Multiformat 11-Bit
A
FEATURES
High definition (HD) input formats
16-bit, 24-bit (4:2:2, 4:4:4) parallel YCrCb
Fully compliant with
SMPTE 274M (1080i, 1080p @ 74.25 MHz)
SMPTE 296M (720p)
SMPTE 240M (1035i)
RGB in 3-bit × 8-bit 4:4:4 input format
HDTV RGB supported
RGB, RGBHV
Other HD formats using async timing mode
Enhanced definition (ED) input formats
8-, 16-, 24-bit (4:2:2, 4:4:4) parallel YCrCb
SMPTE 293M (525p)
BTA T-1004 EDTV2 (525p)
ITU-R BT.1358 (625p/525p)
ITU-R BT.1362 (625p/525p)
RGB in 3-bit × 8-bit 4:4:4 input format
Standard definition (SD) input formats
CCIR-656 4:2:2 8-bit or 16-bit parallel input
HD output formats
YPrPb HDTV (EIA 770.3)
RGB, RGBHV
CGMS-A (720p/1080i)
ED output formats
Macrovision® Rev 1.2 (525p/625p)
CGMS-A (525p/625p)
YPrPb progressive scan (PS), EIA-770.1, EIA-770.2
RGB, RGBHV
SD output formats
Composite NTSC M/N
Composite PAL M/N/B/D/G/H/I, PAL-60
SMPTE 170M NTSC-compatible composite video
ITU-R BT.470 PAL-compatible composite video
S-video (Y/C)
EuroScart RGB
Component YPrPb (Betacam, MII, SMPTE/EBU N10)
Macrovision Rev 7.1.L1
CGMS/WSS
Closed captioning
GENERAL FEATURES
Simultaneous SD/HD or PS/SD inputs and outputs
Oversampling up to 216 MHz
Programmable DAC gain control
HDTV Video Encoder
ADV7322
Sync outputs in all modes
On-board voltage reference
Six 11-bit precision video DACs
2-wire, serial I
Dual I/O supply 2.5 V/3.3 V operation
Analog and digital supply 2.5 V
On-board PLL
64-lead LQFP package
Lead-free (Pb-free) free product
APPLICATIONS
Enhanced versatile disk (EVD) players
SD/PS DVD recorders/players
SD/PS/HDTV display devices
SD/HDTV set-top boxes
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
S7–S0
HSYNC
VSYNC
BLANK
CLKIN_
CLKIN_B
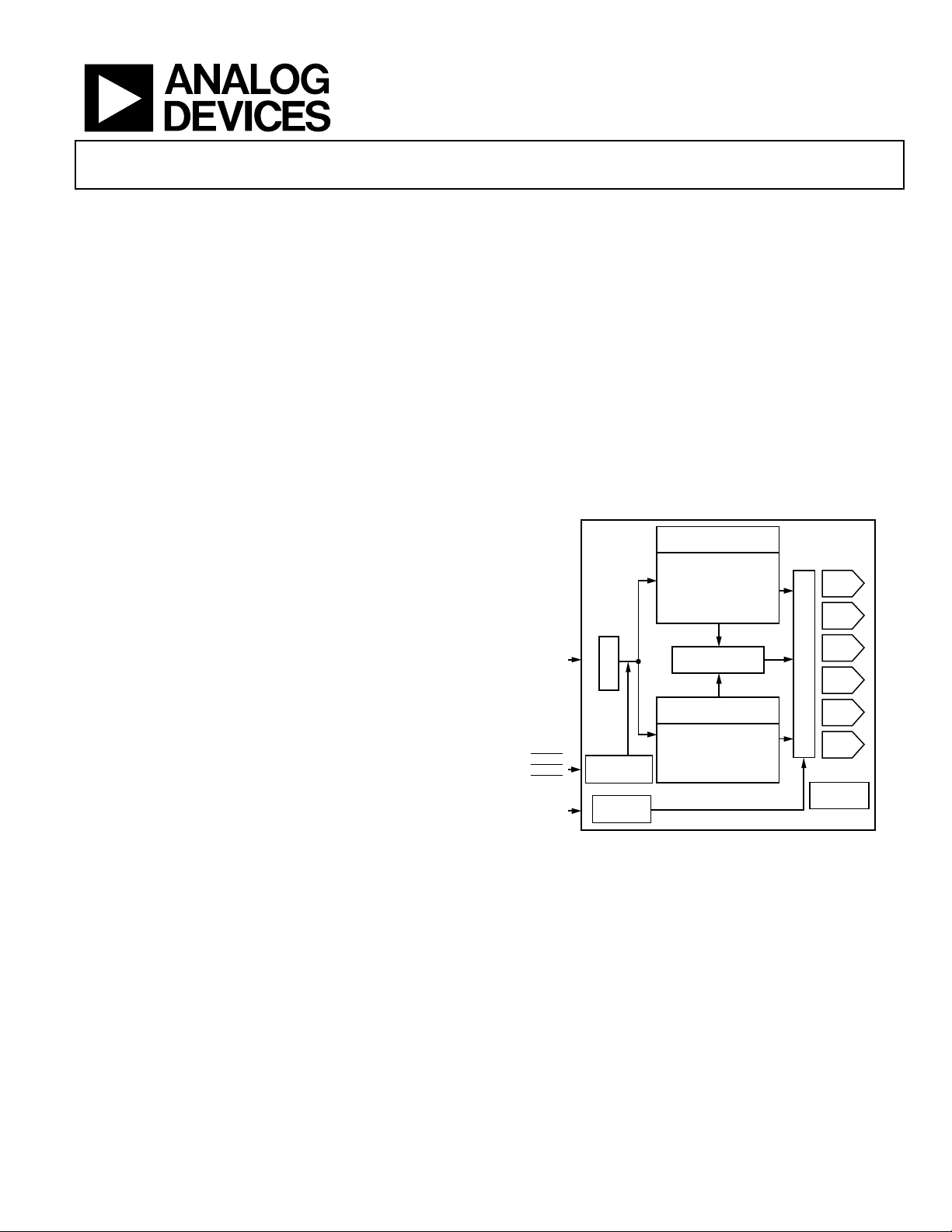
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV7322 is a high speed, digital-to-analog encoder on a
single monolithic chip. It includes six high speed video DACs
with TTL-compatible inputs. It has separate 8-, 16-, and 24-bit
input ports that accept data in high definition (HD) and/or
standard definition (SD) video format. For all standards, external
horizontal, vertical, and blanking signals, or EAV/SAV timing
codes, control the insertion of appropriate synchronization signals
into the digital data stream and, therefore, the output signal.
2
C® interface, open-drain configuration
SD
CONTROL BLOCK
COLOR CONTROL
BRIGHTNESS
DNR
GAMMA
PROGRAMMABLE
FILTERS
SD TEST PATTERN
D
E
M
U
X
TIMING
GENERATOR
PLL
PROGRAMMABLE
RGB MATRIX
HD
CONTROL BLOCK
HD TEST PATTERN
COLOR CONTROL
ADAPTIVE FILTER CTRL
SHARPNESS FILTER
Figure 1. Simplified Functional Block Diagram
ADV7322
11-BIT
DAC
11-BIT
O
DAC
V
E
R
11-BIT
S
DAC
A
M
11-BIT
P
DAC
L
I
N
11-BIT
G
DAC
11-BIT
DAC
I2C
INTERFACE
05135-001
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADV7322
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 6
Gamma Correction .................................................................... 53
Dynamic Specifications ............................................................... 7
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 8
Timing Diagrams.............................................................................. 9
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 16
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................16
ESD Caution................................................................................ 16
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 17
Typical Performance Characteristics ...........................................19
MPU Port Description................................................................... 23
Register Access................................................................................ 25
Register Programming............................................................... 25
Subaddress Registers (SR7 to SR0)........................................... 25
Input Configuration....................................................................... 38
SD-Only mode............................................................................ 38
PS-Only or HDTV-Only Modes .............................................. 38
Simultaneous SD/PS or SD/HDTV Modes............................. 38
PS Mode at 27 MHz (Dual Edge) or 54 MHz......................... 39
Features............................................................................................ 41
Output Configuration................................................................ 41
HD Async Timing Mode........................................................... 42
HD Timing Reset........................................................................ 43
SD Real-Time Control, Subcarrier Reset, and
Timing Reset ............................................................................... 43
HD Sharpness Filter and Adaptive Filter Controls................ 55
HD Sharpness Filter and Adaptive Filter
Application Examples ................................................................ 56
SD Digital Noise Reduction...................................................... 57
Coring Gain Border ................................................................... 58
Coring Gain Data....................................................................... 58
DNR Threshold .......................................................................... 58
Border Area................................................................................. 58
Block Size Control...................................................................... 58
DNR Input Select Control......................................................... 58
DNR Mode Control ................................................................... 59
Block Offset Control.................................................................. 59
SD Active Video Edge................................................................ 59
SAV/EAV Step-Edge Control ................................................... 59
Hsync/Vsync Output Control .................................................. 61
Board Design and Layout.............................................................. 62
DAC Termination and Layout Considerations ...................... 62
Video Output Buffer and Optional Output Filter.................. 62
PCB Board Layout...................................................................... 63
Appendix 1—Copy Generation Management System .............. 65
PS CGMS..................................................................................... 65
HD CGMS................................................................................... 65
SD CGMS .................................................................................... 65
Reset Sequence............................................................................ 45
SD VCR FF/RW Sync................................................................. 45
Vertical Blanking Interval ......................................................... 46
Subcarrier Frequency Registers................................................ 46
Square Pixel Timing Mode........................................................ 47
Filters............................................................................................ 48
Color Controls and RGB Matrix .............................................. 49
Programmable DAC Gain Control .......................................... 53
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 92
CGMS Functionality.................................................................. 65
Appendix 2—SD Wide-Screen Signaling.................................... 68
Appendix 3—SD Closed Captioning ........................................... 70
Appendix 4—Test Patterns............................................................ 71
Appendix 5—SD Timing Modes .................................................. 74
Mode 0 (CCIR-656)—Slave Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 0 0 0) ........................... 74
Mode 0 (CCIR-656)—Master Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 0 0 1) ........................... 75

ADV7322
Mode 1—Slave Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 0 1 0) ............................77
Mode 1—Master Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 0 1 1) ............................78
Mode 2— Slave Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 1 0 0) ............................79
Mode 2—Master Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 1 0 1) ............................80
Mode 3—Master/Slave Option
(Timing Register 0 TR0 = X X X X X 1 1 0 or X X X X X 1 1 1)
.......................................................................................................81
REVISION HISTORY
12/04—Revision 0: Initial Version
Appendix 6—HD Timing..............................................................83
Appendix 7—Video Output Levels...............................................84
HD YPrPb Output Levels ..........................................................84
RGB Output Levels.....................................................................85
YPrPb Levels—SMPTE/EBU N10............................................86
Appendix 8—Video Standards......................................................88
Outline Dimensions........................................................................90
Ordering Guide...........................................................................90
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 92
ADV7322
DETAILED FEATURES
HD programmable features (720p/1080i/1035i)
2× oversampling (148.5 MHz)
Internal test pattern generator
Color hatch, black bar, flat field/frame
Fully programmable YCrCb-to-RGB matrix
Gamma correction
Programmable adaptive filter control
Programmable sharpness filter control
CGMS-A (720p/1080i)
ED programmable features (525p/625p)
8× oversampling (216 MHz output)
Internal test pattern generator
Color hatch, black bar, flat frame
Individual Y and PrPb output delay
Gamma correction
Programmable adaptive filter control
Fully programmable YCrCb-to-RGB matrix
Undershoot limiter
Macrovision Rev 1.2 (525p/625p)
CGMS-A (525p/625p)
SD programmable features
16× oversampling (216 MHz)
Internal test pattern generator
Color bars, black bar
Controlled edge rates for start and end of active video
Individual Y and PrPb output delay
Undershoot limiter
Gamma correction
Digital noise reduction (DNR)
Multiple chroma and luma filters
Luma-SSAF™ filter with programmable gain/attenuation
PrPb SSAF™
Separate pedestal control on component and
composite/S-video output
VCR FF/RW sync mode
Macrovision Rev 7.1.L1
CGMS/WSS
Closed captioning
Table 1. Standards Directly Supported1
Clock
Interlace/
Resolution
720 × 480 I 29.97 27 ITU-R BT.656
720 × 576 I 25 27 ITU-R BT.656
720 × 480 I 29.97 24.54
720 × 576 I 25 29.5
720 × 483 P 59.94 27 SMPTE 293M
720 × 483 P 59.94 27 BTA T-1004
720 × 483 P 59.94 27 ITU-R BT.1358
720 × 576 P 50 27 ITU-R BT.1358
720 × 483 P 59.94 27 ITU-R BT.1362
720 × 576 P 50 27 ITU-R BT.1362
1920 ×
1035
29.97 74.1758
1280 × 720 P
1920 ×
1080
1920 ×
1080
PS
I 30 74.25
I
P
Frame
Rate (Hz)
60, 50, 30,
25, 24
23.97,
59.94,
29.97
30, 25 74.25
29.97 74.1758
30, 25, 24 74.25
23.98,
29.97
Input
(MHz) Standard
NTSC Square
Pixel
PAL Square
Pixel
SMPTE 240M
74.25 SMPTE 296M
74.1758
SMPTE 274M
SMPTE 274M
74.1758
1
Other standards are supported in async timing mode.
