ANALOG DEVICES ADP2118 Service Manual
3 A, 1.2 MHz/600 kHz High Efficiency
Synchronous Step-Down DC-to-DC Regulator
FEATURES
3 A continuous output current
75 mΩ and 40 mΩ integrated FET
±1.5% output accuracy
Input voltage range from 2.3 V to 5.5 V
Output voltage from 0.6 V to V
600 kHz or 1.2 MHz fixed switching frequency
Synchronizable between 600 kHz and 1.4 MHz
Selectable synchronize phase shift: 0
Selectable PWM or PFM mode operation
Current mode architecture
Precision enable input
Power good output
Voltage tracking input
Integrated soft start
Internal compensation
Starts up into a precharged output
UVLO, OVP, OCP, and thermal shutdown
Available in 16-lead 4mm × 4mm LFCSP_WQ package
APPLICATIONS
Point of load conversion
Communications and networking equipments
Industrial and instrumentation
Consumer electronics
Medical appliances
IN
o
or 180o
ADP2118
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADP2118 is a low quiescent current, synchronous, step-down,
dc-to-dc regulator in a compact 4mm × 4mm LFCSP_WQ
package. It uses a current mode, constant frequency pulse-width
modulation (PWM) control scheme for excellent stability and
transient response. Under light loads, the ADP2118 can be
configured to operate in pulse frequency modulation (PFM)
mode that reduces switching frequency to save power.
The ADP2118 runs from input voltages of 2.3 V to 5.5 V. The
output voltage of the ADP2118ACPZ-R7 is adjustable from
0.6 V to input voltage (V
available in preset output voltage options of 3.3 V, 2.5 V, 1.8 V,
1.5 V, 1.2 V, and 1.0 V. The ADP2118 requires minimal external
parts and provides a high efficiency solution with its integrated
power switch, synchronous rectifier, and internal compensation.
The IC draws less than 3 μA from the input source when it is
disabled. Other key features include undervoltage lockout
(UVLO), integrated soft start to limit inrush current at startup,
overvoltage protection (OVP), overcurrent protection (OCP),
and thermal shutdown (TSD).
), and the ADP2118ACPZ-x.x-R7 are
IN
C1
0.1µF
R1
10Ω
R2
10kΩ
16 15 14 13
EN
VIN
VIN
P
12
PVIN
11
SW
10
SW
9
SW
PGND
PGND
PGND
R
BOT
2.21kΩ
1
SYNC/MODE
2
FREQ
3
TRK
4
FB
R
TOP
10kΩ
PGOOD
ADP2118
ND
G
5 6 7 8
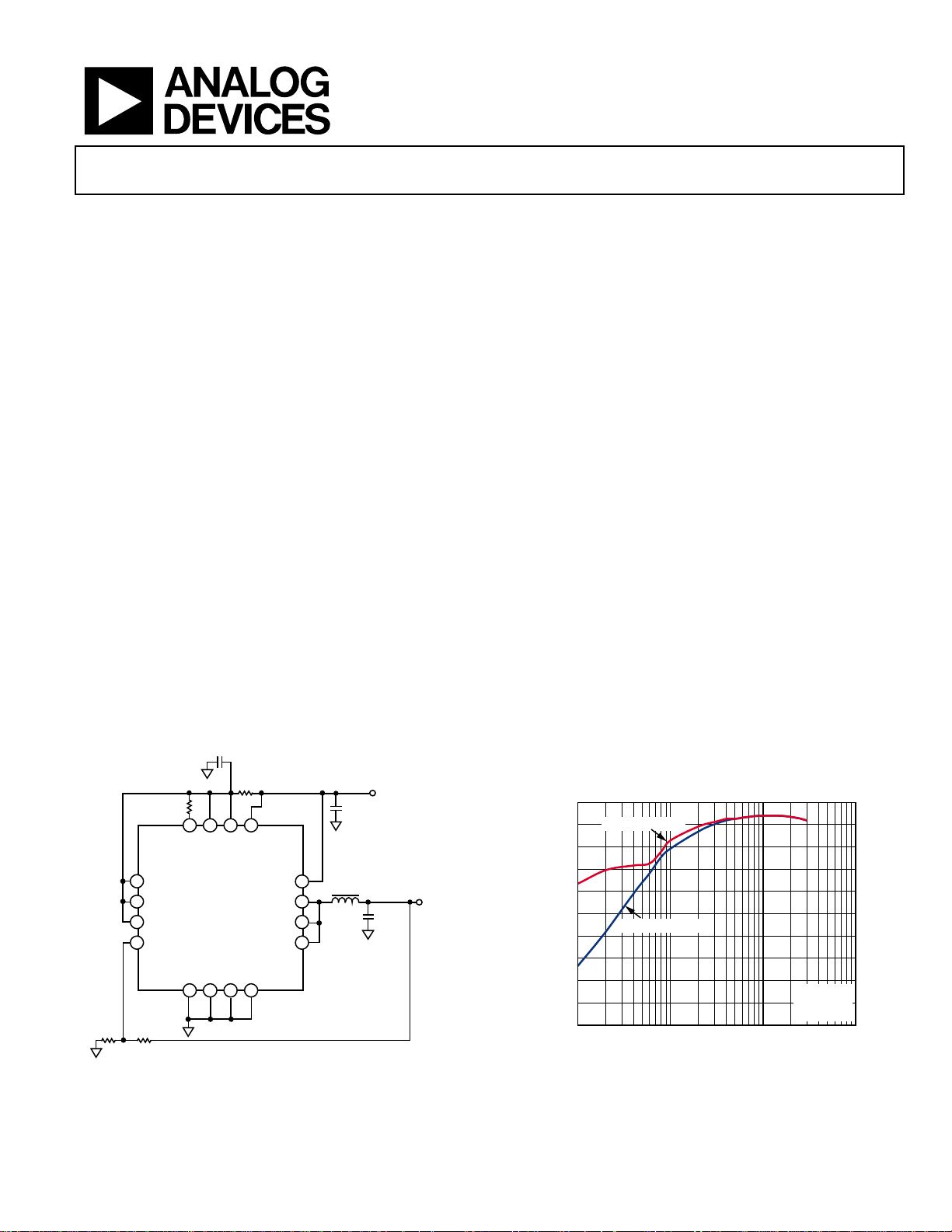
Figure 1. Typical Applications Circuit
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1µH
