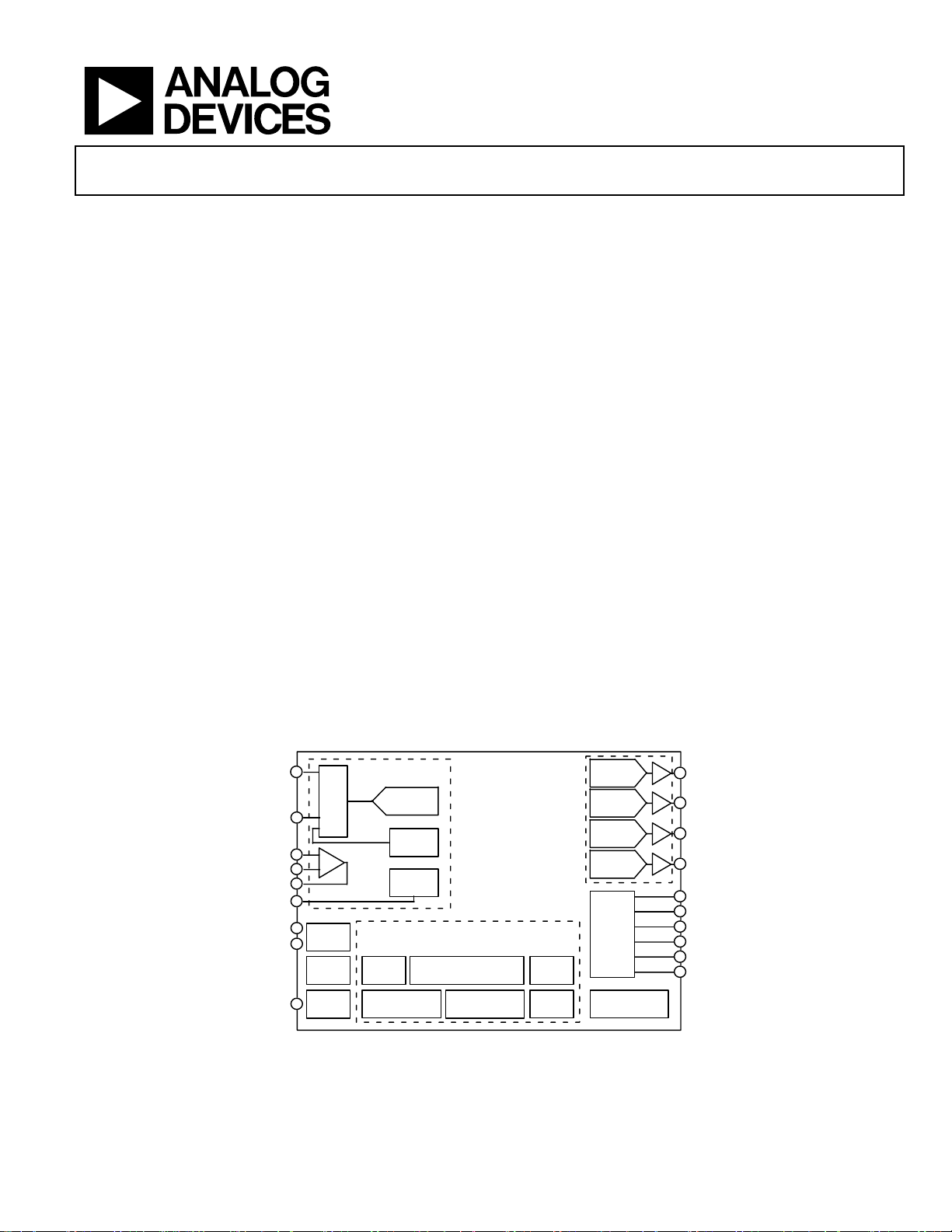
Precision Analog Microcontroller
Preliminary Technical Data
FEATURES
Analog I/O
Multi-Channel, 12-bit, 1MSPS ADC
- Up to 16 ADC channels *
Fully differential and single-ended modes
0 to V
12-bit Voltage Output DACs
- Up to 4 DAC outputs available*
On-Chip 20ppm/°C Voltage Reference
On-Chip Temperature Sensor (±3°C)
Uncommitted Voltage Comparator
Microcontroller
ARM7TDMI Core, 16/32-bit RISC architecture
JTAG Port supports code download and debug
Clocking options: - Trimmed On-Chip Oscillator (± 3%)
45MHz PLL with Programmable Divider
Memory
62k Bytes Flash/EE Memory, 8k Bytes SRAM
In-Circuit Download, JTAG based Debug
Software triggered in-circuit re-programmability
On-Chip Peripherals
UART, 2 X I
Up to 40-Pin GPIO Port*
Analog Input Range
REF
- External Watch crystal
- External clock source
2
C and SPI Serial I/O
12-bit Analog I/O,
ARM7TDMI® MCU
ADuC702x Series
4 X General Purpose Timers
Wake-up and Watchdog Timers
Power Supply Monitor
Three-phase 16-bit PWM generator*
PLA – Programmable Logic (Array)
Power
Specified for 3V operation
Active Mode: 3mA (@1MHz)
50mA (@45MHz)
Packages and Temperature Range
From 40 lead 6x6mm LFCSP to 80 pin LQFP*
Fully specified for –40°C to 125°C operation
Tools
Low-Cost QuickStart Development System
Full Third-Party Support
* Package, PWM, GPIO availability and number of Analog I/O
depend on part model. See page 9.
APPLICATIONS
Industrial Control and Automation Systems
Smart Sensors, Precision Instrumentation
Base Station Systems, Optical Networking
(See general description on page 11)
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADC0
...
...
MUX
ADC11
CMP0
CMP1
CMP
OUT
V
REF
XCLKI
XCLKO
RST
Rev. PrB
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
+
-
OSC
&PLL
PSM
POR
1MSPS
12-BIT ADC
TEMP
SENSOR
BANDGAP
REF
ARM7TDMI-BASED MCU WITH
ADDITIONAL PERIPHERALS
PLA
4 GEN. PUR-
POSE TIMERS
2kX32 SRAM
31kX16 FLASH/EEPROM
UART, SPI, I2C
SERIAL I/O
Figure 1
DAC012-BIT DAC
ADuC7026*
GPIO
JTAG
Threephase
PWM
EXT. MEMORY
INTERFACE
DAC112-BIT DAC
DAC212-BIT DAC
DAC312-BIT DAC
PWM0H
PWM0L
PWM1H
PWM1L
PWM2H
PWM2L
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ADuC702x—Specifications ............................................................ 3
Reset and Remap........................................................................ 36
Terminology ...................................................................................... 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
Ordering Guide............................................................................. 9
Pin function descriptions ..............................................................10
General Description ....................................................................... 19
Overview of the ARM7TDMI core.......................................... 19
Memory organisation................................................................. 21
ADC circuit information............................................................... 26
General Overview....................................................................... 26
ADC Transfer Function............................................................. 26
Typical Operation....................................................................... 27
Converter operation................................................................... 29
Driving the analog inputs.......................................................... 30
ADC Calibration ........................................................................ 30
Temperature Sensor ...................................................................30
Other analog peripherals............................................................... 37
DAC.............................................................................................. 37
Power Supply Monitor............................................................... 39
Comparator................................................................................. 39
Oscillator and PLL - Power control ......................................... 40
Digital peripherals.......................................................................... 42
Three-phase PWM..................................................................... 42
General Purpose I/O.................................................................. 49
Serial Port Mux........................................................................... 52
Programmable Logic Array (PLA)........................................... 62
Processor reference peripherals.................................................... 65
Interrupt System ......................................................................... 65
Timers.......................................................................................... 67
ADuC702x Hardware Design considerations ............................ 75
Power supplies ............................................................................ 75
Bandgap Reference..................................................................... 30
Nonvolatile Flash/EE Memory ..................................................... 32
Flash/EE memory overview ...................................................... 32
Flash/EE Memory and the ADuC702x.................................... 32
Flash/EE memory security ........................................................ 32
Flash/EE Control Interface........................................................ 33
Execution time from SRAM and FLASH/EE .........................34
Grounding and Board Layout Recommendations................. 75
Clock Oscillator.......................................................................... 76
Power-on reset operation .......................................................... 76
Typical sysem configuration ..................................................... 77
Development Tools ........................................................................ 78
In-Circuit Serial Downloader................................................... 78
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 79
Rev. PrB | Page 2 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
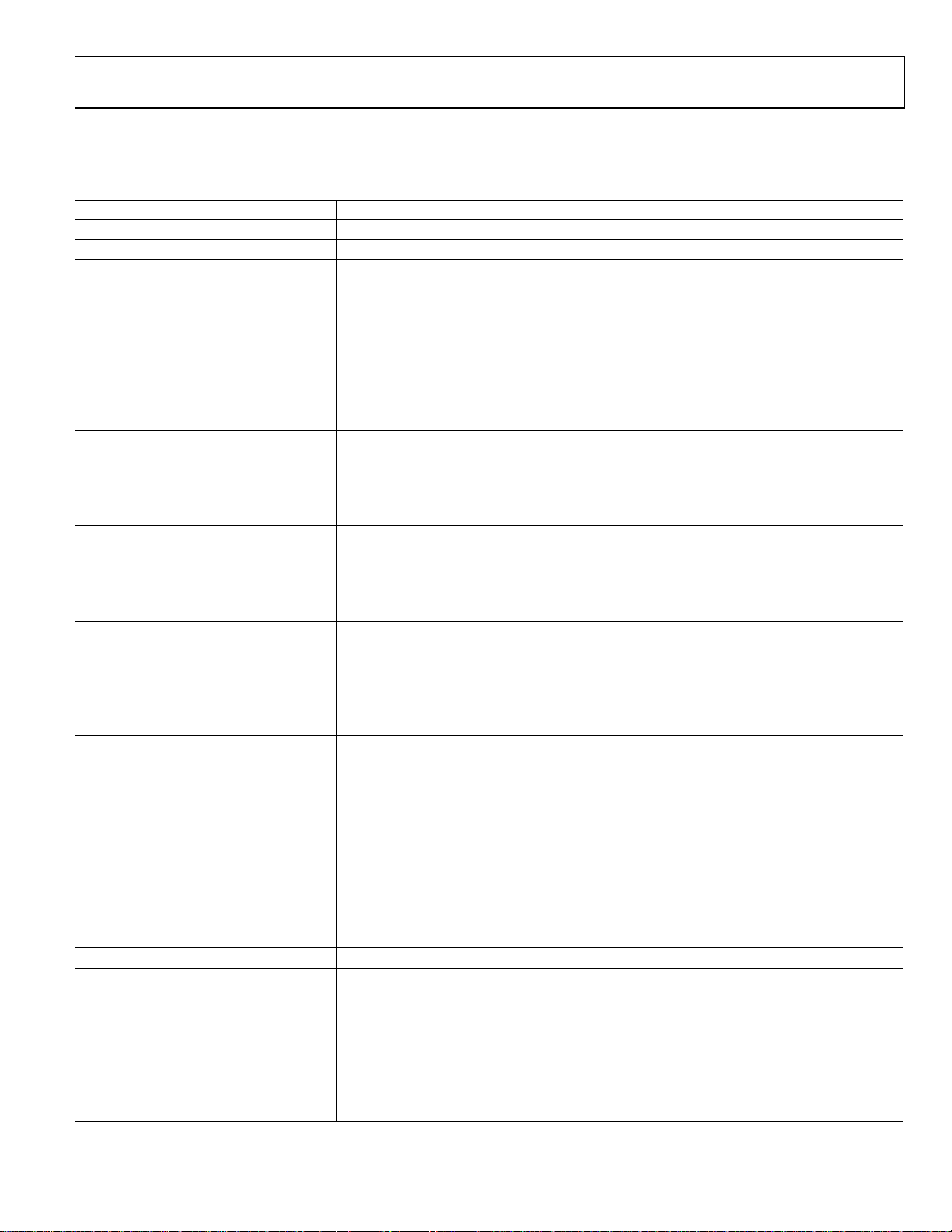
ADUC702X—SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. (AV
unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter ADuC702x Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ADC CHANNEL SPECIFICATIONS
ADC Powerup Time 500 uS
DC Accuracy
Resolution 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity
Integral Nonlinearity
Differential Nonlinearity
Differential Nonlinearity
DC Code Distribution
CALIBRATED ENDPOINT ERRORS
Offset Error
Offset Error Match
Gain Error
Gain Error Match
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE Fin = 10kHz Sine Wave, f
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) -78 dB typ
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Ranges
Differential mode V
Single-ended mode 0 to V
Leakage Current ±5 µA max
Input Capacitance 20 pF typ During ADC Acquisition
ON-CHIP VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage
Accuracy ±10 mV max Measured at TA = 25°C
Reference Temperature Coefficient
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Output Impedance
Internal V
EXTERNAL REFERENCE INPUT9
Input Voltage Range
Input Impedance
DAC CHANNEL SPECIFICATIONS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 12 Bits
Relative Accuracy ±2 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity ±1 LSB max Guaranteed Monotonic
Offset Error
Gain Error
Gain Error Mismatch
= IOVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, V
DD
2, 3
4
4
5
6
7
Power-On Time
REF
1
= 2.5 V Internal Reference, f
REF
f
±1.5
±0.5
±2.0
+1/-0.9
±0.5
+1/-0.9
1
±5
±1
±5
±1
LSB max
LSB typ
LSB max
LSB max
LSB typ
LSB max
LSB typ
LSB max
LSB typ
LSB max
LSB typ
71 dB typ
-78
-80
8
±V
/2 Volts
CM
REF
Volts
REF
2.5
±10
80
10
1
0.625
AV
DD
TBD
dB typ
dB typ
V
ppm/°C typ
dB typ
Ω typ
ms typ
V min
V max
KΩ typ
±2
±5
±0.5
TBD
mV max
mV max
% max
% typ
= 45MHz, All specifications TA = T
CORE
= 1MSPS
SAMPLE
2.5V internal reference
2.5V internal reference
1.0V external reference
2.5V internal reference
2.5V internal reference
1.0V external reference
ADC input is a dc voltage
SAMPLE
0.47µF from V
to AGND
REF
= 5kΩ, CL = 100pF
R
L
DAC output unbuffered
DAC output buffered
% of fullscale on DAC0
MAX
= 1MSPS
to T
MIN
,
Rev. PrB | Page 3 of 80
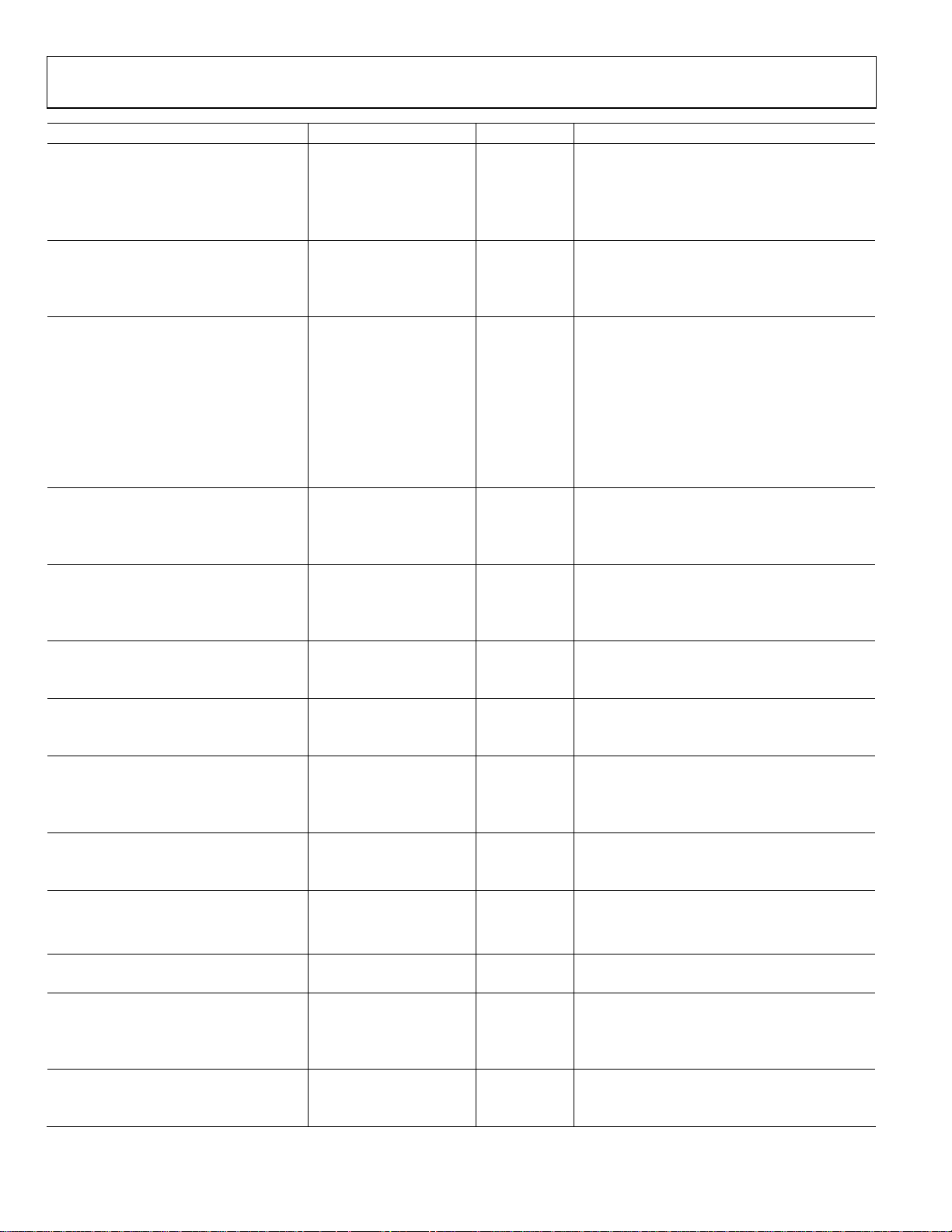
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Parameter ADuC702x Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Output Voltage Range_0
Ouput Voltage Range_1
Output Voltage Range_2
0 to DACREF
0 to 2.5V
0 to DACV
DD
Output Impedance 10
DAC AC CHARACTERISTICS
Voltage Output Settling Time
Voltage Output Settling Time
Digital to Analog Glitch Energy
10
15
TBD
COMPARATOR
Input Offset Voltage
Input Bias Current
Input Voltage Range
Input Capacitance
Hysteresis
Response Time
±10
5
AGND to AV
7
5
10
1
DD
-1.2
10
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Voltage Output at 25°C
Voltage TC
TBD
-1.5
Accuracy ±3 °C typ
POWER SUPPLY MONITOR (PSM)
IOVDD Trip Point Selection 2.79 V Two selectable Trip Points
3.07 V
Power Supply Trip Point Accuracy ±2.5 % max Of the selected nominal Trip Point Voltage
Watchdog Timer (WDT)
Timeout Period
4
0
TBD
Flash/EE MEMORY
Endurance10 10,000 Cycles min
Data Retention11 30 Years min TJ = 55°C
Digital Inputs
Input Leakage Current
Input Capacitance
Logic Inputs4
VINL, Input Low Voltage
VINH, Input High Voltage
±10
±1
10
0.4
2.0
Logic Outputs
VOH, Output High Voltage IOVDD – 400mV V min I
VOL, Output Low Voltage12 0.4 V max I
MCU CLOCK RATE 355.5
45.5
STARTUP TIME
At Power-On
From Idle Mode
From Power-Down Mode
Programmable Logic Array (PLA)
Propagation Delay
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V typ
V typ
V typ
Ω typ
µs typ
µs typ
nV-sec typ
mV
nA typ
Vmin/Vmax
pF typ
mV min
mv max
µs min
µs max
mV typ
mV/°C typ
ms min
ms max
µA max
µA typ
pF typ
V max
V min
kHz min
MHz max
ns typ
DACREF range: DACGND to DACV
DD
DAC Output buffered
DAC Output unbuffered
I LSB change at major carry
Hysteresis can be turned on or off via the
CMPHYST bit in the CMPCON register
Response time may be modified via the CMPRES
bits in the CMPCON register
All digital inputs including XTAL1 and XTAL2
All Logic inputs including XTAL1 and XTAL2
= 1.6mA
SOURCE
= 1.6mA
SINK
8 programmable core clock selections within this
range
Core Clock = TBD MHz
From input pin to output pin
Rev. PrB | Page 4 of 80
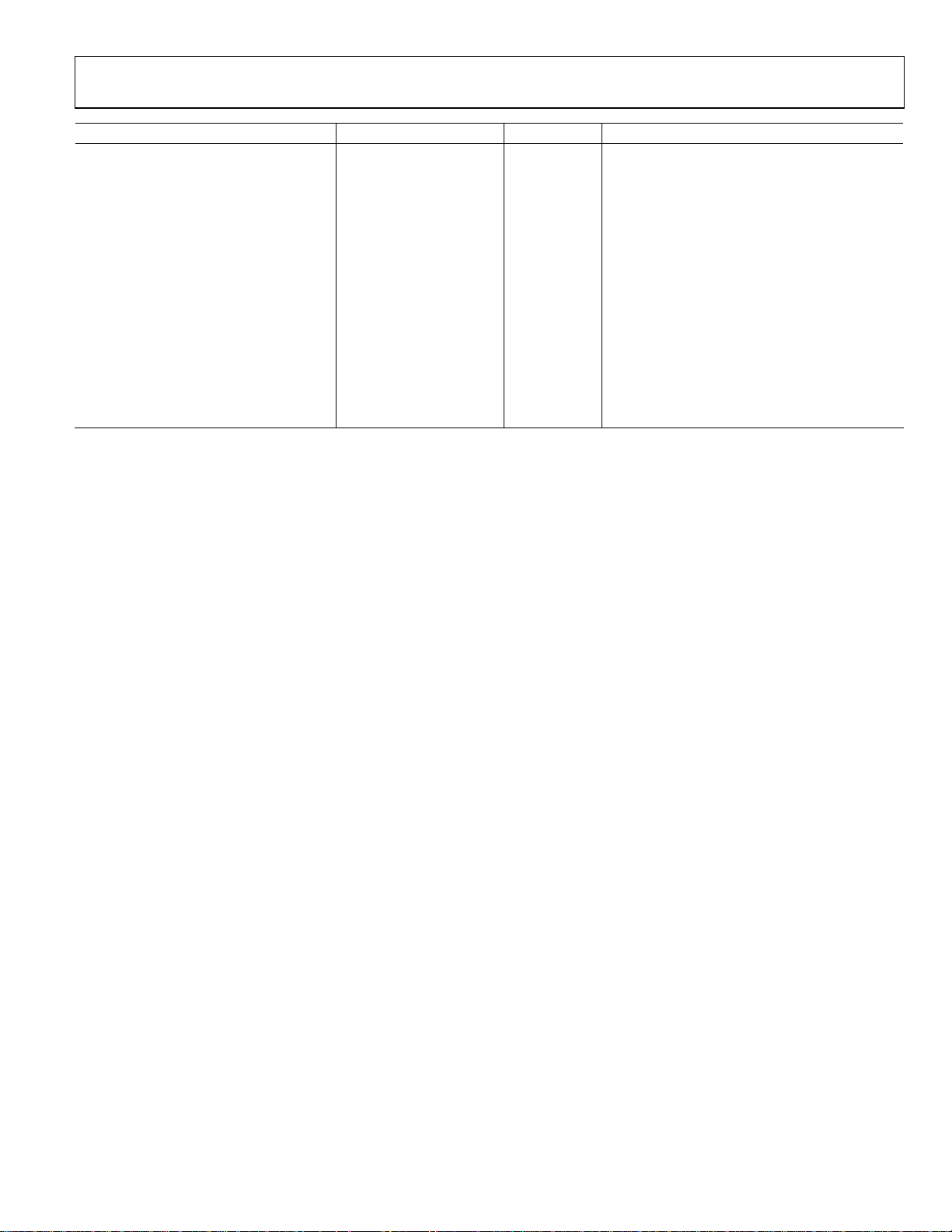
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Parameter ADuC702x Unit Test Conditions/Comments
POWER REQUIREMENTS 13, 14
Power Supply Voltage Range
AVDD – AGND and IOVDD - IOGND 2.7 V min
3.6 V max
Power Supply Current Normal Mode 3mA
Power Supply Current Idle Mode
Power Supply Current Power Down
Mode
1
Temperature Range -40° to +85°C
2
All ADC Channel Specifications are guaranteed during normal MicroConverter core operation.
3
These specification apply to all ADC input channels.
4
These numbers are not production tested but are supported by design and/or characterization data on production release.
5
Based on external ADC system components, the user may need to execute a system calibration to remove external endpoint and achieve these specifications..
6
SNR calculation includes distortion and noise components.
7
Channel-to-channel crosstalk is measured on adjacent channels.
8
The input signal can be centered on any dc common-mode voltage (VCM) as long as this value is within the ADC voltage input range specified.
9
When using an external reference input pin, the internal reference must be disabled by setting the lsb in the REFCON Memeory Mapped Register to 0.
10
Endurance is qualified to 50,000 cycles as per JEDEC Std. 22 method A117 and measured at -40°C, +25°C and +85°C. Typical endurance at 25°C is 70,000 cycles.
11
Retention lifetime equivalent at junction temperature (Tj) = 55°C as per JEDEC Std. 22 method A117. Retention lifetime will derate with junction temperature.
12
Test carried out with a maximum of 20 I/O set to a low output level.
13
Power supply current consumption is measured in normal, idle and power-down modes under the following conditions:
Normal Mode: TBD
Idle Mode: TBD
Power-Down: TBD
14
DVDD power supply current increases typically by TBD mA during a Flash/EE memory program or erase cycle.
1MHz clock
1MHz clock
45MHz clock
5
50
mA typ
mA max
mA typ
60 mA max 45MHz clock
1
30
100
mA max
µA typ
µA max
External Crystal or Internal Osc ON
External Crystal or Internal Osc ON
Rev. PrB | Page 5 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
TERMINOLOGY
ADC Specifications
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation of any code from a straight line
passing through the endpoints of the ADC transfer function.
The endpoints of the transfer function are zero scale, a point 1/2
LSB below the first code transition and full scale, a point 1/2
LSB above the last code transition.
fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all nonfundamental
signals up to half the sampling frequency (fS/2), excluding dc.
The ratio is dependent upon the number of quantization levels
in the digitisation process; the more levels, the smaller the
quantization noise. The theoretical signal to (noise + distortion)
ratio for an ideal N-bit converter with a sine wave input is given
by:
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) = (6.02N + 1.76) dB
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
This is the deviation of the first code transition (0000 . . . 000) to
(0000 . . . 001) from the ideal, i.e., +1/2 LSB.
Gain Error
This is the deviation of the last code transition from the ideal
AIN voltage (Full Scale – 1.5 LSB) after the offset error has been
adjusted out.
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Ratio
This is the measured ratio of signal to (noise + distortion) at the
output of the ADC. The signal is the rms amplitude of the
Thus for a 12-bit converter, this is 74 dB.
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total Harmonic Distortion is the ratio of the rms sum of the
harmonics to the fundamental.
DAC SPECIFICATIONS
Relative Accuracy
Relative accuracy or endpoint linearity is a measure of the
maximum deviation from a straight line passing through the
endpoints of the DAC transfer function. It is measured after
adjusting for zero error and full-scale error.
Voltage Output Settling Time
This is the amount of time it takes for the output to settle to
within a 1 LSB level for a full-scale input change..
