Page 1

FriendlyNET® FM2008/2009
SNMP/Web Managed Switches
User’s Manual
Page 2

Quick Start Guide
Follow these steps to install the switch:
1. Open the box and check the contents. See Chapter 1 for a complete list
of the items included with the switch.
2. Install the switch in an equipment or wall rack, or prepare it for desktop
placement.
3. Connect the power supply.
4. Connect network devices to the switch.
5. Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for configuration and management
capabilities.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
2 User’s Manual
Page 3

FriendlyNET FM2008/2009 SNMP/Web Managed Switches
User’s Manual
Asanté Technologies, Inc.
821 Fox Lane
San Jose, CA 95131
USA
ALES
S
800-662-9686 Home/Office Solutions
800-303-9121 Enterprise Solutions
408-435-8388
sales@asante.com
ECHNICAL SUPPORT
T
801-566-8991 Worldwide
801-566-3787 FAX
www.asante.com
support@asante.com
Copyright © 2002 Asanté Technologies, Inc. Asanté and FriendlyNET are registered trademarks of Asanté Technologies, Inc. The Asanté
logo is a trademark of Asanté Technologies, Inc. All other names or marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
owners. All features and specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Rev. A
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
3 User’s Manual
Page 4

Table of Contents
Quick Start Guide ................................................................................................... 2
1. Introduction......................................................................................................... 5
2. Hardware Description......................................................................................... 9
3. Console Management ...................................................................................... 15
4. Web-Based Management................................................................................. 55
5. Technical Specifications ................................................................................... 82
6. Troubleshooting................................................................................................ 83
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
4 User’s Manual
Page 5

1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the FM2008/2009 SNMP/Web Managed Switch.
The FM2008/2009 switches are compact desktop-sized switches that are
an ideal solution for the SOHO (Small Office or Home Office) network user.
They provide full wire-speed, Fast Ethernet switching that allows a
high-performance, low-cost connection. Each switch features
store-and-forward switching and can auto-learn and store source
addresses on an 8K-entry MAC address table
.
Figure 1-1. The FriendlyNET FM2009 Switch
The FM2008/2009 both provide 8 switched, auto-sensing 10/100
Mbps RJ-45 Ethernet ports. Each switch will automatically detect the
speed of the device(s) connected to it, allowing the user to use both
10 and 100Mbps legacy devices. The 10Mbps bandwidth will
accommodate 10Mbps workgroup hubs while simultaneously
providing the 100Mbps bandwidth needed to accommodate
multimedia applications. In addition, each RJ-45 port supports Auto
MDI/MDI-X function.
The FM2009 switch also provides one 100Base-FX fiber port. Four
types of fiber connectors are available: SC, MT-RJ, VF-45
(multi-mode), and SC (single-mode). The fiber port can be used to
connect to a remote site up to 2 kilometers (multi-mode) or 15–60
kilometers (SC single-mode) away.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
5 User’s Manual
Page 6

With its built-in Web-based Management, managing and configuring
the switch is easy: From cabinet management to port-level control
and monitoring, the user can visually configure and manage the
network via a web browser. Just click your mouse instead of typing
command strings. However, the switch can also be managed via
telnet, console, or SNMP management.
Features
• Conforms to IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, and 802.3x Ethernet
Standards
• 8x auto-sensing 10/100Mbps Ethernet RJ-45 ports
• Automatic MDI/MDI-X crossover for each 10BaseT/
100BaseTX port
• FM2009 only: 1 fixed 100Mbps fiber port (SC/SC single
mode/MT-RJ/VF-45 connector)
• Half-duplex mode for backpressure, and full-duplex for
flow control
• Store-and-forward switching architecture for abnormal
packet filtering
• Automatic address learning, address migration
• 8K-entry MAC address table
• 2Mbit memory buffer sharing
• Performs non-blocking full wire speed switching
• LED indicators for Power, 100Mbps, Link/Activity, Full
duplex
• 10 inch desktop-sized design
Intelligent Management Features
• Web-based management
• SNMP network management
• Console and Telnet management
• IEEE 802.1q Port Base VLAN and Tag VLAN up to 256
static VLANs, or up to 4094 dynamic VLANs
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
6 User’s Manual
Page 7

• IEEE 802.1ad Port Trunking LACP supported
• IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree
• MIB II (RFC1213) supported
• IP Multicast, IGMP Snooping
• Quality of Service (QoS)
• Port Mirror, Broadcast Filter, Static MAC Address, Port
Security, MAC Filtering and GVRP supported
Package Contents
Unpack the contents of the switch and verify them against the
following checklist:
• Switch
• Power Cord
• Rack Mount Kit
• Four Rubber Feet
• RS-232 Cable
• Set-up Guide
• User’s Manual (this document) on CD-ROM
If any item is missing or damaged, please contact your local dealer
immediately for service.
Management Methods
The switch series supports the following management methods:
• Console and Telnet Management
• Web-based Management
• SNMP Network Management
Console and Telnet Management
Console Management is done through the RS-232 Console Port.
Managing the switch in this method requires a direct connection
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
7 User’s Manual
Page 8

between the computer and the switch, while Telnet management is
done over the network. Once the switch is on the network, use Telnet
to log in and change the configuration.
Note: The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.0.1. Both the
default user name and the default password are root.
Web Based Management
The switch provides an embedded HTML web site residing in flash
memory. It offers advanced management features and allows users to
manage the switch from anywhere on the network through a standard
browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
SNMP Network Management
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) provides a means to
remotely manage network devices, and to monitor statistics, performance,
and security.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
8 User’s Manual
Page 9

2. Hardware Description
This section describes the hardware of the FM2008 and 2009. (The
model shown is the FM2009. The FM2008 is identical, except that
there is no fiber uplink port.)
Front Panel
The front panel of the switch consists of 8 auto-sensing 10/100Mbps
Ethernet RJ-45 ports (automatic MDI/MDI-X), one 100Base-FX fiber
port, and the LED indicators.
FM2009 Managed Switch
Figure 2-1. The front panel of the switch
Four types of fiber connectors are available (FM2009 only): SC, SC
single-mode, MT-RJ, and VF-45.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
9 User’s Manual
Page 10
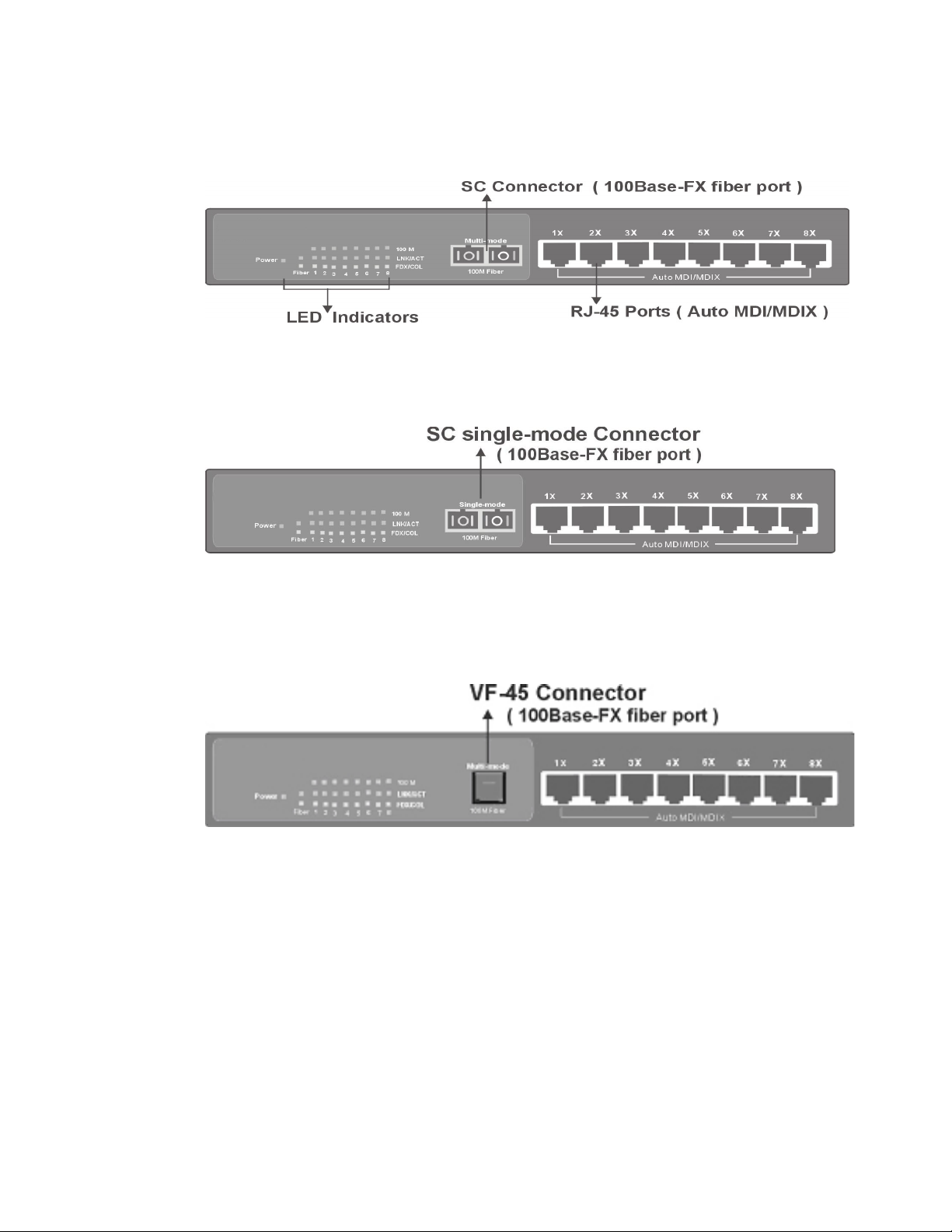
FM2009 managed switch with SC Connector (multi-mode)
Figure 2-2. The front panel of the FM2009 with a SC connector
FM2009 managed switch with SC Connector (single-mode)
Figure 2-3. The front panel of the FM2009 with a SC (single mode) connector
FM2009 managed switch with VF-45 Connector
Figure 2-4. The front panel of the FM2009 with a VF45 connector
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
10 User’s Manual
Page 11

