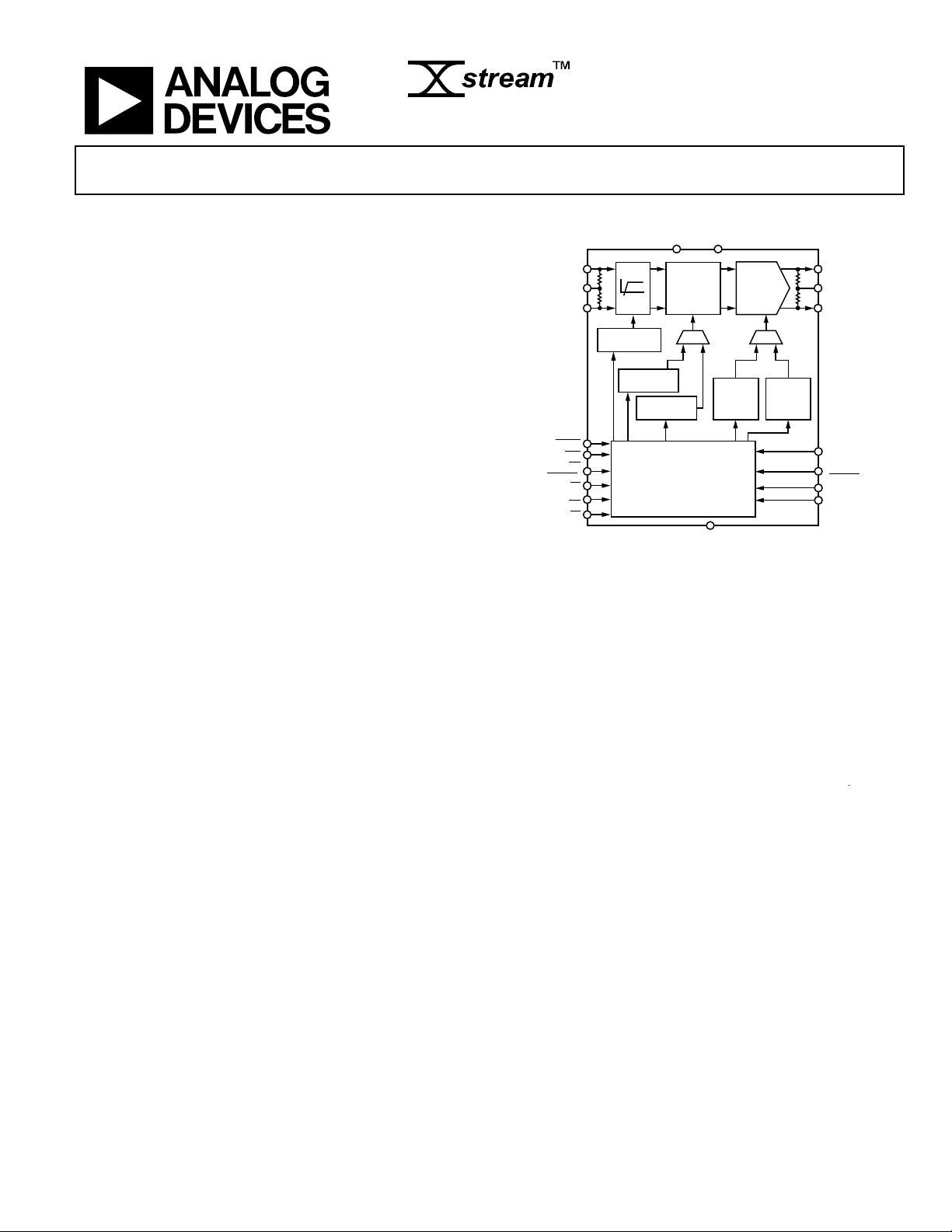
Crosspoint Switch
ADN4605
EQ
Rx Tx
PRE-
EMPHASIS
40 × 40
SWITCH
MATRIX
CONNECTION
MAP 1
CONNECTION
MAP 0
PARALLEL/SERIA L CONTROL
LOGIC INTERFACE
PRE-
EMPHASIS
LEVEL
SETTINGS
OUTPUT
LEVEL
SETTINGS
ADN4605
V
CC
V
EE
DV
CC
OP[39:0]
V
TTOA
,
V
TTOB
ON[39:0]
IP[39:0]
V
TTIA
,
V
TTIB
IN[39:0]
I
2
C/SPI
(UPDATE)
SDI/RE
SCL/SCK/
WE
RESET
SER/PAR
CS
EQUALIZATION
SETTINGS
DATA[1]
(UPDATE)
DATA[0]/
SDA/SDO
DATA[7:2]
ADDR[7:0]
09796-001
Rev. A
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the propert y of their respective owners.
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Data Sheet
FEATURES
DC to 4.25 Gbps per port NRZ data rate
Adjustable receive equalization
3 dB, 6 dB, or 12 dB boost
Compensates over 40 inches of FR4 at 4.25 Gbps
Adjustable transmit preemphasis/deemphasis
Programmable boost and output level
Compensates over 40 inches of FR4 at 4.25 Gbps
Low power
105 mW per channel at 2.5 V (400 mV p-p differential
output level swing)
40 × 40, fully differential, nonblocking array
Double rank connection programming with dual maps
Low jitter, typically <25 ps
Flexible 2.5 V to 3.3 V supply range
DC- or ac-coupled differential PECL/CML inputs
Differential CML outputs
Per-lane polarity inversion for routing ease
50 Ω on-chip I/O termination with disable feature
Supports 8b10b, scrambled or uncoded NRZ data
Serial (IC slave or SPI) control interface
Parallel control interface
4.25 Gbps 40 × 40 Digital
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 1.
APPLICATIONS
Digital video (HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort, 3G/HD/SD-SDI)
Fiber optic network switching
High speed serial backplane routing to OC-48 with FEC
XAUI, 4x Fibre Channel, Infiniband®, and GbE over backplane
Data storage networks
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADN4605 is a 40 × 40 asynchronous, protocol agnostic,
digital crosspoint switch, with 40 differential PECL/CMLcompatible inputs and 40 differential programmable CML
outputs.
The ADN4605 is optimized for NRZ signaling with data rates of
up to 4.25 Gbps per port. Each port offers adjustable levels of
input equalization, programmable output swing, and output
preemphasis/deemphasis.
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The ADN4605 nonblocking switch core implements a 40 × 40
crossbar and supports independent channel switching through
serial and parallel control interfaces. The ADN4605 has low
latency and very low channel-to-channel skew.
An I
the device for control of connectivity and other features.
The ADN4605 is assembled in a 35 mm × 35 mm, 352 BGA
package and operates over a temperature range of −40°C
to +85°C.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
2
C, SPI, or parallel interface is used to communicate with

ADN4605 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Electrical Specifications ............................................................... 3
I2C Timing Specifications ............................................................ 5
SPI Timing Specifications ........................................................... 5
Parallel Mode Specifications ....................................................... 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 7
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 7
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 8
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 18
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 24
Introduction ................................................................................ 24
Receivers ...................................................................................... 25
Polarity Inversion ....................................................................... 26
Switch Core ................................................................................. 27
Reset ............................................................................................. 28
Transmitters ................................................................................ 29
Termination ................................................................................. 32
I2C Serial Control Interface ........................................................... 33
I2C Dat a Write ............................................................................. 33
I2C Data Read .............................................................................. 34
SPI Serial Control Interface .......................................................... 35
Parallel Control Interface .............................................................. 38
Address Inputs: ADDR[7:0] ...................................................... 38
Data Inputs/Outputs: DATA[7:0]............................................. 38
Write Operation.......................................................................... 38
Read Operation........................................................................... 38
Register Map ................................................................................... 39
Applications Information .............................................................. 49
Supply Sequencing ..................................................................... 51
Power Dissipation....................................................................... 51
Output Compliance ................................................................... 51
TX/XPT HEADROOM ............................................................. 51
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Layout Guidelines ................... 54
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 55
Ordering Guide ............................................................................... 55
REVISION HISTORY
11/11—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Layout
Guidelines ........................................................................................ 54
Removed Figure 55, Renumbered Sequentially.......................... 54
6/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 56
Data Sheet ADN4605
Deterministic Jitter
20 ps p-p
Residual Deterministic Jitter with
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 20 in. FR4, PE boost = 5.6 dB
22 ps p-p
Output Rise/Fall Time
20% to 80%
108 ps
Single-ended absolute voltage level, VH
VCC + 0.3
V
TERMINATION CHARACTERISTICS
POWER SUPPLY
V
, V
VEE = 0 V
2.5
VCC + 0.3
V
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
VCC = 2.5 V, V
equalizer (EQ) = 1 (3 dB), data rate = 4.25 Gbps (PRBS7 data pattern), ac-coupled inputs and outputs, differential input swing = 800 mV p-p,
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
T
A
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Data Rate (DR) per Channel (NRZ) dc 4.25 Gbps
Random Jitter RMS, no channel 0.8 ps rms
Residual Deterministic Jitter with
Receive Equalization
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 40 in. FR4, EQ boost = 12 dB 25 ps p-p
= 2.5 V, V
TTIx
= 2.5 V, D VCC = 3.3 V, VEE = 0 V, RL = 50 Ω, output level (OLEV) = 4 (16 mA), preemphasis (PE) = 0 (0 dB),
TTOx
Data rate ≤ 4.25 Gbps, no channel
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 20 in. FR4, EQ boost = 12 dB 14 ps p-p
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 30 in. FR4, EQ boost = 12 dB 15 ps p-p
Transmit Preemphasis
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 30 in. FR4, PE boost = 6.8 dB 28 ps p-p
Data rate = 4.25 Gbps, 40 in. FR4, PE boost = 9.5 dB 32 ps p-p
Propagation Delay Input to output 920 ps
Channel-to-Channel Skew Earliest input/output lane to latest input/output lane 200 ps
Switching Time Update logic switching to 50% output data 20 ns
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
V
Minimum Differential Input
Voltage Swing
Maximum Differential Input
Voltage Swing
1
1
= VCC − 0.6 V 50 mV p-p diff
ICM
= VCC − 0.6 V 2000 mV p-p diff
V
ICM
Input Voltage Range Single-ended absolute voltage level, VL VEE + 1.0 V
Single-ended absolute voltage level, VH VCC + 0.3 V
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing Differential, PE boost = 0 dB, default output level, at dc 670 800 875 mV p-p diff
Output Voltage Range Single-ended absolute voltage level, VL VCC – 1.4 V
Per-Port Output Current PE boost = 0 dB, default output level 16 mA
PE boost = 6 dB, default output level 32 mA
Resistance Differential, VCC = V
MIN
to V
MAX
, TA = T
MIN
to T
88 100 114 Ω
MAX
Temperature Coefficient 0.015 Ω/°C
Operating Range
VCC VEE = 0 V 2.25 2.5 3.6 V
DVCC VEE = 0 V 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
, V
TTIA
TTOA
VEE = 0 V 2.5 VCC + 0.3 V
TTIB
TTOB
Supply Current Inputs/outputs disabled (reset condition)
ICC 55 64 mA
I
0.3 1.1 mA
DVCC
I
+ I
TTIA
I
TTOA
Inputs floating 0 1.5 mA
TTIB
+ I
Outputs floating 0 1.5 mA
TTOB
Rev. A | Page 3 of 56
ADN4605 Data Sheet
I
+ I
11
15
mA
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Supply Current
ICC 1320 1410 mA
I
0.3 1.1 mA
DVCC
I
+ I
11 15 mA
TTIB
+ I
335 360 mA
TTOB
I
TTIA
TTOA
All outputs enabled, ac-coupled I/O,
200 mV I/O swings (400 mV p-p differential),
PE boost = 0 dB, 50 Ω far-end terminations
Supply Current All outputs enabled, ac-coupled I/O,
ICC 1370 1460 mA
I
0.3 1.1 mA
DVCC
I
+ I
11 15 mA
TTIA
TTIB
I
+ I
TTOA
665 715 mA
TTOB
400 mV I/O swings (800 mV p-p differential),
PE boost = 0 dB, 50 Ω far-end terminations
Supply Current All outputs enabled, ac-coupled I/O,
ICC 1850 1960 mA
I
0.3 1.1 mA
DVCC
TTIA
TTIB
I
+ I
TTOA
1340 1380
TTOB
400 mV I/O swings (800 mV p-p differential),
PE boost = 6 dB, 50 Ω far-end terminations
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Operating Temperature2 −40 +85 °C
θJA Still air; JEDEC multilayer test board 11.6 °C/W
θJB 1 m/s air velocity 5.4 °C/W
θJC 1 m/s air velocity 0.72 °C/W
LOGIC CHARACTERISTICS
Input High Voltage Threshold (VIH) DVCC = 3.3 V 0.7 ×
Input Low Voltage Threshold (VIL) DVCC = 3.3 V 0.25 ×
Output High Voltage (VOH) IOH = −3 mA (I2C/SPI mode only) 0.75 ×
Output Low Voltage (VOL) IOL = +3 mA VEE 0.4 V
1
V
is the input common-mode voltage.
ICM
2
Junction temperature cannot exceed 125°C (see the Absolute Maximum Ratings section).