Rev. PrB | Page 6 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted) DVDD = IOVDD , AGND = REFGND = DACGND =
GNDREF
Parameter Rating
AVDD to DVDD -0.3V to +0.3V
AGND to DGND -0.3V to +0.3V
DVDD to DGND, AVDD to AGND -0.3V to +7V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND -0.3V to +5.5V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND -0.3V to +5.5V
VREF to AGND -0.3V to AVDD+0.3V
Analog Inputs to AGND -0.3V to AVDD+0.3V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial ADuC702x
Storage Temperature Range TBD
Junction Temperature 125°C
θJA Thermal Impedance (CSP)
θJA Thermal Impedance (LQFP)
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) TBD
Infrared (15 sec) TBD
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only;
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
–40°C to +125°C
TBD
TBD
ESD Caution
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high-energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. PrB | Page 7 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
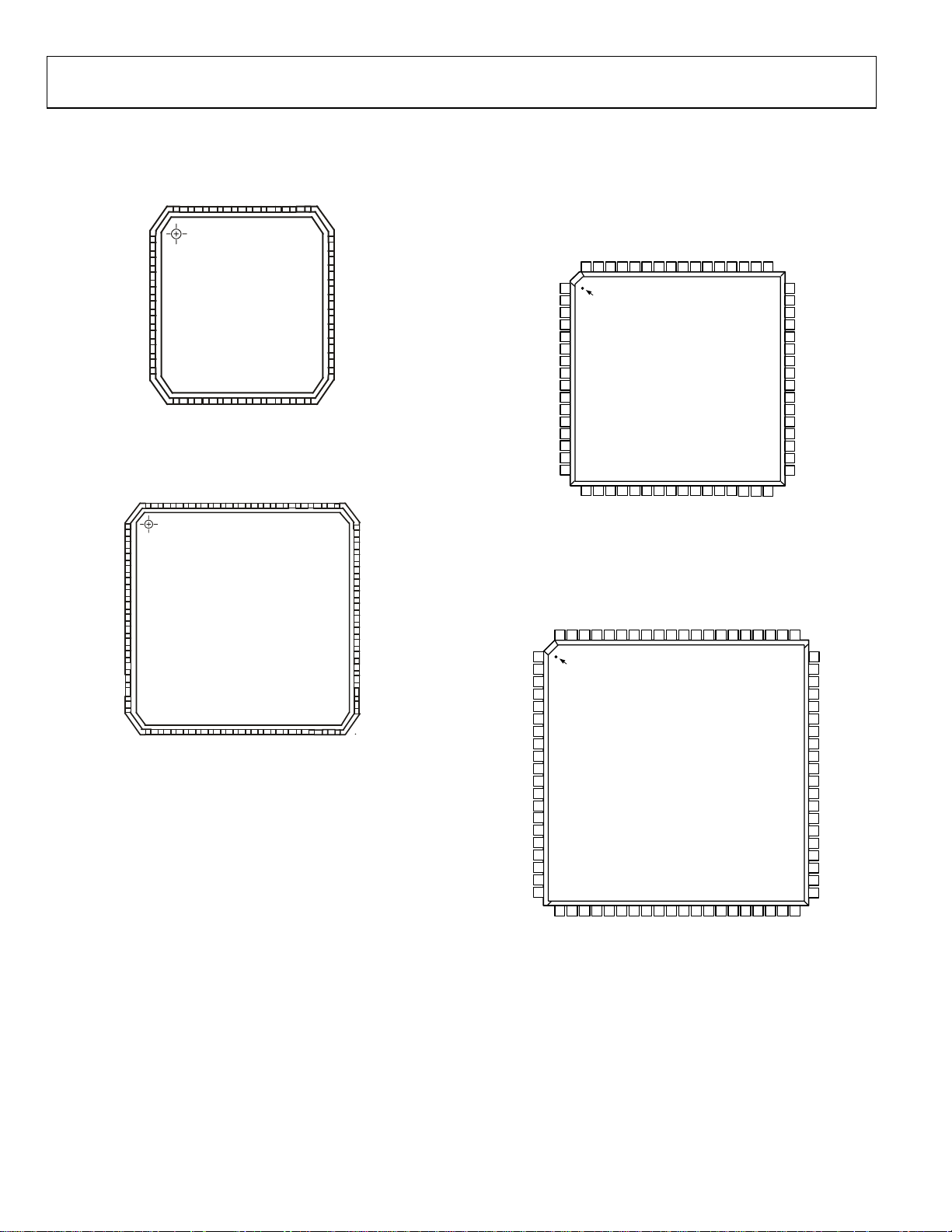
PIN CONFIGURATION
40-Lead CSP
40
31
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
ADuC7020/21/22
30
64
1
TOP VIEW
64-Lead LQFP
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
49
48
(Not to Scale)
10
11
21
20
ADuC7024/ADuC7025
64-LEAD L QFP
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
64-Lead CSP
64
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
49
48
16
17
33
32
ADuC7024/A D u C7025
TOP V IEW
(Not to Scale)
80
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
80-Lead LQFP
61
60
16
17
33
32
ADuC7026/ADuC7027 80-LEAD
LQFP
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
20
21
41
40
Rev. PrB | Page 8 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
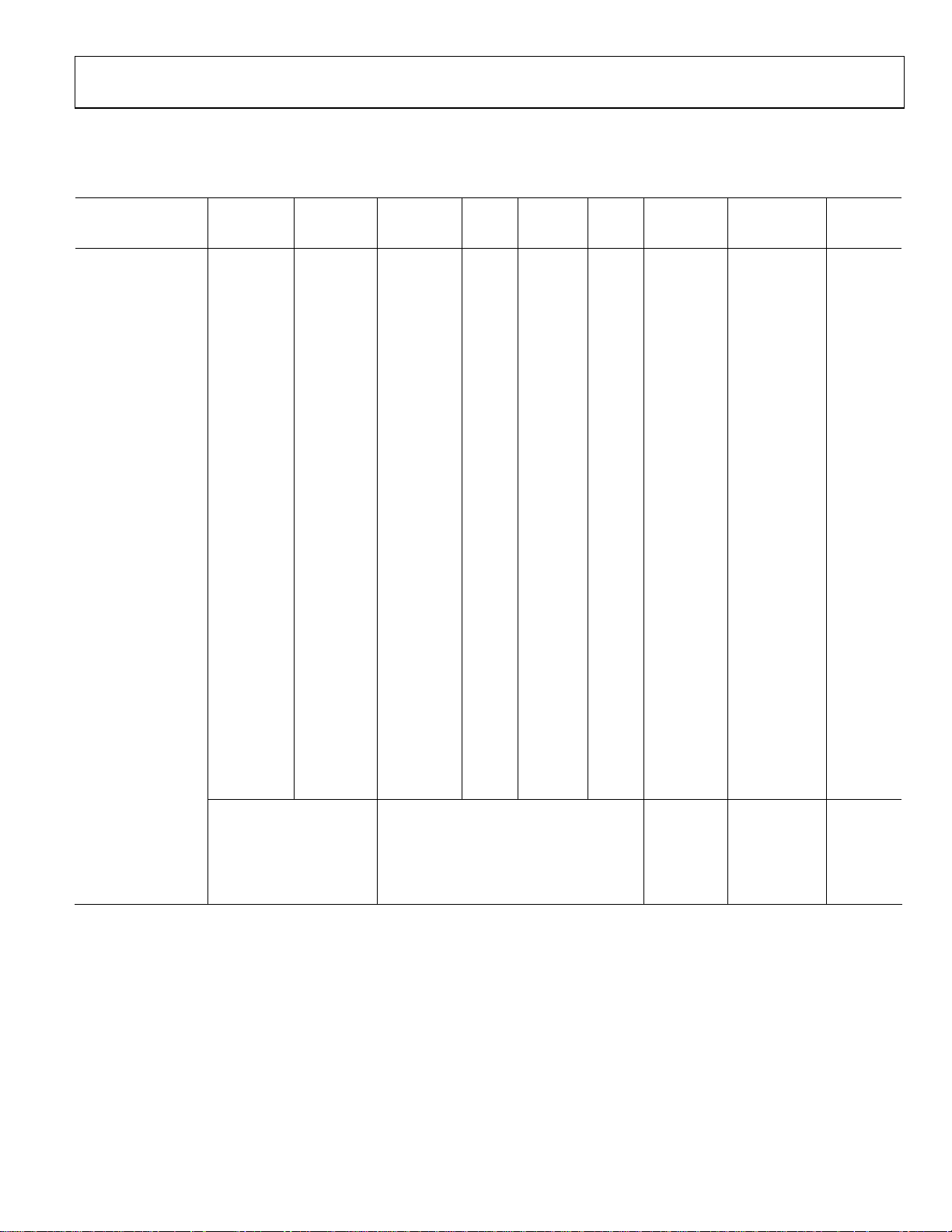
ORDERING GUIDE
Model ADC
Channels
DAC
Channels
FLASH /
RAM
PWM Ext
Memory
GPIO Temp
Range
Package
Description
Package
Option
ADuC7020BCP62 5 4 62kB/8kB Single 14
ADuC7021BCP62 8 2 62kB/8kB Single 13
ADuC7021BCP32 8 2 32kB/4kB Single 13
ADuC7021ACP32
ADuC7022BCP62 10 62kB/8kB Single 13
ADuC7022BCP32 10 32kB/4kB Single 13
ADuC7022ACP32
ADuC7024BCP62 10 2 62kB/8kB
ADuC7024BST62 10 2 62kB/8kB
ADuC7025BCP62 12 62kB/8kB
ADuC7025BCP32 12 32kB/4kB
ADuC7026BST62 12 4 62kB/8kB
ADuC7027BST62 16 62kB/8kB
ADuC7027AST62
EVAL-ADuC7020QS
EVAL-ADuC7024QS
EVAL-ADuC7026QS
8 (10 Bit
NMC)
10 (10 Bit
NMC)
16 (10 Bit
NMC)
2 32kB/4kB Single 13
62kB/8kB Single 13
Three
Phase
Three
Phase
Three
Phase
Three
Phase
Three
Phase
Three
Phase
62kB/8kB
Three
Phase
30
30
30
30
Yes 40
Yes 40
Yes 40
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
125°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
85°C
–40°C to +
125°C
–40°C to +
125°C
–40°C to +
125°C
Contact the factory for chip availability.
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
40-Lead Chip
Scale Package
64-Lead Chip
Scale Package
64 Lead
Plastic Quad
Flatpack
64-Lead Chip
Scale Package
64-Lead Chip
Scale Package
80 Lead
Plastic Quad
Flatpack
80 Lead
Plastic Quad
Flatpack
80 Lead
Plastic Quad
Flatpack
Development
System
Development
System
Development
System
CP-40
CP-40
CP-40
CP-40
CP-40
CP-40
CP-40
CP-64-1
ST-64
CP-64-1
CP-64-1
ST-80
ST-80
ST-80
Rev. PrB | Page 9 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
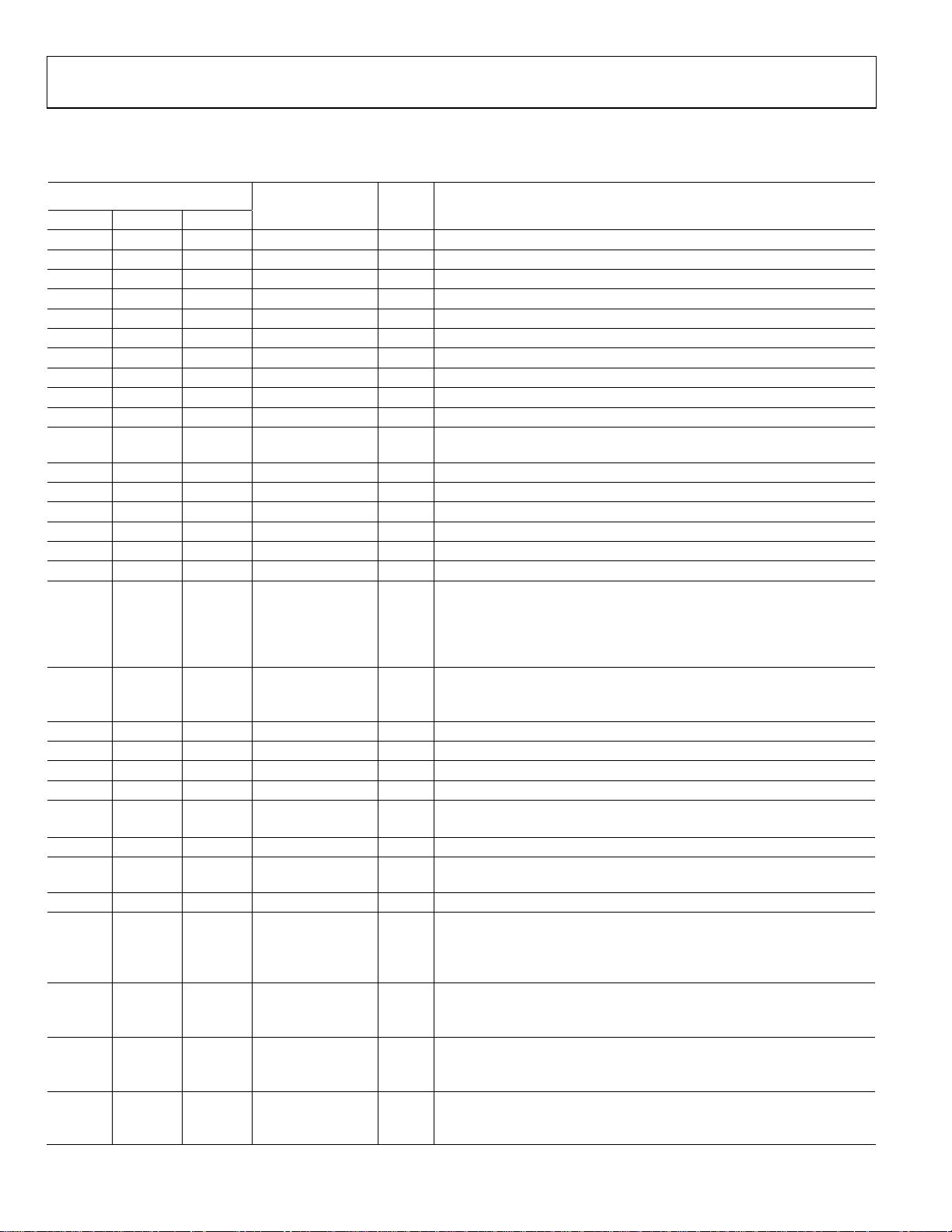
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS – ADUC7020/ADUC7021/ADUC7022
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin# ADuC702X
Mnemonic Type* Function
7020 7021 7022
38 37 36 ADC0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 0
39 38 37 ADC1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 1
40 39 38 ADC2/CMP0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 2 / Comparator Positive Input
1 40 39 ADC3/CMP1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 3 / Comparator Negative Input
2 1 40 ADC4 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 4
- 2 1 ADC5 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 5
- 3 2 ADC6 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 6
- 4 3 ADC7 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 7
- - 4 ADC8 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 8
- - 5 ADC9 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 9
3 5 6 GND
S
REF
Ground voltage reference for the ADC. For optimal performance the
analog power supply should be separated from IOGND and DGND
4 6 - DAC0/ADC12 I/O DAC0 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 12
5 7 - DAC1/ADC13 I/O DAC1 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 13
6 - - DAC2/ADC14 I/O DAC2 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 14
7 - - DAC3/ADC15 I/O DAC3 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 15
8 8 7 TMS I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Mode Select. Debug and download access
9 9 8 TDI I JTAG Test Port Input – Test Data In. Debug and download access
Multifunction I/O pin:
10 10 9
BM/P0.0/CMP
LAI[7]
OUT
/P
Boot Mode. The ADuC702X will enter serial download mode if BM is low
I/O
at reset and will execute code if BM is pulled high at reset through a
1kOhm resistor/ General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.0 / Voltage
Comparator Output/ Programmable Logic Array Input Element 7
11 11 10
P0.6/T1/MRST/PLA
O[3]
Multifunction pin: driven low after reset
O
General Purpose Output Port 0.6 / Timer 1 Input / Power on reset output
/ Programmable Logic Array Output Element 3
12 12 11 TCK I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Clock. Debug and download access
13 13 12 TDO O JTAG Test Port Output - Test Data Out. Debug and download access
14 14 13 IOGND S Ground for GPIO. Typically connected to DGND
15 15 14 IOVDD S 3.3V Supply for GPIO and input of the on-chip voltage regulator.
16 16 15 LVDD S
2.5V. Output of the on-chip voltage regulator. Must be connected to a
0.47µF capacitor to DGND
17 17 16 DGND S Ground for core logic.
18 18 17 P0.3/TRST/ADC
I
BUSY
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.3 / JTAG Test Port Input – Test
Reset. Debug and download access / ADC
signal output
BUSY
19 19 18 RST I Reset Input. (active low)
Multifunction I/O pin:
20 20 19
IRQ0/P0.4/CONV
ART
/PLAO[1]
ST
External Interrupt Request 0, active high / General Purpose Input-Output
I/O
Port 0.4 / Start conversion input signal for ADC / Programmable Logic
Array Output Element 1
21 21 20
22 22 21
23 23 22
IRQ1/P0.5/ADC
/PLAO[2]
P2.0/SPM9/PLAO[
5]/CONV
P0.7/ECLK/SPM8/
PLAO[4]/XCLK
START
BUSY
Multifunction I/O pin:
I/O
External Interrupt Request 1, active high / General Purpose Input-Output
Port 0.5 / ADC
signal / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 2
BUSY
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.0 / UART / Programmable Logic
Array Output Element 5/ Start conversion input signal for ADC
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.7 / Output for External Clock signal
/ UART / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 4/ Input to the
Rev. PrB | Page 10 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Pin# ADuC702X
7020 7021 7022
24 24 23 XCLKO O Output from the crystal oscillator inverter
25 25 24 XCLKI I
26 26 25
27 27 26 P1.6/SPM6/PLAI[6] I/O
28 28 27
29 29 28
30 30 29 P1.3/SPM3/PLAI[3] I/O
31 31 30 P1.2/SPM2/PLAI[2] I/O
32 32 31 P1.1/SPM1/PLAI[1] I/O
33 33 32
34 - - P4.2/PLAO[10] I/O
35 34 33 V
36 35 34 AGND S Analog Ground. Ground reference point for the analog circuitry
37 36 35 AVDD S 3.3V Analog Power
*
I = Input, O = Output, S = Supply.
- No pin assigned.
Mnemonic Type* Function
internal clock generator circuits
Input to the crystal oscillator inverter and input to the internal clock
generator circuits
P1.7/SPM7/PLAO[
0]
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.7 / UART / SPI / Programmable
Logic Array Output Element 0
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.6 / UART / SPI / Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 6
P1.5/SPM5/PLAI[5]
/IRQ3
P1.4/SPM4/PLAI[4]
/IRQ2
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.5 / UART / SPI / Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 5/ External Interrupt Request 3, active high
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.4 / UART / SPI / Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 4/ External Interrupt Request 2, active high
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.3/ UART / I2C1 /Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 3
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.2 / UART / I2C1 /Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 2
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.1 / UART / I2C0 / Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 1
P1.0/T1/SPM0/PLA
I[0]
Serial Port Multiplexed:
I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.0/ Timer 1 Input / UART / I2C0 /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 0
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.2 / Programmable Logic Array
Output Element 10
I/O
REF
2.5V internal Voltage Reference. Must be connected to a 0.47uF capacitor
when using the internal reference.
Rev. PrB | Page 11 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS – ADUC7024/ADUC7025
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
1 ADC4 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 4
2 ADC5 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 5
3 ADC6 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 6
4 ADC7 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 7
5 ADC8 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 8
6 ADC9 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 9
7 GND
8 ADCNEG I
9 DAC0**/ADC12 I/O DAC0 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 12
10 DAC1**/ADC13 I/O DAC1 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 13
11 TMS I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Mode Select. Debug and download access
12 TDI I JTAG Test Port Input – Test Data In. Debug and download access
13 P4.6/PLAO[14] I/O
14 P4.7/PLAO[15] I/O
15 BM/P0.0/CMP
16 P0.6/T1/MRST/PLAO[3] O
17 TCK I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Clock. Debug and download access
18 TDO O JTAG Test Port Output - Test Data Out. Debug and download access
19 IOGND S Ground for GPIO. Typically connected to DGND
20 IOVDD S 3.3V Supply for GPIO and input of the on-chip voltage regulator.
21 LVDD S
22 DGND S Ground for core logic.
23 P3.0/PWM0H/PLAI[8] I/O
24 P3.1/PWM0L/PLAI[9] I/O
25 P3.2/PWM1H/PLAI[10] I/O
26 P3.3/PWM1L/PLAI[11] I/O
27 P0.3/TRST/ADC
28 RST I Reset Input. (active low)
29 P3.4/PWM2H/PLAI[12] I/O
30 P3.5/PWM2L/PLAI[13] I/O
S
REF
/PLAI[7] I/O
OUT
I/O
BUSY
Ground voltage reference for the ADC. For optimal performance the analog
power supply should be separated from IOGND and DGND
Bias point or Negative Analog Input of the ADC in pseudo differential mode.
Must be connected to the ground of the signal to convert. This bias point
must be between 0V and 1V
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.6/ Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 14
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.7/ Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 15
Multifunction I/O pin:
Boot Mode. The ADuC7024/ADuC7025 will enter download mode if BM is low
at reset and will execute code if BM is pulled high at reset through a 1kOhm
resistor/ General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.0 / Voltage Comparator
Output/ Programmable Logic Array Input Element 7
Multifunction pin: driven low after reset
General Purpose Output Port 0.6 / Timer 1 Input / Power on reset output /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 3
2.5V. Output of the on-chip voltage regulator. Must be connected to a 0.47µF
capacitor to DGND
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.0/ PWM phase 0 high side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 8
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.1/ PWM phase 0 low side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 9
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.2/ PWM phase 1 high side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 10
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.3/ PWM phase 1 low side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 11
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.3 / JTAG Test Port Input – Test Reset.
Debug and download access / ADC
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.4 / PWM phase 2 high side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input 12
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.5 / PWM phase 2 low side output /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 13
signal output
BUSY
Rev. PrB | Page 12 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
Multifunction I/O pin:
31 IRQ0/P0.4/CONV
32 IRQ1/P0.5/ADC
33 P2.0/PWM
TRIP
/PLAO[1] I/O
START
/PLAO[2] I/O
BUSY
/SPM9/PLAO[5]/CONV
I/O
START
34 P0.7/ECLK/SPM8/PLAO[4]/XCLK I/O
35 XCLKO O Output from the crystal oscillator inverter
36 XCLKI I
37 P3.6/PWM
/PLAI[14] I/O
TRIP
38 P3.7/PWMSYNC/PLAI[15] I/O
39 P1.7/SPM7/PLAO[0] I/O
40 P1.6/SPM6/PLAI[6] I/O
41 IOGND S Ground for GPIO. Typically connected to DGND
42 IOVDD S 3.3V Supply for GPIO and input of the on-chip voltage regulator.
43 P4.0/PLAO[8] I/O
44 P4.1/PLAO[9] I/O
45 P1.5/SPM5/PLAI[5]/IRQ3 I/O
46 P1.4/SPM4/PLAI[4]/IRQ2 I/O
47 P1.3/SPM3/PLAI[3] I/O
48 P1.2/SPM2/PLAI[2] I/O
49 P1.1/SPM1/PLAI[1] I/O
50 P1.0/T1/SPM0/PLAI[0] I/O
51 P4.2/PLAO[10] I/O
External Interrupt Request 0, active high / General Purpose Input-Output Port
0.4 / Start conversion input signal for ADC / Programmable Logic Array
Output Element 1
Multifunction I/O pin:
External Interrupt Request 1, active high / General Purpose Input-Output Port
0.5 / ADC
signal / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 2
BUSY
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.0 / PWM safety cut off / UART /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 5/ Start conversion input signal
for ADC
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.7 / Output for External Clock signal /
UART / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 4/ Input to the internal
clock generator circuits
Input to the crystal oscillator inverter and input to the internal clock
generator circuits
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.6/ PWM safety cut off / Programmable
Logic Array Input Element 14
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.7/ PWM synchronisation input output
/Programmable Logic Array Input Element 15
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.7 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Output Element 0
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.6 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 6
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.0 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 8
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.1 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 9
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.5 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 5/ External Interrupt Request 3, active high
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.4 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 4/ External Interrupt Request 2, active high
Serial Port Multiplexed:
2
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.3/ UART / I
C1 /Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 3
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.2 / UART / I
2
C1 /Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 2
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.1 / UART / I
2
C0 / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 1
Serial Port Multiplexed:
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.0/ Timer 1 Input / UART / I2C0 /
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 0
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.2 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 10
Rev. PrB | Page 13 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
52 P4.3/PLAO[11] I/O
53 P4.4/PLAO[12] I/O
54 P4.5/PLAO[13] I/O
55 V
56 DAC
I/O
REF
I External Voltage Reference for the DACs. Range: DACGND to DACVDD
REF
57 DACGND S Ground for the DAC. Typically connected to AGND
58 AGND S Analog Ground. Ground reference point for the analog circuitry
59 AVDD S 3.3V Analog Power
60 DACVDD S 3.3V Power Supply for the DACs. Typically connected to AVDD
61 ADC0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 0
62 ADC1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 1
63 ADC2/CMP0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 2/ Comparator positive input
64 ADC3/CMP1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 3/ Comparator negative input
*
I = Input, O = Output, S = Supply.
** DAC outputs not present on ADuC7025
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.3 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 11
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.4 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 12
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.5 / Programmable Logic Array Output
Element 13
2.5V internal Voltage Reference. Must be connected to a 0.47uF capacitor
when using the internal reference.
Rev. PrB | Page 14 of 80
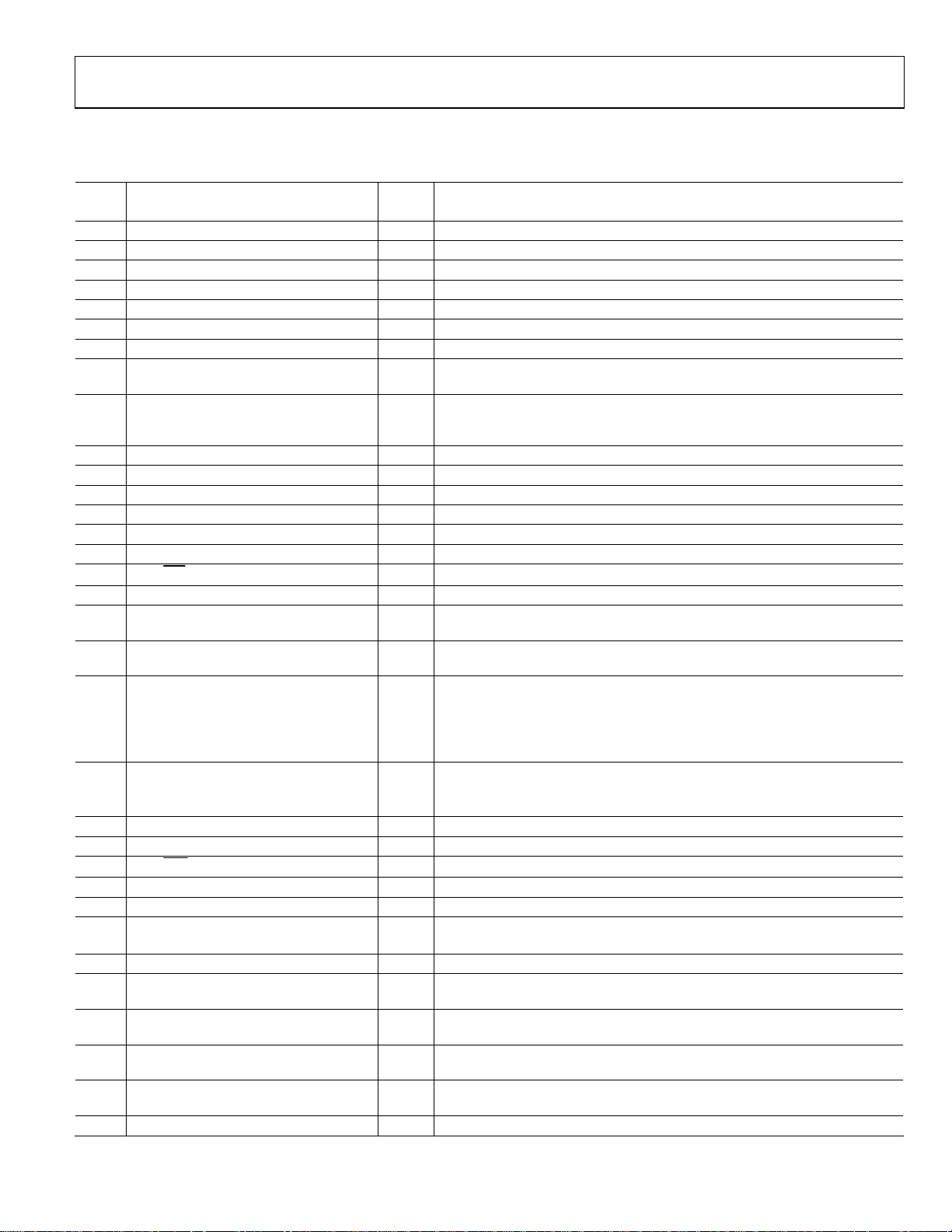
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS – ADUC7026/ADUC7027
Table 5. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
1 ADC4 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 4
2 ADC5 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 5
3 ADC6 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 6
4 ADC7 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 7
5 ADC8 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 8
6 ADC9 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 9
7 ADC10 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 10
8 GND
9 ADCNEG I
10 DAC0/ADC12 I/O DAC0 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 12
11 DAC1/ADC13 I/O DAC1 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 13
12 DAC1/ADC14 I/O DAC2 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 14
13 DAC1/ADC15 I/O DAC3 Voltage Output / Single-ended or differential Analog input 15
14 TMS I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Mode Select. Debug and download access
15 TDI I JTAG Test Port Input – Test Data In. Debug and download access
16
17 P2.3/AE
18 P4.6/AD14/PLAO[14] I/O
19 P4.7/AD15/PLAO[15] I/O
20 BM/P0.0/CMP
21 P0.6/T1/MRST/PLAO[3]/AE O
22 TCK I JTAG Test Port Input - Test Clock. Debug and download access
23 TDO O JTAG Test Port Output - Test Data Out. Debug and download access
24
25 IOGND S Ground for GPIO. Typically connected to DGND
26 IOVDD S 3.3V Supply for GPIO and input of the on-chip voltage regulator.
27 LVDD S
28 DGND S Ground for core logic.
29 P3.0/AD0/PWM0H/PLAI[8] I/O
30 P3.1/AD1/PWM0L/PLAI[9] I/O
31 P3.2/AD2/PWM1H/PLAI[10] I/O
32 P3.3/AD3/PWM1L/PLAI[11] I/O
33 P2.4/MS0 I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.4 / External Memory select 0
S
REF
BLE
P0.1/
P0.2/
BHE
/PLAI[7] I/O
OUT
Ground voltage reference for the ADC. For optimal performance the analog
power supply should be separated from IOGND and DGND
Bias point or Negative Analog Input of the ADC in pseudo differential mode.