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 92
ADV7322
HD PIXEL
INPUT
CLKIN_B
P_HSYNC
P_VSYNC
P_BLANK
S_HSYNC
S_VSYNC
S_BLANK
CLKIN_A
SD PIXEL
INPUT
DEINTERLEAVE
DEINTERLEAVE
CR
CB
CB
CR
Y
Y
TEST
PATTERN
TEST
PATTERN
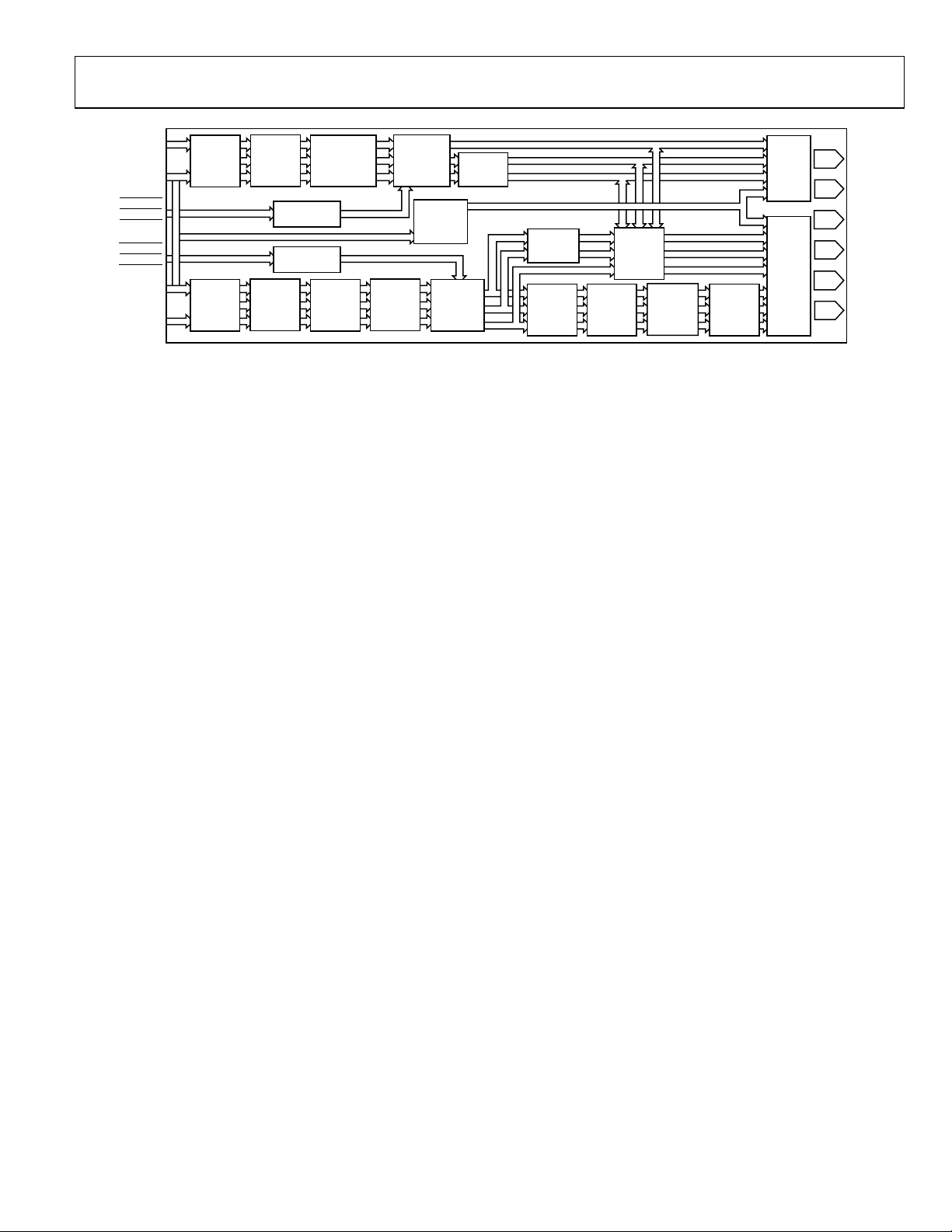
TERMINOLOGY
SD: standard definition video, conforming to
ITU-R BT.601/ITU-R BT.656.
HD: high definition video, i.e., 720p/1080i/1035i.
EDTV: enhanced definition television (525p/625p).
PS: progressive scan video, conforming to SMPTE 293M,
ITU-R BT.1358, BTA T-1004 EDTV2, or ITU-R BT.13621362.
SHARPNESS
ADAPTIVE
CONTROL
TIMING
GENERATOR
TIMING
GENERATOR
GAMMA
AND
FILTER
DNR
Y COLOR
CR COLOR
CB COLOR
COLOR
CONTROL
CLOCK
CONTROL
AND PLL
SYNC
INSERTION
4:2:2
TO
4:4:4
U
UV SSAF
V
LUMA
AND
CHROMA
FILTERS
Figure 2. Detailed Functional Block Diagram
HDTV: high definition television video, conforming to
SMPTE 274M, or SMPTE 296M and SMPTE 240M.
YCrCb SD, PS, or HD component: digital video.
YPrPb SD, PS, or HD component: analog video.
MATRIX
2× OVER-
SAMPLING
RGB
F
SC
MODU-
LATION
CGMS
WSS
PS 8×
HDTV2×
SD 16×
DAC
DAC
DAC
DAC
DAC
DAC
05135-002
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 92
ADV7322
SPECIFICATIONS
VAA = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, VDD = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, V
to T
All specifications T
MIN
(0°C to 70°C), unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 2.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE1
Resolution 11 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity 1.5 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity,2 +ve 0.5 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity,2 −ve 1.0 LSB
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 [0.4]3 V I
Output High Voltage, VOH 2.4 [2.0]3 V I
Three-State Leakage Current ±1.0 µA VIN = 0.4 V, 2.4 V
Three-State Output Capacitance 2 pF
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, VIH 2 V
Input Low Voltage, VIL 0.8 V
Input Leakage Current 10 µA VIN = 2.4 V
Input Capacitance, CIN 2 pF
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Full-Scale Output Current 4.1 4.33 4.6 mA
Output Current Range 4.1 4.33 4.6 mA
DAC-to-DAC Matching 1.0 %
Output Compliance Range, VOC 0 1.0 1.4 V
Output Capacitance, C
7 pF
OUT
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Internal Reference Range, V
External Reference Range, V
V
Current4 ±10 µA
REF
1.15 1.235 1.3 V
REF
1.15 1.235 1.3 V
REF
POWER REQUIREMENTS
Normal Power Mode
5
I
137 mA SD only (16×)
DD
78 mA PS only (8×)
73 mA HDTV only (2×)
140 1906 mA SD (16×, 8-bit) + PS (8×, 16-bit)
I
1.0 mA
DD_IO
7, 8
I
37 45 mA
AA
Sleep Mode
IDD 80 µA
IAA 7 µA
I
250 µA
DD_IO
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO 0.01 %/%
= 2.375 V to 3.6 V, V
DD_IO
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 3040 Ω, R
SET
= 3.2 mA
SINK
SOURCE
LOAD
= 400 µA
= 300 Ω.
1
Oversampling disabled. Static DAC performance improves with increased oversampling ratios.
2
DNL measures the deviation of the actual DAC output voltage step from the ideal. For +ve DNL, the actual step value lies above the ideal step value; for −ve DNL, the
actual step value lies below the ideal step value.
3
For values in brackets, V
4
External current required to overdrive internal V
5
IDD, the circuit current, is the continuous current required to drive the digital core.
6
Guaranteed maximum by characterization.
7
All DACs on.
8
IAA is the total current required to supply all DACs, including the V
= 2.375 V to 2.75 V.
DD_IO
.
REF
circuitry and the PLL circuitry.
REF
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 92
ADV7322
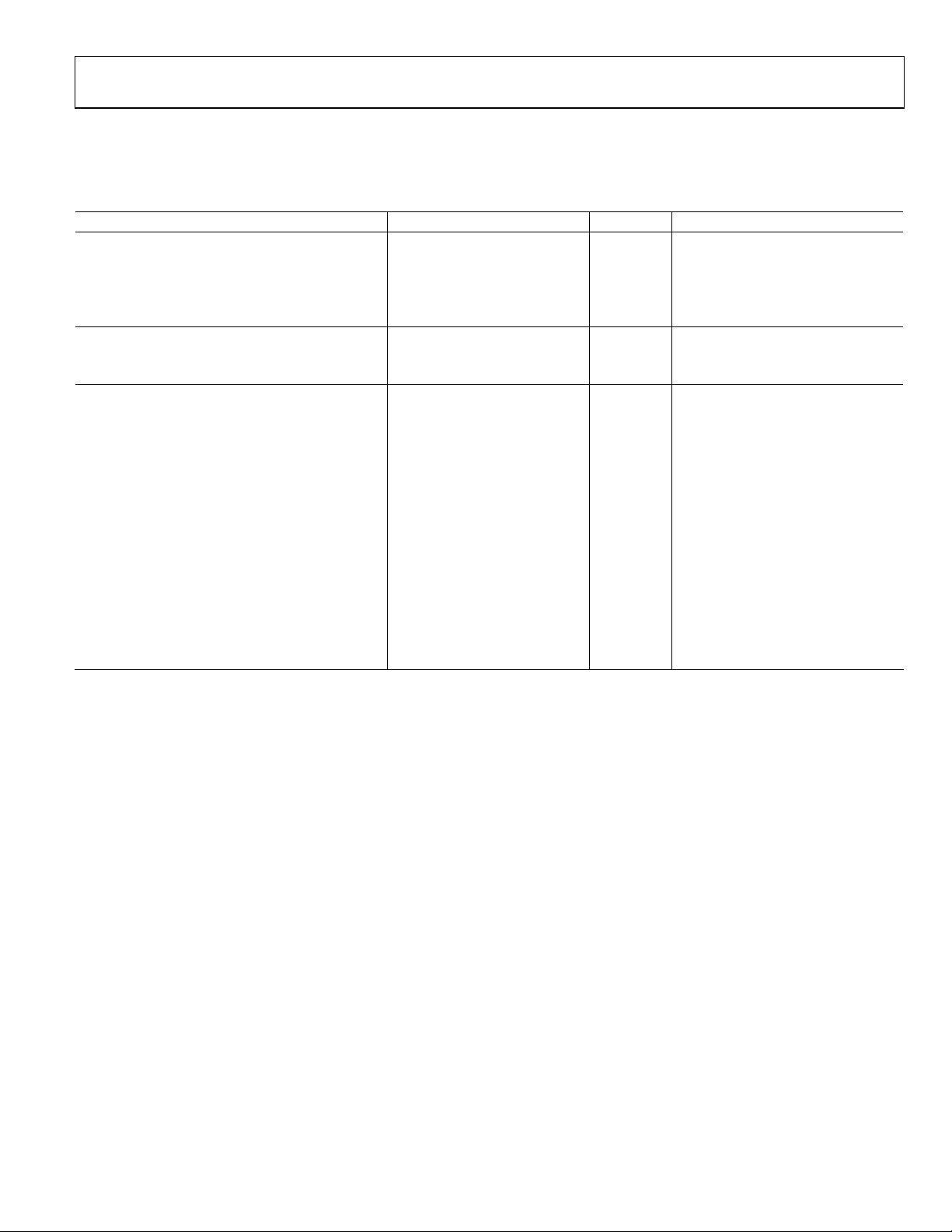
DYNAMIC SPECIFICATIONS
VAA = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, VDD = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, V
All specifications T
MIN
to T
(0°C to 70°C), unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 3.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
PS MODE
Luma Bandwidth 12.5 MHz
Chroma Bandwidth 5.8 MHz
SNR 65.6 dB Luma ramp unweighted
72 dB Flat field, full bandwidth
HDTV MODE
Luma Bandwidth 30 MHz
Chroma Bandwidth 13.75 MHz
SD MODE
Hue Accuracy 0.4 Degrees
Color Saturation Accuracy 0.4 %
Chroma Nonlinear Gain 1.2 ±% Referenced to 40 IRE
Chroma Nonlinear Phase −0.2 ±Degrees
Chroma/Luma Intermodulation 0 ±%
Chroma/Luma Gain Inequality 97.0 ±%
Chroma/Luma Delay Inequality −1.1 ns
Luminance Nonlinearity 0.5 ±%
Chroma AM Noise 84 dB
Chroma PM Noise 75.2 dB
Differential Gain 0.2 % NTSC
Differential Phase 0.15 Degrees NTSC
SNR 59.1 dB Luma ramp
77.1 dB Flat field, full bandwidth
= 2.375 V to 3.6 V, V
DD_IO
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 3040 Ω, R
SET
= 300 Ω.
