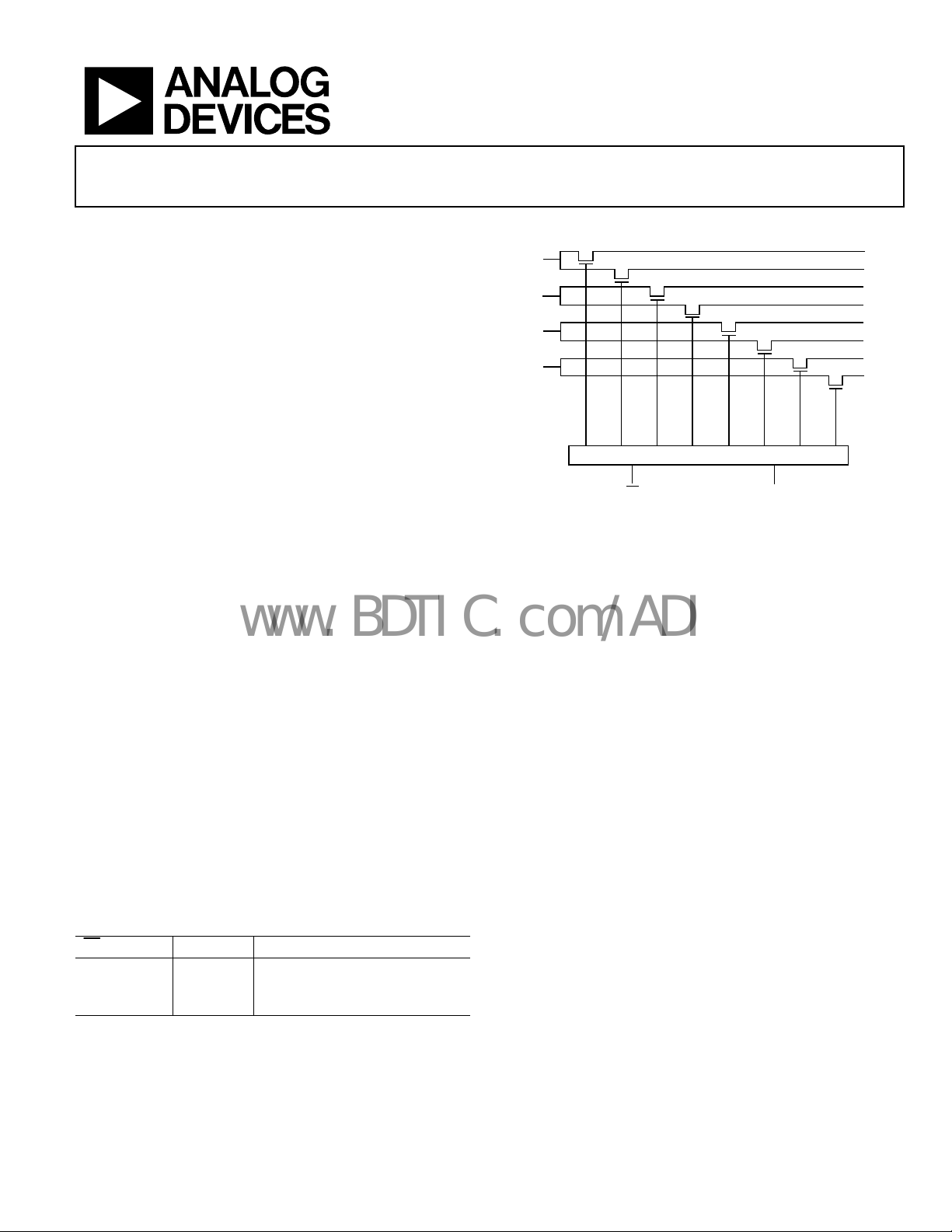
High Speed, 3.3 V/5 V Quad 2:1 Mux/Demux
A
2A3A
4A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
100 ps propagation delay through the switch
2 Ω switches connect inputs to outputs
Data rates up to 933 Mbps
Single 3.3 V/5 V supply operation
Level translation operation
Ultralow quiescent supply current (1 nA typical)
3.5 ns switching
Switches remain in the off state when power is off
Standard 3257 type pinout
APPLICATIONS
Bus switching
Bus isolation
Level translation
Memory switching/interleaving
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADG3257 is a CMOS bus switch comprised of four 2:1
multiplexers/demultiplexers with high impedance outputs. The
device is manufactured on a CMOS process. This provides low
power dissipation yet high switching speed and very low on
resistance, allowing the inputs to be connected to the outputs
without adding propagation delay or generating additional
ground bounce noise.
