Page 1
AN-595
a
APPLICATION NOTE
One Technology Way • P.O. Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106 • Tel: 781/329-4700 • Fax: 781/326-8703 • www.analog.com
Understanding Pin Compatibility in the
TxDAC
®
Line of High Speed D/A Converters
by David Carr
INTRODUCTION
The TxDAC product line is comprised of three generations
of high performance, low power CMOS digital-to-analog
converters (DACs). Products are available in pin compatible 8-, 10-, 12-, and 14-bit versions and are specifically
optimized for the transmit signal path of communication
systems. All of the devices share the same interface
options, small outline package, and pinout, providing an
upward or downward component selection path based on
performance, resolution, and cost.
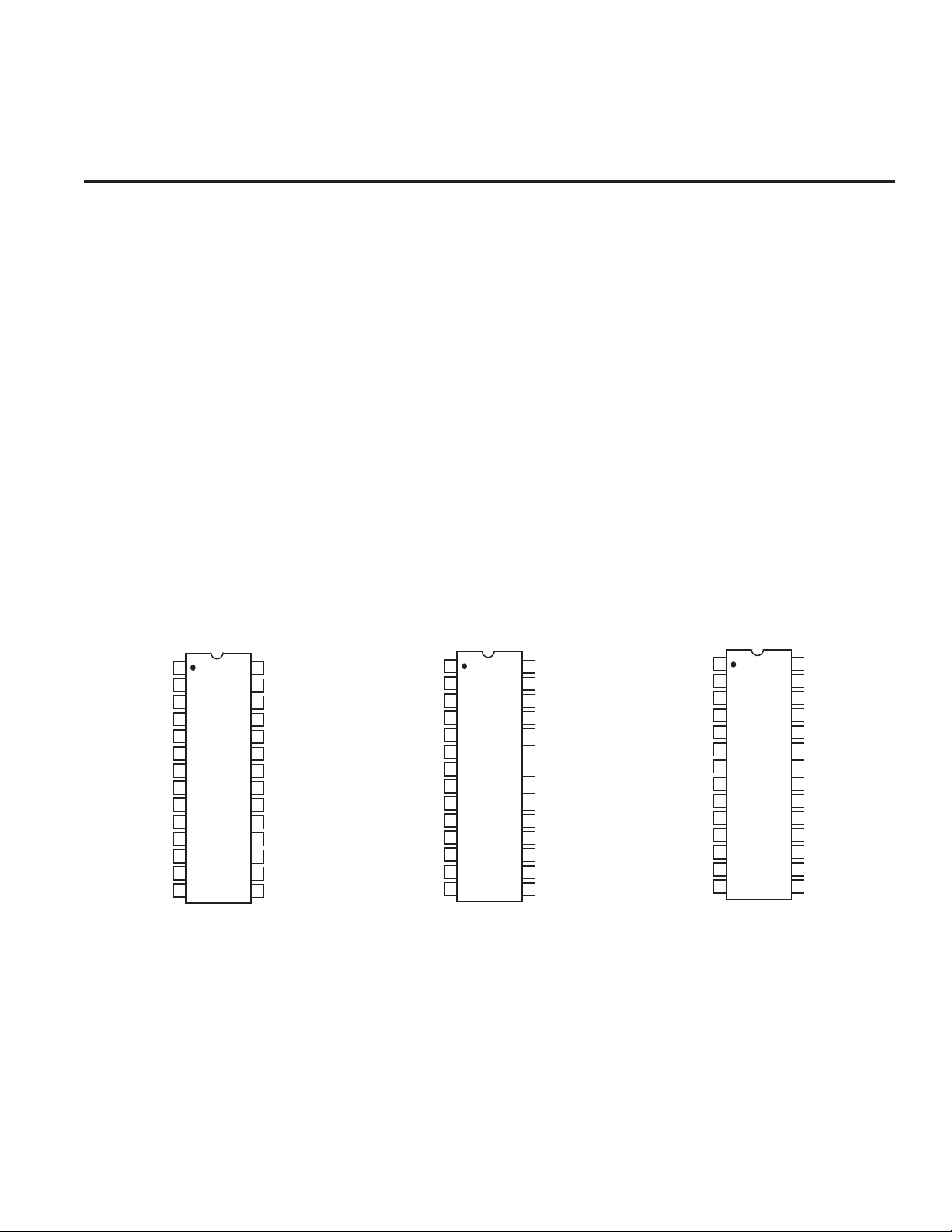
Pin compatibility to previous generations has been maintained throughout the evolution of the TxDAC product
line (refer to Figures 1–3). There are differences in power
supply requirements, as well as functional options and
bypassing requirements that need to be comprehended
when migrating a design between generations.
