Page 1

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction ............................................................................................ 3
Introduction .......................................................................................... 3
Features............................................................................................... 3
Front Panel Controls .............................................................................. 4
Input Gain Control ............................................................................... 4
Input Impedance Control ................................................................. 4-5
Analog Output Control ......................................................................... 5
HPF Control ........................................................................................ 5
Gain Switch ......................................................................................... 5
Phantom Switch ................................................................................... 5
Phase Switch ...................................................................................... 5
Plate Voltage Switch......................................................................... 5-6
Meter Switch........................................................................................ 6
Digital Section Controls ........................................................................ 6
Digital Level Control ............................................................................ 6
Dither Switch ....................................................................................... 6
Sample Rate Control ........................................................................... 7
Optical Switch...................................................................................... 8
Front Panel Connections......................................................................... 8
Instrument Inputs................................................................................. 8
Rear Panel Connections......................................................................... 8
Balanced Inputs................................................................................... 8
Balanced Outputs ............................................................................... 8
Insert Jacks ......................................................................................... 9
Word Clock Jacks................................................................................. 9
ADAT Input .......................................................................................... 9
Optical Output....................................................................................... 9
S/PDIF Output ..................................................................................... 9
AES/EBU Output .................................................................................. 9
Signal Path Flow ................................................................................... 10
Signal Path Flow Diagram .................................................................. 10
Operating Instructions ......................................................................... 10
Obtaining the best noise performance............................................... 10
