ANALOG DEVICES ADV7183A Service Manual
Multiformat SDTV Video Decoder
FEATURES
Multiformat video decoder supports NTSC-(J, M, 4.43),
PAL-(B/D/G/H/I/M/N), SECAM
Integrates three 54 MHz, 10-bit ADCs
Clocked from a single 27 MHz crystal
Line-locked clock-compatible (LLC)
Adaptive Digital Line Length Tracking (ADLLT™)
5-line adaptive comb filters
Proprietary architecture for locking to weak, noisy, and
unstable video sources such as VCRs and tuners
Subcarrier frequency lock and status information output
Integrated AGC with adaptive peak white mode
Macrovision® copy protection detection
CTI (chroma transient improvement)
DNR (digital noise reduction)
Multiple programmable analog input formats:
CVBS (composite video)
S-Video (Y/C)
YPrPb component (VESA, MII, SMPTE, and Betacam)
12 analog video input channels
Automatic NTSC/PAL/SECAM identification
Digital output formats (8-bit or16-bit):
ITU-R BT.656 YCrCb 4:2:2 output + HS, VS, and FIELD
0.5 V to 1.6 V analog signal input range
Differential gain: 0.5% typ
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV7183A integrated video decoder automatically detects
and converts a standard analog baseband television signalcompatible with worldwide standards NTSC, PAL, and SECAM
into 4:2:2 component video data-compatible with 16-/8-bit
CCIR601/CCIR656.
The advanced, highly flexible digital output interface enables
performance video decoding and conversion in line-locked
clock based systems. This makes the device ideally suited for a
broad range of applications with diverse analog video characteristics, including tape based sources, broadcast sources, security/
surveillance cameras, and professional systems.
The 10-bit accurate A/D conversion provides professional
quality video performance and is unmatched. This allows true
8-bit resolution in the 8-bit output mode.
The 12 analog input channels accept standard composite,
S-Video, YPrPb video signals in an extensive number of
combinations. AGC and clamp restore circuitry allow an input
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
ADV7183A
Differential phase: 0.5° typ
Programmable video controls:
Peak-white/hue/brightness/saturation/contrast
Integrated on-chip video timing generator
Free run mode (generates stable video ouput with no I/P)
VBI decode support for
Close captioning, WSS, CGMS, EDTV, Gemstar® 1×/2×
Power-down mode
2-wire serial MPU interface (I
3.3 V analog, 1.8 V digital core; 3.3 V IO supply
2 temperature grades: 0°C to 70°C and –40°C to +85°C
80-lead LQFP Pb-free package
APPLICATIONS
DVD recorders
Video projectors
HDD-based PVRs/DVDRs
LCD TVs
Set-top boxes
Security systems
Digital televisions
AVR receiver
video signal peak-to-peak range of 0.5 V up to 1.6 V.
Alternatively, these can be bypassed for manual settings.
The fixed 54 MHz clocking of the ADCs and datapath for all
modes allows very precise, accurate sampling and digital
filtering. The line-locked clock output allows the output data
rate, timing signals, and output clock signals to be synchronous,
asynchronous, or line locked even with ±5% line length variation.
The output control signals allow glueless interface connections
in almost any application. The ADV7183A modes are set up
over a 2-wire, serial, bidirectional port (I
The ADV7183A is fabricated in a 3.3 V CMOS process. Its
monolithic CMOS construction ensures greater functionality
with lower power dissipation.
The ADV7183A is packaged in a small 80-lead LQFP Pb-free
package.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 © 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
2
C®-compatible)
2
C-compatible).

ADV7183A
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction ...................................................................................... 4
Analog Front End......................................................................... 4
Standard Definition Processor ................................................... 4
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 5
Specifications..................................................................................... 6
Electrical Characteristics ............................................................. 6
Video Specifications..................................................................... 7
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 8
Analog Specifications................................................................... 8
Thermal Specifications ................................................................ 8
Timing Diagrams.......................................................................... 9
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 10
ESD Caution................................................................................ 10
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 11
Analog Front End........................................................................... 13
Color Controls............................................................................ 25
Clamp Operation........................................................................ 27
Luma Filter.................................................................................. 28
Chroma Filter.............................................................................. 31
Gain Operation........................................................................... 32
Chroma Transient Improvement (CTI) .................................. 36
Digital Noise Reduction (DNR)............................................... 37
Comb Filters................................................................................ 37
AV Code Insertion and Controls ............................................. 40
Synchronization Output Signals............................................... 42
Sync Processing .......................................................................... 50
VBI Data Decode ....................................................................... 51
Pixel Port Configuration ............................................................... 62
MPU Port Description................................................................... 63
Register Accesses........................................................................ 64
Analog Input Muxing ................................................................ 13
Global Control Registers ............................................................... 16
Power-Save Modes...................................................................... 16
Reset Control .............................................................................. 16
Global Pin Control..................................................................... 17
Global Status Registers................................................................... 19
Identification............................................................................... 19
Status 1......................................................................................... 19
Status 2......................................................................................... 20
Status 3......................................................................................... 20
Standard Definition Processor (SDP).......................................... 21
SD Luma Path ............................................................................. 21
SD Chroma Path......................................................................... 21
Sync Processing........................................................................... 22
VBI Data Recovery..................................................................... 22
Register Programming............................................................... 64
2
I
C Sequencer.............................................................................. 64
2
I
C Control Register Map.......................................................... 65
2
I
C Register Map Details ........................................................... 69
2
I
C Programming Examples.......................................................... 96
Mode 1—CVBS Input (Composite Video on AIN5)............. 96
Mode 2—S-Video Input (Y on AIN1 and C on AIN4)......... 96
Mode 3—525i/625i YPrPb Input (Y on AIN2, Pr on AIN3,
and Pb on AIN6) ........................................................................ 97
Mode 4—CVBS Tuner Input PAL Only on AIN4 ................. 98
PCB Layout Recommendations.................................................... 99
XTAL and Load Capacitor Value Selection .......................... 100
Typical Circuit Connection......................................................... 101
Outline Dimensions..................................................................... 103
Ordering Guide ........................................................................ 103
General Setup.............................................................................. 22
Rev. B | Page 2 of 104

ADV7183A
REVISION HISTORY
3/05—Rev. A to Rev. B
Added NTSC J ...................................................................................1
Changes to the Analog Specifications Section.........................8
Changes to Figure 5 ........................................................................11
Changes to Table 9........................................................................14
Addition to
Changes to Figures 12.....................................................................30
Changes to Figures 13, 14, 15 .......................................................31
Deleted YPM Section and Renumbered Subsequent Tables .....31
Changes to Figure 16 ......................................................................32
Change to the Luma Gain Section ................................................33
Clamp Section........................................................27
Changes to Table 60......................................................................30
Changes to Table 104 and Table 105 ........................................43
Deleted Table 173 and Renumbered Subsequent Tables............69
Changes to Table 174................................................................73
Changes to Table 183................................................................80
Changes to Table 192................................................................87
Added XTAL and Load Capacitor Value Selection Section ....100
Change to Figure 43......................................................................102
Changes to Ordering Guide.........................................................103
6/04—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Addition to Applications List ..........................................................1
Changes to Table 3 ............................................................................8
Changes to Table 5 ............................................................................8
Change to Drive Strength Selection (Data) Section...................17
Changes to Figure 42....................................................................103
5/04—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 3 of 104

ADV7183A
INTRODUCTION
The ADV7183A is a high quality, single chip, multiformat video
decoder that automatically detects and converts PAL, NTSC,
and SECAM standards in the form of composite, S-Video, and
component video into a digital ITU-R BT.656 format.
The advanced and highly flexible digital output interface
enables performance video decoding and conversion in linelocked clock based systems. This makes the device ideally suited
for a broad range of applications with diverse analog video
characteristics, including tape based sources, broadcast sources,
security/surveillance cameras, and professional systems.
ANALOG FRONT END
The ADV7183A analog front end comprises three 10-bit ADCs
that digitize the analog video signal before applying it to the
standard definition processor. The analog front end employs
differential channels to each ADC to ensure high performance
in mixed-signal applications.
The front end also includes a 12-channel input mux that enables
multiple video signals to be applied to the ADV7183A. Current
and voltage clamps are positioned in front of each ADC to
ensure that the video signal remains within the range of the
converter. Fine clamping of the video signals is performed
downstream by digital fine clamping within the ADV7183A.
The ADCs are configured to run in 4× oversampling mode.
STANDARD DEFINITION PROCESSOR
The ADV7183A is capable of decoding a large selection of
baseband video signals in composite, S-Video, and component
formats. The video standards supported by the ADV7183A
include PAL B /D/I/G / H , PA L60, PAL M , PAL N, PAL Nc,
NTSC M/J, NTSC 4.43, and SECAM B/D/G/K/L. The
ADV7183A can automatically detect the video standard and
process it accordingly.
The ADV7183A has a 5-line, superadaptive, 2D comb filter that
gives superior chrominance and luminance separation when
decoding a composite video signal. This highly adaptive filter
automatically adjusts its processing mode according to video
standard and signal quality with no user intervention required.
Video user controls such as brightness, contrast, saturation, and
hue are also available within the ADV7183A.
The ADV7183A implements a patented adaptive digital linelength tracking (ADLLT) algorithm to track varying video line
lengths from sources such as a VCR. ADLLT enables the
ADV7183A to track and decode poor quality video sources
such as VCRs, noisy sources from tuner outputs, VCD players,
and camcorders. The ADV7183A contains a chroma transient
improvement (CTI) processor that sharpens the edge rate of
chroma transitions, resulting in sharper vertical transitions.
The ADV7183A can process a variety of VBI data services, such
as closed captioning (CC), wide screen signaling (WSS), copy
generation management system (CGMS), EDTV, Gemstar 1×/
2×, and extended data service (XDS). The ADV7183A is fully
Macrovision certified; detection circuitry enables Type I, II, and
III protection levels to be identified and reported to the user.
The decoder is also fully robust to all Macrovision signal inputs.
Rev. B | Page 4 of 104
ADV7183A
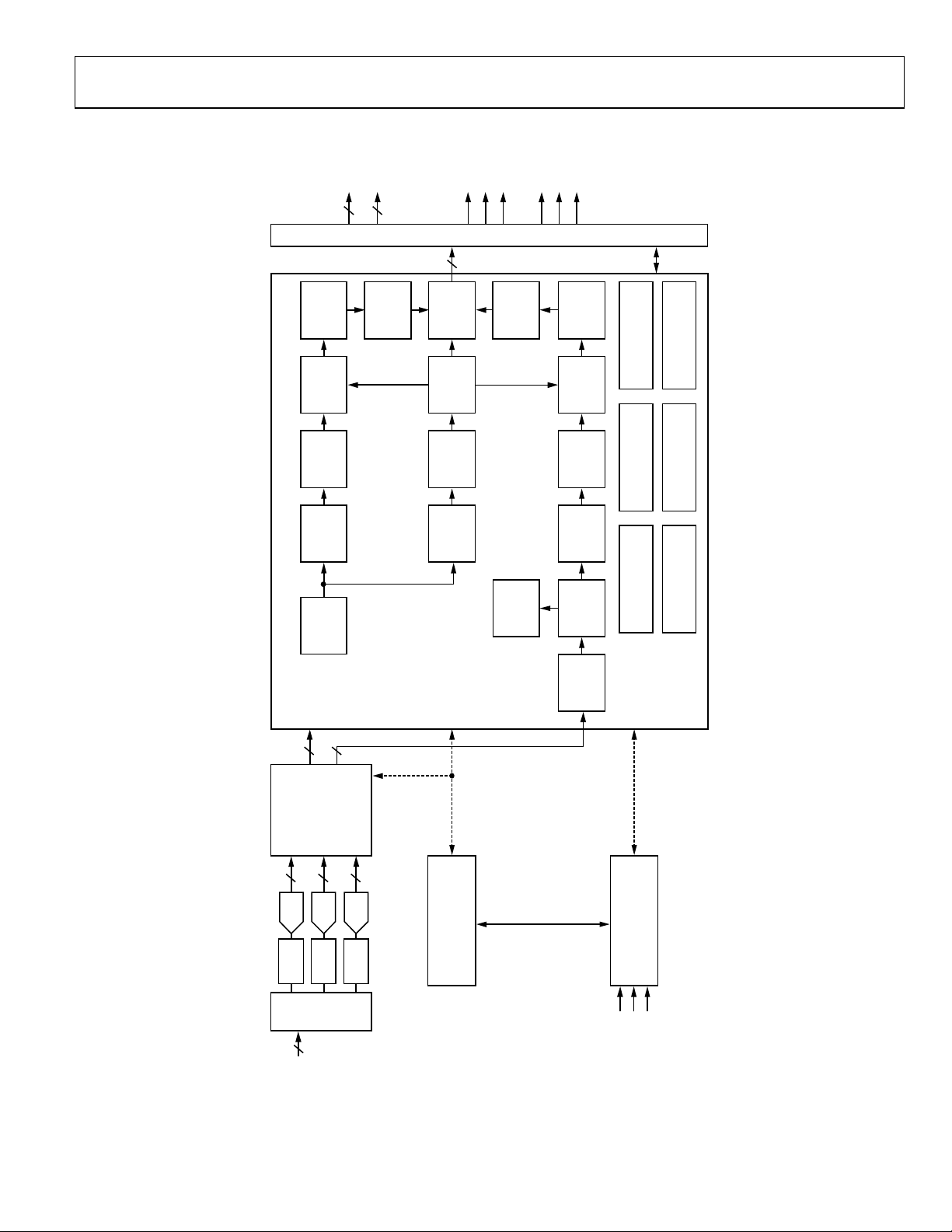
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
04821-001
HS
VS
FIELD
LLC1
LLC2
PIXEL
DATA
8
8
16
SFL
OUTPUT FORMATTER
LUMA
(4H MAX)
2D COMB
LUMA
RESAMPLE
GAIN
CONTROL
LUMA
FILTER
STANDARD DEFINITION PROCESSOR
FINE
LUMA
CLAMP
DIGITAL
10
10
L-DNR
AV
LINE
CODE
INSERTION
CONTROL
RESAMPLE
LENGTH
PREDICTOR
SYNC
EXTRACT
F
CTI
SC
C-DNR
RECOVERY
(4H MAX)
CHROMA
2D COMB
CHROMA
RESAMPLE
GAIN
CONTROL
FILTER
CHROMA
DEMOD
CHROMA
FINE
CLAMP
DIGITAL
CHROMA
FREE RUN
SYNTHESIZED
LLC CONTROL
OUTPUT CONTROL
STANDARD
AUTODETECTION
DETECTION
MACROVISION
VBI DATA RECOVERY GLOBAL CONTROL
DATA
10
12
PREPROCESSOR
A/DCLAMP
AIN1–AIN12
FILTERS
DOWNSAMPLING
DECIMATION AND
10
A/DCLAMP10A/DCLAMP
MUX
INPUT
CVBS
YPrPb
S-VIDEO
SYNC AND
CLK CONTROL
CLOCK GENERATION
SYNC PROCESSING AND
Figure 1.
