600 mA/1000 mA, 2.5 MHz Buck-Boost
2.3V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES FEATURES
1 mm height profile 1 mm height profile
Compact PCB footprint Compact PCB footprint
Seamless transition between modes Seamless transition between modes
38 A typical quiescent current 38 A typical quiescent current
2.5 MHz operation enables 1 µH inductor 2.5 MHz operation enables 1 µH inductor
Input voltage: 2.3 V to 5.5 V Input voltage: 2.3 V to 5.5 V
Fixed output voltage: 2.8 V to 5.0 V Fixed output voltage: 2.8 V to 5.0 V
600 mA (ADP2503) and 1000 mA (ADP2504) output options 600 mA (ADP2503) and 1000 mA (ADP2504) output options
Boost converter configuration with load disconnect Boost converter configuration with load disconnect
SYNC pin with three different modes: SYNC pin with three different modes:
Power save mode (PSM) for improved light load efficiency Power save mode (PSM) for improved light load efficiency
Forced fixed frequency operation mode Forced fixed frequency operation mode
Synchronization with external clock Synchronization with external clock
Internal compensation Internal compensation
Soft start Soft start
Enable/shutdown logic input Enable/shutdown logic input
Overtemperature protection Overtemperature protection
Short-circuit protection Short-circuit protection
Undervoltage lockout protection Undervoltage lockout protection
Small 10-lead 3 mm × 3 mm LFCSP/QFN package Small 10-lead 3 mm × 3 mm LFCSP/QFN package
APPLICATIONS APPLICATIONS
Wireless handsets Wireless handsets
Digital cameras/portable audio players Digital cameras/portable audio players
Miniature hard disk power supplies Miniature hard disk power supplies
USB powered devices USB powered devices
DC-to-DC Converters
ADP2503/ADP2504
GENERAL DESCRIPTION GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADP2503/ADP2504 are high efficiency, low quiescent current
The ADP2503/ADP2504 are high efficiency, low quiescent current
step-up/step-down dc-to-dc converters that can operate at input
step-up/step-down dc-to-dc converters that can operate at input
voltages greater than, less than, or equal to the regulated output
voltages greater than, less than, or equal to the regulated output
voltage. The power switches and synchronous rectifiers are
voltage. The power switches and synchronous rectifiers are
internal to minimize external part count. At high load currents,
internal to minimize external part count. At high load currents,
the ADP2503/ADP2504 use a current-mode, fixed frequency
the ADP2503/ADP2504 use a current-mode, fixed frequency
pulse-width modulation (PWM) control scheme for optimal
pulse-width modulation (PWM) control scheme for optimal
stability and transient response. To ensure the longest battery life
stability and transient response. To ensure the longest battery life
in portable applications, the ADP2503/ADP2504 have an
in portable applications, the ADP2503/ADP2504 have an
optional power save mode that reduces the switching frequency
optional power save mode that reduces the switching frequency
under light load conditions. For wireless and other low noise
under light load conditions. For wireless and other low noise
applications where variable frequency power save mode may
applications where variable frequency power save mode may
cause interference, the logic control input sync forces fixed
cause interference, the logic control input sync forces fixed
frequency PWM operation under all load conditions.
frequency PWM operation under all load conditions.
The ADP2503/ADP2504 can run from input voltages between
The ADP2503/ADP2504 can run from input voltages between
2.3 V and 5.5 V, allowing single lithium or lithium polymer cell,
2.3 V and 5.5 V, allowing single lithium or lithium polymer cell,
multiple alkaline or NiMH cells, PCMCIA, USB, and other
multiple alkaline or NiMH cells, PCMCIA, USB, and other
standard power sources. The ADP2503/ADP2504 have fixed
standard power sources. The ADP2503/ADP2504 have fixed
output options ranging from 2.8 V to 5 V. Compensation is
output options ranging from 2.8 V to 5 V. Compensation is
internal to minimize the number of external components.
internal to minimize the number of external components.
During logic-controlled shutdown, the input is disconnected
During logic-controlled shutdown, the input is disconnected
from the output and draws less than 1 µA from the input source.
from the output and draws less than 1 µA from the input source.
Operating as boost converters, the ADP2503/ADP2504 feature
Operating as boost converters, the ADP2503/ADP2504 feature
a true load disconnect function that isolates the load from the
a true load disconnect function that isolates the load from the
power source. Other key features include undervoltage lockout
power source. Other key features include undervoltage lockout
to prevent deep battery discharge and soft start to prevent input
to prevent deep battery discharge and soft start to prevent input
current overshoot at startup.
current overshoot at startup.