Adjusting the input impedance...................................................... 10-11
Obtaining the perfect digital level setting ........................................... 11
Setting the tube plate voltage ............................................................ 11
Warranty Information ........................................................................... 12
Service .................................................................................................. 12
Specifications ....................................................................................... 13
2
Page 2

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
DIGITAL MPA INTRODUCTION
The ART Digital MPA™ microphone preamplifier features a new low noise, high performance preamplification
circuitry, designed for superior audio fidelity. Building upon the quality and success of great sounding products like
the Pro MPA, ART engineers set out to develop the next generation of professional microphone preamplifier. The
Digital MPA is the culmination of years of research and development, and sets a new standard for quality and value.
Professional features and spectacular tone are what make the Digital MPA a world-class microphone preamplifier.
DIGITAL MPA FEATURES:
• Variable input impedance for flexible microphone voicing (150 Ohms to 2400 Ohms).
• Selectable plate voltage
• Large VU meters
• Front accessible meter trim
• Selectable between output level and tube warmth
• Improved discrete class A input microphone preamplifier
• Lower noise at low gains
• Lower THD
• Wider frequency response
• Front accessible Instrument Input Jack
• Very high input impedance
• Automatically switches to the instrument input when you plug in
The Digital MPA also features digital connectivity for use with various digital processors and digital recording devices.
The Digital interface supports the following features and functions:
• 24-204KHz External sample rate
• 44.1K, 48K, 88.2K, 96K, 176.4K, 192K Internal sample rates
• 24/16 bit switchable dithering
• Wide dynamic range A/D
• Rotary Encoder for quick selection of sample rate and output format
• Separate analog and digital output level controls
• Digital Level LED meters
• ADAT optical I/O
• Sync to incoming ADAT data rate
• Switch selectable optical output (S/PDIF or ADAT)
• Selectable Pro/consumer output format
• AES/EBU output on cannon connector
• Two wordclock jacks allowing loop through
ART Digital MPA – Rear view image (above)
3
Page 3
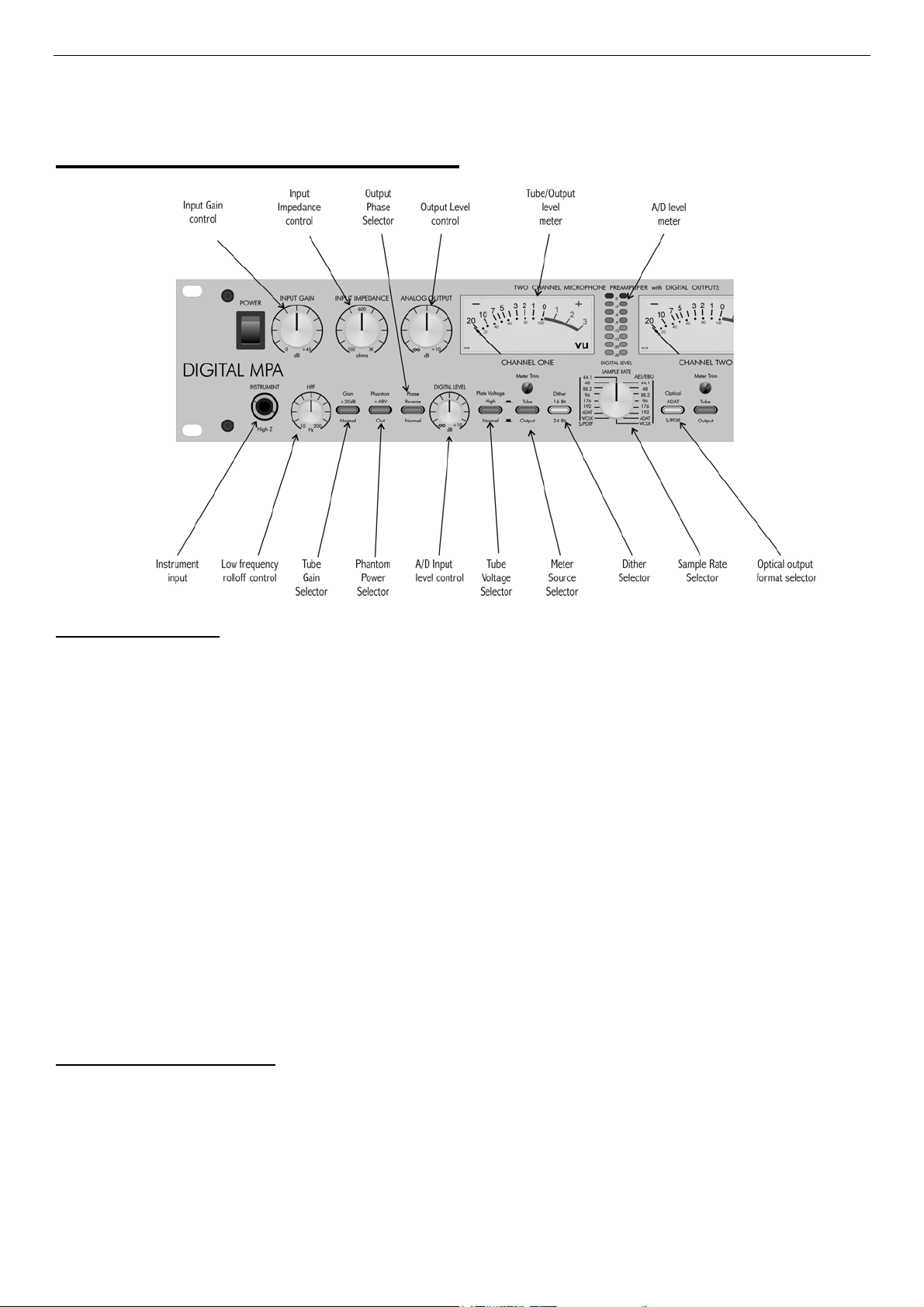
ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
FRONT PANEL CONTROLS
Input Gain Control
This control optimizes the input signal level before the tube gain is applied. Both Microphone and
Instrument input gains remain the same and are affected by this adjustment. Input gain can be
adjusted from 0dB (for line level signals) to 45dB of gain.
Use the analog meters in the TUBE setting to gauge how much input gain is required.
Additional gain is available via the Gain switch (+20dB) and the Analog Output control (+10dB) for
a maximum of 75dB total.
The combination of these controls allows the user to adjust the signal level through the tube
section, providing more or less “tube” sound as needed. To obtain more “tube’ sound, increase
input gain, use the +20dB Gain switch, “normal” plate voltage, and less Analog output gain.
