ANALOG DEVICES ADuM2210 Service Manual
Dual-Channel Digital Isolators, 5 kV
Data Sheet
FEATURES
High isolation voltage: 5000 V rms
Enhanced system-level ESD performance per IEC 61000-4-x
Low power operation
5 V operation
1.6 mA per channel maximum at 0 Mbps to 2 Mbps
3.7 mA per channel maximum at 10 Mbps
3 V operation
1.4 mA per channel maximum at 0 Mbps to 2 Mbps
2.4 mA per channel maximum at 10 Mbps
Bidirectional communication
3 V/5 V level translation
High temperature operation: 125°C
Default low output
High data rate: dc to 10 Mbps (NRZ)
Precise timing characteristics
3 ns maximum pulse width distortion
3 ns maximum channel-to-channel matching
High common-mode transient immunity: >25 kV/μs
16-lead SOIC wide body package version (RW-16)
16-lead SOIC wide body enhanced creepage version (RI-16)
Safety and regulatory approvals (RI-16 package)
UL recognition: 5000 V rms for 1 minute per UL 1577
CSA Component Acceptance Notice #5A
IEC 60601-1: 250 V rms (reinforced)
IEC 60950-1: 400 V rms (reinforced)
VDE Certificate of Conformity
DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12
V
= 846 V peak
IORM
APPLICATIONS
General-purpose, high voltage, multichannel isolation
Medical equipment
Power supplies
RS-232/RS-422/RS-485 transceiver isolation
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADuM221x1 are 2-channel digital isolators based on Analog
Devices, Inc., iCoupler® technology. Combining high speed CMOS
and monolithic air core transformer technology, these isolation
components provide outstanding performance characteristics that
are superior to alternatives such as optocoupler devices.
By avoiding the use of LEDs and photodiodes, iCoupler devices
remove the design difficulties commonly associated with optocouplers. Typical optocoupler concerns regarding uncertain current
transfer ratios, nonlinear transfer functions, and temperature
ADuM2210/ADuM2211
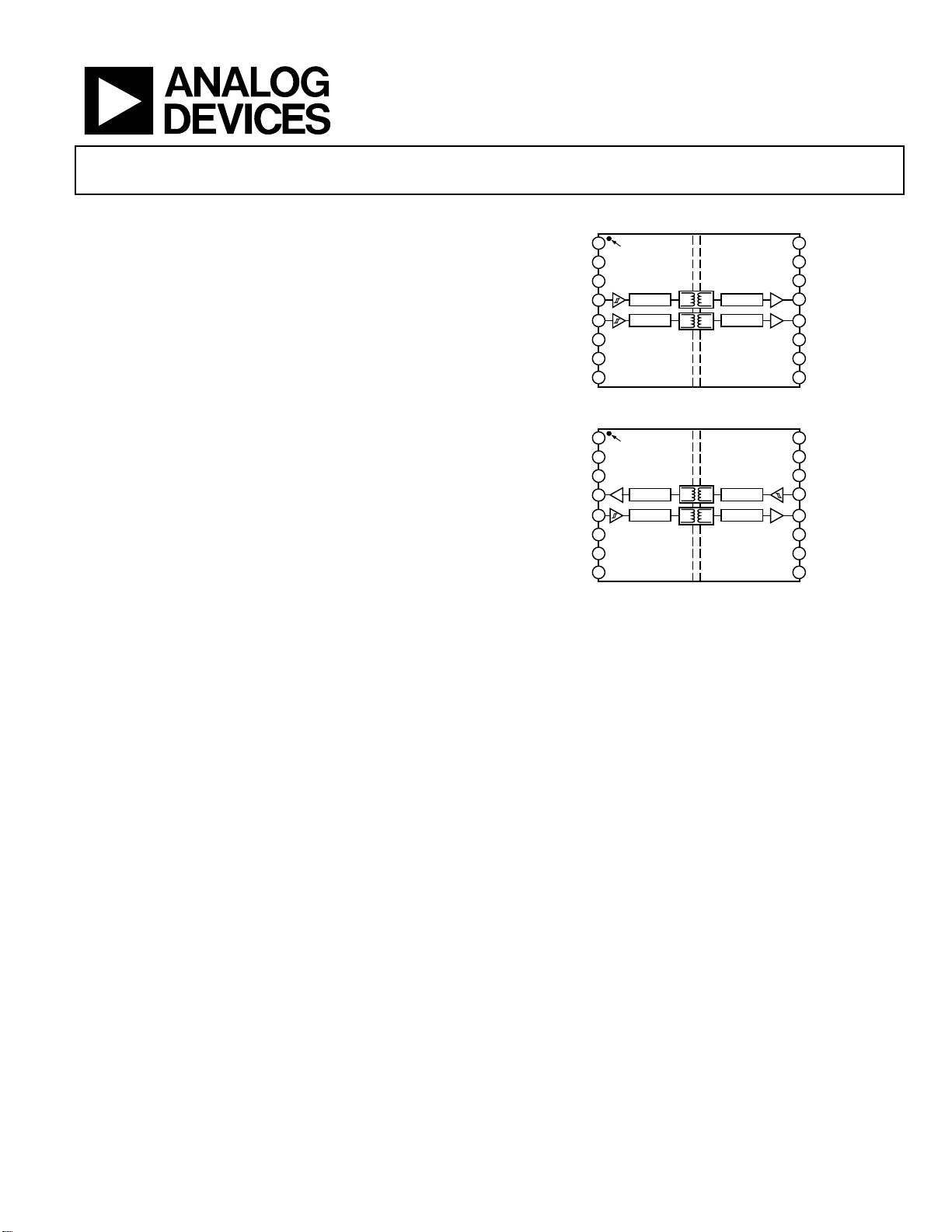
