Page 1
a
a Engineer To Engineer Note EE-130
aa
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781) 461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
The syntax for the ELF assembler directives is
Making a Fast Transition from
ADSP-21xx to ADSP-219x
common across ADI ELF assemblers. The IDE
provides a common environment and options.
The VisualDSP debugger is based on the robust
Contributed by Barbara Zino
and complete DWARF-2 format.
Version 1.2
See also: App Note "A Quick Primer on ELF
and DWARF-2".
Introduction
Whether you are upgrading existing 21xx code
or writing new code, you will want to be aware
of what is new and different with the ADSP219x instruction set and tools.
This application note was written for anyone
who is coming on-board with ADSP-219x and
would like detailed information on the
assembler tools. It is intended to assist in:
1) Upgrading existing 21xx assembly code to
ADSP-219x
2) Writing new assembly code for the ADSP219x
For a complete description of the ADSP-219x,
please see the ADSP-219x DSP Instruction Set
Reference (Part 82-00390-02).
ELF and DWARF-2
The ADSP-219x assembler and linker are part
of the new family of ADI ELF assemblers and
linkers that operate within the VisualDSP IDE
environment.
The tools produce industry standard formats:
• ELF Object File Format
• DWARF-2 Debugging Format
Getting Started
To assist in the upgrade of existing 21xx
applications, the assembler can optionally
process legacy syntax.
If you are using the command line version of the
new assembler or the IDE, the default is the new
ELF assembler directives:
easm219x myNew.asm
Specify the -legacy option to have the 5.x/6.x
syntax accepted by the new assembler: In
addition, you will likely want to specify the -c
option. This makes the 21xx -legacy case
sensitive:
easm219x -legacy -c myLegacy.dsp
The -legacy assembler option processes the
21xx directives and syntax that pre-date the new
family of ELF assemblers. The assembler
legacy option allows you to focus on core issues
and ignore syntax differences.
To enable assemble legacy code within the IDE
build environment:
Project Options
Assemble
Additional Options
Add "-legacy -c"
Copyright 2000, Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Analog Devices assumes no responsibility for customer product design or the use or application of customers’ products or
for any infringements of patents or rights of others which may result from Analog Devices assistance. All trademarks and logos are property of their respective holders. Information
furnished by Analog Devices Applications and Development Tools Engineers is believed to be accurate and reliable, however no responsibility is as sumed by Analog Devices
regarding the technical accuracy of the content provided in all Analog Devices’ Engineer-to-Engineer Notes.
Page 2