LOAD
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 92
ADV7322
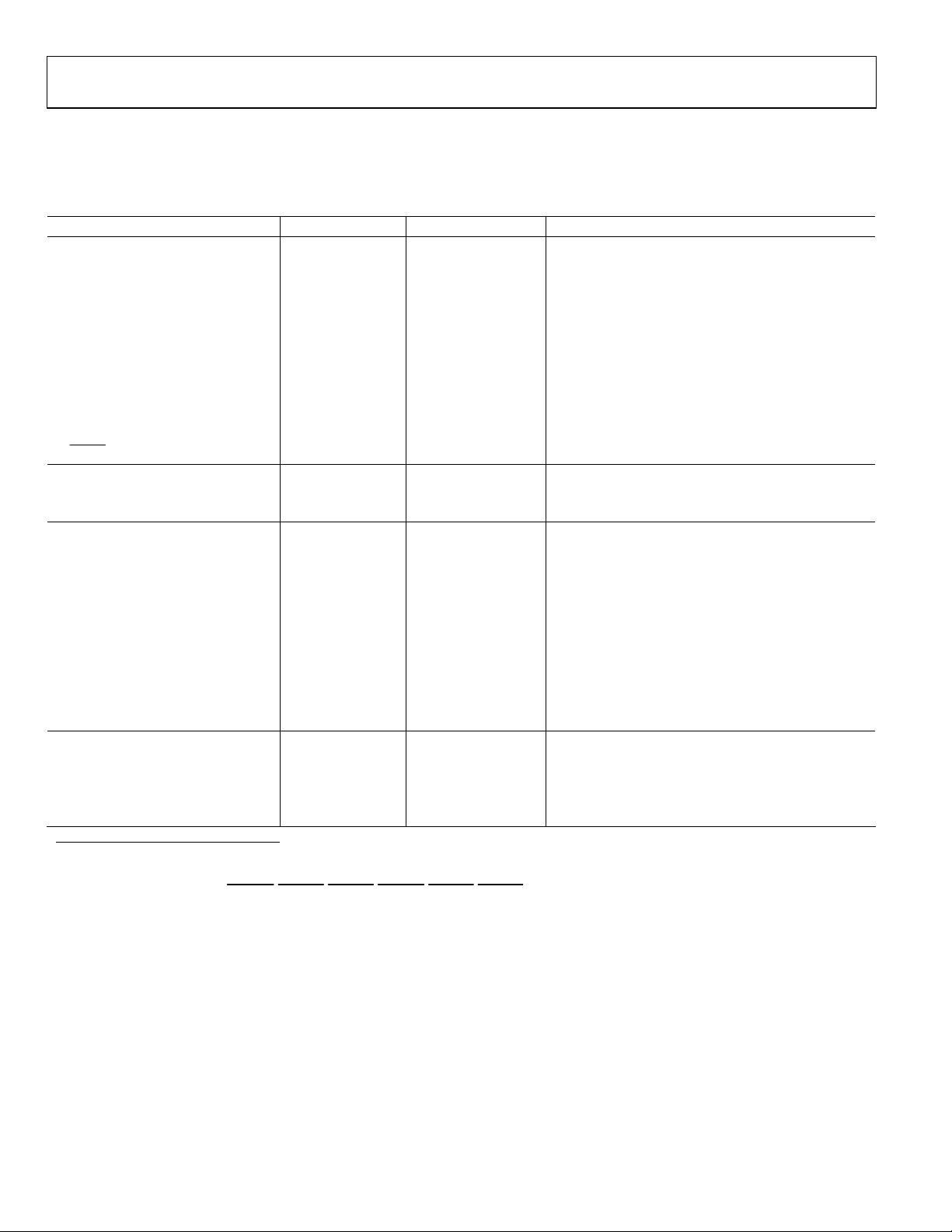
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VAA = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, VDD = 2.375 V to 2.625 V, V
to T
specifications T
MIN
(0°C to 70°C), unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 4.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
MPU PORT1
SCLOCK Frequency 0 400 kHz
SCLOCK High Pulse Width, t1 0.6 µs
SCLOCK Low Pulse Width, t2 1.3 µs
Hold Time (Start Condition), t3 0.6 µs
Setup Time (Start Condition), t4 0.6 µs
Data Setup Time, t5 100 ns
SDATA, SCLOCK Rise Time, t6 300 ns
SDATA, SCLOCK Fall Time, t7 300 ns
Setup Time (Stop Condition), t8 0.6 µs
Low Time 100 ns
RESET
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Analog Output Delay2 7 ns
Output Skew 1 ns
CLOCK CONTROL AND PIXEL PORT3
f
29.5 MHz SD PAL square pixel mode
CLK
f
81 MHz PS/HD async mode
CLK
Clock High Time, t9 40 % of one clock cycle
Clock Low Time, t10 40 % of one clock cycle
Data Setup Time, t
Data Hold Time, t
1
2.0 ns
11
1
2.0 ns
12
SD Output Access Time, t13 15 ns
SD Output Hold Time, t14 5.0 ns
HD Output Access Time, t13 14 ns
HD Output Hold Time, t14 5.0 ns
PIPELINE DELAY4 63 Clock cycles SD (2×, 16×)
76 Clock cycles SD component mode (16×)
35 Clock cycles PS (1×)
41 Clock cycles PS (8×)
36 Clock cycles HD (2×, 1×)
1
Guaranteed by characterization.
2
Output delay measured from the 50% point of the rising edge of CLOCK to the 50% point of DAC output full-scale transition.
3
Data: C[9:0]; Y[9:0], S[9:0]; Control:
4
SD, PS = 27 MHz, HD = 74.25 MHz.
P_HSYNC, P_VSYNC, P_BLANK, S_HSYNC, S_VSYNC, S_BLANK
= 2.375 V to 3.6 V, V
DD_IO
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 3040 Ω, R
SET
LOAD
First clock generated after this period relevant for
repeated start condition
.
= 300 Ω. All
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 92
ADV7322
C
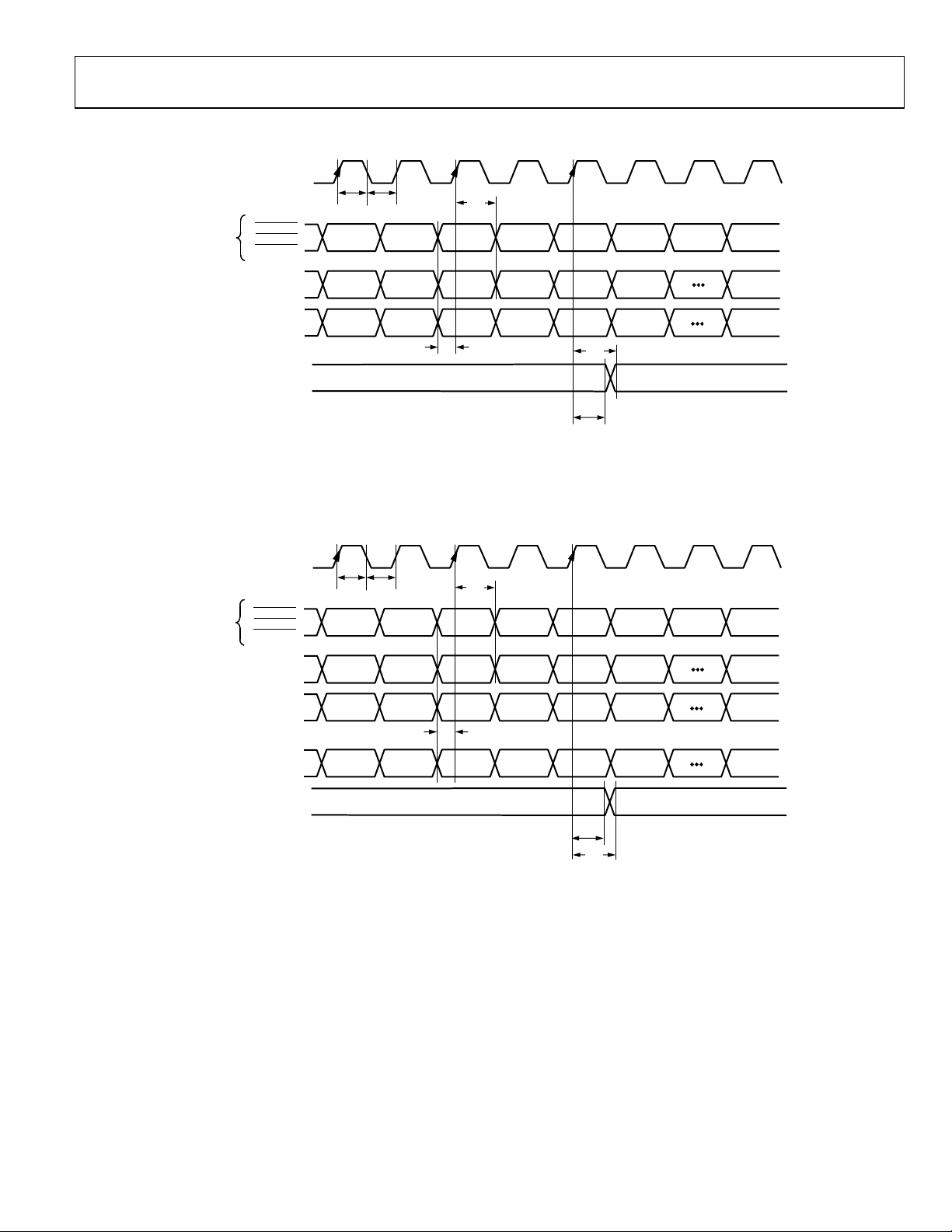
TIMING DIAGRAMS
CLKIN_A
CONTROL
INPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
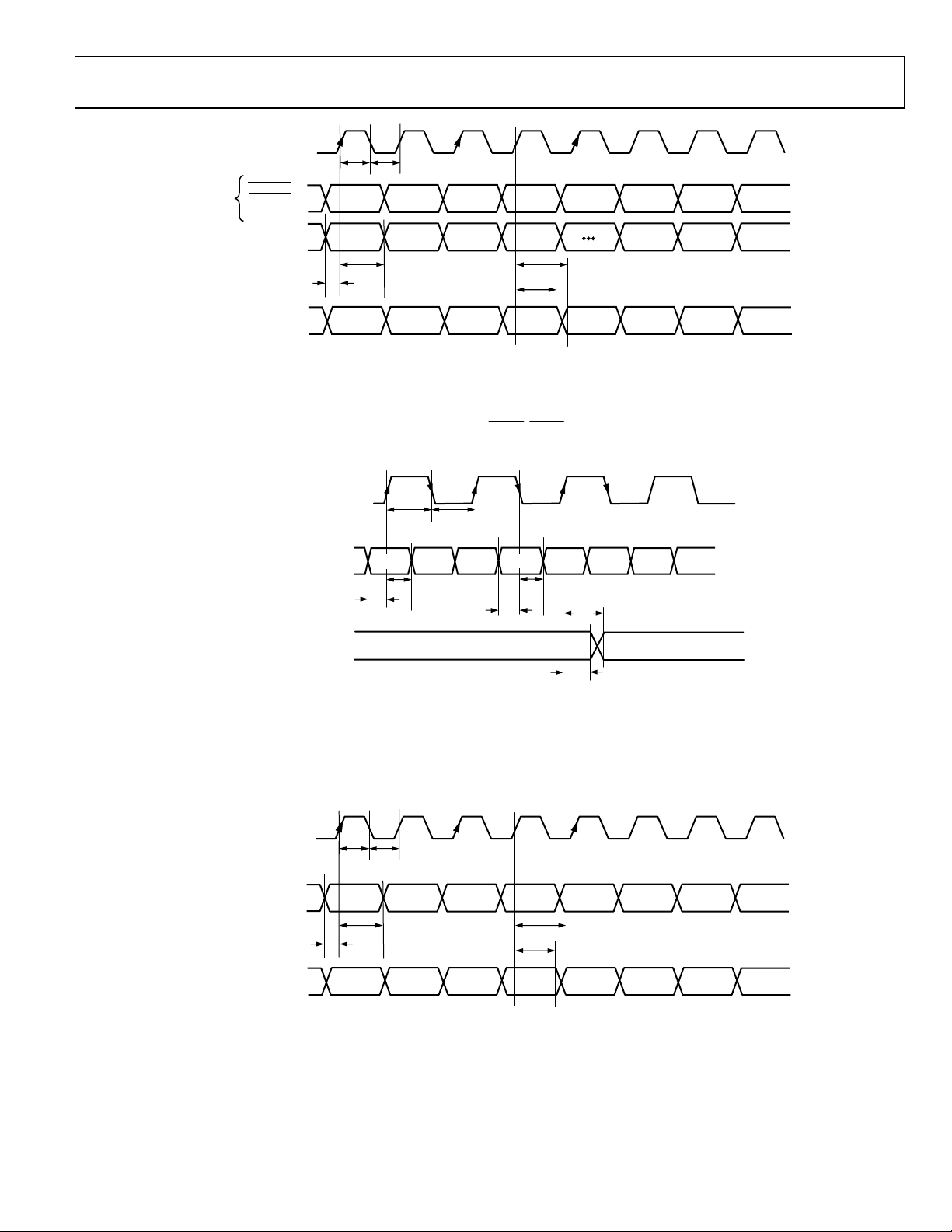
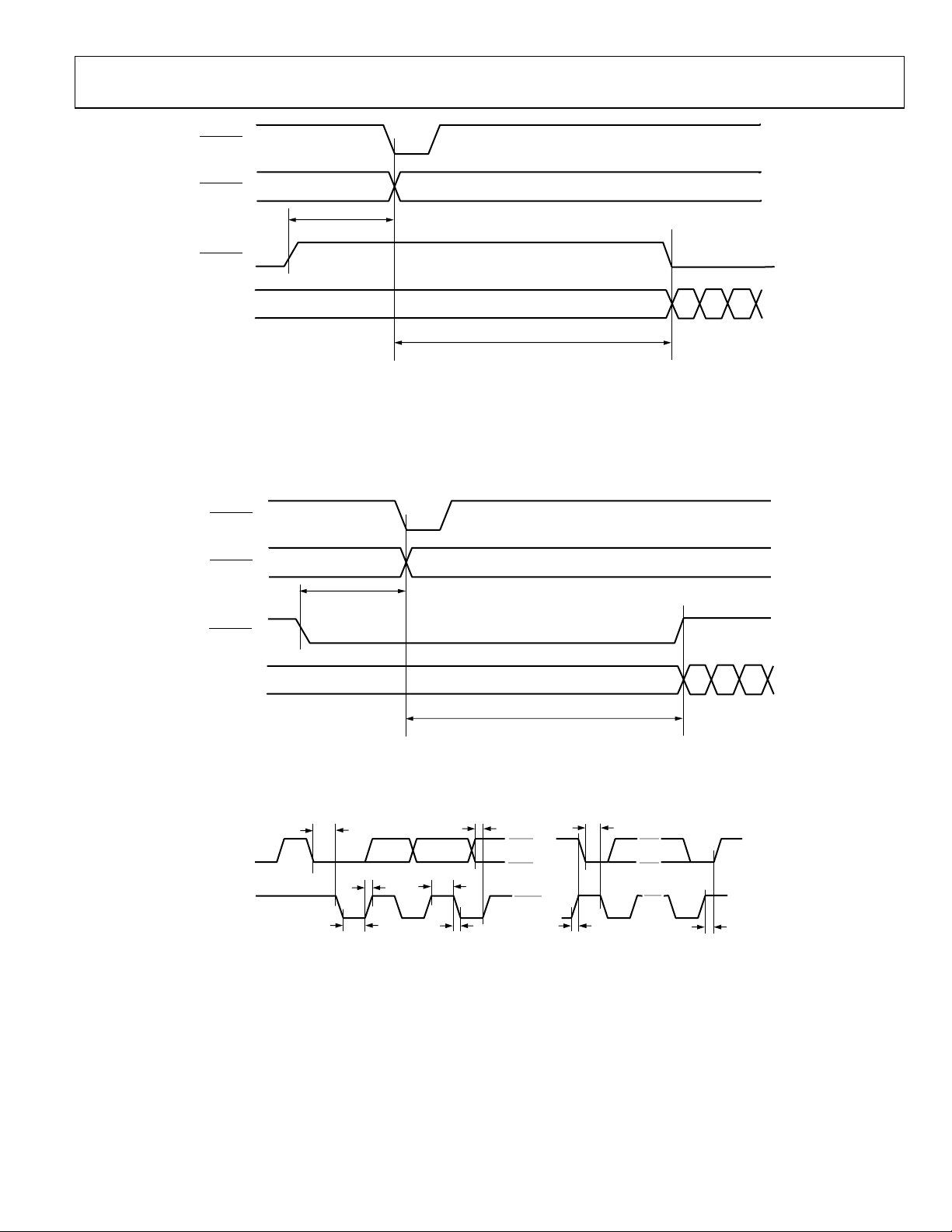
Figure 3. HD Only, 4:2:2 Input Mode (Input Mode 010); PS Only, 4:2:2 Input Mode (Input Mode 001)
CLKIN_A
ONTROL
INPUTS
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
Cb2
t
12
Cr2
Cb4
t
13
t
14
t
t
10
9
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5
Cb0
Cr0
t
11
t
t
9
10
t
12
Cr4
05135-003
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
S7–S0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Figure 4. HD Only, 4:4:4 Input Mode (Input Mode 010); PS Only, 4:4:4 Input Mode (Input Mode 001)
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5
Cb0
Cr0
Cb2Cb1
t
11
Cr2Cr1
Cb4Cb3
Cr4Cr3
t
14
t
13
Cb5
Cr5
05135-004
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 92
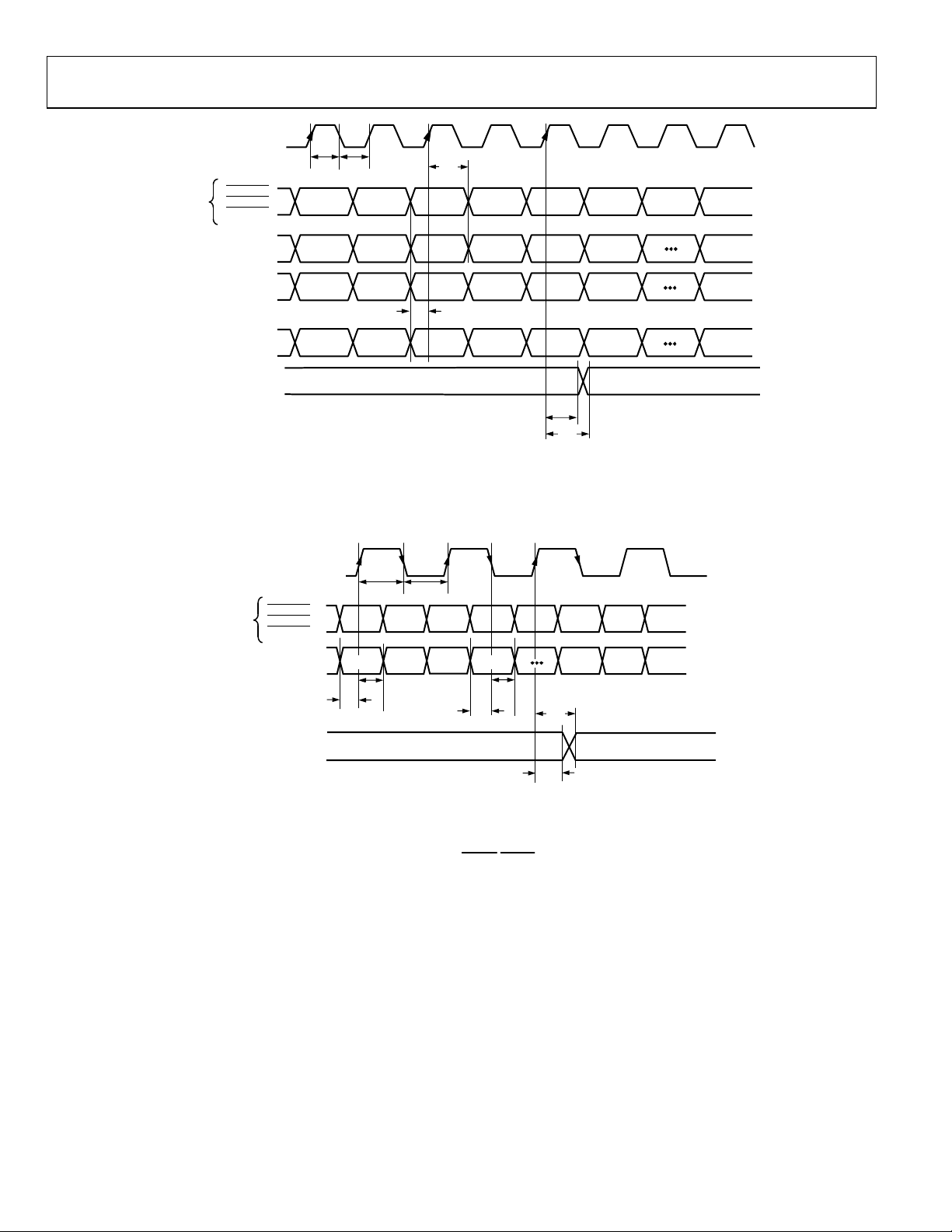
ADV7322
t
t
t
t
t
t
CLKIN_A
CONTROL
INPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
CONTROL
INPUTS
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
S7–S0
CLKIN_B*
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
t
t
9
10
G0 G1 G2 G3 G4 G5