FM2009 managed switch with MT-RJ Connector
Figure 2-5. The front panel of the FM2009 with a MT-RJ connector
•
RJ-45 Ports (Auto MDI/MDI-X):
auto-sensing for 10Base-T or 100Base-TX connections.
In general,
MDI-X
MDI/MDI-X
workstation without changing non-crossover or crossover cabling.
•
100Base-FX Fiber Port:
available for the switch, as shown above. The distance for fiber
cabling can be extended up to 2 kilometers. However, the distance
for SC single-mode fiber port is 60 kilometers.
means connecting to a workstation or PC. Therefore,
means connecting to another hub or switch while
MDI
means that the switch can connect to another switch or
LED Indicators
Eight 10/100Mbps ports;
Auto
There are 4 types of fiber connectors
Figure 2-6. LED Indicators from the FM2009
The fiber port (FM2009) has two LED indicators (Link/Activity, Full
Duplex), and each UTP port has three LED indicators (100Mbps,
Link/Activity, Full Duplex).
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
11 User’s Manual
Page 12
The following table provides descriptions of the LEDs statuses and
meanings. These LEDs provide a real-time indication of systematic
operation status.
LED Status Color Description
Power
On Green Power On
On Green The port is operating at 100Mbps
100Mbps
The port is operating at 10Mbps, or no
device is attached
A valid link has been established on
the port
The port is receiving or transmitting
data
Link/
Activity
Off
On Green
Blinking Green
Off No device attached
The port is operating in full-duplex
On Yellow
mode. This LED is always lit on the
fiber port
Full
Duplex
Table 2-1. The description of LED Indicators
Blinking Yellow Packet collision is occurring on the port
Off
Half-duplex mode or no device
attached
Rear Panel
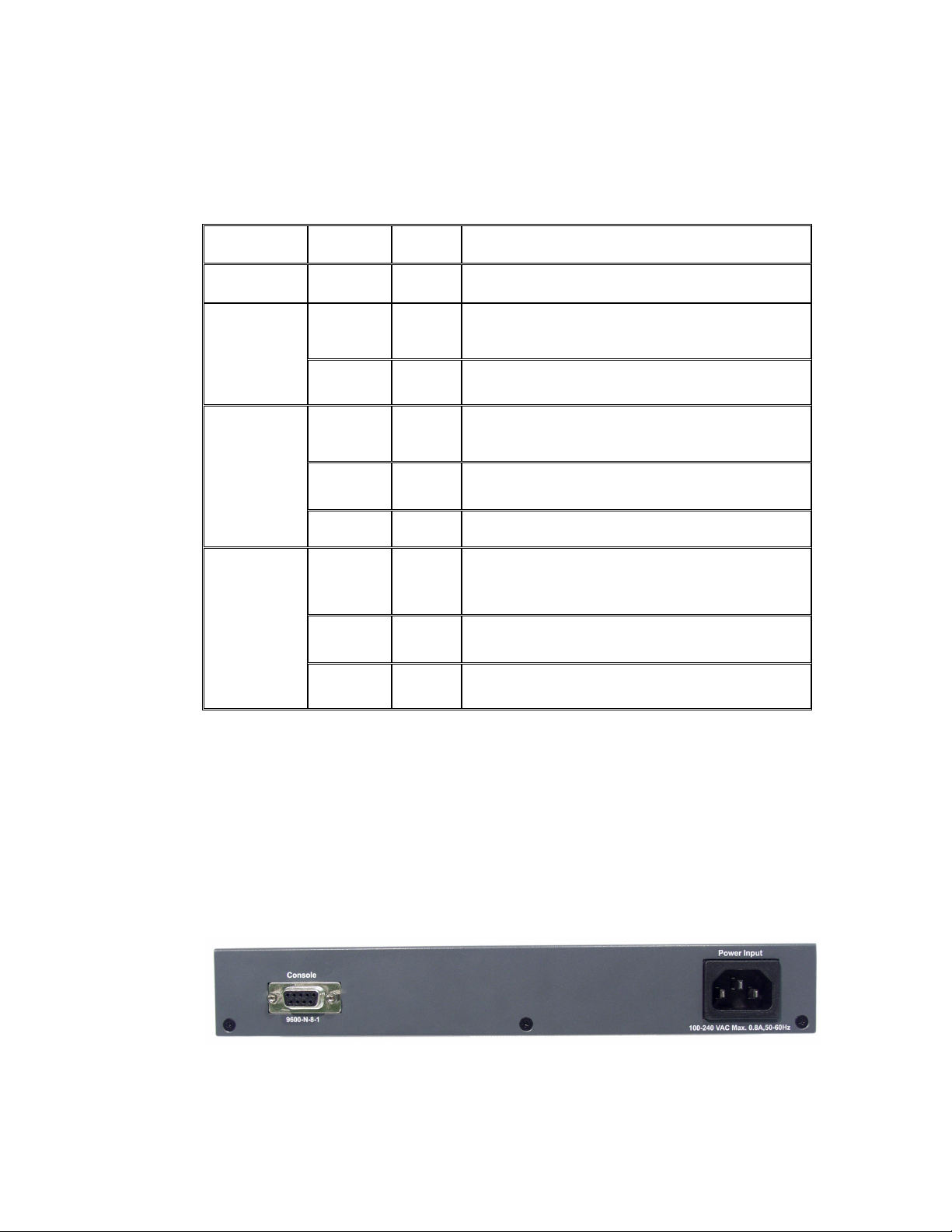
The console port and 3-pronged power plug are located at the rear
panel of the switch as shown in figure 2-7. The switch will work with
AC in the ranges 100–240V AC, 50–60Hz.
Figure 2-7. The rear panel of the switch
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
12 User’s Manual
Page 13

Console Port: Switch management can be done through the console
port. It requires a direct connection between the switch and an end
station (PC) via an RS-232 cable.
Desktop Installation
Set the switch on a sufficiently large flat space with a power outlet
nearby. The surface should be clean, smooth, level, and sturdy.
Make sure there is enough clearance around the switch to allow
attachment of cables, power cord and air circulation.
Attaching Rubber Feet
1. Make sure mounting surface on the bottom of the switch is
grease and dust free.
2. Remove adhesive backing from the rubber feet (supplied).
3. Apply the rubber feet to each corner on the bottom of the switch.
These footpads can prevent the switch from shock/vibration.
Installation Into an Equipment Rack
To mount the switch into an equipment rack:
1. Place the switch on a flat, stable surface.
2. Locate a rack-mounting bracket (supplied) and place it over the
mounting holes on one side of the unit.
3. Use the screws (supplied) to secure the bracket (with a Phillips
screwdriver).
4. Repeat the two previous steps on the other side of the unit.
5. Place the switch in the equipment rack.
6. Secure the switch by securing its mounting brackets onto the
equipment rack.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
13 User’s Manual
Page 14

Important!
for each bracket are secured to the equipment rack. Failure to do so could
cause the unit to fall, which may result in personal injury or damage to the
unit.
Make sure the unit is supported until all of the mounting screws
Equipment Rack Guidelines
• Size: 10.0 x 5.2 x 1.5 inches
• Ventilation: Ensure that the rack is installed in a room in which the
temperature remains below 40° C (104° F). Be sure that no
obstructions, such as other equipment or cables, block airflow to or
from the vents
• Clearance: In addition to providing clearance for ventilation, ensure
that adequate clearance for servicing the switch from the front exists
Power On
Connect the power cord to the power socket on the rear panel of the
switch. The other side of power cord connects to the power outlet. The
internal power supply in the switch works with AC in the voltage
ranges 100-240VAC, frequency 50–60Hz.
Check the power indicator on the front panel to see if power is
properly supplied.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
14 User’s Manual
Page 15