When Upgrading Existing Code
• Assemble with -legacy
• Review instruction diagnostics (if any)
and revise to ADSP-219x
When Writing New Code
• Code with new ELF directives
• Do not use the -legacy option
Please note that you cannot mix "old and new"
syntax in the same assembly source file. You
can combine "old and new" in the same
application by assembling distinct source files
that are then linked together.
Resulting error with 9x assembler:
[Error E24] "MYSQRT.DSP":61
Assembler Error: 218x to 219x incompatibility:
No More POS or NEG.
Must use CCODE register.
Solution:
Use CCODE register.
"SE" IS NO LONGER D-REGISTER
218x code:
AX0=SE, SR=NORM MR1 (HI);
Resulting error with 9x assembler:
[Error E22] "MYSQRT.DSP":32
Illegal Multi Instruction Formation
Instruction Component: register move
Instruction Component: shift
Upgrading Existing Code
Some existing 21xx assembly applications will
require no source code changes. Others may
need changes for the ADSP-219x core
instruction set. Here is a sampling of 21xx
legacy code with invalid ADSP-219x
instructions and the assembler messages that are
reported after passing the code through the
ADSP-219x assembler. These are the places in
the code that you need to change.
The following diagnostics are reported whether
or not the -legacy option is in effect. The -legacy
option in the 9x assembler is for 21xx syntax
compatibility only, not instruction compatibility.
For 8x processing, use the -legacy option with
the 8x assembler.
easm218x -legacy -c myApp.dsp
No NEG or POS CONDITION
218x code:
pwr_ok: IF NEG JUMP frac;
Solution:
Since SE is no longer a DREG (group 0
register), its use in a multi function move is
illegal. Select one of the ADSP-219x DREG.
“MF" REGISTER REPLACED
218x code:
MF=AR*MY0 (RND), MX0=DM(I3,M3);
MR=MR+MX0*MF (SS), MX0=DM(I3,M3);
approx: MF=AR*MF (RND);
Resulting error with 9x assembler:
"MYSQRT.DSP":38 Invalid Register 'MF':
Illegal destination register for MACC instruction
Solution:
The 21xx MF register has been replaced
by the 219x SR2-SR0 dual accumulator
CCODE LATENCY
218x code:
ccode=0x03;
if not swcond ar = mr0 and 8192;
EE-130 Page 2
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 3
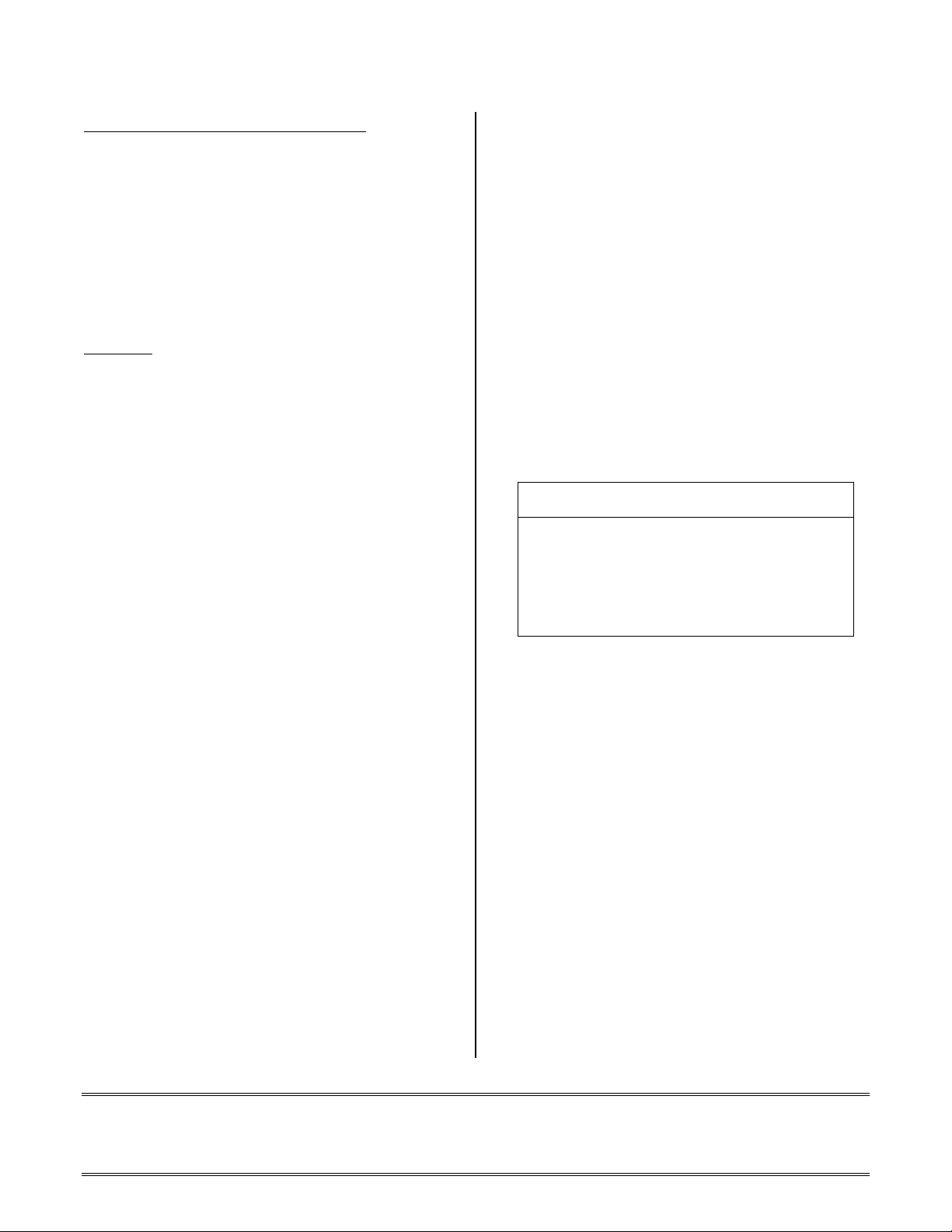
Resulting warning with 9x assembler:
[Warning W35] “CcodeLatency.asm":26
Assembler Warning: Detected a CCODE latency
problem. The CCODE write is immediately followed
by a CCODE conditional check. There is a 1-cycle
latency between writing to the CCODE register and
testing the condition. There is no stall in the
sequencer. If you don't add an instruction after the
CCODE write, your conditional check will be based
on the old CCODE!
Solution:
// CCODE latency accounted for
ccode=0x03;
i0=1;
if not swcond ar = abs ax0;
WRITING NEW CODE
When you write new code, use the ELF
directives that are common across the ADI ELF
assemblers. There are three ELF directives that
are the building blocks of any ELF assembly
program. Think of them as "The Three
Musketeers":
.SECTION DIRECTIVE
Sections are named contiguous locations of
program or data memory.
.section ( sectionQualifiers )+
sectionName sectionType? ;
One or more section qualifiers indicate the
section properties. Section qualifiers begin with
"/". For example "/dm" or "/pm".
The section type is optional and the default is
SHT_PROGBITS. It is unlikely you will ever
need to override the section type for sections in
ELF binary object file for your application so
you can just ignore this paragraph altogether ☺.
.SECTION Examples
.section/pm program;
.section/dm data1;
1) .SECTION
2) .VAR
3) .GLOBAL
NOTATION
The notation used to describe the syntax in this
document:
* 0 or more
+ 1 or more
? Optional item (0 or 1 may appear)
There are some advantages to using .section
directives:
• Permits multiple code sections
• Gives you more control over data placement
• Readable displays via the ElfDump utility
Multiple /pm (/code) .sections are allowed in
219x. In 21xx there was only a single .module
(code section).
In 219x, you determine placement of data
buffers in the assembler source by locating them
within the desired section. This differs from
21xx where the linker placed the data buffers at
locations of its own choosing.
EE-130 Page 3
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 4
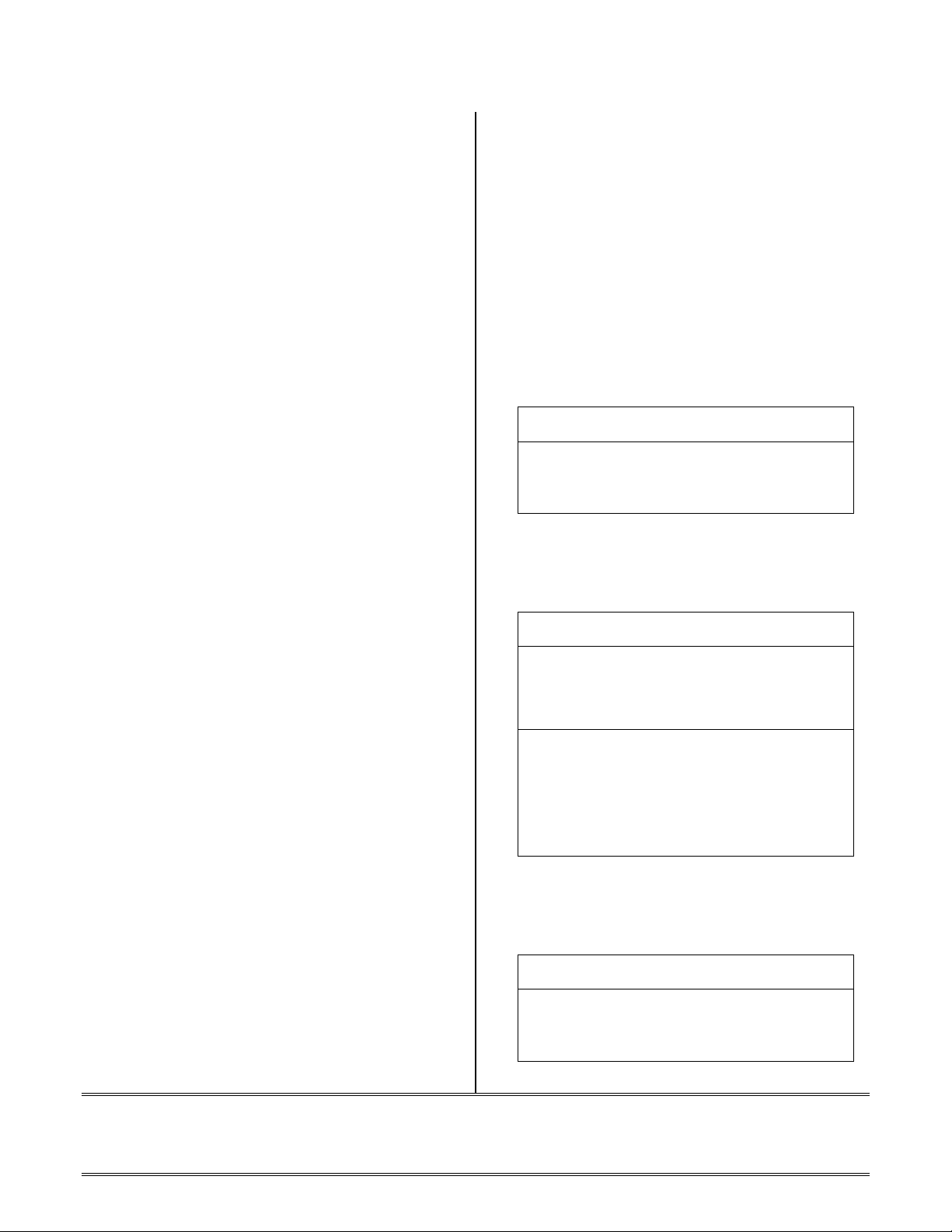
You specify section placement in memory in the
LDF (Linker-Description-File) for your
application. For more info on LDF files, see the
Linker Guide "LDF Programming Examples",
"Linker Description File Reference" and the
Overlay Example for the 2192-12.
ELFDUMP
The ElfDump utility shows the contents of
object and executable files in a readable format.
It has many options. Total section size and
variable placement within each section are
easily viewed via ElfDump section displays.
.VAR INITIALIZATION
The -legacy directives separated the .VAR/DM
and .VAR/PM declarations from the .INIT or
.INIT24 initializations. The new style is an "all
in one" declare and initialize.
The default is to treat the .VAR initializers as 16
bit constants. 24 bit constants are supported via
the /INIT24 qualifier on the .VAR directive.
The default for the .VAR directive initialization
is to treat the initializers as 16 bit constants.
DM Data Variable 16 Bit Initialization
For example, if you want to see a code
disassembly (mnemonic display) of section
"program" in the object file file9x:
elfdump -ni program file9x.doj
Please run ElfDump -help for the complete list
of options.
.VAR DIRECTIVE
The .VAR directive defines and initializes data
objects.
.var ( /init24 )? variableName
( '[' expression ']' )?
( '=' initializerList )? ;
.var ( /init24 )? variableName
(, variableName )* ;
.var ( /init24 )? '=' expression ','
( ',' expression)* ;
.section/dm data1;
.var buffer[2] = 0x1234, 0x4321;
16 bit PM data is correctly padded by the
assembler:
PM Data Variable 16 Bit Initialization
.section/pm program;
.var buffer[3] =
0x1234, 0x3210, 0x2130;
// 16 bit initialization in 24 bit
// memory with padding:
123400
321000
213000
To get a 24 bit constant initialization, specify
.var/init24.
PM Data Variable 24 Bit Initialization
.VAR directives must be within a section.
EE-130 Page 4
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
.section/pm program;
.var/init24 GiveMe24 = 0x123456;
Page 5
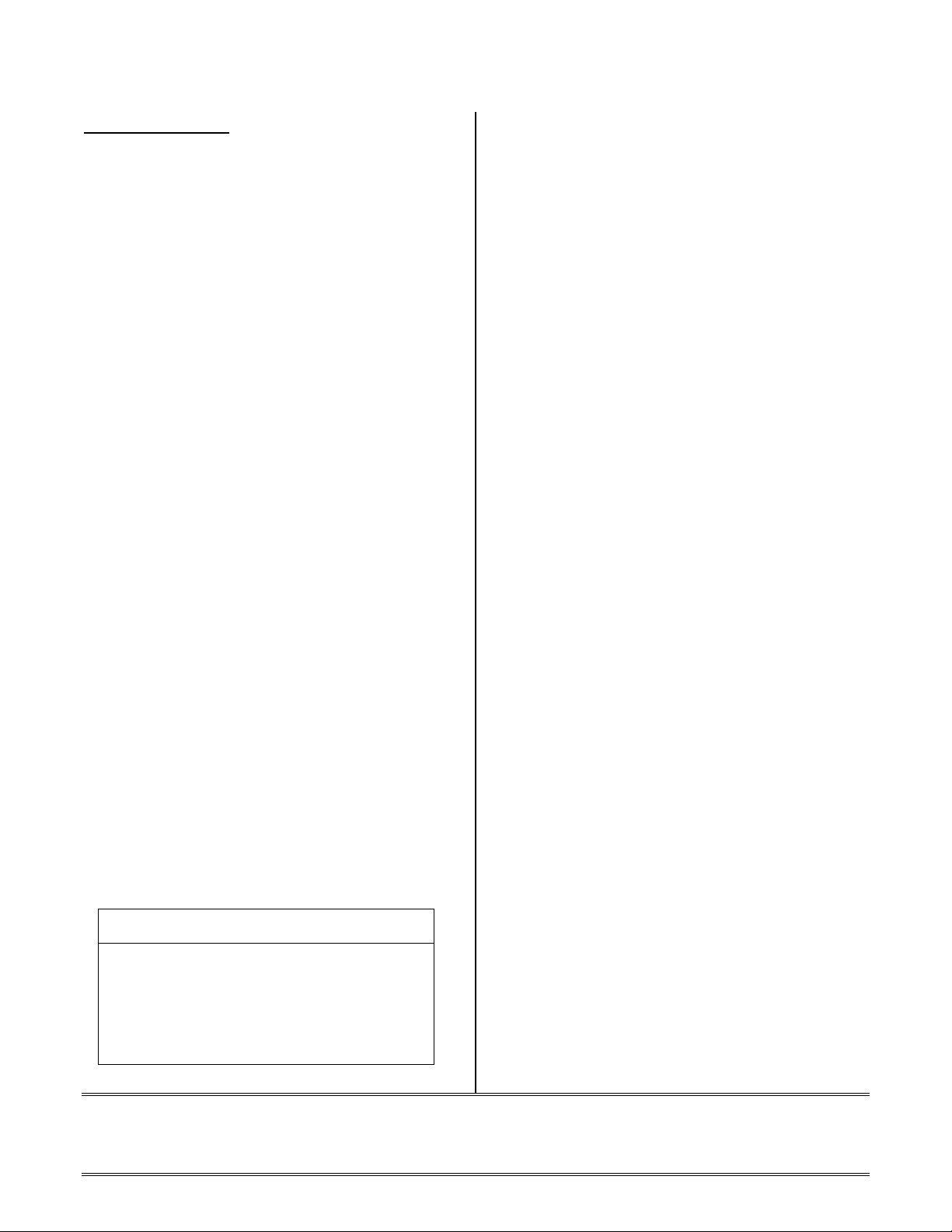
Recommendation:
MEMORY REFERENCE SYNTAX
Use the .VAR form with explicit sizing for
initialization. For example:
#define bufferSize 5
.section/data data1;
.var bufferOk[bufferSize]= 1,2,3,4,5;
.var bufferTooFew[bufferSize]= 1,2,3;
The assembler provides error diagnostics for an
incorrect # of initializers if you use the form of
the syntax with an explicit declarator followed
by its initializers. In the example above, the
bufferTooFew .VAR directive is explicitly
declared with 5 elements. Only 3 elements are
initialized and the assembler reports the
discrepancy.
[Warning W41] "test.asm":4 'bufferTooFew':
Too few initializers specified.
Expected 5 but found 3. The remaining 2
elements were initialized to zero.
.GLOBAL DIRECTIVE
Symbols declared as global are program scope
and are thus visible outside the local file. By
default, symbols are file scope (local). The
.global directive must be used to export a
symbol.
The ELF directives were designed with the
syntax and semantics of C in mind. Memory
reference notation has been extended to the
more familiar C-style. You may find this
notation self-documenting and less prone to
error or you may prefer to keep coding in the
style you are already accustomed to.
Note: The -legacy option is not needed to
process old memory reference syntax where the
ordering of the operands determined the action
taken. The new assembler always accepts both
the old and new memory reference syntax styles.
" SEE APPENDIX A:
MEMORY REFERENCE SYNTAX
The following examples are identified by
description and the instruction type number as
defined in the 219x Instruction Set Guide.
// Type 4 :
// Multifunction ALU or MACC with memory
// read or write using DAG post-modify
//
AF=AF+1,AX0=DM(I0,M1); ! legacy
AF=AF+1,AX0=DM(I0+=M1); // new syntax
// Type 21 : DAG Modify
//
MODIFY(I4,M5); ! legacy
MODIFY(I4+=M5); // new syntax
If another file needs to access the symbol,
specify .global in the file that declares it and
.extern in the file(s) that references it.
.global symbol (, symbol )* ;
.GLOBAL Example
.global Function1, Function2;
Function1:
ax1 = dm(1, i4);
Function2:
EE-130 Page 5
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
// Type 21a : DAG Immediate Modify
//
MODIFY(I4,3); ! legacy
MODIFY(I4+=3); // new syntax
// Type 29: DAG Memory Read/Write
// with Immediate Modify (Post-modify with
// update or offset without update)
//
DM(2,I1)=MR1; ! offset
DM(I1+2)=MR1; // offset, new syntax
// Type 32:
// Pre-modify offset/
// Post-modify Update
// DAG memory read/write
//
DM(M5,I4)=m3; ! pre-modify offset
DM(I4+M5)=m3; // new syntax
Page 6
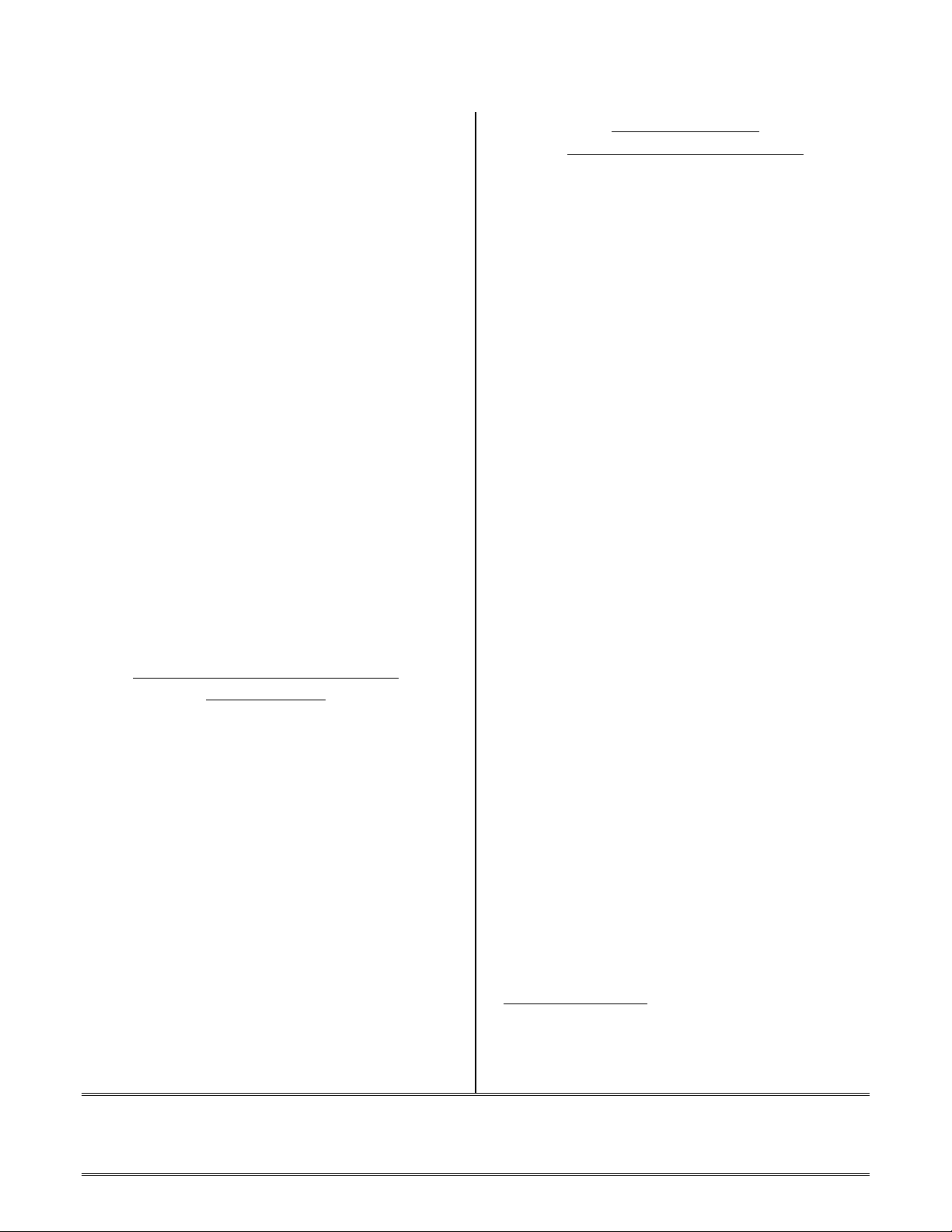
PRE-PROCESSOR
Here are the pre-processor basics:
EASM219x -legacy
Pre-Processing Flow of Control
• The pre-processor for the 219x assembler
and linker is the C style pre-processor
pp.exe. This is the same pre-processor used
by the other ELF assemblers and linkers,
including 21k, 2116x, and TigerSharc.
• The pre-processor for 21xx is asmpp.exe. To
preserve legacy code pre-processing, specify
the -legacy option and the 219x assembler
will call asmpp.exe as an additional preprocessing step after the pp.exe preprocessor.
• Specify the -sp (skip preprocessor) option
and neither pre-processor will be called.
Pre-Processor Flow Of Control
The 219x pre-processor produces "*.is" output
files. The naming convention for ADSP-219x
assembly source suffixes is .ASM.
EXAMPLE.DSP
#
PP.EXE
#
EXAMPLE.IS
#
ASMPP.EXE
#
EXAMPLE.APP
By default, the pre-processor files are written to
the temporary directory as specified by the
environment variable TMP on the PC (or
TMPDIR on Unix). The temporary files are
deleted upon completion of the assembly.
To obtain permanent copies of the pre-processor
temporary files, run the assembler with the preprocessor only option:
easm219x -pp -o example.tmp example.asm
EASM219x Default Pre-Processing
Flow of Control
EXAMPLE.ASM
#
PP.EXE
#
EXAMPLE.IS
When the -legacy option is specified, an
additional pre-processing pass is added after the
*.is is produced. It calls the legacy preprocessor asmpp.exe which processes the
.macro, .const, .include, and .local directives.
The legacy suffix convention for assembly
source was .DSP.
This runs the pre-processor on example.asm and
writes the temporary file example.is to the
current directory. It is not deleted.
easm219x -pp -legacy example.dsp
This runs the pre-processor on example.dsp and
leaves the temporary files example.is and
example.app in the current directory.
.CONST UPGRADE EXAMPLE
The .const directive is replaced by the C-style
#define macro and H# with 0x hex constant
syntax
21xx asmpp.exe
.CONST base=H#0D49,sqrt2=H#5A82;
EE-130 Page 6
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 7
219x pp.exe
#define base 0x0D49
#define sqrt2 0x5A82
uniqueLabel_2:
M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);MR1=DM(I6,M5);
uniqueLabel_3:
M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);MR1=DM(I6,M5);
PRE-PROCESSOR SYNTAX
.MACRO UPGRADE EXAMPLE
The .macro directive is replaced by the C-style
#define macro. The % arguments are replaced
by named arguments.
21xx asmpp.exe
.MACRO getsfirst(%1);
M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);%1=DM(I6,M5)
.ENDMACRO;
getsfirst(MR1);
219x pp.exe
#define getsfirst(Rg) \
M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);Rg=DM(I6,M5)
getsfirst(MR1);
PRE-PROCESSOR "?" EXAMPLE
The question mark "?" can be used to replace
the .local directive to avoid creating duplicate
labels when a macro is expanded multiple times.
219x pp.exe
If you are using the -legacy option, the legacy
pre-processor directives will be processed in
addition to the C pre-processor directives.
Without -legacy, rely solely on the C preprocessor directives.
" SEE APPENDIX B:
PRE_PROCESOR REFERENCE
EXPRESSIONS
There are places in the source where the
assembler processes symbols and literal
constants that may form expressions. We lump
these all under the category of "expressions".
SET POINTER
The "^" set point operator legacy syntax is
recognized when assembled with the -legacy
option. The "^" set point operator is no longer
required. Simply omit it when writing new code
for ADSP-219x.
-legacy Set Pointer
start: I2=^x_input;
#define getsfirst(Rg) \ uniqueLabel?: \ M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);Rg=DM(I6,M5);
// MACRO-INVOCATIONS
//
getsfirst(MR1)
getsfirst(MR1)
getsfirst(MR1)
219x Set Pointer
start: I2=x_input;
DATA INITIALIZATION FILES
The .VAR directive accepts a list of one or more
initializers from an external data file that by
convention is a file ending in ".dat" and referred
to as "dat" files. The legacy behavior for
// POST-EXPANSIONS
// Each label is unique
//
uniqueLabel_1:
M5=1;I6=1;MODIFY(I6,M4);MR1=DM(I6,M5);
EE-130 Page 7
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
initializers in the dat files was quirky. It treated
initializers explicitly typed in.INIT and INIT24
differently than those read in from *.dat files.
Page 8