Must be connected to the ground of the signal to convert. This bias point
must be between 0V and 1V
I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.1/ External memory byte low enable
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.6/ External Memory
Interface/Programmable Logic Array Output Element 14
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.7/ External Memory Interface /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 15
Multifunction I/O pin:
Boot Mode. The ADuC7026 will enter UART download mode if BM is low at
reset and will execute code if BM is pulled high at reset through a 1kOhm
resistor/ General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.0 / Voltage Comparator
Output/ Programmable Logic Array Input Element 7
Multifunction pin: driven low after reset
General Purpose Output Port 0.6 / Timer 1 Input / Power on reset output /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 3
I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.2/ External memory byte high enable
2.5V. Output of the on-chip voltage regulator. Must be connected to a 0.47µF
capacitor to DGND
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.0 / External Memory Interface/ PWM
phase 0 high side output / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 8
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.1 / External Memory Interface / PWM
phase 0 low side output / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 9
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.2 / External Memory Interface / PWM
phase 1 high side output / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 10
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.3 / External Memory Interface / PWM
phase 1 low side output / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 11
Rev. PrB | Page 15 of 80
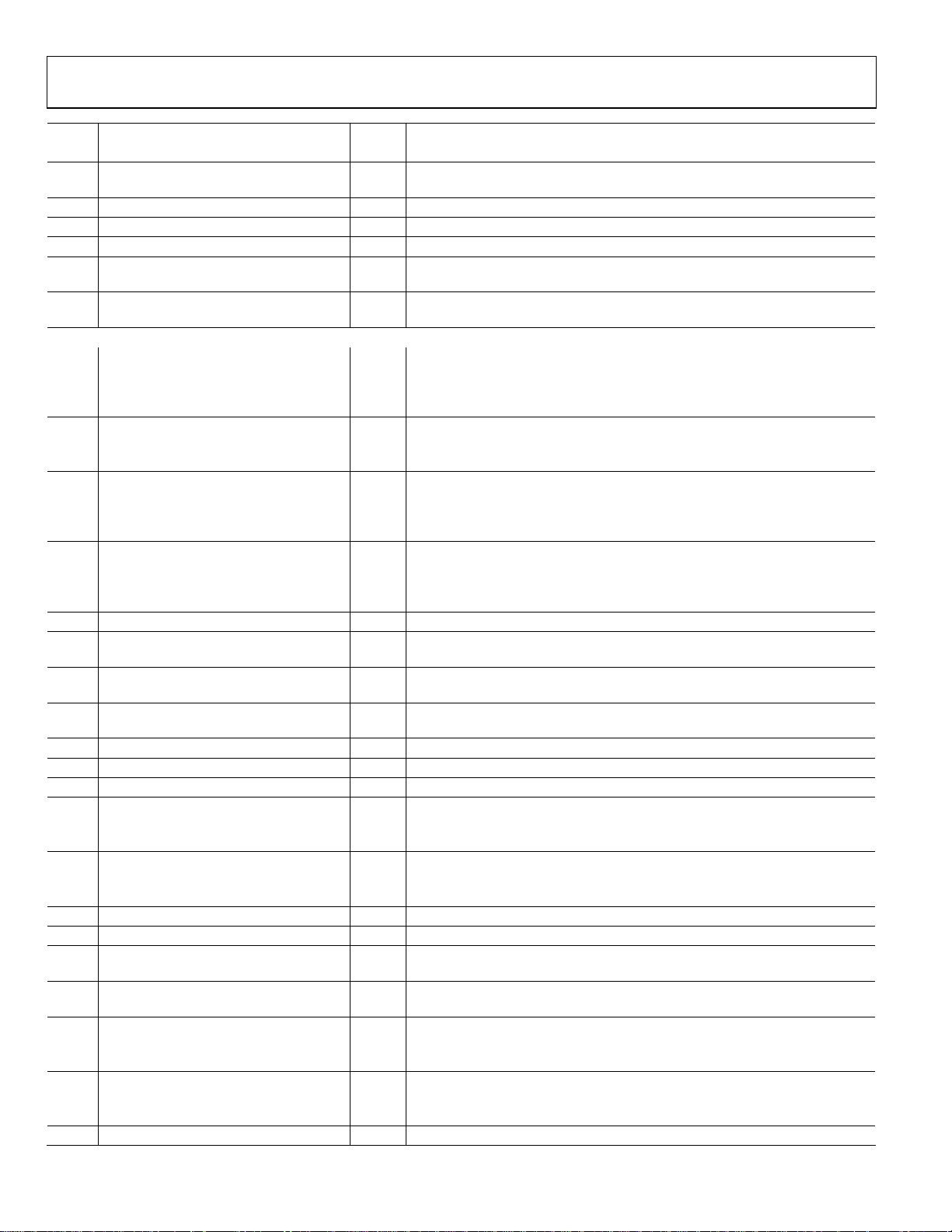
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
34 P0.3/TRST/A16/ADC
I/O
BUSY
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.3 / JTAG Test Port Input – Test Reset.
Debug and download access / ADC
signal output
BUSY
35 P2.5/MS1 I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.5 / External Memory select 1
36 P2.6/MS2 I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.6 / External Memory select 2
37 RST I Reset Input. (active low)
38 P3.4/AD4/PWM2H/PLAI[12] I/O
39 P3.5/AD5/PWM2L/PLAI[13] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.4 / External Memory Interface / PWM
phase 2 high side output / Programmable Logic Array Input 12
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.5 / External Memory Interface /PWM
phase 2 low side output / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 13
Multifunction I/O pin:
40 IRQ0/P0.4/CONV
/PLAO[1] I/O
START
External Interrupt Request 0, active high / General Purpose Input-Output Port
0.4 / Start conversion input signal for ADC / Programmable Logic Array
Output Element 1
Multifunction I/O pin:
41 IRQ1/P0.5/ADC
/PLAO[2] I/O
BUSY
External Interrupt Request 1, active high / General Purpose Input-Output Port
0.5 / ADC
signal / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 2
BUSY
Serial Port Multiplexed:
42 P2.0/PWM
/SPM9/PLAO[5]/CONV
TRIP
I/O
START
General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.0 / PWM safety cut off / UART /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 5/ Start conversion input signal
for ADC
Serial Port Multiplexed:
43 P0.7/ECLK/SPM8/PLAO[4]/XCLK I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 0.7 / Output for External Clock signal /
UART / Programmable Logic Array Output Element 4/ Input to the internal
clock generator circuits.
44 XCLKO O Output from the crystal oscillator inverter
45 XCLKI I
46 P3.6/AD6/PWM
/PLAI[14] I/O
TRIP
47 P3.7/AD7/ECLK/PLAI[15] I/O
Input to the crystal oscillator inverter and input to the internal clock
generator circuits
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.6 / External Memory Interface / PWM
safety cut off / Programmable Logic Array Input Element 14
General Purpose Input-Output Port 3.7/ / External Memory Interface / Output
for External Clock signal /Programmable Logic Array Input Element 15
48 P2.7/MS3 I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.7 / External Memory select 3
49 P2.1/WS I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.1 / External Memory Write Strobe
50 P2.2/RS I/O General Purpose Input-Output Port 2.2 / External Memory Read Strobe
Serial Port Multiplexed:
51 P1.7/SPM7/PLAO[0] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.7 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Output Element 0
Serial Port Multiplexed:
52 P1.6/SPM6/PLAI[6] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.6 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 6
53 IOGND S Ground for GPIO. Typically connected to DGND
54 IOVDD S 3.3V Supply for GPIO and input of the on-chip voltage regulator.
55 P4.0/AD8/PLAO[8] I/O
56 P4.1/AD9/PLAO[9] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.0 / External Memory Interface /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 8
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.1 / External Memory Interface
/Programmable Logic Array Output Element 9
Serial Port Multiplexed:
57 P1.5/SPM5/PLAI[5]/IRQ3 I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.5 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 5/ External Interrupt Request 3, active high
Serial Port Multiplexed:
58 P1.4/SPM4/PLAI[4]/IRQ2 I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.4 / UART / SPI / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 4 / External Interrupt Request 2, active high
59 P1.3/SPM3/PLAI[3] I/O Serial Port Multiplexed:
Rev. PrB | Page 16 of 80
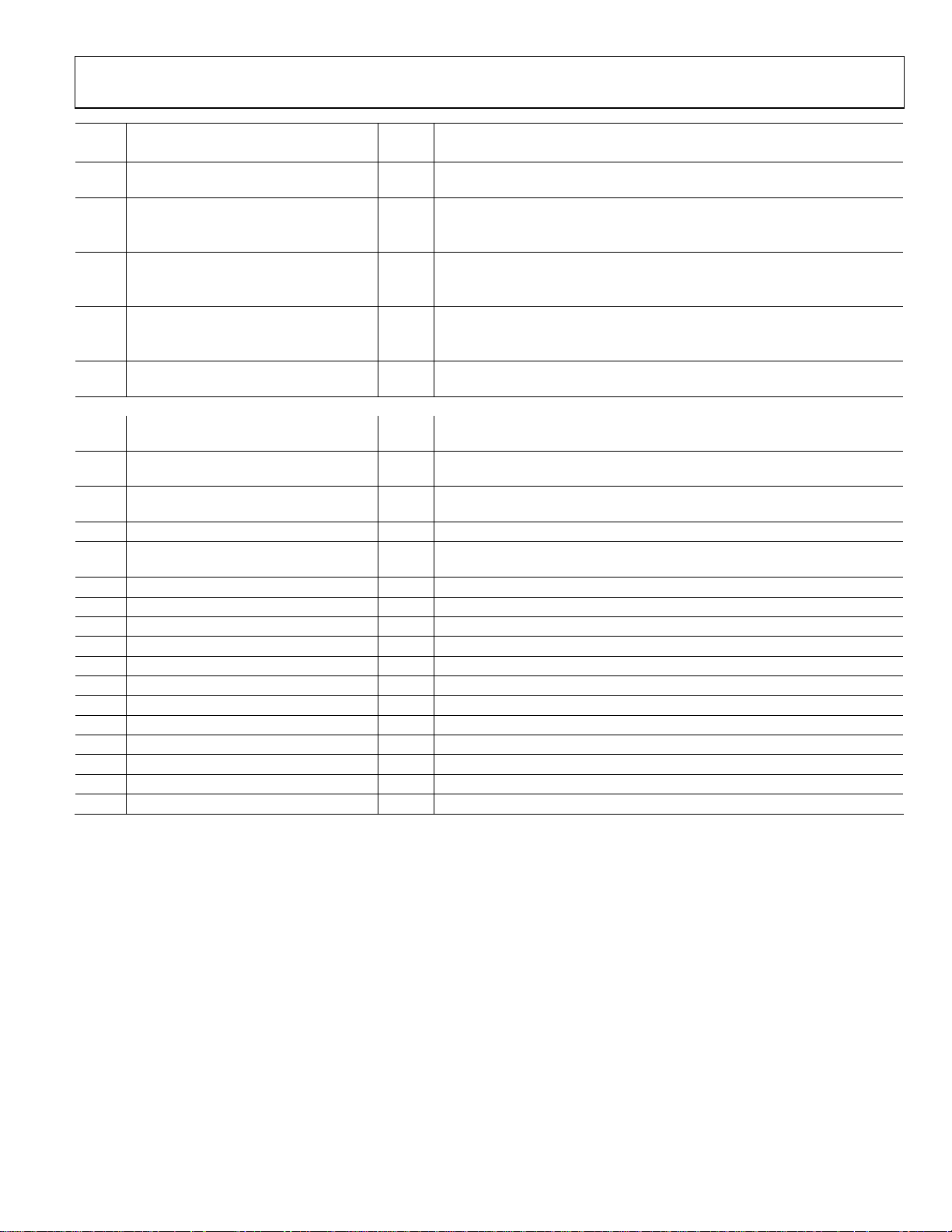
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Pin# Mnemonic Type* Function
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.3/ UART / I2C1 /Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 3
Serial Port Multiplexed:
60 P1.2/SPM2/PLAI[2] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.2 / UART / I
Array Input Element 2
Serial Port Multiplexed:
61 P1.1/SPM1/PLAI[1] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.1 / UART / I2C0 / Programmable Logic
Array Input Element 1
Serial Port Multiplexed:
62 P1.0/T1/SPM0/PLAI[0] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 1.0/ Timer 1 Input / UART / I
Programmable Logic Array Input Element 0
63 P4.2/AD10/PLAO[10] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.2 / External Memory Interface /
Programmable Logic Array Output Element 10
64 P4.3/AD11/PLAO[11] I/O
65 P4.4/AD12/PLAO[12] I/O
66 P4.5/AD13/PLAO[13] I/O
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.3 / External Memory Interface
/Programmable Logic Array Output Element 11
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.4 / External Memory Interface
/Programmable Logic Array Output Element 12
General Purpose Input-Output Port 4.5 / External Memory Interface
/Programmable Logic Array Output Element 13
67 REFGND S Ground for the reference. Typically connected to AGND
68 V
REF
69 DAC
I/O
I External Voltage Reference for the DACs. Range: DACGND to DACVDD
REF
2.5V internal Voltage Reference. Must be connected to a 0.47uF capacitor
when using the internal reference.
70 DACGND S Ground for the DAC. Typically connected to AGND
71 AGND S Analog Ground. Ground reference point for the analog circuitry
72 AGND S Analog Ground. Ground reference point for the analog circuitry
73 AVDD S 3.3V Analog Power
74 AVDD S 3.3V Analog Power
75 DACVDD S 3.3V Power Supply for the DACs. Typically connected to AVDD
76 ADC11 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 11
77 ADC0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 0
78 ADC1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 1
79 ADC2/CMP0 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 2/ Comparator positive input
80 ADC3/CMP1 I Single-ended or differential Analog input 3/ Comparator negative input
*
I = Input, O = Output, S = Supply.
2
C1 /Programmable Logic
2
C0 /
Rev. PrB | Page 17 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
F
E
R
D
N
G
D
N
D
D
D
G
N
G
A
D
N
F
V
V
E
G
A
A
R
A
D
D
D
D
N
D
G
O
I
D
N
D
D
V
V
G
O
O
O
I
I
I
T
D
E
D
N
S
D
E
G
V
R
L
D
D
D
F
N
D
E
R
V
G
C
C
C
A
A
A
D
D
D
BM/P0.0/CMP
P4.6/PLAO/AD14
P4.7/PLAO/AD15
ADC0
ADC1
ADC2/CMP0
ADC3/CMP1
ADC4
ADC5
ADC6
ADC7
ADC8
ADC9
ADC10
ADC11
ADC
NEG
/PLAI
OUT
V
REF
DAC
DAC
PROG. LOGIC
MUX
MUX
MUX
BAND GAP
REFERENCE
ARRAY
12-BIT SAR
ADC 1MSPS
TEMP
SENSOR
62 KBYTES FLASH/EE
/IRQ
CMP
OUT
V
REF
SPI/I2CSERIAL
INTERFACE
8192 BYTES USER RAM
SERIAL PORT MULTIPLEXER
ADC
CONTROL
(31k X 16 bits)
(2k X 32 bits)
DOWNLOADER
UART
SERIAL PORT
ADuC7026*
ARM7TDMI
MCU
CORE
R
O
T
G
A
A
L
T
U
J
M
E
DAC
CONTROL
WAKEUP/
RTC TIMER
POWER SUPPLY
MONITOR
PROG. CLOCK
DIVIDER
POR
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
12-BIT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT DAC
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
Threephase
PWM
PLL
BUF
BUF
BUF
BUF
OSC
DAC0*/ADC12
DAC1*/ADC13
DAC2*/ADC14
DAC3*/ADC15
P3.0/PWM0H/PLAI/AD0
P3.1/PWM0L/PLAI/AD1
P3.2/PWM1H/PLAI/AD2
P3.3/PWM1L/PLAI/AD3
P3.4/PWM2H/PLAI/AD4
P3.5/PWM2L/PLAI/AD5
P3.6/PWM
TRIP
/PLAI/AD6
XCLKO
XCLKI
P3.7/ECLK/PLAI/AD7
IRQ0/P0.4/CONV
IRQ1/P0.5/ADC
P0.0
START
BUSY
/PLAO
/PLAO
I
I
I
I
I
I
0
1
3
8
9
D
D
A
A
/
/
O
O
A
A
L
L
P
P
/
/
0
1
.
.
4
4
P
P
2
1
A
A
A
1
1
1
1
T
/
L
D
D
A
A
/
/
O
O
A
A
L
L
P
P
/
/
2
3
.
.
4
4
P
P
I
D
D
A
/
O
A
L
P
/
4
.
4
P
P
A
A
/
/
L
1
O
P
/
M
A
0
P
L
S
M
P
/
/
P
1
5
.
.
S
/
1
4
0
P
.
P
1
P
A
L
L
L
P
P
P
/
/
/
2
3
4
M
M
M
P
P
P
S
S
S
/
/
/
2
3
4
.
.
.
1
1
1
P
P
P
I
T
A
L
P
/
5
M
P
S
/
5
.
1
P
O
A
A
R
A
L
L
A
L
P
/
6
M
P
S
/
6
.
1
P
T
P
/
P
S
/
7
V
8
M
N
M
P
O
P
S
/
C
S
/
/
7
.
O
K
1
L
A
P
L
C
P
E
/
/
9
7
.
M
0
P
P
S
/
P
I
R
T
M
W
P
/
0
.
2
P
I
S
D
M
T
T
Y
O
K
L
D
T
C
X
/
K
C
T
1
S
E
S
U
B
C
D
A
/
6
1
A
/
T
S
R
T
/
3
.
0
P
S
T
/
E
A
/
O
A
L
P
/
T
S
R
M
/
6
.
0
P
A
R
W
/
/
/
3
2
1
.
.
.
2
2
2
P
P
P
3
0
1
2
E
S
S
M
M
/
/
4
5
.
.
2
2
P
P
* See selection table for
feature availability on
different models.
E
S
S
L
H
B
B
M
M
/
/
/
/
1
2
6
7
.
.
.
.
0
0
2
2
P
P
P
P
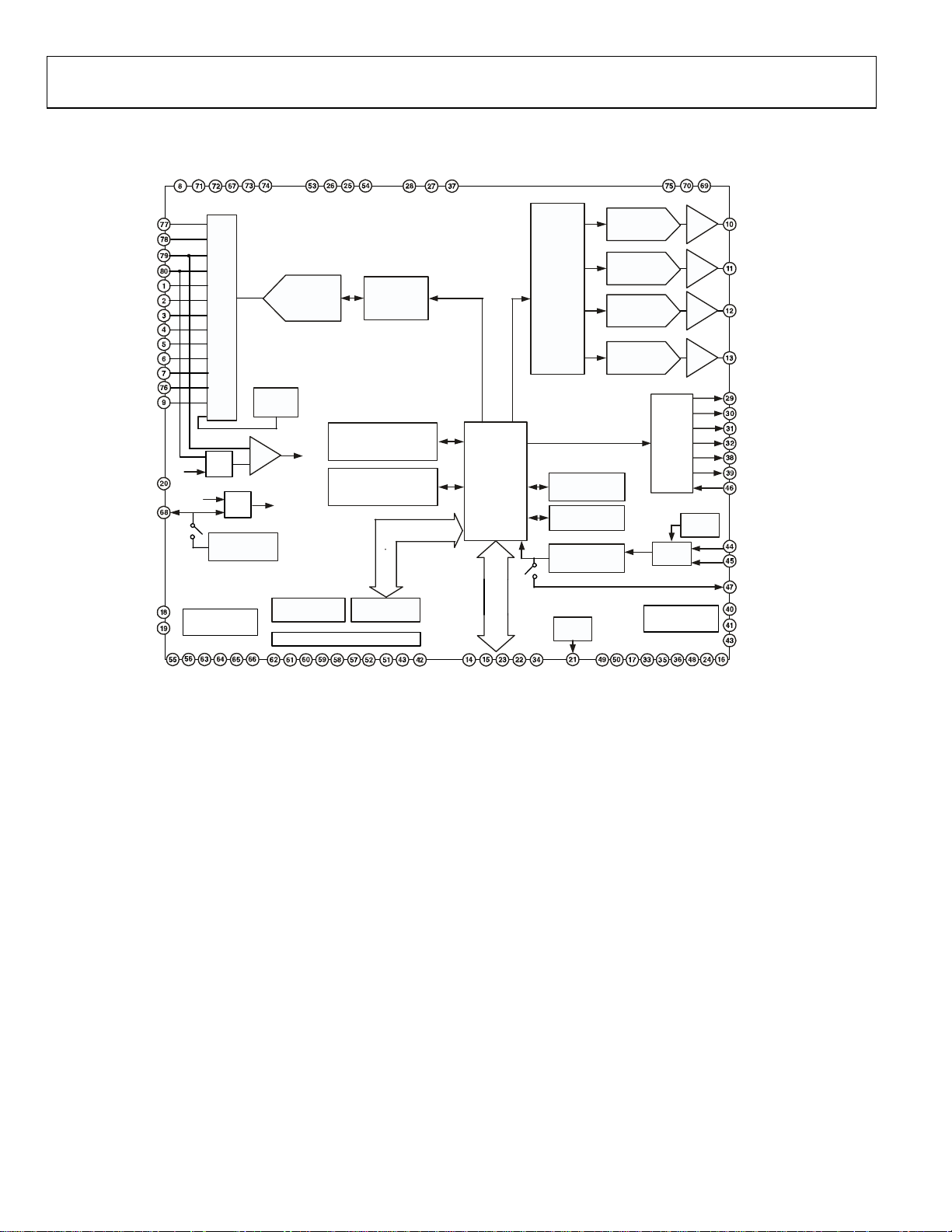
Figure 2: Detailed Block Diagram
Rev. PrB | Page 18 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADuC702x is fully integrated, 1MSPS, 12-bit data
acquisition system incorporating a high performance multichannel ADC, a 16/32-bit MCU and Flash/EE Memory on a
single chip.
The ADC consists of up to 12 single-ended inputs. An
additional 4 inputs are available but are multiplexed with the 4
DAC output pins. The 4 DAC outputs are only available on
certain models of the ADuC702x, though in many cases where
the DAC is not present this pin can still be used as an additional
ADC input, giving a maximum of 16 ADC input channels. The
ADC can operate in single-ended or differential input modes.
The ADC input voltage is 0 to V
reference, temperature sensor and voltage comparator complete
the ADC peripheral set.
The ADuC702x also integrates 4 buffered voltage output DACs
on-chip. The DAC output range is programmable to one of
three voltage ranges.
The device operates from an on-chip oscillator and PLL
generating an internal high-frequency clock of 45 MHz. This
clock is routed through a programmable clock divider from
which the MCU core clock operating frequency is generated.
The microcontroller core is an ARM7TDMI, 16/32-bit RISC
machine, offering up to 45 MIPS peak performance. 62k Bytes
of non-volatile Flash/EE are provided on-chip as well as 8k
Bytes of SRAM. The ARM7TDMI core views all memory and
registers as a single linear array.
On-chip factory firmware supports in-circuit serial download
via the UART and JTAG serial interface ports while nonintrusive emulation is also supported via the JTAG interface.
These features are incorporated into a low-cost QuickStart
Development System supporting this MicroConverter family.
The parts operate from 2.7V to 3.6V and are specified over an
industrial temperature range of -40°C to 125°C. When
operating at 45MHz the power dissipation is 150mW. The
ADuC702x is available in a variety of memory models and
packages. These are detailed on page 9.
. Low drift bandgap
REF
OVERVIEW OF THE ARM7TDMI CORE
The ARM7 core is a 32-bit Reduced Instruction Set Computer
(RISC). It uses a single 32-bit bus for instruction and data. The
length of the data can be 8, 16 or 32 bits and the length of the
instruction word is 32 bits.
The ARM7TDMI is an ARM7 core with 4 additional features:
- T support for the Thumb (16 bit) instruction set.
- D support for debug
- M support for long multiplies
- I include the EmbeddedICE module to support embedded
system debugging.
Thumb mode (T)
An ARM instruction is 32-bits long. The ARM7TDMI
processor supports a second instruction set that has been
compressed into 16-bits, the Thumb instruction set. Faster
execution from 16-bit memory and greater code density can
usually be achieved by using the Thumb instruction set instead
of the ARM instruction set, which makes the ARM7TDMI core
particularly suitable for embedded applications.
However the Thumb mode has two limitations:
- Thumb code usually uses more instructions for the same job,
so ARM code is usually best for maximising the performance
of the time-critical code.
- The Thumb instruction set does not include some
instructions that are needed for exception handling, so the
core will automatically switch to ARM code for exception
handling.
See ARM7TDMI User Guide for details on the core
architecture, the programming model and both the ARM and
ARM Thumb instruction sets.
Long Multiply (M)
The ARM7TDMI instruction set includes four extra
instructions which perform 32-bit by 32-bit multiplication with
64-bit result and 32-bit by 32-bit multiplication-accumulation
(MAC) with 64-bit result. This result is achieved in a reduced
number of cycles than required on a standard ARM7 core.
EmbeddedICE (I)
EmbeddedICE provides integrated on-chip support for the core.
The EmbeddedICE module contains the breakpoint and
watchpoint registers which allow code to be halted for
debugging purposes. These registers are controlled through the
JTAG test port.
When a breakpoint or watchpoint is encountered, the processor
halts and enters debug state. Once in a debug state, the
processor registers may be inspected as well as the Flash/EE, the
SRAM and the Memory Mapped Registers.
Exceptions
ARM supports five types of exceptions, and a privileged
processing mode for each type. The five type of exceptions are:
- Normal interrupt or IRQ. It is provided to service general-
purpose interrupt handling of internal and external events
- Fast interrupt or FIQ. It is provided to service data transfer or
communication channel with low latency. FIQ has priority
over IRQ
Rev. PrB | Page 19 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
- Memory abort
- Attempted execution of an undefined instruction
- Software interrupt (SWI) instruction which can be used to
make a call to an operating system.
Typically the programmer will define interrupts as IRQ but for
higher priority interrupt, i.e. faster response time, the
programmer can define interrupt as FIQ.
ARM Registers
ARM7TDMI has a total of 37 registers, of which 31 are general
purpose registers and six are status registers. Each operating
mode has dedicated banked registers.
When writing user-level programs, 15 general purpose 32-bit
registers (r0 to r14), the program counter (r15) and the current
program status register (CPSR) are usable. The remaining
registers are used only for system-level programming and for
exception handling.
When an exception occurs, some of the standard register are
replaced with registers specific to the exception mode. All
exception modes have replacement banked registers for the
stack pointer (r13) and the link register (r14) as represented in
Figure 3. The fast interrupt mode has more registers (8 to 12)
for fast interrupt processing, so that the interrupt processing
can begin without the need to save or restore these registers and
thus save critical time in the interrupt handling process.
Interrupt latency
The worst case latency for an FIQ consists of the longest time
the request can take to pass through the synchronizer, plus the
time for the longest instruction to complete (the longest
instruction is an LDM) which loads all the registers including
the PC, plus the time for the data abort entry, plus the time for
FIQ entry. At the end of this time, the ARM7TDMI will be
executing the instruction at 0x1C (FIQ interrupt vector
address). The maximum total time is 50 processor cycles, which
is just over 1.1µS in a system using a continuous 45 MHz
processor clock. The maximum IRQ latency calculation is
similar, but must allow for the fact that FIQ has higher priority
and could delay entry into the IRQ handling routine for an
arbitrary length of time. This time can be reduced to 42 cycles
if the LDM command is not used, some compilers have an
option to compile without using this command. Another option
is to run the part in THUMB mode where this is reduced to 22
cycles.
The minimum latency for FIQ or IRQ interrupts is five cycles in
total which consists of the shortest time the request can take
through the synchronizer plus the time to enter the exception
mode.
Note that the ARM7TDMI will always be run in ARM (32-bit)
mode when in privileged modes, i.e. when executing interrupt
service routines.
r0
r1
r2
r3
r4
r5
r6
r7
r8
r9
r10
r11
r12
r13
r14
r15 (PC)
CPSR
user mode fiq
r8_fiq
r9_fiq
r10_fiq
r11_fiq
r12_fiq
r13_fiq
r14_fiq
SPSR_fiq
mode
Figure 3: register organisation
r13_svc
r14_svc
SPSR_svc
svc
mode
r13_abt
r14_abt
SPSR_abt
mode
usablein user mode
system modes only
r13_irq
r14_irq
SPSR_irq
abort
mode
irq
r13_und
r14_und
SPSR_und
undefined
mode
More information relative to the programmer’s model and the
ARM7TDMI core architecture can be found in the following
documents from ARM:
- DDI0029G, ARM7TDMI Technical Reference Manual.
- DDI0100E, ARM Architecture Reference Manual.
Rev. PrB | Page 20 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
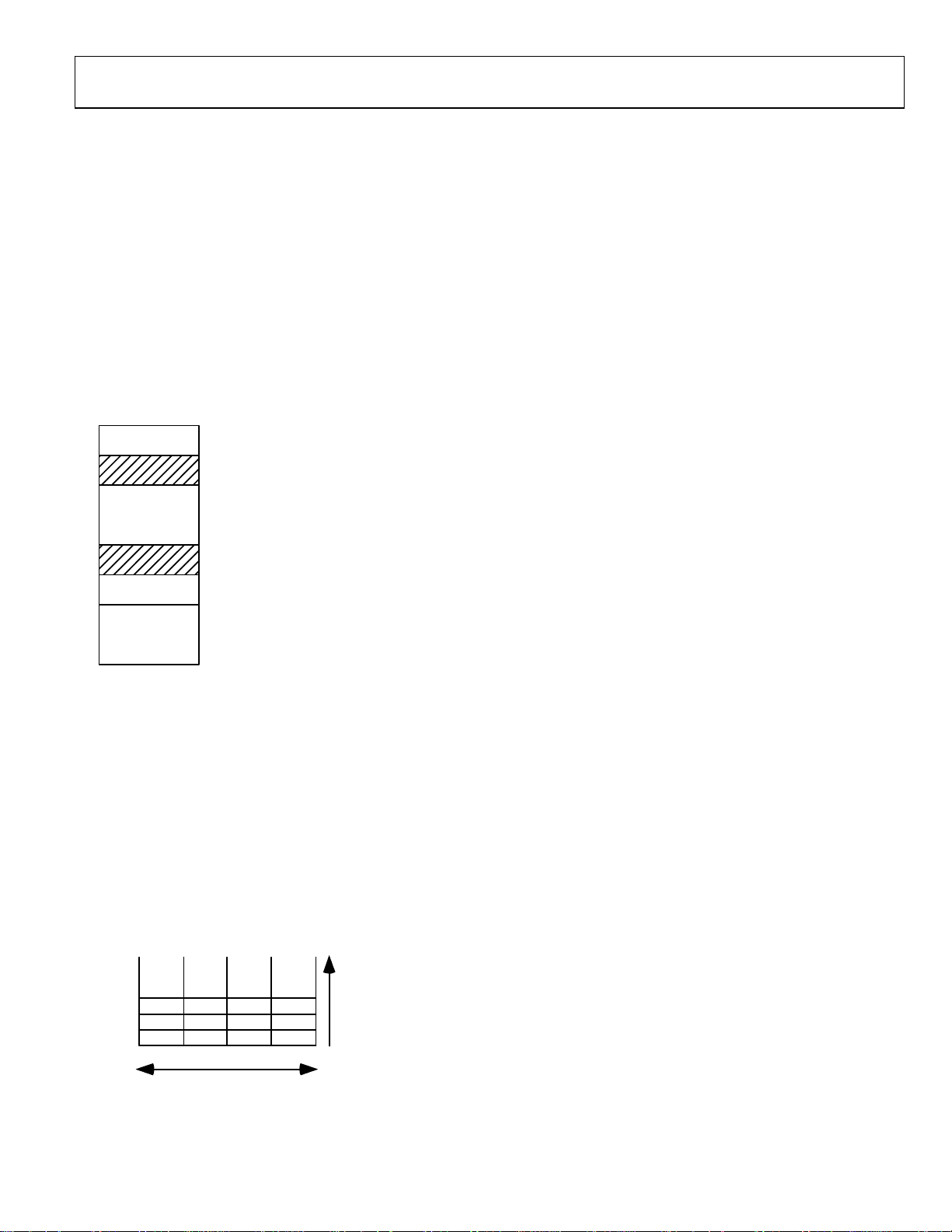
MEMORY ORGANISATION
The part incorporates two separate blocks of memory, 8kByte of
SRAM and 64kByte of On-Chip Flash/EE memory. 62kByte of
On-Chip Flash/EE memory are available to the user, and the
remaining 2kBytes are reserved for the factory configured boot
page. These two blocks are mapped as shown in
.