C
IN
100µF
X5R,
6.3V
L
V
IN
5V
C
OUT
100µF
X5R,
6.3V
V
OUT
3.3V
3A
08301-001
100
90
PFM OPERATION
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.01 0.1 1 10
FPWM OPE RAT I O N
OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
VIN = 5V
V
OUT
f
= 1.2MHz
S
Figure 2. Efficiency vs. Output Current
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
= 3.3V
08301-050

ADP2118
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 7
Functional Block Diagram ............................................................ 13
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 14
Control Scheme .......................................................................... 14
PWM Mode Operation .............................................................. 14
PFM Mode Operation ................................................................ 14
Slope Compensation .................................................................. 14
Enable/Shutdown ....................................................................... 14
Integrated Soft Start ................................................................... 14
Tracking ....................................................................................... 14
Oscillator and Synchronization ................................................ 15
Current Limit and Short-Circuit Protection .......................... 15
Overvoltage Protection (OVP) ................................................. 15
Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) ............................................... 15
Thermal Shutdown .................................................................... 15
Power Good ................................................................................ 15
Applications Information .............................................................. 16
Output Voltage Selection ........................................................... 16
Inductor Selection ...................................................................... 16
Output Capacitor Selection ....................................................... 16
Input Capacitor Selection .......................................................... 17
Voltage Tracking ......................................................................... 17