OLD (21xx)
.var/dm/seg=dmdata x_input[n];
.init x_input : <xin.dat>;
xin.dat
1234
123a
NEW (219x)
.section/dm dmdata;
.var x_input[n] = "xin.dat";
OLD (21xx)
Default is case insensitive
-legacy
CALL AllMixedUp;
CALL allmixedup;
CALL ALLmixedUP;
Will be treated as referencing the same function.
To make case sensitive:
-legacy -c
xin.dat
0x1234
0x123a
There was some legacy behavior that seemed
just plain ol' wrong and the 9x -legacy doesn't
duplicate it. For instance "123" in the old tools
was treated as decimal "1230".
Recommendation:
The -legacy option has trouble with some of the
legacy dat files. It is recommended you change
the dat file constants to be hex prefixed with 0x
or H# whether you are using -legacy or not.
" SEE APPENDIX C:
DATA INITIALIZATION FILES
CASE SENSITIVITY
The 219x assembler is case sensitive, meaning
symbols must have the exact same case letter for
letter to be recognized as the same symbol.
The default for 21xx was case insensitive. It
uppercased all symbol references.
NEW (219x)
Case sensitive
ELF assemblers follow the C rules (case sensitive)
CALL AllMixedUp;
CALL allmixedup;
Will be treated as referencing different functions.
A POSSIBLE SURPRISE
If you are mixing legacy and non-legacy
assemblies you may be surprised by a linker
report for an unresolved reference. The reason
is the default on case sensitivity differs between
the old and new assemblers. You may
unintentionally reference and define a function
in a different case.
Look at the example below. ALLMIXEDUP is
referenced in all upper-case, but the definition is
the case sensitive AllMixedUp. The linker will
report an error for ALLMIXEDUP as
unresolved if these objects are linked together.
Solution: Use -legacy -c when mixing old and
new.
EE-130 Page 8
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 9

