Page 1
GPR-2500 / GPR-2500MO
Oxygen Transmitter
Owner’s Manual
2855 Metropolitan Place, Pomona, CA 91767 USA ♦ Tel: 909-392-6900, Fax: 909-392-3665, e-mail: info@aii2.com, www.aii2.com
Page 2

2
Table of Contents
Introduction
1
Quality Control Certification
2
Safety
3
Features & Specifications
4
Operation
5
Maintenance
6
Spare Parts
7
Troubleshooting
8
Warranty
9
Material Safety Data Sheets
10
Drawings
A/R
Page 3

3
1 Introduction
Your new oxygen transmitter incorporated an advanced electrochemical sensor specific to oxygen along with stateof-the-art digital electronics designed to give you years of reliable precise oxygen measurements in variety of
industrial oxygen applications.
To obtain maximum performance from your new oxygen transmitter, please read and follow the guidelines
provided in this Owner’s Manual.
Every effort has been made to select the most reliable state of the art materials and components, to design the
transmitter for superior performance and minimal cost of ownership. This transmitter was tested thoroughly by the
manufacturer prior to shipment for best performance.
However, modern electronic devices do require service from time to time. The warranty included herein plus a staff
of trained professional technicians to quickly service your transmitter is your assurance that we stand behind every
transmitter sold.
The serial number of this transmitter may be found on the inside the transmitter. You should note the serial
number in the space provided and retains this Owner’s Manual as a permanent record of your purchase, for future
reference and for warranty considerations.
Serial Number: _______________________
Advanced Instruments Inc. appreciates your business and pledges to make every effort to maintain the highest
possible quality standards with respect to product design, manufacturing and service.
Page 4

4
2 Quality Control Certification
Date:
Customer: Order No.: Pass
Model
( ) GPR-2500 Oxygen Transmitter
( ) GPR-2500MO Oxygen Purity Transmitter
Sensor
( ) GPR-11-32-4 Oxygen Sensor (GPR-2500)
( ) XLT-11-24-4 Oxygen Sensor (GPR-2500)
( ) GPR-11-120-OP Oxygen Purity Sensor (GPR-2500MO)
( ) Other _____________________
Serial Nos.:
Analyzer: Sensor:
Accessories:
Owner’s Manual
Configuration:
( ) A-1151-E-L2 PCB Assembly Main / Display (GPR-2500)
( ) A-1151-E-L3 PCB Assembly Main / Display (GPR-2500MO)
Software rev:
( ) Ranges GPR-2500: 0-1%, 0-5%, 0-10%, 0-25%
( ) Range GPR-2500MO: 0-100%
Power: 12-36V DC two wire loop power
NEMA 4 rated wall mount enclosure
Barometric pressure compensation
Test:
Default zero (without sensor)
Default span @ 40uA (GPR-2500) or 20uA (GPR-2500MO)
Analog signal output 4-20mA full scale
Calibrates with adequate span adjustment within 10-50% FS
Baseline drift on zero gas < ± 2% FS over 24 hour period
Noise level < ± 1.0% FS
Span adjustment within 10-50% FS
Final:
Overall inspection for physical defects
Options:
Notes:
1 of 1 analyzer due ASAP
Page 5

5
3 Safety
General
This section summarizes the essential precautions applicable to the GPR-2500/2500MO Oxygen Transmitter.
Additional precautions specific to individual transmitter are contained in the following sections of this manual. To
operate the transmitter safely and obtain maximum performance follow the basic guidelines outlined in this
Owner’s Manual.
Caution: This symbol is used throughout the Owner’s Manual to CAUTION and alert the user to recommended
safety and/or operating guidelines.
Danger: This symbol is used throughout the Owner’s Manual to identify sources of immediate DANGER such as
the presence of hazardous voltages.
Read Instructions: Before operating the transmitter read the instructions.
Retain Instructions: The safety precautions and operating instructions found in the Owner’s Manual should be
retained for future reference.
Heed Warnings: Follow all warnings on the transmitter, accessories (if any) and in this Owner’s Manual.
Follow Instructions: Observe all precautions and operating instructions. Failure to do so may result in personal
injury or damage to the transmitter.
Pressure and Flow
Inlet Pressure: GPR-2500/2500MO ppm Oxygen Transmitters are designed for flowing samples, equipped with
1/8” bulkhead tube fitting connections on the side of the unit (unless otherwise indicated, either fitting can serve as
inlet or vent) and are intended to operate at positive pressure regulated to between 5-30 psig.
Caution: If the GPR-2500 is equipped with the optional H2S sample system, the inlet pressure must not exceed 30
psig.
Outlet Pressure: The sample gas vent pressure should be atmospheric.
Installation
Oxygen Sensor: DO NOT open the sensor. The sensor contains a corrosive liquid electrolyte that could be
harmful if touched or ingested, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet contained in the Owner’s Manual appendix.
Avoid contact with any liquid or crystal type powder in or around the sensor or sensor housing, as either could be a
form of electrolyte. Leaking sensors should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Mounting: The transmitter is approved for indoor or outdoor use. Mount as recommended by the manufacturer.
Power: Supply power to the transmitter only as rated by the specification or markings on the transmitter
enclosure. The wiring that connects the transmitter to the power source should be installed in accordance with
recognized electrical standards and so they are not pinched particularly near the power source and the point where
they attach to the transmitter. Never yank wiring to remove it from an outlet or from the transmitter.
Operating Temperature: The maximum operating temperature is 45º C.
Heat: Situate and store the transmitter away from sources of heat.
Liquid and Object Entry: The transmitter should not be immersed in any liquid. Care should be taken so that
liquids are not spilled into and objects do not fall into the inside of the transmitter.
Page 6

6
Handling: Do not use force when using the switches and knobs. Before moving your transmitter be sure to
disconnect the wiring/power cord and any cables connected to the output terminals located on the transmitter.
Maintenance
Serviceability: Except for replacing the oxygen sensor, there are no parts inside the transmitter for the operator
to service.
Only trained personnel with the authorization of their supervisor should conduct maintenance.
Oxygen Sensor: DO NOT open the sensor. The sensor contains a corrosive liquid electrolyte that could be
harmful if touched or ingested, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet contained in the Owner’s Manual appendix.
Avoid contact with any liquid or crystal type powder in or around the sensor or sensor housing, as either could be a
form of electrolyte. Leaking sensors should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Troubleshooting: Consult the guidelines in Section 8 for advice on the common operating errors before
concluding that your transmitter is faulty.
Do not attempt to service the transmitter beyond those means described in this Owner’s Manual. Do not attempt to
make repairs by yourself as this will void the warranty as per Section 10 and may result in electrical shock, injury or
damage. All other servicing should be referred to qualified service personnel.
Cleaning: The transmitter should be cleaned only as recommended by the manufacturer. Wipe off dust and dirt
from the outside of the unit with a soft damp cloth then dry immediately. Do not use solvents or chemicals.
Nonuse Periods: If the transmitter is equipped with a range switch advance the switch to the OFF position and
disconnect the power when the transmitter is left unused for a long period of time.
4 Features & Specifications
See last page, this page left blank intentionally.
Page 7