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAMS
1
GND
V
GND
NC
DD1
V
V
NC
NC
PIN 1
1
INDICATOR
2
3
4
IA
5
IB
6
7
1
8
NC = NO CONNECT
ENCODE
ENCODE
ADuM2210
DECODE
DECODE
Figure 1. ADuM2210
1
GND
V
V
GND
NC
DD1
OA
V
NC
NC
PIN 1
1
INDICATOR
2
3
4
5
IB
6
7
1
8
NC = NO CONNECT
DECODE
ENCODE
ADuM2211
ENCODE
DECODE
Figure 2. ADuM2211
and lifetime effects are eliminated with the simple iCoupler digital
interfaces and stable performance characteristics. The need for
external drivers and other discrete components is eliminated with
these iCoupler products. Furthermore, iCoupler devices run at
one-tenth to one-sixth the power of optocouplers at comparable
signal data rates.
The ADuM221x isolators provide two independent isolation
channels in a variety of channel configurations and data rates
(see the Ordering Guide). The ADuM221x models operate with
the supply voltage of either side ranging from 3.0 V to 5.5 V,
providing compatibility with lower voltage systems as well as
enabling voltage translation functionality across the isolation
barrier. The ADuM221x isolators have a patented refresh feature
that ensures dc correctness in the absence of input logic transitions and during power-up/power-down conditions.
Similar to the ADuM320x isolators, the ADuM221x isolators
contain various circuit and layout enhancements to provide
increased capability relative to system-level IEC 61000-4-x
testing (ESD, burst, and surge). The precise capability in these
tests for either the ADuM320x or ADuM221x products is strongly
determined by the design and layout of the user’s board or module.
For more information, see the AN-793 Application Note,
ESD/Latch-Up Considerations with iCoupler Isolation Products.
16
GND
2
15
NC
14
V
DD2
13
V
OA
12
V
OB
11
NC
10
NC
9
GND
2
09233-001
16
GND
2
15
NC
14
V
DD2
13
V
IA
12
V
OB
11
NC
10
NC
9
GND
2
09233-002
1
Protected by U.S. Patents 5,952,849; 6,873,065; 6,903,578; and 7,075,329. Other patents pending.