3. Console Management
This chapter explains how to configure console management via a
direct connection to the console port of the switch.
Console management involves the administration of the switch via a
direct connection to the RS-232 console port. This port is a female
DB-9 connector. From the main menu of the console program, user
has access to manage the functions of the switch.
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
Figure 3-1. Connecting the switch to a terminal via an RS-232 cable
Use the supplied RS-232 cable to connect a terminal or PC to the
console port. The terminal or PC to be connected must support the
terminal emulation program.
After the connection between the switch and the PC is finished, turn
on the PC and run a terminal emulation program such as Hyper
Terminal to match the following default characteristics of the console
port:
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
15 User’s Manual
Page 16
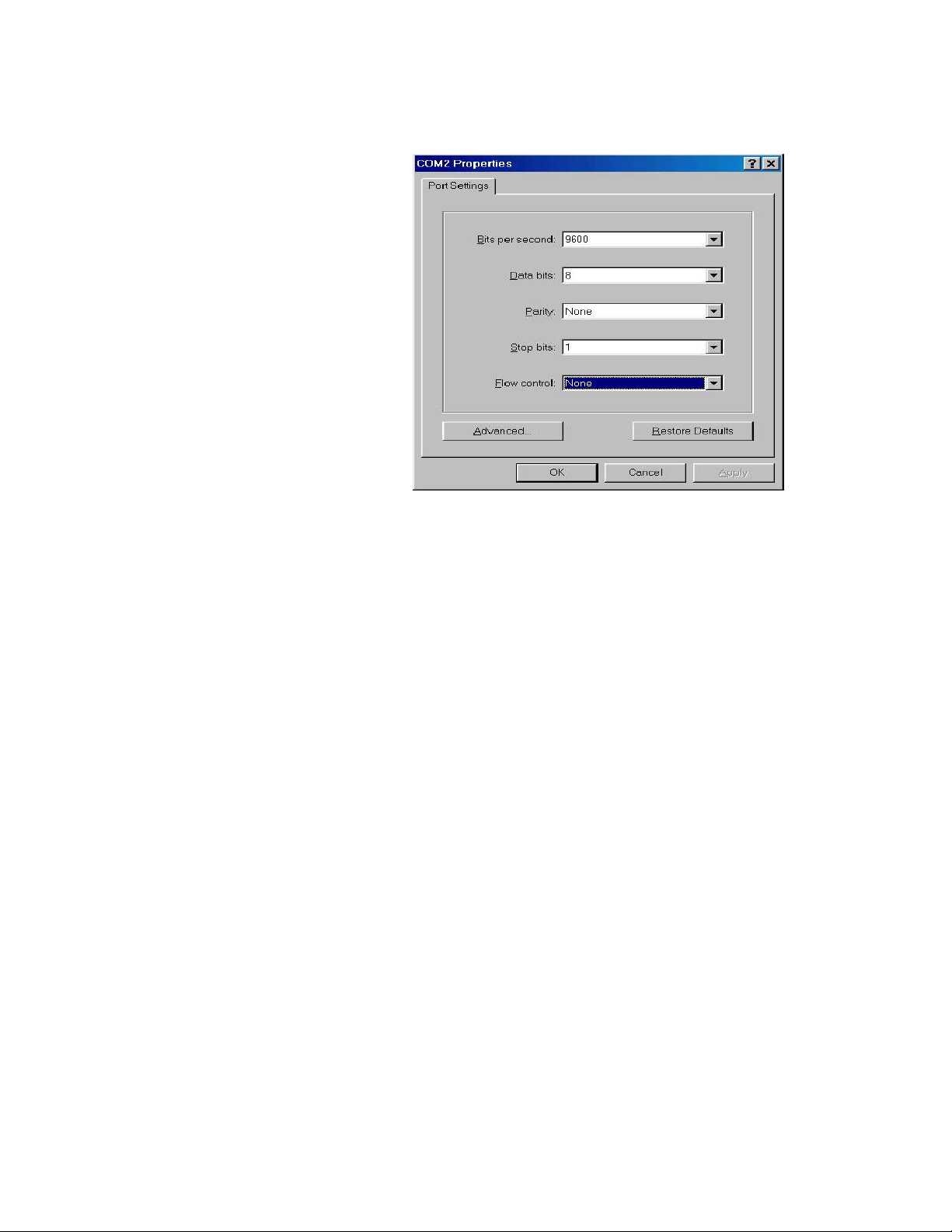
Baud Rate: 9600
bps
Data Bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bit: 1
Control flow: None
Figure 3-2. Communication parameters settings
After entering the parameter settings, press the Enter key and the
Login screen for console management appears.
Console – Menu
The switch provides a serial interface to manage and monitor the
switch. The user can follow the Console Port Information provided by
the web interface to use Windows HyperTerminal program to connect
to the switch.
Type the user name and password to login. The default user name is
root and the default password is also root.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
16 User’s Manual
Page 17

3.1 Main Menu
To move through each screen’s menu, use the Tab key or Backspace
bar to highlight an option, press Enter to select an option, and press
the Spacebar to toggle between configuration options.
The main menu contains the following options:
• Status and Counters: Displays the status of the switch
• Switch Static Configuration: Allows the user to configure the
switch
• Protocol Related Configuration: Allows the user to configure
supported protocols
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
17 User’s Manual
Page 18

• Reboot Switch: Restarts the system or resets switch to default
configuration
• Logout: Exits the menu line program
3.2 Status and Counters
From the main menu, select Status and Counters to configure the
following:
• Port Status
• Port Counters
• System Information
3.2.1 Port Status
This page displays the current status of each port.
• Typ e: Displays the port speed
• Enabled: Displays whether each port is enabled (“Yes”) or
disabled (“No”)
• Status: Displays each port’s link status; “Down” means there is
no link detected, and “Up” means there is a valid link detected
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
18 User’s Manual
Page 19
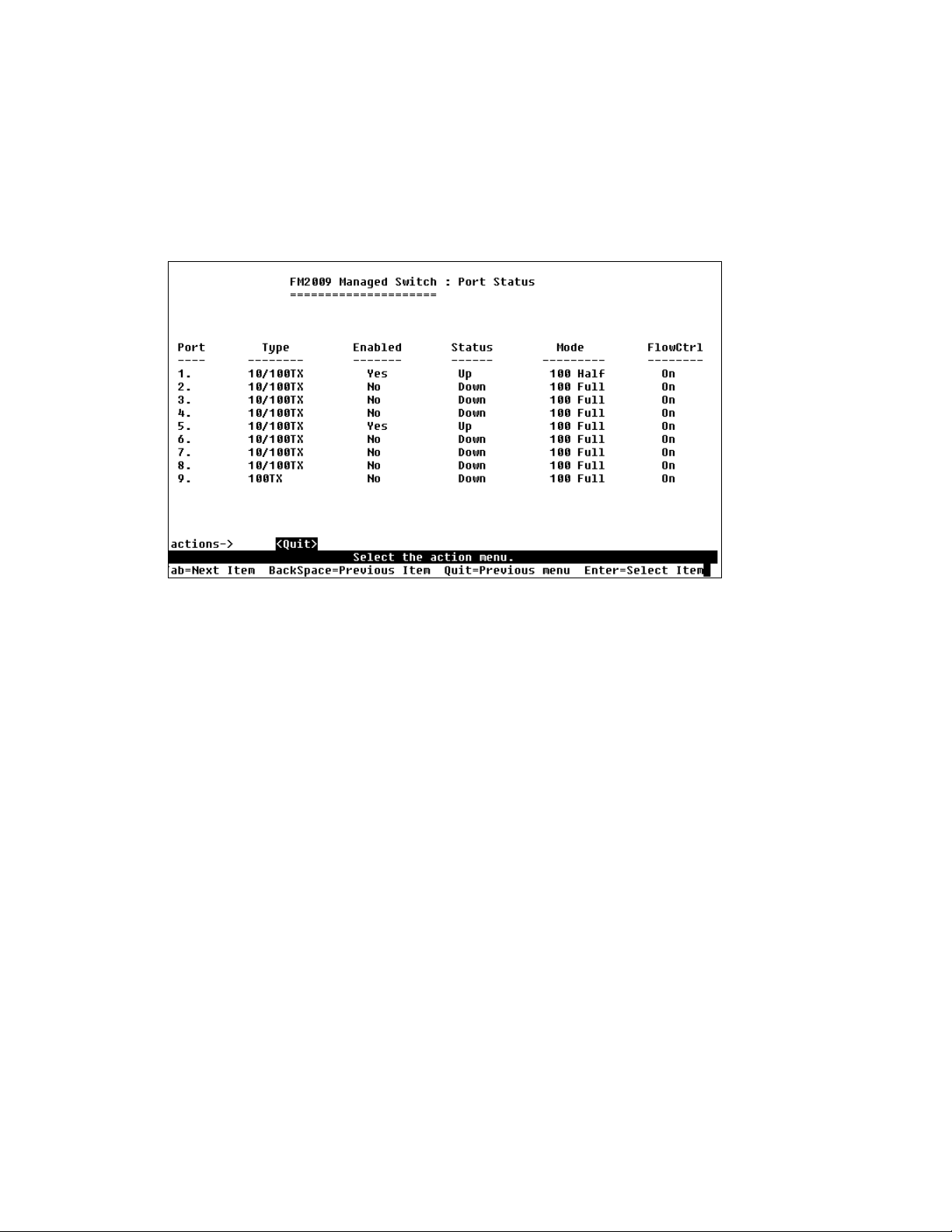
• Mode: Displays each port’s speed and duplex state
• FlowCtrl: Displays the flow control status of each port; “On”
indicates that flow control is enabled and “Off” indicates that it is
disabled
Actions->
Press the Tab or Backspace keys to choose action menu, and press
the Enter key to select an option.
<Quit>: Exits the port status page, and returns to the previous menu
<Previous Page>: Displays the previous page
<Next page>: Displays the next page
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
19 User’s Manual
Page 20

