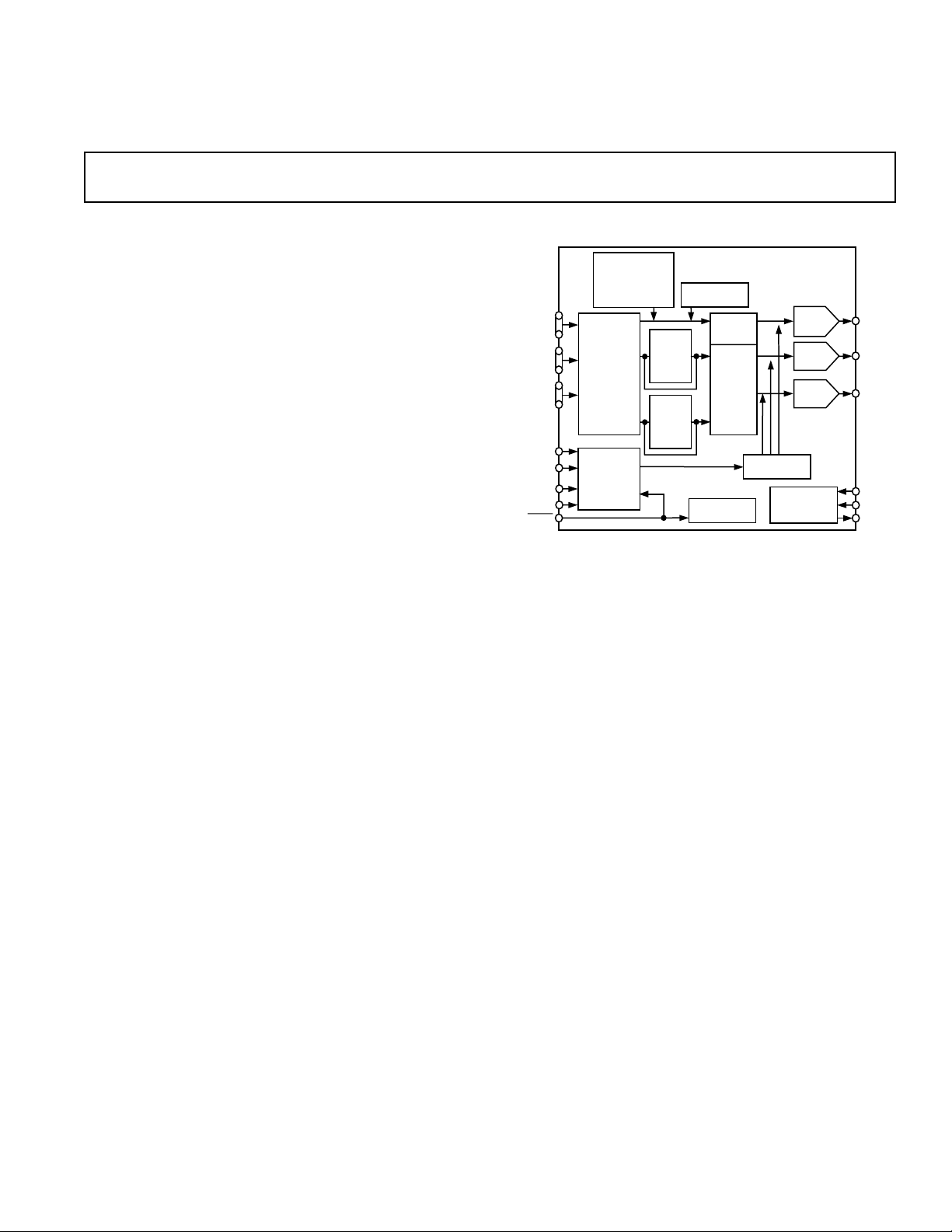
Multiformat Progressive Scan/HDTV
Encoder with Three 11-Bit DACs
a
FEATURES
INPUT FORMATS
YCrCb in 2 10-Bit (4:2:2) or 3 10-Bit (4:4:4) FormatCompliant to SMPTE-293M (525p), ITU-R.BT1358
(625p), SMPTE274M (1080i), SMPTE296M (720p) and
Any Other High-Definition Standard Using Async
Timing Mode
RGB in 3 10 Bit (4:4:4) Format
OUTPUT FORMATS
YPrPb Progressive Scan (EIA-770.1, EIA-770.2)
YPrPb HDTV (EIA-770.3)
RGB Levels Compliant to RS-170 and RS-343A
11-Bit + Sync (DAC A)
11-Bit DACs (DAC B, DAC C)
PROGRAMMABLE FEATURES
Internal Test Pattern Generator with Color Control
Y/C Delay ()
Gamma Correction
Individual DAC On/Off Control
54 MHz Output (2 Oversampling)
Sharpness Filter with Programmable Gain/Attenuation
Programmable Adaptive Filter Control
Undershoot Limiter
VBI Open Control
2C®
Filter
I
CGMS-A (525p)
2-Wire Serial MPU Interface
Single Supply 3.3 V Operation
52-MQFP Package
APPLICATIONS
Progressive Scan/HDTV Display Devices
MPEG at 81 MHz
Progressive Scan/HDTV Projection Systems
Digital Video Systems
High Resolution Color Graphics
Image Processing/Instrumentation
Digital Radio Modulation/Video Signal Reconstruction
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV7195 is a triple high-speed, digital-to-analog encoder
on a single monolithic chip. It consists of three high-speed video
D/A converters with TTL-compatible inputs.
and 10-Bit Data Input
ADV7195
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SHARPNESS
FILTER CONTROL
Y0–Y9
Cr0–Cr9
Cb0–Cb9
CLKIN
HORIZONTAL
SYNC
VERTICAL
SYNC
BLANKING
RESET
AND
ADAPTIVE
FILTER CONTROL
TEST PATTERN
GENERATOR
AND
DELAY
AND
GAMMA
CORRECTION
TIMING
GENERATOR
CHROMA
CHROMA
4:2:2
TO
4:4:4
(SSAF)
4:2:2
TO
4:4:4
(SSAF)
CGMS
MACROVISION
LUMA
SSAF
2 INTERPOLATION
I2C MPU
PORT
The ADV7195 has three separate 10-bit-wide input ports that
accept data in 4:4:4 10-bit YCrCb or RGB or 4:2:2 10-bit YCrCb.
This data is accepted in progressive scan format at 27 MHz or
HDTV format at 74.25 MHz or 74.1758 MHz. For any other
high-definition standard but SMPTE293M, ITU-R BT.1358,
SMPTE274M or SMPTE296M the Async Timing Mode can
be used to input data to the ADV7195. For all standards, external horizontal, vertical, and blanking signals or EAV/SAV codes
control the insertion of appropriate synchronization signals into
the digital data stream and therefore the output signals.
The ADV7195 outputs analog YPrPb progressive scan format
complying to EIA-770.1, EIA-770.2; YPrPb HDTV complying
to EIA-770.3; RGB complying to RS-170/RS-343A.
The ADV7195 requires a single 3.3 V power supply, an
optional external 1.235 V reference and a 27 MHz clock in
Progressive Scan Mode or a 74.25 MHz (or 74.1758 MHz)
clock in HDTV mode.
