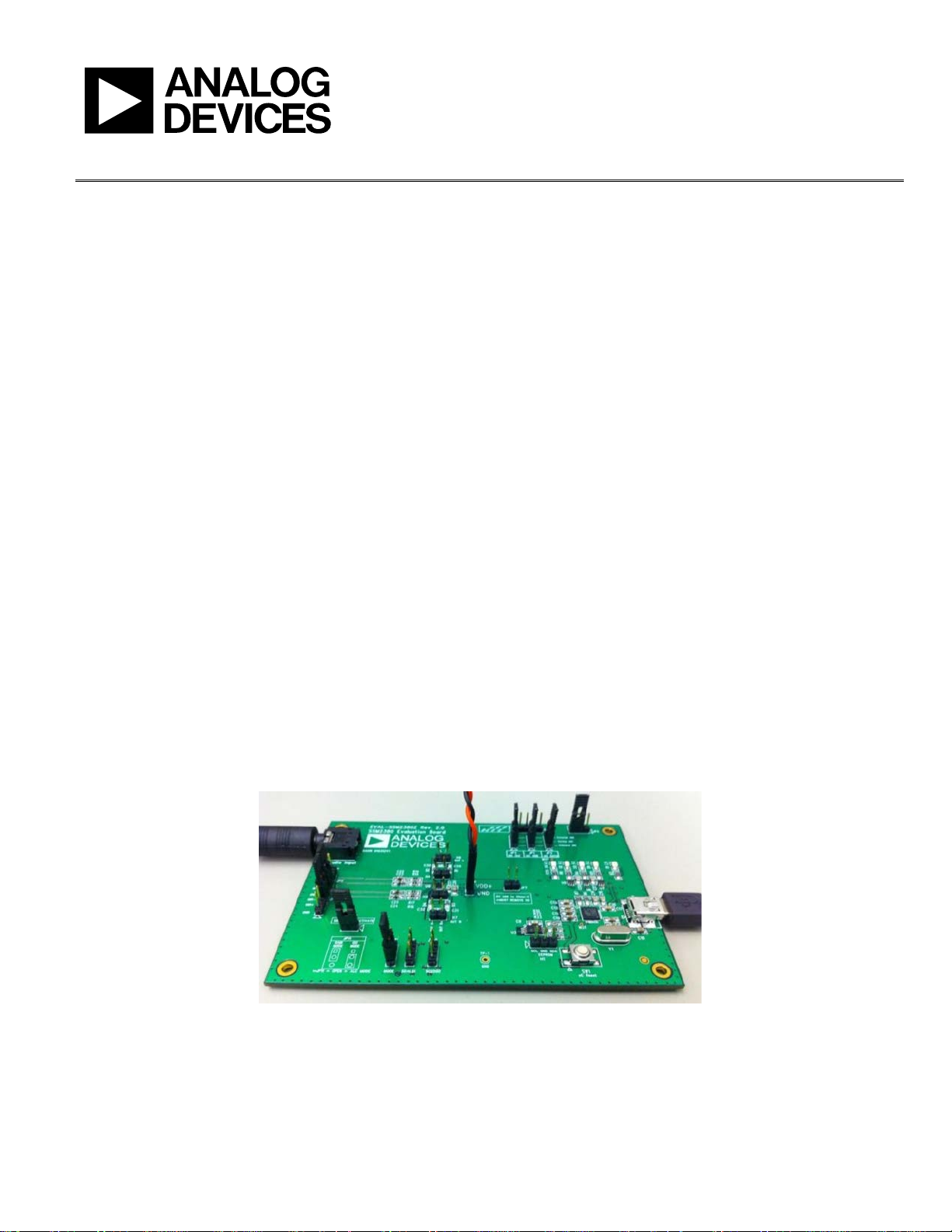
Evaluation Board User Guide
UG-248
09686-001
One Technology Way • P. O. Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel: 781.329.4700 • Fax: 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
Evaluating the SSM2380 Audio Amplifier
FEATURES
Accepts either differential or single-ended inputs
Full featured evaluation board for the SSM2380
PCB footprint for optional EMI filter
Includes USB hardware interface for plug-and-play
operation
Microsoft Windows®-based evaluation software with
simple graphical user interface
EQUIPMENT NEEDED
Audio source with ⅛" male stereo plug or 0.100" header
Power supply (5.0 V, 2.0 A recommended)
EVAL-SSM2380Z evaluation board
PC running Windows XP or later; USB 2.0 port required
Stereo speakers or other load
DOCUMENTS NEEDED
SSM2380 data sheet
SOFTWARE NEEDED
SSM2380 evaluation software
TYPICAL I2C INTERFACE CONFIGURAT ION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2380 evaluation board is a complete solution for
driving two loudspeakers. It includes the SSM2380 amplifier
IC and the additional components needed to connect the I
bus to a personal computer using a universal serial bus (USB)
connection. Figure 1 shows the evaluation board in a simple
configuration with USB and power and audio input connections.
The SSM2380 features an I
settings. Using the I
SSM2380 can be selected from any of 47 values between
1 dB and 24 dB. Other features available when using the I
interface include independent left/right channel shutdown,
EMI emission control modes, automatic level control (ALC),
and stereo-to-mono input mixing.
This user guide describes how to use the EVA L -SSM2380Z to
test the features of the SSM2380 stereo amplifier. It describes
the hardware and software of the SSM2380 evaluation board,
including detailed schematics and PCB layout artwork.
The SSM2380 data sheet, available at www.analog.com/SSM2380,
provides detailed information about the specifications, internal
block diagrams, and application guidance for the amplifier IC.
The SSM2380 evaluation software can be downloaded from
www.analog.com/SSM2380. Click Evaluation Boards & Kits
and choose the appropriate Windows version (32-bit or 64-bit).
2
C interface with many useful
2
C control interface, the gain of the
2
C
2
C
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
Figure 1. EVAL-SSM2380Z Evaluation Board
Rev. 0 | Page 1 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Equipment Needed ........................................................................... 1
Documents Needed .......................................................................... 1
Software Needed ............................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Typ ical I2C Interface Configuration ............................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Evaluation Board Hardware ............................................................ 3
Power Supplies .............................................................................. 3
Input Signals .................................................................................. 3
Output Signals............................................................................... 3
Shutdown and Mode Jumpers .................................................... 3
LEDs ............................................................................................... 4
EEPROM ....................................................................................... 4
USB Power Switch ........................................................................ 4
I2C Source Jumpers ...................................................................... 4
Operating Modes .............................................................................. 5
I2C Control Mode ......................................................................... 5
ALC Mode ..................................................................................... 5
Gain Select Mode .......................................................................... 5
Evaluation Board Software Quick Start Procedures .................... 6
SSM2380 Control Software Setup .............................................. 6
Initial SSM2380 Hardware Setup ................................................6
SSM2380 GUI Functional Blocks ....................................................8
Input Control .................................................................................8
Output Control ..............................................................................8
Auxiliary Functions.......................................................................9
Quick Set Buttons ....................................................................... 10
Direct I2C Register Access ......................................................... 10
USB Power ................................................................................... 10
USB—I2C Interface ......................................................................... 11
General Description ................................................................... 11
USB Connector ........................................................................... 11
Power Regulator ......................................................................... 11
Cypress USB Interface ............................................................... 11
Crystal Oscillator ........................................................................ 11
Passive Component Selection ....................................................... 12
Input Coupling Capacitor Selection (C22 to C25) ............... 12
Output Ferrite Beads (B1 to B4) ............................................... 13
Output Shunting Capacitors (C29 to C32) ............................. 13
Output Inductors (L1 to L4) ..................................................... 13
Evaluation Board Schematics and Artwork ................................ 14
Ordering Information .................................................................... 18
Bill of Materials ........................................................................... 18
REVISION HISTORY
9/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 20
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
1/8” STEREO
INPUT
OR
DIFERENTIAL
AUDIO INPUT
TO PC
EXTERNAL I
2
C
TO LOAD
2.5V TO 5.5V
TO ANALYZER
09686-002
09686-003
EVALUATION BOARD HARDWARE
The SSM2380 evaluation board provides all of the support
circuitry required to operate the SSM2380 amplifier, including
a computer interface for the I
2
C bus. Figure 2 shows the typical
bench characterization setup used to evaluate the audio performance of the SSM2380. See the Evaluation Board Software
Quick Start Procedures section to get started.