V
DV
CC
DV
CC
DV
DV
CC
V
CC
V
Rev. A | Page 4 of 56
Data Sheet ADN4605
SDA
SCL
t
f
t
LOW
t
HD;STA
t
r
t
HD;DAT
t
HIGH
t
SU;DAT
t
f
t
SU;STA
t
HD;STA
t
SP
t
SU;STO
t
r
t
BUF
SPSrS
09796-002
Low Period of the SCL Clock
t
1.4
µs
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
5
t
6
t
4
t
7
t
8
D7
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
09796-003
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Max
Unit
Data Setup Time Prior to SCLK Rising Edge
t5
10 ns
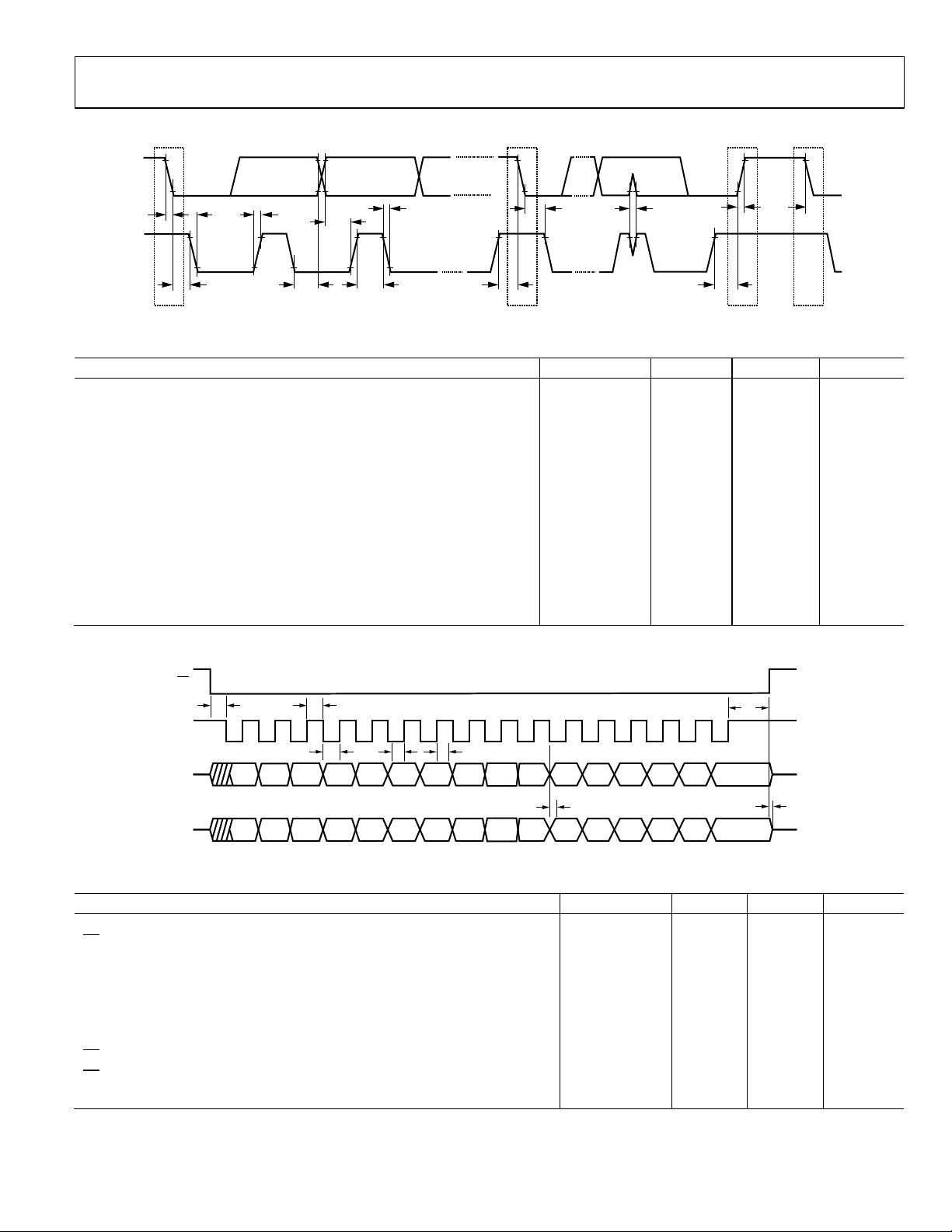
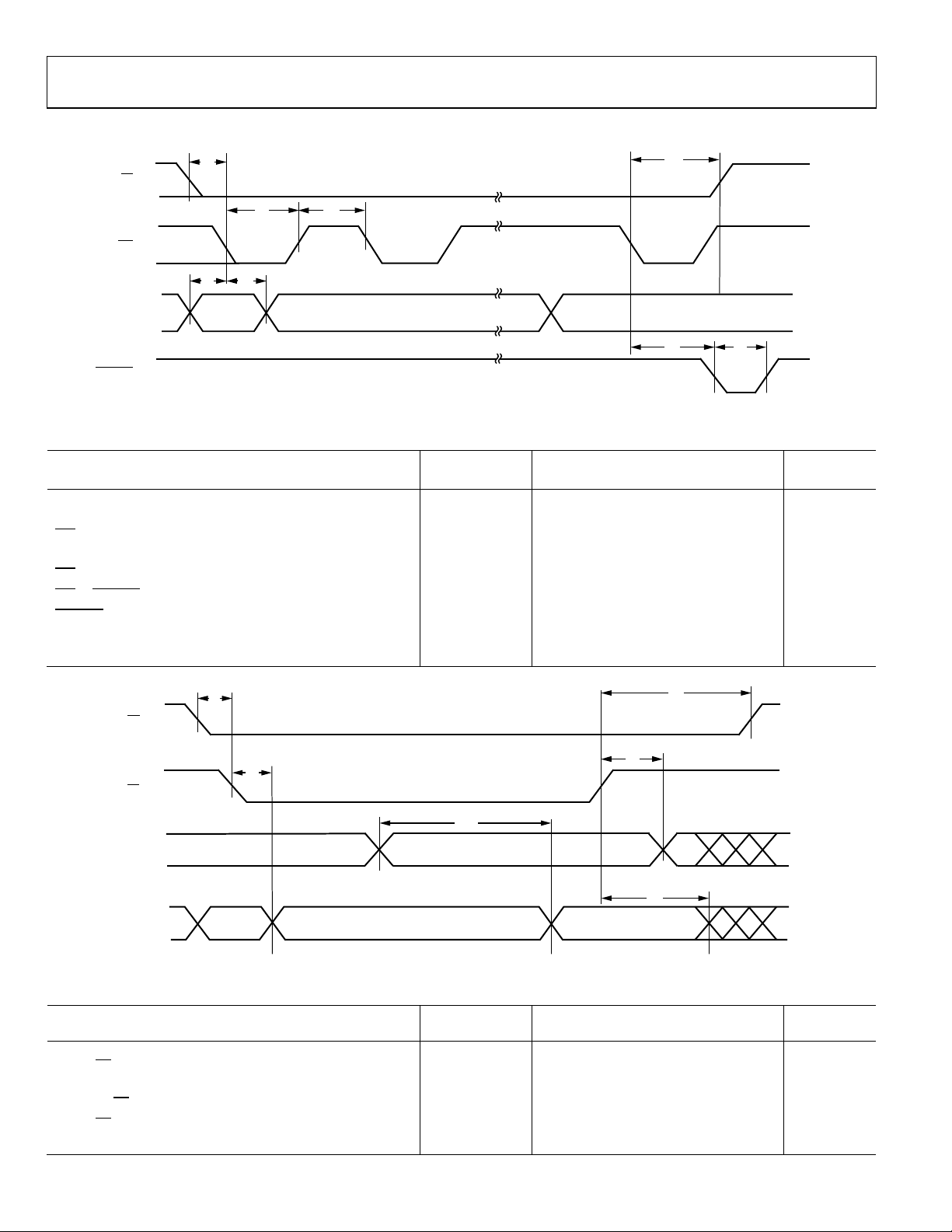
I2C TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
2
Figure 2. I
C Timing Diagram
Table 2. I2C Timing Specifications
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
SCL Clock Frequency f
Hold Time for a Start Condition t
Setup Time for a Repeated Start Condition t
High Period of the SCL Clock t
Data Hold Time t
Data Setup Time t
Rise Time for Both SDA and SCL t
Fall Time for Both SDA and SCL t
Setup Time for Stop Condition t
Bus Free Time Between a Stop Condition and a Start Condition t
0 500+ kHz
SCL
HD; STA
SU; STA
LOW
HIGH
HD; DAT
SU; DAT
r
f
SU; STO
BUF
0.5 µs
0.5 µs
0.6 µs
0.02 µs
0.02 µs
1 300 ns
1 300 ns
0.5 µs
1 ns
Bus Idle Time After a Reset 20 ns
Reset Pulse Width 20 ns
SPI TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3. SPI Timing Specifications
SCK Clock Frequency f
CS to SCLK Setup Time
SCLK High Pulse Width t2 30 ns
SCLK Low Pulse Width t3 30 ns
Data Access Time After SCLK Falling Edge t4 45 ns
Data Hold Time After SCLK Rising Edge t6 30 ns
CS to SCLK Hold Time
CS to SDO High Impedance
Reset Pulse Width 20 ns
Figure 3. SPI Timing Diagram
10 MHz
SCK
0 ns
t
1
t7 0
45
t
8
ns
ns
Rev. A | Page 5 of 56
ADN4605 Data Sheet
UPDATE
1
0
WE
D7:D0
A7:A0
1
0
CS
1
0
0
1
t
6
t
8
t
3
t
5
t
1
t
2
t
4
t
7
09796-004
UPDAT E Pulse Width
t7
30
ns
1
0
RE
CS
1
0
D7:D0 DATA (ADDR 1)
ADDR 1
1
0
ADDR 2
A7:A0
1
0
DATA (ADDR 2)
t
1
t
2
t
6
t
5
t
3
t
4
09796-005
PARALLEL MODE SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 4. Parallel Mode Write Cycle
Table 4. Parallel Mode Write Cycle Timing Specifications
Limit
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Chip Select Setup Time t
1
Parallel Data Setup Time t2 0 ns
t
WE Pulse Width
30 50 ns
3
Parallel Data Hold Time t4 25 ns
WE Pulse Separation
WE to UPDAT E Delay
t
5
t6 40 ns
0 ns
25 ns
Chip Select Hold Time t8 0 ns
Reset Pulse Width 20 ns
Table 5. Parallel Mode Read Cycle Timing Specifications
Limit
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Chip Select Setup Time t
Parallel RE Setup to Valid Time
Data Access Time t3 25 50 ns
Address to RE Hold Time
Data to RE Hold Time
Chip Select Hold Time t
Figure 5. Parallel Mode Read Cycle
1
10 ns
t
2
25 ns
t
4
25 ns
t
5
6
Rev. A | Page 6 of 56
0 ns
5 ns

Data Sheet ADN4605
Storage Temperature Range
−65°C to +125°C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
VCC to VEE 3.7 V
DVCC to VEE 3.7 V
V
, V
VCC + 0.6 V
TTIA
TTIB
V
, V
TTOA
VCC + 0.6 V
TTOB
Internal Power Dissipation1 8.4 W
Differential Input Voltage 2.0 V
Logic Input Voltage VEE – 0.3 V < VIN < VCC + 0.6 V
Junction Temperature 125°C
1
Internal power dissipation is for the device in free air.
TA = 27° C; θJA = 11.6°C/W in still air.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 7 of 56
ADN4605 Data Sheet
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AF
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AF
V
EE
VEEV
EE
VEEV
EE
V
EE
ON39 OP39 ON37 OP37 ON35 OP35 ON33 OP33 ON31 OP31 ON29 OP29 ON27 OP27 ON25 OP25 ON23 OP23 ON21 OP21
ON38 OP38 ON36 OP36 ON34 OP34 ON32 OP32 ON30 OP30 ON28 OP28 ON26 OP26 ON24 OP24 ON22 OP22
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
V
TTOB
ON20 OP20
V
EE
V
EE
VEEV
EE
V
EE
DV
CC
DV
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
CC
CS
RE
WE
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
IP0
IN0IP1
IP2IN1
IN2IP3
IP4IN3
IN4IP5
IP6IN5
IN6IP7
IP8IN7
IN8IP9
IP10IN9
IP12IN11
IN12IP13
IN10IP11
IN14IP15
IP14IN13
IN16IP17
IN18IP19
IP16IN15
IP18IN17
IN19
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
VCCV
CC
VCCV
CC
V
CC
V
CC
VCCV
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
VEEVEEVEEV
EE
V
CCVCC
V
EEVEEVEE
V
EE
V
EEVEE
V
EE
DV
CC
V
EE
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
TTIA
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
DV
CC
V
EE
IN38 IP39
IP38
IN36
IP36
IN37
IP37
IN34
IP34
IN35
IP35
IN32
IP32
IN33
IP33
IN30
IP30
IN31
IP31
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
IN39
IN28 IP29
IP28
IN26
IP26
IN27
IP27
IN24
IP24
IN25
IP25
IN22
IP22
IN23
IP23
IN20
IP20
IN21
IP21
IN29
V
EE
V
EE
V
CC
DV
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
EE
VEEV
EE
V
EE
ON19
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
DATA7
DATA6
DATA5
DATA4
DATA3
DATA2
DATA1
DATA0
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
TTIB
V
EE
V
EE
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
EE
V
EE
V
EEVEE
V
EE
VEEV
EE
OP0 ON0
OP1 ON1
OP2 ON2
OP3 ON3
OP4 ON4
OP5 ON5
OP6 ON6
OP7 ON7
OP8 ON8
OP9 ON9
OP10 ON10
OP11 ON11
OP12 ON12
OP13 ON13
OP14 ON14
OP15 ON15
OP16 ON16
OP17 ON17
OP18 ON18
OP19
VEEVEEV
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
V
EEVEE
V
EE
V
EE
VEEV
EEVEE
V
EE
ADDR7
V
TTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOAVTTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOA
V
TTOAVTTOA
ADDR6
ADDR5
ADDR4
ADDR3
ADDR2
ADDR1
ADDR0
RESET
SER/
PAR
I
2
C/
SPI
ADN4605
TopView
09796-006
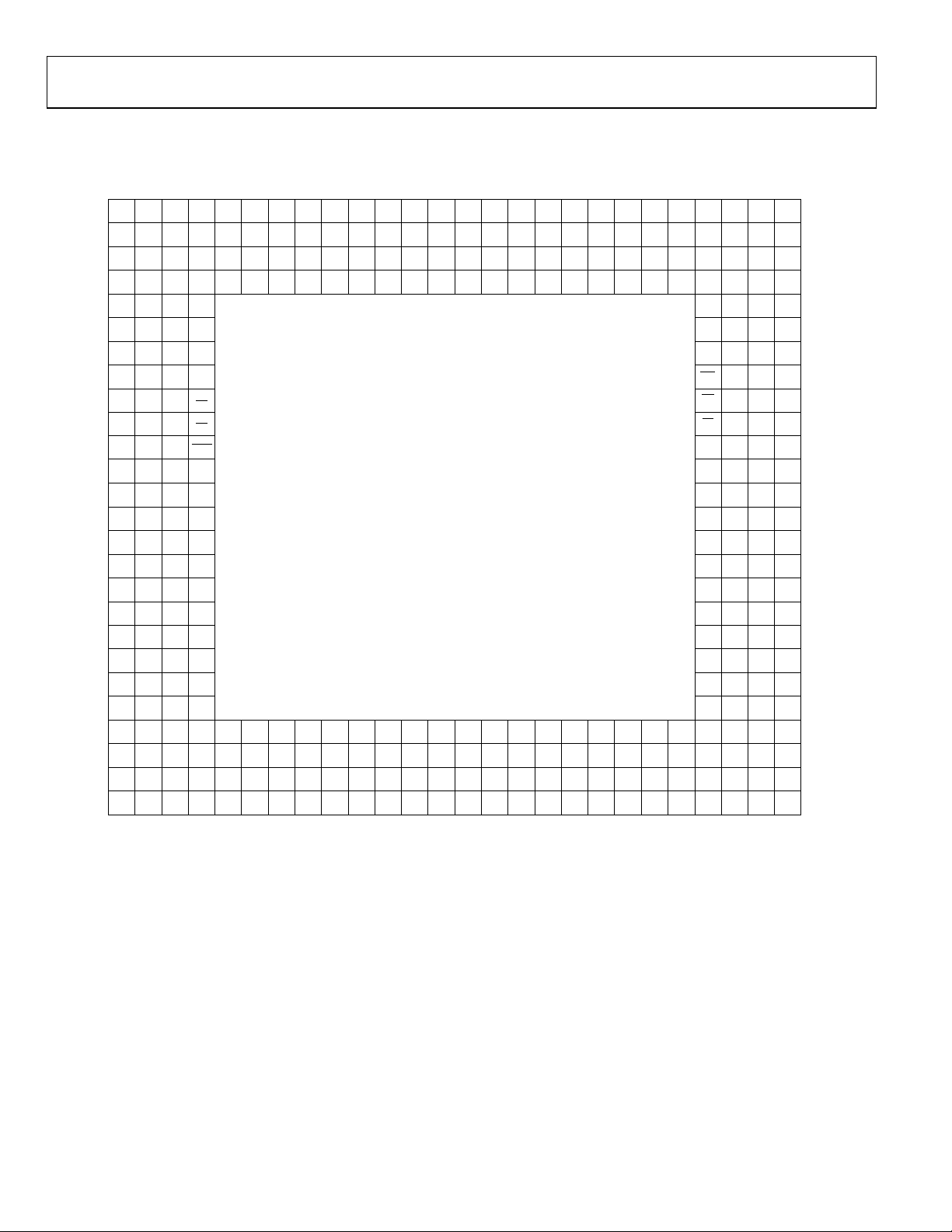
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Figure 6. Pin Configuration
Rev. A | Page 8 of 56
Data Sheet ADN4605
A1
V
Power
Negative Supply.
A2
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
A20
ON23
Output
High Speed Output Complement.
A21
OP23
Output
High Speed Output.
A22
ON21
Output
High Speed Output Complement.
B16
OP28
Output
High Speed Output.
B17
ON26
Output
High Speed Output Complement.
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
EE
A3 VEE Power Negative Supply.
A4 ON39 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A5 OP39 Output High Speed Output.
A6 ON37 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A7 OP37 Output High Speed Output.
A8 ON35 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A9 OP35 Output High Speed Output.
A10 ON33 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A11 OP33 Output High Speed Output.
A12 ON31 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A13 OP31 Output High Speed Output.
A14 ON29 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A15 OP29 Output High Speed Output.
A16 ON27 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A17 OP27 Output High Speed Output.
A18 ON25 Output High Speed Output Complement.
A19 OP25 Output High Speed Output.
A23 OP21 Output High Speed Output.
A24 VEE Power Negative Supply.
A25 VEE Power Negative Supply.
A26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
B1 VEE Power Negative Supply.
B2 VEE Power Negative Supply.
B3 VEE Power Negative Supply.
B4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
B5 ON38 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B6 OP38 Output High Speed Output.
B7 ON36 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B8 OP36 Output High Speed Output.
B9 ON34 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B10 OP34 Output High Speed Output.
B11 ON32 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B12 OP32 Output High Speed Output.
B13 ON30 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B14 OP30 Output High Speed Output.
B15 ON28 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B18 OP26 Output High Speed Output.
B19 ON24 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B20 OP24 Output High Speed Output.
B21 ON22 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B22 OP22 Output High Speed Output.
Rev. A | Page 9 of 56
ADN4605 Data Sheet
B24
OP20
Output
High Speed Output.
B25
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
C13
V
Power
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins are normally tied to the
C16
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
C17
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
D5
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
D6
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
B23 ON20 Output High Speed Output Complement.
B26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
C1 VEE Power Negative Supply.
C2 IP0 Input High Speed Input.
C3 VEE Power Negative Supply.