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5
t
11
R0 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5
t
12
t
14
t
13
Figure 5. HD RGB 4:4:4 Input Mode (Input Mode 010)
t
t
9
10
05135-005
Y7–Y0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Cb0
t
12
t
11
Figure 6. PS 4:2:2 8-Bit Interleaved at 27 MHz
Cr0
t
11
HSYNC
Y1
t
12
t
13
t
14
VSYNC
/
Input Mode (Input Mode 100)
Y0
*CLKIN_B MUST BE USED IN THIS PS MODE
Crxxx
Yxxx
05135-006
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 92
ADV7322
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
CLKIN_A
t
t
10
9
CONTROL
INPUTS
P_VSYNC,
P_HSYNC,
P_BLANK
Y7–Y0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
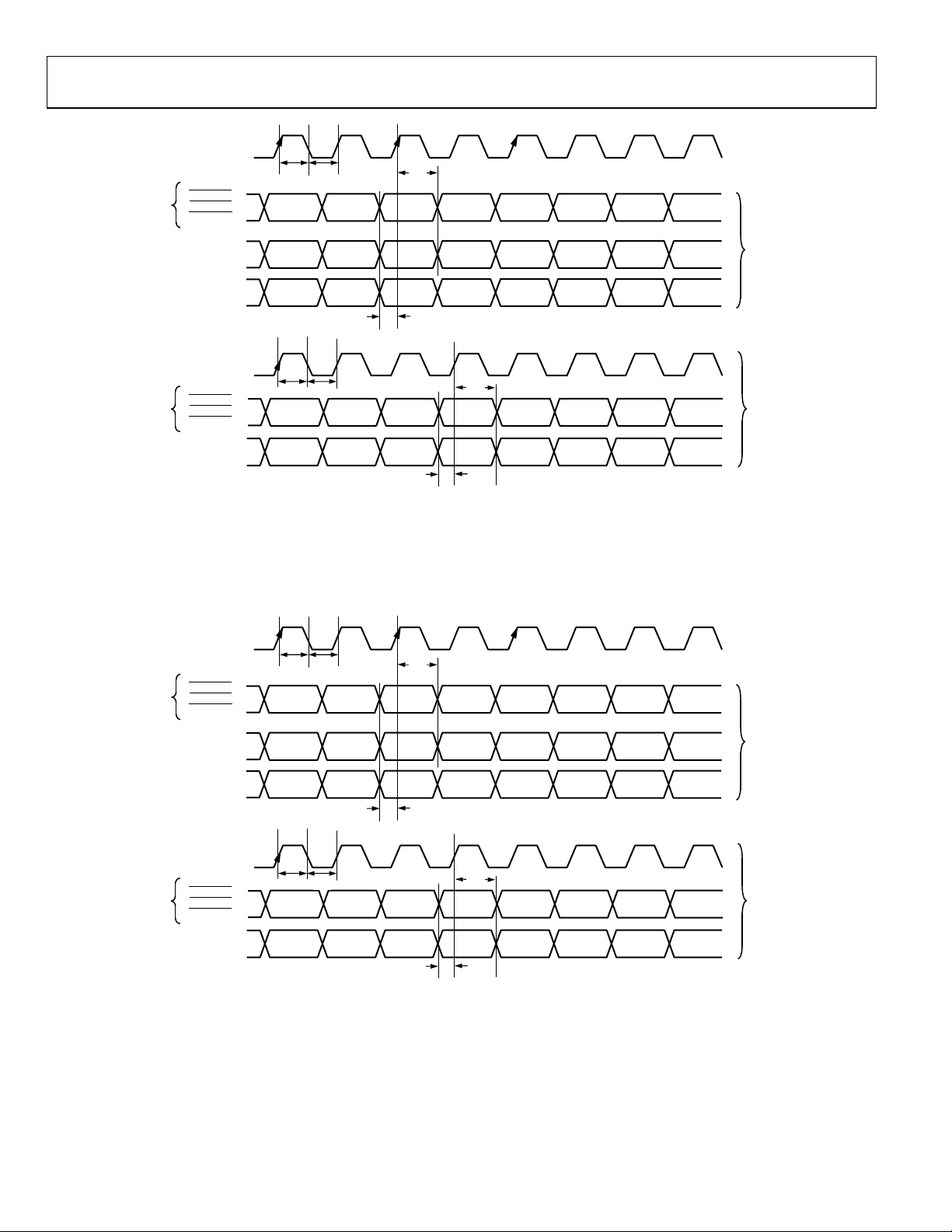
Figure 7. PS 4:2:2 8-Bit Interleaved at 54 MHz
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Figure 8. PS Only, 4:2:2 8-Bit Interleaved at 27 MHz EAV/SAV Input Mode (Input Mode 100)
t
11
CLKIN_B*
Y7–Y0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
Cb0
Crxxx
Yxxx
05135-007
HSYNC
Y1
t
13
t
14
VSYNC
/
Input Mode (Input Mode 111)
Y0
t
12
Cr0
t
t
9
10
Y1
05135-008
t
12
t
11
*CLKIN_B USED IN THIS PS-ONLY MODE
t
Y0Cb0XY0000FF
Cr0
t
12
11
t
13
t
14
CLKIN_A
t
t
10
9
Y7–Y0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
FF
t
12
t
11
00
NOTE: Y0, Cb0 SEQUENCE AS PER SUBADDRESS 0x01, BIT 1
00
XY
t
Cb0
t
13
14
Y0
Cr0
Y1
05135-009
Figure 9. PS Only, 4:2:2 8-Bit Interleaved at 54 MHz EAV/SAV Input Mode (Input Mode 111)
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 92
ADV7322
CONTROL
INPUTS
CLKIN_B
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
t
t
10
9
t
12
CONTROL
INPUTS
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
CLKIN_A
S_HSYNC,
S_VSYNC,
S_BLANK
S7–S0
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Y0 Y1
Cb0
t
9
Cr0
t
10
Y2
t
11
Y0Cb0
Cr0
Y3 Y4 Y5
Cb4Cr2Cb2
t
12
Y1
t
11
Cb1
Cr4
Y2
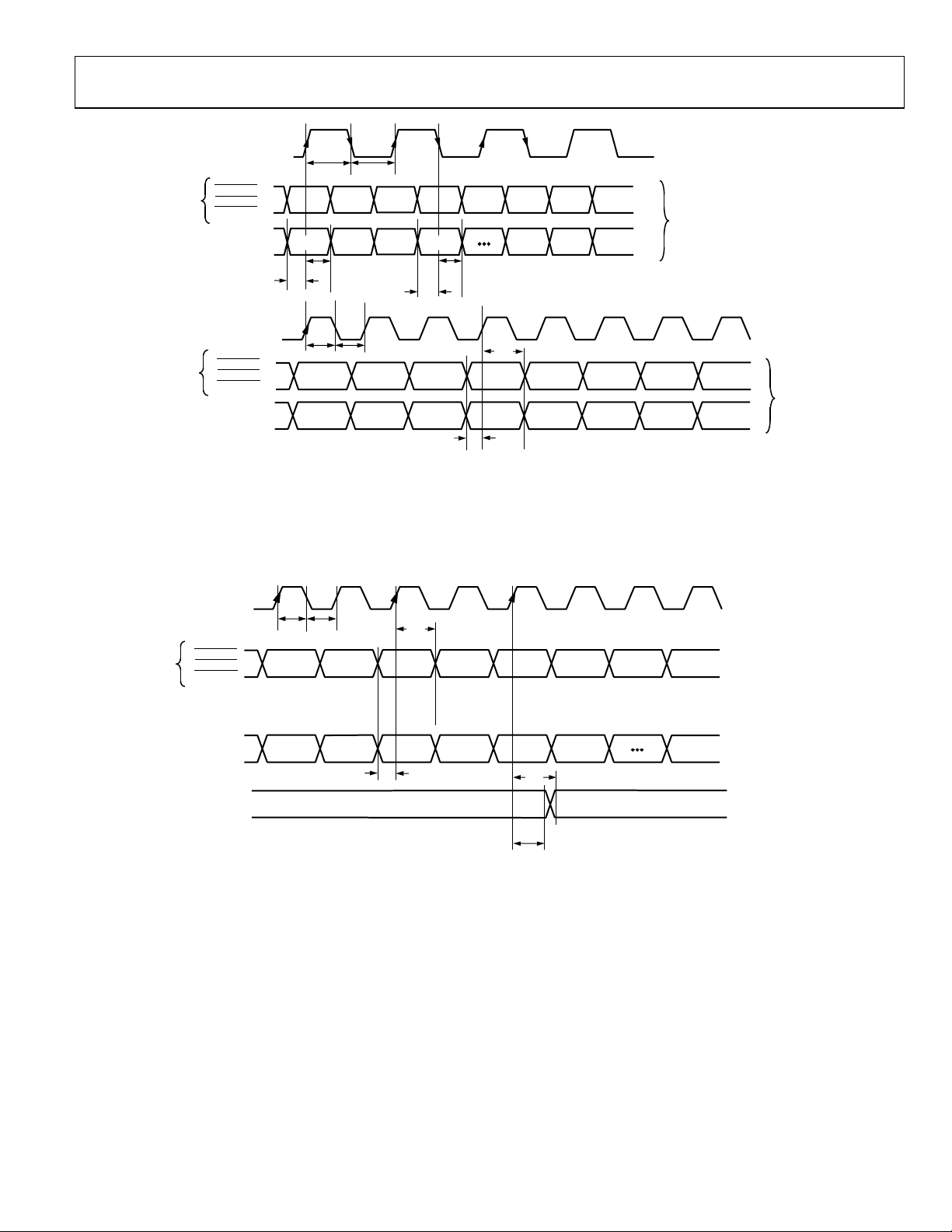
Figure 10. HD 4:2:2 and SD 8-Bit Simultaneous Input Mode (Input Mode 101: SD Oversampled; Input Mode 110: HD Oversampled)
CLKIN_B
t
12
CONTROL
INPUTS
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
t
t
10
9
HD INPUT
SD INPUT
05135-010
CONTROL
INPUTS
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
CLKIN_A
S_HSYNC,
S_VSYNC,
S_BLANK
S7–S0
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Figure 11. PS 4:2:2 and SD 8-Bit Simultaneous Input Mode (Input Mode 011)
Y0 Y1
Cb0
t
9
Cr0
t
10
Y2
t
11
Y0Cb0
Cr0
Y3 Y4 Y5
Cb4Cr2Cb2
t
12
Y1
t
11
Cb1
Cr4
Y2
PS INPUT
SD INPUT
05135-011
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 92
ADV7322
CLKIN_B
t
t
9
10
PS INPUT
Crxxx
Cr0
Y0
Y1
Yxxx
CONTROL
INPUTS
P_HSYNC,
P_VSYNC,
P_BLANK
Y7–Y0
Cb0
CONTROL
CONTROL
INPUTS
INPUTS
CLKIN_A
S_HSYNC,
S_VSYNC,
S_BLANK
S7–S0
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
CLKIN_A
S_HSYNC,
S_VSYNC,
S_BLANK
t
12
t
11
t
t
9
10
Y0Cb0
t
12
t
11
t
12
Cr0
Y1
t
11
Cb1
Y2
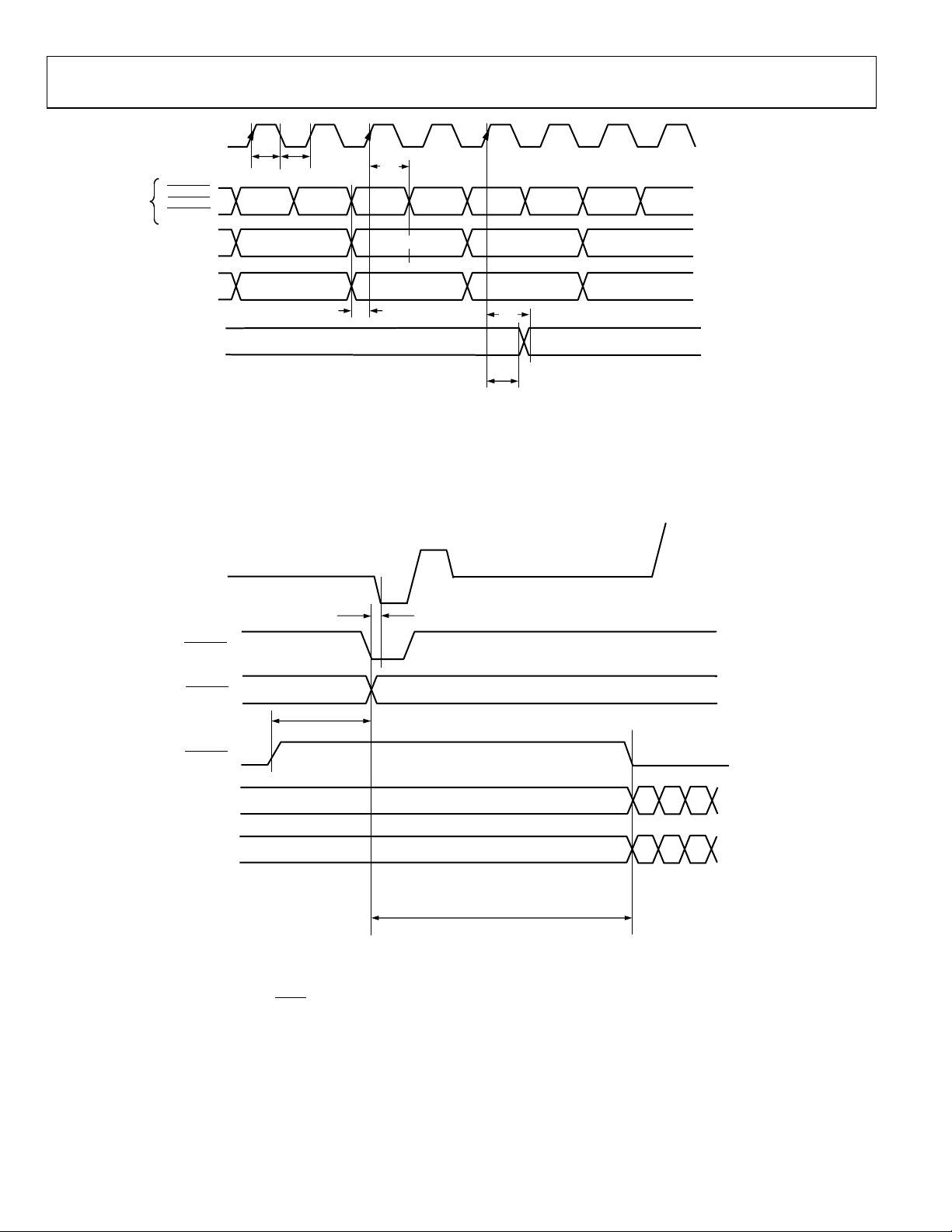
Figure 12. PS 8-Bit and SD 8-Bit Simultaneous Input Mode (Input Mode 100)
t
t
10
9
t
12
SD INPUT
IN SLAVE MODE
05135-012
S7–S0/Y7–Y0*
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Cb0
Cr0
t
11
*SELECTED BY ADDRESS 0x01, BIT 7: SEE TABLE 21.
Cr2Cb2
Cb4
t
14
Cr4
t
13