Figure 2. Diagram View of Evaluation Board Connections
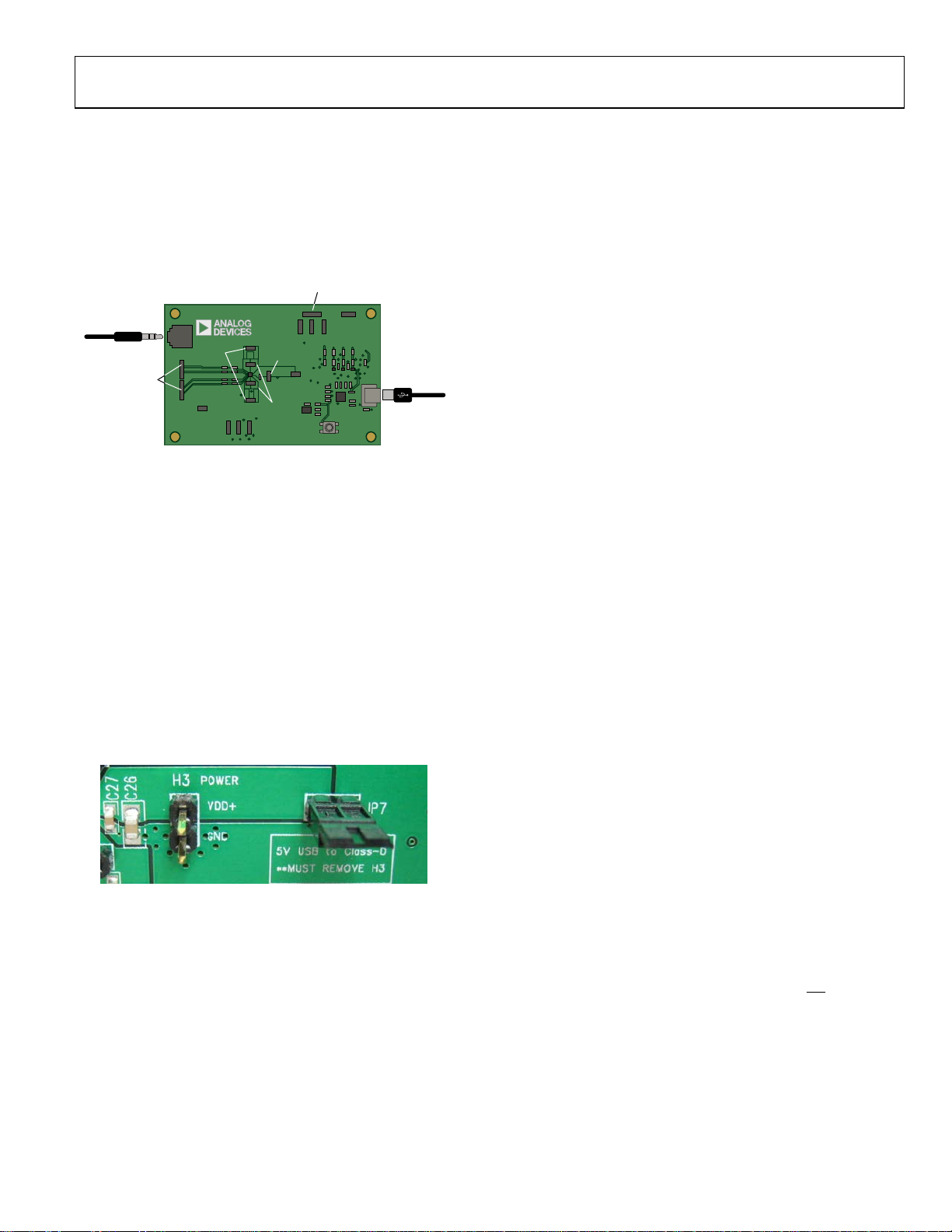
POWER SUPPLIES
The SSM2380 requires an external dc power supply. A 2-pin
0.100" male header, H3, is provided on the evaluation board.
Supply voltages between 2.5 V and 5.5 V are accepted, and
supply currents may exceed 1 A under some conditions.
Alternatively, 5 V USB power supply can be used to power the
chip, although the USB 2.0 specification only allows current
draw up to 500 mA. Be cautious when using the USB port
to supply any significant amount of power. The jumper
configuration used for USB power is shown in Figure 3.
Be sure to remove JP7 when using an external power supply,
as this will short the I
Conversely, be sure to remove the external supply from
H3 when using USB power.
Figure 3. Connecting USB Power Supply to SSM2380
2
C voltage to the external supply.
INPUT SIGNALS
On the left side of the PCB are two 4-pin headers, JP5 and JP6.
These are used to connect the input audio signal to the amplifier. If
the input audio signal is differential, use the two center pins of
JP5 (INL+ and INL−) for left channel audio and the two center
pins of JP6 (INR+ and INR−) for the right channel audio. In
this case, connect either the top or the bottom pin to the source/
signal ground.
For single-ended audio inputs, only two pins of JP5 and two
pins of JP6 are used: ground and the input signal. If a noninverting input is desired, connect the input signals to INL+
and INR+, and place jumpers between Pin 3 and Pin 4 of JP5
and JP6, shorting INL− and INR− to ground.
Conversely, if an inverting input is desired, connect the input
signals to INL− and INR−, and place the jumpers between Pin 1
and Pin 2 of JP5 and JP6, shorting INL+ and INR+ to ground.
Alternatively, single-ended stereo audio can be supplied by
connecting a standard ⅛" stereo plug to the J2 input. In this
case, jumpers must connect INL− and INR− to ground.
OUTPUT SIGNALS
Each channel of the amplifier output is available at two 2-pin
0.100" headers. The speakers are connected in bridge-tied load
(BTL) configuration, and the output pins are labeled with their
polarity; for example, OUTL+ indicates the left channel noninverting terminal.
In the standard filterless configuration, the two headers on
each channel are connected with 0 Ω links on the pads marked
B1 to B4. In this case, the two headers on each channel are tied
together and can be used interchangeably as attachment points
for the load and an audio analyzer. The EMI filtering is not
populated on the SSM2380 evaluation board to allow proper
measurement of key parameters such as SNR and THD.
The top layer of the PCB contains the footprints necessary for a
ferrite bead-based EMI filter configuration, whereas the bottom
layer of the PCB contains the footprints for an inductor-based
EM I filter. If EMI filtering is used, only H6 and H7 connect at
the proper location with respect to the filter components—the
load must be connected to these headers. Measurements of the
unfiltered waveform can be taken at H4 and H5.
SHUTDOWN AND MODE JUMPERS
The 2-pin jumper, JP8, is used to enable and disable the SSM2380
SD
amplifier. Inserting a jumper across JP8 pulls the
SPKVDD supply rail, activating the amplifier. Removing the
jumper from JP8 shuts down both channels of the SSM2380
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 20
so that minimal current (about 20 nA) is drawn from the
power supply.
pin to the
UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
09686-004
LEDS
The LEDs provide feedback to the user about the status of the
Cypress USB microcontroller. The function of each LED is
shown in Tab le 1.
