MicroConverter, 12-Bit ADCs and DACs
FEATURES
ANALOG I/O
8-channel, 247 kSPS, 12-Bit ADC
DC performance: ±1 LSB INL
AC performance: 71 dB SNR
DMA controller for high speed ADC-to-RAM capture
2 12-bit (monotonic) voltage output DACs
Dual output PWM/Σ-∆ DACs
On-chip temperature sensor function: ±3°C
On-chip voltage reference
Memory
62 kB on-chip Flash/EE program memory
4 kB on-chip Flash/EE data memory
Flash/EE, 100 Yr retention, 100,000 cycles of endurance
2304 bytes on-chip data RAM
8051-based core
8051-compatible instruction set (16 MHz maximum)
32 kHz external crystal, on-chip programmable PLL
12 interrupt sources, 2 priority levels
Dual data pointer
Extended 11-bit stack pointer
On-chip peripherals
Time interval counter (TIC)
2
UART, I
Watchdog timer (WDT), power supply monitor (PSM)
Power
Specified for 3 V and 5 V operation
Normal, idle, and power-down modes
Power-down: 25 µA @ 3 V with wake-up timer running
APPLICATIONS
Optical networking—laser power control
Base station systems
Precision instrumentation, smart sensors
Transient capture systems
DAS and communications systems
Upgrade to ADuC812 systems; runs from 32 kHz
External crystal with on-chip PLL.
Also available: ADuC831 pin-compatible upgrade to
existing ADuC812 systems that require additional
code or data memory; runs from 1 MHz to 16 MHz
External crystal
C, and SPI Serial I/O
with Embedded 62 kB Flash MCU
ADuC832
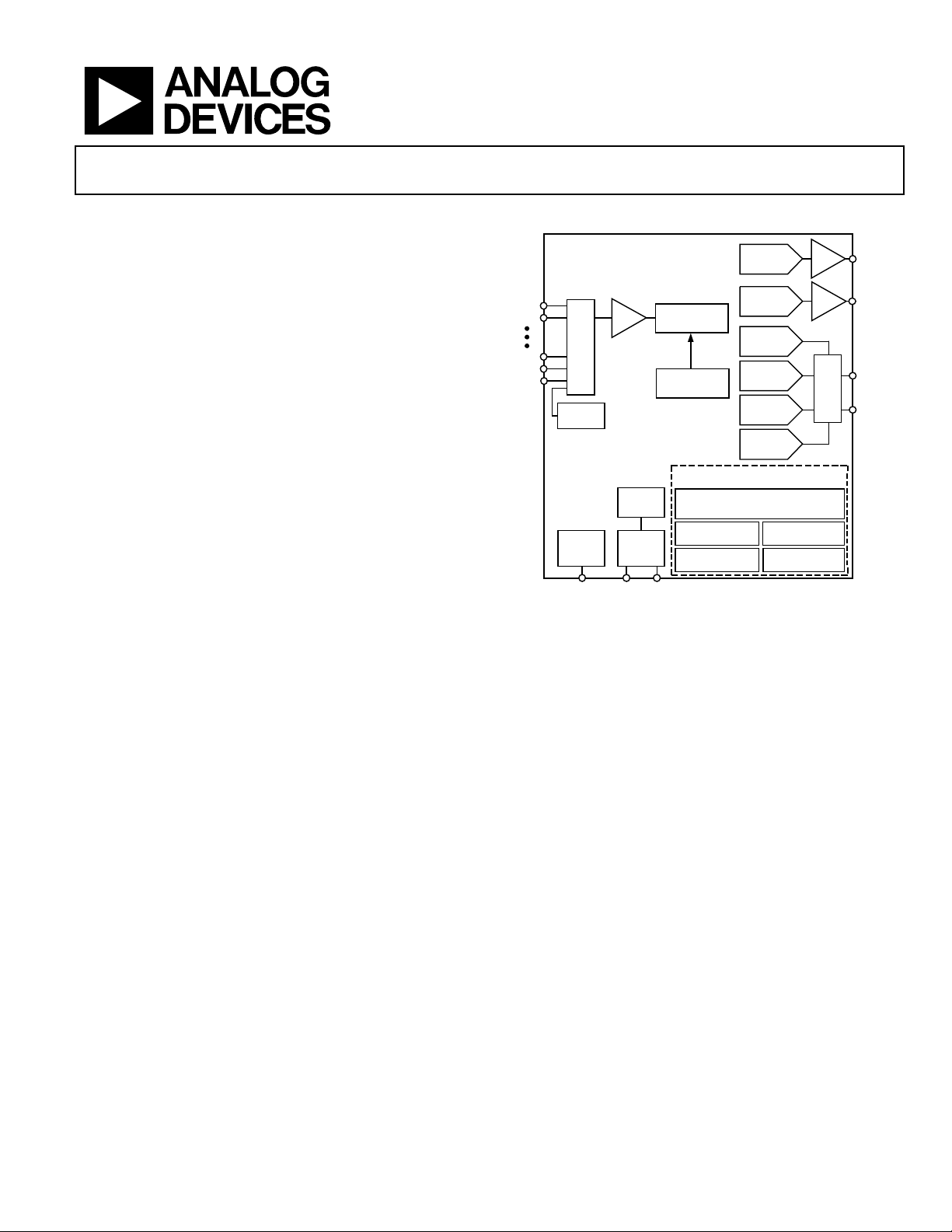
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADuC832
ADC0
ADC1
ADC5
ADC6
ADC7
TEMP
SENSOR
INTERNAL
BAND GAP
VREF
MUX
V
T/H
REF
PLL
OSC
XTAL2XTAL1
12-BIT ADC
HARDWARE
CALIBRATON
8051-BASED MCU WITH ADDITIONAL
62 kB FLASH/EE PROGRAM MEMORY
4 kB FLASH/EE DATA ME M O RY
3 × 16-BIT TIM ERS
1 × REAL-TI M E CL O CK
4 ×PARALLEL
PORTS
Figure 1.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADuC832 is a complete, smart transducer front end,
integrating a high performance self-calibrating multichannel
12-bit ADC, dual 12-bit DACs, and programmable 8-bit MCU
on a single chip.
The device operates from a 32 kHz crystal with an on-chip PLL,
generating a high frequency clock of 16.78 MHz. This clock is,
in turn, routed through a programmable clock divider from
which the MCU core clock operating frequency is generated.
The microcontroller core is an 8052 and is therefore 8051
instruction set compatible with 12 core clock periods per
machine cycle. 62 kB of nonvolatile Flash/EE program memory are
provided on chip. There are also 4 kB of nonvolatile Flash/EE data
memory, 256 bytes of RAM, and 2 kB of extended RAM integrated
on chip.
The ADuC832 also incorporates additional analog functionality
with two 12-bit DACs, a power supply monitor, and a band gap
reference. On-chip digital peripherals include two 16-bit Σ-
DACs, a dual-output 16-bit PWM, a watchdog timer, time
interval counter, three timers/counters, Timer 3 for baud rate
generation, and serial I/O ports (SPI, I
12-BIT
DAC
12-BIT
DAC
16-BIT
Σ-Δ DAC
16-BIT
Σ-Δ DAC
16-BIT
PWM
16-BIT
PWM
PERIPHERALS
2304 BYTES USER RAM
POWER SUPPLY MO N
WATCHDOG TIMER
UART, I
SERIAL I/ O
2
C®, and UART).
BUF
BUF
2
C, AND SPI
MUX
DAC0
DAC1
PWM0
PWM1
2987-001
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2002–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADuC832
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 4
Specifications ..................................................................................... 6
Timing Specifications ................................................................ 10
Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................... 20
ESD Caution ................................................................................ 20
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ........................... 21
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 26
Terminology .................................................................................... 29
ADC Specifications .................................................................... 29
DAC Specifications..................................................................... 29
Explanation of Typical Performance Plots .................................. 30
Memory Organization ................................................................... 31
Flash/EE Program Memory ...................................................... 31
Flash/EE Data Memory ............................................................. 31
General-Purpose RAM .............................................................. 31
External Data Memory (External XRAM) .............................. 32
Internal XRAM ........................................................................... 32
Special Function Registers (SFRs) ................................................ 33
Accumulator SFR (ACC) ........................................................... 33
B SFR (B) ..................................................................................... 33
Stack Pointer (SP and SPH)....................................................... 33
Data Pointer (DPTR) ................................................................. 33
Program Status Word (PSW) .................................................... 33
Power Control SFR (PCON) ..................................................... 33
Special Function Registers ............................................................. 34
ADC Circuit Information .............................................................. 35
General Overview ....................................................................... 35
ADC Transfer Function ............................................................. 35
Typical Operation ....................................................................... 35
Driving the Analog-to-Digital Converter ............................... 39
Voltage Reference Connections ................................................ 40
Configuring the ADC ................................................................ 41
ADC DMA Mode ....................................................................... 41
Micro-Operation During ADC DMA Mode .......................... 42
ADC Offset and Gain Calibration Coefficients ..................... 42
Calibrating the ADC ...................................................................... 43
Rev. A | Page 2 of 92
Initiating Calibration in Code ...................................................... 44
Nonvolatile Flash/EE Memory ..................................................... 45
Flash/EE Memory Overview .................................................... 45
Flash/EE Memory and the ADuC832 ..................................... 45
ADuC832 Flash/EE Memory Reliability ................................. 45
Using the Flash/EE Program Memory .................................... 46
Flash/EE Program Memory Security ....................................... 47
Using The Flash/EE Data Memory .............................................. 48
ECON—Flash/EE Memory Control SFR ................................ 48
Example: Programming the Flash/EE Data Memory ............ 49
Flash/EE Memory Timing ........................................................ 49
ADuC832 Configuration SFR (CFG832) ................................ 50
User Interface to Other On-Chip ADuC832 Peripherals ......... 51
DAC .............................................................................................. 51
Using the DAC ............................................................................ 52
On-Chip PLL................................................................................... 54
PLLCON (PLL Control Register) ............................................. 54
Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM) .................................................. 55
PWMCON (PWM Control SFR) ............................................. 55
PWM Modes of Operation............................................................ 56
Mode 0: PWM Disabled ............................................................ 56
Mode 1: Single Variable Resolution PWM ............................. 56
Mode 2: Twin 8-Bit PWM ......................................................... 56
Mode 3: Twin 16-Bit PWM ....................................................... 56
Mode 4: Dual NRZ 16-Bit Σ- DAC ....................................... 57
Mode 5: Dual 8-Bit PWM ......................................................... 57
Mode 6: Dual RZ 16-Bit Σ- DAC .......................................... 57
Serial Peripheral Interface ............................................................. 58
MISO (Master Input, Slave Output Data Pin) ............................ 58
MOSI (Master Output, Slave Input Pin) ................................. 58
SCLOCK (Serial Clock I/O Pin) .............................................. 58
SS
(Slave Select Input Pin)......................................................... 58
Using the SPI Interface .............................................................. 59
SPI Interface—Master Mode .................................................... 59
SPI Interface—Slave Mode ........................................................ 59
I2C-Compatible Interface .............................................................. 60
I2C Interface SFRs ....................................................................... 60
Overview ..................................................................................... 61
Software Master Mode ............................................................... 61
Hardware Slave Mode ................................................................ 61

ADuC832
Dual Data Pointers .......................................................................... 62
DPCON (Data Pointer Control SFR) ....................................... 62
Power Supply Monitor .................................................................... 63
PSMCON (Power Supply Monitor Control Register ) ........... 63
Watchdog Timer .............................................................................. 64
Time Interval Counter (TIC) ......................................................... 65
TIMECON (TIC Control Register) .......................................... 65
INTVAL (User Time Interval Select Register) ........................ 66
HTHSEC (Hundredths Seconds Time Register) .................... 66
SEC (Seconds Time Register) .................................................... 66
MIN (Minutes Time Register) ................................................... 66
HOUR (Hours Time Register) .................................................. 66
8052-Compatible On-Chip Peripherals ....................................... 67
Parallel I/O ................................................................................... 67
Port 0 ............................................................................................. 67
Port 1 ............................................................................................. 67
Port 2 ............................................................................................. 67
Port 3 ............................................................................................. 68
Additional Digital I/O ................................................................ 68
Read-Modify-Write Instructions .............................................. 69
Timers/Counters ......................................................................... 70
Timer/Counter 0 and Timer/Counter 1 Data Registers ........ 71
Timer/Counter 0 And Timer/Counter 1 Operating Modes ...... 72
Mode 0 (13-Bit Timer/Counter) ............................................... 72
Mode 1 (16-Bit Timer/Counter) ............................................... 72
Mode 2 (8-Bit Timer/Counter with Autoreload) .................... 72
Mode 3 (Two 8-Bit Timer/Counters) ....................................... 72
Timer/Counter 2 ............................................................................. 73
T2CON (Timer/Counter 2 Control Register) ......................... 73
Timer/Counter 2 Data Registers ............................................... 73
Timer/Counter Operation Modes ............................................ 74
UART Serial Interface ..................................................................... 75
SBUF ............................................................................................. 75
SCON (UART Serial Port Control Register) ........................... 75
Mode 0: 8-Bit Shift Register Mode ........................................... 76
Mode 1: 8-Bit UART, Variable Baud Rate ................................ 76
Mode 2: 9-Bit UART with Fixed Baud Rate ............................ 76
Mode 3: 9-Bit UART with Variable Baud Rate ........................ 76
UART Serial Port Baud Rate Generation ................................. 77
Timer 1 Generated Baud Rates ................................................. 77
Timer 2 Generated Baud Rates ................................................. 77
Timer 3 Generated Baud Rates ................................................. 78
Interrupt System .............................................................................. 80
IE (Interrupt Enable Register) ................................................... 80
IP (Interrupt Priority Register ) ................................................ 80
IEIP2 (Secondary Interrupt Enable Register) ......................... 80
Interrupt Priority ........................................................................ 81
Interrupt Vectors ......................................................................... 81
ADuC832 Hardware Design Considerations .............................. 82
Clock Oscillator ........................................................................... 82
External Memory Interface........................................................ 82
Power Supplies ............................................................................. 83
Power Consumption ................................................................... 84
Power Saving Modes ................................................................... 84
Power-On Reset ........................................................................... 84
Grounding and Board Layout Recommendations ................. 85
Other Hardware Considerations ................................................... 87
In-Circuit Serial Download Access .......................................... 87
Embedded Serial Port Debugger .............................................. 87
Single-Pin Emulation Mode ...................................................... 87
Typical System Configuration ................................................... 87
Development Tools ......................................................................... 88
QuickStart Development System .............................................. 88
QuickStart Plus Development System...................................... 88
Outline Dimensions ........................................................................ 89
Ordering Guide ........................................................................... 89
Rev. A | Page 3 of 92

