Page 1

TOSHIBA
WN4301A-LF-JT
Wireless LAN PC Card
User’s Manual
Page 2

Contents
Introduction 1
Features 1
Applications 2
System Requirements 2
Package Checklist 2
Hardware Description 3
LED Indicators 3
Hardware Installation 4
Driver and Utility Installation 5
Windows 98/Me/2000 Installation 5
Windows XP Installation 7
Utility Configuration 10
Using Wireless Card Manager 10
Configuration 11
Link Information 14
IP information 15
Site browse 16
Version information 17
Network Configuration and Planning 18
Network Topologies 18
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN 18
Infrastructure Wireless LAN 19
Setting the Communication Domain 20
Stationary Wireless PCs 20
Roaming Wireless PCs 20
Troubleshooting 21
Adapter Installation Problems 21
Network Connection Problems 22
Compliances 23
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement 23
CE Mark Declaration of Conformance for EMI and Safety (EEC) 24
Specifications 25
i
Page 3

Introduction
The WN4301A-LF-JT is a Wireless LAN PC Card, support a 54 Mbps wireless network
adapter that seamlessly integrates with existing Ethernet networks to support applications
such as mobile users or temporary conferences. This solution offers a high data rate and
reliable wireless connectivity with considerable cost savings over wired LANs (which
include long-term maintenance overhead for cabling). Just install enough wireless access
points to cover your network area, plug wireless cards into your notebooks, and start
networking.
Using this card in conjunction with a wireless access point, gateway or wireless router,
you can create an instant network that integrates seamlessly with 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
LANs. Moreover, moving or expanding your network is as easy as moving or installing
additional access points – no wires!
Features
• Up to 54 Mbps data rate
• Wireless connection without the hassles and cost of cabling
• Greater flexibility to locate or move networked PCs
• Integrates with or replaces wired LANs at dramatically lower cost than wired
alternatives
• Seamless connectivity to wired Ethernet LANs augments existing networks quickly and
easily
• Easy installation and user-friendly configuration
• Complementary Code Keying (CCK) ensures backward compatibility to the existing
802.11b WLAN infrastructure
• Auto fallback data rate under noisy environment
• Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technology provides robust,
interference-resistant wireless connection
• Supports a wide range of systems (Windows 98/Me/2000/XP)
• Enhances your network security with 64/128-bit WEP data encryption
• Domain Channel Selection (DCS) allows access to the channels prescribed by the
regulation of different countries
1
Page 4

