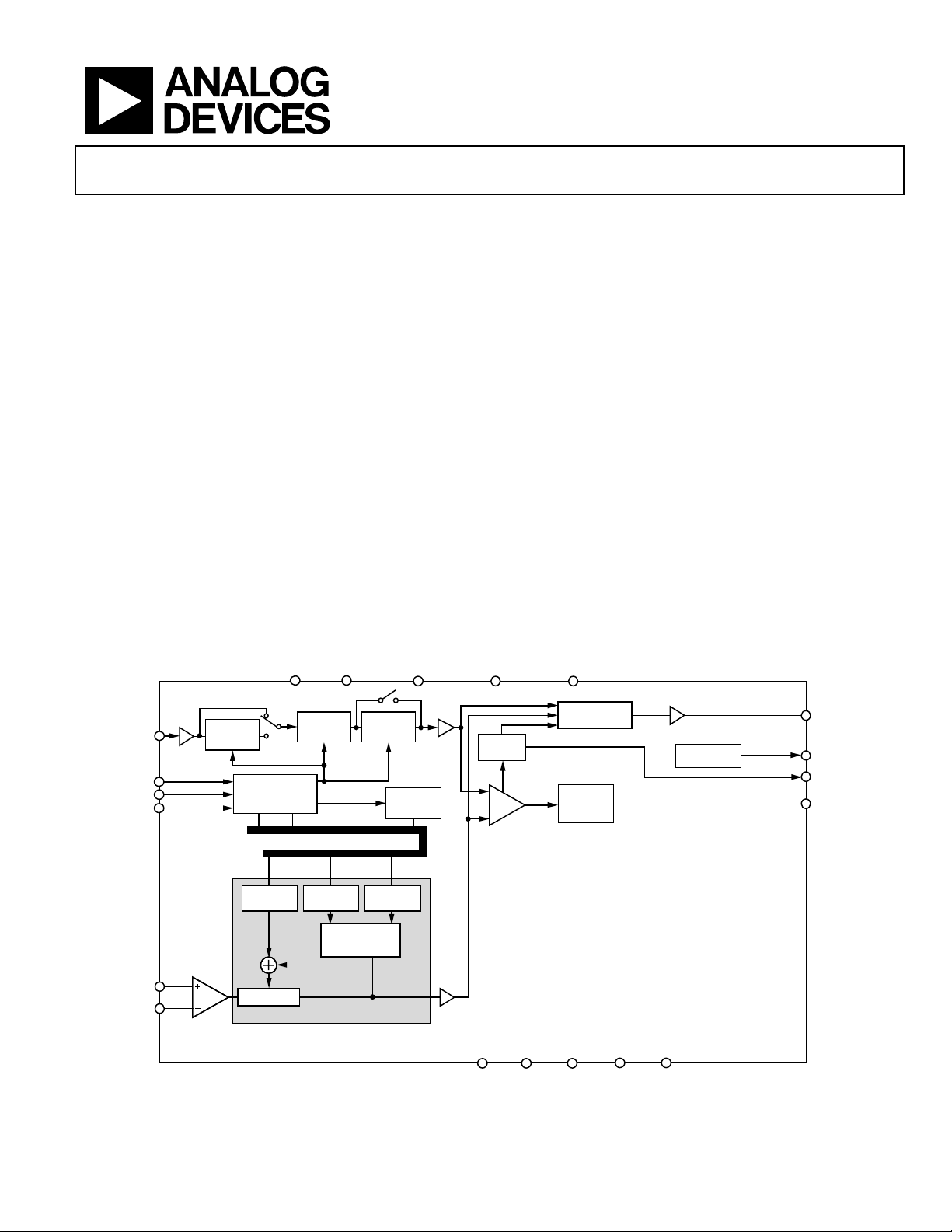
Fractional-N/Integer-N PLL Synthesizer
ADF4151
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
MUXOUT
CP
OUT
LD
SW
REF
IN
CLK
DATA
LE
AV
DD
xSDV
DD
DV
DD
V
P
A
GND
CE CP
GND
SD
GNDDGND
R
SET
RFIN+
RF
IN
–
PHASE
COMPARATOR
FL
O
SWITCH
CHARGE
PUMP
10-BIT R
COUNTER÷2DIVIDER
×2
DOUBLER
FUNCTION
LATCH
DATA REGISTER
INTEGER
REG
N COUNTER
FRACTION
REG
THIRD-ORDER
FRACTIONAL
INTERPOLATOR
MODULUS
REG
MULTIPLEXER
LOCK
DETECT
ADF4151
10265-001
Data Sheet
FEATURES
Fractional-N synthesizer and integer-N synthesizer
RF bandwidth to 3.5 GHz
3.0 V to 3.6 V power supply
1.8 V logic compatibility
Separate charge pump supply (V
voltage (up to 5.5 V) in 3 V systems
Programmable dual-modulus prescaler of 4/5 or 8/9
Programmable RF output phase
3-wire serial interface
Analog and digital lock detect
Switched bandwidth fast lock mode
Cycle slip reduction
APPLICATIONS
Wireless infrastructure (W-CDMA, TD-SCDMA, WiMax, GSM,
PCS, DCS, DECT)
Test equipment
Wireless LANs, CATV equipment
Clock generation
) allows extended tuning
P
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADF4151 allows implementation of fractional-N or
integer-N phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizers
if used with an external voltage controlled oscillator (VCO),
loop filter, and external reference frequency.
The ADF4151 is used with external VCO parts and is footprint
and software compatible with the ADF4350. The part consists
of a low noise digital phase frequency detector (PFD), a precision
charge pump, and a programmable reference divider. There is
a Σ-Δ based fractional interpolator to allow programmable
fractional-N division. The INT, FRAC, and MOD registers
define an overall N divider [N = (INT + (FRAC/MOD))]. The
RF output phase is programmable for applications that require
a particular phase relationship between the output and the
reference. The ADF4151 also features cycle slip reduction
circuitry, leading to faster lock times without the need for
modifications to the loop filter.
Control of all the on-chip registers is through a simple 3-wire
interface. The device operates with a power supply ranging
