Page 1

MX3ZA
User's Guide
Printed in Taiwan
PART NO.: 49.88101.081
DOC. NO.: MX3ZA-1-E9903A
Page 2

Page 3

MX3ZA
Motherboard
User's Guide
Document Number : MX3ZA-1-E9903A
Model and revision : For MX3ZA rev 1.xx
Manual version : English, rev A
Release Date : Mar 18, 1999
More help for latest information:
Taiwan http://www.aopen.com.tw
USA http://www.aopenusa.com
Europe http://www.aopen.nl
Page 4

Copyright
Copyright 1999 by this company. All rights reserved. No part of this
publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval
system, or translated into any language or computer language, in any form or
by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, manual or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of this company.
ii
Page 5

Disclaimer
This company makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or
implied, with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any
warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Any software
described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs
prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its
distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing,
repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect
in the software. Further, this company reserves the right to revise this
publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof
without obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
XT/AT is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
AMI is a registered trademark of American Megatrends Inc.
AWARD is a registered trademark of Award Software Inc.
Other brand and product names are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
iii
Page 6
FCC Class B Radio Frequency
Declaration of Conformity
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
Subassembly -CPU Board device, pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: 1. This device may not cause harmful
interference, and 2. This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Equipment Classification : FCC Class B Subassembly - CPU Board
Type of Product : Intel Celeron PPGA Micro ATX Motherboard
Chipset(s) : Intel 82440LX
MX3L
Test To Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
The limits of FCC Part 15 Class B are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there
is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Notice 1:
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Notice 2:
Shielded interface cables, if any, must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
iv
Page 7

Organization
Chapter 1, Overview, covers the introduction and specifications of the system
board and special features.
Chapter 2, Hardware Installation, describes hardware jumpers, connectors and
memory configuration. There are user friendly drawings to locate jumper and
connector.
Chapter 3, AWARD BIOS, explains the system BIOS and tells how to configure
the system by setting the BIOS parameters.
v
Page 8
Conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual:
Text entered by user,
default settings,
recommended selections
<Enter>, <Tab>,<Ctl>, <Alt>,
<Ins>, <Del>, etc
Represent text input by the user,
default settings and recommended
selections
Represent the actual keys that you
have to press on the keyboard.
Note:
Gives bits and pieces of additional
information related to the current topic.
Warning:
Alerts you to any damage that might
result from doing or not doing specific
actions.
Caution:
Suggests precautionary measures to
avoid potential hardware or software
problems.
Important:
Reminds you to take specific action
relevant to the accomplishment of the
procedure at hand.
Tip:
Tells how to accomplish a procedure
with minimum steps through little
shortcuts.
vi
Page 9

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
1.1
SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................4
1.2
APM SUSPEND TO HARD DRIVE ..............................................................5
1.3
ZERO VOLTAGE WAKE ON MODEM ......................................................... 8
1.4
SYSTEM VOLTAGE MONITORING............................................................ 10
1.5
FAN MONITORING .................................................................................. 10
1.6
CPU THERMAL PROTECTION ................................................................. 11
1.7
BATTERY-LESS DESIGN.......................................................................... 11
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION ...........................................1
2.1
JUMPER AND CONNECTOR LOCATIONS .................................................... 2
2.2
JUMPERS ..................................................................................................4
2.2.1 Selecting the CPU Frequency ..........................................................4
2.2.2 Setting the CPU Voltage ..................................................................5
2.2.3 Clearing the CMOS..........................................................................5
2.2.4 Onboard Audio.................................................................................6
2.2.5 KB/MS Wakeup ................................................................................6
2.3
CONNECTORS ...........................................................................................7
2.3.1 Power Cable.....................................................................................7
2.3.3 Fan……… ........................................................................................7
2.3.4 PS/2 Mouse ......................................................................................8
2.3.5 Keyboard.......................................................................................... 8
2.3.6 Serial Devices (COM1/COM2) ........................................................8
2.3.7 Printer…...........................................................................................9
2.3.8 USB Device ......................................................................................9
2.3.9 Floppy Drive ..................................................................................10
2.3.10 IDE Hard Disk and CD ROM .....................................................10
2.3.11 Panel Connector ..........................................................................11
2.3.12 IrDA Connector............................................................................12
2.3.13 Wake On Modem Connector ........................................................13
2.3.14 Wake On LAN Connector.............................................................13
2.3.15 CD Audio Connector....................................................................14
2.3.16 Mono In/Mic Out Connector........................................................14
2.4
CONFIGURING THE SYSTEM MEMORY ....................................................15
2.5
ONBOARD AUDIO................................................................................... 18
vii
Page 10

2.5.1 Setting Up in Windows 95/98.........................................................20
2.5.2 Setting Up in NT4.0........................................................................21
CHAPTER 3 AWARD BIOS ........................................................................1
3.1
ENTERING THE AWARD BIOS SETUP MENU ............................................2
3.2
STANDARD CMOS SETUP ........................................................................3
3.3
BIOS FEATURES SETUP ........................................................................... 6
3.4
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP ..................................................................... 10
3.5
POWER MANAGEM ENT SETUP ................................................................18
3.6
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION SETUP.......................................................... 25
3.7
LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS .........................................................................30
3.8
LOAD TURBO DEFAULTS........................................................................ 30
3.9
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS .................................................................... 31
3.10
PASSWORD SETTING.............................................................................38
3.11
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION ............................................................... 38
3.12
SAVE & EXIT SETUP.............................................................................38
3.13
LOAD EEPROM DEFAULT................................................................... 39
3.14
SAVE EEPROM DEFAULT ...................................................................39
3.15
EXIT WITHOUT SAVING ........................................................................39
3.16
NCR SCSI BIOS AND DRIVERS........................................................... 39
3.17
BIOS FLASH UTILITY...........................................................................40
viii
Page 11

Chapter 1
Overview
MX3ZA is a new generation Socket 370 based system board that utilizes Intel
82440ZX AGPset on Micro ATX PCI/ISA platform. This AGPset is designed
for Celeron PPGA CPU, and supports new architectures such as a high speed
AGP graphic port, SDRAM, Ultra DMA/33, Bus Master IDE and USB port. It
has two Dual in-line Memory Module (DIMM) slots that allow to install
SDRAMs and expand up to a maximum of 256MB. Also, MX3ZA uses a 2M bit
Flash ROM BIOS to reserve for future new functions.
In addition to the above features, MX3ZA also implements many special
features as follows.
Jumper-less Design Celeron VID signal and SMbus clock generator provide
CPU voltage auto-detection and allows the user to set the CPU frequency
through the CMOS setup, therefore no jumpers or switches are used. The
correct CPU information is saved into the EEPROM. With these technologies,
the disadvantages of the Pentium based jumper-less designs are eliminated.
There will be no worry of wrong CPU voltage detection and no need to re-open
the housing in case of CMOS battery loss. The only jumper left is to clear the
CMOS, which is a safety hook if you forget the password.
Battery-less Motherboard This motherboard implements EEPROM and a
special circuit (patent applied) that allows you to save your current CPU and
CMOS Setup configurations without the need of a battery. The RTC (real time
clock) can also keep running as long as the power cord is plugged. If you lose
your CMOS data by accident, you can just reload the CMOS configurations
from EEPROM and the system will recover as usual.
APM Suspend To Hard Drive "Immediately" turns on system and goes back
to the original screen before power down. You can resume your original work
directly from hard disk without go through the Win95 booting process and run
your application again. Suspend to Hard Drive saves your current work
(system status, memory image) into hard disk. Note that you have to use
VESA compatible PCI VGA, Sound Blaster compatible sound card with APM
driver, for Suspend to Hard Drive to work properly.
1-1
Page 12

Overview
ACPI Suspend to Hard Drive The conventional "Suspend to Hard Drive"
function is a private design of AOpen motherboards, the requirement to run it
is a BIOS revision and correct chipset that supports this function. However,
nowadays "Suspend to Hard Drive" has been become widely known as the "S4
- Hibernation" state defined in the ACPI specification; in this case not only the
BIOS itself but also the operation system (i.e. Windows98) and even the
display card are involved in the execution of this function. With regard to how
to implement this function, please refer to section “1.4 ACPI Suspend to Hard
Drive”.
Zero Voltage Wake on Modem In conjunction with ATX soft power On/Off, it
is possible to have the system totally power off and wakeup to automatically
answer a phone call to serve as an answering machine or to send/receive a
fax. The most important break through is not only an externally cased modem
but also an internal modem card can be used to support Wake On Modem.
This motherboard and MP56 internal modem card implement a special circuit
(patent applied) to make sure the modem card works properly without any
power.
Wake On LAN This feature is very similar as the Wake On Modem feature, but
it is through a local area network. To use the Wake On LAN function, you must
have a network card that supports this feature and have installed proper
network management software.
Wake On RTC Timer The Wake Up Timer is more like an alarm, which
wakes up and powers on your system at a pre-defined time for a specific
application. It can be set to wake up everyday or on specific date within a
month. The date/time is accurate to within a second.
Wake On Keyboard This function allows you to power on your system by
clicking the hot key that you specified. Besides, you also may disable the
function of power button and let the system can only be powered on through
the preset keys (like a password).
Wake On Mouse This function allows you power on the system by clicking a
specified mouse button twice successively.
AC Power Auto Recovery A traditional ATX system should remain at power
off stage when AC power resumes from power failure. This design is
inconvenient for a network server or workstation, without an UPS, that needs
to keep power-on. This motherboard implements an AC Power Auto Recovery
function to solve this problem. In BIOS Setup settings if this item is set to
“Enabled” the system will automatically power-on after AC power resumes.
High Efficiency Synchronous Switching Regulator Most of the current
switching designs are Asynchronous mode, which from a technical point of
view, still consumes very high power and generates heat. This motherboard
implements a high efficient synchronous switching design so that the
temperature of MOS FET is far less than the Schottky diode of the
asynchronous design.
1-2
Page 13
Overview
Over Current Protection The Over Current Protection was very popular
implemented on the Baby AT or ATX 3.3V/5V/12V switching power supply.
However, the new generation Celeron PPGA CPU uses different voltage that
have regulator to transfer 5V to CPU voltage (for example, 2.0V), and make 5V
over current protection useless. MX3ZA with switching regulator onboard
support CPU over current protection, in conjunction with 3.3V/5V/12V power
supply provide the full line over current protection.
CPU and Housing Fan Monitoring This motherboard has one more "fan
monitoring" function to prevent system overheat. There are two fan connectors.
One is for the CPU and the other can be an extra housing fan. The system will
report an alarm fan malfunction through utility software such as Hardware
Monitoring Utility.
CPU Thermal Protection This motherboard has a special thermal detection
circuit to provide warning through application software when the temperature is
higher than a predefined value.
System Voltage Monitoring Further more, this motherboard implements a
voltage monitoring system. As you turn on your system, this smart design will
continue to monitor your system’s working voltage. If any of the system’s
voltage is over the component's standard an alarm will be sounded through
utility software such as a Hardware Monitoring Utility for a warning to user.
Resetable Fuse This motherboard implements resetable fuses to prevent any
accidental short circuit caused by keyboard or USB devices hot plug.
FCC DoC certificate MX3ZA has passed FCC DoC test. The radiation is very
low, you can use any kind of housing.
Powerful Utility Software AOpen Bonus Pack bundled CD contains many
useful utilities, such as Norton Antivirus, AOchip, Hardware Monitoring Utility,
and Suspend to Hard Drive Utility.
註解: Is this a specific
application that comes on
the driver disc? If so, then it
should be specified with the
word ‘the’ not ‘a’
Note: This motherboard is battery-less, that means the RTC
(real time clock) can keep running without battery as long as the
power cord is plugged. But in case of power failure or the power
cord unplugged, you need to reset date and time from "Standard
CMOS Setup" section of BIOS Setup. For more information,
please see "Chapter 3 BIOS Setup".
1-3
Page 14
Overview
1.1 Specifications
Form Factor
Board Size
CPU
System Memory
Chipset
Onboard Audio
Onboard AGP
Expansion Slots
Serial Port
Parallel Port
Floppy Interface
IDE Interface
USB Interface
PS/2 Mouse
Keyboard
RTC and Battery
BIOS
Micro ATX
244 mm x 220 mm
Celeron PPGA
168-pin DIMM x2, maximum 256MB SDRAM.
Intel 82440ZX AGPset
ESS Solo-1
ATI 3D Rage Pro Turbo AGP
ISA x1 and PCI x3
Two serial ports UART 16C550 compatible, and the
3rd UART for IR function.
One parallel port supports standard parallel port (SPP),
enhanced parallel port (EPP) or extended capabilities
port (ECP).
Floppy interface supports 3.5 inches drives with
720KB, 1.44MB or 2.88MB format or 5.25 inches
drives with 360KB, 1.2MB format
Dual-channel IDE interface support maximum 4 IDE
hard disks or CDROM, mode 4 , bus master hard disk
drives and Ultra DMA/33 mode hard drives are also
supported.
Two USB ports supported by USB bracket, the BIOS
also supports USB driver to simulate legacy keyboard.
Mini-Din PS/2 mouse connector onboard.
Mini-Din PS/2 keyboard connector onboard.
RTC within Intel PIIX4E chipset. Lithium (CR-2032)
battery is an option, no battery is needed if power cord
is plugged.
AWARD Plug-and-Play, 2M bit Flash ROM BIOS.
1-4
Page 15

