3.3 V, 100 Mbps, Half- and Full-Duplex,
V
V
Data Sheet
FEATURES
Multipoint LVDS transceivers (low voltage differential
signaling driver and receiver pairs)
Switching rate: 100 Mbps (50 MHz)
Supported bus loads: 30 Ω to 55 Ω
Choice of 2 receiver types
Type 1 (ADN4690E/ADN4692E): hysteresis of 25 mV
Type 2 (ADN4694E/ADN4695E): threshold offset of 100 mV
for open-circuit and bus-idle fail-safe
Conforms to TIA/EIA-899 standard for M-LVDS
Glitch-free power-up/power-down on M-LVDS bus
Controlled transition times on driver output
Common-mode range: −1 V to +3.4 V, allowing
communication with 2 V of ground noise
Driver outputs high-Z when disabled or powered off
Enhanced ESD protection on bus pins
±15 kV HBM (human body model), air discharge
±8 kV HBM (human body model), contact discharge
±10 kV IEC 61000-4-2, air discharge
±8 kV IEC 61000-4-2, contact discharge
Operating temperature range: −40°C to +85°C
Available in 8-lead (ADN4690E/ADN4694E) and 14-lead
(ADN4692E/ADN4695E) SOIC packages
APPLICATIONS
Backplane and cable multipoint data transmission
Multipoint clock distribution
Low power, high speed alternative to shorter RS-485 links
Networking and wireless base station infrastructure
High Speed M-LVDS Transceivers
ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
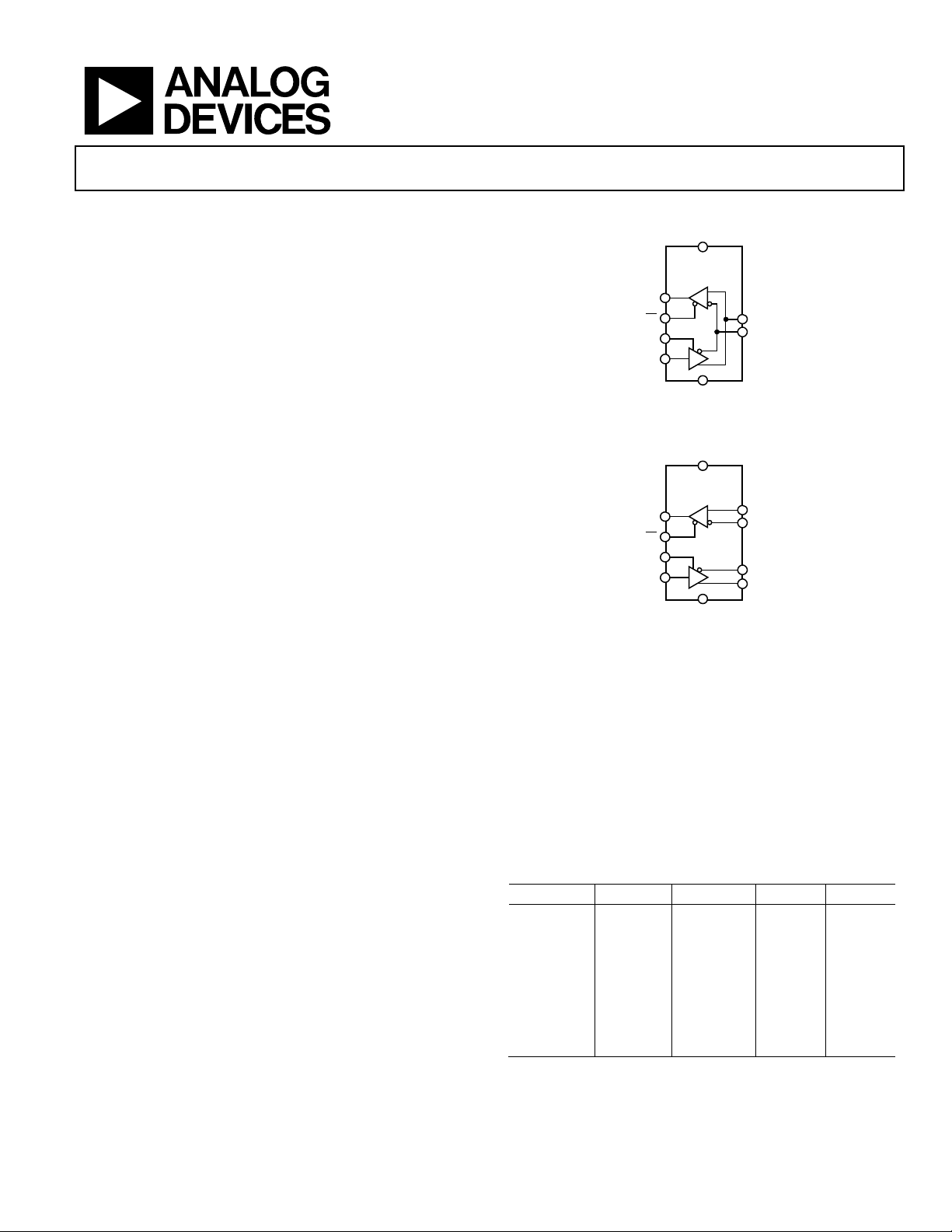
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAMS
CC
ADN4690E/
ADN4694E
RO R
RE
DE
D
DI
GND
Figure 1.