The ADG3257 operates from a single 3.3 V/5 V supply. The
control logic for each switch is shown in Tabl e 1. These switches
are bidirectional when on. In the off state, signal levels are blocked
up to the supplies. When the power supply is off, the switches
remain in the off state, isolating Port A and Port B.
This bus switch is suited to both switching and level translation
applications. It can be used in applications requiring level translation from 3.3 V to 2.5 V when powered from 3.3 V. Additionally,
with a diode connected in series with 5 V V
may also be used in applications requiring 5 V to 3.3 V level
translation.
Table 1. Truth Table
BE
S Function
H X Disable
L L A = B1
L H A = B2
, the ADG3257
DD
(4-Bit, 1 of 2) Bus Switch
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
LOGIC
BE
Figure 1.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. 0.1 ns propagation delay through switch.
2. 2 Ω switches connect inputs to outputs.
3. Bidirectional operation.
4. Ultralow power dissipation.
5. 16-lead QSOP package.
S
ADG3257
1B
1
1B
2
2B
1
2B
2
3B
1
3B
2
4B
1
4B
2
02914-001
Rev. E
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2002–2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADG3257
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 5
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 5
REVISION HISTORY
03/08—Rev. D to Rev. E
Updated Format .................................................................... Universal
Changes to Features .............................................................................1
Changes to General Description .......................................................1
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ..........................................5
Changes to Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ...........6
Changes to Test Circuits .....................................................................9
Changes to Ordering Guide ...............................................................11
11/04—Rev. C to Rev. D
Changes to Specifications ...................................................................2
Changes to Ordering Guide ...............................................................4
04/03—Rev. A to Rev. B
Updated Outline Dimensions ............................................................8