Typical Application Circuits ......................................................... 18
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 21
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 21
REVISION HISTORY
10/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changed Converter to Regulator (Throughout) .......................... 1
Changes to Applications Section .................................................... 1
7/09—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 24
ADP2118
SPECIFICATIONS
VIN = PVIN = 3.3 V, EN = VIN, SYNC/MODE = high @ TJ = −40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TJ = 25oC.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
VIN AND PVIN
VIN Voltage Range VIN 2.3 5.5 V
PVIN Voltage Range PVIN 2.3 5.5 V
Quiescent Current I
Shutdown Current I
VIN Undervoltage Lockout Threshold UVLO VIN rising 2.2 2.3 V
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Load Regulation1 I
Line Regulation1 I
FB
FB Regulation Voltage VFB VIN = 2.3 V to 5.5 V 0.591 0.6 0.609 V
FB Bias Current IFB 0.01 0.1 μA
SW
High-Side On Resistance2 VIN = PVIN = 3.3 V, ISW = 500 mA 75 110 mΩ
Low-Side On Resistance2 VIN = PVIN = 3.3 V, ISW = 500 mA 40 60 mΩ
SW Peak Current Limit High-side switch, VIN = PVIN = 3.3 V 4 5.2 6.4 A
SW Maximum Duty Cycle VIN = PVIN = 5.5 V, full frequency 100 %
SW Minimum On Time3 VIN = PVIN = 5.5 V, full frequency 100 ns
TRK
TRK Input Voltage Range 0 600 mV
TRK to FB Offset Voltage TRK = 0 mV to 500 mV −10 +10 mV
TRK Input Bias Current 100 nA
FREQUENCY
Oscillator Frequency FREQ = VIN 1.0 1.2 1.4 MHz
FREQ Input High Voltage 1.2 V
FREQ Input Low Voltage 0.4 V
SYNC/MODE
Synchronization Range 0.6 1.4 MHz
SYNC Minimum Pulse Width 100 ns
SYNC Minimum Off Time 100 ns
SYNC Input High Voltage 1.2 V
SYNC Input Low Voltage 0.4 V
INTEGRATED SOFT START
Soft Start Time All switching frequency 2048 Clock cycles
PGOOD
Power Good Range FB rising threshold 105 110 115 %
Power Good Deglitch Time From FB to PGOOD 16 Clock cycles
PGOOD Leakage Current V
PGOOD Output Low Voltage I
No switching, SYNC/MODE = GND 100 150 μA
VIN
Switching, no load, SYNC/MODE = high 680 900 μA
VIN = PVIN = 5.5 V, EN = GND 0.3 3 μA
SHDN
VIN falling 2 2.1 V
= 0 A to 3 A 0.08 %/A
o
= 1.5 A 0.05 %/V
o
FREQ = GND 500 600 700 kHz
FB rising hysteresis 2.5 %
FB falling threshold 85 90 94 %