Table 1. LED Functions
Reference
Designator Color Function
D1 Red 5 V power is supplied over the USB bus
D2 Yellow I2C mode is active
D3 Blue GPIO LED, for firmware debug purposes
D4 Yellow SPI mode is active
D5 Blue USB power switch enabled (USB_PWR_ON)
EEPROM
The USBi has an EEPROM on the I2C bus at Address 0x51, which
it uses to indicate its vendor ID and product ID to the PC, as
well as boot its internal program. The EEPROM is an important
system element that identifies the board to the host PC and
stores the firmware for the Cypress USB interface. The EEPROM
is programmed during manufacturing via the H1 connector.
Avoid having any other EEPROMs in your system design at
this address. This EEPROM is not write-protected; therefore,
an attempt to write to Address 0x51 overwrites the USBi's
on-board EEPROM, and the USBi will cease to function. The
USBi cannot be reprogrammed without returning it to Analog
Devices.
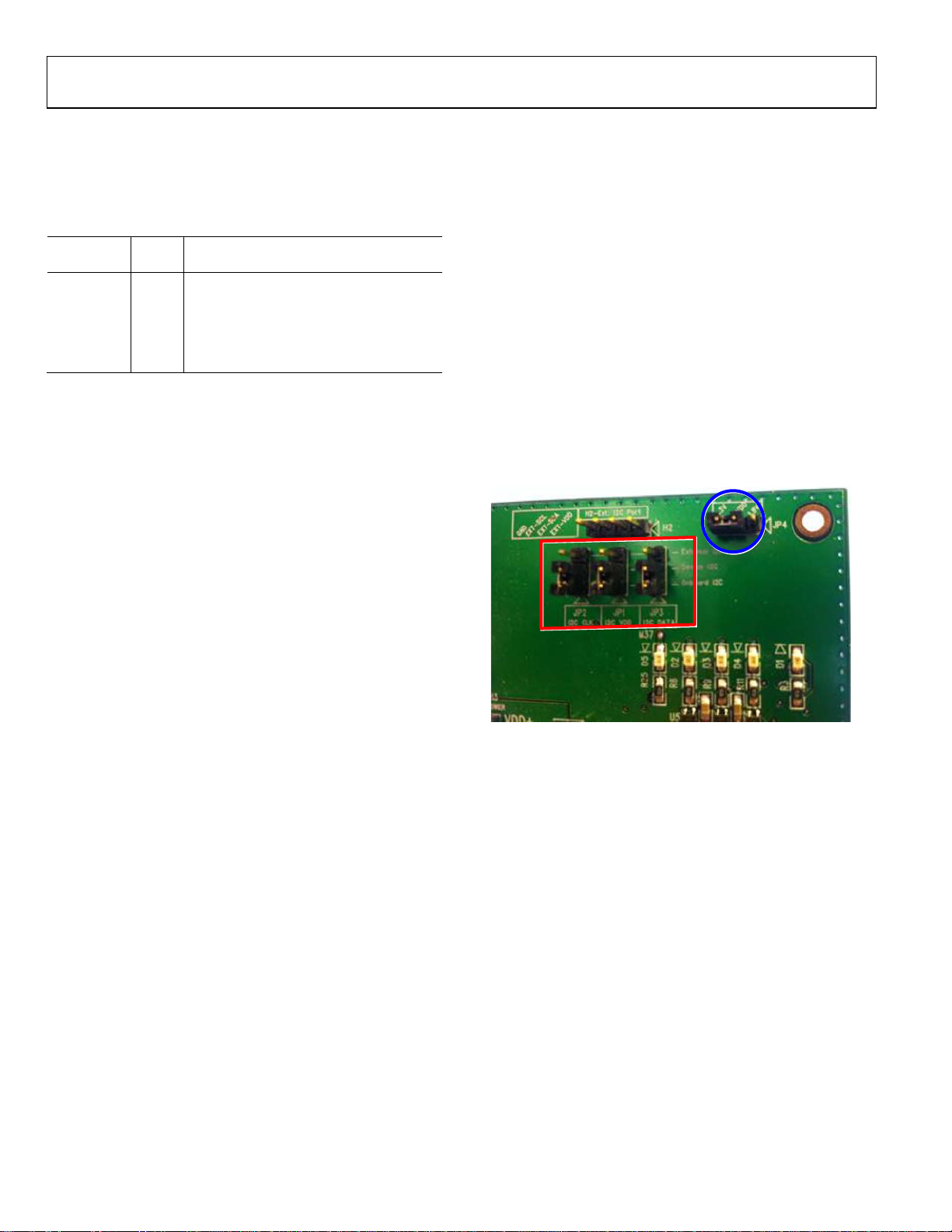
I2C SOURCE JUMPERS
If an external I2C source is to be used, place the JP1, JP2, and
JP3 jumpers such that they connect the device I
external I
2
I
C lines to the on-board I2C lines, as shown in the red
2
C lines. Otherwise, they should connect the device
rectangular area of Figure 4. If an external I
external I
2
C source can be attached to H2, following the
silkscreen labels displayed on the board.
The voltage of the external I
2
C interface should match the
value set on JP4; the two voltages are taken from two separate
on-board regulators. The on-board I
2
C interface works properly
in either configuration.
For the Cypress USB microcontroller to boot properly from the
EEPROM, it may be necessary to power down (or disconnect)
any other devices from the I
2
C bus, including the SSM2380.
In this case, remove the external 5 V supply while the USB
connection is first established, or remove the JP2 and JP3
jumpers and replace them only after the connection is activated.
2
C lines to the
2
C is used, an
USB POWER SWITCH
The SSM2380 evaluation board is capable of taking 5 V power
from the USB port after the Cypress USB microcontroller has
finished its boot up process. The USB_PWR_ON signal, which
can be set in the SSM2380 software, appears on one pin of the
Cypress microcontroller. This signal controls, Q1 and Q2, create
a connection between USB power and the supply rail. D5, a blue
LED, lights up when this supply is activated. Note that the
current available from the USB bus is limited; therefore, the
amplifier power stage may not drive low impedance loads
properly.
Figure 4. Jumpers as Configured for On-Board I
2
C Operation
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 20
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
OPERATING MODES
The SSM2380 has three operating modes: I2C control mode,
ALC mode, and gain select mode. These modes are described
in detail in the SSM2380 data sheet. On the evaluation board,
the 3-pin JP11 jumper allows the user to change between the
available operating modes.