ADuC832
REVISION HISTORY
9/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Figure 1 .......................................................................... 1
Changed 16.77 MHz to 16.78 MHz Throughout ......................... 1
Changes to Reference Input/Output, Output Voltage Parameter,
Endnote 19, and Endnote 20, Table 1 ............................................ 9
Moved Timing Specifications Section ......................................... 10
Changes to Figure 3 ........................................................................ 10
Changes to Table 3 .......................................................................... 11
Changes to Table 4 .......................................................................... 12
Changes to Table 5 .......................................................................... 13
Changes to Table 11 ........................................................................ 19
Changes to Figure 15 and Table 13 ............................................... 21
Changes to Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 20, and Figure 21 ....... 26
Added Explanation of Typical Performance Plots Section ....... 30
Changes to Flash/EE Program Memory, Flash/EE Data
Memory, and General-Purpose RAM Sections .......................... 31
Changes to Figure 36 ...................................................................... 34
Changes to Figure 39 and Figure 40 ............................................. 39
Changes to Table 20 ........................................................................ 40
Changes to A Typical DMA Mode Configuration Example
Section .............................................................................................. 41
Changed 16.777216 MHz to 16.78 MHz Throughout ............... 41
Changes to Table 21 ........................................................................ 48
Changes to Using the DAC Section and Figure 52 .................... 52
Changes to Figure 54 Caption ...................................................... 53
Changes to Figure 56 ...................................................................... 55
Changed 16.77 MHz to 16.78 MHz ............................................. 56
Changes to Figure 60 ...................................................................... 57
Changes to Table 31 ....................................................................... 63
Deleted Figure 65 and Figure 66; Renumbered Sequentially ... 66
Deleted ASPIRE—IDE Section..................................................... 66
Deleted Figure 67 ............................................................................ 67
Changes to Table 34 ....................................................................... 67
Changes to Figure 68, Figure 69, Figure 70, and Table 35 ........ 68
Changes to Figure 84 ...................................................................... 78
Changes to External Memory Interface Section ........................ 82
Changes to Power Supplies Section ............................................. 83
Changes to Table 50 ....................................................................... 84
Changes to Figure 94 ...................................................................... 86
Changes to Single-Pin Emulation Mode Section ....................... 87
Changes to QuickStart Development System Section and
QuickStart Plus Development System Section ........................... 88
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 89
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 89
11/02—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 4 of 92
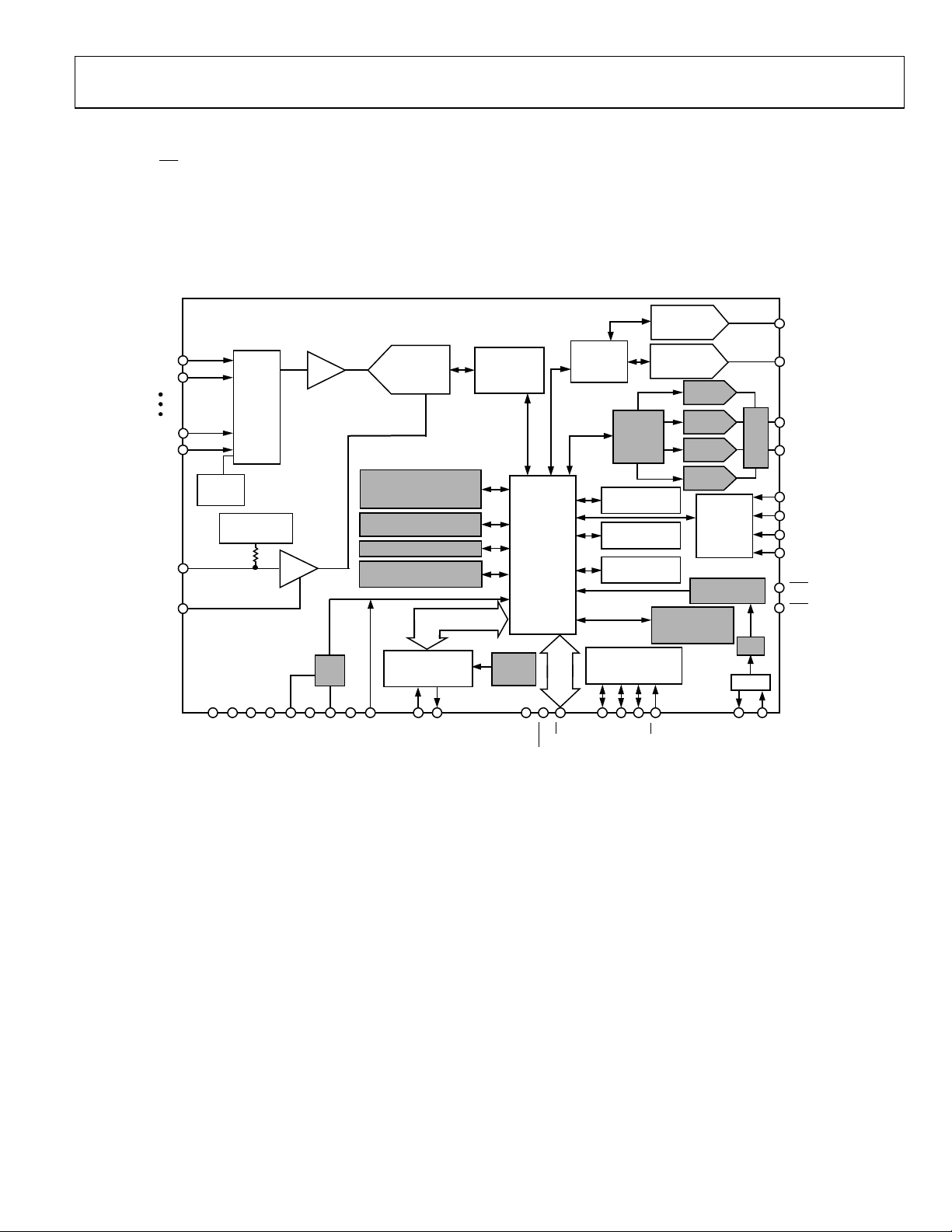
ADuC832
On-chip factory firmware supports in-circuit serial download
and debug modes (via UART) as well as single-pin emulation
mode via the
EA
pin. The ADuC832 is supported by QuickStart™
and QuickStart Plus development systems featuring low cost
software and hardware development tools. A functional block
diagram of the ADuC832 is shown in with a more
detailed block diagram shown in .
The part is specified for 3 V and 5 V operation over the extended
industrial temperature range and is available in a 52-lead metric
quad flat package (MQFP) and a 56-lead lead frame chip scale
package (LFCSP).
Figure 1
Figure 2
PWM
TIMER
DATA/MOSI
2
C )
MISO
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
16-BIT
Σ-Δ DAC
16-BIT
Σ-Δ DAC
16-BIT
PWM
16-BIT
PWM
16-BIT
COUNTER
TIMERS
PROG. CLOCK
DIVIDER
TIME INTERVAL
COUNTER
(WAKEUP C CT)
SS
MUX
PLL
OSC
XTAL1
DAC0
DAC1
PWM0
PWM1
T0
T1
T2
T2EX
INT0
INT1
XTAL2
2987-004
ADC0
ADC1
ADC6
ADC7
V
REF
C
REF
ADuC832
TEMP
SENSOR
BAND GAP
REFERENCE
DD
AV
AGND
MUX
DDDVDDDVDD
DV
BUF
T/H
DGND
FLASH/EE INCLUDING
USER DOWNLO AD M ODE
2 × DATA POINTERS
11-BIT STACK PO I N T ER
POR
DGND
DGND
RESET
12-BIT
ADC
62 kB PROGRAM
4 kB DATA
FLASH/EE
2 kB USER XRAM
DOWNLOADER
DEBUGGER
ASYNCHRONOUS
SERIAL PORT
(UART)
TxD
RxD
ADC
CONTROL
AND
CALIBRATION
CORE
UART
TIMER
ALE
8052
MCU
PSEN
SINGLE-PIN
EMULATOR
EA
CONTROL
DAC
CONTROL
256 BYTES
USER RAM
WATCHDOG
POWER SUPPLY
MONITOR
SYNCHRONOUS
SERIAL INT E RFACE
(SPI OR I
SCLOCK
Figure 2. ADuC832 Block Diagram (Shaded Areas are Features Not Present on the ADuC812)
Rev. A | Page 5 of 92
ADuC832
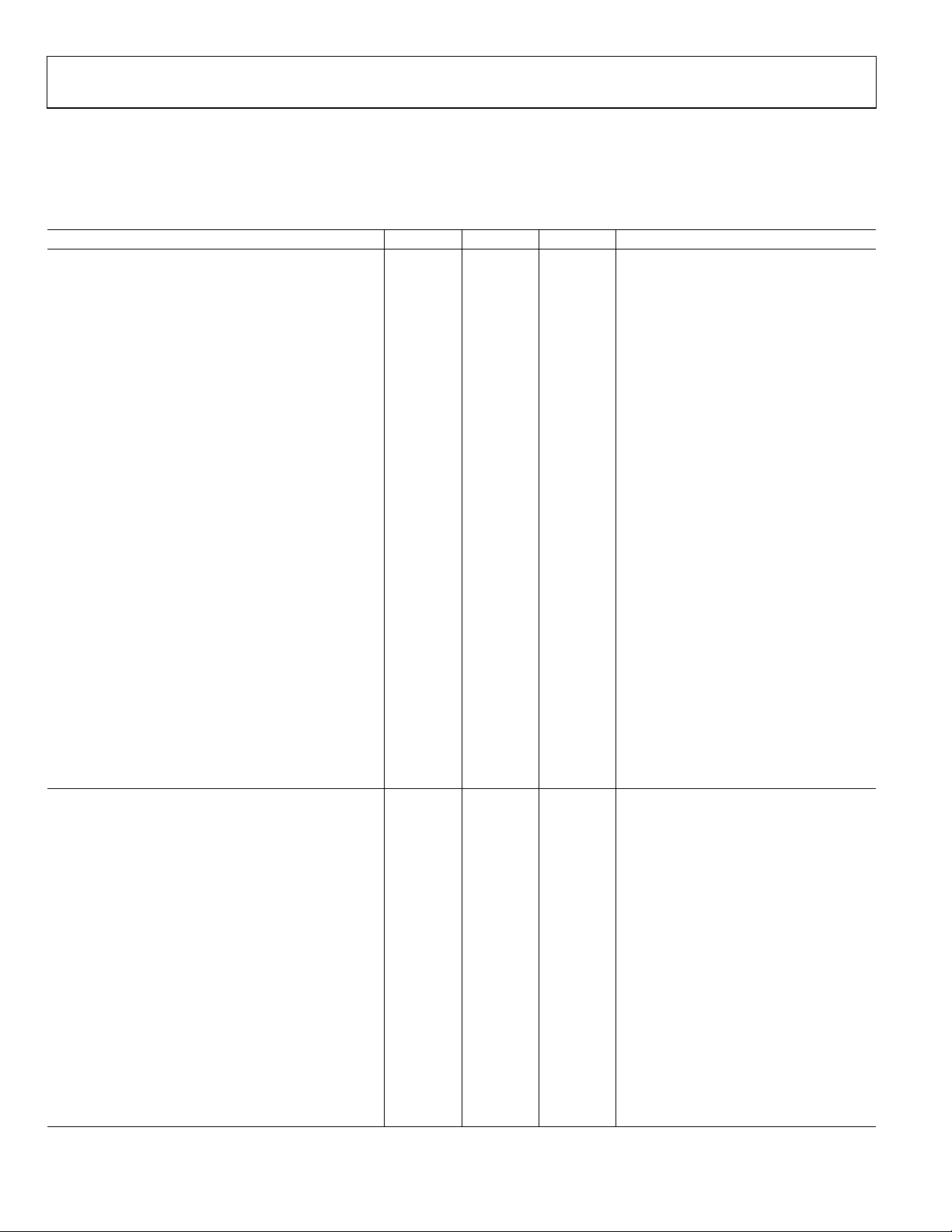
SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V or 4.5 V to 5.5 V; V
unless otherwise noted.
= 2.5 V internal reference, f
REF
= 16.78 MHz; all specifications TA = T
CORE
MIN
to T
MAX
,
Table 1.
Parameter
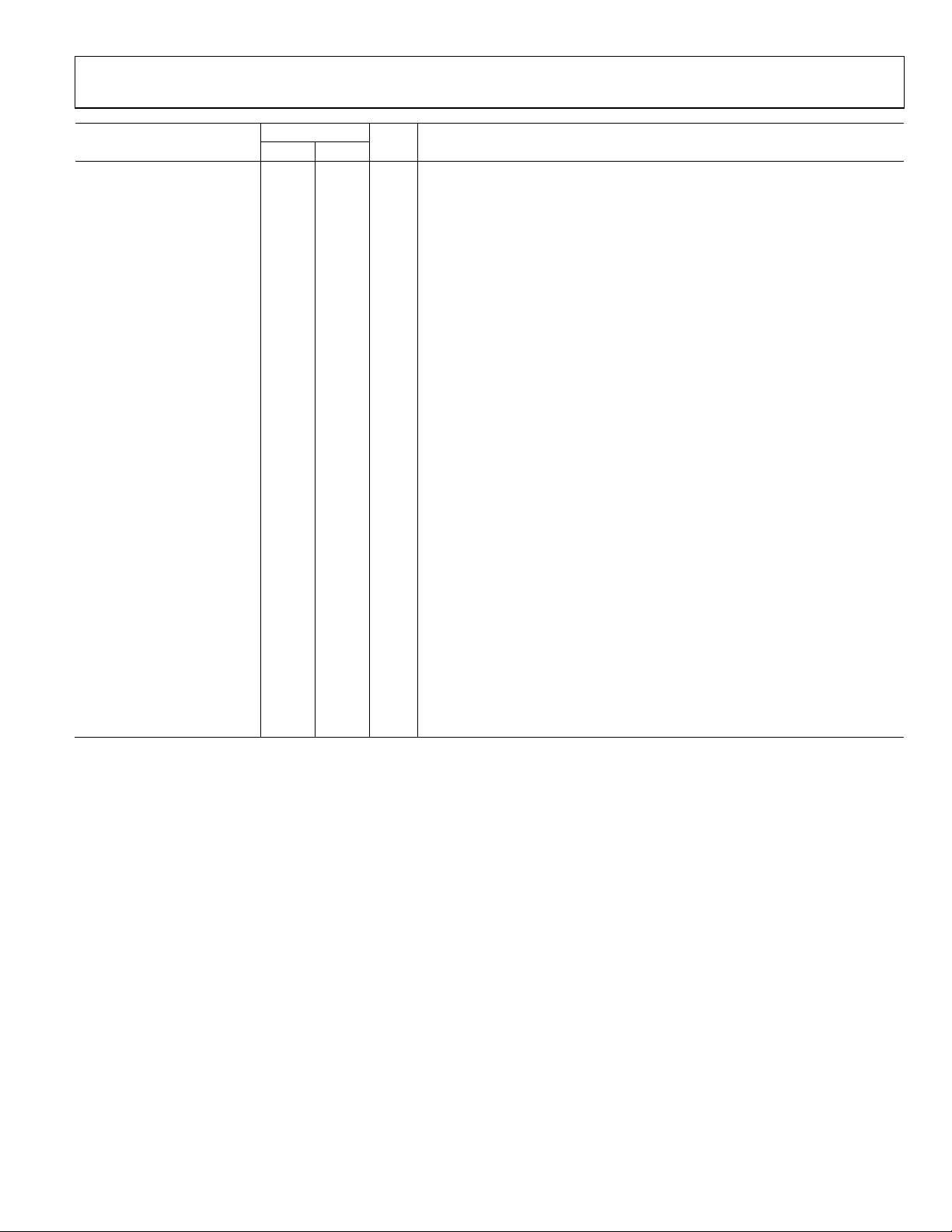
ADC CHANNEL SPECIFICATIONS
DC Accuracy
Calibrated Endpoint Errors
Dynamic Performance fIN = 10 kHz sine wave, fS = 147 kHz
Analog Input
Temperature Sensor
±1.5 ±1.5 °C typ External 2.5 V V
DAC CHANNEL SPECIFICATIONS, INTERNAL BUFFER
ENABLED
DC Accuracy10
Analog Outputs
DAC AC Characteristics
1
2, 3
VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V Unit Test Conditions/Comments
f
= 147 kHz, see Figure 16 to Figure 21 at
S
other f
S
Resolution 12 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 ±1 LSB max For 2.5 V internal reference
±0.3 ±0.3 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity ±0.9 ±0.9 LSB max 2.5 V internal reference
±0.25 ±0.25 LSB typ
Integral Nonlinearity
Differential Nonlinearity
4
4
+1.5/−0.9 +1.5/−0.9 LSB max 1 V external reference
±1.5 ±1.5 LSB max 1 V external reference
Code Distribution 1 1 LSB typ ADC input is a dc voltage
5, 6
Offset Error ±4 ±4 LSB max
Offset Error Match ±1 ±1 LSB typ
Gain Error ±2 ±3 LSB max
Gain Error Match −85 −85 dB typ
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
7
71 71 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) −85 −85 dB typ
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise −85 −85 dB typ
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
Input Voltage Ranges 0 to V
8
−80 −80 dB typ
0 to V
REF
V
REF
Leakage Current ±1 ±1 A max
Input Capacitance 32 32 pF typ
9
Voltage Output at 25°C 650 650 mV typ
Voltage TC −2.0 −2.0 mV/°C typ
Accuracy ±3 ±3 °C typ Internal 2.5 V V
DAC load to AGND, R
REF
REF
= 10 kΩ, CL = 100 pF
L
Resolution 12 12 Bits
Relative Accuracy ±3 ±3 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity11 −1 −1 LSB max Guaranteed 12-bit monotonic
±1/2 ±1/2 LSB typ
Offset Error ±50 ±50 mV max
V
REF
range
Gain Error ±1 ±1 % max AVDD range
±1 ±1 % typ V
range
REF
Gain Error Mismatch 0.5 0.5 % typ % of full scale on DAC1
Voltage Range 0 0 to V
Voltage Range 1 0 to VDD 0 to VDD V typ DAC V
0 to V
REF
V typ DAC V
REF
= 2.5 V
REF
= VDD
REF
Output Impedance 0.5 0.5 Ω typ
Voltage Output Settling Time 15 15 s typ Full-scale settling time to within ½ LSB of final
value
Digital-to-Analog Glitch Energy 10 10 nV sec typ 1 LSB change at major carry
Rev. A | Page 6 of 92
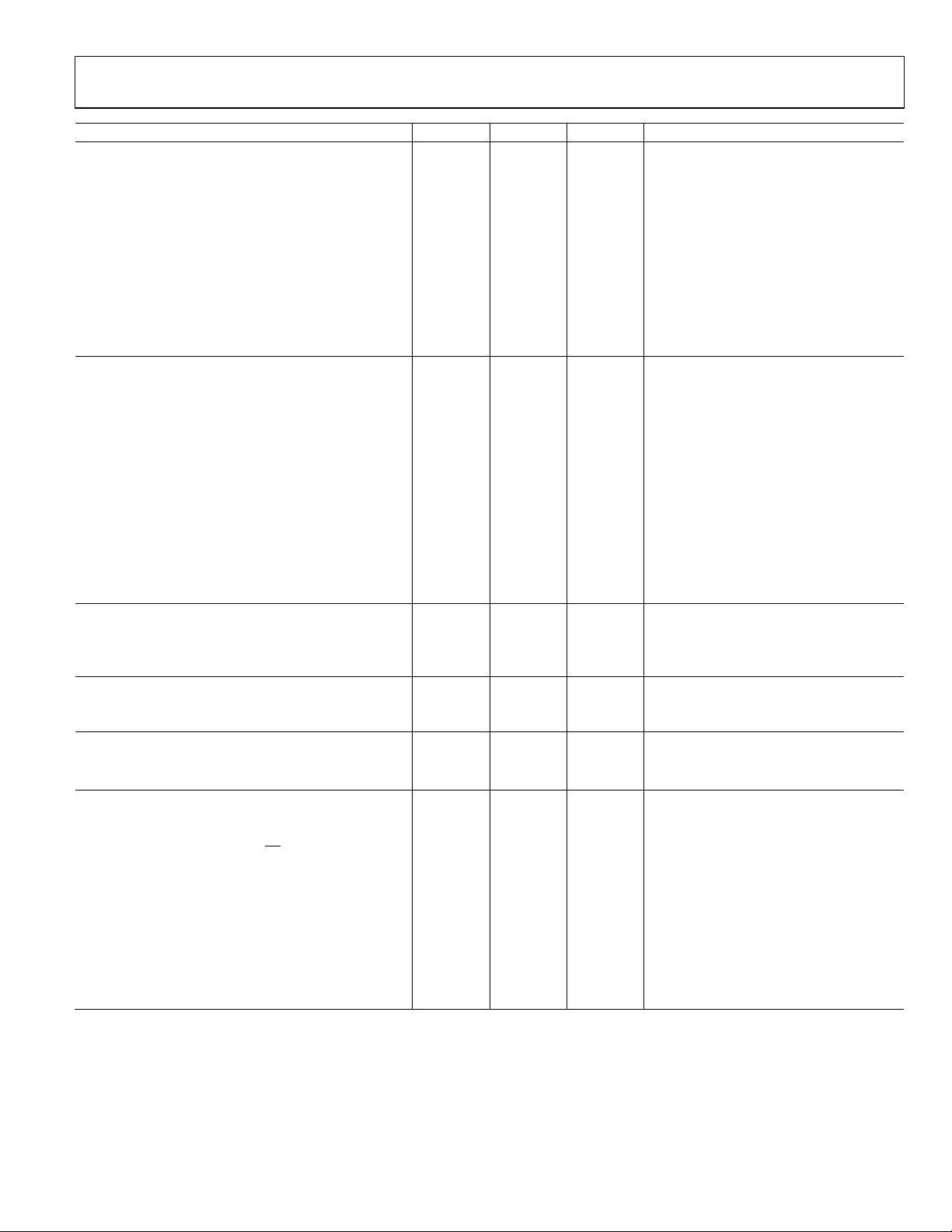
ADuC832
Parameter
DAC CHANNEL SPECIFICATIONS
DISABLED
DC Accuracy
1
12, 13
10
, INTERNAL BUFFER
VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Resolution 12 12 Bits
Relative Accuracy ±3 ±3 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity11 −1 −1 LSB max Guaranteed 12-bit monotonic
±1/2 ±1/2 LSB typ
Offset Error ±5 ±5 mV max V
Gain Error −0.3 −0.3 % typ V
range
REF
range
REF
Gain Error Mismatch4 0.5 0.5 % max % of full scale on DAC1
Analog outputs
Voltage Range 0 0 to V
0 to V
REF
V typ DAC V
REF
= 2.5 V
REF
REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT
Reference Output
Output Voltage (V
Accuracy ±2.5 ±2.5 % max Of V
14
) 2.5 2.5 V typ
REF
measured at the C
REF
REF
pin
Power Supply Rejection 47 47 dB typ
Reference Temperature Coefficient ±100 ±100 ppm/°C
typ
Internal V
External Reference Input
Voltage Range (V
V
Power-On Time 80 80 ms typ
REF
15
4
)
0.1 0.1 V min
REF
V
V
DD
V max
DD
and C
REF
pins shorted
REF
Input Impedance 20 20 kΩ typ
Input Leakage 1 1 A max Internal band gap deselected via
ADCCON1[6]
POWER SUPPLY MONITOR (PSM)
DVDD Trip Point Selection Range 2.63 V min Four trip points selectable in this range
4.37 V max programmed via TPD1 and TPD0 in PSMCON
DVDD Power Supply Trip Point Accuracy ±3.5 % max
WATCHDOG TIMER (WDT)4
Timeout Period 0 0 ms min Nine timeout periods
2000 2000 ms max Selectable in this range
FLASH/EE MEMORY RELIABILITY CHARACTERISTICS
Endurance
Data Retention
17
18
16
100,000 100,000 Cycles min
100 100 Years min
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input High Voltage (V
Input Low Voltage (V
Input Leakage Current (Port 0, EA)
)4 2.4 2 V min
INH
)4 0.8 0.4 V max
INL
±10 ±10 A max V
= 0 V or VDD
IN
±1 ±1 A typ VIN = 0 V or VDD
Logic 1 Input Current (All Digital Inputs)
±10 ±10 A max VIN = VDD
±1 ±1 A typ VIN = VDD
Logic 0 Input Current (Port 1, Port 2, and Port 3) −75 −25 A max
−40 −15 A typ VIL = 450 mV
Logic 1-to-Logic 0 Transition Current (Port 2, Port 3) −660 −250 A max VIL = 2 V
−400 −140 A typ VIL = 2 V
Rev. A | Page 7 of 92
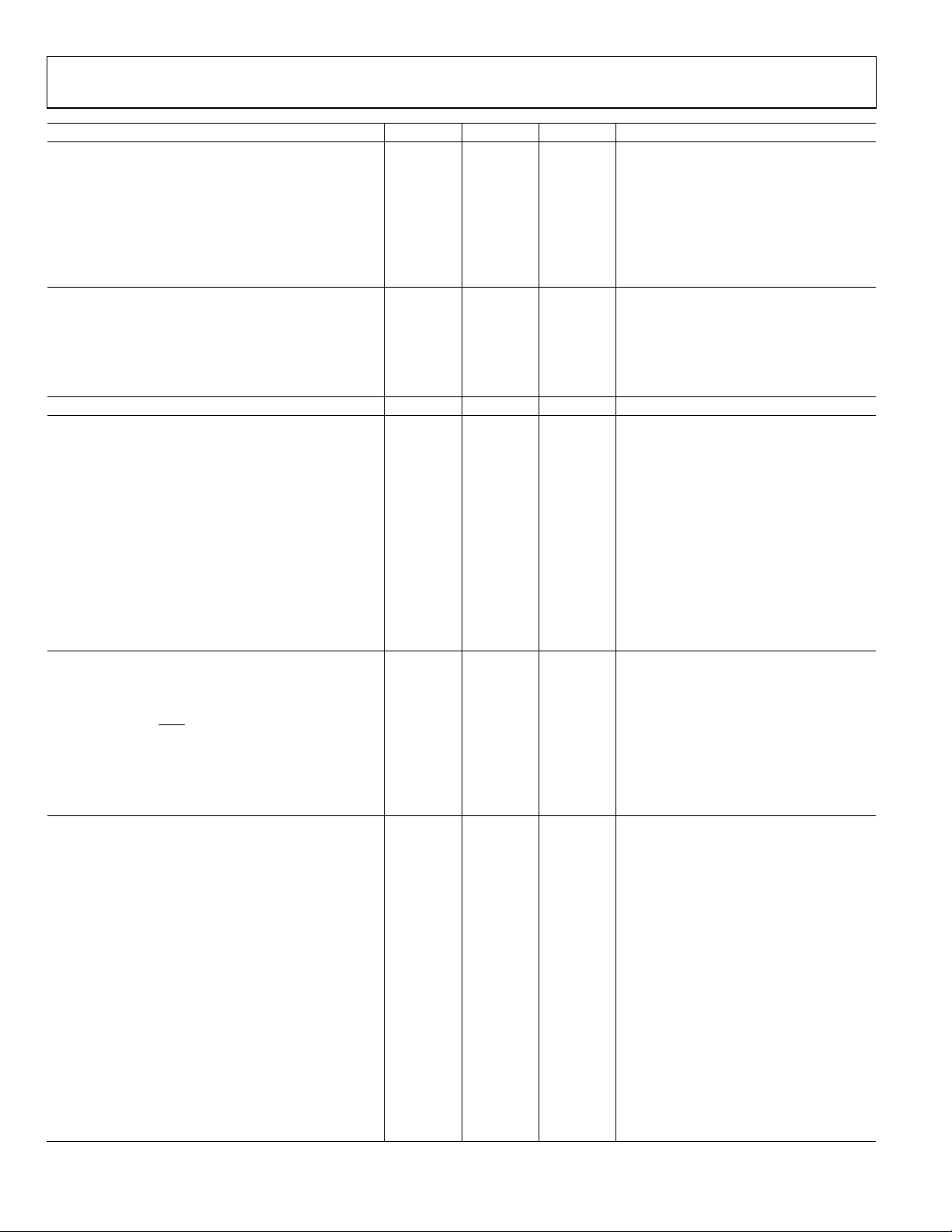
ADuC832
Parameter
1
VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SCLOCK and RESET ONLY4
(Schmitt-Triggered Inputs)
VT+ 1.3 0.95 V min
3.0 2.5 V max
VT− 0.8 0.4 V min
1.4 1.1 V max
VT+ − VT− 0.3 0.3 V min
0.85 0.85 V max
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
Logic Inputs, XTAL1 Only
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 0.4 V typ
INL
V
, Input High Voltage 3.5 2.5 V typ
INH
XTAL1 Input Capacitance 18 18 pF typ
XTAL2 Output Capacitance 18 18 pF typ
MCU CLOCK RATE 16.78 16.78 MHz max Programmable via PLLCON[2:0]
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage (VOH) 2.4 V min VDD = 4.5 V to 5.5 V
4.0 V typ I
SOURCE
= 80 A
2.4 V min VDD = 2.7 V to 3.3 V
2.6 V typ I
SOURCE
= 20 A
Output Low Voltage (VOL)
ALE, Port 0 and Port 2 0.4 0.4 V max I
0.2 0.2 V typ I
Port 3 0.4 0.4 V max I
SCLOCK/SDATA 0.4 0.4 V max I
Floating State Leakage Current
4
±10 ±10 A max
= 1.6 mA
SINK
= 1.6 mA
SINK
= 4 mA
SINK
= 8 mA, I2C enabled
SINK
±1 ±1 A typ
Floating State Output Capacitance 10 10 pF typ
START-UP TIME At any Core_CLK
At Power-On 500 500 ms typ
From Idle Mode 100 100 s typ
From Power-Down Mode
Wakeup with
INT0
Interrupt
150 400 s typ
Wakeup with SPI/I2C Interrupt 150 400 s typ
Wakeup with External Reset 150 400 s typ
After External Reset in Normal Mode 30 30 ms typ
After WDT Reset in Normal Mode 3 3 ms typ Controlled via WDCON SFR
POWER REQUIREMENTS
19, 20
Power Supply Voltages
AVDD/DVDD − AGND 2.7 V min AVDD/DVDD = 3 V nom
3.3 V max
4.5 V min AVDD/DVDD = 5 V nom
5.5 V max
Power Supply Currents Normal Mode
DVDD Current
4
6 3 mA max Core_CLK = 2.097 MHz
AVDD Current 1.7 1.7 mA max Core_CLK = 2.097 MHz
DVDD Current 23 12 mA max Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
20 10 mA typ Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
AVDD Current 1.7 1.7 mA max Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
Power Supply Currents Idle Mode
DVDD Current 4 2 mA typ Core_CLK = 2.097 MHz
AVDD Current 0.14 0.14 mA typ Core_CLK = 2.097 MHz
DVDD Current4 10 5 mA max Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
9 4 mA typ Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
AVDD Current 0.14 0.14 mA typ Core_CLK = 16.78 MHz
Rev. A | Page 8 of 92
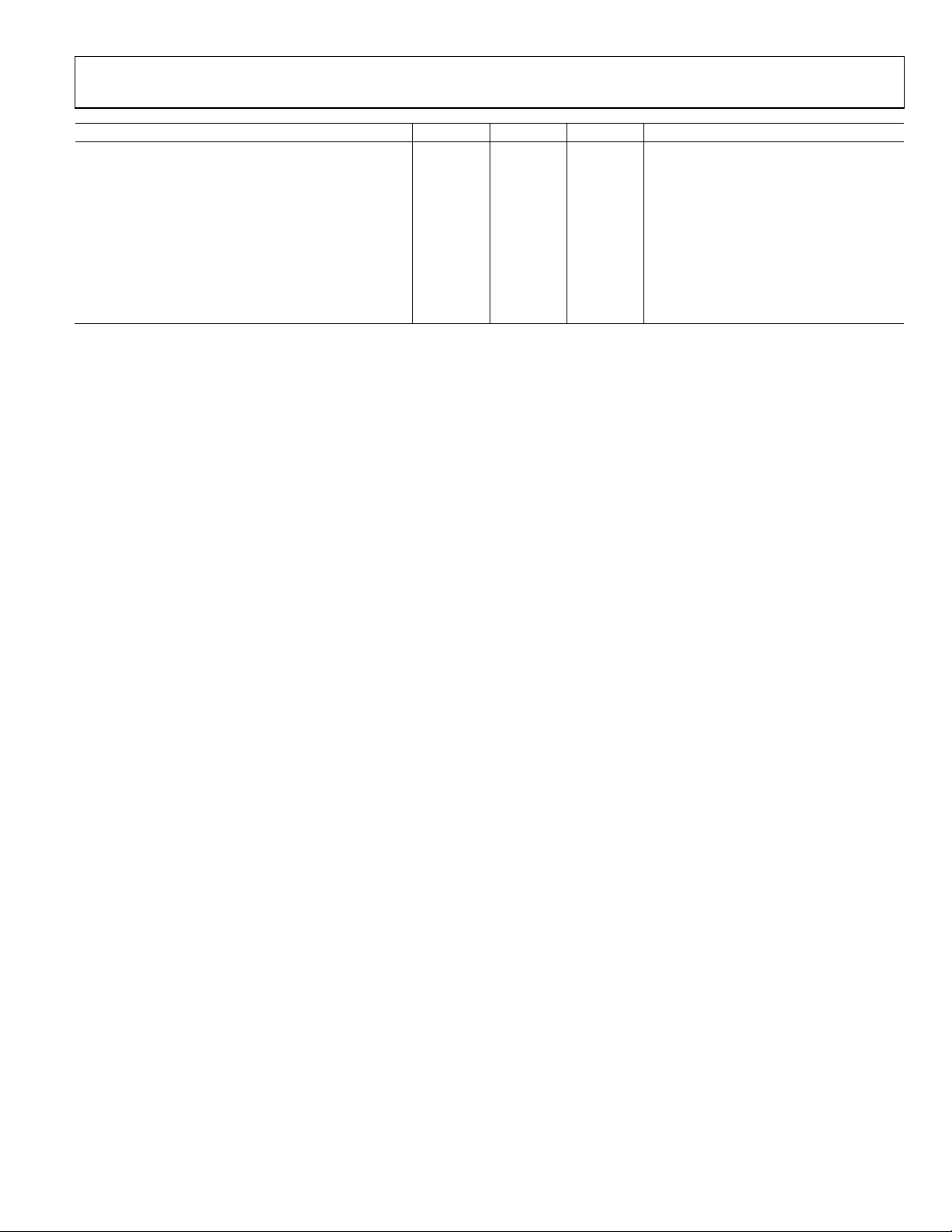
ADuC832
Parameter
1
VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Power Supply Currents Power-Down Mode Core_CLK = 2.097 MHz or 16.78 MHz
DVDD Current
4
80 25 A max Oscillator on
38 14 A typ
AVDD Current 2 1 A typ
DVDD Current 35 20 A max Oscillator off
25 12 A typ
Typical Additional Power Supply Currents AVDD = DVDD = 5 V
PSM Peripheral 50 A typ
ADC 1.5 mA typ
DAC 150 A typ
1
Temperature range: −40°C to +125°C.
2
ADC linearity is guaranteed during normal MicroConverter core operation.
3
ADC LSB size = V
4
Not production tested, but are guaranteed by design and/or characterization data on production release.
5
Offset error, gain error, offset error match, and gain error match are measured after factory calibration.
6
Based on external ADC system components, the user may need to execute a system calibration to remove additional external channel errors and achieve these
specifications.
7
SNR calculation includes distortion and noise components.
8
Channel-to-channel crosstalk is measured on adjacent channels.
9
The temperature sensor gives a measure of the die temperature directly; air temperature can be inferred from this result.
10
DAC linearity is calculated using:
Reduced code range of 100 to 4095, 0 V to V
Reduced code range of 100 to 3945, 0 V to VDD range.
DAC output load = 10 kΩ and 100 pF.
11
DAC differential nonlinearity specified on 0 V to V
12
DAC specification for output impedance in the unbuffered case depends on DAC code.
13
DAC specifications for I
unbuffered mode tested with OP270 external buffer, which has a low input leakage current.
14
Measured with V
capacitor chosen for both the V
15
When using an external reference device, the internal band gap reference input can be bypassed by setting the ADCCON1[6] bit. In this mode, the V
need to be shorted together for correct operation.
16
Flash/EE Memory reliability characteristics apply to both the Flash/EE program memory and the Flash/EE data memory.
17
Endurance is qualified to 100,000 cycles as per JEDEC Std. 22 method A117 and measured at −40°C, +25°C, and +125°C. Typical endurance at 25°C is 700,000 cycles.
18
Retention lifetime equivalent at junction temperature (TJ) = 55°C as per JEDEC Std. 22 Method A117. Retention lifetime based on an activation energy of 0.6 eV
derates with junction temperature as shown in Figure 48 in the ADuC832 Flash/EE Memory Reliability section.
19
Power supply current consumption is measured in normal, idle, and power-down modes under the following conditions:
/212, that is, for internal V
REF
, voltage output settling time, and digital-to-analog glitch energy depend on external buffer implementation in unbuffered mode. DAC in
SINK
and C
REF
pins decoupled with 0.1 µF capacitors to ground. Power-up time for the internal reference is determined by the value of the decoupling
REF
and C
REF
= 2.5 V, 1 LSB = 610 µV and for external V
REF
range.
REF
and 0 V to VDD ranges.
REF
pins.
REF
= 1 V, 1 LSB = 244 µV.
REF
REF
and C
REF
Normal mode: RESET = 0.4 V, digital I/O pins = open circuit, Core_CLK changed via the CD bits in PLLCON[2:0], core executing internal software loop.
Idle mode: RESET = 0.4 V, digital I/O pins = open circuit, Core_CLK changed via the CD bits in PLLCON, PCON[0] = 1, core execution suspended in idle mode.
Power-down mode: RESET = 0.4 V, all Port 0 pins = 0.4 V, all other digital I/O and Port 1 pins are open circuit, Core_CLK changed via the CD bits in PLLCON, PCON[1]
= 1, core execution suspended in power-down mode, oscillator turned on or off via OSC_PD bit (PLLCON[7]).
20
DVDD power supply current increases typically by 3 mA (3 V operation) and 10 mA (5 V operation) during a Flash/EE memory program or erase cycle.
pins
Rev. A | Page 9 of 92
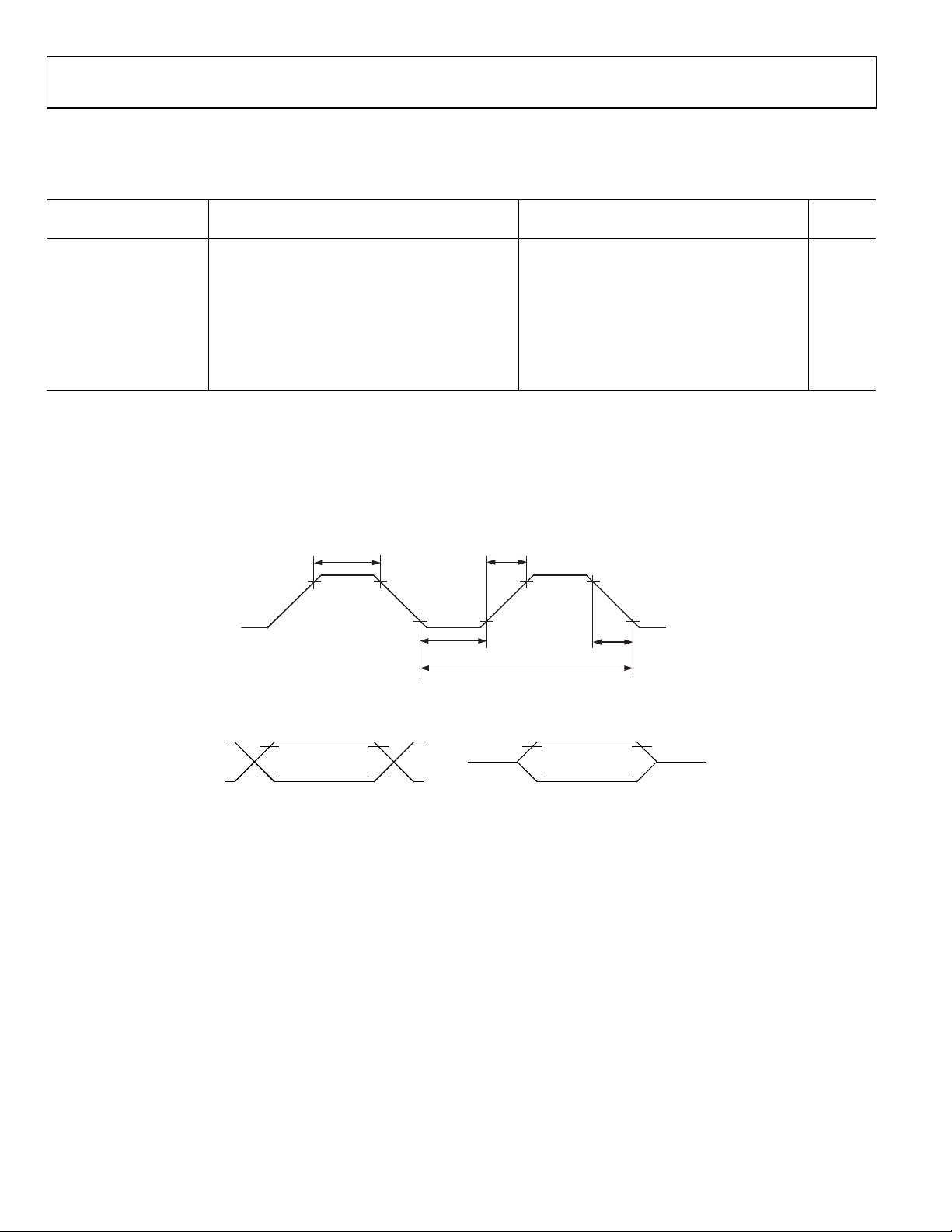
ADuC832
V
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 4.75 V to 5.25 V, DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 4.75 V to 5.25 V; all specifications T
Table 2. Clock Input (External Clock Applied on XTAL1)
32.768 kHz External Crystal
1, 2, 3
Parameter
Description Min Typ Max Unit
tCK XTAL1 period (see Figure 3) 30.52 s
t
XTAL1 width low (see Figure 3) 15.16 s
CKL
t
XTAL1 width high (see Figure 3) 15.16 s
CKH
t
XTAL1 rise time (see Figure 3) 20 ns
CKR
t
XTAL1 fall time (see Figure 3) 20 ns
CKF
1/t
ADuC832 core clock frequency
CORE
t
ADuC832 core clock period
CORE
t
ADuC832 machine cycle time
CYC
1
AC inputs during testing are driven at DVDD − 0.5 V for a Logic 1 and 0.45 V for a Logic 0. Timing measurements are made at VIH minimum for a Logic 1 and VIL maximum for
a Logic 0, as shown in Figure 4.
2
For timing purposes, a port pin is no longer floating when a 100 mV change from load voltage occurs. A port pin begins to float when a 100 mV change from the
loaded VOH/VOL level occurs, as shown in Figure 4.
3
C
for all outputs = 80 pF, unless otherwise noted.
LOAD
4
The ADuC832 internal PLL locks onto a multiple (512 times) the external crystal frequency of 32.768 kHz to provide a stable 16.78 MHz internal clock for the system.
The core can operate at this frequency or at a binary submultiple called Core_CLK, selected via the PLLCON SFR.
5
This number is measured at the default Core_CLK operating frequency of 2.09 MHz.
6
ADuC832 machine cycle time is nominally defined as 12/Core_CLK.
4
5
6
0.131 16.78 MHz
0.476 s
0.72 5.7 91.55 s
t
CKH
t
CKR
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
t
CKL
t
CK
t
CKF
2987-086
Figure 3. XTAL1 Input
DVDD –0.5
0.45V
+ 0.9V
0.2DV
DD
TEST POINTS
– 0.1V
0.2DV
DD
V
LOAD
Figure 4. Timing Waveform Characteristics
V
V
LOAD
LOAD
– 0.1V
+ 0.1V
TIMING
REFERENCE
POINTS
V
V
LOAD
LOAD
– 0.1V
+ 0.1V
V
LOAD
2987-087
Rev. A | Page 10 of 92
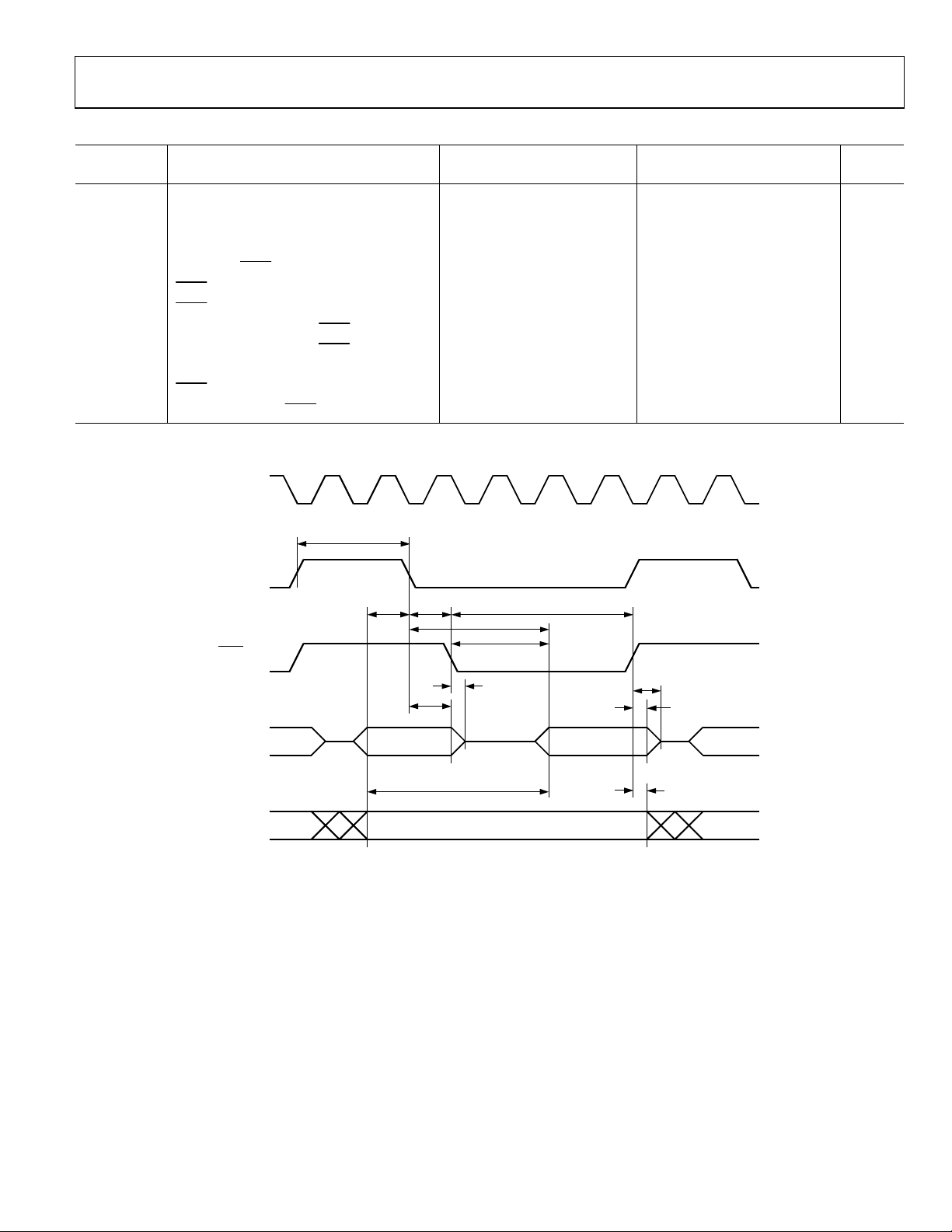
ADuC832
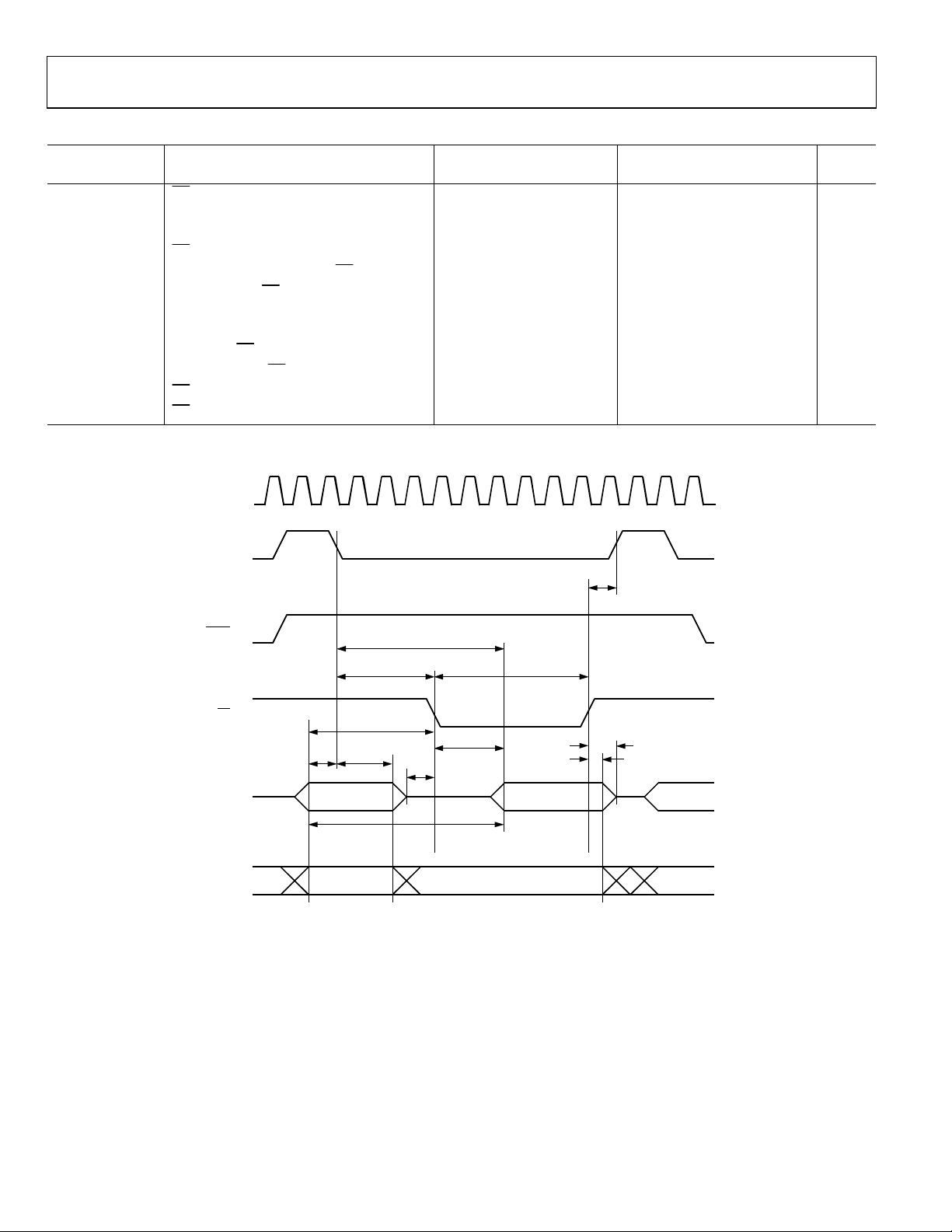
Table 3. External Program Memory Read Cycle
16.78 MHz Core_CLK Variable Clock
Parameter1 Description
t
ALE pulse width 79 2tCK − 40 ns
LHLL
t
Address valid to ALE low 19 tCK − 40 ns
AVLL
t
Address hold after ALE low 29 tCK − 30 ns
LLAX
t
ALE low to valid instruction in 138 4tCK − 100 ns
LLIV
t
LLPL
t
PLPH
t
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
Address to valid instruction in 193 5tCK − 105 ns
AVIV
t
PLAZ
t
PHAX
1
See Figure 5.
ALE low to PSEN
pulse width
PSEN
low to valid instruction in
PSEN
Instruction in, hold after PSEN
Instruction in, float after PSEN
low to address float
PSEN
Address hold after PSEN
low
high
M
CLK
t
LHLL
Min Max Min Max Unit
29 t
133 3t
73 3t
− 30 ns
CK
− 45 ns
CK
− 105 ns
CK
0 0 ns
34 tCK − 25 ns
25 25 ns
0 0 ns
ALE (O )
PSEN (O)
PORT 0 (I/O)
PORT 2 (O)
t
AVLLtLLPL
t
PCL (OUT)
LLAX
t
AVIV
t
PLAZ
PCH
t
PLPH
t
t
LLIV
PLIV
t
PXIX
INSTRUCTION
(IN)
Figure 5. External Program Memory Read Cycle
t
PXIZ
t
PHAX
02987-088
Rev. A | Page 11 of 92
ADuC832
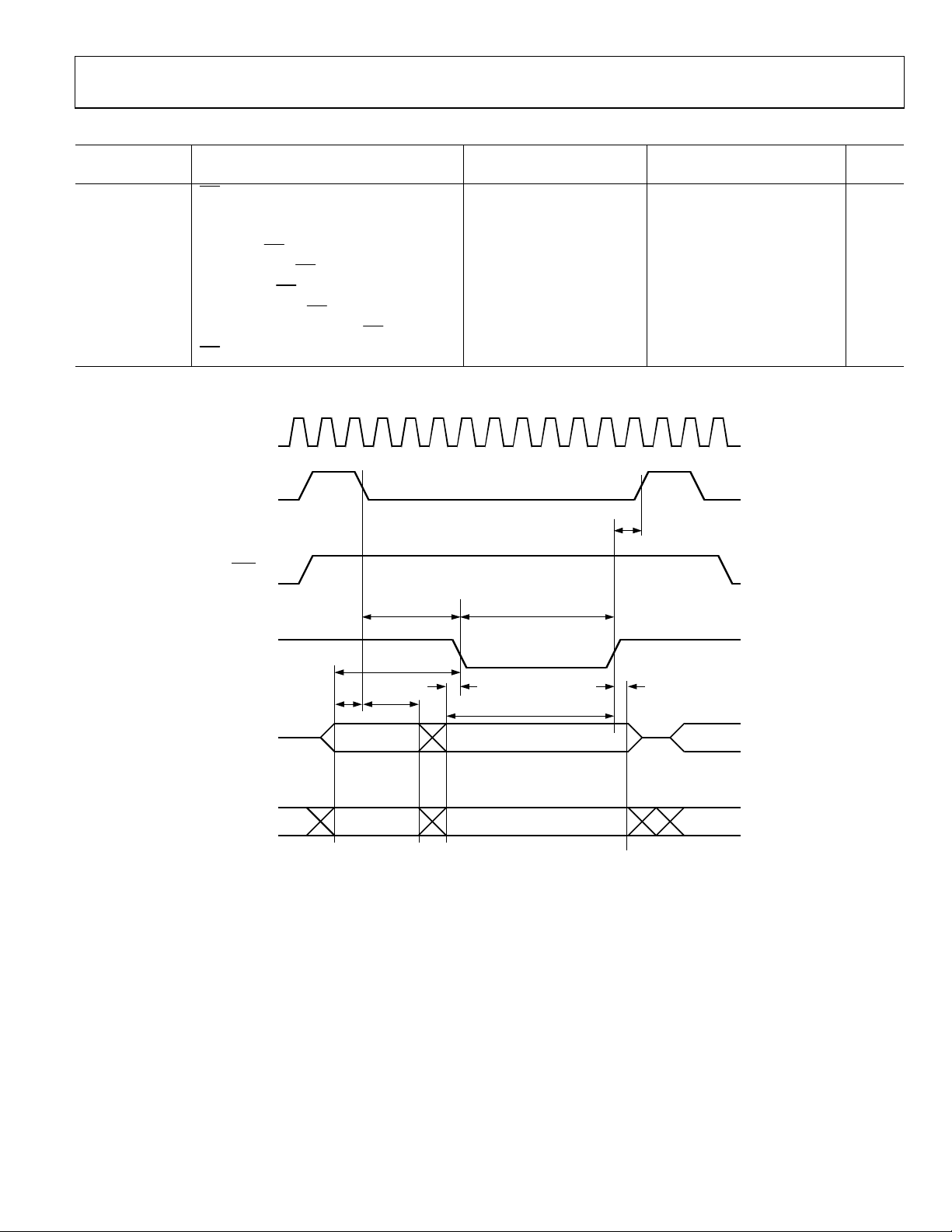
Table 4. External Data Memory Read Cycle
16.78 MHz Core_CLK Variable Clock
Parameter1 Description Min Max Min Max Unit
t
RLRH
t
Address valid before ALE low 19 tCK − 40 ns
AVLL
t
Address hold after ALE low 24 tCK − 35 ns
LLAX
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
ALE low to valid data in 326 8tCK − 150 ns
LLDV
t
Address to valid data in 371 9tCK − 165 ns
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVW L
t
RLAZ
t
WHLH
1
See Figure 6.
pulse width
RD
low to valid data in
RD
Data and address hold after RD
Data float after RD
ALE low to RD
Address valid to RD
low to address float
RD
high to ALE high
RD
low
low
M
CLK
257 6t
133 5t
− 100 ns
CK
− 165 ns
CK
0 0 ns
49 2tCK − 70 ns
128 228 3t
108 4t
− 50 3tCK +50 ns
CK
− 130 ns
CK
0 0 ns
19 257 t
− 40 6tCK − 100 ns
CK
ALE (O )
PSEN (O)
RD (O)
PORT 0 (I/O)
PORT 2 (O)
t
AVLL
t
LLDV
t
LLWL
t
t
AVDV
t
LLAX
AVWL
t
RLAZ
t
RLDV
A8 TO A15A16 TO A23
Figure 6. External Data Memory Read Cycle
t
RLRH
D0 TO D7 (IN)A0 TO A7 (OUT)
t
RHDX
t
WHLH
t
RHDZ
02987-089
Rev. A | Page 12 of 92
ADuC832
Table 5. External Data Memory Write Cycle
16.78 MHz Core_CLK Variable Clock
Parameter1 Description
t
WLWH
t
Address valid before ALE low 19 tCK − 40 ns
AVLL
t
Address hold after ALE low 24 tCK − 35 ns
LLAX
t
LLWL
t
AVW L
t
QVWX
t
QVWH
t
WHQX
t
WHLH
1
See Figure 7.
pulse width
WR
ALE low to WR
Address valid to WR
Data valid to WR
Data setup before WR
low
Low
transition
Data and address hold after WR
high to ALE high
WR
M
CLK
ALE (O)
Min Max Min Max Unit
257 6t
128 228 3t
108 4t
9 t
− 100 ns
CK
− 50 3tCK +50 ns
CK
− 130 ns
CK
− 50 ns
CK
267 7tCK − 150 ns
9 t
19 257 t
− 50 ns
CK
− 40 6tCK − 100 ns
CK
t
WHLH
PSEN (O)
WR (O)
PORT 2 (O)
t
AVLL
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
t
LLAX
A0 TO A7
A16 TO A23
QVWX
DATA
A8 TO A15
Figure 7. External Data Memory Write Cycle
t
WLWH
t
QVWH
t
WHQX
02987-090
Rev. A | Page 13 of 92
ADuC832
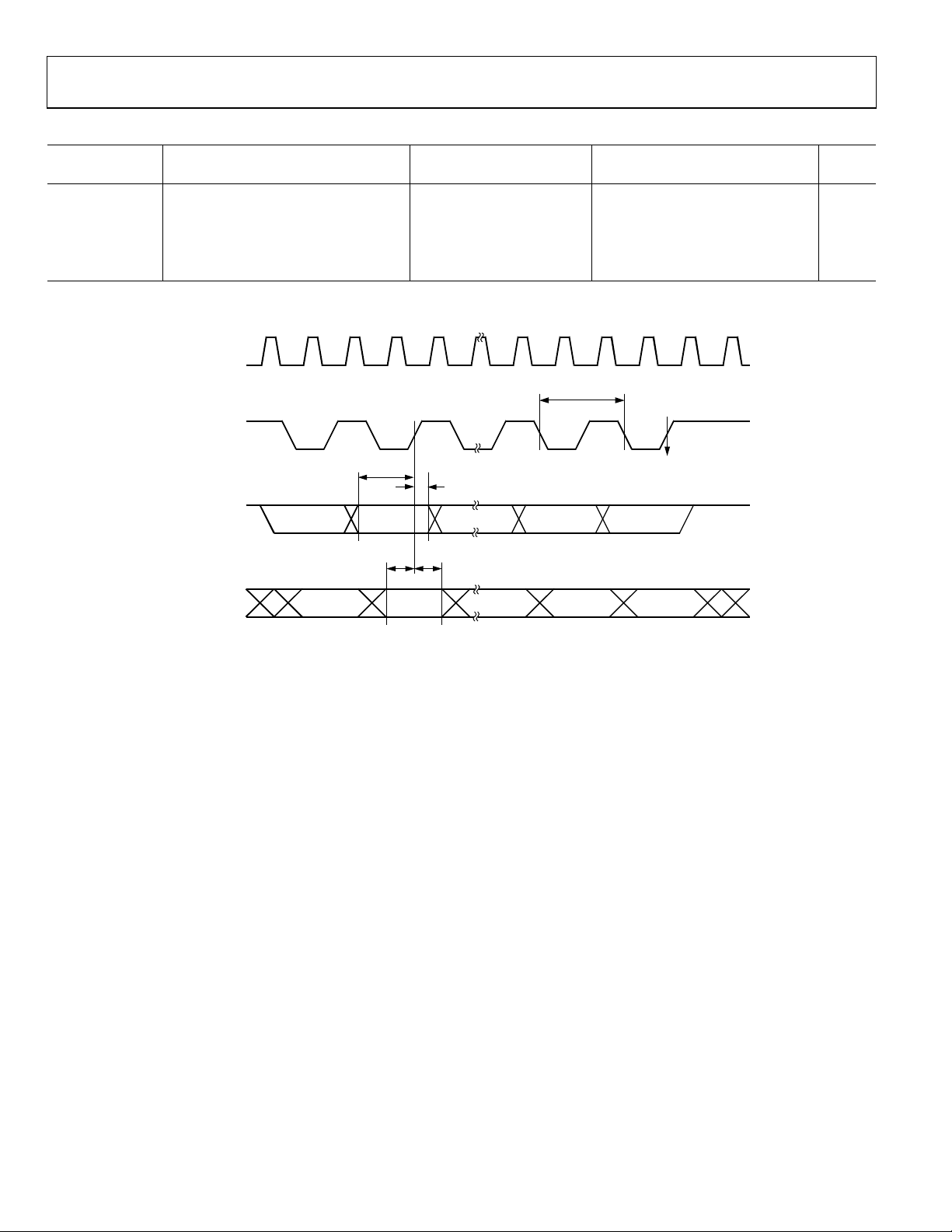
Table 6. UART Timing (Shift Register Mode)
Parameter
t
XLXL
t
QVXH
t
DVXH
t
XHDX
t
XHQX
1
See Figure 8.
1
Description
Serial port clock cycle time 715 12tCK s
Output data setup to clock 463 10tCK − 133 ns
Input data setup to clock 252 2tCK + 133 ns
Input data hold after clock 0 0 ns
Output data hold after clock 22 2tCK − 117 ns
ALE (O)
16.78 MHz Core_CLK Variable Clock
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
t
XLXL
(OUTPUT CLOCK)
(OUTPUT DATA)
TxD
RxD
RxD
(INPUT DATA)
MSB
6
BIT 1BIT 6
BIT 1
t
DVXH
t
QVXH
1
t
XHQX
t
XHDX
BIT 6
0
MSB
LSB
7
SET RI
OR
SET TI
LSB
2987-091
Figure 8. UART Timing in Shift Register Mode
Rev. A | Page 14 of 92
ADuC832
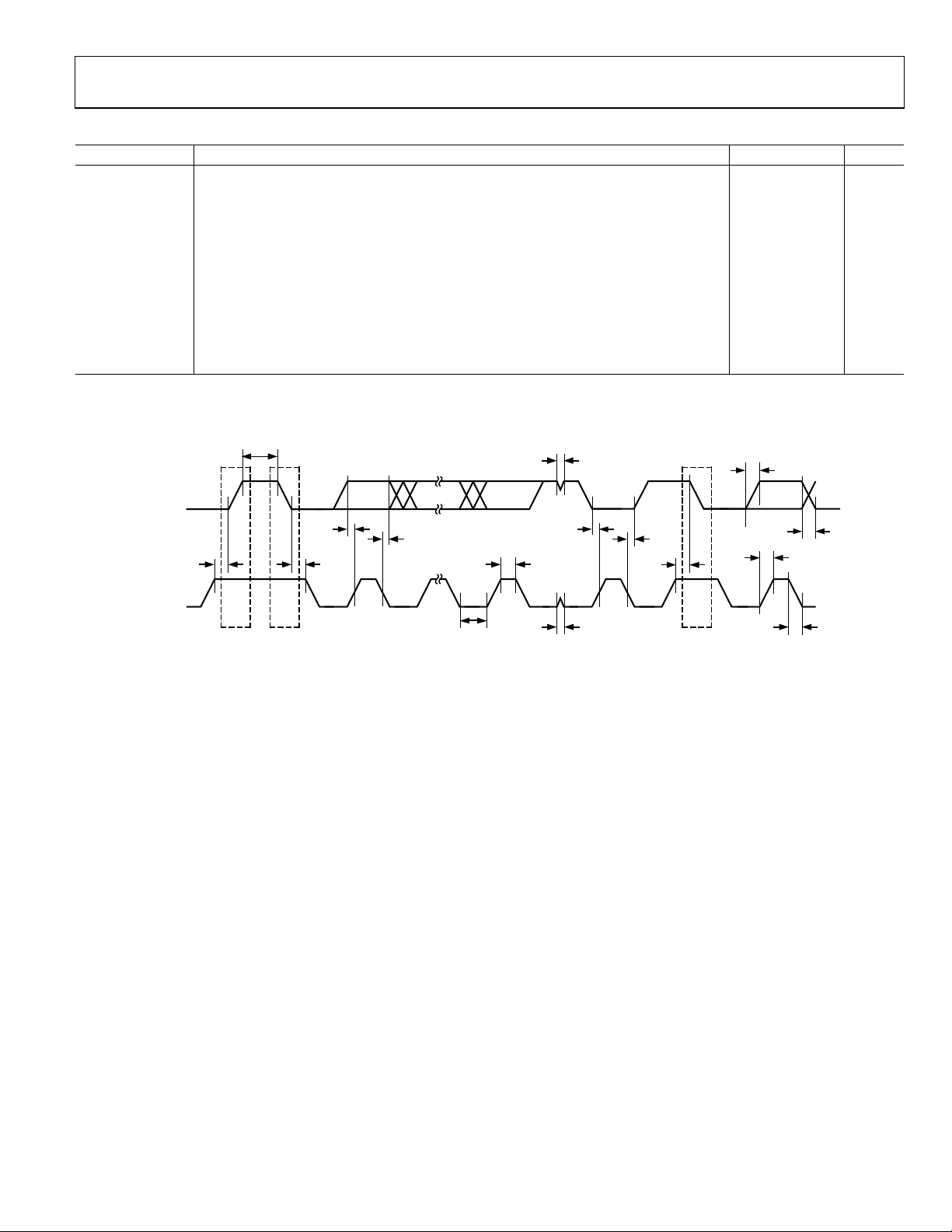
Table 7. I2C-Compatible Interface Timing
Parameter1 Description Min Max Unit
tL SCLOCK low pulse width 4.7 s
tH SCLOCK high pulse width 4.0 s
t
Start condition hold time 0.6 s
SHD
t
Data setup time 100 s
DSU
t
Data hold time 0.9 s
DHD
t
Setup time for repeated start 0.6 s
RSU
t
Stop condition setup time 0.6 s
PSU
t
Bus free time between a stop condition and a start condition 1.3 s
BUF
tR Rise time of both SCLOCK and SDATA 300 ns
tF Fall time of both SCLOCK and SDATA 300 ns
2
t
Pulse width of spike suppressed 50 ns
SUP
1
See Figure 9.
2
Input filtering on both the SCLOCK and SDATA inputs suppresses noise spikes less than 50 ns.
t
SDATA (I/O)
BUF
MSB
LSB
t
SUP
t
R
MSBACK
SCLOCK (I)
t
PSU
PS
STOP
CONDITION
START
CONDITION
t
DSU
t
t
DHD
t
SHD
Figure 9. I
2–7
2
C Compatible Interface Timing
8
t
L
1
DSU
t
H
t
SUP
t
DHD
t
RSU
9
S(R)
REPEATED
START
t
F
t
R
1
t
F
02987-092
Rev. A | Page 15 of 92
ADuC832
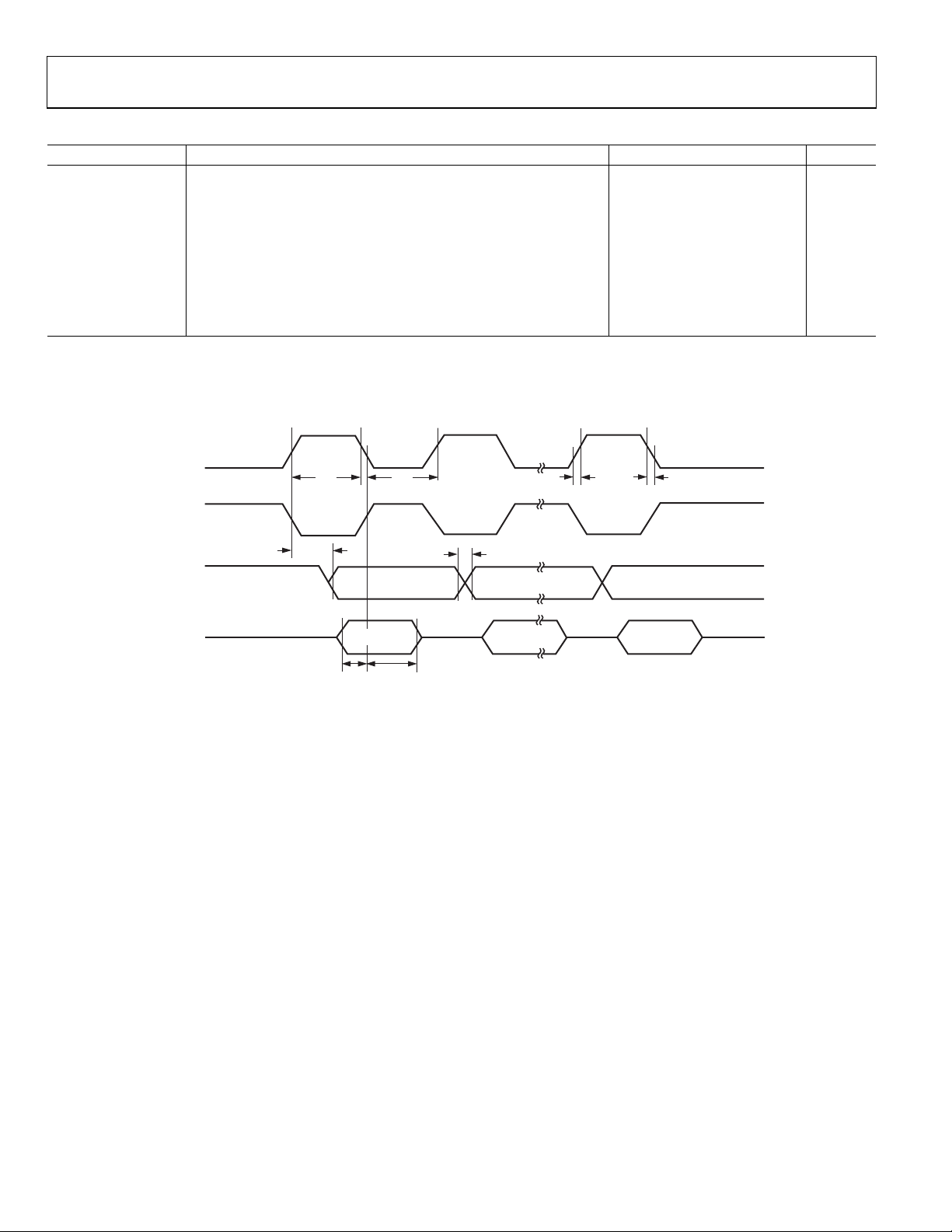
Table 8. SPI Master Mode Timing (CPHA = 1)
Parameter1 Description Min Typ Max Unit
tSL SCLOCK low pulse width
tSH SCLOCK high pulse width
t
Data output valid after SCLOCK edge 50 ns
DAV
t
Data input setup time before SCLOCK edge 100 ns
DSU
t
Data input hold time after SCLOCK edge 100 ns
DHD
tDF Data output fall time 10 25 ns
tDR Data output rise time 10 25 ns
tSR SCLOCK rise time 10 25 ns
tSF SCLOCK fall time 10 25 ns
1
See Figure 10.
2
Characterized under the following conditions:
a. Core clock divider bits (CD2, CD1, and CD0 bits in PLLCON SFR) set to 0, 1, and 1, respectively, that is, core clock frequency = 2.09 MHz
b. SPI bit rate selection bits (SPR1 and SPR0 bits in SPICON SFR) set to 0 and 0, respectively.
SCLOCK (O)
(CPO L = 0)
SCLOCK (O)
(CPO L = 1)
MOSI (O)
2
2
476 ns
t
MSB
SL
t
t
DF
t
DR
BIT 6 TO 1
t
DAV
t
SH
476 ns
SR
t
SF
LSB
MISO (I)
t
DSU
MSB IN
t
DHD
BIT 6 TO 1
Figure 10. SPI Master Mode Timing (CPHA = 1)
LSB IN
2987-093
Rev. A | Page 16 of 92
ADuC832
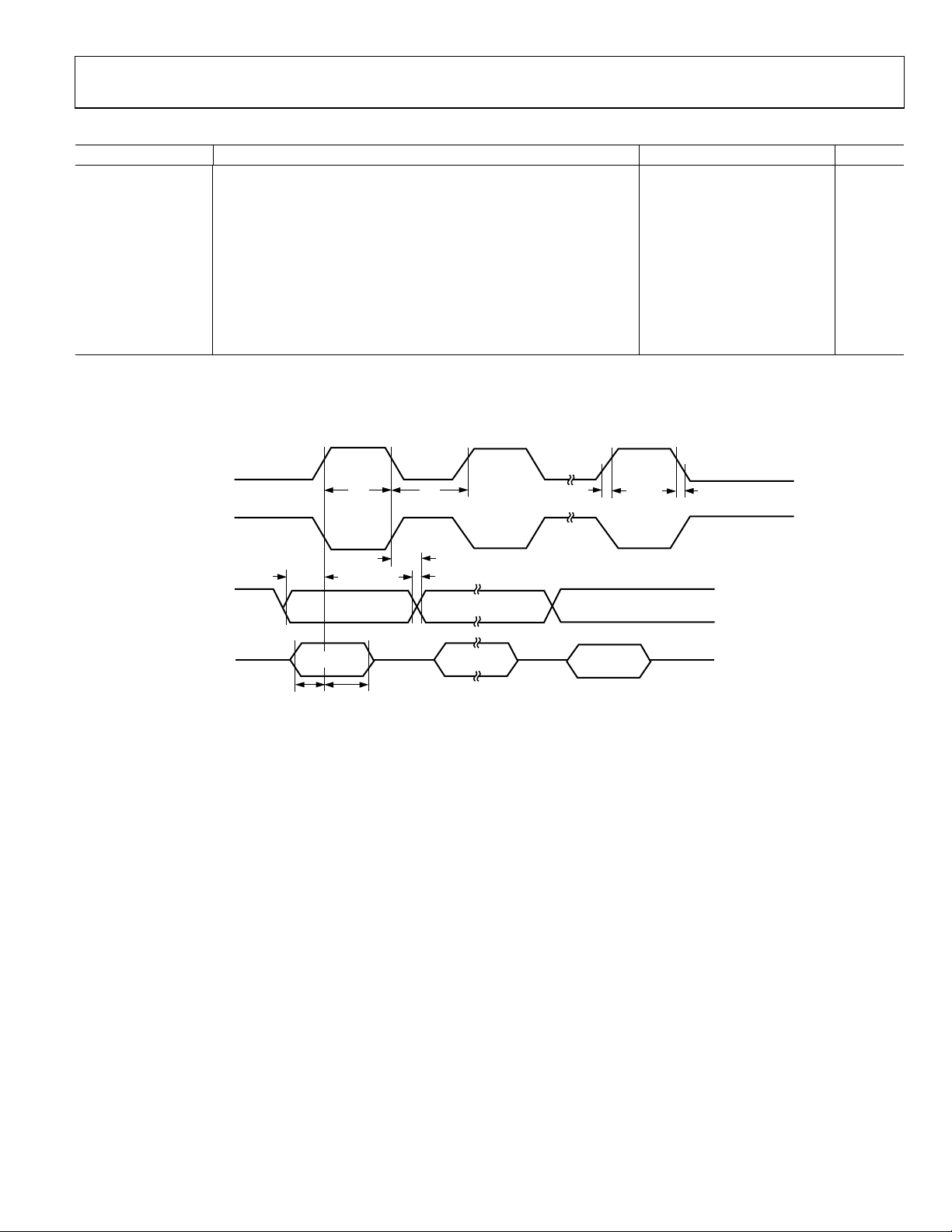
Table 9. SPI Master Mode Timing (CPHA = 0)
Parameter
tSL SCLOCK low pulse width
tSH SCLOCK high pulse width
t
DAV
t
DOSU
t
DSU
t
DHD
tDF Data output fall time 10 25 ns
tDR Data output rise time 10 25 ns
tSR SCLOCK rise time 10 25 ns
tSF SCLOCK fall time 10 25 ns
1
See Figure 11.
2
Characterized under the following conditions:
a. Core clock divider bits (CD2, CD1, and CD0 bits in PLLCON SFR) set to 0, 1, and 1, respectively, that is, core clock frequency = 2.09 MHz
b. SPI bit rate selection bits (SPR1 and SPR0 bits in SPICON SFR) set to 0 and 0, respectively.
1
Description Min Typ Max Unit
2
2
476 ns
476 ns
Data output valid after SCLOCK edge 50 ns
Data output setup before SCLOCK edge 150 ns
Data input setup time before SCLOCK edge 100 ns
Data input hold time after SCLOCK edge 100 ns
SCLOCK (O)
(CPOL = 0)
t
SL
t
DAV
t
DF
t
DR
t
SR
t
SF
SCLOCK (O)
(CPOL = 1)
t
DOSU
t
SH
MISO (O)
MOSI (I)
t
DSU
MSB IN
t
MSB
DHD
BIT 6 TO 1
BIT 6 TO 1
Figure 11. SPI Master Mode Timing (CPHA = 0)
LSB IN
LSB
02987-094
Rev. A | Page 17 of 92
ADuC832
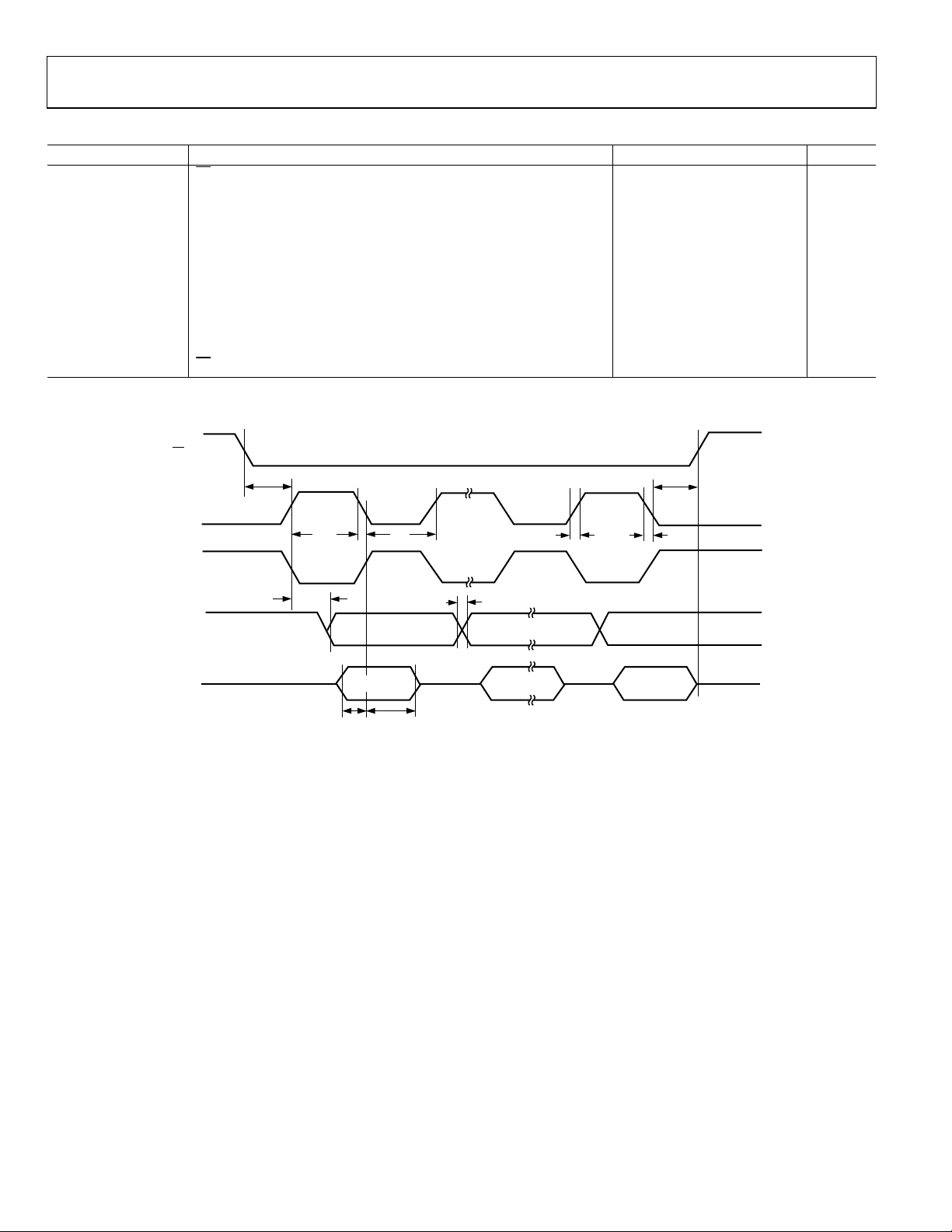
Table 10. SPI Slave Mode Timing (CPHA = 1)
Parameter
tSS
tSL SCLOCK low pulse width 330 ns
tSH SCLOCK high pulse width 330 ns
t
Data output valid after SCLOCK edge 50 ns
DAV
t
Data input setup time before SCLOCK edge 100 ns
DSU
t
DHD
tDF Data output fall time 10 25 ns
tDR Data output rise time 10 25 ns
tSR SCLOCK rise time 10 25 ns
tSF SCLOCK fall time 10 25 ns
t
SFS
1
See Figure 12.
1
Description Min Typ Max Unit
to SCLOCK edge
SS
0 ns
Data input hold time after SCLOCK edge 100 ns
0 ns
t
SFS
t
SR
t
SF
SS (I)
SCLOCK (I)
(CPOL = 0)
SCLOCK (I)
(CPOL = 1)
high after SCLOCK edge
SS
t
SS
t
SH
t
SL
MISO (O)
MOSI (I)
t
DAV
MSB IN
t
DSU
MSB
t
DHD
t
DF
t
DR
BITS 6 TO 1
BITS 6 TO 1
LSB
LSB IN
02987-095
Figure 12. SPI Slave Mode Timing (CPHA = 1)
Rev. A | Page 18 of 92
ADuC832
S
S
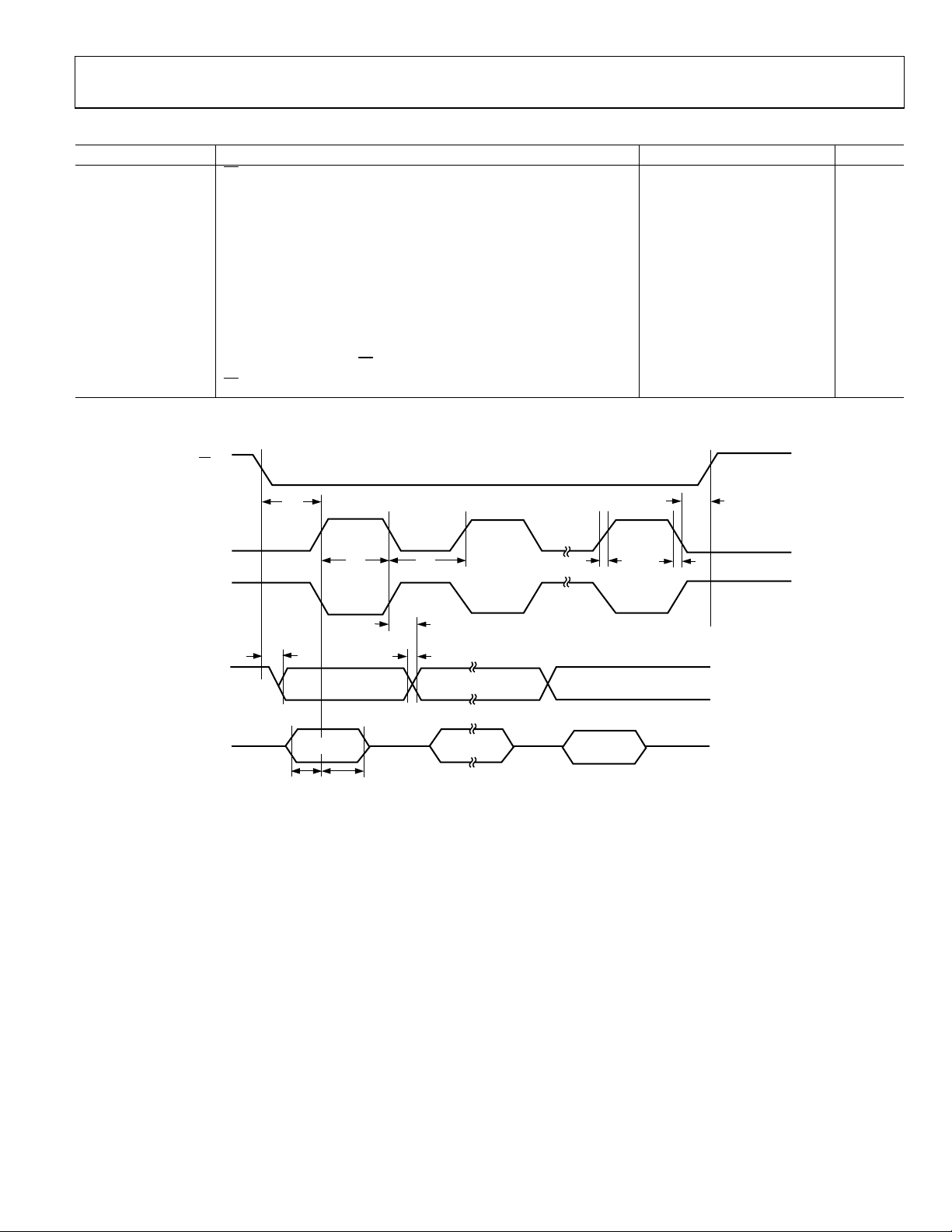
Table 11. SPI Slave Mode Timing (CPHA = 0)
Parameter1 Description Min Typ Max Unit
tSS
to SCLOCK edge
SS
tSL SCLOCK low pulse width 330 ns
tSH SCLOCK high pulse width 330 ns
t
Data output valid after SCLOCK edge 50 ns
DAV
t
Data input setup time before SCLOCK edge 100 ns
DSU
t
Data input hold time after SCLOCK edge 100 ns
DHD
tDF Data output fall time 10 25 ns
tDR Data output rise time 10 25 ns
tSR SCLOCK rise time 10 25 ns
tSF SCLOCK fall time 10 25 ns
t
DOSS
t
SFS
1
See Figure 13.
Data output valid after SS
high after SCLOCK edge
SS
edge
SS (I)
0 ns
20 ns
0 ns
t
SFS
t
SF
02987-096
CLOCK (I)
(CPOL = 0)
CLOCK (I)
(CPOL = 1)
MISO (O)
MOSI (I)
t
DOSS
t
SS
t
SH
MSB LSB
MSB IN
t
t
DSU
DHD
t
SL
t
DAV
t
DF
t
DR
BIT 6 TO BIT 1
BIT 6 TO BIT 1
t
SR
LSB IN
Figure 13. SPI Slave Mode Timing (CPHA = 0)
Rev. A | Page 19 of 92