3.2.2 Port Counters
This page displays the current counter statistics for each port.
Actions->
Press the Tab or Backspace keys to choose action menu, and press
the Enter key to select an option.
<Quit>: Exits the port status page, and returns to the previous menu
<Reset All>: Sets all counters to 0
<Previous Page>: Displays the previous page
<Next page>: Displays the next page
3.2.3 System Information
This page displays the system information. Press the Esc key to
return to the main menu.
• System Description: Displays the name of the device
• MAC Address: Displays the unit’s MAC Address (the unique
hardware address assigned by the manufacturer)
• Firmware Version: Displays the firmware version
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
20 User’s Manual
Page 21

• Hardware Version: Displays the hardware version
• Default config value version: Displays the EEPROM version
3.3 Switch Static Configuration
From the main menu, select Switch Static Configuration to configure
the following options:
• Administration Configuration
• Port/Trunk Configuration
• Port Mirroring Configuration
• VLAN Configuration
• Priority Configuration
• MAC Address Configuration
• Misc. Configuration
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
21 User’s Manual
Page 22

3.3.1 Administration Configuration
From the Switch Static Configuration menu, select Administration
Configuration to configure the following options:
• Device Configuration
• IP Configuration
• Change Username
• Change Password
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
22 User’s Manual
Page 23

3.3.1.1 Device Information
This page displays the device information. Use the action menu line to
change information.
Actions->
<Edit>: Allows the configuration of all items. When finished, press
Esc to return to the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configuration.
<Quit>: Exits the Device Information page and returns to the previous
menu.
3.3.1.2 IP Configuration
From this page, the user can change the IP address from the default
IP address. Use the action menu line to enter the new IP setting.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
23 User’s Manual
Page 24

Actions->
<Edit>: Configures all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configuration.
<Quit>: Exits the IP Configuration page and returns to the previous
menu.
Note: You need to save and restart the computer after finishing IP
configuration.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
24 User’s Manual
Page 25

3.3.1.3 Change Username
From this page the user can change the web management user
name.
3.3.1.4 Change Password
From this page the user can change the web management user
password.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
25 User’s Manual
Page 26
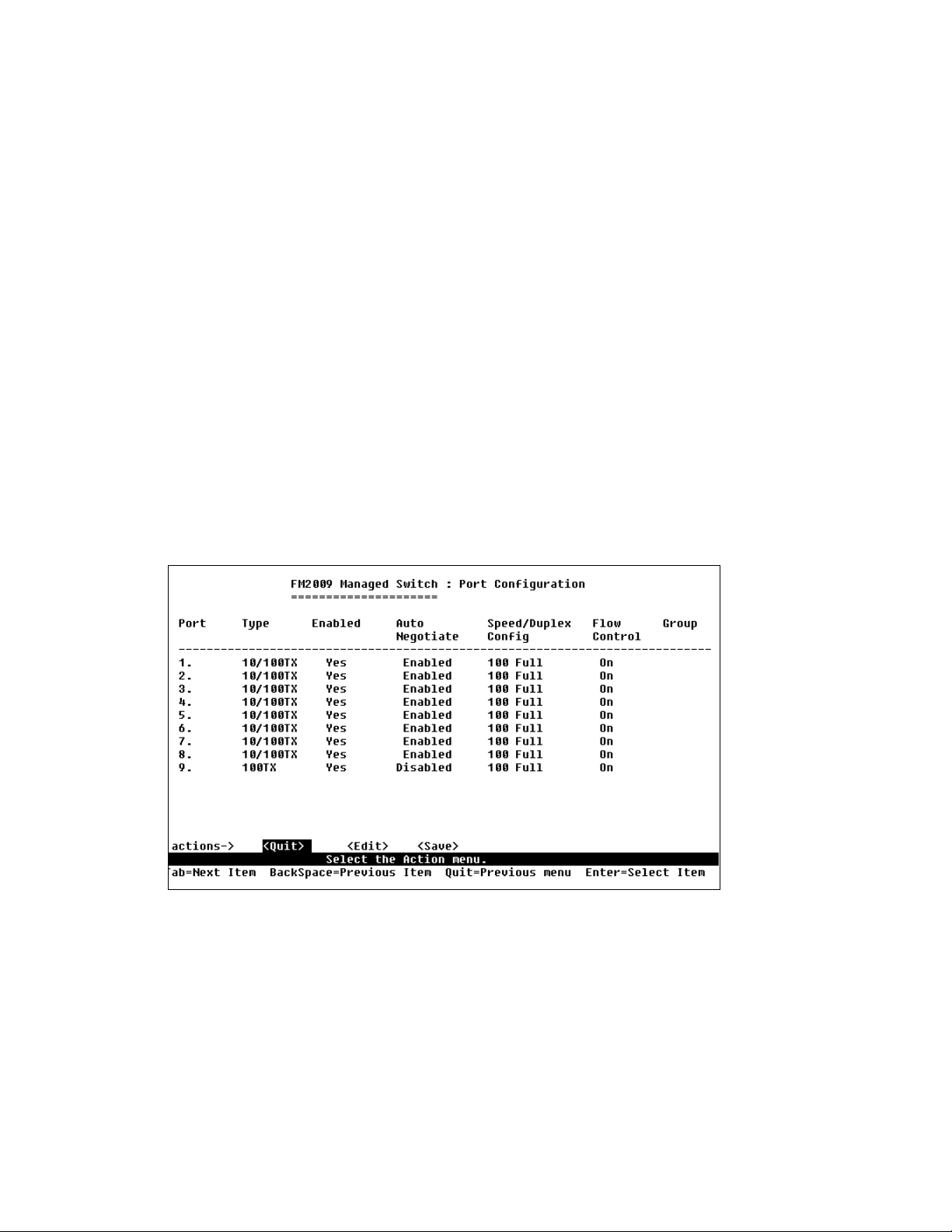
3.3.2 Port/Trunk Configuration
From the Switch Static Configuration page, select Port/Trunk
Configuration to change each port’s status and to configure trunking
groups. Press the Space key to toggle between configuration options.
• Enabled: The user can disable or enable each port
• Auto Negotiate: The user can enable or disable auto
negotiation for each port
• Speed/Duplex Config: The user can set 100Mbps or 10Mbps
speed on ports 1-8 (port 9 is 100Mbps only), and set full-duplex
or half-duplex mode
• Flow Control: The user can enable or disable flow control
• Group: The user can set trunk groups for ports 1-8. There can
be up to four trunk groups
Actions->
<Quit>: Exits the port configuration page and returns to the previous
menu.
<Edit>: Configures all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
26 User’s Manual
Page 27

<Previous Page>: Returns to the previous page.
<Next page>: Goes to the next page.
3.3.3 Port Mirroring Configuration
From the Switch Static Configuration page, select Port Mirroring
Configuration. Port mirroring is a method for monitoring traffic in
switched networks. Traffic through all the ports can be monitored by
one specific port. Press the Space key to toggle between the
configuration options:
• Port mirroring state: Use the space bar to toggle between
“Disabled” and “Enabled”
• Analysis Port: Select which port will act as a “sniffer” port to
monitor port traffic.
• Action: Select the ports to monitor. All monitored port traffic will
be copied to the “sniffer” port. You can select a maximum of 9
monitored ports in the switch. Under the Action option, you
may choose whether you want to monitor RX frames only or TX
frames only, or both.
Actions->
<Quit>: Exits the port monitoring configuration page and returns to
the previous menu.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
27 User’s Manual
Page 28

<Edit>: Configures all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Previous Page>: Returns to the previous page.
<Next page>: Goes to the next page.
3.3.4 VLAN Configuration
From the Switch Static Configuration page, select the VLAN
Configuration option to configure the following:
• VLAN Configure
• Create a VLAN Group
• Edit/Delete a VLAN Group
3.3.4.1 VLAN Configure
Use the console connection to enable VLANs on the switch. Select VLAN
Configure and Edit, then use the space bar to toggle between VLAN modes:
Disabled, Port-Based, 802.1Q, and 802.1QwithGVRP. When using 802.1Q
VLANs, enter the following values:
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
28 User’s Manual
Page 29