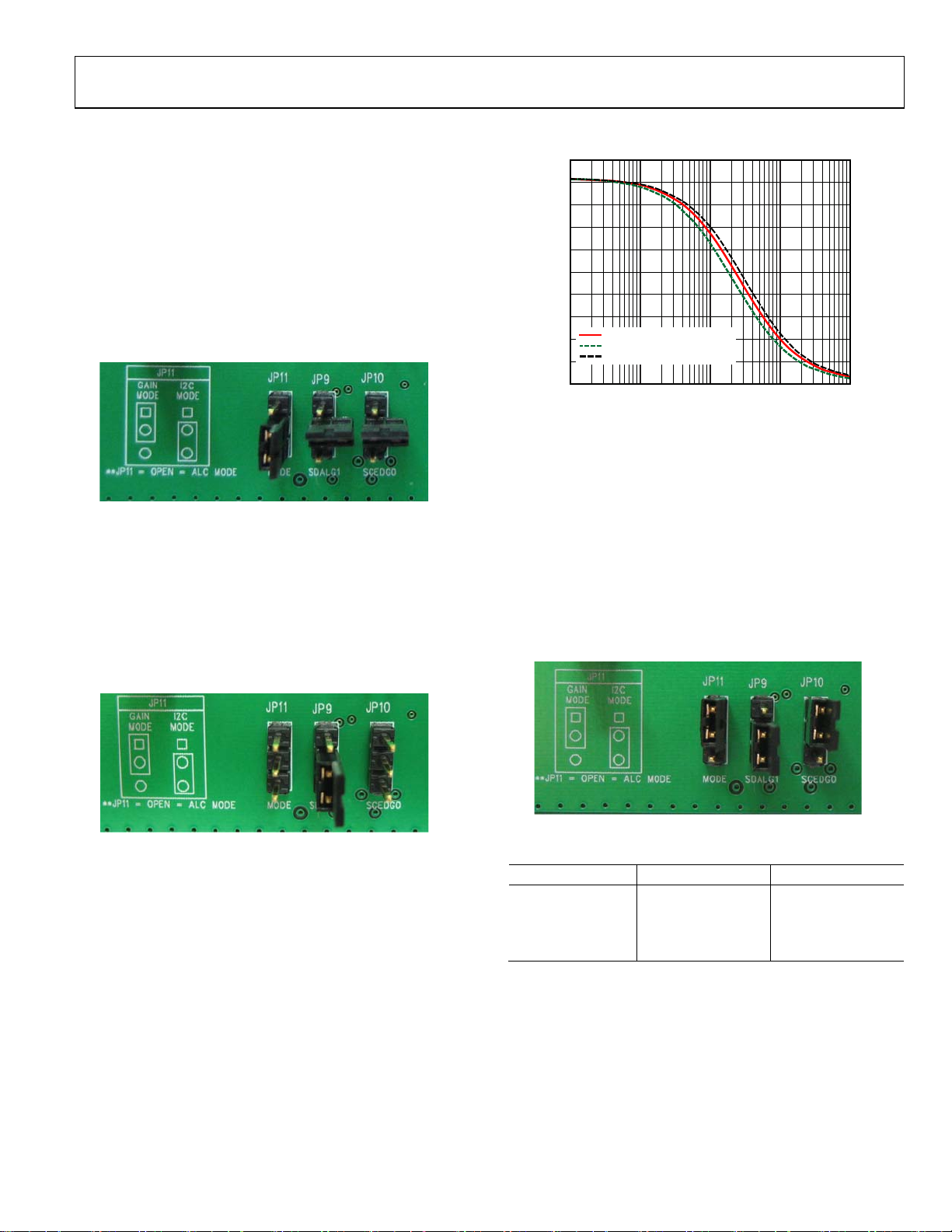
I2C CONTROL MODE
To operate the SSM2380 in I2C control mode, connect JP11 as
shown in Figure 5, connecting the MODE pin to GND. While
2
in I
C control mode, JP9 and JP10 are not used and the jumpers
should be left unconnected.
Figure 5. Jumper Connections for I
ALC MODE
The proper connections for ALC mode are shown in Figure 6.
For this setting, JP11 is open and the middle and bottom pins
of JP9 are shorted. This floats the MODE pin and makes a
connection from the SSM2380 ALCTH pin with Resistor
R24 to GND, setting the SSM2380 ALC limiting range. JP10
is used to activate the radiated emissions reduction mode in
this configuration.
2
C Mode Operation
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
OUTPUT VO LTAGE LIMIT (%)
55
50
45
TYPICAL CO NDITION
INTERNAL RESISTOR – 20%
INTERNAL RESISTOR + 20%
100 1k 10k 100k 1M
Figure 7. Output Voltage Limit (V
RESISTOR (Ω)
) vs. RTH
TH
09686-007
GAIN SELECT MODE
The proper connections for gain select mode are shown in
09686-005
Figure 8. A jumper must be inserted on JP11 from center pin
to top pin. JP9 and JP10 allow the user to select the SSM2380
gain from 6 dB to 24 dB. To connect the appropriate gain select
pin to VDD, place a jumper from the center pin to the top pin
of the header. To select GND, simply move the jumper connection to the center pin and bottom pin of the header. A gain
select table shows all possible settings in Table 2. All other
features (ALC, emissions control, and mixer) are deactivated
while the SSM2380 is in gain select mode.
09686-006
Figure 6. Jumper Connections for ALC Mode Operation
The limiting percentage of the ALC feature is determined by the
value of an external resistor, R24, which should be placed on the
secondary side of the board. The resistor value can be calculated
using the curve shown in Figure 7.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 20
09686-008
Figure 8. Jumper Connections for Gain Select Mode Operation
Table 2. Gain Select Mode Settings for JP9 and JP10
GAIN1 (JP9) GAIN0 (JP10) Gain Setting
GND GND 6 dB
GND VDD 12 dB
VDD GND 18 dB
VDD VDD 24 dB

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
EVALUATION BOARD SOFTWARE QUICK START PROCEDURES
SSM2380 CONTROL SOFTWARE SETUP
Do not connect the evaluation board until software is installed.
The SSM2380 software interface requires Microsoft® .NET
Framework (Version 2.0 or later). The installer automatically
downloads it if .NET Version 2.0 is not already installed.
To install the control software, use the following steps:
1. Go to www.analog.com/SSM2380.
2. Click Evaluation Boards & Kits.
3. Choose the appropriate Windows version (32-bit or 64-bit)
to download.
4. Extract the SSM2380 zipped installation file to a
convenient location and double-click setup.exe to begin
the installation process. Follow the installation instructions
when prompted.
5. The software and USB drivers are installed in C:\Program
Files\Analog Devices Inc\SSM2380.
SSM2380 USB Driver Installation
Before connecting the SSM2380 evaluation board to a PC or
notebook, the following procedure may need to be completed.
(This procedure only needs to be executed once on each computer that uses the SSM2380 software. This procedure can be
skipped if the user has previously installed any SigmaStudio
or USBi related drivers from Analog Devices, Inc.)
1. Exit the SSM2380 user interface software.
2. Remove jumpers from JP1, JP2, and JP3, located at the top
of the evaluation board to completely isolate the Cypress
USB driver from the SSM2380.
3. Connect JP4 in the 3.3 V location as shown in the blue-
circled area of Figure 4. The purpose of this is to power
the Cypress USB controller to establish communication
between the software and the board.
4. Make sure the software was closed. Connect the SSM2380
evaluation board to the PC via the USB cable.
5. The PC recognizes the new hardware. When the hardware
is recognized, a prompt asks to let Windows find the
proper drivers for the hardware.
Do not let Windows install the drivers.
6. The user must direct the driver installation to the following
path by clicking the Browse tab:
C:\Program Files\Analog Devices Inc\SSM2380\
7. After the path has been properly selected, the user can
continue with the driver installation process. Windows
will properly establish the link between the Cypress USB
controller and the PC.
8. After the previous steps are followed, the user can now run
the SSM2380 control software. The software is located at
the following path: C:\Program Files\Analog Devices
Inc\SSM2380\ SSM2380.exe.
9. For quick access to this software, the installer creates a
shortcut from the SSM2380.exe file to the desktop.
10. If all steps were properly followed, at the top of the
SSM2380 software window, a status message of USBi
Connected appears. If the installation was not successful,
a message of USBi – Cannot Find Device appears.
11. After a successful installation, the
recognizes a connection from the PC to the SSM2380
evaluation board. There is no need to adjust the jumper
positions of JP1, JP2, and JP3; but they should be
connected as shown in Figure 4.
SSM2380 software
Uninstall SSM2380 Control Software
1. Locate the directory where the SSM2380 zipped installer
file was extracted.
2. Double-click setup.exe. Simply select Uninstall to remove
the software from the host PC.
