
Synchronous Buck Controller with Constant
V
V
V
FEATURES
Power input voltage range: 2.95 V to 20 V
On-board bias regulator
Minimum output voltage: 0.6 V
0.6 V reference voltage with ±1.0% accuracy
Supports all N-channel MOSFET power stages
Available in 300 kHz, 600 kHz, and 1.0 MHz options
No current-sense resistor required
Power saving mode (PSM) for light loads (ADP1875 only)
Resistor programmable current limit
Power good with internal pull-up resistor
Externally programmable soft start
Thermal overload protection
Short-circuit protection
Standalone precision enable input
Integrated bootstrap diode for high-side drive
Starts into a precharged output
Available in a 16-lead QSOP package
APPLICATIONS
Telecom and networking systems
Mid- to high-end servers
Set-top boxes
DSP core power supplies
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADP1874/ADP1875 are versatile current mode, synchronous
step-down controllers. They provide superior transient response,
optimal stability, and current-limit protection by using a constant
on-time, pseudo fixed frequency with a programmable current
limit, current control scheme. In addition, these devices offer
optimum performance at low duty cycles by using a valley, current
mode control architecture. This allows the ADP1874/ADP1875
to drive all N-channel power stages to regulate output voltages
to as low as 0.6 V.
The ADP1875 is the power saving mode (PSM) version of
the device and is capable of pulse skipping to maintain output
regulation while achieving improved system efficiency at light
loads (see the ADP1875 Power Saving Mode (PSM) section for
more information).
Available in three frequency options (300 kHz, 600 kHz, and
1.0 MHz, plus the PSM option), the ADP1874/ADP1875 are well
suited for a wide range of applications that require a single-input
power supply range from 2.95 V to 20 V. Low voltage biasing is
supplied via a 5 V internal low dropout regulator (LDO).
On-Time and Valley Current Mode
ADP1874/ADP1875
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS CIRCUIT
= 2.95V TO 20
IN
C
C
C
C2
R
C
10k
REG
R
TOP
V
OUT
R
BOT
C
VREG2
C
VREG
R
RES
100
VIN = 5V (PSM)
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
VIN = 13V (PSM)
55
EFFICIENCY (%)
50
45
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
40
35
30
25
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Figure 2. ADP1874/ADP1875 Efficiency vs. Load Current (V
In addition, soft start programmability is included to limit input inrush current from the input supply during startup and to
provide reverse current protection during precharged output
conditions. The low-side current sense, current gain scheme, and
integration of a boost diode, along with the PSM/forced pulsewidth modulation (PWM) option, reduce the external part count
and improve efficiency.
The ADP1874/ADP1875 operate over the −40°C to +125°C
junction temperature range and are available in a 16-lead QSOP
package.
VIN
ADP1874/
ADP1875
COMP BST
EN
DRVH
FB
GND
VREG
VREG_IN
RES
SW
DRVL
PGOOD
TRACK
PGND
SS
C
IN
C
Q1
BST
C
Q2
R
PGD
V
EXT
C
SS
R
TRK2
R
TRK1
Figure 1. Typical Applications Circuit
VIN = 16.5V
VIN = 13V
TA = 25°C
V
= 1.8V
OUT
f
= 300kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744325120, L = 1.2µH, DCR = 1.8m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
L
OUT
LOAD
V
MASTER
= 1.8 V, 300 kHz)
OUT
V
OUT
09347-001
09347-102
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADP1874/ADP1875
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Typical Applications Circuit............................................................ 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 6
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 6
Boundary Condition .................................................................... 6
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 6
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
ADP1874/ADP1875 Block Digram.............................................. 18
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 19
Startup.......................................................................................... 19
Soft Start ...................................................................................... 19
Precision Enable Circuitry ........................................................19
Undervoltage Lockout ............................................................... 19
On-Board Low Dropout Regulator.......................................... 20
Thermal Shutdown..................................................................... 20
Programming Resistor (RES) Detect Circuit.......................... 20
Valley Current-Limit Setting .................................................... 20
Hiccup Mode During Short Circuit......................................... 22
Synchronous Rectifier................................................................ 22
ADP1875 Power Saving Mode (PSM) ..................................... 22
Timer Operation ........................................................................ 23
Pseudo-Fixed Frequency........................................................... 24
Power Good Monitoring ........................................................... 24
Voltage Tracking......................................................................... 25
Applications Information.............................................................. 27
Feedback Resistor Divider ........................................................ 27
Inductor Selection...................................................................... 27
Output Ripple Voltage (VRR) .................................................. 27
Output Capacitor Selection....................................................... 27
Compensation Network ............................................................ 28
Efficiency Consideration........................................................... 29
Input Capacitor Selection.......................................................... 30
Thermal Considerations............................................................ 31
Design Example.......................................................................... 32
External Component Recommendations.................................... 34
Layout Considerations................................................................... 36
IC Section (Left Side of Evaluation Board)............................. 38
Power Section ............................................................................. 38
Differential Sensing.................................................................... 39
Typical Application Circuits ......................................................... 40
12 A, 300 kHz High Current Application Circuit.................. 40
5.5 V Input, 600 kHz Application Circuit ............................... 40