In Progressive Scan Mode, a sharpness filter with programmable
gain allows high-frequency enhancement on the luminance signal.
Programmable Adaptive Filter Control, which may be used,
allows removal of ringing on the incoming Y data. The ADV7195
supports CGMS-A data control generation.
The ADV7195 is packaged in a 52-lead MQFP package.
ADV7195
SYNC
GENERATOR
DAC CONTROL
11-BIT+
SYNC
DAC
11-BIT
DAC
11-BIT
DAC
BLOCK
DAC A ( Y)
DAC B
DAC C
V
REF
RESET
COMP
I2C is a registered trademark of Philips Corporation.
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2001

ADV7195
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
3.3 V SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3 V DYNAMIC–SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3.3 V TIMING–SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
PIN CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Control Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Analog Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Undershoot Limiter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2
C Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
I
Internal Test Pattern Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Y/CrCb Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Gamma Correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
54 MHz Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
PROGRAMMABLE SHARPNESS FILTER . . . . . . . . . . . 10
PROGRAMMABLE ADAPTIVE FILTER CONTROL . . 11
INPUT/OUTPUT CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
MPU PORT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
REGISTER ACCESSES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
REGISTER PROGRAMMING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Subaddress Register (SR7–SR0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Register Select (SR6–SR0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
PROGRESSIVE SCAN MODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MODE REGISTER 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MR0 (MR07–MR00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MR0 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Output Standard Selection (MR00–MR01) . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Input Control Signals (MR02–MR03) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Input Standard (MR04) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Reserved (MR05) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
DV Polarity (MR06) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Reserved (MR07) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MODE REGISTER 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
MR1 (MR17–MR10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
MR1 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Pixel Data Enable (MR10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Input Format (MR11) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Test Pattern Enable (MR12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Test Pattern Hatch/Frame (MR13) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
VBI Open (MR14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Undershoot Limiter (MR15–MR16) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Sharpness Filter (MR17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
MODE REGISTER 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
MR1 (MR27–MR20) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
MR2 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Y Delay (MR20–MR22) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Color Delay (MR23–MR25) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
CGMS Enable (MR26) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
CGMS CRC (MR27) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
14
MODE REGISTER 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR3 (MR37–MR30) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR3 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
