Page 1
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
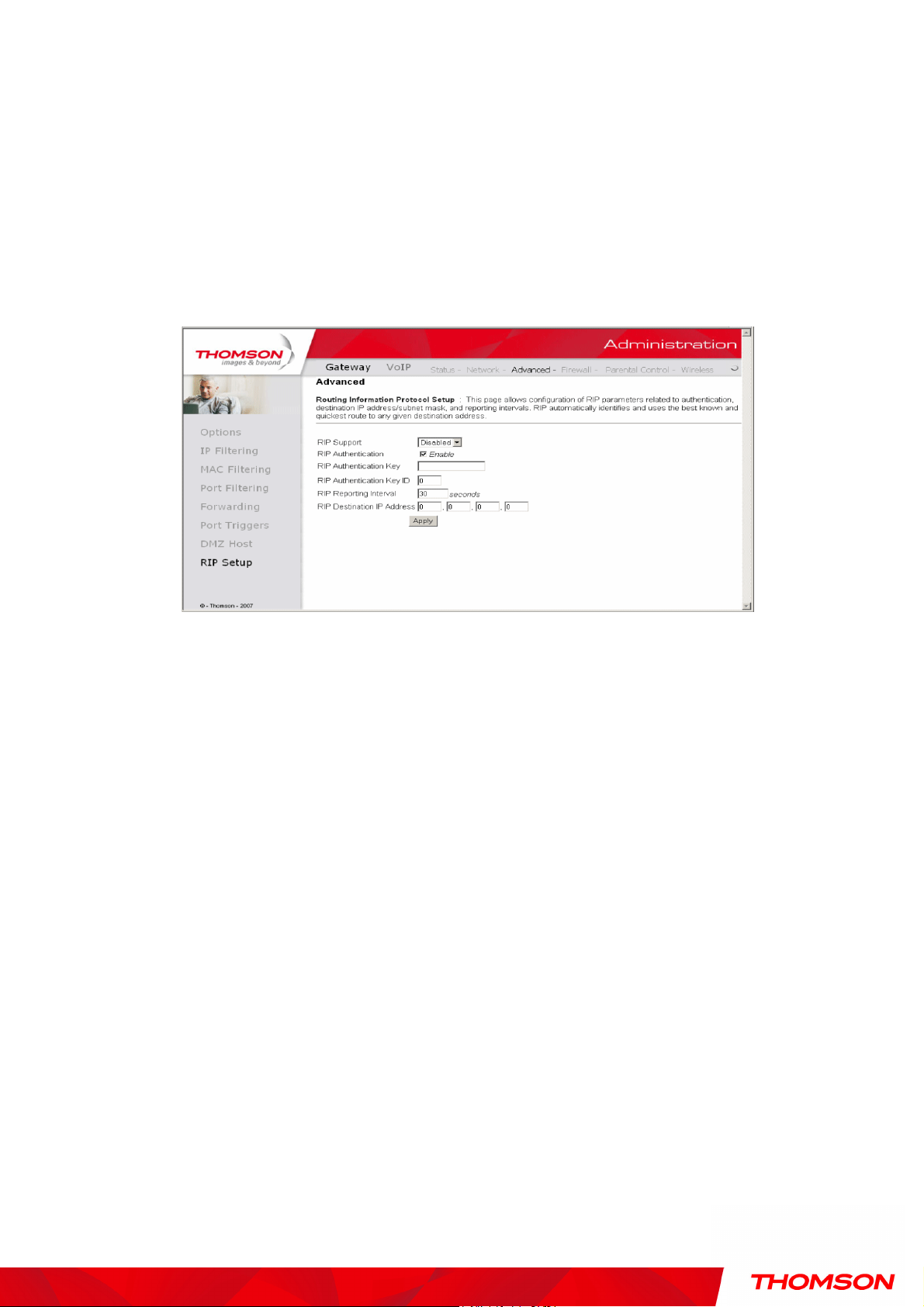
8. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) Setup
This feature enables the gateway to be used in small business situations where more than one LAN
(local area network) is installed. The RIP protocol provides the gateway a means to “advertise”
available IP routes to these LANs to your cable operator, so packets can be routed properly in this
situation.
Your cable operator will advise you during installation if any setting changes are required here.
Fig. 26 Gateway\Advanced\RIP Setup
46
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 2
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Gateway – Firewall Web Page Group
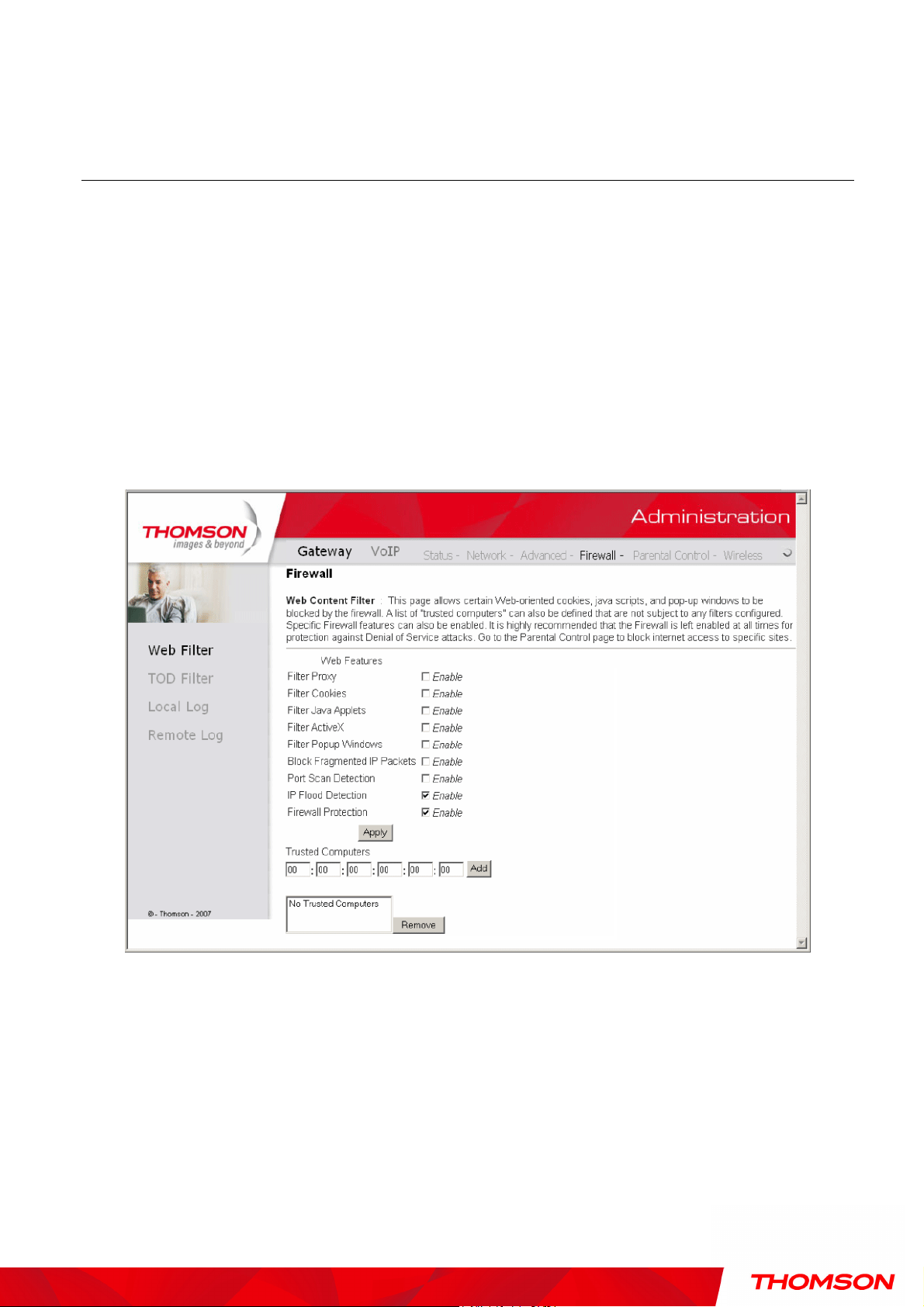
1. Web Content Filtering
These pages allow you to enable, disable, and configure a variety of firewall features associated with
web browsing, which uses the HTTP protocol and transports HTML web pages. On these pages, you
designate the gateway packet types you want to have forwarded or blocked. You can activate settings
by checking them and clicking Apply.
The web-related filtering features you can activate from the Web Content Filter page include Filter
Proxy, Filter Cookies, Filter Java Applets, Filter ActiveX, Filter Popup Windows, and Firewall
Protection.
If you want the gateway to exclude your selected filters to certain computers on your LAN, enter their
MAC addresses in the Trusted Computers area of this page.
Fig. 27 Gateway\Firewall\Web Filter
47
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 3
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
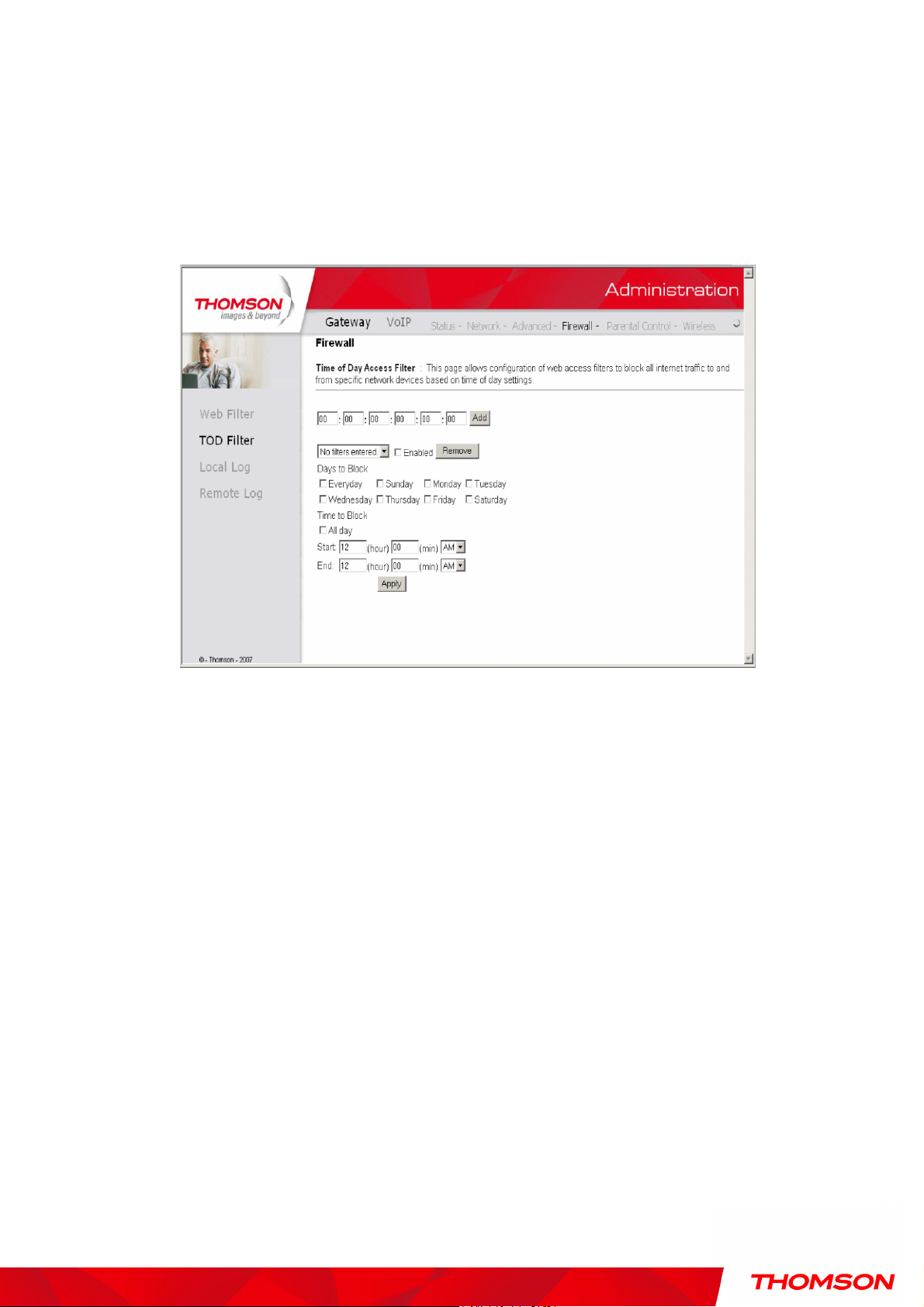
2. TOD Filtering
Use this page to set rules that will block specific LAN side PCs from accessing the Internet, but only
at specific days and times. Specify a PC by its hardware MAC address, and then use the tools to
specify blocking time. Finally, click the Apply button to save your settings.
Fig. 28 Gateway\Firewall\TOD Filtering
48
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 4