• PVID (Port VID): Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to
untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is useful for
accommodating devices that you want to participate in the
VLAN but don’t support tagging. Only one untagged VLAN is
allowed per port
• Ingress Filter 1: Matches Ingress Filtering Rule 1. If enabled,
drops any frame received by the port whose tag doesn’t match
the port’s configured VID. Press Spacebar to toggle between
Enable and Disable
• Ingress Filter 2: Matches Ingress Filtering Rule 2. If enabled,
drops any frame without a VLAN tag. Press Spacebar to toggle
between Enable and Disable
Important! Enabling either of these filters may disrupt communication
through the switch. Please double-check your settings before saving
the VLAN settings.
3.3.4.2 Create a VLAN Group
Create a VLAN and add tagged/untagged member ports to it.
•
VLAN Name:
•
VLAN ID:
•
Protocol VLAN:
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
Enter a name for the new VLAN
Enter a VID (between 2~4094). The default is 1
Press the
Space
key to choose the protocol type
29 User’s Manual
Page 30

•
Member:
Press the
Space
key to toggle each port’s VLAN
membership. There are three options
:
UnTagged
Tagged
: the port is not a member of the VLAN group
No
: the member port is untagged port
: the member port is tagged port
Actions->
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
<Edit>: Configures all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Previous Page>: Returns to the previous page.
<Next page>: Goes to the next page.
3.3.4.3 Edit / Delete a VLAN Group
Access this page to edit or delete a VLAN group.
1. Select <Edit> or <Delete>.
2. Choose the VLAN group that you want to edit or delete and
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
30 User’s Manual
Page 31

then press Enter.
3. Modify the options as desired, or add or remove member ports
as desired.
4. After completing the desired changes to the VLAN, press
<Save> to save the new configuration.
Note: The default VLAN cannot be deleted, nor can the VLAN Name
or VLAN ID be modified.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
31 User’s Manual
Page 32

3.3.5 Priority Configuration
There are 7 priority levels that map traffic to two queues.
Queue Service Ratio (H:L) allows the user to select the ratio of high priority
packets to low priority packets processed by the switch.
The High/Low
First In First Out: The packets are sent out in the order they were
received.
High to Low: High priority packets are sent before low priority
packets.
Ratio: The user may select the precedence given to packets in the
switch's high-priority queue. These options represent the number of
high priority packets sent before one or more low priority packets are
sent. For example, a ratio of 5:2 means that the switch sends 5 high
priority packets before sending 2 low priority packets.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
32 User’s Manual
Page 33

Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.3.6 MAC Address Configuration
3.3.6.1 Static MAC Address
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch's
address table, regardless of whether the device is physically
connected to the switch. This saves the switch from having to re-learn
a device's MAC address when a device is reconnected to the network.
In this page user can add, modify or delete a static MAC address.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
33 User’s Manual
Page 34

Add static MAC address
1. Press <Add> --> <Edit> key to add a static MAC address.
2. Enter the MAC address of a device from which the port should
permanently forward traffic regardless of the device’s network
activity. Enter the address without separators (e.g.
000094abcdef)
3. In the Port num item, enter the port number.
4. If tag-based (802.1Q) VLANs are set up on the switch, static
addresses are associated with individual VLANs. Type the
VLAN ID number associated with the device’s MAC address.
5. Press Esc to go back to the action menu line, and then select
<Save> to save the new configuration.
Edit static MAC address
1. Press the <Edit> key to modify a static MAC address.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to modify and then
press Enter.
3. Press the <Edit> key to modify the desired items.
4. Press Esc to go back to the action menu line, and then select
<Save> to save the new configuration.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
34 User’s Manual
Page 35

Delete static MAC address
1. Press the <Delete> key to delete a static MAC address.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then
press Enter.
3. After deleting the static MAC address, press <Save> to have
the changes take effect.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
35 User’s Manual
Page 36

3.3.6.2 Filter MAC Address
From this screen, add, edit, or delete filter MAC addresses.
3.3.7 Miscellaneous Configuration
3.3.7.1 Port Security
By default, the port security feature is disabled for each port to allow for
address learning. When port security is enabled, the port will only accept
incoming packets from a known static MAC address. The user can enable
port security on a port, and then use the Static MAC Address page to define
a list of MAC addresses that can use the secure port.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
36 User’s Manual
Page 37

Select <Edit> to enable or disable the port security.
Press the Space bar to toggle between enabled and disabled on each
port.
Press Esc to go back to the action menu line, and then select <Save>
to save the new configuration.
3.3.7.2 MAC Age Interval
From this screen, you may enter the time (in seconds) that an inactive
MAC address remains in the switch’s address table. The valid range
is 300–765 seconds. The default is 300 seconds.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
37 User’s Manual
Page 38

Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.3.7.3 Broadcast Storm Filtering
From this page you may configure the broadcast storm filter. Press
<Edit> to proceed to configure the broadcast storm filter.
Press the Spacebar to choose the threshold value. This is the
percentage of total traffic that may be broadcast before the filter takes
effect. Valid threshold values are 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and NO.
Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
38 User’s Manual
Page 39

3.3.7.4 Max bridge transmit delay bound
• Max bridge transmit delay bound: Limits the packet queue
time in the switch. If enabled, the packets will be dropped from
the queue after the time has expired. Press the Space bar to
set the time. The options are 1 second, 2 seconds, 4 seconds
and off. The default is 1 second
• Enable Delay Bound: Limits the low priority packets’ queuing
time in the switch. If enabled, the low priority packets that stay
in the switch past the Max Delay Time will be sent. Press the
Space bar to enable or disable this function
Note: Make sure that Max bridge transit delay bound control is
enabled before enabling Delay Bound.
• Max Delay Time: Sets the time that low priority packets may
queue in switch. The valid range is 1–255 ms.
NOTE: Make sure that “Max bridge transit delay bound control” is
enabled before enabling Delay Bound.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
39 User’s Manual
Page 40

Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.4 Protocol Related Configuration
3.4.1 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
3.4.1.1 STP Enable
On this screen you may enable or disable the Spanning Tree function.
Press the Space bar to toggle between
Enable
and
Disable
.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
40 User’s Manual
Page 41

3.4.1.2 System Configuration
On the left of this screen, you can view the Root Bridge Information.
On the right, you can configure new values for the STP parameters.
Bridge Priority
Setting the Bridge Priority to a low value will increase the likelihood that the
current bridge will become the root bridge. If the current bridge is located
physically near the center of your network, you may wish to decrease the
Bridge Priority from its default value of 32768 to make it become the root
bridge. If the current bridge is near the edge of your network, it is best to
leave the value of the Bridge Priority at its default setting.
Hello Time
This is the time period between BPDUs transmitted by each bridge. The
default setting is 3 seconds.
Maximum Age
Each bridge should receive regular configuration BPDUs from the direction
of the root bridge. If the maximum age timer expires before the bridge
receives another BPDU, it assumes that a change in the topology has
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
41 User’s Manual
Page 42

occurred, and it begins recalculating the spanning tree. The default setting
for Maximum Age is
15 seconds.
Forward Delay
After a recalculation of the spanning tree, the Forward Delay parameter
regulates the delay before each port begins transmitting traffic. If a port
begins forwarding traffic too soon (before a new root bridge has been
selected), the network can be adversely affected. The default value for
Forward Delay is 5 seconds.
: The above parameters (Hello Time, Maximum Age and Forward
Note
Delay) are constrained by the following formula:
(Hello Time + 1) <= Maximum Age <= 2 x (Forward Delay – 1)
In general, reducing the values of these timers will make the spanning tree
react faster when the topology changes, but may cause temporary loops as
the tree stabilizes in its new configuration. Increasing the values of these
timers will make the tree react more slowly to changes in topology, but will
make an unintended reconfiguration less likely. All of the bridges on the
network will use the values set by the root bridge. It is only necessary to
reconfigure that bridge if you wish to change the parameters.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
42 User’s Manual
Page 43

3.4.1.3 Per-port Configuration
PortState: View the spanning tree status for each port.
PathCost:
cost factor to each port. The lower the assigned port path cost is, the more
likely that port will be accessed. The default port path cost for a 10Mbps or
100Mbps port is the result to the equation:
Path cost = 1000/LAN speed (in Mbps)
Therefore, for ports operating at 10Mbps, the default port path cost is 100.
For ports operating at 100Mbps, it is 10.
Port path cost is the spanning tree parameter that assigns a
If you change the value, you
need to restart the switch for the change to take effect.
Priority:
so that if two or more ports have the same path cost, the STP selects the
path with the highest priority (the lowest numerical value). By changing the
priority of a port, you can make it more, or less, likely to become the root
port. The default value is 128, and the value range is 0 – 255.
The port priority is a spanning tree parameter that ranks each port,
If you
change the value, you need to restart the switch for the change to take
effect.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
43 User’s Manual
Page 44

3.4.2 SNMP
Use this page to define management stations as trap managers and
to enter SNMP community strings. You can also define a system
name, location, and contact person for the switch.
4.4.2.1 System Options
Select <Edit> to enter the information, and then select <Save> to
have the changes take effect.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
44 User’s Manual
Page 45

System Name: Enter a name to be used for the switch.
System Contact: Enter the name of contact person or organization.
System Location: Enter the location of the switch.
3.4.2.2 Community Strings
Use this page to enter SNMP community strings.
Community Name: Enter the name of the current string.
Write Access: Designate the access rights of the current string.
• Restricted: Read-only enables requests accompanied by this
string to retrieve MIB object information
• Unrestricted: Read-Write enables requests accompanied by
this string to retrieve MIB object information and to set MIB
objects to a new value
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
45 User’s Manual
Page 46

