Hardware User Guide
UG-216
One Technology Way • P. O . Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel : 781.329.4700 • Fax : 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
Dual Port Xpressview Advantiv HDMI Receiver Functionality and Features
SCOPE
This user guide provides a detailed description of the Advantiv™ ADV7612 HDMI® functionality and features.
DISCLAIMER
Information furnished by Analog Devices, Inc., is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog
Devices for its use, nor any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to
change without notice. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks
and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
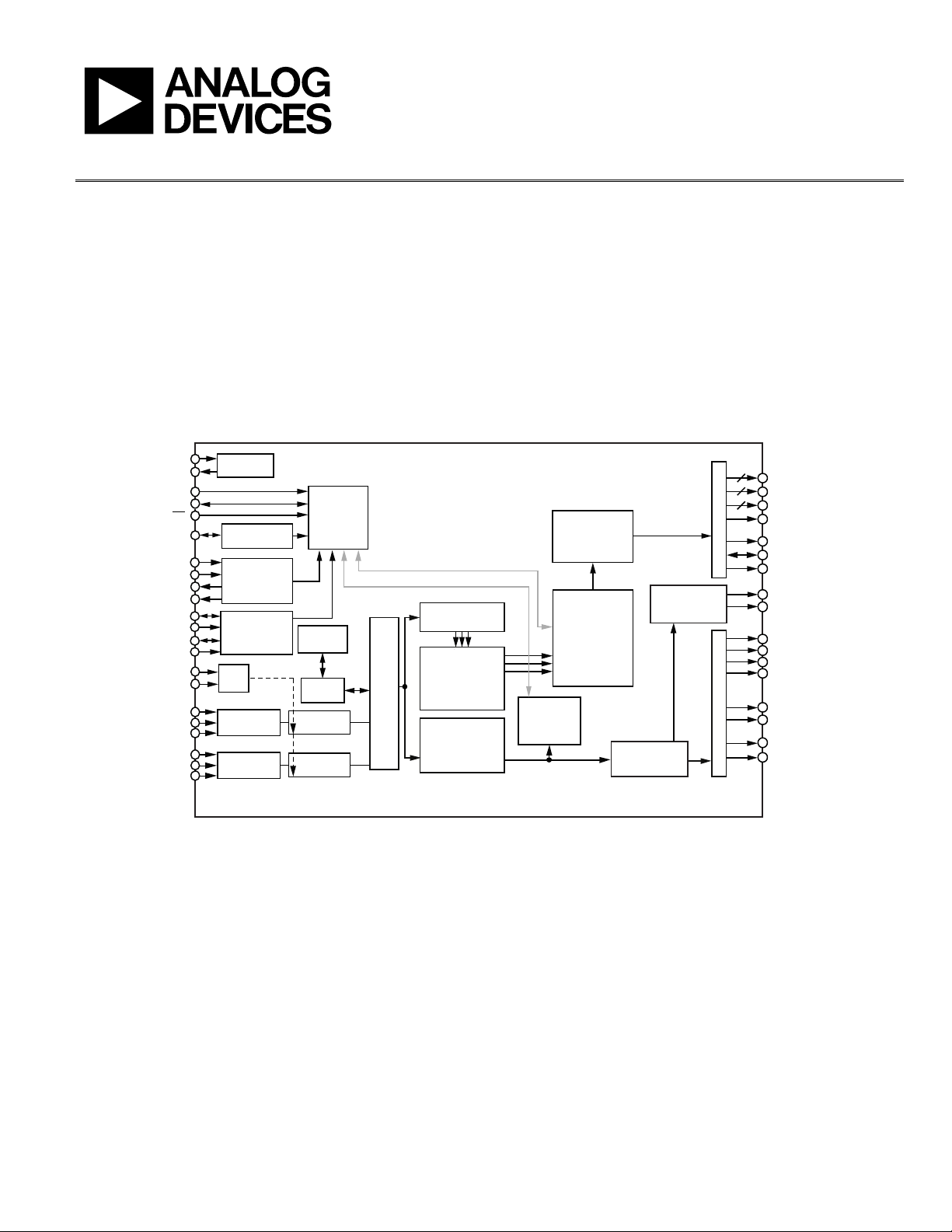
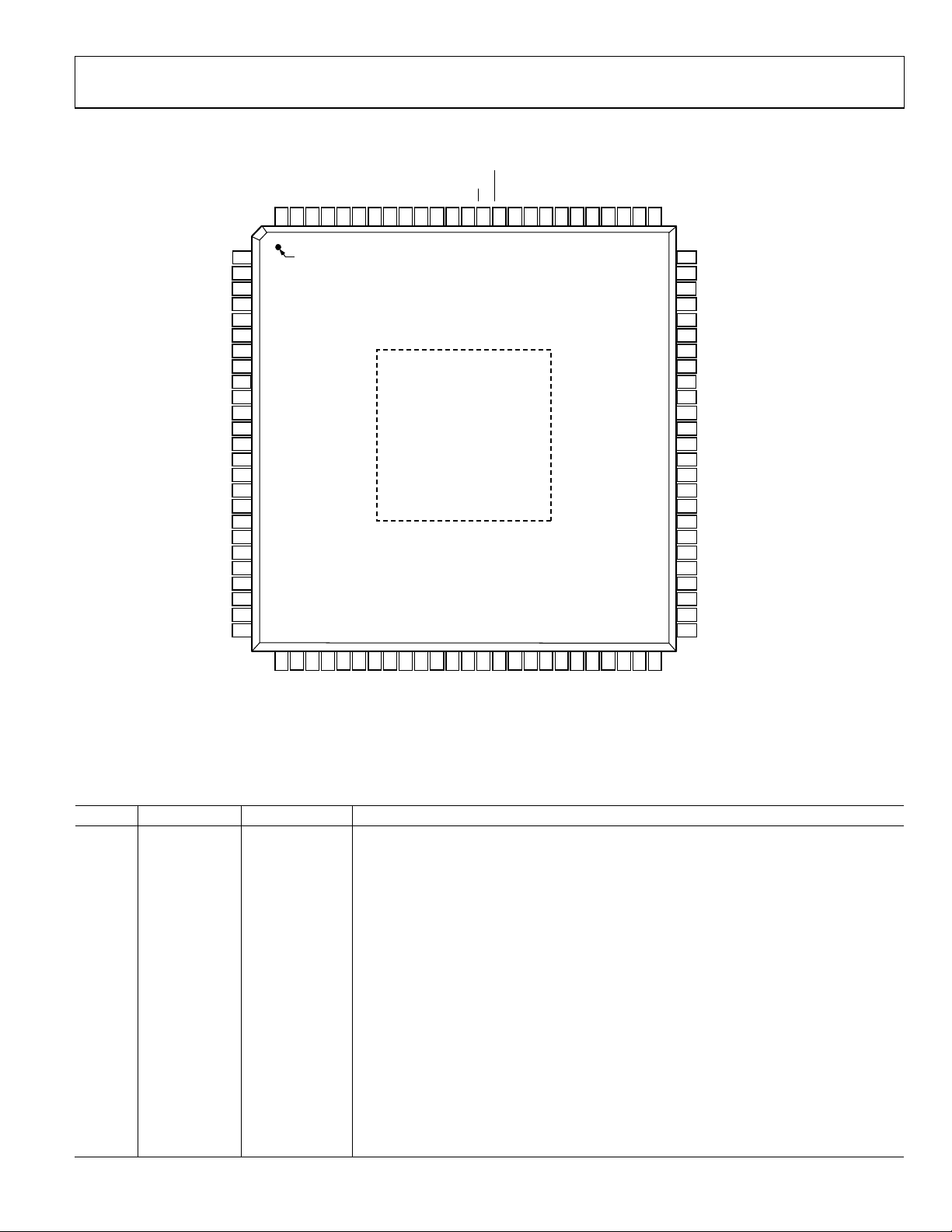
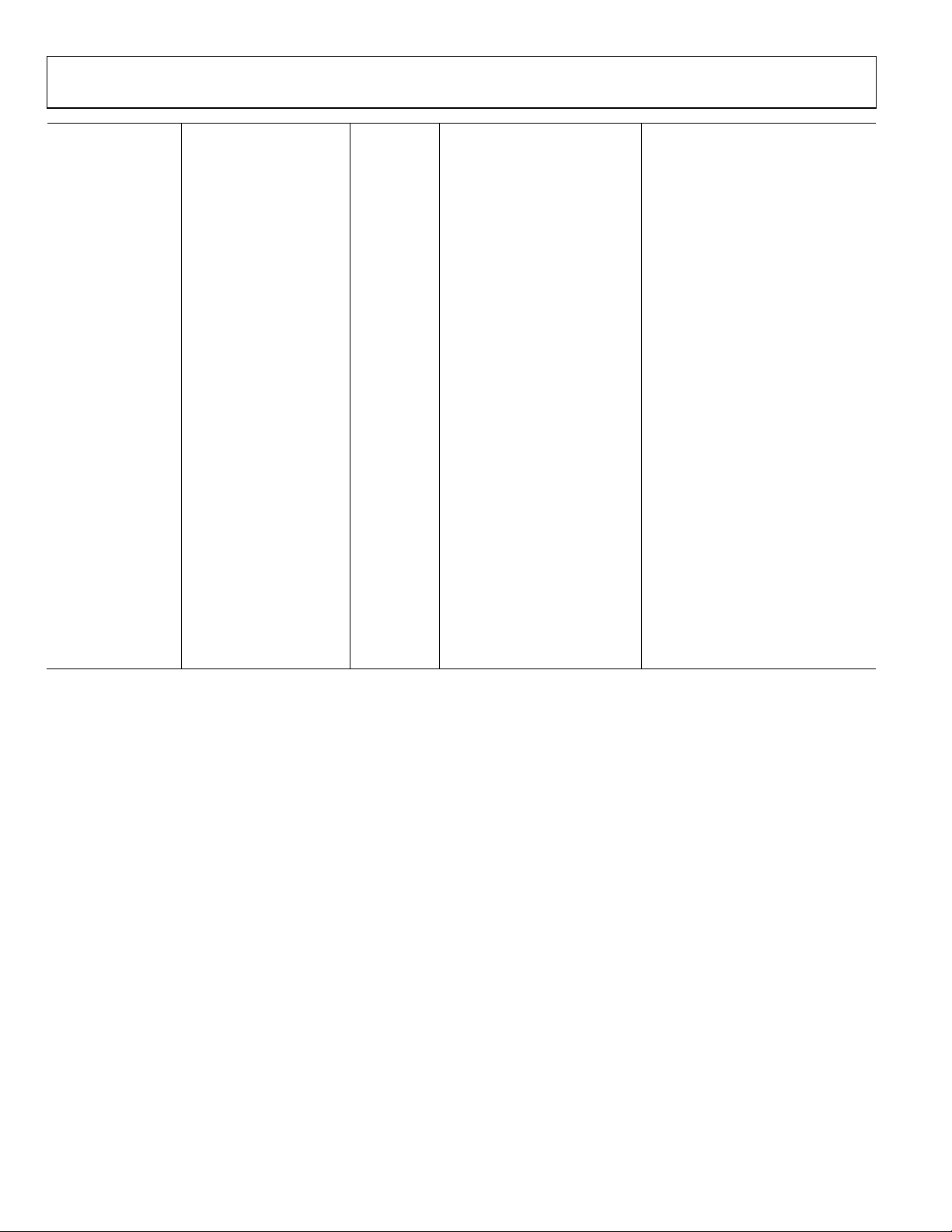
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
XTALP
XTALN
SCL
SDA
CS
CEC
RXA_5V
RXB_5V
HPA_A/INT2*
HPA_B
DDCA_SDA
DDCA_SCL
DDCB_SDA
DDCB_SCL
RXA_C±
RXB_C±
RXA_0±
RXA_1±
RXA_2±
RXB_0±
RXB_1±
RXB_2±
DPLL
CEC
CONTROLLER
5V DETECT
AND HPD
CONTROLLER
EDID
REPEATER
CONTROLLER
PLL
EQUALIZER
EQUALIZER
CONTROL
INTERFACE
I
HDCP
EEPROM
HDCP
ENGINE
SAMPLER
SAMPLER
12
P0 TO P11
12
P12 TO P23
12
P24 TO P25
2
C
CONTROL
AND DATA
HDMI
PROCESSOR
™
XPressView
FAST SWITCHING
DATA
PREPROCESOR
AND COLOR
SPACE
CONVERSION
PACKET
PROCESSOR
COLOR SPACE
CONVERSION
COMPONENT
PROCESSOR
A
B
C
PACKET/
INFOFRAME
MEMORY
BACKEND
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
(INT1, INT2)
MUTE
AUDIO
PROCESSOR
OUTPUT FORMATTER
AUDIO OUTPUT FORMATT ER
LLC
HS
VS/FIELD/ALSB
DE
INT1
INT2*
AP1
AP2
AP3
AP4
AP5
SCLK/INT2*
MCLK/INT2*
AP0
ADV7612
*INT2 CAN BE ONLY OUTPUT O N ONE OF THE PI N S : SCLK/INT2, MCLK/INT2, OR HP A _A/INT2.
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
Rev. B | Page 1 of 204
09486-001

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Scope .................................................................................................. 1
Disclaimer .......................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 5
Using the ADV7612 Hardware User Guide .................................. 6
Number Notations ........................................................................ 6
Register Access Conventions ...................................................... 6
Acronyms and Abbreviations ..................................................... 6
Field Function Descriptions ........................................................ 8
Example Field Function Description ..................................... 8
References ...................................................................................... 8
Introduction to the ADV7612 ........................................................ 9
HDMI Receiver ............................................................................. 9
Component Processor ................................................................. 9
Main Features of ADV7612 ........................................................ 9
HDMI Receiver ......................................................................... 9
Component Video Processing .............................................. 10
Video Output Formats ........................................................... 10
Additional Features ................................................................ 10
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ....................... 11
Global Control Registers ............................................................... 15
ADV7612 Revision Identification ............................................ 15
Power-Down Controls ............................................................... 15
Primary Power-Down Controls ........................................... 15
Secondary Power-Down Controls ....................................... 15
Power-Down Modes .............................................................. 16
Global Pin Control ..................................................................... 17
RESET
Pin ............................................................................... 17
Reset Controls ......................................................................... 17
Tristate Output Drivers ......................................................... 17
Tristate LLC Driver ................................................................ 18
Tristate Synchronization Output Drivers ............................ 18
Tristate Audio Output Drivers.............................................. 18
Drive Strength Selection ........................................................ 19
Output Synchronization Selection ....................................... 20
Output Synchronization Signals Polarity ............................ 20
Digital Synthesizer Controls ................................................. 21
Crystal Frequency Selection ................................................. 21
Primary Mode and Video Standard ............................................. 22
Primary Mode and Video Standard Controls ......................... 22
Rev. B | Page 2 of 204
V_FREQ .................................................................................. 24
HDMI Decimation Modes ........................................................ 24
Primary Mode and Video Standard Configuration for HDMI
Free Run ....................................................................................... 24
Recommended Settings for HDMI Inputs .............................. 25
Pixel Port Configuration ............................................................... 27
Pixel Port Output Modes ........................................................... 27
Bus Rotation and Reordering Controls ............................... 27
Pixel Data and Synchronization Signals Control ............... 28
LLC Controls............................................................................... 28
DLL on LLC Clock Path ............................................................ 28
Adjusting DLL Phase in All Modes ..................................... 28
DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes ........................ 29
HDMI Receiver ............................................................................... 30
+5 V Cable Detect ...................................................................... 30
Hot Plug Assert ........................................................................... 31
E-EDID/Repeater Controller .................................................... 33
E-EDID Data Configuration..................................................... 34
Notes ........................................................................................ 34
E-EDID Support for Power-Down Modes ......................... 34
Transitioning of Power Modes ................................................. 35
Structure of Internal E-EDID for Port A ................................ 35
Structure of Internal E-EDID for Port B ................................. 36
TMDS Equalization ................................................................... 38
Port Selection .............................................................................. 38
Fast Switching and Background Port Selection ...................... 39
TMDS Clock Activity Detection .............................................. 40
Important ................................................................................ 41
Clock and Data Termination Control ................................. 41
HDMI/DVI Status Bits .............................................................. 41
Video 3D Detection ................................................................... 41
TMDS Measurement.................................................................. 42
TMDS Measurement After TMDS PLL .............................. 42
Deep Color Mode Support ........................................................ 45
Notes ........................................................................................ 45
Video FIFO .................................................................................. 46
Pixel Repetition .......................................................................... 47
HDCP Support ........................................................................... 49
HDCP Decryption Engine .................................................... 49
Internal HDCP Key OTP ROM ........................................... 50

Hardware User Guide UG-216
HDCP Keys Access Flags ....................................................... 50
HDCP Ri Expired ................................................................... 53
HDMI Synchronization Parameters ......................................... 53
Notes ......................................................................................... 53
Horizontal Filter and Measurements ................................... 53
Primary Port Horizontal Filter Measurements ................... 53
Background Port Horizontal Filter Measurements ............ 55
Horizontal Filter Locking Mechanism ................................. 55
Vertical Filters and Measurements ....................................... 56
Primary Port Vertical Filter Measurements ........................ 56
Background Port Vertical Filter Measurements ................. 58
Vertical Filter Locking Mechanism ...................................... 59
Low Frequency Formats ......................................................... 60
Audio Control and Configuration ............................................ 60
Important ................................................................................. 60
Audio DPLL ............................................................................. 61
Locking Mechanism ............................................................... 61
ACR Parameters Loading Method ....................................... 61
Audio DPLL Coast Feature .................................................... 61
Audio FIFO .................................................................................. 61
Audio Packet Type Flags ............................................................ 63
Notes ......................................................................................... 64
Audio Output Interface .............................................................. 65
I2S/SPDIF Audio Interface and Output Controls ............... 66
Notes ......................................................................................... 67
DSD Audio Interface and Output Controls ........................ 69
HBR Interface and Output Controls .................................... 71
MCLKOUT Setting ..................................................................... 72
Audio Channel Mode ................................................................. 72
Audio Muting .............................................................................. 73
Delay Line Control ................................................................. 73
Audio Mute Configuration .................................................... 74
Internal Mute Status ............................................................... 75
AV Mute Status ........................................................................ 76
Audio Mute Signal .................................................................. 76
Audio Stream with Incorrect Parity Error ........................... 76
Audio Clock Regeneration Parameters .................................... 77
ACR Parameters Readbacks .................................................. 77
Monitoring ACR Parameters ................................................. 77
Channel Status ............................................................................. 78
Validity Status Flag .................................................................. 78
Rev. B | Page 3 of 204
General Control and Mode Information ............................. 80
Category Code ......................................................................... 80
Source Number and Channel Number ................................ 80
Sampling and Frequency Accuracy ...................................... 81
Word L eng t h ............................................................................ 81
Channel Status Copyright Value Assertion ......................... 82
Monitoring Change of Audio Sampling Frequency ........... 82
Packets and InfoFrames Registers ............................................ 82
InfoFrames Registers .............................................................. 83
InfoFrame Collection Mode .................................................. 83
InfoFrame Checksum Error Flags ........................................ 83
AVI InfoFrame Registers ....................................................... 84
Audio InfoFrame Registers .................................................... 85
SPD InfoFrame Registers ....................................................... 86
MPEG Source InfoFrame Registers ...................................... 87
Vendor Specific InfoFrame Registers ................................... 88
Packet Registers ........................................................................... 89
ACP Packet Registers ............................................................. 89
ISRC Packet Registers............................................................. 90
Gamut Metadata Packets ....................................................... 92
Customizing Packet/InfoFrame Storage Registers ................. 93
Repeater Support ......................................................................... 94
Repeater Routines Performed by the EDID/Repeater
Controller ................................................................................. 94
Repeater Actions Required by External Controller ........... 95
HDCP Registers Available in Repeater Map ....................... 96
Interface to DPP Section .......................................................... 101
Notes ....................................................................................... 102
Pass Through Mode .................................................................. 102
4:2:2 Pass Through ................................................................ 102
4:4:4 Pass Through ................................................................ 102
Color Space Information Sent to the DPP and CP Sections
..................................................................................................... 103
Status Registers .......................................................................... 103
HDMI Section Reset Strategy ................................................. 106
HDMI Packet Detection Flag Reset........................................ 106
Data Preprocessor and Color Space Conversion and Color
Controls .......................................................................................... 107
Color Space Conversion Matrix .............................................. 107
CP CSC Selection .................................................................. 107
Selecting Auto or Manual CP CSC Conversion Mode .... 108
Auto Color Space Conversion Matrix ................................ 108

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
HDMI Automatic CSC Operation ..................................... 110
Manual Color Space Conversion Matrix ........................... 112
CSC in Pass-Through Mode ............................................... 116
Color Controls .......................................................................... 116
Component Processor .................................................................. 118
Introduction to the Component Processor ........................... 118
Clamp Operation ...................................................................... 118
CP Gain Operation................................................................... 120
Features of Manual Gain Control ...................................... 120
Features of Automatic Gain Control ................................. 120
Manual Gain and Automatic Gain Control Selection ..... 120
Manual Gain Control ........................................................... 121
Manual Gain Filter Mode .................................................... 122
Other Gain Controls ............................................................ 123
CP Offset Block......................................................................... 123
Notes ...................................................................................... 124
AV Code Block .......................................................................... 125
CP Data Path for HDMI Modes ............................................. 126
Pregain Block ........................................................................ 127
Sync Processed by CP Section ................................................ 130
Sync Routing from HDMI Section .................................... 130
Standard Detection and Identification .............................. 130
Detailed Mechanism of STDI Block Horizontal/Vertical
Lock Mechanism .................................................................. 132
CP Output Synchronization Signal Positioning ................... 137
CP Synchronization Signals ................................................ 138
HSync Timing Controls ...................................................... 139
VSync Timing Controls ....................................................... 141
DE Timing Controls ............................................................ 142
FIELD Timing Controls ...................................................... 143
HCOUNT Timing Control ................................................. 147
CP HDMI Controls .................................................................. 148
Free Run Mode ......................................................................... 148
Free Run Mode Thresholds ................................................. 148
Free Run Feature in HDMI Mode ...................................... 150
Free Run Default Color Output .......................................... 151
CP Status .................................................................................... 152
CP_REG_FF .......................................................................... 152
CP Core Bypassing ................................................................... 152
Consumer Electronics Control ................................................... 153
Main Controls ........................................................................... 153
CEC Transmit Section ............................................................. 154
CEC Receive Section ................................................................ 156
Logical Address Configuration .......................................... 156
Receive Buffers ..................................................................... 157
CEC Message Reception Overview ................................... 160
Antiglitch Filter Module .......................................................... 161
Typical Operation Flow ........................................................... 162
Initializing CEC Module ..................................................... 162
Using CEC Module as Initiator .......................................... 163
Using CEC Module as Follower ......................................... 164
Low Power CEC Message Monitoring ................................... 165
Interrupts ....................................................................................... 167
Interrupt Architecture Overview ........................................... 167
Interrupt Pins ............................................................................ 170
Notes ...................................................................................... 170
Interrupt Duration ............................................................... 171
Interrupt Drive Level ........................................................... 171
Interrupt Manual Assertion ................................................ 171
Multiple Interrupt Events .................................................... 172
Description of Interrupt Bits .................................................. 173
General Operation ............................................................... 173
HDMI Video Mode .............................................................. 173
CEC ........................................................................................ 173
HDMI Only Mode ............................................................... 173
Additional Explanations .......................................................... 174
STDI_DATA_VALID_RAW ............................................... 174
CP_LOCK, CP_UNLOCK ................................................. 175
HDMI Interrupts Validity Checking Process ................... 175
Storing Masked Interrupts .................................................. 177
Register Access and Serial Ports Description ........................... 189
Main I2C Port ............................................................................ 189
Register Access ..................................................................... 189
IO I2C Map Address ............................................................. 189
Addresses of Other Maps .................................................... 190
Protocol for Main I2C Port .................................................. 191
DDC Ports ................................................................................. 191
I2C Protocols for Access to the Internal EDID ................. 192
I2C Protocols for Access to HDCP Registers .................... 192
DDC Port A .......................................................................... 192
DDC Port B ........................................................................... 192
Appendix A ................................................................................... 193
Rev. B | Page 4 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
PCB Layout Recommendations ............................................. 193
Power Supply Bypassing .......................................................... 193
Example of a Current Loop ................................................ 193
Digital Outputs (Data and Clocks) ........................................ 193
Digital Inputs ............................................................................ 194
XTAL and Load Cap Value Selection .................................... 194
REVISION HISTORY
11/12—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changed Pin 75 from AP1/I2S_TDM to AP1 ................ Unviersal
Changes to Figure 1........................................................................... 1
Deleted TDM from Table 3 .............................................................. 7
Deleted TDM Information from HDMI Reciever Section .......... 9
Changes to Figure 2......................................................................... 11
Changes to Pin 17, Pin 18, Pin 75, Pin 96, and Pin 100 ............. 12
Changes to ADV7612 Revision Identification Section .............. 15
Changes to Table 5 .......................................................................... 16
Changes to Tristate Audio Output Drivers Section .................... 18
Changes to DR_STR Section ......................................................... 19
Changes to INV_F_POL, IO, Address 0x06[3] Section ............. 21
Deleted 0x8D from OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] Table ................... 27
Changes to DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes Section
and Added Table 9 ........................................................................... 29
Changes to E-EDID Data Configuration Section ....................... 34
Changes to Figure 4......................................................................... 35
Added Low Frequency Formats Section and Figure 15 ............. 60
Deleted I2S_TDM_MODE_ENABLE, Addr 68 (HDMI),
Address 0x6D[7] Section ................................................................ 67
Changes to Notes Section ............................................................... 67
Deleted Figure 24 ............................................................................ 69
Deleted Notes Section ..................................................................... 72
Changes to Audio Mute Signal Section ........................................ 76
Changes to XTAL and Load Cap Value Selection Section .......194
Changes to Tab le 7 8 ......................................................................198
Example .................................................................................. 194
Appendix B .................................................................................... 195
Recommended Unused Pin Configurations ......................... 195
Appendix C .................................................................................... 198
Pixel Output Formats ............................................................... 198
2/12—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Change to Video Output Formats Section ................................... 10
Change to Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions
Section, Table 4, Pin 87 ................................................................... 14
Changes to Table 7 .......................................................................... 25
Added Endnote to OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] Table in Pixel
Port Output Modes Section ........................................................... 27
Added LLC_DLL_DOUBLE Section and Table to DLL on
LCC Clock Path Section ................................................................. 28
Added DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes Section ...... 29
Changes to Audio Mute Signal Section ........................................ 75
Added 1001 to CS_DATA[27:24] Table in Sampling and
Frequency Accuracy Section ......................................................... 80
Changes to Check the Value of Each Coefficient Section ....... 114
Changes to CP_HUE[7:0], Addr 44 (CP) Address 0x3D[7:0]
in Color Controls Section; Changes to CP_HUE[7:0] Table ..... 116
Changes to INT2_POL Table in Interrupt Drive Level Section ... 170
Added Figure 75; Renumbered Sequentially ............................. 191
Added Endnote to Table 76 ......................................................... 197
11/10—Revis
ion 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 5 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
R/W
Memory location has read and write access.
HDTV
High definition television.
ISRC
International standard recording code.
USING THE ADV7612 HARDWARE USER GUIDE
NUMBER NOTATIONS
Table 1.
Notation Description
Bit N Bits are numbered in little endian format, that is, the least significant bit of a number is referred to as Bit 0.
V[X:Y] Bit field representation covering Bit X to Bit Y of a value or a field (V).
0xNN Hexadecimal (base-16) numbers are preceded by the prefix ‘0x’.
0bNN Binary (base-2) numbers are preceded by the prefix ‘0b’.
NN Decimal (base-10) are represented using no additional prefixes or suffixes.
REGISTER ACCESS CONVENTIONS
Table 2.
Mode Description
R Memory location is read access only. A read always returns 0 unless otherwise specified.
W Memory location is write access only.
ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Table 3.
Acronym/Abbreviation Description
ACP Audio content protection.
AGC Automatic gain control.
Ainfo HDCP register. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
AKSV HDCP transmitter key selection vector. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References
section.
An 64-bit pseudo-random value generated by HDCP cipher function of Device A.
AP Audio output pin.
AVI Auxiliary video information.
BCAPS HDCP register. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
BKSV HDCP receiver key selection vector. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References
section.
CP Component processor.
CSC Color space converter/conversion.
DDR Double data rate.
DE Data enable.
DLL Delay locked loop.
DPP Data preprocessor.
DVI Digital visual interface.
EAV End of active video.
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility.
EQ Equalizer.
HD High definition.
HDCP High bandwidth digital content protection.
HDMI High bandwidth multimedia interface.
HPA Hot plug assert.
HPD Hot plug detect.
HSync Horizontal synchronization.
IC Integrated circuit.
Rev. B | Page 6 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
I2C
Inter integrated circuit.
STDI
Standard detection and identification.
Acronym/Abbreviation Description
I2S Inter IC sound.
KSV Key selection vector.
LLC Line locked clock.
LSB Least significant bit.
L-PCM Linear pulse coded modulated.
Mbps Megabit per second.
MPEG Moving picture expert group.
ms Millisecond.
MSB Most significant bit.
NC No connect.
OTP One-time programmable.
Pj’ HDCP enhanced link verification response. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the
References section.
Ri’ HDCP link verification response. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
Rx Receiver.
SAV Start of active video.
SDR Single data rate.
SHA-1 Refer to HDCP documentation.
SMPTE Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers.
SOG Sync on green.
SOY Sync on Y.
SPA Source physical address.
SPD Source production descriptor.
TMDS Transition minimized differential signaling.
Tx Transmitter.
VBI Video blanking interval.
VSync Vertical synchronization.
XTAL Crystal oscillator.
Rev. B | Page 7 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
FIELD FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Throughout this user guide, a series of function tables are provided. The function of a field is described in a table preceded by the bit
name, a short function description, the I
The detailed description consists of:
• For a readable field, the values the field can take
• For a writable field, the values the field can be set to
Example Field Function Description
This section provides an example of a field function table followed by a description of each part of the table.
PRIM_MODE[3:0], IO Map, Address 0x01[3:0].
A control to select the primary mode of operation of the decoder.
Function
PRIM_MODE[3:0] Description
0000 Reserved
0001 Reserved
0010 Reserved
0011 Reserved
0100 Reserved
0101 HDMI-Comp
0110 (default) HDMI-GR
0111 to 1111 Reserved
In this example
2
C map, the register location within the I2C map, and a detailed description of the field.
• The name of the field is PRIM_MODE and it is four bit long.
• Address 0x01 is the I
2
C location of the field in big endian format (MSB first, LSB last).
• The address is followed by a detailed description of the field.
• The first column of the table lists values the field can take or can be set to. These values are in binary format if not preceded by 0x or
in hexadecimal format if preceded by 0x.