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
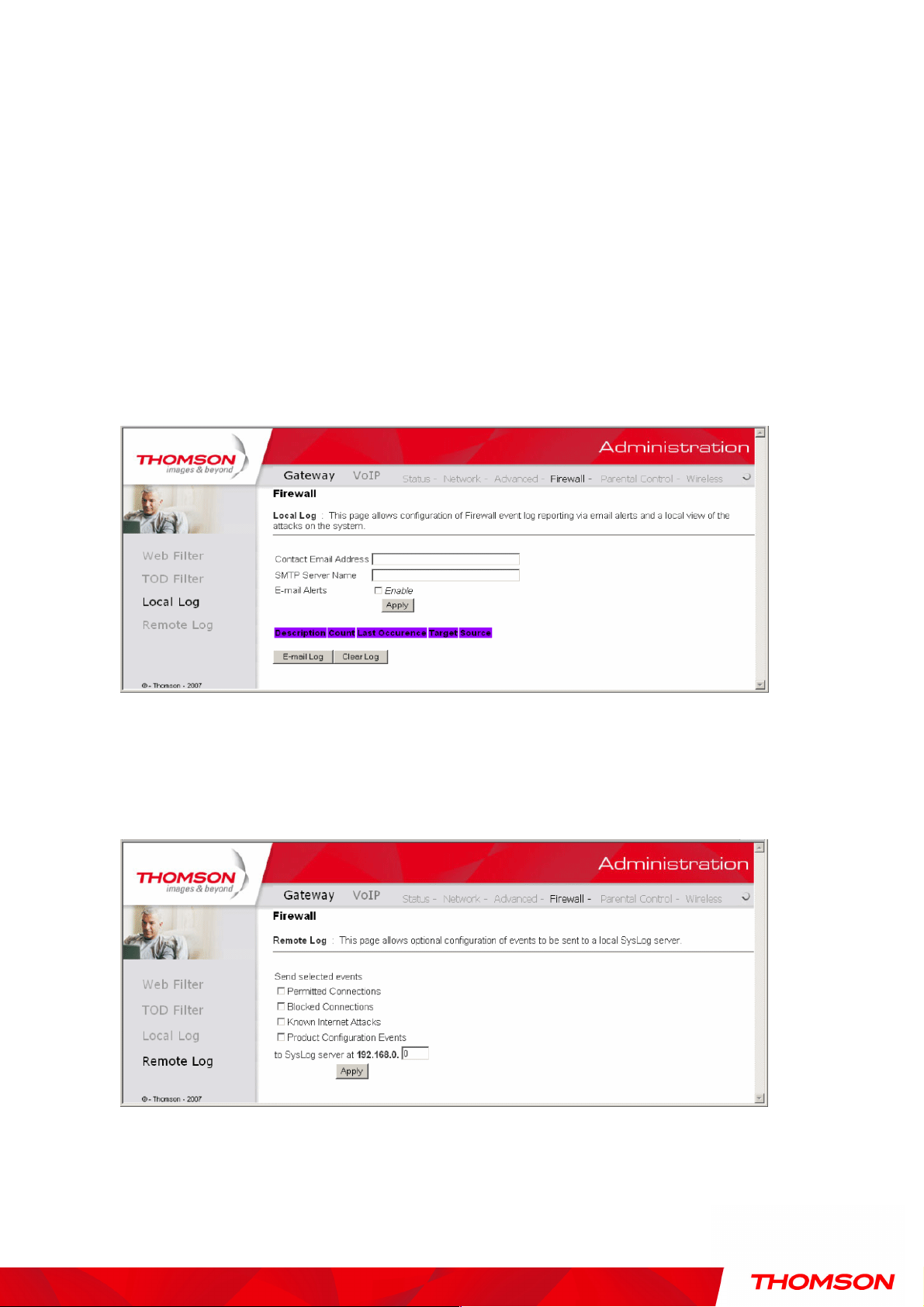
3. Local Log and Remote Log
The gateway builds a log of firewall blocking actions that Firewall has taken.Using the Local Log
page lets you specify an email address to which you want the gateway to email this log. You must also
tell the gateway your outgoing (i.e. SMTP) email server’s name, so it can direct the email to it. Enable
Email Alerts has the gateway forward email notices when Firewall protection events occur. Click
E-mail Log to immediately send the email log. Click Clear Log to clear the table of entries for a fresh
start.
The log of these events is also visible on the screen. For each blocking event type that has taken place
since the table was last cleared, the table shows Description, Count, Last Occurrence, Target, and
Source.
Fig. 29 Gateway\Firewall\Local Log
The Remote Log page allows you to specify the IP address where a SysLog server is located and select
different types of firewall events that may occur. Then, each time such an event occurs, notification is
automatically sent to this log server.
Fig. 30 Gateway\Firewall\Remote Log
49
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 5
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Gateway – Parental Control Web Page Group
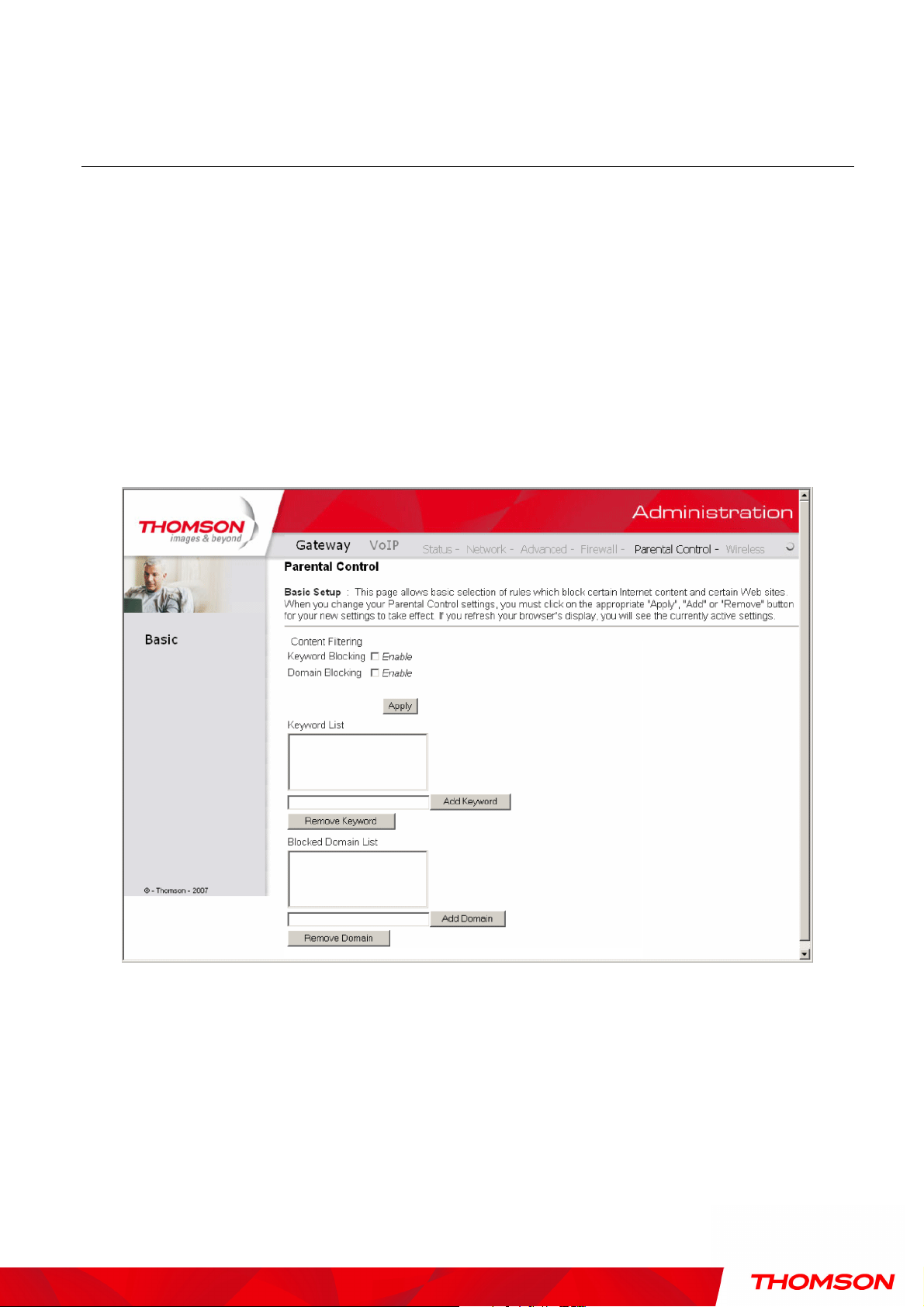
1. Basic
This page allows you to enable, disable, and configure a variety of firewall features associated with
web browsing, which uses the HTTP protocol and transports HTML web pages. On these pages, you
designate the gateway packet types you want to have forwarded or blocked. You can activate settings
by checking them and clicking Apply.
Here are some of your choices on the Parental Control page:
Activate Keyword Blocking and specify some keywords in the Keyword List to cause blocking
of web pages on the WAN side with the specified keyword in the content.
Activate Domain Blocking and specify some Domain Names (e.g. disney.com) in the Domain
List.
Fig. 31 Gateway\Parental Control\Basic
50
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 6