Both the microphone and instrument inputs are optimized for their respective sources as far as
signal levels and noise performance. Running most of the gain on the input generally provides the
best performance of the DMPA. Refer to the section titled “Obtaining the best noise performance
with the DMPA” for more detailed instructions on setting the Input Gain control for the best results.
Input Impedance Control
This knob controls the Mic/line input amplifier impedance. This function allows variable voicing of
any microphone.
Refer to the application section titled “Adjusting the Input Impedance” for more information on
making the most of this function.
4
Page 4

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
The 1/4” instrument input is NOT affected by this control, and remains high (>1M Ohm) impedance.
Analog Output control
The output signal level at the rear output jacks is adjusted by this control. It can provide from
+10dB of gain (fully clockwise) to completely muted. You can see the effects of this adjustment
reflected in the analog meters when the meter switch is set to “output”.
HPF control
The HPF is a single tuned High Pass Filter that is frequency tunable. The input signal can be
filtered to remove “pops” or other extraneous low frequency information. This control moves the
rolloff frequency from 10 Hz (fully CCW) to 200 Hz (fully CW). Since it is single tuned (the same
as single pole, the simplest kind of filter), it preserves some low frequency content so its use is
less obtrusive. It is especially useful in close mic’d applications.
Gain switch
The Gain switch is used in conjunction with the input gain control to adjust signal levels through
the DMPA. When depressed, the tube circuit provides 20dB more gain in the signal path. This also
has the effect of driving the tube harder and making the tube the dominant source of gain and
overload character.
Phantom switch
Phantom power on the microphone input is turned on and off with this switch. Depressing the
switch will power condenser microphones and other 48volt phantom powered devices. Phantom
power is supplied to pins 2 and 3 of the input jack.
NOTE:
1) Dynamic microphones are NOT affected by Phantom power, although it should be turned off when using dynamic
microphones or line level inputs.
2) Although the 48volt phantom power ramps up and down slowly it may still create a pop. Mute the output of the
DMPA when engaging or disengaging phantom power to prevent damage to equipment following the DMPA.
Phase switch
The Phase switch can invert the phase of the audio signal path in either channel. The Phase
switch is located after the tube circuit in the signal path, so you can hear slight differences between different phase selections in the “normal” plate voltage mode near saturation. There are a
number of reasons why adjusting the phase is needed these include, wiring errors and inversions
in some audio equipment. Some microphones sound different depending on the phase chosen.
If two microphones are out of phase, they may cancel at various frequencies (depending on the
distance between them). If this happens, try changing the phase of one of the microphones and
see if there is an improvement.
Plate Voltage switch
This switch sets both the tube bias point and the plate voltage level the balanced differential tube
circuit runs at. The amount of headroom is adjusted by using the Gain switch and the input Gain
5
Page 5

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
control. The DMPA takes about 10-30 seconds to smoothly transition from one mode to the other.
There is a slight increase in gain in the “High” plate voltage mode.
In the “normal” (OUT) position, the tube distortion gradually rises until it smoothly clips. The tube is
run almost completely open-loop in this mode, providing a musical tube “crunch” when overdriven
with a natural recovery from clipping. The tube section can be more easily overdriven when the
gain switch is in. This mode brings out the harmonics in the input sources, particularly stringed
instruments.
The tube circuit runs extremely clean in the “high” (IN) position of the plate voltage switch. As
signal levels rise distortion remains very low until within 6dB of clipping, where the overload characteristics smoothly limit the signal swing. There is increased bandwidth (>100KHz), and headroom in this mode as well.
Meter Switch
The analog meters can monitor either the output signal at the output jacks (“output” position) or the
tube output level (“tube” position).
VU on the meter measures +4dBu at the output jacks in “output” mode.
When in “tube” mode there is 10 to 15dB of headroom above 0VU before the tube saturates (for
“normal” and “high” plate voltage settings respectively).
