
FEATURES
Matched pair of multiplying VGAs
Broad frequency range 20 MHz to 2.4 GHz
Continuous magnitude control from +5 dB to −30 dB
Output third-order intercept 24 dBm
Output 1 dB compression point 11 dBm
Output noise floor −148 dBm/Hz
Adjustable modulation bandwidth up to 230 MHz
Fast output power disable
Single-supply voltage 4.75 V to 5.25 V
APPLICATIONS
PA linearization and predistortion
Amplitude and phase modulation
Variable matched attenuator and/or phase shifter
Cellular base stations
Radio links
Fixed wireless access
Broadband/CATV
RF/IF analog multiplexer
RF/IF Vector Multiplier
ADL5390
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
VPRF
INMQ
INPQ
CMRF
INPI
INMI
CMOP
Figure 1.
VPS2OBBMQBBP
RFOP
RFOM
DSOPIBBMIBBP
04954-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADL5390 vector multiplier consists of a matched pair of
broadband variable gain amplifiers whose outputs are summed.
The separate gain controls for each amplifier are linear-inmagnitude. If the two input RF signals are in quadrature, the
vector multiplier can be configured as a vector modulator or as
a variable attenuator/phase shifter by using the gain control pins
as Cartesian variables. In this case, the output amplitude can be
controlled from a maximum of +5 dB to less than –30 dB, and
the phase can be shifted continuously over the entire 360°
range. Since the signal paths are linear, the original modulation
on the inputs is preserved. If the two signals are independent,
then the vector multiplier can function as a 2:1 multiplexer or
can provide fading from one channel to another.
The ADL5390 operates over a wide frequency range of 20 MHz
to 2400 MHz. For a maximum gain setting on one channel at
380 MHz, the ADL5390 delivers an OP1dB of 11 dBm, an OIP3
of 24 dBm, and an output noise floor of −148 dBm/Hz. The gain
and phase matching between the two VGAs is better than 0.5 dB
and 1°, respectively, over most of the operating range.
The gain control inputs are dc-coupled with a +/−500 mV differential full-scale range centered about a 500 mV common
mode. The maximum modulation bandwidth is 230 MHz,
which can be reduced by adding external capacitors to limit the
noise bandwidth on the control lines.
Both the RF inputs and outputs can be used differentially or
single-ended and must be ac-coupled. The impedance of each
VGA RF input is 250 Ω to ground, and the differential output
impedance is nominally 50 Ω over the operating frequency
range. The DSOP pin allows the output stage to be disabled
quickly to protect subsequent stages from overdrive. The
ADL5390 operates off supply voltages from 4.75 V to 5.25 V
while consuming 135 mA.
The ADL5390 is fabricated on Analog Devices’ proprietary,
high performance 25 GHz SOI complementary bipolar IC
process. It is available in a 24-lead, Pb-free CSP package and
operates over a −40°C to +85°C temperature range. Evaluation
boards are available.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Anal og Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

ADL5390
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
RF Output and Matching .......................................................... 13