Figure 13. 8-Bit, SD-Only Pixel Input Mode (Input Mode 000)
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 92
IN MASTER/SLAVE MODE
05135-013
ADV7322
CLKIN_A
CONTROL
INPUTS
S_HSYNC,
S_VSYNC,
S_BLANK
S7–S0/Y7–Y0*
C7–C0
CONTROL
OUTPUTS
t
= CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
= CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
= DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
= DATA HOLD TIME
12
t
= HD OUTPUT ACCESS TIME
13
t
= HD OUTPUT HOLD TIME
14
Y OUTPUT
t
t
9
10
Y0 Y2 Y3
Cb0 Cr0 Cb2 Cr2
t
11
t
12
Y1
t
13
t
14
*SELECTED BY ADDRESS 0x01, BIT 7: SEE TABLE 21.
Figure 14. 16-Bit, SD-Only Pixel Input Mode (Input Mode 000)
c
IN SLAVE MODE
IN MASTER/SLAVE MODE
05135-014
P_HSYNC
P_VSYNC
a
P_BLANK
Y7–Y0
C7–C0
b
a AND b AS PER RELEVANT STANDARD.
c = PIPELINE DELAY. PLEASE REFER TO RELEVANT PIPELINE DELAY. THIS CAN BE FOUND IN THE TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION OF THE DATA SHEET.
A FALLING EDGE OF HSYNC INTO THE ENCODER GENERATES A FALLING EDGE OF TRILEVEL SYNC ON THE OUTPUT
AFTER A TIME EQUAL TO THE PIPELINE DELAY.
Y0 Y1
Y2 Y3
Cb1Cr1Cr0Cb0
Figure 15. HD 4:2:2 Input Timing Diagram
05135-015
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 92
ADV7322
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
P_HSYNC
P_VSYNC
a
P_BLANK
Y7–Y0 Cb Y
b
a = 32 CLOCK CYCLES FOR 525p
a = 24 CLOCK CYCLES FOR 625p
AS RECOMMENDED BY STANDARD
b(MIN) = 244 CLOCK CYCLES FOR 525p
b(MIN) = 264 CLOCK CYCLES FOR 625p
Figure 16. PS 4:2:2 8-Bit Interleaved Input Timing Diagram
S_HSYNC
S_VSYNC
PAL = 24 CLOCK CYCLES
NTSC = 32 CLOCK CYCLES
S_BLANK
S7–S0/Y7–Y0*
PAL = 264 CLOCK CYCLES
NTSC = 244 CLOCK CYCLES
*SELECTED BY ADDRESS 0x01, BIT 7: SEE TABLE 21.
Figure 17. SD Timing Input for Timing Mode 1
t
3
SDA
t
3
t
5
Cb Y
Cr Y
Cr Y
05135-016
05135-017
t
6
SCLK
t
2
= SCLOCK HIGH PULSE WIDTH
1
= SCLOCK LOW PULSE WIDTH
2
= HOLD TIME (START CONDITION)
3
= SETUP TIME (START CONDITION)
4
= DATA SETUP TIME
5
= SDATA, SCLOCK RISE TIME
6
= SDATA, SCLOCK FALL TIME
7
= SETUP TIME (STOP CONDITION)
8
t
1
t
7
t
4
t
8
05135-018
Figure 18. MPU Port Timing Diagram
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 92
ADV7322
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
Parameter1 Value
VAA to AGND −0.3 V to +3.0 V
VDD to DGND −0.3 V to +3.0 V
V
to GND_IO −0.3 V to +4.6 V
DD_IO
Digital Input Voltage to DGND −0.3 V to V
VAA to VDD −0.3 V to +0.3 V
AGND to DGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
DGND to GND_IO −0.3 V to +0.3 V
AGND to GND_IO −0.3 V to +0.3 V
Ambient Operating Temperature (TA) 0°C to 70°C
Storage Temperature (TS) –65°C to +150°C
Infrared Reflow Soldering (20 s) 260°C
1
Analog output short circuit to any power supply or common can be of
an indefinite duration.
DD_IO
+0.3 V
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
θJC = 11°C/W
= 47°C/W
θ
JA
The ADV7322 is a Pb-free, environmentally friendly product. It
is manufactured using the most up-to-date materials and
processes. The coating on the leads of the device is 100% pure
Sn electroplate. The device is suitable for Pb-free applications and
is able to withstand surface-mount soldering up to 255°C (±5°C).