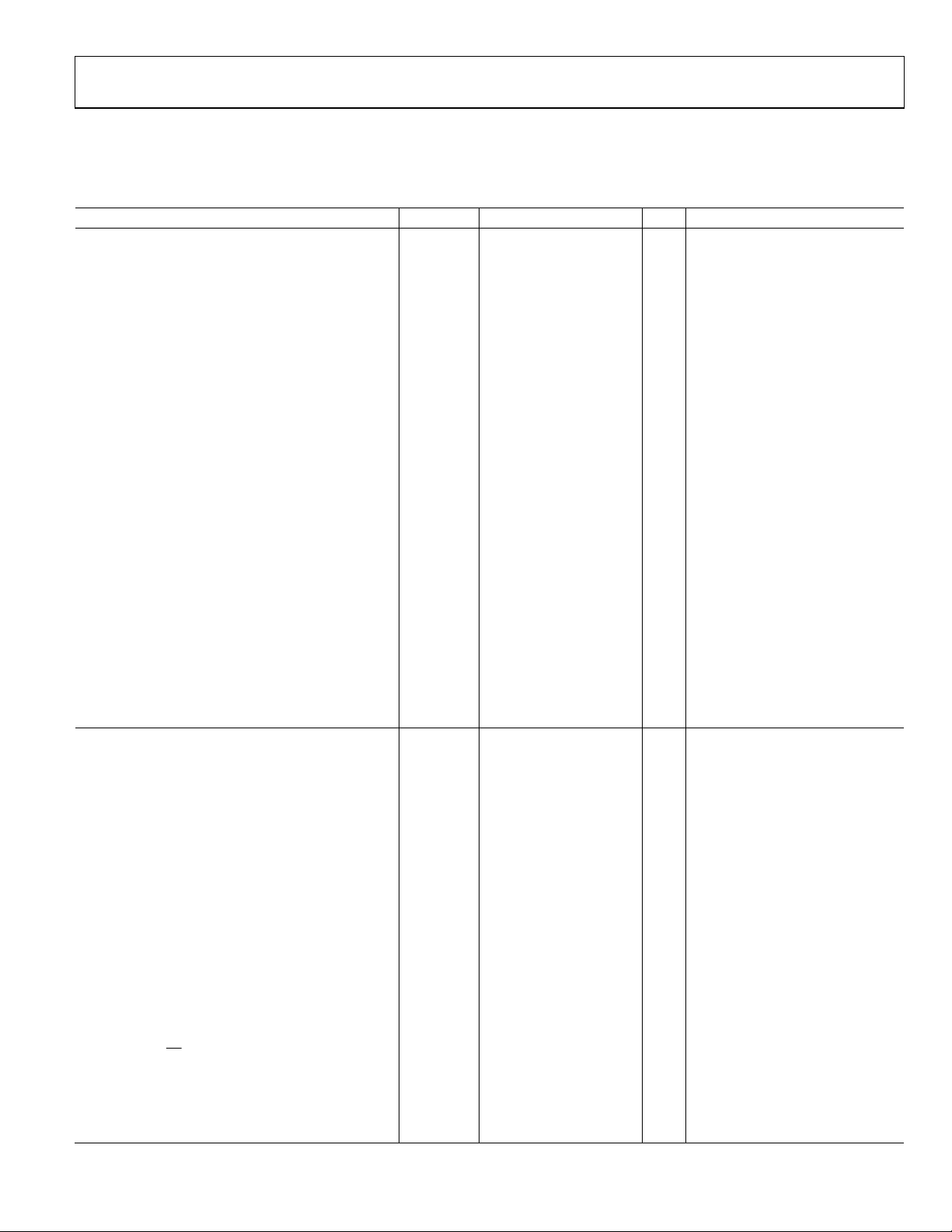
CC
ADN4692E/
ADN4695E
RO R
RE
DE
D
DI
GND
Figure 2.
A
B
10471-001
A
B
Z
Y
10471-102
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E are
multipoint, low voltage differential signaling (M-LVDS)
transceivers (driver and receiver pairs) that can operate at up
to 100 Mbps (50 MHz). Slew rate control is implemented on the
driver outputs. The receivers detect the bus state with a differential
input of as little as 50 mV over a common-mode voltage range of
−1 V to +3.4 V. ESD protection of up to ±15 kV is implemented
on the bus pins. The parts adhere to the TIA/EIA-899 standard for
M-LVDS and complement TIA/EIA-644 LVDS devices with
additional multipoint capabilities.
The ADN4690E/ADN4692E are Type 1 receivers with 25 mV of
hysteresis, so that slow-changing signals or loss of input does
not lead to output oscillations. The ADN4694E/ADN4695E are
Type 2 receivers exhibiting an offset threshold, guaranteeing the
output state when the bus is idle (bus-idle fail-safe) or the
inputs are open (open-circuit fail-safe).
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The parts are available as half-duplex in an 8-lead SOIC package
(the ADN4690E/ADN4694E) or as full-duplex in a 14-lead
SOIC package (the ADN4692E/ADN4695E). A selection table
for the ADN469xE parts is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. ADN469xE Selection Table
Part No. Receiver Data Rate SOIC Duplex
ADN4690E Type 1 100 Mbps 8-lead Half
ADN4691E Type 1 200 Mbps 8-lead Half
ADN4692E Type 1 100 Mbps 14-lead Full
ADN4693E Type 1 200 Mbps 14-lead Full
ADN4694E Type 2 100 Mbps 8-lead Half
ADN4695E Type 2 100 Mbps 14-lead Full
ADN4696E Type 2 200 Mbps 8-lead Half
ADN4697E Type 2 200 Mbps 14-lead Full
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagrams ............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Receiver Input Threshold Test Voltages .................................... 4
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 6
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 6
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 6
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Test Circuits and Switching Characteristics ................................ 11
REVISION HISTORY
3/12—Rev. 0 to R e v. A
Added ADN4694E and ADN4695E ................................. Universal
Change to Features Section, General Description Section,
and Table 1 .......................................................................................... 1
Added Type 2 Receiver Parameters, Table 2 .................................. 3
Added Table 4, Renumbered Sequentially ..................................... 5
Added Type 2 Receiver Parameters, Table 5 .................................. 5
Driver Voltage and Current Measurements ............................ 11
Driver Timing Measurements .................................................. 12
Receiver Timing Measurements ............................................... 13
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 14
Half-Duplex/Full-Duplex Operation ....................................... 14
Three-State Bus Connection ..................................................... 14
Tr u t h Ta b l es ................................................................................. 14
Glitch-Free Power-Up/Power-Down ....................................... 15
Fault Conditions ......................................................................... 15
Receiver Input Thresholds/Fail-Safe ........................................ 15
Applications Information .............................................................. 16
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 17
