Page 1

IntraSpection
™
Personality Module
3Com® SuperStack™ II Switch 1000
User’s Manual
Asanté Technologies, Inc.
821 Fox Lane
San Jose, CA 95131
1.800.662.9686
www.asante.com
September 1997
Part Number 06-00373-00 Rev. A
Page 2

Copyright Notice
Copyright 1997 by Asanté Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this manual, or any associated artwork, software,
product design or design concept, may be copied, reproduced or stored, in whole or in part, in any form or by any means
mechanical, electronic, optical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, including translation to another language or format,
without the express written consent of Asanté Technologies, Inc.
TRADEMARKS
mark of 3Com Corporation. SuperStack II is a trademark of 3Com Corporation. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation. Java is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Netscape and Netscape
Navigator are registered trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Netscape FastTrack Server is also a trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation, which may be registered in other
countries. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, exclusively licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd. All brand names and products are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT
entity) and Asanté Technologies, Inc. By opening the package(s) containing the software you are agreeing to be bound by the
terms of this agreement. If y ou do not agree to the terms of this agreement, promptly return the unopened software package(s)
and the accompanying items including written materials and binders or other container(s) to the place you obtained them for a
full refund.
1. GRANT OF LICENSE.
software program per serial number (the “SOFTWARE” is in “use” on a computer when it is loaded into temporary memory (i.e.,
RAM) or installed into permanent memory (e.g., hard disk, CD-ROM, or other storage device) of that computer. Installation on
a network server for the sole purpose of distribution to one or more other computer(s) shall constitute “use” for which a separate license/serial number is required.
2. COPYRIGHT
laws and international treaty provisions. Therefore, you must treat the SOFTWARE like any other copyrighted material (e.g., a
book or musical recording) except that you may either (a) make one copy of the SOFTWARE solely for backup or archival purposes, or (b) transfer the SOFTWARE to a single hard disk provided you keep the original solely for backup or archival purposes. You may not copy the written materials accompanying the software.
3. OTHER RESTRICTIONS
ing written materials on a permanent basis provided you retain no copies and the recipient agrees to the terms of this Agreement. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the SOFTWARE. If the SOFTWARE is an update or has been
updated, any transfer must include the most recent update and all prior versions.
LIMITED WARRANTY
accordance with the accompanying written materials for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of receipt. Any implied warranties on the SOFTWARE are limited to ninety (90) days. Some states/countries do not allow limitations of duration of an
implied warranty, so the above limitation may not apply to you.
CUSTOMER REMEDIES
be, at Asanté Technologies’ option, either (a) return of the price paid, or (b) repair or replacement of the SOFTWARE that does
not meet Asanté Technologies’ Limited Warranty and which is returned to Asanté Technologies with a copy of your receipt. This
Limited Warranty is void if failure of the SOFTWARE has resulted from accident, abuse, or misapplication. Any replacement
SOFTWARE will be warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period. Outside the United States, these remedies are
not available without proof of purchase from an authorized non-U.S. source.
NO OTHER WARRANTIES
or implied, including, but not limited to, implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, with regard
to the SOFTWARE, the accompanying written materials, and any accompanying hardware. This limited warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may have others which vary from state to state or country to country.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
liability for any indirect or consequential damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interrupted, loss of business information, or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use
this Asanté Technologies product, even if Asanté Technologies has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Any suit or
legal action relating to this Agreement or Licensed Programs must be brought within one (1) year of the date the programs are
purchased by the original licensee. Because some states/countries do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
be limited to a refund of the purchase price. In no event shall Asanté Technologies, Inc. be liable for costs of procurement of
substitute products or services, or for any lost profits, or for any consequential, incidental, direct or indirect damages, however
caused and on any theory of liability, arising from this warranty and sale.
U.S. GOVERNMENT Restricted Rights
RESTRICTED RIGHTS. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the The Rights in Technical Data and Computer Softw ar e c lause at DFARS 52.227-7013 or subparagraphs (c)(1) and
(2) of the Commercial Computer Software—Restricted Rights at 48 CFR 52.227-19, as applicable.
Manufacturer is Asanté Technologies, Inc., 821 Fox Lane, San Jose, California 95131. If you acquired this product in the United
States, this Agreement is governed by the laws of the State of California. Should you have any questions concerning this Agreement, please contact your local Asanté Technologies subsidiary or sales office, or write to Asanté Technologies.
WARRANTY DISCLAIMERS
erwise, regar ding the SuperStack II Switc h 1000 Personality Module, and specifically disclaims any warranty for merchantability
or fitness for a particular purpose. The exclusion of implied warranties is not permitted in some states and the exclusions specified herein may not apply to you. This warranty provides you with specific legal rights. Ther e ma y be other rights that you hav e
which vary from state to state.
Asanté and IntraSpection are trademarks of Asanté Technologies, Inc. 3Com is a registered trade-
This is a legal agreement between you (either an individual or an
Asanté Technologies grants to you the right to use one copy of the enclosed Asanté Technologies
. The SOFTWARE is owned by Asanté Technologies or its suppliers and is protected by United States copyright
. You may not rent or lease the SOFTWARE, but you may transfer the SOFTWARE and accompany-
Asanté Technologies, Inc. warrants that the SOFTWARE will perform substantially in
Asanté Technologies’ and its suppliers’ entire liability and your exclusive remedy shall
Asanté Technologies and its suppliers disclaim all other warranties, either express
Asanté T echnologies expressl y disclaims all
The liability of Asanté Technologies, Inc. arising from this warranty and sale shall
The SOFTWARE and documentation are provided with
Asanté Technologies, Inc. makes no other warranties, express, implied, or oth-
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface..................................................................................vii
About This Manual..........................................................................vii
Chapter Contents............................................................................vii
Document Conventions.................................................................viii
Audience........................................................................................viii
Introduction.........................................................................1-1
IntraSpection Personality Modules ................................................1-1
SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module .............................1-1
Management Options.....................................................................1-2
System Requirements.....................................................................1-3
Server ......................................................................................1-3
Client.......................................................................................1-3
Installation...........................................................................2-1
Installing a Personality Module......................................................2-1
Accessing the Device..........................................................3-1
Accessing the Device Page.............................................................3-1
Device Page Components..............................................................3-3
Device Information.................................................................3-3
VLAN Identification Window..................................................3-4
Front Panel Image ...................................................................3-4
Selecting the Device for Management..............................3-5
Selecting a VLAN Group for Management........................3-5
Selecting a Port for Management......................................3-6
Page iii
Page 4

Menus3-7
Tables......................................................................................3-7
Table Columns........................................................................3-7
Buttons....................................................................................3-7
Management.......................................................................4-1
Performing Basic Management Functions .....................................4-1
Configuration Tasks Overview................................................4-1
Management Tasks Overview.................................................4-1
Setting Community Strings......................................................4-3
Configuring Network Access Parameters ...............................4-5
Configuring Identification Information...................................4-6
Performing a Software Upgrade..............................................4-7
Updating the Device Page.......................................................4-8
Viewing General Device Information .....................................4-9
Resetting the Device.............................................................4-10
Viewing Group Information..................................................4-11
Managing Trap Receivers......................................................4-12
Adding a Trap Receiver..................................................4-12
Deleting a Trap Receiver................................................4-13
Modifying a Trap Receiver.............................................4-13
Viewing SNMP Agent Information........................................4-14
Managing the Port Address Table .........................................4-15
Viewing the Port Address Table.....................................4-15
Specifying Port Access ...................................................4-16
Deleting an Entry............................................................4-17
Viewing Statistics.................................................................4-18
Table Statistics................................................................4-18
Graph Statistics...............................................................4-20
VLAN....................................................................................5-1
VLAN Overview.............................................................................5-1
Viewing VLAN Groups...................................................................5-2
VLAN Groups..........................................................................5-3
VLAN Ports..............................................................................5-3
VLAN Menu Items...................................................................5-4
Creating VLAN Groups ..................................................................5-5
Page iv
Page 5

Managing VLAN Groups.................................................................5-8
Naming a VLAN Group............................................................5-9
Disabling a VLAN Group.......................................................5-11
Viewing Statistics for a VLAN Group ....................................5-12
Menus..................................................................................6-1
VLAN..............................................................................................6-3
Address List....................................................................................6-4
Identify...........................................................................................6-6
Device............................................................................................6-7
Agent..............................................................................................6-8
Slots................................................................................................6-9
Upgrade........................................................................................6-13
Network Access...........................................................................6-14
Trap Receivers .............................................................................6-15
Validate ........................................................................................6-17
Graph...........................................................................................6-18
Table ............................................................................................6-21
VLAN View...................................................................................6-22
Technical Support.............................................................. A-1
Contacting Asanté Technical Support .......................................... A-1
Technical Support Hours.............................................................. A-1
Index ..............................................................................Index-i
Page v
Page 6

Page 7

Preface
About This Manual
This manual introduces the IntraSpection Personality Module for the f ollowing device:
The 3Com SuperStack II Switch 1000
❏
The manual defines a Personality Module and explains how to install
and use the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module.
▲
Important:
IntraSpection, refer to the IntraSpection User’s Manual.
Chapter Contents
This manual is divided into the following chapters:
Chapter 1, “Introduction,” defines an IntraSpection Per-
❏
sonality Module and describes the components of the
SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module.
Chapter 2, “Installation” explains how to install the
❏
SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module.
For additional information on using
Chapter 3, “Accessing the Device,” explains how to
❏
access the SuperStack II Switch 1000 via IntraSpection.
❏
Chapter 4, “Management,” explains how to perform some
basic management functions.
❏
Chapter 5, “VLAN,” provides an overview of VLAN and
explains how use it with the SuperStack II Switch 1000
Personality Module.
Chapter 6, “Menus,” is a reference chapter that describes
❏
the Personality Module’s management menus.
Page vii
Page 8

Preface
Document Conventions
This manual uses the following conventions to convey instructions and
information:
Commands and key words are in
❏
∆
Note:
helpful suggestions or references to other sections
in the manual, is in this format.
Important:
▲
attention to important features or instructions is in
this format.
Noteworthy information, which contains
Significant information that calls
boldface
font.
Audience
This manual uses terms and concepts associated with Ethernet networking and switches; it is recommended that the user of this manual be
familiar with local area networking and Ethernet switches.
This manual also assumes familiarity with IntraSpection Web-based network management.
Page viii
Page 9

