4 Channel High Current LED Driver with
Preliminary Technical Data
FEATURES
Highly integrated feature set gives a high brightness LED
driver solution with minimal external components.
Four current sink channels with adjustable currents from 0 to
500 mA.
DC LED dimming for noiseless operation.
2% (max) matching between LED channels.
5% (max) LED current accuracy.
Operates from Vin of 7.5 V to 30 V. Higher voltages easily
accomplished with small external circuit.
Operates with LED anode supply voltages up to 100 Vdc.
Feedback output controls external power source for optimal
efficiency and safety.
Multiple ADP8140 ICs can be operated in parallel and control
one power supply.
Secondary side control of isolated power supplies without
need of a TL431.
Dedicated DIM pin for output current reduction.
Easy connection of a temperature thermister or light sensor.
Provides robust protection of the entire system:
- Power supply overvoltage protection
- LED Over temperature protection
- LED Short protection
- LED Open protection
- IC Over temperature protection
- Shorted ISET protection
- Open ISET and EN protection
Standby mode for low current consumption
Fault indicator output
Available in a thermally enhanced LFCSP package (4x4 mm)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADP8140 provides high current control of up to four LED
drivers. Each driver can sink up to 500 mA. The sink current
is programmed for all four drivers with one external resistor.
The device features a feedback output which controls an
external power supply for optimal efficiency. The ADP8140
also protects the LEDs, power supply, and itself against thermal
Adaptable Power Control
ADP8140
APPLICATIONS
High brightness LED lighting
Large format LED backlighting
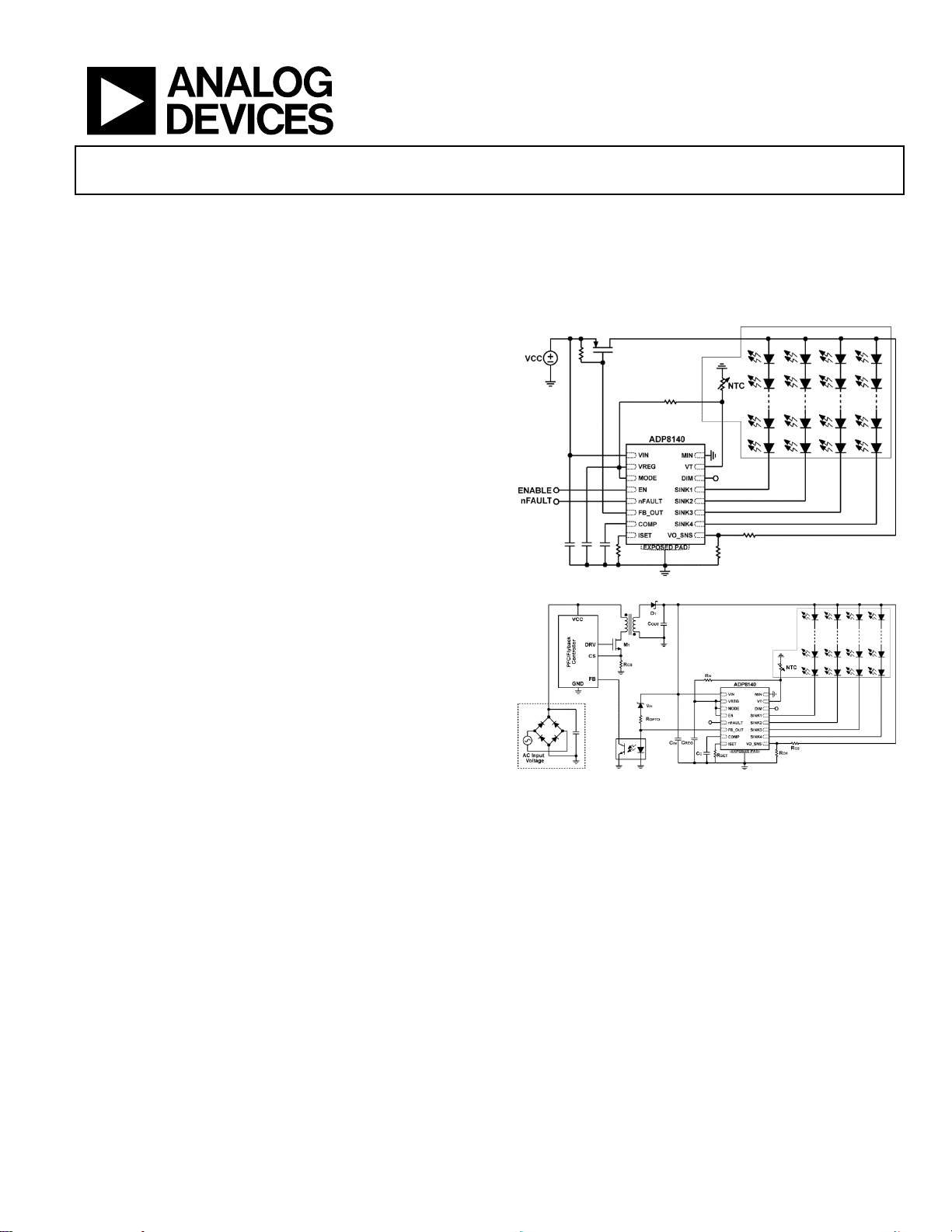
TYPICAL OPERATING CIRCUITS
Figure 1. ADP8140 used with Shunt Regulator
Figure 2. ADP8140 used as Secondary Side Controller
events, short circuits, overvoltages, and LED open circuits.
Multiple ADP8140 ICs are easily connected in parallel to drive
additional LED strings, or higher current LEDs. The ADP8140
is available in a small, thermally enhanced, LFCSP (lead frame
chip scale package).
Rev. PrA
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 © 2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADP8140 Preliminary Technical Data
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Typical Operating CircuitS .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History .......................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 6
Maximum Temperature Ranges ................................................. 6
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 6
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 6
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 7