Wireless LAN PC Card
Applications
Offers a fast, reliable, cost-effective solution for wireless client access to the network in
applications like these:
• Remote access to corporate network information
E-mail, file transfer, and terminal emulation
• Difficult-to-wire environments
Historic or old buildings, asbestos installations, and open areas where wiring is difficult
to employ
• Frequently changing environments
Retailers, manufacturers, and banks who frequently rearrange the workplace and
change location
• Temporary LANs for special projects or peak times
Trade shows, exhibitions, and construction sites that need a temporary setup for a
short time period. Retailers, airline, and shipping companies that need additional
workstations for peak periods. Auditors who require workgroups at customer sites
• Access to databases for mobile workers
Doctors, nurses, retailers, office workers who need access to databases while being
mobile in the hospital, retail store or office campus
• SOHO users
SOHO (Small Office Home Office) users who need easy and quick installation of a
small computer network
System Requirements
Before you install the Wireless LAN PC Card, check your system for the following:
• A laptop with a PCMCIA Type II or Type III slot
• Windows 98/Me/2000/XP
(Prepare the Windows OS installation CD for use during driver and utility installation)
• A minimum of 1500 Kbytes of free disk space for installing the driver and utility program
• Other IEEE 802.11b/g-compliant devices installed in your network
Package Checklist
The Wireless LAN PC Card package includes:
• 1 Wireless PC Card
• 1 driver and utility CD with documentation
• Warrenty card
Please inform your dealer if there are any incorrect, missing, or damaged parts. Please
retain the original packing materials, in case there is a need to return the product.
2
Page 5
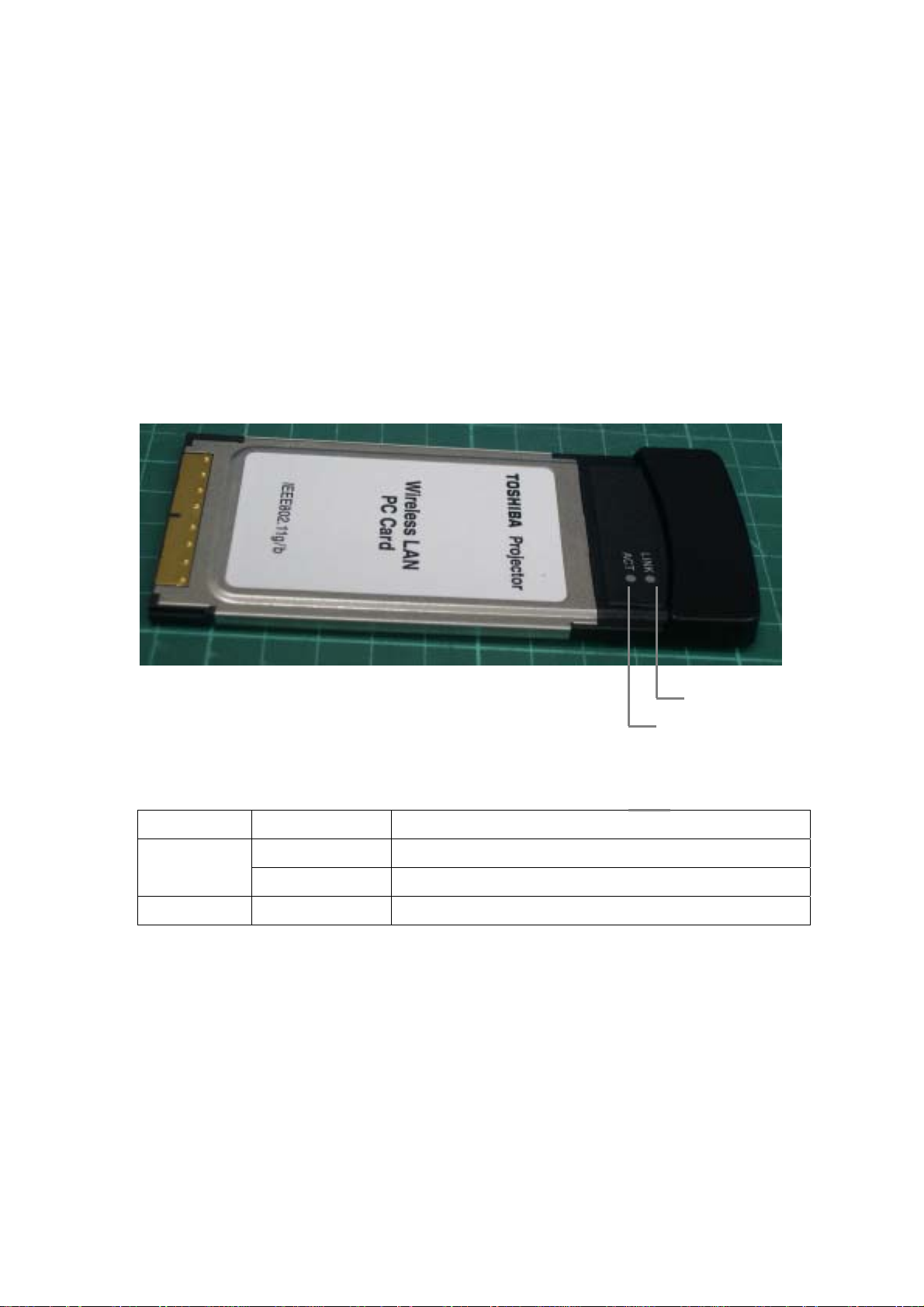
Hardware Description
The Wireless LAN PC Card supports up to 54Mbps connections to Ethernet networks.
This wireless card is fully complient with the specifications defined in IEEE 802.11g.
It can be installed in any notebook with a Type Ⅱ PCMCIA slot. And this card
supports Windows 98/ME/200/XP.
LED Indicators
The Wireless LAN PC Card includes two status LED inducators, as described in the
following figure and table.
Link
Activity
LED Status Description
LINK
ACT Flashing Indicates that the card is transmitting or receiving packets
On Indicates a valid connection
Flashing Indicates that the card is scanning for available networks
Page 6