Overview
1.2 APM Suspend to Hard Drive
Suspend to Hard Drive saves your current work (system status, memory and
screen image) into hard disk, and then the system can be totally power off.
Next time, when power is on, you can resume your original work directly from
hard disk within few seconds without go through the Win95 booting process
and run your application again. If your memory is 16MB, normally, you need to
reserve at least 16MB HDD space to save your memory image. Note that you
have to use VESA compatible PCI VGA (AOpen PV70/PT70), Sound Blaster
compatible sound card and sound driver that supports APM (AOpen
AW32/AW35) for Suspend to Hard Drive to work properly. Of course, we
recommend choosing AOpen products for best compatibility.
To use Suspend to Hard Drive:
1. Go into BIOS setup, Power Management Æ Suspend Mode Option, select
"Suspend to Disk".
2. Go into BIOS setup, PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PnP OS Installed, select
"No". This can give BIOS the capability to allocate system resources for
Suspend to Hard Drive.
3. Boot up your system into DOS command prompt. If you are Win'95 user,
Please restart your Windows 95 under "Command Prompt" by pressing
"F8" while system shows "Windows 95 Starting ...". Choose "Safe Mode
Command Prompt Only" from selection so that system will start in DOS
command prompt.
4. Copy AOZVHDD.EXE to the root directory of your C: drive.
5. Option 1: Use /file switch (applied to FAT16 file system):
Please use following command to create a hidden file in the root directory
of your hard disk for Suspend to Hard Drive to save the system status and
memory image.
C:>AOZVHDD /c /file
Please make sure that you have enough continuous HDD space for
creating this hidden file. For example, if you have 32MB of system memory
and 4MB of VGA memory, you need at least 36MB (32MB + 4MB) of
continuous HDD space. If AOZVHDD failed to allocate the HDD space, you
may run "DEFRAG" Utility or "Disk Defragmenter" which come with MSDOS or Win'95 to free HDD space.
1-5
Page 16
Overview
Option2: Use /partition switch (applied to FAT16/FAT32 file system):
To create a separate partition for Suspend to Hard Drive, please make sure
you have reserved a free partition. We suggest you reserve the free
partition which space is appropriate for your future memory expansion. For
example, if you have 32MB of system memory and 4MB of VGA memory
currently, but you plan to upgrade system memory to 64MB in the near
future, then you may reserve a 68MB (64MB+4MB) space by using a disk
utility (such as fdisk). Next, use following command to create a suspend
partition:
C:>AOZVHDD /c /partition
If there is no extra free partition and you don't want your data lost, please
do not use this partition method.
6. After creating above partition or hidden file, please reboot your system.
7. Push suspend switch (momentary mode) or use Win95 Suspend icon to
force system goes into Suspend to Hard Drive mode and then turn system
power off by power switch of your power supply.
8. Next time when you turn on your system, it will resume to your original work
automatically.
Warning: Note that Intel Bus Master and Ultra
DMA/33 IDE driver are not fully compatible with
Suspend to Hard Drive function, installing these
drivers may cause the system unstable. Under this
situation, please uninstall the drivers.
1-6
Warning: This function does not support SCSI hard
disks.
Page 17

Tip: The following VGA cards have been tested &
recognized as VESA compatible VGA device.
AOpen PV90 (Trident 9680)
AOpen PT60 (S3 Virge/BIOS R1.00-01)
AOpen PV60 (S3 Tiro64V+)
AOpen PT70 (S3 Virge/DX)
ProLink Trident GD-5440
ProLink Cirrus GD-5430
ProLink Cirrus GD-5446
ATI Mach 64 GX
ATI 3D RAGE II
Diamond Stealth64D (S3 868)
Diamond Stealth64V (S3 968)
KuoWei ET-6000
Tip: The following sound cards have been tested OK
for Suspend to Hard Drive.
AOpen AW32
AOpen AW35
AOpen MP32
Creative SB 16 Value PnP
Creative SB AWE32 PnP
ESS 1868 PnP
If your sound card can not work after resume from
Suspend to Hard Drive, check your sound card
vendor see if there is driver to support APM, and
install it again.
Overview
Note: The USB function has not been tested for
Suspend to Hard Drive. If you find any unstable
problem, please go into BIOS, Integrated Peripherals
Æ
USB Legacy Support. Disable the USB Legacy
function.
1-7
Page 18

Overview
1.3 ACPI Suspend to Hard Drive
For a detailed installation procedure please refer to the following procedure to
enable ACPI Suspend to Hard Drive on the AOpen MX3ZA motherboard. First
please check if your system meets the following requirements, then follow the
procedure step by step.
I. Fresh installation of Windows 98 on a new system
1. Execute "Setup.exe /p j" to install Windows 98
2. After Windows 98's installation is complete, go to the Control Panel -->
Power Management.
a. Set All Power Schemes to "Never".
b. Click on "Hibernate" and select "Enable Hibernate Support".
c. Click on the Advance tab and check the "Hibernate" box.
3. Clean boot into DOS and run "AOZVHDD /C /File" to create the suspend
hidden file.
4. Reboot system.
II. Changing from APM to ACPI (Windows 98 only)
1. Run "Regedit.exe"
a. Go through the following path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
SOFTWARE
MICROSOFT
WINDOWS
CURRENT VERSION
DETECT
b. Select "ADD Binary" and name it as "ACPIOPTION".
c. Right click and select Modify, add "01" after "0000" to make it "0000 01".
d. Save changes.
2. Select "Add New Hardware" under Control Panel. Allow Windows 98 to
detect new hardware. (It will find "ACPI BIOS" and remove "Plug and Play
BIOS")
1-8
Page 19

Overview
3. Reboot system.
4. Clean boot into DOS and run "AOZVHDD.EXE /C /File"
III. Changing from ACPI to APM
1. Run "Regedit.exe"
a. Go through the following path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
SOFTWARE
MICROSOFT
WINDOWS
CURRENT VERSION
DETECT
ACPI OPTION
b. Right click and select "Modify, change "01" to "00" to make it "0000 02".
Note: "02" means Windows 98 is ACPI
acknowledged but the ACPI function is disabled.
c. Save changes.
2. Select "Add New Hardware" under Control Panel. Allow Windows 98 to
detect new hardware. (It will find "Plug and Play BIOS" and remove "ACPI
BIOS")
3. Reboot system.
4. Run "Add New Hardware" again and it will find "Advanced Power
Management Resource".
5. Click "OK".
Note: currently we found only ATI 3D Rage Pro AGP
card would support ACPI suspend to disk; if you need
this function implemented be sure to use this card.
1-9
Page 20
Overview
p
(
)
p
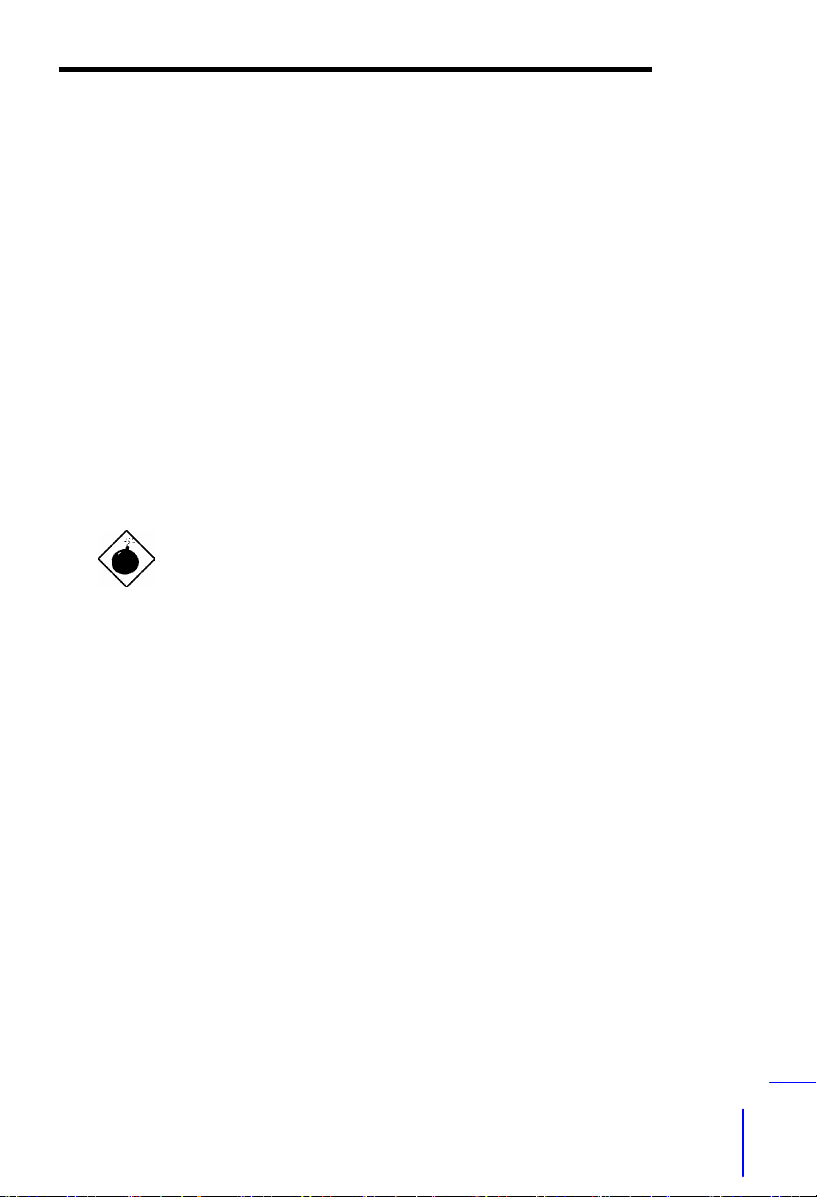
1.4 Zero Voltage Modem Wake Up
The Wake On Modem discussed here is to wakeup from true power off
(defined as the fan of power supply being off), This motherboard still supports
traditional green PC suspend mode but is not discussed here.
With the help of the ATX soft power On/Off, it is possible to have a system
totally power off (The traditional suspend mode of power management function
does not really turn off the system power supply), and wakeup to automatically
answer a phone call as an answering machine or to send/receive a fax. You
may identify whether or not your system is in true power off mode by checking
to see if the fan of your power supply is off. Both an external box modem and
an internal modem card can be used to support Modem Wake Up, but if you
use an external modem, you have to leave your box modem on. The AOpen
MX3ZA and internal modem card implement a special circuit (patent applied)
and make sure the modem card works properly without any power. We
recommend choosing the AOpen modem card (MP56) for Wake On Modem
applications.
TEL Line
COM port
External Box Modem
External Modem WakeU
TEL Line
Internal Modem Card WakeU
1-10
such as MP56
Page 21

Overview
For Internal Modem Card (AOpen MP56):
1. Go into the BIOS Setup, select Power Management and Æ 0V Wake On
Modem. Select “Enabled.”
2. Install your application, put into Windows 95 StartUp.
3. Turn the system power off by soft power switch.
4. Connect the 4-pin Wake On Modem cable from MP56 RING connector to
the MX3ZA WOM connector.
5. Connect your telephone line to the MP56 modem. You are now ready to
use Wake On Modem.
For External Box Modem:
1. Go into the BIOS Setup, select Power Management and Æ 0V Wake On
Modem. Select “Enabled.”
2. Setup your application, put into Windows 95 StartUp.
3. Turn your system power off by soft power switch.
4. Connect your RS232 modem cable from your external box modem to
COM1 or COM2.
5. Connect telephone line to external box modem. Turn on modem power
(you must keep modem power always on). You are now ready to use Wake
On Modem.
Tip: External modem wake up signal is detected through
COM1 or COM2. An internal modem card wake up signal
is detected through a cable from the connector RING (on
the modem card) to WOM (on the mainboard).
Note: If you use an external modem, the power of the
external modem must be kept on to receive a signal from
the telephone line. An internal modem card has no such
limitation.
1-11
Page 22
Overview
1.5 System Voltage Monitoring
This motherboard implements a voltage monitoring system. As you turn on
your system, this smart design will continue to monitor your system’s working
voltage. If any of the system’s voltage is over the component's standard there
will be an alarm through application software such as the Hardware Monitoring
Utility to warn the user. The system voltage monitoring function monitors CPU
core voltage. It is automatically implemented by the BIOS and Hardware
Monitoring Utility (the program’s file name is like aohwxxx.exe, where xxx
means the version number), no hardware installation is needed.
1.6 Fan Monitoring
There are three fan connectors, two is for CPU, the other can be connected to
a housing fan. The fan monitoring function is implemented by connecting fan
to 3-pin fan connector CPUFAN1 or FAN and installing Hardware Monitoring
Utility.
1-12
Note: You need a 3-pin fan that supports SENSE
signal for fan monitoring function to work
properly.
Page 23