• The second column describes the function of each field for each value the field can take or can be set to. Values are in binary format.
REFERENCES
CEA, CEA-861-D, A DTV Profile for Uncompressed High Speed Digital Interfaces, Revision D, July 18, 2006.
Digital Content Protection (DCP) LLC, High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection System, Revision 1.4, July 8, 2009.
HDMI Licensing and LLC, High-Definition Multimedia Interface, Revision 1.4a, March 4, 2010.
ITU, ITU-R BT.656-4, Interface for Digital Component Video Signals in 525-Line and 625-Line Television Systems Operating
at the 4:2:2 Level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601, February 1998.
Rev. B | Page 8 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
INTRODUCTION TO THE ADV7612
The ADV7612 is a high quality, 2:1 multiplexed high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI®) receiver.
The ADV7612 incorporates a dual input HDMI receiver that supports all mandatory 3D TV formats defined in the HDMI specification.
HDTV formats up to 1080p 36-bit deep color and display resolutions up to UXGA (1600 × 1200 at 60 Hz).
The ADV7612 also integrates a CEC controller that supports the capability discovery and control (CDC) feature.
The ADV7612 incorporates Xpressview™ fast switching on both input HDMI ports. Using Analog Devices’ hardware-based HDCP engine
that minimizes software overhead, Xpressview technology allows fast switching between both HDMI input ports in less than 1 second.
Each HDMI port has dedicated +5 V detect and hot plug assert pins. The HDMI receiver also includes an integrated programmable
equalizer that ensures robust operation of the interface with long cables.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the ADV7612 is provided in a 14 mm × 14 mm, 100-pin surface-mount LQFP_EP, RoHScompliant package and is specified over −40°C to +85°C temperature range.
HDMI RECEIVER
The HDMI receiver on the ADV7612 incorporates a fast switching feature that allows inactive ports to be HDCP authenticated to provide
rapid switching between encrypted HDMI sources. The ADV7612 HDMI receiver incorporates active equalization of the HDMI data
signals to compensate for the losses inherent in HDMI and DVI cabling, especially at longer lengths and higher frequencies. The equalizer
is highly effective and is capable of equalizing for long cables to achieve robust receiver performance.
With the inclusion of HDCP, displays can receive encrypted video content. The HDMI interface of the ADV7612 allows a video receiver
to authenticate, decrypt encoded data, and renew that authentication during transmission, as specified by the HDCP v1.4 protocol for
both active and background HDMI ports.
The ADV7612 offers a flexible audio output port for audio data extraction from the HDMI stream. HDMI audio formats, including super
audio CD (SACD) via DSD and HBR are supported by ADV7612. The HDMI receiver has advanced audio functionality, such as a mute
controller, that prevents audible extraneous noise in the audio output.
COMPONENT PROCESSOR
The component processor (CP) is located behind the HDMI receiver. It processes the video data received from the HDMI receiver. The
CP section provides color adjustment features, such as brightness, saturation, and hue. The color space conversion (CSC) matrix allows
the color space to be changed as required. The standard detection and identification (STDI) block allows the detection of video timings.
MAIN FEATURES OF ADV7612
HDMI Receiver
• HDMI features supported
• 3D HDMI video format support
• Full colorimetry, including sYCC601, Adobe RGB, Adobe YCC601, and xvYCC extended gamut color
• CEC-compatible
• 3D video support, including frame packing for all 3D formats up to a 225 MHz TMDS clock and/or up a pixel clock of 165 MHz
• Fast switching between HDMI ports
• Supports deep color
• Supports all display resolutions up to UXGA (1600 × 1200 at 60 Hz, 10-bit)
• Supports multichannel audio with sampling frequency up to 192 kHz
• Programmable front-end equalization for long cable lengths
• Audio mute for removing extraneous noise
• Programmable interrupt generator to detect HDMI packets
• Internal EDID support
• Repeater support
Rev. B | Page 9 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Component Video Processing
• An any-to-any 3 × 3 CSC matrix support YCrCb to RGB and RGB to YCrCb
• Provides color controls, such as saturation, brightness, hue, and contrast
• STDI block that enables format detection
• Free run output mode provides stable timing when no video input is present
Video Output Formats
• Double data rate (DDR) 8-/10-/12-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb
• DDR is supported only up to 50 MHz (an equivalent to ata rate clocked with 100 MHz clock in SDR mode)
• Pseudo DDR (CCIR-656 type stream) 8-/10-/12-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb for 525i, 625i, 525P, and 625P
• SDR 16-/20-/24-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb for all standards
• SDR 24-/30-/36-bit 4:4:4 YCrCb/RGB for all HDMI standards
• DDR 12-/24-/30-/36-bit 4:4:4 RGB
Additional Features
• HS, VS, FIELD, and DE output signals with programmable position, polarity, and width
• Numerous interrupt sources available for the INT1 and INT2 interrupt request output pins, available via one of the selected pins, that
is, SCLK/INT2, MCLK/INT2, or HPA_A/INT2
• Temperature range of −40°C to +85°C
• 14 mm × 14 mm, 100-pin LQFP_EP package
Rev. B | Page 10 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
C
2
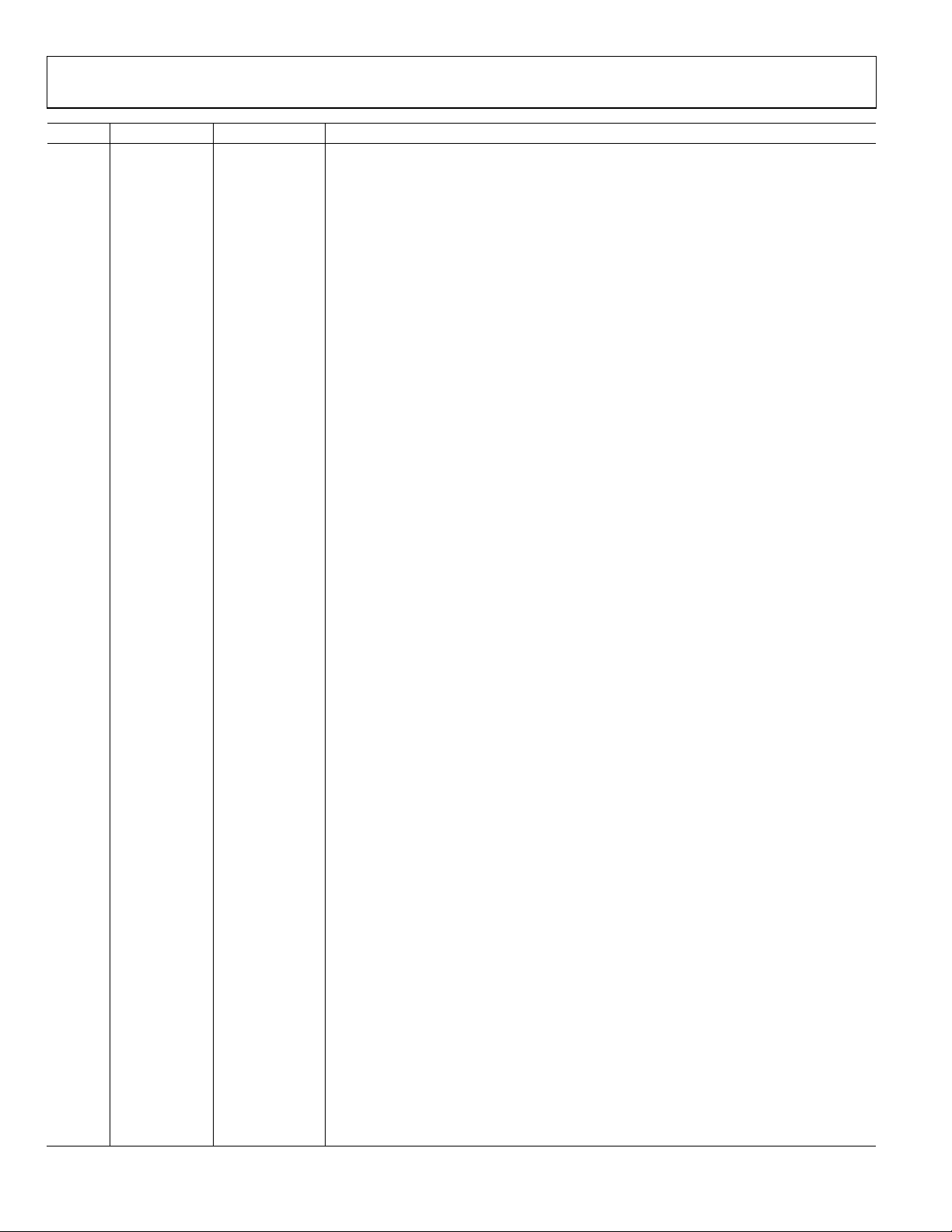
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
HPA_A/INT2
RXA_5V
DDCA_SDA
DDCA_SCL
HPA_B
RXB_5V
DDCB_SDA
DDCB_SCL
CEC
DVDD
XTALN
XTALP
100
PVDDCSRESET
99
98
95
93
97
96
92
94
898887
91
90
INT1
SDA
SCL
DVDD
MCLK/INT2
AP5
SCLK/INT2
AP4
AP3
AP2
84
82
86
85
81
83
787776
80
79
CVDD
RXA_C–
RXA_C+
TVDD
RXA_0–
RXA_0+
TVDD
RXA_1–
RXA_1+
TVDD
RXA_2–
RXA_2+
CVDD
RXB_C–
RXB_C+
TVDD
RXB_0–
RXB_0+
TVDD
RXB_1–
RXB_1+
TVDD
RXB_2–
RXB_2+
CVDD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
PIN 1
INDICATOR
27
26
NC
P35
(Not to Scale)
31
33
29
30
28
P34
P33
34
32
P32
35
P31
P30
P29
P28
DVDDIO
NOTES
1. NC = NO CONNE
. CONNECT EXPOSED PAD (PIN0) TO GROUND (BOTTOM).
T. DO NOT CONNECT TO THI S PIN.
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
ADV7612
TOP VIEW
373839
36
P27
P26
DVDDIO
75
AP1
74
AP0
73
VS/FIELD/ALSB
72
HS
71
DE
70
DVDDIO
69
P0
68
P1
67
P2
66
P3
65
P4
64
P5
63
P6
62
DVDD
61
P7
60
P8
59
P9
58
P10
57
P11
56
P12
55
P13
54
DVDDIO
53
P14
52
P15
51
P16
42
44
40
41
P25
P24
DVDD
45
43
P23
P22
P21
LLC
484950
46
47
P20
P19
NC
P18
P17
09486-003
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
0 GND Ground Ground.
1 CVDD Power HDMI Analogue Block Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
2 RXA_C− HDMI input Digital Input Clock Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
3 RXA_C+ HDMI input Digital Input Clock True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
4 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
5 RXA_0− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 0 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
6 RXA_0+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 0 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
7 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
8 RXA_1− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
9 RXA_1+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
10 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
11 RXA_2− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 2 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
12 RXA_2+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 2 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
13 CVDD Power HDMI Analogue Block Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
14 RXB_C− HDMI input Digital Input Clock Complement of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
15 RXB_C+ HDMI input Digital Input Clock True of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
16 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
Rev. B | Page 11 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
18
RXB_0+
HDMI input
Digital Input Channel 0 True of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
24
RXB_2+
HDMI input
Digital Input Channel 2 True of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
output
31
P32
Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
47
P19
Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
17 RXB_0− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 0 Complement of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
19 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
20 RXB_1− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 Complement of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
21 RXB_1+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 True of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
22 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
23 RXB_2− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 2 Complement of Port B in the HDMI Interface.
25 CVDD Power HDMI Analogue Block Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
26 NC No connect No connect.
27 P35 Digital video
output
28 P34 Digital video
output
29 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
30 P33 Digital video
output
32 P31 Digital video
output
33 P30 Digital video
output
34 P29 Digital video
output
35 P28 Digital video
output
36 P27 Digital video
output
37 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
38 P26 Digital video
output
39 P25 Digital video
output
40 P24 Digital video
output
41 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
42 LLC Digital video
output
43 P23 Digital video
output
44 P22 Digital video
output
45 P21 Digital video
output
46 P20 Digital video
output
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Line-Locked Output Clock for the Pixel Data (Range is 13.5 MHz to 170 MHz).
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
48 P18 Digital video
output
49 P17 Digital video
output
50 NC No connect No connect.
51 P16 Digital video
output
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Rev. B | Page 12 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
59
P9
Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
64
P5
Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
72
HS
Digital video
HS is a horizontal synchronization output signal.
77
AP3
Miscellaneous
Audio Output Pin. Pins AP to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
52 P15 Digital video
output
53 P14 Digital video
output
54 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
55 P13 Digital video
output
56 P12 Digital video
output
57 P11 Digital video
output
58 P10 Digital video
output
output
60 P8 Digital video
output
61 P7 Digital video
output
62 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V ).
63 P6 Digital video
output
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
65 P4 Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
66 P3 Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
67 P2 Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
68 P1 Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
69 P0 Digital video
Video Pixel Output Port.
output
70 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
71 DE Miscellaneous
DE (data enable) is a signal that indicates active pixel data.
digital
output
73 VS/FIELD/ALSB Digital video
output
74 AP0 Miscellaneous Audio Output Pin. Pins AP0 to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
75 AP1 Miscellaneous Audio Output Pin. Pins AP0 to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
76 AP2 Miscellaneous Audio Output Pin. Pins AP to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
VS is a vertical synchronization output signal. FIELD is a field synchronization output signal
in all interlaced video modes. VS or FIELD can be configured for this pin. The ALSB allows
selection of the I
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I
2
C address.
2
2
2
S.
S.
S.
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I2S.
78 AP4 Miscellaneous Audio Output Pin. Pins AP to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I
79 SCLK/INT2 Miscellaneous
digital
A dual function pin that can be configured to output Audio Serial Clock or an Interrupt2
signal.
80 AP5 Miscellaneous Audio Output Pin. Pins AP to AP5 can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output
(SPDIF), High Bit Rate (HBR), Direct Stream Digital (DSD), Direct Stream Transfer (DST) or I2S.
Additionally, Pin AP5 can be configured to provide LRCLK.
Rev. B | Page 13 of 204
2
S.
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
91
DVDD
Power
Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
81 MCLK/INT2 Miscellaneous A dual fuction pin that can be configured to output Audio Master Clock or an Interrupt2
signal.
82 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
83 SCL Miscellaneous
digital
84 SDA Miscellaneous
digital
85 INT1 Miscellaneous
digital
86
87
88 PVDD Power PLL Supply Voltage (1.8 V)
89 XTAL P Miscellaneous
90 XTAL N Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
RESET
digital
Miscellaneous
CS
digital
analog
analog
I2C Port Serial Clock Input. SCL is the clock line for the control port.
I2C Port Serial Data Input/Output Pin. SDA is the data line for the control port.
Interrupt. This pin can be active low or active high. When status bits change, this pin is
triggered. The events that trigger an interrupt are under user configuration.
System Reset Input. Active low. A minimum low reset pulse width of 5 ms is required to
reset the ADV7612 circuitry.
Chip Select. This pin has an internal pull-down. Pulling this line up causes the I2C state
machine to ignore I
Input Pin for 28.63636 MHz Crystal or an External 1.8 V, 28.63636 MHz Clock Oscillator
Source to Clock the ADV7612.
Crystal Input. Input pin for 28.63636 MHz crystal.
2
C transmission.
92 CEC Digital
input/output
93 DDCB_SCL HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Clock Port B. DDCB_SCL is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
94 DDCB_SDA HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Data Port B. DDCB_SDA is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
95 RXB_5V HDMI input 5 V Detect Pin for Port B in the HDMI Interface.
96 HPA_B Miscellaneous
digital
97 DDCA_SCL HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Clock Port A. DDCA_SCL is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
98 DDCA_SDA HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Data Port A. DDCA_SDA is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
99 RXA_5V HDMI input 5 V Detect Pin for Port A in the HDMI Interface.
100 HPA_A/INT2 Miscellaneous
digital
Consumer Electronic Control Channel.
Hot Plug Assert signal output for HDMI port B. This is an open-drain pin.
A dual function open-drain pin that can be configured to output Hot Plug Assert signal (for
HDMI Port A) or an Interrupt2 signal.
Rev. B | Page 14 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Powers down clock to CP core. HDMI block not affected by this bit.
GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTERS
The register control bits described in this section deal with the general control of the chip, and the CP and the HDMI receiver sections of
the ADV7612.
ADV7612 REVISION IDENTIFICATION
RD_INFO[15:0], IO, Address 0xEA[7:0]; Address 0xEB[7:0] (Read Only)
Chip revision code.
Function
RD_INFO[15:0] Description
0x2051 ADV7611 Final Silicon
0x2041 ADV7612 Final Silicon
POWER-DOWN CONTROLS
Primary Power-Down Controls
POWER_DOWN is the main power-down control. It is the main control for power-down Mode 0 and Mode 1. See the Power-Down
Modes section for more details.
POWER_DOWN, IO, Address 0x0C[5]
A control to enable power-down mode. This is the main I
Function
POWER_DOWN Description
0 Chip operational
1 (default) Enables chip power down
Secondary Power-Down Controls
The following controls allow various sections of the ADV7612 to be powered down.
It is possible to stop the clock to the CP to reduce power for a power-sensitive application. The CP_PWRDN bit enables this power-save
mode. The HDMI block is not affected by this power-save mode. This allows the use of limited HDMI, STDI monitoring features while
reducing the power consumption. For full processing of the HDMI input, the CP core needs to be powered up.
CP_PWRDN, IO, Address 0x0C[2]
A power-down control for the CP core.
Function
CP_PWRDN Description
0 (default) Powers up clock to CP core.
2
C power-down control.
XTAL_PDN
XTAL_PDN allows the user to power down the XTAL clock in the following sections:
• STDI blocks
• Free run synchronization generation block
2
• I
C sequencer block, which is used for the configuration of the gain, clamp, and offset
• CP and HDMI section
The XTAL clock is also provided to the HDCP engine, EDID, and the repeater controller within the HDMI receiver. The XTAL clock
within these sections is not affected by XTAL_PDN.
XTAL_PDN, IO, Address 0x0B[0]
A power-down control for the XTAL in the digital blocks.
Function
XTAL_PDN Description
0 (default) Powers up XTAL buffer to digital core
1 Powers down XTAL buffer to digital core
Rev. B | Page 15 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
CORE_PDN
CORE_PDN allows the user to power down clocks, with the exception of the XTAL clock, in the following sections:
• CP block
• Digital section of the HDMI block
CORE_PDN, IO, Address 0x0B[1]
A power-down control for the DPP, CP core, and digital sections of the HDMI core.
Function
CORE_PDN Description
0 (default) Powers up CP and digital sections of HDMI block
1 Powers down CP and digital section of HDMI block
Power-Down Modes
The ADV7612 supports the following power-down modes:
• Power-Down Mode 0
• Power-Down Mode 1
Table 5 shows the power-down and normal modes of ADV7612.
Table 5. Power-Down Modes
POWER_DOWN bit CEC_POWER_UP Bit CEC EDID Power-Down Mode
1 0 Disabled Enabled Power-Down Mode 0
1 1 Enabled Enabled Power-Down Mode 1
0 0 Disabled Enabled1 Normal mode
0 1 Enabled Enabled1 Normal mode
1
Dependent on the values of EDID_X_ENABLE_CPU and EDID_X_ENABLE for the HDMI port (where X is A).
Power-Down Mode 0
In Power-Down Mode 0, selected sections and pads are kept active to provide EDID and +5 V antiglitch filter functionality.
In Power-Down Mode 0, the sections of the ADV7612 are disabled except for the following blocks:
2
• I
C slave section
• EDID/repeater controller
• EDID ring oscillator
The ring oscillator provides a clock to the EDID/repeater controller (refer to the E-EDID/Repeater Controller section) and the +5 V
power supply antiglitch filter. The clock output from the ring oscillator runs at approximately 50 MHz.
The following pads only are enabled in Power-Down Mode 0:
2
• I
C pads
• SDA
• SCL
• +5 V pads
• RXA_5V
• RXB_5V
• HPA_A
• HPA_B
• DDC pads
• DDCA_SCL
• DDCA_SDA
• DDCB_SCL
• DDCB_SDA
• Reset pad
Power-Down Mode 0 is initiated through a software (I
RESET
2
C register) configuration.
Rev. B | Page 16 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
PADS_PDN
Description
Entering Power-Down Mode 0 via Software
The ADV7612 can be put into Power-Down Mode 0 by setting POWER_DOWN to 1 (default value) and CEC_POWER_UP to 0. This
method allows an external processor to put the system in which the ADV7612 is integrated into standby mode. In this case, the CP and
HDMI cores of the ADV7612 are kept powered up from the main power (for example, ac power) and set in or out of power-down Mode 0
through the POWER_DOWN bit.
Power-Down Mode 1
Power-Down Mode 1 is enabled when the following conditions are met:
• POWER_DOWN bit is set to 1
• CEC section is enabled by setting CEC_POWER_UP to 1
Power-Down Mode 1 provides the same functionality as Power-Down Mode 0, with the addition of the following sections:
• XTAL clock
• CEC section
• Interrupt controller section
The following pads are enabled in Power-Down Mode 1:
• Same pads as enabled in Power-Down Mode 0
• CEC pad
• INT1 and INT2 interrupt pads
The internal EDID is also accessible through the DDC bus for Port A and Port B in Power-Down Mode 0 and Power-Down Mode 1.
GLOBAL PIN CONTROL
RESET
Pin
The ADV7612 can be reset by a low reset pulse on the reset pin with a minimum width of 5 ms. It is recommended to wait 5 ms after the
low pulse before an I
Reset Controls
MAIN_RESET, IO, Address 0xFF[7] (Self-Clearing)
Main reset where I
Function
MAIN_RESET Description
0 (default) Normal operation
1 Applies main I2C reset
Tristate Output Drivers
PA DS_PDN , IO, Address 0x0C[0]
A power-down control for pads of the digital output s. When enabled, the pads are tristated and the input path is disabled. This control
applies to the DE, HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, INT1, and LLC pads and to the P0 to P35 pixel pads.
Function
0 (default) Powers up pads of digital output pins
1 Powers down pads of digital output pins
DDC_PWRDN[7:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x73[7:0]
A power-down control for DDC pads.
Function
DDC_PWRDN[7:0] Description
00000000 (default) Powers up DDC pads
xxxxxxx1
xxxxxx1x
2
C write is performed to the ADV7612.
2
C registers are reset to their default values.
Powers down DDC pads on Port A
Powers down DDC pads on Port B
Rev. B | Page 17 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
TRI_PIX
This bit allows the user to tristate the output driver of pixel outputs. Upon setting TRI_PIX, the pixel output P[35:0] is tristated.
TRI_PIX, IO, Address 0x15[1]
A control to tristate the pixel data on the pixel pins, P[35:0].
Function
TRI_PIX Description
0 Pixel bus active
1 (default) Tristates pixel bus
Tristate LLC Driver
TRI_LLC, IO, Address 0x15[2]
A control to tristate the output pixel clock on the LLC pin.
Function
TRI_LLC Description
0 LLC pin active
1 (default) Tristates LLC pin
Tristate Synchronization Output Drivers
The following output synchronization signals are tristated when TRI_SYNCS is set:
• VS/FIELD/ALSB
• HS
• DE
The drive strength controls for these signals are provided via the DR_STR_SYNC bits. The ADV7612 does not support tristating via a
dedicated pin.
TRI_SYNCS, IO, Address 0x15[3]
Synchronization output pins tristate control. The synchronization pins under this control are HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE.
Function
TRI_SYNCS Description
0 Sync output pins active
1 (default) Tristates sync output pins
Tristate Audio Output Drivers
TRI_AUDIO, IO Map, Address 0x15, [4]
TRI_AUDIO allows the user to tristate the drivers of the following audio output signals:
• AP0
• AP1
• AP2
• AP3
• AP4
• AP5
• SCLK/INT2
• MCLK/INT2
The drive strength for the output pins can be controlled by the DR_STR[1:0] bits. The ADV7612 does not support tristating via a
dedicated pin.
Rev. B | Page 18 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1 (default)
Tristates audio output pins
11
High (4×) for LLC greater than 100 MHz
TRI_AUDIO, IO, Address 0x15[4]
A control to tristate the audio output interface pins (AP0, AP1, AP2, … , AP5).
Function
TRI_AUDIO Description
0 Audio output pins active
Drive Strength Selection
DR_STR
It may be desirable to strengthen or weaken the drive strength of the output drivers for Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and
crosstalk reasons. This section describes the controls to adjust the output drivers used by the CP and HDMI modes.
The drive strenth DR_STR_SYNC[1:0] bits allow the user to select the strength of the following synchronization signals:
• DE
• HS
• VS/FIELD
The DR_STR[1:0] drive strength bits affect output drivers for the following output pins:
• P[35:0]
• AP0-AP5
• SCLK
• SDA
• SCL
The drive strength DR_STR_CLK[1:0] bits affect output driver for LLC line.
DR_STR[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[5:4]
A control to set the drive strength of the data output drivers.
Function
DR_STR[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×)
10 (default) Medium high (3×)
11 High (4×)
DR_STR_CLK[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[3:2]
A control to set the drive strength control for the output pixel clock out signal on the LLC pin.
Function
DR_STR_CLK[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×) for LLC up to 60 MHz
10 (default) Medium high (3×) for LLC from 44 MHz to 105 MHz
DR_STR_SYNC[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[1:0]
A control to set the drive strength of the synchronization pins, HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE.
Function
DR_STR_SYNC[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×)
10 (default) Medium high (3×)
11 High (4×)
Rev. B | Page 19 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
Selects DE output on DE pin
1
Positive polarity HS
Output Synchronization Selection
VS_OUT_SEL, IO, Address 0x06[7]
A control to select the VSync or FIELD signal to be output on the VS/FIELD/ALSB pin.
Function
VS_OUT_SEL Description
0 Selects FIELD output on VS/FIELD/ALSB pin
1 (default) Selects VSync output on VS/FIELD/ALSB pin
F_OUT_SEL, IO, Address 0x05[4]
A control to select the DE or FIELD signal to be output on the DE pin.
Function
F_OUT_SEL Description
1 Selects FIELD output on DE pin
Output Synchronization Signals Polarity
INV_LLC_POL, IO Map, Address 0x06, [0]
The polarity of the pixel clock provided by the ADV7612 via the LLC pin can be inverted using the INV_LLC_POL bit. Note that this
inversion affects only the LLC output pin. The other output pins are not affected by INV_LLC_POL.
Changing the polarity of the LLC clock output may be necessary in order to meet the setup and hold time expectations of the downstream
devices processing the output data of the ADV7612. It is expected that these parameters must be matched regardless of the type of video
data that is transmitted. Therefore, INV_LLC_POL is designed to be mode independent.
INV_LLC_POL, IO, Address 0x06[0]
A control to select the polarity of the LLC.
Function
INV_LLC_POL Description
0 (default) Does not invert LLC
1 Inverts LLC
The output synchronization signals HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE can be inverted using the following control bits:
• INV_HS_POL
• INV_VS_POL
• INV_F_POL
INV_HS_POL, IO, Address 0x06[1]
A control to select the polarity of the HS signal.
Function
INV_HS_POL Description
0 (default) Negative polarity HS
INV_VS_POL, IO, Address 0x06[2]
A control to select the polarity of the VS/FIELD/ALSB signal.
Function
INV_VS_POL Description
0 (default) Negative polarity VS/FIELD/ALSB
1 Positive polarity VS/FIELD/ALSB
Rev. B | Page 20 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Inverted FIELD/DE polarity (negative FIELD/DE polarity)
INV_F_POL, IO, Address 0x06[3]
A control to select the polarity of the DE signal.
Function
INV_F_POL Description
0 (default) Default FIELD/DE polarity (positive FIELD/DE polarity)
Digital Synthesizer Controls
The ADV7612 features two digital encoder synthesizers that generate the following clocks:
• Video DPLL: this clock synthesizer generates the pixel clock. It undoes the effect of deep color and pixel repetition that are inherent
to HDMI streams. The output of the LLC pin is either this pixel clock or a divided down version, depending on the datapath
configuration. It takes less than one video frame for this synthesizer to lock.
• Audio DPLL: this clock synthesizer generates the audio clock. As per HDMI specification, the incomming HDMI clock is divided
down by CTS and then multiplied up by N. This audio clock is used as the main clock in the audio stream section. The output of
MCLK represents this clock. It takes less than 5 ms after a valid ACR packet for this synthesizer to lock.
Crystal Frequency Selection
The ADV7612 supports 27.0, 28.63636, 24.576 and 24.0 MHz frequency crystals. Following control allows selecting crystal frequency.
XTAL_FREQ_SEL[1:0], IO, Address 0x04[2:1]
A control to set the XTAL frequency used.
Function
XTAL_FREQ_SEL[1:0] Description
00 27 MHz
01 (default) 28.63636 MHz
10 24.576 MHz
11 24.0 MHz
Rev. B | Page 21 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0011
Reserved
xxxxxx
Reserved
Reserved
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD
Setting the primary mode and choosing a video standard are the most fundamental settings when configuring the ADV7612. There
are two primary modes for the ADV7612: HDMI-component and HDMI-graphic modes. The appropriate mode should be set with
PRIM_MODE[3:0].
In HDMI modes, the ADV7612 can receive and decode HDMI or DVI data throughout the DVI/HDMI receiver front end. Video data
from the HDMI receiver is routed to the CP block while audio data is available on the audio interface. One of these modes is enabled by
selecting either the HDMI-component or the HDMI-graphics primary mode.
Note: The HDMI receiver decodes and processes any applied HDMI stream irrespective of the video resolution. However, many primary
mode and video standard combinations can be used to define how the decoded video data routed to the DPP and CP blocks is processed.
This allows for free run features and data decimation modes that some systems may require.
If free run and decimation are not required, it is recommended to set the following configuration for HDMI mode:
• PRIM_MODE[3:0]: 0x06
• VID_STD[5:0]: 0x02
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD CONTROLS
PRIM_MODE[3:0], IO, Address 0x01[3:0]
A control to select the primary mode of operation of the decoder. Setting the appropriate HDMI mode is important for free run mode to
work properly. This control is used with VID_STD[5:0].
Function
PRIM_MODE[3:0] Description
0000 Reserved
0001 Reserved
0010 Reserved
0011 Reserved
0100 Reserved
0101 HDMI component
0110 (default) HDMI graphics
0111 to 1111 Reserved
VID_STD[5:0], IO, Address 0x00[5:0]
Sets the input video standard mode. Configuration is dependent on PRIM_MODE[3:0]. Setting the appropriate mode is important for
free run mode to work properly.
Function
VID_STD[5:0] Description
000010 Default value
PRIM_MODE[3:0] should be used with VID_STD[5:0] to select the required video mode. These controls are set according to Tab le 6.