The -c option makes it case insensitive and
avoids any potential mismatch of definitions in
non-legacy modules.
-c Assembled with -legacy
.extern AllMixedUp;
Directives -- OLD and NEW
Welcome to the world of legacy directives and
the new ELF directives. This section shows the
legacy directives and how you would rewrite
them using the ELF directives instead. Side by
side examples are presented.
CALL AllMixedUp;
// with -c, case sensitive
// AllMixedUp
// without -c, case insensitive
// so upper-cased
// “ALLMIXEDUP”
Assembled without -legacy:
.global AllMixedUp;
AllMixedUp:
… code …
// case sensitive “as-is”
// “AllMixedUp”
.MODULE DIRECTIVE
In 21xx, every assembly program began with a
.module directive. In the ELF assemblers,
.section directives that define code sections
replace modules.
When the -legacy option is specified, the
assembler translates the .module directive to the
appropriate .section directive. "program" is the
name of the code section in the default *.ldf
(linker-description-file) used by the compilers.
In the absence of a specific /SEG qualifier on
the .module directive, the 219x assembler uses
"program" as the default name.
Use the .section directive when writing new
code. The .ENDMOD directive is not needed.
The beginning of the next section or the end-offile indicates the section ending point.
EXPRESSIONS SYNTAX
Expression syntax is for writing constants and
performing length, pointer, address and page
OLD (21xx)
.MODULE _dummy_;
.ENDMOD;
operations. Legacy expression syntax is
accepted only when the -legacy option is
.MODULE/SEG=myCode _dummy_;
.ENDMOD;
specified.
When writing new code, do not specify the
NEW (219x)
-legacy option and change to the new expression
syntax, where applicable.
" SEE APPENDIX D:
EXPRESSIONS REFERENCE
EE-130 Page 9
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
.SECTION/PM program;
.SECTION/PM myCode;
-orspecify /CODE in place of /PM on .SECTION
Page 10