Theory of Operation ........................................................................ 8
Current Sinks ................................................................................ 9
Power Control Operation ............................................................ 9
MODE Pin Operation .................................................................. 9
Error Amplifier Power Control .................................................. 9
Low gain Buffer Power Control .................................................. 9
Using Multiple ADP8140 ICs ................................................... 10
Reducing the LED Current with the DIM Pin ....................... 10
Implementing LED Thermal Protection ................................. 10
Effect of LED Vf Mismatch ....................................................... 11
Managing the ADP8140’s Power Dissipation ......................... 12
ADP8140 Fault Protections ...................................................... 13
Startup Sequence ........................................................................ 13
Die Temperature Protection ..................................................... 14
Overvoltage Protection .............................................................. 14
Operating the ADP8140 From Higher Input Voltages ......... 14
Layout Guidelines....................................................................... 15
ADP8140 + 24 Vdc Input .......................................................... 16
ADP8140 Secondary Side Control Design example .............. 16
ADP8140 and 24Vdc Rail Design Example ............................ 17
Multiple ADP8140s With a 24Vdc Rail Design Example ..... 17
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 18
Ordering Guide ............................................................................... 18
Rev. PrA | Page 2 of 18
ADP8140 Preliminary Technical Data
SPECIFICATIONS
VIN = 12 V, EN=3.0V. Typical values are at TJ = 25°C and are not guaranteed. Minimum and maximum limits are guaranteed from TJ =
−40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
SUPPLY
Input Voltage
Operating Range VIN 7.5 30.0 V
Undervoltage Lockout V
UVLO Hysteresis V
Quiescent Current IQ
During Standby I
During Operation I
During Operation I
During Operation I
REG Output
REG Output Voltage VREG VIN=7.5, 12, 24 V, IREG=1 mA 2.85 3.0 3.15 V
REG Source Current IREG VIN=7.5, 12, 24 V 15 mA
REG Load Regulation VREG1 VIN=7.5, 12, 24 V, IREG=0.1 mA to 15
FEEDBACK OUTPUT
FB_OUT EA Accuracy VEA 430 450 470 mV
FB_OUT NMOS Pulldown FB_PD SINKx=0V, FB_OUT = 5.0V 12.0 15.0 18.0 mA
FB_OUT Fault Current FB_FC Fault activated, FB_OUT = 3.0 V. TBD 1 µA
Amplifier transconductance COMPgm TBD 50 TBD µmho
Transconductance amplifier
output sink/source current
Transconductance amplifier