300 kHz High Current Application Circuit............................ 41
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 42
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 42
REVISION HISTORY
2/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 44
ADP1874/ADP1875
SPECIFICATIONS
All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard statistical quality control (SQC). VREG = 5 V,
BST − SW = VREG − V
RECT_DROP
unless otherwise specified.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
POWER SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
High Input Voltage Range VIN C
ADP1874ARQZ-0.3/ADP1875ARQZ-0.3 (300 kHz) 2.95 12 20 V
ADP1874ARQZ-0.6/ADP1875ARQZ-0.6 (600 kHz) 2.95 12 20 V
ADP1874ARQZ-1.0/ADP1875ARQZ-1.0 (1.0 MHz) 3.25 12 20 V
Quiescent Current I
Shutdown Current I
Undervoltage Lockout UVLO Rising VIN (see Figure 35 for temperature variation) 2.65 V
UVLO Hysteresis Falling VIN from operational state 190 mV
INTERNAL REGULATOR
CHARACTERISTICS
VREG Operational Output Voltage VREG C
ADP1874ARQZ-0.3/ADP1875ARQZ-0.3 (300 kHz) 2.75 5 5.5 V
ADP1874ARQZ-0.6/ADP1875ARQZ-0.6 (600 kHz) 2.75 5 5.5 V
ADP1874ARQZ-1.0/ADP1875ARQZ-1.0 (1.0 MHz) 3.05 5 5.5 V
VREG Output in Regulation VIN = 7 V, 100 mA 4.82 4.981 5.16 V
V
Load Regulation 0 mA to 100 mA, VIN = 7 V 32 mV
0 mA to 100 mA, VIN = 20 V 34 mV
Line Regulation VIN = 7 V to 20 V, 20 mA 2.5 mV
V
VIN to VREG Dropout Voltage 100 mA out of VREG, VIN ≤ 5 V 300 415 mV
Short VREG to PGND VIN = 20 V 229 320 mA
SOFT START
Soft Start Period Calculation
ERROR AMPLIFER
FB Regulation Voltage VFB T
T
T
Transconductance Gm 320 496 670 μS
FB Input Leakage Current I
CURRENT-SENSE AMPLIFIER GAIN
Programming Resistor (RES)
Value from RES to PGND
RES = 22 kΩ ± 1% 5.5 6 6.5 V/V
RES = none 11 12 13 V/V
RES = 100 kΩ ± 1% 22 24 26 V/V
SWITCHING FREQUENCY
ADP1874ARQZ-0.3/
ADP1875ARQZ-0.3 (300 kHz)
On-Time VIN = 5 V, V
Minimum On-Time VIN = 20 V 145 190 ns
Minimum Off-Time 84% duty cycle (maximum) 340 400 ns
(see Figure 40 to Figure 42). VIN = 12 V. The specifications are valid for TJ = −40°C to +125°C,
= 22 μF(25 V rating) to PGND (at Pin 1)
VIN
+ I
Q_REG
REG,SD
FB = 1.5 V, no switching 1.1 mA
Q_BST
+ I
EN < 600 mV 140 225 μA
BST,SD
VREG and VREG_IN tied together and should not be
loaded externally because they are intended to only
bias internal circuitry
= 4.7 μF to PGND, 0.22 μF to GND, VIN = 2.95 V to 20 V
VREG
= 12 V, 100 mA 4.83 4.982 5.16 V
IN
= 7 V to 20 V, 100 mA 2 mV
IN
Connect external capacitor from SS pin to GND,
= 10 nF/ms
C
SS
= 25°C 600 mV
J
= −40°C to +85°C 596 600 604 mV
J
= −40°C to +125°C 594.2 600 605.8 mV
J
FB = 0.6 V, EN = VREG 1 50 nA
FB, LEAK
10 nF/ms
RES = 47 kΩ ± 1% 2.7 3 3.3 V/V
Typical values measured at 50% time points with
0 nF at DRVH and DRVL; maximum values are
guaranteed by bench evaluation
1
300 kHz
= 2 V, TJ = 25°C 1120 1200 1280 ns
OUT
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 44
ADP1874/ADP1875
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
ADP1874ARQZ-0.6/
ADP1875ARQZ-0.6 (600 kHz)
On-Time VIN = 5 V, V
Minimum On-Time VIN = 20 V, V
Minimum Off-Time 65% duty cycle (maximum) 340 400 ns
ADP1874ARQZ-1.0/
ADP1875ARQZ-1.0 (1.0 MHz)
On-Time VIN = 5 V, V
Minimum On-Time VIN = 20 V 52 85 ns
Minimum Off-Time 45% duty cycle (maximum) 340 400 ns
OUTPUT DRIVER CHARACTERISTICS
High-Side Driver
Output Source Resistance2 I
Output Sink Resistance2 I
Rise Time3 t
Fall Time3 t
Low-Side Driver
Output Source Resistance2 I
Output Sink Resistance2 I
Rise Time3 t
Fall Time3 t
Propagation Delays
DRVL Fall to DRVH Rise3 t
DRVH Fall to DRVL Rise3 t
SW Leakage Current I
Integrated Rectifier
Channel Impedance I
PRECISION ENABLE THRESHOLD
Logic High Level VIN = 2.9 V to 20 V, VREG = 2.75 V to 5.5 V 605 634 663 mV
Enable Hysteresis VIN = 2.9 V to 20 V, VREG = 2.75 V to 5.5 V 31 mV
COMP VOLTAGE
COMP Clamp Low Voltage V
COMP Clamp High Voltage V
COMP Zero Current Threshold V
THERMAL SHUTDOWN T
Thermal Shutdown Threshold Rising temperature 155 °C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis 15 °C
CURRENT LIMIT
Hiccup Current Limit Timing COMP = 2.4 V 6 ms
OVERVOLTAGE AND POWER GOOD
THRESHOLDS
FB Power Good Threshold FB
FB Power Good Hysteresis 30 mV
FB Overvoltage Threshold FBOV V
FB Overvoltage Hysteresis 30 mV
PGOOD Low Voltage During Sink V
PGOOD Leakage Current PGOOD = 5 V 1 400 nA
600 kHz
= 2 V, TJ = 25°C 500 540 580 ns
OUT
= 0.8 V 82 110 ns
OUT
1.0 MHz
= 2 V, TJ = 25°C 285 312 340 ns
OUT
= 1.5 A, 100 ns, positive pulse (0 V to 5 V) 2.25 3 Ω
SOURCE
= 1.5 A, 100 ns, negative pulse (5 V to 0 V) 0.70 1 Ω
SINK
BST − SW = 4.4 V, CIN = 4.3 nF (see Figure 59) 25 ns
r, DR VH
BST − SW = 4.4 V, CIN = 4.3 nF (see Figure 60) 11 ns
f, DRV H
= 1.5 A, 100 ns, positive pulse (0 V to 5 V) 1.6 2.2 Ω
SOURCE
= 1.5 A, 100 ns, negative pulse (5 V to 0 V) 0.7 1 Ω
SINK
VREG = 5.0 V, CIN = 4.3 nF (see Figure 60) 18 ns
r,DR VL
VREG = 5.0 V, CIN = 4.3 nF (see Figure 59) 16 ns
f,DRV L
BST − SW = 4.4 V (see Figure 59) 15.4 ns
tpdhDRVH
BST − SW = 4.4 V (see Figure 60) 18 ns
tpdhDRVL
BST = 25 V, SW = 20 V, VREG = 5 V 110 μA
SWLEAK
= 10 mA 22 Ω
SINK
COMP(LOW )
Tie EN pin to VREG to enable device
0.47 V
(2.75 V ≤ VREG ≤ 5.5 V)
(2.75 V ≤ VREG ≤ 5.5 V) 2.55 V
COMP(H IGH)
(2.75 V ≤ VREG ≤ 5.5 V) 1.15 V
COMP_ZC T
TMSD
PGOOD
PGD
PGOOD
VFB rising during system power-up 542 566 mV
rising during overvoltage event, I
FB
I
= 1 mA 143 200 mV
PGOOD
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 44
= 1 mA 691 710 mV
PGOOD
ADP1874/ADP1875
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
TRACKING
Track Input Voltage Range 0 5 V
FB-to-Tracking Offset Voltage 0.5 V < TRACK < 0.6 V, offset = VFB − V
Leakage Current V
1
The maximum specified values are with the closed loop measured at 10% to 90% time points (see Figure and Figure 60), C
MOSFETs being Infineon BSC042N03MS G.
2
Guaranteed by design.
3
Not automatic test equipment (ATE) tested.
= 5 V 1 50 nA
TRACK
63 mV
TRACK
59
= 4.3 nF, and the upper- and lower-side
GATE
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 44
ADP1874/ADP1875
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
VREG, VREG_IN, TRACK to PGND, GND −0.3 V to +6 V
VIN, EN, PGOOD to PGND −0.3 V to +28 V
FB, COMP, RES, SS to GND −0.3 V to (VREG + 0.3 V)
DRVL to PGND −0.3 V to (VREG + 0.3 V)
SW to PGND −2.0 V to +28 V
BST to SW −0.6 V to (VREG + 0.3 V)
BST to PGND −0.3 V to +28 V
DRVH to SW −0.3 V to VREG
PGND to GND ±0.3 V
PGOOD Input Current 35 mA
θJA (16-Lead QSOP)
4-Layer Board 104°C/W
Operating Junction Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Soldering Conditions JEDEC J-STD-020
Maximum Soldering Lead Temperature
(10 sec)
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Absolute maximum ratings apply individually only, not in
combination. Unless otherwise specified, all other voltages are
referenced to PGND.