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
Typical Performance Characteristics............................................. 7
General Structure ........................................................................... 11
Theory of Operation ..................................................................11
Noise and Distortion.................................................................. 11
Applications..................................................................................... 12
Using the ADL5390.................................................................... 12
RF Input and Matching.............................................................. 12
REVISION HISTORY
10/04—Revision 0: Initial Version
Driving the I-Q Baseband Gain Controls............................... 13
Interfacing to High Speed DACs.............................................. 14
Generalized Modulator ............................................................. 15
Vec t or Mo d ul a t or ....................................................................... 15
Vector Modulator Example—CDMA2000 ............................. 15
Quadrature Modulator.............................................................. 17
RF Multiplexer............................................................................ 18
Evaluation Board ............................................................................ 19
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 23
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 23
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 24
ADL5390
SPECIFICATIONS
VS = 5 V, TA = 25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, FRF = 380 MHz, single-ended source drive to INPI and INPQ, and INMI and INMQ are ac-coupled to
common, unless otherwise noted. 66.5 Ω termination resistors before ac-coupling capacitors on INPI and INPQ. The specifications refer
to one active channel with the other channel input terminated in 50 Ω. The common-mode level for the gain control inputs is 0.5 V. A
maximum gain setpoint of 1.0 refers to a differential gain control voltage of 0.5 V.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
OVERALL FUNCTION
Frequency Range
Gain Control Range Relative to maximum gain 35 dB
GAIN CONTROL INTERFACE (I and Q) QBBP, QBBM, IBBM, IBBP (Pins 4, 5, 14, 15)
Gain Scaling 3.5 1/V
Modulation Bandwidth
Second Harmonic Distortion
Third Harmonic Distortion
Step Response For gain from −15 dB to +5 dB 45 ns
For gain from +5 dB to −15 dB 47 ns
FRF = 70 MHz
Maximum Gain Maximum gain setpoint 4.6 dB
Gain Conformance Over gain setpoint of 0.2 to 1.0 0.25 dB
Output Noise Floor Maximum gain setpoint, no RF input −149 dBm/Hz
RF PIN = −5 dBm, frequency offset = 20 MHz −146 dBm/Hz
Output IP3
Output 1 dB Compression Point Maximum gain setpoint 10.7 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point Gain setpoint = 0.1 6.7 dBm
Gain Flatness Over any 60 MHz bandwidth 0.25 dB
Gain Matching At maximum gain setpoint 0.5 dB
Phase Matching At maximum gain setpoint ±0.25 Degrees
Input Impedance INPI, INMI, INMQ, INMP (Pins 20, 21, 22, 23)
Output Return Loss
FRF = 140 MHz
Maximum Gain Maximum gain setpoint 4.5 dB