Table 6. Primary Mode and Video Standard Selection
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
0000 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0001 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0010 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0100 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
Rev. B | Page 22 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
CP
001011
PR 1×1 625p
720 × 576
CP
001110
XGA
1024 × 768 @ 75
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
0101 HDMI-COMP
(Component video)
0110 HDMI-GR
(Graphics)
CP 000000 SD 1×1 525i 720 × 480 HDMI receiver support
CP 000001 SD 1×1 625i 720 × 576
CP 000010 SD 2×1 525i 720 × 480
CP 000011 SD 2×1 625i 720 × 576
000100 Reserved Reserved
000101 Reserved Reserved
000110 Reserved Reserved
000111 Reserved Reserved
001000 Reserved Reserved
001001 Reserved Reserved
CP 001010 PR 1×1 525p 720 × 480
CP 001100 PR 2×1 525p 720 × 480
CP 001101 PR 2×1 625p 720 × 576
001110 Reserved Reserved
001111 Reserved Reserved
010000 Reserved Reserved
010001 Reserved Reserved
010010 Reserved Reserved
CP 010011 HD 1×1 1280 × 720
CP 010100 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 010101 HD 1×1 1920 × 1035
CP 010110 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 010111 HD 1×1 1920 × 1152
011000 Reserved Reserved
CP 011001 HD 2×1 720p 1280 × 720
CP 011010 HD 2×1 1125 1920 × 1080
CP 011011 HD 2×1 1125 1920 × 1035
CP 011100 HD 2×1 1250 1920 × 1080
CP 011101 HD 2×1 1250 1920 × 1152
CP 011110 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 011111 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 000000 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 56
CP 000001 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 60
CP 000010 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 72
CP 000011 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 75
CP 000100 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 85
CP 000101 SXGA 1280 × 1024 @ 60
CP 000110 SXGA 1280 × 1024 @ 75
000111 Reserved Reserved
CP 001000 VGA 640 × 480 @ 60
CP 001001 VGA 640 × 480 @ 72
CP 001010 VGA 640 × 480 @ 75
CP 001011 VGA 640 × 480 @ 85
CP 001100 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 60
CP 001101 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 70
HDMI receiver support
0111 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1000 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1001 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
CP 001111 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 85
01xxxx Reserved
Rev. B | Page 23 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
1010 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1011 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1100 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1101 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1110 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1111 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
V_FREQ
This control is set to allow free run to work correctly (refer to Tab le 7).
V_FREQ[2:0], IO, Address 0x01[6:4]
A control to set vertical frequency.
Function
V_FREQ[2:0] Description
000 (default) 60 Hz
001 50 Hz
010 30 Hz
011 25 Hz
100 24 Hz
101 Reserved
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
HDMI DECIMATION MODES
Some of the modes defined by VID_STD have an inherent 2×1 decimation. For these modes, the main clock generator and the
decimation filters in the DPP block are configured automatically. This ensures the correct data rate at the input to the CP block. Refer to
the Data Preprocessor and Color Space Conversion and Color Controls section for more information on the automatic configuration of
the DPP block.
The ADV7612 correctly decodes and processes any incoming HDMI stream with the required decimation, irrespective of its video
resolution:
• In 1×1 mode (that is, without decimation), as long the PRIM_MODE and VID_STD registers are programmed for any HDMI mode
without decimation.
For example:
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x00
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x13
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x6 and VID_STD to 0x02
• In 2×1 decimation mode, as long the PRIM_MODE and VID_STD registers are programmed for any HDMI mode with 2×1
decimation. For example:
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x0C
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x19
Note: Decimating the video data from an HDMI stream is optional and should be performed only if it is required by the downstream
devices connected to the ADV7612.
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD CONFIGURATION FOR HDMI FREE RUN
If free run is enabled in HDMI mode, PRIM_MODE[3:0] and VID_STD[5:0] specify the input resolution expected by the ADV7612 (for
free run Mode 1) and/or the output resolution to which the ADV7612 free runs (for free run Mode 0 and Mode 1). Refer to the Free Run
Mode section for additional details on the free run feature for HDMI inputs and to HDMI_FRUN_MODE.
Rev. B | Page 24 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
6, 7
720 (1440) × 480i @ 60 Hz
1
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
33
1920 × 1080p @ 25 Hz
0
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
RECOMMENDED SETTINGS FOR HDMI INPUTS
This section provides the recommended settings for an HDMI input encapsulating a video resolution corresponding to a selection Video
ID Code described in the 861 specification.
Table 7 provides the recommended settings for the following registers:
• PRIM_MODE
• VID_STD
• V_FREQ (V_FREQ should be set to 0x0 if not specified in Tabl e 7.)
• INV_HS_POL = 1 (INV_HS_POL should be set to 1 if not specified in Ta ble 7.)
• INV_VS_POL = 1 (INV_VS_POL should be set to 1 if not specified in Tab le 7.)
Table 7. Recommended Settings for HDMI Inputs
Recommended Settings
Video ID Codes
(861 Specification) Formats
2, 3 720 × 480p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
4 1280 × 720p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
5 1920 × 1080i @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
Pixel
Repetition
if Free Run Used and
DIS_AUTOPARAM_BUFFER = 0
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
Recommended Settings if
Free Run Not Used or Free Run Used
and DIS_AUTO_PARAM_BUFFER = 1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x13
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x14
VID_STD = 0x2
10, 11 2880 × 480i @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
14, 15 1440 × 480p @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
16 1920 × 1080p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
17, 18 720 × 576p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
19 1280 × 720p @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
20 1920 × 1080i @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
21, 22 720 (1440) ×576i @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
25, 26 2880 × 480i @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
29, 30 144 0× 576p @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
31 1920 × 1080p @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
32 1920 × 1080p @ 24 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE=0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xB
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA3
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x14
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE=0x5
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x4
35, 36 2880 × 480p @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
37, 38 2880 × 576p @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
Rev. B | Page 25 of 204
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x3
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
N/A
VGA 640 × 480p @ 60
0
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 56 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 72 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SXGA 1280 × 1024p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A SXGA 1280 × 1024p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x3
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x04
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x05
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x06
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 72 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 70 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x08
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x09
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0A
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0B
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0C
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0D
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0E
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0F
Rev. B | Page 26 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
Function
OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0]
Description
0x00 (default)1
8-bit SDR ITU-656 mode
0x011
10-bit SDR ITU-656 mode
0x021
12-bit SDR ITU-656 Mode 0
0x061
12-bit SDR ITU-656 Mode 1
0x0A1
12-bit SDR ITU Mode 2
0x20
8-bit 4:2:2 DDR mode
0x21
10-bit 4:2:2 DDR Mode
0x22
12-bit 4:2:2 DDR Mode 0
0x23
12-bit 4:2:2 DDR Mode 1
0x24
12-bit 4:2:2 DDR Mode 2
0x40
24-bit 4:4:4 SDR mode
0x41
30-bit 4:4:4 SDR mode
0x42
36-bit 4:4:4 SDR Mode 0
0x46
36-bit SDR 4:4:4 Mode 1
0x4C
24-bit SDR 4:4:4 Mode 3
0x50
24-bit SDR 4:4:4 Mode 4
0x51
30-bit SDR 4:4:4 Mode 4
0x52
36-bit SDR 4:4:4 Mode 4
0x60
24-bit 4:4:4 DDR mode
0x61
30-bit 4:4:4 DDR mode
0x62
36-bit 4:4:4 DDR mode
0x80
16-bit ITU-656 SDR mode
0x81
20-bit ITU-656 SDR mode
0x82
24-bit ITU-656 SDR Mode 0
0x86
24-bit ITU-656 SDR Mode 1
0x8A
24-bit ITU-656 SDR Mode 2
0x90
16-bit SDR 4:2:2 Mode 4
0x91
20-bit SDR 4:2:2 Mode 4
0x92
24-bit SDR 4:2:2 Mode 4
Function
OP_CH_SEL[2:0]
Description
000
P[35:24] Y/G, P[23:12] U/CrCb/B, P[11:0] V/R
001
P[35:24] Y/G, P[23:12] V/R, P[11:0] U/CrCb/B
010
P[35:24] U/CrCb/B, P[23:12] Y/G, P[11:0] V/R
011 (default)
P[35:24] V/R, P[23:12] Y/G, P[11:0] U/CrCb/B
100
P[35:24] U/CrCb/B, P[23:12] V/R, P[11:0]Y/G
101
P[35:24] V/R, P[23:12] U/CrCb/B, P[11:0] Y/G
110
Reserved
111
Reserved
PIXEL PORT CONFIGURATION
The ADV7612 has a very flexible pixel port, which can be configured in a variety of formats to accommodate downstream ICs. The
ADV7612 can provide output modes up to 36 bits.
This section details the controls required to configure the ADV7612 pixel port. Appendix C contains tables describing pixel port
configurations.
PIXEL PORT OUTPUT MODES
OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0], IO, Address 0x03[7:0]
A control to select the data format and pixel bus configuration. for full information on pixel port modes and configuration settings.
1
Refer to the DLL settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-bit modes in the DLL on LLC Clock Path section.
Bus Rotation and Reordering Controls
Bus reordering controls are available for ADV7612. OP_CH_SEL[2:0] allows the three output buses to be rearranged, thus providing six
different output possibilities.
OP_CH_SEL[2:0], IO, Address 0x04[7:5]
A control to select the configuration of the pixel data bus on the pixel pins. Refer to the pixel port configuration for full information on
pixel port modes and configuration settings.
Rev. B | Page 27 of 204
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Pixel Data and Synchronization Signals Control
The polarity of the LLC and synchronization signals can be inverted, and the LLC, the synchronization signals, and the pixel data output
can be tristated. Refer to the information on the following controls:
• INV_F_POL
• INV_VS_POL
• INV_HS_POL
• TRI_PIX
• TRI_LLC
• TRI_SYNCS
OP_SWAP_CB_CR, IO, Address 0x05[0]
Controls the swapping of Cr and Cb data on the pixel buses.
Function
OP_SWAP_CB_CR Description
0 (default) Outputs Cr and Cb as per OP_FORMAT_SEL
1 Inverts the order of Cb and Cr in the interleaved data stream
OP_SWAP_CB_CR swaps the order in which Cb and Cr are interleaved in the output data stream. It caters for cases in which the data on
Channels B and C are swapped. It is effective only if OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] is set to a 4:2:2 compatible output mode.
Note: It has no effect for 36-bit SDR modes and DDR modes.
LLC CONTROLS
The ADV7612 has a limited number of adjustment features available for the line locked clock (LLC) output. The polarity of the LLC can
be inverted and the LLC of the output driver can be tristated. Controls also exist to skew the LLC versus the output data to achieve
suitable setup and hold times for any back end device.
The LLC controls are as follows:
• INV_LLC_POL
• TRI_LLC
• LLC_DLL_EN
• LLC_DLL_MUX
• LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0]
DLL ON LLC CLOCK PATH
A delay locked loop (DLL) block is implemented on the LLC clock path. This DLL allows the changing of the phase of the output pixel
clock on the LLC pin.
LLC_DLL_DOUBLE, IO, Address 0x19[6]
A control to double LLC frequency.
Function
LLC_DLL_DOUBLE Description
0 (default) Normal LLC frequency
1 Double LLC frequency
Adjusting DLL Phase in All Modes
LLC_DLL_EN, IO, Address 0x19[7]
A control to enable the DLL for the output pixel clock.
Function
LLC_DLL_EN Description
1 Enables LLC DLL
0 (default) Disables LLC DLL
Rev. B | Page 28 of 204
Hardware User Guide UG-216
LLC_DLL_MUX
Description
0 (default)
Bypasses the DLL
1
Muxes the DLL output on LLC output
LLC_DLL_MUX, IO, Address 0x33[6]
A control to apply the pixel clock DLL to the pixel clock output on the LLC pin.
Function
LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0], IO, Address 0x19[4:0]
A control to adjust LLC DLL phase in increments of 1/32 of a clock period.
Function
LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0] Description
00000 (default) Default
xxxxx Sets one of 32 phases of DLL to vary LLC CLK
DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes
Table 8 and Table 9 show the settings that must be used to enable 8-/10-/12-bit, 656 output. Note that the 720p 8-/10-/12-bit mode must
use OP_FORMAT_SEL = 0x20 or 0x2A (refer to Ta ble 78). Doubling the clock as per Table 8 undoes the DDR mode.
Table 8. DLL Settings for 8-/12-Bit Pixel Bus Output
Address Setting Description
IO Map Address 0x03[7:0] Refer to Table 9 OP_FORMAT_SEL value
IO Map Address 0x19[7] 1 Enables LLC DLL
IO Map Address 0x33[6] 1 Muxes the DLL output on LLC output
IO Map Address 0x19[6] 1 Doubles the clock
Table 9. OP_FORMAT_SEL Settings for 8-/12-Bit Pixel Bus Output (To Be Used With Settings from Table 8)
Input Video OP_FORMAT_SEL Value Output Clock Frequency after Clock Doubling
480i, 576i 8-bit 0x00 27 MHz
480i, 576i 10-/12-bit 0x0A 27 MHz
480p, 576p 8-bit 0x00 54 MHz
480p, 576p 10-/12-bit 0x0A 54 MHz
720p 8-bit 0x20 148.5 MHz
720p 10-/12-bit 0x2A 148.5 MHz
Rev. B | Page 29 of 204
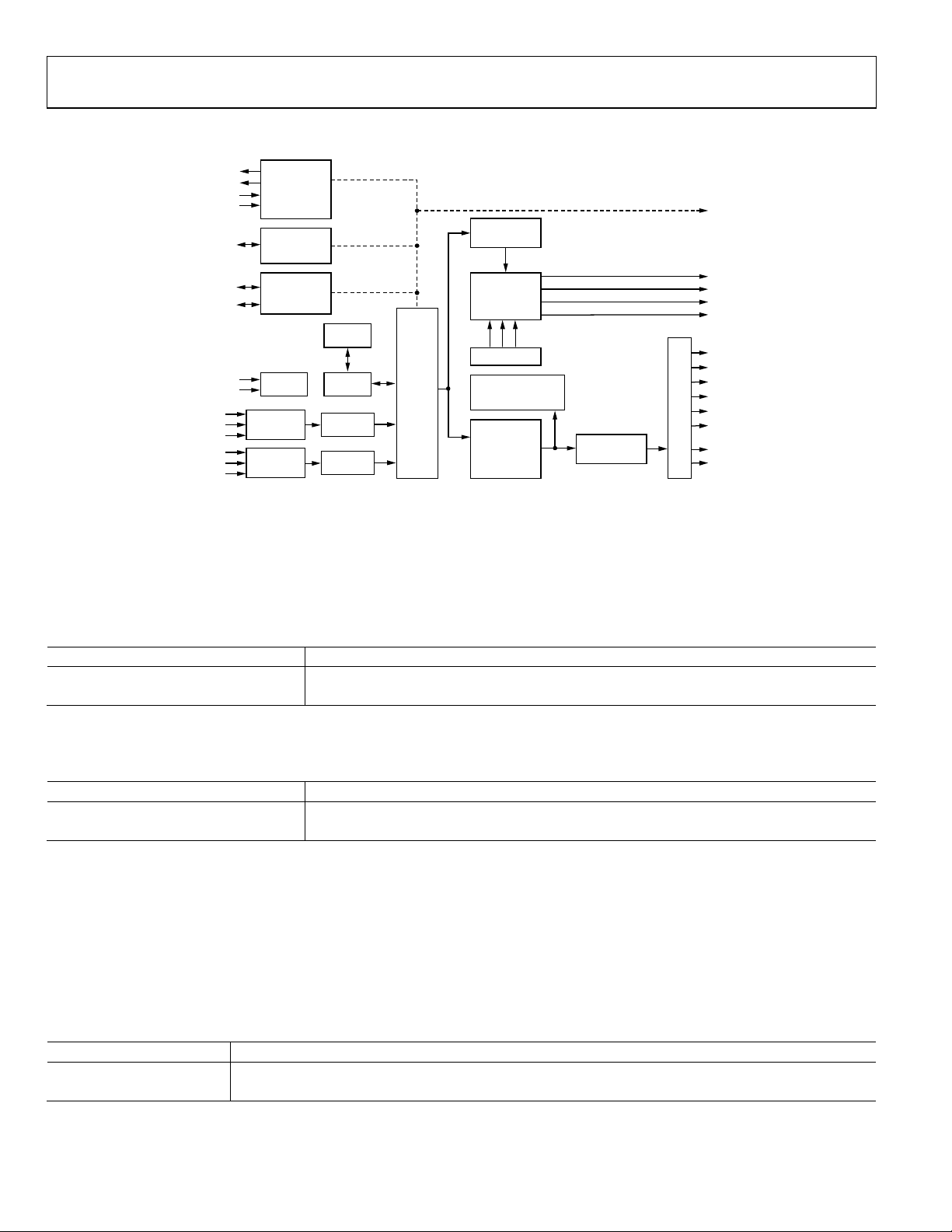
UG-216 Hardware User Guide
HDMI RECEIVER
HPA_A/INT2
HPA_B
RXA_5V
RXB_5V
CEC
DDCA_SDA/DDCA_SC L
DDCA_SDA/DDCB_SC L
RXA_C±
RXB_C±
RXA_0±
RXA_1±
RXA_2±
RXA_0±
RXA_1±
RXA_2±
+5 V CABLE DETECT
The HDMI receiver in the ADV7612 can monitor the level on the +5 V power signal pin of the HDMI port. The results of this detection
can be read back from the following I
CABLE_DET_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x6F[0] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port A +5 V cable detection signal.
Function
CABLE_DET_A_RAW Description
0 (default) No cable detected on Port A
1 Cable detected on Port A (high level on RXA_5V)
CABLE_DET_B_RAW, IO, Address 0x6A[7] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port B +5 V cable detection signal.
Function
CABLE_DET_A_RAW Description
0 (default) No cable detected on Port B
1 Cable detected on Port A (high level on RXB_5V)
The ADV7612 provides a digital glitch filter on the +5 V power signals from the HDMI port. The output of this filter is used to reset the
HDMI block (refer to the HDMI Section Reset Strategy section).
The +5 V power signal must be constantly high for the duration of the timer (controlled by FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0]), otherwise the
output of the filter is low. The output of the filter returns low as soon as any change in the +5 V power signal is detected.
FILT_5V_DET_DIS, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x56[7]
This control is used to disable the digital glitch filter on the HDMI 5 V detect signals. The filtered signals are used as interrupt flags and
used to reset the HDMI section. The filter works from an internal ring oscillator clock and, therefore, is available in power-down mode.
The clock frequency of the ring oscillator is 42 MHz ± 10%.
Function
FILT_5V_DET_DIS Description
0 (default) Enabled
1 Disabled
Note: If the +5 V pins are not used and are left unconnected, the +5 V detect circuitry must be disconnected from the HDMI reset signal
by setting DIS_CABLE_DET_RST to 1. This avoids holding the HDMI section in reset.
5V DETECT
AND HPA
CONTROLLER
CONTROLLER
EDID/
REPEATER
CONTROLLER
PLL
EQUALIZER
CEC
HDCP
EEPROM
HDCP
BLOCK
SAMPLER
SAMPLEREQUALIZER
DEEP COLOR
CONVERSION
DATA
4:2:2 TO 4: 4: 4
CONVERSION
FILTER
PACKET/
INFOFRAME
+ MUX
FAST SWITCHING BLOCK
HDMI DECODE + PORT MEASUR EMENT
MEMORY
PACKET
PROCESSOR
HS
VS
DE
AUDIO
PROCESSOR
AUDIO OUTPOUT FORMATTER
TO INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
TO DPP
TO DPP
TO DPP
TO DPP
AP0
AP1/I2S_TDM
AP2
AP3
AP4
AP5
SCLK/INT2
MCLK/INT2
Figure 3. Functional Block Diagram of HDMI Core
2
C registers. These readbacks are valid even when the part is not configured for HDMI mode.
09486-004
Rev. B | Page 30 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0 (default)
Resets HDMI section if 5 V input pin corresponding to selected HDMI port (for example, RXA_5V for Port A)
1 (default)
High level applied to HPA_A pin
Function
FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x56[6:0]
This control is used to set the timer for the digital glitch filter on the HDMI +5 V detect inputs. The unit of this parameter is two clock
cycles of the ring oscillator (~ 47 ns). The input must be constantly high for the duration of the timer; otherwise, the filter output remains
low. The output of the filter returns low as soon as any change in the +5 V power signal is detected.
Function
FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0] Description
1011000 (default) Approximately 4.2 µs
xxxxxxx Time duration of +5 V deglitch filter. Unit of this parameter is 2 clock cycles of the ring oscillator (~47 ns)
DIS_CABLE_DET_RST, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x48[6]
This control disables the reset effects of cable detection. DIS_CABLE_DET_RST must be set to 1 if the +5 V pins are unused and left
unconnected.
Function
DIS_CABLE_DET_RST Description
is inactive
1 Does not use 5 V input pins as reset signal for HDMI section
HOT PLUG ASSERT
The ADV7612 features hot plug assert ( HPA) control for its HDMI port. The purpose of the control and its corresponding output pin is
to communicate to an HDMI transmitter that it is possible to access the enhanced-extended display identification (E-EDID) connected to
the DDC bus.
HPA_MANUAL, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[0]
Manual control enable for the HPA output pins. Automatic control of these pins is disabled by setting this bit. Manual control is
determined by the HPA_MAN_VALUE_X (where X = A or B).
Function
HPA_MANUAL Description
0 (default) HPA takes its value based on HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID
1 HPA takes its value from HPA_MAN_VALUE_X
HPA_MAN_VALUE_A, IO, Address 0x20[7]
A manual control for the value of HPA on Port A. Valid only if HPA_MANUAL is set to 1.
Function
HPA_MAN_VALUE_A Description
0 0 V applied to HPA_A pin
HPA_MAN_VALUE_B, IO, Address 0x20[6]
A manual control for the value of HPB on Port A. Valid only if HPA_MANUAL is set to 1.
HPA_MAN_VALUE_A Description
0 0 V applied to HPA_B pin
1 (default) High level applied to HPA_B pin
Note: The HPA_A and HPA_B pins is open drain. An external pull-up resistor is required to pull it high.
Rev. B | Page 31 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
HPA_B pin active
HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[2:1]
This control selects the type of automatic control on the HPA output pins. This bit has no effect when HPA_MANUAL is set to 1.
Function
HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID[1:0] Description
00 HPA of an HDMI port asserted high immediately after internal EDID activated for that port. HPA of a specific
HDMI port deasserted low immediately after internal E-EDID is de-activated for that port.
01 (default) HPA of an HDMI port asserted high following a programmable delay after part detects an HDMI cable plug
on that port. HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after part detects a cable disconnect on that
HDMI port.
10 HPA of an HDMI port asserted high after two conditions met.
1. Internal EDID is active for that port.
2. Delayed version of cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is high.
HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after either of these two conditions are met:
1. Internal EDID is de-activated for that port.
2. Cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is low.
11 HPA of an HDMI port is asserted high after three conditions met:
1. Internal EDID is active for that port.
2. Delayed version of cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is high.
3. User has set manual HPA control for that port to 1 via HPA_MAN_VALUE_X controls.
HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after any of these three conditions met:
1. Internal EDID de-activated for that port.
2. Cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is low.
3. User sets the manual HPD control for that port to 0 via HPA_MAN_VALUE_X controls
Note: The delay is programmable via HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0]. Refer to EDID_ENABLE for details on enabling the internal E-EDID for an
HDMI port. In HPA_MAN_VALUE_X and CABLE_DET_X_RAW, X refers to A and B.
HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[7:4]
Sets a delay between +5 V detection and hot plug assertion on the HPA output pins, in increments of 100 ms per bit.
Function
HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0] Description
0000 No delay
0001 100 ms delay
0010 200 ms delay
1010 (default) 1 sec delay
1111 1.5 sec delay
HPA_TRISTATE_A, IO, Address 0x20[3]
Tris tates HPA output pin for Port A.
Function
HPA_TRISTATE_A Description
0 (default) HPA_A pin active
1 Tristates HPA_A pin
HPA_TRISTATE_B, IO, Address 0x20[2]
Tris tates HPA output pin for Port B.
Function
HPA_TRISTATE_B Description
1 Tristates HPA_B pin
Rev. B | Page 32 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
+5 V applied to HPA_A pin by chip
Function
HPA_STATUS_PORT_A, IO, Address 0x21[3] (Read Only)
Readback of HPA status for Port A.
Function
HPA_STATUS_PORT_A Description
0 (default) +5 V not applied to HPA_A pin by chip
HPA_STATUS_PORT_B, IO, Address 0x21[2] (Read Only)
Readback of HPA status for Port B.
HPA_STATUS_PORT_A Description
0 (default) +5 V not applied to HPA_B pin by chip
1 +5 V applied to HPA_B pin by chip
HPA_OVR_TERM, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[3]
A control to set the termination control to be overridden by the HPA setting. When this bit is set, termination on a specific port is set
according to the HPA status of that port.
Function
HPA_OVR_TERM Description
0 (default) Automatic or manual I2C control of port termination
1 Termination controls disabled and overridden by HPA controls
E-EDID/REPEATER CONTROLLER
The HDMI section incorporates an E-EDID/repeater controller, which performs the following tasks:
• Computes the E-EDID checksum
• Performs the repeater routines described in the Repeater Support section
The E-EDID/repeater controller is powered from the DVDD supply and clocked by an internal ring oscillator. The controller and the
internal DDC bus arbiter are kept active in Power-Down Mode 0 and Power-Down Mode 1. This allows the internal E-EDID to be
functional and accessible through the DDC port, even when the part is powered down (refer to the Power-Down Modes section).
These HDMI transmitters can then read the capabilities of the powered-down application integrating the ADV7612 by accessing its
internal E-EDID through the DDC ports.
The E-EDID/repeater controller is reset when the DVDD supplies go low or when HDCP_REPT_EDID_RESET is set high. When the
E-EDID/repeater controller reboots, it performs the following tasks:
• Clears the internal E-EDID and Key Selection Vector (KSV) RAM (refer to the E-EDID Data Configuration section and the Internal
HDCP Key OTP ROM section )
• Computes a checksums for ports (refer to the Structure of Internal E-EDID for Port A section.)
• Updates the SPA registers.
HDCP_REPT_EDID_RESET, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5A[3] (Self-Clearing)
A reset control for the E-EDID/repeater controller. When asserted, it resets the E-EDID/repeater controller.
Function
HDCP_REPT_EDID_RESET Description
0 (default) Normal operation
1 Resets the E-EDID/repeater controller
Rev. B | Page 33 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
EDID_A_ENABLE_CPU
Description
E-EDID DATA CONFIGURATION
The ADV7612 features RAM that can store an E-EDID. This internal E-EDID feature can be used for both HDMI Port A and Port B.
The following controls are provided to enable the internal E-EDID for each of the two HDMI ports.
EDID_A_ENABLE, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x74[0]
2
Enables I
Function
EDID_A_ENABLE Description
0 (default) Disables E-EDID for Port A
1 Enables E-EDID for Port A
EDID_B_ENABLE, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x74[1]
Enables I
Function
EDID_B_ENABLE Description
0 (default) Disables E-EDID for Port B
1 Enables E-EDID for Port B
When the internal E-EDID is enabled on either port, the ADV7612 must first calculate the E-EDID checksums for that port before the EEDID is actually enabled.
EDID_A_ENABLE_CPU, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x76[0] (Read Only)
Flags internal EDID enabling on Port A.
Function
C access to the internal EDID RAM from DDC Port A.
2
C access to the internal EDID RAM from DDC Port B.
0 (default) Disabled
1 Enabled
EDID_B_ENABLE_CPU, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x76[1] (Read Only)
Flags internal EDID enabling on Port B.
Function
EDID_B_ENABLE_CPU Description
0 (default) Disabled
1 Enabled
Notes
• When the internal E-EDID is enabled on more than one port (that is, Port A and Port B), the corresponding enable controls (that is,
EDID_A_ENABLE and EDID_B_ENABLE) should be set high in one single I
2
C write. This ensures the fastest calculation of the
checksums.
• If the internal E-EDID RAM is enabled for one specific port (that is, Port A), an external E-EDID storage device must not be
connected on the DDC bus of that port.
• The internal E-EDID can be read by current address read sequences on the DDC port.
• The ADV7612 supports the segment pointer, which is set at device address 0x60 through the DDC bus, and used in combination
with the internal E-EDID address (0xA0) to access the internal E-EDID.
• The contents of the EDID RAM are not to be trusted after power up or hardware reset. User should write proper contents to the
EDID RAM memory inside the ADV7612 via an external MCU.
E-EDID Support for Power-Down Modes
The ADV7612 supports E-EDID access in Power-Down Mode 0 and Power-Down Mode 1. Using this feature, an application that
integrates the ADV7612 in standby can make its E-EDID available to the HDMI transmitter. This allows support of CEC and provides
compatibility with HDMI transmitters that require the E-EDID to be available when the HDMI receiver is powered down.
In Power-Down Mode 0, the part operates in a very low power state with only the minimum of internal circuitry enabled for the
internal E-EDID.
For more details on E-EDID accessibility in power-down modes, refer to the Power-Down Modes section.
Rev. B | Page 34 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
PORT A E-EDID ST RUCTURE
BLOCK 3 CHECKSUM0x1FF
0x1FE
0x17E
0xFE
0x7E
0x17F
0x180
0x100
0x00
0x80
0xFF
0x7F
BLOCK 2 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 1 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 0 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 3
BLOCK 2
BLOCK 1
BLOCK 0
09486-005
TRANSITIONING OF POWER MODES
If the part starts in Power-Down Mode 0 and then transitions into a different power mode (that is, Power-Down Mode 1 or normal
operation mode), the information in the internal E-EDID is not overwritten. The internal E-EDID remains active on the HDMI port for
which the E-EDID has been accessed. This prevents disturbing E-EDID read requests from HDMI sources connected to the ADV7612
while it is being powered on, or while the power mode is transitioning.
It is possible to disable the automatic enable of internal EDID on the HDMI ports when the part comes out of power-down mode, by
setting the DISABLE_AUTO_EDID bit.
DISABLE_AUTO_EDID, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x7A[1]
Disables all automatic enables for internal E-EDID.
Function
DISABLE_AUTO_EDID Description
0 (default) Automatic enable of internal E-EDID on HDMI port when the part comes out of Power-Down Mode 0
1 Disable automatic enable of internal E-EDID on HDMI port when the part comes out of Power-Down Mode 0
STRUCTURE OF INTERNAL E-EDID FOR PORT A
The internal E-EDID is enabled on Port A by setting EDID_A_ENABLE to 1. The structure of the internal E-EDID that is accessible on
the DDC line of Port A is shown in Figure 4.