C4 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C5 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C6 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C7 V
C8 V
C9 V
C10 V
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
C11 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C12 VCC Power Positive Supply.
TTOB
C14 V
C15 V
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Power
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). T The V
V
pins.
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
V
pins.
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
V
pins.
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
C18 V
C19 V
C20 V
C21 V
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Power
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
V
pins.
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (B). The V
V
pins.
TTOA
C22 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C23 VCC Power Positive Supply.
C24 DVCC Power Digital Positive Supply.
C25 VEE Power Negative Supply.
C26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D1 IP1 Input High Speed Input.
D2 IN0 Input High Speed Input Complement.
D3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D4 DVCC Power Digital Positive Supply.
D7 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D8 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D9 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D10 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D11 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D12 VCC Power Positive Supply.
Rev. A | Page 10 of 56
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
Data Sheet ADN4605
D14
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
D15
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
E26
IP39
Input
High Speed Input
F1
IP3
Input
High Speed Input
F26
IN37
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
G1
IN3
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
G25
IN36
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
G26
IP37
Input
High Speed Input.
H1
IP5
Input
High Speed Input.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
D13 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D16 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D17 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D18 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D19 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D20 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D21 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D22 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D23 DVCC Power Digital Positive Supply.
D24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
D25 VEE Power Negative Supply.
D26 IN39 Input High Speed Input Complement.
E1 IN1 Input High Speed Input Complement.
E2 IP2 Input High Speed Input.
E3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
E4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
E23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
E24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
E25 IN38 Input High Speed Input Complement.
F2 IN2 Input High Speed Input Complement.
F3 V
TTIA
Power
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
F4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
F23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
F24 V
TTIB
Power
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
F25 IP38 Input High Speed Input.
G2 IP4 Input High Speed Input.
G3 V
Power
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTIB
G4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
G23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
G24 V
Power
TTIB
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
H2 IN4 Input High Speed Input Complement.
H3 V
Power
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
H4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
H23
WE/SCL/SCK
Control
Parallel control interface: First-Rank Write Strobe (WE) Active Low.
I2C Control Interface: I2C Clock (SCL).
SPI Control Interface: SPI Clock (SCK).
H24 V
Power
TTIB
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
Rev. A | Page 11 of 56
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB

ADN4605 Data Sheet
H26
IN35
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
J1
IN5
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
J23
RE/SDI
Control
Parallel Control Interface: Read Strobe (RE) Active Low.
K4
Control
Serial Control Interface Selection (SER).
M24
V
Power
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins are normally tied to the
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
H25 IP36 Input High Speed Input.
J2 IP6 Input High Speed Input.
J3 V
J4
J24 V
J25 IN34 Input High Speed Input.
J26 IP35 Input High Speed Input Complement.
K1 IP7 Input High Speed Input.
K2 IN6 Input High Speed Input Complement.
K3 VCC Power Power Supply.
K23
K24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
K25 IP34 Input High Speed Input.
K26 IN33 Input High Speed Input Complement.
L1 IN7 Input High Speed Input Complement.
L2 IP8 Input High Speed Input.
L3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
L4
L23 DATA0/SDA/SDO Control
L24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
L25 IN32 Input High Speed Input Complement.
L26 IP33 Input High Speed Input.
M1 IP9 Input High Speed Input.
M2 IN8 Input High Speed Input Complement.
M3 V
M4 ADDR0 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 0.
M23
M25 IP32 Input High Speed Input
M26 IN31 Input High Speed Input Complement.
N1 IN9 Input High Speed Input Complement.
N2 IP10 Input High Speed Input.
N3 V
N4 ADDR1 Control
Power
TTIA
2
C/SPI/ UPDAT E
I
Power
TTIB
PAR
SER/
CS
RESET
Power
TTIA
UPDAT E
DATA1/
TTIB
Power
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
Control
2
C Control Interface Selection (I2C).
I
SPI Control Interface Selection (
Parallel Control Interface (
SPI Control Interface: Data Input (SDI) SPI Control.
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
Parallel Control Interface Selection (PA R ) Active Low.
Control Chip Select Active Low.
Control
Configuration Registers: Reset (Active Low). This pin is normally pulled
up to DV
Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 0 (DATA0).
2
C Control Interface: Data In (SDA).
I
.
CC
SPI Control Interface: Data Out (SDO).
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTIB
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 0.
I
Control
Parallel Control Interface: Register (DATA1). Data Bit 1.
2
C or SPI Serial Control Interface (U P DAT E). Active Low.
I
V
pins.
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 1.
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 1.
I
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
SPI) Active Low.
UPDAT E) Active Low.
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
Rev. A | Page 12 of 56
Data Sheet ADN4605
N24
V
Power
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins are normally tied to the
T24
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
T25
IP28
Input
High Speed Input.
U23
DATA6
Control
Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 6.
U24
V
Power
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
N23 DATA 2 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 2.
TTIB
V
pins.
TTIA
N25 IN30 Input High Speed Input Complement.
N26 IP31 Input High Speed Input.
P1 IP11 Input High Speed Input.
P2 IN10 Input High Speed Input Complement.
P3 V
P4 ADDR2 Control
Power
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTIB
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 2.
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 2.
I
P23 DATA3 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 3.
P24 V
Power
TTIB
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
P25 IP30 Input High Speed Input.
P26 IN29 Input High Speed Input Complement.
R1 IN11 Input High Speed Input Complement.
R2 IP12 Input High Speed Input.
R3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
R4 ADDR3 Control
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 3.
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 3.
I
R23 DATA4 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 4.
R24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
R25 IN28 Input High Speed Input Complement.
R26 IP29 Input High Speed Input.
T1 IP13 Input High Speed Input.
T2 IN12 Input High Speed Input Complement.
T3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
T4 ADDR4 Control
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 4.
I2C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 4.
T23 DATA 5 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 5.
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
T26 IN27 Input High Speed Input Complement.
U1 IN13 Input High Speed Input Complement.
U2 IP14 Input High Speed Input.
U3 V
Power
TTIA
U4 ADDR5 Control
TTIB
U25 IN26 Input High Speed Input Complement.
U26 IP27 Input High Speed Input.
V1 IP15 Input High Speed Input.
V2 IN14 Input High Speed Input Complement.
V3 V
Power
TTIA
V4 ADDR6 Control
V23 DATA 7 Control Parallel Control Interface: Register Data Bit 7.
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 5.
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 5.
I
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTIB
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 6.
2
C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 6.
I
Rev. A | Page 13 of 56
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
ADN4605 Data Sheet
AA25
IN22
Input
High Speed Input Complement.
AA26
IP23
Input
High Speed Input.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
V24 V
V25 IP26 Input High Speed Input.
V26 IN25 Input High Speed Input Complement.
W1 IN15 Input High Speed Input Complement.
W2 IP16 Input High Speed Input.
W3 V
W4 ADDR7 Control
W23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
W24 V
W25 IN24 Input High Speed Input Complement.
W26 IP25 Input High Speed Input.
Y1 IP17 Input High Speed Input.
Y2 IN16 Input High Speed Input Complement.
Y3 V
Y4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
Y23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
Y24 V
Y25 IP24 Input High Speed Input.
Y26 IN23 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AA1 IN17 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AA2 IP18 Input High Speed Input.
AA3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AA4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AA23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AA24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
Power
TTIB
Power
TTIA
Power
TTIB
Power
TTIA
Power
TTIB
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
Parallel Control Interface: Register Address Bit 7.
I2C Control Interface: Slave Address Bit 7.
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
Input Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTIB
Input Termination Supply (B). The V
pins.
V
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTIB
pins are normally tied to the
TTIA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOB
AB1 IP19 Input High Speed Input.
AB2 IN18 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AB3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AB4 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AB23 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AB24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AB25 IP22 Input High Speed Input.
AB26 IN21 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AC1 IN19 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AC2 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC3 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC4 DVCC Power Digital Positive Supply.
AC5 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC6 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC7 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC8 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC9 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC10 VEE Power Negative Supply.
Rev. A | Page 14 of 56
Data Sheet ADN4605
AC12
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
AC13
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
AD6
VCC
Power
Positive Supply.
AD7
V
Power
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins are normally tied to the
AD19
V
Power
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
AC11 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC14 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC15 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC16 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC17 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC18 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC19 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC20 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC21 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AC22 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC23 DVCC Power Digital Positive Supply.
AC24 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AC25 IN20 Input High Speed Input Complement.
AC26 IP21 Input High Speed Input.
AD1 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AD2 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AD3 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AD4 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD5 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD8 V
AD9 V
AD10 V
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Power
TTOA
V
pins.
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
AD11 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD12 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD13 V
AD14 V
AD15 V
Power
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
AD16 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD17 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD18 V
AD20 V
AD21 V
Power
TTOA
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Power
TTOA
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
pins.
V
TTOB
Output Termination Supply (A). The V
V
pins.
TTOB
AD22 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD23 VCC Power Positive Supply.
AD24 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AD25 IP20 Input High Speed Input.
AD26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
Rev. A | Page 15 of 56
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
pins are normally tied to the
TTOA
ADN4605 Data Sheet
AE2
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
AE3
OP0
Output
High Speed Output.
AE22
ON18
Output
High Speed Output Complement.
AE23
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
AF16
OP13
Output
High Speed Output.
AF17
ON13
Output
High Speed Output Complement.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
AE1 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AE4 ON0 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE5 OP2 Output High Speed Output.
AE6 ON2 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE7 OP4 Output High Speed Output.
AE8 ON4 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE9 OP6 Output High Speed Output.
AE10 ON6 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE11 OP8 Output High Speed Output.
AE12 ON8 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE13 OP10 Output High Speed Output.
AE14 ON10 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE15 OP12 Output High Speed Output.
AE16 ON12 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE17 OP14 Output High Speed Output.
AE18 ON14 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE19 OP16 Output High Speed Output.
AE20 ON16 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AE21 OP18 Output High Speed Output.
AE24 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AE25 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AE26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AF1 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AF2 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AF3 VEE Power Negative Supply.
AF4 OP1 Output High Speed Output.
AF5 ON1 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF6 OP3 Output High Speed Output.
AF7 ON3 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF8 OP5 Output High Speed Output.
AF9 ON5 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF10 OP7 Output High Speed Output.
AF11 ON7 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF12 OP9 Output High Speed Output.
AF13 ON9 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF14 OP11 Output High Speed Output.
AF15 ON11 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF18 OP15 Output High Speed Output.
AF19 ON15 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF20 OP17 Output High Speed Output.
AF21 ON17 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF22 OP19 Output High Speed Output.
Rev. A | Page 16 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
AF24