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 17
Changes to Table 8 ............................................................................. 7
Added Table 13 ................................................................................ 14
Changes to Receiver Input Thresholds/Fail-Safe Section
and Figure 35 .................................................................................... 15
Changes to Figure 36 and Figure 37 and Their Captions .......... 16
Changes to Ordering Guide ........................................................... 18
1/12—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 20
Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
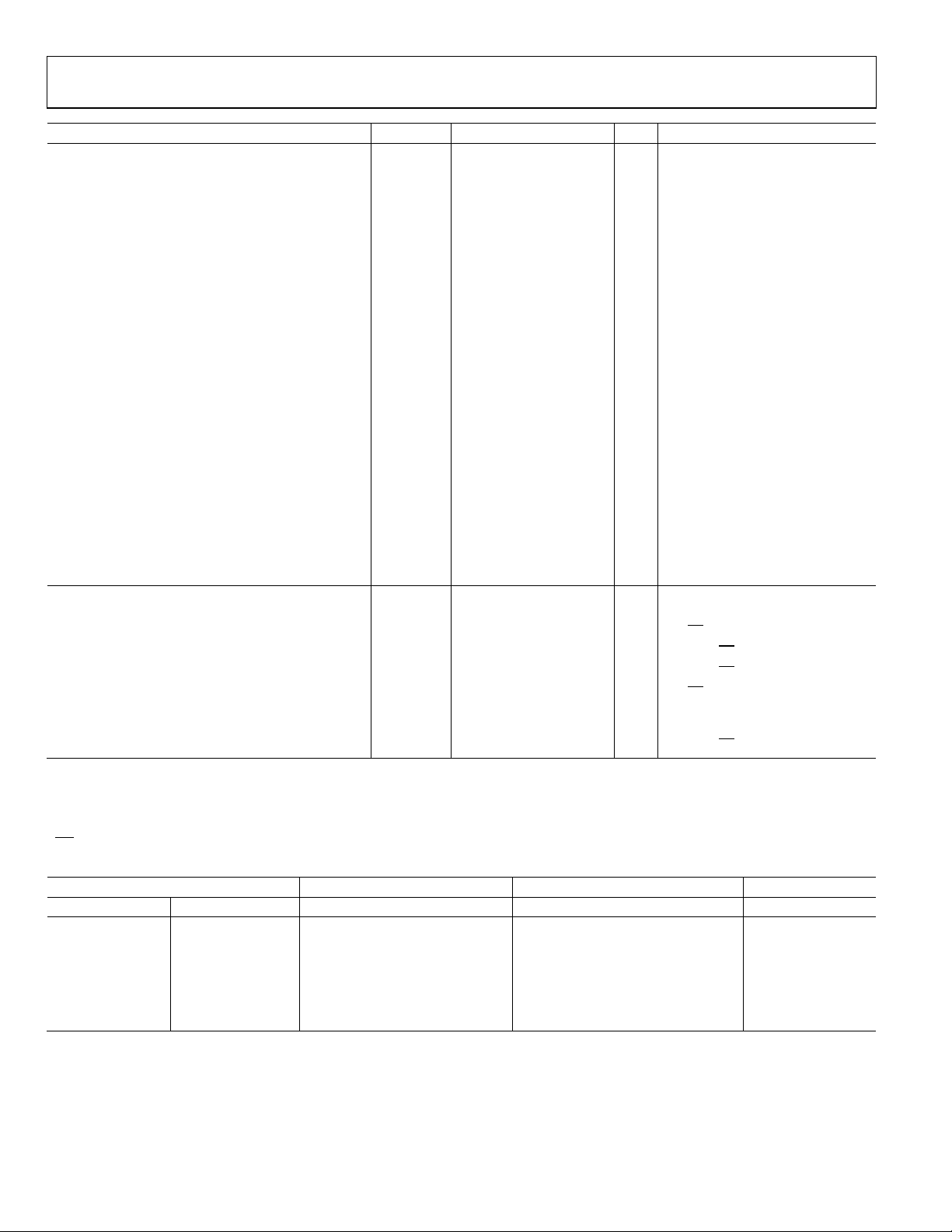
SPECIFICATIONS
VCC = 3.0 V to 3.6 V; RL = 50 Ω; TA = T
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DRIVER
Differential Outputs
Differential Output Voltage Magnitude |VOD| 480 650 mV See Figure 18
∆|VOD| for Complementary Output States ∆|VOD| −50 +50 mV See Figure 18
Common-Mode Output Voltage (Steady State) V
ΔV
for Complementary Output States ΔV
OC(SS)
Peak-to-Peak VOC V
Maximum Steady-State Open-Circuit Output
Voltage
Voltage Overshoot
Low to High VPH 1.2VSS V See Figure 23, Figure 26
High to Low VPL −0.2VSS V See Figure 23, Figure 26
Output Current
Short Circuit |IOS| 24 mA See Figure 21
High Impedance State, Driver Only IOZ −15 +10 μA
Power Off I
Output Capacitance CY or CZ 3 pF
Differential Output Capacitance CYZ 2.5 pF VAB = 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V,2 DE = 0 V
Output Capacitance Balance (CY/CZ) C
Logic Inputs (DI, DE)
Input High Voltage VIH 2 VCC V
Input Low Voltage VIL GND 0.8 V
Input High Current IIH 0 10 μA VIH = 2 V to VCC
Input Low Current IIL 0 10 μA VIL = GND to 0.8 V
RECEIVER
Differential Inputs
Differential Input Threshold Voltage
Type 1 Receiver (ADN4690E, ADN4692E) VTH −50 +50 mV See Table 3, Figure 35
Type 2 Receiver (ADN4694E, ADN4695E) VTH 50 150 mV See Table 4, Figure 35
Input Hysteresis
Type 1 Receiver (ADN4690E, ADN4692E) V
Type 2 Receiver (ADN4694E, ADN4695E) V
Differential Input Voltage Magnitude |VID| 0.05 VCC V
Input Capacitance CA or CB 3 pF
Differential Input Capacitance CAB 2.5 pF VAB = 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V2
Input Capacitance Balance (CA/CB) C
Logic Output RO
Output High Voltage VOH 2.4 V IOH = –8 mA
Output Low Voltage VOL 0.4 V IOL = 8 mA
High Impedance Output Current IOZ −10 +15 μA VO = 0 V or 3.6 V
Logic Input RE
Input High Voltage VIH 2 VCC V
Input Low Voltage VIL GND 0.8 V
Input High Current IIH −10 0 μA VIH = 2 V to VCC
Input Low Current IIL −10 0 μA VIL = GND to 0.8 V
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.1
MAX
0.8 1.2 V See Figure 19, Figure 22
OC(SS)
−50 +50 mV See Figure 19, Figure 22
OC(SS)
150 mV See Figure 19, Figure 22
OC(PP)
V
, V
,
A(O)
B(O)
, or V
V
Y(O)
O(OFF)
Y/Z
HYS
HYS
A/B
Z(O)
−10 +10 μA
0.99 1.01
25 mV
0 mV
0.99 1.01
0 2.4 V See Figure 20
–1.4 V ≤ (V
or VZ) ≤ 3.8 V,
Y
other output = 1.2 V
–1.4 V ≤ (V
or VZ) ≤ 3.8 V,
Y
other output = 1.2 V, 0 V ≤ V
= 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V + 0.5 V,2
V
I
other output = 1.2 V, DE = 0 V
= 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V + 0.5 V,2
V
I
other input = 1.2 V
≤ 1.5 V
CC
Rev. A | Page 3 of 20
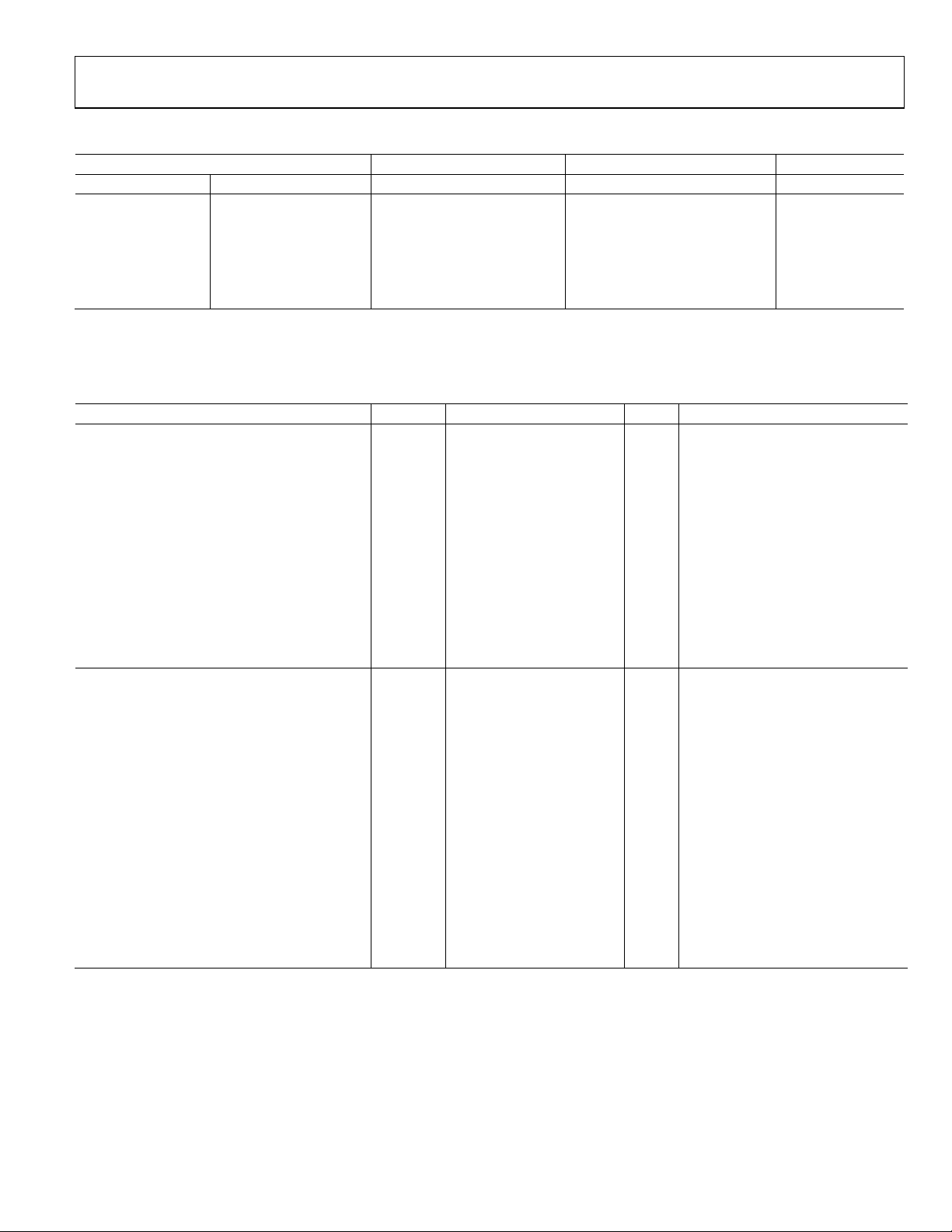
ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
−32 0
µA
VB = 1.2 V, VA = −1.4 V
Power-Off Input Current
0 V ≤ VCC ≤ 1.5 V
POWER SUPPLY
Parameter Symbol Min Ty p Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
BUS INPUT/OUTPUT
Input Current
A (Receiver or Transceiver with Driver Disabled) IA 0 32 µA VB = 1.2 V, VA = 3.8 V