7
5 Operation
Principle of Operation
The GPR-2500/2500MO oxygen transmitter incorporates a variety of ppm range advanced galvanic fuel cell type
sensors. The transmitter is configured in a general purpose NEMA 4X rated enclosure and meets the intrinsic safety
standards required for use in Class 1, Division 1, Groups A, B, C, D hazardous areas when operated in conjunction
with the manufacturer’s recommended optional intrinsic safety barriers.
Advanced Galvanic Sensor Technology:
The sensors function on the same principle and are specific for oxygen. They measure the partial pressure of
oxygen from low ppm to 100% levels in inert gases, gaseous hydrocarbons, helium, hydrogen, mixed gases, acid
gas streams and ambient air. Oxygen, the fuel for this electrochemical transducer, diffusing into the sensor reacts
chemically at the sensing electrode to produce an electrical current output proportional to the oxygen concentration
in the gas phase. The sensor’s signal output is linear over all ranges and remains virtually constant over its useful
life. The sensor requires no maintenance and is easily and safely replaced at the end of its useful life.
Proprietary advancements in design and chemistry add significant advantages to an extremely versatile oxygen
sensing technology. Sensors for low ppm analysis recover from air to ppm levels in minutes, exhibit longer life and
reliable quality. The expected life of our new generation of percentage range sensors now range to five and ten
years with faster response times and greater stability. Another significant development involves expanding the
operating temperature range for percentage range sensors from -30°C to 50°C.
Electronics:
The signal generated by the sensor is processed by state of the art low power micro-processor based digital
circuitry. The first stage amplifies the signal. The second stage eliminates the low frequency noise. The third stage
employs a high frequency filter and compensates for signal output variations caused by ambient temperature
changes. The result is a very stable signal. Sample oxygen is analyzed very accurately. Response time of 90% of
full scale is less than 10 seconds (actual experience may vary due to the integrity of sample line connections, dead
volume and flow rate selected) on all ranges under ambient monitoring conditions. Sensitivity is typically 0.5% of
full scale low range. Oxygen readings may be recorded by an external device via the 0-1V signal output jack.
A 4-20mA signal output is provided from a two-wire 12-36VDC loop power source such as a PLC and is represented
on full scale oxygen readings to an external device. When operated in conjunction with the manufacturer’s
recommended optional intrinsic safety barriers the GPR-2500/GPR-2500MO meets the intrinsic safety standards
required for use in Class 1, Division 1, Groups A, B, C, D hazardous areas.
Sample System:
The GPR-2500/2500MO is supplied without a sample conditioning system for maximum portability. However the
sample must be properly presented to the sensor to ensure an accurate measurement. Users interested in adding
their own sample conditioning system should consult the factory. Advanced Instruments Inc. offers a full line of
sample handling, conditioning and expertise to meet your application requirements. Contact us at 909-392-6900 or
e-mail us at aii2@earthlink.net
Page 8
8
Pressure & Flow
All electrochemical oxygen sensors respond to partial pressure changes in oxygen. The inlet pressure must always
be higher than the pressure at the outlet vent which is normally at atmospheric pressure.
Flow Through Configuration:
The sensor is exposed to sample gas that must flow or be drawn through
metal tubing inside the transmitter. The GPR-2500/2500MO internal
sample system includes 1/8” compression tube inlet and vent fittings, a
stainless steel sensor housing with an o-ring seal to prevent the leakage
of air and stainless steel tubing.
Flow rates of 1-5 SCFH cause no appreciable change in the oxygen
reading. However, flow rates above 5 SCFH generate backpressure and
erroneous oxygen readings because the diameter of the integral tubing
cannot evacuate the sample gas at the higher flow rate. The direction the
sample gas flows is not important, thus either tube fitting can serve as the
inlet or vent – just not simultaneously.
A flow indicator with an integral metering valve upstream of the sensor is
recommended as a means of controlling the flow rate of the sample gas.
A flow rate of 2 SCFH or 1 liter per minute is recommended for optimum
performance.
Caution: Do not place your finger over the vent (it pressurizes the
sensor) to test the flow indicator when gas is flowing to the sensor.
Removing your finger (the restriction) generates a vacuum on the sensor
and may damage the sensor (voiding the sensor warranty).
To avoid generating a vacuum on the sensor (as described above) during operation, always select and install the
vent fitting first and remove the vent fitting last.
Application Pressure - Positive:
A flow indicator with integral metering valve (GPR-2500/2500MO option) positioned upstream of
the sensor is recommended for controlling the sample flow rate between 1-5 SCFH. To reduce the
possibility of leakage for low ppm measurements, position a metering needle valve upstream of
the sensor to control the flow rate and position a flow indicator downstream of the sensor.
If necessary, a pressure regulator (with a metallic diaphragm is recommended for optimum
accuracy, the use of diaphragms of more permeable materials may result in erroneous readings)
upstream of the flow control valve should be used to regulate the inlet pressure between 5-30
psig.
Application Pressure - Atmospheric or Slightly Negative:
For accurate ppm range oxygen measurements, an optional external sampling pump should be positioned
downstream of the sensor to draw the sample from the process, by the sensor and out to atmosphere. A flow
meter is generally not necessary to obtain the recommended flow rate with most sampling pumps.
Caution: If the transmitter is equipped with an optional flow indicator with integral metering valve or a metering
flow control valve upstream of the sensor - open the metering valve completely to avoid drawing a vacuum on the
sensor and placing an undue burden on the pump.
If pump loading is a consideration, a second throttle valve on the pump’s inlet side may be necessary to provide a
bypass path so the sample flow rate is within the above parameters.
Page 9