HDTV Enable (MR30) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Reserved (MR31–MR32) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DAC A Control (MR33) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DAC B Control (MR34) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DAC C Control (MR35) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Interpolation (MR36) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Reserved (MR37) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MODE REGISTER 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR4 (MR47–MR40) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR4 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Timing Reset (MR40) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MODE REGISTER 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR5 (MR57–MR50) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MR5 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Reserved (MR50) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
RGB Mode (MR51) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Sync on PrPb (MR52) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Color Output Swap (MR53) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Gamma Curve (MR54) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Gamma Correction (MR55) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Adaptive Mode Control (MR56) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Adaptive Filter Control (MR57) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
COLOR Y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CY (CY7–CY0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
COLOR CR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CCR (CCR7–CCR0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
COLOR CB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CCB (CCB7–CCB0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
MODE REGISTER 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
MR6 (MR67–MR60) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
MR6 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
MR67–MR60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CGMS DATA REGISTERS 2–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CGMS2 (CGMS27–CGMS20) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CGMS1 (CGMS17–CGMS10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CGMS0 (CGMS07–CGMS00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
FILTER GAIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
FG (FG7–FG0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
FG BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Filter Gain A (FG3–FG0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Filter Gain B (FG4–FG7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
GAMMA CORRECTION REGISTERS 0–13
(GAMMA CORRECTION 0–13) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
SHARPNESS FILTER CONTROL AND
ADAPTIVE FILTER CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
SHARPNESS FILTER MODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ADAPTIVE FILTER MODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ADAPTIVE FILTER GAIN 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFG1 (AFG1)7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ADAPTIVE FILTER GAIN 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFG2 (AFG2)7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ADAPTIVE FILTER GAIN 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFG3 (AFG3)7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
–2–
REV. 0

ADV7195
ADAPTIVE FILTER THRESHOLD A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFTA AFTA7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ADAPTIVE FILTER THRESHOLD B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFTB AFTB7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ADAPTIVE FILTER THRESHOLD C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AFTC AFTC7–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
SHARPNESS FILTER AND ADAPTIVE FILTER
APPLICATIONS EXAMPLES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Sharpness Filter Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Adaptive Filter Control Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
HDTV MODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MODE REGISTER 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
MR0 (MR07–MR00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