−20 +20 µA VB = 1.2 V, VA = 0 V or 2.4 V
B (Receiver or Transceiver with Driver Disabled) IB 0 32 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = 3.8 V
−20 +20 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = 0 V or 2.4 V
−32 0 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = −1.4 V
−4 +4 µA VA = VB, 1.4 ≤ VA ≤ 3.8 V
Differential (Receiver or Transceiver with Driver
Disabled)
I
AB
A (Receiver or Transceiver) I
0 32 µA VB = 1.2 V, VA = 3.8 V
A(OFF)
−20 +20 µA VB = 1.2 V, VA = 0 V or 2.4 V
−32 0 µA VB = 1.2 V, VA = −1.4 V
B (Receiver or Transceiver) I
0 32 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = 3.8 V
B(OFF)
−20 +20 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = 0 V or 2.4 V
−32 0 µA VA = 1.2 V, VB = −1.4 V
Differential (Receiver or Transceiver) I
Input Capacitance (Transceiver with Driver Disabled) CA or CB 5 pF
−4 +4 µA VA = VB, 1.4 V ≤ VA ≤ 3.8 V
AB(OFF)
= 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V + 0.5 V,2
V
I
other input = 1.2 V, DE = 0 V
3 pF VAB = 0.4 sin(30e6πt) V,2 DE = 0 V
Differential Input Capacitance (Transceiver with
C
AB
Driver Disabled)
C
Input Capacitance Balance (CA/CB) (Transceiver
0.99 1.01 DE = 0 V
A/B
with Driver Disabled)
Supply Current ICC
Only Driver Enabled 13 22 mA
Both Driver and Receiver Disabled 1 4 mA
Both Driver and Receiver Enabled 16 24 mA
Only Receiver Enabled 4 13 mA
Total Power Dissipation PD 94 mW
RE
= VCC, RL = 50 Ω
DE,
RE
DE = 0 V,
DE = V
DE,
= 50 Ω, input (DI) = 50 MHz,
R
L
= VCC, RL = no load
, RE = 0 V, RL = 50 Ω
CC
RE
= 0 V, RL = 50 Ω
50% duty cycle square wave;
; RE = 0 V; TA = 85°C
CC
1
All typical values are given for VCC = 3.3 V and TA = 25°C.
2
HP4194A impedance analyzer (or equivalent).
DE = V
RECEIVER INPUT THRESHOLD TEST VOLTAGES
RE
= 0 V, H = high, L = low.
Table 3. Test Voltages for Type 1 Receiver
Applied Voltages Input Voltage, Differential Input Voltage, Common Mode Receiver Output
VA (V) VB (V) VID (V) VIC (V) RO
2.4 0 2.4 1.2 H
0 2.4 −2.4 1.2 L
3.425 3.375 0.05 3.4 H
3.375 3.425 −0.05 3.4 L
−0.975 −1.025 0.05 −1 H
−1.025 −0.975 −0.05 −1 L
Rev. A | Page 4 of 20
Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
Period Jitter, rms (One Standard Deviation)2
t
2 3 ps
50 MHz clock input3 (see Figure 25)
Enable Time to High Level
t
4 7 ns
See Figure 24, Figure 27
Propagation Delay
t
, t
2 6
ns
CL = 15 pF (see Figure 29, Figure 32)
Period Jitter, rms (One Standard Deviation)2
t
4 7 ps
50 MHz clock input3 (see Figure 31)
Table 4. Test Voltages for Type 2 Receiver
Applied Voltages Input Voltage, Differential Input Voltage, Common Mode Receiver Output
VA (V) VB (V) VID (V) VIC (V) RO
2.4 0 2.4 1.2 H
0 2.4 −2.4 1.2 L
3.475 3.325 0.15 3.4 H
3.425 3.375 0.05 3.4 L
−0.925 −1.075 0.15 −1 H
−0.975 −1.025 0.05 −1 L
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VCC = 3.0 V to 3.6 V; TA = T
Table 5.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DRIVER
Maximum Data Rate 100 Mbps
Propagation Delay t
Differential Output Rise/Fall Time tR, tF 2 2.6 3.2 ns See Figure 23, Figure 26
Pulse Skew |t
PHL
− t
PLH
Part-to-Part Skew t
Peak-to-Peak Jitter
2, 4
Disable Time from High Level t
Disable Time from Low Level t
Enable Time to Low Level t
RECEIVER
Rise/Fall Time tR, tF 1 2.3 ns CL = 15 pF (see Figure 29, Figure 32)
Pulse Skew |t
RPHL
– t
Type 1 Receiver (ADN4690E, ADN4692E) tSK 100 300 ps
Type 2 Receiver (ADN4694E, ADN4695E) tSK 300 500 ps
Part-to-Part Skew6 t
Peak-to-Peak Jitter
2, 4
Type 1 Receiver (ADN4690E, ADN4692E) t
Type 2 Receiver (ADN4694E, ADN4695E) t
Disable Time from High Level t
Disable Time from Low Level t
Enable Time to High Level t
Enable Time to Low Level t
1
All typical values are given for VCC = 3.3 V and TA = 25°C.