Digital Section Front Panel Controls
Digital Level Control
The levels driving the A/D converter are adjusted with this control. The topology of the DMPA
lends itself to simultaneous use of the analog and digital outputs, as each has its’ own level control. Common to both is the output signal of the tube circuit.
The Digital level control is variable from +10dB to -∞ (fully muted).
Located before the Digital level control is the insert jack, allowing processing to be added before
digital conversion.
As the Digital Level control is used refer to the Digital level LED meter which indicates both peak
and average level present at the A/D converter input. This meter helps you get the perfect level
adjustment and avoid clipping the A/D. Refer to the section titled “Obtaining the perfect digital level
setting” for more detail on the operation and use of these features.
Dither Switch
The DMPA possesses a 24-bit A/D converter. When the output of the unit goes off to a system
that can handle only 16 bit data, the 8 least significant bits of data are ignored (truncated). This
leaves the sound with gritty “digital” sounding signals at very low levels. Depressing the Dither
switch adds a dither component that when truncated replaces this with a more musical sound as
the levels trail off into the noise floor.
6
Page 6

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
Generally, keep the unit in 24-bit mode (the out position of the switch) unless you are connected to
a system that will truncate the signal to 16 bits. The 24-bit mode has significantly greater dynamic
range.
Sample Rate Control
The Sample rate knob determines both the output sample rate of the DMPA as well as the digital
data format. You can select either AES/EBU (pro) format or S/PDIF (consumer) data format. This
allows the DMPA to interface to a wide variety of digital inputs.
The S/PDIF mode has copy protection turned off, and identifies itself as an A/D converter with 24
bit data.
The AES/EBU mode identifies itself as either locked (when set to an internal sample rate) or
unlocked (when set to Wordclock or ADAT as a sync source). No other channel status data is
sent.
The first step in determining the correct sample rate setting is to choose the data format. If you
plan on using the cannon output (AES/EBU jack) make a sample rate selection on the right half of
the selection range.
If using the coax (RCA jack) output make a selection of the left side of the sample rate knob.
The internal sample rate can be set from 44.1KHz to 192KHz. Simply select the correct rate by
turning the knob to the rate you need and the DMPA will use its’ internal crystal controlled oscillator to accurately generate the selected timing.
Be careful in adjusting this control. Some equipment is not capable of the available sample rates
and may produce damaging side effects. Always turn down levels following the DMPA when
changing the sample rate.
External sync sources are Wordclock and ADAT INPUT.
Wordclock is a 5V logic level signal interfaced by a BNC connector on the rear of the unit. The
Range of wordclock accepted by the DMPA is 28KHZ to 212 kHz. It is recommended that you use
wordclock whenever possible, as this will minimize interface errors with other equipment.
NOTE: When using the ADAT optical output, the maximum sample rate is limited to about 50KHz. If wordclock
exceeds this the ADAT output (if selected) will fail.
The ADAT Input on the rear panel is used as a timing reference as well as a source of data to be
passed on to the ADAT output of the DMPA.
If the unit CANNOT sync to an external source (either out of range, not connected or a system
failure), the optical Output select switch will blink. (You may see this switch flash once between
changing sample rates, indicating the fraction of a second it takes to settle to the new rate. This is
normal). NOTE: When using the ADAT Input as a sync source, the maximum sample rate is
limited to about 50KHz Sample Rate (selection being set to ADA - not wordclock or any other
fixed sample rate).
7
Page 7

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
Optical Switch
The optical output jack of the DMPA can have one of two formats. When this switch is depressed
AND lit blue, this jack will output 8 channels of ADAT. (ADAT cannot be output if the sample rate
exceeds 48KHZ - the Sample Rate selection being set to an internal rate). In this case the switch
cap will NOT be illuminated, and the output format will revert to 2-channel mode (TOSLINK).
When ADAT output is active, The left channel of the DMPA is output on CH1, the right channel of
the DMPA is CH2, and the rest of the channels consist of data received from the ADAT Input jack.
When the switch is in the OUT position OR the switch cap is not lit, the output consists of two
channels of digital audio in the format selected by the Sample Rate Switch.