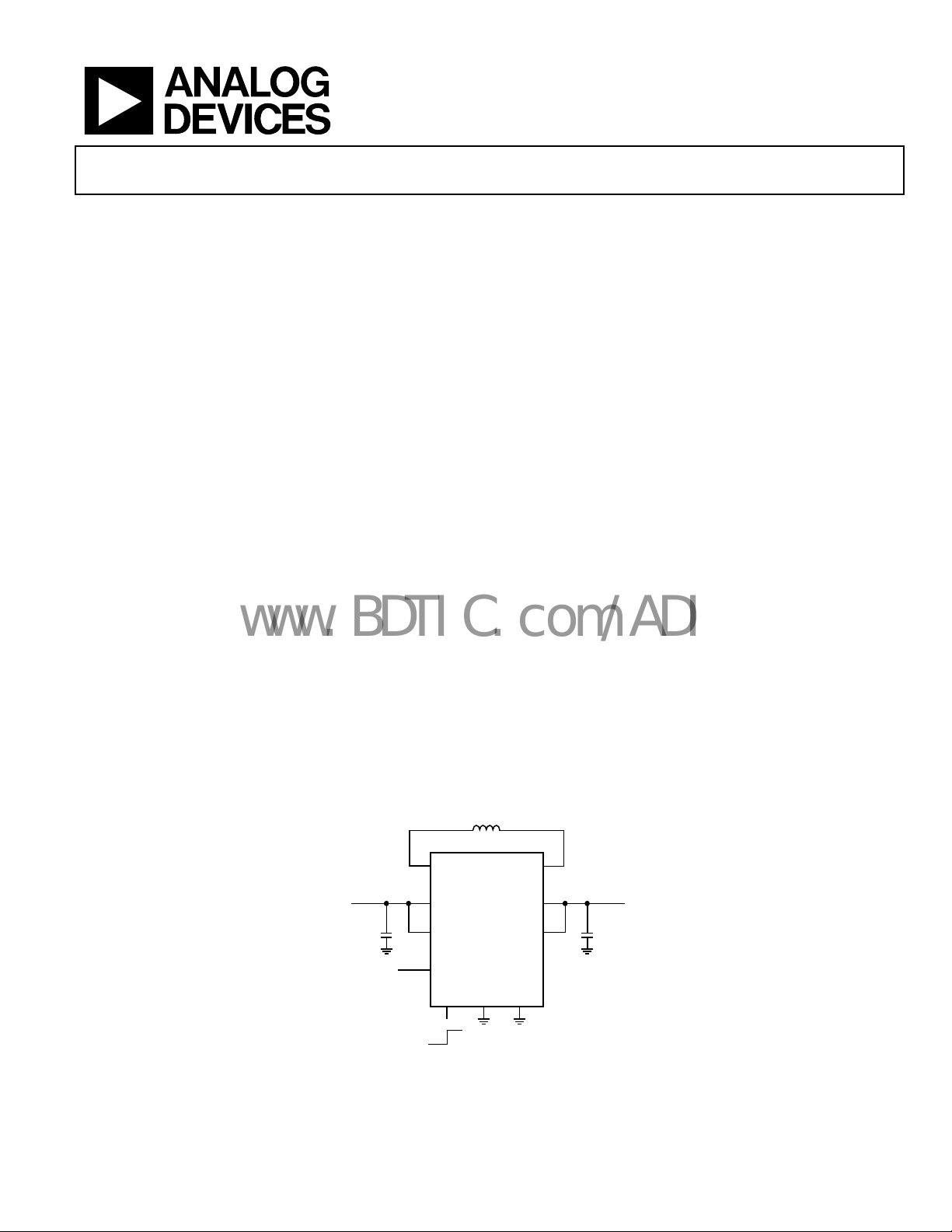
TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
SW1
V
IN
TO 5.5V
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
ADP2503
PVIN
VIN
SYNC
EN
ON
OFF
1.0µH
SW2
V
OUT
VOUT
FB
AGND
PGND
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
2.8V TO 5V
22µF10µF
07475-001

ADP2503/ADP2504
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Typical Application Circuit ............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 4
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 4
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 4
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 5
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 6
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 11
Power Save Mode ........................................................................ 11
REVISION HISTORY
10/08—Revision 0: Initial Version
Soft Start ...................................................................................... 11
Sync Function ............................................................................. 11
Enable ........................................................................................... 11
Undervoltage Lockout ............................................................... 12
Thermal Shutdown .................................................................... 12
Short-Circuit Protection ............................................................ 12
Reverse Current Limit ............................................................... 12
Applications Information .............................................................. 13
Inductor Selection ...................................................................... 13
PCB Layout Guidelines .................................................................. 15
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 16
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 16
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 16

ADP2503/ADP2504
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
VIN = 3.6 V, V
unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameters Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Voltage Range 2.3 5.5 V
Undervoltage Lockout Threshold VIN rising 2.15 2.20 2.25 V
Undervoltage Lockout Threshold VIN falling 2.10 2.14 2.20 V
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Range 2.8 5.0 V
Feedback Impedance 450 kΩ
Output Voltage Initial Accuracy ADP2503/ADP2504 (PWM operation, no load) −2 +2 %