MR0 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Output Standard Selection (MR00-MR01) . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Input Control Signals (MR02–MR03) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Reserved (MR04) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Input Standard (MR05) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
DV Polarity (MR06) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Reserved (MR07) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
MODE REGISTER 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
MR1 (MR17–MR10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
MR1 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Pixel Data Enable (MR10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Input Format (MR11) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Test Pattern Enable (MR12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Test Pattern Hatch/Frame (MR13) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
VBI Open (MR14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Reserved (MR15–MR17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
MODE REGISTER 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MR1 (MR27–MR20) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MR2 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Y Delay (MR20–MR22) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
26
Color Delay (MR23–MR25) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Reserved (MR26–MR27) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MODE REGISTER 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MR3 (MR37–MR30) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MR3 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
HDTV Enable (MR30) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Reserved (MR31–MR32) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
DAC A Control (MR33) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
DAC B Control (MR34) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
DAC C Control (MR35) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Reserved (MR36–MR37) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
MODE REGISTER 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MR4 (MR47–MR40) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MR4 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Timing Reset (MR40) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Reserved (MR41–MR47) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MODE REGISTER 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MR5 (MR57–MR50) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
MR5 BIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Reserved (MR50) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
RGB Mode (MR51) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Sync on PrPb (MR52) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Color Output Swap (MR53) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Reserved (MR54–MR57) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
DAC TERMINATION AND LAYOUT
CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Voltage Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
PC BOARD LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . 30
Supply Decoupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Digital Signal Interconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Analog Signal Interconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Video Output Buffer and Optional Output Filter . . . . . . . 31
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
REV. 0
–3–
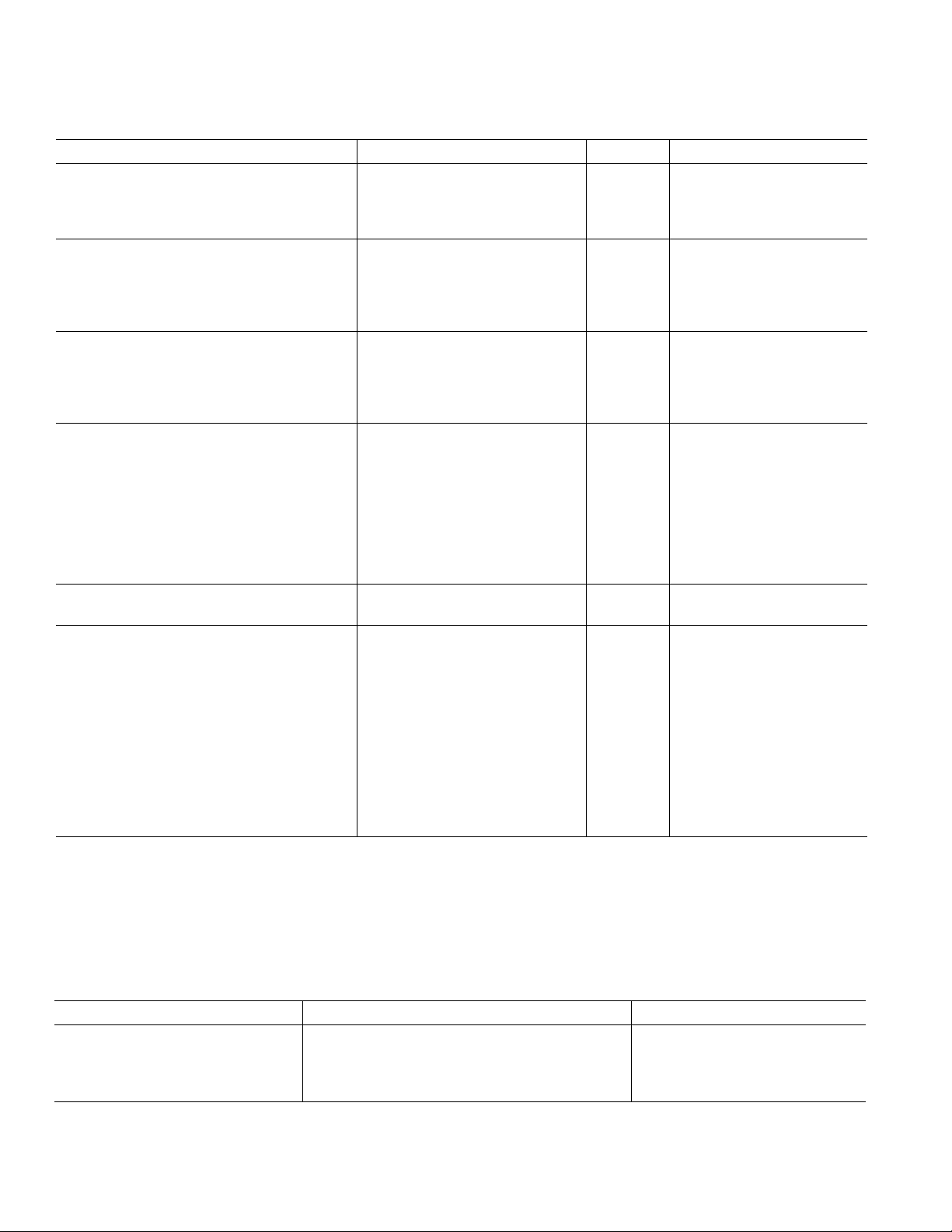
ADV7195–SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, V
3.3 V SPECIFICATIONS
to 70C] unless otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 11 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity
Differential Nonlinearity
1
1
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output Low Voltage, V
Output High Voltage, V
OL
OH
2.4 V I
Three-State Leakage Current 10 µAV
Three-State Output Capacitance 4 pF
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
Input Capacitance, C
IL
IN
IN
IH
2V
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Full-Scale Output Current 3.92 4.25 4.56 mA DAC A
2.54 2.83 3.11 mA DAC B, DAC C