FB falling hysteresis 2.5 %
= 5 V 0.1 1 μA
PGOOD
= 1 mA 140 200 mV
PGOOD
Rev. A | Page 3 of 24
ADP2118
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
EN
EN Input Rising Threshold VIN = 2.3 V to 5.5 V 1.12 1.2 1.28 V
EN Input Hysteresis VIN = 2.3 V to 5.5 V 100 mV
EN Pull-Down Resistor 1 MΩ
THERMAL
Thermal Shutdown Threshold 140 °C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis 15
1
Specified by the circuit in . Figure 45
2
Pin-to-pin measurements.
3
Guaranteed by design.
°C
Rev. A | Page 4 of 24
ADP2118
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
VIN, PVIN −0.3 V to +6 V
SW −0.3 V to +6 V
FB, SYNC/MODE, EN, TRK, FREQ, PGOOD −0.3 V to +6 V
PGND to GND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
Operating Junction Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Soldering Conditions JEDEC J-STD-020
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 3. Thermal Resistance
Package Type
16-Lead LFCSP_WQ 38.3 °C/W
θ
JA
Unit
Boundary Conditions
θJA is measured using natural convection on a JEDEC 4-layer
board, and the exposed pad is soldered to the printed circuit
board with thermal vias.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 5 of 24
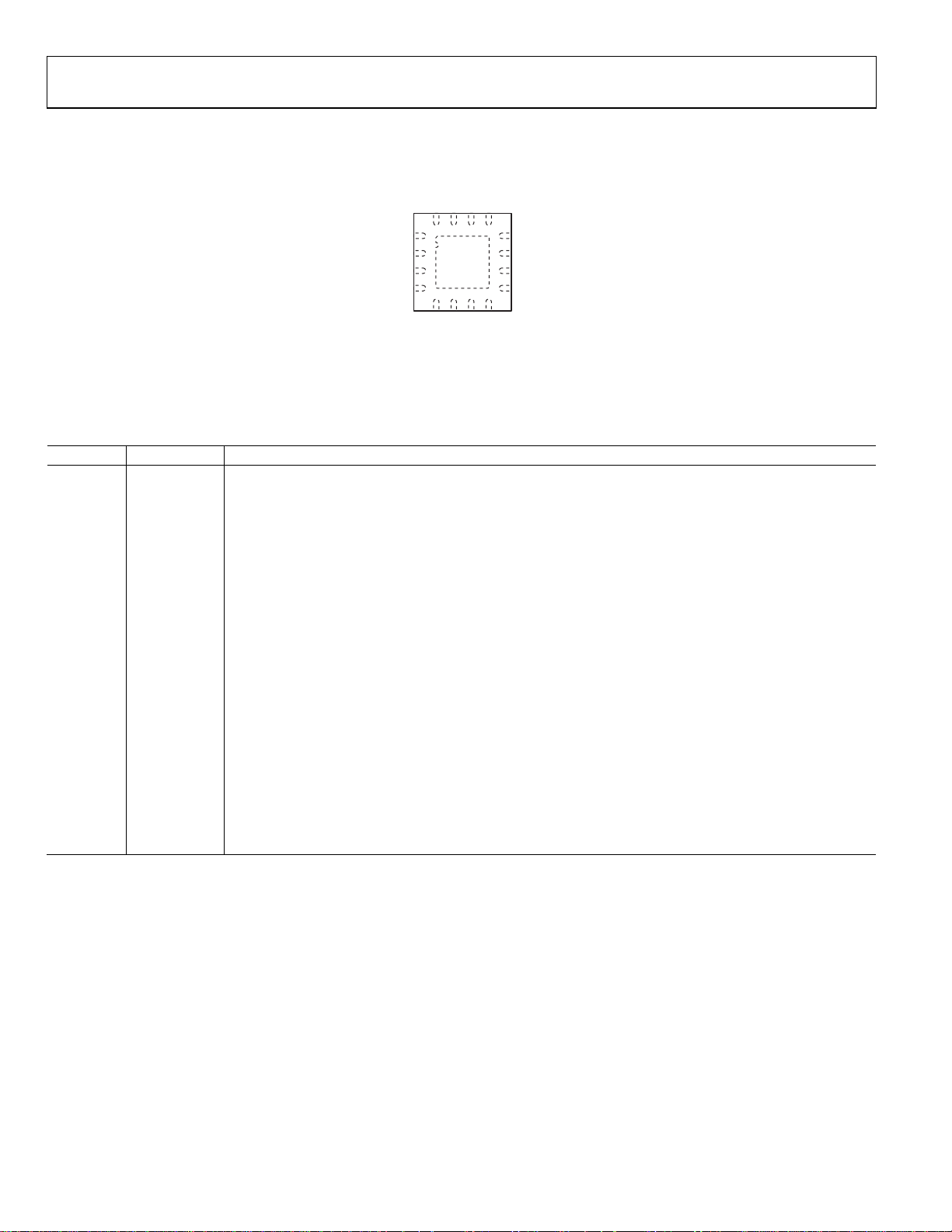
ADP2118
D
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
EN
VIN
16 PGOO
PVIN
13
15
14
FREQ
TRK
FB
1
2
ADP2118
5
GND
TOP
VIEW
6
PGND
3
4
SYNC/MODE
NOTES
1. THE EXPOSED PAD SHOULD BE SOLDERED TO
AN EXTERNAL GROUND PLANE UNDERNEATH
THE IC FOR THERMAL DISSIPATION.
12
PVIN
11
SW
10
SW
9
SW
8
7
PGND
PGND
08301-002
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 SYNC/MODE
Synchronization Input (SYNC). Connect this pin to an external clock between 600 kHz and 1.4 MHz to
synchronize the switching frequency to the external clock (see the Oscillator and Synchronization section for
details).
CCM/PFM Selection (MODE). When this pin is connected to VIN, PFM mode is disabled and the ADP2118 only
works in continuous conduction mode (CCM). When this pin is connected to ground, PFM mode is enabled
and becomes active at light loads.
2 FREQ Frequency Selection. Connect to GND to select 600 kHz and VIN for 1.2 MHz.
3 TRK
Tracking Input. To track a master voltage, drive TRK from a voltage divider from the master voltage. If the
tracking function is not used, connect TRK to VIN.