2
Jitter parameters are guaranteed by design and characterization. Values do not include stimulus jitter.
3
tR = tF = 0.5 ns (10% to 90%), measured over 30,000 samples.
4
Peak-to-peak jitter specifications include jitter due to pulse skew (tSK).
5
tR = tF = 0.5 ns (10% to 90%), measured over 100,000 samples.
6
HP4194A impedance analyzer or equivalent.
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.1
MAX
, t
PLH
PHL
2 2.5 3.5 ns See Figure 23, Figure 26
| tSK 30 150 ps See Figure 23, Figure 26
0.9 ns See Figure 23, Figure 26
SK(PP)
t
J(PER)
150 ps
J(PP)
100 Mbps 2
15
− 1 PRBS input5
(see Figure 28)
4 7 ns See Figure 24, Figure 27
PHZ
4 7 ns See Figure 24, Figure 27
PLZ
PZH
4 7 ns See Figure 24, Figure 27
PZL
RPLH
RPHL
| CL = 15 pF (see Figure 29, Figure 32)
RPLH
1 ns CL = 15 pF (see Figure 29, Figure 32)
SK(PP)
J(PER)
100 Mbps 2
15
− 1 PRBS input5
(see Figure 34)
200 700 ps
J(PP)
225 800 ps
J(PP)
6 10 ns See Figure 30, Figure 33
RPHZ
6 10 ns See Figure 30, Figure 33
RPLZ
10 15 ns See Figure 30, Figure 33
RPZH
10 15 ns See Figure 30, Figure 33
RPZL
Rev. A | Page 5 of 20
ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
–0.5 V to +4 V
Driver Output (A, B, Y, Z) Voltage
–1.8 V to +4 V
IEC 61000-4-2, Air Discharge
±10 kV
Operating Temperature Range
−40°C to +85°C
Package Type
θJA
Unit
14-Lead SOIC
86
°C/W
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
VCC –0.5 V to +4 V
Digital Input Voltage (DE, , DI)
Receiver Input (A, B) Voltage
Half-Duplex (ADN4690E, ADN4694E) –1.8 V to +4 V
Full-Duplex (ADN4692E, ADN4695E) –4 V to +6 V
Receiver Output Voltage (RO) –0.3 V to +4 V
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
8-Lead SOIC 121 °C/W
ESD Rating (A, B, Y, Z Pins)
HBM (Human Body Model)
Air Discharge ±15 kV
Contact Discharge ±8 kV
IEC 61000-4-2, Contact Discharge ±8 kV
ESD Rating (Other Pins, HBM) ±4 kV
ESD Rating (All Pins)
FICDM ±1.25 kV
Machine Model ±400 V
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 6 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
RO
1
RE
2
DE
3
DI
4
V
CC
8
B
7
A
6
GND
5
ADN4690E/
ADN4694E
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
10471-002
Figure 3. ADN4690E/ADN4694E Pin Configuration
NC
1
2
3
4
V
CC
14
13
12
11
5 10
GND
6
Y
9
GND
7
NC
8
NOTES
1. NC = NO CONNEC T. DO NOT
CONNECT TO THIS PIN.
ADN4692E/
ADN4695E
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
RO
RE
DE
DI
V
CC
A
B
Z
10471-104
N/A
11 B Inverting Receiver Input B.
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Figure 4. ADN4692E/ADN4695E Pin Configuration
Table 8. Pin Function Descriptions
ADN4690E/
ADN4694E
Pin No.
1 2 RO Receiver Output. Type 1 receiver (ADN4690E/ADN4692E), when enabled:
2 3
3 4 DE
4 5 DI Driver Input. Half-duplex (ADN4690E/ADN4694E), when enabled:
5 6, 7 GND Ground.
N/A 9 Y Noninverting Driver Output Y.
N/A 10 Z Inverting Driver Output Z.
6 N/A A Noninverting Receiver Input A and Noninverting Driver Output A.
N/A 12 A Noninverting Receiver Input A.
7 N/A B Inverting Receiver Input B and Inverting Driver Output B.
ADN4692E/
ADN4695E
Pin No.
Mnemonic Description
If A − B ≥ 50 mV, then RO = logic high. If A − B ≤ −50 mV, then RO = logic low.
Type 2 receiver (ADN4694E/ADN4695E), when enabled:
If A − B ≥ 150 mV, then RO = logic high. If A − B ≤ 50 mV, then RO = logic low.
Receiver output is undefined outside these conditions.
RE
Receiver Output Enable. A logic low on this pin enables the receiver output, RO.
A logic high on this pin places RO in a high impedance state.
Driver Output Enable. A logic high on this pin enables the driver differential outputs.
A logic low on this pin places the driver differential outputs in a high impedance state.
A logic low on DI forces A low and B high, whereas a logic high on DI forces A high and B low.
Full-duplex (ADN4692E/ADN4695E), when enabled:
A logic low on DI forces Y low and Z high, whereas a logic high on DI forces Y high and Z low.
8 13, 14 VCC Power Supply (3.3 V ± 0.3 V).