.SECTION DIRECTIVES
ELF .SECTION directives provide the
assembler with explicit directions on where to
place the code and data. You can switch back
and forth between sections and the assembler
adds on to the appropriate section wherever it
had left off.
NEW (219x)
.SECTION/DM seg_mydata;
.VAR sqrt_coeff[3] =
0x5D1D, 0xA9ED, 0x46D6;
-or specify /DATA in place of /DM on .SECTION
Note: The ELF directives include a .PREVIOUS
directive for treating the sections as a stack. We
recommend you explicitly specify the section by
name to reduce the chance of an error when
adding new code.
.section/data data1;
.var …
.var …
.section/code program;
label1:
code …
code …
.section/data data1;
.var …
.section/code program;
code …
code …
label2:
code …
.VAR DIRECTIVE WITH SEG
.VAR DIRECTIVE WITHOUT SEG
In 219x, the segment is determined by which
section the .VAR directive is located within.
Every .VAR directive must reside within a
section.
OLD (21xx)
.VAR/DM sqrt_coeff[3];
.INIT sqrt_coeff :
H#5D1D, H#A9ED, H#46D6;
NEW (219x)
.SECTION/DM data1;
.VAR sqrt_coeff[3] =
0x5D1D, 0xA9ED, 0x46D6;
The .VAR directive in 21xx had an optional
-or specify /DATA in place of /DM on .SECTION
/SEG=segName qualifier. In 219x, the segment
is determined by which .section the .VAR
directive is located within. The /seg qualifier
does not appear on the .VAR directive. It is the
section name.
-legacy .VAR WITHOUT /SEG
When the assembler is run in the -legacy mode,
it must determine what section each .VAR
OLD (21xx)
belongs to. If the .var has an explicit
/seg=segName qualifier it creates a section by
.VAR/DM/SEG=seg_mydata sqrt_coeff[3];
.INIT sqrt_coeff :
H#5D1D, H#A9ED, H#46D6;
EE-130 Page 10
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
that name (or adds it to an already existing one
of that name).
Page 11