1
Introduction
IntraSpection Personality Modules
A Personality Module is a “plug-in” to the IntraSpection system that
allows for expanded manag ement of an SNMP (Simple Networ k Management Protocol) device by specifically addressing the device’s proprietary information (the “Private MIB”).
Management capabilities are accessed via the Personality Module’s
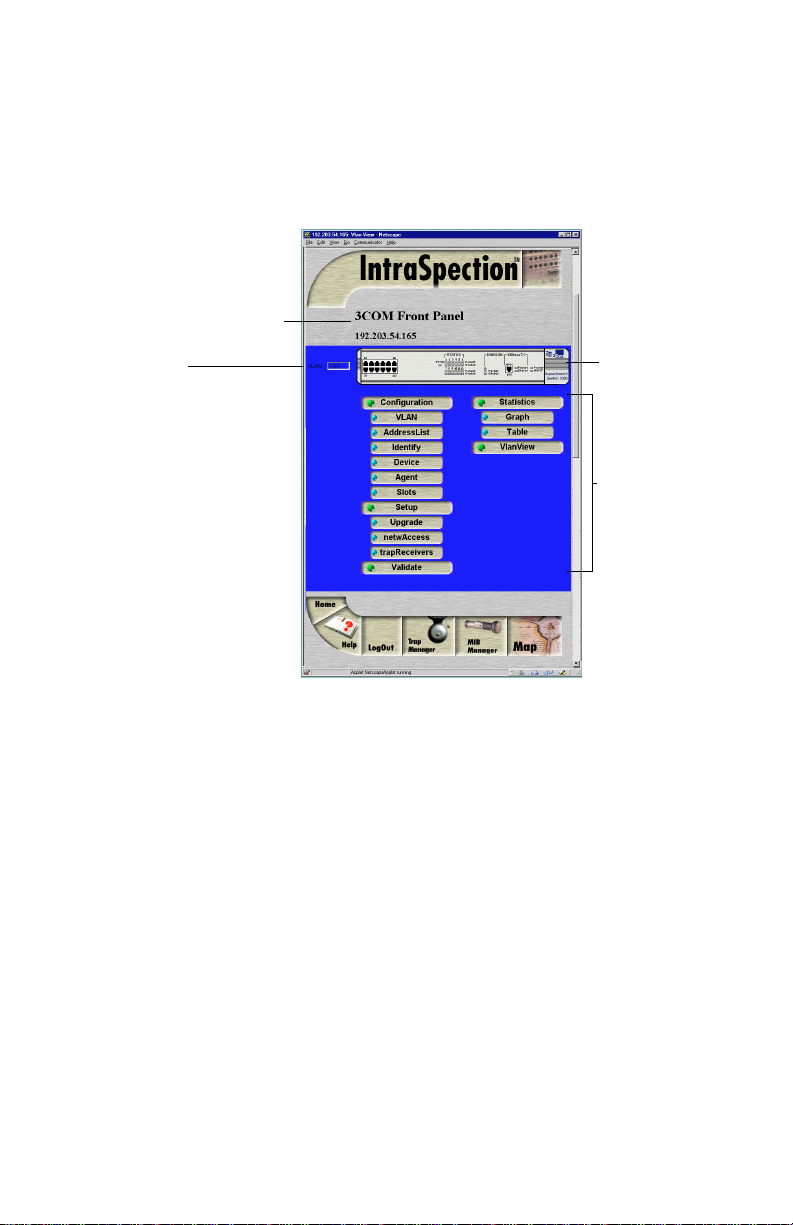
Device Page. See Figure 1-1.
SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module allows for expanded
management of a 3Com SuperStack II Switch 1000.
Device Information
VLAN
Identification
Window
Figure 1-1 SuperStack II Switch 1000 Device Page
Front Panel image
Personality Module
Information
(management menus)
Page 1-1
Page 10

Introduction
Management Options
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module supports the following management options:
VLAN — up to 16 groups
❏
Port address table
❏
Device identification information
❏
General device information
❏
SNMP agent information
❏
Slot (group) configuration information
❏
❏
Software upgrades
Network access configuration
❏
❏
Trap receiver management
Table statistics at the device, VLAN, and port levels
❏
❏
Graph statistics at the device, VLAN, and port levels
See Chapter 4, “Management,” for inf ormation on perf orming some basic
management functions.
See Chapter 5, “VLAN,” for information on using VLAN with the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
See Chapter 6, “Menus,” for a complete description of each management
menu and its contents.
Page 1-2
Page 11

System Requirements
Server
IntraSpection version 1.01.
❏
❏
PC with 80486 or faster microprocessor.
48MB RAM.
❏
❏
100MB free disk space.
Windows NT™ 3.51 or higher or Windows NT 4.0 (rec-
❏
ommended).
❏
Web server that supports Common Gateway Interface
(CGI) 1.1 (such as Netscape FastTrack Server™,
Microsoft IIS, NCSA HTTP, etc.).
Any database management system that supports ODBC
❏
(Open Database Connectivity), such as Microsoft
Access™, Oracle™, or Microsoft SQL Server.
Client
❏
Any Windows™, Windows NT, Macintosh™ or UNIX®
workstation.
Any World Wide Web browser with Java™ and Java-
❏
script support (such as Netscape Navigator® [version
3.0 required, 3.01 recommended] or Microsoft Internet
Explorer™).
IntraSpection Personality Modules
Important:
▲
Module’s
Netscape Communicator™ version 4.0
To access and use the Personality
VLANView
menu, you must use
.
Page 1-3
Page 12

Page 13

2
Installation
This chapter explains how to install the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module.
Installing a Personality Module
Important:
▲
the computer where the IntraSpection Application
Server is installed.
Before installing the Personality Module, make sure
that IntraSpection (websuite.exe) is NOT running on
the computer.
1
Insert the Personality Module CD into the computer
where the IntraSpection Application Server is
installed.
2
Open the CD to display its contents.
3
Double-click the LS1000.exe file.
The Personality Module is installed on
4 Click Yes at the “IntraSpection Personality Module
for LinkSwitch 1000” dialog box.
The “IntraSpection Personality Module for the Link-
Switch 1000” window appears.
5 Click Finish to continue.
The Personality Module files are decompressed.
The “IntraSpection Personality Module Welcome” dia-
log box appears.
6 Click Next to continue.
Page 2-1
Page 14
Installation
The “Software License Agreement” window appears.
Review the agreement carefully.
7 Click Yes to accept the agreement and continue with
the installation or click No to exit the installation.
The “IntraSpection Personality Module Read Me” win-
dow appears. Review the information carefully.
8 Click Next to continue.
The decompressed Personality Module files are
installed onto the computer.
The “Decompression of the Source is Now Complete”
dialog box appears.
9 Click OK to continue with the installation.
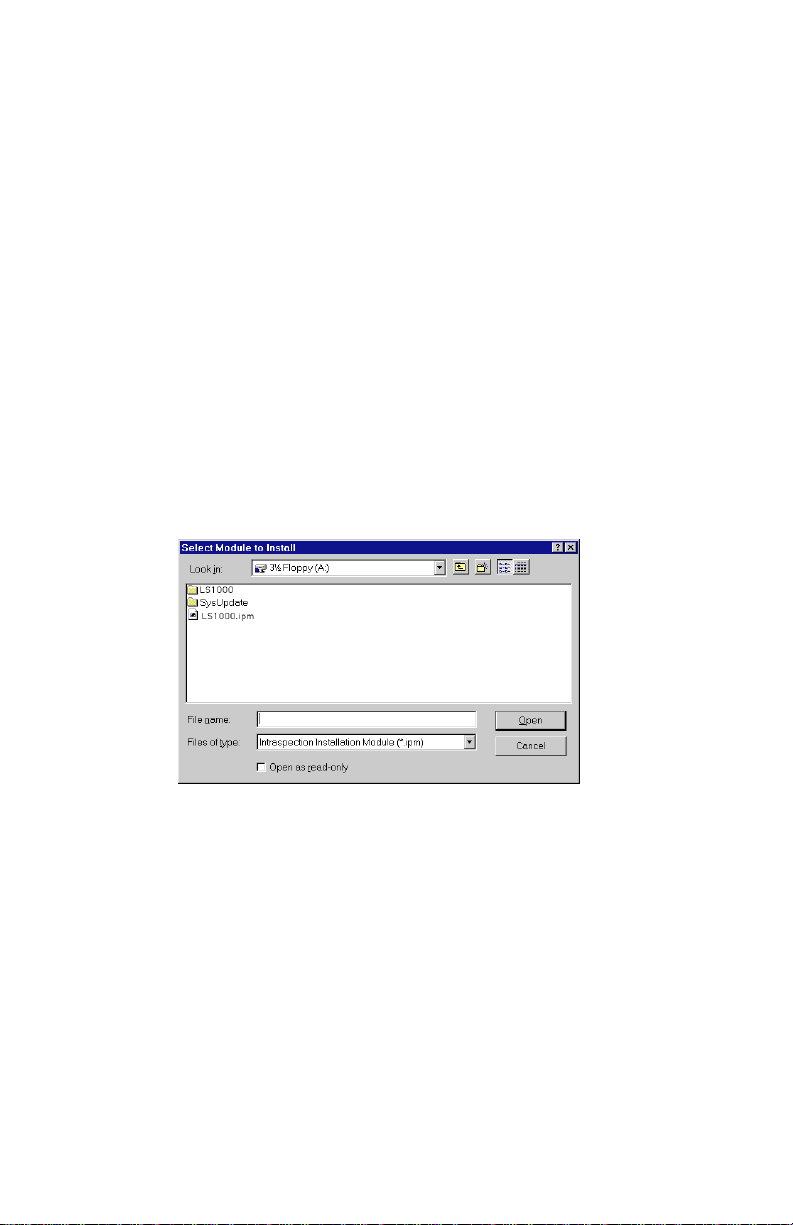
The “Select Module to Install” window appears, displaying the LS1000.ipm file See Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Select Module to Install window
10 Click once on the LS1000.ipm file.
11 Click Open.
The “Enter Product Serial Number” window appears.
12 Enter the serial number that came with your copy of
the Personality Module.
The serial number is located on the inside cover of this
User’s Manual.
▲ Important: The serial number is case-sensitive;
enter it exactly as shown.
Page 2-2
Page 15

Installing a Personality Module
13 Click OK.
The “IntraSpection Module Installation” window
appears.
▲ Important: This window should be pointing
to the directory that contains the IntraSpection
(websuite.exe) program. If it is not, click
Browse and locate that directory.
14 Click OK.
∆ Note: A “Select Database” window may appear.
If it does, select vendor.mdb, then click OK.
∆ Note: An “Updating IntraSpection System Files”
window may appear, if it does, click OK.
The installer program installs the Personality Module
into the IntraSpection Application Server.
Installation is complete when the “Installation Completed Successfully” dialog box appears.
15 Start the IntraSpection Application Server, following
the guidelines below:
❏ Windows NT 3.51 users: double-click the
IntraSpection icon (located in the Programs
group).
❏ Windows NT 4.0 users: open the Start menu,
select Programs, then IntraSpection.
For information on accessing the SuperStack II Switch
1000, see Chapter 3, “Accessing the Device.”
For information on performing some basic management functions, see Chapter 4, “Management.”
Page 2-3
Page 16