9
To avoid erroneous oxygen readings and damaging the sensor:
¾ Do not place your finger over the vent (it pressurizes the sensor) to test the flow indicator when gas is flowing
to the sensor. Removing your finger (the restriction) generates a vacuum on the sensor and may damage the
sensor (voiding the sensor warranty).
¾ Assure there are no restrictions in the sample or vent lines
¾ Avoid drawing a vacuum that exceeds 14” of water column pressure – unless done gradually
¾ Avoid excessive flow rates above 5 SCFH which generate backpressure on the sensor.
¾ Avoid sudden releases of backpressure that can severely damage the sensor.
¾ Avoid the collection of particulates, liquids or condensation collect on the sensor that could block the diffusion
of oxygen into the sensor.
¾ If the transmitter is equipped with an optional integral sampling pump (positioned downstream of the sensor)
and a flow control metering valve (positioned upstream of the sensor), completely open the flow control
metering valve to avoid drawing a vacuum on the sensor and placing an undue burden on the pump.
Page 10
10
Calibration & Accuracy
Single Point Calibration: As previously described the galvanic oxygen sensor generates an electrical current
sensor exhibiting an absolute zero, e.g. the sensor does not generate a current output in the absence of oxygen.
Given these linearity and absolute zero properties, single point calibration is possible.
Pressure: Because sensors are sensitive to the partial pressure of oxygen in the sample gas their output is a
function of the number of molecules of oxygen 'per unit volume'. Readouts in percent are permissible only when
the total pressure of the sample gas being analyzed remains constant. The pressure of the sample gas and that of
the calibration gas(es) must be the same (reality < 1-2 psi).
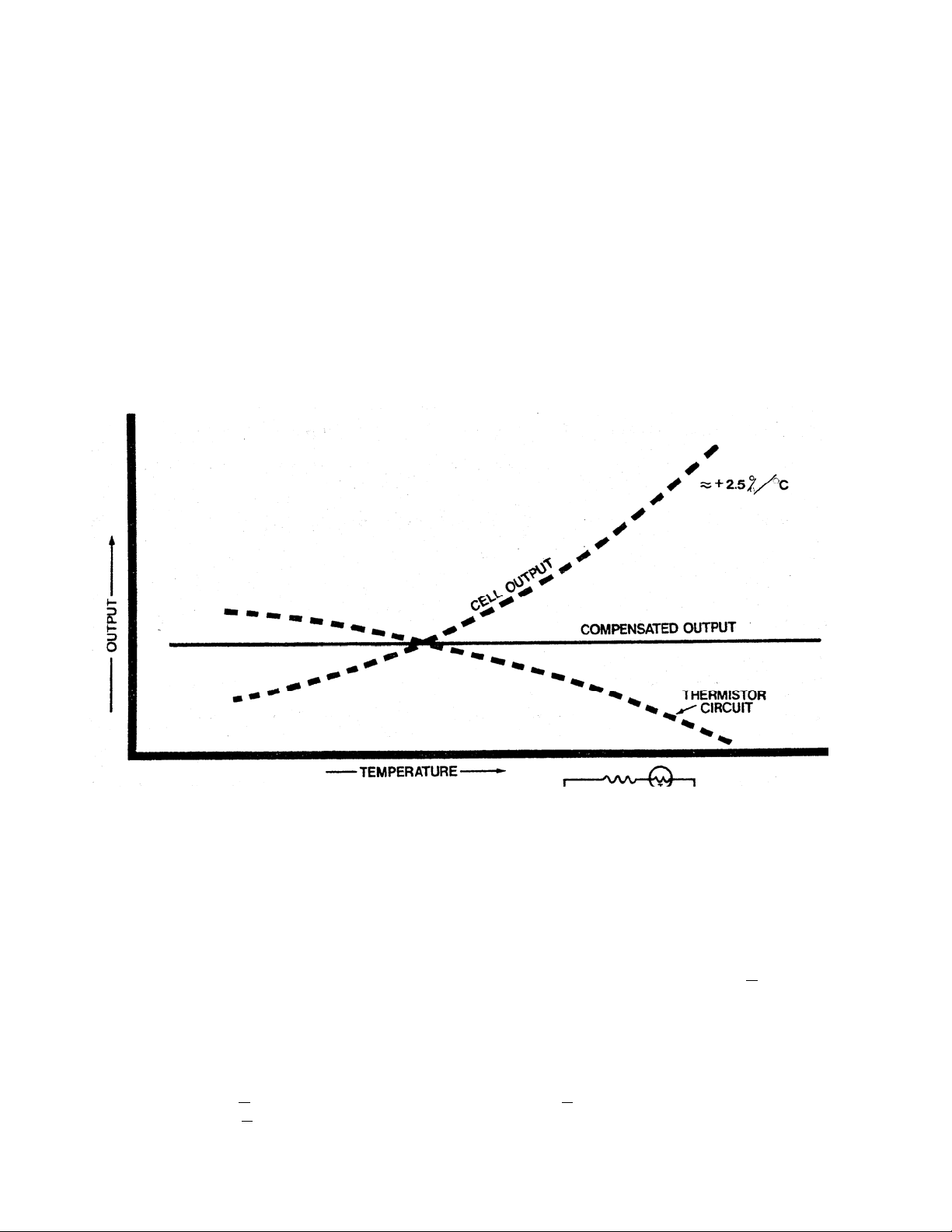
Temperature: The rate oxygen molecules diffuse into the sensor is controlled by a Teflon membrane otherwise
known as an 'oxygen diffusion limiting barrier' and all diffusion processes are temperature sensitive, the fact the
sensor's electrical output will vary with temperature is normal. This variation is relatively constant 2.5% per ºC. A
temperature compensation circuit employing a thermistor offsets this effect with an accuracy of +5% or better and
generates an output function that is independent of temperature. There is no error if the calibration and sampling
are performed at the same temperature or if the measurement is made immediately after calibration. Lastly, small
temperature variations of 10-15º produce < +1% error.
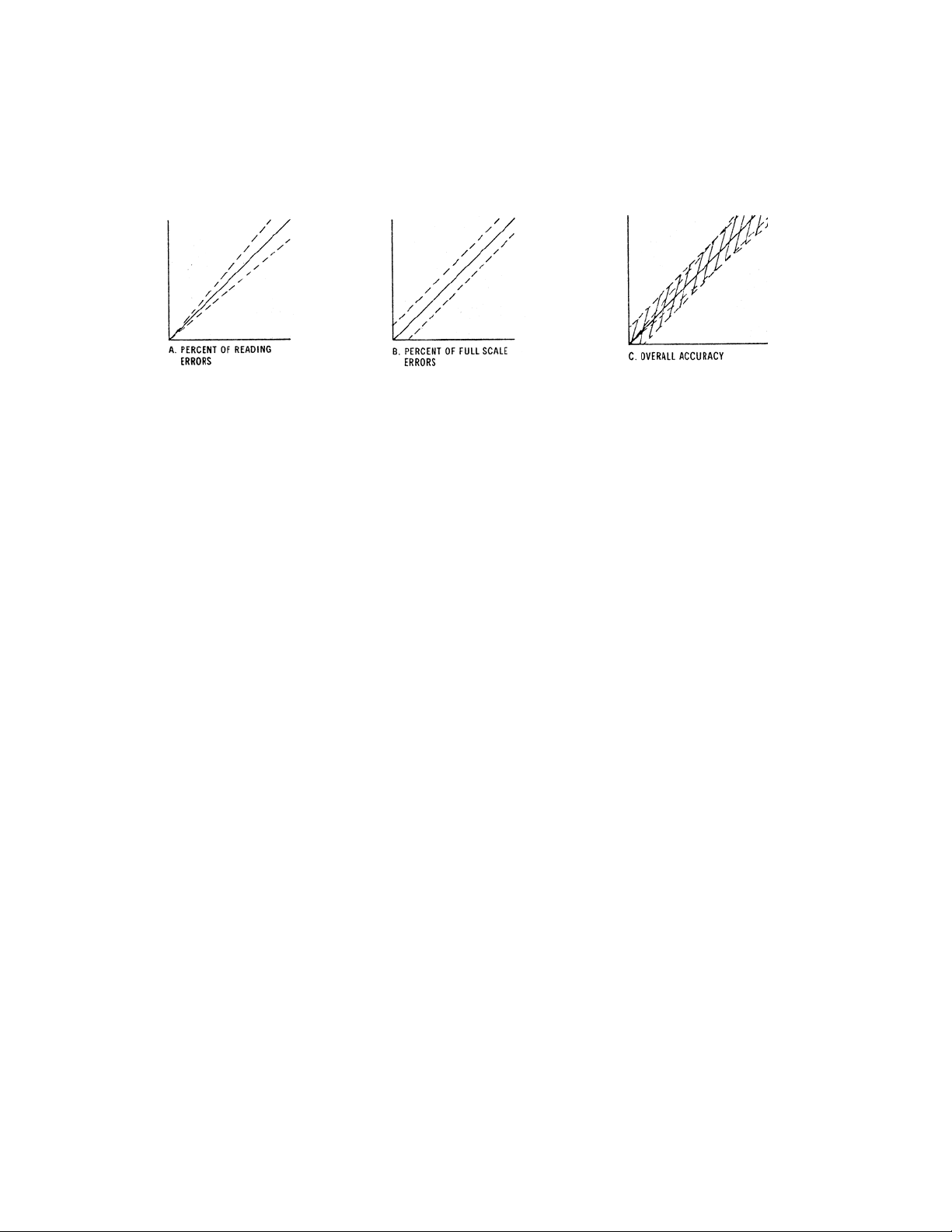
Accuracy:
In light of the above parameters, the overall accuracy of an transmitter is affected by two types of
errors: 1) those producing 'percent of reading errors', illustrated by Graph A below, such as +
5% temperature
compensation
circuit, tolerances of range resistors and the 'play' in the potentiometer used to make span
adjustments and 2) those producing 'percent of full scale errors', illustrated by Graph B, such as +1-2% linearity
errors in readout devices, which are really minimal due to today's technology and the fact that other errors are
'spanned out' during calibration.
Graph C illustrates these 'worse case' specifications that are typically used to develop an transmitter's overall
accuracy statement of +
1% of full scale at constant temperature or +5% over the operating temperature range.
QC testing is typically <+
0.5% prior to shipment.
Page 11
11
Example: As illustrated by Graph A any error, play in the multi-turn span pot or the temperature compensation
circuit, during a span adjustment at 20.9% (air) of full scale range would be multiplied by a factor of 4.78
(100/20.9) if used for measurements of 95-100% oxygen concentrations. Conversely, an error during a span
adjustment at 100% of full scale range is reduced proportionately for measurements of lower oxygen
concentrations.
Recommendation: Calibrating with a span gas approximating 80% of the full scale range one or two ranges
higher than the full scale range of interest is recommended for 'optimum calibration accuracy'. Always calibrate at
the same temperature and pressure of the sample gas stream.
Start-up
The GPR-2500/2500MO Oxygen Transmitters has been calibrated at the factory prior to shipment and is fully
operational from the shipping container. The ppm oxygen sensor has been removed and packaged in a nitrogen
atmosphere to assure optimum performance. Once installed, we recommend the user allow the transmitters to
stabilize for 30 minutes and then recalibrate the device as instructed below.
Installation Considerations:
The GPR-2500/2500MO consists of an electronic module, sensor housing and sample 1/8” sample inlet and vent
connections housed in a 4”W x 9”H x 3”D enclosure NEMA 4 rated enclosure suitable for wall mounting.
For optimum accuracy zero and calibrate a ppm transmitter after it has been allowed to stabilize, typically 24-36
hours after installation. Assuming the initial zero is performed according to the procedure described herein, the
analyzer should not require zeroing again until the either the sensor is replaced or a change is made to the sample
system or gas lines. Following the initial zero and calibration, the analyzer should not require span calibration again
for up to 3 months under “normal” application conditions as described in the published specifications.
Note: As described below, zeroing the transmitter is recommended for measurements below 1 ppm. The low end
sensitivity (zero capability) has been verified at the factory; however, no ZERO OFFSET adjustment has been
made. A factory adjustment would be meaningless because of the difference in sample systems and leakage
factors between the factory set-up and the actual application conditions
¾ Assemble the necessary hardware for mounting the transmitter and optional components - such as coalescing
or particulate filters and pumps, 1/8” metal or plastic tubing for interconnecting the transmitter and optional
components.
¾ Review the application conditions to ensure the sample is suitable for analysis.
¾ Temperature: The sample must be sufficiently cooled before it enters the transmitter and any optional
components. A coiled 10 foot length of ¼” stainless steel tubing is sufficient for cooling sample gases as high
as 1,800ºF to ambient.
Page 12
12
¾ Pressure & Flow: As described above.
¾ Moisture & Particulates: Prevent water and/or particulates from entering the sample system. They can clog the
tubing and damage the optional components such as pumps, scrubbers or sensors. Installation of a suitable
coalescing or particulate filter is required to remove condensation, moisture and/or particulates from the
sample gas to prevent erroneous analysis readings and damage to the sensor or optional components. Consult
the factory for recommendations concerning the proper selection and installation of components.
¾ Contaminants: A gas scrubber and flow indicator with integral metering valve are required upstream of the
transmitter to remove interfering gases such as oxides of sulfur and nitrogen or hydrogen sulfide that can
produce false readings and reduce the expected life of the sensor. Installation of a suitable scrubber is required
to remove the contaminant from the sample gas to prevent erroneous analysis readings and damage to the
sensor or optional components. Consult the factory for recommendations concerning the proper selection and
installation of components.
¾ Gas connections: Inlet and outlet vent gas lines require 1/8” diameter tubing preferably metal.
¾ Power connection: Locate a source of AC power to meet area classification and to plug in the charging adapter.
¾ Zero calibration (required only for very low percentage range measurements).
¾ Span calibration – Users are responsible for certified span gas cylinder, regulator and flow control valve.
Mounting the Transmitter:
The GPR-2500/2500MO enclosure is 4”Wx9”Hx3”D configuration is
designed to be mounted directly to any flat vertical surface, wall or
bulkhead plate with the appropriate screws. To facilitate servicing
the interior of the transmitters, position it approximately 5 feet off
the floor.
1. Remove the four (4) screws securing the top section of the
enclosure, set them aside for reinstallation and raise the hinged
top section 180º until it locks in place.
2. Locate the mounting holes cast into the bottom section of the
enclosure and the black sensor. Orient the enclosure by locating
the sensor at six (6) o’clock.
3. Secure the bottom section of the enclosure to a vertical surface
approximately 5 feet from the floor or a level accessible to
service personnel. This requires the user to supply four (4)
additional proper size screws and anchors.
4. Caution: Do not remove or discard the gaskets from either the
enclosure or junction box. Failure to reinstall either gasket will
void the NEMA 4 rating and RFI protection.
5. The transmitters design provides protection from RFI that is
maintained by leaving specific mating areas of the enclosure unpainted to maintain conductivity the gasket, top
and bottom sections of the enclosure. These unpainted areas are protected by gaskets and contribute to
maintaining the NEMA 4 rating. Do not paint these areas. Painting will negate the RFI protection.
6. As described below the power connection is made through the junction box on the left side of the enclosure.
Page 13