If there is no /seg=segName qualifier, the 9x
assembler defaults to "data1" for DM and
"program" for PM. (These match the section
names the compiler uses).
-legacy .VAR WITH /ABS
To support the -legacy /ABS=address qualifier
on the .var directive, the new assembler
automatically generates the linker commands in
an LDF file that can be included in your
application's LDF.
-legacy .VAR/ABS=address
#define CMN_BASE 0x010000
.VAR/DM/ABS=CMN_BASE+0x22 eq_outq;
.GLOBAL eq_outq;
Auto-Generates RESOLVE for LDF
• RESOLVE commands
OLD (21xx)
.MODULE test;
.VAR/DM myData[3];
.INIT myData : H#001, H#002, H#003;
.ENDMOD;
NEW (219x)
.SECTION/DM data1;
.VAR myData[3] = 0x001, 0x002, 0x003;
.SECTION/PM program;
.VAR AND .INIT24 IN PM SECTION
Declaring and initializing PM data in 21xx was
accomplished via the .VAR directive for the
declaration and the .INIT24 directive for the
initialization.
// .var eq_outq in "cmn.asm", line 12,
// section 'data1', section index 4
//
RESOLVE( eq_outq, 0x10022 )
Include in Application LDF
• LDF INCLUDE command
INCLUDE(resolve_cmn.ldf)
.VAR AND .INIT DIRECTIVES
Declaring and initializing 16 bit data in 21xx
was accomplished via the .VAR directive for the
declaration and the .INIT directive for the
initialization.
With the ELF directives, the .VAR directive
declares and initializes "all in one" directive.
The default is 16-bit initialization.
With the ELF directives, the .VAR directive
declares and initializes. The /INIT24 qualifier is
needed to indicate it is a full 24 bit initialization.
Remember, the .VAR directive default is 16 bits
whether it is DM or PM data.
OLD (21xx)
.MODULE test;
.VAR/PM myPMData;
.INIT24 myPMData: 0x123456;
.ENDMOD;
NEW (219x)
.SECTION/PM program;
.VAR/INIT24 myPMData = 0x123456;
EE-130 Page 11
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 12

"TRICK OF THE TRADE"
.EXTERNAL DIRECTIVES
If you ever need to work-around an assembler
encoding bug, here is a way to do it with the
ELF directives:
.SECTION/PM program;
// You can explicitly assemble an
// instruction, by placing a
// .var/init24 in a code section
// The following is the opcode for
// DM(I4,M5) = AX0;
.VAR/INIT24 myMove = 0x157001;
.VAR WITH BUFFER LENGTH
In 21xx, the unary operator % was used to
obtain the length.
With the ELF directives, use the LENGTH()
keyword. % is the binary operand modulus
operator.
OLD (21xx)
Change the spelling of the .external directive
keyword to .extern. The two directives are
equivalent. This is just a name change.
OLD (21xx)
/* ptr to the Equalizer data */
.EXTERNAL Complex_Filter_Id;
NEW (219x)
/* ptr to the Equalizer data */
.EXTERN Complex_Filter_Id;
DATA DIRECTIVES REFERENCE
Appendix E provides a summary of data
directives from 21xx and other legacy
assemblers and their equivalent in the ELF
directives.
.MODULE test;
.VAR/DM x_input[10];
! % is legacy length operator
start: L2=%x_input;
.ENDMOD;
" SEE APPENDIX E:
DATA DIRECTIVES REFERENCE
JUMP AND CALL OPTIMIZATIONS
A new optimization is available with the ADSP-
NEW (219x)
.SECTION/DM data1;
.VAR x_input[10];
.SECTION/PM program;
start: L2=LENGTH(x_input);
219x tools to automatically convert out of range
jump or call instructions to long.
The jump/call optimization is optional. You can
continue to code with short and long syntax as
you did in 21xx, if you prefer. (The 21xx
method means you must manually optimize the
code).
EE-130 Page 12
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 13

The -legacy option has no bearing on the
jump/call syntax or expansion option.
SHORT VERSUS LONG SYNTAX
The assembler will encode the instructions
based on syntax. It encodes short versus long
jumps and calls based on the keyword that is
specified. The "L" means long.
• LJUMP vs JUMP
• LCALL vs CALL
Out of range short jumps/calls receive errors
is done automatically by the tools. There is no
re-coding needed at the source level.
" SEE APPENDIX F:
JUMP/CALL EXPANSION REFERENCE
UNIVERSAL ELF DIRECTIVES
The set of universal ELF directives are common
among the family of ADI ELF assemblers, but
please keep in mind that some of them have no
meaning for a particular processor. For
example, the floating point directives are not
applicable to 219x which is a fixed point
processor.
[Error E33] ”JumpOutOfRange10.asm":2539
Jump offset out of range: -4096 to 4095
(Type 10). Jump at PC offset 464 to
destination '_L_250512' at PC offset 5764.
Recode with LJUMP or use the -jcs2l
(JumpCallShort2Long) option for automatic
conversion to long jump.
Long jumps/calls range that fit in a short range
receive warnings.
[Warning W32] "LJumpShort.asm":32
Jump doesn't require long range: 24 bit address
(Type 36 2 Word Instruction). LJUMP at PC
offset 58 to destination 'endLabel' at PC offset
154. This can be recoded with a single word
Type 10 JUMP.
-JCS2L OPTION (Jump-Call-Short-2-Long)
A new optimization was introduced in the
ADSP-219x assembler and linker.
easm219x -jcs2l
easm219x -JumpCallShort2Long
The -jcs2l option instructs the tools to change
out of range short jumps and calls to long. This
The Reference chart is complete. Some of these
directives are used by the compiler. You will see
them if you look at the "*.s" intermediate file
produced by the compiler.
" SEE APPENDIX G:
ELF DIRECTIVES REFERENCE
SOFTWARE UPDATE NEWS
The following are new features since the initial
7.0 release that are relevant to upgrading from
5.x/6.x:
• Comment Conversion
• .VAR Blocks and Initialization
CommentConverter
The { } legacy comment syntax is supported for
–legacy assemblies.
It is no longer supported for assemblies without
the –legacy option.
EE-130 Page 13
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 14

A comment conversion utility is available. It
will automatically upgrade sources with legacy
comment styles, converting them to C/C++ style
comments.
Run commentconverter –help for a complete list
of options. Here is a highlight. Note that there is
no space between the –rs and its argument:
The declaration of one or more symbols in a
.VAR directive guarantees consecutive
placement in both 5.x/6.x and the new toolset.
Use C-style initialization syntax to initialize
data buffers that must be kept contiguous by the
linker.
-rsall (default)
replace "{ }" and "!" style comments
-rs{
replace "{ }" style comments
-rs!
replace "!" style comments
Example:
commentconverter –rs{
OldFile.dsp >NewFile.dsp
OLD (21xx)
SendMessage: { transmit data }
NEW (219x)
SendMessage: /* transmit data */
OLD (21xx)
.var/dm LState1[2], LState2[2];
.init Lstate1 : 0x10, 0x11;
.init Lstate2 : 0x20, 0x21;
NEW (219x)
.section/dm data1;
.var Lstate1[2] = { 0x10, 0x11 },
Lstate2[2] = { 0x20, 0x21 };
CONCLUSION
This completes the grand tour of the "old" and
"new" in the ADSP-21xx assembler family.
If you are writing new assembly code for the
ADSP-219x, please see the online Assembler
.VAR Blocks and Initialization
and Linker documentation in your software kit
for more details. They are PDF files located in
By default, all data within a section is placed in
consecutive memory locations by the ELF
linker.
With the linker –ip (individual placement)
option, data maybe re-arranged.
EE-130 Page 14
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
the installation directory:
\Program Files\Analog Devices\
VisualDSP\Docs
They are also available online from within the
VisualDSP IDE.
Page 15