Rev. B | Page 5 of 104
ADV7183A
CONTROL
AND DATA
SERIAL INTERFACE
CONTROL AND VBI DATA
SDA
SCLK
ALSB
ADV7183A
SPECIFICATIONS
Temperature range: T
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
A
= 3.15 V to 3.45 V, D
VDD
otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each ADC) N 10 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity INL BSL at 54 MHz –0.475/+0.6 ±3 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity DNL BSL at 54 MHz –0.25/+0.5 –0.7/+2 LSB
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input High Voltage VIH 2 V
Input Low Voltage VIL 0.8 V
Input Current IIN Pins listed in Note 1 –50 +50 µA
All other pins –10 +10 µA
Input Capacitance CIN 10 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage VOH I
Output Low Voltage VOL I
High Impedance Leakage Current I
All other pins 10 µA
Output Capacitance C
POWER REQUIREMENTS3
Digital Core Power Supply D
Digital I/O Power Supply D
PLL Power Supply P
Analog Power Supply A
Digital Core Supply Current I
Digital I/O Supply Current I
PLL Supply Current I
Analog Supply Current I
YPrPb input5 180 mA
Power-Down Current I
Power-Up Time t
1
Pins 36 and 79.
2
Pins 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 32, 33, 34, 35, 73, 74, 75, 76, and 80.
3
Guaranteed by characterization.
4
ADC1 powered on.
5
All three ADCs powered on.
to T
MIN
MAX
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V, D
VDD
, –40°C to +85°C. The min/max specifications are guaranteed over this range.
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V, P
VDDIO
SOURCE
= 3.2 mA 0.4 V
SINK
Pins listed in Note 2 50 µA
LEAK
20 pF
OUT
1.65 1.8 2 V
VDD
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
VDDIO
1.65 1.8 2.0 V
VDD
3.15 3.3 3.45 V
VDD
82 mA
DVDD
2 mA
DVDDIO
10.5 mA
PVDD
CVBS input4 85 mA
AVDD
1.5 mA
PWRDN
20 ms
PWRUP
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V; operating temperature range, unless
VDD
= 0.4 mA 2.4 V
Rev. B | Page 6 of 104
ADV7183A
VIDEO SPECIFICATIONS
Guaranteed by characterization. A
temperature range, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
NONLINEAR SPECIFICATIONS
Differential Phase DP CVBS I/P, modulate 5-step 0.5 0.7 °
Differential Gain DG CVBS I/P, modulate 5-step 0.5 0.7 %
Luma Nonlinearity LNL CVBS I/P, 5-step 0.5 0.7 %
NOISE SPECIFICATIONS
SNR Unweighted Luma ramp 54 56 dB
Luma flat field 58 60 dB
Analog Front End Crosstalk 60 dB
LOCK TIME SPECIFICATIONS
Horizontal Lock Range –5 +5 %
Vertical Lock Range 40 70 Hz
FSC Subcarrier Lock Range ±1.3 Hz
Color Lock In Time 60 Lines
Sync Depth Range 20 200 %
Color Burst Range 5 200 %
Vertical Lock Time 2 Fields
Autodetection Switch Speed 100 Lines
CHROMA SPECIFICATIONS
Hue Accuracy HUE 1 °
Color Saturation Accuracy CL_AC 1 %
Color AGC Range 5 400 %
Chroma Amplitude Error 0.5 %
Chroma Phase Error 0.4 °
Chroma Luma Intermodulation 0.2 %
LUMA SPECIFICATIONS
Luma Brightness Accuracy CVBS, 1 V I/P 1 %
Luma Contrast Accuracy CVBS, 1 V I/P 1 %
= 3.15 V to 3.45 V, D
VDD
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V, D
VDD
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V, P
VDDIO
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V; operating
VDD
Rev. B | Page 7 of 104
ADV7183A
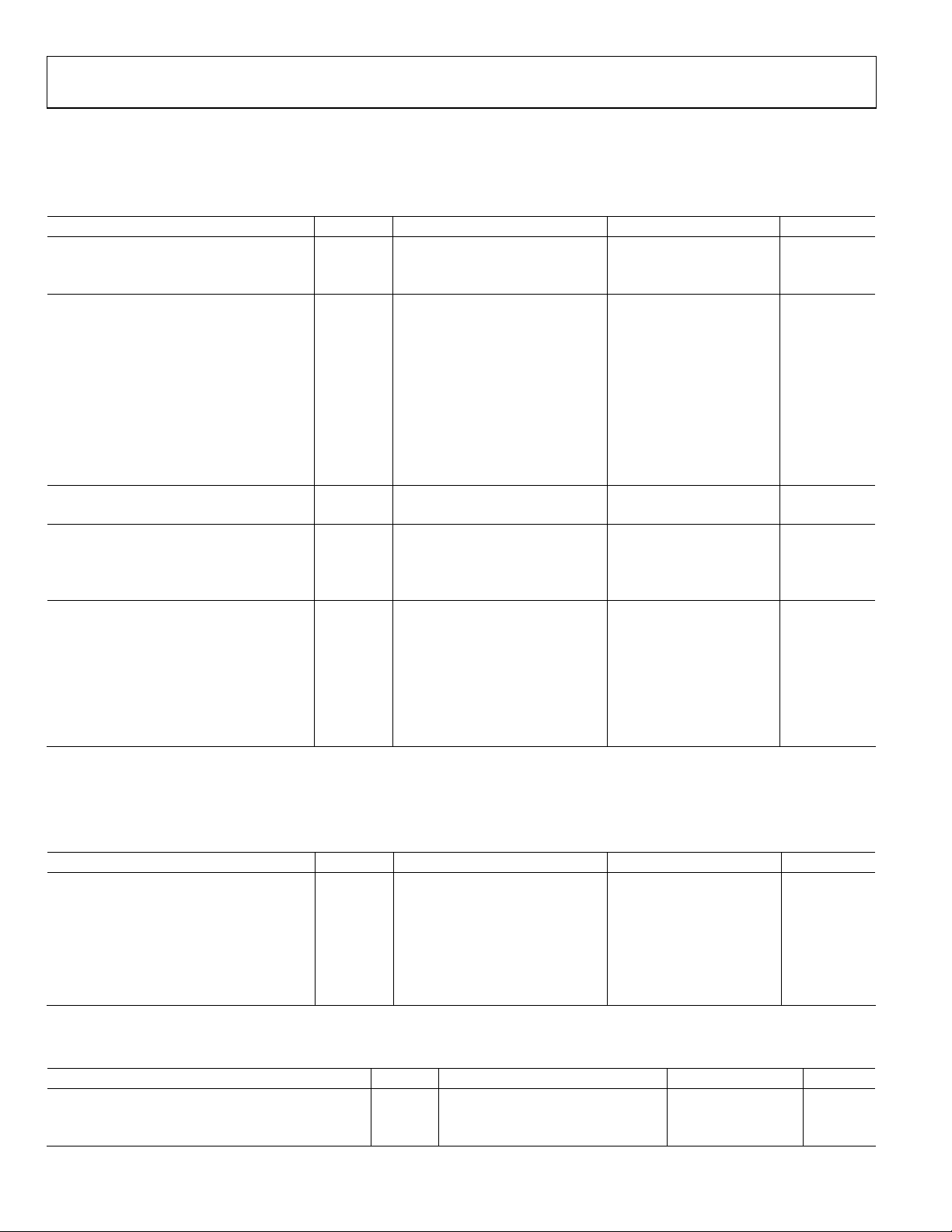
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Guaranteed by characterization. A
temperature range, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
SYSTEM CLOCK AND CRYSTAL
Nominal Frequency 27.00 MHz
Frequency Stability ±50 ppm
I2C PORT
SCLK Frequency 400 kHz
SCLK Min Pulse Width High t1 0.6 µs
SCLK Min Pulse Width Low t2 1.3 µs
Hold Time (Start Condition) t3 0.6 µs
Setup Time (Start Condition) t4 0.6 µs
SDA Setup Time t5 100 ns
SCLK and SDA Rise Time t6 300 ns
SCLK and SDA Fall Time t7 300 ns
Setup Time for Stop Condition t8 0.6 µs
RESET FEATURE
Reset Pulse Width 5 ms
CLOCK OUTPUTS
LLC1 Mark Space Ratio t9:t10 45:55 55:45 % Duty Cycle
LLC1 Rising to LLC2 Rising t11 0.5 ns
LLC1 Rising to LLC2 Falling t12 0.5 ns
DATA AND CONTROL OUTPUTS
Data Output Transitional Time t13
Data Output Transitional Time t14
Propagation Delay to Hi-Z t15 6 ns
Max Output Enable Access Time t16 7 ns
Min Output Enable Access Time t17 4 ns
ANALOG SPECIFICATIONS
Guaranteed by characterization. A
temperature range, unless otherwise noted. Recommended analog input video signal range: 0.5 V – 1.6 V, typically 1 V p-p.
Table 4.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
CLAMP CIRCUITRY
External Clamp Capacitor 0.1 µF
Input Impedance Clamps switched off 10 MΩ
Large Clamp Source Current 0.75 mA
Large Clamp Sink Current 0.75 mA
Fine Clamp Source Current 60 µA
Fine Clamp Sink Current 60 µA
THERMAL SPECIFICATIONS
Table 5.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Junction-to-Case Thermal Resistance θJC 4-layer PCB with solid ground plane 7.6 °C/W
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (Still Air) θJA 4-layer PCB with solid ground plane 38.1 °C/W
= 3.15 V to 3.45 V, D
VDD
= 3.15 V to 3.45 V, D
VDD
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V, D
VDD
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V, P
VDDIO
Negative clock edge to start of
= t
valid data (t
ACCESS
10
– t13)
End of valid data to negative
clock edge (t
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V, D
VDD
= t9 + t14)
HOLD
= 3.0 V to 3.6 V, P
VDDIO
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V; operating
VDD
6 ns
0.6 ns
= 1.65 V to 2.0 V; operating
VDD
Rev. B | Page 8 of 104
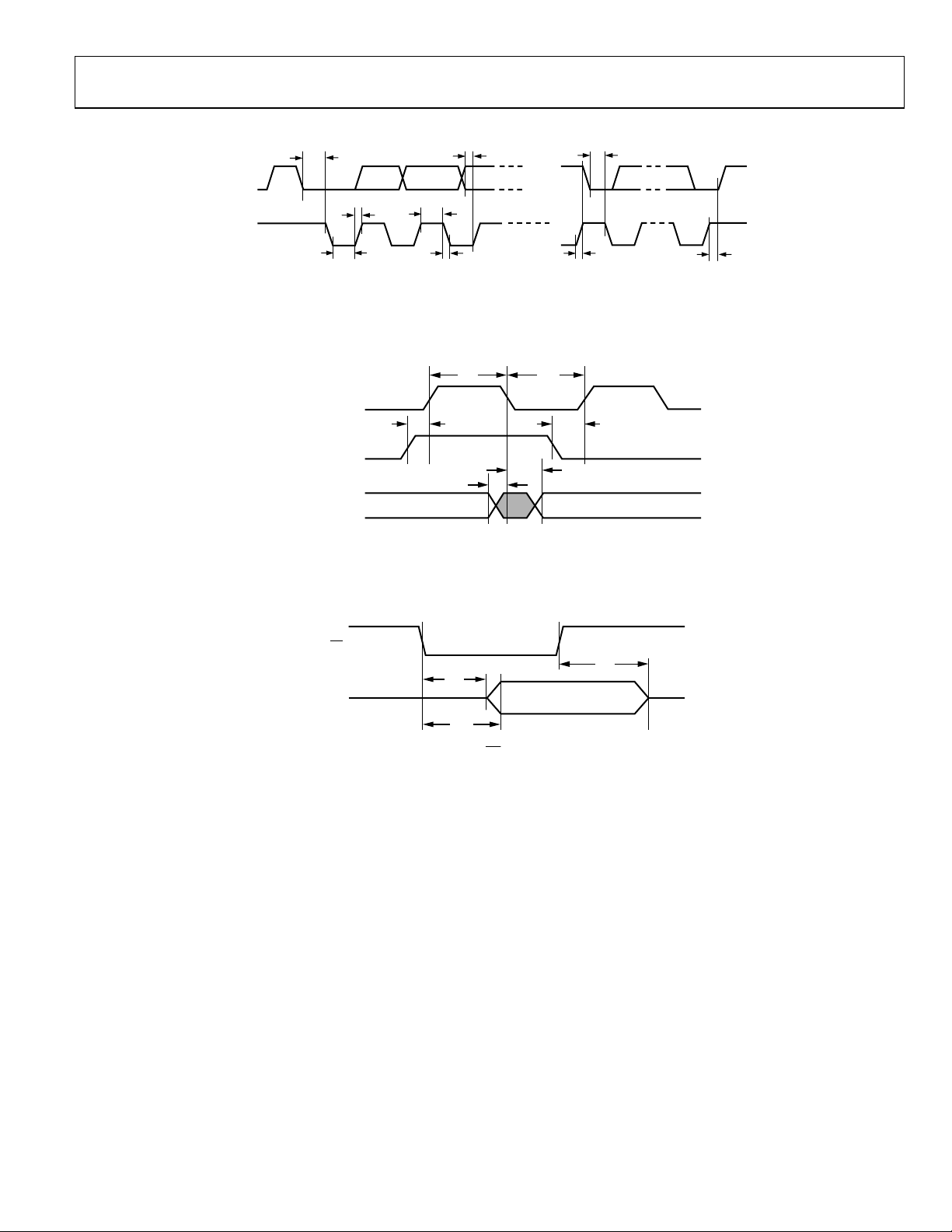
ADV7183A
TIMING DIAGRAMS
t
t
t
7
5
1
Figure 2. I
2
C Timing
SDA
SCLK
t
3
t
6
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
8
04821-002
OUTPUT LLC1
OUTPUT LLC2
OUTPUTS P0–P15, VS,
HS, FIELD, SFL
t
9
t
11
t
14
t
10
t
12
t
13
04821-003
Figure 3. Pixel Port and Control Output Timing
OE
t
15
04821-004
P0–P15, HS,
VS, FIELD, SFL
t
17
t
16
Figure 4.