4 FB
Feedback Voltage Sense Input. Connect to a resistor divider from V
directly.
to V
OUT
. For the fixed output version, connect
OUT
5 GND Analog Ground. Connect to the ground plane.
6, 7, 8 PGND Power Ground. Connect to the ground plane and to the output return side of the output capacitor.
9, 10, 11 SW Switch Node Output. Connect to the output inductor.
12, 13 PVIN
Power Input Pin. Connect this pin to the input power source. Connect a bypass capacitor between this pin
and PGND.
14 VIN
Bias Voltage Input Pin. Connect a bypass capacitor between this pin and GND and a small (10 Ω) resistor
between this pin and PVIN.
15 EN
Precision Enable Pin. The external resistor divider can be used to set the turn-on threshold. To enable the part
automatically, connect the EN pin to VIN. This pin has a 1 MΩ pull-down resistor to GND.
16 PGOOD Power-Good Output (Open Drain). Connect to a resistor to any pull-up voltage <5.5 V.
17 (EPAD) Exposed Pad The exposed pad should be soldered to an external ground plane underneath the IC for thermal dissipation.
Rev. A | Page 6 of 24
ADP2118
C
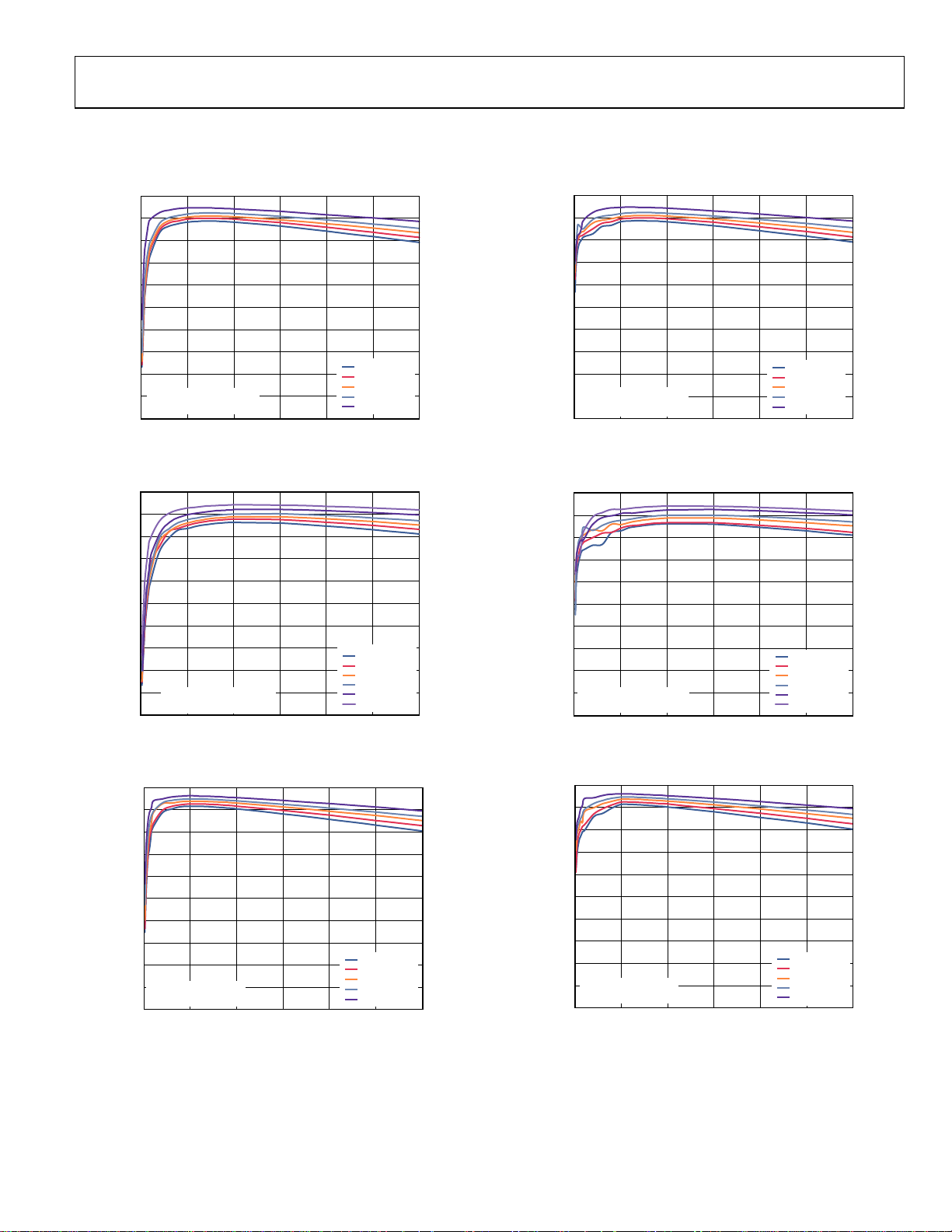
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
TA = 25°C, VIN = 5 V, V
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
INDUCTOR COI LCRAFT
MSS1038-102NL
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
Figure 4. Efficiency (1.2 MHz, VIN = 3.3 V, FPWM) vs. Output Current
= 1.2 V, L = 1 μH, CIN = 100 μF, C
OUT
V
= 1.0V
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