output sink/source current
Transconductance amplifier
output resistance
Low gain EA Gbuff Gain in buffer mode
Low gain BW Low gain buffer mode 100 kHz
ISET
ISET Accuracy 500mA ILED
ISET Accuracy 350mA ILED
ISET Accuracy 100mA ILED
ISET shorted current ISET = GND TBD 570 TBD mA
ISET open current ISET = OPEN 13 TBD mA
CURRENT SINKS
Current sink headroom
voltage at max current
Sink matching at max current I
7.3 7.5 V
UVLO
150 mV
UVLO_HYS
EN = 0 V, all SINKx Zener clamps and
Q(STBY)
TBD 250 A
VREG remain active, IREG=0µA
EN = 3 V, VIN=7.5 V TBD 8.0 mA
Q(ACTIVE1)
EN = 3 V, VIN=12 V TBD 8.0 mA
Q(ACTIVE2)
EN = 3 V, VIN=28 V TBD 8.0 mA
Q(ACTIVE3)
TBD TBD V/mA
mA
COMP
COMP
COMP pin output source current TBD 500 TBD µA
SOURCE
COMP pin output sink current TBD 2.0 TBD mA
SINK
COMPRO 20 MΩ
-5% 4.0 +5%
Gbuff=Vcomp/MIN(Vsinkx)
RSET=5.11 kΩ, SINK
500
RSET=7.32 kΩ, SINK
350
RSET=25.5 kΩ, SINK
100
V
ILED = 95% * ILED
HR_500
Matching = (MAX ISINK – MIN
MATCH1
=450mV -5% 500 +5% mA
1:4
=450mV -5% 350 +5% mA
1:4
=450mV -5% 100 +5% mA
1:4
VEA
500
mV
MIN
TBD 2 %
ISINK)/(MAX ISINK + MIN ISINK)*100
Rev. PrA | Page 3 of 18
ADP8140 Preliminary Technical Data
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
Sink matching at mid current I
SINKx leakage current I
Channel Overvoltage
Threshold
Channel Overvoltage
Hysteresis
Channel Clamp (low) Current
Channel Clamp (high)
Threshold
Channel Clamp (high)
Hysteresis
Channel Clamp (high)
Current
INPUT CONTROLS
Input Threshold (low) VIL EN 0.5 V
Input Threshold (high) VIH EN 1.2 V
EN input resistance REN EN=1.2 V 400 k Ω
Mode pin pullup current IM 0V<Vmode<Vreg 18 20 22 µA
Mode Threshold 1 30.1k VM1 Threshold for increasing mode voltage
Mode Threshold 2 49.9k VM2 Threshold for increasing mode voltage
Mode Threshold 3 VM3 Threshold for increasing mode voltage
LED Scaling Controls
DIM and VT limit voltage VT
Dimming Accuracy VT = 1 V, ILED=350 mA.
DIM pin Frequency Range 140 Hz 40 kHz
MIN comparator hysteresis VMIN
THERMAL FOLDBACK (internal)
Thermal Foldback Threshold TFB
Thermal Shutdown
Hysteresis
FAU LT D ETEC T I O N
Fault Threshold FAULT
VO_SNS Hysteresis VOSNS
Fault Threshold FAULT
Fault Hysteresis FAULT
Fault Filter t
V
bias current I
O_SNS
Matching = (MAX ISINK – MIN
MATCH2
TBD 2 %
ISINK)/(MAX ISINK + MIN ISINK)*100
SINKx pin = 4V. 100 TBD µA
SINK(LKG)
CH
Threshold on SINKx to trigger CH_OVP
CLMP_LO
TBD 5.5 TBD V
fault and Channel Clamp (low)
CH
I
CLMP_LO
CH
Hysteresis after CH
CLMP_HYS
is triggered. TBD 1.0 TBD V
CLMP_LO
Channel pulldown current when
SINKx> CH
Threshold on SINKx to trigger Channel
CLMP_HI
CLMP_LO
-20% ISET +20% mA
13.5 15.0 16.5 V
Clamp (high)
CH
I
CLMP_HI
Hysteresis after CH
CLMP_HYS
is triggered. TBD 2.8 TBD V
CLMP_HI
Channel pulldown current when
SINKx> CH
CLMP_HI
-20% 510 +20% mA
TBD 0.45 TBD V
to enter DC Buffer operation.