OE
Timing
Rev. B | Page 9 of 104
ADV7183A
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
A
to GND 4 V
VDD
A
to AGND 4 V
VDD
D
to DGND 2.2 V
VDD
P
to AGND 2.2 V
VDD
D
to DGND 4 V
VDDIO
D
to AVDD –0.3 V to +0.3 V
VDDIO
P
to D
VDD
D
VDDIO
D
VDDIO
A
VDD
A
VDD
Digital Inputs Voltage to DGND –0.3 V to D
Digital Output Voltage to DGND –0.3 V to D
Analog Inputs to AGND AGND – 0.3 V to A
Maximum Junction Temperature
(T
Storage Temperature Range –65°C to +150°C
Infrared Reflow Soldering (20 sec) 260°C
–0.3 V to +0.3 V
VDD
– P
–0.3V to +2 V
VDD
– D
–0.3 V to +2 V
VDD
– P
–0.3 V to +2 V
VDD
– D
–0.3 V to +2 V
VDD
max)
J
150°C
VDDIO
VDDIO
+ 0.3 V
+ 0.3 V
+ 0.3 V
VDD
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. B | Page 10 of 104
ADV7183A
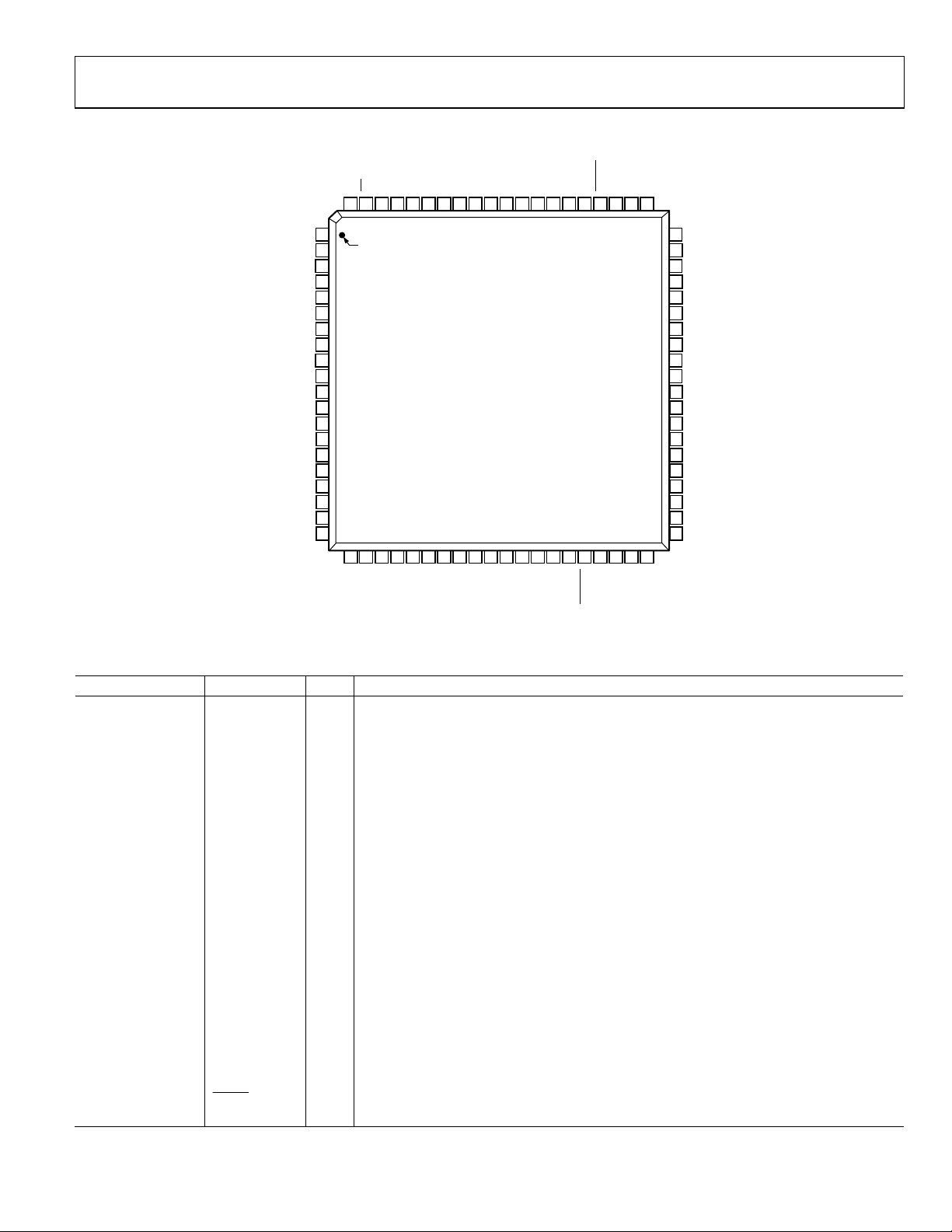
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
FIELD79OE78NC77NC76P1275P1374P1473P1572DVDD71DGND70NC69NC68SCLK67SDA66ALSB65NC64RESET63NC62AIN661AIN12
80
1
VS
HS
DGND
DVDDIO
P11
P10
P9
P8
DGND
DVDD
NC
SFL
NC
DGND
DVDDIO
NC
NC
NC
P7
P6
NC = NO CONNECT
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21P522P423P324P225NC26
PIN 1
28
LLC227LLC1
ADV7183A
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
29
30
31
XTAL
DVDD
XTAL1
32P133P034NC35NC36
DGND
37
PWRDN
38
ELPF
39
PVDD
AGND40AGND
Figure 5. 80-Lead LQFP Pin Configuration
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Function
3, 9, 14, 31, 71 DGND G Digital Ground.
39, 40, 47, 53, 56 AGND G Analog Ground.
4, 15 DVDDIO P Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
10, 30, 72 DVDD P Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
50 AVDD P Analog Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
38 PVDD P PLL Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
42, 44, 46, 58, 60,
AIN1–AIN12 I Analog Video Input Channels.
62, 41, 43, 45, 57,
59, 61
11, 13, 16–18, 25,
NC No Connect Pins.
34, 35, 63, 65, 69,
70, 77, 78
33, 32, 24, 23, 22,
P0–P15 O Video Pixel Output Port.
21, 20, 19, 8, 7, 6, 5,
76, 75, 74, 73
2 HS O Horizontal Synchronization Output Signal.
1 VS O Vertical Synchronization Output Signal.
80 FIELD O Field Synchronization Output Signal.
67 SDA I/O I2C Port Serial Data Input/Output Pin.
68 SCLK I I2C Port Serial Clock Input (Max Clock Rate of 400 kHz).
66 ALSB I
This pin selects the I
2
C address for the ADV7183A. ALSB set to Logic 0 sets the address for a
write as 0x40; for ALSB set to logic high, the address selected is 0x42.
64
RESET
I
System Reset Input, Active Low. A minimum low reset pulse width of 5 ms is required to
reset the ADV7183A circuitry.
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
AIN5
AIN11
AIN4
AIN10
AGND
CAP C2
CAP C1
AGND
CML
REFOUT
AVDD
CAP Y2
CAP Y1
AGND
AIN3
AIN9
AIN2
AIN8
AIN1
AIN7
04821-005
Rev. B | Page 11 of 104
ADV7183A
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Function
27 LLC1 O
26 LLC2 O
29 XTAL I
28 XTAL1 O
36
79
37 ELPF I
12 SFL O
51 REFOUT O
52 CML O
48, 49 CAPY1, CAPY2 I
54, 55 CAPC1, CAPC2 I
PWRDN
OE
I
I
This is a line-locked output clock for the pixel data output by the ADV7183A. Nominally
27 MHz, but varies up or down according to video line length.
This is a divide-by-2 version of the LLC1 output clock for the pixel data output by the
ADV7183A. Nominally 13.5 MHz, but varies up or down according to video line length.
This is the input pin for the 27 MHz crystal, or can be overdriven by an external 3.3 V,
27 MHz clock oscillator source. In crystal mode, the crystal must be a fundamental crystal.
This pin should be connected to the 27 MHz crystal or left as a no connect if an external
3.3 V, 27 MHz clock oscillator source is used to clock the ADV7183A. In crystal mode, the
crystal must be a fundamental crystal.
A logic low on this pin places the ADV7183A in a power-down mode. Refer to the I2C
Control Register Map for more options on power-down modes for the ADV7183A.
When set to a logic low, OE enables the pixel output bus, P15–P0 of the ADV7183A. A logic
high on the OE pin places Pins P15–P0, HS, VS, SFL into a high impedance state.
The recommended external loop filter must be connected to this ELPF pin, as shown in
Figure 43.
Subcarrier Frequency Lock. This pin contains a serial output stream that can be used to lock
the subcarrier frequency when this decoder is connected to any Analog Devices, Inc. digital
video encoder.
Internal Voltage Reference Output. Refer to Figure 43 for a recommended capacitor
network for this pin.
Common-Mode Level for the Internal ADCs. Refer to Figure 43 for a recommended
capacitor network for this pin.
ADC’s Capacitor Network. Refer to Figure 43 for a recommended capacitor network for
this pin.
ADC’s Capacitor Network. Refer to Figure 43 for a recommended capacitor network for
this pin.
Rev. B | Page 12 of 104

ADV7183A
ANALOG FRONT END
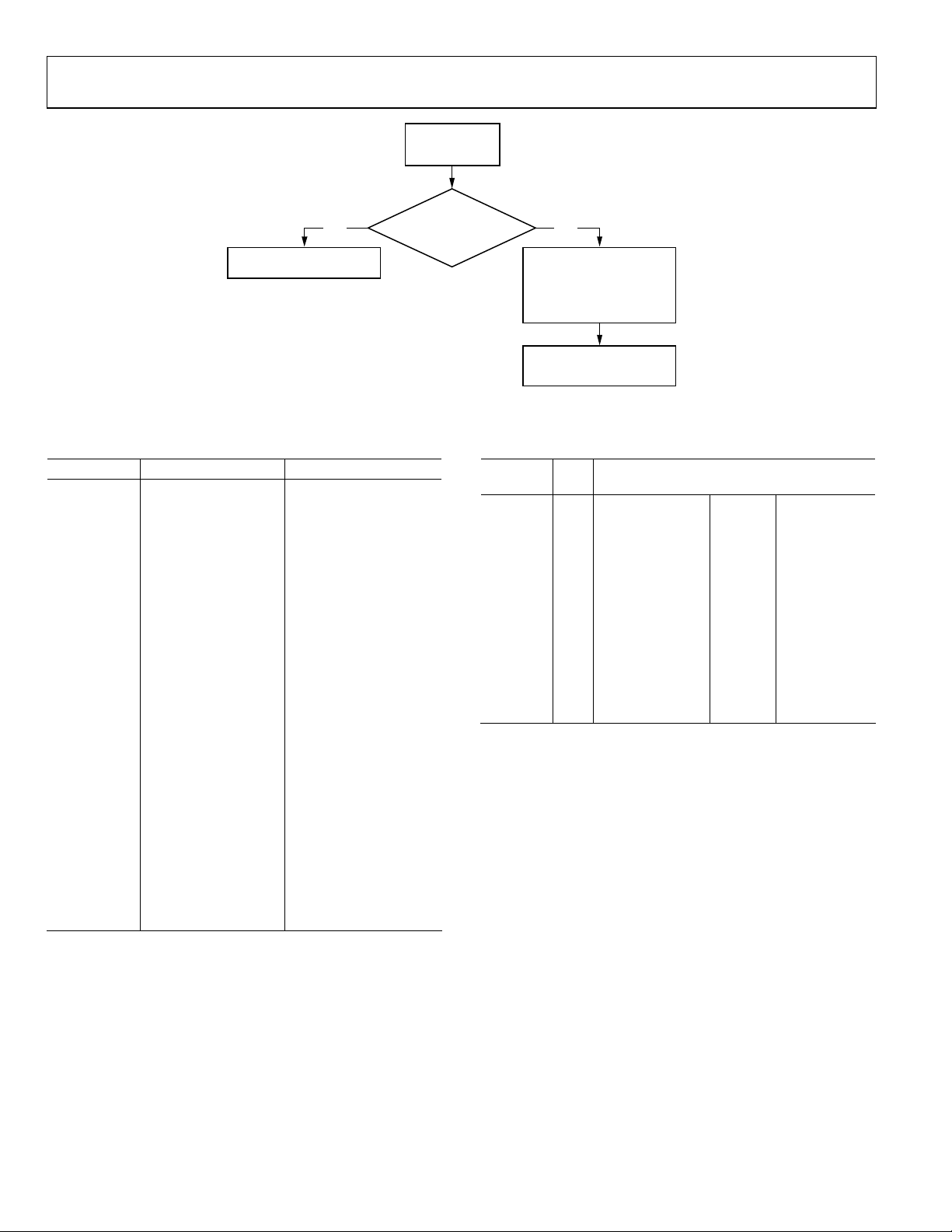
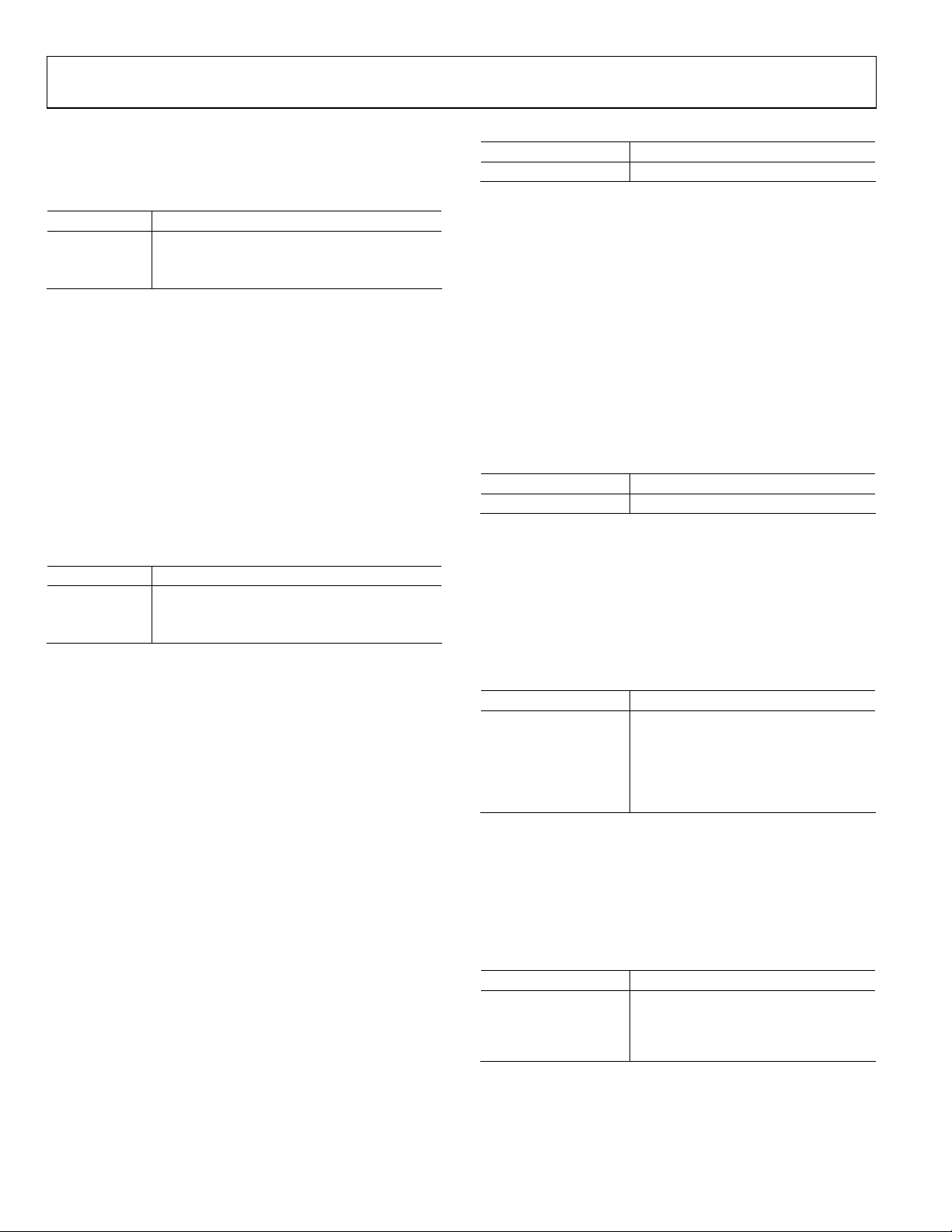
ANALOG INPUT MUXING
ADC_SW_MAN_EN INSEL[3:0]
AIN12
AIN6
AIN11
AIN5
AIN10
AIN4
AIN9
AIN3
AIN8
AIN2
AIN7
AIN1
AIN1
AIN7
AIN2
AIN8
AIN3
AIN9
AIN4
AIN10
AIN5
AIN11
AIN6
AIN12
AIN3
AIN9
AIN4
AIN10
AIN5
AIN11
AIN6
AIN12
1
0
1
0
ADC0_SW[3:0]
ADC0
ADC1_SW[3:0]
ADC1
INTERNAL
MAPPING
FUNCTIONS
Figure 6. Internal Pin Connections
The ADV7183A has an integrated analog muxing section that
allows more than one source of video signal to be connected to
the decoder. Figure 6 outlines the overall structure of the input
muxing provided in the ADV7183A.
