– 16 or 0.8125 – 16 UN 2A 0.0015 0.8110 0.8016 ... 0.7704 0.7655 0.004887 0.7433 0.7249 0.7366 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.7388 0.7301 0.0113 0.0094
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019

Copyrighted material licensed to University of Toronto by Clarivate Analytics (US) LLC, subscriptions.techstreet.com, downloaded on 2020-08-15 07:29:54 +0000 by University of Toronto User.
No further reproduction or distribution is permitted.
Table 2A Limits of Size for Standard Series External Threads (UN, UNR, and UNJ) (Cont’d)
Minor Diameter, d
Reference
Diameter
[Note (6)] Radius Diameter Radius
21
Nominal Size
and
Threads/in.
Series
Designa-
tion
Class
[Note
(1)]
Allowance,
es
Major
Diameter,
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
Pitch Diameter,
d
, and
2
Functional
Diameter
Max.
[Note
(2)] Min.
[Note (4)]
Tolerance,
Td
2
[Note (5)] Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min.
d
Min.
[Note
(3)]
UN UNR UNJ
Reference
Diameter
[Notes (6), (7)]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.8125 0.8031 ... 0.7719 0.7682 0.0037 0.7448 0.7276 0.7381 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.7403 0.7328 0.0113 0.0094
13
(8)
∕16– 20 or 0.8125 – 20 UNEF 2A 0.0013 0.8112 0.8031 ... 0.7787 0.7743 0.004442 0.7571 0.7418 0.7517 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.7534 0.7460 0.0090 0.0075
(8) 20 3A 0.0000 0.8125 0.8044 ... 0.7800 0.7767 0.0033 0.7584 0.7442 0.7530 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.7547 0.7484 0.0090 0.0075
13
∕16– 28 or 0.8125 – 28 UN 2A 0.0012 0.8113 0.8048 ... 0.7881 0.7842 0.003877 0.7726 0.7610 0.7688 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.7701 0.7640 0.0064 0.0054
(8)
(8) 28 3A 0.0000 0.8125 0.8060 ... 0.7893 0.7864 0.0029 0.7738 0.7632 0.7700 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.7713 0.7662 0.0064 0.0054
13
(8)
∕16– 32 or 0.8125 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.8114 0.8054 ... 0.7911 0.7874 0.003683 0.7776 0.7671 0.7742 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.7753 0.7697 0.0056 0.0047
(8) 32 3A 0.0000 0.8125 0.8065 ... 0.7922 0.7894 0.0028 0.7787 0.7691 0.7753 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.7764 0.7717 0.0056 0.0047
7
∕8– 9 or 0.8750 – 9 UNC 1A 0.0019 0.8731 0.8523 ... 0.8009 0.7914 0.0095 0.7528 0.7192 0.7408 … 0.0160 0.0120 ... ... ... ...
9 2A 0.0019 0.8731 0.8592 0.8523 0.8009 0.7946 0.006305 0.7528 0.7224 0.7408 … 0.0160 0.0120 0.7448 0.7317 0.0200 0.0167
9 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8611 ... 0.8028 0.7981 0.0047 0.7547 0.7259 0.7427 … 0.0160 0.0120 0.7467 0.7352 0.0200 0.0167
7
(8)
∕8– 12 or 0.8750 – 12 UN 2A 0.0017 0.8733 0.8619 ... 0.8192 0.8136 0.005596 0.7831 0.7595 0.7741 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.7771 0.7665 0.0150 0.0125
(8) 12 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8636 ... 0.8209 0.8167 0.0042 0.7848 0.7626 0.7758 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.7788 0.7696 0.0150 0.0125
7
∕8– 14 or 0.8750 – 14 UNF 1A 0.0016 0.8734 0.8579 ... 0.8270 0.8189 0.0081 0.7961 0.7725 0.7883 … 0.0103 0.0077 ... ... ... ...
(8)
(8) 14 2A 0.0016 0.8734 0.8631 ... 0.8270 0.8216 0.005420 0.7961 0.7752 0.7883 … 0.0103 0.0077 0.7909 0.7812 0.0129 0.0107
(8) 14 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8647 ... 0.8286 0.8245 0.0041 0.7977 0.7781 0.7899 … 0.0103 0.0077 0.7925 0.7841 0.0129 0.0107
7
(8)
∕8– 16 or 0.8750 – 16 UN 2A 0.0015 0.8735 0.8641 ... 0.8329 0.8280 0.004922 0.8058 0.7874 0.7991 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.8013 0.7926 0.0113 0.0094
(8) 16 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8656 ... 0.8344 0.8307 0.0037 0.8073 0.7901 0.8006 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.8028 0.7953 0.0113 0.0094
7
∕8– 20 or 0.8750 – 20 UNEF 2A 0.0013 0.8737 0.8656 ... 0.8412 0.8367 0.004477 0.8196 0.8042 0.8142 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.8159 0.8084 0.0090 0.0075
(8)
(8) 20 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8669 ... 0.8425 0.8391 0.0034 0.8209 0.8066 0.8155 … 0.0072 0.0054 0.8172 0.8108 0.0090 0.0075
7
(8)
∕8– 28 or 0.8750 – 28 UN 2A 0.0012 0.8738 0.8673 ... 0.8506 0.8467 0.003912 0.8351 0.8235 0.8313 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.8326 0.8265 0.0064 0.0054
(8) 28 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8685 ... 0.8518 0.8489 0.0029 0.8363 0.8257 0.8325 … 0.0052 0.0039 0.8338 0.8287 0.0064 0.0054
7
∕8– 32 or 0.8750 – 32 UN 2A 0.0011 0.8739 0.8679 ... 0.8536 0.8499 0.003718 0.8401 0.8296 0.8367 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.8378 0.8322 0.0056 0.0047
(8)
(8) 32 3A 0.0000 0.8750 0.8690 ... 0.8547 0.8519 0.0028 0.8412 0.8316 0.8378 … 0.0045 0.0034 0.8389 0.8342 0.0056 0.0047
15
(8)
∕16– 12 or 0.9375 – 12 UN 2A 0.0017 0.9358 0.9244 ... 0.8817 0.8761 0.005629 0.8456 0.8220 0.8366 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.8396 0.8290 0.0150 0.0125
(8) 12 3A 0.0000 0.9375 0.9261 ... 0.8834 0.8792 0.0042 0.8473 0.8251 0.8383 … 0.0120 0.0090 0.8413 0.8321 0.0150 0.0125
15
∕16– 16 or 0.9375 – 16 UN 2A 0.0015 0.9360 0.9266 ... 0.8954 0.8904 0.004955 0.8683 0.8498 0.8616 … 0.0090 0.0068 0.8638 0.8550 0.0113 0.0094
(8)
/Root Radius
1
ASME B1.1-2019
 Loading...
Loading...