Gain Conformance Over gain setpoint of 0.2 to 1.0 0.25 dB
Output Noise Floor Maximum gain setpoint, no RF input −144 dBm/Hz
RF PIN = −5 dBm, frequency offset = 20 MHz −145 dBm/Hz
Output IP3
Output 1 dB Compression Point Maximum gain setpoint 11 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point Gain setpoint = 0.1 7.1 dBm
Gain Flatness Over any 60 MHz bandwidth 0.25 dB
Gain Matching At maximum gain setpoint 0.5 dB
Phase Matching At maximum gain setpoint ±0.25 Degrees
Input Impedance INPI, INMI, INMQ, INMP (Pins 20, 21, 22, 23)
Output Return Loss
FRF = 380 MHz
Maximum Gain Maximum gain setpoint 4.1 dB
Gain Conformance Over gain setpoint of 0.2 to 1.0 0.25 dB
20 2400 MHz
500 mV p-p, sinusoidal baseband input single-
230 MHz
ended
500 mV p-p, 1 MHz, sinusoidal baseband input
45 dBc
differential
500 mV p-p, 1 MHz, sinusoidal baseband input
55 dBc
differential
= 70 MHz, F
F
RF1
= 72.5 MHz, maximum gain
RF2
23 dBm
setpoint
Ohms||pF
RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10) measured through
250||1
9.7 dB
balun
= 140 MHz, F
F
RF1
= 142.5 MHz, maximum
RF2
24.4 dBm
gain setpoint
Ohms||pF
RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10) measured through
250||1
9.6 dB
balun
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 24
ADL5390
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Output Noise Floor Maximum gain setpoint, no RF input −147.5 dBm/Hz
RF PIN = −5 dBm, frequency offset = 20 MHz −146 dBm/Hz
Output IP3
= 380 MHz, F
F
RF1
= 382.5 MHz, maximum
RF2
gain setpoint
Output 1 dB Compression Point Maximum gain setpoint 11.3 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point Gain setpoint = 0.1 8.3 dBm
Gain Flatness Over any 60 MHz bandwidth 0.25 dB
Gain Matching At maximum gain setpoint 0.5 dB
Phase Matching At maximum gain setpoint ±0.5 Degrees
Input Impedance INPI, INMI, INMQ, INMP (Pins 20, 21, 22, 23)
Output Return Loss
RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10) measured through
balun
FRF = 900 MHz
Maximum Gain Maximum gain setpoint 4.5 dB
Gain Conformance Over gain setpoint of 0.2 to 1.0 0.4 dB
Output Noise Floor Maximum gain setpoint, no RF input −149.5 dBm/Hz
RF PIN = −5 dBm, frequency offset = 20 MHz −148 dBm/Hz
Output IP3
= 900 MHz, F
F
RF1
= 902.5 MHz, maximum
RF2
gain setpoint
Output 1 dB Compression Point Maximum gain setpoint 11.5 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point Gain setpoint = 0.1 8.5 dBm
Gain Flatness Over any 60 MHz bandwidth 0.25 dB
Gain Matching At maximum gain setpoint 0.6 dB
Phase Matching At maximum gain setpoint ±1 Degrees
Input Impedance INPI, INMI, INMQ, INMP (Pins 20, 21, 22, 23)
Output Return Loss
RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10) measured through
balun
FRF = 2400 MHz
Maximum Gain Maximum gain setpoint 7.0 dB
Gain Conformance Over gain setpoint of 0.2 to 1.0 0.5 dB
Output Noise Floor Maximum gain setpoint, no RF input −147 dBm/Hz
RF PIN = −5 dBm, frequency offset = 20 MHz −144 dBm/Hz
Output IP3
= 2400 MHz, F
F
RF1
= 2402.5 MHz, maximum
RF2
gain setpoint
Output 1 dB Compression Point Maximum gain setpoint 9.6 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point Gain setpoint = 0.1 4.3 dBm
Gain Flatness Over any 60 MHz bandwidth 0.25 dB