06/02—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Edits to Features ...................................................................................1
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ..............................6
Typical Performance Characteristics ..............................................7
Test Circuits ........................................................................................9
Applications Information .............................................................. 10
Mixed Voltage Operation, Level Translation .......................... 10
Memory Switching ..................................................................... 10
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 11
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 11
Rev. E | Page 2 of 12
ADG3257
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
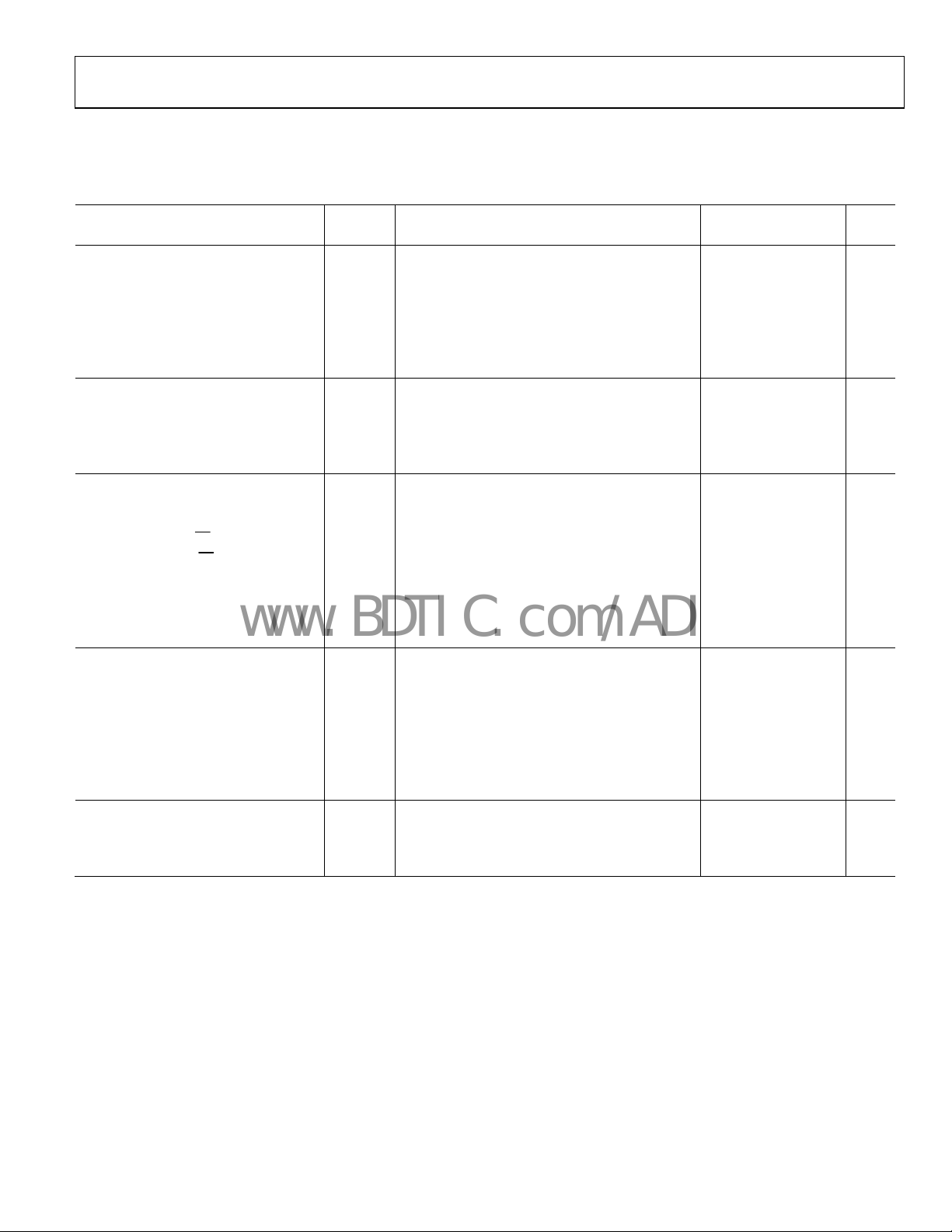
SPECIFICATIONS
VCC = 5.0 V ± 10%, GND = 0 V. All specifications T
Table 2.
Parameter1 Symbol Conditions2
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
2.4 V
INH
−0.3 +0.8 V
INL
Input Leakage Current II 0 ≤ VIN ≤ 5.5 V ±0.01 ±1 μA
Off State Leakage Current IOZ 0 ≤ A, B ≤ VCC ±0.01 ±1 μA
On State Leakage Current IOZ 0 ≤ A, B ≤ VCC ±0.01 ±1 μA
Maximum Pass Voltage4 VP VIN = VCC = 5 V, IO = −5 μA 3.9 4.2 4.4 V
CAPACITANCE4
A Port Off Capacitance CA OFF f = 1 MHz 7 pF
B Port Off Capacitance CB OFF f = 1 MHz 5 pF
A, B Port On Capacitance CA, CB ON f = 1 MHz 11 pF
Control Input Capacitance CIN f = 1 MHz 4 pF
4
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Propagation Delay A to B or B to A, tPD t
, t
PHL
Propagation Delay Matching6 VA = 0 V, CL = 50 pF 0.0075 0.035 ns
t
Bus Enable Time BE to A or B
Bus Disable Time BE to A or B
, t
PZH
t
, t
PHZ
Bus Select Time S to A or B
Enable t
Disable t
SEL_EN
SEL_DIS
Maximum Data Rate VA = 2 V p-p 933 Mbps
DIGITAL SWITCH
On Resistance RON VA = 0 V
I
I
V
I
I
On-Resistance Matching ΔRON VA = 0 V, IO = 48 mA, 15 mA, 8 mA 0.15 Ω
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VCC 3.0 5.5 V
Quiescent Power Supply Current ICC Digital inputs = 0 V or VCC 0.001 1 μA
4, 7
Increase in ICC per Input
1
Temperature range is: Version B: –40°C to +85°C.
2
See Test Circuits section.
3
All typical values are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
4
Guaranteed by design, not subject to production test.