Wireless LAN PC Card
Hardware Installation
Warnings:
Network cards are sensitive to static electricity. To protect the card, always touch the
metal chassis of your computer or the ground before handling the card.
To install the card:
1. Turn on your notebook.
2. Install the driver and utility program into your system. Drivers can be found on the
driver and utility CD. See the following section for more information on driver and
utility installation.
3. Find an available Type II PCMCIA slot in your notebook.
4. With the card’s 68-pin connector facing the PCMCIA slot, slide the card completely
into the slot as shown below.
4
Page 7
Page 8
Wireless LAN PC Card
5. This screen will appear, though the driver is fully compatible with Windows 2000, it
has not yet been Logo tested by Microsoft. Click Yes to continue with the installation.
Do not click No, as this will cancel the installation and the driver will not be installed
Note:
properly.
6. The InstallShield wizard will start copy driver files into your system, this may take a
few minutes. The Country Select window will then appear, click OK to exit the
window. The installation process in now completed.
6
Page 9
Page 10

Wireless LAN PC Card
4. After inserting the card, the Found New Hardware Wizard window appears. Select
Install the software automatically, then click Next.
5. This screen will then appear, though the driver is fully compatible with Windows XP, it
has not yet been Logo tested by Microsoft. Click Continue Anyway.
Note:
Do not click STOP Installation, as this will cancel the installation process, and the driver
will not be installed properly.
8
Page 11

Windows XP Installation
6. The Wizard will start to install the software into your system. This may take a few
minutes.
7. When the wizard has finished installing the driver, the following screen will appear.
Click Finish to exit the window.
8. Select the country in which you are using the Wireless LAN PC Card.
The installation process in now completed.
9
Page 12

Page 13

Page 14

Wireless LAN PC Card
Encryption — Select 64 bit or 128 bit to enable the WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
function. This function is implemented in the card to prevent unauthorized access.
Key Type — Select ASCII or Hex.
Default Key — Choose one key to use for encryption.
Passphrase — Check this box to automatically generate keys for encryption.
Advance — Click this button to set the packet burst duration function. Move the slider bar
to adjust the packet transmission speed. The larger the number, the faster the speed.
How to set up WEP:
The WEP mechanism is based on the RC4 encryption algorithm. The security keys are
provided to ensure data confidentiality. WEP security protects your wireless LAN against
eavesdropping and unauthorized access by intruders. If WEP is in use, all clients on the
same network must use the same WEP key settings in order to communicate with each
other.
To use the WEP function, take the following steps:
Step 1. Select 64 bit or 128 bit in the Encryption field.
Step 2. To automatically generate keys, check the Passphrase box, then type in a string
of characters (a maximum of 32 digits) into the field. If you are using an auto-generated
key, you must use the same passphrase and key on every station within the same
network. Please note that when Encryption is set to 64 bit, 4 keys will be generated.
When 128 bit Encryption is selected, only one key will be auto generated.
Step 3. In the Default Key field, select one number to use as the default key from the
drop-down menu.
Step 4. Click Apply changes to allow the settings to take effect.
Or
12
Page 15

Using Wireless Card Manager
Step 1. Select 64 bit or 128 bit in the Encryption field.
Step 2. Select ASCII or Hex in the Key Type field.
Step 3. In the Default Key field, select one number to use as the default key from the
drop-down menu.
Step 4. Manually type in a string of characters in the corresponding Key # field that you
have selected in step 3.
Step 5. Click Apply changes to allow the settings to take effect.
When setting up WEP without using the Passphrase function, if the Key Type is set to
Note:
Hex, only hexadecimal characters (range: 0~9 and A~F) can be used. When Encryption
is set to 64 bit, 10 Hex characters can be entered in the Key field. And for 128 bit
Encryption setting, a maximum of 26 Hex characters cna be entered to generate the key
string. If the Key Type is set to ASCII, and Encryption is set to 64 bit, then 5 ASCII
characters can be used in the Key field. And for 128 bit Encryption, 13 ASCII characters
can be used.
13
Page 16