As can be seen in Figure 6, there are two ways in which the
analog input muxes can be controlled:
• Control via functional registers (INSEL).
Using INSEL[3:0] simplifies the setup of the muxes, and
minimizes crosstalk between channels by pre-assigning the
input channels. This is referred to as ADI recommended
input muxing.
2
• Control via an I
C manual override
(ADC_sw_man_en, ADC0_sw, ADC1_sw, ADC2_sw).
This is provided for applications with special requirements
(for example, number/combinations of signals) that would
not be served by the pre-assigned input connections. This
is referred to as manual input muxing.
AIN2
AIN8
AIN5
AIN11
AIN6
AIN12
ADC1_SW[3:0]
1
0
ADC2
04821-007
ADI Recommended Input Muxing
A maximum of 12 CVBS inputs can be connected and decoded
by the ADV7183A. As can be seen in Figure 5, the sources have
to be connected to adjacent pins on the IC. This calls for a careful design of the PCB layout, for example, ground shielding
between all signals routed through tracks that are physically
close together.
INSEL[3:0] Input Selection, Address 0x00 [3:0]
The INSEL bits allow the user to select an input channel as well
as the input format. Depending on the PCB connections, only a
subset of the INSEL modes are valid. The INSEL[3:0] does not
only switch the analog input muxing, it also configures the
standard definition processor core to process CVBS (Comp),
S-Video (Y/C), or component (YPbPr) format.
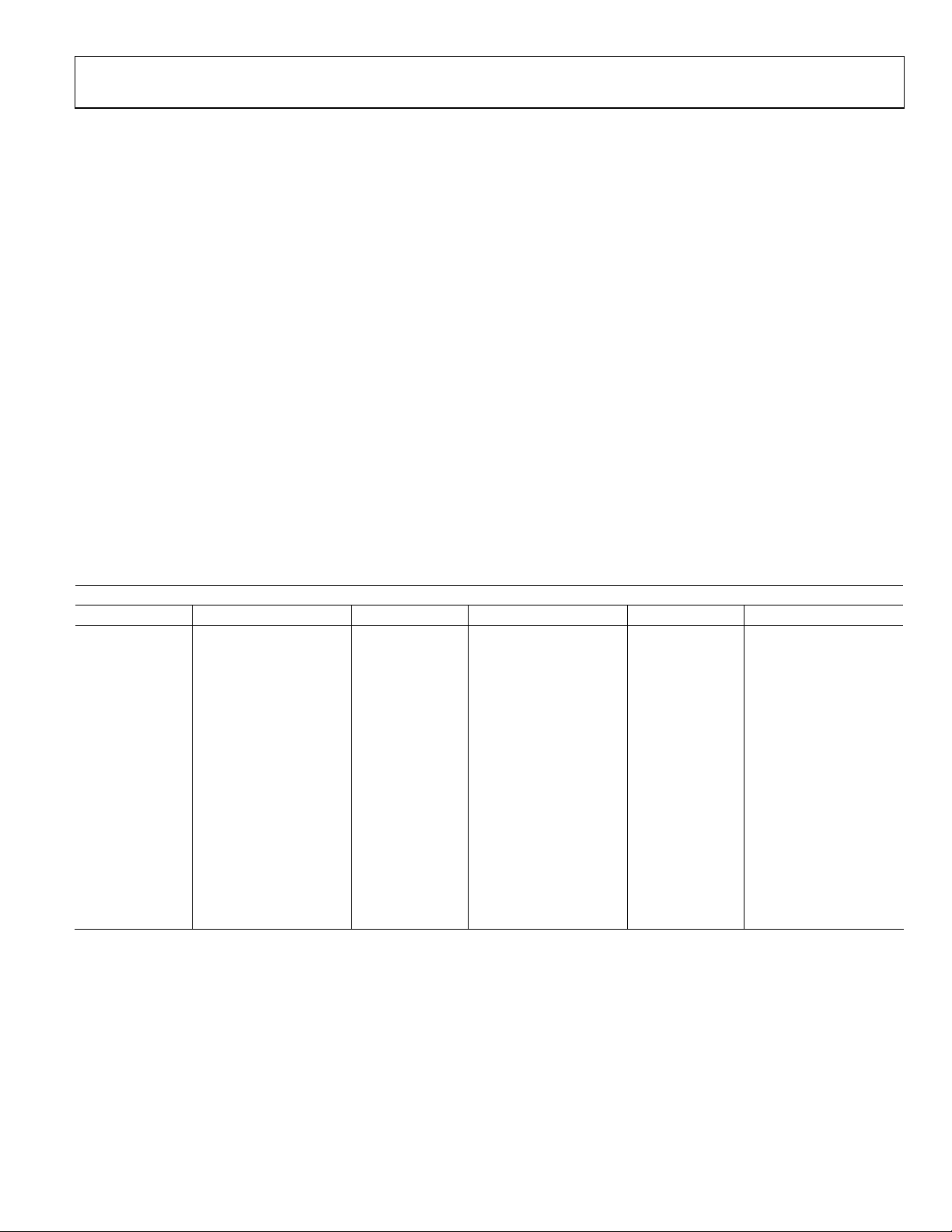
Refer to Figure 7 for an overview of the two methods of
controlling the ADV7183A’s input muxing.
Rev. B | Page 13 of 104
ADV7183A
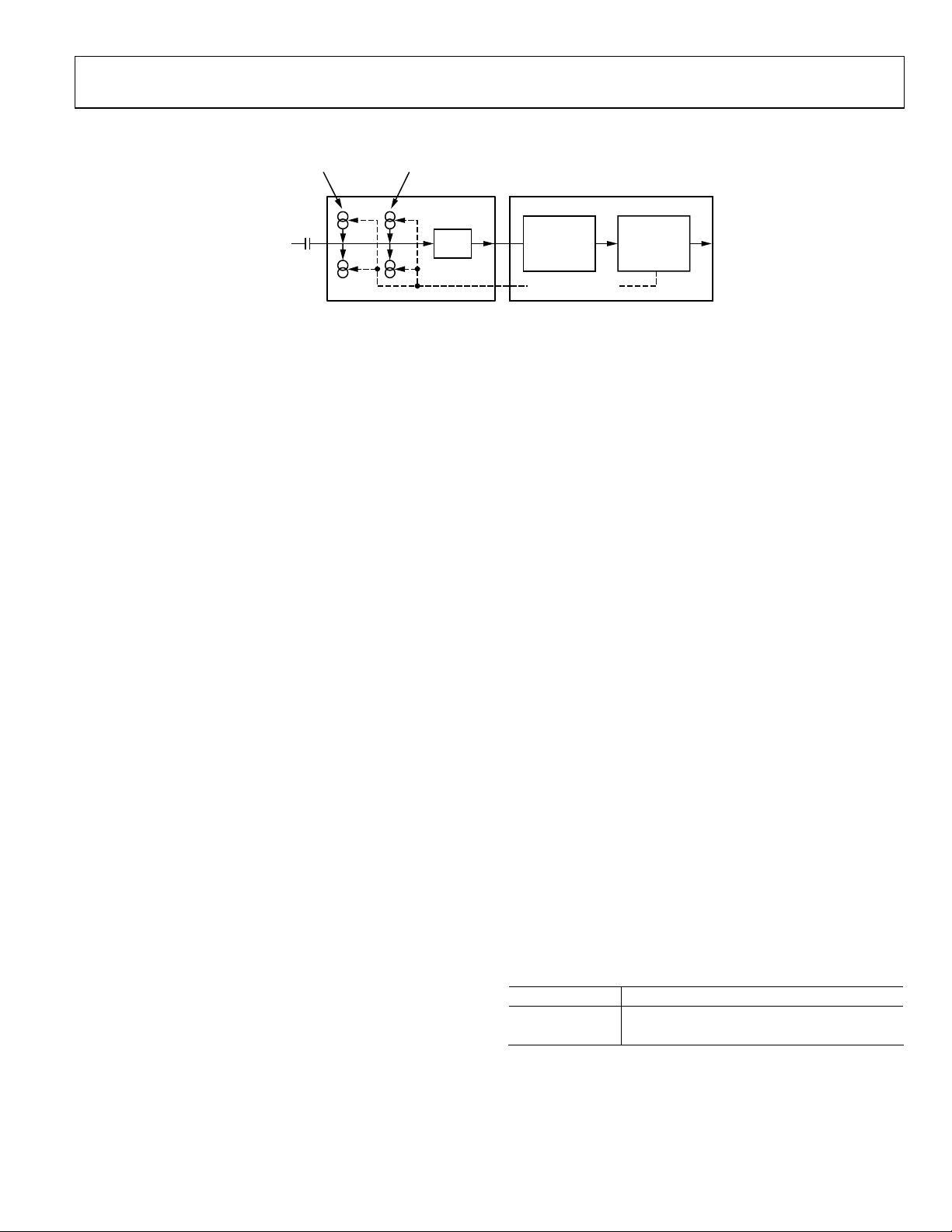
CONNECTING
ANALOG SIGNALS
TO ADV7183A
YES NO
SET INSEL[3:0] FOR REQUIRED
MUXING CONFIGURATION
Table 8. Input Channel Switching Using INSEL[3:0]
INSEL[3:0] Analog Input Pins Video Format
0000
CVBS1 = AIN1 Composite
(default)
0001 CVBS2 = AIN2 Composite
0010 CVBS3 = AIN3 Composite
0011 CVBS4 = AIN4 Composite
0100 CVBS5 = AIN5 Composite
0101 CVBS6 = AIN6 Composite
0110 Y1 = AIN1 YC
C1 = AIN4 YC
0111 Y2 = AIN2 YC
C2 = AIN5 YC
1000 Y3 = AIN3 YC
C3 = AIN6 YC
1001 Y1 = AIN1 YPrPb
PR1 = AIN4 YPrPb
PB1 = AIN5 YPrPb
1010 Y2 = AIN2 YPrPb
PR2 = AIN3 YPrPb
PB2 = AIN6 YPrPb
1011 CVBS7 = AIN7 Composite
1100 CVBS8 = AIN8 Composite
1101 CVBS9 = AIN9 Composite
1110 CVBS10 = AIN10 Composite
1111 CVBS11 = AIN11 Composite
ADI RECOMMENDED
INPUT MUXING; SEE TABLE 9
(ADC_SW_MAN_EN, ADC0_SW,
Figure 7. Input Muxing Overview
Table 9. Input Channel Assignments
Input
Channel
AIN7 41 CVBS7
AIN1 42 CVBS1 YC1-Y YPrPb1-Y
AIN8 43 CVBS8
AIN2 44 CVBS2 YC2-Y YPrPb2-Y
AIN9 45 CVBS9
AIN3 46 CVBS3 YC3-Y YPrPb2-Pr
AIN10 57 CVBS10
AIN4 58 CVBS4 YC1-C YPrPb1-Pr
AIN11 59 CVBS11
AIN5 60 CVBS5 YC2-C YPrPb1-Pb
AIN12 61 Not Available
AIN6 62 CVBS6 YC3-C YPrPb2-Pb
ADI recommended input muxing is designed to minimize
crosstalk between signal channels and to obtain the highest
level of signal integrity. Table 9 summarizes how PCB layout
should connect analog video signals to the ADV7183A.
Notes
• It is strongly recommended to connect any unused analog
input pins to AGND to act as a shield.
• Inputs AIN7 to AIN11 should be connected to AGND in
cases where only six input channels are used. This improves
the quality of the sampling due to better isolation between
the channels.
SET INSEL[3:0] TO
CONFIGURE ADV7183A TO
DECODE VIDEO FORMAT:
CVBS: 0000
YC: 0110
YPrPb: 1001
USE MANUAL INPUT MUXING
ADC1_SW, ADC2_SW)
Pin
ADI Recommended Input Muxing Control
No.
04821-008
INSEL[3:0]
• AIN12 is not under the control of INSEL[3:0]. It can only
Rev. B | Page 14 of 104
be routed to ADC0/ADC1/ADC2 by manual muxing. See
Table 10 for further details.
ADV7183A
Manual Input Muxing
By accessing a set of manual override muxing registers, the
analog input muxes of the ADV7183A can be controlled
directly. This is referred to as manual input muxing.
Notes
• Manual input muxing overrides other input muxing
control bits, for example, INSEL.
• The manual muxing is activated by setting the
ADC_SW_MAN_EN bit. It affects only the analog
switches in front of the ADCs.
This means if the settings of INSEL and the manual input
muxing registers (ADC0/ADC1/ADC2_sw) contradict
each other, the ADC0/ADC1/ADC2_sw settings apply and
INSEL is ignored.
• Manual input muxing only controls the analog input
muxes. INSEL[3:0] still has to be set so the follow-on
blocks process the video data in the correct format.
This means INSEL must still be used to tell the ADV7183A
whether the input signal is of component, YC, or CVBS
format.
Restrictions in the channel routing are imposed by the analog
signal routing inside the IC; every input pin cannot be routed to
each ADC. Refer to Figure 6 for an overview on the routing
capabilities inside the chip. The three mux sections can be
controlled by the reserved control signal buses ADC0/ADC1/
ADC2_sw[3:0]. Table 10 explains the control words used.