Gain Matching At maximum gain setpoint 0.8 dB
Phase Matching At maximum gain setpoint ±2.5 Degrees
Input Impedance INPI, INMI, INMQ, INMP (Pins 20, 21, 22, 23)
Output Return Loss
RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10) measured through
balun
POWER SUPPLY VPRF, VPS2 (Pin 1, 18, 6); RFOP, RFOM (Pins 9, 10)
Positive Supply Voltage 4.75 5 5.25 V
Total Supply Current Includes load current 135 mA
OUTPUT DISABLE DSOP (Pin 13)
Disable Threshold 2.5 V
Maximum Attenuation DSOP = 5 V 40 dB
Enable Response Time
Delay following high-to-low transition until
device meets full specifications
Disable Response Time
Delay following low-to-high transition until
device produces full attenuation
24.2 dBm
200||1
Ohms||pF
8.5 dB
23.3 dBm
180||0.6
Ohms||pF
6.8 dB
18.7 dBm
140||0.5
Ohms||pF
13.5 dB
15 ns
10 ns
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 24

ADL5390
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameters Rating
Supply Voltage VPRF, VPS2 5.5 V
DSOP 5.5 V
IBBP, IBBM, QBBP, QBBM 2.5 V
RFOP, RFOM 5.5 V
RF Input Power at Maximum Gain 10 dBm for 50 Ω
(INPI or INPQ, Single-Ended Drive)
Equivalent Voltage 2.0 V p-p
Internal Power Dissipation 825 mW
θJA (With Pad Soldered to Board) 59°C/W
Maximum Junction Temperature 125°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 24
ADL5390
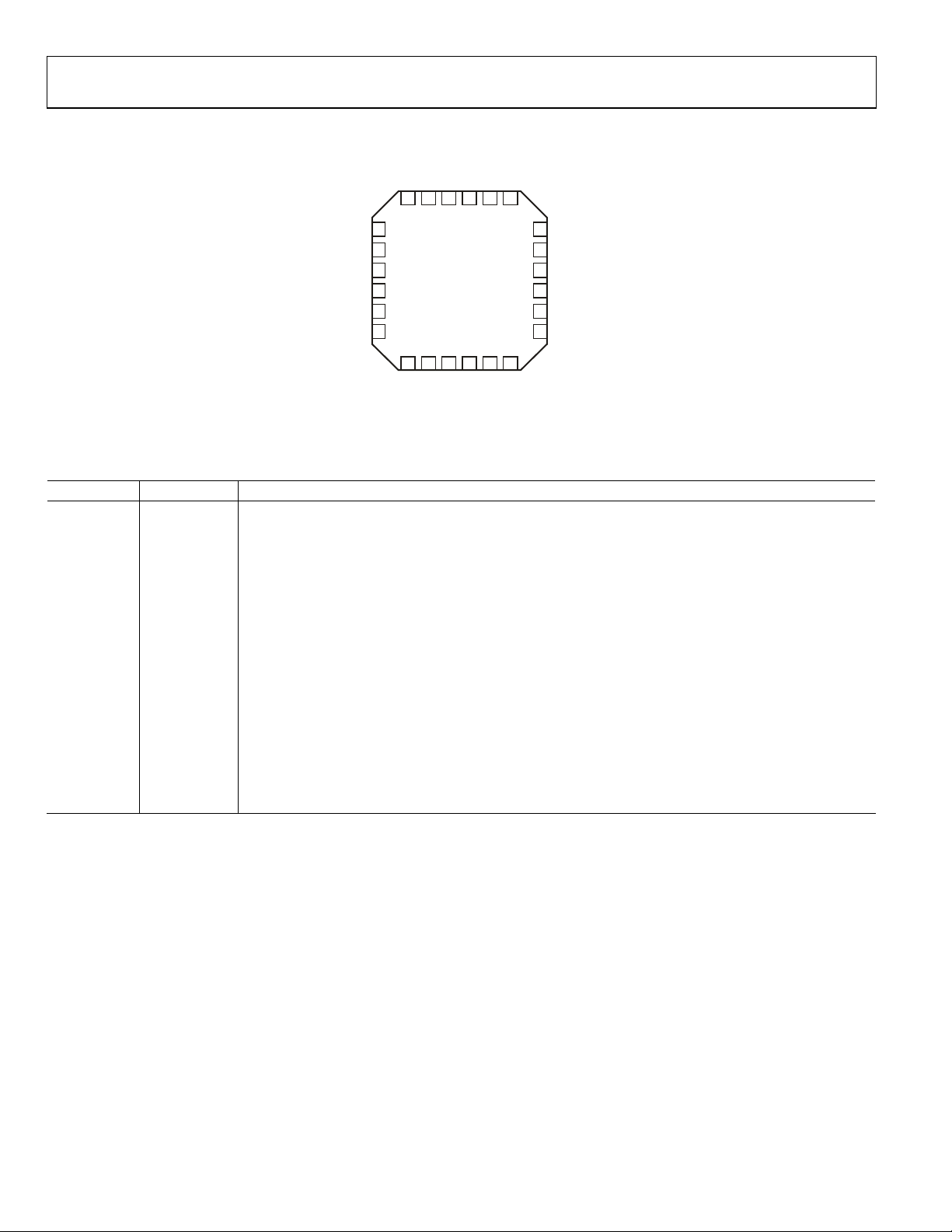
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
CMRF
INPQ
INMQ
INMI
INPI
24
23 22 21 20 19
CMRF
VPRF
QFLP
QFLM
QBBP
QBBM
VPS2
1
2
3
4
5
6
ADL5390
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7 8 9 101112
RFOP
CMOP
CMOP
RFOM
CMOP
CMOP
18
VPRF
17
IFLP
16
IFLM
15
IBBP
14
IBBM
13
DSOP
04954-002
Figure 2. LFCSP Pin Configuration
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
2, 3 QFLP, QFLM
Q Baseband Input Filter Pins. Connect optional capacitor to reduce Q baseband gain control channel low-
pass corner frequency.
4, 5 QBBP, QBBM Q Channel Differential Baseband Gain Control Inputs. Typical common-mode bias level of 0.5 V.
6, 1, 18 VPS2, VPRF Positive Supply Voltage. VP of 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
7, 8, 11, 12,
CMOP, CMRF Device Common. Connect via lowest possible impedance to external circuit common.
19, 24
9, 10 RFOP, RFOM
Differential RF Outputs. Must be ac-coupled. Differential impedance 50 Ω nominal.
13 DSOP Output Disable. Pull high to disable output stage. Connect to common for normal operation.
14, 15 IBBM, IBBP I Channel Differential Baseband Gain Control Inputs. Typical common-mode bias level of 0.5 V.
16, 17 IFLM, IFLP
I Baseband Input Filter Pins. Connect optional capacitor to reduce I baseband gain control channel lowpass corner frequency.
20, 21 INPI, INMI
I Channel Differential RF Inputs. Must be ac-coupled. 250 Ω impedance to common on each pin. These
inputs can be driven single-ended without any performance degradation.
22, 23 INMQ, INPQ
Q Channel Differential RF Inputs. Must be ac-coupled. 250 Ω impedance to common on each pin. These
inputs can be driven single-ended without any performance degradation.
Exposed
Paddle
GND
The exposed paddle on the underside of the package should be soldered to a low thermal and electrical
impedance ground plane.