Page 17

Page 18

Page 19

Page 20

Wireless LAN PC Card
Network Configuration and Planning
This Wireless Solution supports a stand-alone wireless network configuration, as well as
an integrated configuration with Ethernet LANs.
The Wireless LAN PC Card can be configured as:
• Ad hoc for peer-to peer communications
• Infrastructure for connections with wireless LANs
Network Topologies
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN
An ad hoc wireless LAN consists of a group of computers, each equipped with a wireless
adapter, connected via radio signals as an independent wireless LAN. Computers in a
specific ad hoc wireless LAN must be configured to the same radio channel. An ad hoc
wireless LAN can be used for a branch office or SOHO operation.
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN
Notebook with
Wireless USB Adapter
18
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Notebook with
Wireless PC Card
Page 21

Network Topologies
Infrastructure Wireless LAN
The Wireless 802.11g/b Card can also provide wireless workstations with access to a wired
LAN. An integrated wired and wireless LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. A
Basic Service Set (BSS) consists of a group of wireless PC users, and an access point
that is directly connected to the wired LAN. Each wireless PC in this BSS can talk to any
computer in its wireless group via a radio link, or access other computers or network
resources in the wired LAN infrastructure via the access point.
The infrastructure configuration not only extends the accessibility of wireless PCs to the
wired LAN, but also extends the effective wireless transmission range for wireless PCs by
passing their signals through one or more access points.
A wireless infrastructure can be used for access to a central database, or for connection
between mobile workers, as shown in the following figure.
Wired LAN Extension
to Wireless Adapters
File
Server
Desktop PC
Switch
Access Point
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
PC with Wireless
PC I Adapter
19
Page 22

Wireless LAN PC Card
Setting the Communication Domain
Stationary Wireless PCs
The Basic Service Set (BSS) is the communication domain for each access point. For
wireless PCs that do not need to support roaming, set the domain identifier (SSID) for the
wireless card to the SSID of the access point you want to connect to. Check with your
administrator for the SSID of the access point that you are connecting.
Roaming Wireless PCs
A wireless infrastructure can also support roaming for mobile workers. More than one
access point can be configured to create an Extended Service Set (ESS). By placing the
access points so that a continuous coverage area is created, wireless users within this
ESS can roam freely. All wireless adapters and access points within a specific ESS must
be configured with the same SSID and to the same radio channel.
File
Server
Wireless Cell
Coverage Area
Desktop PC
Switch
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
20
<BSS1>
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Notebooks with Wireless
PC Card Adapters
Access Point
Access Point
PC with Wireless
PC I Adapter
<ESS>
Seamless Roaming
<BSS2>
Page 23

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Check the following troubleshooting items before contacting Technical Support.
Adapter Installation Problems
If your laptop cannot find the Wireless PC Card or the driver software does not install
correctly, check the following:
• Make sure the adapter is securely seated in the PCMCIA slot. Check for any hardware
problems, such as physical damage to the card’s connector.
• Try the card in another PCMCIA slot. If this also fails, test your laptop with another
wireless card that is known to operate correctly.
• Make sure your laptop is using the latest BIOS.
• If there are other network adapters in the notebook, they may be causing conflict.
Remove all other network adapters from the laptop and test the EPSON Wireless PC
Card separately.
• Check for a defective notebook or PCMCIA connection by trying the adapter in another
notebook that is known to operate correctly.
If it still does not work, take out the wireless adapter, delete the driver and utility from
your system. Then go to Control Panel and delete the adapter from your network
configuration menu. Restart your notebook and reinstall the Wireless PC Card and the
driver and utility software.
21
Page 24

Wireless LAN PC Card
Network Connection Problems
If the Link LED on the Wireless PC Card does not light, or if you cannot access any
network resources from the notebook, check the following:
• Make sure the correct software driver is installed for your operating system. If
necessary, try reinstalling the driver.
• Make sure the notebook and other network devices are receiving power.
• The access point you want to connect to may be defective. Try connecting with another
access point.
• If you cannot access a Windows or NetWare service on the network, check that you
have enabled and configured the service correctly. If you cannot connect to a particular
server, be sure that you have access rights and a valid ID and password.
• If you cannot access the Internet, be sure you have configured your system for TCP/IP.
If your wireless station cannot communicate with a computer in the Ethernet LAN when
configured for Infrastructure mode, check the following:
• Make sure the access point that the station is associated with is powered on.
• If you still cannot connect, change the access point and all the stations within the BSS
to another radio channel.
• Make sure the SSID is the same as that used by the access point for a station with
roaming disabled, or the same as that used by the access points in the extended
service set (ESS).
22
Page 25