ADuC832
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 12.
Parameter Rating
AVDD to DVDD −0.3 V to +0.3 V
AGND to DGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
DVDD to DGND, AVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +7 V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND −0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND −0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
V
to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
REF
Analog Inputs to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range Industrial
ADuC832BS −40°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range Industrial
ADuC832BCP −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
θJA Thermal Impedance (ADuC832BS) 90°C/W
θJA Thermal Impedance (ADuC832BCP) 52°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 20 of 92
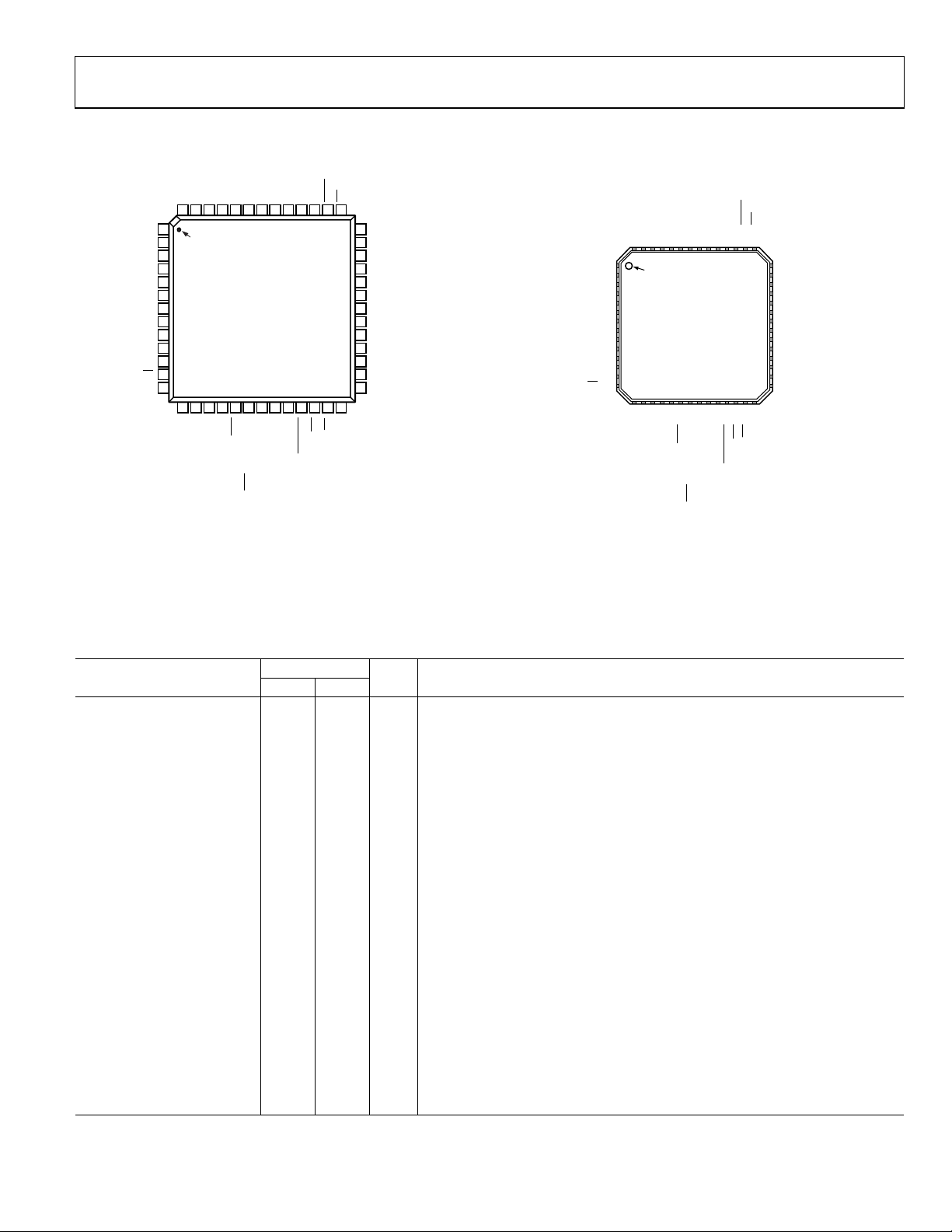
ADuC832
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P0.5/AD5
P0.4/AD4
DVDDDGND
P0.3/AD3
P0.2/AD2
P0.1/AD1
P0.0/AD0
ALE
PSEN
P1.0/ADC0/T2
P1.1/ADC1/T2EX
P1.2/ADC2
P1.3/ADC3
AV
AGND
C
REF
V
REF
DAC0
DAC1
P1.4/ADC4
P1.5/ADC5/SS
P1.6/ADC6
52
51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
2
3
4
5
DD
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
P1.7/ADC7
RESET
(Not to Scale)
P3.1/TxD
P3.0/RxD
ADuC832
TOP VIEW
DD
DV
P3.2/INT0
3.3/INT1/MISO/PWM1
P
DGND
WMC/PWM0/EXTCLK
P3.4/T0/P
EA
39
P2.7/PWM1/A15/A23
38
P2.6/PWM0/A14/A22
37
P2.5/A13/A21
36
P2.4/A12/A20
35
DGND
34
DV
DD
33
XTAL2
32
XTAL1
31
P2.3/A11/A19
30
P2.2/A10/A18
29
P2.1/A9/A17
28
P2.0/A8/A16
27
SDATA/MOSI
26252423222120191817161514
P3.7/RD
P3.6/WR
SCLOCK
P3.5/T1/CONVST
02987-002
NOTES
1. THE LFCSP HAS AN EXPOSED PADDLE THAT MUST BE SOLDERED
AV
DD
AV
DD
AGND
C
REF
V
REF
DAC0
TO THE PCB BUT ELECTRICALLY LEFT UNCONNECTED.
P1.0/ADC0/T2
56
1P1.1/ADC1/T2EX
2P1.2/ADC2
3P1.3/ADC3
4
5
6
7AGND
8AGND
9
10
11
12DAC1
13P1.4/ADC4
14P1.5/ADC5/SS
15
P1.6/ADC6
Figure 14. 52-Lead MQFP
DD
0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P
54
55
PIN 1
INDICATOR
(Not to Scale)
16
17
RESET
P.7/ADC7
P0.4/AD4
P0.5/AD5
P0.3/AD3
DGND
DV
52
53
49
50
51
ADuC832
TOP VIEW
19
21
20
22
18
DD
DV
P3.1/TxD
P3.0/RxD
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1/MISO/PWM1
0.2/AD2
ALE
P0.0/AD0
P0.1/AD1
P
PSEN
44
45
46
47
48
23
24
25
26
27
DGND
P3.7/RD
P3.6/WR
P3.5/T1/CONVST
P3.4/T0/PWMC/PWM0/EXTCLK
Figure 15. 56-Lead LFCSP
EA
43
28
SCLOCK
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
P2.7/PWM1/A15/A23
P2.6/PWM0/A14/A22
P2.5/A13/A21
P2.4/A12/A20
DGND
DGND
DV
DD
XTAL2
XTAL1
P2.3/A11/A19
P2.2/A10/A18
P2.1/A9/A17
P2.0/A8/A16
SDATA/MOSI
7-003
0298
Table 13. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No.
Mnemonic MQFP LFCSP Type Description
Exposed Paddle N/A 0 The LFCSP has an exposed paddle that must be soldered to the PCB but left
P1.0/ADC0/T2 1 56 I Input Port 1 (P1.0). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
I
I
P1.1/ADC1/T2EX 2 1 I
I
I
P1.2/ADC2 3 2 I
I
P1.3/ADC3 4 3 I
I
AV
5 4, 5 P Analog Positive Supply Voltage, 3 V or 5 V Nominal.
DD
AGND 6 6, 7, 8 G
C
7 9 I/O Decoupling Input for On-Chip Reference. Connect 0.1 F between this pin and AGND.
REF
unconnected.
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC0). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
Timer/Counter 2 Digital Input (T2). When enabled, Counter 2 is incremented in
response to a 1-to-0 transition of the T2 input.
Input Port 1 (P1.1). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC1). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
Digital Input (T2EX). Capture/Reload trigger for Counter 2; also functions as an
up/down control input for Counter 2.
Input Port 1 (P1.2). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC2). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
Input Port 1 (P1.3). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC3). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
Analog Ground. Ground reference point for the analog circuitry.
Rev. A | Page 21 of 92
ADuC832
Pin No.
Mnemonic MQFP LFCSP Type Description
V
8 10 I/O Reference Input/Output. This pin is connected to the internal reference through a
REF
DAC0 9 11 O Voltage Output from DAC0.
DAC1 10 12 O Voltage Output from DAC1.
P1.4/ADC4 11 13 I Input Port 1 (P1.4). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
I Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC4). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
P1.5/ADC5/SS
I Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC5). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
I
P1.6/ADC6 13 15 I Input Port 1 (P1.6). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
I Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC6). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
P1.7/ADC7 14 16 I
I Single-Ended Analog Input (ADC7). Channel selection is via ADCCON2 SFR.
RESET 15 17 I Digital Input. A high level on this pin for 24 master clock cycles while the oscillator is
P3.0/RxD 16 18 I/O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.0). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I Receiver Data Input (Asynchronous) or Data Input/Output (Synchronous) of Serial
P3.1/TxD 17 19 I/O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.1). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
O Transmitter Data Output (Asynchronous) or Clock Output (Synchronous) of Serial
INT0
P3.2/
I
P3.3/
I
I/O SPI Master Input/Slave Output Data I/O Pin for SPI Serial Interface (MISO).
O PWM1 Voltage Output (PWM1). See the ADuC832 Configuration SFR (CFG832) section
DVDD 20, 34,
DGND 21, 35,
INT1
/MISO/PWM1
12 14 I Input Port 1 (P1.5). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1 defaults
18 20 I Input/Output Port 3 (P3.2). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
19 21 I Input/Output Port 3 (P3.3). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
48
47
22, 36,
51
23, 37,
38, 50
P Digital Positive Supply Voltage, 3 V or 5 V Nominal.
G Digital Ground. Ground reference point for the digital circuitry.
series resistor and is the reference source for the analog-to-digital converter. The
nominal internal reference voltage is 2.5 V, which appears at the pin. See the Voltage
Reference Connections section on how to connect an external reference.
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
to analog input mode. To configure any of these Port Pins as a digital input, write a 0
to the port bit. Port 1 pins are multifunction and share the following functionality.
Slave Select Input for the SPI Interface (
to analog input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input, write a 0 to the
Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following functionality.
SS
).
Input Port 1 (P1.7). Port 1 is an 8-bit input port only. Unlike other ports, Port 1
defaults to Analog Input mode. To configure any Port 1 pin as a digital input,
write a 0 to the Port 1 bit. Port 1 pins are multifunctional and share the following
functionality.
running resets the device.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
(UART) Port (RxD).
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
(UART) Port (TxD).
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Interrupt 0 (
programmed to one of two priority levels. This pin can also be used as a gate control
input to Timer 0.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Interrupt 1 (
programmed to one of two priority levels. This pin can also be used as a gate control
input to Timer 1.
for further information.
INT0
). This programmable edge or level triggered interrupt input can be
INT1
). This programmable edge or level triggered interrupt input can be
Rev. A | Page 22 of 92
ADuC832
Pin No.
Mnemonic MQFP LFCSP Type Description
P3.4/T0/PWMC/PWM0/EXTCLK 22 24 I/O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.4). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I Timer/Counter 0 Input (T0).
I PWM Clock Input (PWMC).
O PWM0 Voltage Output (PWM0). PWM outputs can be configured to uses
I Input for External Clock Signal (EXTCLK). This pin must be enabled via the CFG832
CONVST
P3.5/T1/
I Timer/Counter 1 Input (T1).
I Active Low Convert Start Logic Input for the ADC Block When the External Convert
P3.6/WR
O
P3.7/RD
O
SCLOCK 26 28 I/O Serial Clock Pin for I2C-Compatible or SPI Serial Interface Clock.
SDATA/MOSI 27 29 I/O User Selectable, I2C-Compatible or SPI Data Input/Output Pin (SDATA).
I/O SPI Master Output/Slave Input Data I/O Pin for SPI Interface (MOSI).
P2.0/A8/A16 28 30 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.0). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A8/A16). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.1/A9/A17 29 31 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.1). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A9/A17). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.2/A10/A18 30 32 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.2). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A10/A18). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.3/A11/A19 31 33 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.3). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A11/A19). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
XTAL1 32 34 I Input to the Inverting Oscillator Amplifier.
23 25 I/O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.5). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
24 26 I/O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.6). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
25 27 O Input/Output Port 3 (P3.7). Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Port 2.6 and Port 2.7, or Port 3.4 and Port 3.3.
register.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
CONVST
Start Function is Enabled (
track-and-hold into its hold mode and starts conversion.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Write Control Signal, Logic Output (
external data memory.
Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Read Control Signal, Logic Output (
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Rev. A | Page 23 of 92
). A low-to-high transition on this input puts the
WR
). Latches the data byte from Port 0 into the
RD
). Enables the external data memory to Port 0.
ADuC832
Pin No.
Mnemonic MQFP LFCSP Type Description
XTAL2 33 35 O Output of the Inverting Oscillator Amplifier.
P2.4/A12/A20 36 39 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.4). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A12/A20). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.5/A13/A21 37 40 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.5). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
I/O External Memory Addresses (A13/A21). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.6/PWM0/A14/A22 38 41 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.6). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
O PWM0 Voltage Output (PWM0). PWM outputs can be configured to use Port 2.6 and
I/O External Memory Addresses (A14/A22). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
P2.7/PWM1/A15/A23 39 42 I/O Input/Output Port 2 (P2.7). Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors.
O PWM1 Voltage Output (PWM1). See the ADuC832 Configuration SFR (CFG832) section
I/O External Memory Addresses (A15/A23). Port 2 emits the high order address bytes
EA
PSEN
ALE 42 45 O Address Latch Enable, Logic Output. This output is used to latch the low byte (and
P0.0/AD0 43 46 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.0). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD0). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.1/AD1 44 47 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.1). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD1). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
40 43 I External Access Enable, Logic Input. When held high, this input enables the device to
41 44 O Program Store Enable, Logic Output. This output is a control signal that enables the
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Port 2.7 or Port 3.4 and Port 3.3
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-up
resistors, and in that state can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins being pulled
externally low sources current because of the internal pull-up resistors.
for further information.
during fetches from external program memory and middle and high order address
bytes during accesses to the external 24-bit external data memory space.
fetch code from internal program memory locations 0000H to 1FFFH. When held low,
this input enables the device to fetch all instructions from external program memory.
This pin should not be left floating.
external program memory to the bus during external fetch operations. It is active
every six oscillator periods except during external data memory accesses. This pin
remains high during internal program execution.
serial download mode when pulled low through a resistor on power-up or reset.
page byte for 24-bit address space accesses) of the address into external memory
during normal operation. It is activated every six oscillator periods except during an
external data memory access.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
PSEN
can also be used to enable
Rev. A | Page 24 of 92
ADuC832
Pin No.
Mnemonic MQFP LFCSP Type Description
P0.2/AD2 45 48 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.2). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
External Memory Address and Data (AD2). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.3/AD3 46 49 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.3). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD3). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.4/AD4 49 52 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.4). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD4). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.5/AD5 50 53 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.5). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD5). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.6/AD6 51 54 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.6). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
I/O External Memory Address and Data (AD6). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
P0.7/AD7 52 56 I/O Input/Output Port 0 (P0.7). Port 0 is an 8-Bit Open-Drain Bidirectional I/O Port. Port 0
External Memory Address and Data (AD7). Port 0 is also the multiplexed low order
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
pins that have 1s written to them float and in that state can be used as high
impedance inputs.
address and data bus during accesses to external program or data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
Rev. A | Page 25 of 92
ADuC832
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4
TYPICAL INL ERROR (LSB)
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 511
1023 2559 3071
ADC CODES
Figure 16. Typical INL Error, VDD = 5 V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4
TYPICAL DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 511
1023 2559 3071
ADC CODES
Figure 17. Typical INL Error, VDD = 3 V
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
WCP–INL (LSB)
0
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
0.5 1.51.0 2.0 5.02.5
EXTERNAL REF E RENCE ( V )
Figure 18. Typical Worst-Case INL Error vs. V
AVDD/DVDD = 5V
f
S
AVDD/DVDD = 3V
f
S
AV
DD
f
= 152kHz
S
WCP INL
WCN INL
= 152kHz
35831535
= 152kHz
35831535
/DVDD = 5V
, VDD = 5 V
REF
40952047
40952047
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
987-005
02
987-006
02
WCN–INL (L SB)
02987-007
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
WCP–INL (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
0.5 1.5 2.5
EXTERNAL REF E RENCE ( V )
Figure 19. Typical Worst-Case INL Error vs. V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4
TYPICAL I NL ERROR (LSB)
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 511
1023 2559 3071
ADC CODES
Figure 20. Typical DNL Error, VDD = 5 V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
–0.4
TYPICAL DNL E RROR (LSB)
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0511
1023 2559 3071
ADC CODES
Figure 21. Typical DNL Error, VDD = 3 V
/DVDD = 3V
AV
DD
f
= 152kHz
S
WCP INL
WCN INL
3.02.01.0
, VDD = 3 V
REF
AVDD/DVDD = 5V
f
= 152kHz
S
AVDD/DVDD = 3V
f
= 152kHz
S
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
WCN–INL (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
02987-008
35831535
40952047
2987-009
35831535
40952047
987-010
02
Rev. A | Page 26 of 92
ADuC832
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
WCP–DNL (LSB)
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
0.5 1.51.0 2.0 5.02.5
EXTERNAL REF E RE NCE (V )
Figure 22. Typical Worst-Case DNL Error vs. V
0.7
0.5
0.3
0.1
–0.1
WCP–DNL (LSB)
–0.3
–0.5
–0.7
0.5 1.51.0 2.0 3.02.5
EXTERNAL REF E RE NCE ( V)
Figure 23. Typical Worst-Case DNL Error vs. V
10,000
8000
6000
4000
OCCURRENCE
2000
0
Figure 24. Code Histogram Plot, VDD = 5 V
CODE
AVDD/DVDD = 5V
f
= 152kHz
S
WCP DNL
WCN DNL
, VDD = 5 V
REF
AV
/DVDD = 3V
DD
f
= 152kHz
S
WCP DNL
WCN DNL
, VDD = 3 V
REF
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
WCN–DNL (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
02987-011
0.7
0.5
0.3
0.1
–0.1
WCN–DNL (LSB)
–0.3
–0.5
–0.7
02987-012
821820819818817
02987-013
10,000
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
OCCURRENCE
3000
2000
1000
0
CODE
Figure 25. Code Histogram Plot, V
20
0
–20
–40
–60
(dB)
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
010
20
FREQUENCY (kHz)
40 50 60
Figure 26. Dynamic Performance at VDD = 5 V
20
0
–20
–40
–60
(dB)
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
01020 7030 40 50 60
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 27. Dynamic Performance at VDD = 3 V
821820819818817
= 3 V
DD
AVDD/DVDD = 5V
f
= 152kHz
S
f
= 9.910kHz
IN
SNR = 71.3dB
THD = –88.0dB
ENOB = 11.6
AVDD/DVDD = 3V
f
= 149.79kHz
S
f
= 9.910kHz
IN
SNR = 71.0dB
THD = –83.0dB
ENOB = 11.5
2987-014
7030
02987-015
02987-016
Rev. A | Page 27 of 92
ADuC832
–
–
–75
–80
–85
–100
–75
–80
–85
–90
–95
–90
–95
70
70
THD (dB)
02987-017
SNR (dB)
80
78
76
74
72
70
68
66
64
62
60
65.476
92.262
119.05 172.62 199.41 226.19
145.83
FREQUENCY (kHz)
AVDD/DVDD = 5V
02987-019
Figure 30. Typical Dynamic Performance vs. Sampling Frequency
0.80
AVDD/DVDD = 3V
SLOPE = –2mV/°C
0.75
0.70
0.65
0.60
THD (dB)
0.55
0.50
SENSOR VOLTAGE OUTPUT (V)
0.45
80
75
70
65
SNR (dB)
60
55
50
0.5 1.51.0 2.0 5.02.5
EXTERNAL REF ERENCE (V)
Figure 28. Typical Dynamic Performance vs. V
80
75
70
65
SNR (dB)
60
55
/DVDD = 5V
AV
DD
f
= 152kHz
S
SNR
THD
, VDD = 5 V
REF
AVDD/DVDD = 3V
f
= 152kHz
S
SNR
THD
50
0.5 1.51.0 2.0 3.02.5
EXTERNAL REFERENCE (V)
Figure 29. Typical Dynamic Performance vs. V
, VDD = 3 V
REF
–100
2987-018
0.40
–40 –20
0255085
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 31. Typical Temperature Sensor Output vs. Temperature
02987-020
Rev. A | Page 28 of 92