300°C
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 3. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA Unit
θJA (16-Lead QSOP)
4-Layer Board 104° °C/W
BOUNDARY CONDITION
In determining the values given in Ta b le 2 and Tabl e 3, natural
convection is used to transfer heat to a 4-layer evaluation board.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 44
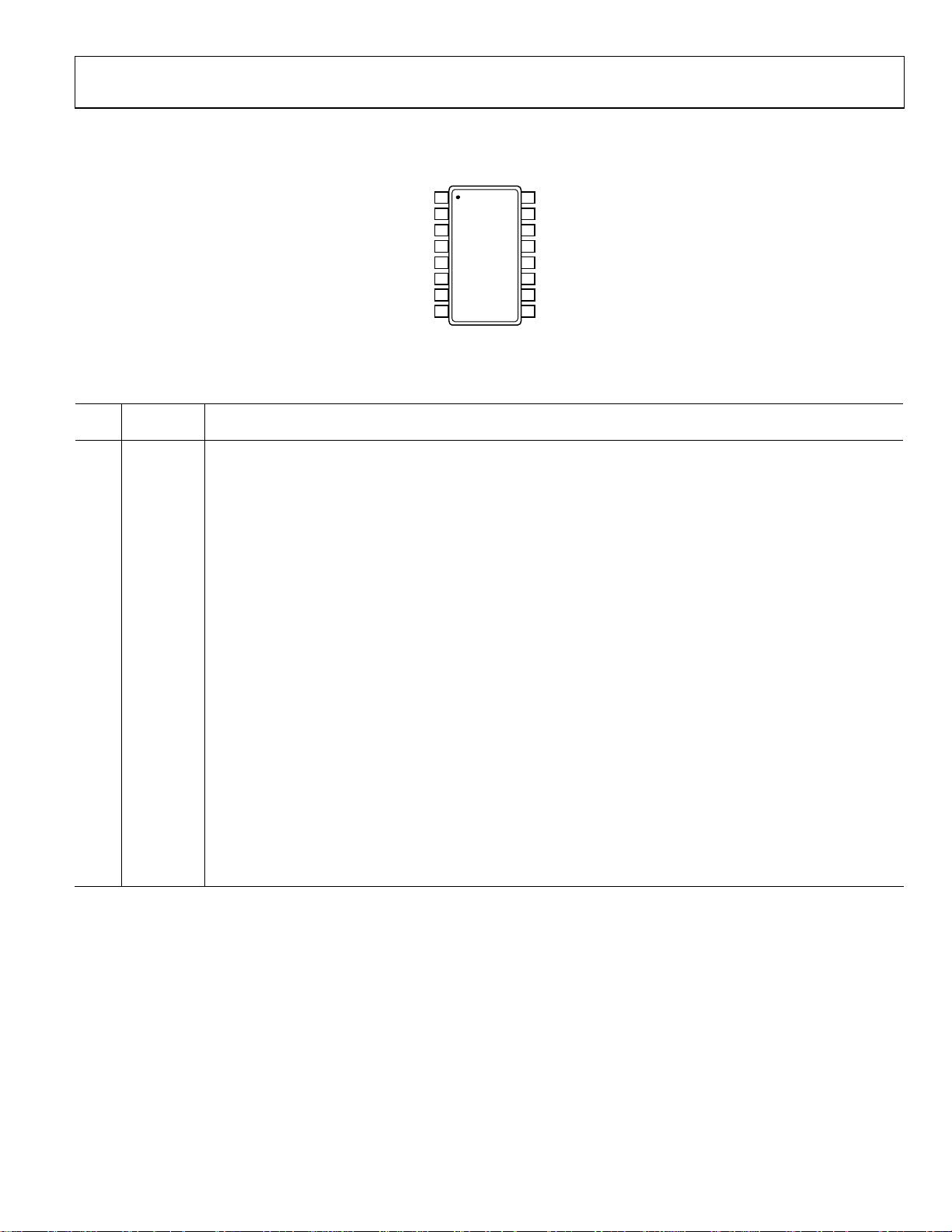
ADP1874/ADP1875
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
VIN
1
COMP
2
3
EN
ADP1874/
ADP1875
FB
4
GND
RES
VREG
VREG_IN
TOP VIEW
5
(Not to Scale)
6
7
8
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin
No.
Mnemonic Description
1 VIN High-Side Input Voltage. Connect VIN to the drain of the upper-side MOSFET.
2 COMP
Output of the Error Amplifier. Connect the compensation network between this pin and AGND to achieve stability
(see the Compensation Network section).
3 EN Connect to VREG to Enable IC. When pulled down to AGND externally, disables the IC.
4 FB Noninverting Input of the Internal Error Amplifier. This is the node where the feedback resistor is connected.
5 GND
Analog Ground Reference Pin of the IC. All sensitive analog components should be connected to this ground plane
(see the Layout Considerations section).
6 RES Current Sense Gain Resistor (External). Connect a resistor between the RES pin and GND (Pin 5).
7 VREG
Internal Regulator Supply Bias Voltage for the ADP1874/ADP1875 Controller (Includes the Output Gate Drivers). A
bypass capacitor of 1 μF directly from this pin to PGND and a 0.1 μF across VREG and GND are recommended.
8 VREG_IN Input to the Internal LDO. Tie this pin directly to Pin 7 (VREG).
9 TRACK
Tracking Input. If the tracking function is not used, it is recommended to connect TRACK to VREG through a resistor
higher than 1 MΩ or simply connect TRACK between 0.7 V and 2 V to reduce the bias current going into the pin.
10 SS
Soft Start Input. Connect an external capacitor to GND to program the soft start period. Capacitance value of 10 nF for
every 1 ms of soft start delay.
11 PGOOD
Open-Drain Power Good Output. Sinks current when FB is out of regulation or during thermal shutdown. Connect a
3 kΩ resistor between PGOOD and VREG. Leave unconnected if not used.
12 DRVL
Drive Output for the External Lower-Side, N-Channel MOSFET. This pin also serves as the current-sense gain setting
pin (see Figure 69).
13 PGND Power GND. Ground for the lower-side gate driver and lower-side, N-channel MOSFET.
14 DRVH Drive Output for the External Upper-Side, N-Channel MOSFET.
15 SW Switch Node Connection.
16 BST
Bootstrap for the Upper-Side MOSFET Gate Drive Circuitry. An internal boot rectifier (diode) is connected between
VREG and BST. A capacitor from BST to SW is required. An external Schottky diode can also be connected between
VREG and BST for increased gate drive capability.