Figure 4
Note that by default, after a reset, the Flash/EE memory is
mirrored at address 0x00000000. It is possible to remap the
SRAM at address 0x00000000 by clearing bit 0 of the REMAP
MMR. This remap function is described in more details in the
Flash/EE memory chapter.
FFFF0000h
00080000h
00010000h
00000000h
FFFFFFFFh
0008FFFFh
00011FFFh
0000FFFFh
MMRs
Reserved
Flash/EE
Reserved
SRAM
Re-mappableMemory Space
(Flash/EE or SRAM)
Figure 4: Physical memory map
Memory Access
The ARM7 core sees memory as a linear array of 232 byte
location where the different blocks of memory are mapped as
outlined in
Figure 4
The ADuC702x memory organisation is configured in little
endian format: the least significant byte is located in the lowest
byte address and the most significant byte in the highest byte
address.
.
Flash/EE Memory
The total 64kBytes of Flash/EE are organised as 32k X 16 bits.
31k X 16 bits are user space and 1k X 16 bits is reserved for the
on chip kernel. The page size of this Flash/EE memory is
512Bytes.
62kBytes of Flash/EE are available to the user as code and nonvolatile data memory. There is no distinction between data and
program as ARM code shares the same space. The real width of
the Flash/EE memory is 16 bits, which means that in ARM
mode (32-bit instruction), two accesses to the Flash/EE are
necessary for each instruction fetch. It is therefore
recommended to use Thumb mode when executing from
Flash/EE memory for optimum access speed. The maximum
access speed for the Flash/EE memory is 45MHz in Thumb
mode and 22.5MHz in full ARM mode. More details on
Flash/EE access time are outlined later in ‘Execution from
SRAM and Flash/EE’ section of this datasheet.
SRAM
8kBytes of SRAM are available to the user, organized as 2k X 32
bits, i.e. 2kWords. ARM code can run directly from SRAM at
45MHz , given that the SRAM array is configured as a 32-bit
wide memory array. More details on SRAM access time are
outlined later in ‘Execution from SRAM and Flash/EE’ section
of this datasheet.
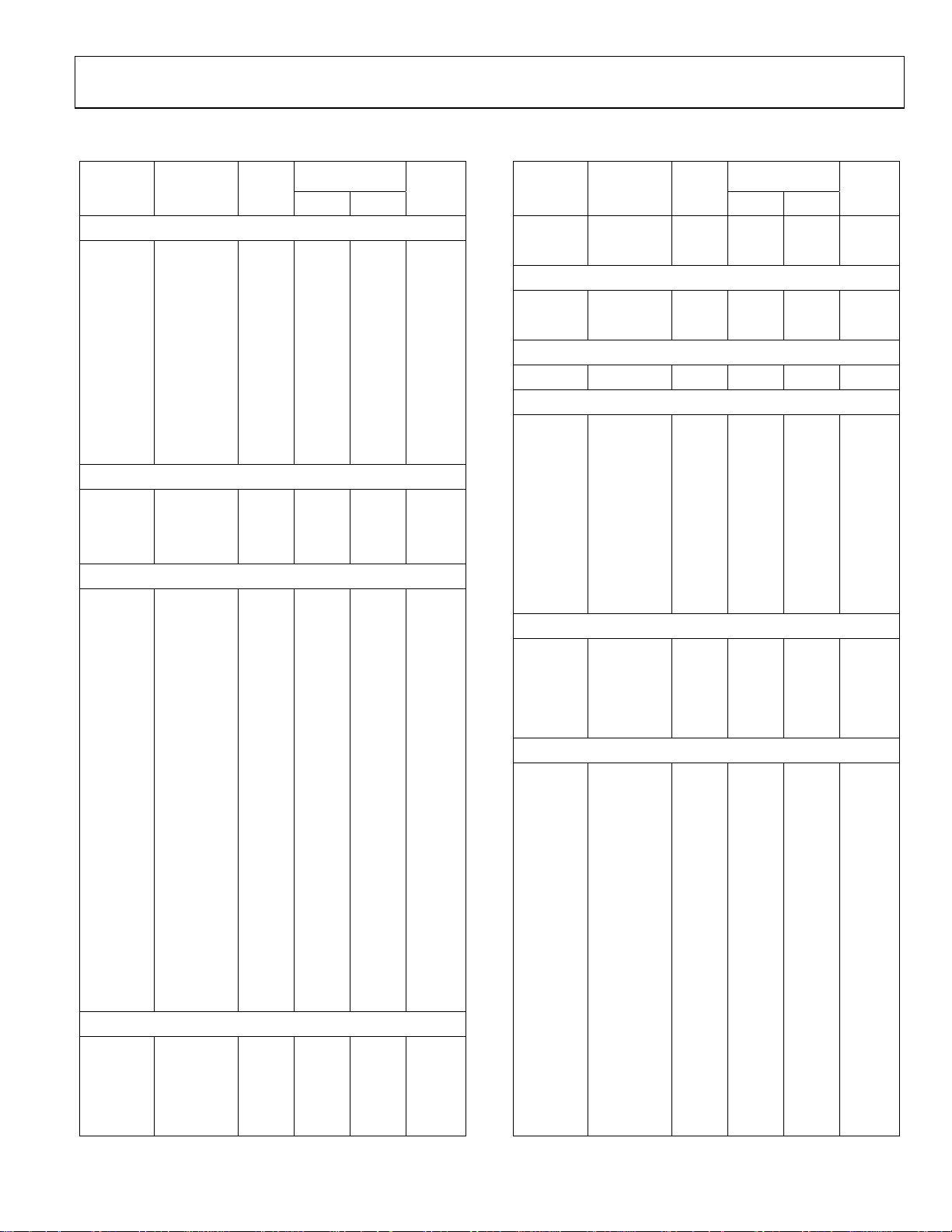
Memory Mapped Registers
The Memory Mapped Register (MMR) space is mapped into
the upper 2 pages of the memory array and accessed by indirect
addressing through the ARM7 banked registers.
The MMR space provides an interface between the CPU and all
on-chip peripherals. All registers except the core registers
reside in the MMR area. All shaded locations shown in Figure 6
are unoccupied or reserved locations and should not be
accessed by user software. Table 6 shows a full MMR memory
map.
Byte0
...
89AB
4567
01
bit0
0xFFFFFFFFh
0x00000004h
0x00000000h
Rev. PrB | Page 21 of 80
bit31
Byte3
...
Byte1Byte2
...
...
23
32 bits
Figure 5: little endian format

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
0xFFFFFFFF
0xFFFFFC3C
0xFFFFFC00
0xFFFFF820
0xFFFFF800
0xFFFFF46C
0xFFFFF400
0xFFFF0B54
0xFFFF0B00
0xFFFF0A14
0xFFFF0A00
0xFFFF0948
0xFFFF0900
0xFFFF0848
0xFFFF0800
0xFFFF0730
0xFFFF0700
0xFFFF0620
0xFFFF0600
0xFFFF0538
0xFFFF0500
0xFFFF0490
0xFFFF048C
0xFFFF0448
0xFFFF0440
0xFFFF0420
0xFFFF0404
0xFFFF0370
0xFFFF0360
0xFFFF0350
0xFFFF0340
0xFFFF0334
0xFFFF0320
0xFFFF0310
0xFFFF0300
0xFFFF0238
0xFFFF0220
0xFFFF0110
0xFFFF0000
PWM
Flash Control
Interface
GPIO
PLA
SPI
I2C1
I2C0
UART
DAC
ADC
Bandgap
Reference
Power Supply
Monitor
PLL &
Oscillator Control
Watchdog
Timer
Wake Up
Timer
General Purpose
Timer
Timer 0
Remap &
System Control
Interrupt
Controller
Figure 6: Memory Mapped
Rev. PrB | Page 22 of 80
Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
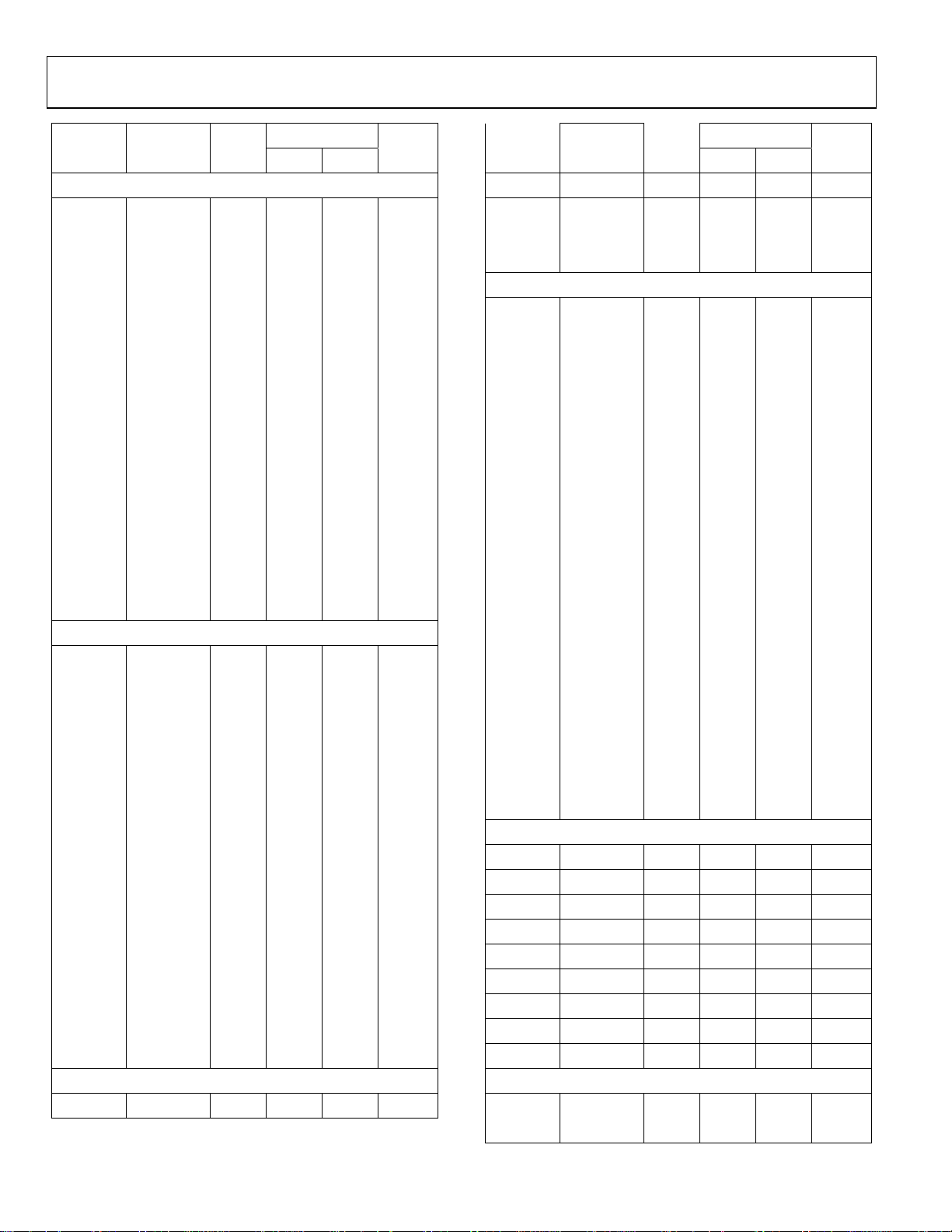
Table 6. Complete MMRs list
Access Address Name Byte
Type Cycle
IRQ address base = 0xFFFF0000
0x0000 IRQSTA 4 R 1 65
0x0004 IRQSIG 4 R 1 65
0x0008 IRQEN 4 RW 1 65
0x000C IRQCLR 4 W 1 65
0x0010 SWICFG 4 W 1 66
0x0100 FIQSTA 4 R 1 65
0x0104 FIQSIG 4 R 1 65
0x0108 FIQEN 4 RW 1 65
0x010C FIQCLR 4 W 1 65
System Control address base = 0xFFFF0200
0x0220 REMAP 1 RW 1 36
0x0230 RSTSTA 1 R 1 36
0x0234 RSTCLR 1 W 1 36
Timer address base = 0xFFFF0300
0x0300 T0LD 2 RW 2 67
0x0304 T0VAL 2 R 2 67
0x0308 T0CON 2 RW 2 67
0x030C T0CLRI 1 W 2 67
0x0320 T1LD 4 RW 2 68
0x0324 T1VAL 4 R 2 68
0x0328 T1CON 2 RW 2 68
0x032C T1CLRI 1 W 2 68
0x0330 T1CAP 4 RW 2 68
0x0340 T2LD 4 RW 2 69
0x0344 T2VAL 4 R 2 69
0x0348 T2CON 2 RW 2 69
0x034C T2CLRI 1 W 2 69
0x0360 T3LD 2 RW 2 70
0x0364 T3VAL 2 R 2 70
0x0368 T3CON 2 RW 2 70
0x036C T3CLRI 1 W 2 70
PLL base address = 0xFFFF0400
0x0404 POWKEY1 2 W 2 41
0x0408 POWCON 2 RW 2 41
0x040C POWKEY2 2 W 2 41
0x0410 PLLKEY1 2 W 2 41
Page
Address Name Byte
0x0414 PLLCON 2 RW 2 41
0x0418 PLLKEY2 2 W 2 41
PSM address base = 0xFFFF0440
0x0440 PSMCON 2 RW 2 39
0x0444 CMPCON 2 RW 2 39
Reference address base = 0xFFFF0480
0x048C REFCON 1 RW 2 31
ADC address base = 0xFFFF0500
0x0500 ADCCON 1 RW 2 27
0x0504 ADCCP 1 RW 2 28
0x0508 ADCCN 1 RW 2 28
0x050C ADCSTA 1 RW 2 27
0x0510 ADCDAT 4 R 2 27
0x0514 ADCRST 1 RW 2 27
0x0530 ADCGN 2 RW 2 30
0x0534 ADCOF 2 RW 2 30
DAC address base = 0xFFFF0600
0x0600 DAC0CON 1 RW 2 37
0x0604 DAC0DAT 4 RW 2 37
0x0608 DAC1CON 1 RW 2 37
0x060C DAC1DAT 4 RW 2 37
UART base address = 0xFFFF0700
0x0700 COMTX 1 RW 2 53
COMRX 1 R 2 53
COMDIV0 1 RW 2 53
0x0704 COMIEN0 1 RW 2 54
COMDIV1 1 R/W 2 53
0x0708 COMIID0 1 R 2 54
0x070C COMCON0 1 RW 2 53
0x0710 COMCON1 1 RW 2 55
0x0714 COMSTA0 1 R 2 54
0x0718 COMSTA1 1 R 2 55
0x071C COMSCR 1 RW 2 53
0x0720 COMIEN1 1 RW 2 56
0x0724 COMIID1 1 R 2 56
0x0728 COMADR 1 RW 2 53
0X072C COMDIV2 2 RW 2 55
Access
Type Cycle
Page
Rev. PrB | Page 23 of 80
ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Access Address Name Byte
Type Cycle
I2C0 base address = 0xFFFF0800
0x0800 I2C0MSTA 1 R 2 60
0x0804 I2C0SSTA 1 R 2 60
0x0808 I2C0SRX 1 R 2 59
0x080C I2C0STX 1 W 2 59
0x0810 I2C0MRX 1 R 2 59
0x0814 I2C0MTX 1 W 2 59
0x0818 I2C0CNT 1 RW 2 59
0x081C I2C0ADR 1 RW 2 59
0x0824 I2C0BYTE 1 RW 2 59
0x0828 I2C0ALT 1 RW 2 59
0x082C I2C0CFG 1 RW 2 59
0x0830 I2C0DIVH 1 RW 2 59
0x0834 I2C0DIVL 1 RW 2 59
0x0838 I2C0ID0 1 RW 2 59
0x083C I2C0ID1 1 RW 2 59
0x0840 I2C0ID2 1 RW 2 59
0x0844 I2C0ID3 1 RW 2 59
I2C1 base address = 0xFFFF0900
0x0900 I2C1MSTA 1 R 2 60
0x0904 I2C1SSTA 1 R 2 60
0x0908 I2C1SRX 1 R 2 59
0x090C I2C1STX 1 W 2 59
0x0910 I2C1MRX 1 R 2 59
0x0914 I2C1MTX 1 W 2 59
0x0918 I2C1CNT 1 RW 2 59
0x091C I2C1ADR 1 RW 2 59
0x0924 I2C1BYTE 1 RW 2 59
0x0928 I2C1ALT 1 RW 2 59
0x092C I2C1CFG 1 RW 2 59
0x0930 I2C1DIVH 1 RW 2 59
0x0934 I2C1DIVL 1 RW 2 59
0x0938 I2C1ID0 1 RW 2 59
0x093C I2C1ID1 1 RW 2 59
0x0940 I2C1ID2 1 RW 2 59
0x0944 I2C1ID3 1 RW 2 59
SPI base address = 0xFFFF0A00
0x0A00 SPISTA 1 R 2 57
Page
Access Address Name Byte
Type Cycle
0x0A04 SPIRX 1 R 2 57
0x0A08 SPITX 1 W 2 57
0x0A0C SPIDIV 1 RW 2 57
0x0A10 SPICON 2 RW 2 57
PLA base address = 0xFFFF0B00
0x0B00 PLAELM0 2 RW 2 62
0x0B04 PLAELM1 2 RW 2 62
0x0B08 PLAELM2 2 RW 2 62
0x0B0C PLAELM3 2 RW 2 62
0x0B10 PLAELM4 2 RW 2 62
0x0B14 PLAELM5 2 RW 2 62
0x0B18 PLAELM6 2 RW 2 62
0x0B1C PLAELM7 2 RW 2 62
0x0B20 PLAELM8 2 RW 2 62
0x0B24 PLAELM9 2 RW 2 62
0x0B28 PLAELM10 2 RW 2 62
0x0B2C PLAELM11 2 RW 2 62
0x0B30 PLAELM12 2 RW 2 62
0x0B34 PLAELM13 2 RW 2 62
0x0B38 PLAELM14 2 RW 2 62
0x0B3C PLAELM15 2 RW 2 62
0x0B40 PLACLK 1 RW 2 63
0x0B44 PLAIRQ 4 RW 2 63
0x0B48 PLAADC 4 RW 2 64
0x0B4C PLADIN 4 R 2 64
0x0B50 PLADOUT 4 RW 2 64
External Memory base address = 0xFFFFF000
0xF000 XMCFG 1 RW 2 71
0xF010 XM0CON 1 RW 2 71
0xF014 XM1CON 1 RW 2 71
0xF018 XM2CON 1 RW 2 71
0xF01C XM3CON 1 RW 2 71
0xF020 XM0PAR 2 RW 2 71
0xF024 XM1PAR 2 RW 2 71
0xF028 XM2PAR 2 RW 2 71
0xF02C XM3PAR 2 RW 2 71
GPIO base address = 0xFFFFF400
0xF400 GP0CON 4 RW 1 49
0xF404 GP1CON 4 RW 1 49
Page
Rev. PrB | Page 24 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Access Address Name Byte
Typ e Cycle
0xF408 GP2CON 4 RW 1 49
0xF40C GP3CON 4 RW 1 49
0xF410 GP4CON 4 RW 1 49
0xF420 GP0DAT 4 RW 1 51
0xF424 GP0SET 1 W 1 51
0xF428 GP0CLR 1 W 1 51
0xF430 GP1DAT 4 RW 1 51
0xF434 GP1SET 1 W 1 51
0xF438 GP1CLR 1 W 1 51
0xF440 GP2DAT 4 RW 1 51
0xF444 GP2SET 1 W 1 51
0xF448 GP2CLR 1 W 1 51
0xF450 GP3DAT 4 RW 1 51
0xF454 GP3SET 1 W 1 51
0xF458 GP3CLR 1 W 1 51
0xF460 GP4DAT 4 RW 1 51
0xF464 GP4SET 1 W 1 51
0xF468 GP4CLR 1 W 1 51
Flash/EE base address = 0xFFFFF800
0xF800 FEESTA 1 R 1 33
0xF804 FEEMOD 1 RW 1 33
0xF808 FEECON 1 RW 1 33
0xF80C FEEDAT 2 RW 1 33
0xF810 FEEADR 2 RW 1 33
0xF818 FEESIGN 3 R 1 33
0xF81C FEEPRO 4 RW 1 34
0xF820 FEEHIDE 4 RW 1 34
PWM base address= 0xFFFFFC00
0xFC00 PWMCON 2 RW 1 47
0xFC04 PWMSTA 2 RW 1 47
0xFC08 PWMDAT0 2 RW 1 47
0xFC0C PWMDAT1 2 RW 1 47
0xFC10 PWMCFG 2 RW 1 47
0xFC14 PWMCH0 2 RW 1 47
0xFC18 PWMCH1 2 RW 1 47
0xFC1C PWMCH2 2 RW 1 47
0xFC20 PWMEN 2 RW 1 48
0xFC24 PWMDAT2 2 RW 1 48
Page
The ‘Access’ column corresponds to the access time reading or
writing a MMR. It depends on the AMBA (Advanced
Microcontroller Bus Architecture) bus used to access the
peripheral. The processor has two AMBA busses, AHB
(Advanced High-performance Bus) used for system modules
and APB (Advanced Peripheral Bus) used for lower
performance peripheral.
Rev. PrB | Page 25 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
A
ADC CIRCUIT INFORMATION
GENERAL OVERVIEW
ADC TRANSFER FUNCTION
The Analog Digital Converter (ADC) incorporates a fast, multichannel, 12-bit ADC. It can operate from 2.7V to 3.6V supplies
and is capable of providing a throughput of up to 1MSPS when
the clock source is 45MHz. This block provides the user with
multi-channel multiplexer, differential track-and-hold, on-chip
reference and ADC.
The ADC consists of a 12-bit successive-approximation
converter based around two capacitor DACs. It can operate in
one of three different modes, depending on the input signal
configuration :
• fully differential mode, for small and balanced signals
• single-ended mode, for any single-ended signals
• pseudo-differential mode, for any single-ended signals,
taking advantage of the common mode rejection
offered by the pseudo differential input.
The converter accepts an analog input range of 0 to V
REF
when
operating in single-ended mode or pseudo-differential mode. In
fully differential mode, the input signal must be balanced
around a common mode voltage V
and with a maximum amplitude of 2 V
V
DD
V
Figure 7: examples of balanced signals for fully differential mode
CM
V
CM
0
, in the range 0V to AVDD
CM
(see Figure 7).
REF
V
CM
2V
REF
2V
REF
2V
REF
A high precision, low drift, and factory calibrated 2.5 V
reference is provided on-chip. An external reference can also be
connected as described later.
Single or continuous conversion modes can be initiated in
software. An external CONV
pin, an output generated from
START
the on-chip PLA or a Timer1 or a Timer2 overflow can also be
used to generate a repetitive trigger for ADC conversions.
A voltage output from an on-chip bandgap reference
proportional to absolute temperature can also be routed
through the front end ADC multiplexer (effectively an
additional ADC channel input) facilitating an internal
temperature sensor channel, measuring die temperature to an
accuracy of ±3°C.
Pseudo-differential and single-ended modes
In pseudo-differential or single-ended mode, the input range is
0 V to V
REF. The output coding is straight binary in pseudo
differential and single-ended modes with 1 LSB = FS/4096 or
2.5 V/4096 = 0.61 mV or 610 µV when V
REF = 2.5 V. The ideal
code transitions occur midway between successive integer LSB
values (i.e. 1/2 LSB, 3/2 LSBs, 5/2 LSBs, . . ., FS –3/2 LSBs). The
ideal input/output transfer characteristic is shown in Figure 8.
OUTPUT
CODE
1111 1111 1111
1111 1111 1110
1111 1111 1101
1111 1111 1100
0000 0000 0011
0000 0000 0010
0000 0000 0001
0000 0000 0000
Figure 8: ADC transfer function in pseudo differential mode or single-ended
0V
1LSB
1LSB =
FS
4096
VOLTAGE INPUT
mode
+FS - 1LSB
Fully differential mode
The amplitude of the differential signal is the difference
between the signals applied to the V
IN–). The maximum amplitude of the differential signal is
V
therefore –V
REF to +VREF p-p (i.e. 2 X VREF). This is regardless of
the common mode (CM). The common mode is the average of
the two signals, i.e. (V
IN+ + VIN–)/2 and is therefore the voltage
that the two inputs are centred on. This results in the span of
each input being CM ± V
REF/2. This voltage has to be set up
externally and its range varies with V
The output coding is two’s complement in fully differential
mode with 1 LSB = 2V
REF = 2.5 V. The designed code transitions occur midway
when V
REF/4096 or 2x2.5 V/4096 = 1.22 mV
between successive integer LSB values (i.e., 1/2 LSB, 3/2 LSBs,
5/2 LSBs, . . ., FS –3/2 LSBs). The ideal input/output transfer
characteristic is shown in Figure 9.
IN+ and VIN– pins (i.e., VIN+ –
REF, (see driving the ADC).
Rev. PrB | Page 26 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
OUTPUT
CODE
0111 1111 1111
0111 1111 1110
0111 1111 1101
0000 0000 0001
0000 0000 0000
1111 1111 1111
1000 0000 0010
1000 0000 0001
1000 0000 0000
Figure 9: ADC transfer function in differential mode
2x
V
1LSB =
-V
REF
REF
4096
+ 1LSB
VOLTAGE INPUT (Vin+ - Vin-)
+V
REF
-1LSB0LSB
TYPICAL OPERATION
Once configured via the ADC control and channel selection
registers, the ADC will convert the analog input and provide a
12-bit result in the ADC data register.
The top 4 bits are the sign bits and the 12-bit result is placed
from bit 16 to 27 as shown in Figure 10. Again, it should be
noted that in fully differential mode, the result is represented in
two’s complement format, and in pseudo differential and singleended mode, the result is represented in straight binary format.
1516 02731
SIGN BITS
Figure 10: ADC Result Format
The same format is used in DACxDAT, simplifying the software.
12-bitADC RESULT
ADC MMRS interface
The ADC is controlled and configured via a number of MMRs
that are listed below and described in detail in the following
pages:
- ADCCON: ADC Control Register allows the programmer to
enable the ADC peripheral, to select the mode of operation of
the ADC, either Single-ended, pseudo-differential or fully
differential mode and the conversion type. This MMR is
described Table 7.
- ADCCP: ADC positive Channel selection Register
- ADCCN: ADC negative Channel selection Register
ADCSTA: ADC Status Register, indicates when an ADC
conversion result is ready. The ADCSTA register contains
only one bit, bit (bit 0), representing the status of the ADC.
This bit is set at the end of an ADC conversion generating an
ADC interrupt, it is cleared automatically by reading the
ADCDAT MMR. When the ADC is performing a conversion,
the status of the ADC can be read externally via the
ADCBusy pin. This pin is high during a conversion. When
the conversion is finished, ADCBusy goes back low. This
information can be available on P0.3 (see chapter on GPIO) if
enabled in ADCCON register.
ADCDAT: ADC Data Result Register, hold the 12-bit ADC
result as shown Figure 10
- ADCRST: ADC Reset Register. Resets all the ADC registers
to their default value.
- ADCOF: Offset calibration register. 10-bit register
- ADCGN: Gain calibration register. 10-bit register
Table 7: ADCCON MMR Bit Designations
Bit Description
7 Enable Conversion
Set by the user to enable conversion mode
Cleared by the user to disable conversion mode
6 Enable ADC
Set by the user to enable the ADC
Cleared by the user to disable the ADC
BUSY
pin
BUSY
pin
BUSY
5 ADC power control:
Set by the user to place the ADC in normal mode, the ADC must be powered up for at least 500uS before it will convert
correctly.
Cleared by the user to place the ADC in power-down mode
Conversion Mode:
4-3
Single Ended Mode
00
Differential Mode
01
10 Pseudo-Differential Mode
Reserved
11
2-0 Conversion Type:
Rev. PrB | Page 27 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
000 Enable CONV
001 Enable timer 1 as a conversion input
010 Enable timer 0 as a conversion input
011 Single software conversion, will be set to 000 after conversion.
100 Continuous software conversion
101 PLA conversion
Other
Reserved
pin as a conversion input
START
Table 8 : AD C CP * MM R b i t d e sig n a tion
Bit Description
7-5
Reserved
Positive Channel Selection Bits 4-0
00000
00001
00010
00011
00100
00101
00110
00111
01000
01001
01010
01011
01100
01101
01110
01111
10000
10001
10010
10011
Others
ADC0
ADC1
ADC2
ADC3
ADC4
ADC5
ADC6
ADC7
ADC8
ADC9
ADC10
ADC11
DAC0/ADC12
DAC1/ADC13
DAC2/ADC14
DAC3/ADC15
Tem perature sensor
AGND
Reference
AVDD/2
Reserved
Table 9 : AD C CN * MM R b i t d e s ig n a t ion
Bit Description
7-5
* ADC and DAC channel availability depends on part model.