from 3.0 V to 3.6 V that can be powered down when not in use.
The ADF4151 is available in a 5 mm × 5 mm package.
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of thi rd parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change with out notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com

ADF4151 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Timing Characteristics ................................................................ 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 6
Transistor Count ........................................................................... 6
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 6
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Circuit Description ......................................................................... 11
Reference Input Section ............................................................. 11
RF N Divider ............................................................................... 11
INT, FRAC, MOD, and R Counter Relationship.................... 11
INT N Mode ................................................................................ 11
R Counter .................................................................................... 11
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump ............ 11
MUXOUT and Lock Detect ...................................................... 12
Input Shift Registers ................................................................... 12
Program Modes .......................................................................... 12
Register Maps .............................................................................. 13
Register 0 ..................................................................................... 17
Register 1 ..................................................................................... 17
Register 2 ..................................................................................... 17
Register 3 ..................................................................................... 19
Register 4 ..................................................................................... 19
Register 5 ..................................................................................... 19
Initialization Sequence .............................................................. 19
RF Synthesizer—A Worked Example ...................................... 20
Modulus ....................................................................................... 20
Reference Doubler and Reference Divider ............................. 20
12-Bit Programmable Modulus ................................................ 20
Cycle Slip Reduction for Faster Lock Times ........................... 21
Spurious Optimization and Fast lock ...................................... 21
Fast Lock Timer and Register Sequences ................................ 21
Fast Lock—An Example ............................................................ 22
Fast Lock—Loop Filter Topology ............................................. 22
Spur Mechanisms ....................................................................... 22
Spur Consistency and Fractional Spur Optimization ........... 23
Phase Resync ............................................................................... 23
Applications Information .............................................................. 24
Direct Conversion Modulator .................................................. 24
Interfacing ................................................................................... 25
PCB Design Guidelines for Chip Scale Package .................... 25
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 26
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 26
REVISION HISTORY
12/11—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changes to Normalized 1/f Noise Parameter, Table 1 ................. 4
11/11—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Figure 28 ...................................................................... 23
10/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 2 of 28
Data Sheet ADF4151
Fractional-N Mode
Input Capacitance, CIN
5.0 pF
Low Power Sleep Mode
1
µA
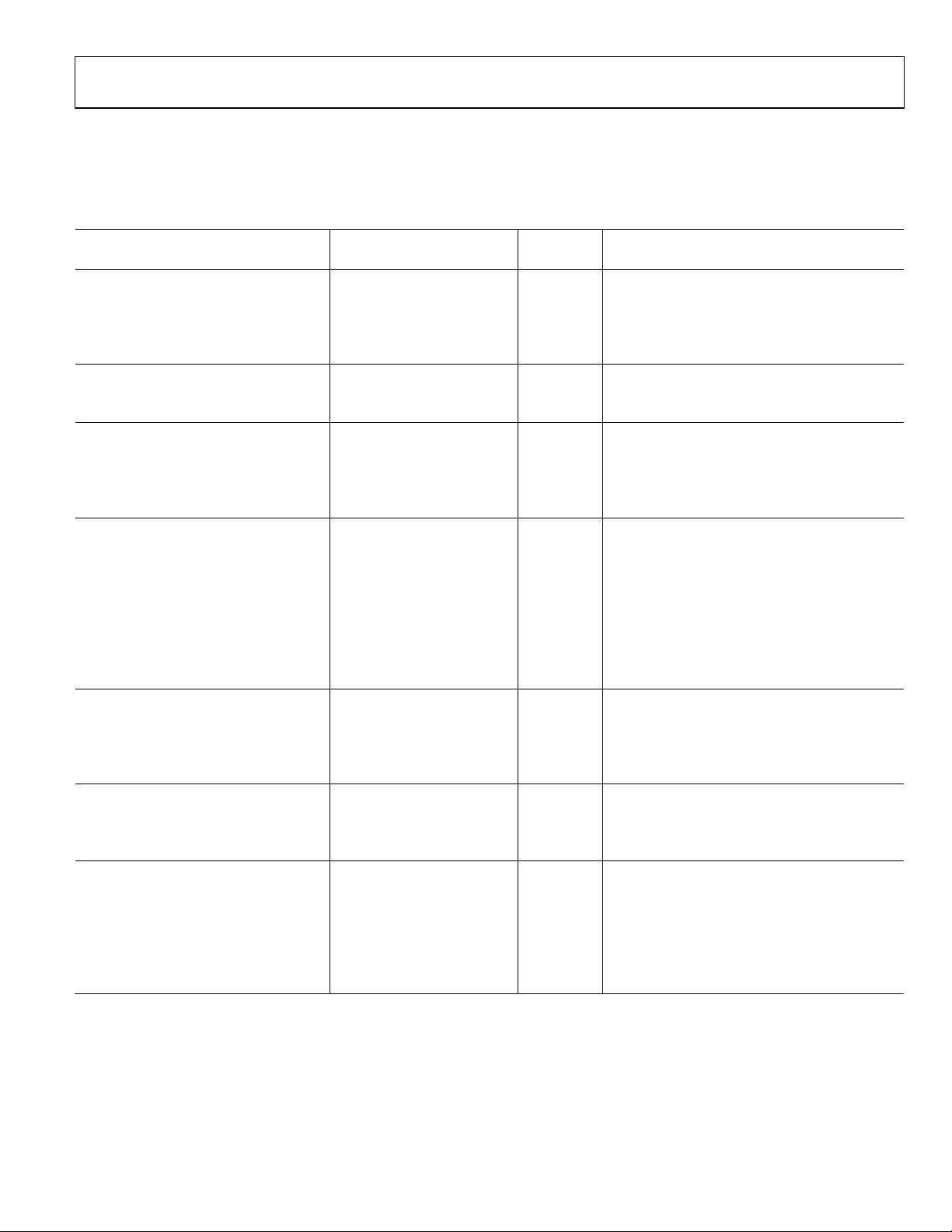
SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = DVDD = SD
temperature range is −40°C to +85°C.