Page 17

3
Accessing the Device
This chapter explains how to access the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module’s Device Page. The Device Page provides access to the
Personality Module’s management options.
Accessing the Device Page
To access the Device Page for a SuperStack II Switch 1000 device, you
must first create a map of your network within IntraSpection.
1 Make sure the Personality Module is installed and the
IntraSpection Application Server is running.
2 Access IntraSpection from any Java-enabled Web
browser (requires logging into IntraSpection).
▲ Important: For help on accessing and logging
into IntraSpection, refer to the IntraSpection
User’s Manual.
3 After you are logged into IntraSpection, click Auto
Discovery on the IntraSpection Main Menu.
The AutoDiscovery Page appears.
4 Complete each field on the AutoDiscovery Page, fol-
lowing the guidelines below:
❏ Type the IP subnet address of the SuperStack II
Switch 1000 to be managed in the Segment field.
❏ Type the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s community
string in the Community field.
❏ Make sure the Enterprise ID field has a value of all.
❏ Type the lowest (beginning) IP address on your
network in the Low IP Address field.
Page 3-1
Page 18

Accessing the Device
❏ Type the highest (last) IP address on your network
in the Hi IP Address field.
❏ Select New in the Discovery Mode field to create a
new map, or select Append to attach this map to the
map that is stored in your system’s buffer (if any).
5 Click Apply.
IntraSpection “discovers” and builds a map of your network. The map contains icons whic h r epr esent eac h SNMP
device on the network. Figure 3-1 is an example map.
Figure 3-1 Discovered network map
6 Click once on the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s device
icon.
∆ Note: The SuperStack II Switch 1000’s device
icon is labeled “3Com” and has the device’s IP
address directly below it.
The Device Page f or the selected SuperStack II Switc h 1000
appears (see Figure 3-2 on page 3-3).
For information on the Device Page’s components, see
“Device Page Components” on page 3-3.
For information on performing basic management func-
tions, see “Performing Basic Management Functions” on
page 4-1.
Page 3-2
Page 19
Device Information
Device Page Components
The Device Page consists of several components, including device information, a front panel image, a VLAN identification window, and management menus. See Figure 3-2.
Device Information
VLAN
Identification
Window
Figure 3-2 Device Page components
Front Panel
Image
Personality
Module
Information
(management
menus)
Device Information
The following device information is displayed at the top of the Device
Page:
❏ Device Description — a description of the device
(i.e., “3Com Front Panel”).
❏ IP Address — the IP address of the SuperStack II
Switch 1000.
Page 3-3
Page 20
Accessing the Device
VLAN Identification Window
The VLAN identification window displays the number of the currently
selected VLAN group. It also allows you to select a configured group of
VLAN by typing the VLAN group’s number in the window.
There are 16 VLAN groups; depending on the number of VLANs you
have created, this number can be from 1001 to 1016.
See “Selecting a VLAN Group for Management” on page 3-5 for information on selecting a VLAN group on the front panel image. See “Creating
VLAN Groups” on page 5-5 for information on creating a VLAN group.
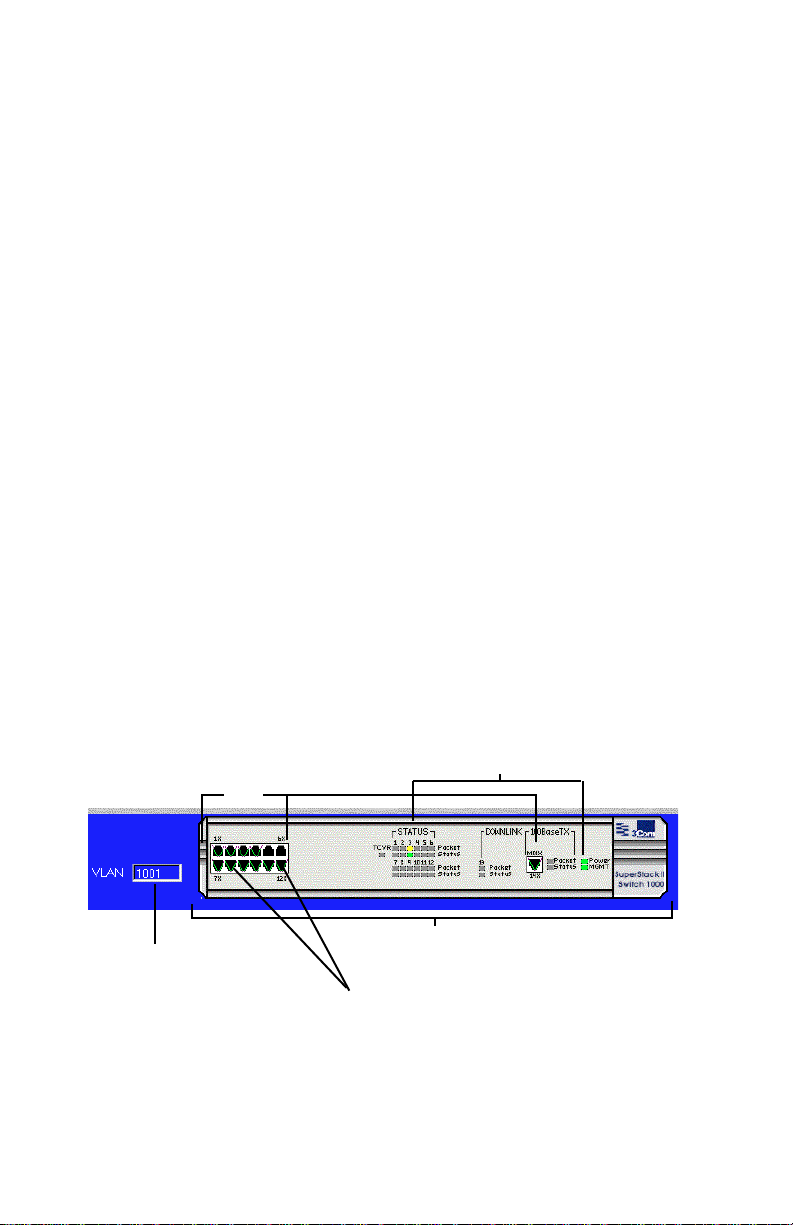
Front Panel Image
The front panel image contains the following components (as illustrated
in Figure 3-3):
❏ Status LEDs — real-time LEDs that represent the LEDs
on the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s front panel. These
LEDs indicate power, management, and port activity.
❏ Device — the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
❏ Port — each port on the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
❏ VLAN groups — groups of configured VLANs on the
SuperStack II Switch 1000. These are identified by a
number (displayed in the VLAN identification window)
and a group marker (a green “v” displayed in each port
that belongs to the VLAN group).
Status LEDs
Ports
Page 3-4
Device
VLAN
Identification
Window
Figure 3-3 Front panel image components
VLAN Group Markers
Page 21

Front Panel Image
Selecting the Device for Management
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 can be managed at different levels; that
is, at the device, VLAN group, or port level.
For example, if you do not select any item on the SuperStack II Switch
1000 and click the Graph menu, statistics for the SuperStack II Switch
1000 are displayed. If you select a VLAN group and click Graph, statistics for the selected VLAN group are displayed.
To select the device:
❏ Do not click anything on the front panel image.
To deselect the device:
❏ Click once on a port.
Selecting a VLAN Group for Management
There are two methods for selecting a VLAN group for management:
❏ Click once on a port that belongs to the VLAN group
you want to manage.
A green VLAN group marker appears in the selected port
and in all of the ports belonging to that group of VLAN. See
Figure 3-4. The number of the VLAN group (1001 to 1016)
appears in the VLAN identification window.
❏ Click once in the VLAN identification window and type
the number of the VLAN group you want to manage.
VLAN Identification Window
click once in the window, then
type the number of the VLAN
group to be managed
Figure 3-4 Selecting a VLAN group
VLAN Group Markers
all ports with this marker belong
to the same VLAN group
To deselect a VLAN group:
❏ Click on any port not belonging to the selected VLAN gr oup.
Page 3-5
Page 22
Accessing the Device
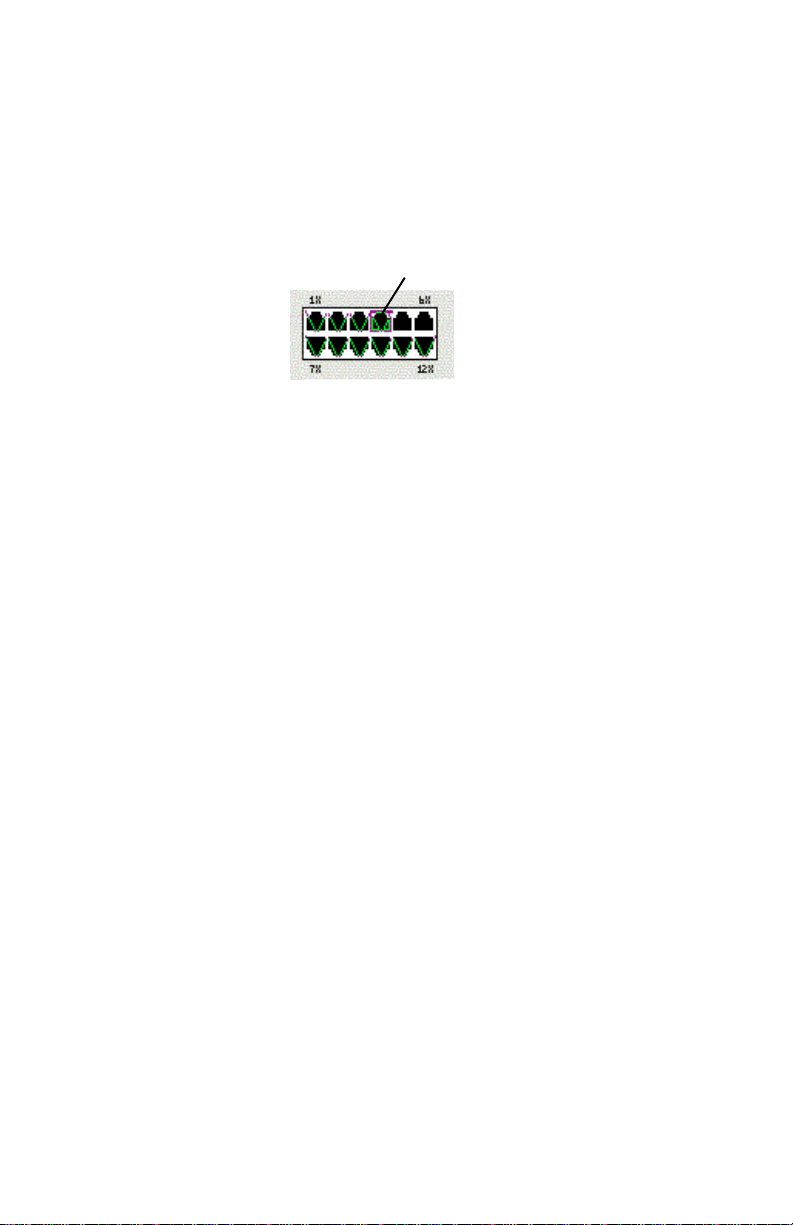
Selecting a Port for Management
To select a port for management:
❏ Click once on a port on the front panel image. If a VLAN
group marker appears, click on the port again until the
port is highlighted by a green box. See Figure 3-5.
Selected Port
Figure 3-5 Selecting a port
To deselect the port:
❏ Click again on the selected port.
Page 3-6
Page 23
Tables
Menus
The menus on the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s Device Page provide
access to the different management options supported by the Personality Module.
Tables
Some menus contain tables with information that is configurable
directly on-screen from your Web browser while others contain information that is read-only.
The tables below describe how to recognize configurable and read-only
fields.
Configurable Information
Menu Item Action
Drop-down menus Select from an available option.
White-colored fields Type information.
Read-only Information
Menu Item Action
Green- or gray-colored fields None; read-only field.
Table Columns
T able columns can be resized by placing the mouse pointer on a column
title’s left or right side (until a double arrow appears) and dragging the
column to the left or to the right, as desired.
Buttons
Some menus contain buttons that allow you to edit and/or update the
page’s table.
The table below describes the different buttons that are available and
their functions.
Button Action
Apply Applies any changes made to the device.
Refresh Updates the page with the latest information.
Modify Modifies a selected entry.
Add Adds an entry into the table.
Page 3-7
Page 24