SETADC_sw_man_en, Manual Input Muxing Enable,
Address 0xC4 [7]
ADC0_sw[3:0], ADC0 mux configuration, Address 0xC3 [3:0]
ADC1_sw[3:0], ADC1 mux configuration, Address 0xC3 [7:4]
ADC2_sw[3:0], ADC2 mux configuration, Address 0xC4 [3:0]
Table 10. Manual Mux Settings for All ADCs
SETADC_sw_man_en = 1
ADC0_sw[3:0] ADC0 Connected To: ADC1_sw[3:0] ADC1 Connected To: ADC2_sw[3:0] ADC2 Connected To:
0000 No Connection 0000 No Connection 0000 No Connection
0001 AIN1 0001 No Connection 0001 No Connection
0010 AIN2 0010 No Connection 0010 AIN2
0011 AIN3 0011 AIN3 0011 No Connection
0100 AIN4 0100 AIN4 0100 No Connection
0101 AIN5 0101 AIN5 0101 AIN5
0110 AIN6 0110 AIN6 0110 AIN6
0111 No Connection 0111 No Connection 0111 No Connection
1000 No Connection 1000 No Connection 1000 No Connection
1001 AIN7 1001 No Connection 1001 No Connection
1010 AIN8 1010 No Connection 1010 AIN8
1011 AIN9 1011 AIN9 1011 No Connection
1100 AIN10 1100 AIN10 1100 No Connection
1101 AIN11 1101 AIN11 1101 AIN11
1110 AIN12 1110 AIN12 1110 AIN12
1111 No Connection 1111 No Connection 1111 No Connection
Rev. B | Page 15 of 104

ADV7183A
GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTERS
Register control bits listed in this section affect the whole chip.
POWER-SAVE MODES
Power-Down
PDBP, Address 0x0F [2]
There are two ways to shut down the digital core of the
ADV7183A: a pin (
PWRDN
The PDBP controls which of the two has the higher priority.
The default is to give the pin (
user to have the ADV7183A powered down by default.
Table 11. PDBP Function
PDBP Description
0 (default)
1 Bit has priority (pin is disregarded).
Digital core power controlled by the PWRDN
(bit is disregarded).
PWRDN, Address 0x0F [5]
Setting the PWRDN bit switches the ADV7183A into a chipwide power-down mode. The power-down stops the clock from
entering the digital section of the chip, thereby freezing its
operation. No I
2
C bits are lost during power-down. The
PWRDN bit also affects the analog blocks and switches them
into low current modes. The I
and remains operational in power-down mode.
The ADV7183A leaves the power-down state if the PWRDN
2
bit is set to 0 (via I
pin.
RESET
C), or if the overall part is reset using the
PDBP must be set to 1 for the PWRDN bit to power down the
ADV7183A.
Table 12. PWRDN Function
PWRDN Description
0 (default) Chip operational.
1 ADV7183A in chip-wide power-down.
ADC Power-Down Control
The ADV7183A contains three 10-bit ADCs (ADC0, ADC1,
and ADC2). If required, it is possible to power down each ADC
individually.
When should the ADCs be powered down?
• CVBS mode. ADC1 and ADC2 should be powered down
to save on power consumption.
• S-Video mode. ADC2 should be powered down to save on
power consumption.
) and a bit (PWRDN see below).
PWRDN
2
C interface itself is unaffected,
) priority. This allows the
pin
PWRDN_ADC_0, Address 0x3A [3]
Table 13. PWRDN_ADC_0 Function
PWRDN_ADC_0 Description
0 (default) ADC normal operation.
1 Power down ADC 0.
PWRDN_ADC_1, Address 0x3A [2]
Table 14. PWRDN_ADC_1 Function
PWRDN_ADC_1 Description
0 (default) ADC normal operation.
1 Power down ADC 1.
PWRDN_ADC_2, Address 0x3A [1]
Table 15. PWRDN_ADC_2 Function
PWRDN_ADC_2 Description
0 (default) ADC normal operation.
1 Power down ADC 2.
RESET CONTROL
Chip Reset (RES), Address 0x0F [7]
Setting this bit, equivalent to controlling the
2
ADV7183A, issues a full chip reset. All I
C registers get reset to
their default values. (Some register bits do not have a reset value
specified. They keep their last written value. Those bits are
marked as having a reset value of x in the register table.) After
the reset sequence, the part immediately starts to acquire the
incoming video signal.
Notes
• After setting the RES bit (or initiating a reset via the pin),
the part returns to the default mode of operation with
respect to its primary mode of operation. All I
loaded with their default values, making this bit selfclearing.
• Executing a software reset takes approximately 2 ms.
However, it is recommended to wait 5 ms before any
2
further I
• The I
C writes are performed.
2
C master controller receives a no acknowledge
condition on the ninth clock cycle when chip reset is
implemented. See the MPU Port Description section.
Table 16. RES Function
RES Description
0 (default) Normal operation.
1 Start reset sequence.
RESET
pin on the
2
C bits are
Rev. B | Page 16 of 104
ADV7183A
GLOBAL PIN CONTROL
Three-State Output Drivers
TOD, Address 0x03 [6]
This bit allows the user to three-state the output drivers of the
ADV7183A.
Upon setting the TOD bit, the P15–P0, HS, VS, FIELD, and SFL
pins are three-stated.
The timing pins (HS/VS/FIELD) can be forced active via the
TIM_OE bit. For more information on three-state control, refer
to the following sections:
• Three-State LLC Driver
• Timing Signals Output Enable
The ADV7183A supports three-stating via a dedicated pin.
When set high, the
P15–P0, HS, VS, FIELD, and SFL. The output drivers are threestated if the TOD bit or the
Table 17. TOD Function
TOD Description
0 (default) Output drivers enabled.
1 Output drivers three-stated.
Three-State LLC Driver
TRI_LLC, Address 0x0E [6]
This bit allows the output drivers for the LLC1 and LLC2 pins
of the ADV7183A to be three-stated. For more information on
three-state control, refer to the following sections:
• Three-State Output Drivers
• Timing Signals Output Enable
Table 18. TRI_LLC Function
TRI_LLC Description
0 (default)
1 LLC pin drivers three-stated.
pin three-states the output drivers for
OE
pin is set high.
OE
LLC pin drivers working according to the
DR_STR_C[1:0] setting (pin enabled).
Timing Signals Output Enable
TIM_OE, Address 0x04 [3]
The TIM_OE bit should be regarded as an addition to the TOD
bit. Setting it high forces the output drivers for HS, VS, and
FIELD into the active (that is, driving) state even if the TOD bit
is set. If set to low, the HS, VS, and FIELD pins are three-stated
dependent on the TOD bit. This functionality is useful if the
decoder is used as a timing generator only. This may be the case
if only the timing signals are extracted from an incoming signal,
or if the part is in free-run mode where a separate chip can
output, for instance, a company logo.
For more information on three-state control, refer to the
following sections:
• Timing Signals Output Enable
• Three-State LLC Driver
Table 19. TIM_OE Function
TIM_OE Description
0 (default)
1
HS, VS, FIELD three-stated according to the
TOD bit.
HS, VS, FIELD are forced active all the time.
The DR_STR_S[1:0] setting determines drive
strength.
Drive Strength Selection (Data)
DR_STR[1:0] Address 0x04 [5:4]
For EMC and crosstalk reasons, it may be desirable to
strengthen or weaken the drive strength of the output drivers.
The DR_STR[1:0] bits affect the P[15:0] output drivers.
For more information on three-state control, refer to the
following sections:
• Drive Strength Selection (Clock)
• Drive Strength Selection (Sync)
Table 20. DR_STR Function
DR_STR[1:0] Description
00 Low drive strength (1×).
01 (default) Medium low drive strength (2×).
10 Medium high drive strength (3×).
11 High drive strength (4×).
Rev. B | Page 17 of 104
ADV7183A
Drive Strength Selection (Clock)
Enable Subcarrier Frequency Lock Pin
DR_STR_C[1:0] Address 0x0E [3:2]
The DR_STR_C[1:0] bits can be used to select the strength of
the clock signal output driver (LLC pin). For more information,
refer to the following sections:
• Drive Strength Selection (Sync)
• Drive Strength Selection (Data)
Table 21. DR_STR Function
DR_STR[1:0] Description
00 Low drive strength (1×).
01 (default) Medium low drive strength (2×).
10 Medium high drive strength (3×).
11 High drive strength (4×).
Drive Strength Selection (Sync)
DR_STR_S[1:0] Address 0x0E [1:0]
The DR_STR_S[1:0] bits allow the user to select the strength of
the synchronization signals with which HS, VS, and F are
driven. For more information, refer to the following sections:
• Drive Strength Selection (Clock)
• Drive Strength Selection (Data)
Table 22. DR_STR Function
DR_STR[1:0] Description
00 Low drive strength (1×).
01 (default) Medium low drive strength (2×).
10 Medium high drive strength (3×).
11 High drive strength (4×).
EN_SFL_PIN Address 0x04 [1]
The EN_SFL_PIN bit enables the output of subcarrier lock
information (also known as GenLock) from the ADV7183A to
an encoder in a decoder/encoder back-to-back arrangement.
Table 23. EN_SFL_PIN
EN_SFL_PIN Description
0 (default) Subcarrier frequency lock output is disabled.
1
Subcarrier frequency lock information is
presented on the SFL pin.
Polarity LLC Pin
PCLK Address 0x37 [0]
The polarity of the clock leaving the ADV7183A via the LLC1
and LLC2 pins can be inverted using the PCLK bit.
Changing the polarity of the LLC clock output may be
necessary to meet the setup-and-hold time expectations of
follow-on chips.
This bit also inverts the polarity of the LLC2 clock.
Table 24. PCLK Function
PCLK Description
0 Invert LLC output polarity.
1 (default)
LLC output polarity normal (as per the Timing
Diagrams)
Rev. B | Page 18 of 104
ADV7183A
GLOBAL STATUS REGISTERS
There are four registers that provide summary information
about the video decoder. The IDENT register allows the user to
identify the revision code of the ADV7183A. The other three
registers contain status bits from the ADV7183A.
IDENTIFICATION
Depending on the setting of the FSCLE bit, the Status[0] and
Status[1] are based solely on horizontal timing info or on the
horizontal timing and lock status of the color subcarrier. See the
FSCLE FSC Lock Enable, Address 0x51 [7] section.
Autodetection Result
IDENT[7:0] Address 0x11 [7:0]
Provides identification of the revision of the ADV7183A.
Review the list of IDENT code readback values for the various
versions shown in Table 25.
Table 25. IDENT Function
IDENT[7:0] Description
0x0D ADV7183A-ES1
0x0E ADV7183A-ES2
0x0F or 0x10 ADV7183A-FT
0x11 ADV7183A (Version 2)
STATUS 1
STATUS_1[7:0] Address 0x10 [7:0]
This read-only register provides information about the internal
status of the ADV7183A.
See CIL[2:0] Count Into Lock, Address 0x51 [2:0] and COL[2:0]
Count Out of Lock, Address 0x51 [5:3] for information on the
timing.
Table 27. STATUS 1 Function
STATUS 1 [7:0] Bit Name Description
0 IN_LOCK In lock (right now).
1 LOST_LOCK Lost lock (since last read of this register).
2 FSC_LOCK FSC locked (right now).
3 FOLLOW_PW AGC follows peak white algorithm.
4 AD_RESULT.0 Result of autodetection.
5 AD_RESULT.1 Result of autodetection.
6 AD_RESULT.2 Result of autodetection.
7 COL_KILL Color kill active.
AD_RESULT[2:0] Address 0x10 [6:4]
The AD_RESULT[2:0] bits report back on the findings from
the autodetection block. Consult the General Setup section for
more information on enabling the autodetection block, and the
Autodetection of SD Modes section to find out how to
configure it.
Table 26. AD_RESULT Function
AD_RESULT[2:0] Description
000 NTSM-MJ
001 NTSC-443
010 PAL-M
011 PAL-60
100 PAL-BGHID
101 SECAM
110 PAL-Combination N
111 SECAM 525
Rev. B | Page 19 of 104
ADV7183A
STATUS 2
STATUS_2[7:0], Address 0x12 [7:0]
Table 28. STATUS 2 Function
STATUS 2 [7:0] Bit Name Description
0 MVCS DET Detected Macrovision color striping.
1 MVCS T3 Macrovision color striping protection. Conforms to Type 3 (if high), and Type 2 (if low).
2 MV_PS DET Detected Macrovision pseudo Sync pulses.
3 MV_AGC DET Detected Macrovision AGC pulses.
4 LL_NSTD Line length is nonstandard.
5 FSC_NSTD FSC frequency is nonstandard.
6 Reserved
7 Reserved
STATUS 3
STATUS_3[7:0], Address 0x13 [7:0]
Table 29. STATUS 3 Function
STATUS 3 [7:0] Bit Name Description
0 INST_HLOCK Horizontal lock indicator (instantaneous).
1 Reserved for future use.
2 Reserved for future use.
3 Reserved for future use.
4 FREE_RUN_ACT
5 STD_FLD_LEN Field length is correct for currently selected video standard.
6 INTERLACED Interlaced video detected (field sequence found).
7 PAL_SW_LOCK Reliable sequence of swinging bursts detected.
ADV7183A outputs a blue screen (see the DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN Default Value Automatic
Enable, Address 0x0C [1] section).