N/A 1, 8 NC No Connect. Do not connect to these pins.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
0
6
4
2
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
SUPPLY CURRENT, I
CC
(mA)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10471-003
DRIVER
RECEIVER (V
ID
= 200mV, VIC = 1V)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
SUPPLY CURRENT, I
CC
(mA)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
10471-004
DRIVER
RECEIVER (VID = 200mV, V
IC
= 1V)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 0.5 1.0 1
.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
RECEIVER LOW LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT, I
OL
(mA)
RECEIVER LOW LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE, VOL(V)
VCC= 3V
VCC= 3.3V
VCC= 3.6V
10471-005
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
RECEIVER HIGH LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
RECEIVER HIGH LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE, VOH (V)
VCC = 3.0V
VCC = 3.3V
V
CC
= 3.6V
10471-006
2.0
2.2
2.4
2.6
3.0
2.8
3.2
3.4
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
DRIVER PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
10471-007
t
PLH
t
PHL
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
5.0
4.5
5.5
6.0
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
RECEIVER PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
10471-008
t
RPLH
t
RPHL
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 5. Power Supply Current vs. Frequency
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C)
(V
CC
Figure 6. Power Supply Current vs. Temperature
(Data Rate = 100 Mbps, V
= 3.3 V)
CC
Figure 8. Receiver Output Current vs. Output Voltage (Output High)
= 25°C)
(T
A
Figure 9. Driver Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
(Data Rate = 2 Mbps, V
= 3.3 V, RL = 50 Ω)
CC
Figure 7. Receiver Output Current vs. Output Voltage (Output Low)
= 25°C)
(T
A
Figure 10. Receiver Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
(Data Rate = 2 Mbps, V
= 3.3 V, VID = 200 mV, VIC = 1 V, CL = 15 pF)
CC
Rev. A | Page 8 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
0
1.0
0.5
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
20 40 60 80 100
ADDED DRIVER PERI OD JITTE R ( ps)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10471-009
0
6
4
2
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
ADDED DRIVER PEAK-TO-P E AK JITTER (ps)
DATA RATE (Mbps)
10471-010
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
80
70
90
100
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
ADDED DRIVER PEAK-TO-P E AK JITTER (ps)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
10471-011
0
3
2
1
4
5
6
7
10 20 30 40 50
ADDED RECEIVER P E RIOD JITT E R ( ps)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10471-012
0
100
200
300
500
400
600
700
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
ADDED RECEIVER P E AK-TO-P E AK JITTER (ps)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
10471-014
Figure 11. Driver Jitter (Period) vs. Frequency
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, Clock Input)
(V
CC
Figure 12. Driver Jitter (Peak-to-Peak) vs. Data Rate
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, PRBS 215 − 1 NRZ Input)
(V
CC
Figure 14. Receiver Jitter (Period) vs. Frequency
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, VIC = 1 V, Clock Input)
(V
CC
Figure 15. Receiver Jitter (Peak-to-Peak) vs. Temperature
= 3.3 V, VIC = 1 V, PRBS 215 − 1 NRZ Input)
(V
CC
Figure 13. Driver Jitter (Peak-to-Peak) vs. Temperature
(Data Rate = 100 Mbps, V
= 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, PRBS 215 − 1 NRZ Input)
CC
Rev. A | Page 9 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
10471-015
2ns/DIV
200mV/DIV
10471-016
2.5ns/DIV
400mV/DIV
Figure 16. ADN4690E Driver Output Eye Pattern
(Data Rate = 100 Mbps, PRBS 2
15
− 1 Input, RL = 50 Ω)
Figure 17. ADN4690E Receiver Output Eye Pattern
(Data Rate = 100 Mbps, PRBS 2
15
− 1, CL = 15 pF)
Rev. A | Page 10 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
DI
NOTES
1. 1% TOL E RANCE FOR ALL RESISTORS.
V
OD
V
TEST
49.9Ω
3.32kΩ
+
–
3.32kΩ
10471-017
A/Y
B/Z
V
TEST
= –1V TO +3. 4V
DI
NOTES
1. C1, C2, AND C3 ARE 20% AND INCLUDE PROBE/ S TRAY
CAPACITANCE < 2cm FROM DU T.
2. R1 AND R2 ARE 1%, METAL FILM, SURFACE MOUNT,
<2cm FROM DUT.
V
OC
R1
24.9Ω
C1
1pF
C2
1pF
C3
2.5pF
R2
24.9Ω
10471-018
A/Y
B/Z
S1 S2
V
A(O)
, V
B(O)
,
V
Y(O)
OR V
Z(O)
A/Y
V
CC
R1
1.62kΩ
±1%
B/ZDE
10471-019
S1
DI
S2
V
TEST
V
CC
I
OS
V
TEST
= –1V OR +3.4V
10471-020
A/Y
B/Z
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: 1MHz; 50% ± 5% DUTY CYCLE; t
R
, t
F
≤ 1ns.
2. V
OC(PP)
MEASURED ON TEST EQUIPMENT WITH –3dB BANDWIDTH ≥ 1GHz.
V
OC(PP)
ΔV
OC(SS)
V
OC
B
A
≈ 0.7V
≈ 1.3V
10471-021
TEST CIRCUITS AND SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
DRIVER VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS
Figure 18. Driver Voltage Measurement over Common-Mode Range
Figure 19. Driver Common-Mode Output Voltage Measurement
Figure 20. Maximum Steady-State Output Voltage Measurement
Figure 21. Driver Short Circuit
Figure 22. Driver Common-Mode Output Voltage (Steady State)
Rev. A | Page 11 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
DI
NOTES
1. C1, C2, AND C3 ARE 20% AND INCLUDE PROBE/ S TRAY
CAPACITANCE < 2cm FROM DU T.
2. R1 IS 1%, METAL FILM, SURFACE MOUNT,
<2cm FROM DUT.
OUT
C1
1pF
C3
0.5pF
C2
1pF
10471-022
R1
50Ω
A/Y
B/Z
DI
DE
S1
V
CC
NOTES
1. C1, C2, C3, AND C4 ARE 20% AND INCLUDE PROBE /STRAY
CAPACITANCE < 2cm F ROM DUT.
2. R1 AND R2 ARE 1%, MET AL FILM , SURFACE MO UNT,
<2cm FROM DUT.
R1
24.9Ω
C1
1pF
C2
1pF
C3
2.5pF
R2
24.9Ω
10471-023
C4
0.5pF
OUT
A/Y
B/Z
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: AGILE NT 8304A STIMULUS SYSTEM;
50MHz; 50% ± 1% DUTY CYCL E .
2. MEASURED USI NG TEK TDS6604 WITH TDS JIT3 SOF TWARE.
V
CC
/2 V
CC
/2
V
CC
0V
1/f0
INPUT
(CLOCK)
10471-024
0V 0V
1/f0
OUTPUT
V
A
– V
B
OR
V
Y
– V
Z
(IDEAL)
0V 0V
t
c(n)
t
J(PER)
= |
t
c(n)
– 1/f0|
OUTPUT
V
A
– V
B
OR
V
Y
– V
Z
(ACTUAL)
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: 1MHz; 50% ± 5% DUTY CYCLE;
t
R
,
t
F
≤ 1ns.
2. MEASURED ON TEST EQUIPMENT WITH –3dB BANDWIDTH ≥ 1GHz.
t
PLH
t
R
t
F
t
PHL
V
CC
V
SS
V
PH
V
PL
0% V
SS
10% V
SS
90% V
SS
0V
0V 0V
OUT
DI
10471-025
10% V
SS
90% V
SS
V
CC
/2 VCC/2
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
V
CC
0V
0V
0V
~ –0.6V
~ +0.6V
–0.1V
0.1V
0.1V
DE
OUT
(DI = 0V)
OUT
(DI = V
CC
)
10471-026
t
PZH
t
PZL
–0.1V
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: 1MHz; 50% ± 5% DUTY CYCLE;
t
R
,
t
F
≤ 1ns.