ADuC832
TERMINOLOGY
ADC SPECIFICATIONS
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation of any code from a straight line
passing through the endpoints of the ADC transfer function.
The endpoints of the transfer function are zero scale, a point
½ LSB below the first code transition, and full scale, a point
½ LSB above the last code transition.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
This is the deviation of the first code transition (0000 … 000) to
(0000 … 001) from the ideal, that is, +½ LSB.
Gain Error
This is the deviation of the last code transition from the ideal
analog input voltage (full scale − 1.5 LSB) after the offset error
has been adjusted out.
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD) Ratio
This is the measured ratio of signal-to-noise and distortion at
the output of the ADC. The signal is the rms amplitude of the
fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all nonfundamental
signals up to half the sampling frequency (f
The ratio is dependent upon the number of quantization levels
in the digitization process; the more levels there are, the smaller
the quantization noise. The theoretical signal to (noise +
distortion) ratio for an ideal N-bit converter with a sine wave
input is given by:
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion = (6.02N + 1.76) dB
Thus for a 12-bit converter, this is 74 dB.
/2), excluding dc.
S
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total harmonic distortion is the ratio of the rms sum of the
harmonics to the fundamental.
DAC SPECIFICATIONS
Relative Accuracy
Relative accuracy or endpoint linearity is a measure of the
maximum deviation from a straight line passing through the
endpoints of the DAC transfer function. It is measured after
adjusting for zero error and full-scale error.
Voltage Output Settling Time
This is the amount of time it takes for the output to settle to a
specified level for a full-scale input change.
Digital-to-Analog Glitch Energy
This is the amount of charge injected into the analog output
when the inputs change state. It is specified as the area of the
glitch in nV sec.
Rev. A | Page 29 of 92

ADuC832
EXPLANATION OF TYPICAL PERFORMANCE PLOTS
The plots presented in the Typical Performance Characteristics
section illustrate typical performance of the ADuC832 under
various operating conditions.
Figure 16 and Figure 17 show typical ADC integral nonlinearity
(INL) errors from ADC Code 0 to Code 4095 at 5 V and 3 V
supplies, respectively. The ADC is using its internal reference
(2.5 V) and operating at a sampling rate of 152 kHz, and the
typically worst-case errors in both plots are slightly less than
0.3 LSBs.
Figure 18 and Figure 19 show the variation in worst-case
positive (WCP) INL and worst-case negative (WCN) INL vs.
external reference input voltage.
Figure 20 and Figure 21 show typical ADC differential nonlinearity (DNL) errors from ADC Code 0 to Code 4095 at 5 V and
3 V supplies, respectively. The ADC is using its internal reference (2.5 V) and operating at a sampling rate of 152 kHz, and
the typically worst-case errors in both plots is slightly less than
0.2 LSBs.
Figure 22 and Figure 23 show the variation in worst-case
positive (WCP) DNL and worst-case negative (WCN) DNL
vs. external reference input voltage.
Figure 24 shows a histogram plot of 10,000 ADC conversion
results on a dc input with V
= 5 V. The plot illustrates an
DD
excellent code distribution pointing to the low noise
performance of the on-chip precision ADC.
Figure 25 shows a histogram plot of 10,000 ADC conversion
results on a dc input for V
= 3 V. The plot again illustrates a
DD
very tight code distribution of 1 LSB with the majority of codes
appearing in one output pin.
Figure 26 and Figure 27 show typical FFT plots for the ADuC832.
These plots were generated using an external clock input. The
ADC is using its internal reference (2.5 V) sampling a full-scale,
10 kHz sine wave test tone input at a sampling rate of 149.79 kHz.
The resultant FFTs shown at 5 V and 3 V supplies illustrate an
excellent 100 dB noise floor, 71 dB or greater signal-to-noise
ratio (SNR), and THD greater than −80 dB.
Figure 28 and Figure 29 show typical dynamic performance vs.
external reference voltages. Again, excellent ac performance can
be observed in both plots with some roll-off being observed as
V
falls below 1 V.
REF
Figure 30 shows typical dynamic performance vs. sampling
frequency. SNR levels of 71 dB are obtained across the sampling
range of the ADuC832.
Figure 31 shows the voltage output of the on-chip temperature
sensor vs. temperature. Although the initial voltage output at
25°C can vary from part to part, the resulting slope of −2 mV/°C is
constant across all parts.
Rev. A | Page 30 of 92

ADuC832
MEMORY ORGANIZATION
The ADuC832 contains four different memory blocks:
• 62 kB of on-chip Flash/EE program memory
• 4 kB of on-chip Flash/EE data memory
• 256 bytes of general-purpose RAM
• 2 kB of internal XRAM
FLASH/EE PROGRAM MEMORY
The ADuC832 provides 62 kB of Flash/EE program memory to
run user code. The user can choose to run code from this
internal memory or from an external program memory.
EA
If the user applies power or resets the device while the
pin
is pulled low, the part executes code from the external program
space; otherwise, the part defaults to code execution from its internal 62 kB of Flash/EE program memory. Unlike the ADuC812,
where code execution can overflow from the internal code space to
external code space once the PC becomes greater than 1FFFH,
the ADuC832 does not support the rollover from F7FFH in
internal code space to F800H in external code space. Instead,
the 2048 bytes between F800H and FFFFH appear as NOP
instructions to user code.
This internal code space can be downloaded via the UART
serial port while the device is in-circuit. During runtime, 56 kB
of the program memory can be reprogrammed; thus the code
space can be upgraded in the field using a user defined protocol, or it can be used as a data memory (for more details, see
the Using the Flash/EE Program Memory section).
FLASH/EE DATA MEMORY
4 kB of Flash/EE data memory are available to the user and can
be accessed indirectly via a group of control registers mapped
into the Special Function Register (SFR) area. Access to the
Flash/EE data memory is discussed in detail in the Using the
Flash/EE Data Memory section.
GENERAL-PURPOSE RAM
The general-purpose RAM is divided into two separate memories, the upper and the lower 128 bytes of RAM. The lower
128 bytes of RAM can be accessed through direct or indirect
addressing. The upper 128 bytes of RAM can only be accessed
through indirect addressing because it shares the same address
space as the SFR space, which can only be accessed through
direct addressing.
The lower 128 bytes of internal data memory are mapped as shown
in Figure 32. The lowest 32 bytes are grouped into four banks of
eight registers addressed as R0 through R7. The next 16 bytes
(128 bits), above the register banks, form a block of bit addressable
memory space at Address 20H through Address 2FH. The stack
can be located anywhere in the internal memory address space,
and the stack depth can be expanded up to 2048 bytes.
A reset initializes the stack pointer to Location 07H and increments it once before loading the stack to start from Location
08H, which is also the first register (R0) of Register Bank 1.
Thus, if using more than one register bank, the stack pointer
should be initialized to an area of RAM not used for data
storage.
7FH
GENERAL-PURPOSE
AREA
30H
2FH
BANKS
SELECTED
VIA
BITS IN PSW
20H
11
18H
10
10H
01
08H
00
00H
Figure 32. Lower 128 Bytes of Internal Data Memory
BIT-ADDRESSABLE
(BIT ADDRESSES)
1FH
17H
FOUR BANKS OF EI G HT
REGISTERS
0FH
R0 TO R7
07H
RESET VALUE OF
STACK POINTER
02987-021
The ADuC832 contains 2048 bytes of internal XRAM,
1792 bytes of which can be configured to be used as an
extended 11-bit stack pointer.
By default, the stack operates exactly like an 8052 in that it rolls
over from FFH to 00H in the general-purpose RAM. On the
ADuC832, however, it is possible (by setting CFG832[7]) to
enable the 11-bit extended stack pointer. In this case, the stack
rolls over from 00FFH in RAM to 0100H in XRAM.
The 11-bit stack pointer is visible in the SP and SPH SFRs. The
SP SFR is located at 81H as with a standard 8052. The SPH SFR
is located at B7H. The three LSBs of this SFR contain the three
extra bits necessary to extend the 8-bit stack pointer into an
11-bit stack pointer.
07FFH
UPPER 1792
BYTES OF
ON-CHIP XRAM
(DATA + STACK
FOR EXSP = 1,
DATA ONLY
FOR EXSP = 0)
CFG832[7] = 0
FFH
00H
Figure 33. Extended Stack Pointer Operation
CFG832[7] = 1
256 BYTES OF
ON-CHIP DATA
RAM
(DATA +
STACK)
100H
00H
LOWER 256
BYTES OF
ON-CHIP XRAM
(DATA ONLY)
02987-022
Rev. A | Page 31 of 92

ADuC832
EXTERNAL DATA MEMORY (EXTERNAL XRAM)
Similar to a standard 8051-compatible core, the ADuC832 can
access external data memory using a MOVX instruction. The
MOVX instruction automatically outputs the various control
strobes required to access the data memory.
The ADuC832, however, can access up to 16 MB of external
data memory. This is an enhancement of the 64 kB external data
memory space available on a standard 8051-compatible core.
The external data memory is discussed in more detail in the
ADuC832 Hardware Design Considerations section.
INTERNAL XRAM
There are 2 kB of on-chip data memory on the ADuC832. This
memory, although on chip, is also accessed via the MOVX instruction. The 2 kB of internal XRAM are mapped into the bottom
2 kB of the external address space if CFG832[0] is set. Otherwise,
access to the external data memory occurs similar to a standard
8051. When using the internal XRAM, Port 0 and Port 2 are
free to be used as general-purpose I/Os.
FFFFFFH
000000H
EXTERNAL
DATA
MEMORY
SPACE
(24-BIT
ADDRESS
SPACE)
CFG832[0] = 0
FFFFFFH
000800H
0007FFH
000000H
EXTERNAL
DATA
MEMORY
SPACE
(24-BIT
ADDRESS
SPACE)
2 kB
ON-CHIP
XRAM
CFG832[0] = 1
02987-023
Figure 34. Internal and External XRAM
Rev. A | Page 32 of 92

ADuC832
SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS (SFRS)
The SFR space is mapped into the upper 128 bytes of internal
data memory space and accessed by direct addressing only.
It provides an interface between the CPU and all on-chip peripherals. A block diagram showing the programming model of the
ADuC832 via the SFR area is shown in Figure 35.
All registers, except the program counter (PC) and the four
general-purpose register banks, reside in the SFR area. The SFR
registers include control, configuration, and data registers that
provide an interface between the CPU and all on-chip peripherals.
4-kB
62-kB
ELECTRICALLY
REPROGRAMMABLE
NONVOLATILE
FLASH/EE PROGRAM
MEMORY
8051-
COMPATIBLE
CORE
2304 BYTES
RAM
128-BYTE
SPECIAL
FUNCTION
REGISTER
AREA
Figure 35. Programming Model
ELECTRICALLY
REPROGRAMMABLE
NONVOLATILE
FLASH/EE DAT A
MEMORY
8-CHANNEL
12-BIT ADC
OTHER ON-CHI P
PERIPHERALS
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
2
12-BIT DACs
SERIAL I/ O
WDT
PSM
TIC
PWM
02987-024
ACCUMULATOR SFR (ACC)
ACC is the accumulator register and is used for math operations
including addition, subtraction, integer multiplication and
division, and Boolean bit manipulations. The mnemonics for
accumulator-specific instructions refer to the accumulator as A.
B SFR (B)
The B register is used with the ACC for multiplication and
division operations. For other instructions, it can be treated
as a general-purpose scratch pad register.
used to provide memory addresses for internal and external
code access and external data access. It can be manipulated as a
16-bit register (DPTR = DPH, DPL), although INC DPTR
instructions automatically carry over to DPP, or as three
independent 8-bit registers (DPP, DPH, and DPL).
The ADuC832 supports dual data pointers. Refer to the Dual
Data Pointers section.
PROGRAM STATUS WORD (PSW)
SFR Address: D0H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
The PSW SFR contains several bits reflecting the current status
of the CPU, as detailed in Table 1 4.
Table 14. PSW SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] CY Carry flag
[6] AC Auxiliary carry flag
[5] F0 General-purpose flag
[4:3] RS[1:0] Register bank select bits
RS1 RS0 Selected Bank
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 2
1 1 3
[2] OV Overflow flag
[1] F1 General-purpose flag
[0] P Parity bit
POWER CONTROL SFR (PCON)
SFR Address: 87H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
STACK POINTER (SP AND SPH)
The SP SFR is the stack pointer and is used to hold an internal
RAM address that is called the top of the stack. The SP register
is incremented before data is stored during push and call
executions. While the stack may reside anywhere in on-chip
RAM, the SP register is initialized to 07H after a reset. This
causes the stack to begin at Location 08H.
As mentioned previously, the ADuC832 offers an extended
11-bit stack pointer. The three extra bits to make up the 11-bit
stack pointer are the three LSBs of the SPH byte located at B7H.
DATA POINTER (DPTR)
The data pointer is made up of three 8-bit registers, named DPP
(page byte), DPH (high byte), and DPL (low byte). These are
Rev. A | Page 33 of 92
The PCON SFR contains bits for power-saving options and
general-purpose status flags, as shown in Ta b le 1 5.
Table 15. PCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] SMOD Double UART baud rate
[6] SERIPD I2C/SPI power-down interrupt enable
INT0
[5] INT0PD
power-down interrupt enable
[4] ALEOFF Disable ALE output
[3] GF1 General-purpose flag bit
[2] GF0 General-purpose flag bit
[1] PD Power-down mode enable
[0] IDL Idle mode enable

ADuC832
SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
All registers except the program counter and the four generalpurpose register banks reside in the special function register
(SFR) area. The SFR registers include control, configuration,
and data registers that provide an interface between the CPU
and other on-chip peripherals.
Figure 36 shows a full SFR memory map and SFR contents on
reset. Unoccupied SFR locations are shown dark-shaded in
Figure 36 (labeled not used). Unoccupied locations in the SFR
address space are not implemented, that is, no register exists at
ISPI
WCOL
SPE
SPIM
CPOL
CPHA
SPR1
SPR0
FFH
0
FEH 0
FDH 0
FCH 0
FBH 0
FAH
F9H 0
1
F7H 0 F6H 0 F5H 0 F4H 0 F3H 0 F2H F1H 0 F0H 0
MCO
MDI
MDO
EFH
0
EEH 0
EDH 0 ECH 0 EBH 0 EAH E9H 0 E8H 0
E7H 0 E6H 0 E5H 0 E4H 0 E3H 0 E2H E1H 0 E0H 0
DMA CCONV SCONV CS3 CS2 CS1 CS0
ADCI
DFH
DEH0DDH0DCH0DBH0DAH D9H0D8H
0
CY
D7H 0ACD6H 0F0D5H 0
TF2
EXF2
CEH 0
PRE2
C6H 0
PADC
BEH 0
EADC
AEH
00
SM1
9EH 0
TR1
8EH 0
RCLK
CDH 0
PRE1
C5H 0 C4H 1
PT2
BDH 0PSBCH 0
ET2
ADHESACH
SM2
9DH 0
TF0
8DH 0
CFH 0
PRE3
C7H 0
BFH 0
RD
B7H 1WRB6H 1T1B5H 1T0B4H 1
EA
AFH
0
A7H A6H A5H 111 A4H 1 A3H 1 A2H A1H 1 A0H 1
SM0
9FH 0
97H 1 96H 1 95H 1 94H 1 93H 1 92H
TF1
8FH 0
87H 1 86H 1 85H 1 84H 1 83H 1 82H 81H 1 80H 1
I2CMMDE
RS1
RS0
D4H 0
D3H 0OVD2HF1D1H 0PD0H 0
TCLK
EXEN2
CCH 0
CBH 0
PRE0
WDIR
C3H 0
PT1
BBH 0
INT1
B3H 1
ET1
ABH
REN
TR0
TB8
9BH 0
IE1
8BH 0
9CH 0
8CH 0
0
I2CTX
I2CRS
0
0
0
0
TR2
CNT2
0
CAH
C9H 0
WDS
WDE
0
C2H
C1H 0
PX1
PT0
0
BAH
B9H 0
INT0
TxD
B2H
B1H 1
1
EX1
ET0
AAH
A9H
000
1
RB8
0
9AHTI99H 0RI98H 0
T2EX
1
91H 1T290H 1
IT1
IE0
0
8AH
89H 0
1
F8H
I2CI
CAP2
C8H 0
WDWR
C0H 0
PX0
B8H 0
RxD
B0H 1
EX0
A8H 00
IT0
88H 0
BITS
0
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
0
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
BITS
SPICON
F8H
F0H 00H
I2CCON
E8H
ACC
E0H
ADCCON2
D8H DAH 00H
PSW
D0H
T2CON
C8H 00H
WDCON
C0H
B8H 00H B9H 00H
P3
B0H
A8H A0HA9H00H
P2
A0H A4H 00H A5H 00H A6H 00H A7H 00H
SCON1SBUF I2CDAT
98H 9BH 55H9AH 00H99H 00H00H
P1
90H FFH
TCON1TMOD TL0 TL1 TH0 TH1
88H 8CH 00H 8DH
P0
80H
that location. If an unoccupied location is read, an unspecified
value is returned. SFR locations reserved for on-chip testing are
shown lighter shaded in Figure 36 (labeled reserved) and should
not be accessed by user software. Sixteen of the SFR locations
are also bit addressable and denoted by Footnote 1 in Figure 36,
that is, the bit addressable SFRs are those whose address ends in
0H or 8H.
1
DAC0L
04H
F9H
1
ADCOFSL
B
F1H
1
00H
1
00H
1
ADCDATAL ADCDATAH
00H D9H 00H
1
00H
1
RESERVED
1
RESERVED
10H
1
IP
ECON EDATA1 EDATA2
1
PWM0L PWM0H PWM1L
FFH
B1H
1
IE
IEIP2
1
TIMECON HTHSEC SEC MIN HOUR DPCON
1, 2
1
FFH
DAC0H DAC1L DAC1H DACCON
FAH 00H00H
3
ADCOFSH3ADCGAINL3ADCGAINH3ADCCON3
00H
D2H
RCAP2L
CAH 00H
FBH 00H
F3H 00HF2H 20H
DMAL DMAH
00H D3H 00H D4H
RCAP2H
CBH
DMAP
TL2
00H 00H 00H
CCH
CHIPID
C2H 2XH
RESERVEDRESERVED
PWM1H
00H
A3H 00HA2H 00HA1H 00HFFH
I2CADD
00H 00H
B4H
NOT USED
B3H
00H
B2H
SP DPL DPH DPP
84H 00H 87H 00H83H 00H82H 00H81H 07H
FDH 04HFCH 00H
F5H
RESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVED
RESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVED
RESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVED
RESERVEDRESERVED
00H
TH2
CDH
RESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVED
BDH
RESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVEDRESERVED
T3FD
9DH 9EH
NOT USEDNO T USEDNOT USEDNO T USEDNOT USED
RESERVED
RESERVED
00HF4H 00H
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
EADRL
EDATA3 EDATA4
00HBCH 00H
NOT USEDNOT USED
PWMCON
AEH 00H
INTVAL
T3CON
00H 00H
NOT USED
00H8BH 00H8AH 00H89H 00H00H
RESERVEDRESERVED
00HC6H
RESERVED
SPIDAT
F7H 00H
ADCCON1
00H
EFH
RESERVED
PSMCON
DFH DEH
PLLCON
D7H
53H
RESERVED
EADRH
00HC7H
00HBFH00HBEH
SPH
00H
B7H
CFG832
AFH 00H
NOT USED
NOT USED
RESERVEDRESERVED
PCON
SFR MAP KEY:
MNEMONIC
SFR ADDRESS
DEFAULT VALUE
1
SFRs WHOSE ADDRESS ENDS IN 0H OR 8H ARE BIT ADDRESSABLE.
2
THE PRIMARY FUNCTION OF PORT1 IS AS AN ANALOG INPUT PORT; THEREFORE, TO ENABLE THE DIGITAL SECONDARY FUNCTIONS ON THESE
PORT PINS, WRITE A 0 TO THE CORRESPONDING PORT 1 SFR BIT.
3
CALIBRATION COEFFICIENTS ARE PRECONFIGURED ON POWER-UP TO FACTORY CALIBRATED VALUES.
THESE BITS ARE CONTAINED IN THIS BYTE.
IE0
89H 0
IT0
88H 0
TCON
88H 00H
MNEMONIC
DEFAULT VALUE
SFR ADDRESS
Figure 36. Special Function Register Locations and Reset Values
Rev. A | Page 34 of 92
2987-025

ADuC832
ADC CIRCUIT INFORMATION
GENERAL OVERVIEW
The ADC conversion block incorporates a fast, 8-channel,
12-bit, single-supply ADC. This block provides the user with
multichannel mux, track/hold, on-chip reference, calibration
features, and an ADC. All components in this block are easily
configured via a three-register SFR interface.
The ADC consists of a conventional successive approximation
converter based around a capacitor DAC. The converter accepts
an analog input range of 0 V to V
and factory calibrated 2.5 V reference is provided on-chip. An
external reference can be connected as described in the Vo lt a g e
Reference Connections section. This external reference can be
in the range of 1 V to AV
DD
.
Single step or continuous conversion modes can be initiated in
software or alternatively by applying a convert signal to an
external pin. Timer 2 can also be configured to generate a
repetitive trigger for ADC conversions. The ADC can be
configured to operate in a DMA mode whereby the ADC block
continuously converts and captures samples to an external
RAM space without any interaction from the MCU core. This
automatic capture facility can extend through a 16 MB external
data memory space.
The ADuC832 is shipped with factory programmed calibration
coefficients that are automatically downloaded to the ADC on
power-up, ensuring optimum ADC performance. The ADC
core contains internal offset and gain calibration registers that
can be hardware calibrated to minimize system errors.
A voltage output from an on-chip band gap reference proportional to absolute temperature can also be routed through the
front-end ADC multiplexer (effectively a ninth ADC channel
input) facilitating a temperature sensor implementation.
. A high precision, low drift,
REF
ADC TRANSFER FUNCTION
The analog input range for the ADC is 0 V to V
the designed code transitions occur midway between successive
integer LSB values (that is, 1/2 LSB, 3/2 LSBs, 5/2 LSBs…FS −
3/2 LSBs). The output coding is straight binary with 1 LSB =
FS/4096 or 2.5 V/4096 = 0.61 mV when V
input/output transfer characteristic for the 0 V to V
shown in Figure 37.
OUTPUT
CODE
111...111
111...110
111...101
111...100
000...011
000...010
000...001
000...000
0V 1LSB
FS
1LSB =
4096
VOLTAGE INPUT
Figure 37. ADC Transfer Function
. For this range,
REF
= 2.5 V. The ideal
REF
range is
REF
+FS
–1LSB
02987-026
TYPICAL OPERATION
Once configured via the ADCCON1 to ADCCON3 SFRs, the
ADC converts the analog input and provides an ADC 12-bit
result word in the ADCDATAH/ADCDATAHL SFRs. The top
four bits of the ADCDATAH SFR are written with the channel
selection bits to identify the channel result. The format of the ADC
12-bit result word is shown in Figure 38.
ADCDATAH SFR
CH–ID
TOP 4 BITS
HIGH 4 BITS OF
ADC RESULT WO RD
ADCDATAL SFR
Rev. A | Page 35 of 92
LOW 8 BITS OF THE
ADC RESULT WORD
Figure 38. ADC Result Format
02987-027

ADuC832
ADCCON1 (ADC Control SFR 1)
SFR Address: EFH
SFR Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Table 16. ADCCON1 SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] MD1
[6] EXT_REF Set by the user to select an external reference. Cleared by the user to use the internal reference.
[5] CK1 The ADC clock divide bits (CK1, CK0) select the divide ratio for the PLL master clock used to generate the
[4] CK0
0 0 8
0 1 4
1 0 16
1 1 32
[3:2] AQ[1:0]
0 0 1
0 1 2
1 0 3
1 1 4
[1] T2C
[0] EXC
The mode bit selects the active operating mode of the ADC. Set by the user to power up the ADC. Cleared by the user
to power down the ADC.
ADC clock. To ensure correct ADC operation, the divider ratio must be chosen to reduce the ADC clock to ≤4.5 MHz. A
typical ADC conversion requires 17 ADC clocks. The divider ratio is selected as follows:
CK1 CK0 MCLK Divider
The ADC acquisition select bits (AQ1, AQ0) select the time provided for the input track-and-hold amplifier to acquire
the input signal. An acquisition of three or more ADC clocks is recommended; clocks are selected as follows:
AQ1 AQ0 Number of ADC Clocks
The Timer 2 conversion bit (T2C) is set by the user to enable the Timer 2 overflow bit to be used as the ADC convert
start trigger input.
The external trigger enable bit (EXC) is set by the user to allow the external Pin P3.5/T1/CONVST to be used as the
active low convert start input. This input should be an active low pulse (minimum pulse width >100 ns) at the required
sample rate.
The ADCCON1 register controls conversion and acquisition
times, hardware conversion modes, and power-down modes as
detailed in Tab le 1 6.
Rev. A | Page 36 of 92

ADuC832
ADCCON2 (ADC Control SFR 2)
SFR Address: D8H
SFR Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Table 17. ADCCON2 SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] ADCI
[6] DMA
[5] CCONV
[4] SCONV
[3:0] CS[3:0]
1 0 0 1 DAC0 (only use with internal DAC output buffer on)
1 0 1 0 DAC1 (only use with internal DAC output buffer on)
1 0 1 1 AGND
1 1 0 0 V
1 1 1 1
All other combinations reserved
The ADC interrupt bit (ADCI) is set by hardware at the end of a single ADC conversion cycle or at the end of a DMA block
conversion. ADCI is cleared by hardware when the PC vectors to the ADC interrupt service routine. Otherwise, the ADCI bit
should be cleared by user code.
The DMA mode enable bit (DMA) is set by the user to enable a preconfigured ADC DMA mode of operation. A more
detailed description of this mode is given in the ADC DMA Mode section. The DMA bit is automatically cleared to 0 at the
end of a DMA cycle. Setting this bit causes the ALE output to cease, starting again when DMA is started, and operates
correctly after DMA is complete.
The continuous conversion bit (CCONV) is set by the user to initiate the ADC into a continuous mode of conversion. In this
mode, the ADC starts converting based on the timing and channel configuration already set up in the ADCCONx SFRs; the
ADC automatically starts another conversion once a previous conversion has completed.
The single conversion bit (SCONV) is set to initiate a single conversion cycle. The SCONV bit is automatically reset to 0 on
completion of the single conversion cycle.
The channel selection bits (CS[3:0] allow the user to program the ADC channel selection under software control. When a
conversion is initiated, the channel converted is the one selected by these channel selection bits. In DMA mode, the
channel selection is derived from the channel ID written to the external memory.
CS3 CS2 CS1 CS0 Channel Number
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 2
0 0 1 1 3
0 1 0 0 4
0 1 0 1 5
0 1 1 0 6
0 1 1 1 7
1 0 0 0 Temperature sensor (requires minimum of 1 s to acquire)
REF
DMA stop (place in XRAM location to finish DMA sequence, see the ADC DMA
Mode section)
The ADCCON2 register controls ADC channel selection and
conversion modes as detailed in Tab l e 1 7 .
Rev. A | Page 37 of 92

ADuC832
ADCCON3 (ADC Control SFR 3)
SFR Address: F5H
SFR Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Table 18. ADCCON3 SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Busy
[6] GNCLD Gain calibration disable bit. Set to 0 to enable gain calibration. Set to 1 to disable gain calibration.
[5:4] AVGS[1:0] Number of averages selection bits. These bits select the number of ADC readings averaged during a calibration cycle.
[3] RSVD Reserved. This bit should always be written as 0.
[2] RSVD This bit should always be written as 1 by the user when performing calibration.
[1] Typical Calibration type select bit. This bit selects between offset (zero-scale) and gain (full-scale) calibration.
Set to 0 for offset calibration.
Set to 1 for gain calibration.
[0] SCAL
The ADC busy status bit is a read-only status bit that is set during a valid ADC conversion or calibration cycle. Busy is
automatically cleared by the core at the end of conversion or calibration.
AVGS1 AVGS0 Number of Averages
0 0 15
0 1 1
1 0 31
1 1 63
Start calibration cycle bit. When set, this bit starts the selected calibration cycle. It is automatically cleared when the
calibration cycle is completed.
The ADCCON3 register controls the operation of various
calibration modes as well as giving an indication of ADC busy
status.
Rev. A | Page 38 of 92

ADuC832
A
DRIVING THE ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
The ADC incorporates a successive approximation (SAR) architecture involving a charge-sampled input stage. Figure 39 shows
the equivalent circuit of the analog input section. Each ADC
conversion is divided into two distinct phases as defined by the
position of the switches in Figure 39. During the sampling
phase (with SW1 and SW2 in the track position), a charge
proportional to the voltage on the analog input is developed
across the input sampling capacitor. During the conversion
phase (with both switches in the hold position) the capacitor
DAC is adjusted via internal SAR logic until the voltage on
Node A is 0, indicating that the sampled charge on the input
capacitor is balanced out by the charge being output by the
capacitor DAC. The digital value finally contained in the SAR
is then latched out as the result of the ADC conversion. Control
of the SAR, and timing of acquisition and sampling modes, is
handled automatically by built-in ADC control logic. Acquisition and conversion times are also fully configurable under user
control.
SW1TRACK
32pF
NODE A
TRACK
ADuC832
SW2
HOLD
CAPACITOR
DAC
COMPARATOR
V
REF
AGND
DAC1
DAC0
TEMPERATURE S ENSOR
ADC7
200Ω
ADC0
HOLD
200Ω
GND
Figure 39. Internal ADC Structure
Note that whenever a new input channel is selected, a residual
charge from the 32 pF sampling capacitor places a transient on
the newly selected input. The signal source must be capable of
recovering from this transient before the sampling switches are
changed to hold mode. Delays can be inserted in software
(between channel selection and conversion request) to account
for input stage settling, but a hardware solution alleviates this
burden from the software design task and ultimately results in a
cleaner system implementation. One hardware solution would
be to choose a very fast settling op amp to drive each analog
input. Such an op amp would need to fully settle from a small
signal transient in less than 300 ns to guarantee adequate
settling under all software configurations. A better solution,
recommended for use with any amplifier, is shown in Figure 40.
02987-028
Though the circuit in Figure 40 may look like a simple
antialiasing filter, it actually serves no such purpose because its
corner frequency is well above the Nyquist frequency, even at a
200 kHz sample rate. Though the R/C does help to reject some
incoming high frequency noise, its primary function is to ensure
that the transient demands of the ADC input stage are met.
ADuC832
10Ω
0.1µF
Figure 40. Buffering Analog Inputs
ADC0
2987-029
It does so by providing a capacitive bank from which the 32 pF
sampling capacitor can draw its charge. Its voltage does not
change by more than one count (1/4096) of the 12-bit transfer
function when the 32 pF charge from a previous channel is
dumped onto it. A larger capacitor can be used if desired, but
not a larger resistor, for the following reasons.
The Schottky diodes in Figure 40 may be necessary to limit
the voltage applied to the analog input pin as per the absolute
maximum ratings (see Tabl e 12). They are not necessary if the
op amp is powered from the same supply as the ADuC832
because in that case the op amp is unable to generate voltages
above V
or below ground. An op amp of some kind is neces-
DD
sary unless the signal source is very low impedance to begin
with. DC leakage currents at the ADuC832 analog inputs can
cause measurable dc errors with external source impedances as
little as ~100 Ω. To ensure accurate ADC operation, keep the
total source impedance at each analog input less than 61 Ω.
Tabl e 19 illustrates examples of how source impedance can
affect dc accuracy.
Table 19. Source Impedance Examples
Source
Impedance
Error from 1 A
Leakage Current
Error from 10 A
Leakage Current
61 Ω 61 V = 0.1 LSB 610 V = 1 LSB
610 Ω 610 V = 1 LSB 6.1 mV = 10 LSB
Although Figure 40 shows the op amp operating at a gain of 1, it
can be configured for any gain needed. Also, an instrumentation
amplifier can be easily used in its place to condition differential
signals. Use any modern amplifier that is capable of delivering
the signal (0 V to V
) with minimal saturation. Some single-
REF
supply rail-to-rail op amps that are useful for this purpose
include, but are not limited to, the ones given in Tab le 2 0 . Visit
www.analog.com for details on these and other op amps and
instrumentation amps.
Rev. A | Page 39 of 92