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2010–2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADuM2210/ADuM2211 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagrams............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Electrical Characteristics—5 V Operation................................ 3
Electrical Characteristics—3 V Operation................................ 5
Electrical Characteristics—Mixed 5 V/3 V or 3 V/5 V
Operation....................................................................................... 7
Package Characteristics .............................................................10
Regulatory Information............................................................. 10
Insulation and Safety-Related Specifications.......................... 10
DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10) Insulation
Characteristics ............................................................................ 11
Recommended Operating Conditions ....................................11
Absolute Maximum Ratings ......................................................... 12
ESD Caution................................................................................ 12
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions......................... 13
Typical Performance Characteristics........................................... 15
Applications Information.............................................................. 16
PCB Layout ................................................................................. 16
Propagation Delay-Related Parameters................................... 16
DC Correctness and Magnetic Field Immunity..................... 16
Power Consumption .................................................................. 17
Insulation Lifetime..................................................................... 18
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 19
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 20
REVISION HISTORY
2/12—Rev. A to Rev. B
Created Hyperlink for Safety and Regulatory Approvals
Entry in Features Section................................................................. 1
Change to PCB Layout Section..................................................... 16
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 19
8/11—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Added 16-Lead SOIC_IC Package ................................... Universal
Changes to Features Section............................................................ 1
Changes to Table 5 and Table 6..................................................... 10
Changes to Endnote 1, Table 8...................................................... 11
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 19
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 20
9/10—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 2 of 20
Data Sheet ADuM2210/ADuM2211
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—5 V OPERATION
All voltages are relative to their respective ground. 4.5 V ≤ V
apply over the entire recommended operation range, unless otherwise noted. All typical specifications are at T
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
DC SPECIFICATIONS
Input Supply Current, per Channel, Quiescent I
Output Supply Current, per Channel, Quiescent I
0.4 0.8 mA
DDI (Q)
DDO (Q)
ADuM2210, Total Supply Current, Two Channels1
DC to 2 Mbps
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (Q)
DD2 (Q)
10 Mbps (TR Grade Only)
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (10)
DD2 (10)
ADuM2211, Total Supply Current, Two Channels1
DC to 2 Mbps
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (Q)
DD2 (Q)
10 Mbps (TR Grade Only)
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (10)
DD2 (10)
For All Models
Input Currents IIA, IIB −10 +0.01 +10 μA 0 V ≤ VIA, VIB ≤ V
Logic High Input Threshold VIH
Logic Low Input Threshold VIL
Logic High Output Voltages V
V
Logic Low Output Voltages V
V
OAH
OBH
0.0 0.1 V IOx = 20 μA, VIx = V
OAL
0.04 0.1 V IOx = 400 μA, VIx = V
OBL
0.2 0.4 V IOx = 4 mA, VIx = V
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
ADuM221xSR
Minimum Pulse Width2 PW 1000 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Maximum Data Rate3 1 Mbps CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay4 t
Pulse Width Distortion, |t
PLH
− t
|4 PWD 40 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PHL
Propagation Delay Skew5 t
Channel-to-Channel Matching6 t
, t
PHL
PLH
100 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSK
PSKCD/tPSKOD
Output Rise/Fall Time (10% to 90%) tR/tF 10 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
≤ 5.5 V, 4.5 V ≤ V
DD1
≤ 5.5 V. All minimum/maximum specifications
DD2
= 25°C, V
A
DD1
= V
DD2
= 5 V.
0.5 0.6 mA
1.3 1.7 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
1.0 1.6 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
3.5 4.6 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
1.7 2.8 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
1.1 1.5 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
1.3 1.8 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
2.6 3.4 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
3.1 4.0 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
or V
DD2
IxH
0.7 (V
or V
(V
DD1
V
DD2
DD2
or
) −
V
DD1
)
V
0.3 (V
DD1
)
or V
DD2
5.0 V I
= −20 μA, VIx = V
Ox
DD1
0.1
(V
V
DD2
DD1
or
) −
4.8 V I
= −4 mA, VIx = V
Ox
IxH
0.5
IxL
IxL
IxL
20 150 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
50 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Rev. B | Page 3 of 20
ADuM2210/ADuM2211 Data Sheet
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
ADuM221xTR
Minimum Pulse Width2 PW 100 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Maximum Data Rate3 10 Mbps CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay4 t
Pulse Width Distortion, |t
PLH
− t
|4 PWD 3 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PHL
Change vs. Temperature 5 ps/°C CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay Skew5 t
Channel-to-Channel Matching,
Codirectional Channels
Channel-to-Channel Matching,
Opposing Directional Channels
6
6
Output Rise/Fall Time (10% to 90%) tR/tF 2.5 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
For All Models
Common-Mode Transient Immunity
at Logic High Output
Common-Mode Transient Immunity
at Logic Low Output
7
7
Refresh Rate fr 1.2 Mbps
Input Dynamic Supply Current, per Channel8 I
Output Dynamic Supply Current, per Channel8 I
1
The supply current values for both channels are combined when running at identical data rates. Output supply current values are specified with no output load
present. The supply current associated with an individual channel operating at a given data rate can be calculated as described in the Power Consumption section. See
Figure 6 through Figure 8 for information on per-channel supply current as a function of data rate for unloaded and loaded conditions. See Figure 9 through Figure 11
for total I
2
The minimum pulse width is the shortest pulse width at which the specified pulse width distortion is guaranteed.