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 24
ADL5390
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
10
5
0
–5
–10
GAIN (dB)
–15
–20
–25
–30
0.250
0.50
GAIN SETPOINT
FRF = 70MHz
= 140MHz
F
RF
= 380MHz
F
RF
= 900MHz
F
RF
= 2400MHz
F
RF
0.75 1.00
04954-003
5
4
3
2
1
0
–1
–2
CHANNEL GAIN MATCH (dB)
–3
–4
–5
0 300 600 900 1200 1500 1800 2100 2400
+3
σ
–3
σ
FREQUENCY (MHz)
04954-006
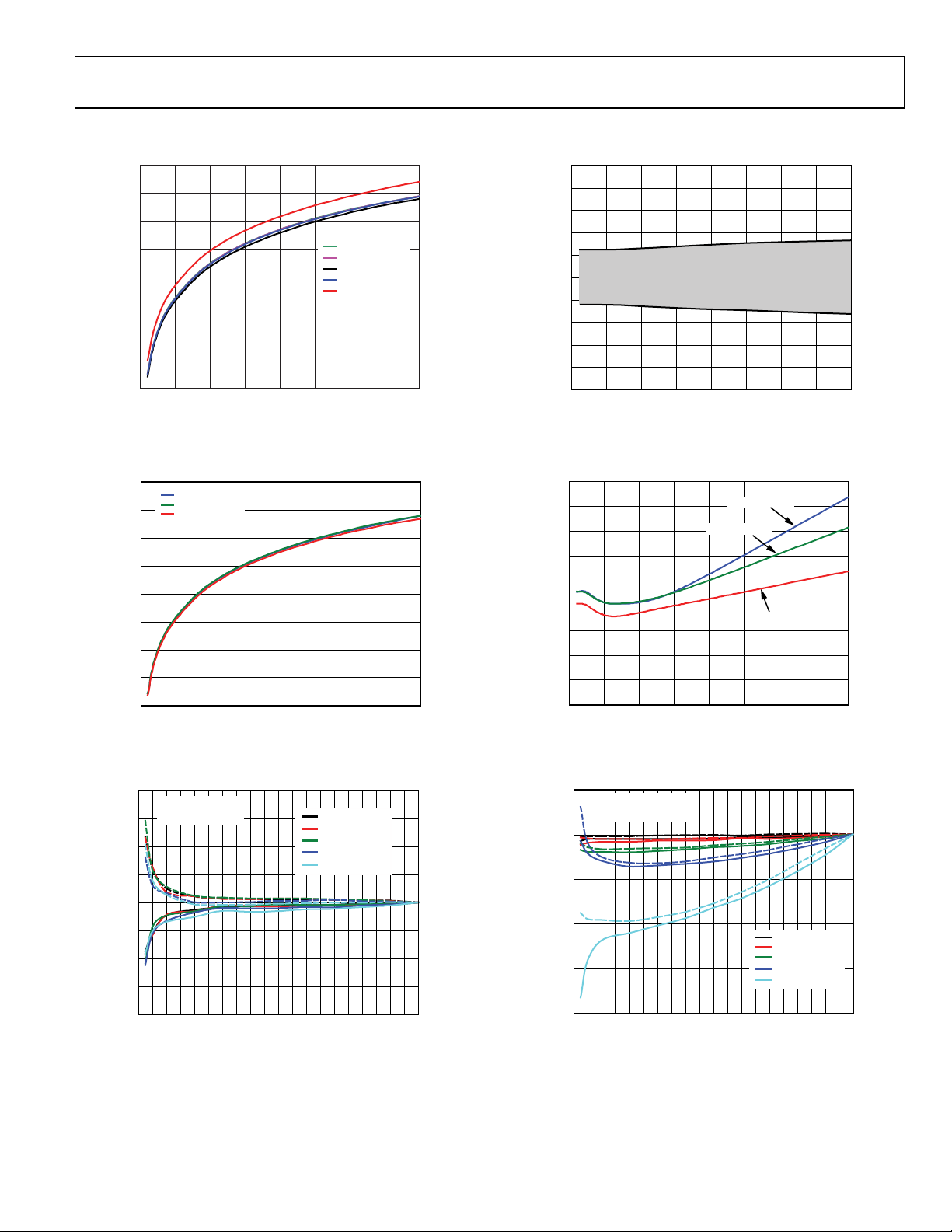
Figure 3. Gain Magnitude vs. Gain Setpoint, RF Frequency = 70 MHz,
140 MHz, 380 MHz, 900 MHz, 2400 MHz (Channel I or Channel Q)
10
–5
–10
GAIN (dB)
–15
–20
–25
–30
TEMP = –40°C
TEMP = +25°C
5
TEMP = +85°C
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
GAIN SETPOINT
04954-004
Figure 4. Gain Magnitude vs. Gain Setpoint, Temp = +85°C, +25°C, −40°C,
RF Frequency = 380 MHz (Channel I or Channel Q)
4
+3σ= DASH LINE
σ
= SOLID LINE
–3
3
2
1
0
–1
GAIN ERROR (dB)
–2
–3
–4
0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.0
GAIN SETPOINT
FRF = 70MHz
FRF = 140MHz
F
= 380MHz
RF
= 900MHz
F
RF
F
= 2400MHz
RF
04954-005
Figure 5. Gain Conformance Error vs. Gain Setpoint, RF Frequency = 70 MHz,
140 MHz, 380 MHz, 900 MHz, 2400 MHz
Figure 6. Channel Gain Matching (I to Q) vs. RF Frequency,
Gain Setpoint = 1.0
9
8
7
6
5
4
GAIN (dB)
3
2
1
0