The Lighting of the optical switch cap serves a second function. If it is blinking, there is a timing
problem in the digital section. This usually happens when there is not a valid external timing input
selected.
Front Panel Connections
Instrument Inputs
The 1/4” jacks on the front panel serve as an instrument input. The input impedance is always
>1M Ohm and the gain can be adjusted by the Input gain control. The maximum input signal level
is +17dBu (5Vrms) @ minimum input gain.
When you plug into this jack it DISABLES the balanced input on the rear of the unit. This feature
allows you to keep the rear input patched in, and use the instrument input to switch to a different
source. The instrument input allows the DMPA to serve as a great DI device as well.
Rear Panel Connections
Balanced Inputs
The DMPA’s XLR connectors follow the AES standard of Pin 1 = Ground, Pin 2 = Hot (+), Pin 3 =
Cold (-). The Balanced inputs have an input impedance that is variable from 150 to 3K Ohms via
the front panel control. The Maximum input level is +19dBu balanced and +17dBu unbalanced.
Balanced Outputs
The DMPA ‘s flexible active balanced outputs are available on both 1/4” and cannon connectors.
They offer low impedance for driving long cable runs and are intelligent so they maintain the same
output level whether it is balanced or unbalanced.
The DMPA’s XLR connectors follow the AES standard of Pin 1= Ground, Pin 2= Hot (+), Pin 3=
Cold (-). The balanced 1/4” phone jacks are typical Tip = Hot (+), Ring = Cold (-), Sleeve = Ground
Maximum output level is +26 balanced and +20 unbalanced.
8
Page 8

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
Insert Jacks
The insert jacks are used to process the audio passed on to the A/D converter. The Insert Jacks
are wired: Tip = Input, Ring = Output, Sleeve = Ground. The input impedance is 10K Ohm and the
output impedance is 1K Ohm. The minimum input signal required to drive the A/D to clip is +12dBu
(3V rms)
Wordclock Jacks
The DMPA offers Wordclock input on a BNC connectors. A 5V logic level signal is required
to drive the digital clock circuitry. Both BNC connectors are tied together allowing you to loop
wordclock through the DMPA saving cabling complexity.
ADAT Input
The ADAT input for the DMPA is a standard optical connector. This input is used when synching to
ADAT for timing purposes. It is also used as a data source for channels 3-8, as the channels NOT
transmitted by the DMPA are passed from this input to the Optical output (when the optical output
is set to ADAT mode).
Optical Output
The Optical output switch selects the data source for this jack. This feature allows the DMPA to
output to multiple units in different formats at the same time.
In S/PDIF mode, two-channel audio is present. The data is identical to the coax and cannon digital
output connectors.
In ADAT mode the DMPA transmits its’ A/D data on the first two channels and passes information
from the ADAT input jack (CH3-8) on to the other channels.
Using the optical output in S/PDIF is recommended over the coax output, as it is the most robust
and reliable of all the digital outputs. When connecting to consumer gear, use a sample rate
selection in the S/PDIF range of the selector knob.
S/PDIF Output
The S/PDIF coax connector allows the DMPA to connect to a wide range of consumer and professional equipment. This output is .5V p-p (peak-to-peak) (when connected) isolated from ground,
and has a 75 Ohm impedance. The same data is sent to both this connector and the AES/EBU
output, but it is recommended that you not use both at the same time, as the AES/EBU output may
work, but there will be too great a loss in level to meet the S/PDIF spec. Choose a sample rate in
the S/PDIF range of the front panel selector when using this jack.
AES/EBU Output
The AES/EBU output of the DMPA is a 5V p-p signal with a 110 Ohm impedance. This cannon
connector is driven by the same drive circuitry and isolation transformer and as the S/PDIF output.
Choose a sample rate in the AES/EBU range of the front panel selector when using this jack. If
this is not done equipment that follows the DMPA may not recognize this data as valid.