In addition, it is backward-compatible with conventional SnPb
soldering processes. This means that the electroplated Sn coating
can be soldered with Sn/Pb solder pastes at conventional reflow
temperatures of 220°C to 235°C.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
this product features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 92
ADV7322
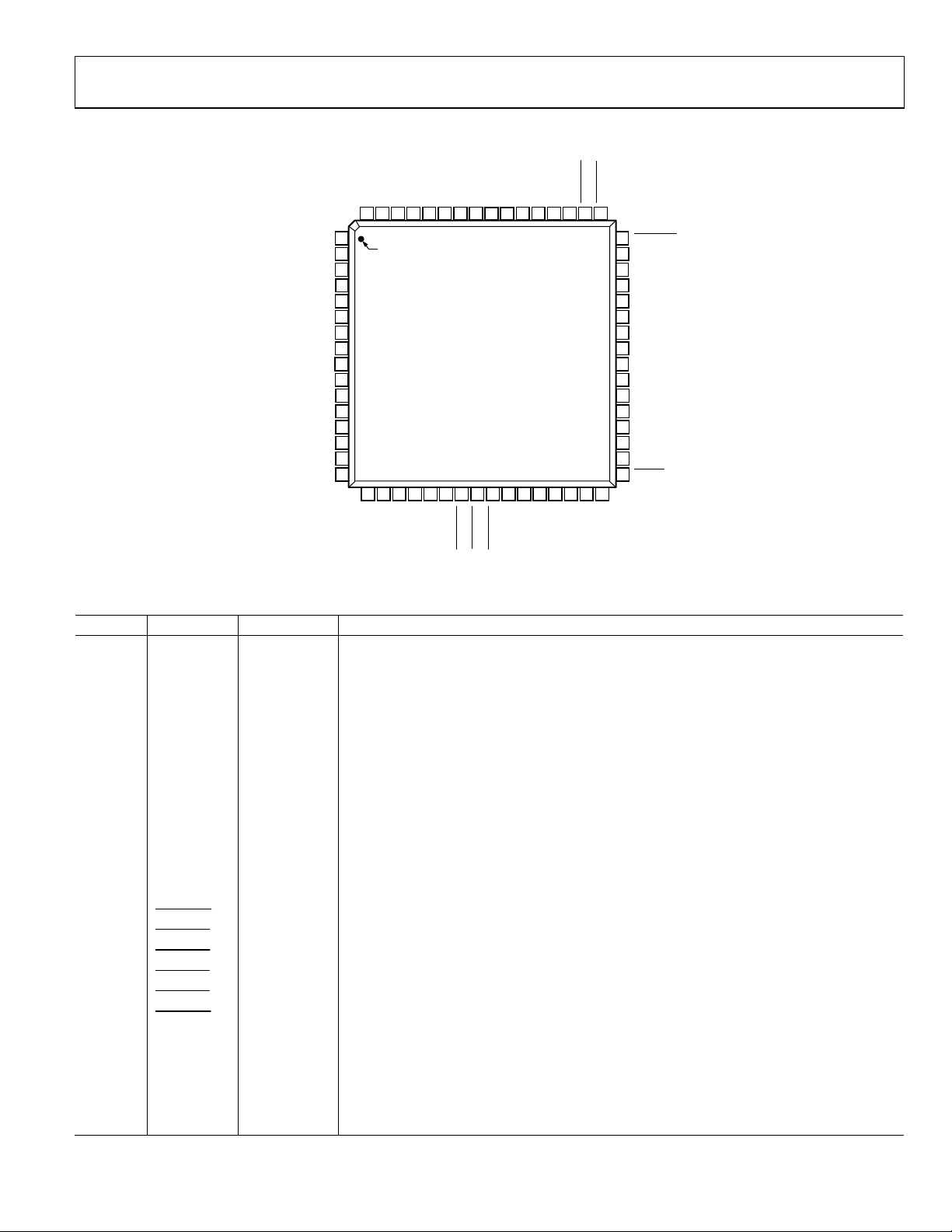
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DD
ADV7322
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
23
24
25
P_VSYNC
P_HSYNC
P_BLANK
55S254S153S052
26C327C428C529C630C731
TEST551TEST450S_HSYNC49S_VSYNC
48
S_BLANK
47
R
SET1
46
V
REF
45
COMP1
44
DAC A
43
DAC B
42
DAC C
41
V
AA
40
AGND
39
DAC D
38
DAC E
37
DAC F
36
COMP2
35
R
SET2
34
EXT_LF
33
RESET
32
CLKIN_A
RTC_SCR_TR
05135-019
V
DD_IO
TEST0
TEST1
V
DGND
TEST2
TEST3
GND_IO63CLKIN_B62S761S660S559S458S357DGND56V
64
1
PIN 1
2
3
4
Y0
5
Y1
6
Y2
7
Y3
8
Y4
9
Y5
10
DD
11
12
Y6
13
Y7
14
15
16
C0
17C118C219
20
21
22
C
2
I
SDA
ALSB
SCLK
Figure 19. Pin Configuration
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Input/Output Description
11, 57 DGND G Digital Ground.
40 AGND G Analog Ground.
32 CLKIN_A I Pixel Clock Input for HD Only (74.25 MHz), PS Only (27 MHz), and SD Only (27 MHz).
63 CLKIN_B I
Pixel Clock Input. Requires a 27 MHz reference clock for PS mode or a 74.25 MHz
(74.1758 MHz) reference clock in HDTV mode. This clock is only used in dual modes.
45, 36 COMP1, 2 O Compensation Pin for DACs. Connect 0.1 µF capacitor from COMP1/2 pin to VAA.
44 DAC A O CVBS/Green/Y/Y Analog Output.
43 DAC B O Chroma/Blue/U/Pb Analog Output.
42 DAC C O Luma/Red/V/Pr Analog Output.
39 DAC D O
In SD-Only Mode: CVBS/Green/Y Analog Output; in HD-Only Mode and Simultaneous HD/SD
Mode: Y/Green [HD] Analog Output.
38 DAC E O
In SD-Only Mode: Luma/Blue/U Analog Output; in HD-Only Mode and Simultaneous HD/SD
Mode: Pr/Red Analog Output.
37 DAC F O
In SD-Only Mode: Chroma/Red/V Analog Output; in HD-Only Mode and Simultaneous HD/SD
Mode: Pb/Blue [HD] Analog Output.
23
24
25
48
49
50
13,12, 9
to 4
30 to 26,
18 to 16
62 to 58,
P_HSYNC
P_VSYNC
P_BLANK
S_BLANK
S_VSYNC
S_HSYNC
Y7 to Y0 I
C7 to C0 I
S7 to S0 I SD or PS/HDTV Input Port for Cr[Red/V] Data in 4:4:4 Input Mode. LSB is set up on Pin S0.
I Video Horizontal Sync Control Signal for HD in Simultaneous SD/HD Mode and HD-Only Mode.
I Video Vertical Sync Control Signal for HD in Simultaneous SD/HD Mode and HD-Only Mode.
I Video Blanking Control Signal for HD in Simultaneous SD/HD Mode and HD-Only Mode.
I/O Video Blanking Control Signal for SD Only.
I/O Video Vertical Sync Control Signal for SD Only.
I/O Video Horizontal Sync Control Signal for SD Only.
SD or PS/HDTV Input Port for Y Data. Input port for interleaved PS data. The LSB is set up on
Pin Y0.
PS/HDTV Input Port 4:4:4 Input Mode. This port is used for the Cb[Blue/U] data. The LSB is set
up on Pin C0.
55 to 53
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 92
ADV7322
Pin No. Mnemonic Input/Output Description
33
47, 35 R
RESET
SET1
, R
SET2
22 SCLK I I2C Port Serial Interface Clock Input.
21 SDA I/O I2C Port Serial Data Input/Output.
20 ALSB I
1 V
P Power Supply for Digital Inputs and Outputs.
DD_IO
10, 56 VDD P Digital Power Supply.
41 VAA P Analog Power Supply.
46 V
I/O Optional External Voltage Reference Input for DACs or Voltage Reference Output (1.235 V).
REF
34 EXT_LF I External Loop Filter for the Internal PLL.
31 RTC_SCR_TR I Multifunctional Input. Real-time control (RTC) input, timing reset input, subcarrier reset input.
19 I2C I This input pin must be tied high (V
64 GND_IO Digital Input/Output Ground.
2,3,14,15,
51,52
TEST0TEST5
I
This input resets the on-chip timing generator and sets the ADV7322 to its default register
setting. RESET
I
A 3040 Ω resistor must be connected from this pin to AGND and is used to control the
amplitudes of the DAC outputs.
TTL Address Input. This signal sets up the LSB of the I
2
C filter is activated, which reduces noise on the I2C interface.
I
I Not Used. Tie to DGND.
is an active low signal.
DD_IO
2
C address. When this pin is tied low, the
) for the ADV7322 to interface over the I2C port.
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 92
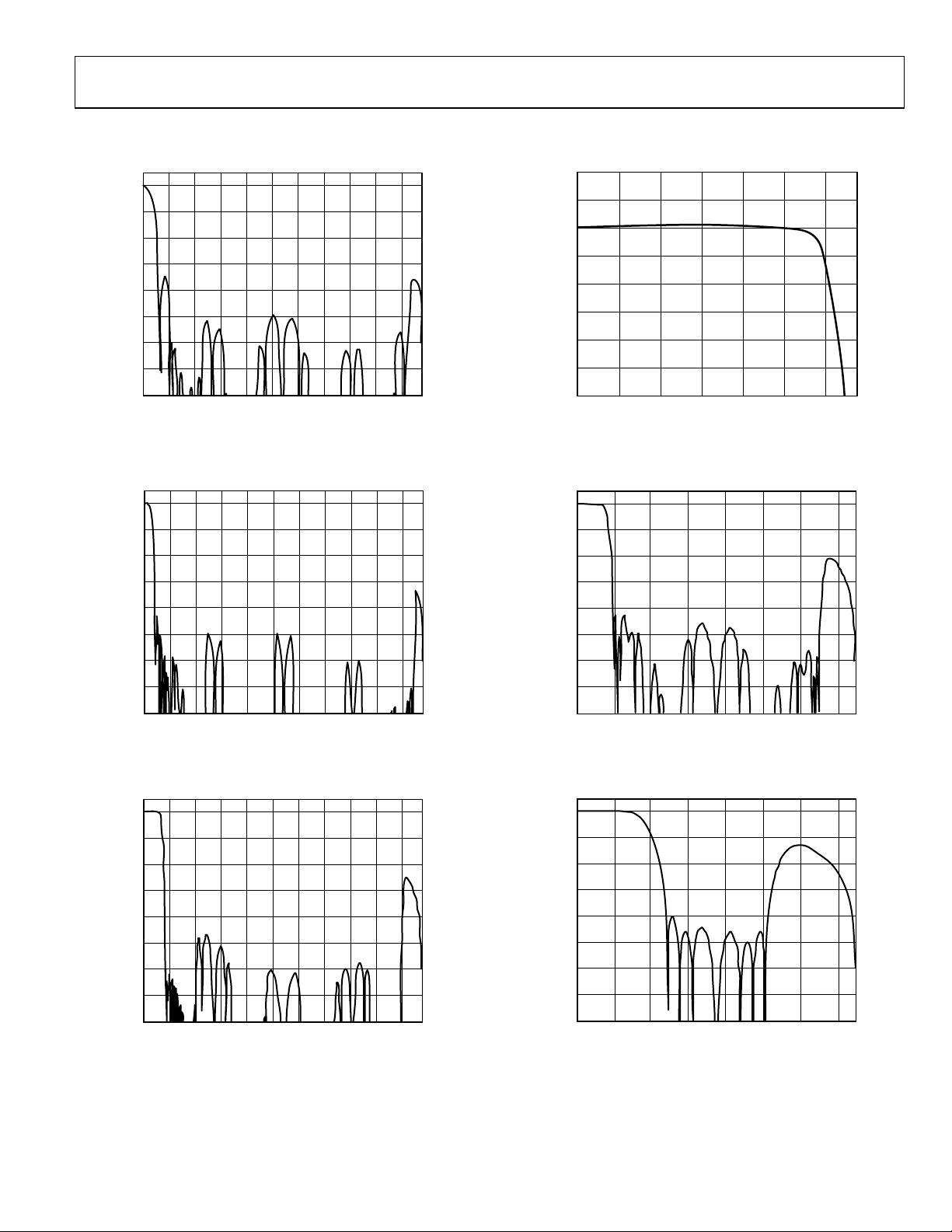
ADV7322
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
PS Pr/Pb RESPONSE. LINEAR INTERPOLATION (4:2:2 TO 4:4:4)
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
–80
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 20. PS—UV: 8× Oversampling Filter (Linear)
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
GAIN (dB)
–1.5
–2.0
–2.5
05135-045
20020 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 1800
–3.0
Y PASS BAND IN PS OVERSAMPLINGMODE
122468100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 23. PS—Y: 8× Oversampling Filter (Pass Band)
05135-048
PS Pr/Pb RESPONSE. SSAF INTERPOLATION(4:2:2 TO4:4:4)
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
–80
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 21. PS—UV: 8× Oversampling Filter (SSAF)
Y RESPONSE IN PS OVERSAMPLINGMODE
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
–80
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 22. PS—Y: 8× Oversampling Filter
Pr/PbRESPONSE IN HDTV OVERSAMPLINGMODE
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