13
Gas Connections:
The GPR-2500/2500MO with its standard flow through configuration is designed for positive pressure samples and
requires connections for incoming sample and outgoing vent lines. Zero and span inlet ports are offered as part of
the optional sample systems. The user is responsible for calibration gases and the required components, see
below.
With the pressure regulated to between 5-30 psig, flow rates of 1-5 SCFH cause no appreciable change in the
oxygen reading. However, flow rates above 5 SCFH generate backpressure and erroneous oxygen readings
because the diameter of the integral tubing cannot evacuate the sample gas at the higher flow rate. A flow
indicator with an integral metering valve upstream of the sensor is recommended as a means of controlling the
flow rate of the sample gas. A flow rate of 2 SCFH or 1 liter per minute is recommended for optimum performance.
Caution: Do not place your finger over the vent (it pressurizes the sensor) to test the flow indicator when gas is
flowing to the sensor. Removing your finger (the restriction) generates a vacuum on the sensor and may damage
the sensor (voiding the sensor warranty).
Procedure:
1. Caution: Do not change the factory setting until instructed to do in this manual.
2. Designate one of the bulkhead tube fittings as the VENT and the other SAMPL E.
3. Regulate the pressure as described in Controlling Pressure & Flow above.
4. Connect a 1/8” vent line to the compression fitting to be used for venting the sample.
5. Connect a 1/8” ZERO, SPAN or SAMPLE line to the fitting designated SAMPLE.
6. If equipped with optional fittings and/or sample system, connect the ZERO and SPAN gas lines.
7. Allow gas to flow through the transmitters and set the flow rate to 2 SCFH.
Page 14

14
Power Connection:
Remove the front cover of the junction box located on left side of the transmitters by removing the four (4) screws
securing the cover and set them aside for reinstallation.
To assure proper grounding, connect the 4-20mA signal output to the external device (PLC, DCS, etc.) before
attempting any zero or span adjustments.
Power requirements consist of a two wire shielded cable and a 12-36V DC with negative ground power supply.
Procedure:
1. Loosen the n u t on the cable gland.
2. Separate the shielding from the wires of the cable.
3. Thread the wires through the cable gland into the inside of the
junction box.
4. Connect the two wires to the two (2) screw type terminals of the
barrier strip inside the junction box.
5. Ensure the positive and negative terminals of the power supply are
connected to the appropriate terminals of the barrier strip as
marked.
6. Connect the shielding of the cable to the copper ground screw inside
the junction box.
7. Replace the junction box cover ensuring the gaskets are in place and
tighten the four (4) screws.
8. Tighten the cable gland to maintain NEMA 4 rating.
Hazardous Area Installation:
The GPR-2500/2500MO transmitters may be installed in a hazardous
area with specific intrinsic safety barriers and a barrier enclosure
approved for use with the safety barrier selected.
MTL 702 type barriers and a 24VDC power supply with two (2) wire shielded cable are recommended.
Requirements include a 4-20mADC two (2) wire signal and a power requirement of 20mADC per channel at 24VDC
minimum.
Refer to drawing A-2439 for wiring instructions. The following chart identifies the required wire based on the
distance from the safety barriers to the two wire transmitters.
4,500 ft. – 22 AWG
7,200 ft. – 20 AWG
11,500 ft. – 18 AWG
18,500 ft. – 16 AWG
29,500 ft. – 14 AWG
Page 15

15
Connections – Optional Intrinsic Safety Barrier:
1. Non-hazardous area: Barrier terminals (1), (2)
2. Hazardous area: Barrier terminals (3), (4)
3. Direct measurement of 4-20mA: Reference (C1), connect the current measuring device at terminal (2) of the
barrier and the negative (-) terminal from the power source as shown below.
4. Convert 4-20mA current to voltage: Reference (C2), connect a resistor (RL) maximum value 850Ω between
terminal (2) of the barrier and the negative (-) terminal from the power source and measure the voltage across
the resistor.
5. Example: To convert the 4-20mA current for output to a PLC requiring 1-5V, follow the above procedure using
a 250Ω resistor (RL).
Hazardous Area Operation:
When used in conjunction with the optional MTL 702, third party certified, intrinsic safety barriers, the design of
the GPR-1500/2500 Series Oxygen Transmitters meet recognized standards as intrinsically safe for operation in
Class I, II, III; Division I, II; Groups A-G hazardous areas.
Note: Locate the optional intrinsic safety barrier as close to the power source in the non-hazardous area as
possible.
Page 16

16
Output connection:
The 4-20mA current output is obtained by connecting the current measuring device between the negative terminal
of power source and the negative terminal, marked (-), located in the junction box of the transmitters. The positive
current flow is from pin 1 to pin 2 and from pin 2 to ground through the external load.
To check the signal output of the 4-20mA E/I integrated circuit connect an ammeter, as illustrated below, as the
measuring device and confirm the output is within +
0.1mA of 4mA.
Power 12-36V DC To Transmitters
Terminal Strip
Caution: To assure proper grounding, connect the 4-20mA signal output to the external device (PLC, DCS, etc.)
before attempting any zero or span adjustments.
Page 17

17
Installing the Oxygen Sensor
The GPR-2500/2500MO Oxygen Transmitter is normally equipped with an integral oxygen sensor. It has been
tested and calibrated by the manufacturer prior to shipment and are fully operational from the shipping container.
However, when the application requires a remote sensor (external to the electronics enclosure) or other special
circumstances, the oxygen sensor will be packaged separately and must be installed prior to operating the
transmitter. If the sensor has not been installed at the factory, it will be necessary to install the sensor in the field.
Caution: All transmitters must be calibrated once the installation has been completed and periodically thereafter
as described below. Following the initial installation and calibration, allow the transmitters to stabilize for 24 hours
and calibrate with certified span gas.
Caution: DO NOT open the oxygen sensor. The sensor contains a corrosive liquid electrolyte that could be harmful
if touched or ingested, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet contained in the Owner’s Manual appendix. Avoid
contact with any liquid or crystal type powder in or around the sensor or sensor housing, as either could be a form
of electrolyte. Leaking sensors should be disposed of in manner similar to that of a common battery in accordance
with local regulations.
Caution: Do not change the factory settings until instructed to do in this manual.
Integral Oxygen Sensor:
1. Remove the four (4) screws securing the top section of
the enclosure, set them aside for reinstallation and raise
the hinged top section 180º until it locks in place.
2. Caution: Do not remove or discard the gaskets from
either the enclosure or junction box. Failure to reinstall
either gasket will void the NEMA 4 rating and RFI
protection.
3. The transmitters design provides protection from RFI
that is maintained by leaving specific mating areas of the
enclosure unpainted to maintain conductivity the gasket,
top and bottom sections of the enclosure. These
unpainted areas are protected by gaskets and contribute
to maintaining the NEMA 4 rating. Do not paint these
areas. Painting will negate the RFI protection.
4. Remove the oxygen sensor from the bag.
5. Screw the oxygen sensor into the sensor flow housing,
equipped with elbows and tubing, finger tighten plus one
half (1/2) turn to ensure a good seal from the o-ring
affixed to the sensor.
6. Remove the shorting device (looped wire) from the receptacle located at the rear of the sensor. Minimize the
time the sensor is exposed to ambient air.
7. Assure the keyway registration of the female plug on the cable and male receptacle on the sensor match up.
8. Push the female plug (including the knurled lock nut) molded to the cable into the male receptacle attached to
the new sensor.
9. Screw the knurled lock nut attached the cable onto to the male connector attached to the sensor, tighten
finger tight plus ¼ turn.
Page 18

18
10. Replace the front cover of the transmitter and ensure that the gasket is replaced as well to maintain CE
approval and NEMA 4 rating.
11. Tighten the four (4) screws to secure the front cover.
12. Connect the gas lines, vent line first, as previously described.
13. Proceed to calibration.
Remote Oxygen Sensor:
Applications requiring the sensor to be located remotely from the electronics dictate the
separate packaging and shipment of the electronics enclosure, oxygen sensor and
sensor flow housing. The appropriate length of cable to connect the sensor to the
electronics is supplied and connected to the electronics. To install the remote sensor:
1. Locate the sensor flow housing and note the through holes in the flanged sections.
2. Identify the spot for installation.
3. Using two (2) 6/32 screws of the appropriate type and length secure the sensor flow
housing to a flat surface, the position illustrated at the right is recommended for
optimum performance.
4. Remove the oxygen sensor from the bag.
5. Screw the oxygen sensor into the sensor flow housing, equipped with elbows and
tubing, finger tighten plus one half (1/2) turn to ensure a good seal from the o-ring
affixed to the sensor.
6. Remove the shorting device (looped wire) from the receptacle located at the rear of
the sensor. Minimize the time the sensor is exposed to ambient air.
7. Assure the keyway registration of the female plug on the cable and male receptacle
on the sensor match up.
8. Push the female plug (including the knurled lock nut) molded to the cable into the
male receptacle attached to the new sensor.
9. Screw the knurled lock nut attached the cable onto to the male connector attached
to the sensor, tighten finger tight plus ¼ turn.
10. Connect the 1/8” diameter gas lines, vent line first, as previously described.
11. Proceed to calibration.
Page 19