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Gateway – Wireless Web Page Group
The Wireless web pages group enables a variety of settings that can provide secure and reliable
wireless communications for even the most demanding tech-savvy user.
The Wireless Voice Gateway offers a choice of 802.1x, WPA and WPA-PSK authentication of your
PCs to the gateway, 64 and 128 bit WEP encryption of communication between the gateway and your
PCs to guaranty security, and an Access Control List function that enables you to restrict wireless
access to only your specific PCs.
The wireless function will probably work in your home as shipped from the factory, but without the
security features activated. In addition, the factory default wireless channel setting may not provide
optimum changes are recommended from the factory defaults, to secure your wireless communications
and provide optimum performance.
Performance
Because your wireless communication travels through the air, the factory default wireless channel
setting may not provide optimum performance in your home if you or your neighbors have other
interfering 2.4GHz devices such as cordless phones. If your wireless PC is experiencing very sluggish
or dramatically slower communication compared with the speed you achieve on your PC that is wired
to the gateway, try changing the channel number. See the 802.11b/g/n Basic Web Page discussion
below for details.
Authentication
Authentication enables you to restrict your gateway from communicating with any remote wireless
PCs that aren’t yours. The following minimum authentication-related changes to factory defaults are
recommended. See the 802.11b/g Basic and Access Control Web Page discussions below for details.
Network Name (SSID) – Set a unique name you choose
Network Type – Set to Open
Access Control List – Enter your wireless PCs’ MAC addresses
Security
Security secures or scrambles messages traveling through the air between your wireless PCs and the
gateway, so they can’t be observed by others. The following minimum security setting changes to
factory defaults are recommended. See the 802.11b/g Security Web Page discussion below for details.
Data Encryption – Set to WEP (64-bit)
PassPhrase – Use this feature to generate security keys
51
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 7
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
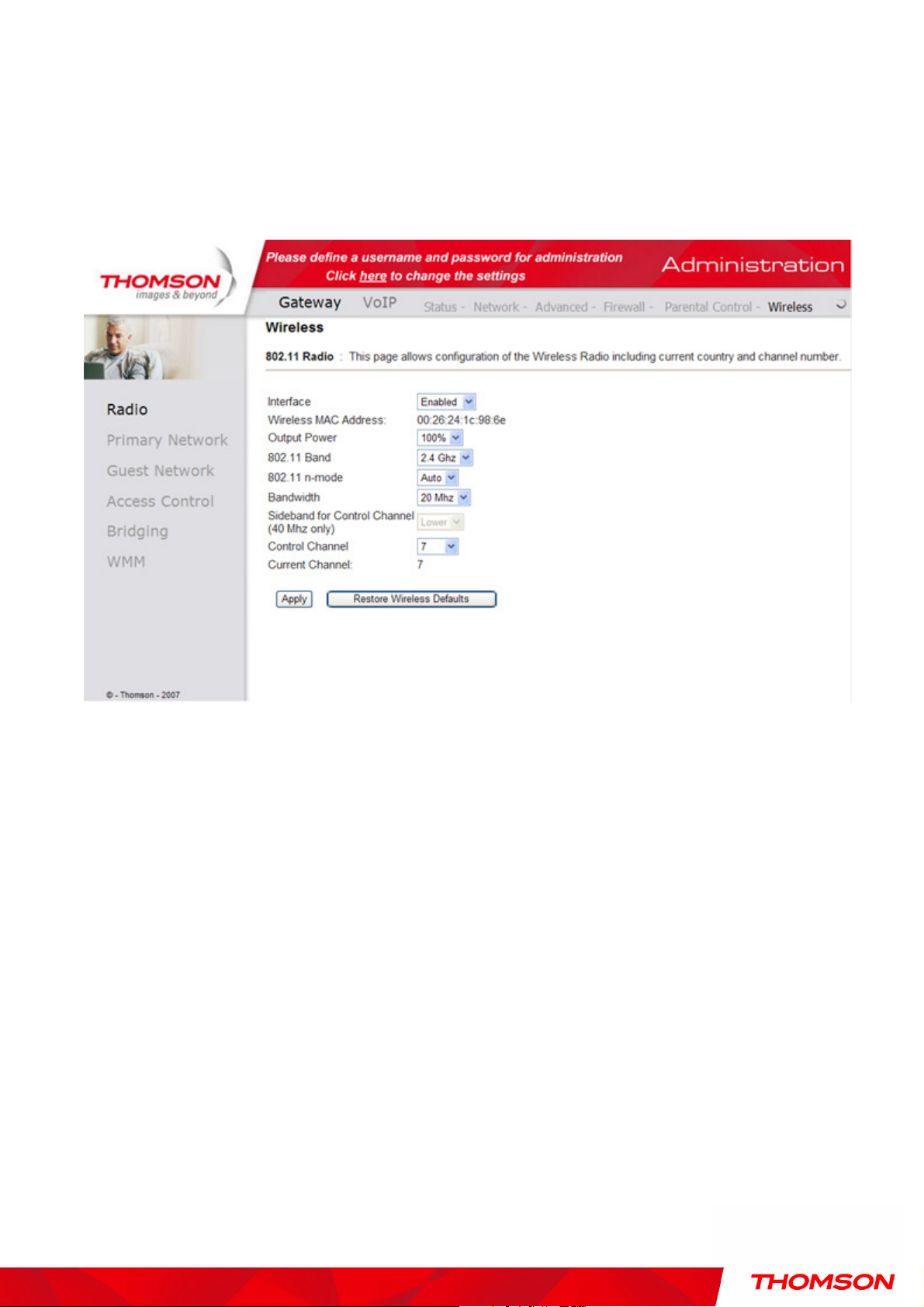
1. 802.11b/g/n Radio
To set the basic configuration for the wireless features, click RADIO from the Wireless menu. These
must match the settings you make on your wireless-equipped PC on the LAN side.
Fig. 32 Gateway\Wireless\Radio
Interface: The wireless radio in your gateway can be completely de-activated by changing Interface to
Disabled. Click the Apply button to save your settings. Activated by changing interface to enabled.
Wireless MAC Address: The MAC address for this wireless device will be displayed in this field
automatically.
Output Power:
This setting decides the output power of this device. You may use it to economize on electricity
by selecting lower percentage of power output. Control the range of the AP by adjusting the radio
output power.
802.11 Band: It can Support 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz exclusively.
802.11n mode: It will help you to Enable or Disable the 11N mode. To enable you need to select Auto, to
disable you need to select Off, and so force the AP to operate in 802.11g mode.
Bandwidth: Select wireless channel width 20Mhz is for default value (bandwidth taken by wireless
signals of this access point.)
52
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 8
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Sideband for Control Channel (40Mhz only): There are “Lower” and “Upper” can be selected if
Bandwidth 40Mhz is Enabled.
Control Channel: There are 13 channels that you can choose. Choose the one that is suitable for this
device.
Current Channel: The channel that you choose will be displayed in this field.
Restore Wireless defaults: To recover to the default settings, press this button to retrieve the settings and
click Apply.
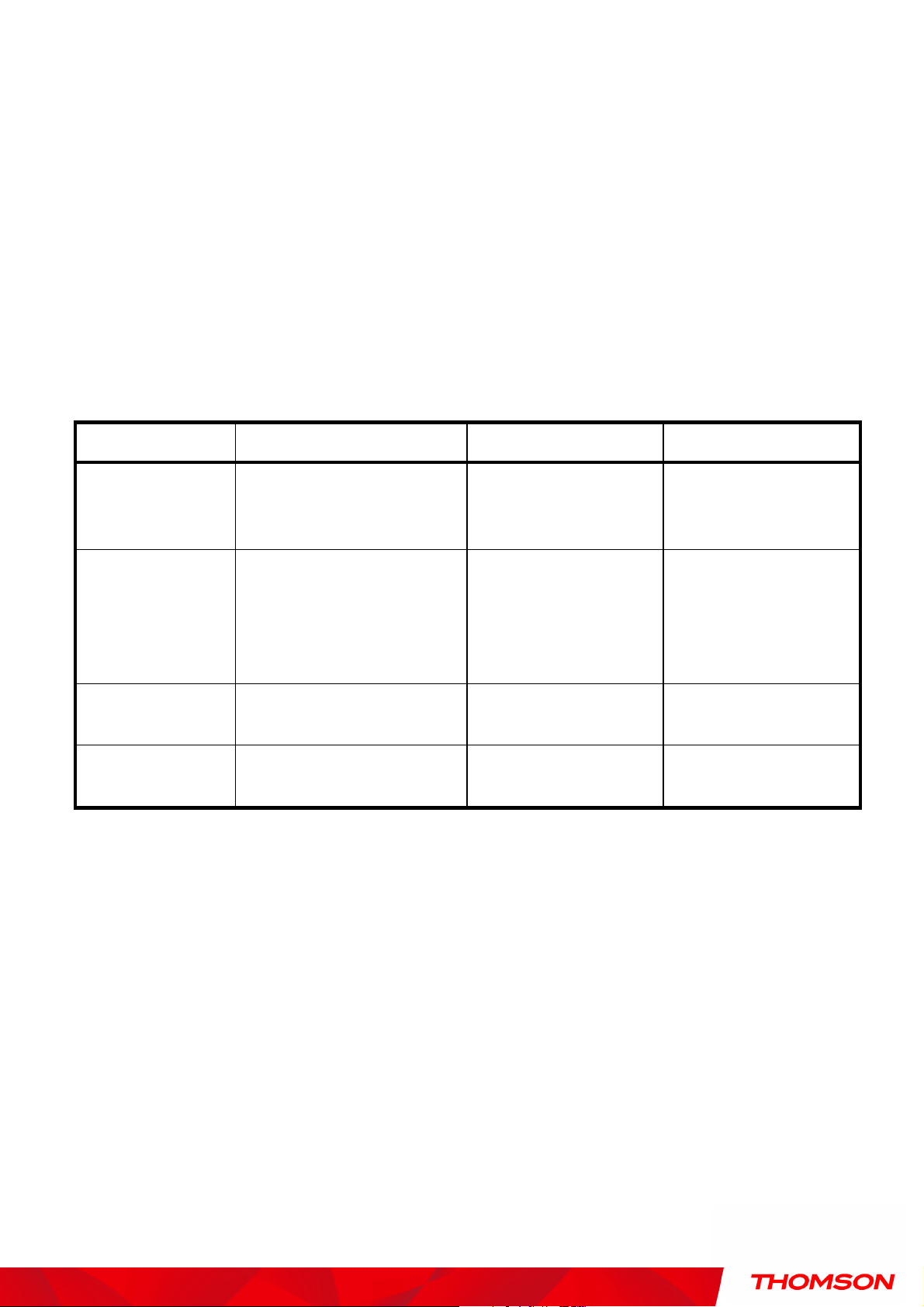
Setting Description Value List or Range
Network Name
(SSID)
Set the Network Name
(also known as SSID) of
this network.
Up to 32-character
string containing
ASCII characters only
THOM-Dxxxxxxx
Default
Select Closed to hide the
network from active
Network Type
scans. Select Open to
Open, Closed Open
reveal the network to
active scans.
New Channel
Interface
Select a particular channel
on which to operate.
Enable or disable the
wireless interface.
Table1. Basic Settings Definitions
1-13 1, 6 or 11
Enabled, Disabled Enabled
Your service provider might enforce different default settings, please check with your provider to insure
proper setup
53
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 9
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
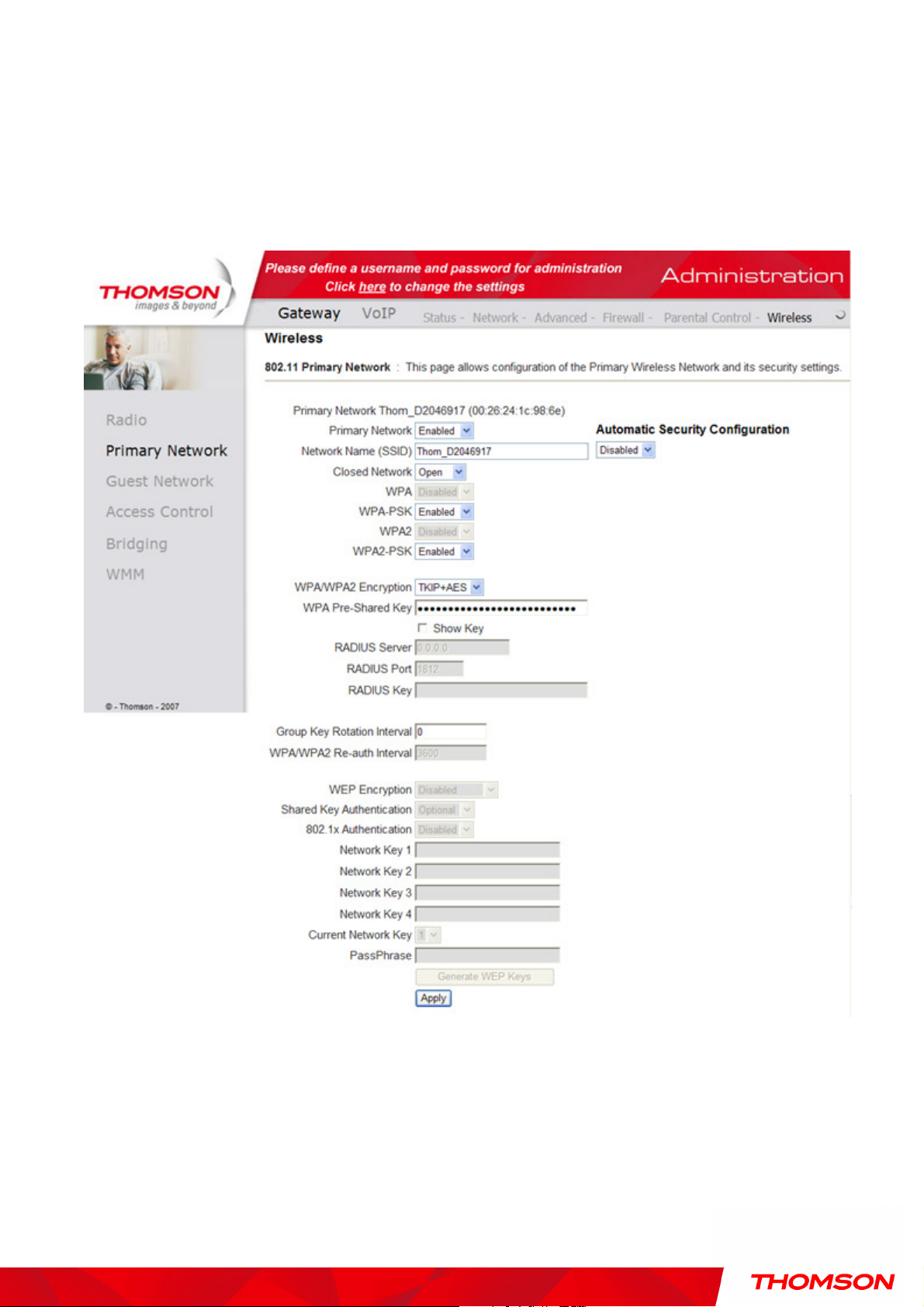
2. 802.11b/g/n Primary Network
This page allows you to configure the Network Authentication. It provides several different
modes of wireless security. You will have to enter proper information according to the mode you
select.
Fig. 33 Gateway\Primary Network
WPA
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)/WPA2
WPA WPA
/WPA2:
/WPA2/WPA2
It must be used in conjunction with an authentication server such as RADIUS to provide centralized
access control and management. It can provide stronger encryption and authentication solution than
54
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 10