Output Current Range 3.92 4.25 4.56 mA DAC A
2.39 2.66 2.93 mA DAC B, DAC C
DAC-to-DAC Matching 1.4 %
Output Compliance Range, V
Output Impedance, R
OUT
Output Capacitance, C
OC
OUT
0 1.4 V
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (External)
Reference Range, V
POWER REQUIREMENTS
2
I
DD
3, 4
I
AA
I
PLL
REF
1.112 1.235 1.359 V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.01 %/%
NOTES
1
Guaranteed by characterization.
2
IDD or the circuit current is the continuous current required to drive the digital core without I
3
IAA is the total current required to supply all DACs, including the V
4
All DACs On.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
circuitry.
REF
= 1.235 V, R
REF
SET
= 110C.)
MAX
= 2470 , R
= 300 . All specifications T
LOAD
1.5 LSB
0.9 2.0 LSB
0.4 V I
SINK
SOURCE
IN
0.8 0.65 V
0 µAV
IN
4pF
100 kΩ
7pF
25 35 mA 1× Interpolation
51 60 mA 2× Interpolation
40 mA HDTV Mode
(With f
11 15 mA 1× Interpolation,
2× Interpolation, and
HDTV Mode
6.0 12 mA 1× Interpolation,
2× Interpolation, and
HDTV Mode
.
PLL
= 3.2 mA
= 400 µA
= 0.4 V
= 0.0 V or V
= 7425 MHz)
CLK
MIN
DD
to T
MAX
[0C
3 V DYNAMIC–SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, V
to T
[0C to 70C] unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 2470 , R
SET
= 300 . All specifications T
LOAD
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Luma Bandwidth 13.5 MHz
Chroma Bandwidth 6.75 MHz
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 64 dB Luma Ramp Unweighted
Chroma/Luma Delay Inequality 0 ns
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–4–
REV. 0
MIN
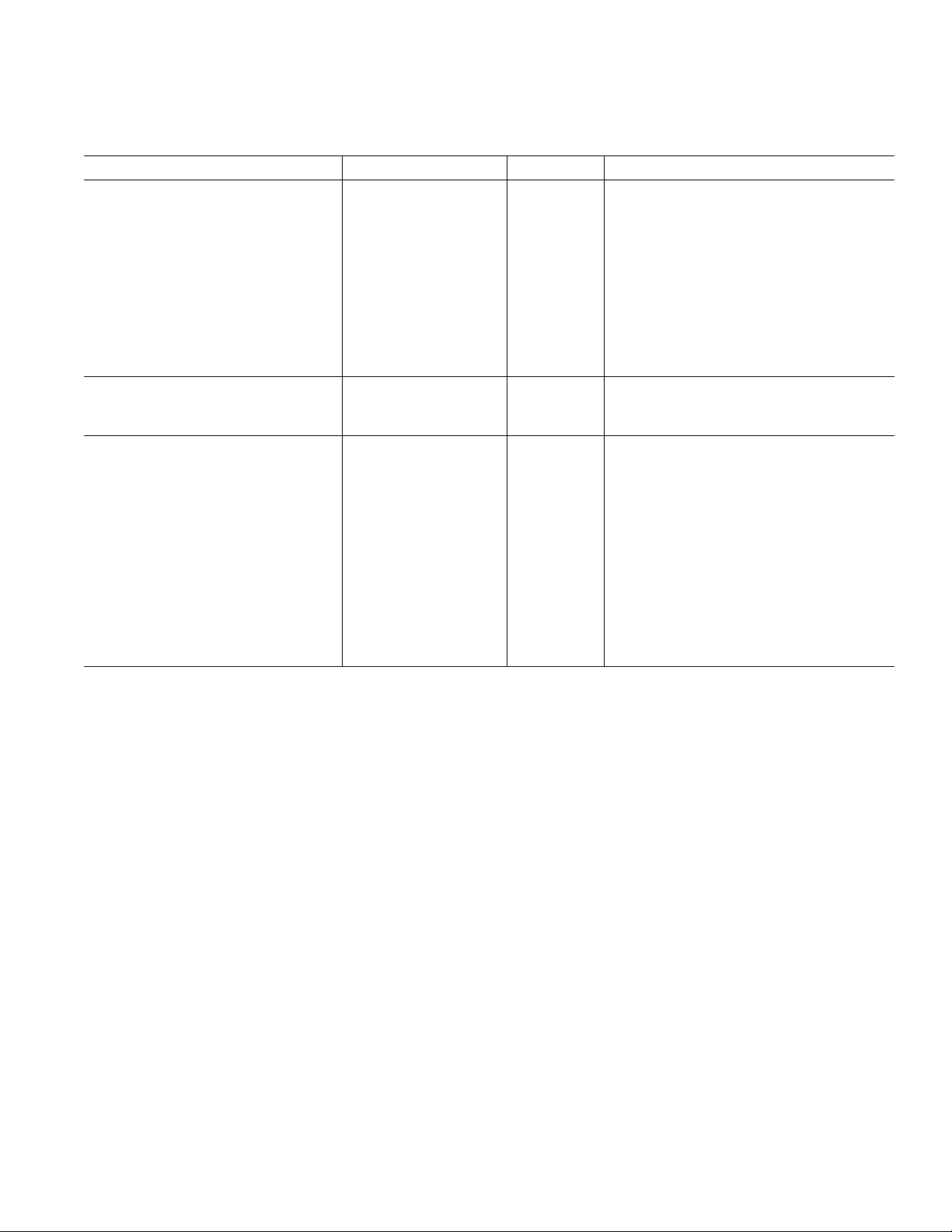
ADV7195
(VAA = 3.15 V to 3.45 V, V
3.3 V TIMING–SPECIFICATIONS
P
arameter Min Typ Max Unit Conditions
MPU PORT
1
T
to T
MIN
[0C to 70C] unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 2470 , R
SET
= 300 . All specifications
LOAD
SCLOCK Frequency 0 400 kHz
SCLOCK High Pulsewidth, t
SCLOCK Low Pulsewidth, t
Hold Time (Start Condition), t
Setup Time (Start Condition), t
Data Setup Time, t
5
SDATA, SCLOCK Rise Time, t
SDATA, SCLOCK Fall Time, t
Setup Time (Stop Condition), t
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
0.6 µs
1.3 µs
0.6 µs After this Period the 1st Clock Is Generated
0.6 µs Relevant for Repeated Start Condition
100 ns
300 ns
300 ns
0.6 µs
RESET Low Time 100 ns
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Analog Output Delay, t
2
6
10 ns
Analog Output Skew 0.5 ns
CLOCK CONTROL AND PIXEL PORT
f
CLK
3
27 MHz Progressive Scan Mode
74.25 MHz HDTV Mode
81 MHz ASYNC Timing Mode and 1× Interpolation
Clock High Time, t
Clock Low Time, t
Data Setup Time, t
Data Hold Time, t
9
10
11
12
Control Setup Time, t
Control Hold Time, t
12
11
5.0 21.5 ns
5.0 22.0 ns
2.0 3.4 ns
4.5 3.2 ns
7.0 3.4 ns
4.0 3.2 ns
Pipeline Delay 16 Clock Cycles For 4:4:4 Pixel Input Format at 1× Oversampling
Pipeline Delay 29 Clock Cycles For 4:4:4 or 4:2:2 Pixel Input Format at
2× Oversampling
NOTES
1
Guaranteed by characterization.
2
Output delay measured from 50% point of rising edge of CLOCK to the 50% point of DAC output full-scale transition.
3
Data: Cb/Cr(9–0), Cr(9–0), Y(9–0); Control: HSYNC/SYNC, VSYNC/TSYNC, DV.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. 0
–5–
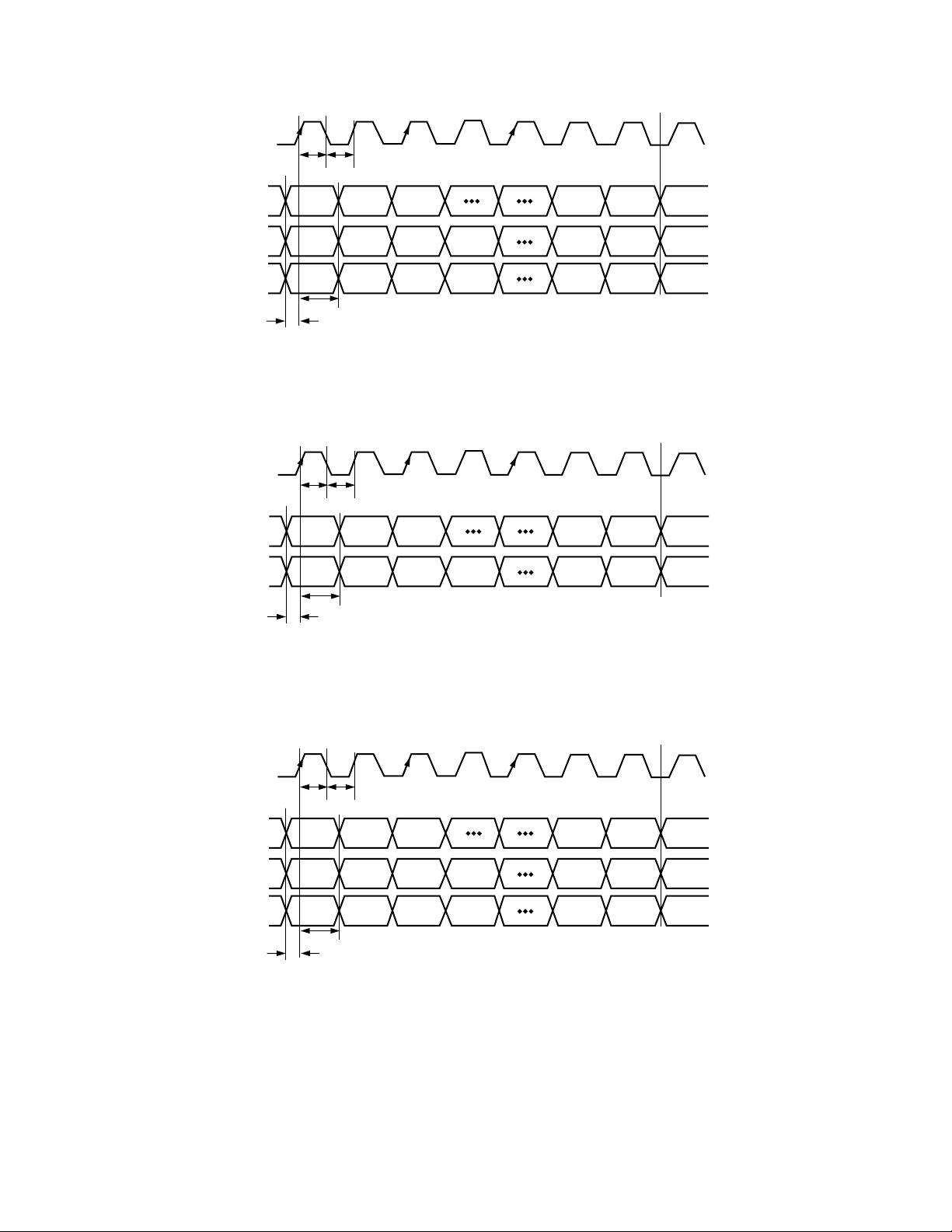
ADV7195
CLOCK
t
t
10
9
PIXEL INPUT
DATA
CLOCK
PIXEL INPUT
DATA
R0 R1 R2 Rxxx
G0 G1 G2 GxxxG3 Gxxx
B0 B1 B2 BxxxB3 Bxxx
t
12
t
11
Rxxx
t
- CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
- CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
- DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
- DATA HOLD TIME
12
Figure 1. 4:4:4 RGB Input Data Format Timing Diagram
t
t
10
9
Y0 Y1 Y2 Yxxx
Cb0 Cr0 Cb1 CrxxxCr1 Cbxxx
t
12
t
11
Yxxx
t
- CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
- CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
- DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
- DATA HOLD TIME
12
Figure 2. 4:2:2 Input Data Format Timing Diagram
CLOCK
PIXEL INPUT
DATA
t
t
10
9
Y0 Y1 Y2 Yxxx
Cb0 Cb1 Cb2 CbxxxCb3 Cbxxx
Cr0
t
t
11
Cr1 Cr2 CrxxxCr3 Crxxx
12
Yxxx
t
- CLOCK HIGH TIME
9
t
- CLOCK LOW TIME
10
t
- DATA SETUP TIME
11
t
- DATA HOLD TIME
12
Figure 3. 4:4:4 YCrCb Input Data Format Timing Diagram
–6–
REV. 0
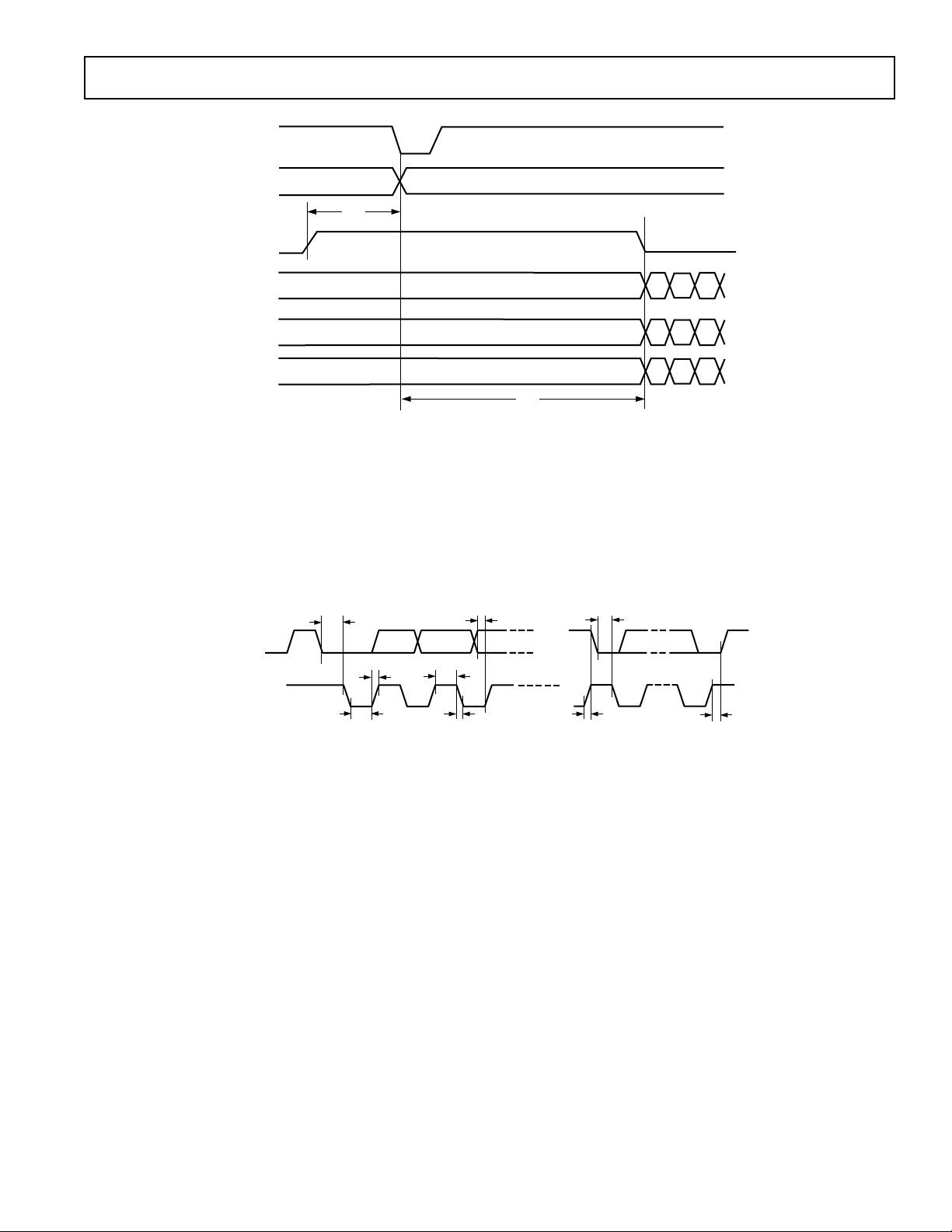