19
Span Gas Preparation
Caution: Do not contaminate the span gas cylinder when connecting the regulator. Bleed the air filled regulator
(faster and more reliable than simply flowing the span gas) before attempting the initial calibration of the
instrument.
Required components:
¾ Certified span gas cylinder with an oxygen concentration, balance nitrogen, approximating 80% of the full scale
range above the intended measuring range.
¾ Regulator to reduce pressure to between 5 and 30 psig.
¾ Flow meter to set the flow between 1-5 SCFH,
¾ 2 lengths of 1/8” dia. metal tubing measuring 4-6 ft. in length.
¾ Suitable fittings and 1/8” dia. metal tubing to connect the regulator to the flow meter inlet
¾ Suitable fitting and 1/8” dia. metal tubing to connect from the flow meter vent to tube fitting designated
SAMPLE IN on the GPR-1200.
Procedure:
1. With the span gas cylinder valve closed, install the regulator on the cylinder.
2. Open the regulator’s exit valve and partially open the pressure regulator’s control knob.
3. Open slightly the cylinder valve.
4. Loosen the nut connecting the regulator to the cylinder and bleed the pressure regulator.
5. Retighten the nut connecting the regulator to the cylinder
6. Adjust the regulator exit valve and slowly bleed the pressure regulator.
7. Open the cylinder valve completely.
8. Set the pressure between 5-30 psig using the pressure regulator’s control knob.
Caution: Do not exceed the recommended flow rate. Excessive flow rate could cause the backpressure on the
sensor and may result in erroneous readings and permanent damage to the sensor.
Page 20

20
Establishing Power to the Electronics:
Once the two wires of the shielded cable are properly connected to the
terminals inside the junction box as described above, connect the other
end of the two wires to a suitable 12-36V DC power supply with
negative ground such as a PLC, DCS, etc.
The digital display responds instantaneously. When power is applied,
the transmitter performs several diagnostic system status checks termed
“START-UP TEST” as illustrated below:
START-UP TEST
ELECTRONICS – PASS
LOOP POWER – PASS
TEMP SENSOR – PASS
BAROMETRIC SENSOR – PASS
REV. 1.61
Note: The transmitter display defaults to the sampling mode when 30
seconds elapses without user interface.
3.3 %
AUTO SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
Menu Navigation:
The four (4) pushbuttons located on the front of the transmitter operate the micro-processor:
1. green ENTER (select)
2. yellow UP ARROW
3. yellow DOWN ARRO W
4. blue MENU (escape)
Main Menu:
Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key:
Page 21

21
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
Range Selection:
The GPR-2500 Oxygen Transmitter is equipped with four (4) standard measuring ranges (see specification) and
provides users with a choice of sampling modes. By accessing the MAIN MENU, users may select either the AUTO
SAMPLING (ranging) or MANUAL SAMPLING (to lock on a single range) mode.
Note: For calibration purposes, use of the AUTO SAMPLE mode is recommended. However, the user can select the
full scale MANUAL SAMPLE RANGE for calibration as dictated by the accuracy of the analysis required – for
example, a span gas with an 8% oxygen concentration with the balance nitrogen would dictate the use of the 010% full scale range for calibration and 0-1%, 0-5% or 0-10% ranges for measuring.
The GPR-2500MO Oxygen Purity Transmitter is equipped with one (1) standard measuring range of 0-100%;
accordingly, there is no difference between auto and manual sampling.
Procedure - Auto Sampling:
1. Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
2. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight AUTO SAMPLE.
3. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
4. The display returns to the sampling mode:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
The display will shift to the next higher range when the oxygen reading (actually the sensor’s signal output)
exceeds 99.9% of the upper limit of the current range. The display will shift to the next lower range when the
oxygen reading drops to 85% of the upper limit of the next lower range.
3.3 %
AUTO SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
For example, if the transmitter is reading 1% on the 0-10% range and an upset occurs, the display will shift to the
0-25% range when the oxygen reading exceeds 9.9%. Conversely, once the upset condition is corrected, the
display will shift back to the 0-10% range when the oxygen reading drops to 8.5%.
Page 22

22
Procedure - Manual Sampling:
1. Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
2. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight MANUAL SAMPLE.
3. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
4. The following displays appears:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
>>>
MANUAL RANGE
25%
10%
5%
1%
5. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight the desired RANGE.
6. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
7. The following display appears with the range selected and oxygen concentration of the sample gas:
3.3 %
MANUAL SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
8. The display will not shift automatically. Instead, when the oxygen reading (actually the sensor’s signal
output) exceeds 110% of the upper limit of the current range an OVER RANGE warning will be displayed.
13.00 %
OVERRANGE
MANUAL SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
Once the OVER RANGE warning appears the user must advance the transmitter to the next higher range via the
menu and keypad Press MENU, select MANUAL SAMPLING, press ENTER, select the appropriate MANUAL RANGE
and press ENTER again.
Page 23

23
An over range condition on a 0-100% range indicates an error introduced during the previous calibration. An over
range condition GPR-2500 transmitters equipped with a 0-100% range indicates an error introduced during the
previous calibration. If the over range condition is less than 100.9%, the OVERRANGE warning is not displayed
If the over range condition exceeds 101.0%, the LCD displays the “OVERRANGE” warning in a reversed black
background. This condition indicates an error introduced during the previous calibration, at this point the analyzer
should be calibrated.
Note: To enhance viewing the LCD display, all analyzers and transmitters are equipped with a backlit LCD display.
Due to the limited power availability of the GPR-2500 series of two wire loop powered transmitters, the backlit LCD
feature does not operate when the signal output is less than 10mA.
Start-Up is complete . . . proceed to Calibration
Page 24

24
Zero Calibration
In theory, the oxygen sensor produces no signal output when exposed to an oxygen free sample gas. However, the
transmitter will generate an oxygen reading when sampling oxygen free sample gas due to:
¾ Contamination or quality of the zero gas
¾ Minor leakage in the sample line connections
¾ Residual oxygen dissolved in the sensor’s electrolyte
¾ Tolerances of the electronic components
Recommendation: Zero calibration is recommended for measurements below 1% on the 0-1% range, as it is not
practical on higher ranges as described below.
Procedure:
Zero calibration should precede the span calibration and once performed should not have to be repeated with
subsequent span calibrations. Normally, zero calibrations are performed when a new sensor is installed or changes
are made in the sample system connections.
Refer to Span Calibration below for the detailed procedure. Differences include the displays illustrated below,
substituting a suitable zero gas for the span gas and allowing the transmitter 24 hours with flowing zero gas to
determine the true zero offset (a stable reading evidenced by a horizontal trend on an external recording device) of
the system before conducting the zero calibration. Note: 24 hours is required for the sensor to consume the
oxygen that has dissolved into the electrolyte inside the sensor (while exposed to air or percentage levels of
oxygen).
Thus, for the reasons above, it is not practical to zero a percent transmitter. Finding the true zero offset is not
always necessary particularly in the case of applications requiring higher level oxygen measurements because of
the low offset value, normally < 0.1 ppm, is not material to the accuracy of higher level measurements.
Note: Prematurely zeroing the transmitter can cause a negative reading in both the ZERO and SAMPLE modes.
1. Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
2. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight CALIBRATE.
3. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
4. Repeat to select ZERO CALIBRATE.
5. The following displays appear:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
>>>
CALIBRATION
SPAN CALIBRATE
ZERO CALIBRATE
DEFAULT SPAN
DEFAULT ZERO
24.5 C 100 KPA
Page 25

25
6. Press the ENTER key to calibrate or MENU key to abort and return to SAMPLING mode.
0.000 PPM
ZERO
CALIBRTION
ENTER TO CALIBRATE
MENU TO ABORT
7. Allow approximately 60 seconds for the calibration process while the processor determines whether the signal
output or reading has stabilized within 60% of the full scale low range.
8. Both the Zero Calibrate and Span Calibrate functions result in the following displays:
PASSED
CALIBRATION
OR
FAILED
CALIBRATION
Satisfying users that the zero offset is reasonably acceptable for their application can be accomplished much
quicker. Unless the zero gas is contaminated or there is a significant leak in the sample connections, the
transmitter should read less than 100 ppm oxygen within 5 minutes after being placed on zero gas.
The maximum zero calibration adjustment permitted is 60% of the lowest full scale range available, which normally
is 1 ppm. Thus the maximum zero calibration adjustment or zero offset is 6 ppm oxygen. Accordingly, the
transmitter’s ZERO has not been adjusted prior to shipment because the factory conditions are different from the
application condition at the user’s installation.
The maximum zero calibration adjustment permitted is 60% of the lowest full scale range available, which normally
is 1%. Thus the maximum zero calibration adjustment or zero offset is 0.6% oxygen. Accordingly, the transmitters’
ZERO has not been adjusted prior to shipment because the factory conditions are different from the application
condition at the user’s installation.
Accuracy due to manufacturer tolerances may result in a slight difference between the LCD display and the analog
output of the 4-20mA integrated circuit. However, the difference is less than 0.25% of range and falls well below
the specified accuracy of the transmitters.
Page 26