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
AF25
VEE
Power
Negative Supply.
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
AF23 ON19 Output High Speed Output Complement.
AF26 VEE Power Negative Supply.
Rev. A | Page 17 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
50Ω CABLES
2
2
HIGH SPEED
SAMPLING
OSCILLOSCOPE
50Ω CABLES
2
2
50Ω
ADN4605
AC-COUPLED
EVALUATION
BOARD
INPUT
PIN
OUTPUT
PIN
PATTERN
GENERATOR
DATA OUT
TP2
TP1
09796-048
09796-035
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-047
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-034
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-046
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
VCC = 2.5 V, V
equalizer (EQ) = 1 (3 dB), data rate = 4.25 Gbps (PRBS7 data pattern), ac-coupled inputs and outputs, differential input swing = 800 mV p-p,
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
T
A
= 2.5 V, V
TTIx
= 2.5 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, VEE = 0 V, RL = 50 Ω, output level (OLEV) = 4 (16 mA), preemphasis (PE) = 0 (0 dB),
TTOx
Figure 7. Standard Test Circuit
Figure 8. 3.25 Gbps Input Eye (TP1 from Figure 7)
Figure 10. 3.25 Gbps Output Eye (TP2 from Figure 7)
Figure 9. 4.25 Gbps Input Eye (TP1 from Figure 7)
Rev. A | Page 18 of 56
Figure 11. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye (TP2 from Figure 7)

Data Sheet ADN4605
50Ω CABLES
2
2
TP3
HIGH
SPEED
SAMPLING
OSCILLOSCOPE
50Ω CABLES
2
2
50Ω
ADN4605
AC-COUPLED
EVALUATION
BOARD
INPUT
PIN
OUTPUT
PIN
PATTERN
GENERATOR
DATA OUT
TP1
50Ω CABLES
2
2
TP2
FR4 TEST BACKP LANE
DIFFERENTIAL
STRIPL INE TRACES
8mils WI DE , 8mils SPACE,
8mils DIELECTRIC HEI GHT
LENGTHS = 10 INCHES, 20 INCHE S ,
30 INCHES, 40 I NCHE S
09796-049
09796-040
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-045
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-038
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-043
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
Figure 12. Equalization Test Circuit
Figure 13. 4.25 Gbps Input Eye, 20 Inch FR4 Input Channel
(TP2 from Figure 12)
Figure 15. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 20-Inch FR4 Input Channel, EQ = 12 dB
(TP3 from Figure 12)
Figure 14. 4.25 Gbps Input Eye, 40-Inch FR4 Input Channel
(TP2 from Figure 12)
Rev. A | Page 19 of 56
Figure 16. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 40-Inch FR4 Input Channel, EQ = 12 dB
(TP3 from Figure 12)

ADN4605 Data Sheet
50Ω CABLES
2
2
TP3
HIGH
SPEED
SAMPLING
OSCILLOSCOPE
50Ω CABLES
2
2
50Ω
ADN4605
AC-COUPLED
EVALUATION
BOARD
INPUT
PIN
OUTPUT
PIN
PATTERN
GENERATOR
DATA OUT
TP1
50Ω CABLES
2
2
TP2
FR4 TEST BACKP LANE
DIFFERENTIAL
STRIPL INE TRACES
8mils WI DE , 8mils SPACE,
8mils DIELECTRIC HEI GHT
LENGTHS = 10 INCHES, 20 INCHE S ,
30 INCHES, 40 I NCHE S
09796-050
09796-039
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-044
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-036
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
09796-041
0.167UI/DIV
200mV/DIV
Figure 18. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 20-Inch FR4 Output Channel, PE = 0 dB
(TP3 from Figure 17)
Figure 17. Preemphasis Test Circuit
Figure 20. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 20-Inch FR4 Input Channel, PE = 5.6 dB
(TP3 from Figure 17)
Figure 19. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 40-Inch FR4 Input Channel, PE = 0 d B
(TP3 from Figure 17)
Rev. A | Page 20 of 56
Figure 21. 4.25 Gbps Output Eye, 40-Inch FR4 Input Channel, PE = 9.5 dB
(TP3 from Figure 17)

Data Sheet ADN4605
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 1 2 3 4 5
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
DATA RATE (Gbps)
09796-033
EQ = 3dB
EQ = 6dB
EQ = 12dB
0
20
40
60
80
100
2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.25 3.50 3.75
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
09796-024
EQ = 3dB
EQ = 6dB
EQ = 12dB
0
20
40
60
80
100
–40 –15 10 35 60 85
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
09796-025
EQ = 3dB
EQ = 6dB
EQ = 12dB
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
0 1 2 3 4 5
EYE HEIGHT (mV p-p DIFF)
DATA RATE (Gbps)
09796-030
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.25 3.50 3.75
EYE HEIGHT (mV p-p DIFF)
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
09796-027
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
–40 –15 10 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
EYE HEIGHT (mV p-p DIFF)
EQ = 3dB
EQ = 6dB
EQ = 12dB
09796-026
Figure 22. Deterministic Jitter vs. Data Rate
Figure 23. Deterministic Jitter vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 25. Eye Height vs. Data Rate
Figure 26. Eye Height vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 24. Deterministic Jitter vs. Temperature
Figure 27. Eye Height vs. Temperature
Rev. A | Page 21 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 10 20 30 40
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
INPUT FR4 TRACE LENGT H ( Inches)
09796-032
EQ = 3dB
EQ = 6dB
EQ = 12dB
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0.01 0.1 1
JITTER (ps)
INPUT SWING (V
DIFF
p-p )
DETERMINISTIC JITTER p-p
RANDOM JITTER RMS
09796-029
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
TERMINATION VOLTAGE (V)
VCC = 2.5V
VCC = 3.3V
09796-022
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 10 20 30 40
50 60 70
DETERMINISTIC JITTER (ps)
OUTPUT FR4 CHANNEL LENGTH (Inches)
09796-031
0dB
2.2dB
3.5dB
5.4dB
6.0dB
7.4dB
9.5dB
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
JITTER (ps)
INPUT COMMON-MODE (V)
RANDOM JITTER RMS
DETERMINISTIC JITTER p-p
09796-028
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
09796-017
LOSS (dB)
FREQUENCY (Hz)
6 INCHES
10 INCHES
20 INCHES
40 INCHES
30 INCHES
Figure 28. Deterministic Jitter vs. Input FR4 Channel Length
Figure 31. Deterministic Jitter vs. Output FR4 Channel Length
Figure 29. Jitter vs. Differential Input Swing
Figure 30. Deterministic Jitter vs. Output Termination Voltage (V
Figure 32. Jitter vs. Input Common-Mode Voltage
TTO)
Figure 33. S21 Test Traces
Rev. A | Page 22 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
RISE/FALL TIME (ps)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
RISE TIME
FALL TIME
09796-018
800
850
900
950
1000
1050
1100
1150
1200
2.375 2.500 3.300 3.630
PROPAGATION DELAY (ps)
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
09796-051
160
152
144
136
128
120
112
104
96
88
80
72
64
56
48
40
32
24
16
8
0
SAMPLES
PROPAGATION DELAY (ps)
700
720
740
760
780
800
820
840
860
880
900
920
940
960
980
1000
1020
1040
1060
1080
1100
PROP DELAY MEAN
922.4ps
09796-023
09796-021
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
–4.0
–3.7
–3.4
–3.0
–2.7
–2.4
–2.1
–1.8
–1.4
–1.1
–0.8
–0.5
–0.2
0.2
0.5
0.8
1.1
1.4
1.8
2.1
2.4
2.7
3.0
3.4
3.7
4.0
SAMPLES
RANDOM JITTER (ps)
STANDARD DEVIATION = 0.81ps
800
850
900
950
1000
1050
1100
1150
1200
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
PROPAGATION DELAY (ps)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
CC
= 2.5V
VCC = 3.3V
09796-020
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10M 100M 1G 10G
RETURN LOS S ( dB)
FREQUENCY (Hz)
S
22
S
11
09796-019
Figure 34. Rise/Fall Time vs. Temperature
Figure 35. Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 37. Random Jitter Histogram
Figure 38. Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
Figure 36. Propagation Delay Histogram
Figure 39. Return Loss (S11, S22)
Rev. A | Page 23 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
EQ
Rx Tx
PRE-
EMPHASIS
40 × 40
SWITCH
MATRIX
CONNECTION
MAP 1
CONNECTION
MAP 0
PARALLEL/SERIA L CONTROL
LOGIC INTERFACE
PRE-
EMPHASIS
LEVEL
SETTINGS
OUTPUT
LEVEL
SETTINGS
ADN4605
V
CC
V
EE
DV
CC
OP[39:0]
V
TTOA
,
V
TTOB
ON[39:0]
IP[39:0]
V
TTIA
,
V
TTIB
IN[39:0]
I
2
C/SPI
(UPDATE)
SDI/RE
SCL/SCK/
WE
RESET
SER/PAR
CS
EQUALIZATION
SETTINGS
DATA[1]
(UPDATE)
DATA[0]/
SDA/SDO
DATA[7:2]
ADDR[7:0]
09796-007
K23
CS
Chip select
N/A
Chip select
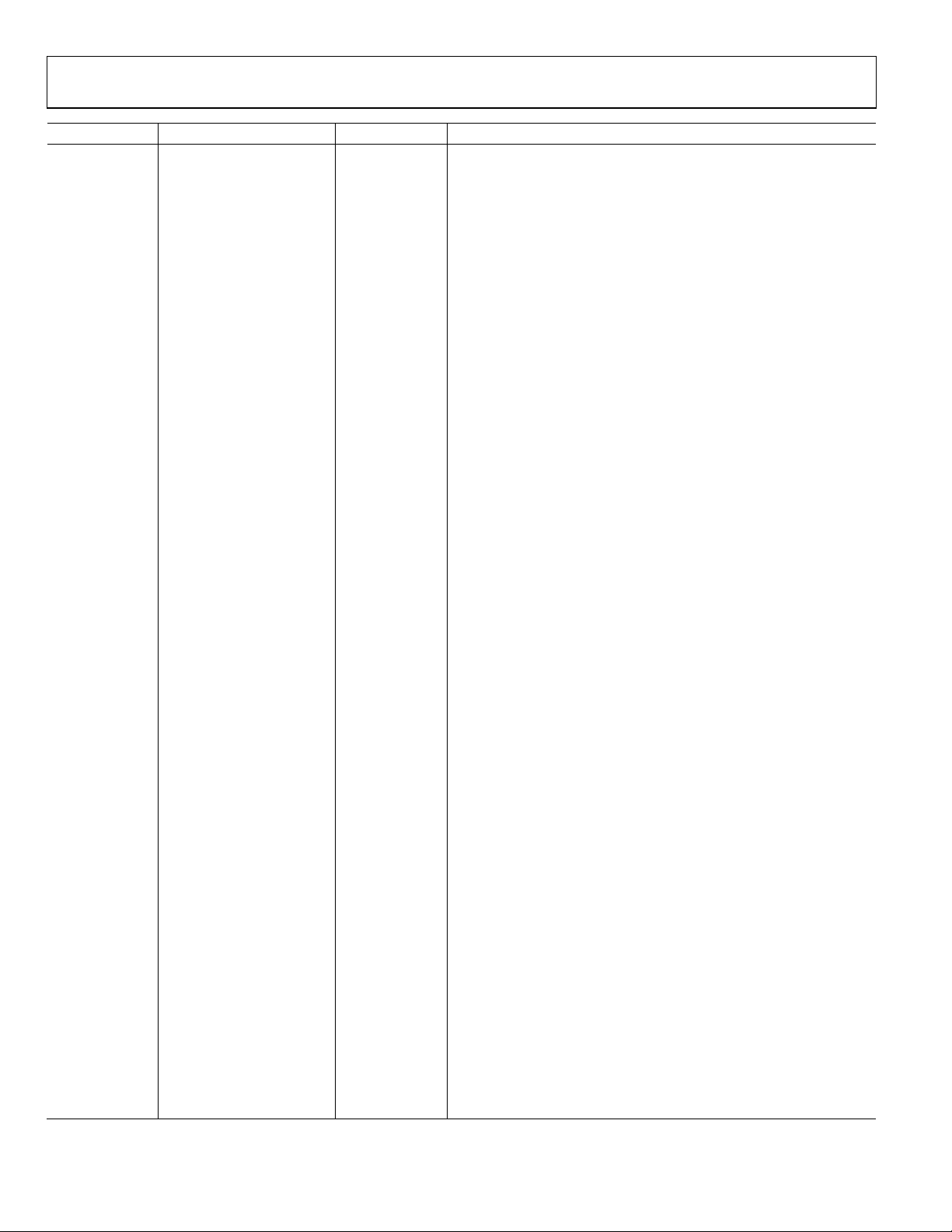
THEORY OF OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
The ADN4605 is a 40 × 40, buffered, asynchronous crosspoint
switch that provides input equalization, output preemphasis,
and output level programming capabilities. The receivers
integrate an equalizer that is optimized to compensate for
typical backplane losses. The switch supports multicast and
broadcast operation, allowing the ADN4605 to work in
redundancy and port replication applications.
The ADN4605 is configured through either the serial or parallel
control interface. The serial or parallel control interface is
selected using the SER/
interface supports both I
2
SPI
I
C/
dedicated control pin. The ADN4605 control pins
function differently depending on which programming
interface is selected, as described in Tabl e 8.
Table 8. Parallel/Serial Interface Pin Control
Pin No. Pin Name
K4
J4
H23
J23
SER/
2
C/SPI/ UPDAT E
I
WE/SCL/SCK
RE/SDI
PAR
dedicated control pin. The serial
2
C and SPI protocols selected using the
Parallel Mode
(SER/
PAR
= 0)
Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function
PAR Serial/parallel control interface
selection
Update strobe
Parallel write strobe I
Parallel read strobe N/A SPI data input
Figure 40. Block Diagram
I2C Mode
(SER/
Serial/parallel control interface
selection
2
C/SPI control interface selection I2C/SPI control interface selection
I
2
C clock SPI clock
= 1, I2C/
PAR
SPI
= 1)
Serial/parallel control interface
selection
(SER/
SPI Mode
= 1, I2C/
PAR
SPI
= 0)
L23 DATA0/SDA/SDO Parallel register data bit (LSB) I2C data input SPI data output
M23
N23, P23,
UPDAT E
DATA1/
DATA2 to DATA7 Parallel register data bits N/A N/A
Parallel register data bits Update strobe Update strobe
R23, T23,
U23, V23
L4
RESET Device register reset (active
Device register reset (active low) Device register reset (active low)
low)
M4 ADDR0
Parallel register address bit
N/A N/A
(LSB)
N4, P4, R4,
T4, U4, V4,
ADDR1to
ADDR7
Parallel register address bits
2
C LSB device address to I2C MSB
I
device address
N/A
W4
Rev. A | Page 24 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
V
CC
V
TTI
IPx
INx
V
EE
R2
210Ω
R4
630Ω
RN
53Ω
RP
53Ω
R1
210Ω
R3
630Ω
600µA 600µA
EQUALIZER
09796-008
RECEIVERS
Input Structure and Input Levels
The ADN4605 receiver inputs incorporate 50 Ω termination
resistors, ESD protection, and a fixed equalizer that is optimized
for operation over long backplane traces. Each receive channel also
provides a positive/negative (P/N) inversion function, which allows
the user to swap the sign of the input signal path to eliminate the
need for board-level crossovers.
Equalization
The ADN4605 receiver incorporates a continuous time equalizer
(EQ) that provides up to 12 dB of high frequency boost to compensate up to 40 inches of FR4 at 4.25 Gbps. Each input has two
equalizer control bits. The receiver is disabled by default. The boost
can be set to defined levels by programming the respective address
register bits (Address 0xC0 through Address 0xC9) for the target
Table 9. Equalization Control Registers
Register
Address
0xC0 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [2]
3:2 RXEQIN [1]
1:0 RXEQIN [0]
0xC1 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [6]
3:2 RXEQIN [5]
1:0 RXEQIN [4]
0xC2 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [10]
3:2 RXEQIN [9]
1:0 RXEQIN [8]
0xC3 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [14]
3:2 RXEQIN [13]
1:0 RXEQIN [12]
0xC4 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [18]
3:2 RXEQIN [17]
1:0 RXEQIN [16]
0xC5 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [22]
3:2 RXEQIN [21]
1:0 RXEQIN [20]
0xC6 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [26]
3:2 RXEQIN [25]
1:0 RXEQIN [24]
Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Functionality Description
(Rx IN 3 to Rx IN 0)
(Rx IN 7 to Rx IN 4)
(Rx IN 11 to Rx IN 8)
(Rx IN 15 to Rx IN 12)
(Rx IN 19 to Rx IN 16)
(Rx IN 23to Rx IN 20)
(Rx IN 27 to Rx IN 24)
Rev. A | Page 25 of 56
input channel to the specified logic combinations as shown in
Tabl e 9.
Figure 41. Simplified Input Circuit
7:6 RXEQIN [3] 00 = Rx disabled (default)
01 = 3 dB boost
10 = 6 dB boost
11 = 12 dB boost
7:6 RXEQIN [7]
7:6 RXEQIN [11]
7:6 RXEQIN [15]
7:6 RXEQIN [19]
7:6 RXEQIN [23]
7:6 RXEQIN [27]

ADN4605 Data Sheet
Register
Address Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Functionality Description
0xC7 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [30]
3:2 RXEQIN [29]
1:0 RXEQIN [28]
0xC8 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [34]
3:2 RXEQIN [33]
1:0 RXEQIN [32]
0xC9 0x0 Rx EQ Control
5:4 RXEQIN [38]
3:2 RXEQIN [37]
1:0 RXEQIN [36]
0xCA 0x0
(Write only)
(Rx IN 31 to Rx IN 28)
(Rx IN35 to Rx IN 32)
(Rx IN 39 to Rx IN 36)
Rx EQ Control
(Rx IN Broadcast)
POLARITY INVERSION
The P/N inversion is a feature intended to allow the user to implement the equivalent of a board-level crossover in a much smaller area
and without additional via impedance discontinuities that degrade the high frequency integrity of the signal path. The P/N inversion is
available independently for each of the 40 input and output channels, which are controlled by writing to the RXSIGN bit of the RX Sign
control registers (Addresses 0xCB through Address 0xCF) and the TXSIGN bit of the TX control registers (Address 0xA9 through
Address 0xAD).
7:6 RXEQIN [31] 00 = Rx disabled (default)
01 = 3 dB boost
10 = 6 dB boost
11 = 12 dB boost
7:6 RXEQIN [35]
7:6 RXEQIN [39]
1:0 RXEQIN BC
Table 10. Signal Path Polarity Control
Register
Address Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Functionality Description
0xCB 0x00 RX SIGN
RX IN 07 to RX IN 00
0xCC 0x00 RX SIGN
RX IN 15 to RX IN 08
0xCD 0x00 RX SIGN
RX IN 23 to RX IN 16
0xCE 0x00 RX SIGN
RX IN31 to RX IN 24
0xCF 0x00 RX SIGN
RX IN 39 to RX IN 32
0xA9 0x00 TX SIGN
TX OUT 07 to TX OUT 00
0xAA 0x00 TX SIGN
TX OUT 15 to TX OUT 08
0xAB 0x00 TX SIGN
TX OUT 23 to TX OUT 16
0xAC 0x00 TX SIGN
TX OUT 31 to TX OUT 24
0xAD 0x00 TX SIGN
TX OUT 39 to TX OUT 32
7: 0 RXSIGN [7]to RXSIGN [0] Signal path polarity inversion (input/output)
7: 0 RXSIGN [15] to RXSIGN [8]
7: 0 RXSIGN[23] to RXSIGN [16]
7: 0 RXSIGN [31] to RXSIGN [24]
7: 0 RXSIGN [39] to RXSIGN [32]
7: 0 TXSIGN [7] to TXSIGN [0]
7: 0 TXSIGN [15] to TXSIGN [8]
7: 0 TXSIGN [23] to TXSIGN [16]
7: 0 TXSIGN [31] to TXSIGN [24]
7: 0 TXSIGN [39] to TXSIGN [32]
0 = noninvert
1 = invert
Rev. A | Page 26 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
0 39
0
39
INPUTSINPUTS
REGIST E R 0x04 TO REGIST E R 0x2B
XPT MAP 0
OUTPUTS
REGIST E R 0x2C TO REGIST E R 0x53
XPT MAP 1
OUTPUTS
0
1
MAP TABLE
SELECT
REGIST E R 0x02
XPT STATUS READ
REGIST E R 0x54 TO REGIST E R 0x7B
UPDATE
REGIST E R 0x01/
EXTERNAL PIN
FIRST RANK RE GISTERS
SECOND
RANK REGIST E RS
0 39
0
39
XPT CORE
OUTPUTS
09796-009
0 39
0
39
INPUTS
SWITCH CORE
The ADN4605 switch core is a fully nonblocking 40 × 40 array
that allows multicast and broadcast configurations. The configuration of the switch core is programmed through either the
serial or parallel control interface. The crosspoint configuration
map, which controls the connectivity of the switch core, consists
of a double rank register architecture, as shown in Figure 42.
The second rank registers contain the current state of the
crosspoint. The first rank registers contain the next state. Each
entry in the connection map stores six bits per output, which
indicates which of the 40 inputs are connected to a given
output. An entire connectivity matrix can be programmed
at once by passing data from the first rank registers into the
second rank by writing 0x01 to the XPT Update register
(Address 0x01). An external
control the data transfer as shown in Tabl e 8.
The first rank registers store connection configurations for
the crosspoint. Map 0 is the default map and is located at
Address 0x04 to Address 0x2B. By default, Map 0 contains
a diagonal connection configuration whereby Input 0 is
connected to Output 0, Input 1 to Output 1, Input 2 to
Output 2, and so on.
UP DATE
pin can also be used to
Similarly, by default, Map 1 contains the opposite diagonal
connection configuration where Input 0 is connected to
Output 39, Input 1 to Output 38, and so on. Both maps are
read/write accessible registers. The active map is selected by
writing to the XPT Map Ta b le Select register (Address 0x02).
The crosspoint is configured by addressing the register assigned
to the desired output and writing the desired connection data
into the first rank of latches in either Map 0 or Map 1. The
connection data is equivalent to the binary coded value of the
input number. This process is repeated until each of the desired
connections is programmed.
In situations where multiple outputs are to be programmed to
a single input, a broadcast command is available. A broadcast
command is issued by writing the binary value of the desired
input to the XPT Broadcast register (Address 0x03). The broadcast is applied to the selected map table.