ADuC832
Table 20. Some Single-Supply Op Amps
Op Amp Model Characteristics
OP281/OP481 Micropower
OP191/OP291/OP491 I/O Good up to VDD, low cost
OP196/OP296/OP496 I/O to VDD, micropower, low cost
OP183/OP249 High gain-bandwidth product (GBP)
OP162/OP262/OP462 High GBP, micro package
AD820/AD822/AD824 FET input, low cost
AD823 FET input, high GBP
Keep in mind that the ADC’s transfer function is 0 V to V
REF
,
and any signal range lost to amplifier saturation near ground
impacts dynamic range. Though the op amps in Ta b le 2 0 are
capable of delivering output signals very closely approaching
ground, no amplifier can deliver signals all the way to ground
when powered by a single supply. Therefore, if a negative supply
is available, consider using it to power the front-end amplifiers.
However, be sure to include the Schottky diodes shown in
Figure 40 (or at least the lower of the two diodes) to protect the
analog input from undervoltage conditions. In summary, use the
circuit of Figure 40 to drive the analog input ADCx pins of the
ADuC832.
VOLTAGE REFERENCE CONNECTIONS
The on-chip 2.5 V band gap voltage reference can be used as
the reference source for the ADC and DACs. To ensure the
accuracy of the voltage reference, the user must decouple the
V
pin to ground with a 0.1 µF capacitor, and the C
REF
ground with a 0.1 µF capacitor, as shown in Figure 41.
ADuC832
2.5V
BAND GAP
REFERENCE
and C
REF
REF
BUFFER
51Ω
V
REF
0.1µF
C
REF
0.1µF
Figure 41. Decoupling V
BUFFER
If the internal voltage reference is to be used as a reference for
external circuitry, the C
output should be used. However, a
REF
buffer must be used in this case to ensure that no current is
drawn from the C
pin itself. The voltage on the C
REF
that of an internal node within the buffer block, and its voltage
is critical to ADC and DAC accuracy. On the ADuC812, V
the recommended output for the external reference; this can be
used but note that there is a gain error between this reference
and that of the ADC.
REF
REF
pin to
pin is
REF
2987-030
is
The ADuC832 powers up with its internal voltage reference in
the on state. This is available at the V
pin, but as noted
REF
previously, there is a gain error between this and that of the
ADC. The C
output becomes available when the ADC is
REF
powered up.
If an external voltage reference is preferred, it should be connected to the V
REF
and C
pins as shown in Figure 42. Bit 6 of
REF
the ADCCON1 SFR must be set to 1 to switch in the external
reference voltage.
To ensure accurate ADC operation, the voltage applied to V
must be between 1 V and AV
. In situations where analog
DD
REF
input signals are proportional to the power supply (such as
some strain gage applications), it may be desirable to connect
the C
REF
and V
pins directly to AVDD.
REF
Operation of the ADC or DACs with a reference voltage below
1 V, however, may incur loss of accuracy, eventually resulting in
missing codes or nonmonotonicity. For that reason, do not use
a reference voltage less than 1 V.
ADuC832
V
DD
EXTERNAL
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
V
REF
0.1µF
C
REF
0.1µF
Figure 42. Using an External Voltage Reference
51Ω
0 = INTERNAL
1 = EXTERNAL
2.5V
BAND GAP
REFERENCE
ADCCON1[6]
BUFFER
2987-031
To maintain compatibility with the ADuC812, the external
reference can also be connected to the V
pin, as shown in
REF
Figure 43, to overdrive the internal reference. Note that this
introduces a gain error for the ADC that has to be calibrated
out; thus the previous method is the recommended one for
most users. For this method to work, ADCCON1[6] should be
configured to use the internal reference. The external reference
then overdrives this.
Rev. A | Page 40 of 92

ADuC832
ADuC832
2.5V
BAND GAP
REFERENCE
02987-032
V
DD
EXTERNAL
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
51Ω
V
REF
0.1µF
C
REF
0.1µF
Figure 43. Using an External Voltage Reference
BUFFER
8
7
CONFIGURING THE ADC
The ADuC832’s successive approximation ADC is driven by a
divided down version of the master clock. To ensure adequate
ADC operation, this ADC clock must be between 400 kHz and
6 MHz, and optimum performance is obtained with ADC clock
between 400 kHz and 4.5 MHz. Frequencies within this range
can easily be achieved with master clock frequencies from 400 kHz
to well above 16 MHz with the four ADC clock divide ratios to
choose from. For example, set the ADC clock divide ratio to 4
(that is, ADCCLK = 16.78 MHz/8 = 2 MHz) by setting the
appropriate bits in ADCCON1 (ADCCON1[5:4] = 00).
The total ADC conversion time is 15 ADC clocks, plus 1 ADC
clock for synchronization, plus the selected acquisition time
(one, two, three, or four ADC clocks). For the preceding example,
with a three-clock acquisition time, total conversion time is
19 ADC clocks (or 9.05 sec for a 2 MHz ADC clock).
In continuous conversion mode, a new conversion begins each
time the previous one finishes. The sample rate is then simply
the inverse of the total conversion time previously described. In
the preceding example, the continuous conversion mode sample
rate would be 110.3 kHz.
If using the temperature sensor as the ADC input, the ADC
should be configured to use an ADCCLK of MCLK/32 and four
acquisition clocks.
Increasing the conversion time on the temperature sensor channel
improves the accuracy of the reading. To further improve the
accuracy, an external reference with low temperature drift
should also be used.
ADC DMA MODE
The on-chip ADC is designed to run at a maximum conversion
speed of 4 µs (247 kSPS sampling rate). When converting at this
rate, the ADuC832 MicroConverter® has 4 µs to read the ADC
result and store the result in memory for further postprocessing;
otherwise, the next ADC sample may be lost. In an interrupt
driven routine, the MicroConverter also has to jump to the ADC
interrupt service routine, which also increases the time required
to store the ADC results. In applications where the ADuC832
Rev. A | Page 41 of 92
cannot sustain the interrupt rate, an ADC DMA mode is
provided.
To enable DMA mode, Bit 6 in ADCCON2 (DMA) must be set.
This allows the ADC results to be written directly to a 16 MB
external static memory SRAM (mapped into data memory
space) without any interaction from the ADuC832 core. This
mode allows the ADuC832 to capture a contiguous sample
stream at full ADC update rates (247 kSPS).
A Typical DMA Mode Configuration Example
To set the ADuC832 into DMA mode, a number of steps must
be followed:
1. The ADC must be powered down. This is done by ensuring
MD1 is set to 0 in ADCCON1.
2. The DMA address pointer must be set to the start address
of where the ADC results are to be written. This is done by
writing to the DMA mode address pointers DMAL, DMAH,
and DMAP. DMAL must be written to first, followed by
DMAH, and then by DMAP.
3. The external memory must be preconfigured. This consists
of writing the required ADC channel IDs into the top four
bits of every second memory location in the external SRAM,
starting at the first address specified by the DMA address
pointer. Because the ADC DMA mode operates independent from the ADuC832 core, it is necessary to provide it
with a stop command. This is done by duplicating the last
channel ID to be converted, followed by 1111 into the next
channel selection field. A typical preconfiguration of
external memory is as follows:
00000AH
000000H
11111
1100
1100
000
010
0010
Figure 44. Typical DMA External Memory Preconfiguration
1
STOP COMM AND
REPEAT LAST CHANNEL
FOR A VALID STOP
CONDITION
CONVERT ADC CH 3
CONVERT TEMP SENSOR
CONVERT ADC CH 5
CONVERT AD
C CH 2
4. Initiate the DMA by writing to the ADC SFRs in the
following sequence:
a. ADCCON2 is written to enable the DMA mode, that
is, MOV ADCCON2, #40H; DMA mode enabled.
b. ADCCON1 is written to configure the conversion
time and power-up of the ADC. It can also enable
Timer 2 driven conversions or external triggered
conversions if required.
c. ADC conversions are initiated. This is done by
starting single conversions, starting Timer 2, running
for Timer 2 conversions, or receiving an external
trigger.
02987-033

ADuC832
When the DMA conversions are completed, the ADC interrupt
bit, ADCI, is set by hardware and the external SRAM contains
the new ADC conversion results as shown in Figure 45. Note
that no result is written to the last two memory locations.
When the DMA mode logic is active, it takes the responsibility
of storing the ADC results away from both the user and ADuC832
core logic. As it writes the results of the ADC conversions to
external memory, it takes over the external memory interface
from the core. Thus, any core instructions that access the external
memory while DMA mode is enabled do not gain access to it.
The core executes the instructions, which take the same time to
execute, but do not gain access to the external memory.
00000AH
000000H
Figure 45. Typical External Memory Configuration Post-ADC DMA Operation
11111
1100
1100
000
010
0010
1
STOP COMMAND
NO CONVERSION
RESULT WRITTEN HERE
CONVERSION RESULT
FOR ADC CH 3
CONVERSION RESULT
FOR TEMP SENSOR
CONVERSION RESULT
FOR ADC CH 5
CONVERS ION RESULT
FOR ADC CH 2
The DMA logic operates from the ADC clock and uses pipelining to perform the ADC conversions and to access the external
memory at the same time. The time it takes to perform one
ADC conversion is called a DMA cycle. The actions performed
by the logic during a typical DMA cycle are shown in Figure 46.
CONVERT CHANNEL RE AD DURI NG PREVIOUS DMA CYCLE
WRITE ADC RESULT
CONVERTED DURING
PREVIOUS DMA CY CL E
Figure 46. DMA Cycle
DMA CYCLE
READ CHANNEL ID
TO BE CONVE RT E D DURING
NEXT DMA CYCLE
02987-035
From Figure 46, it can be seen that during one DMA cycle, the
following actions are performed by the DMA logic:
• An ADC conversion is performed on the channel whose
ID was read during the previous cycle.
• The 12-bit result and the channel ID of the conversion
performed in the previous cycle is written to the external
memory.
• The ID of the next channel to be converted is read from
external memory.
For the previous example, the complete flow of events is shown
in Figure 46. Because the DMA logic uses pipelining, it takes
three cycles before the first correct result is written out.
02987-034
MICRO-OPERATION DURING ADC DMA MODE
During ADC DMA mode, the MicroConverter core is free to
continue code execution, including general housekeeping and
communication tasks. However, note that MCU core accesses to
Port 0 and Port 2 (which are being used by the DMA controller)
are gated off during ADC DMA mode of operation. This means
that even though the instruction that accesses the external Port 0 or
Port 2 appears to execute, no data is seen at these external ports
as a result. Note that during DMA to the internally contained
XRAM, Port 0 and Port 2 are available for use.
The only case in which the MCU is able to access XRAM during
DMA is when the internal XRAM is enabled and the section of
RAM to which the DMA ADC results are being written to lies
in an external XRAM. Then the MCU is able to access only the
internal XRAM. This is also the case for use of the extended
stack pointer.
The MicroConverter core can be configured with an interrupt
to be triggered by the DMA controller when it has finished
filling the requested block of RAM with ADC results, allowing
the service routine for this interrupt to postprocess data without
any real-time timing constraints.
ADC OFFSET AND GAIN CALIBRATION COEFFICIENTS
The ADuC832 has two ADC calibration coefficients, one for
offset calibration and one for gain calibration. Both the offset
and gain calibration coefficients are 14-bit words, and are each
stored in two registers located in the special function register
(SFR) area. The offset calibration coefficient is divided into
ADCOFSH (six bits) and ADCOFSL (eight bits) and the gain
calibration coefficient is divided into ADCGAINH (six bits)
and ADCGAINL (eight bits).
The offset calibration coefficient compensates for dc offset
errors in both the ADC and the input signal. Increasing the
offset coefficient compensates for positive offset, and effectively
pushes the ADC transfer function down. Decreasing the offset
coefficient compensates for negative offset, and effectively
pushes the ADC transfer function up. The maximum offset that
can be compensated is typically ±5% of V
typically ±125 mV with a 2.5 V reference.
Similarly, the gain calibration coefficient compensates for dc
gain errors in both the ADC and the input signal. Increasing the
gain coefficient compensates for a smaller analog input signal
range and scales the ADC transfer function up, effectively
increasing the slope of the transfer function. Decreasing the
gain coefficient compensates for a larger analog input signal
range and scales the ADC transfer function down, effectively
decreasing the slope of the transfer function. The maximum
analog input signal range for which the gain coefficient can
compensate is 1.025 × V
0.975 × V
, which equates to typically ±2.5% of the reference
REF
and the minimum input range is
REF
voltage.
, which equates to
REF
Rev. A | Page 42 of 92

ADuC832
CALIBRATING THE ADC
There are two hardware calibration modes provided that can be
easily initiated by user software. The ADCCON3 SFR is used to
calibrate the ADC. The typical bit (ADCCON3[1]) and the CS3
to CS0 bits (ADCCON2[3:0]) set up the calibration modes.
Device calibration can be initiated to compensate for significant
changes in operating conditions frequency, analog input range,
reference voltage, and supply voltages. In this calibration mode,
offset calibration uses the internal AGND selected via ADCCON2
register bits CS[3:0] = 1011, and gain calibration uses the internal
V
selected by CS[3:0] = 1100. Offset calibration should be
REF
executed first, followed by gain calibration.
System calibration can be initiated to compensate for both internal
and external system errors. To perform system calibration using
an external reference, tie system ground and reference to any
two of the six selectable inputs. Enable external reference mode
(ADCCON1[6]). Select the channel connected to AGND via
CS[3:0] and perform system offset calibration. Select the channel
connected to V
The ADC should be configured to use settings for an ADCCLK
of divide-by-16 and divide-by-4 acquisition clocks.
via CS[3:0] and perform system gain calibration.
REF
Rev. A | Page 43 of 92

ADuC832
INITIATING CALIBRATION IN CODE
When calibrating the ADC using ADCCON1, the ADC should
be set up into the configuration in which it will be used. The
ADCCON3 register can then be used to set up the device and
calibrate the ADC offset and gain.
MOV ADCCON1,#0ACH ;ADC on; ADCCLK set
;to divide by 16,4
;acquisition clock
To calibrate device offset:
MOV ADCCON2,#0BH ;select internal AGND
MOV ADCCON3,#25H ;select offset calibration,
;31 averages per bit,
;offset calibration
To c ali bra t e d e vi ce g ain :
MOV ADCCON2,#0CH ;select internal V
REF
MOV ADCCON3,#27H ;select offset calibration,
;31 averages per bit,
;offset calibration
To calibrate system offset:
Connect system AGND to an ADC channel input (0).
MOV ADCCON2,#00H ;select external AGND
MOV ADCCON3,#25H ;select offset calibration ,
;31 averages per bit
To c ali bra t e sy ste m ga i n:
Connect system V
MOV ADCCON2,#01H ;select external V
to an ADC channel input (1).
REF
REF
MOV ADCCON3,#27H ;select offset calibration
;31 averages per bit,
;offset calibration
The calibration cycle time, t
, is calculated by the following
CAL
equation:
t
= 14 × ADCCLK × NUMAV × (16 + t
CAL
For an ADCCLK/f
divide ratio of 16, with t
CORE
)
ACQ
= 4 ADCCLK,
ACQ
and NUMAV = 15, the calibration cycle time is:
t
= 14 × (1/1,048,576) × 15 × (16 + 4)
CAL
t
= 4.2 ms
CAL
In a calibration cycle, the ADC busy flag (ADCCON3[7]),
instead of framing an individual ADC conversion as in normal
mode, goes high at the start of calibration and only returns to 0
at the end of the calibration cycle. It can therefore be monitored
in code to indicate when the calibration cycle is completed. The
following code can be used to monitor the busy signal during a
calibration cycle:
WAIT:
MOV A, ADCCON3 ;move ADCCON3 to A
JB ACC.7, WAIT ;If Bit 7 is set, jump to
WAIT, else continue
Rev. A | Page 44 of 92

ADuC832
NONVOLATILE FLASH/EE MEMORY
FLASH/EE MEMORY OVERVIEW
The ADuC832 incorporates Flash/EE memory technology on
chip to provide the user with nonvolatile, in-circuit, reprogrammable code and data memory space. Flash/EE memory is a relatively
recent type of nonvolatile memory technology and is based on a
single transistor cell architecture.
This technology is basically an outgrowth of EPROM technology and was developed through the late 1980s. Flash/EE memory
takes the flexible in-circuit reprogrammable features of EEPROM
and combines them with the space efficient/density features of
EPROM (see Figure 47).
Because Flash/EE technology is based on a single transistor cell
architecture, a Flash memory array, like EPROM, can be implemented to achieve the space efficiencies or memory densities
required by a given design. Like EEPROM, Flash memory can
be programmed in-system at a byte level, although it must first
be erased, the erase being performed in page blocks. Thus, Flash
memory is often and more correctly referred to as Flash/EE
memory.
EPROM
TECHNOLOGY
SPACE EFFICIENT /
DENSITY
Figure 47. Flash/EE Memory Development
FLASH/EE MEMORY
TECHNOLOGY
EEPROM
TECHNOLOGY
IN-CIRCUIT
REPROGRAMMABLE
602987-03
Overall, Flash/EE memory represents a step closer to the
ideal memory device that includes nonvolatility, in-circuit
programmability, high density, and low cost. Incorporated in
the ADuC832, Flash/EE memory technology allows the user
to update program code space in-circuit, without the need to
replace one-time programmable (OTP) devices at remote
operating nodes.
FLASH/EE MEMORY AND THE ADUC832
The ADuC832 provides two arrays of Flash/EE memory for
user applications. There are 62 kB of Flash/EE program space
provided on chip to facilitate code execution without any
external discrete ROM device requirements. The program
memory can be programmed in-circuit using the serial download mode provided, using conventional third party memory
programmers, or via a user defined protocol that can configure
it as data if required.
A 4 kB Flash/EE data memory space is also provided on chip.
This can be used as a general-purpose nonvolatile scratchpad
area. User access to this area is via a group of six SFRs. This
space can be programmed at the byte level, although it must
first be erased in 4-byte pages.
ADUC832 FLASH/EE MEMORY RELIABILITY
The Flash/EE program and data memory arrays on the
ADuC832 are fully qualified for two key Flash/EE memory
characteristics, namely Flash/EE memory cycling endurance
and Flash/EE memory data retention.
Endurance quantifies the ability of the Flash/EE memory to be
cycled through many program, read, and erase cycles. In real
terms, a single Flash/EE memory endurance cycle is composed
of the following four independent, sequential events:
• Initial page erase sequence
• Read/verify sequence
• Byte program sequence
• Second read/verify sequence
In reliability qualification, every byte in both the program and
data Flash/EE memory is cycled from 00H to FFH until a first
fail is recorded, signifying the endurance limit of the on-chip
Flash/EE memory.
As indicated in the Specifications section, the ADuC832 Flash/
EE memory endurance qualification has been carried out in
accordance with JEDEC Specification A117 over the industrial
temperature range of −40°C to +25°C and +85°C to +125°C. The
results allow the specification of a minimum endurance value
over supply and temperature of 100,000 cycles, with an endurance value of 700,000 cycles being typical of operation at 25°C.
Retention quantifies the ability of the Flash/EE memory to
retain its programmed data over time. Again, the ADuC832 has
been qualified in accordance with the formal JEDEC retention
lifetime specification (A117) at a specific junction temperature
(T
= 55°C). As part of this qualification procedure, the Flash/
J
EE memory is cycled to its specified endurance limit described
previously, before data retention is characterized. This means
that the Flash/EE memory is guaranteed to retain its data for its
full specified retention lifetime every time the Flash/EE memory is
reprogrammed. It should also be noted that retention lifetime,
based on an activation energy of 0.6 eV, derates with T
in Figure 48.
, as shown
J
Rev. A | Page 45 of 92

ADuC832
300
250
200
150
100
RETENTION (Years)
50
0
5040 60 70 80 90 100 110
Figure 48. Flash/EE Memory Data Retention
ADI SPECIFICATION
100 YEARS MIN.
AT T
= 55°C
J
T
JUNCTION TEM P ERATURE ( °C)
J
02987-037
USING THE FLASH/EE PROGRAM MEMORY
The 62 kB Flash/EE program memory array is mapped into the
lower 62 kB of the 64 kB program space addressable by the
ADuC832, and is used to hold user code in typical applications.
The program memory Flash/EE memory arrays can be
programmed in three ways: serial downloading, parallel
programming, and user download mode.
Serial Downloading (In-Circuit Programming)
The ADuC832 facilitates code download via the standard
UART serial port. The ADuC832 enters serial download mode
after a reset or power cycle if the
through an external 1 kΩ resistor. Once in serial download
mode, the user can download code to the full 62 kB of Flash/EE
program memory while the device is in-circuit in its target
application hardware.
A PC serial download executable is provided as part of the
ADuC832 QuickStart™ development system. The serial
download protocol is detailed in the MicroConverter uC004
Tec hni cal No te , Understanding the Serial Download Protocol.
Parallel Programming
The parallel programming mode is fully compatible with conventional third-party Flash or EEPROM device programmers. In
this mode, Port P0, Port P1, and Port P2 operate as the external
data and address bus interface, ALE operates as the write enable
strobe, and Port P3 is used as a general configuration port that
configures the device for various program and erase operations
during parallel programming. The high voltage (12 V) supply
required for Flash programming is generated using on-chip
charge pumps to supply the high voltage program lines.
The complete parallel programming specification is available at
www.analog.com/microconverters, the MicroConverter home
e.
pag
PSEN
pin is pulled low
User Download Mode (ULOAD)
As shown in Figure 49, it is possible to use the 62 kB of
Flash/EE program memory available to the user as one single
block of memory. In this mode, all of the Flash/EE memory is
read only to user code.
However, the Flash/EE program memory can also be written to
during run time simply by entering ULOAD mode. In ULOAD
mode, the lower 56 kB of program memory can be erased and
reprogrammed by user software as shown in Figure 49. ULOAD
mode can be used to upgrade your code in the field via any user
defined download protocol. Configuring the SPI port on the
ADuC832 as a slave, it is possible to completely reprogram the
56 kB of Flash/EE program memory in only 5 seconds (see the
uC007 Technical Note, User Download (ULOAD) Mode).
Alternatively, ULOAD mode can be used to save data to the
56 kB of Flash/EE memory. This can be extremely useful in data
logging applications where the ADuC832 can provide up to
60 kB of NV data memory on chip (4 kB of dedicated Flash/EE
data memory also exist).
The upper 6 kB of the 62 kB of Flash/EE program memory is
only programmable via serial download or parallel programming.
This means that this space appears as read only to user code.
Therefore, it cannot be accidently erased or reprogrammed by
erroneous code execution. This makes it very suitable to use the
6 kB as a bootloader. A bootload enable option exists in the
serial downloader to always run from E000H after reset. If using
a bootloader, this option is recommended to ensure that the
bootloader always executes correct code after reset.
Programming the Flash/EE program memory via ULOAD
mode is described in more detail in the ECON—Flash/EE
Memory Control SFR section and in the uC007 Technical Note,
User Download (ULOAD) Mode.
EMBEDDED DOWNLOAD/DEBUG KERNEL
PERMANENTLY EMBEDDED FIRMW ARE ALLOWS
CODE TO BE DO WNLOADED TO ANY OF THE
62 kBYTES OF ON-CHIP PROGRAM MEMO RY .
THE KERNEL PROGRAM APPEARS AS 'NOP'
INSTRUCTIONS TO USER CODE.
USER BOOTLOADER SPACE
THE USER BOOTLOADER
SPACE CAN BE PROGRAM MED IN
DOWNLOAD/ DE BUG MODE VIA T HE
62 kBYTES
OF USER
CODE
MEMORY
KERNEL BUT IS RE AD ONLY WHEN
EXECUTING USER CODE
USER DOWNLO AD S P ACE
EITHER THE DOWNLOAD/ DE BUG
KERNEL OR USER CODE (IN
ULOAD MODE) CAN PROGRAM
THIS SPACE.
Figure 49. Flash/EE Program Memory Map in ULOAD Mode
FFFFH
2 kBYTE
F800H
F7FFH
6 kBYTE
E000H
DFFFH
56 kBYTE
0000H
02987-038
Rev. A | Page 46 of 92

ADuC832
FLASH/EE PROGRAM MEMORY SECURITY
The ADuC832 facilitates three modes of Flash/EE program
memory security. These modes can be independently activated,
restricting access to the internal code space. These security modes
can be enabled as part of serial download protocol as described
in Technical Note uC004 or via parallel programming. The
security modes available on the ADuC832 are described as
follows.
Lock Mode
This mode locks the code memory, disabling parallel
programming of the program memory. However, reading the
memory in parallel mode and reading the memory via a MOVC
command from external memory is still allowed. This mode is
deactivated by initiating a code-erase command in serial
download or parallel programming modes.
Secure Mode
This mode locks code in memory, disabling parallel programming
(program and verify/read commands) as well as disabling the
execution of a MOVC instruction from external memory, which
attempts to read the op codes from internal memory. Read/write of
internal data Flash/EE from external memory is also disabled. This
mode is deactivated by initiating a code-erase command in serial
download or parallel programming modes.
Serial Safe Mode
This mode disables serial download capability on the device. If
serial safe mode is activated and an attempt is made to reset the
part into serial download mode, that is, RESET asserted and
deasserted with
download reset as a normal reset only. It therefore does not
enter serial download mode but only executes a normal reset
sequence. Serial safe mode can only be disabled by initiating a
code-erase command in parallel programming mode.
PSEN
low, the part interprets the serial
Rev. A | Page 47 of 92

ADuC832
A
USING THE FLASH/EE DATA MEMORY
The 4 kB of Flash/EE data memory is configured as 1024 pages,
each of four bytes. As with the other ADuC832 peripherals, the
interface to this memory space is via a group of registers
3FFH
3FEH
BYTE 1
(0FFCH)
BYTE 1
(0FF8H)
(0FFDH)
mapped in the SFR space. A group of four data registers
(EDATA1 to EDATA4) are used to hold the four bytes of data at
each page. The page is addressed via the EADRH and EADRL
registers. Finally, ECON is an 8-bit control register that may be
written with one of nine Flash/EE memory access commands to
trigger various read, write, erase, and verify functions.
A block diagram of the SFR interface to the Flash/EE data
(EADRH/L)
PAGE ADDRESS
03H
02H
01H
00H
BYTE 1
(000CH)
BYTE 1
(0008H)
BYTE 1
(0004H)
BYTE 1
(0000H)
memory array is shown in Figure 50.
BYTE
ECON—FLASH/EE MEMORY CONTROL SFR
Programming of either the Flash/EE data memory or the
Flash/EE program memory is done through the Flash/EE
memory control SFR (ECON). This SFR allows the user to read,
ADDRESSES
RE GIVEN IN
BRACKETS
EDATA1 SFR
Figure 50. Flash/EE Data Memory Control and Configuration
write, erase, or verify the 4 kB of Flash/EE data memory or the
56 kB of Flash/EE program memory.
Table 21. ECON—Flash/EE Memory Commands
Command Description (Normal Mode)
ECON Value
01H READPAGE
(Power-On Default) Command Description (ULOAD Mode)
Results in four bytes in the Flash/EE data memory,
Not implemented. Use the MOVC instruction.
addressed by the page address EADRH/L, being read into
EDATA1 to EDATA4.
02H WRITEPAGE
Results in four bytes in EDATA1 to EDATA4 being written to
the Flash/EE data memory at the page address given by
EADRH/L
1
(0 ≤ EADRH/L < 0400H). Note that the four
bytes in the page being addressed must be pre-erased.
Results in Byte 0 to Byte 255 of internal XRAM being
written to the 256 bytes of Flash/EE program memory at
the page address given by EADRH (0 ≤ EADRH < E0H).
Note that the 256 bytes in the page being addressed
must be pre-erased.
03H Reserved command. Reserved command.
04H VERIFYPAGE
Verifies if the data in EDATA[1:4] is contained in the page
address given by EADRH/L. A subsequent read of the
Not implemented. Use the MOVC and MOVX instructions
to verify the WRITE in software.
ECON SFR results in a 0 being read if the verification is
valid, or a nonzero value being read to indicate an invalid
verification.
05H ERASEPAGE
Results in the erase of the 4-byte page of Flash/EE data
memory addressed by the Page Address EADRH/L.
Results in the 64-byte page of Flash/EE program memory,
addressed by the Byte Address EADRH/L being erased.
EADRL can equal any of 64 locations within the page.
A new page starts whenever EADRL is equal to 00H, 40H,
80H, or C0H.
06H ERASEALL
81H READBYTE
Results in the erase of entire 4 kB of Flash/EE data
memory.
Results in the byte in the Flash/EE data memory,
Results in the erase of the entire 56 kB of ULOAD Flash/EE
program memory.
Not implemented. Use the MOVC command.
addressed by the Byte Address EADRH/L, being read into
EDATA1 (0 ≤ EADRH/L ≤ 0FFFH).
82H WRITEBYTE
Results in the byte in EDATA1 being written into Flash/EE
data memory, at the byte address EADRH/L.
Results in the byte in EDATA1 being written into Flash/EE
program memory, at the Byte Address EADRH/L (0 ≤
EADRH/L ≤ DFFFH).
0FH EXULOAD
F0H ULOAD
1
Register EADRH and EADRL form the full address, EADRH/L.
Leaves the ECON instructions to operate on the Flash/EE
data memory.
Enters ULOAD mode, directing subsequent ECON
instructions to operate on the Flash/EE program memory.
Enters normal mode directing subsequent ECON
instructions to operate on the Flash/EE data memory.
Leaves the ECON instructions to operate on the Flash/EE
program memory.
BYTE 2
BYTE 2
(0FF9H)
BYTE 2
(000DH)
BYTE 2
(0009H)
BYTE 2
(0005H)
BYTE 2
(0001H)
EDATA2 SFR
BYTE 3
(0FFEH)
BYTE 3
(0FFAH)
BYTE 3
(000EH)
BYTE 3
(000AH)
BYTE 3
(0006H)
BYTE 3
(0002H)
EDATA3 SFR
BYTE 4
(0FFFH)
BYTE 4
(0FFBH)
BYTE 4
(000FH)
BYTE 4
(000BH)
BYTE 4
(0007H)
BYTE 4
(0003H)
EDATA4 SFR
02987-039
Rev. A | Page 48 of 92

ADuC832
EXAMPLE: PROGRAMMING THE FLASH/EE DATA MEMORY
To program F3H into the second byte on Page 03H of the
Flash/EE data memory space while preserving the other three
bytes already in this page, a typical program of the Flash/EE
data array includes the following steps:
1. Setting EADRH/L with the page address
2. Writing the data to be programmed to EDATA1 to
EDATA4
3. Writing the ECON SFR with the appropriate command
Step 1: Set Up the Page Address
The two address registers, EADRH and EADRL, hold the high
byte address and the low byte address of the page to be
addressed.
The assembly language to set up the address may appear as:
MOV EADRH,#0 ; Set Page Address Pointer
MOV EADRL,#03H
Step 2: Set Up the EDATA Registers
Next, write the four values to be written into the page into the
four SFRs, EDATA1 to EDATA4. Unfortunately, three of these
are unknown. Thus, the current page must be read and the
second byte overwritten.
MOV ECON,#1 ; Read Page into EDATA1 to
EDATA4
MOV EDATA2,#0F3H ; Overwrite Byte 2
Step 3: Program Page
A byte in the Flash/EE array can only be programmed if it has
previously been erased; that is, a byte can only be programmed
if it already holds the value FFH. Because of the Flash/EE architecture, this erase must happen at a page level; therefore, a minimum
of four bytes (one page) is erased when an erase command is
initiated. Once the page is erased, the four bytes can be programmed in-page and then a verification of the data performed.
MOV ECON,#5 ; ERASE Page
MOV ECON,#2 ; WRITE Page
MOV ECON,#4 ; VERIFY Page
MOV A,ECON ; Check if ECON = 0 (OK!)
JNZ ERROR
Although the 4 kB of Flash/EE data memory are shipped from
the factory pre-erased, that is, byte locations set to FFH, it is
nonetheless good programming practice to include an erase-all
routine as part of any configuration/setup code running on the
ADuC832. An erase all command consists of writing 06H to the
ECON SFR, which initiates an erase of the 4 kB Flash/EE array.
This command coded in 8051 assembly appears as:
MOV ECON,#06H ; Erase all Command
; 2 ms Duration
FLASH/EE MEMORY TIMING
Typical program and erase times for the ADuC832 are as
detailed in Tab le 2 2 and Tab l e 2 3.
Table 22. Normal Mode (Operating on Flash/EE Data
Memory)
Instruction Time
READPAGE (4 bytes) −5 machine cycles
WRITEPAGE (4 bytes) −380 s
VERIFYPAGE (4 bytes) −5 machine cycles
ERASEPAGE (4 bytes) −2 ms
ERASEALL (4 kB) −2 ms
READBYTE (1 byte) −3 machine cycle
WRITEBYTE (1 byte) −200 s
Table 23. ULOAD Mode (Operating on Flash/EE Program
Memory)
Instruction Time
WRITEPAGE (256 bytes) −15 ms
ERASEPAGE (64 bytes) −2 ms
ERASEALL (56 kB) −2 ms
WRITEBYTE (1 byte) −200 s
Note that a given mode of operation is initiated as soon as
the command word is written to the ECON SFR. The core
microcontroller operation on the ADuC832 is idled until
the requested program/read or erase mode is completed.
In practice, this means that even though the Flash/EE memory
mode of operation is typically initiated with a two-machine
cycle MOV instruction (to write to the ECON SFR), the next
instruction is not executed until the Flash/EE operation is complete. This means that the core does not respond to interrupt
requests until the Flash/EE operation is complete, although the
core peripheral functions such as counter/timers continue to
count and keep time as configured throughout this period.
Rev. A | Page 49 of 92

ADuC832
ADUC832 CONFIGURATION SFR (CFG832)
The CFG832 SFR contains the necessary bits to configure the
internal XRAM, external clock select, PWM output selection,
DAC buffer, and the extended SP. By default, it configures the
user into 8051 mode; that is, extended SP is disabled and the
internal XRAM is disabled.
Table 24. CFG832 SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] EXSP
[6] PWPO
[5] DBUF
[4] EXTCLK
[3] RSVD Reserved. This bit should always contain 0.
[2] RSVD Reserved. This bit should always contain 0.
[1] RSVD Reserved. This bit should always contain 0.
[0] XRAMEN
Extended SP enable.
When set to 1 by the user, the stack rolls over from SPH/SP = 00FFH to SPH/SP = 0100H.
When set to 0 by the user, the stack rolls over from SP = FFH to SP = 00H.
PWM pinout selection.
When set to 1 by the user, the PWM output pins are selected as P3.4 and P3.3.
When set to 0 by the user, the PWM output pins are selected as P2.6 and P2.7.
DAC output buffer.
When set to 1 by the user, the DAC output buffer is bypassed.
When set to 0 by the user, the DAC output buffer is enabled.
Set by the user to 1 to select an external clock input on P3.4.
Set by the user to 0 to use the internal PLL clock.
XRAM enable bit.
When set to 1 by the user, the internal XRAM is mapped into the lower 2 kB of the external address space.
When set to 0 by the user, the internal XRAM is not accessible and the external data memory is mapped into the lower
2 kB of external data memory.
CFG832 (ADuC832 Configuration SFR)
SFR Address: AFH
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Rev. A | Page 50 of 92

ADuC832
USER INTERFACE TO OTHER ON-CHIP ADUC832 PERIPHERALS
The following section gives a brief overview of the various
peripherals also available on-chip. A summary of the SFRs used
to control and configure these peripherals is also given.
DAC
The ADuC832 incorporates two 12-bit voltage output DACs on
chip. Each DAC has a rail-to-rail voltage output buffer capable
of driving 10 kΩ/100 pF. Each has two selectable ranges, 0 V to
V
(the internal band gap 2.5 V reference) and 0 V to AVDD.
REF
Each can operate in 12-bit or 8-bit mode. Both DACs share a
control register, DACCON, and four data registers, DAC1H,
DAC1L, DAC0H, and DAC0L. Note that in 12-bit asynchronous mode, the DAC voltage output is updated as soon as the
DACL data SFR has been written; therefore, the DAC data
registers should be updated as DACH first, followed by DACL.
Note that for correct DAC operation on the 0 V to V
the ADC must be switched on. This results in the DAC using
the correct reference value.
DACCON (DAC Control Register)
SFR Address: FDH
range,
REF
DACxH/DACxL (DAC Data Registers)
Function: DAC data registers, written by user to
update the DAC output
SFR Address: DAC0L (DAC0 data low byte) = F9H;
DAC1L (DAC1 data low byte) = FBH
DAC0H (DAC0 data high byte) = FAH;
DAC1H (DAC1 data high byte) = FCH
Power-On Default
00H (all four registers)
Va lu e :
Bit Addressable: No (all four registers)
The 12-bit DAC data should be written into DACxH/DACxL
right-justified such that DACxL contains the lower eight bits,
and the lower nibble of DACxH contains the upper four bits.
Power-On Default Value: 04H
Bit Addressable: No
Table 25. DACCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Mode
[6] RNG1
[5] RNG0
[4] CLR1
[3] CLR0 DAC0 clear bit. Set to 0 = DAC1 Output Forced to 0 V. Set to 1 = DAC1 output normal.
[2] SYNC
[1]
[0] PD0
PD1
The DAC MODE bit sets the overriding operating mode for both DACs.
Set to 1 = 8-bit mode (write eight bits to DACxL SFR).
Set to 0 = 12-bit mode.
DAC1 range select bit.
Set to 1 = DAC1 range 0 V − V
Set to 0 = DAC1 range 0 V − V
DAC0 range select bit.
Set to 1 = DAC0 range 0 V − V
Set to 0 = DAC0 range 0 V − V
DAC1 clear bit.
Set to 0 = DAC1 output forced to 0 V.
Set to 1 = DAC1 output normal.
DAC0/DAC1 update synchronization bit.
When set to 1, the DAC outputs update as soon as DACxL SFRs are written. The user can simultaneously update
both DACs by first updating the DACxL/DACxH SFRs while SYNC is 0. Both DACs then update simultaneously
when the SYNC bit is set to 1.
DAC1 Power-down bit.
Set to 1 = power on DAC1.
Set to 0 = power off DAC1.
DAC0 Power-Down Bit.
Set to 1 = power on DAC0.
Set to 0 = power off DAC0.
DD
REF
DD
REF
.
.
.
.
Rev. A | Page 51 of 92