26
Factory Default Zero:
The software will eliminate any previous zero calibration adjustment and display the actual the signal output of the
sensor at a specified oxygen concentration. For example, assuming a zero gas is introduced, the display will reflect
an oxygen reading representing basically the zero calibration adjustment as described above. This feature allows
the user to test the sensor’s signal output without removing it from the sensor housing.
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
>>>
CALIBRATION
SPAN CALIBRATE
ZERO CALIBRATE
DEFAULT SPAN
DEFAULT ZERO
24.5 C 100 KPA
Span Calibration
Maximum drift from calibration temperature is approximately 0.11% of reading per °C. The transmitter has been
calibrated at the factory. However, in order to obtain reliable data, the transmitter must be calibrated at the initial
start-up and periodically thereafter. The maximum calibration interval recommended is approximately 3 months, or
as determined by the user’s application.
Calibration involves adjusting the transmitter electronics to the sensor’s signal output at a given oxygen standard,
e.g. a certified span gas with an oxygen content (balance nitrogen) approximating 80% of the next higher full scale
range above the intended measuring range is recommended for optimum accuracy, see Calibration and Accuracy.
Calibration with ambient or instrument air (20.9% or 209,000 ppm) is recommended when installing a new sensor
or when a certified gas is not available.
GPR-2500 General Service:
In standard configuration, the GPR-2500 can be calibrated by exposing the sensor to the readily available cost
effective and reliable 20.9% (209,000 ppm) oxygen concentration of ordinary atmospheric air or a certified span
gas with an oxygen concentration of 80-100% of full scale range balance nitrogen. For example, for a 0-25%
range, the span gas should be a certified grade between 19-23% oxygen preferably approximately 20.9% oxygen.
Caution: Regardless of configuration to assure proper grounding, connect the 4-20mA signal output to the external
device (PLC, DCS, etc.) before attempting any zero or span adjustments.
GPR-2500MO Medical Grade Oxygen:
For optimum accuracy calibrate (zero and span) the transmitters and then repeat both the zero and span
calibration after the transmitters has been allowed to stabilize for 24-36 hours after the initial calibration.
Caution: Do not attempt to span the transmitters with air or 21% oxygen and then operate it for either elevated
or high purity oxygen measurements – select one of the following recommendations.
Certification of medical grade oxygen: As mandated by the FDA, requires the use of certified zero (99.9% nitrogen
minimum purity) and span (99.2% oxygen minimum purity). For optimum accuracy and to take advantage of the
transmitters’ inherent accuracy of 0.1%, perform the zero and span calibration before each certification. Otherwise
calibrate every eight (8) hours.
Page 27

27
Non-medical grade oxygen: Assuming the initial zero is performed according to the procedure described herein,
the transmitter should not require zeroing again until the either the sensor is replaced or a change is made to the
sample system or gas lines. In most cases, a zero gas of 99% nitrogen purity and a span gas of 95-100% oxygen
purity are sufficient. Following the initial zero and calibration, the transmitters should not require span calibration
again for up to 3 months under “normal” application conditions as described in the published specifications.
Factory Default Span
The software will set the SPAN adjustment based on the average oxygen reading (actually the sensor’s signal
output) at a specified oxygen concentration. For example, when a span gas is introduced, the micro-processor will
display an oxygen reading within +
50% of the span gas value. This feature allows the user to test the sensor’s
signal output without removing it from the sensor housing.
1. Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
2. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight MANUAL SAMPLE.
3. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
4. The following displays appears:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
>>>
CALIBRATION
SPAN CALIBRATE
ZERO CALIBRATE
DEFAULT SPAN
DEFAULT ZERO
24.5 C 100 KPA
Manual Span
The user must ascertain that the oxygen reading (actually the sensor’s signal output) has reached a stable value
within the limits entered below before entering the span adjustment. Failure to do so will result in an error.
Preparation - Required components: Refer to Installing Span Gas section above.
1. Certified span gas cylinder with an oxygen concentration, balance nitrogen, approximating 80% of the full scale
range above the intended measuring range.
2. Regulator to reduce pressure to between 5 and 30 psig.
3. Flow meter to set the flow between 1-5 SCFH,
4. 2 lengths of 1/8” dia. metal tubing measuring 4-6 ft. in length.
5. Suitable fittings and 1/8” dia. metal tubing to connect the regulator to the flow meter inlet
6. Suitable fitting and 1/8” dia. me tal tubing to connect to the flow meter vent
7. 1/8” male NPT to tube adapter fitting to connect the 1/8” dia. metal tubing from the flow meter vent to the
mating male quick disconnect fitting supplied with the GPR-2500/2500MO.
Page 28

28
Procedure:
This procedure assumes a span gas under positive pressure and is recommended for a transmitter without an
optional sampling pump, which if installed downstream of the sensor should be placed in the OFF position and
disconnected so the vent is not restricted during calibration.
To assure an accurate calibration, the temperature and pressure of the span gas must closely approximate the
sample conditions.
For calibration purposes, use of the AUTO SAMPLE mode is recommended. However, the user can select the full
scale MANUAL SAMPLE RANGE for calibration as dictated by the accuracy of the analysis required – for example, a
span gas with an 8% oxygen concentration with the balance nitrogen would dictate the use of the 0-10% full scale
range for calibration and a 0-1%, 0-5% or 0-10% measuring range. Select as described above.
Note: The GPR-2500MO has a single 0-100% range and should be calibrate in accordance with the application as
described above.
1. Access the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
2. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight AUTO SAMPLE.
3. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
4. The following displays appear:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
3.3 %
AUTO SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
5. Return to the MAIN MENU by pressing the MENU key.
6. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight CALIBRATE.
7. Press the EN TER key to select the highlighted menu option.
8. Repeat to select SPAN CALIBRATE
9. The following displays appear:
MAIN MENU
AUTO SAMPLE
MANUAL SAMPLE
CALIBRATE
24.5 C 100 KPA
>>>
CALIBRATION
SPAN CALIBRATE
ZERO CALIBRATE
DEFAULT SPAN
DEFAULT ZERO
24.5 C 100 KPA
10. Assure there are no restrictions in vent line.
Page 29

29
11. Regulate the pressure and control the flow rate as described above at 5-30 psig and a 2 SCFH flow rate.
12. Allow the span gas to flow for 1-2 minutes to purge the air trapped in the span gas line.
13. Disconnect the sample gas line and install the purged span gas line.
14. Caution: Allow the span gas to flow and wait until the reading is stable before proceeding with
calibration. The wait time will vary depending on the amount oxygen introduced to the sensor when the gas
lines were switched.
15. Press the ENTER key to select the SPAN CALIBRATE option.
16. Note: A span gas concentration above 1000 ppm dictates the selection of the PERCENT option.
17. Advance the reverse shade cursor using the ARROW keys to highlight the desired GAS CONCENTRATION.
18. Press the ENTER key to select the highlighted menu option.
GAS CONCENTRATION
PERCENT
PPM
19. The following displays appear:
00.00 %
PRESS UP OR DOWN
TO CHANGE VALUE
SELECT TO SAVE
ESC TO RETURN
>>>
08.00 %
SPAN
CALIBRATION
ENTER TO CALIBRATE
MENU TO ABORT
20. Press the UP/ DOWN ARROWS to enter the first digit of the span value.
21. Press the ENTER key to advance the underline cursor right to the second digit of the span value.
Press the MENU key to advance the underline cursor left to the previous digit.
22. Press the UP/ DOWN ARROWS to enter the second digit of the span value.
23. Repeat steps 21 and 22 until the complete span value has been entered.
24. Allow approximately 60 seconds for the calibration process while the processor determines whether the signal
output or reading has stabilized within 60% of the full scale low range.
Page 30

30
25. Both the Zero Calibrate and Span Calibrate functions result in the following displays:
PASSED
CALIBRATION
OR
FAILED
CALIBRATION
26. If the calibration is successful, the transmitter returns to the SAMPLING mode after 30 seconds.
3.3 %
AUTO SAMPLING
10% RANGE
24.5 C 100 KPA
27. If the calibration is unsuccessful, return to the SAMPLING mode with span gas flowing through the transmitter,
make sure the reading stabilizes and repeat the calibration before concluding the equipment is defective.
28. Before disconnecting the span gas line and connecting the sample gas line, restart if necessary the flow of
sample gas and allow it to flow for 1-2 minutes to purge the air inside the line.
29. Disconnect the span gas line and replace it with the purged sample gas line.
30. Wait 10-15 minutes to ensure the reading is stable and proceed to sampling.
Sampling
GPR-2500/2500MO Oxygen Transmitter requires positive pressure to flow the sample gas by the sensor to measure
the oxygen concentration in a sample gas. If not available see Pressure & Flow section.
Note: Prematurely zeroing the transmitter can cause the transmitter to display a negative reading in both the
ZERO and SAMPLE modes.
Procedure:
Following calibration the transmitter returns to the SAMPLE mode after 30 seconds.
1. Select the desired sampling mode - auto or if manual, the range that provides maximum resolution – as
described above.
2. Use metal tubing to transport the sample gas to the transmitter.
3. The main consideration is to eliminate air leaks which can affect oxygen measurements above or below the
20.9% oxygen concentration in ambient air - ensure the sample gas tubing connections fit tightly into the 1/8”
male NPT to tube adapter, and, the NPT end is taped and securely tightened into the mating male quick
disconnect fittings which mate with the female fittings on the transmitter
Page 31