INITIAL SSM2380 HARDWARE SETUP
To allow the SSM2380 software to control the SSM2380
evaluation board, the user must make a few simple jumper
connections:
1. Connect the bottom and middle terminals of each jumper
JP1, JP2, and JP3. The purpose of this is to connect the
on-board Cypress USB-I
signals connected are I
2. Connect JP4 in one of two positions to choose an I
supply rail, either 1.8 V or 3.3 V. These two voltages
come from separate on-board LDOs. The SSM2380
control interface works well under either of these I
supply voltage conditions.
2
C interface to the SSM2380. The
2
C VDD, I2C CLK, and I2C DATA.
2
C
2
C
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
09686-109
Figure 9. SSM2380 Evaluation Software
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
09686-009
09686-010
SSM2380 GUI FUNCTIONAL BLOCKS
The SSM2380 control software is logically split into several
different functional blocks. Each functional block is split into
the individual subsections.
Note that when the power supply of the SSM2380 is interrupted,
you must reset the SSM2380 software to synchronize with the
device. Simply click the red RESET button at the bottom-left
corner of the software window (see Figure 9).
INPUT CONTROL
This section controls the left and right gain control operation
of SSM2380.
OUTPUT CONTROL
This section controls the auto level control (ALC) of the
SSM2380.
Figure 10. Input Control Section of SSM2380 GUI
Left Gain Control (Register R0)
This is associated with Control Register R0. Options include
mute, left-to-right gain loading (load left gain to right channel),
and left channel gain. The left channel gain can be set from 1 dB
to 24 dB in 0.5 dB increments.
Right Gain Control (Register R1)
This is associated with Control Register R1. Options include
mute, right-to-left gain loading (load right gain to left channel),
and right channel gain. The right channel gain can be set from
1 dB to 24 dB in 0.5 dB increments.
Figure 11. Output Control Section of SSM2380 GUI
ALC Control 1 (Register R3)
This is associated with Control Register R3. This section allows
the user to control the release time and attack time of the
SSM2380.
ALC Control 2 (Register R4)
This is associated with Control Register R4. This section allows
the user to enable ALC operation, to set the compressor operation mode (light to heavy compression and limiting), to set the
limiter level, and to set the limiter mode.
There are two limiter modes: fixed power and supply tracking.
Fixed power mode sets the output limiter level to a fixed value,
independent of the power supply rail. Supply tracking mode
sets the limiter as a percentage of SPKVDD.
Note that if the user intends to change the gain setting registers,
R0 or R1, the user must toggle the ALC Enable check box to
allow the new gain settings to take effect.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
09686-011
AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS
This section allows user access to the power management
control registers, current/thermal fault recovery, mixing
operation, and edge rate control.
Figure 12. Auxiliary Function Section of SSM2380 GUI
Shutdown (Register R5)
To enable the SSM2380, simply click ON for left and/or right
channels.
Mode Control (Register R2)
The Mode Control (Register R2) section, which is associated
with Control Register R2, contains a collection of unrelated
settings, including current and thermal fault recovery, mixers,
and emissions control modes.
Current/Thermal Fault Recovery
The Overcurrent Autorecovery and Overtemperature
Autorecover y check boxes control the autorecovery feature
of the fault detection mode. When selected, the autorecovery
feature is active. When cleared, the device stays in fault
protection mode until the reset register, R8, is written to zero
or the device loses power.
Mixer Modes
When R-to-L Signal Mix is selected, the right input signal is
mixed to both right and left outputs. When L-to-R Signal Mix
is selected, the left input signal is mixed to both left and right
outputs.
Edge Speed
Several different emission control mode levels can be set. The
slowest setting yields the best emission suppression, but it may
degrade SNR and efficiency measurements slightly.
Error (Register R6)
This section is associated with Control Register R6. Each block
is a read-only indicator that is activated when a particular fault
condition is encountered. It does not update unless the R6 Read
button is clicked, as detailed in the Direct I
2
C Register Access
section. This feature is only active if the fault recovery options
(overcurrent autorecovery and overtemperature autorecovery)
are enabled.
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
09686-012
09686-013
09686-021
QUICK SET BUTTONS
The GUI includes a collection of buttons to switch quickly
to several predefined configurations. See Figure 13 and the
following three sections for details.
Figure 13. Preset Button Section of SSM2380 GUI
RESET
RESET first initializes the SSM2380 by writing all 0s to
Control Register R8. It then clears all previously stored
read/write windows and ensures that all registers are set
to the proper default value. The RESET button should be
clicked every time power is disrupted from the SSM2380
to synchronize the SSM2380 to the control software.
Music Optimized
By clicking the Music Optimized preset button, the following
occurs:
• Left and right channels are enabled.
• Gain for both left and right channels is set to 18 dB.
• The ALC operation is enabled and tuned for optimized sound
quality for music playback. A slower attack time is used,
along with heavier compression and a slower release time.
Voice Optimized
By clicking the Voice Optimized preset button, the following
occurs:
• Left and right channels are enabled.
• Gain for both left and right channels is set to 18 dB.
• The ALC operation is enabled and tuned for optimized
SPL level for voice playback. A faster attack time is used,
a small amount of compression before limiter operation,
and a faster release time.
DIRECT I2C REGISTER ACCESS
Within each subsection is direct access to the associated I2C
control register. If the user desires, data can be directly written
to the control register by typing the register data byte in hexadecimal format. Simply type the desired word in hexadecimal
format in the desired register write window. Click the Wri te
button when ready to send this data to the SSM2380. The
associated subsection options from the main GUI section
are also updated. You can also check the register contents by
clicking the Read button. The register contents are displayed
in the text box next to each button.
Figure 14. I
2
C Register Direct Control of SSM2380 GUI
USB POWER
The 5 V power switch, described in the USB Power Switch
section, is activated by clicking 5V USB Power ON as shown
in Figure 15.
Figure 15. USB Power Control
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
09686-014
USB—I2C INTERFACE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The EVAL-ADUSB2EBZ, also known as the USBi, is a standalone communications interface adapter and programmer used
in the evaluation of SigmaDSP® systems. It translates USB
control commands from SigmaStudio to the I
communications protocols.
To simplify bench evaluation, an interface based on the USBi
adapter is included on the SSM2380 evaluation board. This
eliminates the need for a separate interface board and 10-pin
ribbon cable; only a USB mini-B cable is required. This
interface is shown in Figure 16.
2
C and SPI
USB CONNECTOR
The connection between the host PC and the Cypress USB
interface device is via a standard USB cable that carries D+ and
D− signals for data communications, a 5 V power supply, and
ground. The D+ and D− lines are a 1-wire communication
interface carried by half-duplex differential signals on a twisted
pair. The clock is embedded in the data using the nonreturn-tozero inverted (NRZI) line code. These signal lines connect
directly to pins on the Cypress USB interface.
A surface-mounted USB miniature Type B jack was selected
for its low profile and increasing popularity in consumer
electronics.
POWER REGULATOR
The Cypress USB interface I/O ports are capable of operating
in both 1.8 V and 3.3 V modes, depending on the target device
in the system. Two regulators, one for 5 V to 3.3 V regulation
and the other for 5 V to 1.8 V regulation, run simultaneously
when the board is powered. A jumper (JP4) is provided to
easily switch the IOVDD supply between the two regulators.
D1 provides visual feedback that the board is being supplied
with 5 V power from the PC USB port.
The position of Jumper JP4 should not be changed when the
board is connected to the USB bus.
2
Figure 16. USB to I
C Microcontroller and USB interface
The on-board regulators enable both 1.8 V and 3.3 V IOVDD
operation, allowing for increased testing flexibility.