3
The maximum data rate is the fastest data rate at which the specified pulse width distortion is guaranteed.
4
t
PHL
measured from the 50% level of the rising edge of the VIx signal to the 50% level of the rising edge of the VOx signal.
5
t
PSK
load within the recommended operating conditions.
6
Codirectional channel-to-channel matching is the absolute value of the difference in propagation delays between any two channels with inputs on the same side of
and I
DD1
supply currents as a function of data rate for ADuM2210 and ADuM2211 channel configurations.
DD2
propagation delay is measured from the 50% level of the falling edge of the VIx signal to the 50% level of the falling edge of the VOx signal. t
is the magnitude of the worst-case difference in t
PHL
the isolation barrier. Opposing directional channel-to-channel matching is the absolute value of the difference in propagation delays between any two channels with
inputs on opposing sides of the isolation barrier.
7
CMH is the maximum common-mode voltage slew rate that can be sustained while maintaining VO > 0.8 V
that can be sustained while maintaining VO < 0.8 V. The common-mode voltage slew rates apply to both rising and falling common-mode voltage edges. The transient
magnitude is the range over which the common mode is slewed.
8
Dynamic supply current is the incremental amount of supply current required for a 1 Mbps increase in the signal data rate. See Figure 6 through Figure 8 for
information on per-channel supply current for unloaded and loaded conditions. See the Power Consumption section for guidance on calculating per-channel supply
current for a given data rate.
, t
20 50 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PHL
PLH
15 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSK
3 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
t
PSKCD
t
17 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSKOD
| 25 35 kV/μs
|CM
H
= V
V
or V
Ix
DD1
transient magnitude = 800 V
| 25 35 kV/μs
|CM
L
= 0 V, VCM = 1000 V,
V
Ix
transient magnitude = 800 V
0.19 mA/Mbps
DDI (D)
0.05 mA/Mbps
DDO (D)
propagation delay is
PLH
and/or t
that is measured between units at the same operating temperature, supply voltages, and output
PLH
. CML is the maximum common-mode voltage slew rate
DD2
, VCM = 1000 V,
DD2
Rev. B | Page 4 of 20
Data Sheet ADuM2210/ADuM2211
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—3 V OPERATION
All voltages are relative to their respective ground. 3.0 V ≤ V
over the entire recommended operation range, unless otherwise noted. All typical specifications are at T
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
DC SPECIFICATIONS
Input Supply Current, per Channel, Quiescent I
Output Supply Current, per Channel, Quiescent I
DDI (Q)
DDO (Q)
ADuM2210, Total Supply Current, Two Channels1
DC to 2 Mbps
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (Q)
DD2 (Q)
10 Mbps (TR Grade Only)
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (10)
DD2 (10)
ADuM2211, Total Supply Current, Two Channels1
DC to 2 Mbps
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (Q)
DD2 (Q)
10 Mbps (TR Grade Only)
V
Supply Current I
DD1
V
Supply Current I
DD2
DD1 (10)
DD2 (10)
For All Models
Input Currents IIA, IIB −10 +0.01 +10 μA 0 V ≤ VIA, VIB ≤ V
Logic High Input Threshold VIH
Logic Low Input Threshold VIL
Logic High Output Voltages V
V
Logic Low Output Voltages V
V
OAH
OBH
OAL
OBL
0.2 0.42 V IOx = 4 mA, VIx = V
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
ADuM221xSR
Minimum Pulse Width2 PW 1000 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Maximum Data Rate3 1 Mbps CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay4 t
Pulse Width Distortion, |t
PLH
− t
|4 PWD 40 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PHL
Propagation Delay Skew5 t
Channel-to-Channel Matching6 t
, t
PHL
100 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSK
PSKCD/tPSKOD
Output Rise/Fall Time (10% to 90%) tR/tF 10 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
≤ 3.6 V, 3.0 V ≤ V
DD1
≤ 3.6 V. All minimum/maximum specifications apply
DD2
= 25°C, V
A
DD1
= V
= 3.0 V.