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
none WPA modes. WPA2 is the second generation of WPA security
WPA-PSK (WPA-Pre-Shared Key) /WPA2-PSK (WPA2-Pre-Shared Key):
It is useful for small places without authentication servers such as the network at home. It allows the
use of manually-entered keys or passwords and is designed to be easily set up for home users.
WEP Encryption:
WEP Encryption:
WEP Encryption: WEP Encryption:
You can choose 64-bit or 128-bit according to your needs. If you choose Disabled, the Network Keys
will not be shown on this page. If selected, the data is encrypted using the key before being transmitted.
For example, if you set 128-bit in this field, then the receiving station must be set to use the128 Bit
Encryption, and have the same Key value too. Otherwise, it will not be able to decrypt the data.
( Note: You need to connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the back of your
computer, and the other end to the ETHERNET port on the Wireless Voice Gateway. )
If you select WEP (64-bit or 128-bit), you can adjust the following settings-
Shared Key Authentication: Decide whether to set the shared key Optional or Required by
selecting from the drop-down menu.
Network Key 1 to 4: The system allows you to enter four sets of the WEP key. For 64-bit WEP
mode, the key length is 5 characters or 10 hexadecimal digits. As for 128-bit WEP mode, the key
length is 13 characters or 26 hexadecimal digits.
Current Network Key: Select one set of the network key (from 1 to 4) as the default one.
PassPhrase: You can enter ASCII codes into this field. The range is from 8 characters to 64
characters. For ASCII characters, you can key in 63 characters in this field. If you want to key
in 64 characters, only hexadecimal characters can be used.
Generate WEP Keys: Click this button to generate the PassPhrase.
Fig. 34 PassPhrase
Apply: After proper configuration, click Apply to invoke the settings.
55
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 11
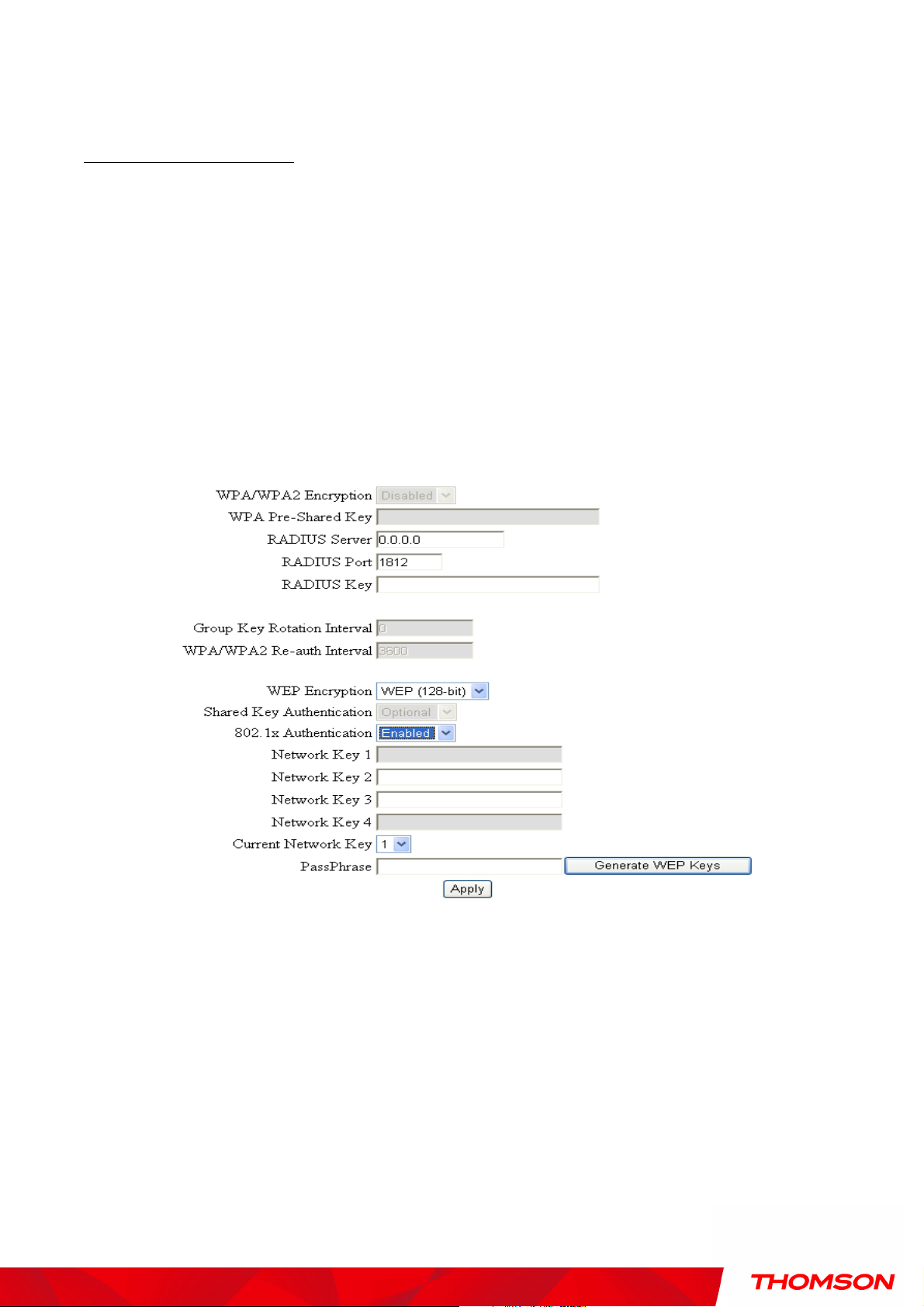
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
802.1x Authentication
If you enable the 802.1x authentication function, you will have to offer the following information-
RADIUS Server: RADIUS Server is a protocol for carrying authentication, authorization, and
configuration information between a Network Access Server which desires to authenticate its
links and a shared Authentication Server. Please key in the IP Address for the RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Port: Besides the IP address of the RADIUS Server, you have to enter the port number
for the server. Port 1812 is the reserved RADIUS-authentication port described in RFC 2138.
Earlier AP (RADIUS clients) use port 1945. The default value will be shown on this box. You
can keep and use it.
RADIUS Key: A RADIUS Key is like a password, which is used between IAS and the specific
RADIUS client to verify identity. Both IAS and the RADIUS client must be use the same
RADIUS Key for successful communication to occur. Enter the RADIUS Key.
Fig. 35 802.1x Authentication
56
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 12