Actions->
<Add>: Creates community strings.
<Edit>: Modifies items. When finished, press Esc to go back to the
action menu line.
<Delete>: Deletes a community string. Press <Save> to have your
changes take effect.
<Save>: Saves the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.4.2.3 Trap Managers
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the
system alerts generated by the switch. If no trap manager is defined,
no traps are issued. Create a trap manager by entering the IP address
of the station and a community string.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
46 User’s Manual
Page 47

Actions->
<Add>: Creates a trap manager.
<Edit>: Modifies all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to the
action menu line.
<Delete>: Deletes a trap manager. Press <Save> to have your
changes take effect.
<Save>: Saves all the new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
47 User’s Manual
Page 48

3.4.3 GVRP
On this page you can enable or disable the GVRP (GARP VLAN
Registration Protocol) support.
Press the Space bar to toggle between Enabled/Disabled.
Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves all new configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
48 User’s Manual
Page 49

3.4.4 Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
3.4.4.1 Aggregator Setting
Group: Displays the trunk group ID.
LACP: Press the Space bar to enable or disable LACP (Link
Aggregation Control Protocol) support. If enabled, the group is a
LACP static trunking group. If disabled, the group is a local static
trunking group.
LACP Work Port Num: The maximum number of ports that can be
aggregated at the same time. If using the LACP static trunking group,
the extra ports are on standby and able to aggregate if a work port
fails. If using a local static trunking group, the number must be the
same as the number of group ports.
Note: Before setting LACP support, you first have to set trunking
groups in the
Port/Trunk Configuration
page.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
49 User’s Manual
Page 50

Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves all configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.4.4.2 State Activity
Active: The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
Passive: The port does not automatically send LACP protocol
packets, but responds only if it receives LACP protocol packets from
another device.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
50 User’s Manual
Page 51

Actions->
<Edit>: Configure all items. When finished, press Esc to go back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Saves all configurations.
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
3.4.4.3 LACP Status
In this page, you may view the trunking group information.
Actions->
<Quit>: Exits this page and returns to the previous menu.
<Previous Page>: Returns to the previous page.
<Next page>: Goes to the next page.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
51 User’s Manual
Page 52

3.5 Reboot Switch
Default: Resets the switch to the default configuration.
Restart: Reboots the switch.
3.6 Xmodem Upgrade
You can load an image file via an Xmodem upgrade during a system
restart. Follow the steps below to perform an Xmodem upgrade via
the console port.
1. Press the X key to start upgrading for Xmodem.
2. Disconnect the terminal and modify the baud rate to 57600bps,
then reconnect to the terminal.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
52 User’s Manual
Page 53

3. Select send file under the transfer menu from the menu bar.
4. Press the Browse button to select the path to the new image
file.
5. Select 1K XModem protocol and press Send button.
6. After successfully upgrading the new firmware, please modify
the baud rate setting of your terminal program to 9600bps.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
53 User’s Manual
Page 54

FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
54 User’s Manual
Page 55

4. Web-Based Management
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the
web-based management of the switch.
The FM2009 provides an embedded HTML website residing in flash
memory that allows users to manage the switch from anywhere on the
network using a standard web browser.
Note: For those who use Windows 2000 and have installed Service
Pack#2, the web management function may have display problems if
the IE version is 5.5 or older.
Web Management Function
1. The web management function uses a web browser to manage
and monitor the switch. The switch has the following default
values:
IP Address: 192.168.0.1
User Name: root
Password: root
If you need to change the IP Address immediately, you can use the
console mode to modify it.
2. Launch your web browser and enter http://192.168.0.1 in the URL
field. When prompted, type the user name and password and click
OK.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
55 User’s Manual
Page 56

4.1 Home Page
After entering the user name and password, you will come to the Home
page, as shown below. The following pages may be accessed from the
Home page:
• Port Status
• Port Statistics
• Administrator
• TFTP Update Firmware
• Configuration Backup
• Reset System
• Reboot
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
56 User’s Manual
Page 57

4.2 Port Status
The following information is displayed in the Port Status page:
• State: Displays each port’s status; off or on depending on the
user’s setting
• Link Status: Displays each port’s link status (up or down)
• Auto Negotiation: Displays each port’s auto-negotiation mode
• Speed status: Displays each port’s link speed: Port 1-8 are
10/100Mbps, Port 9 is 100 Mbps only
• Duplex status: Displays each port’s duplex mode (full or half)
• Flow control: Displays each port’s flow control status (On is
enabled, Off is disabled)
• Config: Displays the current configuration setting
• Actual: Displays the negotiation result
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
57 User’s Manual
Page 58

4.3 Port Statistics
The Port Statistics page provides the current status of the unit.
4.4 Administrator
The management functions include:
IP Address, Switch Settings, Console Port Information, Port Controls,
Link Aggregation, Filter Database, VLAN Configuration, Spanning
Tree, Port Mirror, SNMP, Security Manager, TFTP Update Firmware,
Configuration Backup, Reset System and Reboot.
4.4.1 IP Address
From this page, you can change the IP Address from the default value
(recommended). Fill in the new values, then click the Apply button.
You must reset switch and then enter the new IP address into the
browser’s URL window to access the web management interface. You
may also need to change your computer’s IP address to the same
network as the switch’s new IP address.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
58 User’s Manual
Page 59

4.4.2 Switch Settings
4.4.2.1 Basic
The Basic Switch Settings page displays the current information of the
switch. Click the
following information:
Basic
button on the Switch Settings page to display the
• Description: Displays the name of the device
• MAC Address: Displays the unique hardware address
assigned by the manufacturer
• Firmware Version: Displays the current firmware version
• Hardware Version: Displays the hardware version
• Default config value version: Displays the D
efault config
value version
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
59 User’s Manual
Page 60

4.4.2.2 Advanced
From the Switch Settings page, click the Advanced button to display
or configure the following information:
• MAC Address Age-out Time: Enter the number of seconds
that an inactive MAC address can remain in the switch's
address table. The valid range is 300–765 seconds, the default
is 300 seconds
• Max bridge transit delay bound control: Limits the packets’
queuing time in switch. If enabled, the packets in the queue will
be dropped when the time expires. The valid values are 1
second, 2 seconds, 4 seconds and off (default is 1 second)
• Broadcast Storm Filter: To configure broadcast storm control,
enable it and set the upper threshold for individual ports. The
threshold is the percentage of the port's total bandwidth used
by broadcast traffic. When broadcast traffic for a port rises
above the threshold you set, broadcast storm control becomes
active. The valid threshold values are 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%,
25% and off
.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
60 User’s Manual
Page 61

Priority Queue Service settings:
• First Come First Served: The sequence of packets sent
depends on their order of arrival
• All High before Low: All high priority packets are sent before
any low priority packets
• Weighted Round Robin (WRR): Select the preference given
to packets in the switch's high-priority queue. These options
represent the number of high priority packets sent before one
low priority packet is sent. For example, a 5:2 ratio means that
the switch sends 5 high priority packets before sending 2 low
priority packets
• Enable Delay Bound: Limit the low priority packets queuing
time in switch. Default Max Delay Time is 255ms. If the low
priority packet stays in switch longer than the Max Delay Time,
it will be sent. The valid range is 1–255 ms
Note: Make sure that Max bridge transit delay bound control is
enabled before checking the Enable Delay Bound box
• QoS Policy: High Priority Levels: Select which priority levels
are mapped to the high priority output queue.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
61 User’s Manual
Page 62

Protocol Enable Settings:
• Enable Spanning Tree Protocol: Enabled by default
(recommended)
• Enable Internet Group Multicast Protocol: IGMP protocol
enabled by default
• VLAN Operation Mode: Select Port Based, 802.1Q without
GVRP, 802.1Q with GVRP, or No VLAN
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
62 User’s Manual
Page 63

GVRP (GARP [Generic Attribute Registration Protocol] VLAN
Registration Protocol)
GVRP allows automatic VLAN configuration between the switch and
nodes. If the switch is connected to a device with GVRP enabled, you
can send a GVRP request using the VID of a VLAN defined on the
switch; the switch will automatically add that device to the existing
VLAN.
4.4.3 Console Port Information
The console is a standard UART interface used to communicate with
the serial port. You may use Windows HyperTerminal or a similar
program to link to the switch. From this page, you may view or
configure the desired parameters for your console connection:
Bits per seconds: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bits: 1
Flow control: none
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
63 User’s Manual
Page 64

4.4.4 Port Controls
From this page you can configure the following parameters:
• State: Disable or enable each port
• Auto Negotiation: Disable or enable auto negotiation for each
port
• Speed: Set port speed (100Mbps or 10Mbps) on ports 1-8; port
9 is 100Mbps only
• Duplex: Set full-duplex or half-duplex mode for each port
• Flow Control: Enable or disable flow control for each port
4.4.5 Trunking
Trunking provides a standardized means for exchanging information
between multiple devices on a link. This allows their Link Aggregation
Control to reach an agreement on the identity of the Link Aggregation
Group, move the link to that Link Aggregation Group, and enable its
transmission and reception functions in an orderly manner. Trunk up
to eight consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection. This
feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network. LACP
operation requires full-duplex mode. For more detailed information,
please refer to IEEE 802.3ad.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
64 User’s Manual
Page 65