ADuC832
A
A
USING THE DAC
The on-chip DAC architecture consists of a resistor string DAC
followed by an output buffer amplifier, the functional equivalent
of which is illustrated in Figure 51. Details of the actual DAC
architecture can be found in U.S. Patent Number 5,969,657.
Features of this architecture include inherent guaranteed
monotonicity and excellent differential linearity.
AV
DD
V
REF
Figure 51. Resistor String DAC Functional Equivalent
As illustrated in Figure 51, the reference source for each DAC is
user selectable in software. It can be either AV
mode, the DAC output transfer function spans from 0
to AV
DD
V to the voltage at the AV
output transfer function spans from 0 V to the internal V
if an external reference is applied, the voltage at the V
The DAC output buffer amplifier features a true rail-to-rail
output stage implementation. This means that, unloaded, each
output is capable of swinging to within less than 100 mV of both
AV
and ground. Moreover, the DAC’s linearity specification
DD
(when driving a 10 kΩ resistive load to ground) is guaranteed
through the full transfer function except Code 0 to Code 100,
and, in 0 V to AV
degradation near ground and AV
the output amplifier, and a general representation of its effects
(neglecting offset and gain error) is illustrated in Figure 52. The
dotted line in Figure 52 indicates the ideal transfer function,
and the solid line represents what the transfer function may
look like with endpoint nonlinearities due to saturation of the
output amplifier. Note that Figure 52 represents a transfer
function in 0 V to AV
V
< AVDD), the lower nonlinearity is similar, but the upper
REF
portion of the transfer function follows the ideal line to the end
(V
in this case, not AVDD), showing no signs of endpoint
REF
linearity errors.
ADuC832
R
R
R
R
R
pin. In 0 V to V
DD
mode only, Code 3995 to Code 4095. Linearity
DD
mode only. In 0 V to V
DD
OUTPUT
BUFFER
DAC0
HIGH Z
DISABLE
(FROM MCU)
or V
DD
REF
mode, the DAC
REF
REF
is caused by saturation of
DD
mode (with
REF
2987-040
. In 0 V
REF
pin.
or,
V
DD
AVDD –50mV
VDD –100mV
100mV
50mV
0mV
000H
FFFH
Figure 52. Endpoint Nonlinearities Due to Amplifier Saturation
The endpoint nonlinearities conceptually illustrated in Figure 52
become worse as a function of output loading. Most of the
ADuC832 specifications assume a 10 kΩ resistive load to
ground at the DAC output. As the output is forced to source or
sink more current, the nonlinear regions at the top or bottom
(respectively) of Figure 52 become larger. With larger current
demands, this can significantly limit output voltage swing.
Figure 53 and Figure 54 illustrate this behavior. It should be
noted that the upper trace in each of these figures is only valid
for an output range selection of 0 V to AV
. In 0 V to V
DD
REF
mode, DAC loading does not cause high-side voltage drops as
long as the reference voltage remains below the upper trace in
the corresponding figure. For example, if AV
= 3 V and V
DD
REF
2.5 V, the high-side voltage is not affected by loads less than
5 mA. However, around 7 mA, the upper curve in Figure 54
drops below 2.5 V (V
currents, the output is not capable of reaching V
5
4
3
2
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (V)
1
0
051015
Figure 53. Source and Sink Current Capability with V
), indicating that, at these higher
REF
REF
DAC LOADED WITH 0FFF H
DAC LOADED WI TH 0000H
SOURCE/SINK CURRENT (mA)
REF
.
= AVDD = 5 V
7-042
0298
=
02987-041
Rev. A | Page 52 of
92

ADuC832
4
DAC LOADED WI TH 0FFFH
3
To drive significant loads with the DAC outputs, external
buffering may be required (even with the internal buffer
enabled), as illustrated in Figure 55. A list of recommended op
amps is shown in Tabl e 20 .
DAC0
1
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (V)
DAC LOADED WI TH 0000H
0
0 5 10 15
Figure 54. Source and Sink Current Capability with V
SOURCE/SINK CURRENT ( mA)
= AVDD = 3 V
REF
02987-043
To reduce the effects of the saturation of the output amplifier at
values close to ground and to give reduced offset and gain errors,
the internal buffer can be bypassed. This is done by setting the
DBUF bit in the CFG832 register. This allows a full rail-to-rail
output from the DAC, which should then be buffered externally
using a dual-supply op amp to obtain a rail-to-rail output. This
external buffer should be located as near as physically possible
to the DAC output pin on the PCB. Note that the unbuffered
mode only works in the 0 V to V
range.
REF
ADuC832
DAC1
2987-044
Figure 55. Buffering the DAC Outputs
The DAC output buffer also features a high impedance disable
function. In the chip’s default power-on state, both DACs are
disabled, and their outputs are in a high impedance state (or
three-state) where they remain inactive until enabled in
software. This means that if a zero output is desired during
power-up or power-down transient conditions, then a pulldown resistor must be added to each DAC output. Assuming
this resistor is in place, the DAC outputs remain at ground
potential whenever the DAC is disabled.
Rev. A | Page 53 of 92

ADuC832
ON-CHIP PLL
The ADuC832 is intended for use with a 32.768 kHz watch
crystal. A PLL locks onto a multiple (512) of this to provide a
stable 16.78 MHz clock for the system. The core can operate at
this frequency or at binary submultiples of it to allow power
saving in cases where maximum core performance is not
required. The default core clock is the PLL clock divided by 8 or
2.097152 MHz. The ADC clocks are also derived from the PLL
clock, with the modulator rate being the same as the crystal
oscillator frequency. The choice of frequencies ensures that the
Table 26. PLLCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] OSC_PD
[6] LOCK
[5] Reserved Reserved for future use; should be written with 0.
[4] Reserved Reserved for future use; should be written with 0.
[3] FINT
[2:0] CD[2:0] CPU (core clock) divider bits. These bits determine the frequency at which the microcontroller core operates.
Oscillator power-down bit.
Set by user to halt the 32 kHz oscillator in power-down mode.
Cleared by user to enable the 32 kHz oscillator in power-down mode. This feature allows the TIC to continue counting
even in power-down mode.
PLL lock bit. This is a read-only bit.
Set automatically at power-on to indicate the PLL loop is correctly tracking the crystal clock. If the external crystal
becomes subsequently disconnected, the PLL rails and the core halt.
Cleared automatically at power-on to indicate the PLL is not correctly tracking the crystal clock. This may be due to the
absence of a crystal clock or an external crystal at power-on. In this mode, the PLL output can be 16.78 MHz ± 20%.
Fast interrupt response bit.
Set by user, enabling the response to any interrupt to be executed at the fastest core clock frequency, regardless of the
configuration of the CD[2:0] bits. Once user code has returned from an interrupt, the core resumes code execution at the
core clock selected by the CD[2:0] bits.
Cleared by user to disable the fast interrupt response feature.
CD2 CD1 CD0 Core Clock Frequency, f
0 0 0 16.78
0 0 1 8.388608
0 1 0 4.194304
0 1 1 2.097152 (default core clock frequency)
1 0 0 1.048576
1 0 1 0.524288
1 1 0 0.262144
1 1 1 0.131072
modulators and the core are synchronous, regardless of the core
clock rate. The PLL control register is PLLCON.
PLLCON (PLL CONTROL REGISTER)
SFR Address: D7H
Power-On Default Value: 53H
Bit Addressable: No
(MHz)
CORE
Rev. A | Page 54 of 92

ADuC832
PULSE-WIDTH MODULATOR (PWM)
The PWM on the ADuC832 is a highly flexible PWM offering
programmable resolution and an input clock, and can be configured for any one of six different modes of operation. Two of
these modes allow the PWM to be configured as a Σ- DAC
with up to 16 bits of resolution. A block diagram of the PWM
is shown in Figure 56.
f
f
XTAL
f
VCO
XTAL
/15
CLOCK
SELECT
PROGRAMMABLE
DIVIDER
16-BIT P WM COUNT ER
COMPARE
P2.6
P2.7
T0/EXTERNAL PWM CLOCK
registers that determine the duty cycles of the PWM outputs. The
output pins that the PWM uses are determined by the CFG832
register, and can be either P2.6 and P2.7 or P3.4 and P3.3. In
this section of the data sheet, it is assumed that P2.6 and P2.7
are selected as the PWM outputs.
To use the PWM user software, first write to PWMCON to
select the PWM mode of operation and the PWM input clock.
Writing to PWMCON also resets the PWM counter. In any of
the 16-bit modes of operation (Mode 1, Mode 3, Mode 4, and
Mode 6), user software should write to the PWM0L or PWM1L
SFR first. This value is written to a hidden SFR. Writing to the
PWM0H or PWM1H SFRs updates both the PWMxH and the
PWMxL SFRs but does not change the outputs until the end of
the PWM cycle in progress. The values written to these 16-bit
registers are then used in the next PWM cycle.
MODE PWM0H/L
Figure 56. PWM Block Diagram
PWM1H/L
The PWM uses five SFRs: the control SFR (PWMCON) and
four data SFRs (PWM0H, PWM0L, PWM1H, and PWM1L).
PWMCON (as described in Ta bl e 27) controls the different
modes of operation of the PWM as well as the PWM clock
02987-045
PWMCON (PWM CONTROL SFR)
SFR Address: AEH
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
frequency. PWM0H/PWM0L and PWM1H/PWM1L are the data
Table 27. PWMCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] SNGL Turns off PWM output at P2.6 or P3.4, leaving port pin free for digital I/O.
[6:4] MD[2:0] PWM mode bits. The MD[2:0] bits choose the PWM mode as follows:
MD2 MD1 MD0 Mode
0 0 0 Mode 0: PWM disabled
0 0 1 Mode 1: single variable resolution PWM on P2.7 or P3.3
0 1 0 Mode 2: twin 8-bit PWM
0 1 1 Mode 3: twin 16-bit PWM
1 0 0 Mode 4: dual NRZ 16-bit Σ-∆ DAC
1 0 1 Mode 5: dual 8-bit PWM
1 1 0 Mode 6: dual RZ 16-bit Σ-∆ DAC
1 1 1 Reserved for future use
[3:2] CDIV[1:0] PWM clock divider. These bits scale the clock source for the PWM counter as follows:
CDIV1 CDIV0 PWM Counter
0 0 Selected clock/1
0 1 Selected clock/4
1 0 Selected clock/16
1 1 Selected clock/64
[1:0] CSEL[1:0] PWM clock divider. These bits select the clock source for the PWM as follows:
CSEL1 CSEL0 PWM Clock
0 0 f
0 1 f
XTAL
XTAL
/15
1 0 External input at P3.4/T0
1 1 f
= 16.78 MHz
VCO
Rev. A | Page 55 of 92

ADuC832
PWM MODES OF OPERATION
MODE 0: PWM DISABLED
The PWM is disabled, allowing P2.6 and P2.7 to be used as normal.
MODE 1: SINGLE VARIABLE RESOLUTION PWM
In Mode 1, both the pulse length and the cycle time (period)
are programmable in user code, allowing the resolution of the
PWM to be variable.
PWM1H/PWM1L sets the period of the output waveform. Reducing PWM1H/PWM1L reduces the resolution of the PWM output
but increases the maximum output rate of the PWM. (for example,
setting PWM1H/PWM1L to 65,536 gives a 16-bit PWM with a
maximum output rate of 266 Hz (16.78 MHz/65,536). Setting
PWM1H/PWM1L to 4096 gives a 12-bit PWM with a maximum output rate of 4096 Hz (16.78 MHz/4096).
PWM0H/PWM0L sets the duty cycle of the PWM output
waveform, as shown in Figure 57.
PWM COUNTE R
Figure 57. PWM Mode 1
MODE 2: TWIN 8-BIT PWM
In Mode 2, the duty cycle of the PWM outputs and the resolution of the PWM outputs are both programmable. The maximum
resolution of the PWM output is eight bits.
PWM1L sets the period for both PWM outputs. Typically, this
is set to 255 (FFH) to give an 8-bit PWM although it is possible
to reduce this as necessary. A value of 100 can be loaded here to
give a percentage PWM (that is, the PWM is accurate to 1%).
The outputs of the PWM at P2.6 and P2.7 are shown in Figure 58.
As can be seen, the output of PWM0 (P2.6) goes low when the
PWM counter equals PWM0L. The output of PWM1 (P2.7)
goes high when the PWM counter equals PWM1H and goes
low again when the PWM counter equals PWM0H. Setting
PWM1H to 0 ensures that both PWM outputs start simultaneously.
PWM1H/L
PWM0H/L
0
P2.7
02987-046
PWM CO UNTER
Figure 58. PWM Mode 2
PWM1L
PWM0H
PWM0L
PWM1H
0
P2.6
P2.7
02987-047
MODE 3: TWIN 16-BIT PWM
In Mode 3, the PWM counter is fixed to count from 0 to 65,536,
giving a fixed 16-bit PWM. Operating from the 16.78 MHz core
clock results in a PWM output rate of 256 Hz. The duty cycle of the
PWM outputs at P2.6 and P2.7 is independently programmable.
As shown in Figure 59, while the PWM counter is less than
PWM0H/PWM0L, the output of PWM0 (P2.6) is high. Once
the PWM counter equals PWM0H/PWM0L, PWM0 (P2.6)
goes low and remains low until the PWM counter rolls over.
Similarly, while the PWM counter is less than PWM1H/
PWM1L, the output of PWM1 (P2.7) is high. Once the PWM
counter equals PWM1H/PWM1L, PWM1 (P2.7) goes low and
remains low until the PWM counter rolls over.
In this mode, both PWM outputs are synchronized, that is, once
the PWM counter rolls over to 0, both PWM0 (P2.6) and
PWM1 (P2.7) go high.
65,536
PWM CO UNTER
PWM1H/L
PWM0H/L
0
P2.6
P2.7
Figure 59. PWM Mode 3
2987-048
Rev. A | Page 56 of 92

ADuC832
MODE 4: DUAL NRZ 16-BIT Σ-∆ DAC
Mode 4 provides a high speed PWM output similar to that of a
Σ- DAC. Typically, this mode is used with the PWM clock
equal to 16.777216 MHz.
In this mode, P2.6 and P2.7 are updated every PWM clock
(60 ns in the case of 16 MHz). Over every 65,536 cycles (16-bit
PWM) PWM0 (P2.6) is high for PWM0H/PWM0L cycles and
low for (65,536 − PWM0H/L) cycles. Similarly PWM1 (P2.7) is
high for PWM1H/PWM1L cycles and low for (65,536 −
PWM1H/PWM1L) cycles.
For example, if PWM1H/L was set to 4010H (slightly above one
quarter of FS), then typically P2.7 is low for three clocks and
high for one clock (each clock is approximately 60 ns). Over
every 65,536 clocks, the PWM compensates for the fact that the
output should be slightly above one quarter of full scale by
having a high cycle followed by only two low cycles.
PWM0H/L = C000H
16-BIT
16-BIT
16.78MHz
16-BIT
16-BIT
PWM1H/L = 4000H
CARRY OUT AT P1.0
16-BIT
LATCH
16-BIT
CARRY OUT AT P2.7
0
111 11
60µs
001000
0
60µs
0
Figure 60. PWM Mode 4
For faster DAC outputs (at lower resolution) write 0s to the
LSBs that are not required. If, for example, only 12-bit performance is required, then write 0s to the four LSBs. This means
that a 12-bit accurate Σ- DAC output can occur at 4.096 kHz.
Similarly, writing 0s to the eight LSBs gives an 8-bit accurate
Σ- DAC output at 65 kHz.
MODE 5: DUAL 8-BIT PWM
In Mode 5, the duty cycle of the PWM outputs and the resolution of the PWM outputs are individually programmable. The
maximum resolution of the PWM output is eight bits. The
output resolution is set by the PWM1L and PWM1H SFRs for
the P2.6 and P2.7 outputs, respectively. PWM0L and PWM0H
set the duty cycles of the PWM outputs at P2.6 and P2.7,
respectively. Both PWMs have same clock source and clock
divider.
PWM1L
PWM COUNTERS
PWM1H
PWM0L
PWM0H
0
P2.6
P2.7
02987-050
Figure 61. PWM Mode 5
MODE 6: DUAL RZ 16-BIT Σ-∆ DAC
Mode 6 provides a high speed PWM output similar to that of a
Σ- DAC. Mode 6 operates very similarly to Mode 4. However,
the key difference is that Mode 6 provides return-to-zero (RZ)
Σ- DAC output. Mode 4 provides nonreturn-to-zero Σ- DAC
outputs. The RZ mode ensures that any difference in the rise
and fall times does not affect the Σ- DAC INL. However, the
RZ mode halves the dynamic range of the Σ- DAC outputs
from 0 V − AV
mode should be used with a PWM clock divider of four.
If PWM1H is set to 4010H (slightly above one quarter of FS)
then typically P2.7 is low for three full clocks (3 × 60 ns), high
for half a clock (30 ns), and then low again for half a clock
(30 ns) before repeating itself. Over every 65,536 clocks, the
PWM compensates for the fact that the output should be slightly
above one quarter of full scale by occasionally leaving the
output high for two half clocks in four.
PWM0H/L = C000H
16-BIT
02987-049
16-BIT
4MHz
16-BIT
0, 3/4, 1/ 2, 1/4, 0
16-BIT
PWM1H/L = 40 00H
down to 0 V − AVDD/2. For best results, this
DD
CARRY OUT AT P2. 6
16-BIT
LATCH
16-BIT
CARRY OUT AT P2. 7
0
111 11
s
240
0
001000
240 s
0
Figure 62. PWM Mode 6
02987-051
Rev. A | Page 57 of 92

ADuC832
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
The ADuC832 integrates a complete hardware serial peripheral
interface (SPI) on chip. SPI is an industry standard synchronous
serial interface that allows eight bits of data to be synchronously
transmitted and received simultaneously, that is, full duplex. It
should be noted that the SPI pins are shared with the I
2
C pins.
Therefore, the user can only enable one or the other interface at
any given time (see SPE in Tabl e 28 ). The SPI port can be configured for master or slave operation and typically consists of
four pins: MISO, MOSI, SCLOCK, and
SS
.
MISO (MASTER INPUT, SLAVE OUTPUT DATA PIN)
The MISO (master input, slave output) pin is configured as an
input line in master mode and an output line in slave mode.
The MISO line on the master (data in) should be connected to
the MISO line in the slave device (data out). The data is transferred as byte-wide (8-bit) serial data, MSB first.
MOSI (MASTER OUTPUT, SLAVE INPUT PIN)
The MOSI (master output, slave input) pin is configured as an
output line in master mode and an input line in slave mode.
The MOSI line on the master (data out) should be connected
to the MOSI line in the slave device (data in). The data is transferred as byte-wide (8-bit) serial data, MSB first.
SCLOCK (SERIAL CLOCK I/O PIN)
The master serial clock (SCLOCK) is used to synchronize the
data being transmitted and received through the MOSI and
MISO data lines. A single data bit is transmitted and received in
each SCLOCK period. Therefore, a byte is transmitted/received
after eight SCLOCK periods. The SCLOCK pin is configured as
an output in master mode and as an input in slave mode. In
master mode, the bit rate, polarity, and phase of the clock are
controlled by the CPOL, CPHA, SPR0, and SPR1 bits in the
Table 28. SPICON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] ISPI
[6] WCOL Write collision error bit. Set by MicroConverter if SPIDAT is written to while an SPI transfer is in progress. Cleared by user code.
[5] SPE SPI interface enable bit. Set by user to enable the SPI interface. Cleared by user to enable the I2C pins.
[4] SPIM
[3] CPOL1 Clock polarity select bit. Set by user if SCLOCK idles high. Cleared by user if SCLOCK idles low.
[2] CPHA1
[1:0] SPR[1:0] SPI bit rate select bits. These bits select the SCLOCK rate (bit rate) in master mode as follows:
1
The CPOL and CPHA bits should both contain the same values for master and slave devices.
SPI interrupt bit. Set by MicroConverter at the end of each SPI transfer. Cleared directly by user code or indirectly by
reading the SPIDAT SFR.
SPI master/slave mode select bit. Set by user to enable Master Mode operation (SCLOCK is an output). Cleared by user to
enable slave mode operation (SCLOCK is an input).
Clock phase select bit. Set by user if leading SCLOCK edge is to transmit data. Cleared by user if trailing SCLOCK edge is to
transmit data.
SPR1 SPR0 Selected Bit Rate
0 0 f
0 1 f
1 0 f
1 1 f
In SPI slave mode, that is, SPIM = 0, the logic level on the external
SPICON SFR (see Tab l e 2 8). In slave mode, the SPICON register
must be configured with the phase and polarity (CPHA and
CPOL) of the expected input clock. In both master and slave
modes, the data is transmitted on one edge of the SCLOCK
signal and sampled on the other. It is important therefore that
the CPHA and CPOL are configured the same for the master
and slave devices.
SS (SLAVE SELECT INPUT PIN)
The slave select (SS) input pin is shared with the ADC5 input.
To configure this pin as a digital input, the bit must be cleared,
for example, CLR P1.5.
This line is active low. Data is only received or transmitted in
slave mode when the
used in single master, multislave SPI configurations. If CPHA = 1,
SS
then the
= 0, the
input may be permanently pulled low. With CPHA
SS
input must be driven low before the first bit in a
byte-wide transmission or reception, and return high again after
the last bit in that byte-wide transmission or reception. In SPI
slave mode, the logic level on the external
the SPR0 bit in the SPICON SFR.
The following SFR registers (SPICON and SPIDAT) are used to
control the SPI interface.
SPICON (SPI Control Register)
SFR Address: F8H
Power-On Default Value: 04H
Bit Addressable: Yes
/2
OSC
/4
OSC
/8
OSC
/16
OSC
SS
pin can be read via the SPR0 bit.
SS
pin is low, allowing the ADuC832 to be
SS
pin can be read via
Rev. A | Page 58 of 92

ADuC832
SPIDAT (SPI Data Register)
SFR Address: F7H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
The SPIDAT SFR is written by the user to transmit data over the
SPI interface, or read by the user read data just received by the
SPI interface.
USING THE SPI INTERFACE
Depending on the configuration of the bits in the SPICON SFR
shown in Tab l e 28 , the ADuC832 SPI interface transmits or
receives data in a number of possible modes. Figure 63 shows all
possible ADuC832 SPI configurations and the timing relationships
and synchronization between the signals involved. Also shown
is the SPI interrupt bit (ISPI) and how it is triggered at the end of
each byte-wide communication.
SCLOCK
(CPO L = 1)
SCLOCK
(CPO L = 0)
SS
SAMPLE INPUT
×
(CPHA = 1)
(CPHA = 0)
DATA OUTPUT
ISPI FLAG
SAMPLE INPUT
DATA OUTPUT
MSB BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT2 BIT 1 LSB
MSB BIT 6 BIT 5 ×BIT4 BIT3 BIT2 BIT1 LSB
SPI INTERFACE—MASTER MODE
In master mode, the SCLOCK pin is always an output and
generates a burst of eight clocks whenever user code writes to
the SPIDAT register. The SCLOCK bit rate is determined by
SPR0 and SPR1 in SPICON. It should also be noted that the
SS
pin is not used in master mode. If the ADuC832 needs to assert
SS
the
pin on an external slave device, a port digital output pin
should be used.
In master mode, a byte transmission or reception is initiated by
a write to SPIDAT. Eight clock periods are generated via the
SCLOCK pin and the SPIDAT byte being transmitted via MOSI.
With each SCLOCK period, a data bit is also sampled via MISO.
After eight clocks, the transmitted byte is completely transmitted
and the input byte waits in the input shift register. The ISPI flag
is set automatically and an interrupt occurs if enabled. The
value in the shift register is latched into SPIDAT.
SPI INTERFACE—SLAVE MODE
In slave mode, the SCLOCK is an input. The SS pin must also
be driven low externally during the byte communication.
Transmission is also initiated by a write to SPIDAT. In slave mode,
a data bit is transmitted via MISO and a data bit is received via
MOSI through each input SCLOCK period. After eight clocks,
the transmitted byte is completely transmitted and the input
byte waits in the input shift register. The ISPI flag is set automatically and an interrupt occurs if enabled. The value in the shift
register is latched into SPIDAT only when the transmission/
reception of a byte has been completed. The end of transmission
occurs after the eighth clock has been received if CPHA = 1, or
SS
when
returns high if CPHA = 0.
SPI F
LAG
I
Figure 63. SPI Timing, All Modes
02987-052
Rev. A | Page 59 of 92

ADuC832
I2C-COMPATIBLE INTERFACE
The ADuC832 supports a fully licensed I2C serial interface. The
2
I
C interface is implemented as a full hardware slave and software master. SDATA is the data I/O pin and SCLOCK is the
serial clock. These two pins are shared with the MOSI and
SCLOCK pins of the on-chip SPI interface. Therefore, the user
can only enable one interface or the other at any given time
(see SPE in SPICON in Ta b le 2 8 ). The uC001 Technical Note,
MicroConverter® I
2
C® Compatible Interface, describes the opera-
tion of this interface as implemented, and is available from the
MicroConverter website at www.analog.com/microconverters.
I2C INTERFACE SFRs
Three SFRs are used to control the I2C interface. These are
described in the following sections.
I2CCON (I2Control Register)
SFR Address: E8H
I2CADD (I2C Address Register)
SFR Address: 9BH
Power-On Default Value: 55H
Bit Addressable: No
The I2CADD SFR holds the I
2
C peripheral address for the part.
It can be overwritten by user code. Technical Note uC001 at
www.analog.com/microconverters describes the format of the
2
I
C standard 7-bit address in detail.
I2CDAT (I2C Data Register)
SFR Address: 9AH
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
The I2CDAT SFR is written by the user to transmit data over
2
C interface or read by user code to read data just received
the I
2
by the I
pending I
C interface. Accessing I2CDAT automatically clears any
2
C interrupt and the I2CI bit in the I2CCON SFR. User
software should only access I2CDAT once per interrupt cycle.
Table 29. I2CCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] MDO
2
C software master data output bit (master mode only). This data bit is used to implement a master I2C transmitter interface
I
in software. Data written to this bit is output on the SDATA pin if the data output enable (MDE) bit is set.
[6] MDE
2
C software master data output enable bit (master mode only). Set by user to enable the SDATA pin as an output (Tx).
I
Cleared by the user to enable SDATA pin as an input (Rx).
[5] MCO
2
C software master clock output bit (master mode only). This data bit is used to implement a master I2C transmitter interface
I
in software. Data written to this bit is output on the SCLOCK pin.
[4] MDI
2
C software master data input bit (master mode only). This data bit is used to implement a master I2C receiver interface in
I
software. Data on the SDATA pin is latched into this bit on SCLOCK if the data output enable (MDE) bit is 0.
[3] I2CM
2
C master/slave mode bit set by user to enable I2C software master mode. Cleared by user to enable I2C hardware slave
I
mode.
[2] I2CRS I2C reset bit (slave mode only). Set by user to reset the I2C interface. Cleared by user code for normal I2C operation.
[1] I2CTX
2
C direction transfer bit (slave mode only). Set by the MicroConverter if the interface is transmitting. Cleared by the
I
MicroConverter if the interface is receiving.
[0] I2CI
2
C interrupt bit (slave mode only). Set by the MicroConverter after a byte has been transmitted or received. Cleared
I
automatically when user code reads the I2CDAT SFR (see the I2CADD (I2C Address Register) section).
Rev. A | Page 60 of 92

ADuC832
2
OVERVIEW
The main features of the MicroConverter I2C interface are:
• Only two bus lines are required; a serial data line (SDATA)
and a serial clock line (SCLOCK).
• An I
2
C master can communicate with multiple slave
devices. Because each slave device has a unique 7-bit
address, single master/slave relationships can exist at all
times even in a multislave environment (Figure 64).
• On-chip filtering rejects <50 ns spikes on the SDATA and
the SCLOCK lines to preserve data integrity.
DV
DD
I2CI
MASTER
Figure 64. Typical I
SLAVE 1
SLAVE 2
2
C System
2
C
2
I
C
2987-053
SOFTWARE MASTER MODE
The ADuC832 can be used as an I2C master device by
configuring the I
software to output the data bit by bit. This is referred to as a
software master. Master mode is enabled by setting the I2CM
bit in the I2CCON register.
To transmit data on the SDATA line, MDE must be set to enable
the output driver on the SDATA pin. If MDE is set, then the
SDATA pin is pulled high or low depending on whether the
MDO bit is set or cleared. MCO controls the SCLOCK pin and
is always configured as an output in master mode. In master mode,
the SCLOCK pin is pulled high or low depending on the
whether MCO is set or cleared.
To receive data, MDE must be cleared to disable the output
driver on SDATA. Software must provide the clocks by toggling
the MCO bit and reading the SDATA pin via the MDI bit. If
MDE is cleared, MDI can be used to read the SDATA pin. The
value of the SDATA pin is latched into MDI on a rising edge of
SCLOCK. MDI is set if the SDATA pin was high on the last
rising edge of SCLOCK. MDI is cleared if the SDATA pin was
low on the last rising edge of SCLOCK.
Software must control MDO, MCO, and MDE appropriately to
generate the start condition, slave address, acknowledge bits,
data bytes, and stop conditions appropriately. These functions
are provided in Technical Note uC001.
2
C peripheral in master mode and writing
HARDWARE SLAVE MODE
After reset, the ADuC832 defaults to hardware slave mode.
2
C interface is enabled by clearing the SPE bit in SPICON.
The I
Slave mode is enabled by clearing the I2CM bit in I2CCON.
The ADuC832 has a full hardware slave. In slave mode, the I
address is stored in the I2CADD register. Data received or to be
transmitted is stored in the I2CDAT register.
2
C
Rev. A | Page 61 of 92
Once enabled in I
2
C slave mode, the slave controller waits for a
start condition. If the ADuC832 detects a valid start condition,
followed by a valid address, followed by the R/
W
bit, the I2CI
interrupt bit is automatically set by hardware.
2
C peripheral only generates a core interrupt if the user
The I
has preconfigured the I
2
C interrupt enable bit (ESI) in the IEIP2
SFR, as well as the global interrupt bit (EA) in the IE SFR.
; Enabling I2C Interrupts for the ADuC832
MOV IEIP2,#01H ; enable I
C interrupt
SETB EA
On the ADuC832, an autoclear of the I2CI bit is implemented
so this bit is cleared automatically on a read or write access to
the I2CDAT SFR.
MOV I2CDAT, A ; I2CI autocleared
MOV A, I2CDAT ; I2CI autocleared
If for any reason the user tries to clear the interrupt more than
once, that is, access the data SFR more than once per interrupt,
then the I
2
C controller stops. The interface then must be reset
using the I2CRS bit.
The user can choose to poll the I2CI bit or enable the interrupt.
In the case of the interrupt, the PC counter vectors to 003BH at
the end of each complete byte. For the first byte, when the user
reaches the I2CI interrupt service routine (ISR), the 7-bit
address and the R/
The I2CTX bit contains the R/
W
bit appear in the I2CDAT SFR.
W
bit sent from the master. If
I2CTX is set, then the master waits to receive a byte. Thus the
slave transmits data by writing to the I2CDAT register. If I2CTX
is cleared, the master transmits a byte. Therefore, the slave receives
a serial byte. The software can check the state of I2CTX to
determine whether it should write to or read from I2CDAT.
Once the ADuC832 has received a valid address, the hardware
hold SCLOCK low until the I2CI bit is cleared by software. This
allows the master to wait for the slave to be ready before
transmitting the clocks for the next byte.
The I2CI interrupt bit is set every time a complete data byte is
received or transmitted, provided it is followed by a valid ACK.
If the byte is followed by a NACK, an interrupt is not generated.
The ADuC832 continues to issue interrupts for each complete
data byte transferred until a stop condition is received or the
interface is reset.
When a stop condition is received, the interface resets to a state
where it is waiting to be addressed (idle). Similarly, if the
interface receives a NACK at the end of a sequence, it also returns
to the default idle state. The I2CRS bit can be used to reset the
2
I
C interface. This bit can be used to force the interface back to
the default idle state.
It should be noted that there is no way (in hardware) to distinguish
between an interrupt generated by a received start plus valid
address and an interrupt generated by a received data byte. User
software must be used to distinguish between these interrupts.

ADuC832
DUAL DATA POINTERS
The ADuC832 incorporates two data pointers. The second data
pointer is a shadow data pointer and is selected via the data
pointer control SFR (DPCON). DPCON also includes features
such as automatic hardware postincrement and postdecrement,
as well as automatic data pointer toggle. DPCON is described in
Tabl e 30 .
Table 30. DPCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Reserved Reserved for future use.
[6] DPT
[5:4] DP1m[1:0] Shadow data pointer mode.
[3:2] DP0m[1:0]
[1] Reserved
[0] DPSEL Data pointer select.
Data pointer automatic toggle enable.
Cleared by user to disable auto swapping of the DPTR. Set in user software to enable automatic toggling of the DPTR
after each MOVX or MOVC instruction.
These two bits enable extra modes of the shadow data pointer operation, allowing for more compact and more
efficient code size and execution.
DP1m1 DP1m0 Behavior of Shadow Data Pointer
0 0 8052 behavior
0 1 DPTR is postincremented after a MOVX or a MOVC instruction.
1 0 DPTR is postdecremented after a MOVX or MOVC instruction.
1 1
Main data pointer mode. These two bits enable extra modes of the main data pointer operation, allowing for more
compact and more efficient code size and execution.
DP0m1 DP0m0 Behavior of the Main Data Pointer
0 0 8052 behavior
0 1 1 DPTR is postincremented after a MOVX or a MOVC instruction.
1 0 DPTR is postdecremented after a MOVX or MOVC instruction.
1 1
This bit is not implemented to allow the INC DPCON instruction to toggle the data pointer without incrementing the
rest of the SFR.
Cleared by user to select the main data pointer. This means that the contents of this 24-bit register are placed into the
DPL, DPH, and DPP SFRs.
Set by the user to select the shadow data pointer. This means that the contents of a separate 24-bit register appears in
the DPL, DPH, and DPP SFRs.
DPTR LSB is toggled after a MOVX or MOVC instruction. (This instruction can be useful for moving
8-bit blocks to/from 16-bit devices.)
DPTR LSB is toggled after a MOVX or MOVC instruction. (This instruction can be useful for moving
8-bit blocks to/from 16-bit devices.)
Notes
This is the only section where the main and shadow data
pointers are distinguished. Everywhere else in this data sheet
wherever the DPTR is mentioned, operation on the active
DPTR is implied.
Only MOVC/MOVX @DPTR instructions are relevant in Ta b le 3 0.
MOVC/MOVX PC/@Ri instructions do not cause the DPTR to
automatically postincrement or postdecrement.
To illustrate the operation of DPCON, the following code copies
256 bytes of code memory at Address D000H into XRAM
starting from Address 0000H.
The following code uses 16 bytes and 2054 cycles. To perform
this on a standard 8051 requires approximately 33 bytes and
7172 cycles (depending on how it is implemented).
Rev. A | Page 62 of 92
DPCON (DATA POINTER CONTROL SFR)
SFR Address: A7H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
MOV DPTR,#0 ; Main DPTR = 0
MOV DPCON,#55H ; Select shadow DPTR
; DPTR1 increment mode,
; DPTR0 increment mode
; DPTR auto toggling on
MOV DPTR,#0D000H ; Shadow DPTR = D000H
MOVELOOP:
CLR A
MOVC A,@A+DPTR ; Get data
; Post Inc DPTR
; Swap to Main DPTR (Data)
MOVX @DPTR,A ; Put ACC in XRAM
; Increment main DPTR
; Swap Shadow DPTR (Code)
MOV A, DPL
JNZ
MOVELOOP

ADuC832
POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
As its name suggests, the power supply monitor, once enabled,
monitors the DV
supply on the ADuC832. It indicates when
DD
any of the supply pins drop below one of four user-selectable
voltage trip points from 2.63 V to 4.37 V. For correct operation
of the power supply monitor function, AV
must be equal to
DD
or greater than 2.7 V. The monitor function is controlled via
the PSMCON SFR. If enabled via the IEIP2 SFR, the monitor
interrupts the core using the PSMI bit in the PSMCON SFR.
This bit is not cleared until the failing power supply has returned
above the trip point for at least 250 ms. This monitor function
allows the user to save working registers to avoid possible data
loss due to the low supply condition, and ensures that normal
Table 31. PSMCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Reserved Reserved.
[6] CMPD
[5] PSMI
[4:3] TPD[1:0] DVDD trip point selection bits. These bits select the DVDD trip point voltage as follows:
[2] Reserved Reserved.
[1] Reserved Reserved.
[0] PSMEN
comparator bit.
DV
DD
This is a read-only bit and directly reflects the state of the DV
Read 1 indicates the DV
Read 0 indicates the DV
Power supply monitor interrupt bit.
This bit is set high by the MicroConverter if CMPD is low, indicating low analog or digital supply. The PSMI bit can be
used to interrupt the processor. Once CMPD returns (and remains) high, a 250 ms counter is started. When this counter
times out, the PSMI interrupt is cleared. PSMI can also be written by the user. However, if either comparator output is
low, it is not possible for the user to clear PSMI.
TPD1 TPD0 Selected DVDD Trip Point (V)
0 0 4.37
0 1 3.08
1 0 2.93
1 1 2.63
Power supply monitor enable bit. Set to 1 by the user to enable the power supply monitor circuit. Cleared to 0 by the
user to disable the power supply monitor circuit.
supply is above its selected trip point.
DD
supply is below its selected trip point.
DD
code execution does not resume until a safe supply level has
been well established. The supply monitor is also protected
against spurious glitches triggering the interrupt circuit.
PSMCON (POWER SUPPLY MONITOR CONTROL REGISTER )
SFR Address: DFH
Power-On Default Value: DEH
Bit Addressable : No
comparator.
DD
Rev. A | Page 63 of 92