HSYNC
VSYNC
DV
ADV7195
A
PIXEL
DATA
SDA
SCL
A
= 16 CLK CYCLES (525P)
MIN
= 12 CLK CYCLES (625P)
A
MIN
= 44 CLK CYCLES (1080I)
A
MIN
A
= 70 CLK CYCLES (720P)
MIN
B
B
B
B
Figure 4. Input Timing Diagram
t
t
3
t
6
t
2
5
t
1
t
7
Figure 5. MPU Port Timing Diagram
B
= 122 CLK CYCLES (525P)
MIN
= 132 CLK CYCLES (625P)
MIN
= 236 CLK CYCLES (1080I)
MIN
= 300 CLK CYCLES (720P)
MIN
t
3
t
4
YYYY
Cr Cr Cr Cr
Cb Cb Cb Cb
t
8
REV. 0
–7–
ADV7195
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
VAA to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 V
Voltage on Any Digital Pin . . . . GND – 0.5 V to V
Ambient Operating Temperature (T
Storage Temperature (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
S
) . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
A
+ 0.5 V
AA
Infrared Reflow Soldering (20 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225°C
Vapor Phase Soldering (1 minute) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
to GND2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 V to V
I
OUT
AA
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Analog Output Short Circuit to any Power Supply or Common can be of an
indefinite duration.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADV7195KST 0°C to 70°C Plastic Quad Flatpack S-52
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the ADV7195 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
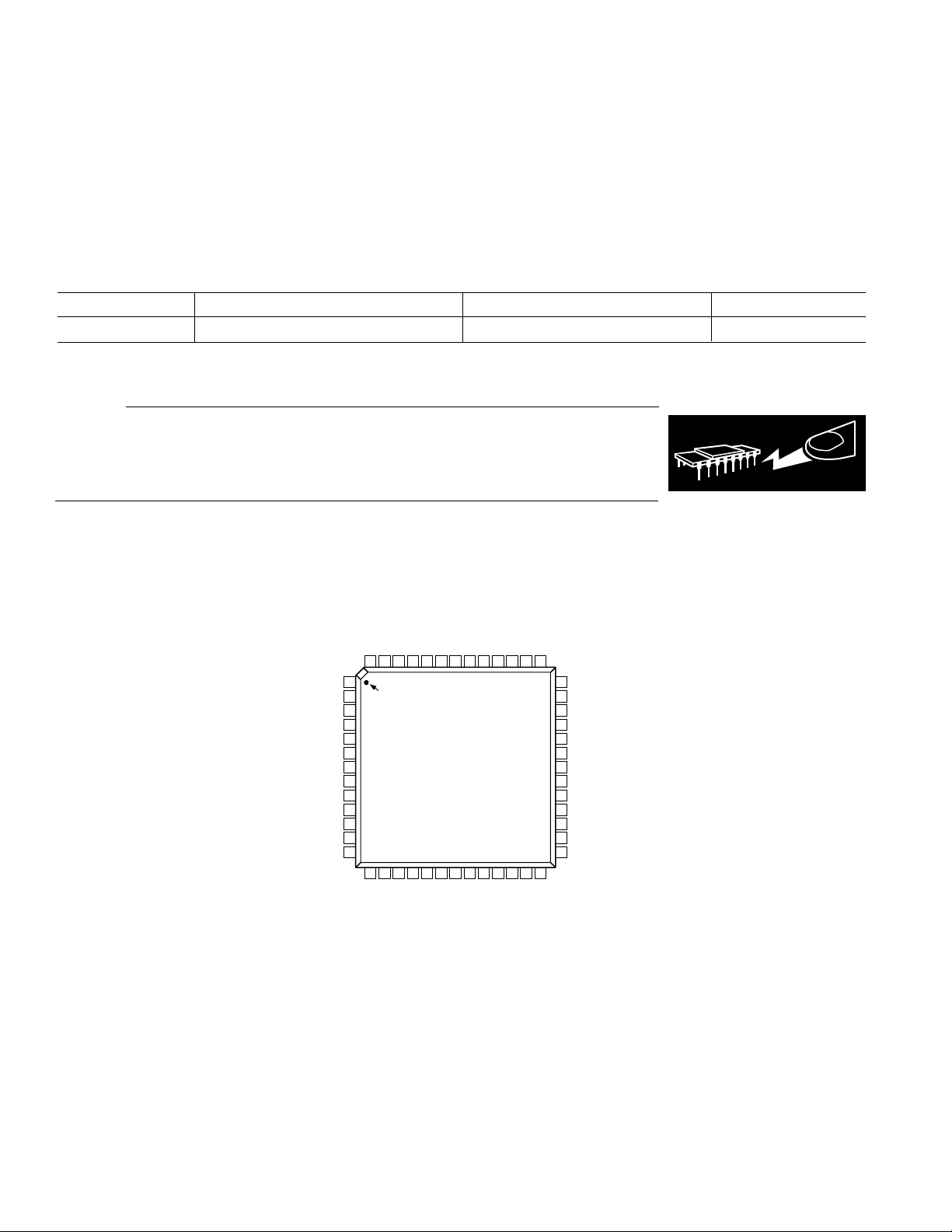
PIN CONFIGURATION
GND
Cb/Cr[0]
Cb/Cr[1]
Cb/Cr[2]
Cr[1]
Cr[2]
Cr[3]
Cb/Cr[3]
ADV7195
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
Cr[4]
52 51 50 49 48 43 42 41 4047 46 45 44
1
V
Y[0]
Y[1]
Y[2]
Y[3]
Y[4]
Y[5]
Y[6]
Y[7]
Y[8]
Y[9]
VDD
GND
DD
PIN 1
2
IDENTIFIER
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
Cr[0]
Cb/Cr[4]
Cb/Cr[5]
Cr[5]
Cr[6]
Cb/Cr[6]
Cb/Cr[7]
Cr[7]
Cr[8]
Cb/Cr[8]
Cb/Cr[9]
AA
V
Cr[9]
ALSB
RESET
AGND
CLKIN
39
V
REF
R
38
SET
37
COMP
36
DAC B
35
V
AA
34
DAC A/Y OUTPUT
33
AGND
32
DAC C
31
SDA
30
SCL
29
HSYNC/SYNC
28
VSYNC/TSYNC
27
DV
–8–
REV. 0
ADV7195
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Mnemonic Input/Output Function
1, 12 V
DD
2–11 Y0–Y9 I 10-bit progressive scan/HDTV input port for Y data. Input for G data when RGB
13, 52 GND G Digital Ground
14–23 Cr0–Cr9 I
24, 35 V
AA
25 CLKIN I Pixel Clock Input. Requires a 27 MHz reference clock for standard operation in
26, 33 AGND G Analog Ground
27 DV I Video Blanking Control Signal Input
28 VSYNC/ I VSYNC, Vertical Sync Control Signal Input or TSYNC Input Control Signal in
TSYNC Async Timing Mode
29 HSYNC/ I HSYNC, Horizontal
SYNC
30 SCL I MPU Port Serial Interface Clock Input
31 SDA I/O MPU Port Serial Data Input/Output
32 DAC C O Color Component Analog Output of Input Data on Cb/Cr9–0 Input Pins
34 DAC A O Y Analog Output
36 DAC B O Color Component Analog Output of Input Data on Cr9–Cr0 Input Pins
37 COMP O Compensation Pin for DACs. Connect 0.1 µF Capacitor from COMP pin to V
38 R
39 V
SET
REF
40 RESET I This input resets the on-chip timing generator and sets the ADV7195 into
41 ALSB I TTL Address Input. This signal sets up the LSB of the MPU address. When this
42–51 Cb/Cr9–0 I
P Digital Power Supply
data is input.
1
0-Bit Progressive Scan/HDTV Input Port for Color Data in 4:4:4 Input Mode.
In 4:2:2 mode this input port is not used. Input port for R data when RGB data
is input.
P Analog Power Supply
Progressive Scan Mode or a 74.25 MHz (74.1758 MHz) reference clock in
HDTV mode.
Sync Control Signal Input or SYNC Input Control Signal in
Async Timing Mode
I A 2470 Ω resistor for input ranges 64–940 and 64–960 (output standards
EIA-770.1–EIA-770.3) must be connected from this pin to ground and is used to
control the amplitudes of the DAC outputs. For input ranges 0–1023 (output
standards RS-170, RS-343A) the R
value must be 2820 Ω.
SET
I/O Optional External Voltage Reference Input for DACs or Voltage Reference
Output (1.235 V)
Default Register setting. Reset is an active low signal.
pin is tied high, the I
When this pin is tied low, the input bandwidth on the I
1
0-Bit Progressive scan/HDTV input port for color data. In 4:2:2 mode the
2
C filter is activated, which reduces noise on the I2C Interface.
2
C interface is increased.
multiplexed CrCb data must be input on these pins. Input port for B data when
RGB is input.
AA
.