The image of the internal E-EDID that is accessed on the DDC bus of Port A corresponds to the data image contained in the internal
E-EDID RAM.
Notes
• After EDID_A_ENABLE is set to 1, the ADV7612 E-EDID/Repeater controller calculates the four checksums of the E-EDID image
• After power up, the ADV7612 E-EDID/Repeater controller sets all bytes in the internal E-EDID RAM to 0; this operation takes less
• When internal E-EDID is enabled on Port A, the hot plug should not be asserted until the EDID map has been completely initialized
• The internal E-EDID can be accessed in read-only mode through the DDC interface at the I
• The internal E-EDID can be accessed in read/write mode through the general I
Figure 4. Port A E-EDID Structure and Mapping
for Port A and updates the internal RAM address locations 0x7F, 0xFF, 0x17F, and 0x1FF in the internal E-EDID RAM with the
computed checksums.
than 1 ms. It is recommended to wait for at least 1 ms before initializing the EDID Map with an E-EDID image.
with E-EDID.
2
C Address 0xA0.
2
C interface at the EDID Map I2C address.
Rev. B | Page 35 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
STRUCTURE OF INTERNAL E-EDID FOR PORT B
This section describes the structure of the internal E-EDID accessible through the DDC bus of Port B.
The internal E-EDID is enabled forPort B by setting the EDID_B_ENABLE bit to 1. The image of the internal E-EDID that is accessed on
the DDC bus of Port B corresponds to the data image contained in the internal E-EDID RAM except for the SPA, SPA location, and the
checksum of the E-EDID block where the SPA is located.
The structure of the internal E-EDID image for Port B is shown in:
Figure 5—SPA located in E-EDID Block 1
Figure 6—SPA located in E-EDID Block 2
Figure 7—SPA located in E-EDID Block 3
PORT B E-EDI D STRUCTURE
BLOCK 3 CHECKSUM0x1FF
0x1FE
BLOCK 3
0x1FF
0x180
0x17F
BLOCK 2 CHECKSUM
0x100
0xFF
BLOCK 1 CHECKSUM
0x80
0x7F
BLOCK 0 CHECKSUM
0x00
BLOCK 2
BLOCK 1
BLOCK 0
0x17E
0xFE
0x7E
0x100
0xFF
PORT_B_CHECKSUM[7:0]
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] + 2
SPA_PORT_B[15:0]
0x80
0x00
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] – 1
0xFE
0x7F
INTERNAL EDID RAM
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
INTERNAL EDID RAM
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
INTERNAL EDID RAM
09486-006
Figure 5. Port B E-EDID Structure and Mapping for SPA Located in E-EDID Block 1
Rev. B | Page 36 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
PORT B E-EDI D STRUCTURE
BLOCK 3 CHECKSUM0x1FF
BLOCK 3
0x180
0x17F
BLOCK 2 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 2
0x100
0xFF
BLOCK 1 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 1
0x80
0x7F
BLOCK 0 CHECKSUM
BLOCK 0
0x00
0x1FE
0x17E
0xFE
0x7E
0x180
0x17F
PORT_B_CHECKSUM[7:0]
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] + 2
SPA_PORT_B[15:0]
0x100
0x00
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] – 1
0x1FF
0x17E
0xFF
INTERNAL EDID RAM
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
INTERNAL EDID RAM
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
INTERNAL EDID RAM
09486-007
Figure 6. Port B E-EDID Structure and Mapping for SPA Located in E-EDID Block 2
PORT B E-EDI D STRUCTURE
BLOCK 3 CHECKSUM0x1FF
0x180
0x17F
BLOCK 2 CHECKSUM
0x1FE
BLOCK 3
0x17E
0x1FF PORT_B_CHECKSUM[7:0]
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] + 2
SPA_PORT_B[15:0]
SPA_LOCATION[8:0] – 1
0x180
0x1FE
0x17F
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
INTERNAL EDID RAM
REPEATER MAP, REG 0x70, REG 0x71
BLOCK 2
0x100
0xFF
BLOCK 1 CHECKSUM
0x80
0x7F
BLOCK 0 CHECKSUM
0x00
0xFE
BLOCK 1
0x7E
BLOCK 0
0x00
INTERNAL EDID RAM
09486-008
Figure 7. Port B E-EDID Structure and Mapping for SPA Located in E-EDID Block 3
The SPA of Port B is programmed in the SPA_PORT_B[15:0] register. The SPA location is programmed in the SPA_LOCATION[7:0]
register. This register should contain a value greater than 0x7F since the SPA is located in an upper block of the E-EDID.
When internal E-EDID is required for Port B, the SPA along with its location address in the E-EDID must be programmed in the
repeater map, Registers SPA_PORT_B[15:0]and SPA_LOCATION[7:0], respectively.
After EDID_B_ENABLE is set to 1, the ADV7612 EDID/Repeater controller computes the four checksums of the E-EDID image for
Port B. The E-EDID controller then updates the checksum registers in the EDID RAM memory location 0x7F and the following
three locations:
0x17F, 0x1FF, and the Register SPA_LOCATION[7:0], which is the SPA located in the EDID Block 1
Rev. B | Page 37 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
PORT_B_CHECKSUM[7:0]
Description
xxxxxxxx
Checksum for E-EDID block containing SPA for Port B
00000000 (default)
Default value
• 0xFF, 0x1FF, and the Register SPA_LOCATION[7:0], which is the SPA located in the EDID Block 2
• 0xFE, 0x17F, and the Register SPA_LOCATION[7:0], which is the SPA located in the EDID Block 3
• After power up, the ADV7612 E-EDID controller sets all bytes in the internal EDID RAM to 0; this operation takes less than 1 ms. It
is recommended to wait for at least 1 ms before initializing the EDID map with E-EDID.
• SPA_LOCATION[7:0] must be programmed with a value greater than 0x7F, as SPA is always located in the E-EDID blocks 1, 2, or 3.
• When internal E-EDID is enabled on Port B, the hot plug should not be asserted until the EDID map has been completely initialized
with E-EDID.
• The internal E-EDID can be accessed in read-only mode through the DDC interface at the I
• The internal E-EDID can be accessed in read/write mode through the general I
2
C interface at the EDID Map I2C address.
• The SPA_PORT_B[15:0] register does not have to be programmed with an actual SPA value. It can be programmed with any value
that must be read from the location SPA_LOCATION[7:0] when the internal E-EDID is accessed from the DDC lines of Port B. This
allows support for non CEA-861 compliant E-EDIDs (that is, VESA-only compliant E-EDID for analog inputs).
The SPA of Port B is the address of the Port B in the CEC interface. The SPA is comprised of four components, A, B, C, and D as defined
in the HDMI specification, which are programmed as follows:
• SPA_PORT_B[15:12] = A
• SPA_PORT_B[11:8] = B
• SPA_PORT_B[7:4] = C
• SPA_PORT_B[3:0] = D
SPA_PORT_B[15:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x52[7:0]; Address 0x53[7:0]
Source physical address for Port B. This is used for CEC and is located in the HDMI vendor specific data block in the E-EDID.
Function
SPA_PORT_B[15:0] Description
0000000000000000 (default) Default value
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Source physical address of Port B
SPA_LOCATION[7:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x70[7:0]
This is the location in the E-EDID record where the SPA is located.
Function
SPA_LOCATION[7:0] Description
11000000 (default) Default value
xxxxxxxx Location of source physical address in internal E-EDID of Port B
PORT_B_CHECKSUM[7:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x61[7:0]
This is the checksum for the second half of the Port B EDID. This is calculated automatically.
Function
2
C Address 0xA0.
TMDS EQUALIZATION
The ADV7612 incorporates active equalization of the HDMI data signals. This equalization compensates for the high frequency losses
inherent in HDMI and DVI cabling, especially at long lengths and higher frequencies. The ADV7612 is capable of equalizing for cable
lengths up to 30 meters and for pixel clock frequencies up to 225 MHz.
PORT SELECTION
HDMI_PORT_SELECT allows the selection of the active HDMI port. This register must be set to activate either HDMI Port A or HDMI
Port B.
Rev. B | Page 38 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
001
Port B
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x00[2:0]
This two bit control is used for HDMI primary port selection.
Function
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0] Description
000 (default) Port A
FAST SWITCHING AND BACKGROUND PORT SELECTION
The ADV7612 incorporates a fast switching feature. This feature allows the user of a system containing the ADV7612 to seamlessly switch
between HDCP encrypted sources. There is no delay in achieving video output which was previously caused by HDCP authentication.
The time required to switch between HDMI sources with HDCP encryption is reduced to a fraction of a second.
If an HDMI port is not selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0], then by default this port is disabled. Asserting EN_BG_PORT_A or
EN_BG_PORT_B allows this unselected port to be enabled in background mode. Once a port is in background mode, the ADV7612
establishes a HDCP link with its source even though it is not selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]. This background authentication
allows for fast switching of the HDMI ports.
Note that EN_BG_PORT_A and EN_BG_PORT_B have no effect if the port is selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT.
EN_BG_PORT_A, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x02[0]
Background mode enable for Port A. Sets Port A in background mode to establish a HDCP link with its source even if the port is not
selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT. This control has no effect if the port is selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
Function
EN_BG_PORT_A Description
0 (default)
1 Port enabled in background mode
EN_BG_PORT_B, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x02[1]
Background mode enable for Port B. Sets Port B in background mode to establish a HDCP link with its source even if the port is not
selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]. This control has no effect if the port is selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
Function
EN_BG_PORT_B Description
0 (default)
1 Port enabled in background mode
The ADV7612 can also perform HDMI parameter measurements on one background port. The following information can then be read
from the background measurement and parameter registers.
• BG_TMDSFREQ[8:0]
• BG_TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0]
• BG_DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0]
• BG_PIX_REP[3:0]
• BG_PARAM_LOCK
• BG_TOTAL_LINE_WIDTH[13:0]
• BG_LINE_WIDTH[12:0]
• BG_TOTAL_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0]
• BG_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0]
• BG_HDMI_INTERLACED
Port disabled, unless selected with
Port disabled, unless selected with
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]
Rev. B | Page 39 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
1
TMDS clock detected on Port A
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x00[5:3]
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[1:0] selects a background port on which HDMI measurements are to be made and provided in the background
measurement registers. The port in question must be set as a background port in order for this setting to be effective. There is no conflict
if this matches the port selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
Function
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0] Description
000 (default) Port A
001 Port B
BG_MEAS_REQ, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5A[5] (Self-Clearing)
This bit must be set to get correct measurements of the selected background port. Setting this control sends a request to update the
synchronization parameter measurements of the currently selected background port. The port on which the measurement will be made
is selected by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0].
Function
BG_MEAS_REQ Description
0 (default) No request to update selected background port synchronization parameter measurements
1 Requests an update of the selected background port synchronization parameter measurements
Note that after setting the self clearing BG_MEAS_REQ bit, the measurements of the TMDS frequency and video parameters of the
background ports are valid when BG_MEAS_DONE_RAW goes high.
BG_MEAS_DONE_RAW, IO, Address 0x8D[1] (Read Only)
Status of background port measurement completed interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates measurements of TMDS frequency and
video parameters on the selected background port have been completed. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via
BG_MEAS_DONE_CLR.
Function
BG_MEAS_DONE_RAW Description
0 (default) Measurements of TMDS frequency and video parameters of background port not finished or not
requested.
1 Measurements of TMDS frequency and video parameters of background port are ready
Note that this bit only informs the user that the measurement is complete and can be read back. One should ensure that
BG_PARAM_LOCK is asserted so that the background parameter filters are locked and the measurement values are valid.
TMDS CLOCK ACTIVITY DETECTION
The ADV7612 provides circuitry to monitor TMDS clock activity on each of its HDMI ports. The firmware can poll the appropriate
registers for TMDS clock activity detection and configure the ADV7612 as desired. TMDS clock detection control is active as soon as
the ADV7612 detects activity above a 25 MHz on the TMDS clock input.
TMDS_CLK_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x6A[4] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port A TMDS clock detection signal.
Function
TMDS_CLK_A_RAW Description
0 (default) No TMDS clock detected on Port A
TMDS_CLK_B_R AW, IO, Address 0x6A[3] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port B TMDS clock detection signal.
Function
TMDS_CLK_B_RAW Description
0 (default) No TMDS clock detected on Port B
1 TMDS clock detected on Port B
Rev. B | Page 40 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0
Enable Termination Port B
Important
• The clock detection flag is valid if the part is powered up or in Power Down Mode 1. Refer to Power-Down Mode 1 section.
• The clock detection flags is valid, irrespective of the mode the part is set into via the PRIM_MODE[3:0] register.
Clock and Data Termination Control
The ADV7612 provides controls for the TMDS clock and data termination on all HDMI ports. The ADV7612 also offers automatic
manual termination closure of the selected port, and individual manual control over the HDMI ports.
Note that the clock termination of the port by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0] must always be enabled.
This part does not support HDMI streams with a clock lower than 25 MHz.
TE RM_AU TO, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x01[0]
This bit allows the user to select automatic or manual control of clock termination. If automatic mode termination is enabled, then the
termination on the port selected via HDMI_PORT_SELECT[1:0] is enabled. The termination is disabled on all other ports
Function
TERM_AUTO Description
0 (default) Disable termination automatic control
1 Enable termination automatic control
Note: To enable the fast switching feature, the termination should be set manually for each port. When manual mode is enabled, the
termination for each port is set individually by the CLOCK_TERMX_DISABLE control bits (where X = A and B)
CLOCK_TERMA_DISABLE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x83[0]
Disable clock termination on Port A. This can be used when TERM_AUTO is set to 0.
Function
CLOCK_TERMA_DISABLE Description
0 Enable Termination Port A
1 (default) Disable Termination Port A
CLOCK_TERMB_DISABLE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x83[1]
Disable clock termination on Port B. This can be used when TERM_AUTO is set to 0.
Function
CLOCK_TERMB_DISABLE Description
1 (default) Disable Termination Port B
HDMI/DVI STATUS BITS
HDMI/DVI status mode is available through HDMI_MODE for active port and BG_HDMI_MODE for background port.
HDMI_MODE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x05[7] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate whether the stream processed by the HDMI core is a DVI or an HDMI stream.
Function
HDMI_MODE Description
0 (default) DVI mode detected
1 HDMI mode detected
BG_HDMI_MODE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xEB[0] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate whether the stream processed by the HDMI core is a DVI or an HDMI stream.
Function
BG_HDMI_MODE Description
0 (default) DVI mode detected
1 HDMI mode detected
VIDEO 3D DETECTION
Status of 3D video is available through VIDEO_3D_RAW bit.
Rev. B | Page 41 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
1
Video 3D detected
128
_ FRACTMDSFREQ
TMDSFREQF
TMDS
+=
VIDEO_3D_RAW, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6A[2] (Read Only)
Raw status of the Video 3D signal.
Function
VIDEO_3D_RAW Description
0 Video 3D not detected
TMDS MEASUREMENT
The ADV7612 contains logic that measures the frequency of the TMDS clock transmitted. The TMDS frequency can be read back via the
TMDSFREQ[8:0] and TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0] registers (described in this section).
TMDS Measurement After TMDS PLL
The TMDSFREQ measurement is provided by a clock measurement circuit located after the TMDS PLL. The TMDS PLL must, therefore,
be locked to the incoming TMDS clock in order for the TMDSFREQ and TMDSFREQ_FRAC registers to return a valid measurement.
The TMDS frequency can be obtained using Equation 1, TMDS Frequency in MHz (Measured after TMDS PLL).
(1)
Notes
• The TMDS PLL lock status can be monitored via TMDS_PLL_LOCKED. Figure 8 shows the algorithm that can be implemented on
an external controller to monitor the TMDS clock frequency.
• The TMDS_PLL_LOCKED flag should be considered valid if a TMDS clock is input on the HDMI port selected via
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
• The NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW flag can be used to monitor if the TMDS frequency on the selected HDMI port changes by a
programmable threshold.
• The ADV7612 can be configured to trigger an interrupt when the Bit NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW changes from 0 to 1. In that
configuration, the interrupt status NEW_TMDS_FRQ_ST indicates that NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW has changed from 0 to 1. Refer to
the Interrupts section for additional information on the configuration of interrupts.
TMDSFREQ[8:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x51[7:0]; Address 0x52[7] (Read Only)
This register provides a full precision integer TMDS frequency measurement.
Function
TMDSFREQ[8:0] Description
000000000 (default) Outputs 9-bit TMDS frequency measurement in MHz
xxxxxxxxx Outputs 9-bit TMDS frequency measurement in MHz
TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x52[6:0] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the fractional bits of measured frequency of PLL recovered TMDS clock. The unit is 1/128 MHz.
Function
TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0] Description
0000000 (default) Outputs 7-bit TMDS fractional frequency measurement in 1/128 MHz
xxxxxxx Outputs 7-bit TMDS fractional frequency measurement in 1/128 MHz
BG_TMDSFREQ[8:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE0[7:0]; Address 0xE1[7] (Read Only)
This register provides a precision integer TMDS frequency measurement on the background port selected by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The
value provided is the result of a single measurement of the TMDS PLL frequency in MHz. This value is updated when an update request
is made via the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit. This measurement is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_TMDSFREQ[8:0] Description
xxxxxxxxx Outputs 9-bit TMDS frequency measurement in MHz
Rev. B | Page 42 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
The TMDS PLL is locked to the TMDS clock input to the selected HDMI port.
Function
BG_TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE1[6:0] (Read Only)
This register provides a precision fractional measurement of the TMDS frequency on the background port selected by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The unit is 1/128 MHz and the value is updated when a update request is made via the BG_MEAS_REQ
control bit. This measurement is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_TMDSFREQ_FRAC[6:0] Description
xxxxxxx Outputs 7-bit TMDS fractional frequency measurement in 1/128 MHz
TMDS_PLL_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[1] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate if the TMDS PLL is locked to the TMDS clock input to the selected HDMI port.
Function
TMDS_PLL_LOCKED Description
0 (default) The TMDS PLL is not locked.
TMDSPLL_LCK_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x6A[6] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the raw status of the Port A TMDS PLL lock signal.
Function
TMDSPLL_LCK_A_RAW Description
0 (default) TMDS PLL on Port A is not locked.
1 TMDS PLL on Port A is locked to the incoming clock.
TMDSPLL_LCK_B_RAW, IO, Address 0x6A[5] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the raw status of the port B TMDS PLL lock signal.
TMDSPLL_LCK_B_RAW Description
0 (default) TMDS PLL on Port B is not locked.
1 TMDS PLL on Port B is locked to the incoming clock.
NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW, IO, Address 0x83[1] (Read Only)
Status of new TMDS frequency interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates the TMDS Frequency has changed by more than the tolerance
set in FREQTOLERANCE[3:0]. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via NEW_TMDS_FREQ_CLR.
Function
NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW Description
0 (default) TMDS frequency has not changed by more than tolerance set in FREQTOLERANCE[3:0] in the HDMI map.
1 TMDS frequency has changed by more than tolerance set in FREQTOLERANCE[3:0] in the HDMI map.
FREQTOLERANCE[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0D[3:0]
Sets the tolerance in MHz for new TMDS frequency detection. This tolerance is used for the audio mute mask MT_MSK_VCLK_CHNG
and the HDMI status bit NEW_TMDS_FRQ_RAW.
Function
FREQTOLERANCE[3:0] Description
0100 (default) Default tolerance in MHz for new TMDS frequency detection
xxxx Tolerance in MHz for new TMDS frequency detection
Rev. B | Page 43 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
NO
ENABLE TMDS _CLK_X_ST
1
INTERRUPT FOR
THE HDMI PORTS THAT ARE USED
TMDS FREQUENCY READ BACK NOT VALID
OR STABLE
READ THE TMDS FREQUENCY
TMDSFREQ
TMDS FREQUENCY READ BACK VALID
AND STABLE
CLEAR TMDS_CLK_X_ST BY
SETTI NG TMDS_CLK_X_CLR TO 1
CLEAR TMDS_P LL_LCK_ST BY
SETTI NG TMDS_PLL_LCK_S_CL R TO 1
IS TMDS_CLK_X_RA
W SET?
START
YES
YES
YES
IS TMDS_P LL_LCK_S
T SET?
IS NEW_T M DS _FRQ_
ST SET?
09486-078
ENABLE TMDS _P LL_LCK_ST INTERRUPT
ENABLE NEW_TMDS_FRQ_ST INTE RRUP T
IS TMDS_CLK_X_RA
W SET?
IS TMDS_P LL_LCK_R
AW SET?
CLEAR NEW_T M DS _FRQ_ST BY
SETTI NG NEW_TMDS_FRQ_ST _CLRTO 1
NO
NO
NO
NOTES
1. THE TM DS _CLK_X_ST INTERRUPTS FOLLOW:
- TMDS_CLK_A_S T (IO MAP, REG Ox6B BIT [3])
- TMDS_CLK_B_S T (IO MAP, REG Ox6B BIT [2])
- TMDS_CLK_C_S T (IO MAP, REG Ox6B BIT [1])
- TMDS_CLK_D_S T (IO MAP, REG Ox6B BIT [0])
YES
Figure 8. Monitoring TMDS Clock Frequency
Rev. B | Page 44 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Override the deep color mode extracted from the general control packet. The HDMI section unpacks
DEEP COLOR MODE SUPPORT
The ADV7612 supports HDMI streams with 24 bit per sample and deep color modes of 30 bits or 36 bits per sample. The addition of a
video FIFO (refer to the Video FIFO section) allows for the robust support of these modes.
The deep color mode information that the ADV7612 extracts from the general control packet can be read back from
DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0]. It is possible to override the deep color mode that the ADV7612 unpacks from the video data encapsulated
in the processed HDMI stream. This is achieved by configuring the OVERRIDE_DEEP_COLOR_MODE and
DEEP_COLOR_MODE_USER[1:0] controls.
DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0B[7:6] (Read Only)
A readback of the deep color mode information extracted from the general control packet
Function
DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0] Description
00 (default) 8-bits per channel
01 10-bits per channel
10 12-bits per channel
OVERRIDE_DEEP_COLOR_MODE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x40[6]
A control to override the deep color mode.
Function
OVERRIDE_DEEP_COLOR_MODE Description
0 (default) The HDMI section unpacks the video data according to the deep-color information extracted from the
General Control packets (normal operation).
the video data according to the deep color mode set in DEEP_COLOR_MODE_USER[1:0].
DEEP_COLOR_MODE_USER[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x40[5:4]
A control to manually set the deep color mode. The value set in this register is effective when OVERRIDE_DEEP_COLOR_MODE is set
to 1.
Function
DEEP_COLOR_MODE_USER[1:0] Description
00 (default) 8 bits per channel
01 10 bits per channel
10 12 bits per channel
Notes
• Deep color mode can be monitored via DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_RAW, which indicates if the color depth of the processed HDMI
stream has changed.
• The ADV7612 can be configured to trigger an interrupt when the DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_RAW bit changes from 0 to 1. In that
configuration, the interrupt status DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_ST indicates that DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_RAW has changed from 0 to 1.
Refer to the Interrupts section for additional information on the configuration of interrupts.
DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_RAW, IO, Address 0x83[7] (Read Only)
Status of deep color mode changed interrupt signal. When set to 1 it indicates a change in the deep color mode has been detected. Once
set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_CLR.
Function
DEEP_COLOR_CHNG_RAW Description
0 (default) Deep color mode has not changed
1 Change in deep color triggered this interrupt
Rev. B | Page 45 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
TMDS
PLL
DIVIDER
TMDS
SAMPLING
AND
DATA
RECOVERY
TMDS
CLOCK
TMDS
DECODING
FIFO
DPLL
TMDS CH0
TMDS CH1
TMDS CH2
10
R
12
G
12
B
12
HS
VS
DE
R
12
G
12
B
12
HS
VS
DE
10
10
TMDS
CHANNEL 0
TMDS
CHANNEL 1
TMDS
CHANNEL 2
09486-009
001
FIFO is about to overflow.
BG_DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xEA[3:2] (Read Only)
This readback provides the deep-color status for the background HDMI port determined by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The readback
provides the HDMI color depth and is updated when an update request is made via the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit. This measurement
is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_DEEP_COLOR_MODE[1:0] Description
00 (default) 8-bit color per channel
01 10-bit color per channel
10 12-bit color per channel
VIDEO FIFO
The ADV7612 contains a FIFO located between the incoming TMDS data and the CP core (refer to Figure 9). Data arriving over the
HDMI link will be at 1X for nondeep color mode (8 bits per channel), and 1.25X, 1.5X, or 2X for deep color modes (30, 36, and 48 bits,
respectively). Data unpacking and data rate reduction must be performed on the incoming HDMI data to provide the CP core with the
correct data rate and data bit width. The video FIFO is used to pass data safely across the clock domains.
The video FIFO also provides extreme robustness to jitter on the TMDS clock. The CP clock is generated by a DPLL running on the
incoming TMDS clock, and the CP clock may contain less jitter than the incoming TMDS clock. The video FIFO provides immunity to
the incoming jitter and the resultant clock phase mismatch between the CP clock and the TMDS clock.
The video FIFO is designed to operate completely autonomously. It automatically resynchronizes the read and write pointers if they are
about to point to the same location. However, it is also possible for the user to observe and control the FIFO operation with a number of
FIFO status and control registers.
DCFIFO_LEVEL[2:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1C[2:0] (Read Only)
A readback that indicates the distance between the read and write pointers. Overflow/underflow would read as Level 0. Ideal centered
functionality would read as 0b100.
Function
DCFIFO_LEVEL[2:0] Description
000 (default) FIFO has underflowed or overflowed.
010 FIFO has some margin.
011 FIFO has some margin.
101 FIFO has some margin.
100 FIFO perfectly balanced
110 FIFO has some margin.
111 FIFO is about to underflow.
Figure 9. HDMI Video FIFO
Rev. B | Page 46 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Video FIFO is locked. Video FIFO did not have to resynchronize between previous two VSyncs.
Function
DCFIFO_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1C[3] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate if video FIFO is locked.
Function
DCFIFO_LOCKED Description
0 (default) Video FIFO is not locked. Video FIFO had to resynchronize between previous two VSyncs.
DCFIFO_RECENTER, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5A[2] (Self-Clearing)
A reset to recenter the video FIFO. This is a self-clearing bit.
DCFIFO_RECENTER Description
0 (default) Video FIFO normal operation
1 Video FIFO to recenter
DCFIFO_KILL_DIS, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1B[2]
The video FIFO output is zeroed if there is more than one resynchronization of the pointers within two FIFO cycles. This behavior can be
disabled with this bit.
Function
DCFIFO_KILL_DIS Description
0 (default) FIFO output set to zero if more than one resynchronization is necessary during two FIFO cycles
1 FIFO output never set to zero regardless of how many resynchronizations occur
DCFIFO_KILL_NOT_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1B[3]
DCFIFO_KILL_NOT_LOCKED controls whether or not the output of the Video FIFO is set to zero when the video PLL is unlocked.
Function
DCFIFO_KILL_NOT_LOCKED Description
0 FIFO data is output regardless of video PLL lock status.
1 (default) FIFO output is zeroed if video PLL is unlocked.
The DCFIFO is programmed to reset itself automatically when the video PLL transitions from unlocked to locked. Note that the video
PLL transition does not necessarily indicate that the overall system is stable.
DCFIFO_RESET_ON_LOCK, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1B[4]
Enables the reset/recentering of video FIFO on video PLL unlock
Function
DCFIFO_RESET_ON_LOCK Description
0 Do not reset on video PLL lock
1 (default) Reset FIFO on video PLL lock
PIXEL REPETITION
In HDMI mode, video formats with TMDS rates below 25 M pixels/sec require pixel repetition in order to be transmitted over the TMDS
link. When the ADV7612 receives this type of video format, it discards repeated pixel data automatically, based on the pixel repetition
field available in the AVI InfoFrame.
When HDMI_PIXEL_REPETITION is nonzero, video pixel data is discarded and the pixel clock frequency is divided by
(HDMI_PIXEL_REPETITION) + 1.
Rev. B | Page 47 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0000 (default)
1×
0011
4x
HDMI_PIXEL_REPETITION[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x05[3:0] (Read Only)
A readback to provide the current HDMI pixel repetition value decoded from the AVI InfoFrame received. The HDMI receiver
automatically discards repeated pixel data and divides the pixel clock frequency appropriately as per the pixel repetition value.
Function
HDMI_PIXEL_REPETITION[3:0] Description
0001 2×
0010 3×
0011 4×
0100 5×
0101 6×
0110 7×
0111 8×
1000 9×
1001 10×
1010 to 1111 Reserved
DEREP_N_OVERRIDE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x41[4]
This control allows the user to override the pixel repetition factor. The ADV7612 then uses DEREP_N instead of
HDMI_PIXEL_REPETITION[3:0] to discard video pixel data from the incoming HDMI stream.
Function
DEREP_N_OVERRIDE Description
0 (default) Automatic detection and processing of procession of pixel repeated modes using the AVI InfoFrame
information.
1 Enables manual setting of the pixel repetition factor as per DEREP_N[3:0].
DEREP_N[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x41[3:0]
Sets the derepetition value if derepetition is overridden by setting DEREP_N_OVERRIDE.
Function
DEREP_N[3:0] Description
0000 (default) DEREP_N+1 indicates the pixel and clock discard factor.
xxxx DEREP_N+1 indicates the pixel and clock discard factor.
BG_PIX_REP[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xEA[7:4] (Read Only)
Background port pixel repetition status for the background HDMI port determined by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The readback
provides the pixel repetition value in AVI Infoframe and is updated when an update request is made via the BG_MEAS_REQcontrol bit.
This measurement is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_PIX_REP[3:0] Description
0000 (default) 1x
0001 2x
0010 3x
0100 5x
0101 6x
0110 7x
0111 8x
1000 9x
1001 10x
1010 - 1111 Reserved
The following registers allow forcing YCrCb 444 and YCrCb 422 regardless of the AVI Infoframe. This feature is useful when source
switches between YCrCb 444 and YCrCb 422 modes without sending appropriate update in AVI Infoframe.
Rev. B | Page 48 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0 (default)
Not forced
1
Forced
0 (default)
The input stream processed by the HDMI core is not HDCP encrypted.
0 (default)
Current frame in Port A is not encrypted.
FORCE_YCRCB_444, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x46[4]
Forces a 4:4:4 interpretation of the video contents, regardless of the description in the AVI infoframe. This bit carries higher priority than
FORCE_YCRCB_422
Function
FORCE_YCRCB_444 Description
1 Forced
FORCE_YCRCB_422, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x47[4]
Forces a 4:2:2 interpretation of the video contents, regardless of the description in the AVI infoframe. This bit is only valid if
FORCE_YCRCB_444 is zero.
Function
FORCE_YCRCB_422 Description
0 (default) Not forced
HDCP SUPPORT
HDCP Decryption Engine
The HDCP decryption engine allows for the reception and decryption of HDCP content-protected video and audio data. In the HDCP
authentication protocol, the transmitter authenticates the receiver by accessing the HDCP registers of the ADV7612 over the DDC bus.