FAMILY DESCRIPTIONS
The first family in the TxDAC line was the AD9708/
AD9760/AD9762/AD9764 (AD976x) series. This was the
first CMOS DAC family on the market designed
specifically for communications applications. It offered
flexibility in the allowable supply voltage (2.7 V to 5.5 V),
with better performance than BiCMOS alternatives that
were prevalent at the time.
(MSB) DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
(LSB) DB0
1
2
3
4
5
AD9764
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
NC = NO CONNECT
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
CLOCK
DVDD
DCOM
NC
AVDD
COMP2
I
OUTA
I
OUTB
ACOM
COMP1
FS ADJ
REFIO
REFLO
SLEEP
(MSB) DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
(LSB) DB0
1
2
3
4
5
AD9754
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
NC = NO CONNECT
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
CLOCK
DVDD
DCOM
NC
AVDD
ICOMP
I
OUTA
I
OUTB
ACOM
NC
FS ADJ
REFIO
REFLO
SLEEP
(MSB) DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
(LSB) DB0
Figure 3. AD9744 PinoutFigure 1. AD9764 Pinout Figure 2. AD9754 Pinout
1
2
3
4
5
AD9744
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
NC = NO CONNECT
28
CLOCK
27
DVDD
26
DCOM
25
MODE
24
AVDD
23
RESERVED
22
I
OUTA
21
I
OUTB
20
ACOM
19
NC
18
FS ADJ
17
REFIO
16
REFLO
15
SLEEP
TxDAC is a registered trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
REV. 0
© Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
Page 2
AN-595
Subsequently the AD9750/AD9752/AD9754 family
(AD975x) was introduced, which provided increased
performance over the first generation. The analog supply voltage was restricted (4.5 V to 5.5 V) to achieve the
performance increase. However, the digital supply
maintained the flexibility from the previous generation
to allow for compatibility with numerous logic families.
The most recent introduction in the TxDAC line is the
AD9740/AD9742/AD9744 (AD974x series). This family
was designed on an advanced submicron CMOS process
supports 3.3 V supplies only. The AD974x series
that
offers the highest performance available in the industrystandard TxDAC pinout.
Power Supply Requirements
Because of the technology advances made in each generation, there are varying requirements for the power
supply voltage. Table I illustrates the requirements for
each generation.
Table I. Power Supply Requirements
Family Analog Supply Digital Supply
AD976x 2.7 V to 5.5 V 2.7 V to 5.5 V
AD975x 4.5 V to 5.5 V 2.7 V to 5.5 V
AD974x 3.0 V to 3.6 V 3.0 V to 3.6 V
Sample Rate
The AD976x and AD975x families were designed on
a 5 V CMOS process and support a maximum data rate
of 125 MSPS. A more advanced 3 V CMOS process that
supports an update rate of 165 MSPS was used for the
AD974x family. Table II summarizes the supported clock
rate for each family.
Table II. Maximum Sample Rate
Family Maximum f
AD976x 125 MSPS
AD975x 125 MSPS
AD974x 165 MSPS
MODE Selection
A MODE pin was added to the AD974x family to allow
either Offset Binary or Two’s Complement data to be
processed. The first two generations supported Offset
Binary only. The MODE function is controlled by Pin 25,
CLOCK
which was designated as a No Connect (NC) in the earlier devices. This pin has an internal pull-down that
results in the part being placed in the Offset Binary data
mode if left floating. Therefore, it is compatible with
existing AD976x and AD975x designs in which Pin 25 is
unconnected. Table III details the allowable external
connections for the MODE pin and the resultant data format that is selected.
Table III. MODE Control for AD974x
MODE Pin Data Format
Float Offset Binary
DCOM Offset Binary
DVDD Two’s Complement
COMP1 and COMP2 Pins
The AD976x family contains two internal bias nodes
(COMP1 and COMP2) that must be externally bypassed.
One of the bias pins was eliminated in the AD975x family. Neither of the internal bias points is externally
decoupled in the AD974x family. However, one of the
pins is declared as RESERVED in the AD974x pinout to
support a factory test mode.
This pin should be disconnected (floated) on the PCB. It
can also be connected to ground through a capacitor but
should not be connected directly (or resistively) to either
ground or the supply rail. The requirements for these
two pins are detailed in Tables IV and V.
Table IV. Name and Connection for Pin 19
Family Pin 19 Name Pin 19 Connection
AD976x COMP1 0.1 µF to AVDD
AD975x NC No Internal Connection
AD974x NC No Internal Connection
Table V. Name and Connection for Pin 23
Family Pin 23 Name Pin 23 Connection
AD976x COMP2 0.1 µF to ACOM
AD975x ICOMP 0.1 µF to ACOM
AD974x RESERVED Float or capacitively
couple to ACOM
E02998–0–6/02(0)
–2–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...