See page 9 for details.
Reserved
Negative Channel Selection Bits 4-0
00000
00001
00010
00011
00100
00101
00110
00111
01000
01001
01010
01011
01100
01101
01110
01111
10000
Others
ADC0
ADC1
ADC2
ADC3
ADC4
ADC5
ADC6
ADC7
ADC8
ADC9
ADC10
ADC11
DAC0/ADC12
DAC1/ADC13
DAC2/ADC14
DAC3/ADC15
Reference
Reserved
Rev. PrB | Page 28 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
CONVERTER OPERATION
The ADC incorporates a successive approximation (SAR)
architecture involving a charge-sampled input stage. This
architecture is described below for the three different modes of
operation.
Differential mode
The ADuC702x contains a successive approximation ADC
based on two capacitive DACs. Figure 11 and Figure 12 show
simplified schematics of the ADC in acquisition and conversion
phase, respectively. The ADC is comprised of control logic, a
SAR, and two capacitive DACs. In Figure 11 (the acquisition
phase), SW3 is closed and SW1 and SW2 are in Position A, the
comparator is held in a balanced condition, and the sampling
capacitor arrays acquire the differential signal on the input.
CAPACITIVE
DAC
AIN0
AIN11
Channel+
.
MUX
.
.
Channel-
B
A
A
B
SW1
SW2
V
REF
C
s
C
s
Figure 11: ADC acquisition phase
When the ADC starts a conversion (Figure 12), SW3 will open
and SW1 and SW2 will move to Position B, causing the
comparator to become unbalanced. Both inputs are
disconnected once the conversion begins. The control logic and
the charge redistribution DACs are used to add and subtract
fixed amounts of charge from the sampling capacitor arrays to
bring the comparator back into a balanced condition. When the
comparator is rebalanced, the conversion is complete. The
control logic generates the ADC’s output code. The output
impedances of the sources driving the V
be matched; otherwise, the two inputs will have different
settling times, resulting in errors.
AIN0
AIN11
Channel+
.
MUX
.
.
Channel-
B
A
A
B
Figure 12: ADC conversion phase
SW1
SW2
V
REF
C
s
C
s
Pseudo-differential mode
In pseudo-differential mode, Channel- is linked to the VIN- pin
COMPARATOR
SW3
IN+ and VIN– pins must
COMPARATOR
SW3
CONTROL
LOGIC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
CONTROL
LOGIC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
of the ADuC702x and SW2 switches between A (Channel-) and
B (VREF). VIN- pin must be connected to Ground or a low
voltage. The input signal on V
V
+ VIN-. Note VIN- must be chosen so that V
REF
not exceed AV
AIN0
.
.
.
MUX
AIN11
VIN-
.
DD
Channel+
Channel-
B
A
SW1
SW2
A
B
V
REF
Figure 13: ADC in pseudo-differential mode
+ can then vary from VIN- to
IN
+ VIN- does
REF
CAPACITIVE
C
s
C
s
COMPARATOR
SW3
CONTROL
LOGIC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
DAC
Single-ended mode
In Single-ended mode, SW2 is always connected internally to
ground. The VIN- pin can be floating. The input signal range on
+ is 0V to V
V
IN
AIN0
.
.
.
MUX
AIN11
VIN-
.
REF
C
Channel+
B
A
Channel-
SW1
s
C
s
Figure 14: ADC in single-ended mode
COMPARATOR
SW3
CAPACITIVE
DAC
CONTROL
LOGIC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
Analog Input Structure
Figure 15 shows the equivalent circuit of the analog input
structure of the ADC. The four diodes provides ESD protection
for the analog inputs. Care must be taken to ensure that the
analog input signals never exceed the supply rails by more than
300 mV. This would cause these diodes to become forward
biased and start conducting into the substrate. These diodes can
conduct up to 10 mA without causing irreversible damage to
the part.
The capacitors C1 in Figure 15 are typically 4 pF and can
primarily be attributed to pin capacitance. The resistors are
lumped components made up of the ON resistance of the
switches. The value of these resistors is typically about 100 Ω .
The capacitors, C2, are the ADC’s sampling capacitors and
have a capacitance of 16 pF typically.
For AC applications, removing high-frequency components
from the analog input signal is recommended by the use of an
RC low-pass filter on the relevant analog input pins. In
applications where harmonic distortion and signal-to-noise
Rev. PrB | Page 29 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
ratio are critical, the analog input should be driven from a low
impedance source. Large source impedances will significantly
affect the AC performance of the ADC. This may necessitate
the use of an input buffer amplifier. The choice of the op amp
will be a function of the particular application.
AV
DD
D
AV
D
DD
D
D
C1
C1
C2
R1
C2
R1
Figure 15: Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
Conversion Phase: Switches Open
Track Phase: Switches Closed
When no amplifier is used to drive the analog input, the source
impedance should be limited to values lower than 1 kΩ . The
maximum source impedance will depend on the amount of
total harmonic distortion (THD) that can be tolerated. The
THD will increase as the source impedance increases and the
performance will degrade.
ADCOF and ADCGN.
For offset error correction, either an external pin must be tied to
AGND (system calibration) or the internal AGND channel
must be selected (device calibration). A software loop must be
implemented to tweak the value in ADCOF register each time
until the transition of ADCDAT reads code 0 to 1. Offset error
correction is done digitally and has a resolution of 0.25 lsb and
a range of +/- 3.125% of VREF.
For gain error correction, either an external pin must be tied to
VREF (system calibration) or the internal reference channel
must be selected (device calibration). A software loop must be
implemented to tweak the value in ADCGN register each time
until the transition of ADCDAT reads code 4094 to 4095.
Similar to the offset calibration, the gain calibration resolution
is 0.25 lsb with a range of +/- 3% of VREF.
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The ADuC702x provides a voltage output from an on-chip
bandgap reference proportional to absolute temperature. It can
also be routed through the front end ADC multiplexer
(effectively an additional ADC channel input) facilitating an
internal temperature sensor channel, measuring die
temperature to an accuracy of ±3°C.
BANDGAP REFERENCE
DRIVING THE ANALOG INPUTS
Internal or external reference can be used for the ADC. In
differential mode of operation, there are restrictions on
common mode input signal (V
) that are dependant on
CM
reference value and supply voltage used to ensure that the signal
remains within the supply rails. Table 10 gives some calculated
min VCM max for some conditions.
V
CM
Table 10: V
AVDD V R E F V
ranges
CM
min VCM max
CM
Signal
Peak-Peak
3.3V
3.0V
2.5V
2.048V
1.25
2.5V
2.048V
1.25
1.25V 2.05V
1.024V 2.276V
0.75V 2.55V
1.25V 1.75V
1.024V 1.976V
0.75V 2.25V
2.5V
2.048V
1.25
2.5V
2.048V
1.25
ADC CALIBRATION
System calibration or device calibration are performed in
software. Two 10-bit registers are available for calibration,
The ADuC702x provides an on-chip bandgap reference of 2.5V,
which can be used for the ADC and for the DAC. This internal
reference also appears on the V
pin. When using the internal
REF
reference, a capacitor of 0.47µF must be connected from the
external V
pin to AGND, to ensure stability and fast response
REF
during ADC conversions. This reference can also be connected
to an external pin (VREF) and used as a reference for other
circuits in the system. An external buffer would be required
because of the low drive capability of the VREF output. A
programmable option also allows an external reference input on
pin.
the V
REF
The bandgap reference interface consists on a 8-bit MMR,
REFCON described in
Table 1 1 .
Rev. PrB | Page 30 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Table 11: REFCON MMR bit designations
Bit Description
7-2
1
0
Reserved
Internal reference powerdown enable
Set by user to place the internal reference in power-down mode and use an external reference
Cleared by user to place the internal reference in normal mode and use it for ADC conversions
Internal reference output enable
Set by user to connect the internal 2.5V reference to the VREF pin. The reference can be used for external component but will
need to be buffered.
Cleared by user to disconnect the reference from the VREF pin.
Rev. PrB | Page 31 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
NONVOLATILE FLASH/EE MEMORY
FLASH/EE MEMORY OVERVIEW
(3) JTAG access
The JTAG protocol uses the on-chip JTAG interface to facilitate
code download and debug.
The ADuC702x incorporates Flash/EE memory technology onchip to provide the user with non-volatile, in-circuit
reprogrammable memory space.
Like EEPROM, Flash memory can be programmed in-system at
a byte level, although it must first be erased; the erase being
performed in page blocks. Thus, Flash memory is often and
more correctly referred to as Flash/EE memory.
Overall, Flash/EE memory represents a step closer to the ideal
memory device that includes non-volatility, in-circuit
programmability, high density, and low cost. Incorporated in
the ADuC702x, Flash/EE memory technology allows the user to
update program code space in-circuit, without the need to
replace one time programmable (OTP) devices at remote
operating nodes.
FLASH/EE MEMORY AND THE ADUC702X
The ADuC702x contains a 64 kByte array of Flash/EE Memory.
The lower 62 Kbytes is available to the user and the upper 2
kBytes of this Flash/EE program memory array contain
permanently embedded firmware, allowing in circuit serial
download. These 2 Kbytes of embedded firmware also contain a
power-on configuration routine that downloads factory
calibrated coefficients to the various calibrated peripherals
(ADC, temperature sensor, bandgap references and so on). This
2 kByte embedded firmware is hidden from user code.
The 62kBytes of Flash/EE memory can be programmed incircuit, using the serial download mode or the JTAG mode
provided or via parallel programming.
(1) Serial Downloading (In-Circuit Programming)
The ADuC702x facilitates code download via the standard
UART serial port or via the I2C port. The ADuC702x will enter
serial download mode after a reset or power cycle if the BM pin
is pulled low through an external 1kOhm resistor. Once in serial
download mode, the user can download code to the full
62kBytes of Flash/EE memory while the device is in circuit in
its target application hardware. A PC serial download
executable is provided as part of the development system for
serial downloading via the UART. An application note is
available at www.analog.com/microconverter
protocol for serial downloading via the UART and I2C.
(2) Parallel Programming
describing the
FLASH/EE MEMORY SECURITY
The 62kByte of Flash/EE memory available to the user can be
read and write protected.
Bit 31 of the FEEPRO/FEEHIDE MMR protects the 62kBytes
from being read through JTAG and also in parallel
programming mode. The other 31 bits of this register protect
writing to the flash memory, each bit protects 4 pages, i.e.
2kBytes. Write protection is activated for all type of access.
There are two levels of protection:
- Protection can be set and removed by writing directly into
FEEHIDE MMR.
- FEEPRO can be protected by a key to avoid direct access to
FEEPRO. The key is saved once and must be entered again to
modify FEEPRO. A mass erase will set the key back to 0xFFFF
but will also erase all the user code.
Sequence to write the key:
1. Enter an address in FEEADR.
2. Do a single READ command, wait for the read to be
successful by monitoring FEESTA.
3. Run a verify command.
4. Write the bit in FEEPRO corresponding to the page to be
protected.
5. Enable key protection by setting bits 7 to 4 of FEEMOD.
6. Write a 32 bit key in FEEADR, FEEDAT
7. Run the write key command 0x0C in FEECON, wait for the
read to be successful by monitoring FEESTA.
To remove or modify the protection the same sequence can be
used with a modified value of FEEPRO.
The sequence above is illustrated in the following example, this
protects writing pages 4 to 7 of the FLASH:
FEEADR = 0x800; //Any address,
FEECON=0x01; //Read command
while (!(FEESTA & 0x01)){} //Wait for read
FEECON=0x04; //Verify Command
FEEPRO=0xFFFFFFFD; //Protect pages 4 to 7
FEEMOD=(FEEMOD & 0xF0); //Write key enable
FEEADR=0xAA55; //16 bit key value
FEEDAT=0xAA55; //16 bit key value
FEECON= 0x0C; // Write key command
while (!(FEESTA & 0x01)){} //Wait for command
The parallel programming protocol allows the on-chip Flash/EE
memory be programmed by industry standard third party
programmers.
Rev. PrB | Page 32 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
FLASH/EE CONTROL INTERFACE
Serial, parallel and JTAG programming use the Flash/EE
Control Interface, which includes seven MMRs:
- FEESTA: read only register, reflects the status of the Flash
Control Interface
- FEEMOD: sets the operating mode of the Flash Control
Interface
- FEECON: 8-bit command register. The commands are
described Table 14
Table 1 2 : FE E STA M M R bit d esi g nati o n s
Bit Description
15-6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Reserved
Burst command enable
Set when the command is a burst command: 0x07, 0x08 or 0x09
Cleared when other command
Reserved
Flash interrupt status bit
Set automatically when an interrupt occurs, i.e. when a command is complete and the Flash/EE interrupt enable bit in the
FEEMOD register is set
Cleared when reading FEESTA register
Flash/EE controller busy
Set automatically when the controller is busy
Cleared automatically when the controller is not busy
Command fail
Set automatically when a command completes unsuccessfully
Cleared automatically when reading FEESTA register
Command complete
Set by MicroConverter when a command is complete
Cleared automatically when reading FEESTA register
- FEEDAT: 16-bit data register.
- FEEADR: 16-bit address register.
- FEESIGN: 24-bit code signature
- FEEPRO: protection following subsequent reset MMR.
Requires software key. See description Table 15
- FEEHIDE: Immediate Protection MMR. Does not require
any software keys. See description Table 15
Bit Description
7-5
4
3-0
Code command Description
0x00* Null Idle state
0x01*
0x02*
0x03*
0x04*
0x05*
Reserved
Flash/EE interrupt enable:
Set by user to enable the Flash/EE interrupt. The interrupt will occur when a command is complete.
Cleared by user to disable the Flash/EE interrupt
Reserved
Single Read Load FEEDAT with the 16-bit data indexed by FEEADR
Single Write
Erase-Write Erase the page indexed by FEEADR and write FEEDAT at the location pointed by FEEADR. This operation
Single Verify Compare the contents of the location pointed by FEEADR to the data in FEEDAT. The result of the
Single Erase Erase the page indexed by FEEADR
Write FEEDAT at the address pointed by FEEADR. This operation takes 20µs.
takes 20ms
comparison is returned in FEESTA bit 1
Table 13: FEEMOD MMR bit designations
Table 14: command codes in FEECON
Rev. PrB | Page 33 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
0x06*
0x07 Burst read Default command. No write is allowed. This operation takes 2 cycles
0x08 Burst read-
0x09 Erase Burst
0x0A Burst
0x0B Signature Give a signature of the 64kBytes of Flash/EE in the 24-bit FEESIGN MMR. This operation takes 32778 clock
0x0C Protect This command can be run only once. The value of FEEPRO is saved and can be removed only with a mass
0x0D
0x0E
0x0F Ping No operation, interrupt generated
*
The FEECON will always read 0x07 immediately after execution of any of these commands.
Command Sequence for executing a Mass Erase
FEEADR = 0x800; //Any address
FEECON=0x01; //Read command
while (!(FEESTA & 0x01)){} //Wait for read
FEECON=0x04; //Verify Command
FEEDAT=0x06; //Mass erase enable
FEECON=0x06; //Mass erase command
Mass erase Erase 62kByte of user space. The 2kByte of kernel are protected. This operation takes 2.48s To prevent
accidental execution a command sequence is required to execute this instruction, this is described below.
write
read-write
termination
Reserved Reserved
Reserved Reserved
Write can handle a maximum of 8 data of 16 bits and takes a maximum of 8 x 20 µs
Will automatically erase the page indexed by the write, allow to write pages without running an erase
command. This command takes 20 ms to erase the page + 20 µs per data to write
Stops the running burst to allow execution from Flash/EE immediately
cycles.
erase (0x06) or with the key
Table 15: FEEPRO and FEEHIDE MMR bit designations
Bit Description
31
30-0
Read protection
Cleared by user to protect all code
Set by user to allow reading the code
Write protection for pages 123 to 120, for pages 119 to 116… and for pages 0 to 3
Cleared by user to protect the pages in writing
Set by user to allow writing the pages
EXECUTION TIME FROM SRAM AND
FLASH/EE
This chapter describes SRAM and Flash/EE access times during
execution for applications where execution time is critical.
Execution from SRAM
Fetching instructions from SRAM takes one clock cycle as the
access time of the SRAM is 2ns and a clock cycle is 22ns
minimum. However, if the instruction involve reading or
writing data to memory, one extra cycle must be added if the
data is in SRAM, or three cycle if the data is in Flash/EE, one
cycle to execute the instruction and two cycles to get the 32-bit
data from Flash/EE. A control flow instruction, for example a
branch instruction will take one cycle to fetch but also two cycle
to fill the pipeline with the new instructions.
Execution from Flash/EE
Because the Flash/EE width is 16-bit and access time for 16-bit
words is 22ns, execution from Flash/EE cannot be done in one
cycle as from SRAM when CD bit =0. Also some dead times are
needed before accessing data for any value of CD bits.
In ARM mode, where instructions are 32 bits, two cycles are
needed to fetch any instruction when CD = 0 and in Thumb
mode, where instructions are 16 bits, one cycle is needed to
fetch any instruction.
Timing is identical in both mode when executing instructions
that involve using the Flash/EE for data memory. If the
instruction to be executed is a control flow instruction, an extra
cycle is needed to decode the new address of the program
counter and then four cycles are needed to fill the pipe-line. A
data processing instruction involving only core register doesn’t
require any extra clock cycle but if it involves data in Flash/EE,
an extra clock cycle is needed to decode the address of the data
and two cycles to get the 32-bit data from Flash/EE. An extra
Rev. PrB | Page 34 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
cycle must also be added before fetching another instruction.
Data transfer instruction are more complex and are
summarised Table 16.
Table 16: execution cycles in ARM/Thumb mode
Instructions
LD 2/1
LDH 2/1
Fetch
cycles
Dead
time
1 2
1 1
Data access
Dead
time
1
1
LDM/PUSH 2/1
STR 2/1
STRH 2/1
STRM/POP 2/1
With 1<N≤16, N number of data to load or store in the multiple
load/store instruction.
The SWAP instruction combine a LD and STR instruction with
only one fetch giving a total of 8 cycles plus 40µs.
N 2 x n
1
1
N
2 x 20µs
20µs
2 x N x 20µs
N
1
1
N
Rev. PrB | Page 35 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
RESET AND REMAP
The ARM exception vectors are all situated at the bottom of the
memory array, from address 0x00000000 to address 0x00000020
as shown Figure 16.
FFFFFFFFh
0008FFFFh
Flash/EE
00011FFFh
SRAM
Mirror Space
interrupt
service routines
interrupt
service routines
ARM exception
vector addresses
kernel
00080000h
00010000h
0x00000020
0x00000000
Figure 16: remap for exception execution
00000000h
By default and after any reset, the Flash/EE is mirrored at the
bottom of the memory array. The remap function allows the
programmer to mirror the SRAM at the bottom of the memory
array, facilitating execution of exception routines from SRAM
instead of from Flash/EE. This means exceptions are executed
twice as fast, exception being executed in ARM mode (32 bit)
and the SRAM being 32-bit wide instead of 16-bit wide
Flash/EE memory.
Remap operation
When a reset occurs on the ADuC702x, execution starts
automatically in factory programmed internal configuration
code. This so called kernel is hidden and cannot be accessed by
user code. If the ADuC702x is in normal mode (BM pin is
high), it will execute the power-on configuration routine of the
kernel and then jump to the reset vector address, 0x00000000, to
execute the users reset exception routine.
Because the Flash/EE is mirrored at the bottom of the memory
array at reset, the reset interrupt routine must always be written
in Flash/EE.
The remap is done from Flash/EE by setting bit0 of the REMAP
register. Precaution must be taken to execute this command
from Flash/EE, above address 0x00080020, and not from the
bottom of the array as this will be replaced by the SRAM.
This operation is reversible: the Flash/EE can be remapped at
address 0x00000000 by clearing Bit0 of the REMAP MMR.
Precaution must again be taken to execute the remap function
from outside the mirrored area. Any kind of reset will remap the
Flash /EE memory at the bottom of the array.
Reset
There are four kinds of reset: external reset, Power-on-reset,
watchdog expiation and software force. The RSTSTA register
indicates the source of the last reset and RSTCLR allows to clear
the RSTSTA register. These registers can be used during a reset
exception service routine to identify the source of the reset. If
RSTSTA is null, the reset was external.
Table 17: REMAP MMR bit designations
Bit Name Description
0 Remap
Remap Bit.
Set by the user to remap the SRAM to address 0x00000000.
Cleared automatically after reset to remap the Flash/EE memory to address 0x00000000.
Table 1 8 : RS T STA M M R bit d esi g nati o n s
Bit Description
7-3
2
Reserved
Software reset
Set by user to force a software reset.
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR
1
Watchdog timeout
Set automatically when a watchdog timeout occurs
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR
0
Power-on-reset
Set automatically when a power-on-reset occurs
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR
Rev. PrB | Page 36 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
OTHER ANALOG PERIPHERALS
DAC. The signal range is 0V to AV
DD
.
DAC
The ADuC702x incorporate dual 12-bit voltage output DACs
on-chip. Each DAC has a rail-to-rail voltage output buffer
capable of driving 5kΩ/100pF. Each buffer can be bypassed.
Each DAC has three selectable ranges, 0V to V
bandgap 2.5V reference), 0V to DAC
AV
. DAC
DD
is equivalent to an external reference for the
REF
(pin 56) and 0V to
REF
Table 19: DAC0CON MMR bit designations
Bit Name Description
6 DACBYP
Buffer bypass bit:
Set by the user to bypass the output buffer.
Cleared by user to buffer the DAC output. By default the DAC is buffered.
5 DACCLK
DAC update rate:
Set by the user to update the DAC using timer1.
Cleared by user to update the DAC using the core clock.
4 DACCLR
DAC clear bit:
Set by the user to enable normal DAC operation.
Cleared by user to reset data register of the DAC to zero.
3 Reserved This bit should be left at ‘0’
2 Reserved This bit should be left at ‘0’
1-0
DAC range bits
00 Power down mode. The DAC output is in tri-state
01 0-DAC
10 0-V
11 0-AV
REF
(2.5V) range
REF
DD
range
range
(internal
REF
DAC MMRs interface
Each DAC is configurable independently through a Control
register and a Data register. These two registers are identical for
the four DACs and only DAC0CON and DAC0DAT will be
described in detail.
Bit Description
31-28
27-16
15-0
Reserved
12-bit data for DAC0
Reserved
Table 20 : DAC0DAT MMR bit designati ons
Rev. PrB | Page 37 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
A
Using the DACs
The on-chip DAC architecture consists of a resistor string DAC
followed by an output buffer amplifier, the functional
equivalent of which is illustrated in Figure 17.
AV
V
DAC
DD
REF
REF
R
R
R
OUTPUT
BUFFER
BYPASSED
FROM MCU
DAC0
that Figure 18 represents a transfer function in 0-to-AV
only. In 0-to-V
< AVDD) the lower nonlinearity would be similar, but
DAC
REF
or 0-to-DAC
REF
modes (with V
REF
the upper portion of the transfer function would follow the
“ideal” line right to the end (V
in this case, not AVDD),
REF
showing no signs of endpoint linearity errors.
AV
DD
VDD-100mV
REF
DD
< AV
mode
or
DD
R
R
Figure 17: DAC structure
As illustrated in Figure 17, the reference source for each DAC is
user selectable in software. It can be either AVDD, VREF or
DACREF. In 0-to-AVDD mode, the DAC output transfer
function spans from 0 V to the voltage at the AVDD pin. In 0to-DACREF mode, the DAC output transfer function spans
from 0 V to the voltage at the DACREF pin. In 0-to-VREF
mode, the DAC output transfer function spans from 0 V to the
internal 2.5V reference, VREF. The DAC output buffer amplifier
features a true rail-to-rail output stage implementation. This
means that, unloaded, each output is capable of swinging to
within less than 5 mV of both AVDD and ground. Moreover,
the DAC’s linearity specification (when driving a 5k resistive
load to ground) is guaranteed through the full transfer function
except codes 0 to 100, and, in 0-to-AVDD mode only, codes
3995 to 4095. Linearity degradation near ground and VDD is
caused by saturation of the output amplifier, and a general
representation of its effects (neglecting offset and gain error) is
illustrated in Figure 18. The dotted line in Figure 18 indicates
the ideal transfer function, and the solid line represents what
the transfer function might look like with endpoint
nonlinearities due to saturation of the output amplifier. Note
~
~
100mV
000h
Figure 18: endpoint nonlinearities due to amplifier saturation
~
~
~
~
FFFh
The endpoint nonlinearities conceptually illustrated in Figure
18 get worse as a function of output loading. Most of the
ADuC702x’s datasheet specifications assume a 5 kΩ resistive
load to ground at the DAC output. As the output is forced to
source or sink more current, the nonlinear regions at
the top or bo t t om (respectively) of Figure 18 become larger.
With larger current demands, this can significantly limit output
voltage swing.
To reduce the effects of the saturation of the output amplifier at
values close to ground and to give reduced offset and gain
errors, the internal buffer can be bypassed in the DAC control
register. This allows a full rail-to-rail output from the DAC
which should then be buffered externally using a dual supply
op-amp in order to get a rail-to-rail output. This external buffer
should be located as near as physically possible to the DAC
output pin on the PCB.
Rev. PrB | Page 38 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
The Power Supply Monitor monitors the IOVDD supply on the
ADuC702x. It indicate when IOV
supply pin drops below one
DD
of two supply trip points. The monitor function is controlled via
the PSMCON register. If enabled in the IRQEN or FIQEN
register, the monitor will interrupt the core using the PSMI bit
in the PSMCON MMR. This bit will be cleared immediately
once CMP goes high.
Table 21: PSMCON MMR bit descriptions
Bit Name Description
3 CMP
Comparator Bit
This is a read-only bit and directly reflects the state of the comparator
supply is above its selected trip point.
DD
supply is below its selected trip point.
DD
2 TP
Read ‘1’ indicates the IOV
Read ‘0’ indicates the IOV
Trip Point Selection Bits
0 - 2.79V
1 - 3.07V
1 PSMEN
Power Supply Monitor Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable the Power Supply Monitor circuit
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to disable the Power Supply Monitor circuit
0 PSMI
Power Supply Monitor Interrupt Bit.
This bit will be set high by the MicroConverter if CMP is low, indicating low I/O supply. The PSMI Bit
can be used to interrupt the processor. Once CMP returns high, the PSMI bit may be cleared by writing
a ‘1’ to this location. A write of ‘0’ has no effect. There is no timeout delay, PSMI may be cleared
immediately once CMP goes high.
This monitor function allows the user to save working registers
to avoid possible data loss due to the low supply or brown-out
conditions, and also ensures that normal code execution will
not resume until a safe supply level has been established.
COMPARATOR
The ADuC702x also integrates an uncommitted voltage
comparator.
The positive input is multiplexed with ADC2 and the negative
input has two options: ADC3 or DAC0. The output of the
comparator can be configured to generate a system interrupt,
can be routed directly to the Programmable Logic Array, can
start an ADC conversion or be on an external pin, CMP
Table 22: CMPCON MMR bit descriptions
Bit Name Description
15-11
10 CMPEN
Reserved
Comparator enable bit:
Set by user to enable the comparator
Cleared by user to disable the comparator
9-8 CMPIN
Comparator negative input select bits:
00 Reserved
01 ADC3 input
OUT
.
MUX
PLA
IRQ
ADC START
CONVERSION
ADC2/CMP0
ADC3/CMP1
P0.0/CMP
OUT
DAC0
MUX
Figure 19: Comparator
The comparator interface consists on a 16-bit MMR, CMPCON
described below.
Rev. PrB | Page 39 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
7-6 CMPOC
5 CMPOL
4-3 CMPRES
2 CMPHYST
1 CMPORI
0 CMPOFI
10 DAC0
11 Reserved
Comparator output configuration bits:
00 Start ADC conversion
01 Reserved
10 Output on CMP
OUT
11 IRQ
Comparator output logic state bit
When low the comparator output is high when the positive input (CMP0) is above the negative input
(CMP1).
When high, the comparator output is high when the positive input is below the negative input
Response time
00
01
10
11
10µs
5µs
1µs
0.5µs
Comparator hysteresis bit:
Set by user to have an hysteresis of about 7.5mV
Cleared by user to have no hysteresis
Comparator output rising edge interrupt
Set automatically when a rising edge occurs on the monitored voltage (CMP0)
Cleared by user by writing a 1 to this bit.
Comparator output falling edge interrupt
Set automatically when a falling edge occurs on the monitored voltage (CMP0)
Cleared by user
OSCILLATOR AND PLL - POWER CONTROL
The ADuC702x integrates a 32.768kHz oscillator, a clock
divider and a PLL. The PLL locks onto a multiple (1376) of the
internal oscillator to provide a stable 45MHz clock for the
system. The core can operate at this frequency, or at binary
submultiples of it, to al low power saving. The default core clock
is the PLL clock divided by 8 (CD = 3) or 5.6 MHz. The core
clock frequency can be output on the ECLK pin as described
Figure 20. A power down mode is available on the ADuC702x.
The operating mode, clocking mode and programmable clock
divider are controlled via two MMRs, PLLCON and POWCON.
PLLCON controls operating mode of the clock system while
POWCON controls the core clock frequency and the powerdown mode.
WAKEUP
TIMER
WATCHDOG
TIMER
* 32.768kHz +/-3%
INT. 32kHz *
OSCILLATOR
32.768kHz
PLL
CD
CORE
Figure 20: clocking system
AT
POWER
UP
45MHz
/2
P0.7/ECLK
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
MDCLK
MDCLK
CD
ANALOG
PERIPHERALS
SCLKS
A certain sequence has to be followed to write in the PLLCON
and POWCON registers, to prevent accidental programming.