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
WPA/WPA2
For the WPA/WPA2 network Authentication, the settings that you can adjust including WPA/WPA2
Encryption, RADIUS Server, RADIUS Port, RADIUS Key, Group Key Rotation Interval, and
WPA/WPA2 Re-auth Interval.
WPA/WPA2 Encryption: There are three types that you can choose, TKIP*, AES**,
TKIP+AES.
TKIP takes the original master key only as a starting point and derives its encryption keys
mathematically from this mater key. Then it regularly changes and rotates the encryption
keys so that the same encryption key will never be used twice
** AES provides security between client workstations operating in ad hoc mode. It uses a
mathematical ciphering algorithm that employs variable key sizes of 128, 192 or 256 bits.
RADIUS Server/RADIUS Port/RADIUS Key: Please refer to the previous page.
Group Key Rotation Interval: Key in the time for the WAP group key rotation interval. The unit
is second. With increasing rekey interval, user bandwidth requirement is reduced.
WPA/WPA2 Re-auth Interval: When a wireless client has associated with the Wireless Voice
Gateway for a period of time longer than the setting here, it would be disconnected and the
authentication will be executed again. The default value is 3600, you may modify it.
Fig. 36 WPA/WPA2
57
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 13

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK
For the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK network Authentication, the settings that you can adjust including
WPA/WPA2 Encryption, WPA Pre-Shared Key, and Group key Rotation Interval.
WPA Pre-Shared Key: Please type the key to be between 8 and 63 characters, or 64
hexadecimal digits. Only the devices with a matching key that you set here can join this network.
WPA/WPA2 Encryption & WPA Group Rekey Interval : Please refer to the WPA/WPA2 part.
Fig. 37 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
58
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 14
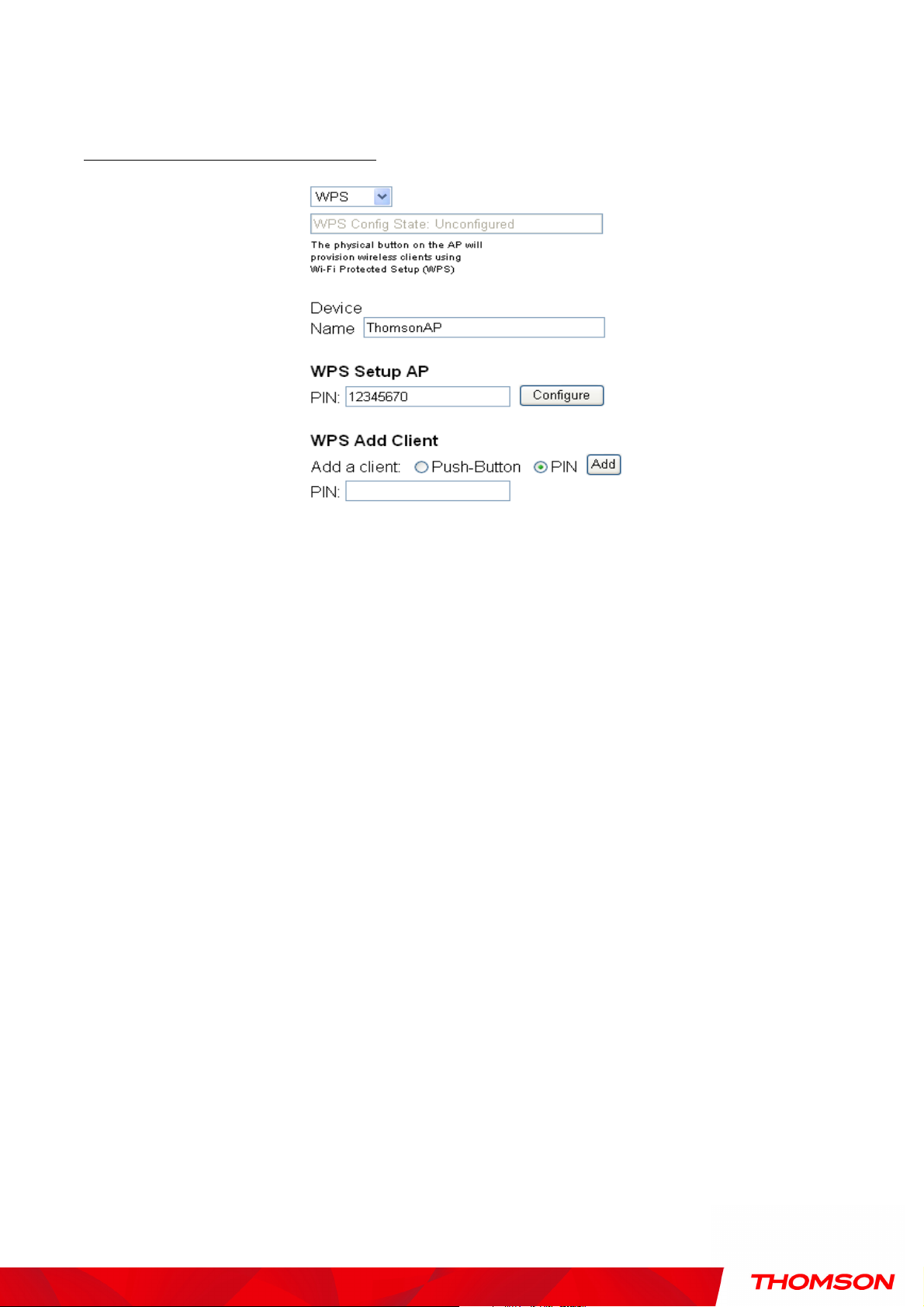
Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Automatic Security Configuration
Fig. 38 Automatic Security Configuration
WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is an easy and secure way of configuring and connecting your WiFi access point.
In your case, the DWG875/DWG875T is the Access Point (AP), and Your PC (or Wifi Device) is called the
STA. When configuring your Wifi Network via WPS, Messages are exchanged between the STA and AP in
order to configure the Security Settings on both devices.
WPS Config: It will help you to Enable or Disable the WPS feature. To enable you need to select WPS,
to disable you need to select Disabled.
Note: After you Enabled the WPS you will get the options as show in Fig.35 and the WPS Config State
box will show its configuration status.
Device Name: By using this you can change the factory default to a name of your choice which is up to 32
characters long as like SSID.
WPS Setup AP: Here you do not need to change anything, just skip this step.
WPS Add Client: T
But, the default selection will be “PIN”.
here are two methods “Push-Button” and “PIN”. Select the method you want.
59
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 15