REV. 0
–9–
ADV7195
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Digital Inputs
The digital inputs of the ADV7195 are TTL-compatible. 30-bit
YCrCb or RGB pixel data in 4:4:4 format or 20-bit YCrCb
pixel data in 4:2:2 format is latched into the device on the rising
edge of each clock cycle at 27 MHz in Progressive Scan Mode or
74.25 MHz or 74.1785 MHz in HDTV mode. It is also possible
to input 3 × bit RGB data in 4:4:4 format to the ADV7195. It
is recommended to input data in 4:2:2 mode to make use of the
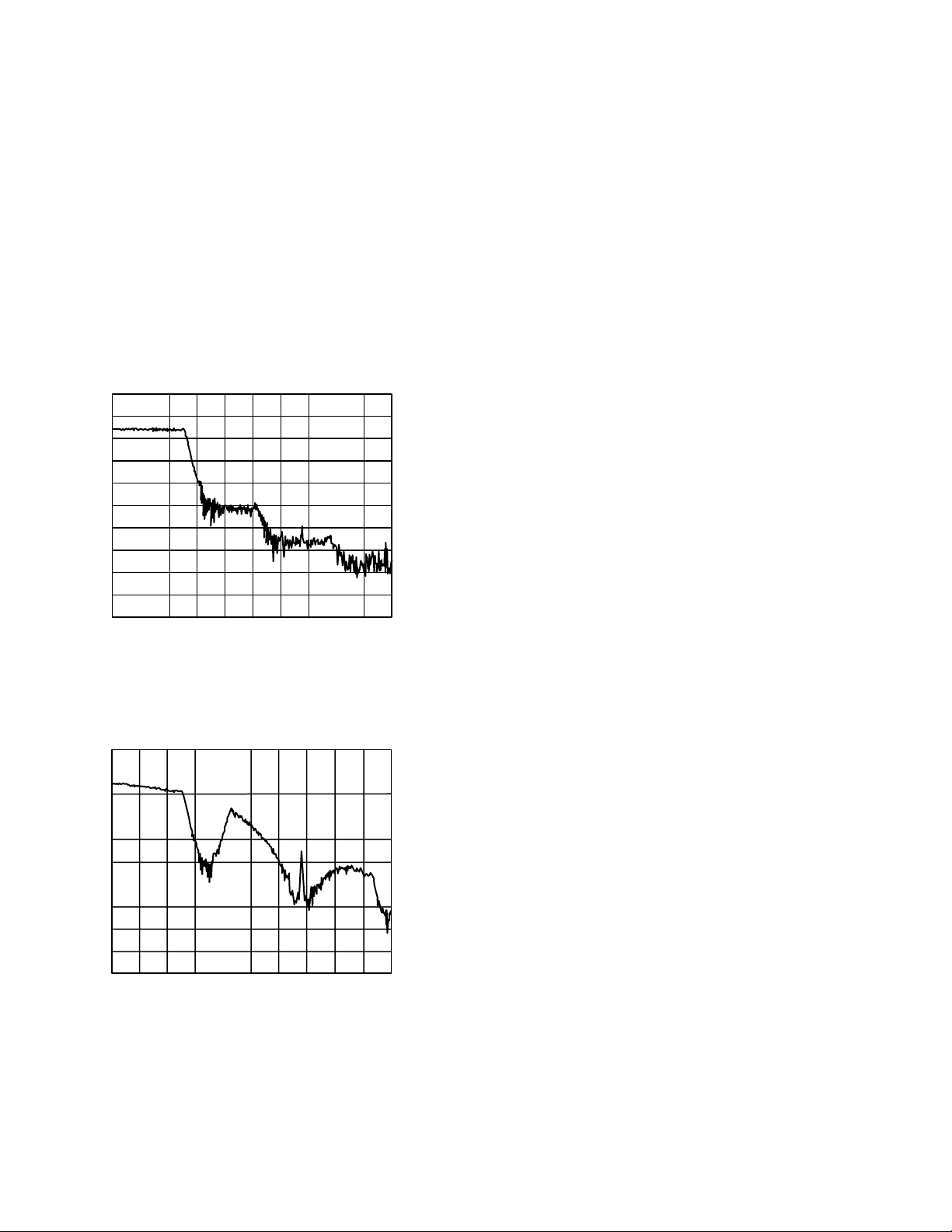
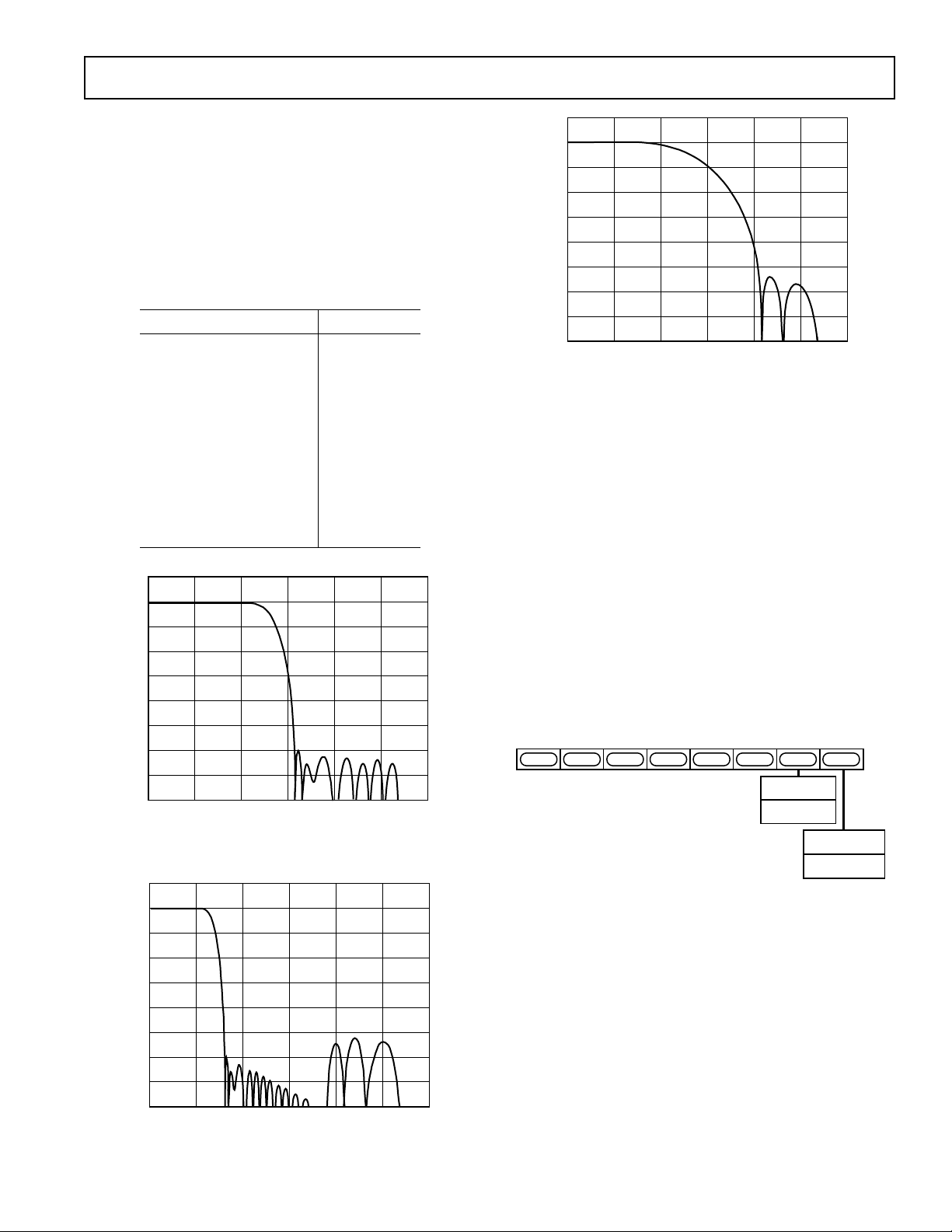
chroma SSAFs on the ADV7195. As can be seen in Figures 6 and
7, this filter has 0 dB passband response and prevents signal components being loaded back into the frequency band. In 4:4:4 input
mode, the video data is already interpolated by the external
input device and the chroma SSAFs of the ADV7195 are bypassed.