PLLCON: POWCON:
PLLKEY1 = 0xAA
PLLCON = 0x01
PLLKEY2 = 0x55
POWKEY1 = 0x01
POWCON = 0x00
POWKEY1 = 0xF4
XCLKO
XCLKI
XCLK
Rev. PrB | Page 40 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Table 23: PLLCON MMR bit designations
Bit Name Description
7-3
2 SCLKS
1-0 MDCLK
Bit Name Description
7
6-4 PC
3 FINT
2-0 CD
Reserved
Slow clock selection for watchdog timer:
Set by the user to use the internal 32kHz for the timer. This bit must be set to use watchdog timer if there
is no external crystal
Cleared by user to use the external 32kHz crystal
Clocking modes
00 Reserved
01 PLL + 32kHz oscillator – default configuration
10 Reserved
11 XCLK pin
Table 24: POWCON MMR bit designations
Reserved
Operating modes:
000 Normal mode
011 Power down mode enable. XIRQ0, XIRQ1, timer2 and timer3 can wake-up the ADuC702x.
Others Reserved
Fast interrupt response bit
Set by user to enable the fast interrupt response. If an interrupt occurs when FINT is set, the CPU will run
at the fastest clock frequency in the interrupt service routine. After completing the ISR, execution resumes
at the clock speed set by the CD bits
Cleared by user to disable the fast interrupt response
CPU clock divider bits
000 45.088 MHz
001 22.544 MHz
010 11.272 MHz
011 5.636 MHz
100 2.818 MHz
101 1.409 MHz
110 704.5 kHz
111 352.2 kHz
Rev. PrB | Page 41 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
DIGITAL PERIPHERALS
THREE-PHASE PWM
General overview
The ADuC702x provides a flexible, programmable, three-phase
PWM waveform generator that can be programmed to generate
the required switching patterns to drive a three-phase voltage
source inverter for ac induction (ACIM) motor control.
The PWM generator produces three pairs of PWM signal on
the six PWM output pins (PWM0H, PWM0L, PWM1H,
PWM1L, PWM2H, and PWM2L). The six PWM output signals
consist of three high-side drive signals and three low-side drive
signals.
The switching frequency and dead time of the generated PWM
patterns are programmable using the PWMDAT0 and
PWMDAT1 MMRs. In addition, three duty-cycle control
registers (PWMCH0, PWMCH1 and PWMCH2) directly
control the duty cycles of the three-pairs of PWM signals.
Each of the six PWM output signals can be enabled or disabled
by separate output enable bits of the PWMEN register. In
addition, three control bits of the PWMEN register permit
crossover of the two signals of a PWM pair. In crossover mode,
the PWM signal destined for the high side switch is diverted to
the complementary low side output and the signal destined for
the low side switch is diverted to the corresponding high side
output signal.
In many applications, there is a need to provide an isolation
barrier in the gate-drive circuits that turns on the power devices
of the inverter. In general, there are two common isolation
techniques, optical isolation using opto-couplers and
transformer isolation using pulse transformers. The PWM
controller permits mixing of the output PWM signals with a
high frequency chopping signal to permit easy interface to such
pulse transformers. The features of this gate-drive chopping
mode can be controlled by the PWMCFG register. An 8-bit
value within the PWMCFG register directly controls the
chopping frequency. High frequency chopping can be
independently enabled for the high-side and the low-side
outputs using separate control bits in the PWMCFG register.
The PWM generator is capable of operating in two distinct
modes, single update mode or double update mode. In single
update mode the duty cycle values are programmable only once
per PWM period, so that the resultant PWM patterns are
symmetrical about the midpoint of the PWM period. In the
double update mode, a second updating of the PWM duty cycle
values is implemented at the midpoint of the PWM period. In
this mode, it is possible to produce asymmetrical PWM
patterns, that produce lower harmonic distortion in three-phase
PWM inverters. This technique also permits closed loop
controllers to change the average voltage applied to the machine
windings at a faster rate and so permits faster closed loop
bandwidths to be achieved. The operating mode of the PWM
block is selected by a control bit in the PWMCON register. In
single update mode a PWMSYNC pulse is produced at the start
of each PWM period. In double update mode, an additional
PWMSYNC pulse is produced at the midpoint of each PWM
period.
The PWM block can also provide an internal synchronisation
pulse on the SYNC pin that is synchronise to the PWM
switching frequency. In single update mode a pulse is produce
at the start of each PWM period. In double update mode, an
additional pulse is also produced at the mid-point of each
PWM period. The width of the pulse is programmable through
the PWMDAT2 register. The PWM block can also accept an
external synchronisation pulse on the SYNC pin. The selection
of external synchronisation or internal synchronisation is in the
PWMCON register. The SYNC input timing can be
synchronised to the internal peripheral clock, which is selected
in the PWMCON register. If the external synchronisation pulse
from the chip pin is asynchronous to the internal peripheral
clock (typical case), the external SYNC is considered
asynchronous and should be synchronised. The synchronisation
logic will add latency add jitter from the external pulse to the
actual PWM outputs. The size of the pulse on the SYNC pin
must be greater than two core clock periods.
The PWM signals produced by the ADuC702x can be shut off
via a dedicated asynchronous PWM shutdown pin, PWMTRIP,
that, when brought low, instantaneously places all six PWM
outputs in the OFF state (high). This hardware shutdown
mechanism is asynchronous so that the associated PWM
disable circuitry does not go through any clocked logic, thereby
ensuring correct PWM shutdown even in the event of a loss of
the core clock.
Status information about the PWM system is available to the
user in the PWMSTA register. In particular, the state of the
PWMTRIP pin is available, as well as a status bit that indicates
whether operation is in the first half or the second half of the
PWM period.
Description of the PWM block
A functional block diagram of the PWM controller is shown in
Figure 21. The generation of the six output PWM signals on
pins PWM0H to PWM2L is controlled by four important
blocks:
• The Three-Phase PWM Timing Unit, which is the core of the
PWM controller. It generates three pairs of complemented and
dead-time-adjusted centre-based PWM signals.
• The Output Control Unit allows the redirection of the outputs
of the Three-Phase Timing Unit for each channel to either the
Rev. PrB | Page 42 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
high-side or the low-side output. In addition, the Output
Control Unit allows individual enabling/disabling of each of the
six PWM output signals.
• The Gate Drive Unit permits the generation of the high
frequency chopping frequency and its subsequent mixing with
the PWM signals.
• The PWM Shutdown Controller takes care of the PWM
shutdown via the PWMTRIP pin and generates the correct
RESET signal for the Timing Unit.
Configuration
Registers
PWMCON
PWMDAT0
PWMDAT1
PWMDAT2
core clock
Duty Cycle
Registers
PWMCH0
PWMCH1
PWMCH2
Three-Phase
PWM Timing
Unit
The PWM sync pulse control unit generates the internal
synchronisation pulse and also controls whether the external
SYNC pin is used or not.
The PWM controller is driven by the ADuC702x core clock
frequency and is capable of generating two interrupts to the
ARM core. One interrupt is generated on the occurrence of a
PWMSYNC pulse and the other is generated on the occurrence
of any PWM shutdown action.
PWMEN
Output
Control
Unit
Sync
PWMCFG
Gate
Drive
Unit
PWM0H
PWM0L
PWM1H
PWM1L
PWM2H
PWM2L
to interrupt
controller
Figure 21: Overview of the PWM controller
Three-phase timing unit
PWM Switching Frequency, PWMDAT0 MMR
The PWM switching frequency is controlled by the PWM
period register, PWMDAT0. The fundamental timing unit of
the PWM controller is t
frequency of the MicroConverter. Therefore, for a 45 MHz
, the fundamental time increment is 21 ns. The value
f
CORE
written to the PWMDAT0 register is effectively the number of
CORE clock increments in half a PWM period. The required
t
PWMDAT0 value is a function of the desired PWM switching
frequency (f
PWM) and is given by:
PWMDAT0 = f
Therefore, the PWM switching period, Ts, can be written as:
Ts = 2 x PWMDAT0 x t
The largest value that can be written to the 16-bit PWMDAT0
MMR is 0xFFFF = 65535 which corresponds to a minimum
PWM switching frequency of:
= 45 x 106 / (2 x 65535) = 343.99 Hz
f
PWM(min)
Note that PWMDAT0 value of 0 and 1 are not defined and
= 1/fCORE where fCORE is the core
CORE
core
/ (2 x f
PWM
CORE
)
PWMSYNC
PWMTRIP
should not be used.
PWM Switching Dead Time, PWMDAT1 MMR
The second important parameter that must be set up in the
initial configuration of the PWM block is the switching dead
time. This is a short delay time introduced between turning off
one PWM signal (e.g. AH) and turning on the complementary
signal (AL). This short time delay is introduced to permit the
power switch being turned off (in this case, AH) to completely
recover its blocking capability before the complementary switch
is turned on. This time delay prevents a potentially destructive
short-circuit condition from developing across the dc link
capacitor of a typical voltage source inverter.
The dead time is controlled by the 10-bit, read/write
PWMDAT1 register. There is only one dead-time register that
controls the dead time inserted into all three pairs of PWM
output signals. The dead time, TD, is related to the value in the
PWMDAT1 register by:
TD = PWMDAT1 × 2 × t
CORE
Therefore, a PWMDAT1 value of 0x00A (= 10), introduces an
426 ns delay between the turn-off on any PWM signal (say, AH)
and the turn-on of its complementary signal (AL). The amount
Rev. PrB | Page 43 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
of the dead time can therefore be programmed in increments of
(or 42 ns for a 45 MHz core clock). The PWMDAT1
2t
CORE
register is a 10-bit register so that its maximum value is 0x3FF
(= 1023), corresponding to a maximum programmed dead time
of:
TD
(max)
= 1023 × 2 × t
= 1023 × 2 × 22 ×10–9 = 45.37 µs
CORE
for a core clock of 45 MHz. Obviously, the dead time can be
programmed to be zero by writing 0 to the PWMDAT1 register.
PWM Operating Mode, PWMCON and PWMSTA MMRs
The PWM controller of the ADuC702x can operate in two
distinct modes, single update mode and double update mode.
The operating mode of the PWM controller is determined by
the state of Bit 2 of the PWMCON register. If this bit is cleared
the PWM operates in the single update mode. Setting Bit 2
places the PWM in the double update mode. The default
operating mode is single update mode.
In single update mode, a single PWMSYNC pulse is produced
in each PWM period. The rising edge of this signal marks the
start of a new PWM cycle and is used to latch new values from
the PWM configuration registers (PWMDAT0 and
PWMDAT1) and the PWM duty cycle registers (PWMCH0,
PWMCH1 and PWMCH2) into the three-phase timing unit. In
addition, the PWMEN register is also latched into the output
control unit on the rising edge of the PWMSYNC pulse. In
effect, this means that the characteristics and resultant duty
cycles of the PWM signals can be updated only once per PWM
period at the start of each cycle. The result is that PWM
patterns that are symmetrical about the midpoint of the
switching period are produced.
The advantage of double update mode is that lower harmonic
voltages can be produced by the PWM process and faster
control bandwidths are possible. However, for a given PWM
switching frequency, the PWMSYNC pulses occur at twice the
rate in the double update mode. Since new duty cycle values
must be computed in each PWMSYNC interrupt service
routine, there is a larger computational burden on the ARM
core in double update mode.
PWM Duty Cycles, PWMCH0, PWMCH1, PWMCH2
MMRs
The duty cycles of the six PWM output signals on pins AH to
CL are controlled by the three 16-bit read/write duty cycle
registers, PWMCH0, PWMCH1 and PWMCH2. The duty cycle
registers are programmed in integer counts of the fundamental
time unit, t
CORE, and define the desired on-time of the high-side
PWM signal produced by the three-phase timing unit over half
the PWM period. The switching signals produced by the threephase timing unit are also adjusted to incorporate the
programmed dead time value in the PWMDAT1 register. The
three-phase timing unit produces active low signals so that a
low level corresponds to a command to turn on the associated
power device.
0H
PWMSYNC
PWMCH0
2x
PWMDAT1
0L
PWMCH0
PWMDAT1
PWMDAT2+1
2x
In double update mode, there is an additional PWMSYNC
pulse produced at the midpoint of each PWM period. The
rising edge of this new PWMSYNC pulse is again used to latch
new values of the PWM configuration registers, duty cycle
registers and the PWMEN register. As a result it is possible to
alter both the characteristics (switching frequency and dead
time) as well as the output duty cycles at the midpoint of each
PWM cycle. Consequently, it is possible to produce PWM
switching patterns that are no longer symmetrical about the
midpoint of the period (asymmetrical PWM patterns). In
double update mode, it may be necessary to know whether
operation at any point in time is in either the first half or the
second half of the PWM cycle. This information is provided by
Bit 0 of the PWMSTA register, which is cleared during
operation in the first half of each PWM period (between the
rising edge of the original PWMSYNC pulse and the rising edge
of the new PWMSYNC pulse introduced in double update
mode). Bit 0 of the PWMSTA register is set during operation in
the second half of each PWM period. This status bit allows the
user to make a determination of the particular half-cycle during
implementation of the PWMSYNC interrupt service routine, if
required.
Rev. PrB | Page 44 of 80
PWMSTA(0)
PWMDAT0
Figure 22: Typical PWM outputs of Three-Phase timing unit in single update
mode
PWMDAT0
A typical pair of PWM outputs (in this case for AH and AL)
from the timing unit are shown in Figure 22 for operation in
single update mode. All illustrated time values indicate the
integer value in the associated register and can be converted to
time by simply multiplying by the fundamental time increment,
CORE. First, it is noted that the switching patterns are perfectly
t
symmetrical about the midpoint of the switching period in this
single update mode since the same values of PWMCH0,
PWMDAT0 and PWMDAT1 are used to define the signals in
both half cycles of the period. It can be seen how the
programmed duty cycles are adjusted to incorporate the desired
dead time into the resultant pair of PWM signals. Clearly, the
dead time is incorporated by moving the switching instants of
both PWM signals (0H and 0L) away from the instant set by the
PWMCH0 register. Both switching edges are moved by an
equal amount (PWMDAT1 x t
CORE) to preserve the

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
symmetrical output patterns.
Also shown is the PWMSYNC pulse and Bit 0 of the PWMSTA
register that indicates whether operation is in the first or
second half cycle of the PWM period.
The resultant on-times of the PWM signals over the full PWM
period (two half periods) produced by the timing unit can be
written as:
= 2 x (PWMCH0 - PWMDAT1) x t
T
0H
T0L = 2 x (PWMDAT0 – PWMCH0 – PWMDAT1) x t
CORE
CORE
And the corresponding duty cycles:
= T0H / Ts = (PWMCH0 – PWMDAT1) / PWMDAT0
d
0H
= T0L / Ts = (PWMDAT0 – PWMCH0 – PWMDAT1) /
d
0L
PWMDAT0
The minimum permissible T0H and T0L values are zero,
corresponding to a 0% duty cycle. In a similar fashion, the
maximum value is T
S, corresponding to a 100% duty cycle.
The output signals from the timing unit for operation in double
update mode are shown in Figure 23. This illustrates a
completely general case where the switching frequency, dead
time and duty cycle are all changed in the second half of the
PWM period. Of course, the same value for any or all of these
quantities could be used in both halves of the PWM cycle.
However, it can be seen that there is no guarantee that
symmetrical PWM signals will be produced by the timing unit
in double update mode. Additionally, it is seen that the dead
time is inserted into the PWM signals in the same way as in the
single update mode.
PWMCH0
0H
2x
PWMDAT1
0L
PWMSYNC
PWMSTA(0)
Figure 23: Typical PWM outputs of the Three-phase timing unit in double
1
PWMDAT0
1
update mode
1
PWMCH0
2
PWMDAT22+1PWMDAT21+1
PWMDAT0
PWMDAT1
2
2x
2
In general the on-times of the PWM signals in double update
mode can be defined as:
= (PWMCH01 + PWMCH02 – PWMDAT11 – PWMDAT12)
T
0H
x t
CORE
T
= (PWMDAT01 + PWMDAT02 - PWMCH01 - PWMCH02 –
0L
PWMDAT1
– PWMDAT12) x t
1
CORE
where the subscript 1 refers to the value of that register during
the first half cycle and the subscript 2 refers to the value during
the second half cycle. The corresponding duty cycles are:
= T0H / Ts = (PWMCH01 + PWMCH02 – PWMDAT11 –
d
0H
PWMDAT1
d
= T0L /Ts = (PWMDAT01 + PWMDAT02 - PWMCH01 -
0L
PWMCH0
PWMDAT0
) / (PWMDAT01 + PWMDAT02)
2
– PWMDAT11 – PWMDAT12) / (PWMDAT01 +
2
)
2
since for the completely general case in double update mode,
the switching period is given by:
Ts = (PWMDAT0
+ PWMDAT02) x t
1
CORE
Again, the values of T0H and T0L are constrained to lie between
zero and T
S.
PWM signals similar to those illustrated in Figure 22 and
Figure 23 can be produced on the 1H, 1L, 2H and 2L outputs by
programming the PWMCH1 and PWMCH2 registers in a
manner identical to that described for PWMCH0. The PWM
controller does not produce any PWM outputs until all of the
PWMDAT0, PWMCH0, PWMCH1 and PWMCH2 registers
have been written to at least once. Once these registers have
been written, internal counting of the timers in the three-phase
timing unit is enabled. Writing to the PWMDAT0 register
starts the internal timing of the main PWM timer. Provided the
PWMDAT0 register is written prior to the PWMCH0,
PWMCH1 and PWMCH2 registers in the initialisation, the
first PWMSYNC pulse and interrupt (if enabled) appear 1.5 x
CORE x PWMDAT0 seconds after the initial write to the
t
PWMDAT0 register in single update mode. In double update
mode, the first PWMSYNC pulse appears after PWMDAT0 x
CORE seconds.
t
Output Control Unit
The operation of the Output Control Unit is controlled by the
9-bit read/write PWMEN register. This register controls two
distinct features of the Output Control Unit that are directly
useful in the control of ECM or BDCM. The PWMEN register
contains three crossover bits, one for each pair of PWM outputs.
Setting Bit 8 of the PWMEN register enables the crossover
mode for the 0H/0L pair of PWM signals, setting Bit 7 enables
crossover on the 1H/1L pair of PWM signals and setting Bit 6
enables crossover on the 2H/2L pair of PWM signals. If
crossover mode is enabled for any pair of PWM signals, the
high-side PWM signal from the timing unit (0H, for example) is
diverted to the associated low-side output of the Output
Control Unit so that the signal will ultimately appear at the 0L
pin. Of course, the corresponding low-side output of the Timing
Unit is also diverted to the complementary high-side output of
Rev. PrB | Page 45 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
the Output Control Unit so that the signal appears at the 0H
pin. Following a reset, the three crossover bits are cleared so that
the crossover mode is disabled on all three pairs of PWM
signals. The PWMEN register also contains six bits (Bits 0 to 5)
that can be used to individually enable or disable each of the six
PWM outputs. If the associated bit of the PWMEN register is
set, the corresponding PWM output is disabled irrespective of
the value of the corresponding duty cycle register. This PWM
output signal will remain in the OFF state as long as the
corresponding enable/disable bit of the PWMEN register is set.
The implementation of this output enable function is
implemented after the crossover function.
Following a reset, all six enable bits of the PWMEN register are
cleared so that all PWM outputs are enabled by default. In a
manner identical to the duty cycle registers, the PWMEN is
latched on the rising edge of the PWMSYNC signal so that
changes to this register only become effective at the start of each
PWM cycle in single update mode. In double update mode, the
PWMEN register can also be updated at the midpoint of the
PWM cycle.
In the control of an ECM only two inverter legs are switched at
any time and often the high-side device in one leg must be
switched ON at the same time as the low-side driver in a second
leg. Therefore, by programming identical duty cycles values for
two PWM channels (e.g. PWMCH0 = PWMCH1) and setting
Bit 7 of the PWMEN register to cross over the 1H/1L pair of
PWM signals, it is possible to turn ON the high-side switch of
Phase A and the low-side switch of Phase B at the same time. In
the control of ECM, it is usual for the third inverter leg (Phase
C in this example) to be disabled for a number of PWM cycles.
This function is implemented by disabling both the 2H and 2L
PWM outputs by setting Bits 0 and 1 of the PWMEN register.
PWMCH0 = PWMCH1, crossover BH/BL pair and disable 0L, 1H, 2H and 2L
outputs. Operation is in single update mode.
In addition, the other four signals (0L, 1H, 2H and 2L) have
been disabled by setting the appropriate enable/disable bits of
the PWMEN register. For the situation illustrated in Figure 24,
the appropriate value for the PWMEN register is 0x00A7. In
normal ECM operation, each inverter leg is disabled for certain
periods of time so that the PWMEN register is changed based
on the position of the rotor shaft (motor commutation).
Gate Drive Unit
The Gate Drive Unit of the PWM controller adds features that
simplify the design of isolated gate drive circuits for PWM
inverters. If a transformer-coupled power device gate drive
amplifier is used then the active PWM signal must be chopped
at a high frequency. The 10-bit read/write PWMCFG register
allows the programming of this high frequency chopping mode.
The chopped active PWM signals may be required for the highside drivers only, for the low-side drivers only or for both the
high-side and low-side switches. Therefore, independent
control of this mode for both high- and low-side switches is
included with two separate control bits in the PWMCFG
register.
Typical PWM output signals with high frequency chopping
enabled on both high-side and low-side signals are shown in
Figure 25. Chopping of the high side PWM outputs (0H, 1H
and 2H) is enabled by setting Bit 8 of the PWMCFG register.
Chopping of the low-side PWM outputs (0L, 1L and 2L) is
enabled by setting Bit 9 of the PWMCFG register. The high
frequency chopping frequency is controlled by the 8-bit word
(GDCLK) placed in Bits 0 to 7 of the PWMCFG register. The
period of this high frequency carrier is:
This situation is illustrated in Figure 24, where it can be seen
that both the 0H and 1L signals are identical, since PWMCH0 =
PWMCH1 and the crossover bit for phase B is set.
PWMCH0
= PWMCH1
0H
0L
1H
1L
2H
2L
PWMDAT0 PWMDAT0
Figure 24. Example active LO PWM signals suitable for ECM control,
PWMCH0
= PWMCH1
2xPWMDAT12xPWMDAT1
Rev. PrB | Page 46 of 80
= (4 x (GDCLK + 1)) x t
T
chop
CORE
and the chopping frequency is therefore an integral subdivision
of the MicroConverter core frequency:
= f
f
chop
/ (4 x (GDCLK + 1))
CORE
The GDCLK value may range from 0 to 255, corresponding to a
programmable chopping frequency rate from 45.9 kHz to 11.75
MHz for a 45 MHz core frequency. The gate drive features
must be programmed before operation of the PWM controller
and typically are not changed during normal operation of the
PWM controller. Following a reset, all bits of the PWMCFG
register are cleared so that high frequency chopping is disabled,
by default.

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
0H
0L
4x(GDCLK+1)xt
PWMDAT0 PWMDAT0
Figure 25: typical PWM signals with high frequency gate chopping enabled
on both high-side and low-side switches
PWMCH0
CORE
PWMCH0
2xPWMDAT12xPWMDAT1
PWM shutdown
In the event of external fault conditions, it is essential that the
PWM system be instantaneously shut down in a safe fashion. A
low level on the PWMTRIP pin provides an instantaneous,
asynchronous (independent of the MicroConverter core clock)
shutdown of the PWM controller. All six PWM outputs are
placed in the OFF state, i.e. high state. In addition, the
PWMSYNC pulse is disabled. The PWMTRIP pin has an
internal pull-down resistor so that if the pin becomes
disconnected the PWM will be disabled. The state of the
PWMTRIP pin can be read from Bit 3 of the PWMSTA
register.
On the occurrence of a PWM shutdown command, a
PWMTRIP interrupt will be generated, internal timing of the
three-phase timing unit of the PWM controller is stopped.
Bit Name Description
7-5
4 PWM_SYNCSEL
3 PWM_EXTSYNC
2 PWMDBL
1 PWM_SYNC_EN
0 PWMEN
Bit Name Description
15-10
9 PWMSYNCINT
Table 25: PWMCON MMR Bit Descriptions
Reserved
External sync select
Set to use external sync
Cleared to use internal sync
External sync select
Set to select external synchronous sync signal
Cleared for asynchronous sync signal
Double Update Mode
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable double update mode
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable single update mode
PWM synchronisation enable
Set by user to enable synchronisation
Cleared by user to disable synchronisation
PWM Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to disable the PWM. Also cleared automatically with PWMTRIP
Table 2 6 : PW M STA M M R Bit D e sc r i pti o n s
Reserved
PWM sync interrupt bit
Following a PWM shutdown, the PWM can only be re-enabled
(in a PWMTRIP interrupt service routine, for example) by
writing to all of the PWMDAT0, PWMCH0, PWMCH1 and
PWMCH2 registers. Provided the external fault has been
cleared and the PWMTRIP has returned to a high level,
internal timing of the three-phase timing unit resumes and new
duty-cycle values are latched on the next PWMSYNC
boundary.
PWM MMRs interface
The PWM block is controlled via the following nine MMRs:
- PWMCON: control register, enable the PWM, choose the
update rate
- PWMSTA: reflects the status of the PWM
- PWMDAT0: unsigned 16-bit register for switching period
- PWMDAT1: unsigned 10-bit register for dead time
- PWMCFG: gate chopping
- PWMCH0,CH1,CH2: channel duty cycle for the three
phases
- PWMEN: allows enabling channel outputs and crossover. See
bit definition Table 28.
- PWMDAT2: unsigned 10-bit register for PWM sync pulse
width.
Rev. PrB | Page 47 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
8 PWMTRIPINT
3 PWMTRIP
2-1
0 PWMPHASE
Bit Name Description
9 CHOPLO
8 CHOPHI
0:7 GDCLK
Bit Name Description
8 0H0L_XOVR
7 1H1L_XOVR
6 2H2L_XOVR
5 0L_EN
4 0H_EN
3 1L_EN
2 1H_EN
1 2L_EN
0 2H_EN
PWM trip interrupt bit
Raw signal from the PWMTRIP pin
Reserved
PWM Phase Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the MicroConverter when the timer is counting down (1
Clear to ‘0’ by the MicroConverter when the timer is counting up (2
Table 27: PWMCFG MMR Bit Descriptions
low-side Gate Chopping enable bit
high-side Gate Chopping enable bit
PWM Gate Chopping Period (unsigned)
Table 28: PWMEN MMR bit descriptions
Channel 0 Output Crossover Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable channel 0 output crossover
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to disable channel 0 output crossover
Channel 1 Output Crossover Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable channel 1 output crossover
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to disable channel 1 output crossover
Channel 2 Output Crossover Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to enable channel 2 output crossover
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to disable channel 2 output crossover
AL Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 0L output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 0L output of the PWM
AH Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 0H output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 0H output of the PWM
BL Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 1L output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 1L output of the PWM
BH Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 1H output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 1H output of the PWM
CL Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 2L output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 2L output of the PWM
CH Output Enable Bit
Set to ‘1’ by the user to disable the 2H output of the PWM
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to enable the 2H output of the PWM
st
half)
nd
half)
Rev. PrB | Page 48 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
g
]
]
[4]
]
]
]
]
]
[0]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
[15]
]
]
]
]
]
]
[14]
GENERAL PURPOSE I/O
The ADuC702x provides 40 General Purpose bi-directional I/O
pins (GPIO). All I/O pins are 5V tolerant which means that the
GPIOs support an input voltage of 5V. In general many of the
GPIO pins have multiple functions, see Table 30 for the pin
function definition. By default the GPIO pins are configured in
GPIO mode. All GPIO pins have internal pull up resistor and
their drive capability is 1.6mA.
The 40 GPIO are grouped in 5 ports, port 0 to 4. Each port is
controlled by four MMRs:
- GPxCON: Port x Control Register, selects the function of
each pin of port x. as described in Table 29
- GPxDAT: Port x Configuration and Data Register. It
configures the direction of the GPIO pins of port x, sets the
output value for the pins configured as output and receives
the stores the input value of the pins configured as input.
- GPxSET: data set port x
- GPxCLR: data clear port x
With x representing the port number.
See Table 6 page 3 for address location of these 20 registers.
The default value of GPxCON is 0x00000000, all port pins are
defined as GPIO, except GP0CON which is 0x01001000 in
order to make the TRST and MRST functions available at reset.