a
a Engineer To Engineer Note EE-130
aa
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781) 461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
APPENDIX A: MEMORY REFERENCE SYNTAX
(Referenced from Page 5)
TYPE OLD NEW
POST MODIFY WITH
UPDATE
PRE MODIFY OFFSET
IMMEDIATE OFFSET
IMMEDIATE MODIFY
DM(<Ireg>,<Mreg>) DM(<Ireg> += <Mreg>)
DM(<Mreg>,<Ireg>) DM(<Ireg> + <Mreg>)
DM(<Expr >, <Ireg>)
<Expr> is an 8 bit 2's compliment number
DM(<Ireg>,<Expr>)
<Expr> is an 8 bit 2's compliment number
DM(<Ireg> + <Expr>)
<Expr> is an 8 bit 2's compliment number
DM(<Ireg> += <Expr>)
<Expr> is an 8 bit 2's compliment number
Copyright 2000, Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Analog Devices assumes no responsibility for customer product design or the use or application of customers’ products or
for any infringements of patents or rights of others which may result from Analog Devices assistance. All trademarks and logos are property of their respective holders. Information
furnished by Analog Devices Applications and Development Tools Engineers is believed to be accurate and reliable, however no responsibility is as sumed by Analog Devices
regarding the technical accuracy of the content provided in all Analog Devices’ Engineer-to-Engineer Notes.
Page 16

APPENDIX B: PRE-PROCESSOR REFERENCE
(Referenced from Page 7)
LEGACY
PURPOSE UPGRADING NEW BEHAVIOR
DIRECTIVE
*.app file Pre-processor output
file is *.app.
.const x Constant definition.
Pre-processor is
asmpp.exe.
.include Pre-processor is
asmpp.exe.
.local symbol; Applies to program
labels in macros to
prevent duplicate
names upon macro
expansion.
.macro ..
.endmacro;
Macro definition.
Pre-processor is
asmpp.exe.
*.is 219x pre-processor output file
is *.is.
#define x C pre-processing style
#include C pre-processing style
Put question mark at
the end of each label
reference within the
macro definition
#define
DoMacro(codeBlock) \
do (pc,macLabel?)
until ce;\
codeBlock \
macLabel?:
(See example)
#define C pre-processing style
%
Example:
.macro alter(%1);
! comment-style 1
{ comment style 2 }
/* multi-line
C comment style */
Macro arguments. Example:
#define alter(x)
M5=x;
Comment syntax
supported in
asmpp.exe.
/* multi-line
C comment style */
// C++ comment style
C style macro arguments
pp.exe supports C and C++
comment syntax only. .
Use the commentconverter
utility to upgrade sources with
legacy comment styles:
! comment style 1
{ comment style 2 }
EE-130 Page 16
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 17

APPENDIX C: DATA INITIALIZATION FILES
(Referenced from Page 8)
The example below is the <xin.dat> data file from the Vect2100.dsp example.
Change the hex prefix 00 to 0x. Commas are allowed and are optional.
-legacy Syntax New Syntax
(with commas)
0001
0002
0003
0004
0005
0006
0007
0008
0009
000A
0x01,
0x02,
0x03,
0x04,
0x05,
0x06,
0x07,
0x08,
0x09,
0x0A
New Syntax
(without commas)
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
0x06
0x07
0x08
0x09
0x0A
EE-130 Page 17
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 18

APPENDIX D: EXPRESSIONS REFERENCE
(Referenced from Page 9)
LEGACY
PURPOSE UPGRADING NEW BEHAVIOR
EXPRESSION
B# prefix
B#01010101
00 prefix
0001, 000A
H# prefix
H#0D49
%symbol LENGTH operation
Binary format. B# prefix
B#01010101
Hex constant. 0x prefix
0x01, 0x0a
Hex constant. 0x prefix
0x0D49
LENGTH(symbol) LENGTH operation
on symbol.
No changes needed.
Same behavior.
New syntax for hex
constants.
New syntax for hex
constants.
on symbol.
^symbol set pointer Omit ^ Operator not
required.
~ Complement ~ No changes needed.
Same behavior.
Address(symbol) Address operation
gets lower 16 bits of
address(symbol) No changes needed.
Same behavior.
address
page symbol
pageof(symbol)
Page operation gets
upper 16 bits of
page(symbol) Use () syntax.
address
label names 1) Reserved words
2) Case insensitive is
default
EE-130 Page 18
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
1) Reserved words
2) Case sensitive!
Case sensitive
Use -legacy -c for
case sensitive
Page 19

APPENDIX E: DATA DIRECTIVES REFERENCE
(Referenced from Page 12)
LEGACY DIRECTIVE PURPOSE UPGRADING NEW BEHAVIOR
.dmseg id; Data memory segment. .section/data id; -or-
or .section/dm id;
.endmod Indicates the end of a
module.
.entry
.export
.external Allows references to
.global Makes symbol visible
Makes label visible outside
the current file.
symbols declared in other
files via .global or .entry.
outside the current file.
-- omit -- No need for an end marker.
.global Makes label visible outside
.extern Allows references to
.global Makes symbol visible
Data memory segment.
the current file by declaring
the symbol with ELF
binding STB_GLOBAL.
symbols declared in other
files via .global.
outside the current file by
declaring the symbol with
ELF binding
STB_GLOBAL.
.init Data initializer(s) are 16
bits.
.init24 Data initializer(s) are 24
bits.
.init x : <fileName> Data initialization from a
file.
EE-130 Page 19
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
.var within either
.section/dm or .section/pm
.var/init24 within
.section/pm
.var x[5] = "fileName"; Quotes replace angle
Data initializer(s) are 16
bits.
Data initializer(s) are 24
bits.
brackets on filename. The
"=" is required.
Page 20