31
4. Assure there are no restrictions in the sample line.
5. For sample gases under positive pressure the user must provide a means of controlling the inlet pressure
between 5-30 psig and the flow of the sample gas between 1-5 SCFH, a flow rate of 2 SCHF is recommended
6. For sample gases under atmospheric or slightly negative pressure an optional sampling pump is recommended
to draw the sample into the transmitter. Generally, no pressure regulation or flow control device is involved.
7. Caution: If the transmitter is equipped with an optional sampling pump and is intended for use in both
positive and atmospheric/slightly negative pressure applications where a flow meter valve is involved – ensure
the valve is completely open when operating the sampling pump. Refer to the Pressure & Flow section above.
8. Assure the sample is adequately vented for optimum response and recovery – and safety.
9. Allow the oxygen reading to stabilize for approximately 10 minutes at each sample point.
To avoid erroneous oxygen readings and damaging the sensor:
¾ Do not place your finger over the vent (it pressurizes the sensor) to test the flow indicator when gas is flowing
to the sensor. Removing your finger (the restriction) generates a vacuum on the sensor and may damage the
sensor (voiding the sensor warranty).
¾ Assure there are no restrictions in the sample or vent lines
¾ Avoid drawing a vacuum that exceeds 14” of water column pressure – unless done gradually
¾ Avoid excessive flow rates above 5 SCFH which generate backpressure on the sensor.
¾ Avoid sudden releases of backpressure that can severely damage the sensor.
¾ Avoid the collection of particulates, liquids or condensation collect on the sensor that could block the diffusion
of oxygen into the sensor.
¾ If the transmitter is equipped with an optional integral sampling pump (positioned downstream of the sensor)
and a flow control metering valve (positioned upstream of the sensor), completely open the flow control
metering valve to avoid drawing a vacuum on the sensor and placing an undue burden on the pump.
Standby
¾ The transmitter has no special storage requirements.
¾ The sensor should remain connected during storage periods.
¾ Store the transmitter with the power OFF.
¾ If storing for an extended period of time, charge before operating.
Page 32

32
6 Maintenance
Generally, cleaning the electrical contacts or replacing filter elements is the extent of the maintenance
requirements of this transmitter.
Sensor Replacement
Periodically, the oxygen sensor will require replacement. The operating life is determined by a number of factors
that are influenced by the user and therefore difficult to predict. The Features & Specifications define the normal
operating conditions and expected life of the standard sensor utilized by the GPR-2500/2500MO transmitter.
Expected sensor life is inversely proportional to changes in oxygen concentration, pressure and temperature.
Serviceability: Except for replacing the oxygen sensor, there are no parts inside the transmitter for the operator
to service. Only trained personnel with the authorization of their supervisor should conduct mainten ance.
Caution: DO NOT open the oxygen sensor. The sensor contains a corrosive liquid electrolyte that could be harmful
if touched or ingested, refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet contained in the Owner’s Manual. Avoid contact with
any liquid or crystal type powder in or around the sensor or sensor housing, as either could be a form of
electrolyte. Leaking sensors should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Procedure:
1. Remove the four (4) screws securing the hinged front panel of the transmitter
and raise it up 180º until it locks into position.
2. Caution: Do not remove or discard the gaskets from the enclosure. Failure to
reinstall the gasket will void the NEMA rating.
3. Unscrew the knurled lock nut connecting the cable to the sensor.
4. Disconnect and remove the female plug (including the knurled lock nut)
molded to the cable from the male receptacle attached to the sensor.
5. Unscrew the old sensor from the threaded hole in the sensor flow housing.
6. Open the barrier bag containing the new sensor.
7. If the sensor is equipped with a shorting loop, remove the shorting wire from
the pins of the female socket attached to the new sensor.
8. Screw the new sensor, finger tight plus 1/2 turn, into the threaded hole in the
flow housing and ensure the o-ring seal is engaged.
9. Assure the keyway registration of the female plug on the cable and male
receptacle on the sensor match up.
10. Push the female plug (including the knurled lock nut) molded to the cable into
the male receptacle attached to the new sensor.
11. Screw and tighten the knurled lock nut attached the cable onto to the male connector attached to the sensor.
12. Replace the front cover of the transmitter, replace the gasket to maintain CE approval and NEMA 4 rating and
tighten the four (4) screws to secure the front cover.
13. Calibrate the transmitter as described in section 5.
Page 33

33
7 Spare Parts
Recommended spare parts for the GPR-2500/2500MO Oxygen Transmitter:
Item No. Description
GPR-11-32-4 Oxygen Sensor (GPR-2500)
XLT-11-24-4 Oxygen Sensor (GPR-2500)
GPR-11-120-OP Oxygen Sensor (GPR-2500MO)
Other spare parts:
Item No. Description
FITN-1018 Connector SS 1/8” MNPT to 1/8” Tube
FITN-1039 Elbow SS 1/8”
A-3051 Housing Flow Adaptor
BARR-1001 Intrinsic Safety Barrier
MTR-1011 Meter Digital Panel LCD Backlight
A-1151-E-L2 PCB Assembly Main / Display (GPR-2500/2500MO)
Page 34

34
8 Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Recommended Action
Reading does not reflect
expected values
Sensor was not calibrated at the
pressure, flow rate and temperature
anticipated in the sample gas stream
Recalibrate the analyzer
Oxygen reading drifts toward
zero or significant number of
turns of the span control
adjustment is required to
calibrate the analyzer.
Indication sensor is nearing the end of
its useful life
Replace sensor, see Section 6 Maintenance.
Slow response time
Erratic oxygen reading
No oxygen reading
Liquid covering sensing membrane
Presence of interference gases.
Unauthorized maintenance
Defective electrical connection
Sensor failure
Gently remove with alcohol and lint
free towel.
Consult factory, replace sensor, and
see Section 6 - Maintenance.
Use voltmeter and determine uA or mV
output and contact factory.
High oxygen reading
Inadequate control of pressure and
flow rate
Abnormality in span gas
See Section 5 - Operation,
Getting Started,
Control of Pressure and Flow
Qualify source
Page 35

35
9 Warranty Policy
What is covered:
Any defect in material and workmanship from normal use in accordance with the Owner’s Manual.
This warranty applies to all transmitter purchased worldwide. Advanced Instruments Inc. reserves the
right in its sole discretion to invalidate this warranty if the serial number does not appear on the
transmitter.
For how long:
One year from shipment by manufacturer or purchase from a distributor with proof of purchase.
Who is warranted:
This warranty is limited to the first customer who submits a claim. Under no circumstances will the
warranty extend to more than one customer.
What we will do:
If your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter is defective with respect to material and workmanship, we
will repair it or, at our option, replace it at no charge to you.
If we choose to replace your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter, we may use new or reconditioned
replacement parts.
If we choose to replace your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter, we may replace it with a new or
reconditioned one of the same or upgraded design.
Limitations:
Implied warranties, including those of fitness for a particular purpose and merchantability (an unwritten
warranty that the product is fit for ordinary use), are limited to one year from the date of shipment by
manufacturer or purchase from a distributor with proof of purchase.
Advanced Instruments Inc. will not pay for: loss of time; inconvenience; loss of use of your Advanced
Instruments Inc. transmitter or property damage caused by your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter
or its failure to work; any special, incidental or consequential damages; or any damage resulting from
alterations, misuse or abuse; lack of proper maintenance; unauthorized repair or modification of the
transmitter; affixing of any attachment not provided with the transmitter or other failure to follow the
Owner’s Manual.
Some states and provinces do not allow limitations on how an implied warranty lasts or the exclusion of
incidental or consequential damages, so the above exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty gives
you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state and province
Page 36

36
to province.
What is not covered:
This warranty does not cover installation; defects resulting from accidents; damage while in transit to our
service location; damage resulting from alterations, misuse or abuse; lack of proper maintenance;
unauthorized repair or modification of the transmitter; affixing of any attachment not provided with the
transmitter; fire, flood, or acts of God; or other failure to follow the Owner’s Manual.
Sole Warranty
This warranty is the only one we will give on your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter, and it sets
forth all our responsibilities regarding your Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter.
There are no other express warranties.
How to obtain warranty service:
Do-It-Yourself-Service:
Call Advanced Instruments Inc. at 909-392-6900 between 8:00am and 5:00pm Pacific Time weekdays.
Trained technicians will assist you in diagnosing the problem and arrange to supply you with the required
parts.
Service from Distributors:
If warranty service is provided by a distributor, Advanced Instruments Inc. will provide all required parts
under warranty at no charge to you, but the distributor is an independent business and may render a
service charge for their services. Advanced Instruments Inc. will not reimburse you or otherwise be
responsible for those charges.
Return to Advanced Instruments Inc.:
You may obtain warranty service by returning you transmitter, postage prepaid to:
Advanced Instruments Inc.
2855 Metropolitan Place
Pomona, Ca 91767 USA
Be sure to pack the transmitter securely. Include your name, address, telephone number, proof of da te
of purchase and a description of the operating problem. After repairing or, at our option, replacing your
Advanced Instruments Inc. transmitter, we will ship it to you at no cost for parts and labor.
Your choice of any one of the service options described above is your exclusive remedy under this
warranty.
Page 37