0 300 600 900 1200 1500 1800 2100 2400
FREQUENCY (MHz)
TEMP = –40°C
TEMP = +25°C
TEMP = +85°C
04954-007
Figure 7. Channel Gain vs. RF Frequency, Temp = +85°C, +25°C, −40°C,
Gain Setpoint = 1.0
5
+3σ= DASH LINE
σ
= SOLID LINE
–3
0
–5
–10
PHASE ERROR (Degrees)
–15
–20
0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.0
GAIN SETPOINT
FRF = 70MHz
= 140MHz
F
RF
F
= 380MHz
RF
= 900MHz
F
RF
= 2400MHz
F
RF
04954-008
Figure 8. Single-Channel Phase Deviation vs. Gain Setpoint, Normalized to
Gain Setpoint = 1.0, RF Frequency = 70 MHz, 140 MHz, 380 MHz,
900 MHz, 2400 MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 24
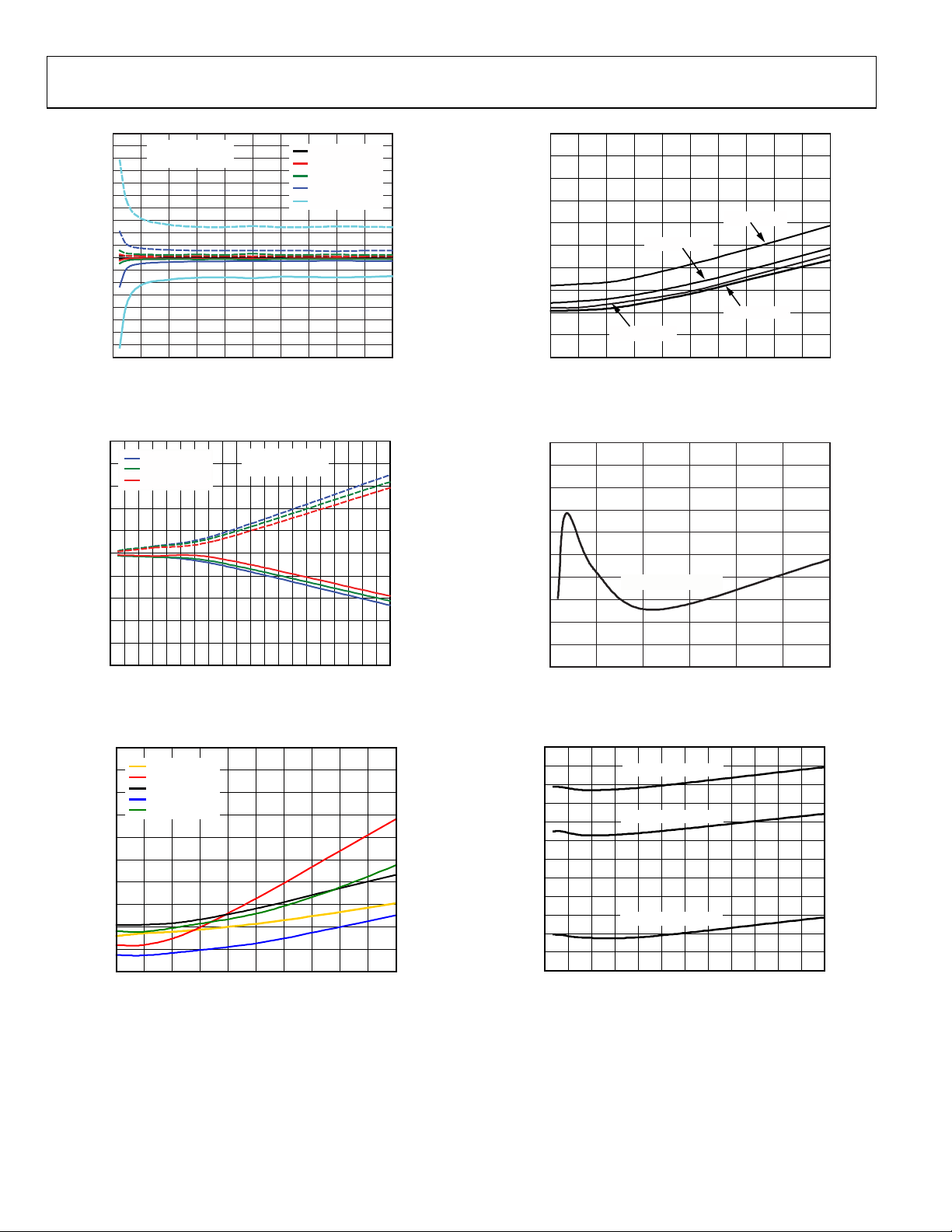
ADL5390
25
20
15
10
–5
–10
PHASE DIFFERRENCE (Degrees)
–15
–20
Figure 9. Channel-to-Channel Phase Matching vs. Gain Setpoint,
RF Frequency = 70 MHz, 140 MHz, 380 MHz, 900 MHz, 2400 MHz
10
8
6
4
2
0
–2
–4
PHASE DIFFERENCE (Degrees)
–6
–8
–10
Figure 10. Channel-to-Channel Phase Matching vs. RF Frequency, Temp =
–142
–143
–144
–145
–146
–147
–148
NOISE (dBm/Hz)
–149
–150
–151
–152
Figure 11. Output Noise Floor vs. Gain Setpoint, No RF Carrier,
RF Frequency = 70 MHz, 140 MHz, 380 MHz, 900 MHz, 2400 MHz
+3σ= DASH LINE
–3
σ
= SOLID LINE
5
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
TEMP = –40°C
TEMP = +25°C
TEMP = +85°C
0 600 1200 1800 2400