Table 1.
Parameter
REFIN CHARACTERISTICS
Input Frequency 10 250 MHz For f < 10 MHz, ensure slew rate > 21 V/µs
Input Sensitivity 0.7 AVDD V p-p Biased at AVDD/21
Input Capacitance 10 pF
Input Current ±60 µA
RF INPUT CHARACTERISTICS For lower frequencies, ensure slew rate > 400 V/µs
RF Input Frequency (RFIN) 0.5 3.5 GHz −10 dBm ≤ RF input power ≤ +5 dBm
Prescaler Output Frequency 750 MHz
MAXIMUM PFD FREQUENCY
Low Spur Mode 26 MHz
Low Noise Mode 32 MHz
Integer-N Mode 32 MHz
CHARGE PUMP
ICP Sink/Source R
High Value 4.5 mA
Low Value 0.281 mA
R
Range 2.7 10 kΩ
SET
ICP Leakage 1 nA VCP = VP/2
Sink and Source Matching 2 % 0.5 V ≤ VCP ≤ VP − 0.5 V
ICP vs. VCP 1.5 % 0.5 V ≤ VCP ≤ VP − 0.5 V
ICP vs. Temperature 2 % VCP = VP/2
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
= 3.3 V ± 10%; VP = AVDD to 5.5 V; A
VDD
GND
= D
= 0 V; TA = T
GND
B Version
Unit Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max
1.5 V
INH
0.6 V
INL
±1 µA
INH/IINL
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted. Operating
MAX
= 5.1 kΩ
SET
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, VOH DVDD − 0.4 V CMOS output chosen
Output High Current, IOH 500 µA
Output Low Voltage, VO 0.4 V IOL = 500 µA
POWER SUPPLIES
AVDD 3.0 3.6 V
DVDD, SD
VP AVDD 5.5 V
DIDD + AI
VPI
DD
AVDD
VDD
2
40 50 mA
DD
2
2 mA VP = 5 V
Rev. B | Page 3 of 28
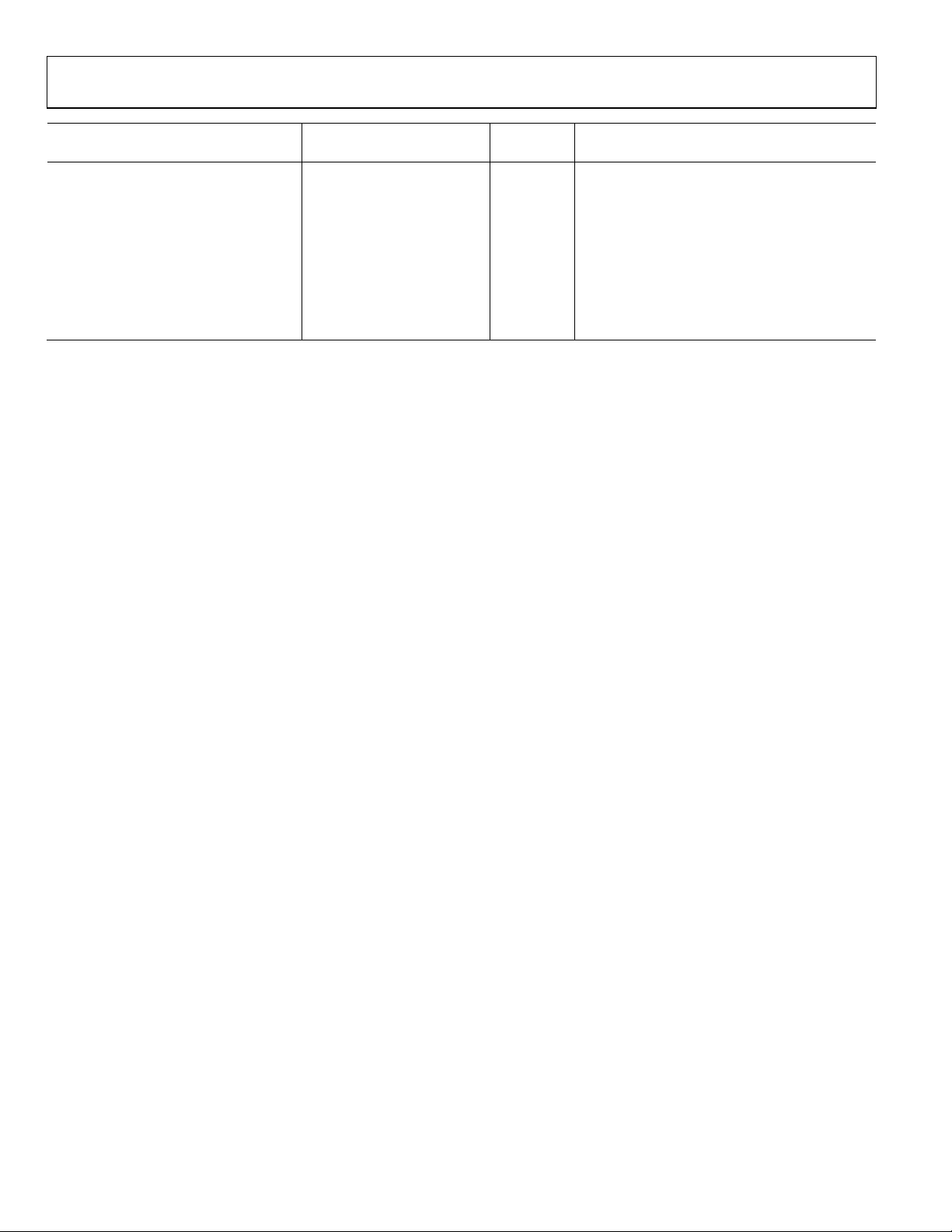
ADF4151 Data Sheet
B Version
Parameter
NOISE CHARACTERISTICS