37
10 Material Safety Data Sheet ( MSDS )
Product Identification
Product Name Oxygen Sensor Models CAD, GPR, PSR, SAF, 67013
Synonyms Galvanic Fuel Cell, Electrochemical Transducer
Manufacturer Analytical Industries Inc.
2855 Metropolitan Place, Pomona, CA 91767 USA
Emergency Phone Number 909-392-6900
Preparation / Revision Date January 1, 1995
Notes Oxygen sensors are sealed, contain protective coverings and in normal
conditions do not present a health hazard. Information applies to
electrolyte unless otherwise noted.
Specific Generic Ingredients
Carcinogens at levels > 0.1% None
Others at levels > 1.0% Potassium Hydroxide, Lead
CAS Number Potassium Hydroxide = KOH 1310-58-3, Lead = Pb 7439-92-1
Chemical (Synonym) and
Family
Physical Properties
Boiling Point Range
Melting Point Range
Freezing Point
Molecular Weight KOH = 56, Lead = 207
Specific Gravity
Vapor Pressure Not applicable
Vapor Density Not applicable
pH > 14
Solubility in H
% Volatiles by Volume None
O Complete
2
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) - Base, Lead (Pb) - Metal
100 to 115° C
KOH -10 to 0° C, Lead 327° C
-40 to 0° C
1.09 @ 20° C
Evaporation Rate Similar to water
Appearance and Odor Colorless, odorless aqueous solution
Page 38

38
General Requirements
Use Potassium Hydroxide - electrolyte, Lead - anode
Handling Rubber or latex gloves and safety glasses
Storage Indefinitely
Fire and Explosion Data
Flash and Fire Points Not applicable
Flammable Limits Not flammable
Extinguishing Method Not applicable
Special Fire Fighting Procedures Not applicable
Unusual Fire and Explosion
Hazards
Not applicable
Reactivity Data
Stability Stable
Conditions Contributing to
Instability
None
Incompatibility Avoid contact with strong acids
Hazardous Decomposition
Products
None
Conditions to Avoid None
Spill or Leak
Steps if material is released Sensor is packaged in a sealed protective plastic bag, check the sensor
inside for electrolyte leakage.
If the sensor leaks inside the protective plastic bag or inside the
transmitter sensor housing do not remove it without rubber or latex
gloves and safety glasses and a source of water.
Flush or wipe all surfaces repeatedly with water or wet paper towel.
Use a fresh towel each time.
Waste Disposal Method In accordance with federal, state and local regulations for battery
disposal
Health Hazard Information
Primary Route(s) of Entry Ingestion, eye and skin contact
Exposure Limits Potassium Hydroxide - ACGIH TLV 2 mg/cubic meter; Lead - OSHA PEL
.05 mg/cubic meter
Effects of Exposure -
Ingestion Electrolyte could be harmful or fatal if swallowed. Oral LD50 (RAT) =
2433 mg/kg
Page 39

39
Eye Electrolyte is corrosive and eye contact could result in permanent loss
of vision.
Skin Electrolyte is corrosive and skin contact could result in a chemical
burn.
Inhalation Liquid inhalation is unlikely.
Symptoms Eye contact - burning sensation; Skin contact - soapy slick feeling.
Medical Conditions Aggravated None
Carcinogenic Reference Data NTP Annual Report on Carcinogens - not listed; LARC Monographs -
not listed; OSHA - not listed
Other Lead is listed as a chemical known to the State of California to cause
birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Emergency First Aid
Ingestion Do not induce vomiting; Give plenty of cold water; Seek medical
attention immediately.
Skin Contact Wash affected area repeatedly with plenty of water; Remove
contaminated clothing; If burning persists, seek medical attention.
Eye Contact Flush repeatedly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes; Seek
medical attention immediately.
Inhalation Liquid inhalation is unlikely.
Special Protection Information
Ventilation Requirements None
Eye Safety glasses
Hand Rubber or latex gloves
Respirator Type Not applicable
Other Protective Equipment None
Special Precautions
Precautions Do not remove the sensor’s protective Teflon and PCB coverings; Do
not probe the sensor with sharp objects; Wash hands thoroughly after
handling; Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing; Empty sensor
body may contain hazardous residue.
Transportation Not applicable
Page 40

40
Product Identification
Product Name Oxygen Sensor Models XLT
Synonyms Galvanic Fuel Cell, Electrochemical Transducer
Manufacturer Analytical Industries Inc.
2855 Metropolitan Place, Pomona, CA 91767 USA
Emergency Phone Number 909-392-6900
Preparation / Revision Date January 1, 1995
Notes Oxygen sensors are sealed, contain protective coverings and in normal
conditions do not present a health hazard.
Information applies to electrolyte unless otherwise noted.
Specific Generic Ingredients
Carcinogens at levels > 0.1% None
Others at levels > 1.0% Acetic Acid, Lead
CAS Number Acetic Acid = 64-19-7, Lead = Pb 7439-92-1
Chemical (Synonym) and
Family
Physical Properties
Boiling Point Range
Melting Point Range
Freezing Point
Molecular Weight Acetic Acid = not applicable, Lead = 207
Specific Gravity
Vapor Pressure
Vapor Density (air = 1) 2.07
pH 2-3
Solubility in H
% Volatiles by Volume None
Evaporation Rate Similar to water
O Complete
2
Acetic Acid (CH3CO2H) - Acid, Lead (Pb) - Metal
100 to 117° C
Acetic Acid = not applicable, Lead 327° C
-40 to -10° C
1.05 @ 20° C
11.4 @ 20° C
Appearance and Odor Colorless, vinegar-like odor aqueous solution
General Requirements
Use Acetic Acid - electrolyte, Lead - anode
Handling Rubber or latex gloves; Safety glasses
Storage Indefinitely
Page 41

41
Fire and Explosion Data
Flash and Fire Points Not applicable
Flammable Limits Not flammable
Extinguishing Method Not applicable
Special Fire Fighting Procedures Not applicable
Unusual Fire and Explosion
Hazards
Not applicable
Reactivity Data
Stability Stable
Conditions Contributing to
Instability
None
Incompatibility Avoid contact with strong bases
Hazardous Decomposition
Products
Emits toxic fumes when heated
Conditions to Avoid Heat
Spill or Leak
Steps if material is released Sensor is packaged in a sealed protective plastic bag, check the sensor
inside for electrolyte leakage. If the sensor leaks inside the protective
plastic bag or inside the transmitter sensor housing do not remove it
without rubber or latex gloves, safety glasses and a source of water.
Flush or wipe all surfaces repeatedly with water or wet paper towel.
Use a fresh towel each time.
Waste Disposal Method In accordance with federal, state and local regulations for battery
disposal.
Health Hazard Information
Primary Route(s) of Entry Ingestion, eye and skin contact
Exposure Limits Acetic Acid - ACGIH TLV / OSHA PEL 10 ppm (TWA); Lead - OSHA PEL
.05 mg/cubic meter
Effects of Exposure -
Ingestion Electrolyte could be harmful or fatal if swallowed; Oral LD50 (RAT) =
6620 mg/kg
Eye Electrolyte is corrosive and eye contact could result in permanent loss
of vision.
Skin Electrolyte is corrosive and skin contact could result in a chemical
burn.
Inhalation Liquid inhalation is unlikely.
Symptoms Eye contact - burning sensation; Skin contact - burning sensation.
Page 42

42
Medical Conditions Aggravated None
Carcinogenic Reference Data NTP Annual Report on Carcinogens - not listed; LARC Monographs -
not listed; OSHA - not listed
Other Lead is listed as a chemical known to the State of California to cause
birth defects or other reproductive harm. Lead acetate formed as the
sensor is used is listed as a chemical known to the State of California
to cause cancer.
Emergency First Aid
Ingestion Do not induce vomiting; Give plenty of cold water or if available milk;
Seek medical attention immediately.
Skin Contact Wash affected area repeatedly with plenty of water; Remove
contaminated clothing; If burning persists, seek medical attention.
Eye Contact Flush repeatedly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes; Seek
medical attention immediately.
Inhalation Liquid inhalation is unlikely.
Special Protection Information
Ventilation Requirements None
Eye Safety glasses
Hand Rubber or latex gloves
Respirator Type Not applicable
Other Protective Equipment None
Special Precautions
Precautions Do not remove the sensor’s protective Teflon and PCB coverings; Do
not probe the sensor with sharp objects; Wash hands thoroughly after
handling; Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing; Empty sensor
body may contain hazardous residue.
Transportation Not applicable
 Loading...
Loading...