GAIN SETPOINT
+3σ= DASH LINE
–3
σ
FREQUENCY (MHz)
FRF= 70MHz
F
F
F
F
= SOLID LINE
=140MHz
RF
=380MHz
RF
= 900MHz
RF
= 2400MHz
RF
+85°C, +25°C, −40°C, Gain Setpoint = 1.0
FRF = 70MHz
F
= 140MHz
RF
F
= 380MHz
RF
F
= 900MHz
RF
F
= 2400MHz
RF
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
GAIN SETPOINT
04954-009
04954-010
04954-011
–142
–143
–144
–145
–146
–147
–148
NOISE (dBm/Hz)
–149
–150
–151
–152
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
PIN=–10dBm
PIN=–15dBm
GAIN SETPOINT
PIN= –5dBm
NO CARRIER
Figure 12. Output Noise Floor vs. Gain Setpoint, No Carrier, with Carrier
(20 MHz Offset), RF P
–142
–143
–144
–145
–146
–147
–148
NOISE (dBm/Hz)
–149
–150
–151
–152
0 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400
= −5, −10, −15, No Carrier, RF Frequency = 380 MHz
IN
GAIN SETPOINT = 1.0
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 13. Output Noise Floor vs. RF Frequency, Gain Setpoint = 1.0,
No RF Carrier
10
5
0
–5
GAIN (dB)
–10
–15
–20
0 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400
GAIN SETPOINT = 1.0
GAIN SETPOINT = 0.5
GAIN SETPOINT = 0.1
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 14. Gain vs. RF Frequency, Gain Setpoint = 1.0, 0.5, 0.1
04954-012
04954-013
04954-014
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...