The current state of the crosspoint connectivity is available
by reading the XPT Status registers (Address 0x54 to Address
0x7B). Register descriptions for Map 0, Map 1, and XPT status
registers are shown in Tab le 11.
Figure 42. Crosspoint Connection Map Block Diagram
Rev. A | Page 27 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
Table 11. XPT Control Registers
Register
Address Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Functionality Description
0x00 0x00
(Write only)
0x01 0x00
(Write only)
0x02 0x00 XPT Map Table Select 0 Map Table Select 0: Map 0 is selected (default)
1: Map 1 is selected
0x03 0x00
(Write only)
0x04 to 0x2B 0x00 to 0x27 XPT Map 0
0x2C to 0x53 0x27 to 0x00 XPT Map 1
0x54 to 0x7B 0x00 to 0x00 XPT Status
RESET
On initial power-up, or at any point in operation, the ADN4605 register set can be restored to the default values by pulling the
low according to the control logic timing specifications. During normal operation, however, the
software reset is also available by writing the value 0x01 to the Reset register at Address 0x00. This register is write-only.
Software Reset 0 Software reset Reset the ADN4605 registers to default values
XPT Update 0 XPT Update Updates XPT switch core (active high)
XPT Broadcast 5:0 XPT BCAST [5:0] Assigns all output values at once for the selected XPT table map
5:0 OUT x [5:0] Output (x = 0 to 39) connection assignments
Control 0 to Control 39
Control 39 to Control 0
Control 39 to Control 0
5:0 OUT x [5:0] Output (x = 39 to 0) connection assignments
5:0 OUT x [5:0] Output (x = 0 to 39) connection status
RESET
pin must be pulled up to DVCC. A
RESET
pin
Rev. A | Page 28 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
ON-CHIP TERMINATION
ESD
V
CC
V
TTOx
OPx
ONx
V
EE
V3
VC
V2
VP
V1
VN
Q1
I
DC
+ I
PE
= I
T
Q2
RP
50Ω
RN
50Ω
09796-010
010: 3 mA
TRANSMITTERS
Output Structure and Output Levels
The ADN4605 transmitter outputs incorporate 50 Ω termination resistors, ESD protection, and output current switches.
Each channel provides independent control of both the absolute
output level and the preemphasis output level. Note that the
choice of output current affects the output common-mode level.
Preemphasis
Transmission line attenuation can be equalized at the transmitter using preemphasis. The transmit equalizer setting can
be chosen by matching the channel loss to the amount of boost
provided by the preemphasis.
Transmitter preemphasis levels, as well as dc output levels, can
be set through either the serial or parallel control interface.
Tabl e 12 summarizes the absolute output levels and
preemphasis level control settings. The output level control sets
the dc current level, and the preemphasis level control sets the
PE current in the transmitter, as shown in Figure 43. The full
resolution of eight settings is available through the serial or
parallel interface. A single setting can be programmed to all
outputs simultaneously by writing to the TX Lane Control
Broadcast Register (Address 0xA8).
In addition to the enabled state, the Tx has three possible
disabled states (standby, squelched, and disabled) controlled
by the Tx Drive Control registers (Address 0xB0 to Address
0xB9) shown in Table 13. Disabled is the lowest power-down
state. When squelched, the output voltage at both the P and N
outputs is the common-mode voltage as defined by the output
current settings. Note that the squelch feature is only available
when using a 3.3 V core supply voltage (V
). In standby, the
CC
output level of both P and N outputs is pulled up to the
termination supply (V
TTOA
or V
TTOB
).
Figure 43. Simplified Tx Output Circuit
Table 12. Preemphasis and Output Level Settings
Register Address Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0x80 (Output 0) to 0xA7 (Output 39)
and 0xA8 (Tx Broadcast)
0x40
Tx Lane Control Output 0 to Tx
Lane Control Output 39 and Tx
Broadcast
7 Reserved
6:4 OLEV
3 Overdrive
Rev. A | Page 29 of 56
2:0 PE 000: 0 mA
001: 2 mA
011: 4 mA
100: 5 mA
101: 6 mA
110: 7 mA
111: 8 mA
0 (Reserve bit)
000: 0 mA
001: 4 mA
010: 8 mA
011: 12 mA
100: 16 mA
101: 20 mA
110: 24 mA
111: (Reserve bit)
1: overdrive (increases OLEV and
PE currents by 25%)
0: no overdrive

ADN4605 Data Sheet
Table 13. Transmitter Output Enable State Settings
Register Address Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Functionality Description
0xB0 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB1 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB2 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB3 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB4 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB5 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB6 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB7 0x00 Tx Drive Control
0xB8 0x00 Drive Control
0xB9 0x00 Drive Control
0xBA 0x00
(Write only)
Tx3 to Tx0
Tx7 to Tx4
Tx11 to Tx8
Tx15 to Tx12
Tx19 to Tx16
Tx23 to Tx20
Tx27 to Tx24
Tx31 to Tx28
Tx35 to Tx32
Tx39 to Tx36
Tx Drive Control 1:0 TXENBC [39]
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
7:6
5:4
3:2
1:0
TXEN [3]
TXEN [2]
TXEN [1]
TXEN [0]
TXEN [7]
TXEN [6]
TXEN [5]
TXEN [4]
TXEN [11]
TXEN [10]
TXEN [9]
TXEN [8]
TXEN [15]
TXEN [14]
TXEN [13]
TXEN [12]
TXEN [19]
TXEN [18]
TXEN [17]
TXEN [16]
TXEN [23]
TXEN [22]
TXEN [21]
TXEN [20]
TXEN [27]
TXEN [26]
TXEN [25]
TXEN [24]
TXEN [31]
TXEN [30]
TXEN [29]
TXEN [28]
TXEN [35]
TXEN [34]
TXEN [33]
TXEN [32]
TXEN [39]
TXEN [38]
TXEN [37]
TXEN [36]
11: enabled
10: Tx standby
01: Tx squelched
00: Tx disabled (default)
Rev. A | Page 30 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
−
+×=
−
−−
V
VV
DCSW
DCSWPESW
Gain 1log20]dB[
10
V
TTO
V
H-PE
V
SW-PE
V
L-PE
V
L-DC
V
SW-DC
V
H-DC
V
OCM
T
PE
09796-011
Delayed Tap
Main Tap
DC Swing
IDC
Programmable
Output current for main tap output level (OLEV)
V
V
− ∆V
− V
/2
DC single-ended output low voltage
The amount of high frequency boost provided by the transmitter is determined by both the output and preemphasis level
settings.
Tabl e 14 provides an example of how the absolute output and
preemphasis level settings determine the amount of high
frequency boost at the Tx output. Note that the OLEV setting
refers to the main tap output current and the PE setting refers to
the delayed tap current.
The preemphasis boost equation follows:
(1)
Figure 44. Signal Level Definitions
Table 14. Preemphasis Boost and Overshoot vs. Setting Example
PE Setting
Current (mA) OLEV Setting
Current (mA) Gain (dB) Overshoot (%)
(mV p-p Diff)
0 0 4 16 0.00 0.00 800
3 4 5 20 3.52 50.00 800
7 8 6 24 6.02 100.00 800
7 8 4 16 9.54 200.00 400
7 8 3 12 13.98 400.00 200
Table 15. Symbol Definitions
Symbol Formula Definition
IPE Programmable Output current for PE delayed tap (PE)
I
IDC + IPE Total transmitter output current
TTO
V
25 Ω × I
DPP-DC
V
25 Ω × I
DPP-PE
V
V
SW-DC
V
V
SW-PE
∆V
OCM_DC-COUPLED
∆V
OCM_AC-COUPLED
V
V
OCM
V
V
H-DC
L-DC
V
V
H-PE
V
V
L-PE
DPP-DC
DPP-PE
25 Ω × I
50 Ω × I
TTO
TTO
TTO
TTO
TTO
× 2 Peak-to-peak differential voltage swing of nonpreemphasized waveform
DC
× 2 Peak-to-peak differential voltage swing of preemphasized waveform
TTO
/2 = V
/2 = V
− ∆V
− ∆V
− ∆V
− ∆V
– V
H-DC
H-PE
/2 Output common-mode shift, dc-coupled outputs
TTO
/2 Output common-mode shift, ac-coupled outputs
TTO
= (V
OCM
+ V
OCM
OCM
+ V
OCM
− V
OCM
DC single-ended voltage swing
L-DC
– V
Preemphasized single-ended voltage swing
L-PE
+ V
H-DC
DPP-DC
DPP-DC
DPP-PE
DPP-PE
)/2 Output common-mode voltage
L-DC
/2 DC single-ended output high voltage
/2 Maximum single-ended output voltage
/2 Minimum single-ended output voltage
Rev. A | Page 31 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
CML
V
EE
V
TTOx
V
TTOx
V
CC
V
TTIx
ADN4605
Rx
50Ω50Ω
50Ω50Ω50Ω
75Ω
75Ω
50Ω
V
TTIx
75Ω75Ω
50Ω
50Ω
09796-012
TERMINATION
The inputs and outputs include integrated 50 Ω termination
resistors. The internal resistors can be disabled for applications that
require external termination resistors. For example, disabling the
integrated 50 Ω termination resistors allow alternative termination
values such as 75 Ω as shown in Figure 45.
Note that the integrated 50 Ω termination resistors are optimal
for high data rate digital signaling. Disabling the terminations
can reduce the overall performance.
The termination control for the receiver inputs can be accessed
through Register Address 0xD0 (Input 0 to Input 19) and
Register Address 0xD1 (Input 20 to Input 39). The termination
control for the transmitter outputs can be accessed through
Register Address 0xBC (Output 0 to Output 19) and Register
Address 0x BD (Output 20 to Output 39).
Tabl e 16 shows the termination control registers. Each bit
controls the terminations settings for four inputs/outputs.
A Logic 0 enables the terminations for the respective group.
A Logic 1 disables the terminations for the respective group.
The terminations are enabled by default.
Figure 45. 75 Ω to 50 Ω Impedance Translator
Table 16. Termination Control Register
Register
Address Default Register Name Bit Bit Name Description Functionality
0xBD 0x00 Tx Termination Control 4
0xBC 0x00 Tx Termination Control 4
0xD1 0x00 Rx Termination Control 4
0xD0 0x00 Rx Termination Control 4
3
2
1
0
3
2
1
0
3
2
1
0
3
2
1
0
TXB_TERM
TXB_TERM
TXB_TERM
TXB_TERM
TXB_TERM
TXA_TERM
TXA_TERM
TXA_TERM
TXA_TERM
TXA_TERM
RXB_TERM
RXB_TERM
RXB_TERM
RXB_TERM
RXB_TERM
RXA_TERM
RXA_TERM
RXA_TERM
RXA_TERM
RXA_TERM
Output [39:36] (B side) termination control
Output [35:32] (B side) termination control
Output [31:28] (B side) termination control
Output [27:24] (B side) termination control
Output [23:20] (B side) termination control
Output [19:16] (A side) termination control
Output [15:12] (A side) termination control
Output [11:8] (A side) termination control
Output [7:4] (A side) termination control
Output [3:0] (A side) termination control
Input [39:36] (B side) termination control
Input [35:32] (B side) termination control
Input [31:28] (B side) termination control
Input [27:24] (B side) termination control
Input [23:20] (B side) termination control
Input [19:16] (A side) termination control
Input [15:12] (A side) termination control
Input [11:8] (A side) termination control
Input [7:4] (A side) termination control
Input [3:0] (A side) termination control
0 = terminations enabled
1= terminations disabled
Rev. A | Page 32 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
START R/W ACK ACK ACK STOPDATA
ADDR
[1:0]
b10010 REGISTER ADDR
SCL
SDA
SDA
EXAMPLE
1 2
2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9a
09796-013
I2C SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE
The ADN4605 register set is controlled through a 2-wire I2C
interface. To a cc e ss the I
2
line and I
acts only as an I
SPI
C/
2
C slave device. Therefore, the I2C bus in the
system needs to include an I
ADN4605 and other I2C devices that may be on the bus.
The ADN4605 I
(100 kHz) and fast (400 kHz) modes. The SDA line only
changes value when the SCL pin is low with two exceptions.
To indicate the beginning or continuation of a transfer, the
SDA pin is driven low while the SCL pin is high; to indicate
the end of a transfer, the SDA line is driven high while the
SCL line is high. Therefore, it is important to control the
SCL clock to toggle only when the SDA line is stable unless
indicating a start, repeated start, or stop condition. To establish
2
I
C communication with the ADN4605, parallel address lines
(ADDR[7:1]) need to be configured to the user-assigned I
device address as shown in Ta b le 17.
Table 17. Example of I
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 I2C Device Address
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 X 0x90
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 X 0x92
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 X 0x94
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 X 0x96
I2C DATA WRITE
To write data to the ADN4605 register set, a microcontroller, or
any other I
to the ADN4605 slave device. The steps to be followed are listed
below; the signals are controlled by the I
wise specified. A diagram of the procedure is shown in Figure 46.
1. Send a start condition (while holding the SCL line high,
2
C m aste r, must send the appropriate control signals
pull the SDA line low).
2
C serial interface, both the SER/
PAR
lines must be held at logic high. The ADN4605
2
C master to configure the
2
C interface can be run in the standard
2
C
2
C Device Address Assignment
2
C master unless other-
2. Send the ADN4605 part address (seven bits) whose bits are
controlled by the input pins ADDR[7:1]. This transfer
should be MSB first.
3. Send the write indicator bit (0).
4. Wait for the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
5. Send the register address (eight bits) to which data is to be
written. This transfer should be MSB first.
6. Wait for the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
7. Send the data (eight bits) to be written to the register
whose address was set in Step 5. This transfer should be
MSB first.
8. Wait for the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
9. Do one or more of the following:
a. Send a stop condition (while holding the SCL line high,
pull the SDA line high) and release control of the bus.
b. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
with Step 2 of the write procedure (see the I2C Data
Write section) to perform a write.
c. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
with Step 2 of this procedure to perform a read from
another address.
d. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
with Step 8 of this procedure to perform a read from
the same address.
The ADN4605 write process is shown in Figure 46. The SCL
signal is shown along with a general write operation and a
specific example. In the example, Data 0x4B is written to
Address 0x6D of an ADN4605 part with a part address of 0x92.
The ADN4605 device address selections are more flexible than
shown. It is important to note that the SDA line only changes
when the SCL line is low, except for the case of sending a start,
stop, or repeated start condition, Step 1 and Step 9 in this case.
2
Figure 46. I
C Write Diagram
Rev. A | Page 33 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
SCL
SDA
SDA
EXAMPLE
1 2 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 8 9
10 11 12 13a
b10010 A A Sr DATA A STOPREGIST E R ADDRSTART
ADDR
[1:0]
ADDR
[1:0]
b10010
R/
W
A
R/
W
09796-014
I2C DATA READ
To read data from the ADN4605 register set, a microcontroller,
or any other I
signals to the ADN4605 slave device. The steps are listed below;
the signals are controlled by the I
specified. A diagram of the procedure is shown in Figure 47.
1. Send a start condition (while holding the SCL line high, pull
the SDA line low).
2. Send the ADN4605 part address (seven bits) whose bits are
controlled by the input pins ADDR[7:1]. This transfer
should be MSB first.
3. Send the write indicator bit (0).
4. Wait for the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
5. Send the register address (eight bits) from which data is
to be read. This transfer should be MSB first. The register
address is kept in memory in the ADN4605 until the part
is reset or the register address is written over with the same
procedure (Step 1 to Step 6).
6. Wa i t fo r the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
7. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the SCL line
high, pull the SDA line low).
8. Send the ADN4605 part address (seven bits) whose bits are
controlled by the input pins ADDR[7:1]. This transfer
should be MSB first.
9. Send the read indicator bit (1).
10. Wait for the ADN4605 to acknowledge the request.
11. The ADN4605 then serially transfers the data (eight bits)
held in the register indicated by the address set in Step 5.
2
C master needs to send the appropriate control
2
C master unless otherwise
12. Acknowledge the data.
13. Do one or more of the following:
a. Send a stop condition (while holding the SCL line high
pull the SDA line high) and release control of the bus.
b. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
2
with Step 2 of the write procedure (see the I
C Data
Write section) to perform a write.
c. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
with Step 2 of this procedure to perform a read from
another address.
d. Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
SCL line high, pull the SDA line low) and continue
with Step 8 of this procedure to perform a read from
the same address.
The ADN4605 read process is shown in Figure 47. The SCL
signal is shown along with a general read operation and a
specific example. In the example, Data 0x49 is read from
Address 0x6D of an ADN4605 part with a part address of 0x92.
The part address is seven bits wide and is composed of the
ADN4605 (ADDR[7:1]). In this example, the ADDR{1:0] bits
are set to b01.