Compliances
Compliances
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the distance between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example - use only shielded interface
cables when connecting to computer or peripheral devices) any changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user’ authority to operate this equipment. This device complies with Part 15
of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment, under 47 CFR 2.1093 paragraph (d)(2).This transmitter must not be co-located
or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
23
Page 26

Wireless LAN PC Card
CE Mark Declaration of Conformance for EMI and Safety (EEC)
This information technology equipment complies with the requirements of the Council
Directive 89/336/EEC on the Approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to
Electromagnetic Compatibility and 73/23/EEC for electrical equipment used within certain
voltage limits and the Amendment Directive 93/68/EEC. For the evaluation of the
compliance with these Directives, the following standards were applied:
RFI
Emission:
Immunity: • Product family standard according to EN 55024:1998
LVD: • EN 60950 (A1/1992; A2/1993; A3/1993; A4/1995; A11/1997)
• Limit class B according to EN 55022:1998
• Limit class B for harmonic current emission according to
EN 61000-3-2/1995
• Limitation of voltage fluctuation and flicker in low-voltage
supply system according to EN 61000-3-3/1995
• Electrostatic Discharge according to EN 61000-4-2:1995
(Contact Discharge: ±4 kV, Air Discharge: ±8 kV)
• Radio-frequency electromagnetic field according to
EN 61000-4-3:1996
(80 - 1000 MHz with 1 kHz AM 80% Modulation: 3 V/m)
• Electrical fast transient/burst according to EN 61000-4-4:1995
(AC/DC power supply: ±1 kV, Data/Signal lines: ±0.5 kV)
• Surge immunity test according to EN 61000-4-5:1995
(AC/DC Line to Line: ±1 kV, AC/DC Line to Earth: ±2 kV)
• Immunity to conducted disturbances, Induced by
radio-frequency fields: EN 61000-4-6:1996
(0.15 - 80 MHz with 1 kHz AM 80% Modulation: 3 V/m)
• Power frequency magnetic field immunity test according to
EN 61000-4-8:1993 (1 A/m at frequency 50 Hz)
• Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations
immunity test according to EN 61000-4-11:1994
(>95% Reduction @10 ms, 30% Reduction @500 ms, >95%
Reduction @5000 ms)
24
Page 27

Specifications
Specifications
Functional Criteria
Data Rate 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps
Operating Range Up to 18 m (60 ft) at 54 Mbps
Up to 40 m (132 ft) at 11 Mbps
Radio Signal
Radio Technology Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Complementary Code Keying (CCK)
Operating Frequency USA (FCC): 2412~2462 MHz
Canada (IC): 2412~2462 MHz
Europe (ETSI): 2412~2472 MHz
Spain: 2457~2462 MHz
France: 2457~2472 MHz
Japan: 2412~2484 MHz
Operating Channel USA, Canada: 11 channels
ETSI: 13 channels
Spain: 2 channels
France: 4 channels
Japan: 14 channels
Sensitivity -68 dBm (typical)
Output Power +10 dBm (minimum)
Physical Characteristics
Power Consumption TX: 480 mA, RX: 420 mA, Power Saving: 20mA
Dimensions 12.8 x 5.3 cm (5.04 x 2.09 in.)
Antenna Built in dual antenna
LED Indicator Link, Power/Activity
Host Interface PCMCIA Type II
Standards Conformance
Wireless Standard IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g
Environmental
Temperature Operating: 0 to 55 °C (32 to 131 °F)
Storage: -20 to 70 °C (-4 to 158 °F)
Humidity 5 to 90% (non-condensing)
Vibration/Shock/Drop IEC 68-2-34, IEC 68-2-27, IEC 68-2-32
25
Page 28

Wireless LAN PC Card
Certification
Emissions EN 50081-1, EN 55022 Class B
EN 50082-1, EN 61000-4-2/3/4/6/11
FCC Part 15(B), ETSI 300-328,
ARIB STD33 & T66
Software Drivers
NDIS Drivers Windows 98
Windows Me
Windows 2000
Windows XP
26
 Loading...
Loading...