Page 25
4
Management
This chapter explains how manage the SuperStack II Switch 1000 via
the IntraSpection Personality Module.
▲ Important: To manage the SuperStack II Switch 1000,
you must first access the switch’s Device Page. See
Chapter 3, “Accessing the Device,” for instructions.
Performing Basic Management Functions
This chapter covers the following tasks:
Configuration Tasks
Configuration Task Page Number
Setting community strings page 4-3
Configuring network access parameters page 4-5
Configuring identification information page 4-6
Performing a software upgrade page 4-7
Management Tasks
Management Task Page Number
Updating the Device Page page 4-8
Viewing general device information page 4-9
Resetting the device page 4-10
Viewing group information page 4-11
Managing trap receivers page 4-12
Viewing SNMP agent information page 4-14
Page 4-1
Page 26

Management
Management Task Page Number
Managing the port address table page 4-15
Viewing statistics page 4-18
▲ Important: For information on using VLAN, see Chap-
ter 5, “VLAN.”
Page 4-2
Page 27

Setting Community Strings
Setting Community Strings
Community strings define access rights for reading and writing SNMP
data objects for a device.
The community strings (read community and write community) for the
SuperStack II Switch 1000 are manually set in the device via its console
port. In order to access the device with IntraSpection, the community
strings must be set in IntraSpection to match those set in the device.
▲ Important: It is recommended that you set the commu-
nity strings for the device in IntraSpection before you
attempt to perform any network management functions.
This section describes how to set the community strings in IntraSpection to match those set in the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
▲ Important: You must know the community strings of
the SuperStack II Switch 1000 in order to correctly set
them in IntraSpection. Refer to the SuperStack II
Switch 1000’s User’s Guide for instructions on viewing
the device’s community strings.
To set the community strings for a SuperStack II Switch 1000 in
IntraSpection:
1 On the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Device Page, click the
map icon on the IntraSpection navigation bar (located at
the bottom of the screen), as shown in Figure 4-1.
Map Icon
Figure 4-1 IntraSpection navigation bar
The most recently “discovered” map appears.
2 Click the Map Manager button.
The Map Manager Page appears, similar to Figure 4-2.
Page 4-3
Page 28

Management
Figure 4-2 IntraSpection Map Manager Page
3 Click the Edit Device button.
The Map Configuration Table appears, similar to Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3 Map Configuration Table
4 Enter the device’s IP address in the IP Address field.
5 Enter the device’s read community string in the Read
Community String field.
6 Enter the device’s write community string in the
Write Community String field.
7 Click Apply.
The read and write community strings are configured.
Page 4-4
Page 29

Configuring Network Access Parameters
Configuring Network Access Parameters
To configure and/or manage the SuperStack II Switch 1000 over the network or via out-of-band access, the device needs to be properly configured with network access parameters. These parameters are initially
configured in the device via the console port; however some can be
modified using IntraSpection.
To view/configure network access parameters:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front panel
image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click netwAccess.
The Network Access Information table appears, similar to
Figure 4-4.
Figure 4-4 Network Access Information table
3 Click once in the field to be edited.
For a description of each field, see “Network Access “ on
page 6-14.
4 Type the new information or select an option (if it’s a
drop-down menu).
5 Click Apply.
The network access parameters are configured. To view
updated information, click Refresh.
Page 4-5
Page 30

Management
Configuring Identification Information
To help with device identification, y ou can add certain details about the
SuperStack II Switch 1000; such as, the device’s physical address, name,
location, and contact information.
To view and/or configure device identification information:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front panel
image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Identify.
The Device Identification table appears, similar to Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 Device Identification table
3 Click once in the field to be edited.
For a description of each field, see “Identify “ on page 6-6.
▲ Important: Only those fields that are colored
white can be edited.
4 Type the new information.
▲ Important: A maximum of 254 characters
(including spaces) is allowed.
5 Click Apply.
The device identification information is modified. To view
updated information, click Refresh.
Page 4-6
Page 31

Performing a Software Upgrade
Performing a Software Upgrade
The SuperStack II Switch 1000’s software can be upgraded via
IntraSpection.
To upgrade the device’s software:
1 Click Upgrade.
The Software Upgrade table appears, similar to Figure 4-6.
Figure 4-6 Software Upgrade table
2 Type the software’s file name and netw ork path in the
Download Filename field.
3 Type the server’s IP address where the software file
resides in the Server Address field.
4 Click Apply.
5 Initiate the downloading via one of the following two
methods:
❏ Physically power the device off and then on.
❏ Open the Slots menu, click once on the row
entry, click Modify, open the Action drop-
down menu and select Reset, then click
Apply.
Page 4-7
Page 32

Management
Updating the Device Page
The files for the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s Personality Module are
stored within the IntraSpection Application Server’s database.
Occasionally, these files should be updated from the Device Page to
ensure that you are viewing the device’s latest information.
To update the Personality Module’s Device Page:
1 Click Validate.
The Device Page is updated with the latest information.
After it is updated, the IntraSpection Map Manager Page
appears.
2 Click AutoDiscovery to rediscover the SuperStack II
Switch 1000.
▲ Important: Refer to page 3-1 for instructions
on discovering devices with AutoDiscovery.
Page 4-8
Page 33

Viewing General Device Information
Viewing General Device Information
General device information includes items such as the device’s chassis
name, object ID, and hardware version number.
To view general device information:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Device.
The Device Information table appears, similar to Figure
4-7.
Figure 4-7 Device Information table
∆ Note: The information displayed on this page is
read-only.
For a description of each field, see “Device” on page 6-7.
3 Click Refresh to view the latest information from the
device.
Page 4-9
Page 34

Management
Resetting the Device
You can reset the SuperStack II Switch 1000 via one of two methods:
❏ By physically powering off the SuperStack II Switch
1000, then powering it on.
❏ Via the Slots menu in IntraSpection.
To reset the SuperStack II Switch 1000 via the Slots menu in IntraSpection:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Slots.
The Slot Configuration Table appears, similar to Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8 Slot Configuration Table
3 Click once on the row containing the group you want
to reset.
∆ Note: For a description of each field, see “Slots”
on page 6-9.
4 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
5 Open the Action drop-down menu and select Reset.
6 Click Apply.
The device is reset.
Page 4-10
Page 35

Viewing Group Information
Viewing Group Information
The Slot Configuration Table displays and allows you to modify group
information about the SuperStack II Switch 1000. The group information contains details about the device as if it were a part of a device
stack.
∆ Note: The SuperStack II Switch 1000 is a stack-
able switch. In a stack of switches, each switch in
the stack is referred to as a “group.”
To view/configure the Slot Configuration Table:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Slots.
The Slot Configuration Table appears, similar to Figure 4-9.
Figure 4-9 Slot Configuration Table
∆ Note: For a description of each field, see “Slots”
on page 6-9.
3 To modify information, click once on a row entry.
4 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
▲ Important: Only those fields that contain drop-
down menus can be edited.
5 Click Apply.
To view updated information, click Refresh.
Page 4-11
Page 36

Management
Managing Trap Receivers
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 can be set to generate traps. Traps are
messages sent across the network to an SNMP network manager (such
as IntraSpection). They alert you to faults or to changes that occur to
the switch device.
▲ Important: Refer to the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s
User’s Guide for instructions on setting traps.
This section describes how to add and delete trap receivers. Trap
receivers are management stations designated to receive traps when
they occur.
Adding a Trap Receiver
To add a trap receiver:
▲ Important: A maximum of four trap receivers is
allowed.
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click trapReceivers.
The Trap Receiver Table appears, similar to Figure 4-10.
Figure 4-10 Trap Receiver Table
3 Click Add.
The Add Dialog box appears.
4 Open the Status drop-down menu and select active.
5 Type the IP address of the management station that is
to receive traps in the Receiver Address field.
Page 4-12
Page 37

Managing Trap Receivers
▲ Important: Do NOT type an IP address of 0.0.0.0.
6 Type the community string of the management station
in the Community String field.
7 Click Apply.
An entry for the management station appears in the table.
If it does not appear, click Refresh.
Deleting a Trap Receiver
To delete a trap receiver entry:
1 Click once on the row containing the entry to be
deleted.
2 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
3 Open the Status drop-down menu and select notIn-
Service.
4 Click Apply.
5 Click Refresh in the Trap Receiver Table.
The trap receiver is deleted.
Modifying a Trap Receiver
To change the IP address of a trap receiver entry:
1 Delete the trap receiver entry, following the directions
above.
2 Add a new trap receiver entry, following the instruc-
tions on page 4-12.
Page 4-13
Page 38

Management
Viewing SNMP Agent Information
SNMP agent information includes items such as the device’s PROM software version number, recent reset action, and last system error.
To view SNMP agent information:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Agent.
The Agent Information table appears, similar to Figure
4-11.
Figure 4-11 Agent Information table
∆ Note: The information displayed in this table is
read-only.
For a description of each field, see “Agent” on page 6-8.
3 To view the latest information, click Refresh.
Page 4-14
Page 39

Managing the Port Address Table
Managing the Port Address Table
The Port Address Table is a table of node addresses that the device
receives on its ports. It uses the information in the table to decide
whether a frame should be forwarded or filtered.
By modifying entries in the Port Address Table, you can restrict access to
certain ports by specifying the physical addresses that are allowed to
connect to the ports.
The table holds a maximum of 500 entries. Initially, all entries are ageing entries (that is, they are removed from the table if, after a period of
time, the device has not transmitted or if the device is reset or powered
off). Entries can be set as “permanent” to remain in the table regardless
of the aging time or if the switch is powered off or reset.
Viewing the Port Address Table
The view the Port Address Table:
1 Do not select any item on the Device Page’s front
panel image. (This selects the entire device.)
2 Click Address List.
The Port Address Table appears, similar to Figure 4-12.
Figure 4-12 Port Address Table
The table displays the last 500 addresses that the device
has received.
Use the table’s scroll bar to navigate up and down the
table. Y ou cannot directl y search f or a specific MAC address
in the table.
3 Click Refresh to view the latest information.
Page 4-15
Page 40