Once the authentication is initiated, the HDCP decryption integrated in the ADV7612 computes and updates a decryption mask for every
video frame. This mask is applied to the incoming data at every clock cycle to yield decrypted video and audio data.
HDCP_A0, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x00[7]
A control to set the second LSB of the HDCP port I
Function
HDCP_A0 Description
0 (default) I2C address for HDCP port is 0x74. Used for single-link mode or first receiver in dual-link mode.
1 I2C address for HDCP port is 0x76. Used only for a second receiver dual-link mode.
HDMI_CONTENT_ENCRYPTED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x05[6] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the use of HDCP encryption.
Function
HDMI_CONTENT_ENCRYPTED Description
2
C address.
1 The input stream processed by the HDMI core is HDCP encrypted.
HDMI_ENCRPT_X_RAW reports the encryption status of the data present on each individual HDMI port (where X = A or B).
Note: These bits are reset to 0 if an HDMI packet detection reset occurs. (Refer to the HDMI Packet Detection Flag Reset section.)
HDMI_ENCRPT_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x6F[2] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port A encryption detection signal.
Function
HDMI_ENCRPT_A_RAW Description
1 Current frame in Port A is encrypted.
HDMI_ENCRPT_B_RAW, IO, Address 0x6F[1] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port B Encryption detection signal.
Function
HDMI_ENCRPT_B_RAW Description
0 (default) Current frame in port B is not encrypted
1 Current frame in port B is encrypted
Rev. B | Page 49 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Notes
• The ADV7612 supports the 1.1_FEATURES, FAST_REAUTHENTICATION, and FAST_I2C speed HDCP features. The BCAPS
register must be initialized appropriately if these features are to be supported by the application integrating the ADV7612, for
example, set BCAPS[0] to 1 to support FAST_REAUTHENTICATION.
• It is recommended to set BCAPS[7:0] Bit [7] to 1 if the ADV7612 is used as the front end of an HDMI receiver. This bit should be set
to 0 for DVI applications.
Internal HDCP Key OTP ROM
The ADV7612 features an on-chip nonvolatile memory that is preprogrammed with a set of HDCP keys.
HDCP Keys Access Flags
The ADV7612 accesses the internal HDCP key OTP ROM (also referred to as HDCP ROM) on two different occasions:
• After a power up, the ADV7612 reads the KSV from the internal HDCP ROM (refer to Figure 10).
• After a KSV update from an HDCP transmitter, the ADV7612 reads the KSV and all keys in order to carry out the link verification
response (refer to Figure 11).
The host processor can read the HDCP_KEYS_READ and HDCP_KEY_ERROR flags to check that the ADV7612 successfully accessed
the HDCP ROM.
HDCP_KEYS_READ, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[5] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate a successful read of the HDCP keys and/or KSV from the internal HDCP Key OTP ROM. A logic high is returned
when the read is successful.
Function
HDCP_KEYS_READ Description
0 (default) HDCP keys and/or KSV not yet read
1 HDCP keys and/or KSV HDCP keys read
HDCP_KEY_ERROR, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[4] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate if a checksum error occurred while reading the HDCP and/or KSV from the HDCP Key ROM Returns 1 when
HDCP Key master encounters an error while reading the HDCP Key OTP ROM
Function
HDCP_KEY_ERROR Description
0 (default) No error occurred while reading HDCP keys
1 HDCP keys read error
Rev. B | Page 50 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
HDCP_KEY_READ = 0
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 0
READ KSV AND CHECKSUM
CS1 FROM HDC P OTP ROM
DERIVE CHECKSUM CS 1'
FROM KSV
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 1
START
(AFTER POWER-UP)
END
CS1 = CS1'
SET BKSV (HDCP REGISTER
ADDRESS 0x00
BKSV = KSV
HDCP_KEY_READ = 1
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 0
NO
YES
09486-010
Figure 10. HDCP ROM Access After Power-Up
Rev. B | Page 51 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
HDCP_KEY_READ = 0
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 0
READ KSV, HDCP KEYS AND
CHECKSUM CS2 FRO M HDCP PROM
DERIVE CHECKSUM CS 2'
FROM KSV AND HDCP KEYS
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 1
START
(AKSV UPDATE
FROM TRANSMITTER)
END
CS1 = CS1'
DERIVE LINK VERIFICATION Ri'
UPDATE BKSV AND Ri' IN
HDCP RESGISTERS
END
NO
YES
HDCP_KEY_READ = 1
HDCP_KEY_ERROR = 0
09486-011
Notes
• After the part has powered up, it is recommended to wait for 1 ms before checking the HDCP_KEYS_READ and
HDCP_KEY_ERROR flag bits. This ensures that the ADV7612 had sufficient time to access the internal HDCP ROM and set the
HDCP_KEYS_READ and HDCP_KEY_ERROR flag bits.
• After an AKSV update from the transmitter, it is recommended to wait for 2 ms before checking the HDCP_KEYS_READ and
HDCP_KEY_ERROR flag bits. This ensures that the ADV7612 had sufficient time to access the internal HDCP ROM, and set the
HDCP_KEYS_READ and HDCP_KEY_ERROR flag bits.
• When the ADV7612 successfully retrieves the HDCP keys and/or KSV from the internal HDCP ROM, the HDCP_KEYS_READ flag
bit is set to 1 and the HDCP_KEY_ERROR flag bit is set to 0.
• The I
2
C controllers for the main I2C lines and the HDCP lines are independent of each other. It is, therefore, possible to access the
internal registers of the ADV7612 while it reads the HDCP keys and/or the KSV from the internal HDCP ROM.
• A hardware reset (that is, reset via the reset pin) does not lead the ADV7612 to read the KSV or the keys from the HDCP ROM.
• The ADV7612 takes 1.8 ms to read the keys from the HDCP ROM
Figure 11. HDCP ROM Access After KSV Update from the Transmitter
Rev. B | Page 52 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
HDCP Ri Expired
Following register allows early detection of HDMI TX failure. Refer to interrupt status controls RI_EXPIRED_A_ST, RI_EXPIRED_B_ST.
HDCP_RI_EXPIRED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[3] (Read Only)
Readback high when a calculated Ri has not been read by the source TX, on the active port. It remains high until next Aksv update.
Function
HDCP_RI_EXPIRED Description
0 (default) Calculated Ri has been read by the source TX.
1 Calculated Ri has not been read by the source TX.
HDMI SYNCHRONIZATION PARAMETERS
The ADV7612 contains the logic required to measure the details of the incoming video resolution. The HDMI synchronization
parameters readback registers from the HDMI Map can be used, in addition to the STDI registers from the CP (refer to the Standard
Detection and Identification section), to estimate the video resolution of the incoming HDMI stream.
Notes
The synchronization parameters are valid if the part is configured in HDMI mode via PRIM_MODE[3:0].
The HDMI synchronization filter readback parameters are valid even while the part free runs (refer to the Free Run Mode section)
on the condition that the measurement filters have locked.
Horizontal Filter and Measurements
The HDMI horizontal filter performs measurements on the DE and HSync of the HDMI stream on the selected port. The ADV7612 also
performs horizontal measurements on the background port as selected by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. These measurements are
available in the HDMI Map and can be used to determine the resolution of the incoming video data streams.
Primary Port Horizontal Filter Measurements
The HDMI horizontal filter performs the measurements described in this section on the HDMI port selected by
HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
Notes
The horizontal measurements are valid only if
DE_REGEN_LCK_RAW is set to 1.
The HDMI horizontal filter is used solely to measure the horizontal synchronization signals decoded from the HDMI stream. The
HDMI horizontal filter is not in the main path of the synchronization processed by the part and does not delay the overall HDMI
data into video data out latency.
The unit for horizontal filter measurement is a pixel, that is, the actual element of the picture content encapsulated in the HDMI/DVI
stream which the ADV7612 processes. A pixel has a duration T
, which is provided in Equation 2, unit time of horizontal filter
PIXEL
measurements.
T
Pixel
= T
× DEEP_COLOR_RATIO × (PIXEL_REPETITION + 1) (2)
FTMDS
where:
T
is the TMDS frequency.
FTMDS
DEEP_COLOR_RATIO = 1 for 24-bit deep color.
DEEP_COLOR_RATIO = 5/4 for 30-bit deep color.
DEEP_COLOR_RATIO = 3/2 for 36-bit deep color.
DEEP_COLOR_RATIO = 2 for 48-bit deep color.
PIXEL_REPETITION is the number of repeated pixels in the input HDMI stream.
DE_REGEN_FILTER_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x07[5] (Read Only)
DE regeneration filter lock status. Indicates that the DE regeneration section has locked to the received DE and horizontal
synchronization parameter measurements are valid for readback.
Function
DE_REGEN_FILTER_LOCKED Description
0 (default) DE regeneration not locked
1 DE regeneration locked to incoming DE
Rev. B | Page 53 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Function
DE_REGEN_LCK_RAW Description
0 (default) DE regeneration block has not been locked.
1 DE regeneration block has been locked to the incoming DE signal.
TOTAL_LINE_WIDTH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1E[5:0]; Address 0x1F[7:0] (Read Only)
Total line width is a horizontal synchronization measurement. This gives the total number of pixels per line. This measurement is valid
only when the DE regeneration filter has locked.
Function
TOTAL_LINE_WIDTH[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxx Total number of pixels per line
LINE_WIDTH[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x07[4:0]; Address 0x08[7:0] (Read Only)
Line width is a horizontal synchronization measurement, which gives the number of active pixels in a line. This measurement is only valid
when the DE regeneration filter is locked.
Function
LINE_WIDTH[12:0] Description
00000000000 (default) Total number of active pixels per line
xxxxxxxxxxx Total number of active pixels per line
HSYNC_FRONT_PORCH[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x20[4:0]; Address 0x21[7:0] (Read Only)
HSync front porch width is a horizontal synchronization measurement. The unit of this measurement is unique pixels. This measurement
is valid only when the DE regeneration filter has locked.
Function
HSYNC_FRONT_PORCH[12:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxx Total number of pixels in the front porch
HSYNC_PULSE_WIDTH[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x22[4:0]; Address 0x23[7:0] (Read Only)
HSync pulse width is a horizontal synchronization measurement. The unit of this measurement is unique pixels. This measurement is
valid only when the DE regeneration filter has locked.
Function
HSYNC_PULSE_WIDTH[12:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxx Total number of pixels in the hsync pulse
HSYNC_BACK_PORCH[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x24[4:0]; Address 0x25[7:0] (Read Only)
HSync back porch width is a horizontal synchronization measurement. The unit of this measurement is unique pixels. This measurement
is valid only when the DE regeneration filter has locked.
Function
HSYNC_BACK_PORCH[12:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxx Total number of pixels in the back porch
DVI_HSYNC_POLARITY, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x05[5] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the polarity of the HSync encoded in the input stream
Function
DVI_HSYNC_POLARITY Description
0 (default) The HSync is active low.
1 The HSync is active high.
Rev. B | Page 54 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
A
B
D
C
E
DATA
ENABLE
HSYNC
NOTE:
A TOTAL NUMBER OF PIXELS PER LINE
B ACTIVE NUMBER OF PIXELS PER LINE
C HSYNC FRONT PORCH WIDTH IN PIXEL UNIT
D HSYNC WIDTH IN PIXEL UNIT
E HSYNC BACK PORCH WIDTH IN PIXEL UNIT
09486-012
1
Horizontal and vertical were locked when measurement for select background HDMI port were taken.
Figure 12. Horizontal Timing Parameters
Background Port Horizontal Filter Measurements
The HDMI horizontal filter performs the measurements described in this section on the HDMI port selected by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. Note that BG_PARAM_LOCK must be high for background horiztonal and vertical measurements to
be valid.
BG_PARAM_LOCK, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xEA[1] (Read Only)
A flag to indicate that vertical and horizontal parameters have been locked during a background measurement.
Function
BG_PARAM_LOCK Description
0 (default) Horizontal and vertical were not locked when measurement for select background HDMI port were
taken.
BG_TOTAL_LINE_WIDTH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE4[5:0]; Address 0xE5[7:0] (Read Only)
Background port total line width, a horizontal synchronization measurement for the background HDMI port determined by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The value represents the total number of pixels in a line and is updated when a update request is made via
the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit. This measurement is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_TOTAL_LINE_WIDTH[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of pixels per line on the background measurement port
BG_LINE_WIDTH[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE2[4:0]; Address 0xE3[7:0] (Read Only)
Background port line width, a horizontal synchronization measurement for the background HDMI Port determined by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The value represents the number of active pixels in a line and is updated when a update request is made
via the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit.
Function
BG_LINE_WIDTH[12:0] Description
0000000000000 (default) The number of active pixels per line on the background measurement port.
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The number of active pixels per line on the background measurement port.
Horizontal Filter Locking Mechanism
The locking/unlocking mechanism of the HDMI horizontal filter is as follows:
• The HDMI horizontal filter locks if the following two conditions are met:
• The DE transitions occur at the exact same pixel count for eight consecutive video lines
• The HSync transitions occur at the exact same pixel count for eight consecutive video lines
• The HDMI horizontal filter unlocks if either of the two following conditions are met:
• The DE transitions occur on different pixels count for 15 consecutive video lines
• The HSync transitions occur on different pixels count for 15 consecutive video lines
Rev. B | Page 55 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
VERT_FILTER_LOCKED
Description
FIELD0_VS_FRONT_PORCH[13:0]
Description
Vertical Filters and Measurements
The ADV7612 integrates a HDMI vertical filter which performs measurements on the VSync of the HDMI stream on the selected port.
The ADV7612 also performs vertical measurements on the background port as selected by BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0].These
measurements are available in the HDMI Map and can be used to determine the resolution of the incoming video data streams.
Primary Port Vertical Filter Measurements
The HDMI vertical filter performs the measurements on the HDMI port selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0].
The Field 0 measurements are adequate to determine the standard of incoming progressive modes. A combination of Field 0 and field 1
measurements should be used to determine the standard of interlaced modes.
Notes
• The vertical measurements are valid only if V_LOCKED_RAW is set to 1.
• The HDMI vertical filter is used solely to measure the vertical synchronization signals decoded from the HDMI stream. This filter is
not in the main path of the synchronization processed by the part and does not delay the overall HDMI data into video data out
latency.
VERT_FILTER_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x07[7] (Read Only)
Vertical filter lock status. Indicates whether the vertical filter is locked and vertical synchronization parameter measurements are valid for
readback.
Function
0 Vertical filter has not locked.
1 Vertical filter has locked.
V_LOCKED_RAW, IO, Address 0x6A[1] (Read Only)
Raw status of the vertical sync filter locked signal.
Function
V_LOCKED_RAW Description
0 Vertical sync filter has not locked and vertical sync parameters are not valid
1 Vertical sync filter has locked and vertical sync parameters are valid
Note: Field 0 measurements are used to determine the video modes that are progressive.
FIELD0_TOTAL_HEIGHT[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x26[5:0]; Address 0x27[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 0 total height is a vertical synchronization measurement. This readback gives the total number of half lines in Field 0. This
measurement is valid only when the vertical filter has locked.
Function
FIELD0_TOTAL_HEIGHT[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in Field 0 (divide readback by 2 to get number of lines)
FIELD0_HEIGHT[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x09[4:0]; Address 0x0A[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 0 height is a vertical filter measurement. This readback gives the number of active lines in Field 0. This measurement is valid only
when the vertical filter has locked.
Function
FIELD0_HEIGHT[12:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The number of active lines in Field 0
FIELD0_VS_FRONT_PORCH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x2A[5:0]; Address 0x2B[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 0 VSync front porch width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit of this measurement is half lines. This measurement
is valid only when the vertical filter has locked.
Function
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in the VSync front porch of Field 0 (divide readback by 2 to get
number of lines)
Rev. B | Page 56 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
A
C
B
DATA
ENABLE
HSYNC
VSYNC
NOTE:
A TOTAL NUMBER OF LINES IN FIELD 0. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
B ACTIVES NUMBER OF LINES IN FIELD 0. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
C VSYNC FRONT PORCH WIDTH IN FIELD 0. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
D VSYNC PULSE WIDTH IN FIELD 0. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
E VSYNC BACK PORCH WIDT H IN FIELD 0. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
ED
09486-013
FIELD0_VS_PULSE_WIDTH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x2E[5:0]; Address 0x2F[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 0 VSync width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit for this measurement is half lines. This measurement is valid
only when the vertical filter has locked.
Function
FIELD0_VS_PULSE_WIDTH[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in the VSync pulse of Field 0 (divide readback by 2 to get
number of lines)
FIELD0_VS_BACK_PORCH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x32[5:0]; Address 0x33[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 0 VSync back porch width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit for this measurement is half lines.
Function
FIELD0_VS_BACK_PORCH[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in the VSync Back Porch of Field 0 (divide readback by 2 to get
number of lines)
DVI_VSYNC_POLARITY, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x05[4] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the polarity of the VSync encoded in the input stream
Function
DVI_VSYNC_POLARITY Description
0 The VSync is active low.
1 The VSync is active high.
Note: Field 1 measurements should not be used for progressive video modes.
FIELD1_TOTAL_HEIGHT[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x28[5:0]; Address 0x29[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 1 total height is a vertical synchronization measurement. This readback gives the total number of half lines in Field 1.
This measurement is valid only when the vertical filter has locked. Field 1 measurements are valid when HDMI_INTERLACED
is set to 1.
Function
FIELD1_TOTAL_HEIGHT[13:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in Field 1 (divide readback by 2 to get number of lines)
FIELD1_HEIGHT[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0B[4:0]; Address 0x0C[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 1 height is a vertical filter measurement. This readback gives the number of active lines in field. This measurement is valid only
when the vertical filter has locked. Field 1 measurements are only valid when HDMI_INTERLACED is set to 1.
Function
FIELD1_HEIGHT[12:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The number of active lines in Field 1
Figure 13. Vertical Parameters for FIELD 0
Rev. B | Page 57 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx
The total number of half lines in the VSync front porch of Field 1 (divide readback by 2 to get
FIELD1_VS_PULSE_WIDTH[13:0]
Description
FIELD1_VS_BACK_PORCH[13:0]
Description
A
C
B
DATA
ENABLE
HSYNC
VSYNC
NOTE:
A TOTAL NUMBER OF LINES IN FIELD 1. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
B ACTIVES NUMBER OF LINES IN FIELD 1. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
C VSYNC FRONT PORCH WIDTH IN FIELD 1. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
D VSYNC PULSE WIDTH IN FIELD 1. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
E VSYNC BACK PORCH WIDT H IN FIELD 1. UNIT IS IN HALF LINES.
E
D
09486-014
FIELD1_VS_FRONT_PORCH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x2C[5:0]; Address 0x2D[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 1 VSync front porch width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit of this measurement is half lines. This measurement is
valid only when the vertical filter has locked. Field 1 measurements are valid when HDMI_INTERLACED is set to 1.
Function
FIELD1_VS_FRONT_PORCH[13:0] Description
number of lines)
FIELD1_VS_PULSE_WIDTH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x30[5:0]; Address 0x31[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 1 VSync width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit for this measurement is half lines. This measurement is valid
only when the vertical filter has locked. Field 1 measurements are valid when HDMI_INTERLACED is set to 1.
Function
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of half lines in the VSync pulse of Field 1 (divide readback by 2 to get number
of lines)
FIELD1_VS_BACK_PORCH[13:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x34[5:0]; Address 0x35[7:0] (Read Only)
Field 1 VSync back porch width is a vertical synchronization measurement. The unit for this measurement is half lines. This measurement is
valid only when the vertical filter has locked. Field 1 measurements are valid when HDMI_INTERLACED is set to 1.
Function
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The number of half lines in the VSync back porch of Field 1 (divide readback by 2 to get number
of lines)
Figure 14. Vertical Parameters for FIELD 1
The vertical filter provides the interlaced status of the video stream. The interlaced status HDMI_INTERLACED is valid only if the
vertical filter is locked and V_LOCKED_RAW is set to 1.
HDMI_INTERLACED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0B[5] (Read Only)
HDMI input Interlace status, a vertical filter measurement.
Function
HDMI_INTERLACED Description
0 Progressive Input
1 Interlaced Input
Background Port Vertical Filter Measurements
The HDMI vertical filter performs the measurements described in this section on the HDMI port selected by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. Note that BG_PARAM_LOCK must be high for background horiztonal and vertical measurements to
be valid.
Rev. B | Page 58 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
xxxxxxxxxxxxx
The number of active lines in a field on the background measurement port
BG_TOTAL_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE8[4:0]; Address 0xE9[7:0] (Read Only)
Background port total field height is a vertical synchronization measurement for the background HDMI port determined by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The value represents the total number of lines in a field and is updated when an update request is made via
the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit.
Function
BG_TOTAL_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0] Description
0000000000000 (default) The total number of lines in a field on the background measurement port
xxxxxxxxxxxxx The total number of lines in a field on the background measurement port
BG_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xE6[4:0]; Address 0xE7[7:0] (Read Only)
Background port field height is a vertical synchronization measurement for a background HDMI Port determined by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The value represents the number of active lines in a field and is updated when a update request is made via
the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit.
Function
BG_FIELD_HEIGHT[12:0] Description
0000000000000 (default) The number of active lines in a field on the background measurement port
BG_HDMI_INTERLACED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0xEA[0] (Read Only)
Background port HDMI input interlace status is a vertical filter measurement for a background HDMI port determined by
BG_MEAS_PORT_SEL[2:0]. The status readback is updated when a update request is made via the BG_MEAS_REQ control bit. This
measurement is only valid when BG_PARAM_LOCK is set to 1.
Function
BG_HDMI_INTERLACED Description
0 (default) Progressive input
1 Interlaced input
Vertical Filter Locking Mechanism
The HDMI vertical filter locks if the input VSync comes at exactly the same line count for two consecutive frames. The HDMI vertical
filter unlocks if the VSync comes at a different pixels count for two consecutive frames.
Rev. B | Page 59 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
DE_REGEN_RAW
INDICATES A CHANGE
IN HSYNC
CALCULATE TOTAL
HORIZO NTAL BLANKING
(HSYNC FRONT PORCH +
HSYNC PULSE WIDTH +
HSYNC BACK PORCH)
IF
TOTAL HORIZONTAL BLANKING
IS GREAT E R THAN
TOTAL LINE LENGTH
SET
NEW_VS_PARAM
TO 0
SET
NEW_VS_PARAM
TO 1
09486-112
ACR PACKET
DATA
AUDIO DPLL
PACKET PROCESSOR
(DISPATCH BLOCK)
AUDIO DATA
VIDEO DATA
AUDIO
FIFO
TO DPP
BLOCK
DELAY
LINE
RAMPED
MUTE/UNMUTE
AUDIO
RECONSTRUCTION,
SERIALIZATIONAND
MUXING
CHANNEL STATUS
BITS COLLECTION
DATA FROM HDCP
ENGINE/MASK
TMDS CLOCK
TMDS CLOCK
N
CTS
MCLK/INT2
AP0
AP1
AP2
AP3
AP4
AP5
SCLK
128fs
09486-015
Low Frequency Formats
To process the low frame rate video formats such as 720p24, 720p25, 720p30, 1080p23, 1080p24, and 1080p30, the NEW_VS_PARAM bit
should be set. Refer to Figure 15.
Figure 15. Low Frame Rate Algorithm
NEW_VS_PARAM, HDMI, Address 0x4C[2]
Enables a new version of vertical parameter extraction for evaluation purposes. That is the version in the background port measurement
blocks.
Function
NEW_VS_PARAM Description
0 NEW_VS_PARAM disabled
1 NEW_VS_PARAM enabled
AUDIO CONTROL AND CONFIGURATION
The ADV7612 extracts an L-PCM, IEC 61937 compressed or DST audio data stream from their corresponding audio packets (that is,
audio sample or DST) encapsulated inside the HDMI data stream.
The ADV7612 also regenerates an audio master clock along with the extraction of the audio data. The clock regeneration is performed by
an integrated DPLL. The regenerated clock is used to output audio data from the 64 stereo sample depth FIFO to the audio interface
configuration pins.
Important
• The ADV7612 supports the extraction of stereo audio data (noncompressed or compressed) at audio sampling frequency up to 192 kHz.
• The ADV7612 supports the extraction of multichannel audio data.
Figure 16. Audio Processor Block Diagram
Rev. B | Page 60 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
Audio DPLL
The audio DPLL generates an internal audio master clock with a frequency of 128 times the audio sampling frequency, usually called fs.
The audio master clock is used to clock the audio processing section.
Locking Mechanism
When the upstream HDMI transmitter outputs a stable TMDS frequency and consistent audio clock regeneration values, the audio DPLL
locks within two cycles of the audio master clock after the following two conditions are met:
• TMDS PLL is locked
• ADV7612 has received an ACR packet with N and CTS parameters within a valid range
The audio DPLL lock status can be monitored via AUDIO_PLL_LOCKED.
AUDIO_PLL_LOCKED, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[0] (Read Only)
A readback to indicate the Audio DPLL lock status.
Function
AUDIO_PLL_LOCKED Description
0 (default) The audio DPLL is not locked.
1 The audio DPLL is locked.
ACR Parameters Loading Method
The N and CTS parameters from the ACR packets are used to regenerate the audio clock and are reloaded into the DPLL anytime they
change. The self-clearing bit FORCE_N_UPDATE provides a means to reset the audio DPLL by forcing a reload of the N and CTS
parameters from the ACR packet into the audio DPLL.
FORCE_N_UPDATE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5A[0] (Self-Clearing)
A control to force an N and CTS value update to the audio DPLL. The audio DPLL regenerates the audio clock.
Function
FORCE_N_UPDATE Description
0 (default) No effect
1 Forces an update on the N and CTS values for audio clock regeneration
Audio DPLL Coast Feature
The audio DPLL incorporates a coast feature that allows it to indefinitely output a stable audio master clock when selectable events occur.
The coast feature allows the audio DPLL to provide an audio master clock when the audio processor mutes the audio following a mute
condition (refer to the Audio Muting section). The events that cause the audio DPLL to coast are selected via the coasts masks listed in
Table 10.
Table 10. Selectable Coast Conditions
HDMI Map
Bit Name
AC_MSK_VCLK_CHNG 0x13[6] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if TMDS clock has any
AC_MSK_VPLL_UNLOCK 0x13[5] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if TMDS PLL unlocks TMDS_PLL_LOCKED
AC_MSK_NEW_CTS 0x13[3] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if CTS changes by more
AC_MSK_NEW_N 0x13[2] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if N changes
AC_MSK_CHNG_PORT 0x13[1] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if active port is changed HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]
AC_MSK_VCLK_DET 0x13[0] When set to 1, audio DPLL coasts if no TMDS clock is detected
Address Description
irregular/missing pulses
than threshold set in CTS_CHANGE_THRESHOLD[5:0]
on the active port
Corresponding Status
Registers(s)
VCLK_CHNG_RAW
CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW
CHANGE_N_RAW
TMDS_CLK_A_RAW
AUDIO FIFO
The audio FIFO can store up to 128 audio stereo data from the audio sample, DSD or HBR packets. Stereo audio data are added into the
FIFO from the audio packet received. Stereo audio data are retrieved from the FIFO at a rate corresponding to 128 times the audio
sampling frequency, f
The status of the audio FIFO can be monitored through the status flags FIFO_UNDERFLO_RAW, FIFO_OVERFLO_RAW,
FIFO_NEAR_OVFL_RAW, and FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_RAW.
.
s
Rev. B | Page 61 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
EMPTY
EMPTY
STEREO DATA N – 1
EMPTY
EMPTY
STEREO DATA N – 2
STEREO DATA 1
STEREO DATA 0
ADDRESS 63
ADDRESS ORDER
ADDRESS N + 2
ADDRESS N + 1
ADDRESS N
ADDRESS 3
ADDRESS 2
ADDRESS 1
ADDRESS 0
WRITE POINTER
READ POINT E R
…
…
…
…
…
…
09486-016
FIFO_UNDERFLO_RAW
Description
FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_RAW
Description
Figure 17. Audio FIFO
FIFO_UNDERFLO_RAW, IO, Address 0x7E[6] (Read Only)
Status of audio FIFO underflow interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates the audio FIFO read pointer has reached the write pointer
causing the audio FIFO to underflow. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via AUDIO_FIFO_UNDERFLO_CLR.
Function
0 (default) Audio FIFO has not underflowed.
1 Audio FIFO has underflowed.
FIFO_OVERFLO_RAW, IO, Address 0x7E[5] (Read Only)
Status of audio FIFO overflow interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates audio FIFO write pointer has reached the read pointer causing
the audio FIFO to overflow. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via AUDIO_FIFO_OVERFLO_CLR.
Function
FIFO_OVERFLO_RAW Description
0 (default) Audio FIFO has not overflowed.
1 Audio FIFO has overflowed.
FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_RAW, IO, Address 0x83[0] (Read Only)
Status of audio FIFO near underflow interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates the audio FIFO is near underflow as the number of FIFO
registers containing stereo data is less or equal to value set in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_EMPTY_THRESHOLD. Once set, this bit will
remain high until it is cleared via FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_CLR.
Function
0 (default) Audio FIFO has not reached low threshold defined in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_EMPTY_THRESHOLD [5:0].
1 Audio FIFO has reached low threshold defined in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_EMPTY_THRESHOLD [5:0].
Rev. B | Page 62 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
FIFO_NEAR_OVFL_RAW, IO, Address 0x7E[7] (Read Only)
Status of audio FIFO near overflow interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates the audio FIFO is near overflow as the number FIFO
registers containing stereo data is greater or equal to value set in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_FULL_THRESHOLD. Once set, this bit will
remain high until it is cleared via FIFO_NEAR_OVFL_CLR.
Function
FIFO_NEAR_OVFL_RAW Description
0 (default) Audio FIFO has not reached high threshold defined in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_FULL_THRESHOLD [5:0]
1 Audio FIFO has reached high threshold defined in AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_FULL_THRESHOLD [5:0]
AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_EMPTY_THRESHOLD[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x12[6:0]
Sets the threshold used for FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_RAW. FIFO_NEAR_UFLO_ST interrupt is triggered if audio FIFO goes below this level.
Function
AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_EMPTY_THRESHOLD[6:0] Description
0x02 (default) Default value
AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_FULL_THRESHOLD[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x11[6:0]
Sets the threshold used for FIFO_NEAR_OVRFL_RAW. FIFO_NEAR_OVRFL_ST interrupt is triggered if audio FIFO reaches this level.