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
If you select “Push-Button”, then the WPS Add Client option will appear as shown below.
Fig. 39 WPS/Push-Button
And then if you click “Add” button then WPS Setup AP page will appear as shown in Fig.38
Fig. 40 WPS Setup AP/PUSH
And WPS Configure Status will be “In progress”, after establishing the connection the WPS Configure
Status will be “Success!” as shown below. After successful connection the client will get IP address from
AP and then internet will be accessible.
Fig. 41 WPS Setup AP successful/PUSH
60
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 16

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
If you select WPS Method to PIN then it will ask for PIN while configuring the WiFi AP by showing a
text box so, you need to enter PIN to establish the connection. You can get the PIN from your connected
Wi-Fi client.
Fig. 42 WPS/PIN
PIN: Use this option to set the PIN, enter 4-8 digits PIN of the device you wish to configure. After
entering the pin click “Add” button, then the WPS Setup AP page will appear as shown in Fig.41
Fig. 43 WPS Setup AP/PIN
And WPS Configure Status will be “In progress”, after establishing the connection the WPS Configure
Status will be “Success!” as shown below. After successful connection the client will get IP address from
AP and then internet will be accessible.
61
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 17

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Fig. 44 WPS Setup AP successful/PIN
62
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 18

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
3. Guest Network
This page allows you to configure a guest network.
You can refer to the details described in previous sections to make the WiFi security settings and guest
LAN settings.
Fig. 45 Gateway\Wireless\Guest Network
63
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 19

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
4. Access Control
This page allows you to make access control to the AP or connected clients by offering the MAC
Addresses of the clients.
Fig. 46 Gateway\Wireless\Access Control
Administration Web Page Access : Select Allow to permit access to Administration Web Page from
PC connected over Wifi; or choose Deny to prevent the clients connected over Wifi from access to
Administration Web Page.
MAC Restrict Mode : Click Disabled to welcome all of the clients on the network; select Allow to
permit only the clients on the list to access the cable modem; or choose Deny to prevent the clients on
the list to access this device.
MAC Address : Your Gateway identifies wireless PCs by their WiFi MAC Address. This address
consists of a string of 6 pairs of numbers 0-9 and letters A-F, such as 00 90 4B F0 FF 50. It is usually
printed on the WiFi card of the device (e.g. the PCMCIA card in a laptop). It can also be determined
from a Windows DOS prompt as explained below.
Enter the MAC addresses of the connected clients into the fields, and then click Apply to add them to
the list for access control.
Apply : After proper configuration, click Apply to invoke the settings.
Connected Clients : The information of currently connected clients will be displayed here.
64
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 20

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
5. Bridging
The Bridging page provides a location where settings can be adjusted related to the WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) feature.
WDS is a system that enables the interconnection of access points wirelessly. It may also be referred
to as repeater mode because it appears to bridge and accept wireless clients at the same time (unlike
traditional bridging).
The wireless gateway can be placed in a mode that allows the gateway to communicate with other
“extender” wireless access points either exclusively or mixed with communications to local PCs. Use
this page to designate the Remote Bridges the gateway is allowed to communicate with, and to select
the Wireless Bridging mode.
Fig. 47 Gateway\Wireless\Bridging
Wireless Bridging:
Choose Disabled to shutdown this function; select Enabled to turn on the function of WDS.
Remote Bridges:
Enter the MAC Addresses of the remote Bridges to relay the signals for each other.
Apply:
After proper configuration, click Apply to invoke the settings.
65
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 21

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
6. 802.11e QoS (WMM) Settings
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) is a component of the IEEE 802.11e wireless LAN standard for quality of
service (QoS). The QoS assigns priority to the selected network traffic and prevents packet collisions and
delays thus improving VoIP calls and watching video over WLANs.
Enable WMM:
This field allows you to enable WMM to improve multimedia transmission.
Enable WMM No-Acknowledgement:
This field allows you to enable WMM No-Ackonwledgement.
Power Save Support:
This field allows you to enable WMM Power-Save-Support.
Fig. 48 Gateway\Wireless\WMM
66
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 22

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
VoIP – Basic Web Page Group
1. Basic LAN
This page displays the basic LAN status of this device, including the downstream and upstream status,
device information, and interface parameters. You can select specific interface from the Interface
Name drop-down menu.
Fig. 49 VoIP\Basic\Basic LAN
67
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 23

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
2. Hardware Info
The hardware Info is displayed on this page.
Fig. 50 VoIP\Basic\Hardware Info
68
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 24

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
3. Event Log
The event logs are displayed on this web page. You can check them whenever you need.
Fig. 51-1 VoIP\Basic\Event log\DOCSIS
69
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 25

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
Fig. 51-2 VoIP\Basic\Event log\PacketCable
70
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 26

Chapter 2: WEB Configuration
4. CM State
This page shows the current state of the cable modem.
Fig. 52 VoIP\Basic\Cm state
71
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 27