Table 29: GPxCON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-30
29-28
27-26
25-24
23-22
21-20
19-18
17-16
15-14
13-12
11-10
9-8
7-6
5-4
3-2
1-0
Reserved
Select function of Px.7 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.6 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.5 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.4 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.3 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.2 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.1 pin
Reserved
Select function of Px.0 pin
Table 30: GPIO pin function Descriptions
Confi
Port Pin
P0.0 GPIO CMP MS2 PLAI[7
P0.1 GPIO PWM2H BLE -
P0.2 GPIO PWM2L BHE -
P0.3 GPIO TRST A16 ADC
P0.4 GPIO
0
P0.5 GPIO
P0.6 GPIO MRST AE PLAO[3
P0.7 GPIO ECLK SIN PLAO
P1.0 GPIO SIN SCL0 PLAI[0
P1.1 GPIO SOUT SDA0 PLAI[1
P1.2 GPIO RTS SCL1 PLAI[2
P1.3 GPIO CTS SDA1 PLAI[3
P1.4 GPIO
1
P1.5 GPIO
P1.6 GPIO DSR MOSI PLAI[6
P1.7 GPIO DTR CSL PLAO
P2.0 GPIO CONVS SOUT PLAO[5
P2.1 GPIO PWM0H WS PLAO[6
P2.2 GPIO PWM0L RS PLAO[7
P2.3 GPIO - AE -
2
P2.4 GPIO PWM0H MS0 -
P2.5 GPIO PWM0L MS1 -
P2.6 GPIO PWM1H MS2 -
P2.7 GPIO PWM1L MS3 -
P3.0 GPIO PWM0H AD0 PLAI[8
P3.1 GPIO PWM0L AD1 PLAI[9
P3.2 GPIO PWM1H AD2 PLAI[10
P3.3 GPIO PWM1L AD3 PLAI[11
3
P3.4 GPIO PWM2H AD4 PLAI[12
P3.5 GPIO PWM2L AD5 PLAI[13
P3.6 GPIO PWMTRIP AD6 PLAI[14
P3.7 GPIO PWMSYNC AD7 PLAI
P4.0 GPIO - AD8 PLAO[8
4
P4.1 GPIO - AD9 PLAO[9
P4.2 GPIO - AD10 PLAO[10
P4.3 GPIO - AD11 PLAO[11
P4.4 GPIO - AD12 PLAO[12
P4.5 GPIO - AD13 PLAO[13
P4.6 GPIO - AD14 PLAO
00 01 10 11
PWMTRIP MS1 PLAO[1]
IRQ0
ADC
IRQ1
IRQ2
DCD MISO PLAI[5]
IRQ3
uration
MS0 PLAO[2]
BUSY
RI CLK PLAI[4]
BUSY
Rev. PrB | Page 49 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
P4.7 GPIO - AD15 PLAO[15]
Rev. PrB | Page 50 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Table 31: GPxDAT MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-24
23-16
15-8
7-0
Bit Description
31-24
23-16
15-0
Direction of the data:
Set to ‘1’ by the user to configure the GPIO pin as an output
Clear to ‘0’ by the user to configure the GPIO pin as an input
Port x data output
Reflect the state of Port x pins at reset (read only)
Port x data input (read only)
Table 32: GPxSET MMR Bit Descriptions
Reserved
Data port x set bit:
Set to ‘1’ by the user to set bit on port x. will also set the corresponding bit in the GPxDAT MMR
Clear to ‘0’ by the user will not affect the data out
Reserved
Bit Description
31-24
23-16
15-0
Reserved
Data port x clear bit:
Set to ‘1’ by the user to clear bit on port x, will also clear the corresponding bit in the GPxDAT MMR
Clear to ‘0’ by the user will not affect the data out
Reserved
Table 33: GPxCLR MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 51 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
g
SERIAL PORT MUX
The Serial Port Mux multiplexes the serial port peripherals (two
2
C, SPI, UART) and the Programmable Logic Array (PLA) to a
I
set of ten GPIO pins. Each pin must be configured to one of its
specific I/O function as described in Table 34.
SPM0 P1.0 SIN I2C0SCL PLAI[0
SPM1 P1.1 SOUT I2C0SDA PLAI[1
SPM2 P1.2 RTS I2C1SCL PLAI[2
SPM3 P1.3 CTS I2C1SDA PLAI[3
SPM4 P1.4 RI SPICLK PLAI[4
SPM5 P1.5 DCD SPIMISO PLAI[5
SPM6 P1.6 DSR SPIMOSI PLAI[6
SPM7 P1.7 DTR SPICSL PLAO[0
SPM8 P0.7 ECLK SIN PLAO[4
SPM9 P2.0 CONV SOUT PLAO[5
Table 34 details the mode for each of the SPMUX GPIO pins.
This configuration has to be done via the GP0CON, GP1CON
and GP2CON MMRs. By default these ten pins are configured
as GPIOs.
GPIO UART UART/I
00 01 10 11
Table 34: SPM configuration
UART SERIAL INTERFACE
The UART peripheral is a full-duplex Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter, fully compatible with the 16450 serial
port standard. The UART performs serial-to-parallel conversion
on data characters received from a peripheral device or a
MODEM, and parallel-to-serial conversion on data characters
received from the CPU. The UART includes a fractional divider
for baudrate generation and has a network addressable mode.
The UART function is made available on the following 10 pins
of the ADuC702x:
Pin Si
SPM0 (mode 1) RTS Request To Send
SPM1 (mode 1) CTS Clear To Send
SPM2 (mode 1) SIN Serial Receive Data
SPM3 (mode 1) SOUT Serial Transmit Data
SPM4 (mode 1) RI Ring Indicator
SPM5 (mode 1) DCD Data Carrier Detect
SPM6 (mode 1) DSR Data Set Ready
SPM7 (mode 1) DTR Data Terminal Ready
SPM8 (mode 2) SIN Serial Receive Data
SPM9 (mode 2) SOUT Serial Transmit Data
The serial communication adopts a asynchronous protocol that
nal Description
Table 35: UART signal description
2
C/SPI PLA
supports various word length, stop bits and parity generation
options selectable in the configuration register.
Baud rate generation
There is two way of generating the UART baudrate.
- Normal 450 UART baudrate generation:
The baudrate is a divided version of the core clock using the
value in COMDIV0 and COMDIV1 MMRs (16-bit value, DL).
MHz
Baudrate
The following table gives some common baudrate values:
Baudrate CD DL Actual
9600 0 92h 9651 0.53%
19200 0 49h 19301 0.53%
115200 0 0Ch 117417 1.92%
9600 3 12h 9785 1.92%
19200 3 9h 19569 1.92%
115200 3 1h 88062 23.55%
Table 36: baudrate using the normal baudrate generator
- Using the fractional divider:
The fractional divider combined with the normal baudrate
generator allows the generating of a wider range of more
accurate baudrates.
Core Clock
Calculation of the baudrate using fractional divider is as follow:
Baudrate
/2
/(M+N/2048)
Figure 26: baudrate generation options
=
=
CD
CD
FBEN
088.45
2162
baudrate
/16DL UART
088.45
MHz
DL
×××
% error
N
(2162
MDL
+××××
)
2048
088.45
M
=+
2048 ××××
Example:
Generation of 9600 baud with CD bits = 3. The previous table
gives DL = 12h.
CD
MHzN
DLBaudrate
2162
Rev. PrB | Page 52 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
088.45
M
=+
2048
M
N
2048
M = 1 and N = 0.019 x 2048 = 39
Baudrate
Baudrate = 9602 bps
Error = 0.02% compared to 1.92% with the normal baudrate
generator.
=
3
MHzN
3
019.1
=+
MHz
088.45
1(218162
+××××
2181629600
××××
39
2048
)
UART registers definition
The UART interface consists on 12 registers namely:
- COMTX: 8-bit transmit register
- COMRX: 8-bit receive register
- COMDIV0: divisor latch (low byte)
COMTX, COMRX and COMDIV0 share the same address
location. COMTX and COMTX can be accessed when bit 7
in COMCON0 register is cleared. COMDIV0 can be accessed
when bit 7 of COMCON0 is set.
- COMDIV1: divisor latch (high byte)
- COMCON0: line control register
- COMSTA0: line status register
- COMIEN0: interrupt enable register
- COMIID0: interrupt identification register
- COMCON1: modem control register
- COMSTA1: modem status register
- COMDIV2: 16-bit fractional baud divide register
- COMSCR: 8-bit scratch register used for temporary storage.
Also used in network addressable UART mode.
Table 37: COMCON0 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
7 DLAB
6 BRK
5 SP
4 EPS
3 PEN
2 STOP
1-0 WLS
Divisor latch access
Set by user to enable access to COMDIV0 and COMDIV1 registers
Cleared by user to disable access to COMDIV0 and COMDIV1 and enable access to COMRX and
COMTX
Set break.
Set by user to force SOUT to 0
Cleared to operate in normal mode
Stick parity
Set by user to force parity to defined values:
1 if EPS = 1 and PEN = 1
0 if EPS = 0 and PEN = 1
Even parity select bit
Set for even parity
Cleared for odd parity
Parity enable bit:
Set by user to transmit and check the parity bit
Cleared by user for no parity transmission or checking
Stop bit
Set by user to transmit 1.5 Stop bit if the Word Length is 5 bits or 2 Stop bits if the word length is 6, 7
or 8 bits. The receiver checks the first Stop bit only, regardless of the number of Stop bits selected
Cleared by user to generate 1 Stop bit in the transmitted data
Word length select:
00 = 5 bits
01 = 6 bits
10 = 7 bits
11 = 8 bits
Rev. PrB | Page 53 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Table 38: COMSTA0 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
7
6 TEMT
5 THRE
4 BI
3 FE
2 PE
1 OE
0 DR
Reserved
COMTX empty status bit
Set automatically if COMTX is empty
Cleared automatically when writing to COMTX
COMTX and COMRX empty
Set automatically if COMTX and COMRX are empty
Cleared automatically when one of the register receives data
Break error
Set when SIN is held low for more than the maximum word length
Cleared automatically
Framing error
Set when invalid stop bit
Cleared automatically
Parity error
Set when a parity error occurs
Cleared automatically
Overrun error
Set automatically if data are overwrite before been read
Cleared automatically
Data ready
Set automatically when COMRX is full
Cleared by reading COMRX
Table 39: COMIEN0 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
7-4
3 EDSSI
2 ELSI
1 ETBEI
0 ERBFI
Bit 2-1
Status bits
00 1
11 0
10 0
01 0
00 0
Bit 0
NINT
Reserved
Modem status interrupt enable bit
Set by user to enable generation of an interrupt if any of COMSTA1[3:0] are set
Cleared by user
RX status interrupt enable bit
Set by user to enable generation of an interrupt if any of COMSTA0[3:0] are set
Cleared by user
Enable transmit buffer empty interrupt
Set by user to enable interrupt when buffer is empty during a transmission
Cleared by user
Enable receive buffer full interrupt
Set by user to enable interrupt when buffer is full during a reception
Cleared by user
Table 40: COMIID0 MMR Bit Descriptions
Priority Definition Clearing operation
No interrupt
1 Receive line status interrupt Read COMSTA0
2 Receive buffer full interrupt Read COMRX
3 Transmit buffer empty interrupt Write data to COMTX or read COMIID0
4 Modem status interrupt Read COMSTA1 register
Rev. PrB | Page 54 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
Table 41: COMCON1 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
7-5
4 LOOPBACK
1 RTS
0 DTR
Bit Name Description
7 DCD
6 RI
5 DSR
4 CTS
3 DDCD
2 TERI
1 DDSR
0 DCTS
Reserved
Loop back
Set by user to enable loop back mode. In loop back mode the SOUT is forced high. Also the modem
signals are directly connected to the status inputs (RTS to CTS, DTR to DSR, OUT1 to RI and OUT2 to
DCD)
Request to send
Set by user to force the RTS output to 0
Cleared by user to force the RTS output to 1
Data terminal ready
Set by user to force the DTR output to 0
Cleared by user to force the DTR output to 1
Table 42: COMSTA1 MMR Bit Descriptions
Data carrier detect
Ring indicator
Data set ready
Clear to send
Delta DCD
Set automatically if DCD changed state since COMSTA1 last read
Cleared automatically by reading COMSTA1
Trailing edge RI
Set if NRI changed from 0 to 1 since COMSTA1 last read
Cleared automatically by reading COMSTA1
Delta DSR
Set automatically if DSR changed state since COMSTA1 last read
Cleared automatically by reading COMSTA1
Delta CTS
Set automatically if CTS changed state since COMSTA1 last read
Cleared automatically by reading COMSTA1
Table 43: COMDIV2 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
15 FBEN
14-13
12-11 FBM[1-0]
10-0 FBN[10-0]
Fractional baudrate generator enable bit
Set by user to enable the fractional baudrate generator
Cleared by user to generate baudrate using the standard 450 UART baudrate generator
Reserved
M. if FBM = 0, M = 4
N
Rev. PrB | Page 55 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
scratch register is the transmitted network address control bit.
Network addressable UART mode
This mode allows connecting the MicroConverter on a 256node serial network, either as a hardware single-master or via
software in a multi-master network. Bit 7 of COMIEN1 (ENAM
bit) must be set to enable UART in network addressable mode.
Note that there is no parity check in this mode, the parity bit is
used for address.
Network addressable UART register definitions
Three additional register:
- COMSCR: 8-bit scratch register used for temporary storage.
In network address mode, the least significant bit of the
Table 44: COMIEN1 MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
7 ENAM
6 E9BT
5 E9BR
4 ENI
3 E9BD
2 ETD
1 NABP
0 NAB
Network address mode Enable bit
set by user to enable network address mode
cleared by user to disable network address mode
9-bit transmit enable bit
Set by user to enable 9-bit transmit. ENAM must be set
Cleared by user to disable 9-bit transmit
9-bit receive enable bit
Set by user to enable 9-bit receive. ENAM must be set
Cleared by user to disable 9-bit receive
network interrupt Enable bit
Word length
Set for 9-bit data. E9BT has to be cleared.
Cleared for 8-bit data
Transmitter pin driver Enable bit
Set by user to enable SOUT pin as an output in slave mode or multi-master mode
Cleared by user, SOUT is three-state
Network address bit, interrupt polarity bit
Network address bit
Set by user to transmit the slave’s address
Cleared by user to transmit data
If set to 1, the device is transmitting an address. If cleared to
0, the device is transmitting data.
- COMIEN1: 8-bit network enable register.
- COMIID1: 8-bit network interrupt register. Bit 7 to 4 are
reserved. See Table 45.
- COMADR: 8-bit read and write network address register.
Holds the address the network addressable UART checks for.
On receiving this address the device interrupts the processor
and/or sets the appropriate status bit in COMIID1.
COMIEN1, COMIID1 and COMADR are used only in
network addressable UART mode.
Bit 3-1
Status bits
000 1
110 0
101 0
011 0
010 0
001 0
000 0
Bit 0
NINT
Table 45: COMIID1 MMR Bit Descriptions
priority Definition Clearing operation
No interrupt
2 Matching network address Read COMRX
3 Address transmitted, buffer empty Write data to COMTX or read COMIID0
1 Receive line status interrupt Read COMSTA0
2 Receive buffer full interrupt Read COMRX
3 Transmit buffer empty interrupt Write data to COMTX or read COMIID0
4 Modem status interrupt Read COMSTA1 register
Rev. PrB | Page 56 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
SPIDIV register as follow:
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
f
The ADuC702x integrates a complete hardware Serial
Peripheral Interface (SPI) on-chip. SPI is an industry standard
synchronous serial interface that allows eight bits of data to be
synchronously transmitted and received simultaneously, i.e., full
duplex up to a maximum bit rate of 5.6Mbs. The SPI Port can
be configured for Master or Slave operation and typically
consists of four pins, namely:
MISO (Master In, Slave Out Data I/O Pin)
The MISO (master in slave out) pin is configured as an input
line in master mode and an output line in slave mode. The
MISO line on the master (data in) should be connected to the
MISO line in the slave device (data out). The data is transferred
as byte wide (8-bit) serial data, MSB first.
MOSI (Master Out, Slave In Pin)
The MOSI (master out slave in) pin is configured as an output
line in master mode and an input line in slave mode.
The MOSI line on the master (data out) should be connected to
the MOSI line in the slave device (data in). The data is
transferred as byte wide (8-bit) serial data, MSB first.
SCL (Serial Clock I/O Pin)
The master serial clock (SCL) is used to synchronize the data
being transmitted and received through the MOSI SCL period.
Therefore, a byte is transmitted/received after eight SCL
periods. The SCL pin is configured as an output in master mode
and as an input in slave mode.
In master mode polarity and phase of the clock are controlled
by the SPICON register, and the bit-rate is defined in the
f
The maximum serial bit clock frequency is 1/8 of the core clock
which, based on a maximum core clock frequency of 45MHz is
just above 5.6Mbs.
In slave mode the SPICON register must be configured with the
phase and polarity of the expected input clock.
In both master and slave modes, the data is transmitted on one
edge of the SCL signal and sampled on the other. It is important
therefore that the polarity and phase are configured the same
for the master and slave devices.
=
kserialcloc
Chip Select (CS) Input Pin
In SPI Slave Mode, a transfer is initiated by the assertion of CS
which is an active low input signal. The SPI port will then
transmit and receive 8-bit data until the transfer is concluded by
desassertion of
CS
. In slave mode CS is always an input.
SPI registers definition
The following MMR registers are used to control the SPI
interface:
- SPICON: 16-bit control register
- SPISTA: 8-bit read only status register
- SPIDIV: 8-bit serial clock divider register
- SPITX: 8-bit write only transmit register
- SPIRX: 8-bit read only receive register
coreclock
+×
)1(2 SPIDIV
Bit Description
15-13
12
11
10
9
8
Reserved
Continuous transfer enable
Set by user to enable continuous transfer.
In master mode the transfer will continue until no valid data is available in the TX register. CS will be asserted and remain
asserted for the duration of each 8-bit serial transfer until TX is empty
Cleared by user to disable continuous transfer. Each transfer consists of a single 8-bit serial transfer. If valid data exists in
the SPITX register then a new transfer is initiated after a stall period
Loop back enable
Set by user to connect MISO to MOSI and test software
Cleared by user to be in normal mode
Slave output enable
Set by user to enable the slave output
Cleared by user to disable slave output
Slave select input enable
Set by user in master mode to enable the output
SPIRX overflow overwrite enable
Set by user, the valid data in the RX register is overwritten by the new serial byte received
Table 46: SPICON MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 57 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Cleared by user, the new serial byte received is discarded
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
SPITX underflow mode
Set by user to transmit the previous data
Cleared by user to transmit 0
Transfer and interrupt mode (master mode)
Set by user to initiate transfer with a write to the SPITX register. Interrupt will occur when TX is empty
Cleared by user to initiate transfer with a read of the COMRX register. Interrupt will occur when RX is full
LSB first transfer enable bit
Set by user the LSB is transmitted first
Cleared by user the MSB is transmitted first
Reserved
Serial clock polarity mode bit
Set by user, the serial clock idles high
Cleared by user the serial clock idles low
Serial clock phase mode bit
Set by user, the serial clock pulses at the beginning of each serial bit transfer
Cleared by user, the serial clock pulses eat end of each serial bit transfer
Master mode enable bit
Set by user to enable master mode
Cleared by user to enable slave mode
SPI enable bit
Set by user to enable the SPI
Cleared to disable the SPI
Bit Description
7-6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Reserved
SPIRX data register overflow status bit
Set if SPIRX is overflowing
Cleared by reading SPISRX register
SPIRX data register IRQ
Set automatically if bit 3 or 5 are set
Cleared by reading SPIRX register
SPIRX data register full status bit
Set automatically if a valid data is present in the SPIRX register
Cleared by reading SPIRX register
SPITX data register underflow status bit
Set automatically if SPITX is under flowing
Cleared by writing in the SPITX register
SPITX data register IRQ
Set automatically if bit 0 is clear or bit 2 is set
Cleared by writing in the SPITX register or if finished transmission disabling the SPI
SPITX data register empty status bit
Set by writing to SPITX to send data. This bit is set during transmission of data
Cleared when SPITX is empty
Table 47: SPISTA MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 58 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
f
coreclock
++×
)02022(2 DIVLCIDIVHCI
I2C COMPATIBLE INTERFACES
The ADuC702x supports two ful l y l i c e n s e d* I2C int e r fa c e s. The I2C
interfaces are both implemented as a full hardware master and
slave interface. The two I
document will describe only I
The two pins used for data transfer, SDA and SCL are
configured in a Wired-AND format that allows arbitration in a
multi-master system.
2
C bus peripheral’s addresses in the I2C bus system is
The I
programmed by the user. This ID can be modified at any time
while a transfer is not in progress. The user can configure the
interface to respond to four slave addresses.
The transfer sequence of a I
initiating a transfer by generating a START condition while the
bus is idle. The master transmits the address of the slave device
and the direction of the data transfer in the initial address
transfer. If the master does not loose arbitration and the slave
acknowledges then the data transfer is initiated. This continues
until the master issues a STOP condition and the bus becomes
idle.
2
C peripheral master and slave functionality are
The I
independent and may be active simultaneously.
A slave is activated when a transfer has been initiated on the
bus. If it is not being addressed it will remain inactive until
another transfer is initiated. This also allows a master device
which looses arbitration to respond as a slave in the same cycle.
Serial Clock Generation
The I2C master in the system generates the serial clock for a
transfer. The master channel can be configured to operate in
Fast mode (400 kHz) or Standard mode (100 kHz).
The bit-rate is defined in the I2C0DIVH and I2C0DIVL
MMRs as follow :
Bit Description
7
Master serial clock enable bit
Set by user to enable generation of the serial clock in master mode
Cleared by user to disable serial clock in master mode
6
Loop back enable bit
Set by user to internally connect the transition to the reception, to test user software
Cleared by user to operate in normal mode
5
START back-off disable bit
Set by user in multi-master mode. If losing arbitration the master will try to transmit again straight away
Cleared by user to enable START back-off. The master after losing arbitration will wait before trying to transmit again
4
Hardware general call enable (bit 3 must be set)
Set by user to enable hardware general call
Cleared by user to disable hardware general call
2
C interfaces being identical, this
2
C0 in detail.
2
C system consists of a master device
Table 48: I2C0CFG MMR Bit Descriptions
f
=
kserialcloc
Slave addresses
The registers I2C0ID0, I2C0ID1, I2C0ID2 and I2C0ID3
contain the device IDs. The device compares the four I2C0IDx
registers to the address byte. The 7 most significant bits of
either ID register must be identical to that of the 7 most
significant bits of the first address byte received to be correctly
addressed. The LSB of the ID registers, transfer direction bit, is
ignored in the process of address recognition.
2
I
C registers description
The I2C peripheral interface consists on 17 8-bit MMRs:
- I2C0CFG: configuration register described Table 48
- I2C0DIVH, I2C0DIVL: clock divider registers
- I2C0SRX, I2C0STX, and I2C0SSTA: respectively receive,
transmit and status register for the slave channel. The status
register is described Table 49.
- I2C0ID0, I2C0ID1, I2C0ID2 and I2C0ID3: slave address
device ID register
- I2C0MRX, I2C0MTX, and I2C0MSTA: respectively receive,
transmit and status register for the master channel. The status
register is described Table 50.
- I2C0CNT: Master receive data count register. If a master read
transfer sequence is initiated, the I2C0CNT register denotes
the number of bytes to be read from the slave device.
- I2C0ADR: master address byte register. The I2C0ADR value
is the address of the device the master wants to communicate
with, it will be transmitted automatically at the start of a
master transfer sequence if there is no valid data in the
I2C0MTX register when setting the master enable bit.
- I2C0ALT: hardware general call ID register, used in slave
mode
Rev. PrB | Page 59 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
3
2
1
0
Bit Description
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
General call enable bit
Set by user to address every device on the I
2
C bus
Cleared by user to operate in normal mode
Reserved
Master enable bit
Set by user to enable the master I
Cleared by user to disable the master I
2
C channel
2
C channel
Slave enable bit
Set by user to enable the slave I
2
C channel. A slave transfer sequence will be monitored for the device address in I2C0ID0,
I2C0ID1, I2C0ID2 and I2C0ID3. if the device address is recognised the part will participate in the slave transfer sequence
2
Cleared by user to disable the slave I
C channel
Table 4 9 : I2 C 0 SS TA M MR B i t De s cri p t i ons
Transmit FIFO flush
Set by user to flush the transmit FIFO
Cleared by user to operate in normal mode
Slave busy
Set automatically if the slave is busy
Cleared automatically
No ACK
Set if master asking for data and no data is available
Cleared automatically
Slave receive FIFO overflow
Set automatically if the slave receive FIFO is overflowing
Cleared automatically by reading I2C0SRX
Slave receive IRQ
Set after receiving data
Cleared automatically by reading the I2C0SRX register
Slave transmit IRQ
Set at the end of a transmission
Cleared automatically by writing to the I2C0STX register
Slave transmit FIFO underflow
Set automatically if the slave transmit FIFO is underflowing
Cleared automatically by writing to the I2C0STX register
Slave transmit FIFO empty
Set automatically if the slave transmit FIFO is empty
Cleared automatically by writing to the I2C0STX register
Bit Description
7
Transmit FIFO flush
Set by user to flush the transmit FIFO
Cleared by user to operate in normal mode
6
Master busy
Set automatically if the master is busy
Cleared automatically
5
Arbitration loss
Set in multi-master mode if another master has the bus
Cleared when the bus becomes available
Table 5 0 : I2 C 0 MS TA M MR B i t Des cri p t i ons
Rev. PrB | Page 60 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
4
3
2
1
0
*
Purchase of licensed I2C components of Analog Devices or one of its
sublicensed Associated Companies conveys a license for the purchaser
under the Philips I2C Patent Rights to use the ADuC702X in an I2C system,
provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as
defined by Philips.
No ACK
Set automatically, if the master receive FIFO is full, the master doesn’t acknowledge the data received
Cleared automatically
Master receive FIFO overflow
Set automatically if the master receive FIFO is overflowing
Cleared automatically by reading I2C0MRX
Master receive IRQ
Set after receiving data
Cleared automatically by reading the I2C0MRX register
Master transmit IRQ
Set at the end of a transmission
Cleared automatically by writing to the I2C0MTX register
Master TX FIFO empty
Set automatically if the master transmit FIFO is empty
Cleared automatically by writing to the I2C0MTX register
Rev. PrB | Page 61 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC ARRAY (PLA)
The ADuC702x integrates a fully Programmable Logic Array
(PLA) which consists of two independent but interconnected
PLA blocks. Each block consists of eight PLA elements, which
gives a total of 16 PLA elements.
A PLA element contains a two-input lookup table that can be
configured to generate any logic output function based on two
inputs and a flip-flop as represented in Figure 27 below.
0
1
A
2
LOOK-UP
TABLE
B
3
4
of block 0 is fed back to the input 0 of mux 0 of element 0 of
block 1.
PLA Block 0 PLA Block 1
Element Input Output Element Input Output
0 P1.0 P1.7 8 P3.0 P4.0
1 P1.1 P0.4 9 P3.1 P4.1
2 P1.2 P0.5 10 P3.2 P4.2
3 P1.3 P0.6 11 P3.3 P4.3
4 P1.4 P0.7 12 P3.4 P4.4
5 P1.5 P2.0 13 P3.5 P4.5
6 P1.6 P2.1 14 P3.6 P4.6
7 P0.0 P2.2 15 P3.7 P4.7
Table 51: element input/output
Figure 27: PLA element
In total, 30 GPIO pins are available on the ADuC702x for the
PLA. These include 16 input pins and 14 output pins. They need
to be configured in the GPxCON register as PLA pins before
using the PLA. Note that the comparator output is also included
as one of the 16 input pins.
The PLA is configured via a set of user MMRs and the output(s)
of the PLA can be routed to the internal interrupt system, to the
CONV
signal of the ADC, to a MMR or to any of the 16
START
PLA output pins.
The interconnection between the two blocks is supported by
connecting output of element 7 of block 1 fed back to the input
0 of mux 0 of element 0 of block 0, and the output of element 7
PLA MMRs interface
The PLA peripheral interface consists on 21 MMRs:
- PLAELMx: element0 to element 15 control registers,
configure the input and output mux of each element, select
the function in the lookup table and bypass/use the flip-flop.
- PLACLK: clock selection for the flip-flops of block 0 and
clock selection for the flip-flops of block 1
- PLAIRQ: enable IRQ0 or/and IRQ1 and select the source of
the IRQ
- PLAADC: PLA source fro ADC start conversion signal
- PLADIN: data input MMR for PLA
- PLADOUT: data output MMR for PLA. This register is
always updated.
A PLA tool is provided in the development system to easily
configure the PLA.
Table 52: PLAELMx MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description PLAELM0 PLAELM1 - 7 PLAELM8 PLAELM9-15
31-11
10-9
Reserved
Mux (0) control, select feedback from:
00 – element 15 element 0 element 7 element 8
01 – element 2 element 2 element 10 element 10
10 – element 4 element 4 element 12 element 12
11 – element 6 element 6 element 14 element 14
8-7
Mux (1) control, select feedback from:
00 – element 1 element 1 element 9 element 9
01 – element 3 element 3 element 11 element 11
10 – element 5 element 5 element 13 element 13
11 – element 7 element 7 element 15 element 15
6
Mux (2) control
Set by user to select the output of mux (1)
Cleared by user to select the bit value from PLADIN
5
Mux (3) control
Set by user to select the input pin of the particular element
Cleared by user to select the output of mux (0)
4-1
Look-up table control
0000 – 0
0001 – NOR
0010 – B AND NOT A
Rev. PrB | Page 62 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
0
Bit Description
7
6-4
3
2-0
Mux (4) control
Set by user to bypass the flip-flop
Cleared by user to select the flip-flop. Cleared by default
Reserved
Block1 clock source selection:
000 – GPIO clock on P0.5
001 – GPIO clock on P0.0
010 – GPIO clock on P0.7
011 – HCLK
100 – OCLK
101 - Timer 1 overflow
Other – Reserved
Reserved
Block0 clock source selection:
000 – GPIO clock on P0.5
001 – GPIO clock on P0.0
010 – GPIO clock on P0.7
011 – HCLK
100 – OCLK
101 - Timer 1 overflow
Other – Reserved
0011 – NOT A
0100 – A AND NOT B
0101 – NOT B
0110 – EXOR
0111 – NAND
1000 – AND
1001 – EXNOR
1010 – B
1011 – NOT A OR B
1100 – A
1101 – A OR NOT B
1110 – OR
1111 – 1
Table 53: PLACLK MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
15-13
12
11-8
7-5
4
Reserved
PLA IRQ1 enable bit
Set by user to enable IRQ1 output from PLA
Cleared by user to disable IRQ1 output from PLA
PLA IRQ1 source
0000 – PLA element 0
0001 – PLA element 1
…
1111 – PLA element 15
Reserved
PLA IRQ0 enable bit
Set by user to enable IRQ0 output from PLA
Cleared by user to disable IRQ0 output from PLA
Table 54: PLAIRQ MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 63 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
3-0
Bit Description
31-5
4
3-0
Bit Description
31-16
15-0
PLA IRQ0 source
0000 – PLA element 0
0001 – PLA element 1
…
1111 – PLA element 15
Table 55: PLAADC MMR Bit Descriptions
Reserved
ADC start conversion enable bit
Set by user to enable ADC start conversion from PLA
Cleared by user to disable ADC start conversion from PLA
ADC start conversion source
0000 – PLA element 0
0001 – PLA element 1
…
1111 – PLA element 15
Table 56: PLADIN MMR Bit Descriptions
Reserved
Input Bit to element 15-0
Bit Description
31-16
15-0
Reserved
Output Bit from element 15-0
Table 57: PLADOUT MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 64 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
PROCESSOR REFERENCE PERIPHERALS
INTERRUPT SYSTEM
There are 24 interrupt sources on the ADuC702x which are
controlled by the Interrupt Controller. Most interrupts are
generated from the on-chip peripherals like ADC, UART, etc.
and two additional interrupt sources are generated from
external interrupt request pins, XIRQ0 and XIRQ1. The
ARM7TDMI CPU core will only recognise interrupts as one of
two types, a normal interrupt request IRQ and a fast interrupt
request FIQ. All the interrupts can be masked separately.