= 100 μF, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
INDUCTOR COI LCRAFT
MSS1038-102NL
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
08301-014
Figure 7. Efficiency (1.2 MHz, VIN = 3.3 V, PFM) vs. Output Current
OUTPUT CURRENT ( A)
V
= 1.0V
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
08301-017
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
INDUCTOR COI LCRAFT
MSS1038-102NL
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
OUTPUT CURRENT ( A)
V
= 1.0V
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
V
= 3.3V
OUT
Figure 5. Efficiency (1.2 MHz, VIN = 5 V, FPWM) vs. Output Current
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
V
= 1.0V
20
10
INDUCTOR SUMI DA
CDRH105R2R2NC
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
Figure 6. Efficiency (600 kHz, VIN = 3.3 V, FPWM) vs. Output Current
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
INDUCTOR COI LCRAFT
MSS1038-102NL
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
08301-015
OUTPUT CURRENT ( A)
V
= 1.0V
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
V
= 3.3V
OUT
8301-018
Figure 8. Efficiency (1.2 MHz, VIN = 5 V, PFM) vs. Output Current
100
90
80
70
60
Y (%)
50
40
EFFICIEN
30
V
= 1.0V
20
10
INDUCTOR SUMIDA
CDRH105R2R2NC
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
08301-016
Figure 9. Efficiency (600 kHz, V
OUTPUT CURRENT ( A)
= 3.3 V, PFM) vs. Output Current
IN
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
8301-019
Rev. A | Page 7 of 24
ADP2118
C
C
100
90
80
70
60
Y (%)
50
40
EFFICIEN
30
20
10
INDUCTOR SUMIDA