Rev. B | Page 20 of 104
ADV7183A
STANDARD DEFINITION PROCESSOR (SDP)
STANDARD DEFINITION PROCESSOR
DIGITIZED CVBS
DIGITIZED Y (YC)
DIGITIZED CVBS
DIGITIZED C (YC)
MACROVISION
DETECTION
LUMA
DIGITAL
FINE
CLAMP
CHROMA
DIGITAL
FINE
CLAMP
RECOVERY
CHROMA
DEMOD
F
SC
RECOVERY
VBI DATA
LUMA
FILTER
EXTRACT
CHROMA
FILTER
AUTODETECTION
SYNC
STANDARD
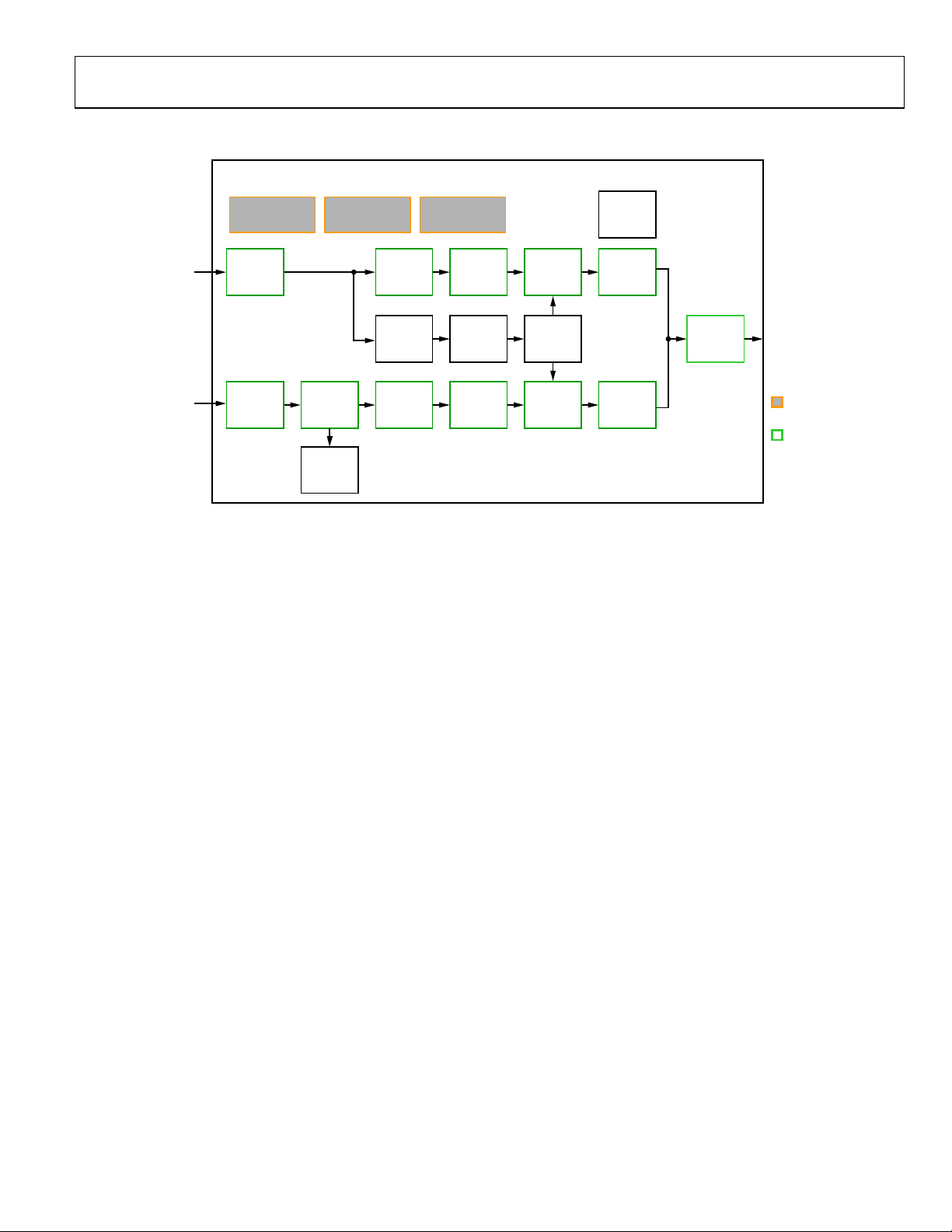
Figure 8. Block Diagram of the Standard Definition Processor
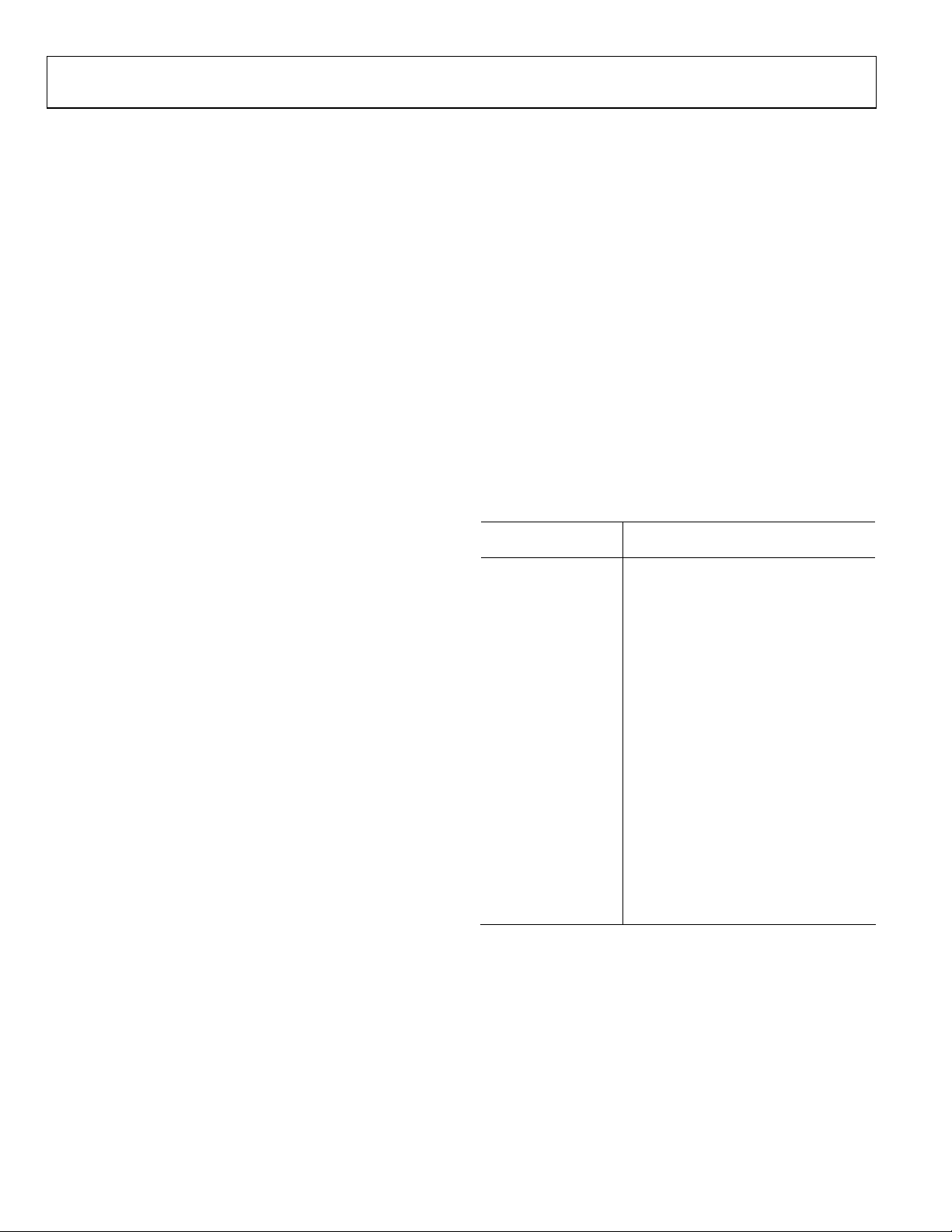
A block diagram of the ADV7183A’s standard definition
processor (SDP) is shown in Figure 8.
The SDP block can handle standard definition video in CVBS,
YC, and YPrPb formats. It can be divided into a luminance and
chrominance path. If the input video is of a composite type
(CVBS), both processing paths are fed with the CVBS input.
SD LUMA PATH
The input signal is processed by the following blocks:
• Digital Fine Clamp. This block uses a high precision
algorithm to clamp the video signal.
• Luma Filter Block. This block contains a luma decimation
filter (YAA) with a fixed response, and some shaping filters
(YSH) that have selectable responses.
• Luma Gain Control. The automatic gain control (AGC)
can operate on a variety of different modes, including gain
based on the depth of the horizontal sync pulse, peak white
mode, and fixed manual gain.
• Luma Resample. To correct for line-length errors as well as
dynamic line-length changes, the data is digitally
resampled.
• Luma 2D Comb. The two-dimensional comb filter
provides YC separation.
• AV Code Insertion. At this point, the decoded luma (Y)
signal is merged with the retrieved chroma values. AV
codes (as per ITU-R. BT-656) can be inserted.
GAIN
CONTROL
LINE
LENGTH
PREDICTOR
GAIN
CONTROL
SLLC
CONTROL
LUMA
RESAMPLE
RESAMPLE
CONTROL
CHROMA
RESAMPLE
LUMA
2D COMB
CHROMA
2D COMB
AV
CODE
INSERTION
VIDEO DATA
OUTPUT
MEASUREMENT
BLOCK (= >1
VIDEO DATA
PROCESSING
BLOCK
2
C)
04821-009
SD CHROMA PATH
The input signal is processed by the following blocks:
• Digital Fine Clamp. This block uses a high precision
algorithm to clamp the video signal.
• Chroma Demodulation. This block employs a color
subcarrier (F
subcarrier for any modulated chroma scheme. The
demodulation block then performs an AM demodulation
for PAL and NTSC and an FM demodulation for SECAM.
• Chroma Filter Block. This block contains a chroma
decimation filter (CAA) with a fixed response, and some
shaping filters (CSH) that have selectable responses.
• Gain Control. Automatic gain control (AGC) can operate
on several different modes, including gain based on the
color subcarrier’s amplitude, gain based on the depth of the
horizontal sync pulse on the luma channel, or fixed manual
gain.
• Chroma Resample. The chroma data is digitally resampled
to keep it perfectly aligned with the luma data. The
resampling is done to correct for static and dynamic linelength errors of the incoming video signal.
• Chroma 2D Comb. The two-dimensional, 5-line,
superadaptive comb filter provides high quality YC
separation in case the input signal is CVBS.
• AV Code Insertion. At this point, the demodulated chroma
(Cr and Cb) signal is merged with the retrieved luma
values. AV codes (as per ITU-R. BT-656) can be inserted.
) recovery unit to regenerate the color
SC
Rev. B | Page 21 of 104
ADV7183A
SYNC PROCESSING
The ADV7183A extracts syncs embedded in the video data
stream. There is currently no support for external HS/VS
inputs. The sync extraction has been optimized to support
imperfect video sources, for example videocassette recorders
with head switches. The actual algorithm uses a coarse
detection based on a threshold crossing followed by a more
detailed detection using an adaptive interpolation algorithm.
The raw sync information is sent to a line-length measurement
and prediction block. The output of this is then used to drive
the digital resampling section to ensure that the ADV7183A
outputs 720 active pixels per line.
The sync processing on the ADV7183A also includes two
specialized postprocessing blocks that filter and condition the
raw sync information retrieved from the digitized analog video.
• VSync Processor. This block provides extra filtering of the
detected VSyncs to give improved vertical lock.
• HSync Processor. The HSync processor is designed to filter
incoming HSyncs that have been corrupted by noise,
providing much improved performance for video signals
with stable time base but poor SNR.
VBI DATA RECOVERY
The ADV7183A can retrieve the following information from
the input video:
• Wide-screen signaling (WSS)
• Copy generation management system (CGMS)
• Closed caption (CC)
• Macrovision protection presence
• EDTV data
• Gemstar-compatible data slicing
The ADV7183A is also capable of automatically detecting the
incoming video standard with respect to color subcarrier frequency, field rate, and line rate. It can configure itself to support
PAL-BGHID, PAL-M/N, PAL-combination N, NTSC-M, NTSCJ, SECAM 50 Hz/60 Hz, NTSC4.43, and PAL60.
GENERAL SETUP
Video Standard Selection
The VID_SEL[3:0] register allows the user to force the digital
core into a specific video standard. Under normal circumstances, this should not be necessary. The VID_SEL[3:0] bits
default to an autodetection mode that supports PAL, NTSC,
SECAM, and variants thereof.
Refer to the Autodetection of SD Modes section for more
information on the autodetection system.
Autodetection of SD Modes
In order to guide the autodetect system, individual enable bits
are provided for each of the supported video standards. Setting
the relevant bit to 0 inhibits the standard from being detected
automatically. Instead, the system picks the closest of the
remaining enabled standards. The autodetection result can be
read back via the status registers. See the Global Status Registers
section for more information.
Table 30. VID_SEL Function
VID_SEL[3:0]
Address 0x00 [7:4] Description
0000 (default)
0001
0010
0011
0100 NTSC J (1)
0101 NTSC M (1).
0110 PAL 60.
0111 NTSC 4.43 (1).
1000 PAL BGHID.
1001 PAL N ( = PAL BGHID (with pedestal)).
1010 PAL M (without pedestal).
1011 PAL M.
1100 PAL combination N.
1101 PAL combination N (with pedestal).
1110 SECAM.
1111 SECAM (with pedestal).
Autodetect (PAL BGHID) <–> NTSC J (no
pedestal), SECAM.
Autodetect (PAL BGHID) <–> NTSC M
(pedestal), SECAM.
Autodetect (PAL N) <–> NTSC J (no
pedestal), SECAM.
Autodetect (PAL N) <–> NTSC M
(pedestal), SECAM.
Rev. B | Page 22 of 104
ADV7183A
AD_SEC525_EN Enable Autodetection of SECAM 525 Line
Video, Address 0x07 [7]
Table 31. AD_SEC525_EN Function
AD_SEC525_EN Description
0 (default)
1 Enable the detection.
Disable the autodetection of a 525-line
system with a SECAM style, FM-modulated
color component.
AD_SECAM_EN Enable Autodetection of SECAM,
Address 0x07 [6]
Table 32. AD_SECAM_EN Function
AD_SECAM_EN Description
0 Disable the autodetection of SECAM.
1 (default) Enable the detection.
AD_N443_EN Enable Autodetection of NTSC 443,
Address 0x07 [5]
Table 33. AD_N443_EN Function
AD_N443_EN Description
0
1 (default) Enable the detection.
Disable the autodetection of NTSC style
systems with a 4.43 MHz color subcarrier.
AD_P60_EN Enable Autodetection of PAL60,
Address 0x07 [4]
Table 34. AD_P60_EN Function
AD_P60_EN Description
0
1 (default) Enable the detection.
Disable the autodetection of PAL systems
with a 60 Hz field rate.
AD_PALN_EN Enable Autodetection of PAL N,
Address 0x07 [3]
Table 35. AD_PALN_EN Function
AD_PALN_EN Description
0 Disable the detection of the PAL N standard.
1 (default) Enable the detection.
AD_PALM_EN Enable Autodetection of PAL M,
Address 0x07 [2]
Table 36. AD_PALM_EN Function
AD_PALM_EN Description
0 Disable the autodetection of PAL M.
1 (default) Enable the detection.
AD_NTSC_EN Enable Autodetection of NTSC,
Address 0x07 [1]
Table 37. AD_NTSC_EN Function
AD_NTSC_EN Description
0 Disable the detection of standard NTSC.
1 (default) Enable the detection.
AD_PAL_EN Enable Autodetection of PAL,
Address 0x07 [0]
Table 38. AD_PAL_EN Function
AD_PAL_EN Description
0 Disable the detection of standard PAL.
1 (default) Enable the detection.
SFL_INV Subcarrier Frequency Lock Inversion
This bit controls the behavior of the PAL switch bit in the SFL
(GenLock Telegram) data stream. It was implemented to solve
some compatibility issues with video encoders. It solves two
problems:
• The PAL switch bit is only meaningful in PAL. Some
encoders (including Analog Devices encoders) also look at
the state of this bit in NTSC.
• There was a design change in Analog Devices encoders
from ADV717x to ADV719x. The older versions used the
SFL (GenLock Telegram) bit directly, while the later ones
invert the bit prior to using it. The reason for this is that
the inversion compensated for the 1-line delay of an SFL
(GenLock Telegram) transmission.
As a result:
• ADV717x encoders need the PAL switch bit in the SFL
(GenLock Telegram) to be 1 for NTSC to work.
• ADV7190/ADV7191/ADV7194 encoders need the PAL
switch bit in the SFL to be 0 to work in NTSC.
If the state of the PAL switch bit is wrong, a 180° phase shift
occurs.
In a decoder/encoder back-to-back system in which SFL is
used, this bit must be set up properly for the specific encoder
used.
Table 39. SFL_INV Function
SFL_INV
Address 0x41 [6]
0
1 (default)
Description
SFL-compatible with ADV7190/ADV7191/
ADV7194 encoders.
SFL-compatible with ADV717x/ADV7173x
encoders.