5
The digital switch contributes no propagation delay other than the RC delay of the typical RON of the switch and the load capacitance when driven by an ideal voltage
source. Because the time constant is much smaller than the rise/fall times of typical driving signals, it adds very little propagation delay to the system. Propagation
delay of the digital switch, when used in a system, is determined by the driving circuit on the driving side of the switch and its interaction with the load on the driven side.
6
Propagation delay matching between channels is calculated from on-resistance matching of worst-case channel combinations and load capacitance.
7
This current applies to the control pins only and represents the current required to switch internal capacitance at the specified frequency. The A and B ports contribute
no significant ac or dc currents as they transition.
ΔICC V
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
B Version
5
VA = 0 V, CL = 50 pF 0.10 ns
PLH
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 1 5 7.5 ns
PZL
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 1 3.5 7 ns
PLZ
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 8 12 ns
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 5 8 ns
= 48 mA, 15 mA, 8 mA, TA = 25°C 2 4 Ω
O
= 48 mA, 15 mA, 8 mA 5 Ω
O
= 2.4 V
A
= 48 mA, 15 mA, 8 mA, TA = 25°C 3 6 Ω
O
= 48 mA, 15 mA, 8 mA 7 Ω
O
= 5.5 V, one input at 3.0 V; others at VCC or GND 200 μA
CC
Unit Min Typ3Max
Rev. E | Page 3 of 12
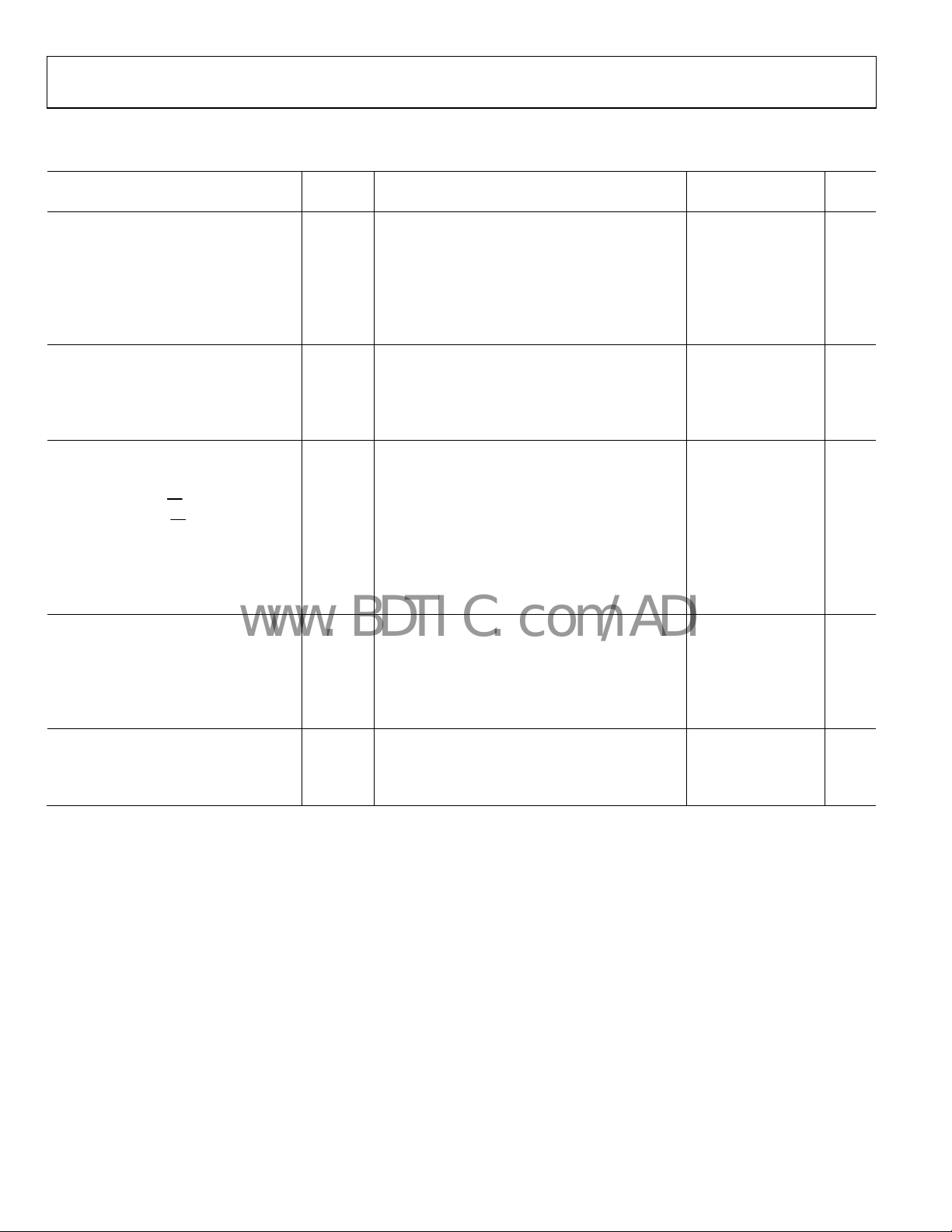
ADG3257
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VCC = 3.3 V ± 10%, GND = 0 V. All specifications T
Table 3.