Page 28
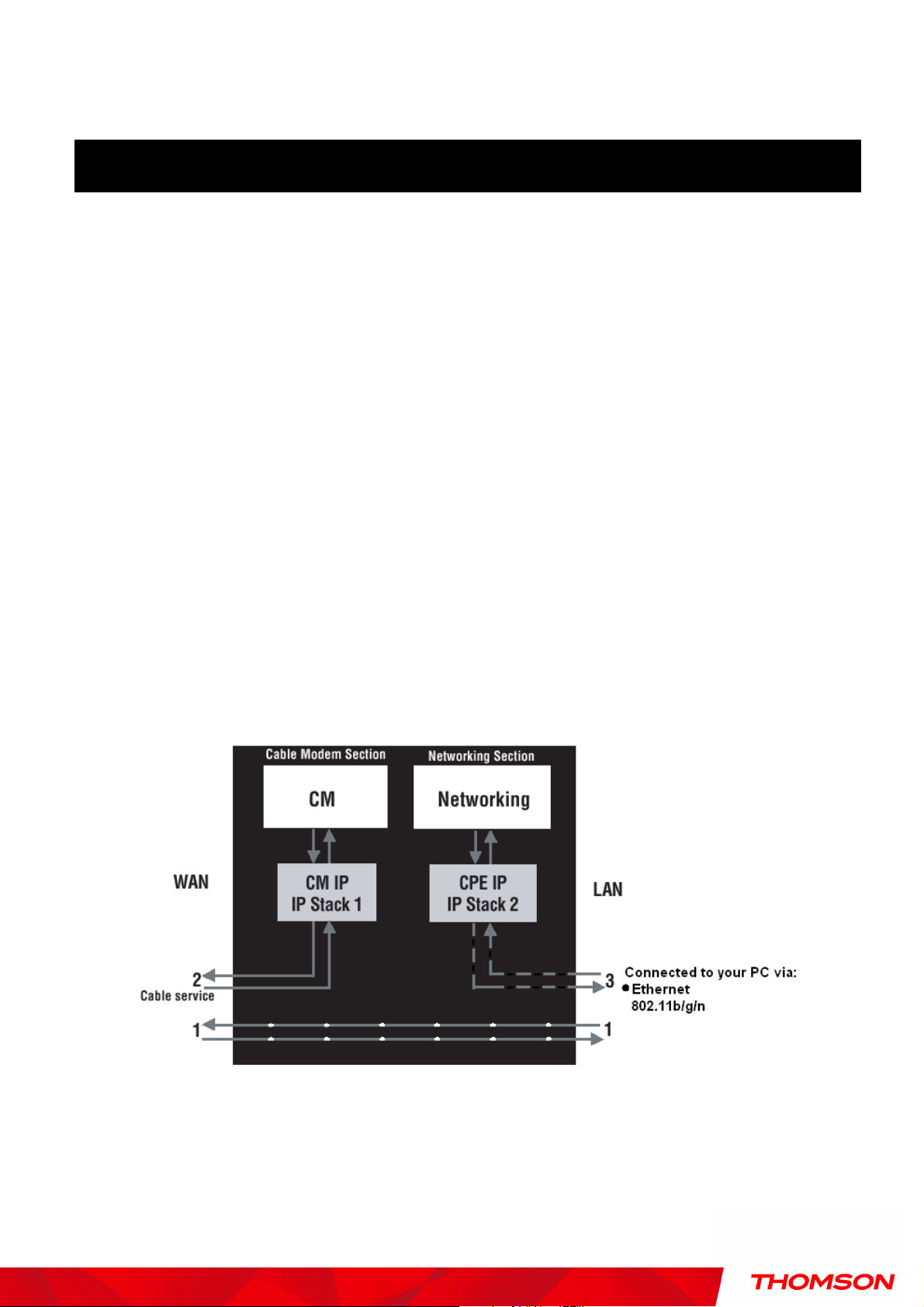
Chapter 3: Networking
Chapter 3: Networking
Communications
Data communication involves the flow of packets of data from one device to another. These
devices include personal computers, Ethernet and USB hubs, cable modems, digital routers
and switches, and highly integrated devices that combine functions, like the Wireless Cable
Gateway.
The gateway integrates the functionality often found in two separate devices into one. It’s
both a cable modem and an intelligent wireless gateway networking device that can provide a
host of networking features, such as NAT and firewall. Figure 2 illustrates this concept, with
the cable modem (CM) functionality on the left, and networking functionality on the right. In
this figure, the numbered arrows represent communication based on source and destination,
as follows:
Type of Communication
1. Communication between the Internet and your PCs
Example: The packets created by your request for a page stored at a web site, and the
contents of that page sent to your PC.
2. Communication between your cable company and the cable modem side
Example: When your cable modem starts up, it must initialize with the cable company,
which requires the cable company to communicate directly with the cable modem itself.
3. Communication between your PCs and the networking side
Fig.53 Communication between your PCs and the network side
Example: The Wireless Cable Gateway offers a number of built-in web pages which you
73
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 29

Chapter 3: Networking
can use to configure its networking side; when you communicate with the networking
side, your communication is following this path.
Each packet on the Internet addressed to a PC in your home travels from the Internet downstream on the cable company’s system to the WAN side of your Wireless Cable Gateway. There
it enters the Cable Modem section, which inspects the packet, and, based on the results,
proceeds to either forward or block the packet from proceeding on to the Networking section.
Similarly, the Networking section then decides whether to forward or block the packet from
proceeding on to your PC. Communication from your home device to an Internet device works
similarly, but in reverse, with the packet traveling upstream on the cable system.
Cable Modem (CM) Section
The cable modem (or CM) section of your gateway uses DOCSIS Standard cable modem
technology. DOCSIS specifies that TCP/IP over Ethernet style data communication be used
between the WAN interface of your cable modem and your cable company.
A DOCSIS modem, when connected to a Cable System equipped to support such modems,
performs a fully automated initialization process that requires no user intervention. Part of
this initialization configures the cable modem with a CM IP (Cable Modem Internet Protocol)
address, as shown in Figure 3, so the cable company can communicate directly with the CM
itself.
Networking Section
The Networking section of your gateway also uses TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/
Internet Protocol) for the PCs you connected on the LAN side. TCP/IP is a networking protocol
that provides communication across interconnected networks, between computers with
diverse hardware architectures and various operating systems.
TCP/IP requires that each communicating device be configured with one or more TCP/IP
stacks, as illustrated by Figure 4. On a PC, you often use software that came with the PC or its
network interface (if you purchased a network interface card separately) to perform this
configuration. To communicate with the Internet, the stack must also be assigned an IP
(Internet Protocol) address. 192.168.100.1 is an example of an IP address. A TCP/IP stack can
be configured to get this IP address by various means, including a DHCP server, by you
directly entering it, or sometimes by a PC generating one of its own.
Ethernet requires that each TCP/IP stack on the Wireless Cable Gateway also have associated
with it an Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address. MAC addresses are permanently
fixed into network devices at the time of their manufacture. 00:90:64:12:B1:91 is an example
of a MAC address.
Data packets enter and exit a device through one of its network interfaces. The gateway offers
Ethernet, USB, and 802.11b/g wireless network interfaces on the LAN side and the DOCSIS
network interface on the WAN side.
When a packet enters a network interface, it is offered to all the TCP/IP stacks associated with
the device side from which it entered. But only one stack can accept it — a stack whose
74
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 30

Chapter 3: Networking
configured Ethernet address matches the Ethernet destination address inside the packet.
Furthermore, at a packet’s final destination, its destination IP address must also match the IP
address of the stack.
Each packet that enters a device contains source MAC and IP addresses telling where it came
from, and destination MAC and IP addresses telling where it is going to. In addition, the
packet contains all or part of a message destined for some application that is running on the
destination device. IRC used in an Internet instant messaging program, HTTP used by a web
browser, and FTP used by a file transfer program are all examples of applications. Inside the
packet, these applications are designated by their port number. Port 80, the standard HTTP
port, is an example of a port number.
The Networking section of the router performs many elegant functions by recognizing
different packet types based upon their contents, such as source and destination MAC
address, IP address, and ports.
Three Networking Modes
Your gateway can be configured to provide connectivity between your cable company and
your home LAN in any one of three Networking Modes: CM, RG, and CH. This mode setting is
under the control of your cable company, who can select the mode to match the level of home
networking support for which you have subscribed. All units ship from the factory set for the
RG mode, but a configuration file which the cable company sends the cable modem section
during its initialization can change it.
Cable Modem (CM) Mode
Fig. 54 Cable Modem Mode
75
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 31

Chapter 3: Networking
Fig. 55 Two IP stacks are activated in cable modem mode
CM (Cable Modem) Mode provides basic home networking. In this mode, two IP stacks are
active:
• IP Stack 1 - for use by the cable company to communicate with the cable modem section
only. This stack receives its IP address from the cable company during CM initialization. It
uses the MAC address printed on the label attached to the Wireless Cable gateway.
• IP Stack 2 - for use by you, the end user, to communicate with the cable modem and
Networking sections, to access the internal web page diagnostics and con guration. This
stack uses a fixed IP address: 192.168.100.1. It uses a MAC address of MAC label + 1 (the
MAC label is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is
00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:92.
With CM Mode, your cable company must provide one IP address for the CM section, plus one
for each PC you connect from their pool of available addresses. Your cable company may have
you or your installer manually enter these assigned addresses into your PC, or use a DHCP
Server to communicate them to your PCs, or use a method that involves you entering host
names into your PCs.
Note that in CM Mode, packets passing to the Internet to/from your PCs do not travel through
any of the IP stacks; instead they are directly bridged between the WAN and LAN sides.
76
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 32

Chapter 3: Networking
Residential Gateway (RG) Mode
Fig. 56 Residential Gateway Mode
Fig. 57 Three IP stacks are activated in Residential mode
RG (Residential Gateway) Mode provides basic home networking plus NAT (Network Address
Translation). In this mode, three IP stacks are active:
• IP Stack 1 - for use by the cable company to communicate with the Cable Modem section
only. This stack receives its IP address from the cable company during CM initialization. It
uses the MAC address printed on the label attached to the Wireless Cable Gateway.
• IP Stack 3 - for use by you to remotely (i.e. from somewhere on the WAN side, such as at
your remote workplace) communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to
remotely access the internal web page diagnostics and configuration. This stack is also
77
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 33

Chapter 3: Networking
used by your cable company to deliver packets between the Internet and the gateway’s
networking section so they can be routed to/from your PCs. This stack requires an IP
address assigned by the cable company from their pool of available addresses. Your cable
company may have you or your installer manually enter assigned addresses into your
gateway, or use a DHCP Server to communicate them, or use a method that involves you
entering host names. This stack uses a MAC address of MAC label + 2 (the MAC label is
found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is 00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC
address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:93.
• IP Stack 5 - for use by you to locally (i.e. from somewhere on the LAN side in your home)
communicate with the Cable Modem and Networking sections, to access the internal web
page diagnostics and configuration. This stack is also used by the gateway’s networking
section to route packets between the gateway’s Networking section and your PCs. This
stack uses a fixed IP address: 192.168.0.1. It uses a MAC address of MAC label + 4 (the
MAC label is found on the bottom of the unit). E.g., if the MAC address is
00:90:64:12:B1:91, this MAC address would be 00:90:64:12:B1:95.
With RG Mode, your cable company must provide one IP address for the CM section, plus one
for the Networking section, from their pool of available addresses. With RG Mode, each PC you
connect gets an IP address from a DHCP Server that is part of the Networking section of the
gateway.
78
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 34