In Figure 47, the corresponding step number is visible in the
circle under the waveform. The SCL line is driven by the I
2
C
master and never by the ADN4605 slave. As for the SDA line,
the data in the shaded polygons is driven by the ADN4605,
whereas the data in the nonshaded polygons is driven by the I
master. The end phase case shown is that of Step13a.
Note that the SDA line only changes when the SCL line is low,
except for the case of sending a start, stop, or repeated start
condition, as in Step 1, Step 7, and Step 13. In Figure 47, A is
the same as ACK. Equally, Sr represents a repeated start where
the SDA line is brought high before SCL is raised. SDA is then
dropped while SCL is still high.
2
C
2
Figure 47. I
C Read Diagram
Rev. A | Page 34 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
SPI SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE
The SPI serial interface of the ADN4605 consists of four wires:
CS
, SCK, SDI, and SDO. In order to access the SPI interface the
PAR
SER/
must be held at logic low. The
when more than one device is connected to the serial clock and
data lines and must be held at logic low to enable write/read
capability to the device when in SPI control mode.
The SCK is used to clock data in and out of the part. The SDI
line is used to write to the registers, and the SDO line is used to
read data back from the registers. Data on SDI line is clocked on
the rising edge of SCK. Data on SDO changes on the falling
edge of SCK. The recommended pull-up resistor value is
between 500 Ω and 1 kΩ. Strong pull-ups are needed when
serial clock speeds that are close to the maximum limit are used
or when the SPI interface lines are experiencing large capacitive
loading. Larger resistor values can be used for pull-up resistors
when the serial clock speed is reduced.
The part operates in a slave mode and requires an externally
applied serial clock to the SCK input. The serial interface is
designed to allow the part to be interfaced to systems that
provide a serial clock that is synchronized to the serial data.
There are two types of serial operations, a read and a write.
Command words are used to distinguish between a read and a
write operation as shown in Table 18.
line must be held at logic high and the I2C/
CS
pin is used to select the device
SPI
line
Table 18. SPI Command Words
Write Command 0x02 (0000 0010)
Read Command 0x03 (0000 0011)
Write Operation
Figure 48 shows the diagram for a write operation to the
ADN4605. Data is clocked into the registers on the rising edge
of SCK. When the
three-state mode. Only when the
does the part accept any data on the SDI line. The 8-bit write
command must precede the register address byte. The register
address byte is then followed by the data byte as shown in
Figure 48.
To allow continuous writes, the address pointer register autoincrements by one without having to load the address pointer
register each time. Subsequent data bytes are written into
sequential registers. Note that not all registers in the 256-byte
address space exist and not all registers are writable. Zeroes
should be entered for nonexistent address fields when implementing a continuous write operation. Address space 0xE0 to
Address 0xFF is reserved and should not be overwritten.
CS
line is high, the SDI and SDO lines are in
CS
goes from a high to a low
Read Operation
To read back from a register, first send the read command
followed by the desired register address. Subsequent clock
cycles, with
desired register address onto SDO, MSB first. SDO changes on
the falling edge of SCK. Multiple data reads are possible in SPI
interface mode because the address pointer register is autoincremented.
CS
asserted low, stream data starting from the
Rev. A | Page 35 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
WRITE COMMAND
START
STOP
REGIST E R ADDRE S S
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
CS
SCK
SDI
SDO
DATA BYTE
X X X X X X X X
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CS (CONTI NUE D)
SCK (CONTI NUE D)
SDI (CONT INUED)
SDO (CONT INUED)
1 8 1 8
1 8
09796-015
Figure 48. SPI–Writing to the Address Pointer Register Followed by a Single Byte of Data to the Selected Register
Rev. A | Page 36 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
READ COMMAND
START
STOP
REGIST E R ADDRE S S
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
CS
SCK
SDI
SDO
DATA BYTE
X X X X X X X X
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CS (CONTI NUE D)
SCK (CONTI NUE D)
SDI (CONT INUED)
SDO (CONT INUED)
1 8 1 8
1 8
09796-016
Figure 49. SPI–Reading a Single Byte of Data from a Selected Register
Rev. A | Page 37 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
PARALLEL CONTROL INTERFACE
The parallel control interface of the ADN4605 consists of
nineteen wires: ADDR[7:0], DATA[7:0],
access the parallel control interface, the SER/
be held at logic low. The
one or more devices share the same address and data lines. The
CS
line must be held at logic low to enable write/read capability
to the device when in parallel control mode.
CS
line is used to select a device when
WE, RE
PAR
, and CS. To
line must
ADDRESS INPUTS: ADDR[7:0]
The binary coded address applied to the address lines
determines which device registers are being programmed or
read back.
DATA INPUTS/OUTPUTS: DATA[7:0]
In write mode, the binary encoded data applied to the data lines
(DATA[7:0]) determine the configuration setting of the register
specified by the address lines (ADDR[7:0]).
In read mode, data lines (DATA [7:0]) are low impedance
outputs indicating the data byte stored in the register specified
by the address lines (ADDR[7:0]). Note that some registers are
write only and may not be read from (see Ta b l e 19) The readback drivers are designed to drive high impedances only
(>1 kΩ).
WRITE OPERATION
For first rank write enable, forcing this pin to logic low allows
the data on the DATA[7:0] lines to be stored in the first rank
latch for the register specified by the address lines (ADDR[7:0]).
The data is latched during the high-to-low transition of the
write enable pulse. The
high state after the write cycle to avoid overwriting the first
rank data.
WE
line must be returned to a logic
READ OPERATION
For second rank read enable, forcing this line to a logic low state
enables the output drivers on the bidirectional data lines
(DATA[7:0]), placing the logic in readback mode of operation.
The register selected to read from is determined by the binary
encoded data configured on the address lines (ADDR[7:0]).
When the read enable line is at a logic low, the data stored in
the specified register will be latched onto the data lines
(DATA[7:0]). The
therefore, first rank programming is not possible while in
readback mode. Note that some registers are defined as write
only and are not accessible in readback mode (see
RE
line is higher priority than the WE line;
Tabl e 19).
Rev. A | Page 38 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
0x00
0x00
Software Reset
0
Reset
Software reset
0x08
0x04
XPT Map 0 Control 4
5:0
OUT 4 [5:0]
Output 4 connection assignment
0x0E
0x0A
XPT Map 0 Control 10
5:0
OUT 10 [5:0]
Output 10 connection assignment
0x19
0x15
XPT Map 0 Control 21
5:0
OUT 21 [5:0]
Output 21 connection assignment
0x24
0x20
XPT Map 0 Control 32
5:0
OUT 32 [5:0]
Output 32 connection assignment
REGISTER MAP
In the Register Map, when settings are provided in the Description column for the first bit, note that these settings apply to all bits with
the same function.
Table 19. Register Map
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
Write only
0x01 0x0 XPT Update 0 XPT Update Updates crosspoint switch core
Write only
0x02 0x00 XPT Map Table 0 Map Table Select 0: Map 0 is selected
Select 1: Map 1 is selected
0x03 Write only XPT Broadcast 5:0 XPT BCAST [5:0] All outputs connection assignment
0x04 0x00 XPT Map 0 Control 0 5:0 OUT 0 [5:0] Output 0 connection assignment
0x05 0x01 XPT Map 0 Control 1 5:0 OUT 1 [5:0] Output 1 connection assignment
0x06 0x02 XPT Map 0 Control 2 5:0 OUT 2 [5:0] Output 2 connection assignment
0x07 0x03 XPT Map 0 Control 3 5:0 OUT 3 [5:0] Output 3 connection assignment
0x09 0x05 XPT Map 0 Control 5 5:0 OUT 5 [5:0] Output 5 connection assignment
0x0A 0x06 XPT Map 0 Control 6 5:0 OUT 6 [5:0] Output 6 connection assignment
0x0B 0x07 XPT Map 0 Control 7 5:0 OUT 7 [5:0] Output 7 connection assignment
0x0C 0x08 XPT Map 0 Control 8 5:0 OUT 8 [5:0] Output 8 connection assignment
0x0D 0x09 XPT Map 0 Control 9 5:0 OUT 9 [5:0] Output 9 connection assignment
0x0F 0x0B XPT Map 0 Control 11 5:0 OUT 11 [5:0] Output 11 connection assignment
0x10 0x0C XPT Map 0 Control 12 5:0 OUT 12 [5:0] Output 12 connection assignment
0x11 0x0D XPT Map 0 Control 13 5:0 OUT 13 [5:0] Output 13 connection assignment
0x12 0x0E XPT Map 0 Control 14 5:0 OUT 14 [5:0] Output 14 connection assignment
0x13 0x0F XPT Map 0 Control 15 5:0 OUT 15 [5:0] Output 15 connection assignment
0x14 0x10 XPT Map 0 Control 16 5:0 OUT 16 [5:0] Output 16 connection assignment
0x15 0x11 XPT Map 0 Control 17 5:0 OUT 17 [5:0] Output 17 connection assignment
0x16 0x12 XPT Map 0 Control 18 5:0 OUT 18 [5:0] Output 18 connection assignment
0x17 0x13 XPT Map 0 Control 19 5:0 OUT 19 [5:0] Output 19 connection assignment
0x18 0x14 XPT Map 0 Control 20 5:0 OUT 20 [5:0] Output 20 connection assignment
0x1A 0x16 XPT Map 0 Control 22 5:0 OUT 22 [5:0] Output 22 connection assignment
0x1B 0x17 XPT Map 0 Control 23 5:0 OUT 23 [5:0] Output 23 connection assignment
0x1C 0x18 XPT Map 0 Control 24 5:0 OUT 24 [5:0] Output 24 connection assignment
0x1D 0x19 XPT Map 0 Control 25 5:0 OUT 25 [5:0] Output 25 connection assignment
0x1E 0x1A XPT Map 0 Control 26 5:0 OUT 26 [5:0] Output 26 connection assignment
0x1F 0x1B XPT Map 0 Control 27 5:0 OUT 27 [5:0] Output 27 connection assignment
0x20 0x1C XPT Map 0 Control 28 5:0 OUT 28 [5:0] Output 28 connection assignment
0x21 0x1D XPT Map 0 Control 29 5:0 OUT 29 [5:0] Output 29 connection assignment
0x22 0x1E XPT Map 0 Control 30 5:0 OUT 30 [5:0] Output 30 connection assignment
0x23 0x1F XPT Map 0 Control 31 5:0 OUT 31 [5:0] Output 31 connection assignment
0x25 0x21 XPT Map 0 Control 33 5:0 OUT 33 [5:0] Output 33 connection assignment
0x26 0x22 XPT Map 0 Control 34 5:0 OUT 34 [5:0] Output 34 connection assignment
0x27 0x23 XPT Map 0 Control 35 5:0 OUT 35 [5:0] Output 35 connection assignment
0x28 0x24 XPT Map 0 Control 36 5:0 OUT 36 [5:0] Output 36 connection assignment
0x29 0x25 XPT Map 0 Control 37 5:0 OUT 37[5:0] Output 37 connection assignment
0x2A 0x26 XPT Map 0 Control 38 5:0 OUT 38 [5:0] Output 38 connection assignment
0x2B 0x27 XPT Map 0 Control 39 5:0 OUT 39 [5:0] Output 39 connection assignment
Rev. A | Page 39 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
0x30
0x23
XPT Map 1 Control 4
5:0
OUT 4 [5:0]
Output 4 connection assignment
0x36
0x1D
XPT Map 1 Control 10
5:0
OUT 10 [5:0]
Output 10 connection assignment
0x41
0x12
XPT Map 1 Control 21
5:0
OUT 21 [5:0]
Output 21 connection assignment
0x47
0x0C
XPT Map 1 Control 27
5:0
OUT 27 [5:0]
Output 27 connection assignment
0x52
0x01
XPT Map 1 Control 38
5:0
OUT 38 [5:0]
Output 38 connection assignment
0x55
0x00
XPT Status 1
5:0
OUT 1 [5:0]
Output 1 connection status
0x60
0x00
XPT Status 12
5:0
OUT 12 [5:0]
Output 12 connection status
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0x2C 0x27 XPT Map 1 Control 0 5:0 OUT 0 [5:0] Output 0 connection assignment
0x2D 0x26 XPT Map 1 Control 1 5:0 OUT 1 [5:0] Output 1 connection assignment
0x2E 0x25 XPT Map 1 Control 2 5:0 OUT 2 [5:0] Output 2 connection assignment
0x2F 0x24 XPT Map 1 Control 3 5:0 OUT 3 [5:0] Output 3 connection assignment
0x31 0x22 XPT Map 1 Control 5 5:0 OUT 5 [5:0] Output 5 connection assignment
0x32 0x21 XPT Map 1 Control 6 5:0 OUT 6 [5:0] Output 6 connection assignment
0x33 0x20 XPT Map 1 Control 7 5:0 OUT 7 [5:0] Output 7 connection assignment
0x34 0x1F XPT Map 1 Control 8 5:0 OUT 8 [5:0] Output 8 connection assignment
0x35 0x1E XPT Map 1 Control 9 5:0 OUT 9 [5:0] Output 9 connection assignment
0x37 0x1C XPT Map 1 Control 11 5:0 OUT 11 [5:0] Output 11 connection assignment
0x38 0x1B XPT Map 1 Control 12 5:0 OUT 12 [5:0] Output 12 connection assignment
0x39 0x1A XPT Map 1 Control 13 5:0 OUT 13 [5:0] Output 13 connection assignment
0x3A 0x19 XPT Map 1 Control 14 5:0 OUT 14 [5:0] Output 14 connection assignment
0x3B 0x18 XPT Map 1 Control 15 5:0 OUT 15 [5:0] Output 15 connection assignment
0x3C 0x17 XPT Map 1 Control 16 5:0 OUT 16 [5:0] Output 16 connection assignment
0x3D 0x16 XPT Map 1 Control 17 5:0 OUT 17 [5:0] Output 17 connection assignment
0x3E 0x15 XPT Map 1 Control 18 5:0 OUT 18 [5:0] Output 18 connection assignment
0x3F 0x14 XPT Map 1 Control 19 5:0 OUT 19 [5:0] Output 19 connection assignment
0x40 0x13 XPT Map 1 Control 20 5:0 OUT 20 [5:0] Output 20 connection assignment
0x42 0x11 XPT Map 1 Control 22 5:0 OUT 22 [5:0] Output 22 connection assignment
0x43 0x10 XPT Map 1 Control 23 5:0 OUT 23 [5:0] Output 23 connection assignment
0x44 0x0F XPT Map 1 Control 24 5:0 OUT 24 [5:0] Output 24 connection assignment
0x45 0x0E XPT Map 1 Control 25 5:0 OUT 25 [5:0] Output 25 connection assignment
0x46 0x0D XPT Map 1 Control 26 5:0 OUT 26 [5:0] Output 26 connection assignment
0x48 0x0B XPT Map 1 Control 28 5:0 OUT 28 [5:0] Output 28 connection assignment
0x49 0x0A XPT Map 1 Control 29 5:0 OUT 29 [5:0] Output 29 connection assignment
0x4A 0x09 XPT Map 1 Control 30 5:0 OUT 30 [5:0] Output 30 connection assignment
0x4B 0x08 XPT Map 1 Control 31 5:0 OUT 31 [5:0] Output 31 connection assignment
0x4C 0x07 XPT Map 1 Control 32 5:0 OUT 32 [5:0] Output 32 connection assignment
0x4D 0x06 XPT Map 1 Control 33 5:0 OUT 33 [5:0] Output 33 connection assignment
0x4E 0x05 XPT Map 1 Control 34 5:0 OUT 34 [5:0] Output 34 connection assignment
0x4F 0x04 XPT Map 1 Control 35 5:0 OUT 35 [5:0] Output 35 connection assignment
0x50 0x03 XPT Map 1 Control 36 5:0 OUT 36 [5:0] Output 36 connection assignment
0x51 0x02 XPT Map 1 Control 37 5:0 OUT 37[5:0] Output 37 connection assignment
0x53 0x00 XPT Map 1 Control 39 5:0 OUT 39 [5:0] Output 39 connection assignment
0x54 0x00 XPT Status 0 5:0 OUT 0 [5:0] Output 0 connection status
0x56 0x00 XPT Status 2 5:0 OUT 2 [5:0] Output 2 connection status
0x57 0x00 XPT Status 3 5:0 OUT 3 [5:0] Output 3 connection status
0x58 0x00 XPT Status 4 5:0 OUT 4 [5:0] Output 4 connection status
0x59 0x00 XPT Status 5 5:0 OUT 5 [5:0] Output 5 connection status
0x5A 0x00 XPT Status 6 5:0 OUT 6 [5:0] Output 6 connection status
0x5B 0x00 XPT Status 7 5:0 OUT 7 [5:0] Output 7 connection status
0x5C 0x00 XPT Status 8 5:0 OUT 8 [5:0] Output 8 connection status
0x5D 0x00 XPT Status 9 5:0 OUT 9 [5:0] Output 9 connection status
0x5E 0x00 XPT Status 10 5:0 OUT 10 [5:0] Output 10 connection status
0x5F 0x00 XPT Status 11 5:0 OUT 11 [5:0] Output 11 connection status
Rev. A | Page 40 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
0x65
0x00
XPT Status 17
5:0
OUT 17 [5:0]
Output 17 connection status
0x6B
0x00
XPT Status 23
5:0
OUT 23 [5:0]
Output 23 connection status
0x76
0x00
XPT Status 34
5:0
OUT 34 [5:0]
Output 34 connection status
0x84: Output 4
0x40
Tx Lane Control
011: 12 mA
0x8A: Output 10
0x40
Tx Lane Control
0x95: Output 21
0x40
Tx Lane Control
110: 7 mA
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0x61 0x00 XPT Status 13 5:0 OUT 13 [5:0] Output 13 connection status
0x62 0x00 XPT Status 14 5:0 OUT 14 [5:0] Output 14 connection status
0x63 0x00 XPT Status 15 5:0 OUT 15 [5:0] Output 15 connection status
0x64 0x00 XPT Status 16 5:0 OUT 16 [5:0] Output 16 connection status
0x66 0x00 XPT Status 18 5:0 OUT 18 [5:0] Output 18 connection status
0x67 0x00 XPT Status 19 5:0 OUT 19 [5:0] Output 19 connection status
0x68 0x00 XPT Status 20 5:0 OUT 20 [5:0] Output 20 connection status
0x69 0x00 XPT Status 21 5:0 OUT 21 [5:0] Output 21 connection status
0x6A 0x00 XPT Status 22 5:0 OUT 22 [5:0] Output 22 connection status
0x6C 0x00 XPT Status 24 5:0 OUT 24 [5:0] Output 24 connection status
0x6D 0x00 XPT Status 25 5:0 OUT 25 [5:0] Output 25 connection status
0x6E 0x00 XPT Status 26 5:0 OUT 26 [5:0] Output 26 connection status
0x6F 0x00 XPT Status 27 5:0 OUT 27 [5:0] Output 27 connection status
0x70 0x00 XPT Status 28 5:0 OUT 28 [5:0] Output 28 connection status
0x71 0x00 XPT Status 29 5:0 OUT 29 [5:0] Output 29 connection status
0x72 0x00 XPT Status 30 5:0 OUT 30 [5:0] Output 30 connection status
0x73 0x00 XPT Status 31 5:0 OUT 31 [5:0] Output 31 connection status