DD2
0.3 0.5 mA
0.3 0.5 mA
0.8 1.3 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
0.7 1.0 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
2.0 3.2 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
1.1 1.7 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
0.7 1.3 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
0.8 1.6 mA
DC to 1 MHz logic signal
frequency
1.5 2.1 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
1.9 2.4 mA 5 MHz logic signal frequency
or V
DD1
V
0.7 (V
DD1
)
or V
DD2
V
0.3 (V
DD1
)
or V
DD2
(V
V
DD2
DD1
) −
3.0 V IOx = −20 μA, VIx = V
or
IxH
0.1
(V
V
DD2
DD1
) −
2.8 V I
or
= −4 mA, VIx = V
Ox
IxH
0.5
0.0 0.1 V IOx = 20 μA, VIx = V
0.04 0.1 V IOx = 400 μA, VIx = V
20 150 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PLH
IxL
IxL
IxL
50 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
DD2
Rev. B | Page 5 of 20
ADuM2210/ADuM2211 Data Sheet
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
ADuM221xTR
Minimum Pulse Width2 PW 100 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Maximum Data Rate3 10 Mbps CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay4 t
Pulse Width Distortion, |t
−t
|4 PWD 3 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PLH
PHL
Change vs. Temperature 5 ps/°C CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
Propagation Delay Skew5 t
Channel-to-Channel Matching,
Codirectional Channels
Channel-to-Channel Matching,
Opposing Directional Channels
6
6
Output Rise/Fall Time (10% to 90%) tR/tF 3.0 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
For All Models
Common-Mode Transient Immunity
at Logic High Output
Common-Mode Transient Immunity
at Logic Low Output
7
7
Refresh Rate fr 1.1 Mbps
Input Dynamic Supply Current, per Channel8 I
Output Dynamic Supply Current, per
1
The supply current values for both channels are combined when running at identical data rates. Output supply current values are specified with no output load
present. The supply current associated with an individual channel operating at a given data rate can be calculated as described in the section. See
Figure 6
for total I
2
The minimum pulse width is the shortest pulse width at which the specified pulse width distortion is guaranteed.
3
The maximum data rate is the fastest data rate at which the specified pulse width distortion is guaranteed.
4
t
propagation delay is measured from the 50% level of the falling edge of the VIx signal to the 50% level of the falling edge of the VOx signal. t
PHL
measured from the 50% level of the rising edge of the VIx signal to the 50% level of the rising edge of the VOx signal.
5
t
is the magnitude of the worst-case difference in t
PSK
load within the recommended operating conditions.
6
Codirectional channel-to-channel matching is the absolute value of the difference in propagation delays between any two channels with inputs on the same side of
the isolation barrier. Opposing directional channel-to-channel matching is the absolute value of the difference in propagation delays between any two channels with
inputs on opposing sides of the isolation barrier.
7
CMH is the maximum common-mode voltage slew rate that can be sustained while maintaining VO > 0.8 V
that can be sustained while maintaining VO < 0.8 V. The common-mode voltage slew rates apply to both rising and falling common-mode voltage edges. The transient
magnitude is the range over which the common mode is slewed.
8
Dynamic supply current is the incremental amount of supply current required for a 1 Mbps increase in the signal data rate. See through for
information on per-channel supply current for unloaded and loaded conditions. See the section for guidance on calculating per-channel supply
current for a given data rate.
8
Channel
through for information on per-channel supply current as a function of data rate for unloaded and loaded conditions. See through
DD1
Figure 8
and I
supply currents as a function of data rate for ADuM2210 and ADuM2211 channel configurations.
DD2
PHL
, t
20 60 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PHL
PLH
22 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSK
3 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
t
PSKCD
t
22 ns CL = 15 pF, CMOS signal levels
PSKOD
| 25 35 kV/μs
|CM
H
= V
V
or V
Ix
DD1
DD2
transient magnitude = 800 V
| 25 35 kV/μs
|CM
L
= 0 V, VCM = 1000 V,
V
Ix
transient magnitude = 800 V
0.10 mA/Mbps
DDI (D)
I
0.03 mA/Mbps
DDO (D)
Power Consumption
Figure 9 Figure 11
propagation delay is
PLH
and/or t
that is measured between units at the same operating temperature, supply voltages, and output
PLH
. CML is the maximum common-mode voltage slew rate
DD2
Figure 6
Figure 8
Power Consumption
, VCM = 1000 V,
Rev. B | Page 6 of 20
 Loading...
Loading...