The control and configuration of the interrupt system is
managed through nine interrupt-related registers, four
dedicated to IRQ, four dedicated to FIQ. An additional MMR is
used to select the programmed interrupt source. The bits in
each IRQ and FIQ registers represent the same interrupt source
as described in Table 58.
Table 58: IRQ/FIQ MMRs bit description
Bit Description
0 All interrupts OR’ed
1 SWI:
not used in IRQEN/CLR
and FIQEN/CLR
2 Timer 0
3 Timer 1
4 Wake Up timer – Timer 2
5 Watchdog timer – Timer 3
6 Flash control
7 ADC channel
8 PLL lock
9 I2C0 Slave
10 I2C0 Master
11 I2C1 Master
12 SPI Slave
13 SPI Master
14 UART
15 External IRQ0
16 Comparator
17 PSM
18 External IRQ1
19 PLA IRQ0
20 PLA IRQ1
21 External IRQ2
22 External IRQ3
23 PWM trip
24 PWM sync
IRQ
The IRQ is the exception signal to enter the IRQ mode of the
processor. It is used to service general purpose interrupt
handling of internal and external events.
The four 32-bit registers dedicated to IRQ are:
- IRQSIG, reflects the status of the different IRQ sources. If a
peripheral generate an IRQ signal, the corresponding bit in
the IRQSIG will be set, otherwise it is cleared. The IRQSIG
bits are cleared when the interrupt in the particular
peripheral is cleared. All IRQ sources can be masked in the
IRQEN MMR. IRQSIG is read-only.
- IRQEN, provides the value of the current enable mask. When
bit is set to 1, the source request is enabled to create an IRQ
exception. When bit is set to 0, the source request is disabled
or masked which will not
- IRQCLR, (write-only register) allows clearing the IRQEN
register in order to mask an interrupt source. Each bit set to 1
will clear the corresponding bit in the IRQEN register
without affecting the remaining bits. The pair of registers
IRQEN and IRQCLR allows independent manipulation of
the enable mask without requiring an atomic read-modifywrite.
- IRQSTA, (read-only register) provides the current enabled
IRQ source status. When set to 1 that source should generate
an active IRQ request to the ARM7TDMI core. There is no
priority encoder or interrupt vector generation. This function
is implemented in software in a common interrupt handler
routine. All 32 bits are logically OR’ed to create the IRQ signal
to the ARM7TDMI core.
create an IRQ exception.
FIQ
The FIQ (Fast Interrupt reQuest) is the exception signal to
enter the FIQ mode of the processor. It is provided to service
data transferor communication channel tasks with low latency.
The FIQ interface is identical to the IRQ interface providing the
second level interrupt (highest priority). Four 32-bit registers
are dedicated to FIQ, FIQSIG, FIQEN, FIQCLR and FIQSTA.
Bit 31 to 1 of FIQSTA are logically OR’ed to create the FIQ
signal to the core and the bit 0 of both the FIQ and IRQ
registers (FIQ source).
The logic for FIQEN and FIQCLR will not allow an interrupt
source to be enabled in both IRQ and FIQ masks. A bit set to ‘1’
in FIQEN will, as a side-effect, clear the same bit in IRQEN. A
bit set to ‘1’ in IRQEN will, as a side-effect, clear the same bit in
FIQEN. An interrupt source can be disabled in both IRQEN
and FIQEN masks.
Programmed interrupts
As the programmed interrupts are non-mask-able, they are
controlled by another register, SWICFG, which write into both
IRQSTA and IRQSIG registers or/and FIQSTA and FIQSIG
Rev. PrB | Page 65 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
registers at the same time.
programmed source interrupt.
The 32-bit register dedicated to software interrupt is SWICFG
described Table 59. This MMR allows the control of
Table 59: SWICFG MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-3
2
1
0
Note that any interrupt signal must be active for at least the
equivalent of the interrupt latency time, to be detected by the
interrupt controller and to be detected by user in the
IRQSTA/FIQSTA register.
Reserved
Programmed Interrupt-FIQ
Setting/clearing this bit correspond in setting/clearing bit 1 of FIQSTA and FIQSIG
Programmed Interrupt-IRQ
Setting/clearing this bit correspond in setting/clearing bit 1 of IRQSTA and IRQSIG
Reserved
Rev. PrB | Page 66 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
TIMERS
The ADuC702x has four general purpose Timer/Counters:
- Timer0,
- Timer1,
- Timer2 or Wake-up Timer,
- Timer3 or Watchdog Timer.
The four timers in their normal mode of operation can be
either free-running or periodic.
- In free-running mode the counter decrements/increments
from the maximum/minimum value until zero/full scale and
starts again at the maximum /minimum value.
- In periodic mode the counter decrements/increments from
the value in the Load Register(TxLD MMR,) until zero/full
scale and starts again at the value stored in the Load Register.
The value of a counter can be read at any time by accessing its
value register (TxVAL). Timers are started by writing in the
Control register of the corresponding timer (TxCON).
In normal mode, an IRQ is generated each time the value of the
counter reaches zero, if counting down, or full-scale, if count ing
up. An IRQ can be cleared by writing any value to Clear register
of the particular timer (TxCLRI).
Timer0 – RTOS timer
Timer0 is a general purpose 16-bit count-down timer with a
programmable prescaler. The prescaler source is the core clock
frequency and can be scaled by factors of 1, 16 or 256.
16-bitLoad
Core Clock 16-bit Down Co u nter
Timer0 interface consists in four MMRS:
- T0LD and T0VAL are 16-bit registers (bit 0 to 15) and hold
16-bit unsigned integers. T0VAL is read-only.
- T0CLRI is an 8-bit register. Writing any value to this register
will clear the interrupt
- T0CON is the configuration MMR described in Table 60
below
Prescaler
/1,16or256
Timer0 Value
Figure 28:timer 0 block diagram
Timer0IRQ
Table 60: T0CON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Name Description
31-8
7
Reserved
Timer0 enable bit:
Set by user to enable timer 0
Cleared by user to disable timer 0. by default.
6
Timer 0 mode:
Set by user to operate in periodic mode
Cleared by user to operate in free-running mode. Default mode
5-4
3-2
Reserved
Prescale:
00 Core clock / 1. value by default
01 Core clock / 16
10 Core clock / 256
11 Undefined. Equivalent to 00
1-0
Reserved
Timer1
Timer1 is a 32-bit general purpose timer, count-down or countup, with a programmable prescaler. The prescaler source can be
the 32kHz Oscillator, the core clock frequency, or an external
GPIO, P1.0 or P0.6. This source can be scaled by a factor of 1,
16, 256 or 32768.
The counter can be formatted as a standard 32-bit value or as
Hours:Minutes:Seconds:Hundreths.
Timer1 has a capture register (T1CAP), which can be triggered
by a selected IRQ source initial assertion. This feature can be
used to determine the assertion of an event with more accuracy
than the precision allowed by the RTOS timer at the time the
IRQ is serviced.
Timer 1 can be used to start ADC conversions as shown in the
block diagramFigure 29.
Timer1 interface consists in five MMRS:
- T1LD, T1VAL and T1CAP are 32-bit registers and hold 32-
Rev. PrB | Page 67 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
bit unsigned integers. T1VAL and T1CAP are read-only.
- T1CLRI is an 8-bit register. Writing any value to this register
will clear the timer1 interrupt.
- T1CON is the configuration MMR described in Table 61
below.
32-bitLoad
32kHz Oscillator
Core Clock Frequency
P0.6
P1.0
Prescaler
/1,16,256
or 32768
IRQ[31:0]
Figure 29:timer 1 block diagram
Table 61: T1CON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-18
17
Reserved
Event Select bit:
Set by user to enable time capture of an event
Cleared by user to disable time capture of an event
16-12
Event select range, 0 to 31
The events are as described in Ta b l e 5 8 . All events are offset by 2, i.e. event 2 in Tabl e 5 8 becomes event zero for the
purposes of timer 1.
11-9
Clock select:
000 Core clock
001 Oscillator 32.768kHz
010 P1.0 raising edge triggered
011 P0.6 raising edge triggered
8
Count up:
Set by user for timer 1 to count up
Cleared by user for timer 1 to count down. by default
7
Timer1 enable bit:
Set by user to enable timer 1
Cleared by user to disable timer 1. by default.
6
Timer 1 mode:
Set by user to operate in periodic mode
Cleared by user to operate in free-running mode. Default mode
5-4
Format:
00 Binary
01
Reserved
10 Hr:Min:Sec:Hundredths – 23 hours to 0 hour
11 Hr:Min:Sec:Hundredths – 255 hours to 0 hour
3-0
Prescale:
0000 Source clock / 1
0100 Source clock / 16
1000 Source clock / 256
1111 Source clock / 32768
Timer2 - Wake-Up Timer
Timer2 is a 32-bit wake-up timer, count-down or count-up,
with a programmable prescaler. It is clocked directly by the
32-bit Up/Down Counter
Timer1 Value
Capture
Timer1IRQ
ADC conversion
internal 32.768kHz oscillator. The wake-up timer will continue
to run when the core clock is disabled. The clock source can be
scaled by a factor of 1, 16, 256 or 32768.
Rev. PrB | Page 68 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
The counter can be formatted as plain 32-bit value or as
Hours:Minutes:Seconds:Hundreths.
Timer 2 can be used to start ADC conversions as shown in the
block diagram Figure 30..
Timer2 interface consists in four MMRS:
- T2LD and T2VAL are 32-bit registers and hold 32-bit
unsigned integers. T2VAL is read-only.
- T2CLRI is an 8-bit register. Writing any value to this register
will clear the timer2 interrupt.
- T2CON is the configuration MMR described in Table 62
below.
Table 62: T2CON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-9
8
Reserved
Count up:
Set by user for timer 2 to count up
Cleared by user for timer 2 to count down. by default
7
Timer2 enable bit:
Set by user to enable timer 2
Cleared by user to disable timer 2. by default.
6
Timer 2 mode:
Set by user to operate in periodic mode
Cleared by user to operate in free-running mode. Default mode
5-4
Format:
00 Binary
01
Reserved
10 Hr:Min:Sec:Hundredths – 23 hours to 0 hour
11 Hr:Min:Sec:Hundredths – 255 hours to 0 hour
3-0
Prescale:
0000 Source clock / 1 by default
0100 Source clock / 16
1000 Source clock / 256 expected for format 2 and 3
1111 Source clock / 32768
Timer3 - Watchdog Timer
32.768kHz
Oscillator
Prescaler
/1,16,256
or 32768
Figure 30:timer 2 block diagram
32-bitLoad
Timer2IRQ
32-bit Up/Down Counter
ADC conversion
Timer2 Value
16-bitLoad
Timer3 has two modes of operation, normal mode and
watchdog mode. The Watchdog timer is used to recover from
an illegal software state. Once enabled it requires periodic
servicing to prevent it from forcing a reset of the processor.
Normal mode:
The Timer3 in normal mode is identical to Timer0 except for
the clock source and the count-up functionality. The clock
source is 32kHz from the PLL and can be scaled by a factor of 1,
16 or 256.
Rev. PrB | Page 69 of 80
32.768kHz
Prescaler
/1,16or256
Figure 31:timer 3 block diagram
16-bit Up/Down Counter
Timer3 Value
Watchdog Reset
Timer3IRQ
Watchdog mode:
Watchdog mode is entered by setting bit 5 in T3CON MMR.
Timer3 decrements from the value present in T3LD Register
until zero. T3LD is used as timeout. The timeout can be 512
seconds maximum, using the maximum prescaler, /256, fullscale in T3LD. Timer3 is clocked by the internal 32kHZ crystal
when operating in the Watchdog mode.
If the timer reaches 0, a reset or an interrupt occurs, depending
on bit 1 in T3CON register. To avoid reset or interrupt, any

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
value must be written to T3ICLR before the expiration period.
This reloads the counter with T3LD and begins a new timeout
period.
As soon watchdog mode is entered, T3LD and T3CON are
write-protected. These two registers can not be modified until a
reset clears the watchdog enable bit and causes Timer3 to exit
watchdog mode.
Timer3 interface:
It consists in four MMRS:
- T3LD and T3VAL are 16-bit registers (bit 0 to 15) and hold
16-bit unsigned integers. T0VAL is read-only.
- T3CLRI is an 8-bit register. Writing any value to this register
will clear the timer3 interrupt in normal mode or will reset a
new timeout period in watchdog mode.
- T3CON is the configuration MMR described in Table 63.
initial value or seed is written to T3ICLR before entering
watchdog mode. After entering watchdog mode, a write to
T3ICLR must match this expected value. If it matches, the
LFSR is advanced to the next state when the counter reload
happens. If it fails to match the expected state, reset is
immediately generated, even if the count has not yet expired.
The value 0x00 should not be used as an initial seed due to the
properties of the polynomial. The value 0x00 will always be
guaranteed to force an immediate reset. The value of the LFSR
can not be read; it must be tracked/generated in software.
DQ
Clock
DQ
6
7
DQ
5
Figure 32: 8-bit LFSR
DQ
3
4
DQ1DQ2DQ
DQ
0
Example of sequence:
Secure bit clear (watchdog mode only):
The secure clear bit is provided for a higher level of protection.
When set, a specific sequential value must be written to
T3ICLR to avoid a watchdog reset. The value is a sequence
generated by the 8-bit LFSR (Linear Feedback Shift Register)
polynomial = X8 + X6 + X5 + X + 1 as shown Figure 32. The
Table 63: T3CON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
31-9
8
Reserved
Count up:
Set by user for timer 3 to count up
Cleared by user for timer 3 to count down. by default
7
Timer3 enable bit:
Set by user to enable timer 3
Cleared by user to disable timer 3. by default.
6
Timer 3 mode:
Set by user to operate in periodic mode
Cleared by user to operate in free-running mode. Default mode
5
Watchdog mode enable bit:
Set by user to enable watchdog mode
Cleared by user to disable watchdog mode. by default.
4
Secure Clear bit:
Set by user to use the secure clear option
Cleared by user to disable the secure clear option. by default.
3-2
Prescale:
00 Source clock / 1 by default
01 Source clock / 16
10 Source clock / 256
11 Undefined. Equivalent to 00
1
Watchdog IRQ option bit:
Set by user to produce an IRQ instead of a reset when the watchdog reaches 0
Cleared by user to disable the IRQ option.
0
Reserved
1) entered initial seed in T3ICLR, 0xAA, before starting timer 3
in watchdog mode
2) enter 0xAA in T3ICLR, timer 3 is reloaded
3) enter 0x37 in T3ICLR, timer 3 is reloaded
4) enter 0x6E in T3ICLR, timer 3 is reloaded
5) enter 0x66. 0xDC was expected, the watchdog reset the chip.
Rev. PrB | Page 70 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
External Memory Interfacing
The only ADuC702x models which feature an external memory
interface are the ADuC7026 and ADuC7027. The external
memory interface requires a larger number of pins, this is why it
is only available on larger pin count package.
documented in the table below.
Address Start Address End Contents
0x10000000 0x1001FFFF External Memory 0
The pins required for interfacing to an external memory are:
Pin Function
AD[15:0} Address/Data Bus
A16 Extended Addressing
MS[3:0} Memory Select Pins
WR Write Strobe
RS Read Strobe
AE Address Latch Enable
BHE, BLE Byte Write Capability
There are four external memory regions available. These are
Table 64: XMxCON MMR Bit Descriptions
Bit Description
1
0
Selects between 8 and 16 bit data bus width.
Set by the user to select a 16 bit data bus
Cleared by the user to select an 8 bit data bus.
Enables Memory Region
Set by the user to enable memory region
Cleared by the user to disable the memory region
0x20000000 0x2001FFFF External Memory 1
0x30000000 0x3001FFFF External Memory 2
0x40000000 0x4001FFFF External Memory 3
Each external memory region can be controlled through the
following three MMRs
XMCFG is set to 1 to enable external memory access. This
must be set to 1 before any port pins will function as external
memory access pins. The port pins must also be individually
enabled via the GPxCON MMR
XMxCON are registers that enable/disable a memory region.
This register also controls the data bus width of the memory
region.
XMxPAR are registers that define the protocol used for
accessing the external memory for each memory region.
Bit Description
15
14-12
11
10
9
Enable Byte write strobe
Set by the user gates the BHE and BLE outputs with the WR output. This allows byte write capability without using
Number of wait states on the Address latch enable strobe.
Enable dynamic addressing
Set by the user to enable 16 bit addressing mode
Cleared by the user to enable 8 bit addressing mode
Extra address hold time
Set by the user to disable extra hold time
Cleared by the user to enable one clock cycle of hold on address in read and write
Extra bus transition time on Read
Set by the user to disable extra bus transition time
Table 65: XMxPAR MMR Bit Descriptions
Rev. PrB | Page 71 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
Cleared by the user to enable one extra clock before and after the Read Strobe, RS
8
7-4
3-0
Extra bus transition time on Write
Set by the user to disable extra bus transition time
Cleared by the user to enable one extra clock before and after the Write Strobe, WS
Number of Write Wait States
Set by the user to select the number of wait states added to the length of the WS pulse.
0x0 is 1clock
0xF is 16 clock cycles (default value)
Number of Read Wait States
Set by the user to select the number of wait states added to the length of the RS pulse.
0x0 is 1clock
0xF is 16 clock cycles (default value)
EPROM
A16
D0-D15
A0:15
CS
WE
OE
ADuC7026
ADuC7027
A16
AD15:0
MS0
MS1
WS
AE
RS
LATCH
RAM
A16
D0-D15
A0:15
CS
WE
OE
Figure 33 Interfacing to external EPROM/RAM
Rev. PrB | Page 72 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
MCLK
AD 16:0
MSx
AE
RS
WS
ADDRE S S
Figure 34: External Memory Read Cycle
DATA
MCLK
AD 16:0
MSx
AE
RS
WS
ADDRE SS
Figure 35: External Memory Read cycle with Address hold and Bus turn cycles
DATA
Rev. PrB | Page 73 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
MCLK
AD 16:0
MSx
AE
RS
WS
ADDRE SS
Figure 36: External Memory Write Cycle with address and write hold cycles
MCLK
DATA
AD 16:0
MSx
AE
RS
WS
ADDRESS
Figure 37: External Memory Write Cycle with wait states
DATA
Rev. PrB | Page 74 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
ANA
A
Y
DD pin with trace lengths as short as possible. Connect the
ADUC702X HARDWARE DESIGN
CONSIDERATIONS
POWER SUPPLIES
The ADuC702X operational power supply voltage range is 2.7V
to 3.6V. Separate analog and digital power supply pins (AV
and IOVDD, respectively) allow AVDD to be kept relatively free
of noisy digital signals often present on the system IOV
In this mode, the part can also operate with split supplies; that
is, using different voltage supply levels for each supply. For
example, this means that the system can be designed to operate
with a IOV
DD voltage level of 3.3 V while the AVDD level can be
at 3 V, or vice versa if required. A typical split supply
configuration is shown in Figure 38.
DIGITAL SUPPLY
10µF
+
-
0.1µF
ADuC7026
AV
IOV
DD
IOGND
Figure 38: External dual supply connections
DD
DACV
DD
GND
REF
DACGND
AGND
REFGND
LOG SUPPLY
10µF
As an alternative to providing two separate power supplies, the
user can help keep AV
and/or ferrite bead between it and IOV
DD separately to ground. An example of this configuration is
AV
DD quiet by placing a small series resistor
DD, and then decoupling
shown in Figure 39. With this configuration other analog
circuitry (such as op amps, voltage reference, and so on) can be
powered from the AV
DIGIT
LSUPPL
+
-
10uF
0.1uF
Figure 39: external single supply connections
DD supply line as well.
BEAD
ADuC7026
AV
IOV
IOGND
DD
DD
DACV
GND
REF
DACGND
AGND
REFGND
DD
1.6V
10uF
Notice that in both Figure 38 and Figure 39, a large value (10
µF) reservoir capacitor sits on IOV
DD and a separate 10 µF
capacitor sits on AVDD. Also, local small-value (0.1 µF)
capacitors are located at each AV
and IOVDD pin of the chip.
DD
As per standard design practice, be sure to include all of these
capacitors, and ensure the smaller capacitors are close to each
DD line.
+
-
0.1µF
0.1uF
DD
AV
ground terminal of each of these capacitors directly to the
underlying ground plane. Finally, it should also be noted that,
at all times, the analog and digital ground pins on the
ADuC702x must be referenced to the same system ground
reference point.
Linear Voltage regulator
The ADuC702x requires a single 3.3V supply but the core logic
requires a 2.5V supply. An on-chip linear regulator generates the
2.5V from IOV
for the core logic. LVDD pin 21 is the 2.5V
DD
supply for the core logic. An external compensation capacitor of
0.47 µF must be connected between LV
and DGND (as close
DD
as possible to these pins) to act as a tank of charge as shown
Figure 40.
ADuC7026
LV
0.47µF
DD
DGND
Figure 40: voltage regulator connections
The LVDD pin should not be used for any other chip. It is also
recommended that the IOV
has excellent power supply
DD
decoupling this to help improving line regulation performance
of the on-chip voltage regulator.
GROUNDING AND BOARD LAYOUT
RECOMMENDATIONS
As with all high resolution data converters, special attention
must be paid to grounding and PC board layout of ADuC702xbased designs in order to achieve optimum performance from
the ADCs and DAC.
Although the ADuC702x has separate pins for analog and
digital ground (AGND and IOGND), the user must not tie
these to two separate ground planes unless the two ground
planes are connected together very close to the ADuC702x, as
illustrated in the simplified example of Figure 41a. In systems
where digital and analog ground planes are connected together
somewhere else (at the system’s power supply for example),
they cannot be connected again near the ADuC702x since a
ground loop would result. In these cases, tie the ADuC702x’s
AGND and IOGND Pins all to the analog ground plane, as
illustrated in Figure 41b. In systems with only one ground
plane, ensure that the digital and analog components are
physically separated onto separate halves of the board such that
digital return currents do not flow near analog circuitry and
vice versa. The ADuC702x can then be placed between the
Rev. PrB | Page 75 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
digital and analog sections, as illustrated in Figure 41c.
a.
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS HERE
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS HERE
XCLKI and XCLKO and connect a capacitor from each pin to
ground as shown Figure 42 This crystal allows the PLL to lock
correctly to give a frequency of 45.088MHz. If no external
crystal is present, the internal oscillator will be used to give a
frequency of 45.088MHz ±5% typically.
DGND
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS
HERE
DGNDAGND
PLACE DIGITAL
COMPONENTS
HERE
b.
c.
AGND
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS
HERE
PLACE ANALOG
COMPONENTS
HERE
GND
Figure 41:. System grounding schemes
In all of these scenarios, and in more complicated real-life
applications, keep in mind the flow of current from the supplies
and back to ground. Make sure the return paths for all currents
are as close as possible to the paths the currents took to reach
their destinations. For example, do not power components on
the analog side of Figure 41b with IOV
return currents from IOV
DD to flow through AGND. Also, try
DD since that would force
to avoid digital currents flowing under analog circuitry, which
could happen if the user placed a noisy digital chip on the left
half of the board in Figure 41c. Whenever possible, avoid large
discontinuities in the ground plane(s) (such as are formed by a
long trace on the same layer), since they force return signals to
travel a longer path. And of course, make all connections to the
ground plane directly, with little or no trace separating the pin
from its via to ground.
If the user plans to connect fast logic signals (rise/fall time < 5
ns) to any of the ADuC702x’s digital inputs, add a series
resistor to each relevant line to keep rise and fall times longer
than 5 ns at the ADuC702x input pins. A value of 100Ω or
200Ω is usually sufficient to prevent high speed signals from
coupling capacitively into the ADuC702x and affecting the
accuracy of ADC conversions.
ADuC7026
XCLKO
12pF
12pF
32.768kHz
XCLKI
TO INTERNAL
PLL
Figure 42: external parallel resonant crystal connections
To use an external source clock input instead of the PLL, bit 1
and bit 0 of PLLCON must be modified. The external clock
uses pin 17, XCLK.
ADuC7026
XCLKI
EXTERNAL
CLOCK
SOURCE
XCLK
TO FREQUENCY
DIVIDER
Figure 43:connecting an external clock source
Whether using the internal PLL or an external clock source, the
ADuC702x’s specified operational clock speed range is 50kHz
to 20MHz to ensure correct operation of the analog peripherals
and Flash/EE.
POWER-ON RESET OPERATION
An internal POR (Power-On Reset) is implemented on the
ADuC702x. For LV
the ADuC702x in reset. As LV
timer will time out for typically 128 ms before the part is
released from reset. The user must ensure that the power
supply IOV
DD has reached a stable 2.7 V minimum level by this
time. Likewise on power-down, the internal POR will hold the
ADuC702x in reset until LV
Figure 44 illustrates the operation of the internal POR in detail.
DD below 1.98 V, the internal POR will hold
DD rises above 1.98 V, an internal
DD has dropped below 1.98V.
CLOCK OSCILLATOR
The clock source for the ADuC702x can be generated by the
internal PLL or by an external clock input. To use the internal
PLL, connect a 32.768kHz parallel resonant crystal between
Rev. PrB | Page 76 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
3.3
V
IOV
DD
1.98V TYP
LV
DD
POR
MRST
Figure 44:. ADuC7024/ADuC7025 Internal Power-on-Reset operation
128msTYP
0.12ms TYP
TYPICAL SYSEM CONFIGURATION
A typical ADuC7024/ADuC7025 configuration is shown in Figure 45. It summarizes some of the hardware considerations discussed in
the previous paragraphs.
2.5V
1.98V TYP
Figure 45:. Typical System Configuration
Rev. PrB | Page 77 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
An entry level, low cost development system is available for the
ADuC702X family. This system consists of the following PCbased (Windows® compatible) hardware and software
development tools:
Hardware:
- ADuC702x Evaluation board
- Serial Port programming cable
- JTAG emulator
Software:
- Integrated Development Environment, incorporating
assembler, compiler and non intrusive JTAG-based
debugger
- Serial Downloader software
- Example Code
Miscellaneous:
- CD-ROM Documentation
IN-CIRCUIT SERIAL DOWNLOADER
The Serial Downloader is a Windows application that allows
the user to serially download an assembled program to the onchip program FLASH/EE memory via the serial port on a
standard PC.
Rev. PrB | Page 78 of 80

Preliminary Technical Data ADuC702x Series
c
k
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
a
40-LeadLeadFrame ChipScale Pa
6x 6 mm Body
Dimensions shown in millimeters
(CP-40)
age[LFCSP]
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1.00
0.85
0.80
128MAX
SEATING
PLANE
6.00
BSCSQ
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VJ JD-2
5.75
BSCSQ
0.20 REF
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.60 MAX
0.50
BSC
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.08
0.60 MAX
31
30
EXPOSED
(BOTTOM VIEW)
21
20
PAD
4.50
REF
PIN 1
40
11
INDICATOR
1
4.25
4.10 SQ
3.95
10
0.25 MIN
Figure 6. 40-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP] (CP-40)—Dimensions shown in millimetres
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
VIEW
64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP]
9.00
TOP
9 x 9 mm Body
8.75
BSC SQ
(CP-64-1)
0.60 MAX
48
Dimensions shown in millimeters
0.60 MAX
49
EXPOSED PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
0.30
0.25
0.18
64
1
PIN 1
INDICATOR
4.85
4.70 SQ
4.55
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
0.45
0.40
0.35
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VMMD
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
33
32
7.50
REF
16
17
Figure 46. 64-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP] (CP-64-1)—Dimensions shown in millimetres
Rev. 0 | Page 79 of 80

ADuC702x Series Preliminary Technical Data
(
)
PR04955-0-8/04(PrB)
0.063 (1.60) MAX
0.006(0.15)
0.002(0.05)
0.47(12.0)
BSC
0.39(10.0) BSC
0.024 ± 0.006
(0.60 ± 0.15)
12
TYP
o
1
4964
48
SEATING
PLANE
TOP VIEW
o
0
3.5o±3.5
16
17
o
0.02 (0.50)
0.0087 ± 0.002
BSC
33
32
(0.22 ± 0.05)
Figure 47. 64-Lead LQF Package [LQFP] (S-64)—Dimensions shown in millimetres
0.559 (14.20)
0.543 (13.80)
0.480 (12.20)
0.465 (11.80)
TOP V IE W
(PINS DOW N )
6180
60
)
)
)
0
0
0
0
8
2
2
8
.
.
.
.
3
2
4
1
1
1
1
1
(
(
(
0
3
5
3
8
4
6
4
4
5
4
5
.
.
.
.
0
0
0
0
0.030 (0.75)
0.020 (0.50)
SEATING
PLANE
0.063 (1.60)
MAX
1
0.003
(0.08)
MAX
0.006 (0.15)
0.002 (0.05)
0.057 (1.45)
0.053 (1.35)
20
21
0.019 (0.50) BSC
0.011 (0.27)
0.007 (0.17)
40
41
Figure 2. 80-Lead LQF Package [LQFP] (S-80)—Dimensions shown in millimetres
Rev. PrB | Page 80 of 80
 Loading...
Loading...