Function
AUDIO_FIFO_ALMOST_FULL_THRESHOLD[6:0] Description
0x7D (default) Default value
AUDIO PACKET TYPE FLAGS
The ADV7612 can receive the following audio packets:
• Audio sample packets—receive and process
• HBR packets—receive and process
• DSD packets— receive and process
• DST packets—detection only
The following flags are provided to monitor the type of audio packets received by the ADV7612. Figure 18 shows the algorithm that can
be implemented to monitor the type of audio packet processed by the ADV7612.
AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_RAW, IO, Address 0x83[5] (Read Only)
Status of audio mode change interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that the type of audio packet received has changed. The following
are considered audio modes, no audio packets, audio sample packet, DSD packet, HBR packet or DST packet. Once set, this bit remains
high until it is cleared via AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_CLR.
Function
AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_RAW Description
0 (default) Audio mode has not changed.
1 Audio mode has changed.
Rev. B | Page 63 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
No L_PCM or IEC 61937 compressed audio sample packet received within the last 10 HSync
1
DSD packet received within the last 10 HSync
Function
AUDIO_SAMPLE_PCKT_DET, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x18[0] (Read Only)
Audio sample packet detection bit. This bit resets to zero on the 11th HSync leading edge following an audio packet if a subsequent audio
sample packet has not been received or if a DSD, DST, or HBR audio packet sample packet has been received.
Function
AUDIO_SAMPLE_PCKT_DET Description
1 L_PCM or IEC 61937 compressed audio sample packet received within the last 10 HSyncs
DSD_PACKET_DET, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x18[1] (Read Only)
DSD audio packet detection bit. This bit resets to zero on the 11th HSync leading edge following a DSD packet or if an audio, DST, or
HBR packet sample packet has been received or after an HDMI reset condition.
Function
DSD_PACKET_DET Description
0 (default) No DSD packet received within the last 10 HSync
DST_AUDIO_PCKT_DET, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x18[2] (Read Only)
DST audio packet detection bit. This bit resets to zero on the 11th HSync leading edge following a DST packet if a subsequent DST has
not been received. Or if an audio, DSD, or HBR packet sample packet has been received or after an HDMI reset condition.
Function
DST_AUDIO_PCKT_DET Description
0 (default) No DST packet received within the last 10 HSync
1 DST packet received within the last 10 HSync
HBR_AUDIO_PCKT_DET, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x18[3] (Read Only)
HBR Packet detection bit. This bit resets to zero on the 11th HSync leading edge following an HBR packet if a subsequent HBR packet has
not been detected. It also resets if an Audio, DSD or DST packet sample packet has been received and after an HDMI reset condition.
HBR_AUDIO_PCKT_DET Description
0 (default) No HBR audio packet received within the last 10 HSync
1 HBR audio packet received within the last 10 HSync
Notes
• The ADV7612 processes only one type of audio packet at a time.
• The ADV7612 processes the latest type of audio packet that it received.
• AUDIO_SAMPL_PCKT_DET, DSD_PACKET_DET, DST_AUDIO_PCKT_DET, and HBR_AUDIO_PCKT_DET are reset to 0
when a HDMI packet detect reset condition occurs.
• A corresponding interrupt can be enabled for AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_RAW by setting the mask AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_MB1 or
AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_MB2. Refer to the Interrupts section for additional information on the interrupt feature.
Rev. B | Page 64 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
ENABLE THE AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_ST
INTERRUPT
SET AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_CLR TO 1
NO AUDIO S AM P LE PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
AUDIO SAMPLE PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
AUDIO_MODE_CH
NG_ST INTERRUPT?
IS
AUDIO_SAMPLE
PCKT_DET?
START
YES
NO YES
NO DSD PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
DSD PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
NO YES
NO DST PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
DST PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
NO
YES
NO HBR PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
HBR PACKETS ARE
BEING RECEIVED
IS
HBR_PACKET_DET?
IS
DST_PACKET_DET?
IS
DSD_PACKET_DET?
NO YES
09486-017
Figure 18. Monitoring Audio Packet Type Processed by ADV7612
AUDIO OUTPUT INTERFACE
The ADV7612 has a dedicated 3-pin audio output interface. The output pin names and descriptions are shown in Table 11.
Table 11. Audio Outputs and Clocks
Output Pixel Port Description
AP0 Audio Output Port 0
AP1 Audio Output Port 1
AP2 Audio Output Port 2
AP3 Audio Output Port 3
AP4 Audio Output Port 4
AP5 Audio Output Port 5
SCLK/INT2 Bit Clock
MCLK/INT2 Audio Master Clock
Table 12 shows the default configurations for the various possible output interfaces.
Rev. B | Page 65 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Function
Table 12. Default Audio Output Pixel Port Mapping
Output Pixel Port I2S/SPDIF Interface DSD Interface
AP0 SPDIF0 DSD0A
AP1 I2S0/SDPIF0 DSD0B
AP2 I2S1/SDPIF1 DSD1A
AP3 I2S2/SPDIF2 DSD1B
AP4 I2S3/SPDIF3 DSD2A
AP5 LRCLK DSD2B
Note: It is possible to tristate the audio pins using the global controls, as described in the Tristate Audio Output Drivers section. It is
possible to output AP0 signal (SPDIF0) to the AP1 pin using MUX_SPDIF_TO_I2S_ENABLE.
MUX_SPDIF_TO_I2S_ENABLE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6E[3]
Enables muxing SPDF data into I2S pins (AP1)
Function
MUX_SPDIF_TO_I2S_ENABLE Description
0 (default) Don’t modify I2S outputs
1 Mux SPDIF into I2S pins
I2S/SPDIF Audio Interface and Output Controls
Two controls are provided to change the mapping between the audio output ports and the I2S and SPDIF (IEC60958) signals.
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6D[5:4]
A control to select the arrangement of the I
Function
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0] Description
00 (default) [I2S0/SPDIF0 on AP1] [I2S1/SPDIF1 on AP2] [I2S2/SPDIF2 on AP3] [I2S3/SPDIF3 on AP4]
01 [I2S3/SPDIF3 on AP1] [I2S0/SPDIF0 on AP2] [I2S1/SPDIF1 on AP3] [I2S2/SPDIF2 on AP4]
10 [I2S2/SPDIF2 on AP1] [I2S3/SPDIF3 on AP2] [I2S0/SPDIF0 on AP3] [I2S1/SPDIF1 on AP4]
11 [I2S1/SPDIF1 on AP1] [I2S2/SPDIF2 on AP2] [I2S3/SPDIF3 on AP3] [I2S0/SPDIF0 on AP4]
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6D[6]
A control to invert the arrangement of the I
interface on the audio output port pins is determined by I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT.
2
S/SPDIF interface on the audio output port pins.
2
S/SPDIF interface on the audio output port pins. Note the arrangement of the I2S/SPDIF
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV Description
0 (default) Do not invert arrangement of I2S/SPDIF channels in audio output port pins
1 Invert arrangement of I2S/SPDIF channels in audio output port pins
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0] and I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV are independent controls. Any combination of values is therefore allowed for
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0] and I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV. Table 13 and Tabl e 14 show examples of mappings for the I
2
S/SPDIF signals.
Table 13. Audio Mappings for I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT = 00, I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV = 0 (Default)
Output Pixel Port I2S/SPDIF Interface
AP1 I2S0/SDPIF0
AP2 I2S1/SDPIF1
AP3 I2S2/SDPIF2
AP4 I2S3/SDPIF3
Rev. B | Page 66 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
…
…
Table 14. Audio Mappings for I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT = 00, I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV = 1
Output Pixel Port I2S/SPDIF Interface
AP1 I2S3/SDPIF3
AP2 I2S2/SDPIF2
AP3 I2S1/SDPIF1
AP4 I2S0/SDPIF0
I2SBITWIDTH[4:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x03[4:0]
2
A control to adjust the bit width for right justified mode on the I
Function
I2SBITWIDTH[4:0] Description
00000 0 bit
00001 1 bit
00010 2 bits
11000 (default) 24 bits
11110 30 bits
11111 31 bits
I2SOUTMODE[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x03[6:5]
2
A control to configure the I
Function
I2SOUTMODE[1:0] Description
00 (default) I2S mode
01 Right justified
10 Left justified
11 Raw SPDIF (IEC60958) mode
S output interface.
Notes
I2SOUTMODE[1:0] is effective when the ADV7612 is configured to output I2S streams or AES3 streams. This is the case in the following
situation:
S interface.
• The ADV7612 receives audio sample packets.
• The ADV7612 receives HBR packets, OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1, and MUX_HBR_OUT is set to 2’b00, 2’b01, 2’b10 or 2’b11.
• In HBR mode, it is required that the part outputs four SPDIF, I
2
S, or raw IEC60958 streams encapsulating a 24-bit audio sample
word. Therefore, 12SBITWIDTH[4:0] should always be set to 0b11000.
The following audio formats can be output when the ADV7612 receives audio sample packets:
• L-PCM audio data is output on the audio output pins if the part received audio sample packets with L-PCM encoded audio data.
Each audio output pin carries stereo data that can be output in I
and Figure 21). The I2SOUTMODE[1:0] control must be set to 0x0, 0x01 or 0x2 to output I
2
S, right justified, or left justified mode (refer to Figure 19, Figure 20,
2
S, right justified, and left justified
respectively on the audio output pins.
• A stream conforming to the IEC60958 specification when the part receives audio sample packets with L-PCM encoded data (refer to
Figure 22).
• An AES3 stream if the I2SOUTMODE[1:0] control is set to 0x3 (refer to Figure 23 and Figure 24). Note that AES3 is also referred to
as raw SPDIF. Each AES3 stream may encapsulate stereo L-PCM audio data or multichannel non L-PCM audio data (for example,
5.1 Dolby Digital).
• Binary stream on the audio output pins when the part receives audio sample packets with non L-PCM encoded audio data (that is,
AC-3 compressed audio) and if the following configuration is used:
• I2SOUTMODE must be set to 0x0, 0x01, or 0x2 for I
2
S, right justified, and left justified format, respectively (refer to Figure 19,
Figure 20, and Figure 21).
• MT_MSK_COMPRS_AUD is set to 0.
Note that no audio flags are output by the part in that configuration. Each binary stream output by the part may encapsulate stereo LPCM audio data or multichannel non L-PCM audio data (for example, 5.1 Dolby Digital).
Rev. B | Page 67 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
A stream conforming to the IEC61937 specification when the part receives audio sample packets with non L-PCM encoded audio
data (for example, AC-3 compressed audio). The audio outputs can carry an audio stream that may be stereo or multichannel audio
(for example, 5.1 Dolby Digital).
Table 15. I
I2S/SPDIF Interface IO Function
SPDIF0 SPDIF audio output
I2S0/SDPIF0 I2S audio (Channel 1, Channel 2)/SPDIF0
I2S1/SDPIF1 I2S audio (Channel 3, Channel 4)/SPDIF1
I2S2/SDPIF2 I2S audio (Channel 5, Channel 6)/SPDIF2
I2S3/SDPIF3 I2S audio (Channel 7, Channel 8)/SPDIF3
SCLK Bit clock
LRCLK Data output clock for left and right channel
MCLKOUT Audio master clock output
2
S/SPDIF Interface Description
LEFT RIGHTLRCLK
SCLK
ISx
MSB MSB LSBLSB
32 CLOCK SLO TS 32 CLOCK S LOTS
Figure 19. Timing Audio Data Output in I
2
S Mode
09486-018
LEFT RIGHT
MSB MSB MSB
MSB
MSB EXTENDED
32 CLOCK SLO TS 32 CLOCK SLOTS
MSB – 1 MSB – 1
MSB MSB MSBLSB LSBMSB
MSB EXTENDED
09486-019
Figure 20. Timing Audio Data Output in Right Justified Mode
LEFT RIGHT
MSB
32 CLOCK SLOTS 32 CL OCK SLOTS
MSB LSBLSB
09486-020
Figure 21. Timing Audio Data Output in Left Justified Mode
Rev. B | Page 68 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
SYNC
PREAMBLE
L
S
B
AUDIO SAMPLE WORD
VALIDITY FLAG
USER DATA
CHANNEL STATUS
PARITY BIT
M
VUCP
S
B
312827034
09486-021
Figure 22. IEC 60958 Subframe Timing Diagram
27 3124230
L
S
B
DATA
VALIDITY FLAG
USER DATA
CHANNEL STATUS
BLOCK START FLAG
Figure 23. AES3 Subframe Timing Diagram
CHANNEL A CHANNEL B
M
VUCB0000
S
B
ZERO PADDING
09486-022
LSB MSB V U C
32 CLOCK SLO TS 32 CLOCK SLOTS
FRAME N FRAME N + 1
MSBLSB BB
UVC
09486-023
Figure 24. AES3 Stream Timing Diagram
DSD Audio Interface and Output Controls
The ADV7612 incorporates a 6-DSD channel interface used to output the audio stream extracted from DSD packets. Each of the DSD
channels carries an over-sampled 1-bit representation of the audio signal as delivered on Super Audio CDs (SACDs).
Table 16. DSD Interface Description
DSD Interface IO Function
DSD0A 1st DSD data channel
DSD0B 2nd DSD data channel
DSD1A 3rd DSD data channel
DSD1B 4th DSD data channel
DSD2A 5th DSD data channel
DSD2B 6th DSD data channel
SCLK Bit clock
MCLKOUT Audio master clock output
Two controls are provided to change the mapping between the audio output ports and DSD signals.
Rev. B | Page 69 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
001
[DSD2B on AP0] [DSD0A on AP1] [DSD0B on AP2] [DSD1A on AP3] [DSD1B on AP4] [DSD2A on AP5]
DSD_MAP_INV
Description
1
Invert arrangement of the DSD channels on the audio output port pins
AP3
DSD1B
SCLK
DSDxx
09486-025
DSD_MAP_ROT[2:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6D[2:0]
A control to select the arrangement of the DSD interface on the audio output port pins.
Function
DSD_MAP_ROT[2:0]
000 (default) [DSD0A on AP0] [DSD0B on AP1] [DSD1A on AP2] [DSD1B on AP3] [DSD2A on AP4] [DSD2B on AP5]
010 [DSD2A on AP0] [DSD2B on AP1] [DSD0A on AP2] [DSD0B on AP3] [DSD1A on AP4] [DSD1B on AP5]
011 [DSD1B on AP0] [DSD2A on AP1] [DSD2B on AP2] [DSD0A on AP3] [DSD0B on AP4] [DSD1A on AP5]
100 [DSD1A on AP0] [DSD1B on AP1] [DSD2A on AP2] [DSD2B on AP3] [DSD0A on AP4] [DSD0B on AP5]
101 [DSD0B on AP0] [DSD1A on AP1] [DSD1B on AP2] [DSD2A on AP3] [DSD2B on AP4] [DSD0A on AP5]
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
DSD_MAP_INV, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6D[3]
A control to invert the arrangement of the DSD interface on the audio output port pins. Note the arrangement of the DSD interface on
the audio output port pins is determined by DSD_MAP_ROT[2:0].
Function
0 (default) Do not invert arrangement of the DSD channels on the audio output port pins
DSD_MAP_ROT[2:0] and DSD_MAP_INV are independent controls. Any combination of values is therefore allowed for
DSD_MAP_ROT[2:0] and DSD_MAP_INV. Tabl e 17 and Tab le 18 show examples of mappings for the DSD signals.
Description
Table 17. Audio Mapping for DSD_MAP_ROT = 00, DSD_MAP_INV = 0 (Default)
Output Pixel Port Name DSD Interface
AP0 DSD0A
AP1 DSD0B
AP2 DSD1A
AP4 DSD2A
AP5 DSD2B
Table 18. Audio Mapping for DSD_MAP_ROT = 00, DSD_MAP_INV = 1
Output Pixel Port Name DSD Interface
AP0 DSD2B
AP1 DSD2A
AP2 DSD1B
AP3 DSD1A
AP4 DSD0B
AP5 DSD0A
Note that DSD0A and DSD0B output must be used when in stereo mode only. DSD0A and DSD0B always carry the main 2-channel
audio data. DSD1A, DSD1B, DSD2A, and DSD2B are the surround channels where: xx is the channel, for example, 0A, 0B.
Figure 25. DSD Timing Diagram
By default, the ADV7612 automatically enables the DSD interface if it receives DSD packets. The ADV7612 also automatically enables the
2
I
S interface if it receives audio sample packets or if it does not receive any audio packets. However, it is possible to override the audio
interface that is used via the OVR_AUTO_MUX_DSD_OUT and MUX_DSD_OUT controls.
Rev. B | Page 70 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Override by outputting DSD/DST data
OVR_AUTO_MUX_DSD_OUT, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x01[3]
DSD/DST override control. In automatic control, DSD or I
interface enabled if part receives DSD or DST audio sample packet. I
when no packet is received. In manual mode, MUX_DSD_OUT selects the output interface.
Function
OVR_AUTO_MUX_DSD_OUT Description
0 (default) Automatic DSD/DST output control
1 Override DSD/DST output control
MUX_DSD_OUT, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x01[4]
An override control for the DSD output.
Function
MUX_DSD_OUT Description
0 (default) Override by outputting I2S data
HBR Interface and Output Controls
The ADV7612 can receive HBR audio stream packets. The ADV7612 outputs HBR data over four of the audio output pins in any of the
following formats:
• An SDPIF stream conforming to the IEC60958 specification (refer to Figure 22). The following configuration is required to output
an SPDIF stream on the HBR output pins:
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 0 or
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1 and MUX_HBR_OUT is set to 1.
• A binary stream if one of the following configurations is used:
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1, MUX_HBR_OUT is set to 0, and I2SOUTMODE[1:0] is set to 0x0 for an I
(refer to Figure 19).
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1, MUX_HBR_OUT is set to 0, and I2SOUTMODE[1:0] is set to 0x1 for a right justified stream
(refer to Figure 20).
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1, MUX_HBR_OUT is set to 0, and I2SOUTMODE[1:0] is set to 0x2 for a left justified stream (refer
to Figure 21).
• No audio flags are output by the part in these configuration.
• An AES3 stream on each HBR interface output pin (refer to Figure 23 and Figure 24). The following configuration is required to
output AES3 streams:
• OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1.
• I2SOUTMODE[1:0] is set to 0b11.
2
S interface is selected according to the type of packet received. DSD/DST
2
S interface is enabled when part receives audio sample packets or
2
S mode binary stream
It is important to note that:
• Each of the four HBR outputs carry one of four consecutive blocks of the HBR stream.
• The four streams on the four HBR pin are output at one quarter of the audio sample rate, f
Table 19. HBR Interface Description
HBR Interface IO Function
AP1 1st block of HBR stream.
AP2 2nd block of HBR stream
AP3 3rd block of HBR stream
AP4 4th block of HBR stream
SCLK Bit clock
LRCLK Data output clock for left and right channel
MCLKOUT Audio master clock output
Rev. B | Page 71 of 204
.
s

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
OVR_MUX_HBR
Description
1
Manual HBR output control
0
The last audio packets received have a layout value of 1. (For example, Layout-1 corresponds to
Notes
• The audio output mapping controls: I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0] and I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV also apply to the HBR output signals.
• The audio output interface pin AP0 will also carry the SPDIF0 output, regardless of I2S_SPDIF_MAP_ROT[1:0] and
I2S_SPDIF_MAP_INV.
OVR_MUX_HBR, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x01[2]
A control to select automatic or manual configuration for HBR outputs. Automatically, HBR outputs are encoded as SPDIF streams. In
manual mode, MUX_HBR_OUT selects the audio output interface.
Function
0 (default) Automatic HBR output control
MUX_HBR_OUT, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x01[1]
A control to manually select the audio output interface for HBR data. Valid when OVR_MUX_HBR is set to 1.
Function
MUX_HBR_OUT Description
0 (default) Override by outputting I2S data
1 Override by outputting SPDIF data
MCLKOUT SETTING
The frequency of audio master clock MCLKOUT is set using the MCLK_FS_N[2:0] register, as shown in Equation 3, relationship between
MCLKOUT, MCLKFS_N, and f
MCLKOUT = (MCLKFS_N[2:0] + 1) × 128 × f
MCLK_FS_N[2:0], Addr 4C (DPLL), Address 0xB5[2:0]
Selects the frequency of MCLK out as multiple of 128 fs.
Function
MCLK_FS_N[2:0] Description
000 128 fs
001 (default) 256 fs
010 384 fs
011 512 fs
100 640 fs
101 768 fs
110 Not valid
111 Not valid
AUDIO CHANNEL MODE
AUDIO_CH_MD_RAW indicates if 2-channel audio data or multichannel audio data is received.
AUDIO_CH_MD_RAW, IO, Address 0x65[4] (Read Only)
Raw status signal indicating the layout value of the audio packets that were last received.
Function
AUDIO_CH_MD_RAW Description
.
s
S
(3)
2-channel audio when audio sample packets are received).
1 The last audio packets received have a layout value of 0. (For example, Layout-0 corresponds to
8-channel audio when audio sample packets are received.)
Note: The Audio CH_MD_RAW flag is valid for audio sample packets and DSD packets.
Rev. B | Page 72 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
1
Multichannel uncompressed audio detected (Channel 3 to Channel 8).
AUDIO_CHANNEL_MODE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x07[6] (Read Only)
Flags stereo or multichannel audio packets. Note stereo packets may carry compressed multichannel audio.
Function
AUDIO_CHANNEL_MODE Description
0 Stereo audio (may be compressed multichannel)
AUDIO MUTING
The ADV7612 integrates an advanced audio mute function that is designed to remove all extraneous noise and pops from a 2-channel
L-PCM audio stream at sample frequencies up to 48 kHz.
The hardware for audio mute function is composed of the following three blocks:
• Audio delay line that delays Channel 1 and Channel 2 by 512 stereo samples.
• Audio mute controller takes in event detection signals that can be used to determine when an audio mute is needed. The controller
generates a mute signal to the ramped audio block and a coast signal to the digital PLL generating the audio clock.
• Ramped audio mute block that can mute the audio over the course of 512 stereo samples.
The ADV7612 mutes only the noncompressed data from the audio sample packets output through the I
The audio delay line is automatically bypassed when the ADV7612 receives multichannel audio or when it receives the following audio
packets:
• DSD packets
• HBR packets
2
S and the SPDIF interface.
The ramped audio mute block is always bypassed when the part received compressed audio or when it received the following audio
packets:
• DSD packets
• HBR packets
Delay Line Control
The audio delay line should be enabled when the ADV7612 is configured for automatic mute. The audio delay line is controlled by the
MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS and AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS bits.
MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0F[7]
Audio delay bypass manual enable. The audio delay line is automatically active for stereo samples and bypassed for multichannel samples.
By setting MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS to 1, the audio delay bypass configuration can be set by the user with the AUDIO_DELAY_
LINE_BYPASS control.
Function
MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS Description
0 (default) Audio delay line is automatically bypassed if multichannel audio is received. The audio delay line is
automatically enabled if stereo audio is received.
1 Overrides automatic bypass of audio delay line. Audio delay line is applied depending on the
AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS control.
AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0F[6]
Manual bypass control for the audio delay line. Only valid if MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS is set to 1.
Function
AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS Description
0 (default) Enables the audio delay line
1 Bypasses the audio delay line
Rev. B | Page 73 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Audio Mute Configuration
The ADV7612 can be configured to automatically mute an L-PCM audio stream when selectable mute conditions occur. The audio
muting is configured as follows:
• Set the audio muting speed via AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED[4:0].
• Set NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE, as follows:
• Set AUDIO_UNMUTE[2:0] to 0 if the audio must be unmuted automatically after a delay set in WAIT_UNMUTE[2:0] after all
selected mute conditions have become inactive.
• Se t NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE to 1 if the audio must be unmuted manually (for example, by an external controller) when all
selected mute conditions have become inactive.
• Select the mute conditions that trigger an audio mute (refer to Table 20).
• Select the Audio PLL coast conditions (refer to the Audio DPLL Coast Feature section).
• Set WAIT_UNMUTE[2:0] to configure the audio counter that triggers the audio unmute when it has timed out after all selected
mute conditions have become inactive.
The ADV7612 internally unmutes the audio if the following three conditions (listed in order of priority) are met:
• Mute conditions are inactive.
• NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE is set to 0.
• Audio unmute counter has finished counting down or is disabled.
Notes
• Both Table 10 and Tabl e 20 provide a column for Corresponding Status Register(s) This column lists the status registers that convey
information related to their corresponding audio mute masks or coast masks.
• The ADV7612 also mutes the DSD stream when one of the selected mute conditions occurs (refer to Table 20) by outputting the
DSD mute pattern 0101010101…. A DSD decoder receiving this stream outputs a 0 V mean analog stream.
• The ADV7612 can mute the audio data with compressed audio data or HBR packets. In these cases, mute outputs constant streams
of 0.
• For the best audio muting performance, the following setting is recommended when the ADV7612 receives multichannel sample
packets:
• Set AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED to 1
• For best audio muting performance, the following settings are recommended when the audio sampling frequency of the audio stream
is greater than 48 kHz:
• Set AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED to 1
• Set MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS to 1
• Set AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS to 1
• For best audio muting performance, the following settings are recommended when the audio sampling frequency of the audio stream
is equal to or lower than 48 kHz:
• Set AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED to 0x1F
• Set MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS to 0
MUTE_AUDIO, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1A[4]
A control to force an internal mute independently of the mute mask conditions
Function
MUTE_AUDIO Description
0 (default) Audio in normal operation
1 Force audio mute
AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED[4:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x0F[4:0]
Number of samples between each volume change of 1.5dB when muting and unmuting
Function
AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED[4:0] Description
0x1F (default) Default value
Rev. B | Page 74 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0 (default)
Audio unmutes following a delay set by WAIT_UNMUTE after all mute conditions have become inactive
001
Unmutes 250 ms after all mute conditions become inactive.
MT_MSK_COMPRS_AUD
0x14[5]
Causes audio mute if audio is compressed
CS_DATA[1]
MT_MSK_FLATLINE_DET
0x15[3]
Causes audio mute if flatline bit in audio packets is set
AUDIO_FLT_LINE_RAW
NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1A[0]
A control to disable the auto unmute feature. When set to 1, audio can be unmuted manually if all mute conditions are inactive by setting
NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE to 0 and then back to 1.
Function
NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE Description
1 Prevents audio from unmuting automatically
WAIT_UNMUTE[2:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1A[3:1]
A control to delay audio unmute. Once all mute conditions are inactive WAIT_UNMUTE[2:0] can specify a further delay time before
unmuting. NOT_AUTO_UNMUTE must be set to 0 for this control to be effective.
Function
WAIT_UNMUTE[2:0] Description
000 (default) Disables/cancels delayed unmute. Audio unmutes directly after all mute conditions become inactive.
010 Unmutes 500 ms after all mute conditions become inactive.
011 Unmutes 750 ms after all mute conditions become inactive.
100 Unmutes 1 sec after all mute conditions become inactive.
Table 20. Selectable Mute Conditions
Bit Name
HDMI Map
Address
Description
Corresponding Status
Register(s)
MT_MSK_AUD_MODE_CHNG 0x14[4] Causes audio mute if audio mode changes between
PCM, DSD, DST, or HBR formats
MT_MSK_PARITY_ERR 0x14[1] Causes audio mute if parity bits in audio samples are
not correct
MT_MSK_VCLK_CHNG 0x14[0] Causes audio mute if TMDS clock has irregular/missing
pulses
MT_MSK_APLL_UNLOCK 0x15[7] Causes audio mute if audio PLL unlocks AUDIO_PLL_LOCKED
MT_MSK_VPLL_UNLOCK 0x15[6] Causes audio mute if TMDS PLL unlocks TMDS_PLL_LOCKED
MT_MSK_ACR_NOT_DET 0x15[5] Causes audio mute if ACR packets are not received
within one VSync
MT_MSK_FIFO_UNDERFLOW 0x15[1] Causes audio mute if audio FIFO underflows FIFO_UNDERFLO_RAW
MT_MSK_FIFO_OVERFLOW 0x15[0] Causes audio mute if audio FIFO overflows FIFO_OVERFLO_RAW
MT_MSK_AVMUTE 0x16[7] Causes audio mute if AVMute is set in the general
control packet
MT_MSK_NOT_HDMIMODE 0x16[6] Causes audio mute if HDMI_MODE bit goes low HDMI_MODE
MT_MSK_NEW_CTS 0x16[5] Causes audio mute if CTS changes by more than the
threshold set in CTS_CHANGE_THRESHOLD[5:0]
MT_MSK_NEW_N 0x16[4] Causes audio mute if N changes
MT_MSK_CHMODE_CHNG 0x16[3] Causes audio mute if the channel mode changes from
stereo to multichannel, or vice versa
MT_MSK_APCKT_ECC_ERR 0x16[2] Causes audio mute if uncorrectable error is detected in
the audio packets by the ECC block
MT_MSK_CHNG_PORT 0x16[1] Causes audio mute if HDMI port is changed HDMI_PORT_SELECT[2:0]
MT_MSK_VCLK_DET 0x16[0] Causes audio mute if TMDS clock is not detected TMDS_CLK_A_RAW
AUDIO_SAMPLE_PCKT_DET
PARITY_ERROR_RAW
VCLK_CHNG_RAW
AUDIO_C_PCKT_RAW
AV_MUTE_RAW
CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW
CHANGE_N_RAW
AUDIO_MODE_CHNG_RAW
AUDIO_PCKT_ERR_RAW
Internal Mute Status
The internal mute status is provided through the INTERNAL_MUTE_RAW bit.
Rev. B | Page 75 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
1
Audio is muted
INTERNAL_MUTE_RAW, IO, Address 0x65[6] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of internal mute signal.
Function
INTERNAL_MUTE_RAW Description
0 (default) Audio is not muted
AV Mute Status
AV_MUTE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x04[6] (Read Only)
Readback of AVMUTE status received in the last general control packet received.
Function
AV_ MUTE Description
0 (default) AVMUTE not set
1 AVMUTE set
Audio Mute Signal
The ADV7612 can output an audio mute signal that can be used to control the muting in a back end audio device processing the audio
data output by the ADV7612 (for example, DSP).
The audio mute signal is output on the INT1 pin by setting EN_MUTE_RAW_INTRQ to 1. The mute signal is active high.
The audio mute signal can also be output on the INT2 signal (via one of the following pins: SCLK/INT2, HPA_A/INT2 or MCLK/INT2)
by setting INTRQ2_MUX_SEL[1:0] to 1 and EN_MUTE_OUT_INTRQ2 to 1.
Important
The ADV7612 may interface with an audio processor (for example, DSP) in which the muting of the audio is implemented. In this case,
the audio processor typically features a delay line followed by a mute block for audio mute and unmuting purposes. The following
hardware and software configuration is recommended for optimum muting performance of the ADV7612 and audio processor system:
• Connect the mute signal of the ADV7612 to the audio processor mute input. The ADV7612 mute signal can now drive the
muting/unmuting of the audio data inside the audio processor.
• Bypass the audio delay line of the ADV7612 with the following settings:
• Set MAN_AUDIO_DL_BYPASS to 1.