Management
Specifying Port Access
To restrict access to a port by specifying the physical address that is
authorized to connect to the port:
1 Select the number of the port you want to control
access to by clicking once on a row containing that
port number.
For example, to specify access to port number 3, c lick on a
row entry that contains a Port ID of 3.
2 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
3 Type the MAC address that is authorized to connect to
this port in the Address field.
4 Determine the status of the address by opening the
Address Status drop-down menu and selecting one
of the following options:
❏ nonPermanent — sets the address to be a
non-permanent entry in the table; the IP
address is deleted after the specified aging time
or when the device is reset or powered off.
❏ permanent — sets the address to be a perma-
nent entry in the table; the IP address is not
deleted regardless of time or power off/reset.
5 Determine the priority of the address by opening the
Address Priority drop-down menu and selecting one
of the following options:
❏ normalPriority — sets the address to filter
normally through the device.
❏ highPriority — sets the address to filter at a
high priority through the device.
6 Click Apply.
Access for the port is configured. To view updated information, click Refresh.
Page 4-16
Page 41

Deleting an Entry
To manually delete an entry in the Port Address Table:
1 Select an entry to be deleted by clicking once on its
row in the table.
2 Click Modify.
3 Open the Address Status drop-down menu and
select delete.
4 Click Apply.
The entry is deleted.
Page 4-17
Page 42

Management
Viewing Statistics
Statistics for a SuperStack II Switch 1000, one of its VLAN g roups, or one
of its ports can be viewed in two different formats: table or graph. Statistics collected include runts, alignment errors, collisions, short events,
and readable frames.
Table Statistics
1 To view statistics for the SuperStack II Switch 1000,
do not select anything on the Device Page’s front
panel image.
To view statistics for a VLAN group, click once on a port
belonging to that VLAN group.
To view statistics for a port, click on the port until it is
highlighted with a green box.
∆ Note: For more information about selecting a
VLAN group, see “Selecting a VLAN Group for Management” on page 3-5.
2 Click Table.
The Table Statistics page appears for the device, the
selected VLAN, group or the selected port, similar to Figure
4-13.
Figure 4-13 Table Statistics
For a complete description of each object in the table, see
“Table” on page 6-21.
3 Select the number of seconds to poll for statistics in
the Sampling Interval drop-down menu.
Page 4-18
Page 43

Viewing Statistics
Statistics are gathered in the following columns:
❏ Curr — (current) the number of occurrences
each second.
❏ Peak — the largest number of occurrences
since opening or resetting the screen.
❏ Avg — the average number of occurrences
since opening or resetting the screen.
❏ Total — the total number of occurrences
since opening or resetting the screen.
4 To reset the object counters to zero, click Reset.
Page 4-19
Page 44

Management
Graph Statistics
1 To view statistics for the SuperStack II Switch 1000,
do not select anything on the Device Page’s front
panel image.
To view statistics for a VLAN group, click once on a port
belonging to that VLAN group.
To view statistics for a port, click on the port until it is
highlighted with a green box.
2 Click Graph.
The Graph Statistics page appears, similar to Figure 4-14.
Count-PerSecond
Display
Figure 4-14 Graph Statistics
Scroll Bar
Drop-Down
Menus:
Seconds
Statistics
3 Select the object to be monitored in the Statistics
drop-down menu.
For a description of each object, see “Graph” on page 6-18.
4 Select the number of seconds for which statistics are
to be gathered in the Seconds drop-down menu.
The graph automatically begins gathering statistics.
5 Use the scroll bar to change the graph’s count-per-sec-
ond display (scroll up to increase the count-per-second, scroll down to decrease it).
❏ Average per Second — the average number of
occurrences since opening or resetting the screen.
❏ Peak per Second — the largest number of occur-
rences since opening or resetting the screen.
6 To reset the statistics in the graph, click Reset.
Page 4-20
Page 45

5
VLAN
This chapter provides an overview of VLAN and explains how to use it
with the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
VLAN Overview
VLAN stands for virtual local area network. VLAN is a netw or k configuration tool that allows you to “group” together specific ports on the same
switch, designating them as their own virtual network segments.
With the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Personality Module, the use of
VLAN lets you:
❏ Create up to 16 separate user groups
❏ Limit broadcast and multicast traffic
❏ Increase security (by specifying which segments
can communicate with each other)
❏ Allocate network resources (such as servers)
❏ Designate specific application groups
You can create up to 16 separate VLANs on the SuperStack II Switch
1000 by assigning each port on the switch to a VLAN number . By grouping certain ports together, you effectively “cut” the switch into completely independent segments.
For example, you can designate ports 2, 6, and 8 to be on VLAN1 and
ports 1, 10, and 12 to be on VLAN2. As a result, each group of ports will
have its own workgroup and resources within its domain. You can create and reconfigure these workgroups, reallocate resources as required,
and gather statistics at the VLAN group and port levels.
Page 5-1
Page 46

VLAN
Viewing VLAN Groups
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 comes with 16 groups of VLAN. At startup, all of the switch’ s ports are on vlan1 (displa yed as 1001 in the VLAN
Identification Window).
▲ Important: You can delete VLAN groups; however, it
is not recommended.
To view the VLAN groups:
▲ Important: To access and use the VLAN groups via the
VLAN View menu, you must use Netscape Communi-
cator v. 4.0.
❏ Click VLANView on the SuperStack II Switch 1000
Device Page.
The VLAN View Page appears. Figure 5-1 is an example
of the VLAN View Page configured with eight groups of
VLAN.
VLAN
Groups
VLAN Group Button
Figure 5-1 VLAN View Page
Page 5-2
Port
LED
Status
Menu
Items
Port Button
Page 47

VLAN Groups
VLAN Groups
The 16 VLAN groups are identified by a number (vlan1, vlan2, etc ) and
a corresponding button, as shown in Figure 5-2.
VLAN Group Number
identifies the VLAN group;
this number cannot be
selected
VLAN Group Button
select this button for
management; drag and
drop a port button here
to place the port within
this VLAN group
Figure 5-2 VLAN groups
The VLAN group button is used to select the VLAN group for management. It is also used as a place to “drop” a port number.
See “Viewing Statistics for a VLAN Group” on page 5-12 and “Creating
VLAN Groups” on page 5-5 for more information
VLAN Ports
Each of the switch’s ports are identified by a port button. The port button contains a group number and a port number. (The group number
represents the device — in this case the SuperStack II Switch 1000 —
and is always labeled “1”).
Each port button also has a corresponding real-time LED status box,
which displays activity on the port.
(no activity on this port)
VLAN Port Button
identifies the port
by group and port number;
“drag and drop” this
port button onto a VLAN
group button to assign the
port to that VLAN group
(activity on this port)
VLAN Port LED
Status Box
lights when there
is activity on the
port
Figure 5-3 VLAN ports
You can drag and drop a port button onto a VLAN group button to reassign the port to a VLAN group. See “Creating VLAN Groups” on
page 5-5 for more information.
Page 5-3
Page 48

VLAN
VLAN Menu Items
The menu items on the VLANView screen allow for individual management of each of the 16 groups of VLAN.
The menu items are identical to those on the SuperStack II Switch 1000
Device Page. Each menu can be opened or closed by clicking once on
its menu-level indicator. See Figure 5-4.
Closed Menu
Opened Menu
Menu-Level Indicator
+ indicates menu is closed
- indicates menu is open
Figure 5-4 VLAN menus
Page 5-4
Page 49

VLAN Groups
Creating VLAN Groups
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 comes with 16 groups of VLAN. By
default, all of the switch’s ports are assigned to vlan1.
To create more groups of VLANs, “group” together the ports that you
want to have on the same segment by dragging and dropping a port button onto a VLAN group button.
To create a VLAN group:
1 Open the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s Device Page.
2 Wait for the page to validate (it is validated when you
see flashing LEDs).
∆ Note: The front panel image on the Device Page
displays the currently selected VLAN group (such as
1001) as well as the ports that are assigned to that
VLAN. See “Selecting a VLAN Group for Management” on page 3-5 for more information.
3 Click once on the VlanView menu.
The VLAN View Page appears.
4 Locate the port you want to assign to a VLAN by find-
ing its port button on the VLAN window.
Use the scroll bar at the bottom of the VLAN window to
scroll to the right and locate port buttons that are not
visible on the screen.
5 Click once on the port’s button and hold down the
left mouse button until a small dot appears next to the
screen’s pointer. See Figure 5-5.
Page 5-5
Page 50

VLAN
Port Button Selection;
click on the port button and hold down
the left mouse button until a dot appears
next to the screen’s pointer
Figure 5-5 Selecting a port button
6 While holding down the mouse button, drag the dot
onto the VLAN group button that you want to assign
the port to, then release the mouse button. See
Figure 5-6.
Page 5-6
drag the button
to the VLAN group
drop the button
on the VLAN group
Figure 5-6 Assigning a port to a VLAN group
The port is now assigned to that VLAN g roup. The port’s
button and status LED box will be aligned with the
VLAN group number. See Figure 5-7.
Page 51

VLAN Groups
the port is assigned
to the VLAN group
Figure 5-7 New VLAN group
7 Repeat steps 1 – 6 for each port you want to assign to
a VLAN group.
Page 5-7
Page 52

VLAN
Managing VLAN Groups
There are two ways to manage each configured group of VLAN on the
SuperStack II Switch 1000:
❏ via the VLANView Page
❏ via the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s Device Page
The management menu items on the VLAN View Page are identical to
those on the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s Device Page.
▲ Important: To access and use the VLAN View screen,
you must use Netscape Communicator v. 4.0.
This section describes how to perform the following management tasks
via the VLAN View Page:
Management Task Page Number
Naming a VLAN group page 5-9
Disabling a VLAN group page 5-11
Viewing statistics for a VLAN group page 5-12
Page 5-8
Page 53

Naming a VLAN Group
Naming a VLAN Group
For identification purposes, configured groups of VLAN can be assigned
a name (such as “Marketing” or “Payroll”).
To assign a name to a VLAN group via the VLAN View Page:
1 In the VLAN View Page, select the VLAN group you
want to name by clicking once on its VLAN group button. See Figure 5-8.
Click once on the VLAN group button;
the button turns green when selected
Figure 5-8 Selecting a VLAN group
2 Open the Configuration menu (if it’s not already
opened) by clicking once on its menu-level indicator.
See Figure 5-9.
Figure 5-9 VLAN menu-level indicator
3 Click once on the VLAN menu item.
The VLAN Workgroup Table appears, similar to Figure 5-10.
Menu-Level
Indicator
Page 5-9
Page 54

VLAN
Figure 5-10 VLAN Workgroup Table
4 Select the VLAN group to be named by clicking once
on its row entry.
5 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
6 Type a name for the VLAN group in the WGroup-
Name field.
7 Click Apply.
The VLAN’s group name is changed and appears in the
Workgroup Table. If it does not appear, click Refresh.
Page 5-10
Page 55