APPENDIX E: DATA DIRECTIVES REFERENCE (continued)
LEGACY DIRECTIVE PURPOSE UPGRADING NEW BEHAVIOR
.module qualifiers
0 or more qualifiers:
/ABS = addr
/BOOT =0-7
/RAM or /ROM
/SEG = id
/STATIC
.page
.pmseg Program memory segment. .section/code id; -or-
.port/dm pName1;
.port/pm pName2;
/push and /pop section
qualifiers
.setdata expr
A single .module for code
definition.
Appears before the .module
directive for paged memory
system.
Declares a memory mapped
I/O port.
Keeps a stack of sections. Explicitly reference the
Appears to be an
undocumented feature in
a2100 to specify a data or
instruction encoding
explicitly.
.section qualifiers
0 or more qualifiers and
LDF linker file
/ABS = addr
/BOOT =0-7
/RAM or /ROM
/SEG = id
/STATIC
-- --
.section/pm id;
Use .var and create a
section in the linker *.LDF
file for each port variable.
section by name
.var/init24 = expr; 219x equivalent to encode
One or more code sections
of contiguous memory.
Program memory segment.
Treat as any other external
variable for linker to
resolve.
219x equivalent.
an instruction explicitly.
.var qualifiers
0 or more qualifiers:
/ROM or /RAM
/PM or /DM
/CIRC
/ABS = expr
/SEG = id
/STATIC
.var/abs=100 Declare symbol with
.var/circ Declare a circular buffer. .var 219x has base registers.
EE-130 Page 20
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
21xx used .var qualifiers. .var qualifiers:
/init24
.section/abs=100 …;
absolute placement.
.var
Use .section qualifiers, not
.var qualifiers.
If DAG related, may not
need to use the .var/abs in
9x.
Page 21
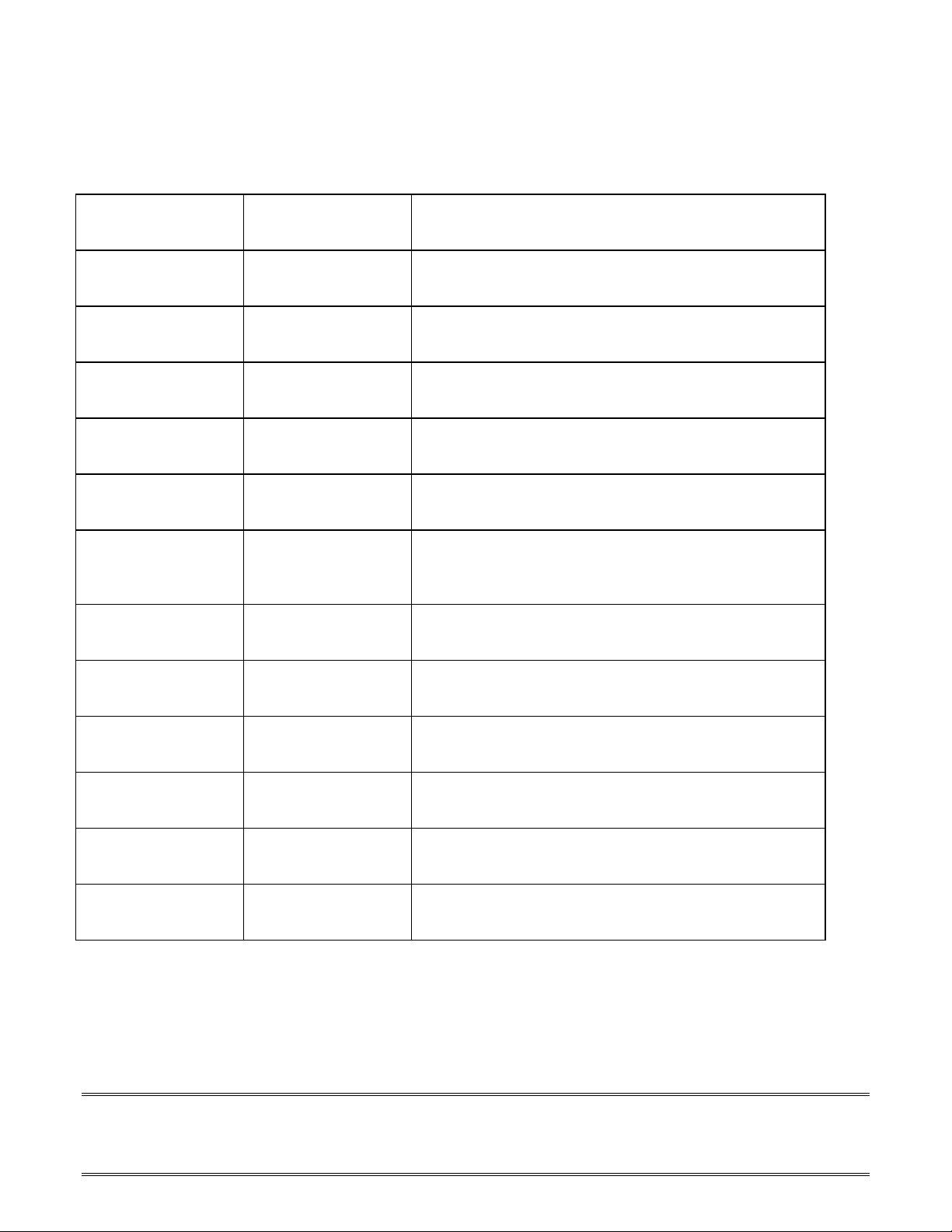
APPENDIX F: UNIVERSAL ELF DIRECTIVES
DIRECTIVE 219X (Supported) BEHAVIOR
.align Yes Specifies a byte alignment requirement.
.extern Yes Variable is imported (not defined in file scope).
.file Yes Override the filename given on the command line.
.global Yes Variable is program scope (exported).
.leftmargin Yes Left margin of listing page.
#line Yes Output from pre-processor for tracking line numbers of the
original source before pre-processing.
.newpage Yes Page break in listing.
.pagelength Yes Length of listing page.
.pagewidth Yes Width of listing page.
.precision N/A Number of significant bits in floating point constant.
.previous Yes Reverts to the previous section.
.round_minus N/A IEEE 754 Round to negative infinity.
EE-130 Page 21
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 22

APPENDIX F: UNIVERSAL ELF DIRECTIVES (continued)
DIRECTIVE 219X (Supported) BEHAVIOR
.round_nearest N/A IEEE 754 Round to nearest (the default).
.round_plus N/A IEEE 754 Round to positive infinity.
.round_zero N/A IEEE 754 Round to zero.
.section Yes Names a contiguous block of program or data memory
.section qualifiers
/data or /DM
/code or /PM
/ABS = expr
/BOOT = expr
/RAM or /ROM
/SEG = id
/STATIC
.size Yes Size calculation for sizing functions
.type Yes Changes a default data symbol type
.size directive Yes Specifies the calculation for the size of a function
Var symbol qualifiers
/INIT24 for 24 bit
initialization
Yes Section qualifiers for 219x
(for C compiler).
(for EPC compiler)
Yes Symbol qualifiers for 219x
EE-130 Page 22
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Page 23

APPENDIX G: JUMP/CALL EXPANSION
JUMP INSTRUCTIONS DELAY BRANCH SLOTS RANGE
Type 10
13-Bit Relative Conditional Jump
Yes (Optional)
PC Relative
IF NE JUMP label1 (DB);
// slot 1
// slot 2
IF NE JUMP label1;
Type 10a
16-Bit Unconditional Jump
JUMP label2 (DB);
// slot 1
// slot 2
JUMP label2;
Type 36 (2 Word)
Far (long) Conditional Jump
IF AV JUMP labelFarAway;
JUMP labelFarAway;
IF NOT CE LJUMP labelFar;
LJUMP labelFarAway;
CALL INSTRUCTIONS DELAY BRANCH SLOTS RANGE
Type 10
There is no 13-Bit Conditional
CALL
DB slots are executed whether the
JUMP is taken or not.
Yes (Optional) PC Relative
No Absolute Address
N/A N/A
-4096 to +4095
-32768 - +32767
Can reach any portion of the 24bit address space.
Type 10a
16-Bit Unconditional CALL
CALL funcNextDoor (DB);
// slot 1
// slot 2
CALL funcNextDoor;
Type 36 (2 Word)
Far (long) Conditional CALL
IF AV CALL FuncFarAway;
CALL FuncFarAway;
IF NOT CE LCALL FuncFar;
LCALL FuncFarAway;
EE-130 Page 23
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices’ DSP components and development tools
Phone: (800) ANALOG-D, FAX: (781)461-3010, EMAIL: dsp.support@analog.com, FTP: ftp.analog.com, WEB: www.analog.com/dsp
Yes (Optional) PC Relative
-32768 - +32767
No Absolute Address
Can reach any portion of the 24bit address space.
 Loading...
Loading...