2. MEASURED ON TEST EQUIPMENT WITH –3dB BANDWIDTH ≥ 1GHz.
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: AGIL E NT 8304A STIMULUS SYSTEM;
100Mbps; 2
15
– 1PRBS.
2. MEASURED USING TEK T DS 6604 WITH TDS JIT3 SOF TWARE.
V
A
– V
B
OR
VY – V
Z
VA – V
B
OR
VY – V
Z
V
CC
OUTPUT
INPUT
(PRBS)
0V
V
CC
/2
t
J(PP)
0V 0V
V
CC
/2
10471-027
DRIVER TIMING MEASUREMENTS
Figure 23. Driver Timing Measurement
Figure 26. Driver Propagation, Rise/Fall Times and Voltage Overshoot
Figure 24. Driver Enable/Disable Time Test Circuit
Figure 25. Driver Period Jitter Characteristics
Figure 27. Driver Enable/Disable Times
Figure 28. Driver Peak-to-Peak Jitter Characteristics
Rev. A | Page 12 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
A
NOTES
1. C
L
IS 20%, CERAMI C, SURFACE MO UNT, AND
INCLUDES PRO BE /STRAY CAPACI TANCE
< 2cm FROM DUT.
V
OUT
C
L
15pF
B
10471-028
RO
RE
V
ID
A
1.4V
1.0V
S1
1.2V
RE INPUT
NOTES
1. C
L
IS 20% AND INCLUDES P ROBE/STRAY
CAPACITANCE < 2cm F ROM DUT.
2. R
L
IS 1% METAL FILM, S URFACE MOUNT, <2cm FROM DUT.
V
OUT
C
L
15pF
R
L
499Ω
B
10471-029
RO
RE
V
TEST
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: AGILE NT 8304A STIMULUS SYSTEM;
50MHz; 50% ± 1% DUTY CYCL E .
2. MEASURED USI NG TEK TDS6604 WITH TDS JIT3 SOF TWARE.
V
OH
V
OL
1/f0
INPUT
(V
A
– VB)
10471-030
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
1/f0
OUTPUT
(IDEAL)
V
OH
V
OL
OUTPUT
(ACTUAL)
t
c(n)
t
J(PER)
= |
t
c(n)
– 1/f0|
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: 1MHz; 50% ± 5% DUTY CYCLE; t
R
, t
F
≤ 1ns.
2. MEASURED ON TEST EQUIPMENT WITH –3dB BANDWIDTH ≥ 1GHz.
V
CC
/2 V
CC
/2
V
OH
V
ID
V
B
V
A
V
OL
V
OUT
90%
0V 0V
10%
90%
10%
t
F
t
R
t
RPLH
t
RPHL
10471-031
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
V
CC
0V
V
CC
0V
V
OL
V
OH
0.5V
CC
0.5V
CC
V
OH
– 0.5V
RE INPUT
(V
TEST
= V
CC
)
(A = 1V)
V
OUT
V
OUT
(V
TEST
= 0V)
(A = 1.4V)
10471-032
t
RPZH
t
RPZL
V
OL
+ 0.5V
t
RPHZ
t
RPLZ
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: 1MHz; 50 ± 5% DUTY CYCLE;
t
R
,
t
F
≤ 1ns.
NOTES
1. INPUT PULSE GENERATOR: AGILE NT 8304A STIMULUS SYSTEM;
100Mbps; 2
15
– 1PRBS.
2. MEASURED USI NG TEK TDS6604 WITH TDS JIT3 SOF TWARE.
V
OH
V
OL
V
A
V
B
OUTPUT
INPUT
(PRBS)
t
J(PP)
V
CC
/2VCC/2
10471-033
Figure 34. Receiver Peak-to-Peak Jitter Characteristics
RECEIVER TIMING MEASUREMENTS
Figure 29. Receiver Timing Measurement
Figure 32. Receiver Propagation and Rise/Fall Times
Figure 30. Receiver Enable/Disable Time
Figure 31. Receiver Period Jitter Characteristics
Figure 33. Receiver Enable/Disable Times
Rev. A | Page 13 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
Yes H H H L
Yes
NC L I
Yes
≤50 mV
L
L
THEORY OF OPERATION
The ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E are
transceivers for transmitting and receiving multipoint, low
voltage differential signaling (M-LVDS) at high speed (data
rates up to 100 Mbps). Each device has a differential line driver
and a differential line receiver, allowing each device to send and
receive data.
Multipoint LVDS expands on the established LVDS low voltage
differential signaling method by allowing bidirectional communication between more than two nodes. Up to 32 nodes can be
connected on an M-LVDS bus.
HALF-DUPLEX/FULL-DUPLEX OPERATION
Half-duplex operation allows a transceiver to transmit or
receive, but not both at the same time. However, with fullduplex operation, a transceiver can transmit and receive
simultaneously. The ADN4690E/ADN4694E are half-duplex
devices in which the driver and the receiver share differential
bus terminals. The ADN4692E/ADN4695E are full-duplex
devices that have dedicated driver output and receiver input
pins. Figure 36 and Figure 37 show typical half- and full-duplex
bus topologies, respectively, for M-LVDS.
THREE-STATE BUS CONNECTION
The outputs of the device can be placed in a high impedance
state by disabling the driver or receiver. This allows several driver
outputs to be connected to a single M-LVDS bus. Note that, on
each bus line, only one driver can be enabled at a time, but
many receivers can be enabled at the same time.
The driver can be enabled or disabled using the driver enable
pin (DE). DE enables the driver outputs when taken high; when
taken low, DE puts the driver outputs into a high impedance state.
Similarly, an active low receiver enable pin (
RE
) controls the
receiver. Taking this pin low enables the receiver, whereas taking
it high puts the receiver outputs into a high impedance state.
Truth tables for driver and receiver output states under various
conditions are shown in Ta ble 10, Tabl e 11, Tab l e 12, and
Tabl e 13.