The USBi interface can also control SigmaDSP systems in
real time via SigmaStudio, and it is capable of programming
an EEPROM in self-boot systems. It is an ideal solution for
in-circuit programming and tuning of prototype systems.
The USBi only supports USB 2.0 interfaces; it does not
work with PCs that only support USB Version 1.0 and
USB Version 1.1.
CYPRESS USB INTERFACE
The Cypress USB interface is the core of the system, including
all of the necessary functionality to convert USB commands
into corresponding I
2
C or SPI read/write transfers, and acts as a
FIFO to route data between the host PC and the target device.
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
The Cypress USB interface is its own clock master, and the board
includes a crystal oscillator circuit with a 24 MHz crystal
resonator to provide stability to the oscillator circuit. The
crystal resonator is driven by the XTALOUT and XTALIN
pins of the Cypress USB interface.
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
PASSIVE COMPONENT SELECTION
Although the evaluation board is preloaded with the passive
components required for a basic configuration, the user may
wish to evaluate the same circuit with different component
values or filter designs. Selecting the proper components is the
key to achieving the performance required at the budgeted cost.
INPUT COUPLING CAPACITOR SELECTION (C22 TO C25)
The input coupling capacitors, C22 to C25, should be large
enough to couple the low frequency signal components in the
incoming signal and small enough to filter out unnecessary
low frequency signals. For music signals, the cutoff frequency
chosen is often between 20 Hz and 30 Hz to preserve the low
frequency components of the signal; for applications with small
speakers, a higher cutoff frequency is often chosen to reduce
the power wasted on audio that cannot be reproduced by the
speaker.
The value of each input capacitor is calculated by
C = 1/(2R
where:
R
is the amplifier’s input resistance.
IN
f
is the cutoff frequency.
C
Because R
IN
to 55 kΩ over the entire gain range of the SSM2380, this
calculation must be performed carefully to ensure that the
low frequency performance is acceptable at all gain levels.
The relationship between gain and input resistance is shown
in Table 3.
As an example calculation, suppose that the low frequency
cutoff is to be no higher than 200 Hz and that the amplifier
gain varies between 6 dB and 18 dB. In this case, the input
resistance is between 39.6 kΩ and 13.6 kΩ. Because the cutoff
frequency is highest when the input resistance is small, the
calculation should be done using the minimum value—in
this case, giving a minimum capacitance of approximately
59 nF. A larger standard value (perhaps 100 nF) should be
used to account for the ordinary variation due to tolerance,
temperature coefficient, and so on.
)
INfC
varies with amplifier gain value from 7.3 kΩ
Table 3. Input Impedance for I
LGAIN[5:0], RGAIN[5:0] Gain (dB) RIN (kΩ)
101110 24.0 7.3
101101 23.5 7.7
101100 23.0 8.1
101011 22.5 8.5
101010 22.0 9.0
101001 21.5 9.5
101000 21.0 10.0
100111 20.5 10.5
100110 20.0 11.1
100101 19.5 11.7
100100 19.0 12.3
100011 18.5 12.9
100010 18.0 13.6
100001 17.5 14.3
100000 17.0 15.0
011111 16.5 15.8
011110 16.0 16.6
011101 15.5 17.4
011100 15.0 18.3
011011 14.5 19.2
011010 14.0 20.1
011001 13.5 21.1
011000 13.0 22.1
010111 12.5 23.1
010110 12.0 24.2
010101 11.5 25.3
010100 11.0 26.4
010011 10.5 27.6
010010 10.0 28.8
010001 9.5 30.0
010000 9.0 31.3
001111 8.5 32.6
001110 8.0 34.0
001101 7.5 35.3
001100 7.0 36.7
001011 6.5 38.1
001010 6.0 39.6
001001 5.5 41.1
001000 5.0 42.6
000111 4.5 44.1
000110 4.0 45.6
000101 3.5 47.1
000100 3.0 48.7
2
C Control Mode
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
OUTPUT FERRITE BEADS (B1 TO B4)
The output beads, B1 to B4, are suggested components for
filtering out the EMI caused at the switching output nodes. The
penalty for using ferrite beads for EMI filtering is slightly worse
noise and distortion performance at the system level due to the
nonlinearity of the beads. Ensure that these beads have enough
current conducting capability while providing sufficient EMI
attenuation. The current rating needed for an 8 Ω load is approximately 420 mA, and impedance at 100 MHz must be ≥120 Ω. In
addition, the lower the dc resistance (DCR) of these beads, the
better for minimizing their power consumption. Table 4
describes suggested beads.
OUTPUT SHUNTING CAPACITORS (C29 TO C32)
There are four output shunting capacitors, C29 to C32, that
work with the B1 to B4 ferrite beads or with the L1 to L4
inductors, if they are used. Use small size (0603 or 0402),
Table 4. Suggested Output Beads
Part No. Manufacturer Z (Ω) I
BLM18PG121SN1D Murata 120 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
MPZ1608S101A TDK 100 3000 0.03 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
MPZ1608S221A TDK 220 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
BLM18EG221SN1D Murata 220 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
multilayer ceramic capacitors that are made of X7R or C0G
(NP0) materials. Note that the capacitors can be used in pairs: a
capacitor with small capacitance (up to 100 pF) plus a capacitor
with a larger capacitance (less than 1 nF). This configuration
provides thorough EMI reduction for the entire frequency spectrum. Alternatively, a single capacitor of approximately 470 pF
can be used if BOM reduction is a priority.
OUTPUT INDUCTORS (L1 TO L4)
If inductors are preferred for EMI filtering at the output nodes,
choose a component value less than 2.2 µH for these inductors.
The higher the inductance, the lower the EMI is at the output;
however, the cost and power consumption by the inductors are
higher. Using 0.47 µH to 2.2 µH inductors is recommended, and
the saturation current rating must be larger than 600 mA for an
8 Ω load. Table 5 shows suggested inductors.
(mA) DCR (Ω) Size (mm)
MAX
Table 5. Suggested Output Inductors
Part No. Manufacturer L (µH) I
LQM31PNR47M00 Murata 0.47 1400 0.07 3.2 × 1.6 × 0.85
LQM31PN1R0M00 Murata 1.0 1200 0.12 3.2 × 1.6 × 0.85
LQM21PNR47MC0 Murata 0.47 1100 0.12 2.0 × 1.25 × 0.5
LQM21PN1R0MC0 Murata 1.0 800 0.19 2.0 × 1.25 × 0.5
LQH32CN2R2M53 Murata 2.2 790 0.1 3.2 × 2.5 × 1.55
LBC2518T2R2M Taiyo Yuden 2.2 630 0.13 2.5 × 1.8 × 2
1033AS-4R7M
Toko 4.7 680 0.31 3.8 × 3.8 × 1
(mA) DCR (Ω) Size (mm)
MAX
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
PO SI TI ON O
F J UMPE
RS
:
1- 2: INTERNA L I 2C CONTR OL LE R
2- 3: EXTERNA L I 2C CON TR OL L
ER
Ex te rn al I2C
Co nn ec
to r
Vo la tg e Sele ct or
EE PR OM
Co nn ec tor
Re se t
U
S
B_ PW R_ON
SD A1SC L1
5V 0DD
1LCS
D
DVOI
EX
VD D
SD A2
SC L2
EX VD
D
SC L2
SDA1SD A
2
SC L1
SD A1
SV DD
SC L
SD A
IOVDD
3
V3 D
D
IOVDD
3V 3DD
IOVDD
3
V3 D
D
5V 0DD_U SB
3V 3DD
IOVDD
3
V3
DD
IOVDD
3
V3 DD
IOVDD
IOVDD
IOVDD
3V 3DD
1V 8DD
1V
8D D
IOVDD
3V
3D D
1V 8DD
SW 1
P
US HB TN
C1 7
22
pF
JP1
HD R1X3
1
2
3
JP3
HD R1X3
123
M31
C1 3
0.1 uF
U7
FXLP3
4P
5X
1
2
3
4
5
VC C1
A
GN D
Y
VC C
JP2
HD R1X3
1
2
3
U5
FXLP34P5X
1
2
3
4
5
VC C1
A
GN D
Y
VC C
D4
YE LLO W
C1
1uF
C1 6
0.1 uF
C8
10nF
R
25
475
U1
AD P1
711-3.3
1
3
2
4
5
IN
EN
GN D
BY P
OU T
U6FXLP34P5X
1
2
3
4
5
VC C1
A
GN D
Y
VC C
H1
HD R1X3
1
2
3
R1 1
4
75
R1
100k
Q1
FZ T70 5/S OT
R8
475
C7
10nF
C9
0.