TBD 0.75 TBD V
to enter PWM Buffer operation.
TBD 1.25 TBD V
to enter PWM EA operation.
VT (and DIM if MODE=GND) voltage to
LIMIT
TBD 2.0 TBD V
produce 100% Iout
TBD 175 TBD mA
DIM=1V, MODE=GND, ILED=350mA.
DIM=50%, 32kHz, MODE=VREG.
70 mV
HYS
TBD 130 TBD °C
THRES
TSD
TBD 20 TBD °C
HYS
Threshold for VO_SNS comparator -2% 1.2 +2% V
THRESH
Hysteresis for VO_SNS comparator 50 mV
HYS
Threshold for nFAULT comparator -5% 1.2 +5% V
THRESH
Hysteresis for nFAULT comparator 100 mV
HYS
Vo_sns and nFAULT shutdown noise
FAULT
10 Us
filter
0 TBD µA
VOSNS
Rev. PrA | Page 4 of 18
ADP8140 Preliminary Technical Data
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
nFAULT pulldown nFAULTPD Fault activated, nFAULT=0.5V TBD 3.0 TBD mA
SINK Fault Threshold SFD
Threshold to remove a sink from the
THRESH
FB loop after a CH_OVP or VOUT_OVP
fault
TBD 75 100 mV
Rev. PrA | Page 5 of 18
ADP8140 Preliminary Technical Data
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
VIN, FB_OUT to GND −0.3 V to +31 V
SINK1,2,3,4 to GND −0.3 V to +21 V
VREG, COMP, ISET, VMIN to GND −0.3 V to +3.6 V
DIM, VT to GND −0.3 V to +5.0 V
All other pins to GND −0.3 V to +6.0 V
Operating Ambient Temperature Range –40°C to +105°C1
Operating Junction Temperature Range –40°C to +125°C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Storage Temperature Range –45°C to +150°C
Soldering Conditions JEDEC J-STD-020
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)
Human Body Model (HBM) ± 2.0 kV
Machine Model (MM) ± TBD V
Charged Device Model (CDM) ± TBD kV
1
The maximum operating junction temperature (T
maximum operating ambient temperature (T
Temperature Ranges section for more information.
) supersedes the
J(MAX)
). See the Maximum
A(MAX)
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Absolute maximum ratings apply individually only, not in
combination. Unless otherwise specified, all voltages are
referenced to GND.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA (junction to air) is specified for the worst-case conditions,
that is, a device soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount
packages. The θ
and θJC (junction to case) are determined
JA
according to JESD51-9 on a 4-layer printed circuit board (PCB)
with natural convection cooling. The LFCSP exposed pad must
be soldered to GND.
Table 3. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA θJB θ
Unit
JC
LFCSP 33.2 12.4 2.4 °C/W
ESD CAUTION
MAXIMUM TEMPERATURE RANGES
The maximum operating junction temperature (T
supersedes the maximum operating ambient temperature
(T
). Therefore, in situations where the ADP8866 is
A(MAX)
exposed to poor thermal resistance and a high power
dissipation (P
), the maximum ambient temperature may need
D
to be derated. In these cases, the ambient temperature
maximum can be calculated with the following equation:
T
A(MAX)
= T
J(MAX)
− (θJA × P
D(MAX)
).
J(MAX)
)
Rev. PrA | Page 6 of 18
 Loading...
Loading...