Load and Line Regulation VIN = 2.3 V to 3.6 V, I
V
CURRENT CHARACTERISTICS
Quiescent Current (VIN) I
Shutdown Current TA = TJ = −40°C to +85°C 0.2 1 µA
SWITCH CHARACTERISTICS
N-Channel Switches (LFCSP) VIN = 3.6 V 150 mΩ
P-Channel Switches (LFCSP) VIN = V
P-Channel Leakage TJ = −40°C to +85°C 1 µA
Switch Current Limit
ADP2504 1.3 2.0 A
ADP2503 1.0 1.4 A
Reverse Current Limit 1.1 A
OSCILLATOR AND STARTUP
Oscillator Frequency 2.1 2.5 2.9 MHz
On Time PMOS1 (Buck Mode) Minimum duty cycle = 30% 130 ns
On Time NMOS2 (Boost Mode) Maximum duty cycle = 50% (×2) 200 ns
Sync Clock Frequency 2.2 2.8 MHz
Sync Clock Minimum Off Time 160 ns
LOGIC LEVEL CHARACTERISTICS
EN, SYNC Input High Threshold 1.2 V
EN, SYNC Input Low Threshold 0.4 V
EN, SYNC Leakage Current VIN = VEN −1 +0.1 +1 µA
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Thermal Shutdown Threshold 150 °C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis 25 °C
1
All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard statistical quality control (SQC).
= 3.3 V, @ TA = TJ = −40°C to +125°C for minimum/maximum specifications and TA = 25°C for typical specifications,
OUT
1
= 0 mA to 500 mA, forced PWM mode 0.5 %
LOAD
= 2.3 V to 5.5 V, I
IN
= 0 mA, V mode = EN = VIN = 3.6 V, device not switching 38 50 µA
OUT
= 3.6 V 150 mΩ
OUT
= 0 mA to 500 mA, forced PWM mode 0.6 %
LOAD
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 16
ADP2503/ADP2504
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
PVIN, VIN, SW1, SW2, VOUT, SYNC,
EN, FB
PGND to AGND −0.3 V to 0.3 V
Operating Ambient Temperature −40°C to +85°C
Operating Junction Temperature −40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature −65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature
Soldering (10 sec) 300°C
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
ESD Human Body Model ±2000 V
ESD Charged Device Model ±1500 V
ESD Machine Model ±100 V
−0.3 V to +6 V
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for a device soldered to a standard JEDEC2S2P
PCB. For a typical printed circuit board of a handset, the total
thermal resistance is higher. For correct operation up to 85°C
ambient temperature the total thermal resistance must not
exceed 100 K/W.
Table 3.
Package Type
10-Lead LFCSP (QFN) 84 °C/W
θ
JA
Unit
ESD CAUTION
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Absolute maximum ratings apply individually only, not in
combination. Unless otherwise specified, all other voltages
are referenced to GND.