Disabling a VLAN Group
Disabling a VLAN Group
Disabling a VLAN g roup prevents all of the ports belonging to that gr oup
from communicating with each other.
To disable a VLAN group:
1 In the VLAN View Page, select the VLAN group you
want to disable by clicking once on its VLAN group
button.
The VLAN group button turns green when selected.
2 Open the Configuration menu (if it’s not already
opened) by clicking once on its menu-level indicator.
3 Click once on the VLAN menu item.
The W orkgroup T able appears.
4 Select the VLAN group to be disabled by clic king once
on its row entry.
5 Click Modify.
The Modify Dialog box appears.
6 Open the Status drop-down menu and select notIn-
Service.
7 Click Apply.
The VLAN group is disabled.
Page 5-11
Page 56

VLAN
Viewing Statistics for a VLAN Group
You can view statistics — in table and graph formats — for each of the
configured groups of VLAN on the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
To view statistics for a VLAN group:
1 In the VLAN View Page, select the VLAN group for
which you want to view statistics by clicking once on
its VLAN group button.
The group number button turns green when selected.
2 Open the Statistics menu (if it’s not already opened)
by clicking once on its menu-level indicator.
3 Click once on Graph (to view statistics in graph for-
mat) or Table (to view statistics in table format).
The Statistics Table or Graph Page appears for the
selected VLAN group.
See “Viewing Statistics” on page 4-18 for more informa-
tion on using the Statistics Page.
Page 5-12
Page 57

6
Menus
This chapter describes each management menu on the SuperStack II
Switch 1000 Personality Module’s Device Page.
The table below provides a brief description of each menu; the sections
that follow explain each menu in detail.
Table 6-1 Device Page Menu Descriptions
Menu Description
Configuration Title for the submenus listed below it; this menu cannot be
selected.
VLAN Allows you to name, disable or enable any of the 16 groups
of VLAN. See “VLAN” on page 6-3.
AddressList Allows you to view the last 500 addresses that the device
received. Also allows you to restrict access to each port.
See “Address List” on page 6-4.
Identify Allows you to configure device identification information.
See “Identify” on page 6-6.
Device Allows you to view general device information. See
“Device” on page 6-7.
Agent Allows you to view information on the device’s SNMP
agent. See “Agent” on page 6-8.
Slots Allows you to view and configure the device’s group infor-
mation. See “Slots” on page 6-9.
Setup Title for the submenus listed below it; this menu cannot be
selected.
Upgrade Allows you to determine the download file name and server
address for upgrading the device’s software. See
“Upgrade” on page 6-13.
Page 6-1
Page 58

Menus
Menu Description
NetwAccess Allows you to view and configure network access informa-
tion (both in-band and out-of-band) for the device. See
“Network Access” on page 6-14.
TrapReceivers
Validate Updates the Device Page with its latest information from
Statistics Title for the submenus listed below it; this menu cannot be
Graph Allows you to view real-time statistical data — in a graph
Table Allows you to view real-time statistical data — in a table for-
VlanView Allows you to view, configure, and manage the 16 groups of
Allows you to determine the management stations can
receive traps from the device. See “Trap Receivers” on
page 6-15.
the IntraSpection Application Server database. See “Validate” on page 6-17.
selected.
format — on the device or a selected group of VLAN. See
“Graph” on page 6-18.
mat — on the device or a selected group of VLAN. See
“Table” on page 6-21.
VLAN. See “VLAN View” on page 6-22.
Page 6-2
Page 59

VLAN
VLAN
This menu allows you to name, disable or enable any of the SuperStack
II Switch 1000’s 16 groups of VLAN.
Table 6-2 describes each field in the VLAN menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Naming a
VLAN Group” on page 5-9, “Disabling a VLAN Group” on
page 5-11, or “Viewing Statistics for a VLAN Group” on
page 5-12.
Table 6-2 VLAN Menu
Field Description
WGroupIndex (Workgroup Index) Read-only field; displays the num-
ber of the VLAN group (from 1001 to 1016).
WGroupName Configurable field; determines a name for the VLAN
group.
See “Naming a VLAN Group” on page 5-9 for instruc-
tions.
UnitID Read-only field; displays the identity of the unit on
which the VLAN group’s downlink resides.
DownLinkPortID Read-only field; displays the identity of the downlink
port for the VLAN group.
Status Configurable field; enables or disables the group of
VLAN.
See “Disabling a VLAN Group” on page 5-11 for
instructions.
❏ active — enables the group of VLAN.
Note:
Refer to the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s MIB
(Management Information Base) for more information
on the options available in this field.
DBaseAction Configurable field; allows you to carry out operations
on the VLAN group’s address list in the forwarding
database.
❏ FreezeAddrs — makes all addresses in the
workgroup permanent.
Page 6-3
Page 60

Menus
Address List
This menu displays the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s MAC address table.
The MAC address table is a table of node addresses that the device
receives on its ports. It uses the information in this table to decide
whether a frame should be forwarded or filtered. Each entry consists of
the MAC address of the device and an identifier f or the port on which it
was received.
▲ Important: The MAC address table holds a maxi-
mum of 500 entries.
The SuperStack II Switch 1000 learns entries automatically by listening
to and learning the information that is broadcast when a new node logs
onto the network. The SuperStac k II Switch 1000 chec ks the source and
destination address as packets pass through it and records the information in the table.
▲ Important: You cannot manually add an entry into
the Port Address Table.
Table 6-3 describes each field in the Address List menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Managing
the Port Address Table” on page 4-15.
Table 6-3 Address List Menu
Field Description
Index Read-only field; displays the number of the entry in
the Port Address Table (from 1 to 500).
Unit ID Read-only field; displays the number of the unit in the
SuperStack II Switch 1000.
Note:
This number is always 1.
Port ID Read-only field; displays the number of the port for
which MAC address mapping information is displayed.
Address index Read-only field; displays the number of the address
entry for a port.
Address Configurable field; determines the MAC address of
the network station that is authorized to communicate
with the port.
Page 6-4
Page 61

Address List
Field Description
Address Status Configurable field; determines the status of the MAC
address in the Port Address Table.
❏ nonPermanent — the address is not perma-
nent; it is removed if, after a period of time
(aging time), the device has not transmitted.
NonPermanent entries are removed from the
table if the device is reset or a power off/on
cycle occurs.
❏ permanent — the address entry is permanent;
it remains in the address table even if the
device is reset or a power off/on cycle occurs.
❏ delete — manually removes the selected
address entry from the address table.
Address Priority Configurable field; determines the priority of the MAC
address in the Port Address Table.
❏ normalPriority — the address filters at a nor-
mal rate through the device.
❏ highPriority — the address filters at a faster-
than-normal rate through the device.
Page 6-5
Page 62

Menus
Identify
This menu allows you to view and configure identification information
for the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
Table 6-4 describes each field in the Identify menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Config-
uring Identification Information” on page 4-6.
Table 6-4 Identify Menu
Field Description
Physical Address Read-only field; displays the device’s hardware
address.
Object ID Read-only field; displays the device’s SNMP identify-
ing number.
Description Read-only field; displays a description of the device.
Name Configurable field; assigns a name to the device.
Note:
A maximum of 254 characters, including
spaces, is allowed.
Location Configurable field; assigns a physical location to the
device.
Note:
A maximum of 254 characters, including
spaces, is allowed.
Contact Configurable field; assigns a name of the person
responsible for the device.
Note:
A maximum of 254 characters, including
spaces, is allowed.
Up Time Read-only field; displays the amount of time the
device has been operational since the last time it was
off-line.
Interfaces Read-only field; displays the number of network inter-
faces present on the device.
Page 6-6
Page 63

Device
Device
This menu allows you to view general information for the SuperStack II
Switch 1000.
Table 6-5 describes each field in the Device menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Viewing
General Device Information” on page 4-9.
Table 6-5 Device Menu
Field Description
Number of Groups Read-only field; displays the number of groups the
device contains.
Chassis Name Read-only field; displays the name of the device’s
chassis.
Note:
This field always displays LinkSwitch 1000 Sta
ChassisObjid Read-only field; displays the device’s object ID num-
ber.
ChassisHWVers Read-only field; displays the device’s hardware ver-
sion number.
Page 6-7
Page 64

Menus
Agent
This menu displays read-only SNMP agent information for the SuperStack Switch 1000.
Table 6-6 describes each field in the Agent menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Viewing
SNMP Agent Information” on page 4-14.
Table 6-6 Agent Menu
Field Description
Heartbeat Interval Read-only field; displays the time, in seconds,
between successive heartbeat events sent to the management station.
An interval of 0 indicates that no heartbeat events are
to be generated.
Note:
A heartbeat event is an event generated at a
regular interval to inform the manager that this device
is still operating and can be reached on the network.
PROM SWVer Read-only field; displays the software version number
of the device’s SNMP agent.
Restart Count Read-only field; displays the number of restarts the
device has undergone (either power on/off or reset).
Last Restart Type Read-only field; displays the reason for the last sys-
tem restart (which may be caused by a management
command, a timeout, a power interruption, or system
error).
Reset Action Read-only field; displays the system’s reset setting.
Last System Error Read-only field; displays the last system error experi-
enced by the system.
Page 6-8
Page 65

Slots
Slots
This menu allows you to view and configure group information for the
SuperStack II Switch 1000. The group information includes details
about the switch as if it were a part of a device stack.
Table 6-7 describes each field in the Slots menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Viewing
Group Information” on page 4-11.
Table 6-7 Slots Menu
Field Description
LocationType Read-only field; displays the types of physical enti-
ties (and their locations) that the device can contain.
Note:
A stack/chassis (such as the SuperStack II
Switch 1000) contains a number of physical entities
(such as power supplies and cards/units).
Each physical entity resides at some location. A stack/
chassis can contain a number of types of locations.
Each type of location is specialized to a different purpose.
There are five types of locations defined:
❏ (1) modular-slot — a location of this type can
take a number of different entities. They are
general purpose and are often the purpose of
the device.
❏ (2) power-supply-bay — contains a power
supply.
❏ (3) fan-position — holds a fan.
❏ (4) backplane-position — contains only a
backplane.
❏ (5) stackableUnit-position — a stack has only
entities of type stackableUnit.
Location Read-only field; displays the location within the
device.
Note:
A location is where a physical entity (such as a
power supply or a card/unit) resides.
SysObjid Read-only field; displays the object ID of the entity at
this location.
Page 6-9
Page 66