TRUTH TABLES
Table 9. Truth Table Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
H High level
L Low level
X Don’t care
I Indeterminate
Z High impedance (off)
NC Disconnected
Driver, Half Duplex (ADN4690E/ADN4694E)
Table 10. Transmitting (see Table 9 for Abbreviations)
Inputs Outputs
Power
Yes H L L H
Yes H NC L H
Yes L X Z Z
Yes NC X Z Z
≤1.5 V X X Z Z
DE DI A B
Driver, Full Duplex (ADN4692E/ADN4695E)
Table 11. Transmitting (see Table 9 for Abbreviations)
Inputs Outputs
Power
Yes H H H L
Yes H L L H
Yes H NC L H
Yes L X Z Z
Yes NC X Z Z
≤1.5 V X X Z Z
DE DI Y Z
Type 1 Receiver (ADN4690E/ADN4692E)
Table 12. Receiving (see Table 9 for Abbreviations)
Inputs Output
Power
Yes ≥50 mV L
Yes ≤−50 mV L L
Yes −50 mV < A − B < 50 mV L I
Yes X H
Yes X NC Z
No X X Z
A − B
RE
RO
H
Z
Type 2 Receiver (ADN4694E/ADN4695E)
Table 13. Receiving (see Table 9 for Abbreviations)
Inputs Output
Power
Yes ≥150 mV L H
Yes 50 mV < A − B < 150 mV L
Yes NC L
Yes X H Z
Yes X NC Z
No X X Z
A − B
RO
RE
I
L
Rev. A | Page 14 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
TYPE 1 RECEIVER
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE (V
– V
) [V]
TYPE 2 RECEIVER
GLITCH-FREE POWER-UP/POWER-DOWN
To minimize disruption to the bus when adding nodes, the
M-LVDS outputs of the device are kept glitch-free when the
device is powering up or down. This feature allows insertion
of devices onto a live M-LVDS bus because the bus outputs are
not switched on before the device is fully powered. In addition,
all outputs are placed in a high impedance state when the device is
powered off.
FAULT CONDITIONS
The ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E contain
short-circuit current protection that protects the part under fault
conditions in the case of short circuits on the bus. This protection
limits the current in a fault condition to 24 mA at the transmitter
outputs for short-circuit faults between −1 V and +3.4 V. Any
network fault must be cleared to avoid data transmission errors
and to ensure reliable operation of the data network and any
devices that are connected to the network.
RECEIVER INPUT THRESHOLDS/FAIL-SAFE
Two receiver types are available, both of which incorporate
protection against short circuits.
The Type 1 receivers of the ADN4690E/ADN4692E incorporate
25 mV of hysteresis. This ensures that slow-changing signals or
a loss of input does not result in oscillation of the receiver output.
Type 1 receiver thresholds are ±50 mV; therefore, the state of the
receiver output is indeterminate if the differential between A and
B is about 0 V. This state occurs if the bus is idle (approximately 0 V
on both A and B), with no drivers enabled on the attached nodes.
Type 2 receivers (ADN4694E/ADN4695E) have an open circuit
and bus-idle fail-safe. The input threshold is offset by 100 mV
so that a logic low is present on the receiver output when the
bus is idle or when the receiver inputs are open.
The different receiver thresholds for the two receiver types are
illustrated in Figure 35. See Tabl e 12 and Tab l e 13 for receiver
output states under various conditions.
OUTPUT
IB
0.25
IA
0.15
0.05
–0.05
–0.15
LOGIC 1
UNDEFINED
0
LOGIC 0
Figure 35. Input Threshold Voltages
OUTPUT
LOGIC 1
UNDEFINED
LOGIC 0
10471-034
Rev. A | Page 15 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
RO
NOTES
1. MAXIMUM NUM BE R OF NODES: 32.
2. R
T
IS EQUAL TO THE CHARACTERI S TIC IMPE DANCE OF THE CABL E US E D.
RE
A B
R
T
R
T
ADN4694E
DE DI
RO RE
A B
ADN4694E
DE DI
RO RE
A B
ADN4694E
DE DI
RO RE
A B
ADN4694E
DE DI
10471-035
RO
NOTES
1. MAXIMUM NUM BE R OF NODES: 32.
2. R
T
IS EQUAL TO THE CHARACTERI S TIC IMPE DANCE OF THE CABL E US E D.
RE
A B Z Y
MASTER SLAVE SLAVE SLAVE
R
T
R
T
ADN4695E
DE DI
RO RE DE DI
RO RE DE DI
A B Z Y
ADN4695E
A B Z Y
ADN4695E
A B Z Y
ADN4695E
R
T
R
T
RO RE DE DI
10471-036
R
D
R
D
R
D
R
D
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
M-LVDS extends the low power, high speed, differential signaling of LVD S ( low voltage differential signaling) to multipoint
systems where multiple nodes are connected over short distances
in a bus topology network.
With M-LVDS, a transmitting node drives a differential signal
across a transmission medium such as a twisted pair cable. The
transmitted differential signal allows other receiving nodes that
are connected along the bus to detect a differential voltage that
can then be converted back into a single-ended logic signal by
the receiver.
The communication line is typically terminated at both ends
by resistors (R
), the value of which is chosen to match the
T
characteristic impedance of the medium (typically 100 Ω).
For half-duplex multipoint applications such as the one shown
in Figure 36, only one driver can be enabled at any time. Fullduplex nodes allow a master slave topology, as shown in Figure 37.
In this configuration, a master node can concurrently send and
receive data to/from slave nodes. At any time, only one slave
node can have its driver enabled to concurrently transmit data
back to the master node.
Figure 36. ADN4694E Typical Half-Duplex M-LVDS Network (Type 2 Receivers with Threshold Offset for Bus-Idle Fail-Safe)
Figure 37. ADN4695E Typical Full-Duplex M-LVDS Master-Slave Network (Type 2 Receivers with Threshold Offset for Bus-Idle Fail-Safe)
Rev. A | Page 16 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLYAND ARE NOT APPROPRIATEFOR USE IN DESIGN.
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDSMS-012-AA
012407-A
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
0.50 (0.0196)
0.25 (0.0099)
45°
8°
0°
1.75 (0.0688)
1.35 (0.0532)
SEATING
PLANE
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0040)
4
1
8 5
5.00(0.1968)
4.80(0.1890)
4.00 (0.1574)
3.80 (0.1497)
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2284)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
COPLANARITY
0.10
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONSARE IN MI LLIMETERS; INCH DI M E NS IONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLYAND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-AB
060606-A
14
8
7
1
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2283)
4.00 (0.1575)
3.80 (0.1496)
8.75 (0.3445)
8.55 (0.3366)
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0039)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
1.75 (0.0689)
1.35 (0.0531)
0.50 (0.0197)
0.25 (0.0098)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
COPLANARITY
0.10
8°
0°
45°
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADN4690EBRZ –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-8
ADN4690EBRZ-RL7 –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-8
ADN4692EBRZ –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-14
ADN4692EBRZ-RL7 –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-14
ADN4694EBRZ –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-8
ADN4694EBRZ-RL7 –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-8
ADN4695EBRZ –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-14
ADN4695EBRZ-RL7 –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package (SOIC_N) R-14
EVA L-ADN469xEHDEBZ Evaluation Board for Half-Duplex M-LVDS (ADN4690E, ADN4694E)
EVA L-ADN469xEFDEBZ Evaluation Board for Full-Duplex M-LVDS (ADN4692E, ADN4695E)
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
Figure 38. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
(R-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Figure 39. 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
(R-14)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Rev. A | Page 17 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 18 of 20

Data Sheet ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 19 of 20

ADN4690E/ADN4692E/ADN4694E/ADN4695E Data Sheet
NOTES
©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D10471-0-3/12(A)
Rev. A | Page 20 of 20
 Loading...
Loading...