4.4.5.1 Aggregator setting
1. System Priority: A value used to identify the active LACP. The
switch with the lowest value has the highest priority and is
selected as the active LACP.
2. Group ID: To create an aggregated link across two or more
ports, choose the "Group ID" and click Get.
3. LACP: If enabled, the selected group becomes an LACP static
trunking group. If disabled, the selected group becomes a local
static trunking group.
All ports support LACP dynamic trunking groups. If connecting
to a device that also supports LACP, the LACP dynamic
trunking group will be created automatically.
4. Work ports: The maximum number of ports that can be
aggregated at the same time. If utilizing a LACP static trunking
group, the extra ports are on standby and able to aggregate if
another working port fails. If using a local static trunking group,
the number must be the same as group ports.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
65 User’s Manual
Page 66

5. Select the ports to join the trunking group
6. If LACP is enabled, you can configure the LACP Active/Passive
status on each port.
7. Click Apply.
4.4.5.2 Aggregator Information
When setting the LACP aggregator, you can view the related
information by clicking Aggregator Information.
4.4.5.3 State Activity
Click on
protocol packets.
State Activity
to configure each port to automatically send LACP
Active (Status box selected): Check the box in each port to have that
port automatically send the LACP protocol packets.
Passive (
Status
box unselected): With the box unchecked, the port
will not automatically send the LACP protocol packets, and responds
only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device.
A link having either two active LACP ports or one active port can
perform dynamic LACP trunking.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
66 User’s Manual
Page 67

A link that has two passive LACP ports will not perform dynamic LACP
trunking because both ports are waiting for a LACP protocol packet
from the opposite device.
If you select active LACP, the active status will be created
automatically when you select the trunking port.
4.4.6 Filter Database
4.4.6.1 IGMP Snooping
The switch supports IP multicasting. Enable the IGMP protocol on the web
interface’s Switch Setting/Advanced page, and then click the
Snooping
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
button to view the multicast group, VID and member port. IP
67 User’s Manual
IGMP
Page 68

multicast addresses range from 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of
the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using
switches, routers, and hosts that support IGMP. Enabling IGMP allows the
ports to detect IGMP queries and report packets and manage IP multicast
traffic through the switch. IGMP has three types of messages, as described
in the table below
:
Message Description
Query
Report
Leave
Group
4.4.6.2 Static MAC Address
Click the
addresses currently defined on the switch.
A message sent from the IGMP router or switch asking for a response from
each host belonging to the multicast group.
A message sent by a host to the IGMP router or switch
wants to be or is a member of a given group indicated in the report message.
A message sent by a host to the IGMP router or switch to indicate that the host
has quit to be a member of a specific multicast group.
Static MAC Addresses
button to view or configure the static
to indicate that the host
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch's
address table, regardless of whether the device is physically
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
68 User’s Manual
Page 69

connected to the switch. This saves the switch from having to re-learn
a device's MAC address when the device is active on the network
again.
To add a static MAC address:
1. From the main menu, click Administrator, and then click Filter
Database.
2. Click Static MAC Addresses. In the MAC address box, enter
the MAC address to and from which the port should
permanently forward traffic, regardless of the network activity of
the device.
3. In the Port Number box, select a port number.
4. If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLANs are set up on the switch,
static addresses are associated with individual VLANs. Type
the VID (tag-based VLANs) associated with the MAC address.
5. Click Add.
4.4.6.3 Port Security
Click the Port Security button to enable security. A port in security
mode will be “locked” to traffic from devices whose MAC addresses
are not in the Static MAC Addresses table. Only incoming packets
with Source MAC already existing in the address table can be
forwarded normally. First, disable the port from learning any new MAC
addresses by checking the Enable Security box, and then use the
static MAC addresses screen to define a list of MAC addresses that
can use the secure port. After you are finished entering the settings,
click Submit to apply the changes to this page.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
69 User’s Manual
Page 70

4.4.6.4 MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is
filtered based on the source or destination addresses. For example, if your
network is congested because of high utilization from one MAC address,
you can filter all traffic transmitted from that MAC address, restoring
network flow while you troubleshoot the problem.
To add a MAC address filter
1. From the main menu, click
Database
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
.
Administrator
70 User’s Manual
, then click
Filtering
Page 71

2. Click
MAC Filtering
.
3. Click
4. In the MAC Address box, type the MAC address (without hyphens) to
filter.
5. Select the port that will filter traffic from this address.
6. If port-based or tag-based VLANs are configured on the switch, type
the name or VID of the VLAN to use the filter.
7. Click
.
Add
Apply
.
4.4.7 VLAN configuration
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast
domain. It allows you to isolate network traffic so only members of the same
VLAN receive traffic from other VLAN members. Creating a VLAN from a
switch is logically equivalent to reconnecting a group of network devices to
another Layer 2 switch. However, all the network devices are still plugged
into the same switch physically. The switch supports port-based and
protocol-based VLANs. In the default configuration, VLAN support is
enabled and all ports on the switch belong to the default VLAN, whose
VLAN ID (VID) is 1.
Note: The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
Port-based VLANs (IEEE 802.1Q VLAN)
This feature is an IEEE 802.1Q specification standard. Therefore, it is
possible to create a VLAN across devices from different switch vendors.
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN uses a technique to insert a “tag” into the Ethernet
frames. The tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that indicates the VLAN
numbers.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
71 User’s Manual
Page 72

Protocol-based VLANs
In order for an end station to send packets to different VLANs, it itself
has to be capable of tagging packets it sends with VLAN tags, or it
must be attached to a VLAN-aware bridge that is capable of
classifying and tagging the packets with different VLAN IDs, based on
not only on the default PVID but also other information about the
packet, such as the protocol.
4.4.7.1 Basic
Create a VLAN and add tagged member ports to it.
1. From the main menu, click Administrator -- VLAN
Configuration.
2. Click Add.
3. Type a name for the new VLAN.
4. Type a VID (between 2-4094). The default is 1.
5. From the
Available Ports
box, select ports to add to the switch
and click Add.
6. Click Apply.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
72 User’s Manual
Page 73

4.4.7.2 Port VID
Configure port VID settings
From the main Tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN page, click Port VID
Settings.
Port VID (PVID)
From this page, you can set the Port VLAN ID that will be assigned to
untagged traffic on a given port. For example, if port 9's Default PVID
is 100, all untagged packets on port 9 will belong to VLAN 100. The
default setting for all ports is VID 1.
This feature is useful for accommodating devices that you want to
participate in the VLAN but that don't support tagging. Only one
untagged VLAN is allowed per port.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
73 User’s Manual
Page 74

Ingress Filtering
Ingress filtering lets frames belonging to a specific VLAN to be
forwarded if the port belongs to that VLAN. The switch has two
ingress filtering rules, as follows:
Ingress Filtering Rule 1: Forward only packets with a VID matching
this port's configured VID.
Ingress Filtering Rule 2: Drop untagged Frames.
4.4.8 Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a standardized method (IEEE 802.1D)
for avoiding loops in switched networks. When STP is enabled, it ensures
that only one path at a time is active between any two nodes on the network.
You can enable Spanning Tree Protocol on the web interface Switch Setting
Advanced item by selecting
recommended that you enable STP on all switches to ensure a single active
path on the network.
Enable Spanning Tree protocol
. It is
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
74 User’s Manual
Page 75

1. You can view Spanning Tree information about the Root
Bridge, as in the following screen:
2. You can view Spanning Tree port status, as in the following
screen:
3. You can configure new values for the STP parameters, and
then click the Apply button to modify.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
75 User’s Manual
Page 76

Parameter Description
You can change the priority value used to identify the root bridge. The
Priority
Max Age
Hello Time
Forward
Delay time
Note: Only users familiar with the operation of Spanning Tree Protocol should change
these values.
bridge with the lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the
root. Enter a number 1 through 65535.
You can change the Max Age value, the number of seconds a bridge
waits without receiving Spanning Tree Protocol configuration messages
before attempting a reconfiguration. Enter a number 6 through 40.
You can change the Hello time value, the number of seconds between
the transmission of Spanning Tree Protocol configuration messages.
Enter a number 1 through 10.
You can change the forward delay time, the number of seconds a port
waits before changing from its Spanning Tree Protocol learning and
listening states to the forwarding state. Enter a number 4 through 30.
4. The following parameters can be configured on each port.
Click the Apply button to have the changes take effect.
Parameter Description
Port
Priority
Path Cost
Note: Only users familiar with the operation of Spanning Tree Protocol should change
these values.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
You can make a port more or less likely to become the root port, by
adjusting the priority setting. The rage is 0-255, with the default
setting is 128.
The lower the number the higher priority the port is given, making it
more likely to be the root port. If you change the value, you must
reboot the switch.
Specifies the path cost of the port that the switch uses to determine
which ports are the forwarding ports.
The port with the lowest path cost becomes the forwarding port. The
rage is 1-65535 and default value base on IEEE802.1D
10Mb/s = 50-600 100Mb/s = 10-60
If you change the value, you MUST reboot the switch.
76 User’s Manual
Page 77