Overview
1.7 CPU Thermal Protection
This motherboard implements special thermal protection circuits. When
temperature is higher than a predefined value, there will be warning through
application software such as the Hardware Monitor utility to notify the user. It is
automatically implemented by the BIOS and the Hardware Monitoring Utility,
no hardware installation is needed.
1.8 Battery-less Design
To preserve the earth, this motherboard implements the battery-less
motherboard design. There is no need to have a battery for RTC (real time
clock) and CMOS Setup as long as the ATX power cable is plugged in. In case
the AC power is shutdown or the power cord is removed by accident, the
CMOS Setup and system configuration can be restored from EEPROM, only
the system clock needs to be re-set to current date/time.
For the convenience of the end user, the MX3ZA still ships with one Lithium
(CR-2032) battery. If you prefer to use a battery, you can still insert it into
battery socket. The RTC will still keep running even when the power cord is
removed.
1-13
Page 24

Overview
1.9 Wake On Keyboard/Mouse
This function allows you to power on your system by clicking a hot key or a
mouse button that you specified. Besides, you can also disable the function of
the power button and only the preset keys (like a password) can boot your
system.
Please follow the procedure below to enable Wake on Keyboard/Mouse
function.
1. Set JP28 at pin 2-3 is to enable this function
2. Go to BIOS Setup Æ Integrated Peripherals Æ Power On Function. You
can select different wake up mode. For detailed information, please refer to
“Chapter 3 AWAED BIOS”
3. Save CMOS setup and Exit.
4. Successfully boot your system to Windows or DOS.
5. Now you can proceed the normal shutdown and next time you can use this
function to boot your system.
1-14
Page 25

Overview
Caution: To implement this function, the 5V Stand
By current of ATX power supply must be greater
than 800mA.
Caution: Wake On Mouse function applies to PS/2
mouse only
Caution: The mouse can’t be moved between
double clicking.
Caution: If you set a Password but forget it, please
clear CMOS.
Caution: If you want to use Wake On Mouse
function in DOS, it is necessary to install the DOS
driver of the mouse.
1-15
Page 26

Chapter 2
Hardware Installation
This chapter gives you a step-by-step procedure on how to install your system.
Follow each section accordingly.
Caution: Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can
damage your processor, disk drives,
expansion boards, and other components.
Always observe the following precautions
before you install a system component.
1. Do not remove a component from its
protective packaging until you are ready
to install it.
2. Wear a wrist ground strap and attach it to
a metal part of the system unit before
handling a component. If a wrist strap is
not available, maintain contact with the
system unit throughout any procedure
requiring ESD protection.
2-1
Page 27
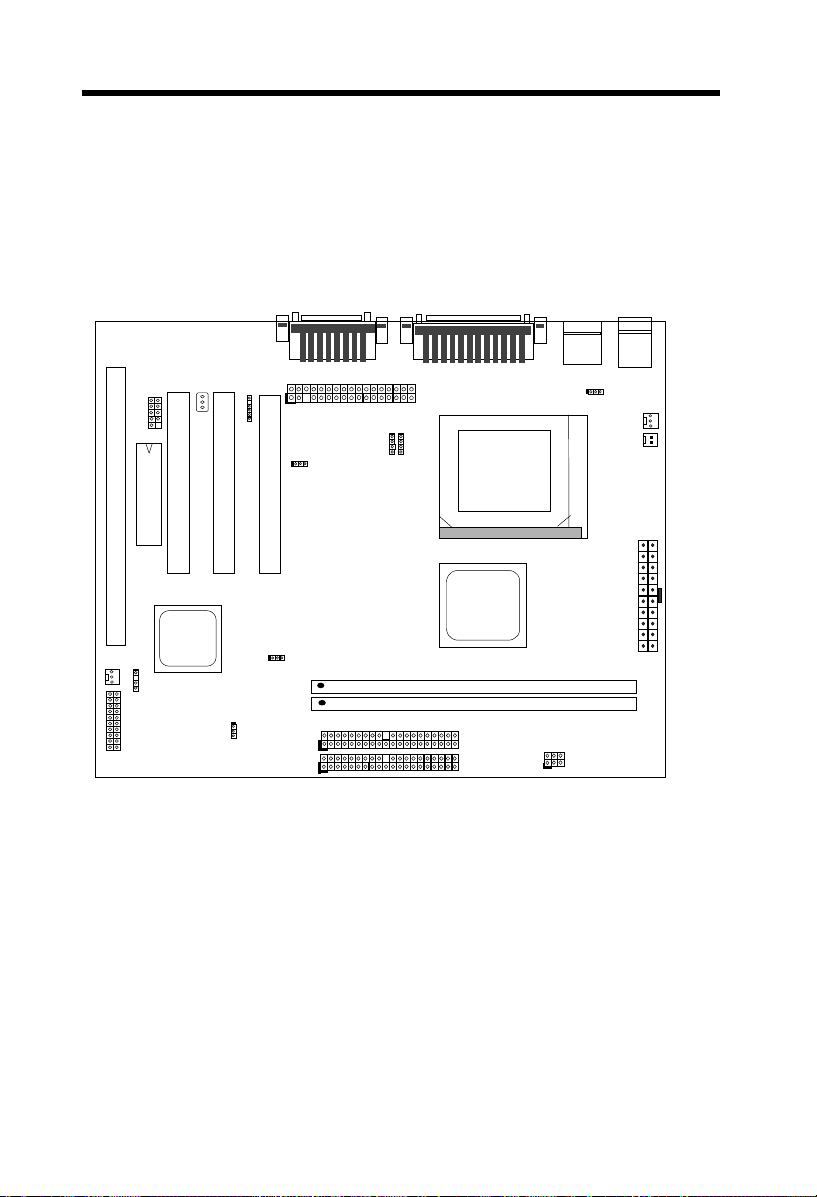
Hardware Installation
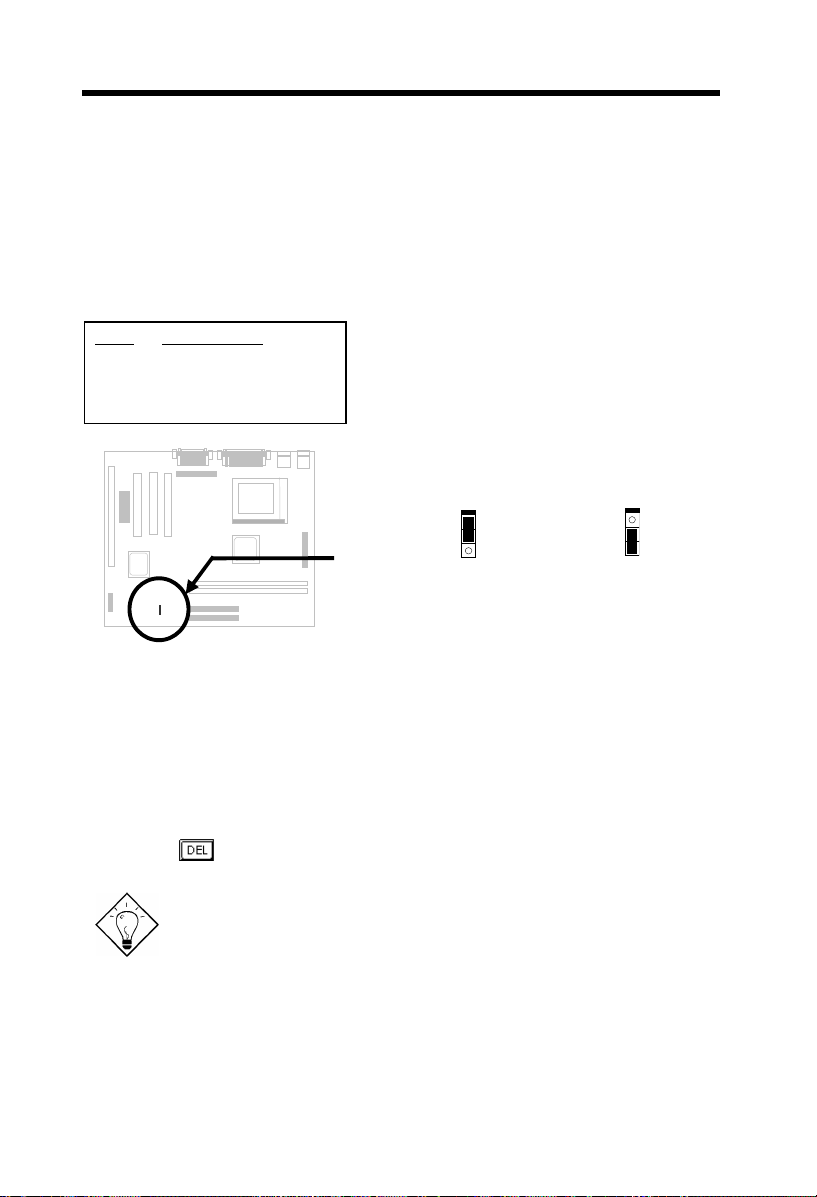
2.1 Jumper and Connector Locations
The following figure shows the locations of the jumpers and connectors on the
system board:
I
S
A
FAN
PANEL
COM2
BIOS
WOM
VGA
IrDA
WOL
P
C
2
I
JP14
P
C
I
1
JP11
JP12
IDE2
IDE1
FDC
MODEM-CN
CD-IN
P
C
I
3
PRINTER
COM1
JP23
USB
DIMM1
DIMM2
JP28
CPU FAN1
KB2
PS/2 MS
CPUFAN2
2-2
Page 28

Hardware Installation
Jumpers:
JP11: Enable/Disable Onboard AGP
JP12: Enable/Disable Onboard Audio
JP14: Clear CMOS
JP23: AGP Ratio
JP28: Enable/Disable KB/MS Wake Up
Connectors:
PS2: PS/2 mouse connector
KB: PS/2 keyboard connector
COM1: COM1 connector
COM2: COM2 connector
PRINTER: Printer connector
PWR2: ATX power connector
USB: USB connector
FDC: Floppy drive connector
IDE1: IDE1 primary channel
IDE2: IDE2 secondary channel
CPUFAN1: CPU fan connector
CDUFAN2: CPU fan connector
FAN: Housing Fan Connector
IrDA: IrDA (Infrared) connector
PANEL: Front panel (Multifunction) connector
CD-IN: CD-audio connector
MODEM-CN: Mono in (Pin 1-2) and Mic out (Pin 3-4)
WOM: Wake On Modem connector
WOL: Wake On LAN connector
2-3
Page 29
Hardware Installation
2.2 Jumpers
With the help of VID signal and SMbus, this motherboard is jumper-less design.
2.2.1 Selecting the CPU Frequency
Celeron PPGA VID signal and SMbus clock generator provide CPU voltage
auto-detection and allow user to set CPU frequency through CMOS setup, no
jumper or switch is needed. The correct CPU information is saved into
EEPROM, with these technologies, the disadvantages of Pentium base
jumper-less design are eliminated. There will be no worry of wrong CPU
voltage detection and no need to re-open the housing if CMOS battery loss.
The CPU frequency selection is set by going into:
BOIS Setup Æ Chipset Features Setup Æ CPU Clock Frequency
(The possible setting is 66.8, 75, 83.3, 100, 103, 105, 110, 112, 120, 124, 133,
140, 150 MHz)
BOIS Setup Æ Chipset Features Setup Æ CPU Clock Ratio
(The possible setting is 1.5x, 2x, 2.5x, 3x, 3.5x, 4x, 4.5x, 5x, 5.5x, 6x, 6.5x, 7x,
7.5x, and 8x)
Core frequency = Ratio * External bus clock
INTEL Celeron PPGA CPU Core Frequency Ratio External Bus Clock
Celeron PPGA 300A 300MHz= 4.5x 66MHz
Celeron PPGA 333 333MHz= 5x 66MHz
Celeron PPGA 350 350MHz= 3.5x 100MHz
Celeron PPGA 366 366MHz= 5.5x 66MHz
Celeron PPGA 400 400MHz= 6x 66MHz
Celeron PPGA 433 433MHz= 6.5x 66MHz
Warning: INTEL 440ZX chipset supports maximum 100MHz FSB
clock, the higher clock settings are for internal test only. These
settings exceed the specification of ZX chipset, which may
cause serious system damage.
2-4
Page 30
Hardware Installation
2.2.2 Setting the CPU Voltage
This motherboard supports Celeron PPGA VID function, the CPU core voltage
is automatically detected, the range is from 1.3V to 2.05V.
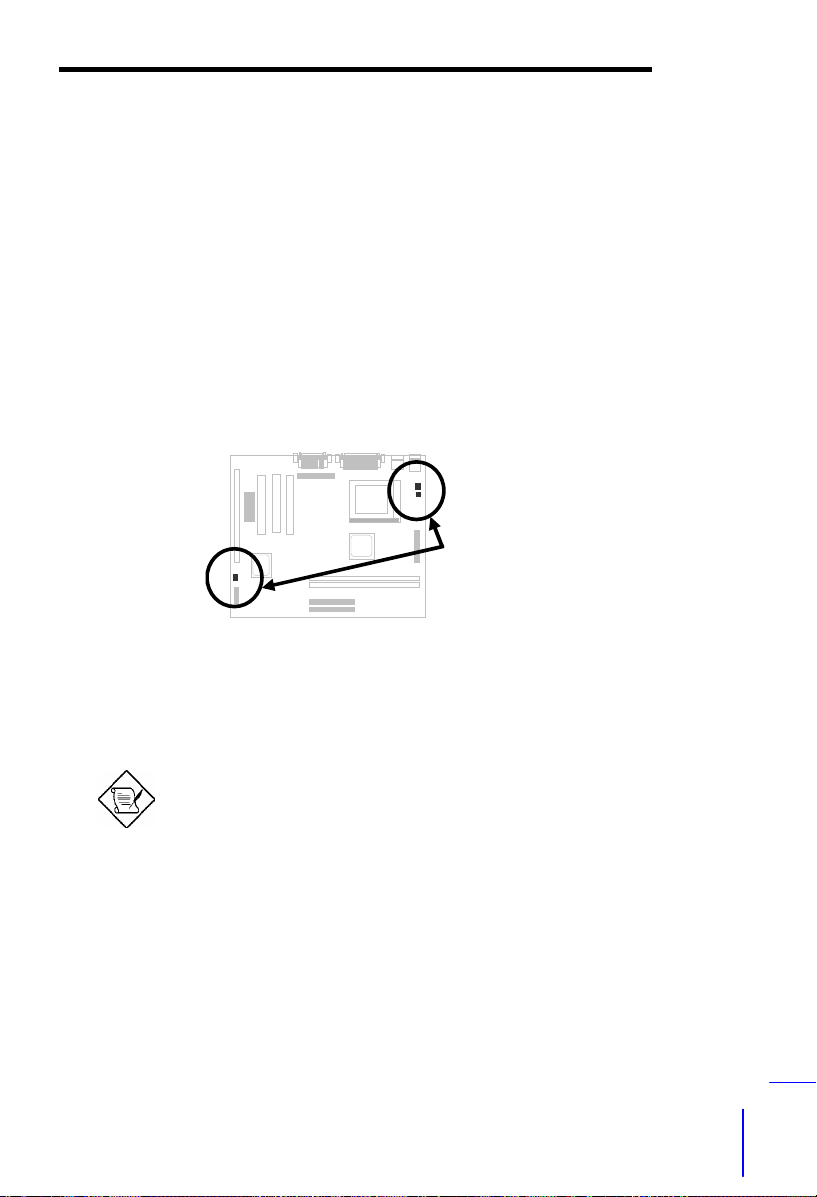
2.2.3 Clearing the CMOS
JP14
1-2
2-3
Clear CMOS
Normal operation
(default)
Clear CMOS
You need to clear the CMOS if you forget your
system password. To clear the CMOS, follow
the procedures listed below:
JP14
1
2
3
Normal Operation
(default)
The procedure to clear CMOS:
1. Turn off the system and unplug the AC power.
2. Remove ATX power cable from connector PWR2.
3. Locate JP14 and short pins 2-3 for a few seconds.
4. Return JP14 to its normal setting by shorting pins 1-2.
5. Connect ATX power cable back to connector PWR2.
6. Turn on the system power.
7. Press
during bootup to enter the BIOS Setup Utility and specify a
new password, if needed.
Tip: If your system hangs or fails to boot because of overclocking, please clear CMOS and the system will go back to
default setting (300MHz).
Tip: If your system hangs or fails to boot because of overclocking, simply use <Home> key to restore to the default
setting (300MHz). By this smart design, it would be more
convenient to clear CPU frequency setting. For using this
function, you just need to press <Home> key first and then
JP14
1
2
3
Clear CMOS
2-5
Page 31