ATTEN 10dB VAVG 1 MKR 0dB
RL –10.0dBm 10dB/ 3.18MHz
START 100kHz STOP 20.00MHz
RBW 10kHz VBW 300Hz SWP 17.0SEC
Figure 6. ADV7195 SSAF Response to a 2.5 MHz Chroma
Sweep Using 4:2:2 Input Mode
ATTEN 10dB VAVG 4 MKR –3.00dB
RL –10.0dBm 10dB/ 3.12MHz
START 100kHz STOP 20.00MHz
RBW 10kHz VBW 300Hz SWP 17.0SEC
Figure 7. Conventional Filter Response to a 2.5 MHz
Chroma Sweep Using 4:4:4 Input Mode
Control Signals
The ADV7195 accepts sync control signals accompanied by
valid 4:2:2 or 4:4:4 data. These external horizontal, vertical, and
blanking pulses (or EAV/SAV codes) control the insertion of
appropriate sync information into the output signals.
Analog Outputs
The analog Y signal is output on the 11-bit + Sync DAC A,
the color component analog signals on the 11-bit DAC B and
DAC C conforming to EIA-770.1 or EIA-770.2 standards in PS
mode or EIA-770.3 in HDTV mode. R
(EIA-770.1, EIA-770.2, EIA-770.3), R
has a value of 2470 Ω
SET
has a value of 300 Ω.
LOAD
For RGB outputs conforming to RS-170/RS-343A output standards R
must have a value of 2820 Ω.
SET
Undershoot Limiter
A limiter can be applied to the Y data before it is applied to the
DACs. Available limit values are –1.5 IRE, –6 IRE, –11 IRE below
blanking. This functionality is available in Progressive Scan
mode only.
I2C Filter
A selectable internal I2C filter allows significant noise reductions
on the I
on the I
passed to the I
input bandwidth on the I
2
C interface. In setting ALSB high, the input bandwidth
2
C lines is reduced and pulses of less than 50 ns are not
2
C controller. Setting ALSB low allows greater
2
C lines.
Internal Test Pattern Generator
The ADV7195 can generate a cross-hatch pattern (white lines
against a black background). Additionally, the ADV7195 can
output a uniform color pattern. The color of the lines or uniform field/frame can be programmed by the user.
Y/CrCb Delay
The Y output and the color component outputs can be delayed
wrt the falling edge of the horizontal sync signal by up to four
clock cycles.
Gamma Correction
Gamma correction may be performed on the luma data. The
user has the choice to use either of two different gamma curves,
A or B. At any one time one of these curves is operational if
gamma correction is enabled. Gamma correction allows the
mapping of the luma data to a user-defined function.
54 MHz Operation
In Progressive Scan mode, it is possible to operate the three
output DACs at 54 MHz or 27 MHz. The ADV7195 is supplied with a 27 MHz clock synced with the incoming data. If
required, a second stage interpolation filter interpolates the data
to 54 MHz before it is applied to the three output DACs.
The second stage interpolation filter is controlled by MR36. After
applying a Reset, it is recommended to toggle this bit. Before
toggling this bit, 3Ehex must be written to Address 09hex.
PROGRAMMABLE SHARPNESS FILTER
Sharpness Filter Mode is applicable to the Y data only in
Progressive Scan mode.
The desired frequency response can be chosen by the user in
programming the correct value via the I
2
C. The variation of
frequency responses can be seen in the figures on the following pages.
–10–
REV. 0
ADV7195
PROGRAMMABLE ADAPTIVE FILTER CONTROL
If the Adaptive Filter Mode is enabled (Progressive Scan mode
only), it is possible to compensate for large edge transitions on
the incoming Y data. Sensitivity and attenuation are all programmable over the I
2
C. For further information refer to
Sharpness Filter Control and Adaptive Filter Control section.
INPUT/OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
Table I shows possible input/output configurations when using
the ADV7195.
Table I.
Input Format Output
YCrCb Progressive Scan
4:2:2 2×
4:4:4 1× or 2×
YCrCb HDTV
4:2:2 1×
4:4:4 1×
RGB Progressive Scan
4:4:4 2×
RGB HDTV
4:4:4 1×
Async Timing Mode
All Inputs 1×
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
5 10152025030
Figure 8. 2× Interpolation Filter 4-Channel
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
0
5 10152025
30
Figure 9. Interpolation Filter–CrCb Channels/Cr 4:2:2
Input Data
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
5 10152025
0
30
Figure 10. Interpolation Filter–CrCb Channels/Cr 4:4:4
Input Data
MPU PORT DESCRIPTION
The ADV7195 support a 2-wire serial (I2C-compatible) microprocessor bus driving multiple peripherals. Two inputs, Serial
Data (SDA) and Serial Clock (SCL), carry information between
any device connected to the bus. Each slave device is recognized
by a unique address. The ADV7195 has four possible slave
addresses for both read and write operations. These are unique
addresses for each device and are illustrated in Figure 11. The
LSB sets either a read or write operation. Logic Level “1” corresponds to a read operation while Logic Level “0” corresponds to
a write operation. A1 is set by setting the ALSB pin of the
ADV7195 to Logic Level “0” or Logic Level “1.” When ALSB is
set to “0,” there is greater input bandwidth on the I
which allows high-speed data transfers on this bus. When ALSB
is set to “1,” there is reduced input bandwidth on the I
lines, which means that pulses of less than 50 ns will not pass
into the I
2
C internal controller. This mode is recommended
2
C lines,
2
C
for noisy systems.
1 X1010 1A1
ADDRESS
CONTROL
SETUP BY
ALSB
READ/ WRITE
CONTROL
0 WRITE
1 READ
Figure 11. Slave Address
To control the various devices on the bus the following protocol
must be followed. First the master initiates a data transfer by
establishing a Start condition, defined by a high-to-low transition on SDA while SCL remains high. This indicates that an
address/data stream will follow. All peripherals respond to the
Start condition and shift the next eight bits (7-bit address + R/W
bit). The bits are transferred from MSB down to LSB. The
peripheral that recognizes the transmitted address responds by
pulling the data line low during the ninth clock pulse. This is
known as an acknowledge bit. All other devices withdraw from
the bus at this point and maintain an idle condition. The idle
condition is where the device monitors the SDA and SCL lines
waiting for the Start condition and the correct transmitted
address. The R/W bit determines the direction of the data.
REV. 0
–11–
 Loading...
Loading...