CDRH105R2R2NC
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
OUTPUT CURRENT( A)
V
OUT
V
OUT
V
OUT
V
OUT
V
OUT
V
OUT
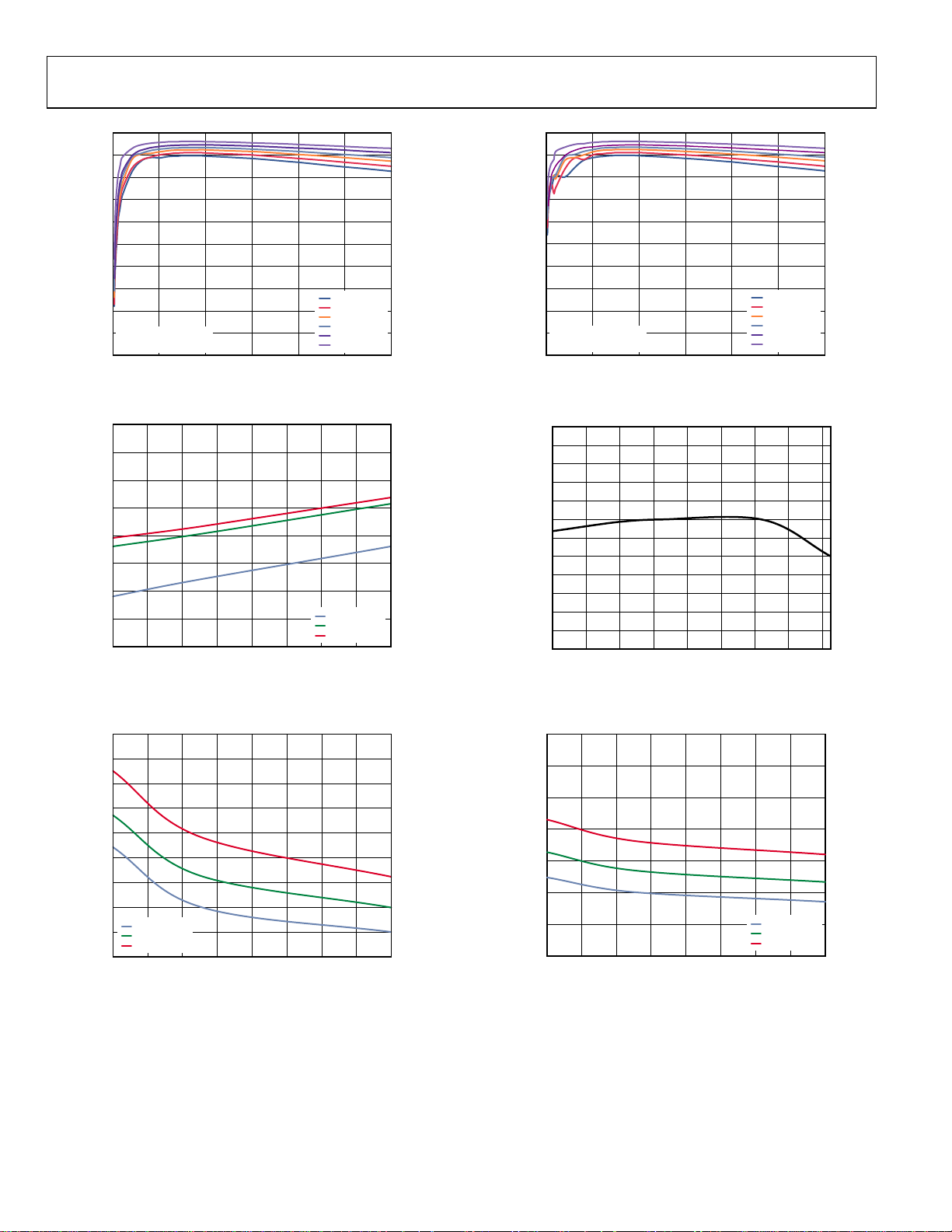
Figure 10. Efficiency (600 kHz, VIN = 5 V, FPWM) vs. Output Current
120
115
110
105
100
95
90
QUIESCENT CURRENT (µA)
85
80
2.32.73.13.53.94.34.75.15.5
VIN (V)
Figure 11. Quiescent Current vs. V
TJ = –40°C
= +25°C
T
J
= +125°C
T
J
(No Switching)
IN
= 1.0V
= 1.2V
= 1.5V
= 1.8V
= 2.5V
= 3.3V
100
90
80
70
60
Y (%)
50
40
EFFICIEN
30
20
10
INDUCTOR SUMI DA
CDRH105R2R2NC
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
08301-020
OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
V
= 1.0V
OUT
V
= 1.2V
OUT
V
= 1.5V
OUT
V
= 1.8V
OUT
V
= 2.5V
OUT
V
= 3.3V
OUT
08301-023
Figure 13. Efficiency (600 kHz, VIN = 5 V, PFM) vs. Output Current
606
605
604
603
602
601
600
599
598
597
FEEDBACK VOLTAGE (mV)
596
595
594
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
08301-021
TEMPERATURE (°C )
8301-024
Figure 14. Feedback Voltage vs. Temperature (VIN = 3.3 V)
130
120
80
70
110
100
90
80
70
PFET RESISTOR (mΩ)
60
50
40
NFET RESISTOR (mΩ)
30
60
TJ = –40°C
50
T
= +25°C
J
T
= +125°C
J
40
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7 5.1 5.5
(V)
V
IN
Figure 12. PFET Resistor vs. VIN (Pin-to-Pin Measurements)
20
10
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7 5.1 5.5
08301-022
VIN (V)
Figure 15. NFET Resistor vs. VIN (Pin-to-Pin Measurements)
TJ = –40°C
T
= +25°C
J
T
= +125°C
J
08301-025
Rev. A | Page 8 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...