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Chapter 4: Additional Information
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What if I don’t subscribe to cable TV?
A. If cable TV is available in your area, data and voice service may be made available with or without
cable TV service. Contact your local cable company for complete information on cable services,
including high-speed internet access.
Q. How do I get the system installed?
A. Professional installation from your cable provider is strongly recommended. They will ensure proper
cable connection to the modem and your computer. However, your retailer may have offered a self
installation kit, including the necessary software to communicate with your cable ISP.
Q. My modem is connected to the power sector but does not work
A. Check the ON/OFF button on the rear panel of your modem. It should be set to “1”.
Q. Once my Wireless Voice Gateway is connected, how do I get access to the Internet?
A. Your local cable company provides your internet service*, offering a wide range of services including
email, chat, and news and information services, and a connection to the World Wide Web.
Q. It seems that the wireless network is not working
A. Check the WiFi LED on the front panel. If it is no lighted, press on the WPS button (on the side of the
modem) during 3 seconds and then check again the WiFi LED. If it is lighted, then the WiFi is enabled.
Q. Can I watch TV, surf the Internet, and talk to my friends through the Wireless Voice
Gateway at the same time?
A. Absolutely!
Q. What do you mean by “Broadband?”
A. Simply put, it means you’ll be getting information through a “bigger pipe,” with more bandwidth, than
a standard phone line can offer. A wider, “broader” band means more information, more quickly.
Q. What is DOCSIS and what does it mean?
A. “Data over Cable Service Interface Specifications” is the industry standard that most cable companies
are adopting as they upgrade their systems. Should you ever decide to move, the Wireless Voice Gateway
79
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 35

Chapter 4: Additional Information
will work with all upgraded cable systems that are DOCSIS-compliant.
Q. What is PacketCable and what does it mean?
A. PacketCable is the industry standard for telephony services that most cable companies are adopting as
they upgrade their systems. Should you ever decide to move, the Wireless Voice Gateway will work with
all upgraded cable systems that are PacketCable compliant.
Q. What is Xpress Technology and what does it mean?
A. It is one of the popular performance-enhancing WiFi technologies, designed to improve wireless
network efficiency and boost throughput. It is more efficient in mixed environments, and it can work with
802.11a/b/g networks. When Xpress is turned on, aggregate throughput (the sum of the individual
throughput speeds of each client on the network) can improve by up to 27% in 802.11g-only networks,
and up to 75% in mixed networks comprised of 802.11g and 802.11b standard equipment. The
technology achieves higher throughput by by re-packaging data, reducing the number of overhead control
packets, so that more useful data can be sent during a given amount of time.
* Monthly subscription fee applies.
**
Additional equipment required. Contact your cable company and ISP for any restrictions or additional
fees.
80
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 36

Chapter 4: Additional Information
General Troubleshooting
You can correct most problems you have with your product by consulting the troubleshooting list that
follows.
I can’t access the internet.
Check all of the connections to your Wireless Voice Gateway.
Your Ethernet card or USB port may not be working. Check each product’s documentation for more
information.
The Network Properties of your operating system may not be installed correctly or the settings may
be incorrect. Check with your ISP or cable company.
All of the lights are flashing in sequence.
This means the Wireless Voice Gateway is automatically updating its system software. Please wait
for the lights to stop flashing. The updating process typically lasts less than one minute.
Do not remove the power supply or reset the Wireless Voice Gateway during this process.
I can’t get the modem to establish an Ethernet connection.
Even new computers don’t always have Ethernet capabilities – be sure to verify that your computer
has a properly installed Ethernet card and the driver software to support it.
Check to see that you are using the right type of Ethernet cable.
The modem won’t register a cable connection.
If the modem is in Initialization Mode, the INTERNET light will be flashing. Call your Cable
Company if it has not completed this 5-step process within 30 minutes, and note which step it is
getting stuck on.
The modem should work with a standard RG-6 coaxial cable, but if you’re using a cable other than
the one your Cable Company recommends, or if the terminal connections are loose, it may not work.
Check with your Cable Company to determine whether you’re using the correct cable.
If you subscribe to video service over cable, the cable signal may not be reaching the modem.
Confirm that good quality cable television pictures are available to the coaxial connector you are
using by connecting a television to it. If your cable outlet is “dead”, call your Cable Company.
Verify that the Cable Modem service is DOCSIS compliant and PacketCable compliant by calling
your cable provider.
81
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 37

Chapter 4: Additional Information
I don’t hear a dial tone when I use a telephone.
Telephone service is not activated. If the rightmost light on the Wireless Voice Gateway stays on
while others flash, check with your TSP or cable company.
If the Wireless Voice Gateway is connected to existing house telephone wiring, make sure that
another telephone service is not connected. The other service can normally be disconnected at the
Network Interface Device located on the outside of the house.
If using the second line on a two-line telephone, use a 2-line to 1-line adapter cable.
For more Usage and Troubleshooting Tips use the web site links provided on the CD-ROM:
http://www.Technicolor.net/GlobalEnglish/Deliver/Cable/cable-modems-routers-gateways/Pages/default.aspx
82
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 38

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Service Information
If you purchased or leased your Wireless Voice Gateway directly from your cable company, then warranty
service for the Digital Cable Modem may be provided through your cable provider or its authorized
representative. For information on 1) Ordering Service, 2) Obtaining Customer Support, or 3) Additional
Service Information, please contact your cable company. If you purchased your Wireless Voice Gateway
from a retailer, see the enclosed warranty card.
83
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 39

Chapter 4: Additional Information
Glossary
10/100/1000 Mbps – Unshielded, twisted pair cable with an RJ-45 connector, used with Ethernet LAN
(Local Area Network). “10/100/1000” indicates speed (10/100/1000 Mbps), “Base” refers to baseband
technology, and “T” means twisted pair cable.
Authentication - The process of verifying the identity of an entity on a network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) – A protocol which allows a server to dynamically assign IP
addresses to workstations on the fly.
Ethernet adapters – A plug-in circuit board installed in an expansion slot of a personal computer. The
Ethernet card (sometimes called a Network Interface Card , network adapter or NIC) takes parallel data
from the computer, converts it to serial data, puts it into a packet format, and sends it over the
10/100/1000 Mbps LAN cable.
DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications) – A project with the objective of
developing a set of necessary specifications and operations support interface specifications for Cable
Modems and associated equipment.
F Connector – A type of coaxial connector, labeled CABLE IN on the rear of the Wireless Voice
Gateway that connects the modem to the cable system.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) – Invisible to the user, HTTP is used by servers and clients to
communicate and display information on a client browser.
Hub – A device used to connect multiple computers to the Wireless Voice Gateway.
IP Address – A unique, 32-bit address assigned to every device in a network. An IP (Internet Protocol)
address has two parts: a network address and a host address. This modem receives a new IP address from
your cable operator via DHCP each time it goes through Initialization Mode.
Key exchange - The swapping of mathematical values between entities on a network in order to allow
encrypted communication between them.
MAC Address – The permanent “identity” for a device programmed into the Media Access Control layer
in the network architecture during the modem’s manufacture.
NID - Network Interface Device, the interconnection between the internal house telephone wiring and a
conventional telephone service provider’s equipment. These wiring connections are normally housed in a
small plastic box located on an outer wall of the house. It is the legal
demarcation between the
subscriber’s property and the service provider’s property.
84
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 40

Chapter 4: Additional Information
PacketCable – A project with the objective of developing a set of necessary telephony specifications and
operations support interface specifications for Wireless Voice Gateways and associated equipment used
over the DOCSIS based cable network.
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) – The worldwide voice telephone network which provides
dial tone, ringing, full-duplex voice band audio and optional services using standard telephones.
Provisioning - The process of enabling the Media Terminal Adapter (MTA) to register and provide
services over the network.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) – A networking protocol that provides
communication across interconnected networks, between computers with diverse hardware architectures
and various operating systems.
TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol, the system by which the Media Terminal Adapter’s configuration
data file is downloaded.
TSP - Telephony Service Provider, an organization that provides telephone services such as dial tone,
local service, long distance, billing and records, and maintenance.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) – USB is a “plug-and-play” interface between a computer and add-on
devices, such as a Wireless Voice Gateway.
Xpress Technology - One of the popular performance-enhancing WiFi technologies, designed to improve
wireless network efficiency and boost throughput. It is more efficient in mixed environments, and it can
work with 802.11a/b/g networks.
Please do not send any products to the Indianapolis address listed in this manual or on the carton. This
will only add delays in service for your product.
THOMSON
101 West 103rd Street,
Indianapolis, IN 46290, USA
85
Illustrations contained in this document are for representation only.
Page 41

For more information
THOMSON
101 West 103rd Street,
Indianapolis, IN 46290, USA http://www.technicolor.com
2006 Thomson Inc.- Trademark(s) ® Registered\ -Marca(s) Registada(s)\
C
○
Photos and features subject to change without notice.
Illustration of product finish may vary from actual color.
 Loading...
Loading...