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
BST
SW
DRVH
PGND
DRVL
PGOOD
SS
TRACK
09347-003
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 44
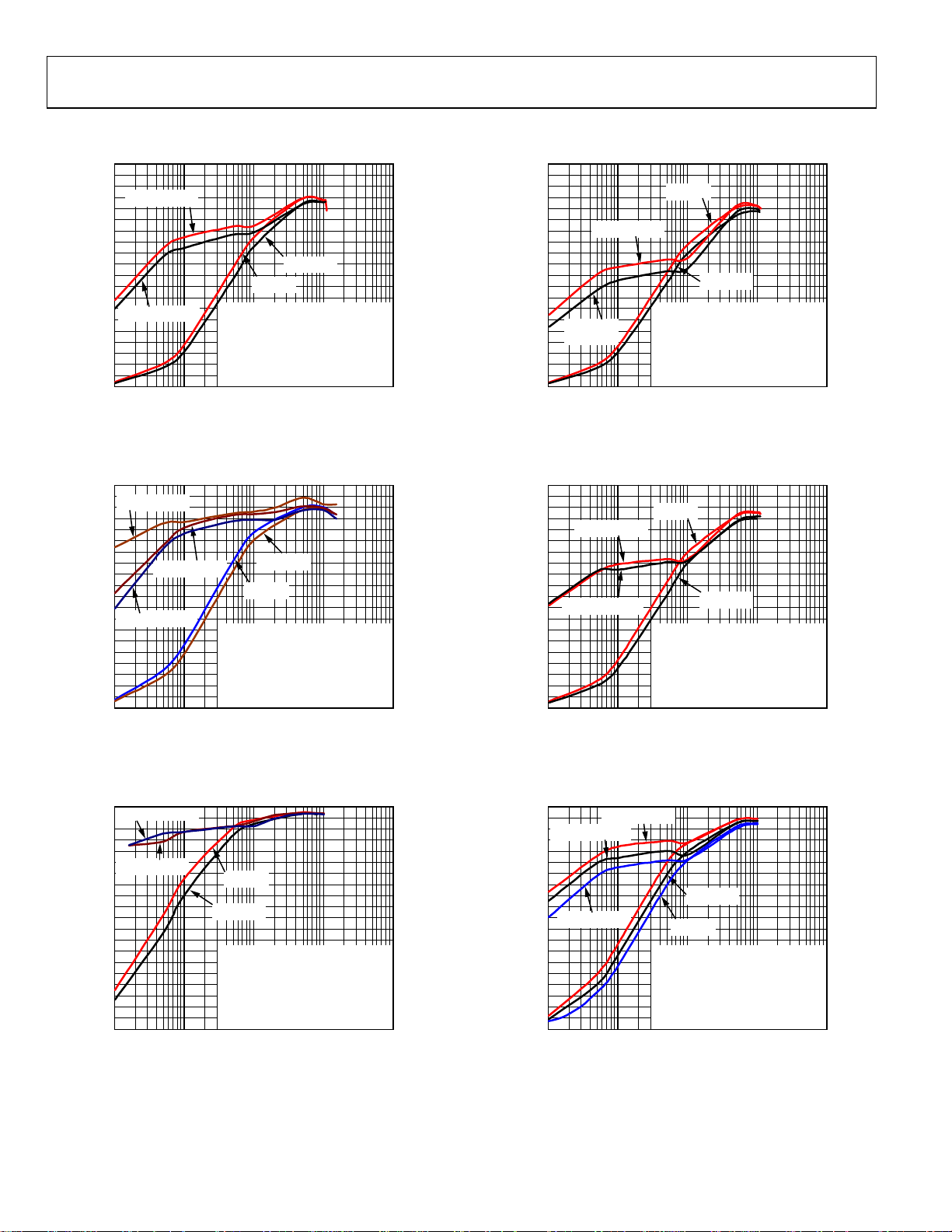
ADP1874/ADP1875
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
100
95
90
VIN = 13V (PSM)
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
TA = 25°C
V
OUT
f
= 300kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744325072, L = 0.72µH, DCR = 1.3m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 4. Efficiency—300 kHz, V
VIN = 13V
= 0.8V
VIN = 16.5V
= 0.8 V
OUT
09347-104
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
VIN = 13V (PSM)
VIN = 16.5V
(PSM)
Figure 7. Efficiency—600 kHz, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
TA = 25°C
= 0.8V
V
OUT
f
= 600kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744355147, L = 0.47µH, DCR = 0.67m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 0.8 V
OUT
09347-107
100
95
VIN = 5V (PSM)
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
VIN = 13V (PSM)
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
10 100 1k 10k 100k
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 5. Efficiency—300 kHz, V
VIN = 16.5V
VIN = 13V
TA = 25°C
= 1.8V
V
OUT
f
= 300kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744325120, L = 1.2µH, DCR = 1.8m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
= 1.8 V
OUT
100
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
95
90
85
80
75
VIN = 13V (PSM)
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Figure 6. Efficiency—300 kHz, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
TA = 25°C
= 7V
V
OUT
f
= 300kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
7443551200, L = 2.0µH, DCR = 2.6m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 7 V
OUT
100
95
90
85
VIN = 13V (PSM)
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
09347-105
Figure 8. Efficiency—600 kHz, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
TA = 25°C
= 1.8V
V
OUT
f
= 600kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744325072, L = 0.72µH, DCR = 1.3m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 1.8 V
OUT
09347-108
100
95
90
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
09347-106
VIN = 13V (PSM)
VIN = 20V (PSM)
VIN = 20V
TA = 25°C
V
OUT
f
= 600kHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744318180, L = 1.4µH, DCR = 3.2m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 9. Efficiency—600 kHz, V
VIN = 16.5V
= 5V
OUT
= 5 V
09347-109
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 44
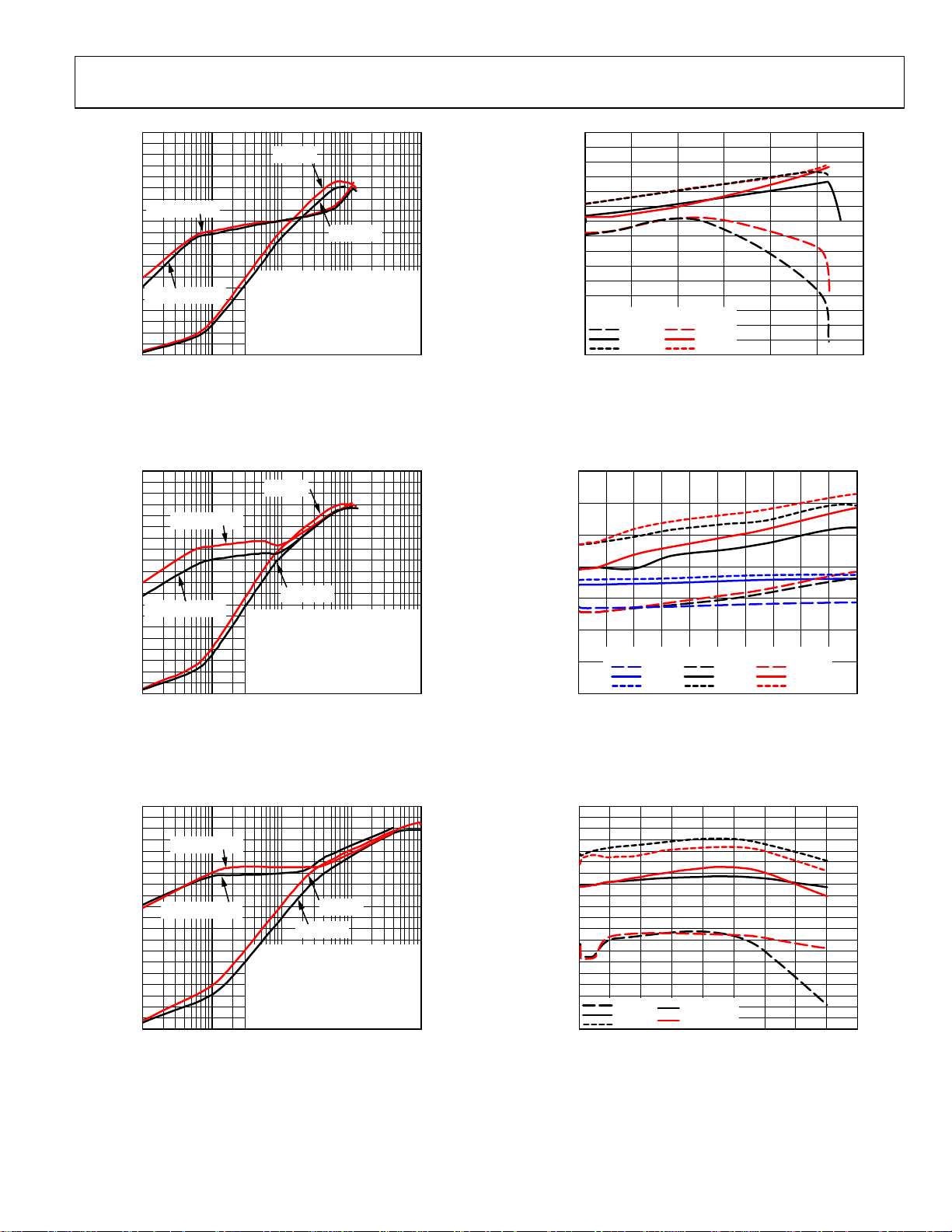
ADP1874/ADP1875
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