Menus
Field Description
Service Type Read-only field; displays what kind of entity is present
at this location.
❏ (1) unmanaged 802.3 repeater
❏ (2) IEEE 802.3 repeater
❏ (3) IEEE 802.5 mau module
❏ (4) IEEE 802.5 ring builder
❏ (5) FDDI concentrator
❏ (6) management module
❏ (12) standard backplane
❏ (13) extended backplane
❏ (14) display panel
❏ (17) fan
❏ (18) power supply
❏ (19) standard bridge
❏ (20) bridge per port
❏ (21) terminal server
❏ (22) remote bridge
❏ (23) switched Ethernet
Entity Type Read-only field; in conjunction with Service Type,
uniquely identifies the specific physical entity. For
example, the Service Type may be “802.3 repeater”
while the Entity Type may be “12 port UTP card.”
Smart 802.3 Repeater:
❏ (1) 4-port RLC coax
❏ (2) 8-port UTP
❏ (3) 4-port fiber
❏ (4) 8-port STP
❏ (6) 4-port fanout
❏ (7) 12-port UTP
❏ (8) 12-port STP
❏ (9) 12-port secure UTP
❏ (10) 12-port secure STP
❏ (11) 6-port fiber
❏ (12) 4-port coax
Page 6-10
Page 67

Field Description
Slots
Entity Type
(continued)
❏ (32) 6-port resilient fiber
❏ (65) 12-port UTP, RJ45 connector
❏ (66) 12-port UTP, RJ45 connector (expand-
able)
❏ (67) 13-port UTP, Telco + module
❏ (68) 24-port TUP, 2xTelco
❏ (69) 6-port fiber, ST connector (expandable)
❏ (70) 6-port fiber, SMA connector (expandable)
❏ (71) 6-port coax (expandable)
❏ (72) 4-port fanout
IEEE 802.5 Mau Module:
❏ (1) 12-port UTP, RJ-45 connector
❏ (2) 12-port STP, RJ-45 connector
IEEE 802.5 Ring Builder:
❏ (1) ring builder, STP rin/rout, RJ-45 connec-
tors
Management Module:
❏ (1) standard management module
❏ (2) enhanced management module
Standard Backplane:
❏ (1) standard backplane
Display Panel:
❏ (1) first release front panel
Fan:
❏ (1) standard fan tray
Power Supply:
❏ (2) standard power supply
Switched Ethernet:
❏ (1) headend unit
❏ (2) expansion unit
HwVersion Read-only field; displays the major and minor revision
level of the entity at this location.
Page 6-11
Page 68

Menus
Field Description
SwVersion Read-only field; displays the software version number
of the entity at this location if the entity contains a
processor. If an entity has no software, the value of
this parameter is “none.”
Serviceid Read-only field; displays the number of the service in
the device. This ID can be used to reference the service elsewhere in the MIB.
EntityName Read-only field; displays the name of the entity at this
location.
PowerReq Read-only field; displays the power consumption
requirement of the entity.
NumberofPorts Read-only field; displays the number of ports on the
entity at this location.
LampTest Configurable field; displays the status of the test that
can be performed on entities contained in the rack.
EntityState Read-only field; displays the state of the entity in the
stack.
Each entity in the stack/chassis has a basic state inde-
pendent of what function that entity performs within
the stack/chassis (initializing, operational, failure). If
the agent cannot determine the state of a particular
entity, the value is unknown.
Action Configurable field; resets the specified unitcard.
POSTtype Configurable field; displays the type of power-on self
tests which an entity carries out during power-up.
❏ normalPOST — a basic confidence check of
the entity (5 seconds) is performed.
❏ extendedPOST — a comprehensive set of
tests (3 minutes) are performed.
PlugInType Read-only field; displays the type of plug-in module (if
any) attached to this entity.
If a plug-in module can never be attached to this
entity, the value notApplicable is displayed.
Page 6-12
Page 69

Upgrade
Upgrade
This menu allows you to set the download file name and server address
for upgrading the device’s software.
Table 6-8 describes each field in the Upgrade menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Performing
a Software Upgrade” on page 4-7.
Table 6-8 Upgrade Menu
Field Description
Load Status Read-only field; displays the status of the last soft-
ware download.
❏ success — software download completed suc-
cessfully.
SW Version Read-only field; displays the device’ s current software
version number.
HW Version Read-only field; displays the device’s current hard-
ware version number.
Download Filename
Server Address Configurable field; sets the boot server’s IP address.
Configurable field; sets the file name and network
path of the software image file.
Page 6-13
Page 70

Menus
Network Access
This menu allows you to view and configure network access information (both in-band and out-of-band) for the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
Table 6-9 describes each field in the Network Access menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Configur-
ing Network Access Parameters” on page 4-5.
Table 6-9 Network Access Menu
Field Description
IP Address Configurable field; sets the device’s in-band IP
address.
Subnet Mask Configurable field; sets the device’s in-band subnet
address.
Note:
A subnet mask, in the IP addressing scheme, is
a group of selected bits whose values serve to identify
a subnetwork. All members of the subnetwork share
the mask value.
Router Address Configurable field; sets the address of the default
gateway to which the device belongs.
Bootp Mode Configurable field; sets the device’s method for
retrieving an IP address.
❏ enabled — sets the device to request an IP
address from a BootP server.
❏ disabled — sets the device to NOT request
an IP address from a BootP server; the IP
address must be configured manually via
the device’s console port.
IP Address Configurable field; sets the device’s out-of-band IP
address.
Subnet Mask Configurable field; sets the device’s out-of-band sub-
net address.
Page 6-14
Page 71

Trap Receivers
Trap Receivers
This menu allows you to determine the management stations that will
receive traps from the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
▲ Important: Refer to the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s
User Guide for instructions on setting traps.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Managing
Trap Receivers” on page 4-12.
Table 6-10 describes each field in the Trap Receivers menu.
Table 6-10 Trap Receivers Menu
Field Description
Trap index Read-only field; displays the number of the trap
receiver entry.
Status Configurable field; displays the status of the trap
receiving station’s entry.
❏ active — trap receiving station’s entry is
active.
❏ notInService — trap receiving station’s entry is
not active (deletes the trap receiving station
when selected).
Note:
Refer to the SuperStack II Switch 1000’s MIB for
information on the other options available in this field.
Receiver Address Configurable field; displays the IP address of the man-
agement station that can receive traps.
Community String Configurable field; displays the write community
string of the receiving management station.
Category Configurable field; determines which traps are to be
received by the trap receiving station.
▲ Important: This is a 32-bit mask field.
❏ FF:FF:FF:FF — enables all traps
❏ ‘00000001’h — high priority configuration
traps.
❏ ‘00000002’h — low priority configuration traps
❏ ‘00000004’h — high priority security traps
❏ ‘00000008’h — low priority security traps
❏ ‘00000010’h — alarms and polling traps
Page 6-15
Page 72

Menus
Field Description
Category
(continued)
❏ ‘00000020’h — regular heartbeat traps
❏ ‘00000040’h — end station table traps
❏ ‘00000080’h — reserved
❏ ‘00000100’h — physical entity traps
❏ ‘00000200’h — facility traps
❏ ‘00000400’h — service related traps
Protocol Read-only field; displays what protocol is being used
to send the trap (IP or IPX).
Throttle Interval Configurable field; determines the time interval for
the device to send traps.
Note:
This field is in milliseconds.
Page 6-16
Page 73

Validate
Validate
This menu updates the SuperStack II Switch 1000 Device Page with the
latest information from the IntraSpection Application Server database.
Occasionally, these files should be updated to ensure that you are viewing the device’s latest information.
When this option is selected, you are returned to the IntraSpection map
page.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Updating
the Device Page” on page 4-8.
Page 6-17
Page 74

Menus
Graph
This menu allows you to view real-time statistical information — in a
graph format — on the SuperStack II Switch 1000, one of its VLAN
groups, or one of its ports.
Table 6-11 describes each field in the Graph menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Viewing
Statistics” on page 4-18 or “Viewing Statistics for a VLAN
Group” on page 5-12.
Table 6-11 Graph Menu
Field Description
Seconds Drop-down menu; specifies the amount of time (in
seconds) that the device is polled for information.
Statistics Drop-down menu; determines the object for which
statistics are gathered.
Device Statistics
❏ Readable Frames — displays the total number
of good or readable frames (frames without
error).
❏ Unicast Frames — displays the number of
frames seen by the card that is addressed to a
unicast (non-card) address.
❏ Broadcast Frames — displays the total num-
ber of frames that were successfully received
and were directed to the broadcast group
address.
❏ FCS Errors — displays the number of frames
that failed Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
❏ Alignment Errors — displays the number of
frames that were an integral number of octets
in length and did not pass the FCS check.
❏ FramesTooLong — displays the number of
frames that exceeded 1,518 bytes.
❏ Short Events — displays the number of data
bursts (data less than 10 bytes in length).
❏ Runts — displays the number of frames
shorter than 64 bytes.
❏ TX Collision — displays the total number of
collisions that occurred when transmitting
from the device.
Page 6-18
Page 75

Field Description
Graph
Statistics
(continued)
Group Statistics
❏ Readable Frames — displays the total number
of good or readable frames (frames without
error).
❏ Unicast Frames — displays the number of
frames seen by the card that is addressed to a
unicast (non-card) address.
❏ Broadcast Frames — displays the total num-
ber of frames that were successfully received
and were directed to the broadcast group
address.
❏ FCS Errors — displays the number of frames
that failed Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
❏ Alignment Errors — displays the number of
frames that were an integral number of octets
in length and did not pass the FCS check.
❏ FramesTooLong — displays the number of
frames that exceeded 1,518 bytes.
❏ Short Events — displays the number of data
bursts, (data is less than 10 bytes in length).
❏ Runts — displays the number of frames
shorter than 64 bytes.
❏ Auto Partitions — displays the number of
times the device has automatically partitioned
a port.
❏ Total Errors — displays the total number of
errors which have occurred on all ports on all
groups in this device.
Port Statistics
❏ Readable Frames — displays the total number
of good or readable frames (frames without
error).
❏ Transmitted Frames — displays the number of
frames (including error frames) which were
transmitted by ports in this workgroup.
❏ Filtered Frames — displays the total number
of frames within a workgroup that were filtered because the destination station was on
the same segment (port) as the source station.
Page 6-19
Page 76

Menus
Field Description
Statistics
(continued)
Port Statistics (continued)
❏ Forwarded Frames — displays the total num-
ber of frames that were forwarded successfully by ports in this workgroup to their
destinations.
❏ RX Congestion — displays the number of
frames that were dropped due to congestion
(lack of buffer resource) on the receive side of
ports in this workgroup.
❏ TX Congestion — displays the number of
frames that were dropped due to congestion
(lack of buffer resource) on the transmit side
of ports in this workgroup.
❏ TX Multicast — displays the number of multi-
cast/braodcast frames that were transmitted
by ports in this workgroup.
Average per second
Reset Statistics Button; resets the counters to zero.
Peak per second Displays the largest number of occurrences since
Count-per-second
display
Displays the average number of occurrences since
opening or resetting the screen.
opening or resetting the screen.
Displays the amount of counts per second displayed
on the graph.
Note:
To control the count-per-second display, use
the scroll bar on the right side of the graph (scroll up
to increase the count-per-second; scroll down to
decrease it).
Page 6-20
Page 77