1u
F
D1
RE D
U4
CY 7C680
53-5
6
BA XI
2E
1E
3F
3G
1A
1B
7H7G8H
2B
2G
2C
1C
7B
8B
8G
6G
8
F
7F6F8C
7C6C3H
4F
4H4G
5H5G5F
6H
8A
7A
6B
6A3B3A
3C
2A
2D
1D
5A
5B
7E
8E
5C
1G
1F
2F
1H
2H
4A
4B
4C
7D
8D
DP LUS
DM INUS
SC L
SD A
RD Y0/SL
RD
RD Y1/S
LW R
CT L
0/F LAGA
CT L1/F
L
AG B
C
TL2/F
LA GC
CL KOUT
IFC LK
XT ALOUT
XT ALIN
WAKE UP
RE SET
P
A0 /
IN
T0
PA 1/I
NT 1
P
A2 /SLOE
PA 3/W U2
PA 4/F IF
OA DR 0
PA 5/F IFO
AD R
1
PA 6/P KT
EN D
PA 7/F LAG D/SL
CS
PB 0/F D[0 ]
PB 1/F D[1 ]
PB 2/F D[2 ]
PB 3/F D
[3
]
PB 4/F D
[
4]
PB 5/F D[5]PB 6/F D[6]PB 7/
FD [7
]
PD 0/F D[8 ]
PD 1/F D[9 ]
PD
2/F
D[10]
PD 3/F D[1 1]
PD
4/
F
D[12]
PD 5/F D[13]PD 6/F D[14]PD 7/F D[1 5]
AV CC
AV CC
VC C_ IO
VC C_IO
VC C_ IO
VC C_IO
VC C_ D
VC C_ A
AG ND
AG ND
GN D
GN D
GN D
GN D
GN D
GN D
GN D
U2
AD P1711-1.8
1
3
2
4
5
IN
EN
GN D
BY P
OU T
Y1
24MHz
C
11
10uF
D2
YE LLO W
U3
24AA2 56
123
4
5
678
A0A1A2
GN D SD A
SC
L
WP
VC C
R9
4
75
H2
HD R1X4
123
4
C5
1uF
C3
10uF
J1US B_MIN I
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
VB US
DM
DP
ID
GN D
6
789
10
11
C1 9
1uF
C1 5
0.1 uF
R
6
4.9 9k
R5
10k
R3
475
C2
1uF
C1822pF
C4
1uF
C1 0
10uF
C2 0
0
.1u F
C6
10uF
R1 0
100k
D3
B
L
U
E
C1 2
0.1 uF
R2
2k
R4
10k
R2 3
0
R74
.99 k
C1 4
0.1 uF
Q2
MM BT3904
LT1 G
C2 1
0.1 uF
JP 4
HD
R1
X3
123
D5
BL UE
R2
2
0
09686-019
EVALUATION BOARD SCHEMATICS AND ARTWORK
Figure 17. USB Interface Schematic
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
J2P
HONEJACK STEREO
JP5
HDR1X4
JP6
HDR1X4
5V0DD_USB
1
2
3
C22
R14
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
A
SPKVDD
0.22uF
C23
0.22uF
C24
0.22uF
C25
0.22uF
JP8
HDR1X2
R15
R16
R17
0
0
0
0
SDA
SCL
SVDD
JP7
HDR1X2
D1
D4
D3
R18
R19
SPKVDD
H3
HDR1X2
C26
10uF
Merge all grounds here.
C27
0.1uF
S
A
SPKG
A3
A2
VDD
VDD
INL P
U8
SSM2380
INR P
INR N
GND
GND
B3
B2
SPKG
0
0
R20
4.99k
mble
A
OUTLP
OUTLNINL N
OUTRP
OUTRN
MODE
SDALG1STDN
SCEDG0
C28
0.1uF
R21
4.99k
A1
B1D2
A4
B4
C2
C4C1
C3
SPKVDD
JP9
1
2
3
HDR1X3
R24
12k
1
2
3
HDR1X3
A
JP10
SPKVDD
1
2
3
A
JP11
HDR1X3
L1
LQM31P NR4 7M00
B1
MPZ1608S 221A
H4
HDR1X2
B2
MPZ1608S 221A
L2
LQM31P NR4 7M00
L3
LQM31P NR4 7M00
B3
MPZ1608S 221A
H5
HDR1X2
B4
MPZ1608S 221A
L4
LQM31P NR4 7M00
C29
510pF
C30
510pF
C31
510pF
C32
510pF
C33
510pF
C34
510pF
C35
510pF
C36
510pF
SPKG
SPKG
OUT_L+
OUT_L-
OUT_R+
OUT_R-
H6
HDR1X2
H7
HDR1X2
09686-020
Figure 18. SSM2380 Schematic
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
09686-015
09686-016
Figure 19. Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Side (Layer 1)
Figure 20. Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane (Layer 2)
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
09686-017
09686-018
Figure 21. Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane (Layer 3)
Figure 22. Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Side (Layer 4)
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
7 4 C22, C23, C24, C25
Ceramic capacitor, 0.22 µF, 16 V, X7R, 0805
Panasonic - ECG
ECJ-2VB1C224K
19 1 Q1
Transistor PNP, −120 V, −2000 mA, SOT-223
Diodes/Zetex
FZT705TA
20 1 Q2
Transistor, GP NPN AMP SOT-23
Fairchild
MMBT3904
22 1 R2
Yageo
RC0805FR-072KL
Semiconductor
ORDERING INFORMATION
BILL OF MATERIALS
Table 6.