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 16
ADP2503/ADP2504
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
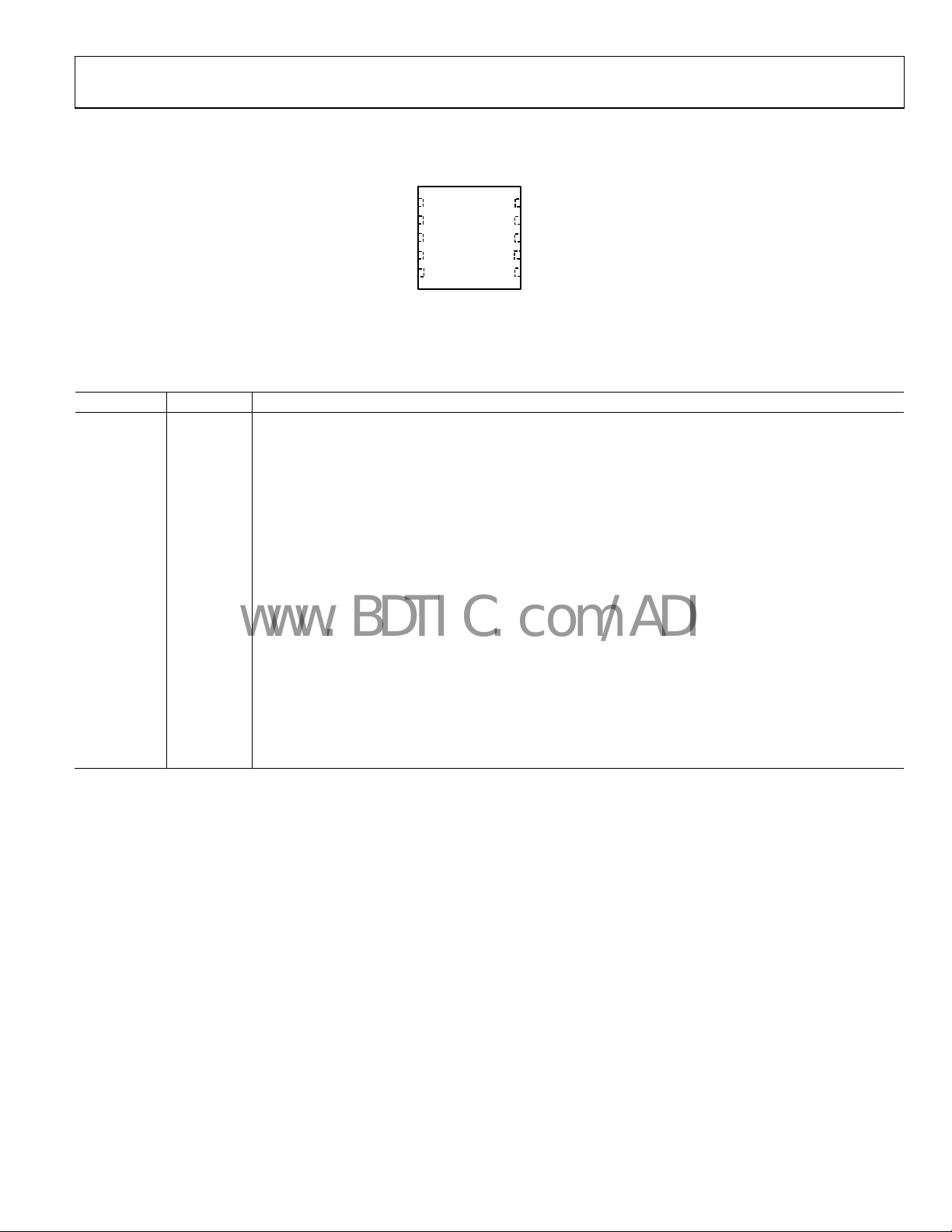
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
1VOUT
ADP2503/
2SW2
ADP2504
3PGND
TOP VIEW
4SW1
(Not to scale)
5PVIN
*CONNECT PADDLETO GND.
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
10 FB
9AGND
8VIN
7SYNC
6EN
07475-003
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 VOUT Output of the ADP2503/ADP2504. Connect the output capacitor between VOUT and PGND.
2 SW2
Power Switch 2 Connection. This is the internal connection to the input PMOS and NMOS switches. Connect
SW2 to the inductor with a short, wide track.
3 PGND Power GND. Connect the input and output capacitors and the PGND pin to a PGND plane.
4 SW1
Power Switch 1 Connection. This is the internal connection to the output PMOS and NMOS switches. Connect
SW1 to the inductor with a short, wide track.
5 PVIN
Power Input. This the input to the buck-boost power switches. Place a 10 F capacitor between PVIN and
PGND as close as possible to the ADP2503/ADP2504.
6 EN Enable. Drive EN high to turn on the ADP2503/ADP2504. Bring EN low to put the part into shutdown mode.
7 SYNC The SYNC pin permits the ADP2503/ADP2504 to operate in three different modes.
Normal operation: with SYNC driven low, the ADP2503/ADP2504 operate at 2.5 MHz PWM mode for heavy
and medium loads, and moves to power save mode (PSM) mode for light loads.
Forced PWM operation: with SYNC driven high, the ADP2503/ADP2504 operate at fixed 2.5 MHz PWM mode
for all load conditions.
SYNC mode: to synchronize the ADP2503/ADP2504 switching to an external signal, drive this pin with a clock
between 2.2 MHz and 2.8 MHz. The SYNC signal must have on and off times greater than 160 ns.
8 VIN Analog Power Supply. This is the supply for the ADP2503/ADP2504 internal circuitry.
9 AGND Analog Ground.
10 FB Output Feedback. This is an input to the internal error amplifier.
EP Paddle Connect the paddle to PGND.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...