ADuC832
WATCHDOG TIMER
The purpose of the watchdog timer is to generate a device reset
or interrupt within a reasonable amount of time if the ADuC832
enters an erroneous state, possibly due to a programming error
or electrical noise. The watchdog function can be disabled by
clearing the watchdog enable (WDE) bit in the watchdog
control (WDCON) SFR. When enabled, the watchdog circuit
generates a system reset or interrupt (WDS) if the user program
fails to set the watchdog (WDE) bit within a predetermined
amount of time (see the PRE[3:0] bits in WDCON). The
watchdog timer itself is a 16-bit counter that is clocked directly
from the 32.768 kHz external crystal. The watchdog timeout
interval can be adjusted via the PRE[3:0] bits in WDCON. Full
control and status of the watchdog timer function can be con-
Table 32. WDCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7:4] PRE[3:0] Watchdog timer prescale bits.
The watchdog timeout period is given by the following equation:
tWD = (2
where 0 ≤ PRE ≤ 7 and f
PRE3 PRE2 PRE1 PRE0 Timeout Period (ms) Action
0 0 0 0 15.6 Reset or Interrupt
0 0 0 1 31.2 Reset or Interrupt
0 0 1 0 62.5 Reset or Interrupt
PRE[3:0] > 1000 = reserved.
[3] WDIR
[2] WDS
[1] WDE
[0] WDWR
0 0 1 1 125 Reset or Interrupt
0 1 0 0 250 Reset or Interrupt
0 1 0 1 500 Reset or Interrupt
0 1 1 0 1000 Reset or Interrupt
0 1 1 1 2000 Reset or Interrupt
1 0 0 0 0.0 Immediate Reset
Watchdog interrupt response enable bit.
If this bit is set by the user, the watchdog generates an interrupt response instead of a system reset when the watchdog
timeout period has expired. This interrupt is not disabled by the CLR EA instruction and it is also a fixed, high priority
interrupt. If the watchdog is not being used to monitor the system, it can alternatively be used as a timer. The prescaler is
used to set the timeout period in which an interrupt is generated.
Watchdog status bit.
Set by the watchdog controller to indicate that a watchdog timeout has occurred.
Cleared by writing a 0 or by an external hardware reset. It is not cleared by a watchdog reset.
Watchdog enable bit.
Set by user to enable the watchdog and clear its counters. If this bit is not set by the user within the watchdog timeout
period, the watchdog generates a reset or interrupt, depending on WDIR.
Cleared under the following conditions: user writes 0, watchdog reset (WDIR = 0), hardware reset, or PSM interrupt.
Watchdog write enable bit.
To write data into the WDCON SFR involves a double instruction sequence. The WDWR bit must be set and the very next
instruction must be a write instruction to the WDCON SFR. See the Example Write Instruction section.
PRE
× (29/f
)).
XTAL
= 32.768 kHz).
XTAL
Example Write Instruction
CLR EA ;disable interrupts while writing
;to WDT
SETB WDWR ;allow write to WDCON
MOV WDCON, #72H ;enable WDT for 2.0 sec timeout
SETB EA ;enable interrupts again (if rqd)
trolled via the watchdog timer control SFR (WDCON). The
WDCON SFR can only be written by user software if the double
write sequence described in the WDWR description (see Tab le 3 2)
is initiated on every write access to the WDCON SFR.
WDCON (Watchdog Timer Control Register)
SFR Address: C0H
Power-On Default Value: 10H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Rev. A | Page 64 of 92

ADuC832
TIME INTERVAL COUNTER (TIC)
A time interval counter is provided on chip for counting longer
intervals than the standard 8051-compatible timers are capable of.
The TIC is capable of timeout intervals ranging from 1/128 second
to 255 hours. Furthermore, this counter is clocked by the external 32.768 kHz crystal rather than the core clock, and has the
ability to remain active in power-down mode and time long
power-down intervals. This has obvious applications for remote
battery-powered sensors where regular widely spaced readings
are required. Note that instructions to the TIC SFRs are also
clocked at 32.768 kHz, and sufficient time must be allowed in
user code for these instructions to execute.
Six SFRs are associated with the time interval counter, TIMECON
being its control register. Depending on the configuration of the
ITS0 and ITS1 bits in TIMECON, the selected time counter register overflow clocks the interval counter. When this counter is
equal to the time interval value loaded in the INTVAL SFR, the
TII bit (TIMECON[2]) is set and generates an interrupt if
enabled. If the ADuC832 is in power-down mode, again with
the TIC interrupt enabled, the TII bit wakes up the device and
resumes code execution by vectoring directly to the TIC interrupt
service vector address at 0053H. The TIC-related SFRs are
described in the following sections. Note also that the timebase
SFRs can be written initially with the current time; the TIC can
then be controlled and accessed by user software. In effect, this
facilitates the implementation of a real-time clock. A block
diagram of the TIC is shown in Figure 65.
32.768kHz EXTERNAL CRYSTAL
TCEN
8-BIT
PRESCALER
HUNDREDTHS COUNTER
HTHSEC
SECOND COUNTER
SEC
MINUTE COUNTER
MIN
HOUR COUNTER
HOUR
INTERVAL TI M EOUT
TIME INTE RVAL CO UNT E R I NT ERRUP T
Figure 65. TIC, Simplified Block Diagram
SELECTION
8-BIT
INTERVAL COUNTER
COMPARE
COUNT = INTVAL
TIMER INTVAL
INTVAL
TIMECON (TIC CONTROL REGISTER)
SFR Address: A1H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
ITS0, ITS1
INTERVAL
TIMEBASE
MUX
TIEN
02987-054
Table 33. TIMECON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Reserved Reserved for future use.
[6] TFH
Twenty-four hour select bit. Set by the user to enable the hour counter to count from 0 to 23. Cleared by the user to
enable the hour counter to count from 0 to 255.
[5:4] ITS[1:0] Interval timebase selection bits. Written by user to determine the interval counter update rate.
ITS1 ITS0 Interval Timebase
0 0 1/128 second
0 1 Seconds
1 0 Minutes
1 1 Hours
[3] STI
Single-time interval bit. Set by the user to generate a single interval timeout. If set, a timeout clears the TIEN bit. Cleared
by the user to allow the interval counter to be automatically reloaded and starts counting again at each interval timeout.
[2] TII TIC interrupt bit. Set when the 8-bit interval counter matches the value in the INTVAL SFR. Cleared by user software.
[1] TIEN
Time interval enable bit. Set by the user to enable the 8-bit time interval counter. Cleared by the user to disable the
interval counter.
[0] TCEN
Time clock enable bit. Set by the user to enable the time clock to the time interval counters. Cleared by the user to
disable the clock to the time interval counters and to reset the time interval SFRs to the last value written to them by the
user. The time registers (HTHSEC, SEC, MIN, and hour) can be written while TCEN is low.
Rev. A | Page 65 of 92

ADuC832
INTVAL (USER TIME INTERVAL SELECT REGISTER)
SFR Address: A6H
MIN (MINUTES TIME REGISTER)
SFR Address: A4H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Valid Value: 0 to 255 decimal
User code writes the required time interval to this register.
When the 8-bit interval counter is equal to the time interval
value loaded in the INTVAL SFR, the TII bit (TIMECON[2]) is
set and generates an interrupt if enabled.
HTHSEC (HUNDREDTHS SECONDS TIME REGISTER)
SFR Address: A2H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Valid Value: 0 to 127 decimal
This register is incremented in 1/128 second intervals when
TCEN in TIMECON is active. The HTHSEC SFR counts from 0
to 127 before rolling over to increment the SEC time register.
SEC (SECONDS TIME REGISTER)
SFR Address: A3H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Valid Value: 0 to 59 decimal
This register is incremented in 1 minute intervals when TCEN
in TIMECON is active. The MIN counts from 0 to 59 before
rolling over to increment the hour time register.
HOUR (HOURS TIME REGISTER)
SFR Address: A5H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Valid Value: 0 to 23 decimal
This register is incremented in 1 hour intervals when TCEN in
TIMECON is active. The hour SFR counts from 0 to 23 before
rolling over to 0.
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
Valid Value: 0 to 59 decimal
This register is incremented in 1 second intervals when TCEN
in TIMECON is active. The SEC SFR counts from 0 to 59 before
rolling over to increment the MIN time register.
Rev. A | Page 66 of 92

ADuC832
L
T
L
8052-COMPATIBLE ON-CHIP PERIPHERALS
This section gives a brief overview of the various secondary
peripheral circuits that are also available to the user on chip.
These remaining functions are mostly 8052 compatible (with a
few additional features) and are controlled via standard 8052 SFR
bit definitions.
PARALLEL I/O
The ADuC832 uses four input/output ports to exchange data
with external devices. In addition to performing general-purpose
I/O, some ports are capable of external memory operations
whereas others are multiplexed with alternate functions for the
peripheral features on the device. In general, when a peripheral
is enabled, that pin cannot be used as a general-purpose I/O pin.
PORT 0
Port 0 is an 8-bit, open-drain, bidirectional I/O port that is directly
controlled via the Port 0 SFR. Port 0 is also the multiplexed low
order address and data bus during accesses to external program
or data memory.
Figure 66 shows a typical bit latch and I/O buffer for a Port 0
port pin. The bit latch (one bit in the port’s SFR) is represented
as a Type D flip-flop, which clocks in a value from the internal
bus in response to a write-to-latch signal from the CPU. The Q
output of the flip-flop is placed on the internal bus in response
to a read latch signal from the CPU. The level of the port pin
itself is placed on the internal bus in response to a read pin
signal from the CPU. Some instructions that read a port activate
the read latch signal, and others activate the read pin signal. See
the Read-Modify-Write Instructions section for more details.
ADDR/DATA
READ
LATCH
INTERNA
BUS
WRITE
O LATCH
READ
DCLQ
LATCH
PIN
Figure 66. Port 0 Bit Latch and I/O Buffer
CONTROL
Q
As shown in Figure 66, the output drivers of Port 0 pins are
switchable to an internal ADDR and ADDR/data bus by an
internal control signal for use in external memory accesses.
During external memory accesses, 1s are written to the P0 SFR
(that is, all of its bit latches become 1). When accessing external
memory, the control signal in Figure 66 goes high, enabling
push-pull operation of the output pin from the internal address
or data bus (ADDR/data line). Therefore, no external pull-ups
are required on Port 0 for it to access external memory.
In general-purpose I/O port mode, Port 0 pins that have 1s
written to them via the Port 0 SFR are configured as open drain
and therefore float. In this state, Port 0 pins can be used as high
impedance inputs. This is represented in Figure 66 by the
DV
DD
P0.x
PIN
2987-055
NAND gate whose output remains high as long as the control
signal is low, thereby disabling the top FET. External pull-up
resistors are therefore required when Port 0 pins are used as
general-purpose outputs. Port 0 pins with 0s written to them drive
a logic low output voltage (V
) and are capable of sinking 1.6 mA.
OL
PORT 1
Port 1 is also an 8-bit port directly controlled via the P1 SFR.
Port 1 digital output capability is not supported on this device.
Port 1 pins can be configured as digital inputs or analog inputs.
By (power-on) default, these pins are configured as analog
inputs, that is, 1 written in the corresponding Port 1 register bit.
To configure any of these pins as digital inputs, write a 0 to
these port bits to configure the corresponding pin as a high
impedance digital input.
These pins also have various secondary functions described in
Tabl e 34 .
Table 34. Port 1, Alternate Pin Functions
Pin Alternate Function
P1.0
T2 (Timer/Counter 2 external input) or ADC0 (single-
ended analog input)
P1.1 T2EX (Timer/Counter 2 capture/reload trigger) or ADC1
P1.5
SS (slave select for the SPI interface) or ADC5
READ
LATCH
INTERNA
BUS
WRITE
TO LATCH
READ
PIN
Figure 67. Port 1 Bit Latch and I/O Buffer
DCLQ
LATCH
TO ADC
Q
P1.x
PIN
02987-056
PORT 2
Port 2 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-up resistors
directly controlled via the P2 SFR. Port 2 also emits the high
order address bytes during fetches from external program
memory and middle and high order address bytes during
accesses to the 24-bit external data memory space.
As shown in Figure 68, the output drivers of Port 2 are
switchable to an internal ADDR and ADDR/data bus by an
internal control signal for use in external memory accesses (as
for Port 0). In external memory addressing mode (control = 1), the
port pins feature push-pull operation controlled by the internal
address bus (ADDR line). However, unlike the P0 SFR during
external memory accesses, the P2 SFR remains unchanged.
In general-purpose I/O port mode, Port 2 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups
(see Figure 69) and, in that state, can be used as inputs. As
inputs, Port 2 pins pulled externally low source current because
of the internal pull-up resistors. Port 2 pins with 0s written to
Rev. A | Page 67 of 92

ADuC832
them drive a logic low output voltage (VOL) and are capable of
sinking 1.6 mA.
P2.6 and P2.7 can also be used as PWM outputs. If they are
selected as the PWM outputs via the CFG832 SFR, the PWM
outputs overwrite anything written to P2.6 or P2.7.
DCLQ
LATCH
ADDR
CONTROL
Q
*SEE FIGURE 69 FOR
DETAILS O F INTERNAL PULL-UP
DV
DV
DD
DD
INTERNAL
PULL-UP*
P2.x
PIN
READ
LATCH
INTERNAL
BUS
WRITE
TO LATCH
READ
PIN
Figure 68. Port 2 Bit Latch and I/O Buffer
DV
DV
DD
DDDVDD
Q2 Q3
P2.x
PIN
02987-058
FROM
PORT
LATCH
2 CLK
DELAY
Q
Q1
Q4
Figure 69. Internal Pull-Up Configuration
PORT 3
Port 3 is a bidirectional port with internal pull-ups directly
controlled via the P3 SFR. Port 3 pins that have 1s written to
them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and, in that state,
can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 3 pins pulled externally
low source current because of the internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins
with 0s written to them drive a logic low output voltage (V
and are capable of sinking 4 mA.
Port 3 pins also have various secondary functions described in
Tabl e 35 . The alternate functions of Port 3 pins can only be
activated if the corresponding bit latch in the P3 SFR contains a 1.
Otherwise, the port pin is stuck at 0.
Table 35. Port 3, Alternate Pin Functions
Pin Alternate Function
P3.0 RxD (UART input pin or serial data I/O in Mode 0)
P3.1 TxD (UART output pin or serial clock output in Mode 0)
P3.2
P3.3
P3.4
(External Interrupt 0)
INT0
(External Interrupt 1) or PWM1/MISO
INT1
T0 (Timer/Counter 0 external input), PWMC, PWM0, or
EXTCLK
P3.5
P3.6
P3.7
T1 (Timer/Counter 1 external input) or CONVST
(external data memory write strobe)
WR
(external data memory read strobe)
RD
P3.3 and P3.4 can also be used as PWM outputs. If they are
selected as the PWM outputs via the CFG832 SFR, the PWM
outputs overwrite anything written to P3.4 or P3.3.
)
OL
DV
DD
READ
LATCH
INTERNAL
BUS
WRITE
TO LATCH
READ
PIN
DCLQ
LATCH
ALTERNATE
OUTPUT
FUNCTION
Q
ALTERNATE
FUNCTION
INPUT
INTERNAL
PULL-UP*
P3.x
PIN
*SEE FIGURE 69
FOR DETAI LS OF
INTERNAL PULL-UP
02987-059
Figure 70. Port 3 Bit Latch and I/O Buffer
7-057
0298
ADDITIONAL DIGITAL I/O
In addition to the port pins, the dedicated SPI/I2C pins
(SCLOCK and SDATA/MOSI) also feature both input and
output functions. Their equivalent I/O architectures are
illustrated in Figure 71 and Figure 73, respectively, for SPI
operation and in Figure 72 and Figure 74 for I
2
Notice that in I
C mode (SPE, SPICON[5] = 0), the strong pull-
2
C operation.
up FET (Q1) is disabled, leaving only a weak pull-up (Q2)
present. By contrast, in SPI mode (SPE = 1) the strong pull-up
FET (Q1) is controlled directly by SPI hardware, giving the pin
push-pull capability.
2
In I
C mode (SPE = 0), two pull-down FETs (Q3 and Q4)
operate in parallel to provide an extra 60% or 70% of current
sinking capability. In SPI mode, however, (SPE = 1) only one of
the pull-down FETs (Q3) operates on each pin, resulting in sink
capabilities identical to that of Port 0 and Port 2 pins. On the
input path of SCLOCK, notice that a Schmitt trigger conditions
the signal going to the SPI hardware to prevent false triggers
(double triggers) on slow incoming edges. For incoming signals
from the SCLOCK and SDATA pins going to I
2
C hardware, a filter
conditions the signals in order to reject glitches of up to 50 ns in
duration.
Notice also that direct access to the SCLOCK and SDATA/MOSI
pins is afforded through the SFR interface in I
Therefore, if the SPI or I
2
C functions are not used, these two
2
C master mode.
pins can be used to give additional high current digital outputs.
DV
Q1
Q3
DD
Q2 (OFF)
Q4 (OFF)
SCLOCK
PIN
02987-060
SPE = 1 (SPI E NABLE)
HARDWARE SPI
(MASTER/SLAVE)
SCHMITT
TRIGGER
Figure 71. SCLOCK Pin I/O Functional Equivalent in SPI Mode
Rev. A | Page 68 of 92

ADuC832
SPE = 0 (I2C ENABLE)
HARDWARE I2C
(SLAVE ONLY)
SFR
BITS
MCO
I2CM
50ns GLI TCH
REJECTION F I LTER
DV
DD
Q1
(OFF)
Q3
Q2
SCLOCK
Q4
Figure 72. SCLOCK Pin I/O Functional Equivalent in I
DV
DD
SPE = 1 (SPI ENABLE)
Q1
HARDWARE SPI
(MASTER/SLAVE)
Q3
Figure 73. SDATA/MOSI Pin I/O Functional Equivalent in SPI Mode
SPE = 0 (I2C ENABLE)
HARDWARE I2C
(SLAVE ONLY)
SFR
BITS
MDI
MDO
MDE
I2CM
50ns GLITCH
REJECTION FILTE R
Figure 74. SDATA/MOSI Pin I/O Functional Equivalent in I
Q2 (OFF)
Q4 (OFF)
DV
Q1
(OFF)
Q3
DD
PIN
2
C Mode
SDATA/
MOSI
Q2
Q4
2
PIN
SDATA/
MOSI
PIN
C Mode
MISO is shared with P3.3 and as such has the same configuration
as that shown in Figure 70.
READ-MODIFY-WRITE INSTRUCTIONS
Some 8051 instructions that read a port read the latch while
others read the pin. The instructions that read the latch rather
than the pins are the ones that read a value, possibly change it,
and then rewrite it to the latch. These are called read-modify-write
7-061
0298
02987-062
2987-063
instructions. Listed below are the read-modify-write instructions.
When the destination operand is a port, or a port bit, these
instructions read the latch rather than the pin.
Instruction Description
ANL Logical AND, for example, ANL P1, A
ORL Logical OR, for example, ORL P2, A
XRL Logical EX-OR, for example., XRL P3, A
JBC
Jump if bit = 1 and clear bit, for example, JBC
P1.1, LABEL
CPL Complement bit, for example, CPL P3.0
INC Increment, for example, INC P2
DEC Decrement, for example, DEC P2
DJNZ
Decrement and jump if not zero, for example,
DJNZ P3, LABEL
MOV PX.Y, C1 Move carry to Bit Y of Port X
CLR PX.Y1 Clear Bit Y of Port X
SETB PX.Y1 Set Bit Y of Port X
1
These instructions read the port byte (all 8 bits), modify the addressed bit
and then write the new byte back to the latch.
The reason that read-modify-write instructions are directed to
the latch rather than the pin is to avoid a possible misinterpretation
of the voltage level of a pin. For example, a port pin might be
used to drive the base of a transistor. When a 1 is written to the
bit, the transistor is turned on. If the CPU then reads the same
port bit at the pin rather than the latch, it will read the base
voltage of the transistor and interpret it as a logic 0. Reading the
latch rather than the pin will return the correct value of 1.
Rev. A | Page 69 of 92

ADuC832
TIMERS/COUNTERS
The ADuC832 has three 16-bit timer/counters: Timer 0, Timer 1,
and Timer 2. The timer/counter hardware has been included on
chip to relieve the processor core of the overhead inherent in
implementing timer/counter functionality in software. Each
timer/counter consists of two 8-bit registers THx and TLx (x =
0, 1, and 2). All three can be configured to operate either as
timers or event counters.
In the timer function, the TLx register is incremented every
machine cycle. Thus, it can be thought of as counting machine
cycles. Because a machine cycle consists of 12 core clock
periods, the maximum count rate is 1/12 the core clock
frequency.
In a counter function, the TLx register is incremented by a 1-to0 transition at its corresponding external input pin, T0, T1, or
T2. In this function, the external input is sampled during S5P2
of every machine cycle. When the samples show a high in one
cycle and a low in the next cycle, the count is incremented. The
new count value appears in the register during S3P1 of the cycle
following the one in which the transition was detected. Because
two machine cycles (24 core clock periods) are needed to
Table 36. TMOD SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Gate
[6] C/T
[5:4 M[1:0] Timer 1 Mode Select Bit 1 and Bit 0.
[3] Gate
[2] C/T
[1:0] M[1:0] Timer 0 Mode Select Bit 1 and Bit 0.
Timer 1 gating control. Set by software to enable Timer/Counter 1 only while INT1
Cleared by software to enable Timer 1 whenever TR1 control bit is set.
Timer 1 timer or counter select bit. Set by software to select counter operation (input from T1 pin). Cleared by software to
select timer operation (input from internal system clock).
M1 M0 Description
0 0 TH1 operates as an 8-bit timer/counter. TL1 serves as a 5-bit prescaler.
0 1 16-bit timer/counter. TH1 and TL1 are cascaded; there is no prescaler.
1 0 8-bit autoreload timer/counter. TH1 holds a value that is to be reloaded into TL1 each time it overflows.
1 1 Timer/Counter 1 stopped.
Timer 0 gating control. Set by software to enable Timer/Counter 0 only while INT0
Cleared by software to enable Timer 0 whenever TR0 control bit is set.
Timer 0 timer or counter select bit. Set by software to select counter operation (input from T0 pin). Cleared by software to
select timer operation (input from internal system clock).
M1 M0 Description
0 0 TH0 operates as an 8-bit timer/counter. TL0 serves as a 5-bit prescaler.
0 1 16-bit timer/counter. TH0 and TL0 are cascaded; there is no prescaler.
1 0 8-Bit autoreload timer/counter. TH0 holds a value that is to be reloaded into TL0 each time it overflows.
1 1 TL0 is an 8-bit timer/counter controlled by the standard timer 0 control bits.
TH0 is an 8-bit timer only, controlled by Timer 1 control bits.
recognize a 1-to-0 transition, the maximum count rate is 1/24
the core clock frequency. There are no restrictions on the duty
cycle of the external input signal, but to ensure that a given level
is sampled at least once before it changes, it must be held for a
minimum of one full machine cycle.
User configuration and control of all timer operating modes is
achieved via three SFRs: TMOD and TCON, which control and
configure Timer 0 and Timer 1, and T2CON, which controls and
configures Timer 2.
TMOD (Timer/Counter 0 and Timer/Counter 1 Mode Register)
SFR Address: 89H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: No
pin is high and TR1 control bit is set.
pin is high and TR0 control bit is set.
Rev. A | Page 70 of 92

ADuC832
TCON (Timer/Counter 0 and Timer/Counter 1 Control Register)
SFR Address: 88H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Table 37. TCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] TF1
Timer 1 overflow flag.
Set by hardware on a Timer/Counter 1 overflow.
Cleared by hardware when the program counter (PC) vectors to the interrupt service routine.
[6] TR1
Timer 1 run control bit.
Set by the user to turn on Timer/Counter 1.
Cleared by the user to turn off Timer/Counter 1.
[5] TF0
Timer 0 overflow flag.
Set by hardware on a Timer/Counter 0 overflow.
Cleared by hardware when the PC vectors to the interrupt service routine.
[4] TR0
Timer 0 run control bit.
Set by the user to turn on Timer/Counter 0.
Cleared by the user to turn off Timer/Counter 0.
[3] IE1
1
External Interrupt 1 (INT1) flag.
Set by hardware by a falling edge or zero level being applied to external interrupt Pin INT1
Cleared by hardware when the PC vectors to the interrupt service routine only if the interrupt was transition-activated. If
level-activated, the external requesting source controls the request flag, rather than the on-chip hardware.
[2] IT1
1
External Interrupt 1 (IE1) trigger type.
Set by software to specify edge-sensitive detection (that is, a 1-to-0 transition).
Cleared by software to specify level-sensitive detection (that is, zero level).
[1] IE01
External Interrupt 0 (INT0
) flag.
Set by hardware by a falling edge or zero level being applied to external interrupt Pin INT0
Cleared by hardware when the PC vectors to the interrupt service routine only if the interrupt was transition-activated.
If level-activated, the external requesting source controls the request flag, rather than the on-chip hardware.
[0] IT0
1
External Interrupt 0 (IE0) trigger type.
Set by software to specify edge-sensitive detection (that is, 1-to-0 transition).
Cleared by software to specify level-sensitive detection (that is, zero level).
1
These bits are not used in the control of Timer/Counter 0 and Timer/Counter 1, but are used instead in the control and monitoring of the external INT0 and INT1
interrupt pins.
TIMER/COUNTER 0 AND TIMER/COUNTER 1 DATA REGISTERS
Each timer consists of two 8-bit registers. These can be used as
independent registers or combined to be a single 16-bit register,
depending on the timer mode configuration.
TH0 and TL0
TH0 is the Timer 0 high byte and TL0 is the low byte. The SFR
addresses for TH0 and TL0 are 8CH and 8AH, respectively.
TH1 and TL1
TH1 is the Timer 1 high byte and TH0 is the low byte. The SFR
addresses for TH1 and TL1 are 8DH and 8BH, respectively.
, depending on the state of Bit IT1.
, depending on the state of Bit IT0.
Rev. A | Page 71 of 92

ADuC832
*
*
*
TIMER/COUNTER 0 AND TIMER/COUNTER 1 OPERATING MODES
The following sections describe the operating modes for
Timer/Counter 0 and Timer/Counter 1. Unless otherwise
noted, it should be assumed that these modes of operation are
the same for Timer 0 as for Timer 1.
MODE 0 (13-BIT TIMER/COUNTER)
Mode 0 configures an 8-bit timer/counter with a divide-by-32
prescaler. Figure 75 shows Mode 0 operation.
CORE
CLK*
P3.4/T0
GATE
P3.2/INT0
CORE CLK IS DEFINED BY THE CD BIT S IN PLLCON.
÷
12
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
CONTROL
TR0
Figure 75. Timer/Counter 0, Mode 0
TL0
(5 BITS)
TH0
(8 BITS)
TF0
INTERRUPT
In this mode, the timer register is configured as a 13-bit register.
As the count rolls over from all 1s to all 0s, it sets the timer
overflow flag, TF0. The overflow flag, TF0, can then be used to
request an interrupt. The counted input is enabled to the timer
when TR0 = 1 and either gate = 0 or
allows the timer to be controlled by external Input
INT0
= 1. Setting gate = 1
INT0
to
facilitate pulse width measurements. TR0 is a control bit in the
TCON SFR; gate is in TMOD. The 13-bit register consists of all
eight bits of TH0 and the lower five bits of TL0. The upper three
bits of TL0 are indeterminate and should be ignored. Setting the
run flag (TR0) does not clear the registers.
MODE 1 (16-BIT TIMER/COUNTER)
Mode 1 is the same as Mode 0, except that the timer register is
running with all 16 bits. Mode 1 is shown in Figure 76.
CORE
CLK*
P3.4/T0
÷12
TR0
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
(8 BITS)
CONTROL
TL0
TH0
(8 BITS)
TF0
INTERRUPT
02987-064
MODE 2 (8-BIT TIMER/COUNTER WITH AUTORELOAD)
Mode 2 configures the timer register as an 8-bit counter (TL0)
with automatic reload, as shown in Figure 77. Overflow from
TL0 not only sets TF0, but also reloads TL0 with the contents
of TH0, which is preset by software. The reload leaves TH0
unchanged.
CORE
CLK
P3.4/T0
GATE
P3.2/INT0
CORE CLK IS DEFINED BY T HE CD BI TS IN PLLCON.
12
*
TR0
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
CONTROL
TL0
(8 BITS)
RELOAD
TH0
(8 BITS)
TF0
INTERRUPT
Figure 77. Timer/Counter 0, Mode 2
MODE 3 (TWO 8-BIT TIMER/COUNTERS)
Mode 3 has different effects on Timer 0 and Timer 1. Timer 1 in
Mode 3 simply holds its count. The effect is the same as setting
TR1 = 0. Timer 0 in Mode 3 establishes TL0 and TH0 as two
separate counters. This configuration is shown in Figure 78.
TL0 uses the Timer 0 control bits: C/T, gate, TR0,
TF0. TH0 is locked into a timer function (counting machine
cycles) and takes over the use of TR1 and TF1 from Timer 1.
Thus, TH0 now controls the Timer 1 interrupt. Mode 3 is
provided for applications requiring an extra 8-bit timer or counter.
When Timer 0 is in Mode 3, Timer 1 can be turned on and off
by switching it out of and into its own Mode 3, or it can still be
used by the serial interface as a baud rate generator. It can be used
in any application not requiring an interrupt from Timer 1 itself.
CORE
CLK
P3.4/T0
12
*
TR0
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
CORE
CLK/12
CONTROL
TL0
(8 BITS)
INT0
TF0
, and
INTERRUPT
02987-066
GATE
P3.2/INT0
CORE CLK IS DE FINED BY THE CD BITS IN PLLCON.
Figure 76. Timer/Counter 0, Mode 1
502987-06
GATE
P3.2/INT0
CORE
CLK/12
TR1
*CORE CLK IS DE FINED BY THE CD BITS IN PL LCON
TH0
(8 BITS)
TF1
INTERRUPT
02987-067
Figure 78. Timer/Counter 0, Mode 3
Rev. A | Page 72 of 92

ADuC832
TIMER/COUNTER 2
T2CON (TIMER/COUNTER 2 CONTROL REGISTER)
SFR Address: C8H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Table 38. T2CON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] TF2
[6] EXF2
[5] RCLK
[4] TCLK
[3] EXEN2
[2] TR2
[1] CNT2
[0] CAP2
Timer 2 overflow flag.
Set by hardware on a Timer 2 overflow. TF2 is not set when either RCLK = 1 or TCLK = 1.
Cleared by user software.
Timer 2 external flag.
Set by hardware when either a capture or reload is caused by a negative transition on T2EX and EXEN2 = 1.
Cleared by user software.
Receive clock enable bit.
Set by the user to enable the serial port to use Timer 2 overflow pulses for its receive clock in serial port Mode 1 and Mode 3.
Cleared by the user to enable Timer 1 overflow to be used for the receive clock.
Transmit clock enable bit.
Set by the user to enable the serial port to use Timer 2 overflow pulses for its transmit clock in serial port Mode 1 and
Mode 3. Cleared by the user to enable Timer 1 overflow to be used for the transmit clock.
Timer 2 external enable flag.
Set by the user to enable a capture or reload to occur as a result of a negative transition on T2EX if Timer 2 is not being used
to clock the serial port.
Cleared by the user for Timer 2 to ignore events at T2EX.
Timer 2 start/stop control bit.
Set by the user to start Timer 2.
Cleared by the user to stop Timer 2.
Timer 2 timer or counter function select bit.
Set by the user to select counter function (input from external T2 pin).
Cleared by the user to select timer function (input from on-chip core clock).
Timer 2 capture/reload select bit.
Set by the user to enable captures on negative transitions at T2EX if EXEN2 = 1.
Cleared by the user to enable autoreloads with Timer 2 overflows or negative transitions at T2EX when EXEN2 = 1. When
either RCLK = 1 or TCLK = 1, this bit is ignored and the timer is forced to autoreload on Timer 2 overflow.
TIMER/COUNTER 2 DATA REGISTERS
Timer/Counter 2 also has two pairs of 8-bit data registers
associated with it. These are used as both timer data registers
and timer capture/reload registers.
TH2 and TL2
TH2 is the Timer 2 data high byte and TL2 is the low byte. The
SFR addresses for TH2 and TL2 are CDH and CCH, respectively.
RCAP2H and RCAP2L
RCAP2H is the Timer 2 capture/reload high byte and RCAP2L
is the low byte. The SFR addresses for RCAP2H and RCAP2L
are CBH and CAH, respectively.
Rev. A | Page 73 of 92

ADuC832
TIMER/COUNTER OPERATION MODES
The following sections describe the operating modes for Timer/
Counter 2. The operating modes are selected by bits in the T2CON
SFR as shown in Ta b le 3 9 .
Table 39. T2CON Operating Modes
RCLK (or) TCLK CAP2 TR2 Mode
0 0 1 16-bit autoreload
0 1 1 16-bit capture
1 X 1 Baud rate
X X 0 Off
16-Bit Autoreload Mode
In autoreload mode, there are two options, which are selected
by Bit EXEN2 in T2CON. If EXEN2 = 0, then when Timer 2
rolls over, it not only sets TF2 but also causes the Timer 2 registers to be reloaded with the 16-bit value in Register RCAP2L and
Register RCAP2H, which are preset by software. If EXEN2 = 1,
then Timer 2 still performs the same function as EXEN2 = 0,
but with the added feature that a 1-to-0 transition at External
Input T2EX also triggers the 16-bit reload and sets EXF2. The
autoreload mode is illustrated in Figure 79.
CORE
PIN
T2EX
PIN
CLK*
T2
÷12
TRANSITION
DETECTOR
C/T2 = 0
C/T2 = 1
CONTROL
TR2
RELOAD
16-Bit Capture Mode
In the capture mode, there are again two options, which are
selected by Bit EXEN2 in T2CON. If EXEN2 = 0, then Timer 2
is a 16-bit timer or counter that, upon overflowing, sets Bit TF2,
the Timer 2 overflow bit, which can be used to generate an interrupt. If EXEN2 = 1, then Timer 2 still performs the same function
as EXEN2 = 0, but a l-to-0 transition on External Input T2EX
causes the current value in the Timer 2 registers, TL2 and TH2,
to be captured into Register RCAP2L and Register RCAP2H,
respectively. In addition, the transition at T2EX causes Bit EXF2
in T2CON to be set, and EXF2, like TF2, can generate an interrupt. The capture mode is illustrated in Figure 80.
The baud rate generator mode is selected by RCLK = 1 and/or
TCLK = 1.
In either case, if Timer 2 is being used to generate the baud rate,
the TF2 interrupt flag does not occur. Therefore, Timer 2 interrupts
do not occur, so they do not have to be disabled. In this mode,
the EXF2 flag, however, can still cause interrupts, and this can
be used as a third external interrupt.
Baud rate generation is described as part of the UART serial
port operation in the UART Serial Interface section.
TL2
(8 BITS)
RCAP2L
TH2
(8 BITS)
RCAP2H
TF2
EXF2
TIMER
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
EXEN2
*CORE CLK IS DEFINED BY THE CD BITS IN PLLCON.
02987-068
Figure 79. Timer/Counter 2, 16-Bit Autoreload Mode
CORE
CLK*
T2
PIN
T2EX
PIN
*CORE CLK IS DEFINED BY THE CD BI TS IN PLL CON.
÷12
TRANSITION
DETECTOR
C/T2 = 0
C/T2 = 1
CONTROL
TR2
CAPTURE
CONTROL
EXEN2
TL2
(8 BITS)
RCAP2L RCAP2H
Figure 80. Timer/Counter 2, 16-Bit Capture Mode
Rev. A | Page 74 of 92
TH2
(8 BITS)
TF2
EXF2
TIMER
INTERRUPT
02987-069

ADuC832
UART SERIAL INTERFACE
The serial port is full duplex, meaning it can transmit and
receive simultaneously. It is also receive-buffered, meaning it
can commence reception of a second byte before a previously
received byte has been read from the receive register. However,
if the first byte still has not been read by the time reception of
the second byte is complete, the first byte is lost. The physical
interface to the serial data network is via the RXD and TXD
pins, and the SFR interface to the UART is comprised of SBUF
and SCON.
Table 40. SCON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7:6] SM[0:1] UART serial mode select bits. These bits select the serial port operating mode as follows:
[5] SM2
[4] REN
[3] TB8
[2] RB8
[1] TI
[0] RI
SM0 SM1 Selected Operating Mode
0 0 Mode 0: shift register, fixed baud rate (Core_CLK/2)
0 1 Mode 1: 8-bit UART, variable baud rate
1 0 Mode 2: 9-bit UART, fixed baud rate (Core_CLK/64) or (Core_CLK/32)
1 1 Mode 3: 9-bit UART, variable baud rate
Multiprocessor communication enable bit.
Enables multiprocessor communication in Mode 2 and Mode 3. In Mode 0, SM2 should be cleared. In Mode 1, if SM2 is set,
RI is not activated if a valid stop bit was not received. If SM2 is cleared, RI is set as soon as the byte of data has been
received. In Mode 2 or Mode 3, if SM2 is set, RI is not activated if the received ninth data bit in RB8 is 0. If SM2 is cleared, RI
is set as soon as the byte of data has been received.
Serial port receive enable bit.
Set by user software to enable serial port reception.
Cleared by user software to disable serial port reception.
Serial Port Transmit Bit 9.
The data loaded into TB8 is the ninth data bit that is transmitted in Mode 2 and Mode 3.
Serial Port Receiver Bit 9.
The ninth data bit received in Mode 2 and Mode 3 is latched into RB8. For Mode 1, the stop bit is latched into RB8.
Serial port transmit interrupt flag.
Set by hardware at the end of the eighth bit in Mode 0, or at the beginning of the stop bit in Mode 1, Mode 2, and Mode 3.
TI must be cleared by user software.
Serial port receive interrupt flag.
Set by hardware at the end of the eighth bit in Mode 0, or halfway through the stop bit in Mode 1, Mode 2, and Mode 3.
RI must be cleared by software.
SBUF
The serial port receive and transmit registers are both accessed
through the SBUF SFR (SFR address = 99H). Writing to SBUF
loads the transmit register and reading SBUF accesses a
physically separate receive register.
SCON (UART SERIAL PORT CONTROL REGISTER)
SFR Address: 98H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Rev. A | Page 75 of 92