9
Page 9

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
SIGNAL PATH FLOW DIAGRAM
The signal path of the DMPA consists of a discrete class A microphone pre-amp followed by a Hi
Pass Filter, a balanced differential tube circuit with a 20dB Gain switch and then the phase switch.
At this point the signal passes to both the analog output and the Insert jacks. The insert jacks
allow processing of the signal before its’ level is adjusted by the Digital Level control and passed
to the A/D. You can use the A/D converters of the DMPA independent of the analog functions by
simply inserting a signal into this insert point.
DMPA OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Obtaining the best noise performance with the DMPA
Start by turning down the Input Gain knob and centering the Analog Output knob. Use the analog
meter to view the operating level by depressing the switch under the center of the analog meter.
The meter will now indicate how much tube headroom there is. Set the +20dB switch to the out
position.
Increase the Input Level knob until the meter reads above –10dB. If you have turned the input
knob fully clockwise and the indicated level is still below –10dB on the meter, center the input knob
and depress the Gain switch. Increase the Input Gain until there is sufficient level.
This procedure optimizes the gain elements to provide the widest dynamic range possible.
Adjusting the Input Impedance
The same microphone can sound different on various pre-amps. One reason is that every pre-amp
presents a different load to on its’ input, some even change as gain is changed! Our third generation discrete front end was designed to be absolutely transparent. Every nuance of the microphone
is maintained providing detail masked by inferior pre-amps. The Input Impedance control is one
key element in providing new versatility in voicing microphones.
10
Page 10

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
NOTE: the Input impedance control only affects the cannon connector inputs. The 1/4” instrument input on the front
panel is NOT affected by this control in any way. The instrument input impedance is ALWAYS >
1M Ohm.
Dynamic microphones are affected as much as phantom powered units.
We provide a continuously variable impedance control to allow you to fine-tune the voicing, finding
the perfect interaction between microphone and pre-amp.
Start by setting the centering the Input Impedance knob. This provides a 600-Ohm load.
Lower impedance loads will reject more noise picked up by cabling, and dampen microphone
resonance. Lower impedances tend to focus the sound more. Higher impedance settings provide
a more “open” sound.
Obtaining the perfect digital level setting
The Digital level meter indicates both peak and average levels present at the A/D converter. The
0dB LED indicates that there is less than 1dB of headroom before clipping. The highest peak level
reached is held for 1 second by a single LED and the average level is indicated by the remaining
LEDs, lit in series.
It is recommended you start with the digital level control centered. Adjust the input gain and +20dB
switch such that the digital meter holds peaks at –3dB and occasionally hits the red 0dB LED. This
setting will provide the best dynamic range AND the tube will saturate before the A/D clips (on
heavy overloads).
If you want more tube headroom, set the digital level control fully clockwise.
If you need to compress the input signal before it is converted to a digital signal, use the rear panel
Insert Jacks. The insert point is located between the tube output and the Digital Level control. This
allows insertion of a dynamics processor with the ability to tweak the A/D input sensitivity from the
DMPA front panel.
Setting the Tube Plate Voltage
The DMPA allows the user select between one of two vastly different tube bias and power supply
levels. The transition between either setting is smooth and quiet and the gain variation is minimal.
NOTE: It takes 15-30 seconds for the tube circuit to fully transition between either mode. During this time, the unit
passes a signal and the only noticeable change is a slight increase in level in the “HIGH” setting.
The “Warm” setting produces a smooth transition from very clean low levels up to a “round” saturated clipping on peaks. This setting is reminiscent of old tube gear, and used to get the most
tube-like sound out of the unit. Common uses include tracking with instruments.
The “High” setting of the plate voltage switch has increased bandwidth and headroom, very low
distortion and runs extremely clean until it reaches a point of saturated clipping. The clipping is
well controlled and still sounds natural. This setting is incredible on vocals.