Hardware Installation
press Power button at the same time. Note that do not release
<Home> key until POST screen appearing.
2.2.4 Onboard AGP
JP11
1-2
2-3
Onboard AGP
Enabled (default)
Disabled
2.2.5 Onboard Audio
JP12
1-2
2-3
Onboard Audio
Enabled (default)
Disabled
If you want to install another VGA card, you
have to disable the onboard AGP by setting
this jumper to Disabled.
JP11
1 2 3
Enabled (default)
If you want to install another sound card,
you have to disable the onboard audio by
setting this jumper to Disabled.
JP12
Enabled (default)
1 2 3
JP11
1 2 3
Disabled
JP12
1 2 3
Disabled
2-6
Page 32

2.2.6 KB/MS Wakeup
Hardware Installation
JP28
1-2
2-3
KB/MS Wakeup
Disabled
Enabled
This jumper is used to enable or disable
Keyboard/Mouse Power ON function. If you
select Enabled, you may decide the wakeup
mode from BIOS Setup. To implement this
function, the 5V Stand By current must be
greater than 800mA.
Note that only PS/2 mouse supports Wake On
Mouse function.
JP28
1
2
3
Disabled
JP28
1
2
3
Enabled
2-7
Page 33

Hardware Installation
2.3 Connectors
2.3.1 Power Cable
The ATX power supply uses 20-pin connector shown below. Make sure you
plug in the right direction.
Caution: Make sure that the power supply is off
before connecting or disconnecting the power cable.
+5V
3.3V
5V SB
3.3V
PWR2
+5V
2.3.2 Fan
Plug in the fan cable to the fan connectors onboard. The fan connectors are
marked CPUFAN1, CPUFAN2 and FAN on the system board. You can plug
the CPU fan cable to both the 3-pin fan connector CPUFAN1 and the 2-pin fan
connector CPUFAN2. FAN can be reserved for the housing fan. Note that only
CPUFAN1 and FAN support the fan monitoring function, because a 3-pin fan
has an extra pin called SENSE, which periodically sends fan signal out.
SENSE
+12V
GND
CPUFAN1 & FAN
GND
+12V
CPUFAN2
2-8
Page 34

Hardware Installation
2.3.3 PS/2 Mouse
The onboard PS/2 mouse connector is a 6-pin Mini-Din connector marked
PS2. The view angle of drawing shown here is from back panel of the housing.
PCB
PS/2 Mouse
2.3.4 Keyboard
The onboard PS/2 keyboard connector is a 6-pin Mini-Din connector marked
KB2. The view angle of drawing shown here is from back panel of the housing.
PCB
PS/2 KB
2-9
Page 35

Hardware Installation
2.3.5 Serial Devices (COM1/COM2)
The onboard serial connectors are 9-pin D-type connectors on the back panel
of mainboard. The serial port 1 connector is marked as COM1 and the serial
port 2 connector is marked as COM2.
PCB
COM1
2.3.6 Serial Devices (COM2)
Plug in the 10-pin flat cable to the COM2 connectors.
1 2
9 10
COM2
2-10
Page 36

Hardware Installation
2.3.7 Printer
The onboard printer connector is a 25-pin D-type connector marked
PRINTER. The view angle of drawing shown here is from back panel of the
housing.
PRINTER
PCB
2.3.8 USB Device
You can attach USB devices to the USB connector. The motherboard
contains two USB connectors, which are marked as USB.
PCB
USB
2-11
Page 37

Hardware Installation
2.3.9 Floppy Drive
Connect the 34-pin floppy drive cable to the floppy drive connector marked as
FDC on the system board.
342
1
33
FDC
2.3.10 IDE Hard Disk and CD ROM
This mainboard supports two 40 pin IDE connectors marked as IDE1 and
IDE2. IDE1 is also known as primary channel and IDE2 as secondary
channel, each channel supports two IDE devices that make total of four
devices.
In order to work together, the two devices on each channel must be set
differently to master and slave mode, either one can be hard disk or CDROM.
The setting as master or slave mode depends on the jumper on your IDE
device, please refer to your hard disk and CDROM manual accordingly.
Connect your first IDE hard disk to master mode of the primary channel. If you
have second IDE device to install in your system, connect it as slave mode on
the same channel, and the third and fourth device can be connected on
secondary channel as master and slave mode respectively.
402
1
IDE1
1
IDE2
39
402
39
2-12
Page 38

Hardware Installation
(
)
(
)
Caution: The specification of IDE cable is
maximum 46cm (18 inches), make sure your
cable does not excess this length.
Caution: For better signal quality, it is
recommended to set far end side device to
master mode and follow the suggested
sequence to install your new device. Please
refer to the following figure.
IDE1 (Primary Channel)
IDE2 (Second Channel)
Slave
(4th)
2.3.11 Panel Connector
The Panel (multifunction) connector is
a 20-pin connector marked as PANEL
on the board. Attach the power LED,
keylock, speaker, SPWR, IDE LED
and reset switch to the corresponding
pins as shown in the figure. If your
ATX housing supports ACPI
specification, the ACPI & Power LED
will keep flashing if you have enabled
“suspend mode” item in BIOS Setup.
Slave
2nd
1
11
GND
KEYLOCK
+5V
IDE LED
IDE LED
+5V
+5V
GND
NC
SPEAKER
10 20
PANEL
Master
1st
Master
(3rd)
SPWR
GND
ACPI & POWER LED
GND
+5V
NC
NC
GND
RESET
GND
2-13
Page 39

Hardware Installation
Keylock
IDE LED
1
11
+
+
+
SPWR
+
ACPI &
Power LED
+
+
Speaker
10 20
Reset
PANEL
2.3.12 IrDA Connector
The IrDA connector can be configured to support wireless infrared module,
with this module and application software such as Laplink or Win95 Direct
Cable Connection, user can transfer files to or from laptops, notebooks,
PDA and printers. This connector supports HPSIR (115.2Kbps, 2 meters),
ASK-IR (56Kbps) and Fast IR (4Mbps, 2 meters).
Install infrared module onto IrDA
connector and enable infrared function
from BIOS setup, make sure to have
correct orientation when you plug onto
IrDA connector.
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
5
6
IrDA
3
4
Description
+5V
NC
IRRX
GND
IRTX
NC
2-14
Page 40

Hardware Installation
2.3.13 Wake On Modem Connector
This mainboard implements special circuit to support
Wake On Modem, both Internal Modem Card (AOpen
MP56) and external box Modem are supported. Since
Internal Modem card consumes no power when system
power is off, it is recommended to use Internal Modem.
To use AOpen MP56, connect 4-pin cable from RING
connector of MP56 to WOM connector on the
mainboard.
1
2
3
4
2.3.14 Wake On LAN Connector
This mainboard implements a WOL connector. To use
Wake On LAN function, you need a network card that
supports this feature. In addition, you also need to
install a network management software.
WOM
Pin
1
2
3
4
Pin
1
2
3
Description
+5V SB
NC
RING
GND
Description
+5V SB
GND
LID
1
2
3
WOL
2-15
Page 41

Hardware Installation
2.3.15 CD Audio Connector
This connector is used to connect CD audio cable.
1
2
3
4
CD-IN
2.3.16 Mono In/Mic Out Connector
This connector is used to connect Mono In/Mic Out
connector of an internal modem card. The pin 1-2 is
Mono In, and the pin 3-4 is Mic Out. Please note
that there is no standard for this kind of connector
yet, only some internal modem cards implement
this connector.
Please see the pin definitions to connect the cable.
1
2
3
4
MODEM-CN
Pin
Description
1
L
2
GND
3
GND
4
R
Pin
Description
1
Mono In
2
GND
3
GND
4
Mic Out
2-16
Page 42

Hardware Installation
2.4 Configuring the System Memory
The DIMM types supported are SDRAM
(Synchronous DRAM) only. This
motherboard has two 168 pin DIMM
sockets (Dual-in-line Memory Module)
that allow you to install system memory
up to 256MB.
Pin1
DIMM modules can be identified by the following factors:
I. Size: single side, 1Mx64 (8MB), 2Mx64 (16MB), 4Mx64 (32MB), 8Mx64
(64MB), 16Mx64 (128MB), and double side, 1Mx64x2 (16MB), 2Mx64x2
(32MB), 4Mx64x2 (64MB), 8Mx64x2 (128MB).
Tip: Here is a trick to check if your DIMM is
single-side or double-side -- if there are traces
connected to golden finger pin 114 and pin 129 of
the DIMM, the DIMM is probably double-side;
otherwise, it is single-side. The following figure is
for your reference.
168
Pin 129
II. Speed:
normally marked as -12, which means the clock cycle time is 12ns and
maximum clock of this SDRAM is 83MHz. Sometimes you can also find the
SDRAM marked as -67, which means maximum clock is 67MHz.
Pin 114
2-17
Page 43

Hardware Installation
III. Buffered and non-buffered: This motherboard supports non-buffered
DIMMs. You can identify non-buffered DIMMs and buffered DIMMs
according to the position of the notch, following figure is for your reference:
buffered
non-buffere d
Reserved
Because the positions are different, only non-buffered DIMMs can be
inserted into the DIMM sockets on this motherboard. Although most of
DIMMs on current market are non-buffered, we still suggest you to ask your
dealer for the correct type.
IV. 2-clock and 4-clock signals: Although both of 2-clock and 4-clock signals
are supported by this motherboard, we strongly recommend choosing 4clock SDRAM in consideration of reliability.
Tip: To identify 2-clock and 4-clock SDRAM, you
may check if there are traces connected to
golden finger pin 79 and pin 163 of the SDRAM. If
there are traces, the SDRAM is probably 4-clock;
Otherwise, it is 2-clock.
V. Parity: This motherboard supports standard 64 bit wide (without parity)
DIMM modules.
VI. SPD support: BIOS will automatically detect DIMM with SPD, and set to
appropriate timing. DIMMs without SPD are still able to work fine on this
board, but BIOS POST screen will give you a warning message that you
use a DIMM without SPD.
There is no jumper setting required for the memory size or type. It is
automatically detected by the system BIOS, and the total memory size is to
add them together. The maximum is 256MB.
Total Memory Size = Size of DIMM1 + Size of DIMM2
2-18
Page 44