• Set AUDIO_DELAY_LINE_BYPASS to 1.
• Configure the ADV7612 to mute the audio over one audio sample clock as follows:
• Set AUDIO_MUTE_SPEED[4:0] to 1. This ensures that the ADV7612 never outputs invalid audio data out to the audio
proc es sor.
EN_MUTE_RAW_INTRQ, IO Map, Address 0x40[3]
A control to apply the internal audio mute signal on the INT1 interrupt pin.
Function
EN_MUTE_RAW_INTRQ Description
0 (default) Does not output audio mute signal on INT1
1 Outputs output audio mute signal on INT1
EN_MUTE_RAW_INTRQ2, IO Map, Address 0x41[3]
A control to apply the internal audio mute signal on INT2 interrupt pin.
Function
EN_MUTE_RAW_INTRQ2 Description
0 (default) Does not output audio mute signal on INT2
1 Outputs output audio mute signal on INT2
Audio Stream with Incorrect Parity Error
The ADV7612 discards audio sample packets that have an incorrect parity bit. When these samples are received, the ADV7612 repeats the
previous audio sample with a valid parity bit. The audio stream out of the ADV7612 can be muted in this situation if the audio mute mask
MT_MSK_PARITY_ERR is set.
Rev. B | Page 76 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
CTS[19:0]
Description
00000000000000000000 (default)
Default CTS value readback from HDMI stream
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CTS value readback from HDMI stream
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
N value readback from HDMI stream
It is possible to configure the ADV7612 so that it processes audio sample packets that have an incorrect parity bit and corrects the parity
bit. The ADV7612 can then output an audio stream even when the parity bits from the audio sample packet are invalid. This
configuration is activated by setting MT_MSK_PARITY_ERR to 0 and IGNORE_PARITY_ERR to 1.
IGNORE_PARITY_ERR, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x1A[6]
A control to select the processing of audio samples even when they have a parity error.
Function
IGNORE_PARITY_ERR Description
0 (default) Discard audio sample packets that have an invalid parity bit
1 Process audio sample packets that have an invalid parity bit
MT_MSK_PARITY_ERR, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x14[1]
Audio mute mask for a parity error. It sets the audio mutes if an audio sample packet is received with an incorrect parity bit.
Function
MT_MSK_PARITY_ERR Description
1 (default) Audio mute occurs if an audio sample packet is received with an incorrect parity bit
AUDIO CLOCK REGENERATION PARAMETERS
The ADV7612 recreates an internal audio master clock using audio clock regeneration (ACR) values transmitted by the HDMI source.
ACR Parameters Readbacks
The registers N and CTS can be read back from the HDMI map.
CTS[19:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5B[7:0]; Address 0x5C[7:0]; Address 0x5D[7:4] (Read Only)
A readback for the CTS value received in the HDMI data stream.
Function
N[19:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x5D[3:0]; Address 0x5E[7:0]; Address 0x5F[7:0] (Read Only)
A readback for the N value received in the HDMI data stream.
Function
N[19:0] Description
00000000000000000000 (default) Default N value readback from HDMI stream
Note: A buffer has been implemented for the N and CTS readback registers. A read of the HDMI map, Address 0x5B register updates the
buffer that stores the N and CTS readback registers. The buffer implemented for N and CTS readback allows the reading of both N and
CTS registers within an I
2
C block read.
Monitoring ACR Parameters
The reception of ACR packets can be notified via the AUDIO_C_PCKT_RAW flag. Changes in N and CTS can be monitored via the
CHANGE_N_RAW and CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW flags, as described in this section.
AUDIO_C_PCKT_RAW, IO, Address 0x65[1] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of audio clock regeneration packet detection signal.
Function
AUDIO_C_PCKT_RAW Description
0 (default) No audio clock regeneration packets received since the last HDMI reset condition
1 Audio clock regeneration packets received
Rev. B | Page 77 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
Audio clock regeneration N value has not changed.
CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW
Description
CTS_CHANGE_THRESHOLD[5:0]
Description
CHANGE_N_RAW, IO, Address 0x7E[3] (Read Only)
Status of the ACR N Value changed interrupt signal. When set to 1 it indicates the N Value of the ACR packets has changed. Once set, this
bit will remain high until it is cleared via CHANGE_N_CLR.
Function
CHANGE_N_RAW Description
1 Audio clock regeneration N value has changed.
CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW, IO, Address 0x7E[4] (Read Only)
Status of the ACR CTS value exceed threshold interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates the CTS Value of the ACR packets has exceeded
the threshold set by CTS_CHANGE_THRESHOLD. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via CTS_PASS_THRSH_CLR.
Function
0 (default) Audio clock regeneration CTS value has not passed the threshold.
1 Audio clock regeneration CTS value has changed more than threshold.
CTS_CHANGE_THRESHOLD[5:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x10[5:0]
Sets the tolerance for change in the CTS value. This tolerance is used for the audio mute mask MT_MSK_NEW_CTS and the HDMI
status bit CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW and the HDMI interrupt status bit CTS_PASS_THRSH_ST. This register controls the amounts of
LSBs that the CTS can change before an audio mute, status change or interrupt is triggered.
Function
100101 (default) Tolerance of CTS value for CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW and MT_MSK_NEW_CTS
xxxxxx Tolerance of CTS value for CTS_PASS_THRSH_RAW and MT_MSK_NEW_CTS
CHANNEL STATUS
Channel status bits are extracted from the HDMI audio packets of the 1st audio channel (that is, Channel 0) and stored in registers
CHANNEL_STATUS_DATA_X of the HDMI Map (where X = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5).
Validity Status Flag
The channel status readback described in the Channel Status section should be considered valid if CS_DATA_VALID_RAW is set to 1.
Figure 26 shows the algorithm that can be implemented to monitor the read valid channel status bit using the CS_DATA_VALID_RAW flag.
CS_DATA_VALID_RAW, IO, Address 0x65[7] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of channel status data valid signal.
Function
CS_DATA_VALID_RAW Description
0 (default) Channel status data is not valid.
1 Channel status data is valid.
Rev. B | Page 78 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
YES
ENABLE THE CS _DATA_VALID_ST
INTERRUPT
SET CS_DATA_VALID_CLR TO 1
IS
CS_DATA_VALID_S
T SET TO 1?
IS
CS_DATA_VALID_R
AW SET TO 1?
START
THE CHANNE L STATUS BITS PREVIOUSLY
READ ARE VALID
IS
CS_DATA_VALID_S
T SET TO 1?
NO
THE CHANNE L STATUS BITS PREVIOUSLY
READ ARE NOT VALID
NO
NO
READ THE CHANNEL STATUS BITS IN
HDMI MAP 0x36 TO 0x3A
YES
INITIALIZATION
CHECK IF THE CS _DATA_VALID
INTERRUPT HAS TRIGGERED
READ THE CHANNEL STATUS BITS
AND DECIDE IF THEYARE VALID
09486-027
Notes
• CS_DATA_VALID_RAW indicates that the first 40 of the channel status bits sent by the upstream transmitter have been correctly
collected. This bit does not indicate if the content of the channel status bit is corrupted as this is indeterminable.
• A corresponding interrupt can be enabled for CS_DATA_VALID_RAW by setting the mask CS_DATA_VALID_MB1 or
CS_DATA_VALID_MB2. Refer to the Interrupts section for additional information on the interrupt feature.
Figure 26. Reading Valid Channel Status Flags
Rev. B | Page 79 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
xxxx xxxx
Category code1
xxxx
Source number1
General Control and Mode Information
The general control and mode information are specified in Byte 0 of the channel status. For more information, refer to the IEC60958
standards.
CS_DATA[0], Consumer/Professional Application, HDMI Map, Address 0x36[0]
Function
CS_DATA[0] Description
0 (default) Consumer application
1 Professional application
CS_DATA[1], PCM/non-PCM Audio Sample, HDMI Map, Address 0x36[1]
Function
CS_DATA[1] Description
0 (default) Audio sample word represents linear PCM samples
1 Audio sample word used for other purposes
CS_DATA[2], Copyright, HDMI Map, Address 0x36[2]
Function
CS_DATA[2] Description
0 (default) Software for which copyright is asserted
1 Software for which no copyright is asserted
CS_DATA[5:3], Emphasis, HDMI Map, Address 0x36[5:3]
Function
CS_DATA[5:3]
000 (default) Two audio channels without pre-emphasis
001 Two audio channels with 50/15 pre-emphasis
1
Unspecified values are reserved.
CS_DATA[7:6], Channel Status Mode, HDMI Map, Address 0x36[7:6]
Function
CS_DATA[7:6]1 Description
00 (default) Mode 0
1
Unspecified values are reserved.
Category Code
The category code is specified in Byte 1 of the channel status. The category code indicates the type of equipment that generates the digital
audio interface signal. For more information, refer to the IEC60958 standards.
CS_DATA[15:8], Category Code, HDMI Map, Address 0x37[7:0]
Function
CS_DATA[15:8] Description
1
Description
0000 0000 (default) Reset value
1
Refer to IEC60958-3 standards.
Source Number and Channel Number
CS_DATA[19:16], Source Number, HDMI Map, Address 0x38[3:0]
Function
CS_DATA[19:16] Description
0000 (default) Reset value
1
Refer to IEC60958-3 standards.
Rev. B | Page 80 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
Function
(default)
(default)
Function
(default)
(default)
(default)
CS_DATA[23:20], Channel Number, HDMI Map, Address 0x38[7:4]
CS_DATA[23:20] Description
xxxxx Channel number1
00000
1
Refer to IEC60958-3 standards.
Sampling and Frequency Accuracy
The sampling frequency and clock accuracy are specified by Byte 3 of the channel status. For additional information, refer to the
IEC60958 standards.
CS_DATA[27:24], Sampling Frequency, HDMI Map, Address 0x39[3:0]
Function
1
CS_DATA[27:24]
0000
Description
0010 48 kHz
0011 32 kHz
1000 88.2 kHz
1001 768 kHz
1010 96 kHz
1100 176 kHz
1110 192 kHz
1
Unspecified values are reserved.
CS_DATA[29:28], Clock Accuracy, HDMI Map, Address 0x39[5:4]
Reset value
44.1 kHz
CS_DATA[29:28] Description
00
Level II, ±1000 ppm
01 Level I, ±50 ppm
10 Level III, variable pitch shifted
11 Reserved
CS_DATA[31:30], Reserved Register, HDMI Map, Address 0x39[7:6]
Function
CS_DATA[31:30] Description
XX Reserved
00
Reset value
Word Length
Word length information is specified in Byte 4 of the channel status bit. For more information, refer to the IEC60958 standards.
CS_DATA[32], Maximum Word Length Size, HDMI Map, Address 0x3A, [0]
Function
CS_DATA[32] Description
0
Maximum audio sample word length is 20 bits.
1 Maximum audio sample word length is 24 bits.
Rev. B | Page 81 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
Function
(default)
Word length not indicated
Word length not indicated
010
22 bits
18 bits
CS_COPYRIGHT_MANUAL
Description
0 (default)
Automatic CS copyright control.
0 (default)
Sampling rate bits of the channel status data on audio Channel 0 have not changed.
CS_DATA[35:33], Word Length, HDMI Map, Address 0x3A, [3:1]
CS_DATA[35:33]1 Description
Audio sample word length if maximum length is 24 as
indicated by CS_DATA_[32]
000
001 20 bits 16 bits
100 23 bits 19 bits
101 24 bits 20 bits
110 21 bits 21 bits
1
Unspecified values are reserved.
Channel Status Copyright Value Assertion
It is possible to overwrite the copyright value of the channel status bit that is passed to the SPDIF output. This is done via the
CS_COPYRIGHT_MANUAL and CS_COPYRIGHT_VALUE controls.
CS_COPYRIGHT_MANUAL, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x50[1]
A control to select automatic or manual setting of the copyright value of the channel status bit that is passed to the SPDIF output. Manual
control is set with the CS_COPYRIGHT_VALUE bit.
Function
Audio sample word length if maximum length is 20 as
indicated by CS_DATA_[32]
1 Manual CS copyright control. Manual value is set by CS_COPYRIGHT_VALUE.
CS_COPYRIGHT_VALUE, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x50[0]
A control to set the CS copyright value when in manual configuration of the CS copyright bit that is passed to the SPDIF output.
Function
CS_COPYRIGHT_VALUE Description
0 (default) Copyright value of channel status bit is 0. Valid only if CS_COPYRIGHT_MANUAL is set to 1.
1 Copyright value of channel status bit is 1. Valid only if CS_COPYRIGHT_MANUAL is set to 1.
Monitoring Change of Audio Sampling Frequency
The ADV7612 features the NEW_SAMP_RT_RAW flag to monitor changes in the audio sampling frequency field of the channel status bits.
NEW_SAMP_RT_RAW, IO, Address 0x83[3] (Read Only)
Status of new sampling rate interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that audio sampling frequency field in channel status data has
changed. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via NEW_SAMP_RT _CLR.
Function
NEW_SAMP_RT_RAW Description
1 Sampling rate bits of the channel status data on audio Channel 0 have changed.
Important
The NEW_SAMP_RT_RAW flag does not trigger if CS_DATA_VALID_RAW is set to 0. This prevents the notification of a change from a
valid to an invalid audio sampling frequency readback in the channel status bits, and vice versa.
PACKETS AND INFOFRAMES REGISTERS
In HDMI, auxiliary data is carried across the digital link using a series of packets. The ADV7612automatically detects and stores the
following HDMI packets:
• InfoFrames
• Audio content protection (ACP)
• International standard recording code (ISRC)
• Gamut metadata
Rev. B | Page 82 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0 (default)
No AVI InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
AUD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW
Description
When the ADV7612 receives one of these packets, it computes the packet checksum and compares it with the checksum available in the
packet. If these checksums are the same, the packets are stored in the corresponding registers. If the checksums are not the same, the
packets are discarded. Refer to the EIA/CEA-861D specifications for more information on the packets fields.
InfoFrames Registers
The ADV7612 can store the following InfoFrames:
• Auxiliary video information (AVI) InfoFrame
• Source production descriptor (SPD) InfoFrame
• Audio InfoFrame
• Moving picture expert group (MPEG) source InfoFrame
InfoFrame Collection Mode
The ADV7612 has two modes for storing the InfoFrame packet sent from the source into the internal memory. By default, the ADV7612
only stores the InfoFrame packets received if the checksum is correct for each InfoFrame.
The ADV7612 also provides a mode to store every InfoFrame sent from the source, regardless of a InfoFrame packet checksum error.
ALWAYS_STORE_INF, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x47[0]
A control to force InfoFrames with checksum errors to be stored.
Function
ALWAYS_STORE_INF Description
0 (default) Stores data from received InfoFrames only if their checksum is correct
1 Always store the data from received InfoFrame regardless of their checksum
InfoFrame Checksum Error Flags
The following checksum error status registers flag when the last InfoFrame received has a checksum error. Once set, these bits remain
high until the interrupt is cleared via their corresponding clear bits.
AVI_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[4] (Read Only)
Status of AVI InfoFrame checksum error interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that a checksum error has been detected for an AVI
InfoFrame. Once set, this bit remains high until it is cleared via AVI_INF_CKS_ERR_CLR.
Function
AVI_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW Description
1 An AVI InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
AUD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[5] (Read Only)
Status of audio InfoFrame checksum error interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that a checksum error has been detected for an
audio InfoFrame. Once set, this bit remains high until it is cleared via AUDIO_INF_CKS_ERR_CLR.
Function
0 (default) No audio InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
1 An audio InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
SPD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[6] (Read Only)
Status of SPD InfoFrame checksum error interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that a checksum error has been detected for an SPD
InfoFrame. Once set, this bit remains high until it is cleared via ASPD_INF_CKS_ERR_CLR.
Function
SPD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW Description
0 (default) No SPD InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
1 An SPD InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
Rev. B | Page 83 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
No MPEG source InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
VS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW
Description
InfoFrame Map Address
Access Type
Register Name
Byte Name1
0xE0
R/W
AVI_PACKET_ID[7:0]
Packet type value
0x09 R AVI_INF_PB_0_10
Data Byte 9
0x1A
R
AVI_INF_PB_0_27
Data Byte 26
MS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[7] (Read Only)
Status of MPEG source InfoFrame checksum error interrupt signal. When set to 1. it indicates that a checksum error has been detected for
an MPEG source InfoFrame. Once set, this bit remains high until it is cleared via MS_INF_CKS_ERR_CLR.
Function
MS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW Description
1 An MPEG source InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
VS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW, IO, Address 0x8D[0] (Read Only)
Status of vendor specific InfoFrame checksum error interrupt signal. When set to 1, it indicates that a checksum error has been detected
for an Vendor Specific InfoFrame. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via VS_INF_CKS_ERR_CLR.
Function
0 (default) No VS InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
1 A VS InfoFrame checksum error has occurred.
AVI InfoFrame Registers
Table 21 provides a list of readback registers for the AVI InfoFrame data. Refer to the EIA/CEA-861D specifications for a detailed
explanation of the AVI InfoFrame fields.
Table 21. AVI InfoFrame Registers
0xE1 R AVI_INF_VER InfoFrame version number
0xE2 R AVI_INF_LEN InfoFrame length
0x00 R AVI_INF_PB_0_1 Checksum
0x01 R AVI_INF_PB_0_2 Data Byte 1
0x02 R AVI_INF_PB_0_3 Data Byte 2
0x03 R AVI_INF_PB_0_4 Data Byte 3
0x04 R AVI_INF_PB_0_5 Data Byte 4
0x05 R AVI_INF_PB_0_6 Data Byte 5
0x06 R AVI_INF_PB_0_7 Data Byte 6
0x07 R AVI_INF_PB_0_8 Data Byte 7
0x08 R AVI_INF_PB_0_9 Data Byte 8
0x0A R AVI_INF_PB_0_11 Data Byte 10
0x0B R AVI_INF_PB_0_12 Data Byte 11
0x0C R AVI_INF_PB_0_13 Data Byte 12
0x0D R AVI_INF_PB_0_14 Data Byte 13
0x0E R AVI_INF_PB_0_15 Data Byte 14
0x0F R AVI_INF_PB_0_16 Data Byte 15
0x10 R AVI_INF_PB_0_17 Data Byte 16
0x11 R AVI_INF_PB_0_18 Data Byte 17
0x12 R AVI_INF_PB_0_19 Data Byte 18
0x13 R AVI_INF_PB_0_20 Data Byte 19
0x14 R AVI_INF_PB_0_21 Data Byte 20
0x15 R AVI_INF_PB_0_22 Data Byte 21
0x16 R AVI_INF_PB_0_23 Data Byte 22
0x17 R AVI_INF_PB_0_24 Data Byte 23
0x18 R AVI_INF_PB_0_25 Data Byte 24
0x19 R AVI_INF_PB_0_26 Data Byte 25
0x1B R AVI_INF_PB_0_28 Data Byte 27
1
As defined by the EIA/CEA-861D specifications.
Rev. B | Page 84 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0x23 R AUD_INF_PB_0_8
Data Byte 7
The AVI InfoFrame registers are considered valid if the following two conditions are met:
• AVI_I NFO_ RAW is 1.
• AVI_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW is 0. This condition applies only if ALWAYS_STORE_INF is set to 1.
AVI_I NFO_ RAW is described in the Interrupt Architecture Overview section.
Audio InfoFrame Registers
Table 22 provides the list of readback registers available for the Audio InfoFrame. Refer to the EIA/CEA-861D specifications for a detailed
explanation of the audio InfoFrame fields.
Table 22. Audio InfoFrame Registers
InfoFrame Map Address Access Type Register Name Byte Name1
0xE3 R/W AUD_PACKET_ID[7:0] Packet type value
0xE4 R AUD_INF_VERS InfoFrame version number
0xE5 R AUD_INF_LEN InfoFrame length
0x1C R AUD_INF_PB_0_1 Checksum
0x1D R AUD_INF_PB_0_2 Data Byte 1
0x1E R AUD_INF_PB_0_3 Data Byte 2
0x1F R AUD_INF_PB_0_4 Data Byte 3
0x20 R AUD_INF_PB_0_5 Data Byte 4
0x21 R AUD_INF_PB_0_6 Data Byte 5
0x22 R AUD_INF_PB_0_7 Data Byte 6
0x24 R AUD_INF_PB_0_9 Data Byte 8
0x25 R AUD_INF_PB_0_10 Data Byte 9
0x26 R AUD_INF_PB_0_11 Data Byte 10
0x27 R AUD_INF_PB_0_12 Data Byte 11
0x28 R AUD_INF_PB_0_13 Data Byte 12
0x29 R AUD_INF_PB_0_14 Data Byte 13
1
As defined by the EIA/CEA-861D specifications.
The audio InfoFrame registers are considered valid if the following two conditions are met:
• AU DIO _INF O _RAW is 1.
• AUD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW is 0. This condition applies only if ALWAYS _STORE_INF is set to 1.
AUDIO_INFO_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[1] (Read Only)
Raw status of audio InfoFrame detected signal.
Function
AUDIO_INFO_RAW Description
0 (default) No AVI InfoFrame has been received within the last three VSyncs or since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 An Audio InfoFrame has been received within the last three VSyncs. This bit will reset to zero on the fourth VSync
leading edge following an Audio InfoFrame, after an HDMI packet detection reset or upon writing to
AUD_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 85 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0xE6
R/W
SPD_PACKET_ID[7:0]
Packet type value
0x2C
R
SPD_INF_PB_0_3
Data Byte 2
0x38 R SPD_INF_PB_0_15
Data Byte 14
0x3D
R
SPD_INF_PB_0_20
Data Byte 19
SPD InfoFrame Registers
Table 23 provides a list of readback registers available for the SPD InfoFrame. Refer to the EIA/CEA-861D specifications for a detailed
explanation of the SPD InfoFrame fields.
Table 23. SPD InfoFrame Registers
InfoFrame Map Address Access Type Register Name Byte Name1
0xE7 R SPD_INF_VER InfoFrame version number
0xE8 R SPD_INF_LEN InfoFrame length
0x2A R SPD_INF_PB_0_1 Checksum
0x2B R SPD_INF_PB_0_2 Data Byte 1
0x2D R SPD_INF_PB_0_4 Data Byte 3
0x2E R SPD_INF_PB_0_5 Data Byte 4
0x2F R SPD_INF_PB_0_6 Data Byte 5
0x30 R SPD_INF_PB_0_7 Data Byte 6
0x31 R SPD_INF_PB_0_8 Data Byte 7
0x32 R SPD_INF_PB_0_9 Data Byte 8
0x33 R SPD_INF_PB_0_10 Data Byte 9
0x34 R SPD_INF_PB_0_11 Data Byte 10
0x35 R SPD_INF_PB_0_12 Data Byte 11
0x36 R SPD_INF_PB_0_13 Data Byte 12
0x37 R SPD_INF_PB_0_14 Data Byte 13
0x39 R SPD_INF_PB_0_16 Data Byte 15
0x3A R SPD_INF_PB_0_17 Data Byte 16
0x3B R SPD_INF_PB_0_18 Data Byte 17
0x3C R SPD_INF_PB_0_19 Data Byte 18
0x3E R SPD_INF_PB_0_21 Data Byte 20
0x3F R SPD_INF_PB_0_22 Data Byte 21
0x40 R SPD_INF_PB_0_23 Data Byte 22
0x41 R SPD_INF_PB_0_24 Data Byte 23
0x42 R SPD_INF_PB_0_25 Data Byte 24
0x43 R SPD_INF_PB_0_26 Data Byte 25
0x44 R SPD_INF_PB_0_27 Data Byte 26
0x45 R SPD_INF_PB_0_28 Data Byte 27
1
As defined by the EIA/CEA-861D specifications.
The Source Product Descriptor InfoFrame registers are considered valid if the following two conditions are met:
• SPD_INFO_RAW is 1.
• SPD_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW is 0. This condition only applies if ALWAYS_STORE_INF is set to 1.
SPD_INFO_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[2] (Read Only)
Raw status of SPD InfoFrame detected signal.
Function
SPD_INFO_RAW Description
0 (default) No source product description InfoFrame received since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 Source product description InfoFrame received. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection reset
or upon writing to SPD_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 86 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0xE9
R/W
MS_PACKET_ID[7:0]
Packet type value
0x48 R MS_INF_PB_0_3
Data Byte 2
MS_INFO_RAW
Description
No source product description InfoFrame received within the last three VSyncs or since the last HDMI packet
MPEG Source InfoFrame Registers
Table 24 provides a list of readback registers available for the MPEG InfoFrame. Refer to the EIA/CEA-861D specifications for a detailed
explanation of the MPEG InfoFrame fields.
Table 24. MPEG InfoFrame Registers
InfoFrame Map Address Access Type Register Name Byte Name1
0xEA R MS_INF_VERS InfoFrame version number
0xEB R MS_INF_LEN InfoFrame length
0x46 R MS_INF_PB_0_1 Checksum
0x47 R MS_INF_PB_0_2 Data Byte 1
0x49 R MS_INF_PB_0_4 Data Byte 3
0x4A R MS_INF_PB_0_5 Data Byte 4
0x4B R MS_INF_PB_0_6 Data Byte 5
0x4C R MS_INF_PB_0_7 Data Byte 6
0x4D R MS_INF_PB_0_8 Data Byte 7
0x4E R MS_INF_PB_0_9 Data Byte 8
0x4F R MS_INF_PB_0_10 Data Byte 9
0x50 R MS_INF_PB_0_11 Data Byte 10
0x51 R MS_INF_PB_0_12 Data Byte 11
0x52 R MS_INF_PB_0_13 Data Byte 12
0x53 R MS_INF_PB_0_14 Data Byte 13
1
As defined by the EIA/CEA-861D specifications.
The MPEG InfoFrame registers are considered valid if the following two conditions are met:
• MS_ IN FO_ RAW is 1.
• MS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW is 0. This condition applies only if ALWAYS_STORE_INF is set to 1.
MS_INFO_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[3] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of MPEG source InfoFrame detection signal.
Function
0 (default)
detection reset.
1 MPEG Source InfoFrame received. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection reset or upon
writing to MS_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 87 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0x57 R VS_INF_PB_0_4
Data Byte 3
0x68 R VS_INF_PB_0_21
Data Byte 20
Vendor Specific InfoFrame Registers
Table 25 provides a list of readback registers available for the vendor specific InfoFrame.
Table 25. VS InfoFrame Registers
InfoFrame Map Address R/W Register Name Byte Name
0xEC R VS_PACKET_ID[7:0] Packet type value
0xED R VS_INF_VERS InfoFrame version number
0xEE R VS_INF_LEN InfoFrame length
0x54 R VS_INF_PB_0_1 Checksum
0x55 R VS_INF_PB_0_2 Data Byte 1
0x56 R VS_INF_PB_0_3 Data Byte 2
0x58 R VS_INF_PB_0_5 Data Byte 4
0x59 R VS_INF_PB_0_6 Data Byte 5
0x5A R VS_INF_PB_0_7 Data Byte 6
0x5B R VS_INF_PB_0_8 Data Byte 7
0x5C R VS_INF_PB_0_9 Data Byte 8
0x5D R VS_INF_PB_0_10 Data Byte 9
0x5E R VS_INF_PB_0_11 Data Byte 10
0x5F R VS_INF_PB_0_12 Data Byte 11
0x60 R VS_INF_PB_0_13 Data Byte 12
0x61 R VS_INF_PB_0_14 Data Byte 13
0x62 R VS_INF_PB_0_15 Data Byte 14
0x63 R VS_INF_PB_0_16 Data Byte 15
0x64 R VS_INF_PB_0_17 Data Byte 16
0x65 R VS_INF_PB_0_18 Data Byte 17
0x66 R VS_INF_PB_0_19 Data Byte 18
0x67 R VS_INF_PB_0_20 Data Byte 19
0x69 R VS_INF_PB_0_22 Data Byte 21
0x6A R VS_INF_PB_0_23 Data Byte 22
0x6B R VS_INF_PB_0_24 Data Byte 23
0x6C R VS_INF_PB_0_25 Data Byte 24
0x6D R VS_INF_PB_0_26 Data Byte 25
0x6E R VS_INF_PB_0_27 Data Byte 26
0x6F R VS_INF_PB_0_28 Data Byte 27
The vendor specific InfoFrame registers are considered valid if the following two conditions are met:
• VS_INFO_RAW is 1.
• VS_INF_CKS_ERR_RAW is 0. This condition applies only if ALWAYS_STORE_INF is set to 1.
VS_INFO_R AW, IO, Address 0x60[4] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of vendor specific InfoFrame detection signal.
Function
VS_INFO_RAW Description
0 (default) No new VS InfoFrame has been received since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 A new VS InfoFrame has been received. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection reset or
upon writing to VS_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 88 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0xF0 R ACP_TYPE
HB1
0x7A
R
ACP_PB_0_11
PB10
0x8B
R
ACP_PB_0_28
PB27
PACKET REGISTERS
ACP Packet Registers
Table 26 provides the list of readback registers available for the ACP packets. Refer to the HDMI specifications for a detailed explanation
of the ACP packet fields.
Table 26. ACP Packet Registers
InfoFrame Map Address R/W Register Name Packet Byte No.1
0xEF R/W ACP_PACKET_ID[7:0] Packet type value
0xF1 R ACP_HEADER2 HB2
0x70 R ACP_PB_0_1 PB0
0x71 R ACP_PB_0_2 PB1
0x72 R ACP_PB_0_3 PB2
0x73 R ACP_PB_0_4 PB3
0x74 R ACP_PB_0_5 PB4
0x75 R ACP_PB_0_6 PB5
0x76 R ACP_PB_0_7 PB6
0x77 R ACP_PB_0_8 PB7
0x78 R ACP_PB_0_9 PB8
0x79 R ACP_PB_0_10 PB9
0x7B R ACP_PB_0_12 PB11
0x7C R ACP_PB_0_13 PB12
0x7D R ACP_PB_0_14 PB13
0x7E R ACP_PB_0_15 PB14
0x7F R ACP_PB_0_16 PB15
0x80 R ACP_PB_0_17 PB16
0x81 R ACP_PB_0_18 PB17
0x82 R ACP_PB_0_19 PB18
0x83 R ACP_PB_0_20 PB19
0x84 R ACP_PB_0_21 PB20
0x85 R ACP_PB_0_22 PB21
0x86 R ACP_PB_0_23 PB22
0x87 R ACP_PB_0_24 PB23
0x88 R ACP_PB_0_25 PB24
0x89 R ACP_PB_0_26 PB25
0x8A R ACP_PB_0_27 PB26
1
As defined by the HDMI specifications.
The ACP InfoFrame registers are considered valid if ACP_PCKT_RAW is set to 1.
ACP_PCKT_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[5] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of audio content protection packet detection signal.