VIN = 13V (PSM)
65
60
55
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Figure 10. Efficiency—1.0 MHz, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
TA = 25°C
= 0.8V
V
OUT
f
= 1.0MHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744303012, L = 0.12µH, DCR = 0.33m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 0.8 V
OUT
09347-110
0.807
0.806
0.805
0.804
0.803
0.802
0.801
0.800
0.799
0.798
0.797
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.796
0.795
VIN = 13V
0.794
0.793
0.792
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10,000
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 13. Output Voltage Accuracy—300 kHz, V
OUT
= 0.8 V
09347-013
100
95
90
85
80
VIN = 13V (PSM)
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Figure 11. Efficiency—1.0 MHz, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
TA = 25°C
= 1.8V
V
OUT
f
= 1.0MHz
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744303022, L = 0.22µH, DCR = 0.33m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 1.8 V
OUT
100
95
90
85
VIN = 13V (PSM)
80
75
70
65
60
55
VIN = 16.5V (PSM)
50
45
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1k 10k 100k
TA = 25°C
V
OUT
f
SW
WÜRTH INDUCTOR:
744355090, L = 0.9µH, DCR = 1.6m
INFINEON FETs:
BSC042N03MS G (UPPER/LOWER)
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 12. Efficiency—1.0 MHz, V
VIN = 16.5V
= 5V
= 1.0MHz
VIN = 13V
= 5 V
OUT
1.821
1.816
1.811
1.806
1.801
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1.796
1.791
1.786
0 1500 3000 4500 6000 7500 9000 10,500 12,000 13,500 15,000
09347-111
VIN = 5.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 14. Output Voltage Accuracy—300 kHz, V
VIN = 13V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
OUT
= 1.8 V
09347-014
7.100
7.095
7.090
7.085
7.080
7.075
7.070
7.065
7.060
7.055
7.050
7.045
7.040
7.035
7.030
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
7.025
7.020
7.015
7.010
7.005
7.000
09347-112
Figure 15. Output Voltage Accuracy—300 kHz, V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
OUT
= 7 V
09347-015
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 44
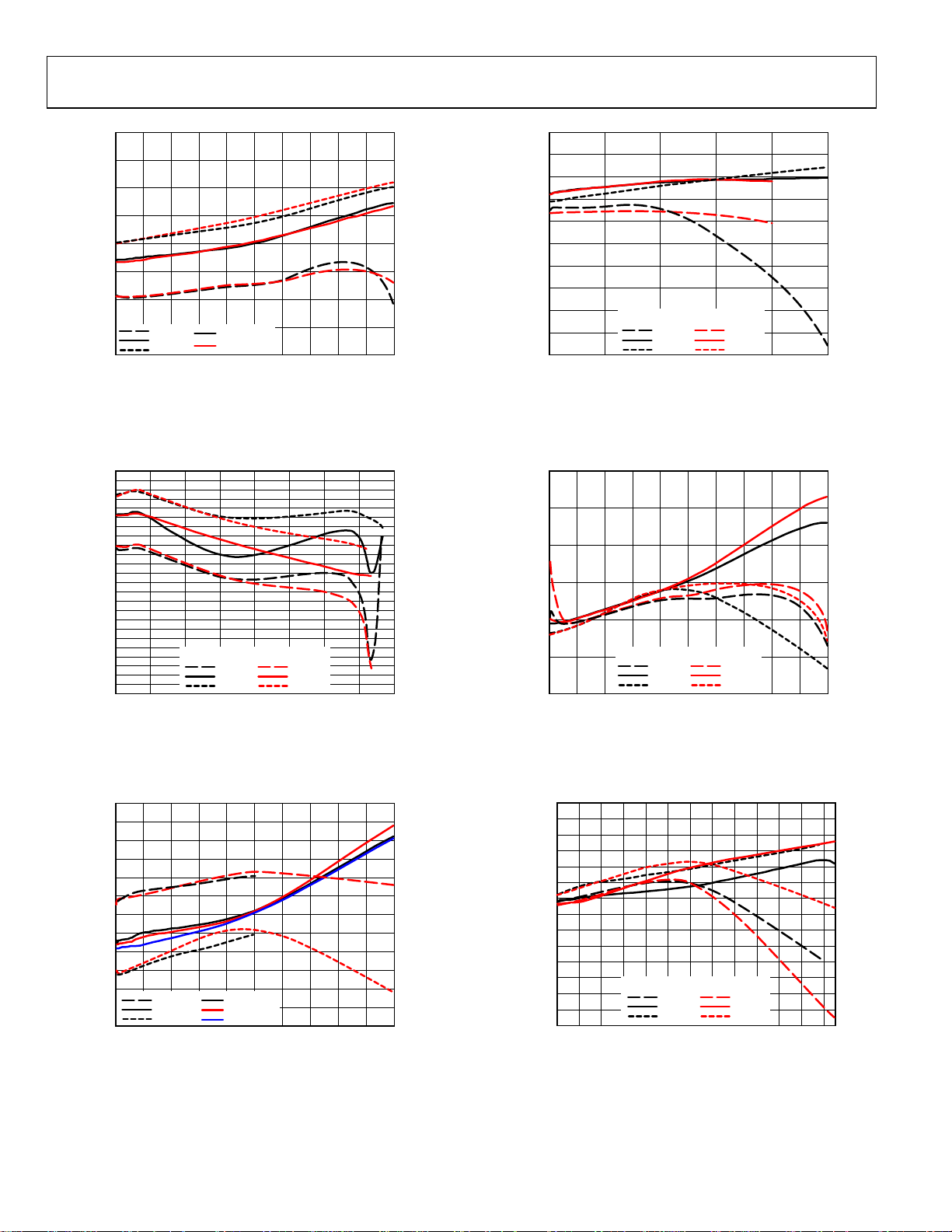
ADP1874/ADP1875
0.808
0.806
0.804
0.802
0.800
0.798
FREQUENCY (kHz)
0.796
0.794
0.792
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 10,0009000
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 16. Output Voltage Accuracy—600 kHz, V
OUT
= 0.8 V
09347-115
0.807
0.805
0.803
0.801
0.799
0.797
0.795
0.793
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.791
0.789
0.787
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10,000