Reference
Item Qty
1 4 B1, B2, B3, B41 Ferrite chip, 220 Ω, 2A, 0603 TDK Corporation MPZ1608S221A
2 5 C1, C2, C4, C5, C19 Ceramic capacitor, 1.0 µF, 10 V, X7R, 0805 Kemet C0805C105K8RACTU
3 5 C3, C6, C10, C11, C26 Ceramic capacitor, 10 µF, 10 V, 10%, X5R, 0805 Murata Electronics GRM21BR61A106KE19L
4 2 C7, C8 Ceramic capacitor, 0.01 µF, 10%, 50 V, X7R, 0603 AVX Corporation 06035C103KAT2A
5 8 C9, C12, C13, C14,
6 2 C17, C18 Ceramic capacitor, 22 pF, 50 V, 0603, SMD Panasonic - ECG ECJ-1VC1H220J
8 2 C27, C282 Ceramic capacitor, 0.10 µF, 25 V, X5R, 0603 Taiyo Yuden TMK107BJ104KA-T
9 8 C29, C30, C31, C32,
10 1 D1 LED MINISMD, red, 7.5 MCD, GAASP/GAP Vishay/Semiconductors TLMS2100-GS08
11 2 D2, D4 LED MINISMD, yellow, 7.5 MCD, GAASP/GAP Vishay/Semiconductors TLMY2100-GS08
12 2 D3, D5 LED, blue, 471 NM, clear, SMD OSRAM Opto
13 8 JP1, H1, JP2, JP3, JP4,
14 3 H2, JP5, JP6 Connector, header, breakaway, 0.100 04POS, STR Tyco Electronics 4-103747-0-04
15 7 H3, H4, H5, H6, JP7,
16 1 J1 Connector mini USB, RCPT, RA, Type B, SMD Tyco Electronics 1734035-2
17 1 J2 Connector jack stereo RA 3-pin 3.5 mm CUI Inc. SJ1-3523N
18 4 L1, L2, L3, L44 0.47 μH, 1.4A, 80 mΩ, 3.2 mm × 1.6 mm Murata Electronics LQM31PNR47M00
Designator Description Manufacturer Part Number
Ceramic capacitor, 0.10 µF, 25 V, X5R, 0603 Taiyo Yuden TMK107BJ104KA-T
C15, C16, C20, C21
Ceramic capacitor, 510 pF, 50 V, 5%, C0G, 0603 Murata Electronics GRM1885C1H511JA01D
C33, C34, C35, C36
3
LB M673-L1M2-35-Z
Semiconductors
Connector, header, breakaway, 0.100, 03POS, STR Tyco Electronics 4-103747-0-03
JP9, JP10, JP11
Connector, header, breakaway, 0.100 02POS, STR Tyco Electronics 4-103747-0-02
H7, JP8
Semiconductor
21 2 R1, R10
Resistor, 100 kΩ, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
Panasonic - ECG ERJ-6ENF1003V
Resistor, 2.00 kΩ, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
23 5 R3, R8, R9, R11, R25
24 2 R4, R5
25 4 R6, R7, R20, R215
26 8 R14, R15, R16, R17,
R18, R19, R22, R23
27 1 R24
Resistor, 475 Ω, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
Resistor, 10.0 kΩ, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
Resistor, 4.99 kΩ, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
Resistor, 0.0 Ω, ⅛ W, 0805, SMD
5
Resistor, 4.99 kΩ, ⅛ W, 1%, 0805, SMD
Panasonic - ECG ERJ-6ENF4750V
Yageo RC0805FR-0710KL
Yageo RC0805FR-074K99L
Panasonic - ECG ERJ-6GEY0R00V
Yageo RC0805FR-074K99L
28 1 SW1 Switch TACT SMD, W/O GND, 160 g Omron Electronics Inc B3SN-3012P
29 1 U1 IC REG LDO, 150 mA, 3.3 V, TSOT-23-5 Analog Devices Inc ADP1711AUJZ-3.3-R7
30 1 U2 IC REG LDO, 150 mA, 1.8 V, TSOT-23-5 Analog Devices Inc ADP1711AUJZ-1.8-R7
31 1 U3 IC EEPROM, 256 Kb, 400 kHz, 8 TSSOP Microchip Technology 24AA256-I/ST
32 1 U4 IC MCU MOBL-USB 56-VFBGA Cypress
36 3 U5, U6, U7 Translator, 1-bit, unidirect, SC70-5 Fairchild
CY7C68053-56BAXIT
FXLP34P5X
Semiconductor
37 1 U8 Class-D audio amplifier with ALC + I2C Analog Devices Inc. SSM2380CBZ
38 1 Y1 Crystal, 24.000 MHz, 20 pF, 49 µs ECS Inc. ECS-240-20-4X
1
B1 to B4 use 0 Ω links.
2
C28 is not populated.
3
C29 to C36 are not populated.
4
L1 to L4 are not populated.
5
R18 to R21 are not populated.
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 20

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-248
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 20

UG-248 Evaluation Board User Guide
ense granted is expressly made subject to the following additional
NATION. ADI may terminate this Agreement at any time upon giving written notice
TS OR LOSS OF GOODWILL. ADI’S TOTAL LIABILITY FROM ANY AND ALL CAUSES SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE
NOTES
ESD Caution
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Charged devices and circuit boards can discharge without detection. Although this product features patented or proprietary protection
circuitry, damage may occur on devices subjected to high e nergy ESD. Therefore, proper ESD precaution s should be taken to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Legal Terms and Conditions
By using the evaluation board discussed herein (together with any tools, components documentation or support materials, the “Evaluation Board”), you are agreeing to be bound by th e terms and conditions
set forth below (“Agreement”) unless you have purchased the Evaluation Board, in which case the Analog Devices Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale shall govern. Do not use the Evaluation Board until you
have read and agreed to the Agreement. Your use of the Evaluation Board shall signify your acceptance of the Agreement. This Agreement is made by and between you (“Customer”) and Analog Devices, Inc.
(“ADI”), with its principal place of business at One Technology Way, Norwood, MA 02062, USA. Subject to the terms and conditions of the Agreement, ADI hereby grants to Customer a free, limited, personal,
temporary, non-exclusive, non-sublicensable, non-transferable license to use the Evaluation Board FOR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY. Customer understands and agrees that the Evaluation Board is provided
for the sole and exclusive purpose referenced above, and agrees not to use the Evaluation Board for any other purpose. Further more, the lic
limitations: Customer shall not (i) rent, lease, display, sell, transfer, assign, sublicense, or distribute the Evaluation Board; and (ii) permit any Third Party to access the Evaluation Board. As used herein, the ter m
“Third Party” includes any entity other than ADI, Customer, their employees, affiliates and in-house consultants. The Evaluation Board is NOT sold to Customer; all rights not expressly granted herein, including
ownership of the Evaluation Board, are reserved by ADI. CONFIDENTIALITY. This Agreement and the Evaluation Board shall all be considered the confidential and proprietary information of ADI. Customer may
not disclose or transfer any portion of the Evaluation Board to any other party for any reason. Upon discontinuation of use of the Evaluation Board or termination of this Agreement, Customer agrees to
promptly return the Evaluation Board to ADI. ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS. Customer may not disassemble, decompile or reverse engineer chips on the Evaluation Board. Customer shall inform ADI of any
occurred damages or any modifications or alterations it makes to the Evaluation Board, including but not limited to soldering or any other activity that affects the material content of the Evaluation Board.
Modifications to the Evaluation Board must comply with applicable law, including but not limited to the RoHS Directive. TERMI
to Customer. Customer agrees to return to ADI the Evaluation Board at that time. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. THE EVALUATION BOARD PROVIDED HEREUNDER IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND ADI MAKES NO
WARRANTIES OR REPRES ENTATIONS OF ANY KIND WITH RESPECT TO IT. ADI SPECIFICAL LY DISC LAIMS ANY REPRESENTATIONS, ENDORSEMENTS, GUAR ANTEES, OR WARRANT IES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, RELATED
TO THE EVALUATION BOARD INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, TITLE, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NONINFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL
PROPERTY RIGHTS. IN NO EVENT WILL ADI AND ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM CUSTOMER’S POSSESSION OR USE OF
THE EVALUATION BOARD, INCLUDING B UT NOT LIMITED TO LOST PR OFITS, DELAY COSTS, LAB OR COS
AMOUNT OF ONE HUNDRED US DOLLARS ($100.00). EXPORT. Customer agrees that it will not directly or indirectly export the Evaluation Board to another country, and that it will comply with all applicable
United States federal laws and regulations relating to exports. GOVERNING LAW. This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the substantive laws of the Commonwealth of
Massachusetts (excluding conflict of law rules). Any legal action regarding this Agreement will be heard in the stat e or federal courts having jurisdiction in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, and Customer hereby
submits to the personal jurisdiction and venue of such courts. The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement and is expressly disclaimed.
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
UG09686-0-9/11(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 20
 Loading...
Loading...