05135-046
20020 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 1800
–80
FREQUENCY (MHz)
05135-049
14020 40 60 80 100 1200
Figure 24. HDTV—UV: 2× Oversampling Filter
Y RESPONSE IN HDTV OVERSAMPLINGMODE
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
05135-047
20020 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 1800
–80
FREQUENCY (MHz)
05135-050
14020 40 60 80 100 1200
Figure 25. HDTV—Y: 2× Oversampling Filter
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 92
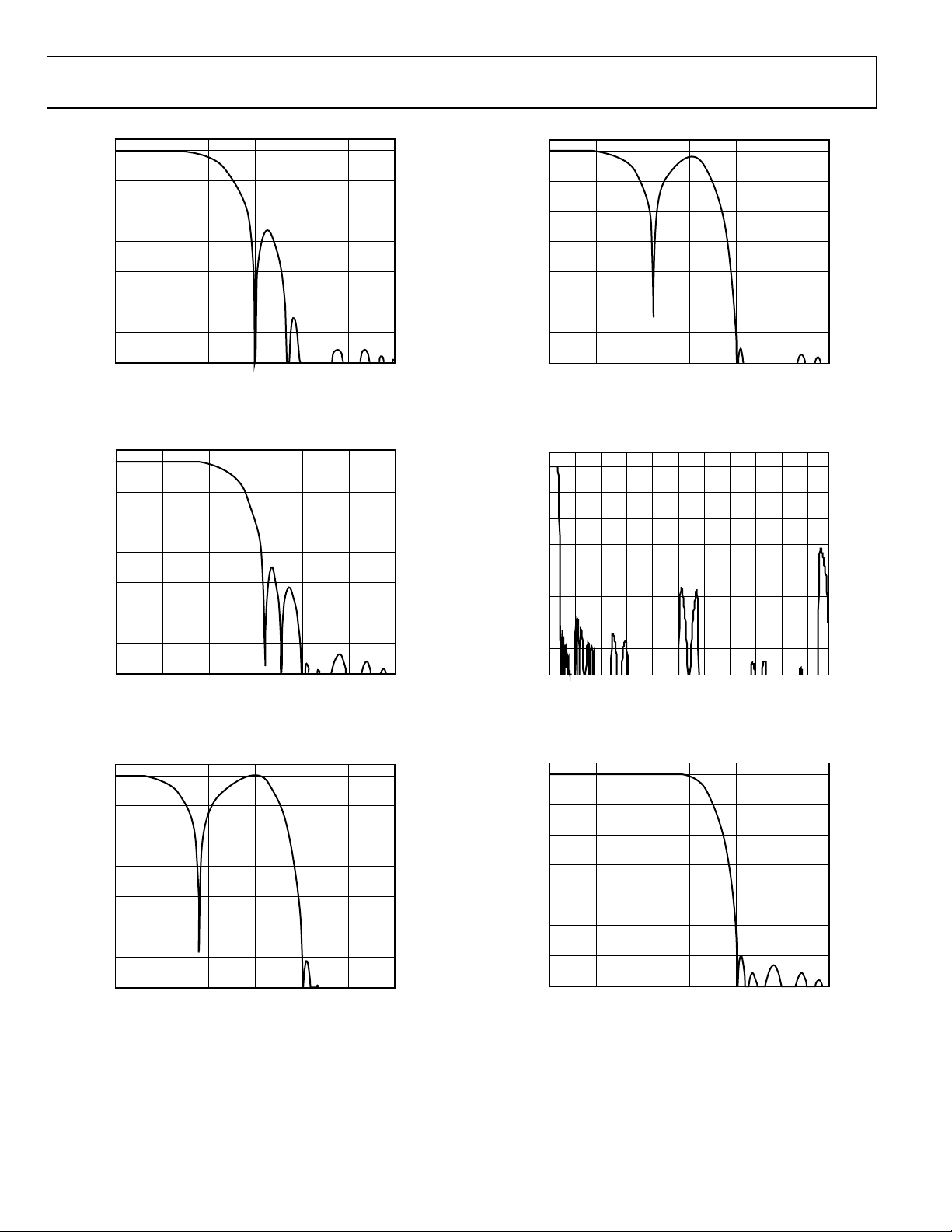
ADV7322
MAGNITUDE (dB)
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
0
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 26. Luma NT SC Low-Pass Filter
0
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 27. Luma PAL Low-Pass Filter
121086420
121086420
05135-051
05135-052
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
–70
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 29. Luma PAL Notch Filter
Y RESPONSE IN SD OVERSAMPLINGMODE
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
GAIN (dB)
–50
–60
–70
–80
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 30. SD—Y: 16× Oversampling Filter
05135-054
121086420
05135-055
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
0
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 31. Luma SSAF Filter up to 12 MHz
05135-056
121086420
0
05135-053
FREQUENCY (MHz)
121086420
Figure 28. Luma NTSC Notch Filter
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 92
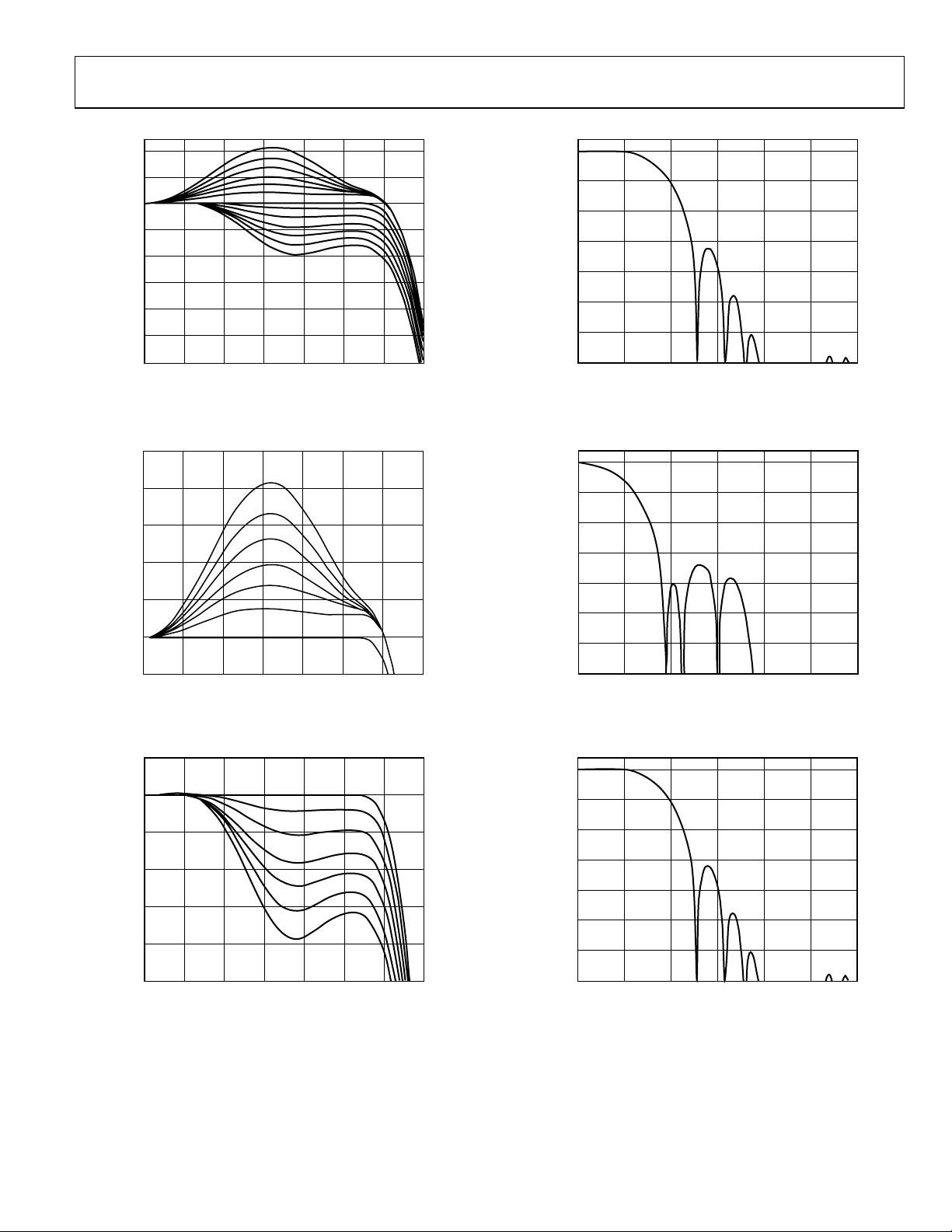
ADV7322
4
2
0
–2
–4
–6
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–8
–10
–12
0
234
1
FREQUENCY (MHz)
5
Figure 32. Luma SSAF Filter—Programmable Responses
5
4
3
2
MAGNITUDE (dB)
1
0
–1
0
234
1
FREQUENCY (MHz)
5
Figure 33. Luma SSAF Filter—Programmable Gain
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
6
05135-057
7
–70
620
FREQUENCY (MHz)
84
10
05135-060
12
Figure 35. Luma CI F Low-Pass Filter
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
05135-058
6
7
–70
4
620
FREQUENCY (MHz)
8
10
05135-061
12
Figure 36. Luma QCIF Low-Pass Filter
1
0
–1
–2
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–3
–4
–5
0
1
23
FREQUENCY (MHz)
4
5
Figure 34. Luma SSAF Filter—Programmable Attenuation
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
05135-059
6
7
–70
4
620
FREQUENCY (MHz)
8
10
05135-062
12
Figure 37. Chroma 3.0 MHz Low-Pass Filter
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 92
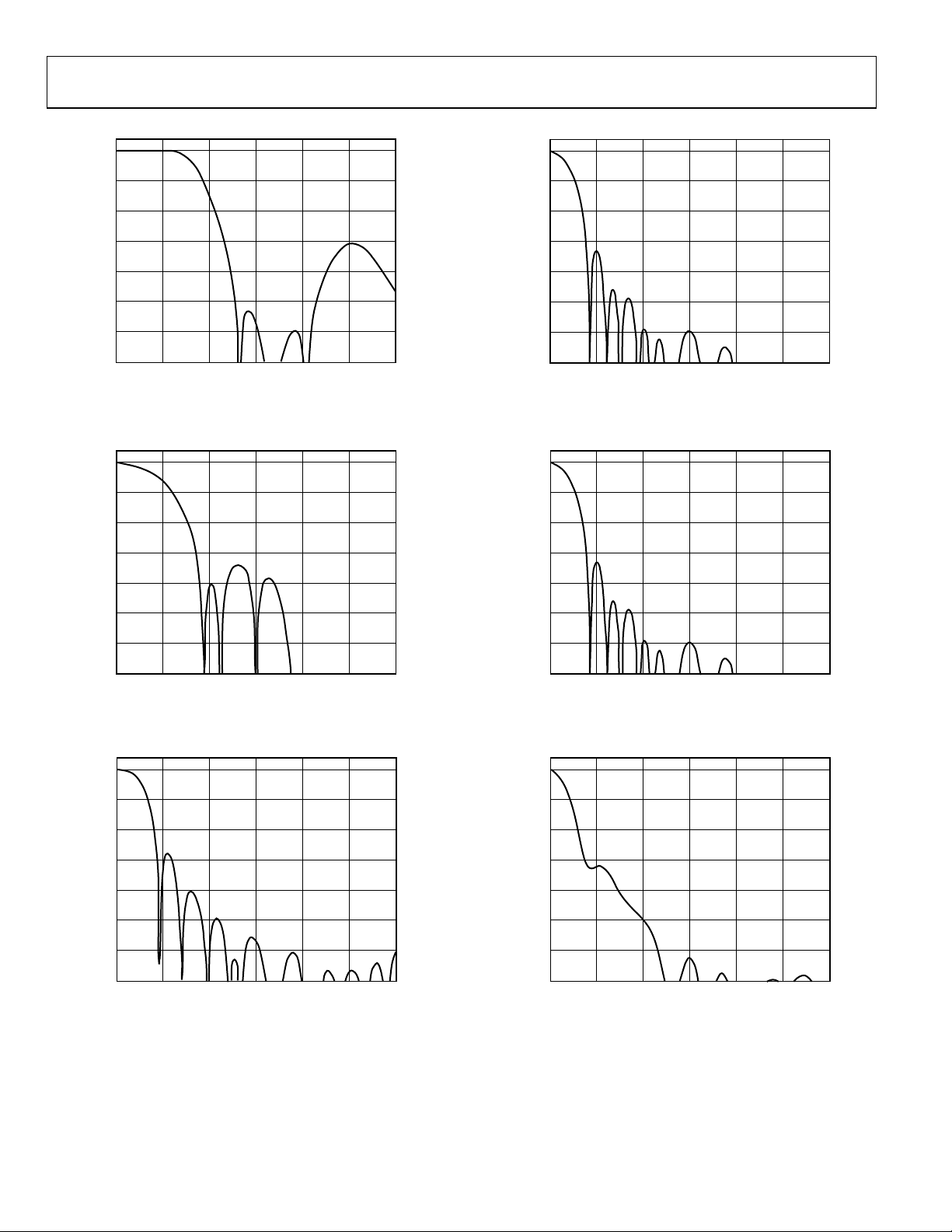
ADV7322
MAGNITUDE (dB)
MAGNITUDE (dB)
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
4
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 38. Chroma 2.0 MHz Low-Pass Filter
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
10
8
620
05135-063
12
–70
4
620
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10
8
05135-066
12
Figure 41. Chroma 0.65 MHz Low-Pass Filter
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–50
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–60
–70
4
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 39. Chroma 1.3 MHz Low-Pass Filter
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
4
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 40. Chroma 1.0 MHz Low-Pass Filter
10
8
620
05135-064
12
05135-065
10
620
8
12
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–60
–70
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
4
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 42. Chroma CIF Low-Pass Filter
0
4
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 43. Chroma QCIF Low-Pass Filter
05135-067
620
8
10
12
620
8
10
05135-068
12
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 92
ADV7322
MPU PORT DESCRIPTION
The ADV7322 supports a 2-wire serial (I2C-compatible)
microprocessor bus for driving multiple peripherals. This port
operates in an open-drain configuration. Two inputs, serial data
(SDA) and serial clock (SCL), carry information between any
device connected to the bus and the ADV7322. Each slave
device is recognized by a unique address. The ADV7322 has
four possible slave addresses for both read and write operations.
These are unique addresses for each device and are illustrated in
Figure 44. The LSB sets either a read or write operation. Logic 1
corresponds to a read operation, while Logic 0 corresponds to a
write operation. A1 is enabled by setting the ALSB pin of the
ADV7322 to Logic 0 or Logic 1. When ALSB is set to 1, there is
2
greater input bandwidth on the I
C lines, which allows high
speed data transfers on this bus. When ALSB is set to 0, there is
2
reduced input bandwidth on the I
pulses of less than 50 ns are not passed into the I
C lines, which means that
2
C internal
controller. This mode is recommended for noisy systems.
1 1 0 1 0 1 A1 X
ADDRESS
CONTROL
SET UP BY
ALSB PIN
READ/WRITE
CONTROL
0 WRITE
1 READ
Figure 44. ADV7322 Slave Address = 0xD4
05135-020
To control the various devices on the bus, the following
protocol must be followed. First, the master initiates a data
transfer by establishing a start condition, defined by a high-tolow transition on SDA while SCL remains high. This indicates
that an address/data stream will follow. All peripherals respond
to the start condition and shift the next eight bits (7-bit address
bit). The bits are transferred from MSB down to LSB.