Hardware Installation
The following table lists the recommended DRAM combinations of DIMM:
DIMM
Data chip
1M by 16 1Mx64 x1 4 8MB Yes
1M by 16 1Mx64 x2 8 16MB Yes
2M by 8 2Mx64 x1 8 16MB Yes
2M by 8 2Mx64 x2 16 32MB Yes
4M by 16 4Mx64 x1 4 32MB Yes
4M by 16 4Mx64 x2 8 64MB Yes
8M by 8 8Mx64 x1 8 64MB Yes
8M by 8 8Mx64 x2 16 128MB Yes
Bit size
per side
Single/
Double side
Chip
count
DIMM size Recommended
DIMM
Data chip
2M by 32 2Mx64 x1 2 16MB Yes, but not tested.
2M by 32 2Mx64 x2 4 32MB Yes, but not tested.
Bit size
per side
Single/
Double side
Chip
count
DIMM size Recommended
The following table lists the possible DRAM combinations that is NOT
recommended:
DIMM
Data chip
4M by 4 4Mx64 x1 16 32MB No
4M by 4 4Mx64 x2 32 64MB No
16M by 4 16Mx64 x1 16 128MB No
Bit size
per side
Single/
Double side
Chip
count
DIMM
size
Recommended
Tip: The parity mode uses 1 parity bit for each byte, normally
it is even parity mode, that is, each time the memory data is
updated, parity bit will be adjusted to have even count "1" for
each byte. When next time, if memory is read with odd
number of "1", the parity error is occurred and this is called
single bit error detection.
2-19
Page 45

Chapter 3
Software Installation
This chapter gives you a step-by-step procedure on how to install the driver
and utility of this motherboard. Because chipset and technology improvement
is faster than operating system, sometimes we need certain procedures to
successfully install necessary software. Please follow each section accordingly.
3-1
Page 46

Software Installation
r
3.1 Onboard Audio
This motherboard comes with a 16-bit sound processor (ESS Solo-1) onboard.
Game Port
PCB
SPK
MIC
LINE-IN
To fully utilize the audio functions, you may connect various peripheral devices
that the audio chip supports. The following figure shows the different devices
that you can connect.
SPK
Line-in
Mic
Stereo
Amplifier
Microphone
Headphones
Speakers
CD Playe
Tape Deck,
Synthesizer,
etc.
3-2
Page 47

Software Installation
The onboard audio has the following features:
Advanced technology support
ESS Solo-1 PCI audio accelerator in 16 bits stereo chip
High-quality ESFM music synthesizer
64 voices software wavetable
3-D stereo effects processor
Support DLS (downloadable sound)
Support Microsoft DirectMusic
Support Microsoft positional 3D
Support DirectSound and DirectSound 3D
ADPCM data compression
Internal modem connector
Full DOS game compatibility
Plug and Play
Record, compress, and play back voice, sound, and music
16-bit stereo ADC and DAC
Programmable independent sample rate from 6 KHz up to 48 KHz for
record and playback
Full duplex operation for simultaneous record and playback
Support full DOS compatible modes: PC/PCI, TDMA, DDMA
Sound Blaster Pro & Windows Sound System compatible
Stereo Input for Line-in, CD-Audio, Auxiliary in and a mono microphone in
MPU-401(UART mode) interface for wavetable synthesizers and MIDI
devices
Integrated dual game port
Separate mono input (MONO-IN) and mono output (MONO-OUT) for
speakerphone
Support windows95/98 or windows NT 4.0
WDM streaming driver support windows98 and windows NT 5.0
Software-controllable audio
Supports various audio devices all controllable through software
Adjusts master volume, CD audio, line-in, AUX, mono in, mono out,
synthesis wave and microphone inputs
Stereo digitized voice channel
Full-duplex operation for simultaneous record and playback
3-3
Page 48

Software Installation
3.1.1 Setting Up in Windows 95/98
This motherboard comes with CD-ROM disc (AOpen Bonus Pack) containing
the Windows 95/98 drivers and software (including the Music Center
application). Refer to their online help for details.
Note: Refer to your Windows 95/98 manual or
online help for any questions on Windows 95/98.
Installing the Drivers and the Application
After turning on the system, Windows 95/98 begins loading and starts
detecting new hardware installed on the system.
1. When Windows 95/98 detects the presence of the onboard audio chip, it
begins to build the driver database. The New Hardware Found dialog box
displays.
2. Select Driver from disk provided by hardware manufacturer and click
on OK. Windows 95/98 prompts you for the driver disk.
3. Insert the driver disk in the appropriate drive and specify another drive, if
required. Then click on OK. The system copies the necessary driver files
to your hard disk drive.
Tip: Prepare the Windows 95/98 CD-ROM disk before
setting up the sound card. Windows 95/98 will prompt
you to insert the Windows 95/98 CD-ROM disk when
you install the joystick or MIDI device.
Note: If the file being copied is older than the file
currently existing in your system, we recommend that
you keep the existing file.
4. Windows 95/98 makes changes to the system settings and begins
detecting the following new hardware components:
• ES1941 PCI AudioDrive
• ES1941 DOS Enumlation
• Gameport Joystick
Windows 95/98 makes final changes to the system settings.
3-4
Page 49

Software Installation
Install the Application
1. Insert AOpen Bonus Pack disc, setup the applications from “Motherboard
Drivers” of the autorun program, or browse CD and select X:\Mx3za\
Sound\Setup.exe.
Dos Legacy mode Setup
1. Insert AOpen Bonus Pack disc, setup the applications from “Motherboard
Drivers” of the autorun program, or browse CD and select X:\Mx3za\
Sound\Setup.exe. Select Application button from setup menu.
2. Choose Dos Legacy Support item to begin setup.
3. If the system reboot under windows98, please select the driver form
Windows98 instead of AOpen Bonus Pack disc.
3.1.2 Setting Up in NT4.0
The card package also comes with NT4.0 drivers. Please refer to your NT4.0
manual or online help for any questions on NT4.0.
Installing the Audio Drivers
Follow these steps to install the audio drivers:
1. Select MULTIMEDIA from control panel and click on the Devices tab.
2. Press the ADD button. Select Unlisted or Updated Drivers and press
OK.
3. Browse and select X:\Mx3za\Sound\Driver\NT40.
4. Press OK to continue with the installation.
5. An Audio Setup dialog box will appear. Select the default configuration
resource and press OK.
6. Click on the Restart Now button.
Install MPU-401/Joystick Driver
Follow these steps to install the MPU401 or joystick drivers:
1. Select MULTIMEDIA from control panel and click on the Devices tab.
2. Press the ADD button. Select MPU-401 Compatible Driver /Microsoft
Sidewinder 3D Pro Joystick and press OK..
3-5
Page 50

Software Installation
3. Place your NT4.0 installation CD and press OK (the default path is the
i386 directory).
4. The Generic MPU-401/Joystick Setup dialog box will pop up. Select the
default configuration resource and press OK.
5. Click on the Restart Now button.
Note: X: means your CD drive letter, please change it
according to the actual drive letter.
3-6
Page 51

3.2 Onboard AGP
Software Installation
PCB
VGA
This motherboard comes with a high performance onboard graphics
accelerator (ATI 3D Rage Pro Turbo AGP).
3.2.1 Installing ATI enhanced driver in Win95/98
1. Place the CD disc into the CDROM drive.
2. In the Taskbar, click Start.
3. Click Run.
4. Type D:\Mx3za\Agp\Win9x\Disk1\Setup.exe in the text entry area, and
press OK. (If D is not your CDROM drive, substitute D with the correct drive
letter.)
5. Follow the instructions displayed in the help.
3.2.2 Installing ATI enhanced driver in Windows NT
1. Run the Windows NT Display program located in the Control Panel, under
"Settings" in the Start menu. Alternatively, position the cursor on the
background of the desktop, click the right mouse button, then select
"Properties" from the popup menu.
2. Select the "Settings" page.
3. Select "Display Type...".
4. Select "Change..." from the display options.
5. Select "Have Disk..."
3-7
Page 52

Software Installation
6. NT will prompt you for the correct path, enter D:\Mx3za\Agp\Win9x. (If D is
not your CDROM drive, substitute D with the correct drive letter.)
7. A list of ATI graphics accelerators will be displayed. Select the one you are
using, then click on the "OK" button.
8. Windows NT will once again prompt for confirmation. All appropriate files
are then copied to the hard disk.
9. Restart Windows NT. Windows NT will start up using the mach64 drivers.
10. NT will boot into a default mode and start the Display applet allowing for
mode selection.
Note: If you select a color depth or resolution not supported by the onboard
AGP, NT will substitute 640x480 in 256 colors for the display.
Caution: You need to setup Windows NT 4.0
Service Pack 3 for installing an AGP card.
3-8
Page 53

Software Installation
3.3 Install Hardware Monitoring Utility
There are four high-valued "Hardware Monitoring" features being implemented
on this motherboard.
1. Over Current Protection: Providing over current protection for CPU
Vcore. In conjunction with the over current protection provided by ATX
power supply on 3.3V/5V/12V, it gives the full line over current protection.
2. System Voltage Monitoring: As you turn your system on, this smart
design will continue to monitor your system working voltage. If any of the
system voltage is over the component's standard, there will be warning
alarm from PC speaker when Hardware Monitoring Utility or ADM
installed.
3. Thermal Protection: The higher speed of CPU, the more heat
dissipation ability is needed to be taken into consideration. If the user
does not use a correct fan for the CPU cooling, it is highly possible the
CPU will be overheating and cause system unstable. AOpen
motherboard monitors CPU temperature by using a thermal sensor.
4. Fan Monitoring: There are two three-pin fan connectors, one is for CPU
and the other one can be connected to the housing fan. The system will
report the rotational speed of the fan and alarm fan malfunction though
Hardware Monitoring Utility or ADM.
The hardware monitoring function is automatically implemented by the BIOS
and utility software (such as Hardware Monitoring Utility or ADM), no hardware
installation is needed.
Hardware Monitoring Utility (the program’s file name is like aohwxxx.exe,
where xxx means the version number) is developed by AOpen which monitors
the status of system voltage, thermal, & fan. Instead of using ADM, which
supports network administration, this utility is especially designed for personal
user. You may install it on your AOpen motherboard based system which
comes with Hardware Monitoring features. To install Hardware Monitoring
Utility, please follow the procedure below.
Choose “Hardware Monitoring Utility” from the autorun menu of AOpen Bonus
Pack CD disc.
~ 0r ~
Run \HwMon\95\aohw120.exe
3-9
Page 54

Software Installation
3-10
Page 55

Software Installation
3.4 Install Norton AntiVirus
You can install this antivirus software from AOpen Bonus Pack CD disc,
please follow the procedure below.
To install Norton Antivirus, please follow the procedure below.
To run AOchip, please follow the procedure below.
1. Choose “Norton Antivirus” from the autorun menu of AOpen Bonus Pack CD
disc.
2. Choose one language version accordingly and click “OK” button.
~ 0r ~
Brazilian version: Run \Nav\Brazilian\Setup.exe
Chinese version: Run \Nav\Chinese\Disk1\Setup.exe
Dutch version: Run \Nav\Dutch\Setup.exe
English version: Run \Nav\English\Setup.exe
French version: Run \Nav\French\Setup.exe
German version: Run \Nav\German\Setup.exe
Italian version: Run \Nav\Italian\Setup.exe
Japanese version: Run \Nav\Japanese\Setup.exe
Korean version: Run \Nav\Korean\Disk1\Setup.exe
Spanish version: Run \Nav\Spanish\Setup.exe
3-11
Page 56

Software Installation
3-12
Page 57

Software Installation
3.5 Install Docucom Reader
The AOpen Bonus Pack CD disc includes an online manual of this
motherboard, which is PDF file format. You must use Docucom Reader to read
these PDF files.
To install Docucom Reader, please follow the procedure below.
Choose “Docucom Reader” from the autorun menu of AOpen Bonus Pack CD
disc.
~ 0r ~
Run \Utility\Docucom\Setup\Setup.exe
3-13
Page 58

Software Installation
3.6 Eliminate “?” mark in Win95
VIA has introduced Apollo Pro Plus chipset with latest feature of "ACPI", "USB"
& "Ultra DMA/33". Since these devices are so new that Win'95 did not
anticipate to support them on Aug. of '95 which Win'95 initially is being
released, there will be question marks or "standard IDE controller" presented
under Device Manager after installing Win'95 on this board.
Even though your system will work fine with this "?" marks, we received many
requests about how to eliminate it. AOpen software team developed an utility
AOchip.exe for the convenience of Win95 users. It is very user friendly and
can be used on any TX/LX/BX/ZX/MVP3/Apollo Pro Plus/5591 chipset based
motherboard, not limited to AOpen products. You are welcome to distribute it,
if you like it, simply say thanks to our software team. Note that you need USB
driver for USB devices to work properly if your OS is Win95.
To run AOchip, please follow the procedure below.
1. Choose “AOChip” from the autorun menu of AOpen Bonus Pack CD disc.
2. Click “Install” button to execute AOChip.
~ 0r ~
Run \Utility\AOchip\AOchip.exe
3-14
Page 59