ADuC832
MODE 0: 8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER MODE
Mode 0 is selected by clearing both the SM0 and SM1 bits in
the SCON SFR. Serial data enter and exit through RxD. TxD
outputs the shift clock. Eight data bits are transmitted or received.
Transmission is initiated by any instruction that writes to SBUF.
The data is shifted out of the RxD line. The eight bits are transmitted with the least significant bit (LSB) first, as shown in Figure 81.
MACHINE
CYCLE 8
S6S5S4S3S2S1S6S5S4S4S3S2S1S6S5S4S3S2S1
CORE
CLK
ALE
RxD
(DATA
OUT)
TxD
(SHIFT
CLOCK)
MACHINE
CYCLE 1
DATA BIT 0 DATA BIT 1 DATA BIT 6 DATA BI T 7
Figure 81. UART Serial Port Transmission, Mode 0
MACHINE
CYCLE 2
MACHINE
CYCLE 7
Reception is initiated when the receive enable bit (REN) is 1
and the receive interrupt bit (RI) is 0. When RI is cleared, the
data is clocked into the RxD line and the clock pulses are output
from the TxD line.
MODE 1: 8-BIT UART, VARIABLE BAUD RATE
Mode 1 is selected by clearing SM0 and setting SM1. Each data
byte (LSB first) is preceded by a start bit (0), followed by a stop
bit (1). Therefore, 10 bits are transmitted on TxD or received on
RxD. The baud rate is set by the Timer 1 or Timer 2 overflow
rate, or a combination of the two (one for transmission and the
other for reception).
Transmission is initiated by writing to SBUF. The write to SBUF
signal also loads a 1 (stop bit) into the ninth bit position of the
transmit shift register. The data is output bit by bit until the stop
bit appears on TxD and the transmit interrupt flag (TI) is
automatically set, as shown in Figure 82.
START
BIT
TxD
(SCON[1])
TI
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
THAT IS, READY FOR M ORE DATA
Figure 82. UART Serial Port Transmission, Mode 0
Reception is initiated when a 1-to-0 transition is detected on
RxD. Assuming a valid start bit was detected, character reception continues. The start bit is skipped and the eight data bits
are clocked into the serial port shift register. When all eight bits
have been clocked in, the following events occur:
• The eight bits in the receive shift register are latched
into SBUF.
• The ninth bit (stop bit) is clocked into RB8 in SCON.
• The receiver interrupt flag (RI) is set.
STOP BIT
SET INTERRUPT
02987-070
02987-097
These events occur only if the following conditions are met at
the time the final shift pulse is generated:
• RI = 0 and either SM2 = 0 or SM2 = 1
• The received stop bit = 1
If either of these conditions is not met, the received frame is
irretrievably lost, and RI is not set.
MODE 2: 9-BIT UART WITH FIXED BAUD RATE
Mode 2 is selected by setting SM0 and clearing SM1. In this
mode, the UART operates in 9-bit mode with a fixed baud rate.
The baud rate is fixed at Core_CLK/64 by default, although by
setting the SMOD bit in PCON, the frequency can be doubled
to Core_CLK/32. Eleven bits are transmitted or received, a start
bit (0), eight data bits, a programmable ninth bit, and a stop bit
(1). The ninth bit is most often used as a parity bit, although it
can be used for anything, including a ninth data bit if required.
To transmit, the eight data bits must be written into SBUF. The
ninth bit must be written to TB8 in SCON. When transmission
is initiated, the eight data bits (from SBUF) are loaded onto the
transmit shift register (LSB first). The contents of TB8 are loaded
into the ninth bit position of the transmit shift register. The
transmission starts at the next valid baud rate clock. The TI flag
is set as soon as the stop bit appears on TxD.
Reception for Mode 2 is similar to that of Mode 1. The eight
data bytes are input at RxD (LSB first) and loaded onto the
receive shift register. When all eight bits have been clocked in,
the following events occur:
• The eight bits in the receive shift register are latched
into SBUF.
• The ninth data bit is latched into RB8 in SCON.
• The receiver interrupt flag (RI) is set.
These events occur only if the following conditions are met at
the time the final shift pulse is generated:
• RI = 0 and either SM2 = 0 or SM2 = 1
• The received stop bit = 1
If either of these conditions is not met, the received frame is
irretrievably lost, and RI is not set.
MODE 3: 9-BIT UART WITH VARIABLE BAUD RATE
Mode 3 is selected by setting both SM0 and SM1. In this mode,
the 8051 UART serial port operates in 9-bit mode with a variable
baud rate determined by either Timer 1 or Timer 2. The operation
of the 9-bit UART is the same as for Mode 2 but the baud rate
can be varied as for Mode 1.
In all four modes, transmission is initiated by any instruction
that uses SBUF as a destination register. Reception is initiated in
Mode 0 by the condition RI = 0 and REN = 1. Reception is
initiated in the other modes by the incoming start bit if REN = 1.
Rev. A | Page 76 of 92

ADuC832
UART SERIAL PORT BAUD RATE GENERATION
Mode 0 Baud Rate Generation
The baud rate in Mode 0 is fixed.
Mode 0 Baud Rate = (Core_CLK Frequency/12)
Mode 2 Baud Rate Generation
The baud rate in Mode 2 depends on the value of the SMOD bit
in the PCON SFR. If SMOD = 0, the baud rate is 1/64 of the
core clock. If SMOD = 1, the baud rate is 1/32 of the core clock:
SMOD
Mode 2 Baud Rate = (2
/64) × (Core_CLK Frequency)
Mode 1 and Mode 3 Baud Rate Generation
The baud rates in Mode 1 and Mode 3 are determined by the
overflow rate in Timer 1 or Timer 2, or both (one for transmit
and the other for receive).
TIMER 1 GENERATED BAUD RATES
When Timer 1 is used as the baud rate generator, the baud rates
in Mode 1 and Mode 3 are determined by the Timer 1 overflow
rate and the value of SMOD as follows:
Mode 1 and Mode 3 Baud Rate =
SMOD
(2
/32) × (Timer 1 Overflow Rate)
The Timer 1 interrupt should be disabled in this application.
The timer itself can be configured for either timer or counter
operation, and in any of its three running modes. In the most
typical application, it is configured for timer operation in the
autoreload mode (high nibble of TMOD = 0010 binary). In that
case, the baud rate is given by the formula:
Modes 1 and 3 Baud Rate =
SMOD
(2
/32) × (Core_CLK/(12 × [256 − TH1]))
Tabl e 41 shows some commonly used baud rates and how they
can be calculated from a core clock frequency of 16.78 MHz
and 2.0971 MHz. A 5% error is tolerable using asynchronous
(start/stop) communications.
Table 41. Commonly Used Baud Rates, Timer 1
Ideal
Baud
9600 16.78 1 −9 (F9H) 9709 1.14
2400 16.78 1 −36 (DCH) 2427 1.14
1200 16.78 1 −73 (B7H) 1197 0.25
1200 2.10 0 −9 (F4H) 1213 1.14
Core_CLK
(MHz)
SMOD
Value
TH1 Reload
Value
Actual
Baud % Error
TIMER 2 GENERATED BAUD RATES
Baud rates can also be generated using Timer 2. Using Timer 2
is similar to using Timer 1 in that the timer must overflow 16
times before a bit is transmitted/received. Because Timer 2 has a
16-bit autoreload mode, a wider range of baud rates is possible
using Timer 2.
Mode 1 and Mode 3 Baud Rate =
(1/16) × (Timer 2 Overflow Rate)
Therefore, when Timer 2 is used to generate baud rates, the timer
increments every two clock cycles and not every core machine
cycle. Thus, it increments six times faster than Timer 1, and
therefore baud rates six times faster are possible. Because Timer
2 has 16-bit autoreload capability, very low baud rates are still
possible.
Timer 2 is selected as the baud rate generator by setting the
TCLK and/or RCLK bit in T2CON. The baud rates for transmit
and receive can be simultaneously different. Setting RCLK and/or
TCLK puts Timer 2 into its baud rate generator mode, as shown
in Figure 83.
In this case, the baud rate is given by the following formula:
Modes 1 and 3 Baud Rate =
(Core_CLK)/(32 × [6556 − (RCAP2H, RCAP2L)])
Tabl e 42 shows some commonly used baud rates and how they
can be calculated from a core clock frequency of 16.78 MHz
and 2.10 MHz.
Table 42. Commonly Used Baud Rates, Timer 2
Ideal
Baud
19,200 16.78 −1 (FFH) −27 (E5H) 19418 1.14
9600 16.78 −1 (FFH) −55 (C9H) 9532 0.7
2400 16.78 −1 (FFH) −218 (26H) 2405 0.21
1200 16.78 −2 (FEH) −181 (4BH) 1199 0.02
9600 2.10 −1 (FFH) −7 (FBH) 9362 2.4
2400 2.10 −1 (FFH) −27 (ECH) 2427 1.14
1200 2.10 −1 (FFH) −55 (C9H) 1191 0.7
Core_CLK
(MHz)
RCAP2H
Value
RCAP2L
Value
Actual
Baud % Error
Rev. A | Page 77 of 92

ADuC832
×
OSC. FREQ. IS DIVIDED BY 2, NOT 12.
EXEN2
CONTROL
TR2
CONTROL
EXF 2
TL2
(8 BITS)
RCAP2L
CORE
CLK
T2
PIN
NOTE AVAIL ABILITY OF ADDITI ONAL
EXTERNAL INTERRUPT
T2EX
PIN
TRANSITION
DETECTOR
*
CORE CLK IS DE F INED BY THE CD BITS IN PLL CON.
2
*
C/T2 = 0
C/T2 = 1
Figure 83. Timer 2, UART Baud Rates
TIMER 3 GENERATED BAUD RATES
The high integer dividers in a UART block mean that high
speed baud rates are not always possible using some particular
crystals. For example, using a 12 MHz crystal, a baud rate of
115,200 is not possible. To address this problem, the ADuC832
has a dedicated baud rate timer (Timer 3) specifically for
generating highly accurate baud rates.
Timer 3 can be used instead of Timer 1 or Timer 2 for generating
very accurate high speed UART baud rates including 115,200
and 230,400. Timer 3 also allows a much wider range of baud
rates to be obtained. Every desired bit rate from 12 bits/sec to
393,216 bits/sec can be generated to within an error of ±0.8%.
Timer 3 also frees up the other three timers, allowing them to
be used for different applications. A block diagram of Timer 3 is
shown in Figure 84.
CORE
CLK
FRACTIONAL
DIVIDER
*CORE CLK IS DEFINED BY THE CD BITS IN PLLCON.
Two SFRs (T3CON and T3FD) are used to control Timer 3.
T3CON is the baud rate control SFR, allowing Timer 3 to be
used to set up the UART baud rate, and setting up the binary
divider (DIV).
÷2
*
÷ (1 + T3FD/64)
DIV
÷2
÷16
TIMER 1/TIMER 2
RX CLOCK (FIG 83)
T3 RX/TX
CLOCK
Figure 84. Timer 3, UART Baud Rates
TIMER 1/TIMER 2
TX CLOCK (F IG 83)
001
1
T3EN
RX
CLOCK
TX CLOCK
TIMER 2
INTERRUPT
02987-072
TIMER 1
OVERFLOW
2
10
SMOD
TIMER 2
TH2
(8 BITS)
RCAP2H
OVERFLOW
RELOAD
0
1
1
RCLK
RX
16
0
TCLK
CLOCK
TX
16
CLOCK
02987-071
Table 43. T3CON SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] T3BAUDEN
T3 UART baud rate enable. Set to enable
Timer 3 to generate the baud rate. When
set, PCON[7], T2CON[4], and T2CON[5] are
ignored. Cleared to let the baud rate be
generated as per a standard 8052.
[6:4] Reserved
[2:0] DIV[2:0] Binary divider factor
DIV2 DIV1 DIV0 Binary Divider
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1
The appropriate value to write to the DIV[2:0] bits can be
calculated using the following formula
DIV
where f
⎛
f
CORE
⎜
log
⎜
×
32
⎝
=
is defined in the PLLCON SFR, PLLCON[2:0].
CORE
⎞
⎟
⎟
RateBaud
⎠
)2log(
Note that the DIV value must be rounded down.
T3FD is the fractional divider ratio required to achieve the
required baud rate. The appropriate value for T3FD can be
calculated using the following formula:
2
f
DIV
CORE
×
=
3
FDT
2
RateBaud
Note that T3FD should be rounded to the nearest integer.
Rev. A | Page 78 of 92

ADuC832
After the values for DIV and T3FD are calculated, the actual
baud rate can be calculated using the following formula:
2+××
f
=
RateBaudActual
DIV
CORE
FDT
)643(2
For example, to obtain a baud rate of 115,200 while operating at
16.78 MHz,
DIV = log(11,059,200/(32 × 115,200))/log(2) = 1.58 = 1
T3FD = (2 × 11,059,200)/(21 × 115,200) − 64 = 32 = 20H
Therefore, the actual baud rate is 114,912 bits/sec.
Table 44. Commonly Used Baud Rates Using Timer 3
Ideal Baud CD DIV T3CON T3FD % Error
230,400 0 1 81H 09H 0.25
115,200 0 2 82H 09H 0.25
115,200 1 1 81H 09H 0.25
115,200 2 0 80H 09H 0.25
57,600 0 3 83H 09H 0.25
57,600 1 2 82H 09H 0.25
57,600 2 1 81H 09H 0.25
57,600 3 0 80H 09H 0.25
38,400 0 3 83H 2DH 0.2
38,400 1 2 82H 2DH 0.2
38,400 2 1 81H 2DH 0.2
38,400 3 0 80H 2DH 0.2
19,200 0 4 84H 2DH 0.2
19,200 1 3 83H 2DH 0.2
19,200 2 2 82H 2DH 0.2
19,200 3 1 81H 2DH 0.2
19,200 4 0 80H 2DH 0.2
9600 0 5 85H 2DH 0.2
9600 1 4 84H 2DH 0.2
9600 2 3 83H 2DH 0.2
9600 3 2 82H 2DH 0.2
9600 4 1 81H 2DH 0.2
9600 5 0 80H 2DH 0.2
Rev. A | Page 79 of 92

ADuC832
INTERRUPT SYSTEM
The ADuC832 provides a total of nine interrupt sources with
two priority levels. The control and configuration of the interrupt system is carried out through three interrupt-related SFRs:
• IE—interrupt enable register
• IP—interrupt priority register
• IEIP2—secondary interrupt enable register
Table 45. IE SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] EA Written by user to enable or disable all interrupt sources (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[6] EADC Written by user to enable or disable ADC interrupt (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[5] ET2 Written by user to enable or disable Timer 2 interrupt (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[4] ES Written by user to enable or disable UART serial port interrupt (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[3] ET1 Written by user to enable or disable Timer 1 interrupt (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[2] EX1 Written by user to enable or disable External Interrupt 1 (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[1] ET0 Written by user to enable or disable Timer 0 interrupt (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[0] EX0 Written by user to enable or disable External Interrupt 0 (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
IP (INTERRUPT PRIORITY REGISTER )
SFR Address: B8H
IE (INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER)
SFR Address: A8H
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Power-On Default Value: 00H
Bit Addressable: Yes
Table 46. IP SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Reserved Reserved for future use.
[6] PADC Written by user to select ADC interrupt priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[5] PT2 Written by user to select Timer 2 interrupt priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[4] PS Written by user to select UART serial port interrupt priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[3] PT1 Written by user to select Timer 1 interrupt priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[2] PX1 Written by user to select External Interrupt 1 priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[1] PT0 Written by user to select Timer 0 interrupt priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
[0] PX0 Written by user to select External Interrupt 0 priority (1 = high; 0 = low)
IEIP2 (SECONDARY INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER)
SFR Address A9H
Power-On Default Value A0H
Bit Addressable No
Table 47. IEIP2 SFR Bit Designations
Bit Name Description
[7] Reserved Reserved for future use
[6] PTI Priority for time interval interrupt
[5] PPSM Priority for power supply monitor interrupt
[4] PSI Priority for SPI/I2C interrupt
[3] Reserved This bit must contain 0.
[2] ETI Written by user to enable or disable time interval counter interrupt. (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[1] EPSMI Written by user to enable or disable power supply monitor interrupt. (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
[0] ESI Written by user to enable or disable SPI or I2C serial port interrupt. (1 = enable; 0 = disable)
Rev. A | Page 80 of 92

ADuC832
INTERRUPT PRIORITY
The interrupt enable registers are written by the user to enable
individual interrupt sources, whereas the interrupt priority
registers allow the user to select one of two priority levels for
each interrupt. An interrupt of a high priority may interrupt the
service routine of a low priority interrupt, and if two interrupts
of different priority occur at the same time, the higher level
interrupt is serviced first. An interrupt cannot be interrupted by
another interrupt of the same priority level. If two interrupts of
the same priority level occur simultaneously, a polling sequence
is observed, as shown in Tab l e 4 8 .
Table 48. Priority Within an Interrupt Level
Source Priority Description
PSMI 1 (highest) Power supply monitor interrupt
WDS 2 Watchdog timer interrupt
IE0 2 External Interrupt 0
ADCI 3 ADC interrupt
TF0 4 Timer/Counter 0 interrupt
IE1 5 External Interrupt 1
TF1 6 Timer/Counter 1 interrupt
ISPI/I2CI 7 SPI Interrupt/I2C interrupt
RI + TI 8 Serial interrupt
TF2 + EXF2 9 (lowest) Timer/Counter 2 interrupt
TII 11 (lowest) Time interval counter interrupt
INTERRUPT VECTORS
When an interrupt occurs, the program counter is pushed onto
the stack and the corresponding interrupt vector address is
loaded into the program counter. The interrupt vector addresses
are shown in Ta bl e 4 9 .
Table 49. Interrupt Vector Addresses
Source Vector Address
IE0 0003H
TF0 000BH
IE1 0013H
TF1 001BH
RI + TI 0023H
TF2 + EXF2 002BH
ADCI 0033H
ISPI/I2CI 003BH
PSMI 0043H
TII 0053H
WDS 005BH
Rev. A | Page 81 of 92

ADuC832
ADUC832 HARDWARE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
This section outlines some of the key hardware design
considerations that must be addressed when integrating the
ADuC832 into any hardware system.
CLOCK OSCILLATOR
The clock source for the ADuC832 can be generated by the
internal PLL or by an external clock input. To use the internal
PLL, connect a 32.768 kHz parallel resonant crystal between
XTAL1 and XTAL2, and connect a capacitor from each pin to
ground as shown in Figure 85. This crystal allows the PLL to
lock correctly to give a f
the PLL free runs, giving a f
of 16.78 MHz. If no crystal is present,
VCO
of 16.7 MHz ± 20%. This is
VCO
useful if an external clock input is required. The part powers up
and the PLL free runs; the user can then write to the CFG832
SFR in the software to enable the external clock input on P3.4.
XTAL1
XTAL2
Figure 85. External Parallel Resonant Crystal Connections
ADuC832
TO INTERNAL
TIMING CIRCUITS
02987-073
EXTERNAL
CLOCK
SOURCE
P3.4
Figure 86. Connecting an External Clock Source
ADuC832
TO INTE RNAL
TIMING CI RCUITS
02987-074
Whether using the internal PLL or an external clock source, the
ADuC832 specified operational clock speed range is 400 kHz to
16.78 MHz. The core itself is static, and functions all the way
down to dc. However, at clock speeds slower than 400 kHz, the
ADC no longer functions correctly. Therefore, to ensure specified
operation, use a clock frequency of at least 400 kHz and no
more than 16.78 MHz.
EXTERNAL MEMORY INTERFACE
In addition to its internal program and data memories, the
ADuC832 can access up to 64 kB of external program memory
(such as ROM and PROM) and up to 16 MB of external data
memory (SRAM).
To select from which code space (internal or external program
memory) to begin executing instructions, tie the
access) pin high or low, respectively. When
up to DV
), the user program execution starts at Address 0 of
DD
the internal 62 kB of Flash/EE code space. When
to ground), the user program execution starts at Address 0 of
the external code space.
EA
(external
EA
is high (pulled
EA
is low (tied
Rev. A | Page 82 of 92
A second very important function of the
the Single Pin Emulation Mode section.
External program memory (if used) must be connected to the
ADuC832 as illustrated in Figure 87. Note that 16 I/O lines
(Port 0 and Port 2) are dedicated to bus functions during
external program memory fetches. Port 0 (P0) serves as a
multiplexed address/data bus. It emits the low byte of the
program counter as an address, and then goes into a float state
awaiting the arrival of the code byte from the program memory.
During the time that the low byte of the program counter is
valid on P0, the signal address latch enable (ALE) clocks this
byte into an address latch. Meanwhile, Port 2 (P2) emits the
high byte of the program counter, then
EPROM and the code byte is read into the ADuC832.
ADuC832
P0
LATCH
ALE
P2
PSEN
Figure 87. External Program Memory Interface
Note that program memory addresses are always 16 bits wide,
even in cases where the actual amount of program memory
used is less than 64 kB. External program execution sacrifices two
of the 8-bit ports (P0 and P2) to the function of addressing the
program memory. While executing from external program
memory, Port 0 and Port 2 can be used simultaneously for
read/write access to external data memory, but not for generalpurpose I/O.
Though both external program memory and external data
memory are accessed by some of the same pins, the two are
completely independent of each other from a software point
of view. For example, the chip can read/write external data
memory while executing from external program memory.
Figure 88 shows a hardware configuration for accessing up to
64 kB of external RAM. This interface is standard to any 8051compatible MCU.
EA
pin is described in
PSEN
strobes the
EPROM
D0 TO D7
(INSTRUCTION)
A0 TO A7
A8 TO A15
OE
02987-075

ADuC832
ADuC832
P0
LATCH
ALE
P2
RD
WR
SRAM
D0 TO D7
(DATA)
A0 TO A7
A8 TO A15
OE
WE
02987-076
Figure 88. External Data Memory Interface (64 kB Address Space)
If access to more than 64 kB of RAM is desired, a feature unique
to the ADuC832 allows addressing up to 16 MB of external
RAM simply by adding an additional latch, as illustrated in
Figure 89.
ADuC832
P0
LATCH
ALE
P2
LATCH
RD
WR
Figure 89. External Data Memory Interface (16 MB Address Space)
SRAM
D0 TO D7
(DATA)
A0 TO A7
A8 TO A15
A16 TO A23
OE
WE
2987-077
In either implementation, Port 0 (P0) serves as a multiplexed
address/data bus. It emits the low byte of the data pointer (DPL)
as an address, which is latched by a pulse of ALE prior to data
being placed on the bus by the ADuC832 (write operation) or
the SRAM (read operation). Port 2 (P2) provides the data
pointer page byte (DPP) to be latched by ALE, followed by the
data pointer high byte (DPH). If no latch is connected to P2,
DPP is ignored by the SRAM, and the 8051 standard of 64 kB
external data memory access is maintained.
POWER SUPPLIES
The ADuC832 operational power supply voltage range is 2.7 V
to 5.25 V. Although the guaranteed data sheet specifications are
given only for power supplies within 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 10% of
the nominal 5 V level, the chip functions equally well at any
power supply level between 2.7 V and 5.5 V.
Note that Figure 90 and Figure 91 refer to the MQFP package.
For the LFCSP package, connect the extra DV
and AGND in the same manner.
Separate analog and digital power supply pins (AV
respectively) allow AV
often present on the system DV
and DV
can be powered from two separate supplies if desired,
DD
to be relatively free of noisy digital signals
DD
line. However, though AVDD
DD
they must remain within 0.3 V of one another at all times to
, DGND, AVDD,
DD
and DVDD,
DD
Rev. A | Page 83 of 92
avoid damaging the chip (as per the Absolute Maximum Ratings
section). Therefore, it is recommended that, unless AV
DV
are connected directly together, back-to-back Schottky
DD
DD
and
diodes be connected between them as shown in Figure 90.
DIGITAL SUPPLY
10µF
ADuC832
DV
DD
0.1µF
DGND
Figure 90. External Dual-Supply Connections
ANALOG SUPPLY
10µF
AV
DD
AGND
0.1µF
02987-078
As an alternative to providing two separate power supplies,
the user can keep AV
and/or ferrite bead between it and DV
AV
separately to ground. An example of this configuration is
DD
quiet by placing a small series resistor
DD
, and then decoupling
DD
shown in Figure 91. With this configuration, other analog circuitry
(such as op amps and voltage reference) can be powered from
the AV
to-back Schottky diodes between AV
supply line as well. The user should still include back-
DD
and DVDD to protect
DD
from power-up and power-down transient conditions that may
separate the two supply voltages momentarily.
DIGITAL SUPPLY
1.6Ω
10µF
BEAD
10µF
ADuC832
AV
AGND
DD
0.1µF
2987-079
0.1µF
DV
DD
DGND
Figure 91. External Single-Supply Connections
Note that, in both Figure 90 and Figure 91, a large value (10 µF)
reservoir capacitor is connected to DV
capacitor is connected to AV
capacitors are located at each AV
. Also, local small-value (0.1 µF)
DD
DD
and a separate 10 µF
DD
pin of the chip. As per standard design practice, be sure to include all of these capacitors,
and ensure that the smaller capacitors are close to each AV
DD
pin with trace lengths as short as possible. Connect the ground
terminal of each of these capacitors directly to the underlying
ground plane. Finally, it should also be noted that, at all times,
the analog and digital ground pins on the ADuC832 must be
referenced to the same system ground reference point.

ADuC832
POWER CONSUMPTION
The currents consumed by the various sections of the ADuC832
are shown in Ta bl e 5 0 . The core values given represent the
current drawn by DV
reference) are pulled by the AV
, and the rest (ADC, DAC, voltage
DD
pin and can be disabled in
DD
software when not in use. The other on-chip peripherals (for
example, watchdog timer and power supply monitor) consume
negligible current and are therefore included with the core
operating current. The user must add any currents sourced by
the parallel and serial I/O pins and by the DAC to determine
the total current needed at the ADuC832 supply pins. Also,
current drawn from the DV
supply increases by approx-
DD
imately 10 mA during Flash/EE erase and program cycles.
Table 50. Typical I
of Core and Peripherals
DD
Core/Peripherals VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V
Core, Normal Mode
Core, Idle Mode
(1.6 nA × M
6 mA
(0.75 nA × M
5 mA
CLK
CLK
) +
) +
(0.8 nA × M
3 mA
(0.25 nA × M
3 mA
CLK
CLK
) +
) +
ADC 1.3 mA 1.0 mA
DAC (Each) 250 µA 200 µA
Voltage Reference 200 µA 150 µA
Because the operating DVDD current is primarily a function of
clock speed, the expressions for core supply current in Ta b le 5 0
are given as functions of M
value for M
in hertz to determine the current consumed by
CLK
, the core clock frequency. Use a
CLK
the core at that oscillator frequency. Because the ADC and
DACs can be enabled or disabled in software, add only the
currents from the peripherals that are expected to be used. Do
not forget to include current sourced by I/O pins, serial port
pins, and DAC outputs, plus the additional current drawn
during Flash/EE erase and program cycles. A software switch
allows the chip to be switched from normal mode into idle
mode, and into full power-down mode. The following sections
provide brief descriptions of power-down and idle modes.
POWER SAVING MODES
In idle mode, the oscillator continues to run but the core clock
generated from the PLL is halted. The on-chip peripherals
continue to receive the clock, and remain functional. The CPU
status is preserved with the stack pointer and program counter,
and all other internal registers maintain their data during idle
mode. Port pins and DAC output pins retain their states in this
mode. The chip recovers from idle mode upon receiving any
enabled interrupt, or upon receiving a hardware reset.
In full power-down mode, both the PLL and the clock to the
core are stopped. The on-chip oscillator can be halted or can
continue to oscillate depending on the state of the oscillator
power-down bit (OSC_PD) in the PLLCON SFR. The TIC,
being driven directly from the oscillator, can also be enabled
during power-down. All other on-chip peripherals, however, are
shut down. Port pins retain their logic levels in this mode, but
the DAC output goes to a high impedance state (three-state).
Rev. A | Page 84 of 92
During full power-down mode, the ADuC832 consumes a total
of approximately 20 µA. There are five ways of terminating
power-down mode.
Asserting the RESET Pin
Asserting the RESET pin returns the part to normal mode. All
registers are set to their default state and program execution
starts at the reset vector when the RESET pin is deasserted.
Cycling Power
All registers are set to their default state and program execution
starts at the reset vector approximately 128 ms later.
Time Interval Counter (TIC) Interrupt
Power-down mode is terminated and the CPU services the TIC
interrupt. The RETI at the end of the TIC ISR returns the core
to the instruction following the one that enabled power-down.
I2C or SPI Interrupt
Power-down mode is terminated and the CPU services the
2
C/SPI interrupt. The RETI at the end of the ISR returns the
I
core to the instruction following the one that enabled powerdown. It should be noted that the I
2
C/SPI power-down
interrupt enable bit (SERIPD) in the PCON SFR must first be
set to allow this mode of operation.
INT0
Interrupt
Power-down mode is terminated and the CPU services the
INT0
interrupt. The RETI at the end of the ISR returns the core
to the instruction following the one that enabled power-down.
INT0
The
pin must not be driven low during or within two
machine cycles of the instruction that initiates power-down
mode. It should be noted that the
INT0
power-down interrupt
enable bit (INT0PD) in the PCON SFR must first be set to allow
this mode of operation.
POWER-ON RESET
An internal power-on reset (POR) is implemented on the
ADuC832. For DV
the ADuC832 in reset. As DV
timer times out for approximately 128 ms before the part is
released from reset. The user must ensure that the power supply
has reached a stable 2.7 V minimum level by this time. Likewise
upon power-down, the internal POR holds the ADuC832 in reset
until the power supply drops below 1 V. Figure 92 illustrates the
operation of the internal POR in detail.
2.45V TYP
DV
DD
1.0V TYP
INTERNAL
CORE RESET
below 2.45 V, the internal POR holds
DD
rises above 2.45 V, an internal
DD
128ms TYP
Figure 92. Internal POR Operation
128ms TYP
1.0V TYP
2987-080

ADuC832
GROUNDING AND BOARD LAYOUT RECOMMENDATIONS
As with all high resolution data converters, special attention
must be paid to grounding and PCB layout of ADuC832- based
designs to achieve optimum performance from the ADC and
DACs. Although the ADuC832 has separate pins for analog and
digital ground (AGND and DGND), the user must not tie these
to two separate ground planes unless the two ground planes are
connected together very close to the ADuC832, as illustrated in
the simplified example of Figure 93a. In systems where digital
and analog ground planes are connected together at some other
location (at the system’s power supply, for example), they cannot
be connected again near the ADuC832 because a ground loop then
results. In these cases, tie all the ADuC832 AGND and DGND
pins to the analog ground plane, as illustrated in Figure 93b. In
systems with only one ground plane, ensure that the digital and
analog components are physically separated onto separate halves
of the board such that digital return currents do not flow near
analog circuitry and vice versa. The ADuC832 can then be
placed between the digital and analog sections, as illustrated in
Figure 93c.
In all of these scenarios, and in more complicated real-life
applications, keep in mind the flow of current from the supplies
and back to ground. Make sure the return paths for all currents
are as close as possible to the paths the currents traveled to reach
their destinations. For example, do not power components on
the analog side of Figure 93b with DV
return currents from DV
to flow through AGND. Also, try
DD
to avoid digital currents flowing under analog circuitry, which
may happen if the user places a noisy digital chip on the left
half of the board in Figure 93c. Whenever possible, avoid large
discontinuities in the ground plane(s) (such as are formed by a
long trace on the same layer), because they force return signals
because that forces
DD
to travel a longer path. Also, make all connections to the ground
plane directly, with little or no trace separating the pin from its
via to ground.
To connect fast logic signals (rise/fall time < 5 ns) to any of the
ADuC832 digital inputs, add a series resistor to each relevant
line to keep rise and fall times longer than 5 ns at the ADuC832
input pins. A value of 100 Ω or 200 Ω is usually sufficient to
prevent high speed signals from coupling capacitively into the
ADuC832 and affecting the accuracy of ADC conversions.
a.
b.
c.
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS
HERE
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS
HERE
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS
HERE
GND
Figure 93. System Grounding Schemes
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS
HERE
DGNDAGND
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS
HERE
DGNDAGND
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS
HERE
02987-081
Rev. A | Page 85 of 92

ADuC832
DV
DD
5251504948
ANALOG INPUT
V
OUTPUT
REF
DAC OUTPUT
AV
P1.0ADC0/T2
DD
AV
DD
AGND
C
REF
V
REF
DAC0
10
DAC1
P1.7/ADC7
RESET
14
DD
DV
ADuC832
P3.0/RxD
P3.1/TxD
16
19 62028124
DV
47
45
46
DGND
DVDDDGND
DD
DOWNLOAD/DEBUG
ENABLE JUMPER
(NORMALLY OPEN)
DV
1kΩ
DD
1kΩ
40
444342
41
PSEN
DGND
DV
XTAL2
XTAL1
EA
39
38
37
36
35
34
DD
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
NOT CONNECTE D IN THIS EXAMP LE
2-PIN HEADER FOR
EMULATIO N ACCESS
(NORMALLY OPEN)
DV
DD
32.768kHz
C1+
V+
C1–
C2+
C2–
V–
T2
R2
OUT
IN
ADM202
GND
T1
R1
R1
R2
V
OUT
OUT
T1
T2
OUT
DV
CC
DD
9-PIN D- S UB
FEMALE
1
2
IN
3
4
IN
IN
5
6
7
8
9
02987-082
Figure 94. Example ADuC832 System (MQFP Package)
Rev. A | Page 86 of 92

ADuC832
OTHER HARDWARE CONSIDERATIONS
To facilitate in-circuit programming, plus in-circuit debug and
emulation options, implement some simple connection points
in the hardware that allow easy access to download, debug, and
emulation modes.
IN-CIRCUIT SERIAL DOWNLOAD ACCESS
Nearly all ADuC832 designs can take advantage of the in-circuit
reprogrammability of the chip. This is accomplished by a
connection to the ADuC832 UART, which requires an external
RS-232 chip for level translation if downloading code from a
PC. Basic configuration of an RS-232 connection is illustrated
in Figure 94 with a simple ADM202-based circuit. To avoid
designing an RS-232 chip onto a board, refer to the uC006
Tec hni cal No te , A 4-Wire UART-to-PC Interface, available at
www.analog.com, for a simple (and zero-cost-per-board)
method of gaining in-circuit serial download access to the
ADuC832.
In addition to the basic UART connections, users also need a way
to trigger the chip into download mode. This is accomplished via a
PSEN
PSEN
pin low,
1 k pull-down resistor that can be jumpered onto the
pin, as shown in . To put the ADuC832 into download
mode, connect this jumper and power-cycle the device (or
manually reset the device, if a manual reset button is available)
so that it can receive a new program serially. With the jumper
removed, the device comes up in normal mode (and runs the
program) whenever power is cycled or RESET is toggled.
Note that
External Memory Interface
only on the falling edge of RESET (that is, at power-up or upon
an external manual reset). Note also that if any external circuitry
unintentionally pulls
may cause the chip to enter download mode and therefore fail
to begin user code execution as it should. To prevent this, ensure
that no external signals are capable of pulling the
except for the external
Figure 94
PSEN
is normally an output (as described in the
section) and is sampled as an input
PSEN
low during power-up or reset events, it
PSEN
jumper itself.
EMBEDDED SERIAL PORT DEBUGGER
From a hardware perspective, entry into serial port debug mode
is identical to the serial download entry sequence described in
the In-Circuit Serial Download Access section. In fact, both
serial download and serial port debug modes can be thought of
as essentially one mode of operation used in two different ways.
Note that the serial port debugger is fully contained on the
ADuC832 device (unlike ROM monitor type debuggers) and
therefore no external memory is needed to enable in-system
debug sessions.
SINGLE-PIN EMULATION MODE
Also built into the ADuC832 is a dedicated controller for single-pin
in-circuit emulation (ICE) using standard production ADuC832
devices. In this mode, emulation access is gained by connection
to a single pin, the
either high or low to select execution from internal or external
program memory space. To enable single-pin emulation mode,
however, users need to pull the
resistor, as shown in . The emulator then connects to
the 2-pin header, also shown in . To be compatible with
the standard connector that comes with the single-pin emulator,
use a 2-pin 0.1 inch pitch friction lock header from Molex such as
Part Number 22-27-2021. Be sure to observe the polarity of this
header. As represented in , when the friction lock tab is
located on the right, the ground pin should be the lower of the
two pins (when viewed from the top).
EA
pin. Normally, this pin is hardwired
EA
pin high through a 1 k
Figure 94
Figure 94
Figure 94
TYPICAL SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
A typical ADuC832 configuration is shown in Figure 94. It
summarizes some of the hardware considerations discussed in
the Single-Pin Emulation Mode section.
Rev. A | Page 87 of 92

ADuC832
DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
There are two models of development tools available for the
ADuC832.
• QuickStart—entry-level development system
• QuickStart Plus—comprehensive development system
QUICKSTART DEVELOPMENT SYSTEM
The QuickStart development system is an entry-level, low cost
development tool suite supporting the ADuC832. The system
consists of the following PC-based (Windows® compatible)
hardware and software development tools.
Table 51. QuickStart Components
Component Description
Hardware
Software
Miscellaneous CD-ROM documentation and prototype device
Hardware contents include:
• Evaluation board
• Serial download/debug cable
• International power supply
ADuC832 evaluation board and serial port
programming cable
Serial download software; incorporates 8051
assembler and serial port debugger
Download—In-Circuit Serial Downloader
The serial downloader is a Windows application that allows the
user to serially download an assembled program (Intel Hex
format file) to the on-chip program FLASH memory via the
serial COM1 port on a standard PC. The uC004 technical note,
which details this serial download protocol, is available from
www.analog.com.
QUICKSTART PLUS DEVELOPMENT SYSTEM
The QuickStart Plus Development system offers users enhanced
nonintrusive debug and emulation tools. The system consists of
the following PC-based (Windows compatible) hardware and
software development tools.
Table 52. QuickStart Plus Components
Component Description
Hardware ADuC832 prototype board
Software Features full C code
Miscellaneous CD-ROM documentation
Software contents include:
• Serial downloader
• Analog performance analysis package
• Example code, function libraries, data sheets, and
application notes
Visit www.analog.com/microcontroller for details on a typical
debug session.
Rev. A | Page 88 of 92

ADuC832
0
0
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
39
PIN 1
1
0.65 BSC
LEAD PITCH
0.60 MAX
43
42
14.15
13.90 SQ
13.65
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
27
26
14
13
0.38
0.22
LEAD WIDTH
0.30
0.23
0.18
56
7.80
REF
10.20
10.00 SQ
9.80
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1
10°
2.10
2.00
1.95
0.25
MIN
VIEW A
ROTATED 90° CCW
6°
2°
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
2.45
1.03
MAX
0.88
0.73
SEATING
PLANE
0.23
VIEW A
0.11
7°
0°
0.10
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-112-AC-1
40
52
Figure 95. 52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Package [MQFP]
(S-52-2)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
8.00
0.60 MAX
6.25
6.10 SQ
5.95
14
0.25 MIN
030509-A
1.00
.85
.80
SEATING
PLANE
12° MAX
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VL L D- 2
7.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.08
(BOTTOM VIEW)
29
28
EXPOSED
PAD
15
6.50
REF
FOR PROPER CONNECTION O F
THE EXPOSE D P AD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONF IGURATION AND
FUNCTION DES CRI PTIONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
Figure 96. 56-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
8 mm × 8 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-56-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADuC832BCP −40°C to +85°C 52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Pack age [MQFP] S-52-2
ADuC832BCP-REEL −40°C to +85°C 52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Pack age [MQFP] S-52-2
ADuC832BCPZ1 −40°C to +85°C 52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Pack age [MQFP] S-52-2
ADuC832BCPZ-REEL
ADuC832BSZ1 −40°C to +125°C 56-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-56-1
ADuC832BSZ-REEL
EVAL-ADuC832QSZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
1
1
QuickStart Development System
−40°C to +85°C 52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Pack age [MQFP] S-52-2
−40°C to +125°C 56-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-56-1
Rev. A | Page 89 of 92

ADuC832
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 90 of 92

ADuC832
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 91 of 92

ADuC832
NOTES
Purchase of licensed I2C components of Analog Devices or one of its sublicensed associated companies conveys a license for the purchaser under the Philips I2C Patent
Rights to use the ADuC832 in an I
2
C system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
©2002–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D02987-0-9/09(A)
Rev. A | Page 92 of 92
 Loading...
Loading...