Table
Table
This menu allows you to view real-time statistical information, in table
format, on the SuperStack II Switch 1000, one of its VLAN groups, or
one of its ports.
Table 6-12 describes each field in the Table menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see “Viewing
Statistics” on page 4-18 or “Viewing Statistics for a VLAN
Group” on page 5-12.
Table 6-12 Table Menu
Field Description
Sampling Interval Configurable field; allows you to set the amount of
time (in seconds) that the device is polled for information.
Reset Button; resets the counters to zero.
Object Read-only fields; displays the objects for which statis-
tics are gathered.
For a description of each object, see “Statistics” on
page 6-18.
Curr (Current) Read-only field; displays the number of
counter occurrences each second.
Peak Read-only field; displays the largest number of
counter occurrences since opening or resetting the
screen.
Avg (Average) Read-only field; displays the average num-
ber of counter occurrences since opening or resetting
the screen.
Total Read-only field; displays the total number of counter
occurrences since opening or resetting the screen.
Page 6-21
Page 78

Menus
VLAN View
This menu allows you to view, configure, and manage the 16 groups of
VLAN that are supported by the SuperStack II Switch 1000.
Table 6-13 describes each field in the VLAN View menu.
∆ Note: For instructions on using this menu, see Chapter 5,
“VLAN.”
Table 6-13 VLAN View Menu
Field Description
Group Number/
Port Number
Vlan1 – Vlan 16 Buttons; represent each of the device’s 16 groups of
Menu Items Menus; allow you to manage each configured group
Buttons; represent each of the device’s ports.
VLAN.
of VLAN (groups that contain at least one port) or the
entire device. These menus are identical to those on
the Device Page.
❏ Configuration
❏ VLAN — allows you to name, disable or
enable the selected VLAN group. See
“VLAN” on page 6-3.
❏ Address List — allows you to view the
last 500 IP addresses that the device
received and allows you to restrict access
to each port. See “Address List” on page
6-4.
❏ Identify — allows you to configure identi-
fication information for the device. See
“Identify” on page 6-6.
❏ Device — allows you to view general
information on the device. See “Device”
on page 6-7.
❏ Agent — allows you to view SNMP agent
information on the device. See “Agent”
on page 6-8.
❏ Slots — allows you to view and configure
the device’s group information. See
“Slots” on page 6-9.
Page 6-22
Page 79

Field Description
❏ Setup
❏ Upgrade — allows you to set the down-
load file name and server address for
upgrading the device’s software. See
“Upgrade” on page 6-13.
❏ NetwAccess — allows you to view and
configure network access information for
the device. See “Network Access” on
page 6-14.
❏ TrapReceivers — allows you to determine
which management stations can receive
traps from the device. See “Trap Receivers” on page 6-15.
❏ Validate — updates the Device Page with the
latest information stored in the IntraSpection
Application Server database. See “Validate”
on page 6-17.
❏ Statistics
❏ Table — allows you to view real-time
statistical data — in a table format — on
the selected VLAN group. See “T able” on
page 6-21.
❏ Graph — allows you to view real-time sta-
tistical data — in a graph format — on the
selected VLAN group. See “Graph” on
page 6-18.
VLAN View
Page 6-23
Page 80

Page 81

Technical Support
Contacting Asanté Technical Support
To contact Asanté Technical Support:
Telephone (800) 622-7464
Fax (408) 432-6018
Fax-Back (800) 741-8607
(408) 954-8607
Internet Mail support@asante.com
W orld Wide W eb http://www .asante.com
Bulletin Board Service (BBS) (408) 432-1416
ARA BBS (guest log in) (408) 894-0765
AppleLink mail/BBS ASANTE
FTP Archive ftp.asante.com
A
Technical Support Hours
6:00 A.M. to 5:00 P.M. Pacific Standard Time USA, Monday – Friday.
.
Page A-1
Page 82

Page 83

Index
A
about this manual vii
access to ports, restricting 4-16
action field, slots menu 6-12
add button 3-7
address
field, address list
index field, address list 6-4
list menu 6-4
priority field 6-5
status field 6-5
table 4-15
deleting an entry 4-17
managing 4-15
agent
menu, description of fields
information, viewing 4-14
alignment errors 6-18, 6-19
apply button 3-7
assistance. See technical support
audience, intended
6-4
6-8
viii
B
bootp mode 6-14
broadcast frames 6-18, 6-19
buttons
add
3-7
apply 3-7
modify 3-7
refresh 3-7
C
CGI 1-3
chapter contents vii
chassis name field 6-7
chassisHWVers 6-7
chassisObjid 6-7
client requirements 1-3
common gateway interface. See CGI
community string
configuring
trap receivers 6-15
configurable information, within a
menu
configuration tasks 4-1
4-3
3-7
contact
field, identify menu
information, configuring 4-6
counters, description of 6-21
6-6
D
database management system 1-3
dbaseAction field, VLAN 6-3
description field, identify menu 6-6
device
defined
information, viewing 3-3, 4-9
menu, description of fields 6-7
page
selecting for management 3-5
disk space required 1-3
document conventions viii
downLinkPortID field, VLAN 6-3
download Filename field, slots
3-4
accessing
components 3-3
menus
updating 4-8
menu
3-1
components of
overview 6-1
tables 3-7
resizing 3-7
6-13
3-7
E
entity
type field, slots menu
name field, slots menu 6-12
state field, slots menu 6-12
6-10
F
fcs errors 6-18, 6-19
frames too long 6-18, 6-19
front panel image 3-4
G
graph menu 6-18
graphic, of device. See front panel
image
group
defined
numbering 3-4
3-4
Index-i
Page 84

groups of VLAN
creating
disabling 5-11
naming 5-9
statistics, viewing 5-12
viewing 3-4
5-5
H
hardware requirements 1-3
heartbeat interval field, agent
menu
help. See technical support
hw version field, upgrade menu 6-13
hw version field, slots menu 6-11
6-8
I
identification information,
configuring
identify menu 6-6
image, front panel 3-4
in-band parameters, configuring 4-5
installation 2-1
IntraSpection Application
Server
requirements 1-3
select database window 2-3
serial number, entering 2-2
intended audience viii
interfaces field, identify menu 6-6
IntraSpection
application server, starting
map icon 4-3
map manager 4-3
IP address
configuring manually
field, network access menu 6-14
out-of-band 6-14
requesting from server 6-14
4-6
2-3
2-3
6-14
J
Java 1-3
L
lamptest field, slots menu 6-12
last
restart type field, agent menu
system error field, agent menu 6-8
6-8
LEDs, status, viewing 3-4
load status field, upgrade menu 6-13
location
field, identify menu
information, configuring 4-6
type field, slots menu 6-9
6-6
M
MAC addresses, viewing table of 4-15
management
accessing the device
address list menu 6-4
agent menu 6-8
device menu 6-7
device page, components 3-3
graph menu 6-18
identify menu 6-6
menus
components of
overview 6-1
network access menu 6-14
performing basic functions,
overview
port
address table
selecting 3-6
resetting the device 4-10
slots menu 6-9
software upgrades 4-7
statistics
graph, viewing
table, viewing 4-18
switch, selecting 3-5
table menu 6-21
tasks 4-1
trap receivers menu 6-15
updating device page 4-8
upgrade menu 6-13
validate menu 6-17
vlan view menu 6-22
map
icon, IntraSpection
manager, IntraSpection 4-3
memory required for installation 1-3
menus
buttons
3-7
3-1
3-7
4-1
4-15
4-20
4-3
Index-ii
Page 85

menus (continued)
components of
overview of 6-1
tables
components of
resizing 3-7
MIB, private 1-1
Microsoft
Access
IIS 1-3
Internet Explorer 1-3
SQL Server 1-3
modify button 3-7
1-3
3-7
3-7
N
name
field, identify menu
information, configuring 4-6
NCSA HTTP 1-3
Netscape
FastTrack Server
Navigator 1-3
network
access
parameters, configuring
menu 6-14
map, creating 3-1
number
of groups field
of ports field 6-12
6-6
1-3
4-5
6-7
O
object ID field, identify menu 6-6
ODBC 1-3
Oracle 1-3
out-of-band parameters,
configuring
overview, personality modules 1-1
4-5
P
personality module
accessing device 3-1
device page, components of
menus
overview
using for management 3-1
6-1
3-3
personality module (continued)
installing
overview 1-1
physical address
configuring
field 6-6
plugInType field, slots menu 6-12
port
access to, restricting
address table
defined 3-4
ID field, address list 6-4
selecting for management 3-6
viewing image of 3-4
post type field, slots menu 6-12
powerReq field, slots menu 6-12
private MIB 1-1
prom SWVer field, agent menu 6-8
2-1
4-6
deleting an entry
managing 4-15
4-16
4-17
R
RAM, required 1-3
read community string,
configuring
readable frames 6-18, 6-19
read-only information, tables 3-7
receiver address field, trap receivers
menu
refresh button 3-7
requirements
client
server 1-3
resetting the device 4-10
reset action field, agent menu 6-8
restart count field, agent menu 6-8
router address field, network access
runts 6-18, 6-19
1-3
menu
4-3
6-15
6-14
S
segmenting switch 5-5
select database window 2-3
selecting
port for management
switch for management 3-5
3-6
Index-iii
Page 86

selecting (continued)
VLAN for management
serial number, location of 2-2
server
address field, upgrade menu
requirements 1-3
service
ID field, slots menu
type field, slots menu 6-10
short events 6-18, 6-19
slots menu 6-9
SNMP
agent information, viewing
community strings. See
community strings
software
requirements
upgrading 4-7
statistics
graph
table 4-18, 6-21
status
field, VLAN
LEDs, viewing 3-4
subnet mask field, network access
menu
sw Version field
upgrade menu
slots menu 6-12
switch information, viewing 4-9
sys objid field, slots menu 6-9
system requirements 1-3
1-3
4-20, 6-18
6-3
6-14
6-13
3-5
6-13
6-12
T
table menu 6-21
tables, within menus
components of
resizing 3-7
technical support A-1
trap
index field
receivers
adding
deleting 4-13
menu 6-15
modifying 4-13
3-7
6-15
4-12
4-14
traps 4-12
TX Collision 6-18
U
unicast frames 6-18, 6-19
unit ID field
address list
VLAN 6-3
UNIX 1-3
up time field, identify menu 6-6
upgrade menu 6-13
upgrading switch software 4-7
6-4
V
validate menu 6-17
virtual local area network. See VLAN
VLAN
creating groups of
group
button
number 5-3
groups
disabling
identifying on image 3-4
naming 5-9
statistics, viewing 5-12
viewing 3-4
identification window 3-4
LED status box 5-3
managing groups of, overview 5-8
menu, description of fields 6-3
menus with 5-4
overview of 5-1
port button 5-3
selecting for management 3-5
use of 5-1
view menu, picture of 5-2
viewing groups 5-2
VLAN View menu 6-22
5-5
5-3
5-11
W
wGroupIndex field, VLAN 6-3
wGroupName field, VLAN 6-3
Windows NT
3.51
1-3
starting server 2-3
Index-iv
Page 87

Windows NT (continued)
4.0
1-3
starting server 2-3
World Wide Web browsers
supported
write community string,
configuring
1-3
4-3
Index-v
Page 88

 Loading...
Loading...