Rev. B | Page 23 of 104
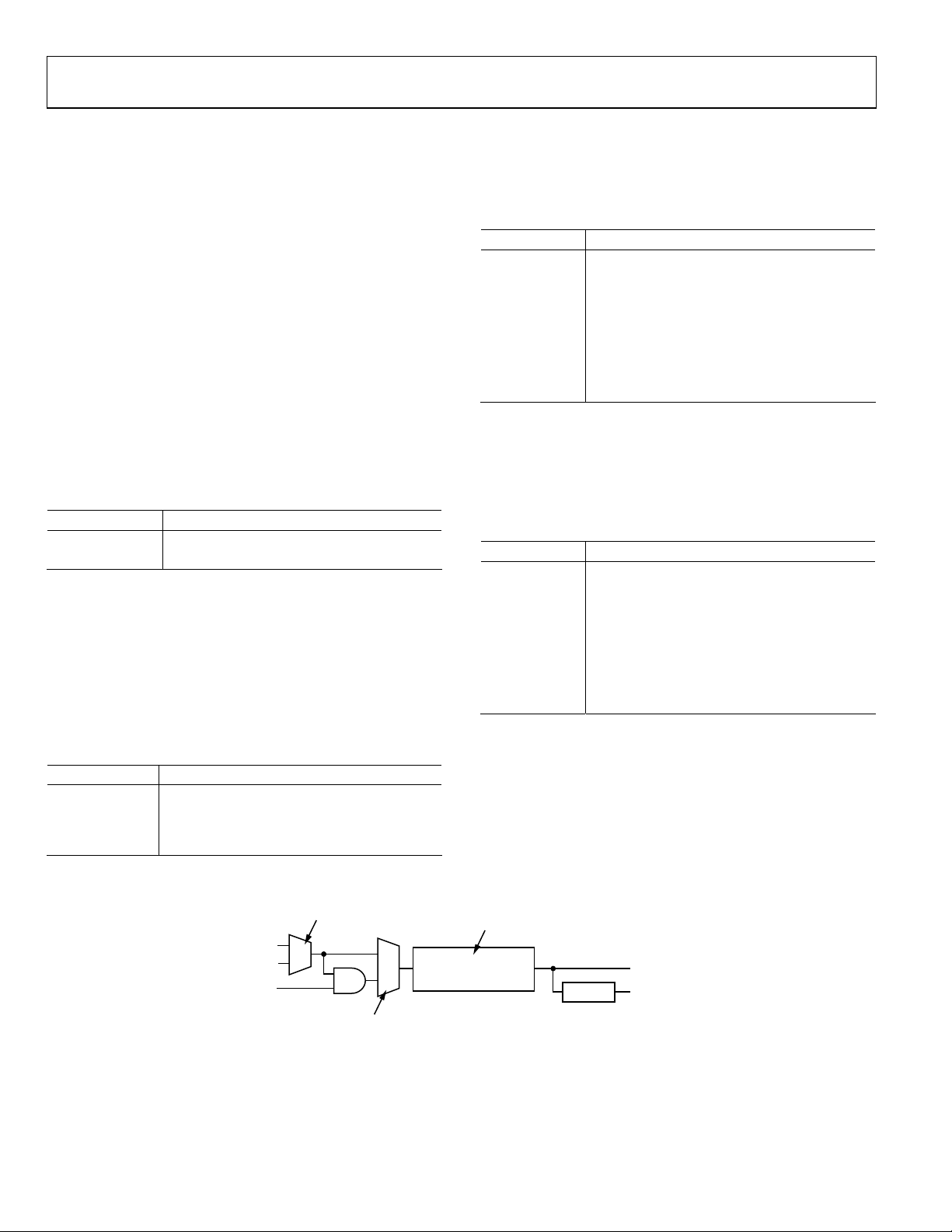
ADV7183A
Lock Related Controls
Lock information is presented to the user through Bits [1:0] of
the Status 1 register. See the STATUS_1[7:0] Address 0x10 [7:0]
section. Figure 9 outlines the signal flow and the controls
available to influence the way the lock status information is
generated.
SRLS Select Raw Lock Signal, Address 0x51 [6]
Using the SRLS bit, the user can choose between two sources for
determining the lock status (per Bits [1:0] in the Status 1 register).
• The time_win signal is based on a line-to-line evaluation of
the horizontal synchronization pulse of the incoming
video. It reacts quite quickly.
• The free_run signal evaluates the properties of the
incoming video over several fields, and takes vertical
synchronization information into account.
Table 40. SRLS Function
SRLS Description
0 (default) Select the free_run signal.
1 Select the time_win signal.
FSCLE FSC Lock Enable, Address 0x51 [7]
The FSCLE bit allows the user to choose whether the status of
the color subcarrier loop is taken into account when the overall
lock status is determined and presented via Bits [1:0] in Status
Register 1. This bit must be set to 0 when operating the
ADV7183A in YPrPb component mode in order to generate a
reliable HLOCK status bit.
Table 41. FSCLE Function
FSCLE Description
0
1 (default)
Overall lock status only dependent on
horizontal sync lock.
Overall lock status dependent on horizontal
sync lock and F
SC
TIME_WIN
FREE_RUN
F
LOCK
SC
Lock.
SELECT THE RAW LOCK SIGNAL
SRLS
1
0
0
1
COUNTER INTO LOCK
COUNTER OUT OF LOCK
CIL[2:0] Count Into Lock, Address 0x51 [2:0]
CIL[2:0] determines the number of consecutive lines for which
the into lock condition must be true before the system switches
into the locked state, and reports this via Status 0 [1:0].
Table 42. CIL Function
CIL[2:0] Description (Count Value in Lines of Video)
000 1
001 2
010 5
011 10
100 (default) 100
101 500
110 1000
111 100000
COL[2:0] Count Out of Lock, Address 0x51 [5:3]
COL[2:0] determines the number of consecutive lines for which
the out of lock condition must be true before the system
switches into unlocked state, and reports this via Status 0 [1:0].
Table 43. COL Function
COL[2:0] Description (Count Value in Lines of Video)
000 1
001 2
010 5
011 10
100 (default) 100
101 500
110 1000
111 100000
FILTER THE RAW LOCK SIGNAL
CIL[2:0], COL[2:0]
STATUS 1 [0]
MEMORY
STATUS 1 [1]
LOCK INTO ACCOUNT
TAKE F
SC
FSCLE
Figure 9. Lock Related Signal Path
04821-006
Rev. B | Page 24 of 104
ADV7183A
COLOR CONTROLS
The following registers provide user control over the picture
appearance, including control of the active data in the event of
video being lost. They are independent of any other controls.
For instance, brightness control is independent from picture
clamping, although both controls affect the signal’s dc level.
SD_SAT_Cr[7:0] SD Saturation Cr Channel,
Address 0xE4 [7:0]
This register allows the user to control the gain of the Cr
channel only.
CON[7:0] Contrast Adjust, Address 0x08 [7:0]
This register allows the user to adjust the contrast of the picture.
Table 44. CON Function
CON[7:0] Description (Adjust Contrast of the Picture)
0x80 (default) Gain on luma channel = 1.
0x00 Gain on luma channel = 0.
0xFF Gain on luma channel = 2.
SAT[7:0] Saturation Adjust, Address 0x09 [7:0]
The user can adjust the saturation of the color output using this
register.
ADI encourages users not to use the SAT[7:0] register, which
may be removed in future revisions of the ADV7183A. Instead,
the SD_SAT_Cb and SD_SAT_Cr registers should be used.
Table 45. SAT Function
SAT[7:0] Description (Adjust Saturation of the Picture)
0x80 (default) Chroma gain = 0 dB.
0x00 Chroma gain = –42 dB.
0xFF Chroma gain = +6 dB.
SD_SAT_Cb[7:0] SD Saturation Cb Channel,
Address 0xE3 [7:0]
This register allows the user to control the gain of the Cb
channel only.
For this register to be active, SAT[7:0] must be programmed
with its default value of 0x80. If SAT[7:0] is programmed with a
different value, SD_SAT_Cb[7:0] and SD_SAT_Cr[7:0] are
inactive.
Table 46. SD_SAT_Cb Function
Description
SD_SAT_Cb[7:0]
0x80 (default) Gain on Cb channel = 0 dB.
0x00 Gain on Cb channel = –42 dB.
0xFF Gain on Cb channel = +6 dB.
(Adjust Saturation of the Picture)
For this register to be active, SAT[7:0] must be programmed
with its default value of 0x80. If SAT[7:0] is programmed with a
different value, SD_SAT_Cb[7:0] and SD_SAT_Cr[7:0] are
inactive.
Table 47. SD_SAT_Cr Function
Description
SD_SAT_Cr[7:0]
0x80 (default) Gain on Cr channel = 0 dB.
0x00 Gain on Cr channel = –42 dB.
0xFF Gain on Cr channel = +6 dB.
(Adjust Saturation of the Picture)
SD_OFF_Cb[7:0] SD Offset Cb Channel, Address 0xE1 [7:0]
This register allows the user to select an offset for the Cb
channel only. There is a functional overlap with the Hue [7:0]
register.
Table 48. SD_OFF_Cb Function
Description
(Adjust Hue of the Picture by Selecting an
SD_OFF_Cb[7:0]
0x80 (default) 0 offset applied to the Cb channel.
0x00 –312 mV offset applied to the Cb channel.
0xFF +312 mV offset applied to the Cb channel.
Offset for Data on the Cb Channel)
SD_OFF_Cr [7:0] SD Offset Cr Chan, Address 0xE2 [7:0]
This register allows the user to select an offset for the Cr
channel only. There is a functional overlap with the Hue [7:0]
register.
Table 49. SD_OFF_Cr Function
Description
(Adjust Hue of the Picture by Selecting an
SD_OFF_Cr[7:0]
0x80 (default) 0 offset applied to the Cb channel.
0x00 –312 mV offset applied to the Cr channel.
0xFF +312 mV offset applied to the Cr channel.
Offset for Data on Cr Channel)
Rev. B | Page 25 of 104
ADV7183A
BRI[7:0] Brightness Adjust, Address 0x0A [7:0]
This register controls the brightness of the video signal through
the ADV7183A.
Table 50. BRI Function
BRI[7:0]
0x00 (default) Offset of the luma channel = +0IRE.
0x7F Offset of the luma channel = +100IRE.
0x80 Offset of the luma channel = –100IRE.
HUE[7:0] Hue Adjust, Address 0x0B [7:0]
This register contains the value for the color hue adjustment.
HUE[7:0] has a range of ±90°, with 0x00 equivalent to an
adjustment of 0°. The resolution of HUE[7:0] is 1 bit = 0.7°.
The hue adjustment value is fed into the AM color demodulation block. Therefore, it only applies to video signals that
contain chroma information in the form of an AM modulated
carrier (CVBS or Y/C in PAL or NTSC). It does not affect
SECAM and does not work on component video inputs
(YPrPb).
Table 51. HUE Function
HUE[7:0] Description (Adjust Hue of the Picture)
0x00 (default) Phase of the chroma signal = 0°.
0x7F Phase of the chroma signal = –90°.
0x80 Phase of the chroma signal = +90°.
DEF_Y[5:0] Default Value Y, Address 0x0C [7:2]
In cases where the ADV7183A loses lock on the incoming video
signal or where there is no input signal, the DEF_Y[5:0] register
allows the user to specify a default luma value to be output.
This value is used under the following conditions:
• If DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN bit is set to high and the
ADV7183A lost lock to the input video signal. This is the
intended mode of operation (automatic mode).
• The DEF_VAL_EN bit is set, regardless of the lock status of
the video decoder. This is a forced mode that may be useful
during configuration.
The DEF_Y[5:0] values define the 6 MSBs of the output video.
The remaining LSBs are padded with 0s. For example, in 8-bit
mode, the output is Y[7:0] = {DEF_Y[5:0], 0, 0}.
Description (Adjust Brightness of the Picture)
Table 52. DEF_Y Function
DEF_Y[5:0] Description
0x0D (blue) (default) Default value of Y.
DEF_C[7:0] Default Value C, Address 0x0D [7:0]
The DEF_C[7:0] register complements the DEF_Y[5:0] value. It
defines the 4 MSBs of Cr and Cb values to be output if
• The DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN bit is set to high and the
ADV7183A cannot lock to the input video (automatic
mode).
• DEF_VAL_EN bit is set to high (forced output).
The data that is finally output from the ADV7183A for the
chroma side is Cr[7:0] = {DEF_C[7:4], 0, 0, 0, 0}, Cb[7:0] =
{DEF_C[3:0], 0, 0, 0, 0}.
Table 53. DEF_C Function
DEF_C[7:0] Description
0x7C (blue) (default) Default values for Cr and Cb.
DEF_VAL_EN Default Value Enable,
Address 0x0C [0]
This bit forces the use of the default values for Y, Cr, and Cb.
Refer to the descriptions for DEF_Y and DEF_C for additional
information. The decoder also outputs a stable 27 MHz clock,
HS, and VS in this mode.
Table 54. DEF_VAL_EN Function
DEF_VAL_EN Description
0 (default)
1
Do not force the use of default Y, Cr,
and Cb values. Output colors
dependent on DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN.
Always use default Y, Cr, and Cb values.
Override picture data even if the video
decoder is locked.
DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN Default Value Automatic Enable,
Address 0x0C [1]
This bit enables the automatic usage of the default values for Y,
Cr, and Cb in cases where the ADV7183A cannot lock to the
video signal.
Table 55. DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN Function
DEF_VAL_AUTO_EN Description
0
1 (default)
Do not use default Y, Cr, and Cb values.
If unlocked, output noise.
Use default Y, Cr, and Cb values when
decoder loses lock.
Rev. B | Page 26 of 104
ADV7183A
A
G
CLAMP OPERATION
FINE
CURRENT
SOURCES
COARSE
CURRENT
SOURCES
NALO
VIDEO
INPUT
ADC
Figure 10. Clamping Overview
The input video is ac-coupled into the ADV7183A through a
0.1 µF capacitor. It is recommended that the range of the input
video signal is 0.5 V to 1.6 V (typically 1 V p-p). If the signal
exceeds this range, it cannot be processed correctly in the
decoder. Since the input signal is ac-coupled into the decoder,
its dc value needs to be restored. This process is referred to as
clamping the video. This section explains the general process of
clamping on the ADV7183A, and shows the different ways in
which a user can configure its behavior.
The ADV7183A uses a combination of current sources and a
digital processing block for clamping, as shown in Figure 10.
The analog processing channel shown is replicated three times
inside the IC. While only one single channel (and only one
ADC) would be needed for a CVBS signal, two independent
channels are needed for YC (S-VHS) type signals, and three
independent channels are needed to allow component signals
(YPrPb) to be processed.
The clamping can be divided into two sections:
• Clamping before the ADC (analog domain): current
sources.
DATA
PRE
PROCESSOR
(DPP)
CLAMP CONTROL
SDP
WITH DIGITAL
FINE CLAMP
04821-010
The clamping scheme has to complete two tasks: it must be able
to acquire a newly connected video signal with a completely
unknown dc level, and it must maintain the dc level during
normal operation.
For a fast acquiring of an unknown video signal, the large current
clamps may be activated. (It is assumed that the amplitude of
the video signal at this point is of a nominal value.) Control of
the coarse and fine current clamp parameters is performed
automatically by the decoder.