VIN = 13V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 19. Output Voltage Accuracy—1.0 MHz, V
OUT
= 0.8 V
09347-118
1.818
1.816
1.814
1.812
1.810
1.808
1.806
1.804
1.802
1.800
1.798
1.796
1.794
1.792
1.790
1.788
1.786
1.784
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1.782
1.780
1.778
1.776
1.774
1.772
1.770
0 12,00010,500900075006000450030001500
VIN = 13V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 17. Output Voltage Accuracy—600 kHz, V
5.030
5.025
5.020
5.015
5.010
5.005
5.000
4.995
4.990
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
4.985
4.980
4.975
4.970
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10,000
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
VIN = 20V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 18. Output Voltage Accuracy—600 kHz, V
OUT
OUT
= 1.8 V
= 5 V
1.820
1.815
1.810
1.805
1.800
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1.795
1.790
0
09347-016
VIN = 13V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 20. Output Voltage Accuracy—1.0 MHz, V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
OUT
= 1.8 V
10,0000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000
09347-019
5.04
5.03
5.02
5.01
5.00
4.99
4.98
4.97
4.96
4.95
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
4.94
4.93
4.92
4.91
4.90
09347-017
Figure 21. Output Voltage Accuracy—1.0 MHz, V
VIN = 13V
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
7200640056004800400024001600 32000 960088008000800
OUT
=5 V
09347-020
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 44
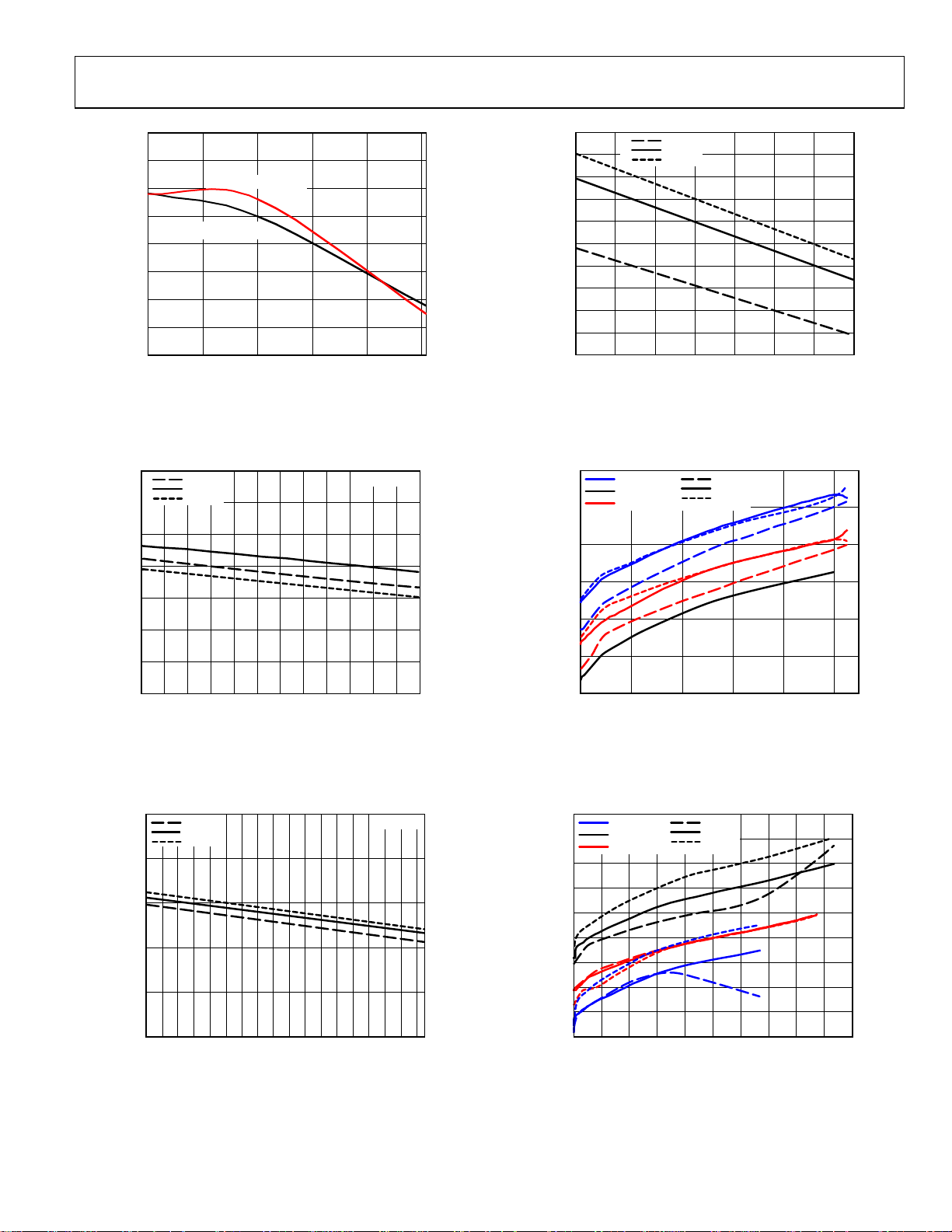
ADP1874/ADP1875
601.0
600.5
600.0
599.5
599.0
598.5
FEEDBACK VOLTAGE (V)
598.0
597.5
597.0
–40.0 –7.5 25.0 57.5 90.0 122.5
VREG = 5V, V
VREG = 5V, VIN = 13V
= 20V
IN
TEMPERATURE (° C)
Figure 22. Feedback Voltage vs. Temperature
09347-121
900
880
860
840
820
800
780
760
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz)
740
720
700
13.0 13.5 14. 0 14.5 15. 0 15.5 16.0 16.5
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN (V)
Figure 25. Switching Frequency vs. High Input Voltage, 1.0 MHz,
Range = 13 V to 16.5 V
V
IN
09347-124
325
315
305
295
285
275
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz)
265
255
10.8 11. 0 11.2 11.4 11.6 11.8 12.0 12.2 12.4 12.6 12.8 13.0 13.2
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN (V)
NO LOAD
09347-022
Figure 23. Switching Frequency vs. High Input Voltage, 300 kHz, ±10% of 12 V
650
600
550
500
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz)
450
400
13.0 13.4 13.8 14.2 14.6 15.0 15.4 15.8 16. 2 16.5
Figure 24. Switching Frequency vs. High Input Voltage, 600 kHz, V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