Software Installation
3.7 Install Bus Master IDE Driver
The traditional PIO (Programmable I/O) IDE requires the CPU to involve in all
the activities of the IDE access including waiting for the mechanical events. To
reduce the workload of the CPU, the bus master IDE device transfers data
from/to memory without interrupting the CPU and releases CPU to operate
concurrently while data is transferring between memory and IDE device. You
need the bus master IDE driver and the bus master IDE HDD to support bus
master IDE mode.
To install Intel Bus Master IDE driver, please follow the procedure below.
1. Choose “Motherboard Drivers” from the autorun menu of AOpen Bonus
Pack CD disc.
2. Select “Intel Bus Master IDE Driver” from the combo box.
~ 0r ~
Run \Mx3za\Driver\Win95\Setup.exe
3-15
Page 60

Chapter 4
Award BIOS
This chapter tells how to configure the system parameters and upgrade the
BIOS.
Important: Because the BIOS code is the most
often changed part of the mainboard design, the
BIOS information contained in this chapter
(especially the Chipset Setup parameters) may be
a little different compared to the actual BIOS that
came with your motherboard.
4-1
Page 61

AWARD BIOS
4.1 Entering the Award BIOS Setup Menu
The BIOS setup utility is a segment of codes/routines residing in the BIOS
Flash ROM. This routine allows you to configure the system parameters and
save the configuration into the 128 byte CMOS area, (normally in the RTC chip
or directly in the main chipset). To enter the BIOS Setup, press
POST (Power-On Self Test). The BIOS Setup Main Menu appears as follows.
during
Tip: Choose "Load Setup Defaults" for
recommended optimal performance. Choose
"Load Turbo Defaults" for best performance
with light system loading. Refer to section 4.7.
The section at the bottom of the screen tells how to control the screen. Use the
arrow keys to move between items, F9 to change language, ESC to exit, and
F10 to save the changes before exiting. Another section at the bottom of the
screen displays a brief description of the highlighted item.
After selecting an item, press Enter to select or enter a submenu.
4-2
Page 62

AWARD BIOS
4.2 Standard CMOS Setup
The "Standard CMOS Setup" sets the basic system parameters such as the
date, time, and the hard disk type. Use the arrow keys to highlight an item and
or to select the value for each item.
Standard CMOS Æ Date
To set the date, highlight the Date parameter. Press or to set the
current date. The date format is month, date, and year.
Standard CMOS Æ Time
To set the time, highlight the Time parameter. Press or to set the
current time in hour, minute, and second format. The time is based on the 24
hour military clock.
4-3
Page 63

AWARD BIOS
Standard CMOS Æ Primary Master Æ Type
Standard CMOS Æ Primary Slave Æ Type
Standard CMOS Æ Secondary Master Æ Type
Standard CMOS Æ Secondary Slave Æ Type
Type
Auto
User
None
This item lets you select the IDE hard disk parameters
that your system supports. These parameters are Size,
Number of Cylinder, Number of Head, Start Cylinder for
Pre-compensation, Cylinder number of Head Landing
Zone and Number of Sector per Track. The default
setting is Auto, which enables BIOS to automatically
detect the parameters of installed HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
at POST (Power-On Self Test). If you prefer to enter HDD
parameters manually, select User. Select None if no
HDD is connected to the system.
The IDE CDROM is always automatically detected.
Tip: For an IDE hard disk, we recommend that
you use the "IDE HDD Auto Detection" to enter
the drive specifications automatically. See the
section "IDE HDD Auto Detection".
Standard CMOS Æ Primary Master Æ Mode
Standard CMOS Æ Primary Slave Æ Mode
Standard CMOS Æ Secondary Master Æ Mode
Standard CMOS Æ Secondary Slave Æ Mode
Mode
Auto
Normal
LBA
Large
The enhanced IDE feature allows the system to use a
hard disk with a capacity of more than 528MB. This is
made possible through the Logical Block Address (LBA)
mode translation. The LBA is now considered a standard
feature of current IDE hard disk on the market because of
its capability to support capacity larger than 528MB.
Note that if a HDD is formatted with LBA On, it will not be
able to boot with LBA Off.
4-4
Page 64

Standard CMOS Æ Drive A
Standard CMOS Æ Drive B
AWARD BIOS
Drive A
None
360KB 5.25"
1.2MB 5.25"
720KB 3.5"
1.44MB 3.5"
2.88MB 3.5"
These items select the floppy drive type. The available
settings and types supported by the mainboard are listed
to the left.
Standard CMOS Æ Video
Video
EGA/VGA
CGA40
CGA80
Mono
This item specifies the type of video card in use. The
default setting is VGA/EGA. Since current PCs use VGA
only, this function is almost useless and may be disregarded
in the future.
Standard CMOS Æ Halt On
Halt On
No Errors
All Errors
All, But Keyboard
All, But Diskette
All, But Disk/Key
This parameter enables you to control the system stops in
case of Power-On Self Test (POST) error.
4-5
Page 65

AWARD BIOS
4.3 BIOS Features Setup
This screen appears when you select the option "BIOS Features Setup" from
the main menu.
BIOS Features Æ Virus Warning
Virus Warning
Enabled
Disabled
Type "Y" to accept write, or "N" to abort write
4-6
Set this parameter to Enabled to activate the warning
message. This feature protects the boot sector and
partition table of your hard disk from virus intrusion. Any
attempt during boot up to write to the boot sector of the
hard disk drive stops the system and the following warning
message appears on the screen. Run an anti-virus program
to locate the problem.
! WARNING !
Disk Boot Sector is to be modified
Award Software, Inc.
Page 66

BIOS Features Æ External Cache
AWARD BIOS
External Cache
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling this parameter activates the secondary
cache (currently, PBSRAM cache). Disabling the
parameter slows down the system. Therefore, we
recommend that you leave it enabled unless you are
troubleshooting a problem.
BIOS Features Æ CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
CPU L2 Cache
ECC Checking
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you enable or disable L2 Cache ECC
checking.
BIOS Features Æ Processor Number Feature
Processor Number
Feature
Enabled
Disabled
This item is used to enable or disable Pentium III CPU
Number Feature.
BIOS Features Æ Quick Power On Self Test
Quick Power on
Self test
Enable
Disabled
This parameter speeds up POST by skipping some
items that are normally checked.
4-7
Page 67

AWARD BIOS
BIOS Features Æ Boot Sequence
Boot Sequence
A,C,SCSI
C,A,SCSI
C,CDROM,A
CDROM,C,A
CDROM,A,C
D,A,SCSI
E,A,SCSI
F,A,SCSI
SCSI,A,C
SCSI,C,A
C only
LS/ZIP,C
This parameter allows you to specify the system boot
up search sequence. The hard disk ID are listed below:
C: Primary master
D: Primary slave
E: Secondary master
F: Secondary slave
LS: LS120
Zip: IOMEGA ZIP Drive
BIOS Features Æ Swap Floppy Drive
Swap Floppy Drive
Enabled
Disabled
This item allows you to swap floppy drives. For
example, if you have two floppy drives (A and B), you
can assign the first drive as drive B and the second
drive as drive A or vice-versa.
BIOS Features Æ Boot Up NumLock Status
Boot Up NumLock
Status
On
Off
Setting this parameter to On enables the numeric
function of the numeric keypad. Set this parameter to
Off to disregard the function. Disabling the numeric
function allows you to use the numeric keypad for
cursor control.
BIOS Features Æ Security Option
Security Option
Setup
System
4-8
The System option limits access to both the System
boot and BIOS setup. A prompt asking you to enter
your password appears on the screen every time you
boot the system.
The Setup option limits access only to BIOS setup.
To disable the security option, select Password
Setting from the main menu, don't type anything and
just press <Enter>.
Page 68

BIOS Features Æ PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
AWARD BIOS
PCI/VGA Palette
Snoop
Enabled
Disabled
Enabling this item informs the PCI VGA card to keep
silent (and to prevent conflict) when palette register is
updated (i.e., accepts data without responding any
communication signals). This is useful only when two
display cards use the same palette address and
plugged in the PCI bus at the same time (such as
MPEQ or Video capture). In such case, PCI VGA is
silent while MPEQ/Video capture is set to function
normally.
BIOS Features Æ OS Select for DRAM > 64MB
OS Select for
DRAM > 64MB
OS/2
Non-OS/2
Set to OS/2 if your system is utilizing an OS/2
operating system and has a memory size of more than
64 MB.
4-9
Page 69

AWARD BIOS
BIOS Features Æ Show Logo On Screen
Show Logo On
Screen
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you show or hide AOpen logo on the
POST screen.
BIOS Features Æ Video BIOS Shadow
Video BIOS
Shadow
Enabled
Disabled
VGA BIOS Shadowing means to copy video display
card BIOS into the DRAM area. This enhances system
performance because DRAM access time is faster than
ROM.
BIOS Features Æ C800-CBFF Shadow
BIOS Features Æ CC00-CFFF Shadow
BIOS Features Æ D000-D3FF Shadow
BIOS Features Æ D400-D7FF Shadow
BIOS Features Æ D800-DBFF Shadow
BIOS Features Æ DC00-DFFF Shadow
C8000-CBFFF
Shadow
Enabled
Disabled
These six items are for shadowing ROM code on other
expansion cards. Before you set these parameters, you
need to know the specific addresses of that ROM code.
If you do not know this information, enable all the ROM
shadow settings.
4-10
Note: The F000 and E000 segments are
always shadowed because BIOS code
occupies these areas.
Page 70

AWARD BIOS
4.4 Chipset Features Setup
The "Chipset Features Setup" includes settings for the chipset dependent
features. These features are related to system performance.
Caution: Make sure you fully understand the
items contained in this menu before you try to
change anything. You may change the
parameter settings to improve system
performance. However, it may cause your
system to be unstable if the setting is not
correct for your system configuration.
4-11
Page 71

AWARD BIOS
Chipset Features Æ SDRAM CAS Latency
Chipset Features Æ SDRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
SDRAM CAS
Latency
2T
3T
Auto
These are timing of SDRAM CAS Latency and RAS
to CAS Delay, calculated by clocks. They are
important parameters affects SDRAM performance,
default is Auto. If you install DIMMs with SPD and set
this item to Auto, BIOS will automatically detect your
DIMMs and then set to a appropriate timing; If you
use DIMMs without SPD and set this item to Auto,
BIOS will set it to 3/3.To make sure all of these
settings in BIOS are correct, it is recommended to
use DIMMs with SPD.
Chipset Features Æ SDRAM RAS# Precharge
SDRAM RAS#
Prechatge
2T
3T
Auto
The RAS Precharge means the timing to inactive
RAS and the timing for DRAM to do precharge before
next RAS can be issued. RAS is the address latch
control signal of DRAM row address. The default
setting is Auto.
Chipset Features Æ Video BIOS Cacheable
Video BIOS
Cacheable
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you cache Video RAM C000.
Chipset Features Æ Video RAM Cacheable
Video RAM
Cacheable
Enabled
Disabled
4-12
This item lets you cache Video RAM A000 and B000.
Page 72

Chipset Features Æ 8 Bit I/O Recovery Time
AWARD BIOS
8 Bit I/O Recovery
Time
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
NA
For some old I/O chips, after the execution of an I/O
command, the device requires a certain amount of
time (recovery time) before the execution of the next
I/O command. Because of new generation CPU and
mainboard chipset, the assertion of I/O command is
faster, and sometimes shorter than specified I/O
recovery time of old I/O devices. This item lets you
specify the delay of 8-bit I/O command by count of
ISA bus clock. If you find any unstable 8-bit I/O card,
you may try to extend the I/O recovery time via this
item. The BIOS default value is 4 ISA clock. If set to
NA, the chipset will insert 3.5 system clocks.
Chipset Features Æ 16 Bit I/O Recovery Time
16 Bit I/O Recovery
Time
1
2
3
4
NA
The same as 16-bit I/O recovery time. This item lets
you specify the recovery time for the execution of 16bit I/O commands by count of ISA bus clock. If you
find any of the installed 16-bit I/O cards unstable, try
extending the I/O recovery time via this item. The
BIOS default value is 1 ISA clocks. If set to NA, the
chipset will automatically insert 3.5 system clocks.
Chipset Features Æ Memory Hole At 15M-16M
Memory Hole At
15M-16M
Enabled
Disabled
This option lets you reserve system memory area for
special ISA cards. The chipset accesses code/data
of these areas from the ISA bus directly. Normally,
these areas are reserved for memory mapped I/O
card.
Chipset Features Æ Passive Release
Passive Release
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you control the Passive Release
function of the PIIX4E chipset (Intel PCI to ISA
bridge). This function is used to meet latency of ISA
bus master. Try to enable or disable it, if you have
ISA card compatibility problem.
4-13
Page 73

AWARD BIOS
Chipset Features Æ Delayed Transaction
Delayed Transaction
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you control the Delayed Transaction
function of the PIIX4E chipset (Intel PCI to ISA
bridge). This function is used to meet latency of PCI
cycles to or from ISA bus. Try to enable or disable it,
if you have ISA card compatibility problem.
Chipset Features Æ AGP Aperture Size (MB)
AGP Aperture Size
(MB)
4
8
16
32
64
128
256
This item lets you determine the effective size of the
AGP Graphic Aperture.
Chipset Features Æ Pentium II Micro Codes
Pentium II Micro
Codes
Enabled
Disabled
The micro codes are used to fix bugs of Pentium II
CPU, we strongly recommend to enable this item for
system reliability reason. However, this microcode
may slightly reduce CPU performance. We provide
this option for your convenience if you like to test it.
Chipset Features Æ Manufacture Frequency Default
Manufacture
Frequency Default
Depends on the CPU
type
This item only reminds you of the actual CPU
frequency while clearing CMOS or pressing "Home”
key. The default setting is 233 MHz, you can modify it
to match the actual CPU frequency by using the utility
- flash.exe.
Chipset Features Æ Clock Spread Spectrum
Clock Spread
Spectrum
On
Off
4-14
This item is used to set clock spread spectrum for
EMI testing. Normally, you don’t need to change the
default setting.
Page 74