4.4.9 Port Mirroring
The Port Mirror is a method for monitoring traffic in switched networks.
Traffic through the ports can be monitored by one specific port. That is,
traffic that goes into or out of the monitored ports will be duplicated
into the analysis port.
Port Mirroring State: Enable or disable the port mirror function.
Analysis Port: Select which port will copy all monitored ports’ traffic.
Mirror Ports: The ports you want to monitor. All monitored ports’
traffic will be copied to the analysis port. You can select a maximum of
9 monitor ports in the switch. To disable this function, set the monitor
port to none.
Monitor Rx: Monitor received frames from the port.
Monitor Tx: Monitor sent frames from the port.
4.4.10 SNMP
Any workstation running the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
can manage the switch, provided the Management Information Base (MIB)
is installed correctly on the management station. The SNMP is a protocol
that governs the transfer of information between management and the
SNMP agent. The switch supports SNMP v1.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
77 User’s Manual
Page 78

Use this page to define management stations as trap managers and
to enter SNMP community strings. You can also define a name,
location, and contact person for the switch. Fill in the system options
data, and then click Apply to update the changes on this page.
4.4.10.1 System Options
• Name: Enter a name to be used for the switch
• Location: Enter the location of the switch
• Contact: Enter the name of a person or organization
4.4.10.2 Community Strings
Community strings serve as passwords and can be entered as one of
the following:
• Read only (RO): Enables requests accompanied by this string
to display MIB-object information
• Read-write (RW): Enables requests accompanied by this
string to display MIB-object information and to set MIB objects
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
78 User’s Manual
Page 79

4.4.10.3 Trap Manager
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system
alerts generated by the switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps are
issued. Create a trap manager by entering the IP address of the station and
a community string.
4.4.11 Security Manager
Use this page to change the web management user name and
password.
Default User name: root
Default Password: root
4.5 TFTP Update Firmware
TFTP is the Trivial File Transfer Protocol.
Use this page to set the TFTP server IP address (the new image code must
have been saved to the TFTP server). Enter the file name and click
The switch will download the new flash image from the server.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
79 User’s Manual
Apply
.
Page 80

4.6 Configuration Backup
4.6.1 TFTP Restore Configuration
Use this page to set TFTP server address. You can restore the EEPROM
value from here, but you must put the back image in TFTP server, the switch
will download the back flash image.
4.6.2 TFTP Backup Configuration
Use this page to set the TFTP server IP address. You can save the
current EEPROM value from here, then go to the TFTP restore
configuration page to restore the EEPROM value.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
80 User’s Manual
Page 81

4.7 Reset System
Reset the switch to the default configuration.
4.8 Reboot
Reboot the switch in software reset.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
81 User’s Manual
Page 82

5. Technical Specifications
Standards
Compliance
Protocol
Max Forwarding and
Max Filtering Rate
LED Indicators
Copper Network
Cables
Fiber Link Max.
IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet,
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX/FX Fast Ethernet
CSMA/CD
14,880 pps per Ethernet port
148,800 pps per Fast Ethernet port
Per Port: (10/100 UTP): 100Mbps,
Link/Activity, Full Duplex (3 LEDs)
Fiber Port (FM2009 only): 100Mbps,
Link/Activity, Full Duplex (3 LEDs)
Per Unit: Power
10Base-T: 2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 3, 4, 5 cable
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (100m)
100Base-TX: 2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5 cable
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (100m)
SC/MT-RJ/VF-45 Multi-mode: Half-duplex:
Distance (FM2009
only)
Dimensions
Weight
Storage Temp.
Operational Temp.
Operational Humidity
Power
Power Consumption
EMI
Safety
Warranty
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
412m, Full-duplex: 2Km
SC Single-mode: Half-duplex: 412m,
Full-duplex: 15~60Km
254mm x 132mm x 37mm (10.0 x 5.2 x 1.5 in.)
1080 ±20 g (approximately 2.4 lbs ± 1 oz.)
-40ºC to 85ºC
0ºC to 45ºC (32ºF to 113ºF)
10% to 90% (Non-condensing)
110-240VAC 50-60Hz
17 Watts (Max)
FCC Class A, CE Mark
UL, cUL
2 years limited warranty
82 User’s Manual
Page 83

6. Troubleshooting
This section is intended to help you solve the most common problems
with installation of the FM2008/2009 switch.
Incorrect connections
Faulty or loose cables
Look for loose or obviously faulty connections. If they appear to
be OK, make sure the connections are snug. If that does not
correct the problem, try a different cable.
Non-standard cables
Non-standard and miswired cables may cause numerous
network collisions and other network problems, and can
seriously impair network performance. A Category 5 cable tester
is a recommended tool for every 100Base-T network installation.
Improper Network Topologies
It is important to make sure that you have a valid network
topology. Common topology faults include excessive cable
length and too many repeaters (hubs) between end nodes. In
addition, you should make sure that your network topology
contains no data path loops. Between any two ends nodes,
should be only one active cabling path at any time. Data path
loops will cause broadcast storms that will severely impact your
network performance.
there
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
83 User’s Manual
Page 84

Diagnosing LED Indicators
The switch can be easily monitored through LED indicators, which
assist in identifying common problems that you may encounter.
If the power LED indicator does not turn on when the power cord is
plugged in, you may have a problem with the power outlet or with the
power cord. However, if the switch powers off after having been
running for a while, check for loose power connections, power losses,
or surges at the power outlet. If you still cannot resolve the problem,
contact your local dealer for assistance.
Cabling
RJ-45 ports: Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded
twisted-pair (STP) cable for RJ-45 connections: Category 3, 4 or
5 cable for 10Mbps connections or Category 5 or better cable for
100Mbps connections. Also be sure that the length of any
twisted-pair connection does not exceed 100 meters (328 feet).
100Base-FX fiber port (FM2009 only): Fiber multi-mode
connectors must use 50/125 or 62.5/125 um multi-mode fiber
cable. You can connect two devices over a 2–kilometer distance.
However, fiber single-mode connectors must use 9/125 um
single-mode fiber cable. With single-mode, you can connect two
devices over a 15–60-kilometer distance in full duplex operation.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
84 User’s Manual
Page 85

FriendlyNET 2-Year Limited Warranty
Subject to the following limitations and exclusions, Asanté warrants to the
original end user purchaser that the covered products will be free from
defects in title, materials, and manufacturing workmanship for a period of
two years from the date of purchase. This warranty excludes fans, power
supplies, non-integrated software, and accessories. Asanté warrants that
the fans and power supplies will be free from defects in title, materials, and
manufacturing workmanship for two years from date of purchase. Asanté
warrants that non-integrated software included with its products will be free
from defects in title, materials, and workmanship for a period of 90 days
from date of purchase, and the company will support such software for the
purpose for which it was intended for a period of 90 days from the date of
purchase. This warranty expressly excludes problems arising due to
compatibility with other vendors’ products, or future compatibility due to
third party software or driver updates. To take advantage of this warranty,
you must contact Asanté for a return materials authorization (RMA) number.
The RMA number must be clearly written on the outside of the returned
package. Product must be sent to Asanté postage paid. In the event of a
defect, Asanté will repair or replace defective product or components with
new, refurbished, or equivalent product or components as deemed
appropriate by Asanté. The foregoing is your sole remedy, and Asanté's
only obligation, with respect to any defect or non-conformity. Asanté makes
no warranty with respect to accessories (including but not limited to cables,
brackets, and fasteners) included with the covered product, nor to any
discontinued product, i.e., product purchased more than thirty days after
Asanté has removed such product from its price list or discontinued
shipments of such product. This warranty is exclusive and is limited to the
original end user purchaser only. This warranty shall not apply to
secondhand products or to products that have been subjected to abuse,
misuse, abnormal electrical or environmental conditions, or any condition
other than what can be considered normal use.
ASANTÉ MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR
OTHERWISE, REGARDING THE ASANTÉ PRODUCTS. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT
PROHIBITED BY APPLICABLE LAW ALL WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
85 User’s Manual
Page 86

MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE HEREBY
DISCLAIMED. ASANTÉ'S LIABILITY ARISING FROM OR RELATING TO THE
PURCHASE, USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCTS IS LIMITED TO A
REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID. IN NO EVENT WILL ASANTÉ BE
LIABLE FOR INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
FOR THE BREACH OF ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, INCLUDING
ECONOMIC LOSS, DAMAGE TO PROPERTY AND, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED
BY LAW, DAMAGES FOR PERSONAL INJURY, HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE). THESE LIMITATIONS SHALL
APPLY EVEN IF ASANTÉ HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES OR IF THIS WARRANTY IS FOUND TO FAIL OF ITS ESSENTIAL
PURPOSE.
Some jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts,
so the previous limitations or exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty
gives you specific legal rights, and you may have other rights, which vary
from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
FriendlyNET FM2008/2009
86 User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...