Standard definition video signals may have excessive noise on
them. In particular, CVBS signals transmitted by terrestrial
broadcast and demodulated using a tuner usually show very
large levels of noise (>100 mV). A voltage clamp would be
unsuitable for this type of video signal. Instead, the ADV7183A
employs a set of four current sources that can cause coarse
(>0.5 mA) and fine (<0.1 mA) currents to flow into and away
from the high impedance node that carries the video signal (see
Figure 10).
2
The following sections describe the I
C signals that can be used
to influence the behavior of the clamping.
• Clamping after the ADC (digital domain): digital
processing block.
The ADCs can digitize an input signal only if it resides within
the ADC’s 1.6 V input voltage range. An input signal with a dc
level that is too large or too small is clipped at the top or bottom
of the ADC range.
The primary task of the analog clamping circuits is to ensure
that the video signal stays within the valid ADC input window
so the analog-to-digital conversion can take place. It is not necessary to clamp the input signal with a very high accuracy in the
analog domain as long as the video signal fits the ADC range.
After digitization, the digital fine clamp block corrects for any
remaining variations in dc level. Since the dc level of an input
video signal refers directly to the brightness of the picture
transmitted, it is important to perform a fine clamp with high
accuracy; otherwise, brightness variations may occur. Furthermore, dynamic changes in the dc level almost certainly lead to
visually objectionable artifacts and must, therefore, be prohibited.
Rev. B | Page 27 of 104
Previous revisions of the ADV7183A had controls (FACL/FICL,
fast and fine clamp length) to allow configuration of the length
for which the coarse (fast) and fine current sources are switched
on. These controls were removed on the ADV7183A-FT and
replaced by an adaptive scheme.
CCLEN Current Clamp Enable, Address 0x14 [4]
The current clamp enable bit allows the user to switch off the
current sources in the analog front end altogether. This may be
useful if the incoming analog video signal is clamped externally.
Table 56. CCLEN Function
CCLEN Description
0 Current sources switched off.
1 (default) Current sources enabled.

ADV7183A
DCT[1:0] Digital Clamp Timing, Address 0x15 [6:5]
The Clamp Timing register determines the time constant of the
digital fine clamp circuitry. It is important to realize that the
digital fine clamp reacts very fast since it is supposed to immediately correct any residual dc level error for the active line. The
time constant of the digital fine clamp must be much quicker
than the one from the analog blocks.
By default, the time constant of the digital fine clamp is adjusted
dynamically to suit the currently connected input signal.
Table 57. DCT Function
DCT[1:0] Description
00 Slow (TC = 1 sec).
01 Medium (TC = 0.5 sec).
10 (default) Fast (TC = 0.1 sec).
11
DCFE Digital Clamp Freeze Enable, Address 0x15 [4]
This register bit allows the user to freeze the digital clamp loop
at any time. It is intended for users who would like to do their
own clamping. Users should disable the current sources for
analog clamping via the appropriate register bits, wait until the
digital clamp loop settles, and then freeze it via the DCFE bit.
Table 58. DCFE Function
DCFE Description
0 (default) Digital clamp operational.
1 Digital clamp loop frozen.
LUMA FILTER
Data from the digital fine clamp block is processed by three sets
of filters. The data format at this point is CVBS for CVBS input
or luma only for Y/C and YPrPb input formats.
• Luma Antialias Filter (YAA). The ADV7183A receives
video at a rate of 27 MHz. (In 4× oversampled video, the
ADCs sample at 54 MHz, and the first decimation is
performed inside the DPP filters. Therefore, the data rate
into the ADV7183A is always 27 MHz.) The ITU-R BT.601
recommends a sampling frequency of 13.5 MHz. The luma
antialias filter decimates the oversampled video using a
high quality, linear phase, low-pass filter that preserves the
luma signal while at the same time attenuating out-of-band
components. The luma antialias filter (YAA) has a fixed
response.
• Luma Shaping Filters (YSH). The shaping filter block is a
programmable low-pass filter with a wide variety of
responses. It can be used to selectively reduce the luma
Determined by ADV7183A dependent on video
parameters.
video signal bandwidth (needed prior to scaling, for
example). For some video sources that contain high
frequency noise, reducing the bandwidth of the luma
signal improves visual picture quality. A follow-on video
compression stage may work more efficiently if the video is
low-pass filtered.
The ADV7183A allows selection of two responses for the
shaping filter: one that is used for good quality CVBS,
component, and S-VHS type sources, and a second for
nonstandard CVBS signals.
The YSH filter responses also include a set of notches for
PAL and NTSC. However, it is recommended to use the
comb filters for YC separation.
• Digital Resampling Filter. This block is used to allow
dynamic resampling of the video signal to alter parameters
such as the time base of a line of video. Fundamentally, the
resampler is a set of low-pass filters. The actual response is
chosen by the system with no requirement for user
intervention.
Figure 12 through Figure 15 show the overall response of all
filters together. Unless otherwise noted, the filters are set into a
typical wideband mode.
Y Shaping Filter
For input signals in CVBS format, the luma shaping filters play
an essential role in removing the chroma component from a
composite signal. YC separation must aim for best possible
crosstalk reduction while still retaining as much bandwidth
(especially on the luma component) as possible. High quality
YC separation can be achieved by using the internal comb filters
of the ADV7183A. Comb filtering, however, relies on the
frequency relationship of the luma component (multiples of the
video line rate) and the color subcarrier (F
). For good quality
SC
CVBS signals, this relationship is known; the comb filter
algorithms can be used to separate out luma and chroma with
high accuracy.
In the case of nonstandard video signals, the frequency
relationship may be disturbed and the comb filters may not be
able to remove all crosstalk artifacts in an optimum fashion
without the assistance of the shaping filter block.
An automatic mode is provided. Here, the ADV7183A evaluates
the quality of the incoming video signal and selects the filter
responses in accordance with the signal quality and video
standard. YFSM, WYSFMOVR, and WYSFM allow the user to
manually override the automatic decisions in part or in full.
Rev. B | Page 28 of 104
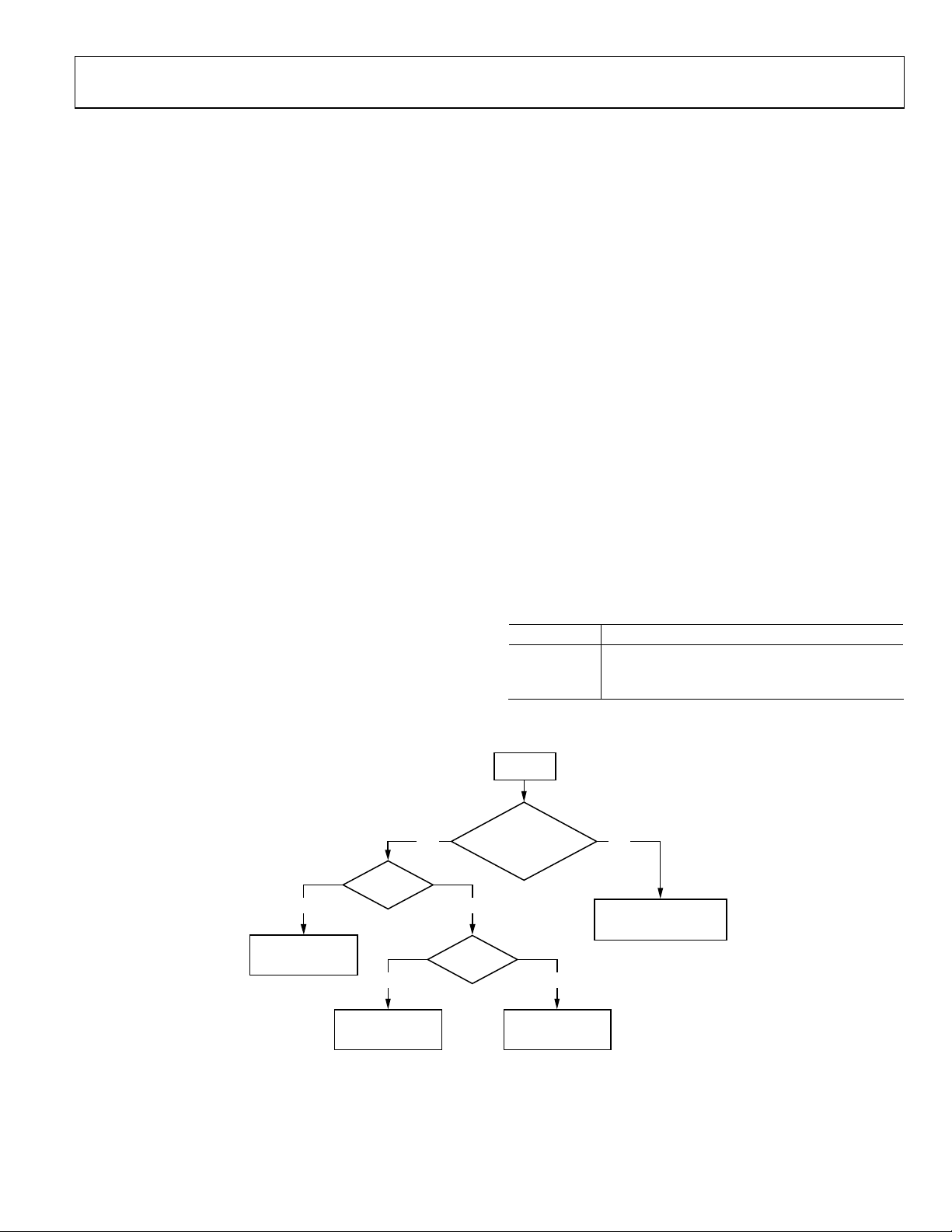
ADV7183A
The luma shaping filter has three control registers:
• YSFM[4:0] allows the user to manually select a shaping
filter mode (applied to all video signals) or to enable an
automatic selection (dependent on video quality and video
standard).
• WYSFMOVR allows the user to manually override the
WYSFM decision.
• WYSFM[4:0] allows the user to select a different shaping
filter mode for good quality CVBS, component (YPrPb),
and S-VHS (YC) input signals.
In automatic mode, the system preserves the maximum possible
bandwidth for good CVBS sources (since they can successfully
be combed) as well as for luma components of YPrPb and YC
sources, since they need not be combed. For poor quality
signals, the system selects from a set of proprietary shaping
filter responses that complements comb filter operation in order
to reduce visual artifacts.
The decisions of the control logic are shown in Figure 11.
YSFM[4:0] Y Shaping Filter Mode, Address 0x17 [4:0]
The Y shaping filter mode bits allow the user to select from a
wide range of low-pass and notch filters. When switched in
automatic mode, the filter is selected based on other register
selections, for example, detected video standard, as well as
properties extracted from the incoming video itself, for
ex ample, quality, time b ase stability. The automatic s election
always picks the widest possible bandwidth for the video input
encountered.
• If the YSFM settings specify a filter (that is, YSFM is set to
values other than 00000 or 00001), the chosen filter is
applied to all video, regardless of its quality.
• In automatic selection mode, the notch filters are only used
for bad quality video signals. For all other video signals,
wideband filters are used.
WYSFMOVR Wideband Y Shaping Filter Override,
Address 0x18 [7]
Setting the WYSFMOVR bit enables the use of the
WYSFM[4:0] settings for good quality video signals. For more
information, refer to the general discussion of the luma shaping
filters in the Y Shaping Filter section and the flowchart shown
in Figure 11.
Table 59. WYSFMOVR Function
WYSFMOVR Description
0
Automatic selection of shaping filter for good
quality video signals.
1 (default) Enable manual override via WYSFM[4:0].
SET YSFM
YSFM IN AUTO MODE?
00000 OR 00001
WYSFMOVR
SELECT AUTOMATIC
WIDEBAND FILTER
USE YSFM SELECTED
FILTER REGARDLESS FOR
GOOD AND BAD VIDEO
04821-011
VIDEO
BAD GOOD
AUTO SELECT LUMA
SHAPING FILTER TO
COMPLEMENT COMB
QUALITY
1 0
SELECT WIDEBAND
FILTER AS PER
WYSFM[4:0]
Figure 11. YSFM and WYSFM Control Flowchart
YES NO
Rev. B | Page 29 of 104
ADV7183A
Table 60. YSFM Function
YSFM[4:0] Description
0'0000
0'0001
0'0010 SVHS 1
0'0011 SVHS 2
0'0100 SVHS 3
0'0101 SVHS 4
0'0110 SVHS 5
0'0111 SVHS 6
0'1000 SVHS 7
0'1001 SVHS 8
0'1010 SVHS 9
0'1011 SVHS 10
0'1100 SVHS 11
0'1101 SVHS 12
0'1110 SVHS 13
0'1111 SVHS 14
1'0000 SVHS 15
1'0001 SVHS 16
1'0010 SVHS 17
1'0011 (default) SVHS 18 (CCIR 601)
1'0100 PAL NN 1
1'0101 PAL NN 2
1'0110 PAL NN 3
1'0111 PAL WN 1
1'1000 PAL WN 2
1'1001 NTSC NN 1
1'1010 NTSC NN 2
1'1011 NTSC NN 3
1'1100 NTSC WN 1
1'1101 NTSC WN 2
1'1110 NTSC WN 3
1'1111 Reserved
WYSFM[4:0] Wide Band Y Shaping Filter Mode,
Address 0x18 [4:0]
The WYSFM[4:0] bits allow the user to manually select a
shaping filter for good quality video signals, for example, CVBS
with stable time base, luma component of YPrPb, luma
component of YC. The WYSFM bits are only active if the
WYSFMOVR bit is set to 1. See the general discussion of the
shaping filter settings in the Y Shaping Filter section.
Automatic selection including a wide notch
response (PAL/NTSC/SECAM)
Automatic selection including a narrow
notch response (PAL/NTSC/SECAM)
Table 61. WYSFM Function
WYSFM[4:0] Description
0'0000 Do not use
0'0001 Do not use
0'0010 SVHS 1
0'0011 SVHS 2
0'0100 SVHS 3
0'0101 SVHS 4
0'0110 SVHS 5
0'0111 SVHS 6
0'1000 SVHS 7
0'1001 SVHS 8
0'1010 SVHS 9
0'1011 SVHS 10
0'1100 SVHS 11
0'1101 SVHS 12
0'1110 SVHS 13
0'1111 SVHS 14
1'0000 SVHS 15
1'0001 SVHS 16
1'0010 SVHS 17
1'0011 (default) SVHS 18 (CCIR 601)
1'0100–1’1111 Do not use
COMBINED Y ANTIALIAS, S-VHS LOW-PASS FILTERS,
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
AMPLITUDE (dB)
–50
–60
–70
010864212
Figure 12. Y S-VHS Combined Responses
Y RESAMPLE
04821-012
FREQUENCY (MHz)
The filter plots in Figure 12 show the S-VHS 1 (narrowest) to
S-VHS 18 (widest) shaping filter settings. Figure 14 shows the
PAL notch filter responses. The NTSC-compatible notches are
shown in Figure 15.
Rev. B | Page 30 of 104
 Loading...
Loading...