Chipset Features Æ System Frequency
AWARD BIOS
System Frequency
233 MHz
266 MHz
300 MHz
333 MHz
350 / 100
366 MHz
400 MHz
400 / 100
433 MHz
450 / 100
466 MHz
500 MHz
500 / 100
Manual
This item lets you set CPU frequency. If you want to
set to other values, please choose "Manual " to set
CPU clock frequency and clock ratio manually.
/100 indicates the setting supports a 100MHz FSB
CPU.
Chipset Features Æ CPU Clock Frequency
CPU Clock Frequency
66.8 MHz
75.0 MHz
83.3 MHz
100 MHz
103 MHz
105 MHz
110 MHz
112 MHz
115 MHz
120 MHz
124 / 31
124 / 41
133 / 33
133 / 44
140 MHz
150 MHz
This item lets you set FSB (Front Side Bus). The
correct setting may vary because of different CPU
products, refer to your CPU specification for more
details.
/xx means the corresponding PCI clock..
4-15
Page 75

AWARD BIOS
Chipset Features Æ CPU Clock Ratio
CPU Clock Ratio
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0
Intel Pentium II is designed to have different Internal
(Core) and External (Bus) frequency. This item lets
you select the ratio of Core/Bus frequency. The
default value is 3.5x.
Chipset Features Æ Y2K CMOS Update
Y2K CMOS Update
Enabled
Disabled
This item is designed for some Y2K testing
programs, for example, Check It 98. If you are using
this kind of program to test your system and fails,
enable this item and redo the test again.
4-16
Page 76

AWARD BIOS
4.5 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup screen enables you to control the motherboard
green features. See the following screen.
Power Management Æ ACPI Function
ACPI Function
Enabled
Disabled
If your OS is ACPI enabled you have to set this item
to Enabled, or there may be unexpected errors. If
your OS is APM mode, you can remain the Disabled
setting.
Power Management Æ Power Management
Power Management
Max Saving
Mix Saving
User Define
Disabled
Mode Doze Standby Suspend HDD Power Down
4-17
This function allows you to set the default parameters
of power-saving modes. Set to Disable to turn off
power management function. Set to User Define to
choose your own parameters.
Page 77

AWARD BIOS
Min Saving 1 hour 1 hour 1 hour 15 min
Max Saving 1 min 1 min 1 min 1 min
Power Management Æ PM Controlled by APM
PM Controlled by
APM
Yes
No
If "Max Saving" is selected, you can turn on this
item, transfer power management control to APM
(Advanced Power Management) and enhance power
saving function. For example, stop CPU internal
clock.
Power Management Æ Video Off Method
Video Off Method
V/H SYNC + Blank
DPMS
Blank Screen
This determines the way that the monitor is off.
Blank Screen writes blanks to video buffer. V/H
SYNC + Blank allows BIOS to control VSYNC and
HSYNC signals. This function applies only for DPMS
(Display Power Management Standard) monitor. The
DPMS mode uses DPMS functions provided by the
VGA card.
Power Management Æ Video Off After
Video Off After
N/A
Doze
Standby
Suspend
To turn off video monitor at which power down
mode.
4-18
Page 78

Power Management Æ Doze Mode
AWARD BIOS
Doze Mode
Disabled
1 Min
2 Min
4 Min
8 Min
12 Min
20 Min
30 Min
40 Min
1 Hour
This item lets you set the period of time after which
the system enters into Doze mode. The system
activity (or event) is detected by monitoring the IRQ
signals or other events (such as I/O).
Power Management Æ Standby Mode
Standby Mode
Disabled
1 Min
2 Min
4 Min
8 Min
12 Min
20 Min
30 Min
40 Min
1 Hour
This item lets you set the period of time after which
the system enters into Standby mode. In this mode,
the monitor power-saving feature activates. Any
activity detected returns the system to full power.
The system activity (or event) is detected by
monitoring the IRQ signals or other events (such as
I/O).
Power Management Æ Suspend Mode
Suspend Mode
Disabled
1 Min
2 Min
4 Min
8 Min
12 Min
20 Min
30 Min
40 Min
1 Hour
This item lets you set the period of time after which
the system enters into Suspend mode. The Suspend
mode can be Power On Suspend or Suspend to Hard
Drive, selected by "Suspend Mode Option".
4-19
Page 79

AWARD BIOS
Power Management Æ HDD Power Down
HDD Power Down
Disabled
1 Min
.....
15 Min
This option lets you specify the IDE HDD idle time
before the device enters the power down state. This
item is independent from the power states previously
described in this section (Standby and Suspend).
Power Management Æ 0V Wake On Modem
0V Wake On Modem
Enabled
Disabled
This option lets you specify enable or disable Wake
On Modem function.
Power Management Æ Wake On LAN
Wake On LAN
Enabled
Disabled
This option lets you specify enable or disable Wake
On LAN function.
Power Management Æ Suspend Mode Option
Suspend Modem
Option
PowerOn Suspend
Suspend to Disk
You can select suspend mode by this item. Power
On Suspend is the traditional Green PC suspend
mode, the CPU clock is stop, all other devices are
shut off. But power must be kept On to detect
activities from modem, keyboard/mouse and returns
the system to full power. The system activities is
detected by monitoring the IRQ signals or I/O.
Suspend to Hard Drive saves system status,
memory and screen image into hard disk, then the
power can be totally Off. Next time, when power is
turned On, the system goes back to your original
work within just few seconds, which depending on
your memory size. You need utility AOZVHDD to
reserve disk space.
4-20
Page 80

Power Management Æ Throttle Duty Cycle
AWARD BIOS
Throttle Duty Cycle
12.5 %
25.0 %
37.5 %
50.0 %
62.5 %
75.0 %
87.5 %
Clock Throttling means at the Doze/Standby state,
the CPU clock count in a given time (not the
frequency) is reduced to the ratio specified in this
parameter. Actually, the period per CPU clock is not
changed. For example, a 66MHz CPU clock remains
the same 30ns clock period when system goes into
Doze/Suspend. The chipset generates the STPCLK
(stop clock) signal periodically to prevent CPU for
accepting clock from clock generator. For full power
on, the CPU can receive 66M count in one second. If
the Slow Clock Ratio is set to 50%, the CPU will only
receive 33M clock count in one second. This will
effectively reduce CPU speed as well as CPU power.
Power Management Æ VGA Active Monitor
VGA Active Monitor
Enabled
Disabled
To enable or disable the detection of VGA activity for
power down state transition.
Power Management Æ Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
Soft-Off by PWRBTTN
Delay 4 sec.
Instant-Off
This is a specification of ACPI and supported by
hardware. When Delay 4 sec. is selected, the soft
power switch on the front panel can be used to
control power On, Suspend and Off. If the switch is
pressed for less than 4 seconds during power On,
the system will go into Suspend mode. If the switch is
pressed for longer than 4 seconds, the system will be
turned Off. The default setting is Instant-Off. If
Instant-Off is selected the soft power switch is only
used to control On and Off, so there is no need to
press it for 4 seconds, and there is no Suspend.
Power Management Æ Wake On RTC Timer
Wake On RTC Timer
By Date
By Week
Disabled
4-21
This option lets you enable or disable the RTC Wake
Up function.
Page 81

AWARD BIOS
Power Management Æ Date (of Month)
Date (of Month)
0
1
.....
31
This item is displayed when you enable the Wake On
RTC Timer option. Here you can specify what date
you want to wake up the system. For Example,
setting to 15 will wake up the system on the 15th day
of every month.
Note: Setting this item to 0 will wake up the
system on the specified time (which can be
set in the Wake On RTC Timer ) every day.
Power Management Æ Time (hh:mm:ss)
Time (hh:mm:ss)
hh:mm:ss
This item is displayed when you enable the Wake On
RTC Timer option. Here you can specify what time
you want to wake up the system.
Power Management Æ IRQ 8 Break Suspend
IRQ 8 Break Suspend
Enabled
Disabled
To enable or disable the detection of IRQ8 (RTC)
event for power down state transition. OS2 has
periodically IRQ8 (RTC) interruptions, If IRQ8 is not
set to Disabled, OS/2 may fail to go into
Doze/Standby/Suspend mode.
Power Management Æ IRQ [3-7,9-15],NMI
IRQ [3-7,9-15],NMI
Enabled
Disabled
4-22
To enable or disable the detection of IRQ3-7, IRQ915 or NMI interrupt events for power down state
transition.
Page 82

Power Management Æ Primary IDE 0
Power Management Æ Primary IDE 1
Power Management Æ Secondary IDE 0
Power Management Æ Secondary IDE 1
Power Management Æ Floppy Disk
Power Management Æ Serial Port
Power Management Æ Parallel Port
AWARD BIOS
Primary IDE 0
Enabled
Disabled
These items enable or disable the detection of IDE,
floppy, serial and parallel port activities for power
down state transition. Actually it detects the
read/write to/from I/O port.
4-23
Page 83

AWARD BIOS
4.6 PNP/PCI Configuration Setup
The PNP/PCI Configuration Setup allows you to configure the ISA and PCI
devices installed in your system. The following screen appears if you select
the option "PNP/PCI Configuration Setup" from the main menu.
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PnP OS Installed
PnP OS Installed
Yes
No
Normally, the PnP resources are allocated by BIOS
during POST (Power-On Self Test). If you are using
a PnP operating system (such as Windows 95), set
this item to Yes to inform BIOS to configure only the
resources needed for booting (VGA/IDE or SCSI).
The rest of system resources will be allocated by PnP
operating system.
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Resources Controlled By
Resources Controlled
by
Auto
Manual
4-24
Setting this option to Manual allows you to
individually assign the IRQs and DMAs to the ISA
and PCI devices. Set this to Auto to enable the autoconfiguration function.
Page 84

AWARD BIOS
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Reset Configuration Data
Reset Configuration
Data
Enabled
Disabled
In case conflict occurs after you assign the IRQs or
after you configure your system, you can enable this
function, allow your system to automatically reset
your configuration and reassign the IRQs, DMAs, and
I/O address.
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ3 (COM2)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ4 (COM1)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ5 (Network/Sound or Others)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ7 (Printer or Others)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ9 (Video or Others)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ10 (SCSI or Others)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ11 (SCSI or Others)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ12 (PS/2 Mouse)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ14 (IDE1)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ IRQ15 (IDE2)
IRQ 3
Legacy ISA
PCI/ISA PnP
If your ISA card is not PnP compatible and requires a
special IRQ to support its function, set the selected
IRQ to Legacy ISA. This setting informs the PnP
BIOS to reserve the selected IRQ for the installed
legacy ISA card. The default is PCI/ISA PnP. Take
note that PCI cards are always PnP compatible
(except old PCI IDE card).
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 0
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 1
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 3
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 5
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 6
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ DMA 7
DMA 0
Legacy ISA
PCI/ISA PnP
4-25
If your ISA card is not PnP compatible and requires a
special DMA channel to support its function, set the
selected DMA channel to Legacy ISA. This setting informs
the PnP BIOS to reserve the selected DMA channel for the
installed legacy ISA card. The default is PCI/ISA PnP.
Take note that PCI card does not require DMA channel.
Page 85

AWARD BIOS
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PCI IDE IRQ Map To
PCI IDE IRQ Map
To
ISA
PCI-Slot1
PCI-Slot2
PCI-Slot3
PCI-Slot4
PCI-Auto
Some old PCI IDE add-on cards are not fully PnP
compatible. These cards require you to specify the
slot in use to enable BIOS to properly configure the
PnP resources. This function allows you to select the
PCI slot for any PCI IDE add-on card present in your
system. Set this item to
automatically configure the installed PCI IDE card(s).
Auto to allow BIOS to
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Primary IDE INT#
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Secondary IDE INT#
Primary IDE INT#
A
B
C
D
These two items, in conjunction with item "PCI IDE
IRQ Map To", specify the IRQ routing of the primary or
secondary channel of the PCI IDE add-on card (not
the onboard IDE). Each PCI slot has four PCI
interrupts aligned as listed in the table below. You
must specify the slot in the "PCI IDE IRQ Map To",
and set the PCI interrupt (INTx) here according to the
interrupt connection on the card.
4-26
Page 86

AWARD BIOS
PCI Slot Location 1
(pin A6)
Slot 1 INTA INTB INTC INTD
Slot 2 INTB INTC INTD INTA
Slot 3 INTC INTD INTA INTB
Slot 4 INTD INTA INTB INTC
Slot 5 (if any) INTD INTA INTB INTC
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Modem Use IRQ
Location 2
(pin B7)
Location 3
(pin A7)
Location 4
(pin B8)
Modem Use IRQ
N/A
3
4
5
7
9
10
11
This item lets you set an IRQ for the modem.
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Used MEM Base Addr
Used MEM base addr
N/A
C800
CC00
D000
D400
D800
DC00
This item, in conjunction with the "Used MEM
Length", lets you set a memory space for non-PnP
compatible ISA card. This item specifies the
memory base (start address) of the reserved
memory space. The memory size is specified in the
"Used MEM Length"
.
4-27
Page 87