0x74 0x00 XPT Status 32 5:0 OUT 32 [5:0] Output 32 connection status
0x75 0x00 XPT Status 33 5:0 OUT 33 [5:0] Output 33 connection status
0x77 0x00 XPT Status 35 5:0 OUT 35 [5:0] Output 35 connection status
0x78 0x00 XPT Status 36 5:0 OUT 36 [5:0] Output 36 connection status
0x79 0x00 XPT Status 37 5:0 OUT 37[5:0] Output 37 connection status
0x7A 0x00 XPT Status 38 5:0 OUT 38 [5:0] Output 38 connection status
0x7B 0x00 XPT Status 39 5:0 OUT 39 [5:0] Output 39 connection status
0x7D 0x00 XPT Headroom 0 XPT_HDROOM 0 = disabled, 1 = enabled (required when V
0x80: Output 0 0x40 Tx Lane Control 7 Reserved 0 (Reserve bit)
0x81: Output 1 0x40 Tx Lane Control 6:4 OLEV [2:0] 000: 0 mA
0x82: Output 2 0x40 Tx Lane Control 001: 4 mA
0x83: Output 3 0x40 Tx Lane Control 010: 8 mA
0x85: Output 5 0x40 Tx Lane Control 100: 16 mA (default)
0x86: Output 6 0x40 Tx Lane Control 101: 20 mA
0x87: Output 7 0x40 Tx Lane Control 110: 24 mA
0x88: Output 8 0x40 Tx Lane Control 111: (Reserve bit)
0x89: Output 9 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x8B: Output 11 0x40 Tx Lane Control 3 Overdrive 1: overdrive (increases OLEV and PE currents by 25%)
0x8C: Output 12 0x40 Tx Lane Control 0: no overdrive (default)
0x8D: Output 13 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x8E Output 14 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x8F: Output 15 0x40 Tx Lane Control 2:0 PE [2:0] 000: 0 mA (default)
0x90: Output 16 0x40 Tx Lane Control 001: 2 mA
0x91: Output 17 0x40 Tx Lane Control 010: 3 mA
0x92: Output 18 0x40 Tx Lane Control 011: 4 mA
0x93: Output 19 0x40 Tx Lane Control 100: 5 mA
0x94: Output 20 0x40 Tx Lane Control 101: 6 mA
> 2.7 V)
CC
0x96: Output 22 0x40 Tx Lane Control 111: 8 mA
0x97: Output 23 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x98: Output 24 0x40 Tx Lane Control
Rev. A | Page 41 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
0x9D: Output 29
0x40
Tx Lane Control
0xA3: Output 35
0x40
Tx Lane Control
1 = inverting
1 TXSIGN [1]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 1
6 TXSIGN [14]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 14
1 TXSIGN [9]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 9
6 TXSIGN [22]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 22
0 TXSIGN [16]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 16
0 TXSIGN [24]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 24
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0x99: Output 25 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x9A: Output 26 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x9B: Output 27 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x9C: Output 28 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x9E: Output 30 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0x9F: Output 31 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA0: Output 32 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA1: Output 33 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA2: Output 34 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA4: Output 36 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA5: Output 37 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA6: Output 38 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA7: Output 39 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA8: Tx Broadcast 0x40 Tx Lane Control
0xA9 0x0 Tx Sign Control 7 TXSIGN [7] Signal path polarity inversion Output 7
0 = noninverting
6 TXSIGN [6] Signal path polarity inversion Output 6
5 TXSIGN [5] Signal path polarity inversion Output 5
4 TXSIGN [4] Signal path polarity inversion Output 4
3 TXSIGN [3] Signal path polarity inversion Output 3
2 TXSIGN [2] Signal path polarity inversion Output 2
0 TXSIGN [0] Signal path polarity inversion Output 0
0xAA 0x0 Tx Sign Control 7 TXSIGN [15] Signal path polarity inversion Output 15
5 TXSIGN [13] Signal path polarity inversion Output 13
4 TXSIGN [12] Signal path polarity inversion Output 12
3 TXSIGN [11] Signal path polarity inversion Output 11
2 TXSIGN [10] Signal path polarity inversion Output 10
0 TXSIGN [8] Signal path polarity inversion Output 8
0xAB 0x0 Tx Sign Control 7 TXSIGN [23] Signal path polarity inversion Output 23
5 TXSIGN [21] Signal path polarity inversion Output 21
4 TXSIGN [20] Signal path polarity inversion Output 20
3 TXSIGN [19] Signal path polarity inversion Output 19
2 TXSIGN [18] Signal path polarity inversion Output 18
1 TXSIGN [17] Signal path polarity inversion Output 17
0xAC 0x0 Tx Sign Control 7 TXSIGN [31] Signal path polarity inversion Output 31
6 TXSIGN [30] Signal path polarity inversion Output 30
5 TXSIGN [29] Signal path polarity inversion Output 29
4 TXSIGN [28] Signal path polarity inversion Output 28
3 TXSIGN [27] Signal path polarity inversion Output 27
2 TXSIGN [26] Signal path polarity inversion Output 26
1 TXSIGN [25] Signal path polarity inversion Output 25
Rev. A | Page 42 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
3 TXSIGN [35]
Signal path polarity inversion Output 35
5:4
TXEN [2]
Tx enable state Output 2
5:4
TXEN [6]
Tx enable state Output 6
0xB2
0x0
Tx Drive Control
7:6
TXEN [11]
Tx enable state Output 11
0xB3
0x0
Tx Drive Control
7:6
TXEN [15]
Tx enable state Output 15
3:2
TXEN [13]
Tx enable state Output 13
3:2
TXEN [17]
Tx enable state Output 17
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xAD 0x0 Tx Sign Control 7 TXSIGN [39] Signal path polarity inversion Output 39
6 TXSIGN [38] Signal path polarity inversion Output 38
5 TXSIGN [37] Signal path polarity inversion Output 37
4 TXSIGN [36] Signal path polarity inversion Output 36
2 TXSIGN [34] Signal path polarity inversion Output 34
1 TXSIGN [33] Signal path polarity inversion Output 33
0 TXSIGN [32] Signal path polarity inversion Output 32
0xB0 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [3] Tx enable state Output 3
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
3:2 TXEN [1] Tx enable state Output 1
1:0 TXEN [0] Tx enable state Output 0
0xB1 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [7] Tx enable state Output 7
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
3:2 TXEN [5] Tx enable state Output 5
1:0 TXEN [4] Tx enable state Output 4
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
5:4 TXEN [10] Tx enable state Output 10
3:2 TXEN [9] Tx enable state Output 9
1:0 TXEN [8] Tx enable state Output 8
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
5:4 TXEN [14] Tx enable state Output 14
1:0 TXEN [12] Tx enable state Output 12
0xB4 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [19] Tx enable state Output 19
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
5:4 TXEN [18] Tx enable state Output 18
1:0 TXEN [16] Tx enable state Output 16
Rev. A | Page 43 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
00 = disabled
5:4
TXEN [26]
Tx enable state Output 26
5:4
TXEN [30]
Tx enable state Output 30
0xB8
0x0
Tx Drive Control
7:6
TXEN [35]
Tx enable state Output 35
0xB9
0x0
Tx Drive Control
7:6
TXEN [39]
Tx enable state Output 39
3:2
TXEN [37]
Tx enable state Output 37
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xB5 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [23] Tx enable state Output 23
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
5:4 TXEN [22] Tx enable state Output 22
3:2 TXEN [21] Tx enable state Output 21
1:0 TXEN [20] Tx enable state Output 20
0xB6 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [27] Tx enable state Output 27
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
3:2 TXEN [25] Tx enable state Output 25
1:0 TXEN [24] Tx enable state Output 24
0xB7 0x0 Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXEN [31] Tx enable state Output 31
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
3:2 TXEN [29] Tx enable state Output 29
1:0 TXEN [28] Tx enable state Output 28
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
5:4 TXEN [34] Tx enable state Output 34
3:2 TXEN [33] Tx enable state Output 33
1:0 TXEN [32] Tx enable state Output 32
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
5:4 TXEN [38] Tx enable state Output 38
1:0 TXEN [36] Tx enable state Output 36
0xBA Write Only Tx Drive Control 7:6 TXENBC [39] Tx enable state broadcast
11 = enabled
10 = standby
01 = squelch
00 = disabled
0xBB 0x0 Tx Headroom 0 TX_HDROOM 0 = disabled, 1 = enabled (required when VCC > 2.7 V)
Rev. A | Page 44 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
2 TXA_TERM [11:8]
Output[11:8] (B side) termination control
0xBD
0x0
Tx Termination
4
TXB_TERM [39:36]
Output[39:36] (B side) termination control
0 TXB_TERM [23:20]
1:0
RXEQIN [0]
Equalizer boost control for Input 0
10 = 6 dB
10 = 6 dB
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xBC 0x0 Tx Termination 4 TXA_TERM [19:16] Output[19:16] (B side) termination control
Control 0: terminations enabled
1: terminations disabled
3 TXA_TERM [15:12] Output[15:12] (B side) termination control
1 TXA_TERM [7:4] Output[7:4] (B side) termination control
0 TXA_TERM [3:0] Output[3:0] (B side) termination control
Control 0: terminations enabled
1: terminations disabled
3 TXB_TERM [35:32] Output[35:32] (B side) termination control
2 TXB_TERM [31:28] Output[31:28] (B side) termination control
1 TXB_TERM [27:24] Output[27:24] (B side) termination control
Output[23:20] (B side) termination control
0xC0 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [3] Equalizer boost control for Input 3
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [2] Equalizer boost control for Input 2
3:2 RXEQIN [1] Equalizer boost control for Input 1
0xC1 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [7] Equalizer boost control for Input 7
11 = 12 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [6] Equalizer boost control for Input 6
3:2 RXEQIN [5] Equalizer boost control for Input 5
1:0 RXEQIN [4] Equalizer boost control for Input 4
0xC2 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [11] Equalizer boost control for Input 11
11 = 12 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [10] Equalizer boost control for Input 10
3:2 RXEQIN [9] Equalizer boost control for Input 9
1:0 RXEQIN [8] Equalizer boost control for Input 8
0xC3 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [15] Equalizer boost control for Input 15
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [14] Equalizer boost control for Input 14
3:2 RXEQIN [13] Equalizer boost control for Input 13
1:0 RXEQIN [12] Equalizer boost control for Input 12
Rev. A | Page 45 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
00 = disabled
5:4
RXEQIN [22]
Equalizer boost control for Input 22
5:4
RXEQIN [26]
Equalizer boost control for Input 26
0xC7
0x0
Rx EQ Control
7:6
RXEQIN [31]
Equalizer boost control for Input 31
0xC8
0x0
Rx EQ Control
7:6
RXEQIN [35]
Equalizer boost control for Input 35
3:2
RXEQIN [33]
Equalizer boost control for Input 33
3:2
RXEQIN [37]
Equalizer boost control for Input 37
11 = 12 dB
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xC4 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [19] Equalizer boost control for Input 19
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
5:4 RXEQIN [18] Equalizer boost control for Input 18
3:2 RXEQIN [17] Equalizer boost control for Input 17
1:0 RXEQIN [16] Equalizer boost control for Input 16
0xC5 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [23] Equalizer boost control for Input 23
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
3:2 RXEQIN [21] Equalizer boost control for Input 21
1:0 RXEQIN [20] Equalizer boost control for Input 20
0xC6 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [27] Equalizer boost control for Input 27
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
3:2 RXEQIN [25] Equalizer boost control for Input 25
1:0 RXEQIN [24] Equalizer boost control for Input 24
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [30] Equalizer boost control for Input 30
3:2 RXEQIN [29] Equalizer boost control for Input 29
1:0 RXEQIN [28] Equalizer boost control for Input 28
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [34] Equalizer boost control for Input 34
1:0 RXEQIN [32] Equalizer boost control for Input 32
0xC9 0x0 Rx EQ Control 7:6 RXEQIN [39] Equalizer boost control for Input 39
11 = 12 dB
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
5:4 RXEQIN [38] Equalizer boost control for Input 38
1:0 RXEQIN [36] Equalizer boost control for Input 36
0xCA 0x0 Rx EQ Control 1:0 RXEQIN BC Equalizer boost control for all inputs
10 = 6 dB
01 = 3 dB
00 = disabled
Rev. A | Page 46 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
3 RXSIGN [3]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 3
2 RXSIGN [10]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 10
2 RXSIGN [18]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 18
0xCE
0x0
Rx Sign Control
7
RXSIGN [31]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 31
0xCF
0x0
Rx Sign Control
7
RXSIGN [39]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 39
1 RXSIGN [33]
Signal path polarity inversion Input 33
0 RXA_TERM [3:0]
Input [3:0] (A side) termination control
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xCB 0x0 Rx Sign Control 7 RXSIGN [7] Signal path polarity inversion Input 7
6 RXSIGN [6] Signal path polarity inversion Input 6
5 RXSIGN [5] Signal path polarity inversion Input 5
4 RXSIGN [4] Signal path polarity inversion Input 4
2 RXSIGN [2] Signal path polarity inversion Input 2
1 RXSIGN [1] Signal path polarity inversion Input 1
0 RXSIGN [0] Signal path polarity inversion Input 0
0xCC 0x0 Rx Sign Control 7 RXSIGN [15] Signal path polarity inversion Input 15
6 RXSIGN [14] Signal path polarity inversion Input 14
5 RXSIGN [13] Signal path polarity inversion Input 13
4 RXSIGN [12] Signal path polarity inversion Input 12
3 RXSIGN [11] Signal path polarity inversion Input 11
1 RXSIGN [9] Signal path polarity inversion Input 9
0 RXSIGN [8] Signal path polarity inversion Input 8
0xCD 0x0 Rx Sign Control 7 RXSIGN [23] Signal path polarity inversion Input 23
6 RXSIGN [22] Signal path polarity inversion Input 22
5 RXSIGN [21] Signal path polarity inversion Input 21
4 RXSIGN [20] Signal path polarity inversion Input 20
3 RXSIGN [19] Signal path polarity inversion Input 19
1 RXSIGN [17] Signal path polarity inversion Input 17
0 RXSIGN [16] Signal path polarity inversion Input 16
6 RXSIGN [30] Signal path polarity inversion Input 30
5 RXSIGN [29] Signal path polarity inversion Input 29
4 RXSIGN [28] Signal path polarity inversion Input 28
3 RXSIGN [27] Signal path polarity inversion Input 27
2 RXSIGN [26] Signal path polarity inversion Input 26
1 RXSIGN [25] Signal path polarity inversion Input 25
0 RXSIGN [24] Signal path polarity inversion Input 24
6 RXSIGN [38] Signal path polarity inversion Input 38
5 RXSIGN [37] Signal path polarity inversion Input 37
4 RXSIGN [36] Signal path polarity inversion Input 36
3 RXSIGN [35] Signal path polarity inversion Input 35
2 RXSIGN [34] Signal path polarity inversion Input 34
0 RXSIGN [32] Signal path polarity inversion Input 32
0xD0 0x0 Rx Termination 4 RXA_TERM [19:16] Input[19:16] (A Side) termination control
Control 0: termination control enabled
1: termination control disabled
3 RXA_TERM [15:12] Input [15:12] (A side) termination control
2 RXA_TERM [11:8] Input [11:8] (A side) termination control
1 RXA_TERM [7:4] Input [7:4] (A side) termination control
Rev. A | Page 47 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
2 RXB_TERM [31:28]
Input [31:28] (B Side) termination control
Address: Channel Default Register Name Bits Bit Name Description
0xD1 0x0 Rx Termination 4 RXB_TERM [39:36] Input [39:36] (B Side) termination control
Control 0: terminations enabled
1: terminations disabled
3 RXB_TERM [35:32] Input [35:32] (B Side) termination control
1 RXB_TERM [27:24] Input [27:24] (B Side) termination control
0 RXB_TERM [23:20] Input [23:20] (B Side) termination control
Rev. A | Page 48 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
ADN4605
IN 0
IN 1
IN 39
OUT 0
OUT 1
OUT 39
ADN4605
IN 0
IN 1
IN 39
OUT 0
OUT 1
OUT 39
ADN4605
IN 0
IN 1
IN 39
OUT 0
OUT 1
OUT 39
ADN4605
IN 0
IN 1
IN 39
OUT 0
OUT 1
OUT 39
SOURCE 1
SOURCE 2
SOURCE 40
SOURCE 39
DISPLAY 1
DISPLAY 2
DISPLAY 40
DISPL
AY 39
09796-052
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The ADN4605 is an asynchronous and protocol agnostic digital
switch and, therefore, is applicable to a wide range of applications including network routing and digital video switching.