11
Page 11

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
WARRANTY INFORMATION
Limited Warranty
Applied Research and Technology will provide warranty and service for this unit in accordance
with the following warrants:
Applied Research and Technology (A R T) warrants to the original purchaser that this product and
the components thereof will be free from defects in workmanship and materials for a period of five
years from the date of purchase. Applied Research and Technology will, without charge, repair or
replace, at its option, defective product or component parts upon prepaid delivery to the factory
service department or authorized service center, accompanied by proof of purchase date in the
form of a valid sales receipt.
Exclusions
This warranty does not apply in the event of misuse or abuse of the product or as a result of
unauthorized alterations or repairs. This warranty is void if the serial number is altered, defaced, or
removed.
A R T reserves the right to make changes in design or make additions to or improvements upon
this product without any obligation to install the same on products previously manufactured.
A R T shall not be liable for any consequential damages, including without limitation damages
resulting from loss of use. Some states do not allow limitations of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to you. This warranty gives you
specific rights and you may have other rights, which vary from state to state.
For units purchased outside the United States, an authorized distributor of Applied Research and
Technology will provide service.
SERVICE
The following information is provided in the unlikely event that your unit requires service.
1) Be sure that the unit is the cause of the problem. Check to make sure the unit has power
supplied, all cables are connected correctly, and the cables themselves are in working condition.
2) If you find the unit to be at fault, write down a complete description of the problem, including
how and when the problem occurs. Please write down a description of your complete setup before
calling Customer Service.
3) Call the factory (585-436-2720) for a Return Authorization (RA) number.
4) Pack the unit in its original carton or a reasonable substitute. The packing box is not recommended as a shipping carton. Put the packaged unit in another box for shipping. Print the RA
number clearly on the outside of the shipping box. Print your return shipping address on the
outside of the box.
12
Page 12

ART Digital MPA™ Microphone Preamplifier
5) Include with your unit: a return shipping address (we cannot ship to a P.O. Box), a copy of your
purchase receipt, a daytime phone number, and a description of the problem.
6) Ship only your unit and its power supply (keep your manual!) to:
APPLIED RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
215 TREMONT STREET ROCHESTER, NEW YORK 14608 ATTN: REPAIR DEPARTMENT, RA# ____________________
7) Contact our Customer Service department at (585) 436-2720 for your Return Authorization
number or questions regarding technical assistance or repairs. Customer Service hours are 9:00
AM to 5:00 PM Eastern Time, Monday through Friday.
DMPA SPECIFICATIONS
Dimensions........................................................... 6.5” D x 19.0” W x 3.5” H
Weight ..................................................................12 Lb.
Frequency Response……………………………….15Hz to 48 kHz (+0, -1dB) @ normal plate voltage
15Hz to 120 kHz (+0, -1dB) @ high plate voltage
Dynamic range .....................................................>110dB (“A” weighted)
CMRR...................................................................>90dB
THD ......................................................................<0.005% (typical)
Equivalent Input Noise..........................................-133dBu (XLR, “A” weighted)
Maximum Input Level............................................+20dBu (cannon)
Maximum Instrument Input ...................................+17dBu
Input Impedance...................................................150-3000 Ohms adjustable (XLR) >800K Ohms (Instrument)
Maximum Output Level.........................................+27dBu (XLR)
Output Impedance ................................................< 47 Ohms (XLR)
Maximum Gain .....................................................75dB
Meter Calibration ..................................................0 VU = +4dBu output
High Pass Filter ....................................................single pole, 10-200 Hz adjustable
Power Requirements ............................................100-125 VAC, 25W. Export Units configured for country of destination
Digital Section:
A/D Frequency Response
@44.1KHz sample rate.........................................10Hz to 21.25KHz (+0, -1dB)
@88.2KHz sample rate.........................................10Hz to 42.50KHz (+0, -1dB)
@196KHz sample rate..........................................10Hz to 81KHz (+0, -1dB)
A/D Dynamic Range .............................................>115dB “A” weighted (typ.)
A/D THD ...............................................................<0.001% @1K (typ.)
A/D Input Sensitivity..............................................+12dBu min
A/D Insert Input Impedance…………………………>10K Ohms
The ART Digital MPA™ is ADAT licensed.
13
 Loading...
Loading...