Range = 13 V to 16.5 V
V
IN
VIN (V)
NO LOAD
= 1.8 V,
OUT
09347-123
280
265
250
235
220
FREQUENCY (kHz)
205
190
VIN = 13V
VIN = 20V
VIN = 16.5V
0 10,0008000600040002000
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 26. Frequency vs. Load Current, 300 kHz, V
330
320
310
300
290
280
270
FREQUENCY (kHz)
260
250
240
0 15,00012,000 13,50010,500900075006000450030001500
VIN = 20V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 27. Frequency vs. Load Current, 300 kHz, V
OUT
OUT
= 0.8 V
= 1.8 V
09347-025
09347-026
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 44
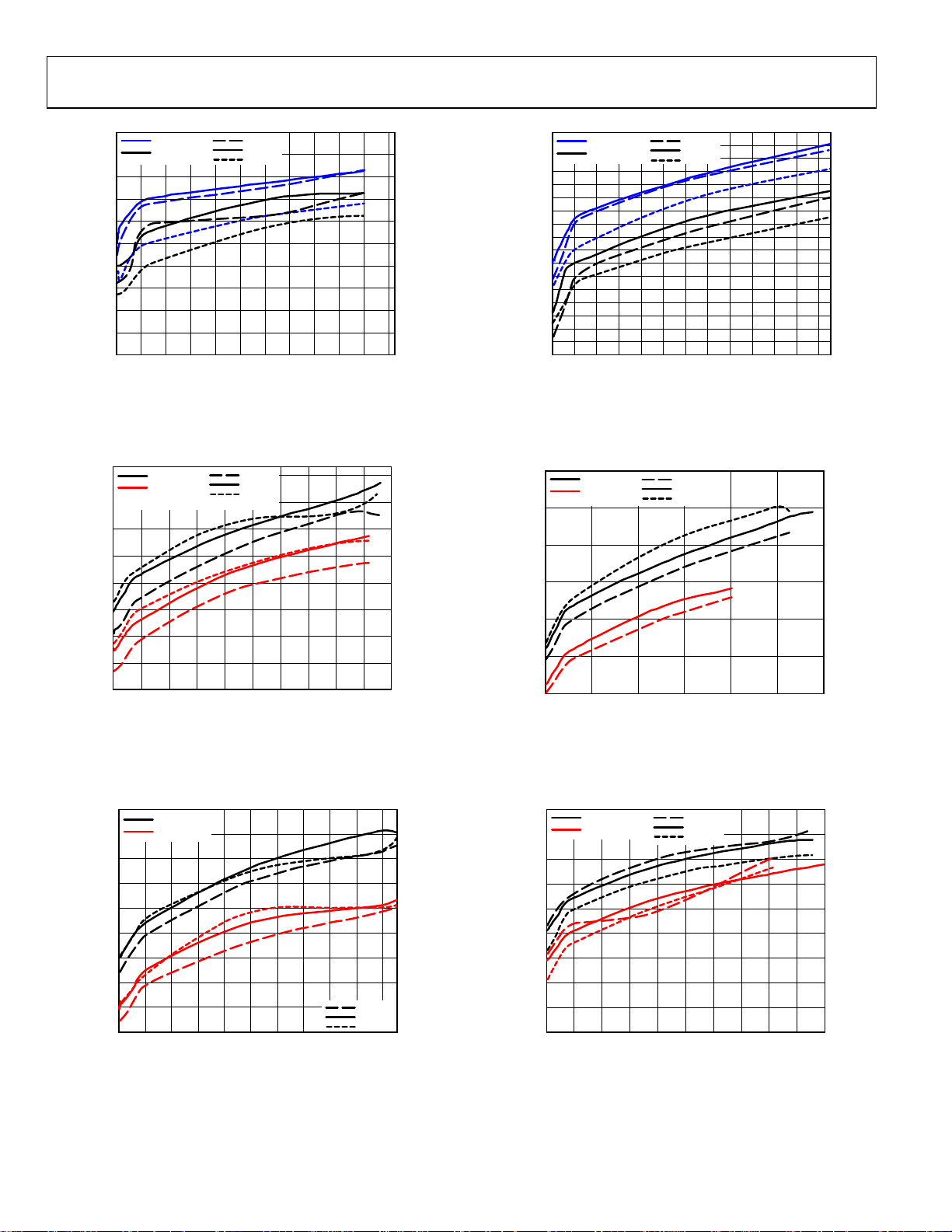
ADP1874/ADP1875
338
334
330
326
322
318
314
FREQUENCY (kHz)
310
306
302
298
0 6400 7200 8000 8800560048004000320024001600800
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 28. Frequency vs. Load Current, 300 kHz, V
OUT
= 7 V
09347-027
740
733
726
719
712
705
698
691
684
677
670
663
FREQUENCY (kHz)
656
649
642
635
628
621
0 96008800800072006400560048004000320024001600800
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 31. Frequency vs. Load Current, 600 kHz, V
OUT
= 5 V
09347-030
540
510
480
450
420
390
FREQUENCY (kHz)
360
330
300
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
0 12,0001200 2400 3600 4800 6000 7200 8400 9600 10,800
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 29. Frequency vs. Load Current, 600 kHz, V
675
655
635
615
595
575
555
FREQUENCY (kHz)
535
515
495
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10,000
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 30. Frequency vs. Load Current, 600 kHz, V
OUT
OUT
= 0.8 V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
= 1.8 V
850
775
700
625
550
FREQUENCY (kHz)
475
400
09347-028
Figure 32. Frequency vs. Load Current, V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
0 12,00010,0008000600040002000
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 1.0 MHz, 0.8 V
OUT
09347-031
1225
1150
1075
1000
925
850
775
FREQUENCY (kHz)
700
625
550
09347-029
Figure 33. Frequency vs. Load Current, 1.0 MHz, V
VIN = 13V +125°C
VIN = 16.5V
0 12,0009600 10,8008400720060004800360024001200
+25°C
–40°C
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 1.8 V
OUT
09347-032
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 44
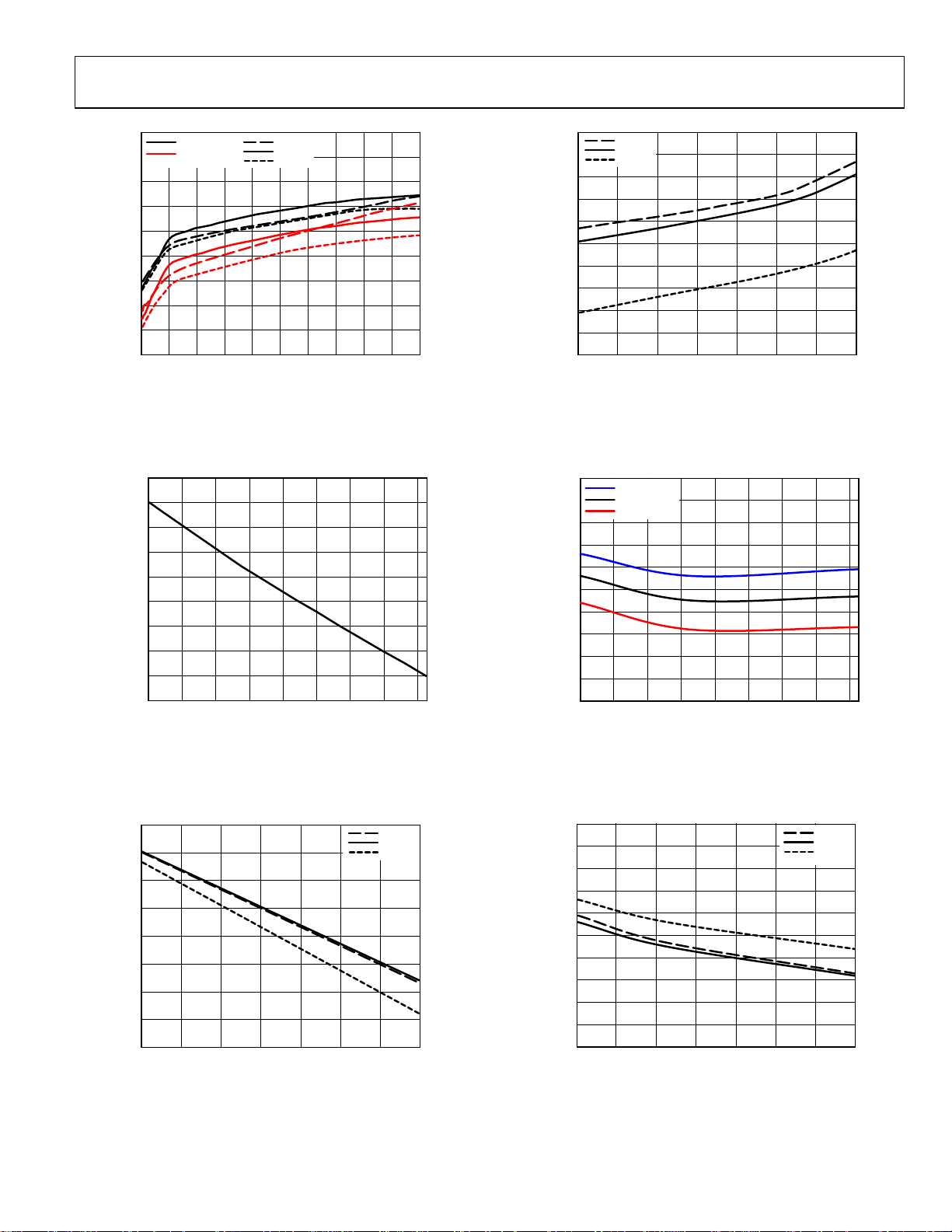
ADP1874/ADP1875
1450
1400
1350
1300
1250
1200
1150
FREQUENCY (kHz)
1100
1050
1000
08000
Figure 34. Frequency vs. Load Current, 1.0 MHz, V
= 13V +125°C
V
IN
= 16.5V
V
IN
800 1600 2400 3200 4000 4800 5600 6400 7200
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
+25°C
–40°C
OUT
= 5 V
09347-033
82
80
78
76
74
72
70
68