+ R/
W
The peripheral that recognizes the transmitted address
responds by pulling the data line low during the ninth clock
pulse. This is known as an acknowledge bit. All other devices
withdraw from the bus at this point and maintain an idle
condition. The idle condition is where the device monitors the
SDA and SCL lines, waiting for the start condition and the
correct transmitted address. The R/
bit determines the
W
direction of the data.
Logic 0 on the LSB of the first byte means that the master writes
information to the peripheral. Logic 1 on the LSB of the first byte
means that the master reads information from the peripheral.
The ADV7322 acts as a standard slave device on the bus. The
data on the SDA pin is eight bits long, supporting the 7-bit
address and the R/
bit. It interprets the first byte as the device
W
address and the second byte as the starting subaddress. There is
a subaddress auto-increment facility. This allows data to be
written to or read from registers in ascending subaddress
sequence, starting at any valid subaddress. A data transfer is
always terminated by a stop condition. The user can also access
any unique subaddress register on a one-by-one basis without
updating all of the registers.
Stop and start conditions can be detected at any stage during
the data transfer. If these conditions are asserted out of
sequence with normal read and write operations, they cause the
device to immediately jump to the idle condition. During a
given SCL high period, the user should only issue a start
condition, a stop condition, or a stop condition followed by a
start condition. If an invalid subaddress is issued by the user,
the ADV7322 does not issue an acknowledge and returns to the
idle condition. If the user utilizes the auto-increment method of
addressing the encoder and exceeds the highest subaddress, the
following actions are taken:
• In read mode, the highest subaddress register contents are
output until the master device issues a no acknowledge. This
indicates the end of a read. A no acknowledge condition is
when the SDA line is not pulled low on the ninth pulse.
• In write mode, the data for the invalid byte is not loaded into
any subaddress register, a no acknowledge is issued by the
ADV7322, and the part returns to the idle condition.
Before writing to the subcarrier frequency registers, the
ADV7322 must be reset at least once after power-up.
The four subcarrier frequency registers must be updated,
starting with Subcarrier Frequency Register 0 and ending with
Subcarrier Frequency Register 3. The subcarrier frequency only
updates after the last subcarrier frequency register byte has been
received by the ADV7322.
Figure 45 illustrates a data transfer for a write sequence and
the start and stop conditions. Figure 46 shows bus write and
read sequences.
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 92

ADV7322
SDATA
SCLOCK
1–7 8
START ADRR R/W ACK SUBADDRESS ACK DATA ACK STOP
9S1–7
9
8
1–7
8
P
9
05135-022
Figure 45. Bus Data Transfer
WRITE
SEQUENCE
READ
SEQUENCE
S SLAVE ADDR A(S) SUBADDR A(S) DATA DATA A(S) P
LSB = 0
S SLAVE ADDR A(S) SUBADDR A(S) S SLAVE ADDR A(S) DATA DATAA(M) A(M) P
S = START BIT
P = STOP BIT
A(S) = ACKNOWLEDGE BY SLAVE
A(M) = ACKNOWLEDGE BY MASTER
A(S)
LSB = 1
A(S) = NO ACKNOWLEDGE BY SLAVE
A(M) = NO ACKNOWLEDGE BY MASTER
05135-023
Figure 46. Read and Write Sequences
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 92
ADV7322
REGISTER ACCESS
The MPU can write to or read from all registers of the
ADV7322 except the subaddress registers, which are write-only
registers. The subaddress register selected determines which
register the next read or write operation accesses. All
communication with the part through the bus starts with an
access to the subaddress register. A read/write operation is then
performed from/to the target address, which increments to the
next address until a stop command is performed on the bus.
Table 7. Registers 0x00 to 0x01
SR7–
SR0
Register Bit Description Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Register Setting
Power
0x00 0 Sleep mode off. 0xFC
Mode
Register
PLL and Oversampling
DAC F: Power On/Off. 0 DAC F off.
1 DAC F on.
DAC E: Power On/Off. 0 DAC E off.
1 DAC E on.
DAC D: Power On/Off. 0 DAC D off.
1 DAC D on.
DAC C: Power On/Off. 0 DAC C off.
1 DAC C on.
DAC B: Power On/Off. 0 DAC B off.
1 DAC B on.
DAC A: Power On/Off. 0 DAC A off.
1 DAC A on.
0x01 Mode
Select
Register
Clock Edge.
1 Y clocked upon rising edge.
Reserved. 0
Clock Align. 0
Only if two input clocks
Input Mode. 0 0 0 SD input only. 0x38
0 0 1 PS input only.
0 1 0 HDTV input only.
0 1 1 SD and PS (16-bit).
1 0 0 SD and PS (8-bit).
1 0 1 SD and HDTV
1 1 0 SD and HDTV
1 1 1 PS only (at 54 MHz).
Y/C/S Bus Swap. 0
1
Sleep Mode. With this
control enabled, current
consumption is reduced
to µA level. All DACs and
the internal PLL circuit are
disabled. I
be read from and written
to in sleep mode.
Control. This control
allows the internal PLL
circuit to be powered
down and the
oversampling to be
switched off.
Reserved. 0 Reserved.
Only for PS interleaved
input at 27 MHz.
are used.
2
C registers can
1 Sleep mode on.
0 1 PLL on.
0 Cb clocked upon rising edge.
1 Must be set if the phase
REGISTER PROGRAMMING
The following tables describe the functionality of each register.
All registers can be read from and written to, unless otherwise
stated.
SUBADDRESS REGISTERS (SR7 TO SR0)
Each subaddress register is an 8-bit, write-only register. After
the encoder’s bus is accessed and a read or write operation is
selected, the subaddress is set up. The subaddress register
determines to or from which register the operation takes place.
Reset Value
(Shaded)
PLL off.
delay between the two input
clocks is <9.25 ns
or >27.75 ns.
(SD oversampled).
(HDTV oversampled).
Allows data to be applied to
data ports in various configurations (SD feature only).
See Table
21.
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 92
ADV7322
Table 8. Registers 0x02 to 0x0F
SR7–
SR0 Register Bit Description Bit 7
0x02 Mode Register 0 Reserved 0 0 Zero must be written to
Test Pattern Black Bar 0 Dis abled.
1 Enabled.
Manual RGB Matrix
1 Enable manual RGB matrix
Sync on RGB2 0 No sync.
1 Sync on all RGB outputs.
RGB/YPrPb Output 0 RGB component outputs.
1 YPrPb component outputs.
SD Sync 0 No sync output.
1 Output SD syncs on
HD Sync 0 No sync output.
1 Output HD, ED, syncs on
0x03 RGB Matrix 0 x x LSB for GY. 0x03
0x04 RGB Matrix 1
0x05 RGB Matrix 2 x x x x x x x x Bit 9 to Bit 2 for GY. 0x4E
0x06 RGB Matrix 3 x x x x x x x x Bit 9 to Bit 2 for GU. 0x0E
0x07 RGB Matrix 4 x x x x x x x x Bit 9 to Bit 2 for GV. 0x24
0x08 RGB Matrix 5 x x x x x x x x Bit 9 to Bit 2 for BU. 0x92
0x09 RGB Matrix 6 x x x x x x x x Bit 9 to Bit 2 for RV. 0x7C
0x0A DAC A, B, C
Output Level
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 +0.018%
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 +0.036%
… …
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 +7.382%
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 +7.5%
Negative Gain to
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 −7.382%
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 −7.364%
… …
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 −0.018%
0x0B DAC D, E, F
Output Level
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 +0.018%
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 +0.036%
… …
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 +7.382%
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 +7.5%
Negative Gain to
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 −7.382%
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 −7.364%
… …
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 −0.018%
0x0C Reserved 0x00
0x0D Reserved 0x00
0x0E Reserved 0x00
0x0F Reserved 0x00
Adjust
Positive Gain to DAC
3
Output Voltage
DAC Output Voltage
Positive Gain to DAC
Output Voltage
DAC Output Voltage
0 Disable manual RGB matrix
x x LSB for RV. 0xF0
x x LSB for BU.
x x LSB for GV.
x x LSB for GU.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0%
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 −7.5%
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0% 0x00
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 −7.5%
1
x = bit can be custom programmed by the user. See the Gamma Correction section.
2
For more detail, refer to Appendix 7.
3
For more detail on the programmable output levels, refer to the Programmable DAC Gain Control section.
1
1
Bit 51 Bit 41 Bit 31 Bit 21 Bit 11 Bit 01
Bit 6
Register Setting Reset Value
these bits.
adjust.
adjust.
,
S_HSYNC
S_BLANK
S_HSYNC
pins.
S_VSYNC
,
S_VSYNC
,
.
0x20
0x11, Bit 2 must
also be enabled.
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 92
ADV7322
Table 9. Registers 0x10 to 0x11
SR7–
SR0 Register Bit Description Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Register Setting Note
0x10
HD Mode
Register 1
0 1 EIA770.1 output
1 0
1 1 Reserved
1 EAV/SAV codes
0 0 0 0 1 Async mode
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 1 ITU-R BT. 1358
0 0 1 0 0 ITU-R BT. 1362
0 0 1 0 1 SMPTE 296M-1/2
0 0 1 1 0 SMPTE 296M-3
0 0 1 1 1 SMPTE 296M-4/5
0 1 0 0 0 SMPTE 296M-6
0 1 0 0 1 SMPTE 296M-7/8
0 1 0 1 0 SMPTE 240M
0 1 0 1 1 Reserved
0 1 1 0 0 Reserved
0 1 1 0 1 SMPTE 274M-4/5
0 1 1 1 0 SMPTE 274M-6
0 1 1 1 1 SMPTE 274M-7/8
1 0 0 0 0 SMPTE 274M-9
1 0 0 0 1 SMPTE 274M-10/11
10010–11111 Reserved
0x11
HD Mode
Register 2
1 Pixel data valid on
0 Reserved
1 HD test pattern on
1 Field/frame
HD VBI Open 0 Disabled
1 Enabled
0 1 −11 IRE
1 0 −6 IRE
1 1 −1.5 IRE
0 Disabled
HD Output
Standard
Input Sync
Format
HD/ED Input
Mode
HD Pixel Data
Valid
HD Test Pattern
Enable
HD Test Pattern
Hatch/Field
HD Undershoot
Limiter
HD Sharpness
Filter
0 0 EIA770.2 output
Output levels for
full input range
0
0 0 0 0 0
0 Pixel data valid off
0 HD test pattern off
0 Hatch
0 0 Disabled
1 Enabled
,
VSYNC
HSYNC
BLANK
SMPTE 293M,
ITU-R BT. 1358
BTA-1004,
ITU-R BT. 1362
,
525p @
59.94 Hz
525p @
59.94 Hz
625p @
50 Hz
625p @
50 Hz
720p @
60/59.94 Hz
720p @
50 Hz
720p @
30/29.97 Hz
720p @
25 Hz
720p @
24/23.98 Hz
1035i @
60/59.94 Hz
1080i @
30/29.97 Hz
1080i @
25 Hz
1080p @
30/29.97 Hz
1080p @
25 Hz
1080p @
24/23.98 Hz
Only
available in
EDTV
(525p/625p)
Reset
Value
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 92
ADV7322
Table 10. Register 0x12
SR7–
SR0 Register Bit Description Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Register Setting
0x12
HD Mode
Register 3
HD Y Delay with Respect
to Falling Edge of
HD Color Delay with
Respect to Falling Edge of
HSYNC
HD CGMS CRC
HSYNC
0 0 0 0 clock cycles 0x00
0 0 1 1 clock cycles
0 1 0 2 clock cycles
0 1 1 3 clock cycles
1 0 0 4 clock cycles
0 0 0 0 clock cycles
0 0 1 1 clock cycle
0 1 0 2 clock cycles
0 1 1 3 clock cycles
1 0 0 4 clock cycles
0 Disabled HD CGMS
1 Enabled
0 Disabled
1 Enabled
Table 11. Registers 0x13 to 0x14
SR7–
SR0 Register Bit Description Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Register Setting
0x13
HD Mode
Register 4
1 Cr after falling edge of
Reserved 0 0 must be written to this bit.
Reserved 0 0 must be written here
Sinc Filter on DAC D, E, F 0 Disabled.
1 Enabled.
Reserved 0 0 must be written here
HD Chroma SSAF 0 Disabled.
1 Enabled.
HD Chroma Input 0 4:4:4
1 4:2:2
HD Double Buffering 0 Disabled.
1 Enabled.
0x14
HD Mode
Register 5
HD Hsync Generation1 0
1
HD Vsync Generation1 0
1
HD Blank Polarity 0
1
1 Macrovision enabled.
Reserved 0 0 must be written to these bits.
HD
1 1 =
1 Field/line counter free running.
HD Cr/Cb Sequence 0 Cb after falling edge of
HD Timing Reset x
HD Macrovision for 525p
and 625p
/Field Input 0 0 = field input.
VSYNC
Horizontal/Vertical
2
Counters
0 Macrovision disabled.
0 Update field/line counter.
A low-high-low transition
resets the internal HD timing
counters.
HSYNC
Refer to the
Output Control section.
active high.
BLANK
active low.
BLANK
VSYNC
VSYNC
/
input.
HSYNC
HSYNC
1
Used in conjunction with HD SYNC in Register 0x02, Bit 7, set to 1.
2
When set to 0, the horizontal/vertical counters automatically wrap around at the end of the line/field/frame of the standard selected. When set to 1, the
horizontal/vertical counters are free running and wrap around when external sync signals indicate to do so.
Reset
Value
Reset
Value
. 0x4C
.
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 92
 Loading...
Loading...