Parameter1 Symbol Conditions2
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
INH
INL
Input Leakage Current II 0 ≤ VIN ≤ 3.6 V ±0.01 ±1 μA
Off State Leakage Current IOZ 0 ≤ A, B ≤ VCC ±0.01 ±1 μA
On State Leakage Current IOZ 0 ≤ A, B ≤ VCC ±0.01 ±1 μA
Maximum Pass Voltage4 VP VIN = VCC = 3.3 V, IO = −5 μA 2.3 2.6 2.8 V
CAPACITANCE4
A Port Off Capacitance CA OFF f = 1 MHz 7 pF
B Port Off Capacitance CB OFF f = 1 MHz 5 pF
A, B Port On Capacitance CA, CB ON f = 1 MHz 11 pF
Control Input Capacitance CIN f = 1 MHz 4 pF
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS4
Propagation Delay A to B or B to A, tPD t
PHL
Propagation Delay Matching6 VA = 0 V, CL = 50 pF 0.01 0.04 ns
Bus Enable Time BE to A or B
Bus Disable Time BE to A or B
t
PZH
t
PHZ
Bus Select Time S to A or B
Enable t
Disable t
SEL_EN
SEL_DIS
Maximum Data Rate VA = 2 V p-p 933 Mbps
DIGITAL SWITCH
On Resistance RON V
V
V
V
On-Resistance Matching ΔR
ON
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VCC 3.0 5.5 V
Quiescent Power Supply Current ICC Digital inputs = 0 V or VCC 0.001 1 μA
Increase in ICC per Input
1
Temperature range is: Version B: −40°C to +85°C.
2
See Test Circuits section.
3
All typical values are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
4
Guaranteed by design, not subject to production test.
5
The digital switch contributes no propagation delay other than the RC delay of the typical RON of the switch and the load capacitance when driven by an ideal voltage
source. Because the time constant is much smaller than the rise/fall times of typical driving signals, it adds very little propagation delay to the system. Propagation
delay of the digital switch, when used in a system, is determined by the driving circuit on the driving side of the switch and its interaction with the load on the driven sid e.
6
Propagation delay matching between channels is calculated from on-resistance matching of worst-case channel combinations and load capacitance.
7
This current applies to the control pins only and represents the current required to switch internal capacitance at the specified frequency. The A and B ports contribute
no significant ac or dc currents as they transition.
4, 7
ΔICC V
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
B Version
Unit Min Typ3Max
2.0 V
−0.3 +0.8 V
5
, t
VA = 0 V, CL = 50 pF 0.10 ns
PLH
, t
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 1 5.5 9 ns
PZL
, t
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 1 4.5 8.5 ns
PLZ
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 8 12 ns
CL = 50 pF, RL = 500 Ω 6 9 ns
= 0 V, IO = 15 mA, 8 mA, TA = 25°C 2 4 Ω
A
= 0 V, Io = 15 mA, 8 mA 5 Ω
A
= 1 V, IO = 15 mA, 8 mA, TA = 25°C 4 7 Ω
A
= 1 V, Io = 15 mA, 8 mA 8 Ω
A
V
= 0 V, IO = 15 mA, 8 mA 0.2 Ω
A
= 3.3 V, one input at 3.0 V; others at VCC or GND 200 μA
CC
Rev. E | Page 4 of 12
 Loading...
Loading...