The ADN4605 supports the data rates and signaling levels of
HDMI®, DVI®, DisplayPort and SD-, HD-, and 3G-SDI digital
video. The ADN4605 can be used to create matrix switches. An
example block diagram of a 40 × 40 matrix switch is shown in
Figure 50. Since HDMI, DVI, and DisplayPort are quad lane
protocols, four ADN4605s are used to create a full 40 × 40
matrix switch. Smaller arrays, such as 10 × 10 and 20 × 20,
require one and two ADN4605 devices, respectively. Proper
high speed PCB design techniques should be used to maintain
the signal integrity of the high data rate signals. It is important
to minimize the lane-to-lane skew and crosstalk in these
applications.
Figure 50. ADN4605 Digital Video (DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort) Matrix Switch Block Diagram
Rev. A | Page 49 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
O/E
O/E
E/O
E/O
CDR
CDR
O/E E/OCDR
ADN4605
40 × 40
CROSSPOINT
SWITCH
IN 1
IN 2
IN 39
OUT 1
OUT 2
OUT 39
09796-053
PE EQ
LOSSY CHANNEL
8 LANE UPLI NK PATH
8 LANE DOWNLINK PATH
LOSSY CHANNEL
ASIC 2
EQ
PE
ASIC 1
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
07934-053
Figure 51. ADN4605 Networking Switch Application Block Diagram
Figure 52. Multilane Signal Conditioning Application Diagram
Rev. A | Page 50 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
SUPPLY SEQUENCING
Ideally, all power supplies should be brought up to the appropriate levels simultaneously (power supply requirements are set by
the supply limits in Ta ble 1 and the absolute maximum ratings
listed in Tabl e 6). If the power supplies to the ADN4605 are
brought up separately, the supply power-up sequence is as
follows: DV
termination supplies (V
powered first, followed by VCC, and, last the
CC
, V
, V
TTIA
TTIB
TTOA
, and V
TTOB
).
The power-down sequence is reversed with termination
supplies being powered off first. The termination supplies
contain ESD protection diodes to the V
power domain. To
CC
avoid a sustained high current condition in these devices, the
V
and V
TTIx
should be powered off before V
supplies should be powered on after VCC and
TTOx
.
CC
If the system power supplies have a high impedance in the
powered off state, then supply sequencing is not required
provided the following limits are observed:
• Peak current from V
• Sustained current from V
TTIx
or V
TTIx
to VCC < 200 mA
TTOx
or V
to VCC < 100 mA
TTOx
POWER DISSIPATION
The power dissipation of the ADN4605 depends on the supply
voltages, I/O coupling type, and device configuration. The input
termination resistors dissipate power depending on the
differential input swing and common-mode voltage. When accoupled, the common-mode voltage is equal to the termination
supply voltage (V
the input termination supply is effectively zero, there is still
power and heat dissipated in the termination resistors as a result
of the differential signal swing. The core supply current and
output termination current are strongly dependent on device
configuration, such as the number of channels enabled, output
level setting, and output preemphasis setting.
In high ambient temperature operating conditions, it is important to avoid exceeding the maximum junction temperature of
the device. Limiting the total power dissipation can be achieved
by the following:
• Reducing the output swing
• Reducing the preemphasis level
• Decreasing the supply voltages within the allowable ranges
defined in Ta b le 1
• Disabling unused channels
TTIx
or V
). While the current drawn from
TTOx
OUTPUT COMPLIANCE
In low voltage applications, users must pay careful attention
to both the differential and common-mode signal levels. The
choice of output voltage swing, preemphasis setting, supply
voltages (V
and V
CC
), and output coupling (ac or dc) affect
TTOx
peak and settled single-ended voltage swings and the commonmode shift measured across the output termination resistors.
These choices also affect output current and, consequently,
power consumption.
Tabl e 20 shows the change in output common mode (ΔV
V
− V
CC
ended output levels are calculated for V
) with output level and preemphasis setting. Single-
OCM
supplies of 3.3 V
TTOx
OCM
=
and 2.5 V to illustrate practical challenges of reducing the
supply voltage. The minimum V
(min VL) cannot be below the
L
absolute minimum level specified in Ta b le 1.
Since the absolute minimum output voltage specified in Tabl e 1
is relative to V
, decreasing VCC is required to maintain the
CC
output levels within the specified limits when lower output
termination voltages are required. V
voltages as low as 1.8 V
TTOx
are allowable for output swings less than or equal to 400 mV
(single-ended).
Figure 53 illustrates an application where the ADN4605 is used
as a dc-coupled level translator to interface a 3.3 V CML driver
to an ASIC with 1.8 V I/Os. The diode in series with V
reduces the voltage at V
for improved output compliance.
CC
CC
TX/XPT HEADROOM
The Tx Headroom and XPT Headroom registers are provided
to improve the output compliance range of the ADN4605 when
the core supply voltage (V
the XPT Headroom and Tx Headroom registers allows the
transmitter an extra 300 mV of output compliance. The
headroom circuitry should not be enabled when the core
supply voltage (V
) is less than or equal to 2.7 V.
CC
When set to 1, the XPT Headroom (Address 0x7D) and Tx
Headroom (Address 0xBB) registers are enabled for all
transmitter outputs. A value of 0 disables the headroom
generating circuitry. Note that both registers (XPT Headroom
and Tx Headroom) must be set for the headroom circuitry to
function properly.
) is greater than 2.7 V. Enabling
CC
Alternatively, the thermal resistance can be reduced by
• Adding an external heat sink
• Increasing the airflow
Refer to the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Layout Guidelines
section for recommendations for proper thermal stencil layout
and fabrication.
Rev. A | Page 51 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
Example: VCC = 3.3 V, V
TTOx
= 2.5 V
In a typical application, the user can select a default output level
of 200 mV single-ended (400 mVp-p differential) and may want
the option to choose preemphasis settings of 0 dB and 9.5 dB.
With preemphasis disabled, a dc-coupled transmitter causes a
100 mV common-mode shift across the termination resistors,
whereas an ac-coupled transmitter causes twice the commonmode shift. When dc-coupled, the single-ended output voltage
swings between 2.5 V and 2.3 V and between 2.4 V and 2.2 V
when ac-coupled. In both cases, these levels are greater than the
minimum V
limit of 1.9 V (VL = VCC − 1.4 V).
L
With a PE setting of 9.5 dB, the ac-coupled transmitter has
single-ended swings from 2.2 V and 1.6 V, whereas the dccoupled transmitter outputs swing between 2.5 V and 1.9 V.
The minimum single-ended output voltage (V
ac-coupled transmitter case exceeds the minimum V
) of the
L-PE
limit of
L
1.9 V by 300 mV, violating the device specification.
Enabling the TX_HDROOM and XPT_HDROOM bit lowers
the minimum V
limit by approximately 300 mV to 1.6 V. This
L
transmitter configuration now complies with the output voltage
range specification.
Rev. A | Page 52 of 56

Data Sheet ADN4605
CML
V
EE
V
TTOx
1.8V
1.8V3.3V
3.3V
V
CC
V
TTIx
ADN4605
CML
3.3V
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
Z
0
ASIC
Rx
09796-055
VCC = V
=
150
250
66.67
4.44
0x02
0x01
10
250
3.175
2.925
2.375
2.125
125
3.3
3.15
2.5
2.25
200
400
100.00
6.02
0x03
0x03
16
400
3.1
2.7
2.30
1.90
200
3.3
2.9
2.5
2.1
Figure 53. DC-Coupled Level Translator Application Circuit
Table 20. Output Voltage Range and Output Common-Mode Shift vs. Output Level and PE Setting
AC-Coupled Outputs DC-Coupled Outputs
Single-Ended Output Levels and
PE Boost
V
SW-DC1
(mV)
V
SW-PE
(mV)
1
PE Boost % PE
(dB) OLEV [2:0] PE [2:0]
Tx Lane Control
Register Settings
Output
Current
1
I
TTO
(mA)
∆V
(mV)
OCM
1
100 100 0.00 0.00 0x01 0x00 4 100 3.25 3.15 2.45 2.35 50 3.3 3.2 2.5 2.4
100 300 200.00 9.54 0x02 0x03 12 300 3.15 2.85 2.35 2.05 150 3.3 3.0 2.5 2.2
100 500 400.00 13.98 0x03 0x07 20 500 3.05 2.55 2.25 1.75 250 3.3 2.8 2.5 2.0
150 450 200.00 9.54 0x03 0x05 18 450 3.075 2.625 2.275 1.825 225 3.3 2.85 2.5 2.05
200 200 0.00 0.00 0x02 0x00 8 200 3.2 3.0 2.40 2.20 100 3.3 3.1 2.5 2.3
200 600 200.00 9.54 0x04 0x07 24 600 3 2.4 2.20 1.60 300 3.3 2.7 2.5 1.9
250 350 40.00 2.92 0x03 0x01 14 350 3.125 2.775 2.325 1.975 175 3.3 2.95 2.5 2.15
250 550 200.00 6.85 0x04 0x05 22 550 3.025 2.475 2.225 1.675 275 3.3 2.75 2.5 1.95
300 300 0.00 0.00 0x03 0x00 12 300 3.15 2.85 2.35 2.05 150 3.3 3.0 2.5 2.2
300 500 66.67 4.44 0x04 0x03 20 500 3.05 2.55 2.25 1.75 250 3.3 2.8 2.5 2.0
300 700 133.33 7.36 0x05 0x07 28 700 2.95 2.25 2.15 1.45 350 3.3 2.6 2.5 1.8
350 450 28.57 2.18 0x04 0x01 18 450 3.075 2.625 2.275 1.825 225 3.3 2.85 2.5 2.05
350 650 85.71 5.38 0x05 0x05 26 650 2.975 2.325 2.175 1.525 325 3.3 2.65 2.5 1.85
400 400 0.00 0.00 0x04 0x00 16 400 3.1 2.7 2.3 1.9 200 3.3 2.9 2.5 2.1
400 600 50.00 3.52 0x05 0x03 24 600 3.0 2.4 2.2 1.6 300 3.3 2.7 2.5 1.9
400 800 100.00 6.02 0x06 0x07 32 800 2.9 2.1 2.1 1.3 400 3.3 2.5 2.5 1.7
450 550 22.22 1.74 0x05 0x01 22 550 3.025 2.475 2.225 1.675 275 3.3 2.75 2.5 1.95
450 750 66.67 4.44 0x06 0x05 30 750 2.925 2.175 2.125 1.375 375 3.3 2.55 2.5 1.75
500 500 0.00 0.00 0x05 0x00 20 500 3.05 2.55 2.25 1.75 250 3.3 2.8 2.5 2.0
500 700 40.00 2.92 0x06 0x03 28 700 2.95 2.25 2.15 1.45 350 3.3 2.6 2.5 1.8
550 650 18.18 1.45 0x06 0x01 26 650 2.975 2.325 2.175 1.525 325 3.3 2.65 2.5 1.85
600 600 0.00 0.00 0x06 0x00 24 600 3.0 2.4 2.2 1.6 300 3.3 2.7 2.5 1.9
1
Symbol definitions are shown in Table 15.
TTO
3.3 V
1
V
V
H-PE
(V)
(V)
L-PE
1
VCC = V
TTO
=
2.5 V
1
V
(V)
H-PE
1
V
L-PE
(V)
∆V
OCM
(mV)
1
VCC = V
3.3 V
1
V
H-PE
(V)
TTO
=
VCC = V
TTO
=
2.5 V
1
V
L-PE
(V)
V
(V)
H-PE
1
V
L-PE
(V)
1
Rev. A | Page 53 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
PCB DIELECTRIC
SIGNAL (MICROSTRIP)
SOLDERMASK
PCB DIELECTRIC
PCB DIELECTRIC
PCB DIELECTRIC
REFERENCE PLANE
REFERENCE PLANE
SIGNAL (STRIPLINE)
WSW
H
WSW
09796-100
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD (PCB) LAYOUT GUIDELINES
The high speed differential inputs and outputs should be routed
with 100 Ω controlled impedance differential transmission
lines. The transmission lines, either microstrip or stripline,
should be referenced to a solid low impedance reference plane.
An example of a PCB cross-section is shown in Figure 54. The
trace width (W), differential spacing (S), height above reference
plane (H), and dielectric constant of the PCB material determine
the characteristic impedance. Adjacent channels should be kept
apart by a distance greater than 3 W to minimize crosstalk.
Figure 54. Example of a PCB Cross-Section
Rev. A | Page 54 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
DETAIL A
1.27
BSC
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AF
1
4
6
8
10
12
3579
11
2
161820
22
15
17
19
2123
14
13
242526
31.85
31.75 SQ
31.65
35.10
35.00 SQ
34.90
BALL A1
INDICATOR
TOP VIEW
BOTTOM
VIEW
A1 CORNER
INDEX AREA
0.20 MIN
0.70
0.60
0.50
1.00
0.80
0.60
COPLANARITY
0.35
0.90
0.75
0.60
SEATING
PLANE
BALL DIAMETER
DETAIL A
1.70 MAX
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO - 192- BAL-2
022206-A
0.25 MIN
(4 )
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Figure 55. 352-Ball Grid Array, Thermally Enhanced [BGA_ED]
(BP-352)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADN4605ABPZ
ADN4605-EVA LZ Evaluation Board
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
−40°C to +85°C 352-Ball Ball Grid Array, Thermally Enhanced [BGA_ED] BP-352
Rev. A | Page 55 of 56

ADN4605 Data Sheet
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
NOTES
I2C refers to a communications protocol originally developed by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors).
HDMI, the HDMI Logo, and High-Definition Multimedia Interface are trademarks or registered trademarks of HDMI Licensing LLC in the United States and other
countries.
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D09796-0-11/11(A)
Rev. A | Page 56 of 56
 Loading...
Loading...