Function
ACP_PCKT_RAW Description
0 (default) No ACP packet received within the last 600 ms or since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 ACP packets have been received within the last 600 ms. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection
reset or upon writing to ACP_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 89 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0xF2
R/W
ISRC1_PACKET_ID[7:0]
Packet type value
0x8E R ISRC1_PB_0_3
PB2
0x9A
R
ISRC1_PB_0_15
PB14
0x9F R ISRC1_PB_0_20
PB19
ISRC Packet Registers
Table 27 and Table 28 provide lists of readback registers available for the ISRC packets. Refer to the HDMI specifications for a detailed
explanation of the ISRC packet fields.
Table 27. ISRC1 Packet Registers
InfoFrame Map Address R/W Register Name Packet Byte No.1
0xF3 R ISRC1_HEADER1 HB1
0xF4 R ISRC1_HEADER2 HB2
0x8C R ISRC1_PB_0_1 PB0
0x8D R ISRC1_PB_0_2 PB1
0x8F R ISRC1_PB_0_4 PB3
0x90 R ISRC1_PB_0_5 PB4
0x91 R ISRC1_PB_0_6 PB5
0x92 R ISRC1_PB_0_7 PB6
0x93 R ISRC1_PB_0_8 PB7
0x94 R ISRC1_PB_0_9 PB8
0x95 R ISRC1_PB_0_10 PB9
0x96 R ISRC1_PB_0_11 PB10
0x97 R ISRC1_PB_0_12 PB11
0x98 R ISRC1_PB_0_13 PB12
0x99 R ISRC1_PB_0_14 PB13
0x9B R ISRC1_PB_0_16 PB15
0x9C R ISRC1_PB_0_17 PB16
0x9D R ISRC1_PB_0_18 PB17
0x9E R ISRC1_PB_0_19 PB18
0xA0 R ISRC1_PB_0_21 PB20
0xA1 R ISRC1_PB_0_22 PB21
0xA2 R ISRC1_PB_0_23 PB22
0xA3 R ISRC1_PB_0_24 PB23
0xA4 R ISRC1_PB_0_25 PB24
0xA5 R ISRC1_PB_0_26 PB25
0xA6 R ISRC1_PB_0_27 PB26
0xA7 R ISRC1_PB_0_28 PB27
1
As defined by the HDMI specifications.
Rev. B | Page 90 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
0 (default)
No ISRC1 packets received since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
0xA8
R
ISRC2_PB_0_1
PB0
0xB3
R
ISRC2_PB_0_12
PB11
0xB9
R
ISRC2_PB_0_18
PB17
The ISRC1 packet registers are considered valid if ISRC1_PCKT_RAW is set to 1.
ISRC1_PCKT_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[6] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of International Standard Recording Code 1 (ISRC1) packet detection signal.
Function
ISRC1_PCKT_RAW Description
1 ISRC1 packets have been received. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection reset or
upon writing to ISRC1_PACKET_ID.
Table 28. ISRC2 Packet Registers
InfoFrame Map Address R/W Register Name Packet Byte No.1
0xF5 R/W ISRC2_PACKET_ID[7:0] Packet type value
0xF6 R ISRC2_HEADER1 HB1
0xF7 R ISRC2_HEADER2 HB2
0xA9 R ISRC2_PB_0_2 PB1
0xAA R ISRC2_PB_0_3 PB2
0xAB R ISRC2_PB_0_4 PB3
0xAC R ISRC2_PB_0_5 PB4
0xAD R ISRC2_PB_0_6 PB5
0xAE R ISRC2_PB_0_7 PB6
0xAF R ISRC2_PB_0_8 PB7
0xB0 R ISRC2_PB_0_9 PB8
0xB1 R ISRC2_PB_0_10 PB9
0xB2 R ISRC2_PB_0_11 PB10
0xB4 R ISRC2_PB_0_13 PB12
0xB5 R ISRC2_PB_0_14 PB13
0xB6 R ISRC2_PB_0_15 PB14
0xB7 R ISRC2_PB_0_16 PB15
0xB8 R ISRC2_PB_0_17 PB16
0xBA R ISRC2_PB_0_19 PB18
0xBB R ISRC2_PB_0_20 PB19
0xBC R ISRC2_PB_0_21 PB20
0xBD R ISRC2_PB_0_22 PB21
0xBE R ISRC2_PB_0_23 PB22
0xBF R ISRC2_PB_0_24 PB23
0xC0 R ISRC2_PB_0_25 PB24
0xC1 R ISRC2_PB_0_26 PB25
0xC2 R ISRC2_PB_0_27 PB26
0xC3 R ISRC2_PB_0_28 PB27
1
As defined by the HDMI specifications.
The ISRC2 packet registers are considered valid if, and only, if ISRC1_PCKT_RAW is set to 1.
ISRC2_PCKT_RAW, IO, Address 0x60[7] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of International Standard Recording Code 2 (ISRC2) packet detection signal.
Function
ISRC2_PCKT_RAW Description
0 (default) No ISRC2 packets received since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 ISRC2 packets have been received. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet detection reset or
upon writing to ISRC2_PACKET_ID.
Rev. B | Page 91 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0xC7
R
GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_4
PB3
0xD8
R
GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_21
PB20
0 (default)
Interrupt flag indicates that gamut packet is new.
Gamut Metadata Packets
Refer to the HDMI specifications for a detailed explanation of the gamut metadata packet fields.
Table 29. Gamut Metadata Packet Registers
HDMI Map Address R/W Register Name Packet Byte No.1
0xF8 R/W GAMUT_PACKET_ID[7:0] Packet type value
0xF9 R GAMUT_HEADER1 HB1
0x FA R GAMUT_HEADER2 HB2
0xC4 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_1 PB0
0xC5 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_2 PB1
0xC6 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_3 PB2
0xC8 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_5 PB4
0xC9 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_6 PB5
0xCA R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_7 PB6
0xCB R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_8 PB7
0xCC R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_9 PB8
0xCD R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_10 PB9
0xCE R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_11 PB10
0xCF R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_12 PB11
0xD0 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_13 PB12
0xD1 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_14 PB13
0xD2 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_15 PB14
0xD3 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_16 PB15
0xD4 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_17 PB16
0xD5 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_18 PB17
0xD6 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_19 PB18
0xD7 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_20 PB19
0xD9 R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_22 PB21
0xDA R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_23 PB22
0xDB R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_24 PB23
0xDC R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_25 PB24
0xDD R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_26 PB25
0xDE R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_27 PB26
0xDF R GAMUT_MDATA_PB_0_28 PB27
1
As defined by the HDMI specifications.
The gamut metadata packet registers are considered valid if GAMUT_MDATA_RAW is set to 1.
GAMUT_MDATA_RAW, IO, Address 0x65[0] (Read Only)
Raw status signal of gamut metadata packet detection signal.
Function
GAMUT_MDATA_RAW Description
0 (default) No gamut metadata packet has been received in the last video frame or since the last HDMI packet detection reset.
1 A gamut metadata packet has been received in the last video frame. This bit resets to zero after an HDMI packet
detection reset or upon writing to GAMUT_PACKET_ID.
GAMUT_IRQ_NEXT_FIELD, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x50[4]
A control set the NEW_GAMUT_MDATA_RAW interrupt to detect when the new contents are applicable to next field or to indicate that
the gamut packet is new. This is done using header information of the gamut packet.
Function
GAMUT_IRQ_NEXT_FIELD Description
1 Interrupt flag indicates that gamut packet is to be applied next field.
Rev. B | Page 92 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
AUD_PACKET_ID[7:0]
Description
CUSTOMIZING PACKET/INFOFRAME STORAGE REGISTERS
The packet type value of each set of packet and InfoFrame registers in the InfoFrame Map is programmable. This allows the user to
configure the ADV7612 to store the payload data of any packet and InfoFrames sent by the transmitter connected on the selected
HDMI port.
Note: Writing to any of the nine following packet ID registers also clears the corresponding raw InfoFrame / Packet detection bit. For
example, writing 0x82, or any other value, to AVI_PACKET_ID clears AVI_ INFO _RAW.
AVI_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xE0[7:0]
AVI InfoFrame ID.
Function
AVI_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x00 to 0x1B
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x00 to 0x1B
AUD_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xE3[7:0]
Audio InfoFrame ID.
Function
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x1C to 0x29
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x1C to 0x29
SPD_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xE6[7:0]
Source Prod InfoFrame ID.
Function
SPD_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x2A to 0x45
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x2A to 0x45
MS_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xE9[7:0]
MPEG source InfoFrame ID.
Function
MS_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x46 to 0x53
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x46 to 0x53
VS_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xEC[7:0]
Vend or specific InfoFrame ID.
Function
VS_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x54 to 0x6F
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x54 to 0x6F
ACP_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xEF[7:0]
ACP InfoFrame ID.
Function
ACP_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame Map, Address 0x70 to 0x8B
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame Map, Address 0x70 to 0x8B
Rev. B | Page 93 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
1xxxxxxx
Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x8C to 0xA7
Function
ISRC1_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xF2[7:0]
ISRC1 InfoFrame ID.
Function
ISRC1_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0x8C to 0xA7
ISRC2_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xF5[7:0]
ISRC2 InfoFrame ID.
ISRC2_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0xA8 to 0xC3
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0xA8 to 0xC3
GAMUT_PACKET_ID[7:0], Addr 7C (InfoFrame), Address 0xF8[7:0]
Gamut InfoFrame ID.
Function
GAMUT_PACKET_ID[7:0] Description
0xxxxxxx Packet type value of packet stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0xC4 to 0xDF
1xxxxxxx Packet type value of InfoFrame stored in InfoFrame map, Address 0xC4 to 0xDF
Note: The packet type values and corresponding packets should not be programmed in the packet type values registers. These packets are
always processed internally and cannot be stored in the packet/InfoFrame registers in the InfoFrame map:
• 0x01: audio clock regeneration packet
• 0x02: audio sample packet
• 0x03: general control packet
• 0x07: DSD audio sample packet
• 0x08: DST audio packet
• 0x09: HBR audio stream packet
REPEATER SUPPORT
The ADV7612 incorporates an EDID/repeater controller that provides all the features required for a receiver front end of a fully HDCP
1.4 compliant repeater system. The ADV7612 has a RAM that can store up to 127 KSVs, which allows it to handle up to 127 downstream
devices in repeater mode (refer to Table 30).
The ADV7612 features a set of HDCP registers, defined in the HDCP specifications, which are accessible through the DDC bus (refer to
the DDC Ports section) of the selected port. A subset of the HDCP registers (defined in the following subsections) are also available in the
Repeater Map and are accessible through the main I
Repeater Routines Performed by the EDID/Repeater Controller
Power-Up
A power-on reset circuitry on the DVDD supply is used to reset the EDID/repeater controller when the ADV7612 is powered up. When
the EDID/repeater controller reboots after reset, it resets all the KSV registers listed in Table 30 to 0x00.
AKSV Update
The EDID/repeater controller resets automatically the BCAPS [5] bit to 0 when an HDCP transmitter writes its AKSV into the ADV7612
HDCP registers through the DDC bus of the HDMI port.
Note: Writing a value in the AKSV[39:32] triggers an AKSV update and AKSV_UPDATE_ST interrupt if AKSV_UPDATE_MB1 or
AKSV_UPDATE_MB2 has been set to 1 This triggers the EDID/repeater controller to reset the BCAPS [5] bit back to 0.
KSV List Ready
The KSV_LIST_READY bit is set by an external controller driving the ADV7612. This notifies the ADV7612 on-chip EDID/repeater
controller that the KSV list registers have been updated with the KSV’s of the attached and active downstream HDCP devices.
2
C port (refer to the Main I2C Port section).
Rev. B | Page 94 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
When KSV_LIST_READY is set to 1, the EDID/repeater controller computes the SHA-1 hash value V’, updates the corresponding V’
registers (refer to Tab le 31), and sets the READY bit (that is, BCAPS[5]) to 1. This indicates to the transmitter attached to the ADV7612
that the KSV FIFO and SHA-1 hash value V’ are ready to be read.
KSV_LIST_READY, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x71[7]
The system sets this bit in order to indicate that the KSV list has been read from the Tx IC(s) and written into the repeater map. The
system must also set Bits[11:0] of BSTATUS before setting this bit.
Function
KSV_LIST_READY Description
0 (default) Not ready
1 Ready
Notes
• The SHA-1 hash value will be computed if the bit KSV_LIST_READY is set after the part has received an AKSV update from the
upstream source. The external controller should therefore set KSV_LST_READY to 1 only after the part has received an AKSV
update from the upstream source.
• The ADV7612 does not automatically clear KSV_LIST_READY to 0, after it has finished computed the SHA-1 has value. Therefore,
the external controller needs to clear KSV_LIST_READY.
HDMI Mode
The BSTATUS[12]bit is updated automatically by the ADV7612 and follows the HDMI mode status of the HDMI/DVI stream input
on the active HDMI port. B STATUS [12] is set to 1 if the ADV7612 receives an HDMI stream, and set to 0 if the ADV7612 receives a
DVI stream.
Repeater Actions Required by External Controller
The external controller must set the BCAPS register and notify the ADV7612 when the KSV list is updated, as described in the following
sections: Repeater Bit, KSV FIFO Read from HDCP Registers, First AKSV Update, and AKSV_UPDATE_B_RAW.
Note that many more routines must be implemented into the external controller driving the ADV7612 to implement a full repeater. Such
routines are described in the HDCP and HDMI specifications (for example, copying InfoFrame and packet data image from the HDMI
receiver into the HDMI transmitter, momentarily deasserting the hot plug detect and disabling the clock termination on a change of
downstream topology, and so on).
Repeater Bit
The REPEATER bit (that is, BCAPS[6]) must be set to 1 by the external controller in the routine that initializes the ADV7612. The
repeater bit must be left as such as long as the ADV7612 is configured as the front end of a repeater system.
Note: The registers in the KSV list (refer to Table 30) should always be set to 0x0 if the REPEATER bit is set to 0. The firmware running
on the external controller, therefore, always sets the registers in the KSV list to 0x0 if the repeater bit is changed from 1 to 0.
KSV FIFO Read from HDCP Registers
The KSV FIFO read at address 0x43 through the HDCP port of the selected HDMI port is dependent on the value of the REPEATER bit
(that is, BCAPS[6]):
• When the REPEATER bit is set to 0, the KSV FIFO read from the HDCP port always returns 0x0
• When the REPEATER bit is set to 1, the KSV FIFO read from the HDCP port matches the KSV list which is set in the Repeater Map
at addresses 0x80 to 0xF7 (refer to Table 30)
First AKSV Update
When the upstream transmitter writes its AKSV for the first time into the ADV7612 HDCP registers, the external controller driving the
ADV7612 should perform the following tasks:
• Update B STATUS[11:0] according to the topology of the downstream device attached to the repeater.
• Update the KSV list (refer to Tabl e 30) with the KSV from the transmitter on the back end of the repeater as well as the KSV from all
the downstream devices connected to the repeater.
• Set KSV_LIST_READY to 1.
• The external controller can monitor the AKSV_UPDATE_X_RAW bits to be notified when the transmitter writes its AKSV into the
HDCP registers of the ADV7612 (where X = A and B).
Rev. B | Page 95 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
0 (default)
No AKSV updates on Port A
1
Detected a write access to the AKSV register on Port B
0x04[7:0]
BKSV[39:32]
AKSV_UPDATE_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[0] (Read Only)
Status of Port A AKSV update interrupt signal. When set to 1 it indicates that transmitter has written its AKSV into HDCP registers for
Port A. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via AKSV_UPDATE_A_CLR.
Function
AKSV_UPDATE_A_RAW Description
1 Detected a write access to the AKSV register on Port A
AKSV_UPDATE_B_RAW, IO, Address 0x88[1] (Read Only)
Status of Port B AKSV Update Interrupt signal. When set to 1 it indicates that transmitter has written its AKSV into HDCP registers for
Port B. Once set, this bit will remain high until it is cleared via AKSV_UPDATE_B_CLR.
Function
AKSV_UPDATE_B_RAW Description
0 (default) No AKSV updates on Port B
Second and Subsequent AKSV Updates
When the upstream transmitter writes its AKSV for the second time or more into the ADV7612 HDCP registers, the external controller
driving the ADV7612 should set KSV_LIST_READY to 1.
HDCP Registers Available in Repeater Map
In order to enable fast switching of the HDCP encrypted HDMI ports, the registers 0x00 to 0x42 in the repeater map are replicated for
each port. AUTO_HDCP_MAP_ENABLE and HDCP_MAP_SELECT[2:0] determine which port is currently visible to the user.
AUTO_HDCP_MAP_ENABLE, Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x79[3]
Selects which port will be accessed for HDCP addresses: the HDMI active port (selected by HDMI_PORT_SELECT, HDMI map) or the
one selected in HDCP_MAP_SELECT.
Function
AUTO_HDCP_MAP_ENABLE Description
0 HDCP data read from port given by HDCP_MAP_SELECT
1 (default) HDCP data read from the active HDMI port
HDCP_MAP_SELECT[2:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x79[2:0]
Selects which port will be accessed for HDCP addresses (0x00 to 0x42 in Repeater map). This only takes effect when AUTO HDCP MAN
ENABLE is 0.
Function
HDCP_MAP_SELECT[2:0] Description
000 (default) Select Port A
001 Select Port B
BKSV[39:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x04[7:0]; Address 0x03[7:0]; Address 0x02[7:0]; Address 0x01[7:0]; Address 0x00[7:0] (Read Only)
The receiver key selection vector (BKSV) can be read back once the part has successfully accessed the HDCP ROM. The following
registers contain the BKSV read from the EEPROM.
Function
BKSV[39:0] Description
0x00[7:0] BKSV[7:0]
0x01[7:0] BKSV[15:8]
0x02[7:0 ] BKSV[23:16]
0x03[7:0] BKSV[31:24]
AKSV[39:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x14[7:0]; Address 0x13[7:0]; Address 0x12[7:0]; Address 0x11[7:0]; Address 0x10[7:0]
The AKSV of the transmitter attached to the active HDMI port can be read back after an AKSV update. The following registers contain
the AKSV written by the Tx.
Rev. B | Page 96 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
Function
AKSV[39:0] Description
0x10[7:0] AKSV[7:0]
0x11[7:0] AKSV[15:8]
0x12[7:0] AKSV[23:16]
0x13[7:0] AKSV[31:24]
0x14[7:0] AKSV[39:32]
BCAPS[7:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x40[7:0]
This is the BCAPS register presented to the Tx attached to the active HDMI port.
Function
BCAPS[7:0] Description
10000011 (default) Default BCAPS register value presented to the Tx
xxxxxxxx BCAPS register value presented to the Tx
BSTATUS[15:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x42[7:0]; Address 0x41[7:0]
These registers contain the BSTATUS information presented to the Tx attached to the active HDMI port. Bits [11:0] must be set by the
system software acting as a repeater.
Function
BSTATUS[15:0] Description
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx BSTATUS register presented to Tx.
0000000000000000 (default) Reset value. BSTATUS register is reset only after power up.
0x41[7:0] BSTATUS[7:0].
0x42[7:0] BSTATUS[15:8].
KSV registers are stored consecutively in RAM, which is split into 5x128 bytes bank maps. Maps are accessible through KSV_BYTE_0 to
KSV_BYTE_127. Proper segment can be selected via KSV_MAP_SELECT[2:0] register, as shown in Figure 27.
0x00 TO 0x04 KSV0
0x05 TO 0x09 KSV1
0x0A TO 0x0E KSV2
…
0x7D TO 0x81 KSV25
0x82 TO 0x86 KSV26
…
0xF5 TO 0xF 9 KS V 49
0xFA TO 0xF E KSV50
0xFF TO 0x10 3 KS V 51
…
0x00
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 0
0x79
0x80
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 1
0xFF
0x100
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 2
0x80 KSV_BYTE_0
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 0
0xFF KSV_BYTE_127
0x17C TO 0x180 KSV76
0x181 TO 0x185 KSV77
0x186 TO 0x18A KSV78
…
0x1FE TO 0x 202 KS V 1 02
0x203 TO 0x207 KSV103
0x208 TO 0x20C KSV104
…
0x276 TO 0x27A KSV126
0x17F
0x180
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 3
0x200
0x201
KSV_MAP_SELECT = 4
0x27A
Figure 27. Addressing Block Using KSV_MAP_SELECT and Register KSV_BYTE_0 to Register KSV_BYTE_127
Rev. B | Page 97 of 204
09486-028

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
000 (default)
KSV Map 0 selected
2
KSV_BYTE_2[7:0]
0x82[7:0]
3
KSV_BYTE_3[7:0]
0x83[7:0]
14
KSV_BYTE_14[7:0]
0x8E[7:0]
31
KSV_BYTE_31[7:0]
0x9F[7:0]
KSV_MAP_SELECT[2:0], Addr 64 (Repeater), Address 0x79[6:4]
Selects which 128 bytes of KSV list will be accessed when reading or writing to addresses 0x80 to 0xFF in this map. Values from 5 and
upwards are not valid
Function
KSV_MAP_SELECT[2:0] Description
001 KSV Map 1 selected
010 KSV Map 2 selected
011 KSV Map 3 selected
100 KSV Map 4 selected
101 Reserved
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
Table 30. KSV Byte Registers Location
KSV Byte Number Register Name Register Addresses1
0 KSV_BYTE_0[7:0] 0x80[7:0]
1 KSV_BYTE_1[7:0] 0x81[7:0]
4 KSV_BYTE_4[7:0] 0x84[7:0]
5 KSV_BYTE_5[7:0] 0x85[7:0]
6 KSV_BYTE_6[7:0] 0x86[7:0]
7 KSV_BYTE_7[7:0] 0x87[7:0]
8 KSV_BYTE_8[7:0] 0x88[7:0]
9 KSV_BYTE_9[7:0] 0x89[7:0]
10 KSV_BYTE_10[7:0] 0x8A[7:0]
11 KSV_BYTE_11[7:0] 0x8B[7:0]
12 KSV_BYTE_12[7:0] 0x8C[7:0]
13 KSV_BYTE_13[7:0] 0x8D[7:0]
15 KSV_BYTE_15[7:0] 0x8F[7:0]
16 KSV_BYTE_16[7:0] 0x90[7:0]
17 KSV_BYTE_17[7:0] 0x91[7:0]
18 KSV_BYTE_18[7:0] 0x92[7:0]
19 KSV_BYTE_19[7:0] 0x93[7:0]
20 KSV_BYTE_20[7:0] 0x94[7:0]
21 KSV_BYTE_21[7:0] 0x95[7:0]
22 KSV_BYTE_22[7:0] 0x96[7:0]
23 KSV_BYTE_23[7:0] 0x97[7:0]
24 KSV_BYTE_24[7:0] 0x98[7:0]
25 KSV_BYTE_25[7:0] 0x99[7:0]
26 KSV_BYTE_26[7:0] 0x9A[7:0]
27 KSV_BYTE_27[7:0] 0x9B[7:0]
28 KSV_BYTE_28[7:0] 0x9C[7:0]
29 KSV_BYTE_29[7:0] 0x9D[7:0]
30 KSV_BYTE_30[7:0] 0x9E[7:0]
32 KSV_BYTE_32[7:0] 0xA0[7:0]
33 KSV_BYTE_33[7:0] 0xA1[7:0]
34 KSV_BYTE_34[7:0] 0xA2[7:0]
35 KSV_BYTE_35[7:0] 0xA3[7:0]
Rev. B | Page 98 of 204

Hardware User Guide UG-216
40
KSV_BYTE_40[7:0]
0xA8[7:0]
57
KSV_BYTE_57[7:0]
0xB9[7:0]
68
KSV_BYTE_68[7:0]
0xC4[7:0]
88
KSV_BYTE_88[7:0]
0xD8[7:0]
KSV Byte Number Register Name Register Addresses1
36 KSV_BYTE_36[7:0] 0xA4[7:0]
37 KSV_BYTE_37[7:0] 0xA5[7:0]
38 KSV_BYTE_38[7:0] 0xA6[7:0]
39 KSV_BYTE_39[7:0] 0xA7[7:0]
41 KSV_BYTE_41[7:0] 0xA9[7:0]
42 KSV_BYTE_42[7:0] 0xAA[7:0]
43 KSV_BYTE_43[7:0] 0xAB[7:0]
44 KSV_BYTE_44[7:0] 0xAC[7:0]
45 KSV_BYTE_45[7:0] 0xAD[7:0]
46 KSV_BYTE_46[7:0] 0xAE[7:0]
47 KSV_BYTE_47[7:0] 0xAF[7:0]
48 KSV_BYTE_48[7:0] 0xB0[7:0]
49 KSV_BYTE_49[7:0] 0xB1[7:0]
50 KSV_BYTE_50[7:0] 0xB2[7:0]
51 KSV_BYTE_51[7:0] 0xB3[7:0]
52 KSV_BYTE_52[7:0] 0xB4[7:0]
53 KSV_BYTE_53[7:0] 0xB5[7:0]
54 KSV_BYTE_54[7:0] 0xB6[7:0]
55 KSV_BYTE_55[7:0] 0xB7[7:0]
56 KSV_BYTE_56[7:0] 0xB8[7:0]
58 KSV_BYTE_58[7:0] 0xBA[7:0]
59 KSV_BYTE_59[7:0] 0xBB[7:0]
60 KSV_BYTE_60[7:0] 0xBC[7:0]
61 KSV_BYTE_61[7:0] 0xBD[7:0]
62 KSV_BYTE_62[7:0] 0xBE[7:0]
63 KSV_BYTE_63[7:0] 0xBF[7:0]
64 KSV_BYTE_64[7:0] 0xC0[7:0]
65 KSV_BYTE_65[7:0] 0xC1[7:0]
66 KSV_BYTE_66[7:0] 0xC2[7:0]
67 KSV_BYTE_67[7:0] 0xC3[7:0]
69 KSV_BYTE_69[7:0] 0xC5[7:0]
70 KSV_BYTE_70[7:0] 0xC6[7:0]
71 KSV_BYTE_71[7:0] 0xC7[7:0]
72 KSV_BYTE_72[7:0] 0xC8[7:0]
73 KSV_BYTE_73[7:0] 0xC9[7:0]
74 KSV_BYTE_74[7:0] 0xCA[7:0]
75 KSV_BYTE_75[7:0] 0xCB[7:0]
76 KSV_BYTE_76[7:0] 0xCC[7:0]
77 KSV_BYTE_77[7:0] 0xCD[7:0]
78 KSV_BYTE_78[7:0] 0xCE[7:0]
79 KSV_BYTE_79[7:0] 0xCF[7:0]
80 KSV_BYTE_80[7:0] 0xD0[7:0]
81 KSV_BYTE_81[7:0] 0xD1[7:0]
82 KSV_BYTE_82[7:0] 0xD2[7:0]
83 KSV_BYTE_83[7:0] 0xD3[7:0]
84 KSV_BYTE_84[7:0] 0xD4[7:0]
85 KSV_BYTE_85[7:0] 0xD5[7:0]
86 KSV_BYTE_86[7:0] 0xD6[7:0]
87 KSV_BYTE_87[7:0] 0xD7[7:0]
Rev. B | Page 99 of 204

UG-216 Hardware User Guide
93
KSV_BYTE_93[7:0]
0xDD[7:0]
110
KSV_BYTE_110[7:0]
0xEE[7:0]
121
KSV_BYTE_121[7:0]
0xF9[7:0]
KSV Byte Number Register Name Register Addresses1
89 KSV_BYTE_89[7:0] 0xD9[7:0]
90 KSV_BYTE_90[7:0] 0xDA[7:0]
91 KSV_BYTE_91[7:0] 0xDB[7:0]
92 KSV_BYTE_92[7:0] 0xDC[7:0]
94 KSV_BYTE_94[7:0] 0xDE[7:0]
95 KSV_BYTE_95[7:0] 0xDF[7:0]
96 KSV_BYTE_96[7:0] 0xE0[7:0]
97 KSV_BYTE_97[7:0] 0xE1[7:0]
98 KSV_BYTE_98[7:0] 0xE2[7:0]
99 KSV_BYTE_99[7:0] 0xE3[7:0]
100 KSV_BYTE_100[7:0] 0xE4[7:0]
101 KSV_BYTE_101[7:0] 0xE5[7:0]
102 KSV_BYTE_102[7:0] 0xE6[7:0]
103 KSV_BYTE_103[7:0] 0xE7[7:0]
104 KSV_BYTE_104[7:0] 0xE8[7:0]
105 KSV_BYTE_105[7:0] 0xE9[7:0]
106 KSV_BYTE_106[7:0] 0xEA[7:0]
107 KSV_BYTE_107[7:0] 0xEB[7:0]
108 KSV_BYTE_108[7:0] 0xEC[7:0]
109 KSV_BYTE_109[7:0] 0xED[7:0]
111 KSV_BYTE_111[7:0] 0xEF[7:0]
112 KSV_BYTE_112[7:0] 0xF0[7:0]
113 KSV_BYTE_113[7:0] 0xF1[7:0]
114 KSV_BYTE_114[7:0] 0xF2[7:0]
115 KSV_BYTE_115[7:0] 0xF3[7:0]
116 KSV_BYTE_116[7:0] 0xF4[7:0]
117 KSV_BYTE_117[7:0] 0xF5[7:0]
118 KSV_BYTE_118[7:0] 0xF6[7:0]
119 KSV_BYTE_119[7:0] 0xF7[7:0]
120 KSV_BYTE_120[7:0] 0xF8[7:0]
122 KSV_BYTE_122[7:0] 0xFA[7:0]
123 KSV_BYTE_123[7:0] 0xFB[7:0]
124 KSV_BYTE_124[7:0] 0xFC[7:0]
125 KSV_BYTE_125[7:0] 0xFD[7:0]
126 KSV_BYTE_126[7:0] 0xFE[7:0]
127 KSV_BYTE_127[7:0] 0xFF[7:0]
1
All KSVs are located in the repeater map.
Table 31. Registers Location for SHA-1 Hash Value V’
Register Name Address Location1 Function
SHA_A[31:0] 0x20[7:0]: SHA_A[7:0]
H0 part of SHA-1 hash value V’. Register also called (V’.H1)2
0x21[7:0]: SHA_A[15:8]
0x22[7:0]: SHA_A[23:16]
0x23[7:0]: SHA_A[31:24]
SHA_B[31:0] 0x24[7:0]: SHA_B[7:0]
H1 part of SHA-1 hash value V’. Register also called (V’.H1)2
0x25[7:0]: SHA_B[15:8]
0x26[7:0]: SHA_B[23:16]
0x27[7:0]: SHA_B[31:24]
SHA_C[31:0] 0x28[7:0]: SHA_C[7:0]
H2 part of SHA-1 hash value V’. Register also called (V’.H2)2
0x29[7:0]: SHA_C[15:8]
0x2A[7:0]: SHA_C[23:16]
Rev. B | Page 100 of 204
 Loading...
Loading...