MAXIMUM DUTY CYCLE (%)
66
64
62
5.5 6.7 7.9 9.1 10.3 11.5 12.7 13.9 15.1 16.3
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
VIN (V)
Figure 37. Maximum Duty Cycle vs. High Voltage Input (V
09347-036
)
IN
2.658
2.657
2.656
2.655
2.654
2.653
UVLO (V)
2.652
2.651
2.650
2.649
–40 120100806040200–20
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 35. UVLO vs. Temperature
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
MAXIMUM DUTY CYCLE (%)
60
55
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 36. Maximum Duty Cycle vs. Frequency
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
680
630
580
530
480
430
380
330
MINUMUM OFF-TIME (ns)
280
230
180
–40 120100806040200–20
09347-034
VREG = 2.7V
VREG = 3.6V
VREG = 5.5V
TEMPERATURE (° C)
09347-037
Figure 38. Minimum Off-Time vs. Temperature
680
630
580
530
480
430
380
330
MINUMUM OFF-TIME (ns)
280
230
180
2.7 5.55.14.74.33.93.53.1
09347-035
VREG (V)
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
09347-038
Figure 39. Minimum Off-Time vs. VREG (Low Input Voltage)
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 44
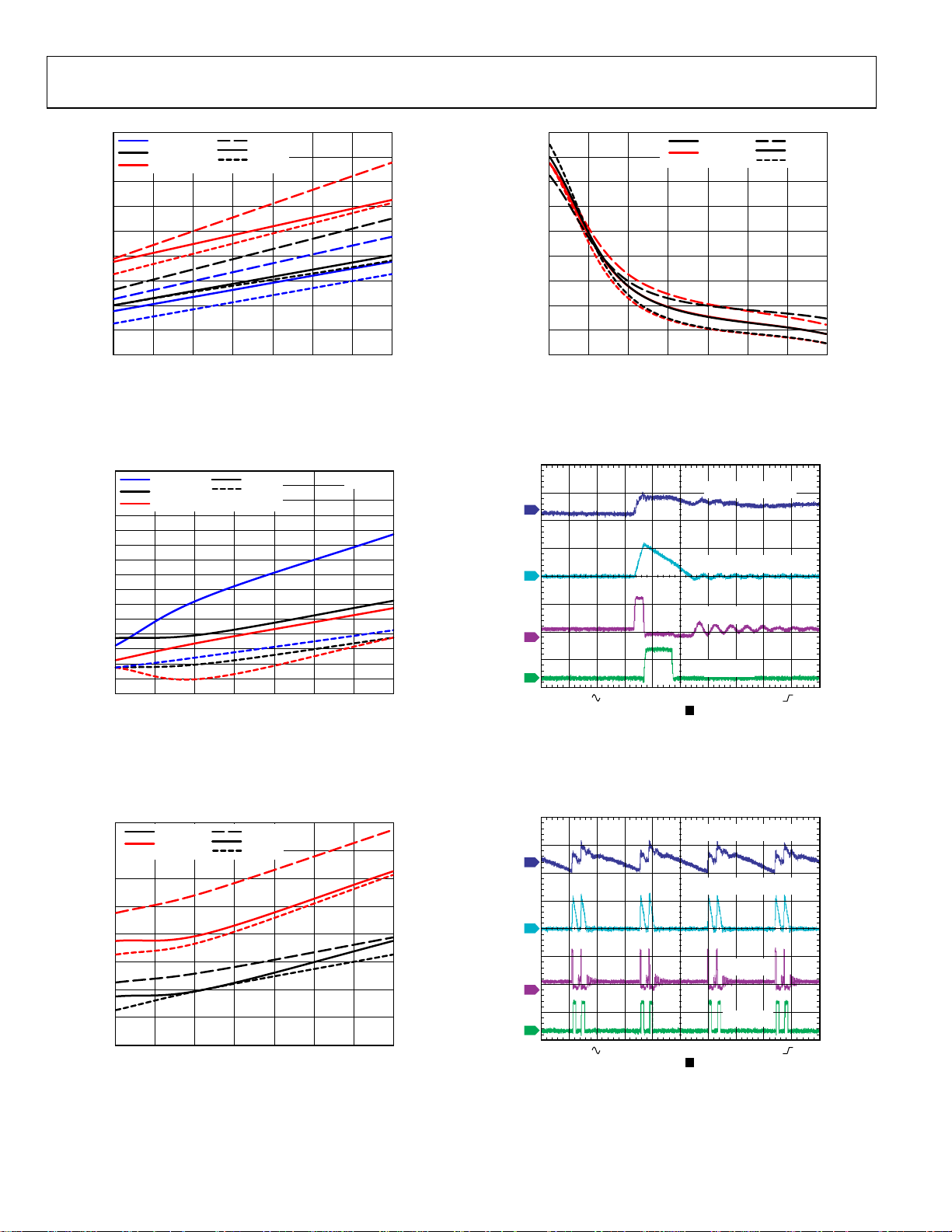
ADP1874/ADP1875
800
720
640
560
480
400
320
RECTIFIER DROP (mV)
240
160
80
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
VREG = 2.7V
VREG = 3.6V
VREG = 5.5V
+125°C
+25°C
–40°C
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 40. Internal Rectifier Drop vs. Frequency
09347-039
80
72
64
56
48
40
32
24
BODY DIODE CONDUCTION TIME (ns)
16
8
2.73.13.53.94.34.75.15.5
300kHz +125°C
1MHz
VREG (V)
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 43. Lower-Side MOSFET Body Diode Conduction Time vs. VREG
09347-042
1280
1200
1120
1040
960
880
800
720
640
560
480
RECTIFIER DROP (mV)
400
320
240
160
80
2.73.13.53.94.34.75.15.5
VIN = 5.5V
VIN = 13V
VIN = 16.5V
1MHz
300kHz
VREG (V)
TA = 25°C
Figure 41. Internal Boost Rectifier Drop vs. VREG (Low Input Voltage)
Variation
Over V
IN
720
640
560
480
400
300kHz +125°C
1MHz
+25°C
–40°C
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
1
2
3
4
CH1 50mV
09347-040
CH3 10V
B
CH2 5A
W
B
CH4 5V
W
INDUCTOR CURRENT
SW NODE
LOW SIDE
M400ns A CH2 3.90A
T 35.8%
09347-043
Figure 44. Power Saving Mode (PSM) Operational Waveform, 100 mA
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
1
INDUCTOR CURRENT
2
320
RECTIFIER DROP (mV)
240
160
80
2.73.13.53.94.34.75.15.5
VREG (V)
Figure 42. Internal Boost Rectifier Drop vs. VREG
09347-041
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 44
3
4
CH1 50mV
CH3 10V
B
CH2 5A
W
B
CH4 5V
W
M4.0µs A CH2 3.90A
T 35.8%
Figure 45. PSM Waveform at Light Load, 500 mA
SW NODE
LOW SIDE
09347-044
 Loading...
Loading...