AWARD BIOS
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ Used MEM Length
Used MEM Length
8K
16K
32K
64K
If your ISA card is not PnP compatible and requires
special memory space to support its function, specify
the memory size in this parameter to inform the PnP
BIOS to reserve the specified memory space for
installed legacy ISA card.
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PCI Slot1 IRQ (Right)
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PCI Slot2 IRQ
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PCI Slot3 IRQ
PNP/PCI Configuration Æ PCI Slot4 IRQ (Left)
PCI Slot1 IRQ
3
4
5
7
9
10
11
12
14
15
Auto
This item is reserved for engineering purpose to let
you assign an IRQ manually to the add-on card on
each PCI slot. If you select Auto, system will
automatically assign an available value to the device.
It is suggested to use default setting, which is Auto,
in order to comply with PnP specification completely.
4-28
Page 88

AWARD BIOS
4.7 Load Setup Defaults
The "Load Setup Defaults" option loads optimized settings for optimum system
performance. Optimal settings are relatively safer than the Turbo settings. All
the product verification, compatibility/reliability test report and manufacture
quality control are based on "Load Setup Defaults". We recommend you to use
this settings for normal operation. "Load Setup Defaults" is not the slowest
setting for this motherboard. If you need to verify an unstable problem, you
may manually set the parameter in the "BIOS Features Setup" and "Chipset
Features Setup" to get slowest and safer setting.
4.8 Load Turbo Defaults
The "Load Turbo Defaults" option gives better performance than "Load Setup
Defaults". It is provided for the convenience of power user who wants to push
the motherboard to get better performance. Turbo setting does not go though
all the detail reliability and compatibility test, it is tested only with limited
configuration and loading (for example, a system that contains only a VGA
card and two DIMMs). Use Turbo setting only when you fully understand the
items in Chipset Setup menu. The performance improvement of Turbo setting
is normally around 3% to 5%, depending on the chipset and the application.
4-29
Page 89

AWARD BIOS
4.9 Integrated Peripherals
The following screen appears if you select the option "Integrated Peripherals"
from the main menu. This option allows you to configure the I/O features.
Integrated Peripherals Æ IDE HDD Block Mode
IDE HDD Block
Mode
Enabled
Disabled
4-30
This feature enhances disk performance by allowing
multisector data transfers and eliminates the interrupt
handling time for each sector. Most IDE drives,
except with old designs, can support this feature.
Page 90

AWARD BIOS
Integrated Peripherals Æ IDE Primary Master UDMA
Integrated Peripherals Æ IDE Primary Slave UDMA
Integrated Peripherals Æ IDE Secondary Master UDMA
Integrated Peripherals Æ IDE Secondary Slave UDMA
IDE Primary Master
UDMA
Auto
Disabled
This item allows you to set the Ultra DMA/33 mode
supported by the hard disk drive connected to your
primary IDE connector.
Integrated Peripherals Æ On-Chip Primary PCI IDE
Integrated Peripherals Æ On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE
On-Chip Primary
PCI IDE
Enabled
Disabled
This parameter lets you enable or disable the IDE
device connected to the primary IDE connector.
Integrated Peripherals Æ USB Keyboard Support
USB Keyboard
Support
Enabled
Disabled
This item lets you enable or disable the USB
keyboard driver within the onboard BIOS. The
keyboard driver simulates legacy keyboard command
and let you use USB keyboard during POST or after
boot if you don't have USB driver in the operating
system.
Caution: You can not use both USB driver
and USB legacy keyboard at the same time.
Disable "USB Keyboard Support" if you have
USB driver in the operating system.
Integrated Peripherals Æ Init Display First
Init Display First
PCI
AGP
4-31
If you installed a PCI VGA card and an AGP card at
the same time, this item lets you decide which one is
the initial display card.
Page 91

AWARD BIOS
Integrated Peripherals Æ Power On Function
Power On Function
Button Only
Keyboard 98
Password
Hot Key
Mouse Left
Mouse Right
This item is used to select Wake on
Keyboard/Mouse mode.
Button Only: Disable Wake on KB/MS function. You
can boot up your system by power button only.
Keyboard 98: If selecting this option, you can boot
up the system by power button and the “Wake” key
on keyboard which complies to Keyboard 98
standard.
Password: Disable the function of power button and
let the system can only be powered on through the
preset keys (like a password).
Hot Key: If selecting this option, you also need to
specify the hot key from “Hot Key Power On” item.
Mouse Left: This function allows you wake up the
system by clicking left mouse button twice
successively. Note that the mouse can’t be moved
while double clicking.
Mouse Right: This function allows you wake up the
system by clicking right mouse button twice
successively. Note that the mouse can’t be moved
while double clicking.
Caution: Whenever you change this item, it will only
take effect after you restart the system and
successfully boot the Windows or DOS.
Caution: To implement Wake On Keyboard/Mouse
function, you must set JP28 to Enabled.
Caution: Wake On Mouse function applies to PS/2
mouse only.
Caution: If you set a Password but forget it, please
clear CMOS.
Caution: If you want to use Wake On Mouse function
in DOS, it is necessary to install the DOS driver of the
mouse.
4-32
Page 92

AWARD BIOS
Integrated Peripherals Æ Keyboard Power On Password
Keyboard Power On
Password
You can specify 1-5 keys as a password.
Note: Before setting a password you have to
make sure JP28 has been enabled, or your
system cannot be boot up properly any more.
Under this situation, the only solution is to
clear CMOS.
Integrated Peripherals Æ Hot Key Power On
Hot Key Power On
Ctrl-F1
Ctrl-F2
Ctrl-F3
Ctrl-F4
Ctrl-F5
Ctrl-F6
Ctrl-F7
Ctrl-F8
Ctrl-F9
Ctrl-F10
Ctrl-F11
Ctrl-F12
If you select “Hot Key” option in “Power On Function”
Item, you need to specify a hot key here.
4-33
Page 93

AWARD BIOS
Power Management Æ AC PWR Auto Recovery
AC PWR Auto
Recovey
Former-Sts
On
Off
A traditional ATX system should remain at power off
stage when AC power resumes from power failure.
This design is inconvenient for a network server or
workstation, without an UPS, that needs to keep
power-on. This item is used to solve this problem.
Selecting On lets the system can automatically
power-on after AC power resumes; in the other hand,
the system will power-off if you select Off. If FormerSts option is selected, the system will power-on or
power-off based on the original state.
Integrated Peripherals Æ Onboard FDC Controller
Onboard FDC
Controller
Enabled
Disabled
Setting this parameter to Enabled allows you to
connect your floppy disk drives to the onboard floppy
disk connector instead of a separate controller card.
Change the setting to Disabled if you want to use a
separate controller card.
Integrated Peripherals Æ Onboard Serial Port 1
Integrated Peripherals Æ Onboard Serial Port 2
Onboard Serial Port 1
Auto
3F8/IRQ4
2F8/IRQ3
3E8/IRQ4
2E8/IRQ3
Disabled
This item allow you to assign address and interrupt
for the board serial port. Default is Auto.
4-34
Note: If you are using a network card, make
sure that the interrupt does not conflict.
Page 94

Integrated Peripherals Æ UART Mode Select
AWARD BIOS
UART Mode Select
Standard
HPSIR
ASKIR
This item is configurable only if the "Onboard UART
is enabled. This allows you to specify the mode
2"
of serial port2. The available mode selections are:
• Standard - Sets serial port 2 to operate in normal mode. This is the
default setting.
• HPSIR - Select this setting if you installed an Infrared module in your
system via IrDA connector (refer to section 2.3 "Connectors"). This
setting allows infrared serial communication at a maximum baud rate of
115K baud.
• ASKIR - Select this setting if you installed an Infrared module via IrDA
connector (refer to section 2.3 "Connectors"). This setting allows infrared
serial communication at a maximum baud rate of 19.2K baud.
Integrated Peripherals Æ RxD, TxD Active
RxD, TxD Active
Hi, Hi
Hi, Lo,
Lo, Hi
Lo, Lo
This item is used to select RxD (Receive Data) and
TxD (Transmit Data) mode for UART, for instance, IR
device, modem, etc. Normally, we suggest you keep
the default setting. Please see the documentation
that comes with your device.
Integrated Peripherals Æ IR Transmission Delay
IR Transmission
Delay
Enabled
Disabled
4-35
If Enabled is selected, there will be a 4 characters
delay when SIR is changed from TX mode to RX
mode.
Page 95

AWARD BIOS
Integrated Peripherals Æ Onboard Parallel Port
Onboard Parallel
Port
3BC/IRQ7
378/IRQ7
278/IRQ5
Disabled
This item controls the onboard parallel port address
and interrupt.
Note: If you are using an I/O card with a
parallel port, make sure that the addresses
and IRQ do not conflict.
Integrated Peripherals Æ Parallel Port Mode
Parallel Port Mode
SPP
EPP
ECP
ECP + EPP
This item lets you set the parallel port mode. The
mode options are SPP (Standard and Bidirection
Parallel Port), EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and
ECP (Extended Parallel Port). SPP is the IBM AT
and PS/2 compatible mode. EPP enhances the
parallel port throughput by directly writing/reading
data to/from parallel port without latch. ECP supports
DMA and RLE (Run Length Encoded) compression
and decompression.
Integrated Peripherals Æ ECP Mode Use DMA
ECP Mode Use DMA
3
1
This item lets you set the DMA channel of ECP
mode.
Integrated Peripherals Æ EPP Mode Select
EPP Mode Select
EPP1.7
EPP1.9
4-36
This item lets you select EPP mode.
Page 96

AWARD BIOS
4.10 Password Setting
Password prevents unauthorized use of your computer. If you set a password,
the system prompts for the correct password before boot or access to Setup.
To set a password:
1. At the prompt, type your password. Your password can be up to 8
alphanumeric characters. When you type the characters, they appear as
asterisks on the password screen box.
2. After typing the password, press.
3. At the next prompt, re-type your password and press again to confirm the
new password. After the password entry, the screen automatically
reverts to the main screen.
To disable the password, press when prompted to enter the password. The
screen displays a message confirming that the password has been disabled.
4.11 IDE HDD Auto Detection
If your system has an IDE hard drive, you can use this function to detect its
parameters and enter them into the "Standard CMOS Setup" automatically.
This routine only detects one set of parameters for your IDE hard drive. Some
IDE drives can use more than one set of parameters. If your hard disk is
formatted using different parameters than those detected, you have to enter
the parameters manually. If the parameters listed do not match the ones used
to format the disk, the information on that disk will not be accessible. If the
auto-detected parameters displayed do not match those that used for your
drive, ignore them. Type
manually from the Standard CMOS Setup screen.
N to reject the values and enter the correct ones
4.12 Save & Exit Setup
This function automatically saves all CMOS values before leaving Setup.
4-37
Page 97

AWARD BIOS
4.13 Load EEPROM Default
Except "Load Setup Default" and "Load Turbo Default", you may also use
"Save EEPROM Default " to save your own settings into EEPROM, and reload
by using this item.
4.14 Save EEPROM Default
You may use this item to save your own settings into EEPROM. Then, if the
data in CMOS is lost or you forget the previous settings, you may use "Load
EEPROM Default " to reload.
4.15 Exit without Saving
Use this function to exit Setup without saving the CMOS value changes. Do
not use this option if you want to save the new configuration.
4.16 NCR SCSI BIOS and Drivers
The NCR 53C810 SCSI BIOS resides in the same flash memory chip as the
system BIOS. The onboard NCR SCSI BIOS is used to support NCR 53C810
SCSI control card without BIOS code.
The NCR SCSI BIOS directly supports DOS, Windows 3.1 and OS/2. For
better system performance, you may use the drivers that come with the NCR
SCSI card or with your operating system. For details, refer to the installation
manual of your NCR 53C810 SCSI card.
4-38
Page 98

AWARD BIOS
4.17 How to Upgrade the BIOS
AOpen Easy Flash is more user friendly than traditional flash method. The
BIOS binary file and flash routine are combined together and you simply run a
single file to complete the flash process.
1. Get new BIOS upgrade program from AOpen's web site. For example,
MX3ZA200.EXE. It is recommended to save it to a bootable DOS floppy
diskette for error recovery.
2. Reboot the system to DOS mode without loading any memory handler
(such as EMM386) or device driver. It needs around 520K free memory
space.
3. Execute A:> MX3ZA200
DO NOT turn off the power during FLASH PROCESS.
4. Reboot the system by turn off the power after flash is completed.
5. Reload the "BIOS SETUP DEFAULT" and reconfigure other items as
previous set. Save & Exit. Done!
Note: If you encounter BIOS flash fail, use
PCI VGA card to check if it can be boot from
floppy and flash again.
Note: The upgrade of new BIOS will
permanently replace your original BIOS
content after flashing. The original BIOS
setting and Win95/Win98 PnP information will
be refreshed and you probably need to reconfigure your system.
4-39
 Loading...
Loading...