Normalized In-Band Phase Noise
Floor (PN
Normalized 1/f Noise (PN
SYNTH
)3
)4 −118 dBc/Hz 10 kHz offset. Normalized to 1 GHz (ABP = 3 ns)
1_f
Normalized In-Band Phase Noise
Floor (PN
Normalized 1/f Noise (PN
Spurious Signals Due to PFD
Frequency
1
AC coupling ensures AVDD/2 bias.
2
TA = 25°C; AVDD = DVDD = 3.6 V; prescaler = 4/5; f
3
The synthesizer phase noise floor is estimated by measuring the in-band phase noise at the output of the VCO and subtracting 20 log N (where N is the N divider
value) and 10 log F
4
The PLL phase noise is composed of 1/f (flicker) noise plus the normalized PLL noise floor. The formula for calculating the 1/f noise contribution at an RF frequency (fRF)
and at a frequ ency offset (f) is given by PN = P
5
Spurious measured on EVAL-ADF4151EB1Z with RF buffer between VCO output and RF input by-passed, using a Rohde & Schwarz FSUP signal source analyzer.
SYNTH
5
)3
)4 −115 dBc/Hz 10 kHz offset; normalized to 1 GHz (ABP = 6 ns);
1_f
. PN
= PN
PFD
SYNTH
– 10 log f
TOT
−221 dBc/Hz PLL loop BW = 500 kHz (ABP = 3 ns)
−220 dBc/Hz PLL loop BW = 500 kHz (ABP = 6 ns);
−107 dBc PFD = 25 MHz
= 130 MHz; f
REFIN
– 20 log N
PFD
+ 10 log(10 kHz/f) + 20 log(fRF/1 GHz). Both the normalized phase noise floor and flicker noise are modeled in ADIsimPLL
1_f
= 26 MHz; fRF = 1.742 GHz.
PFD
Unit Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max
low noise mode
low noise mode
Rev. B | Page 4 of 28
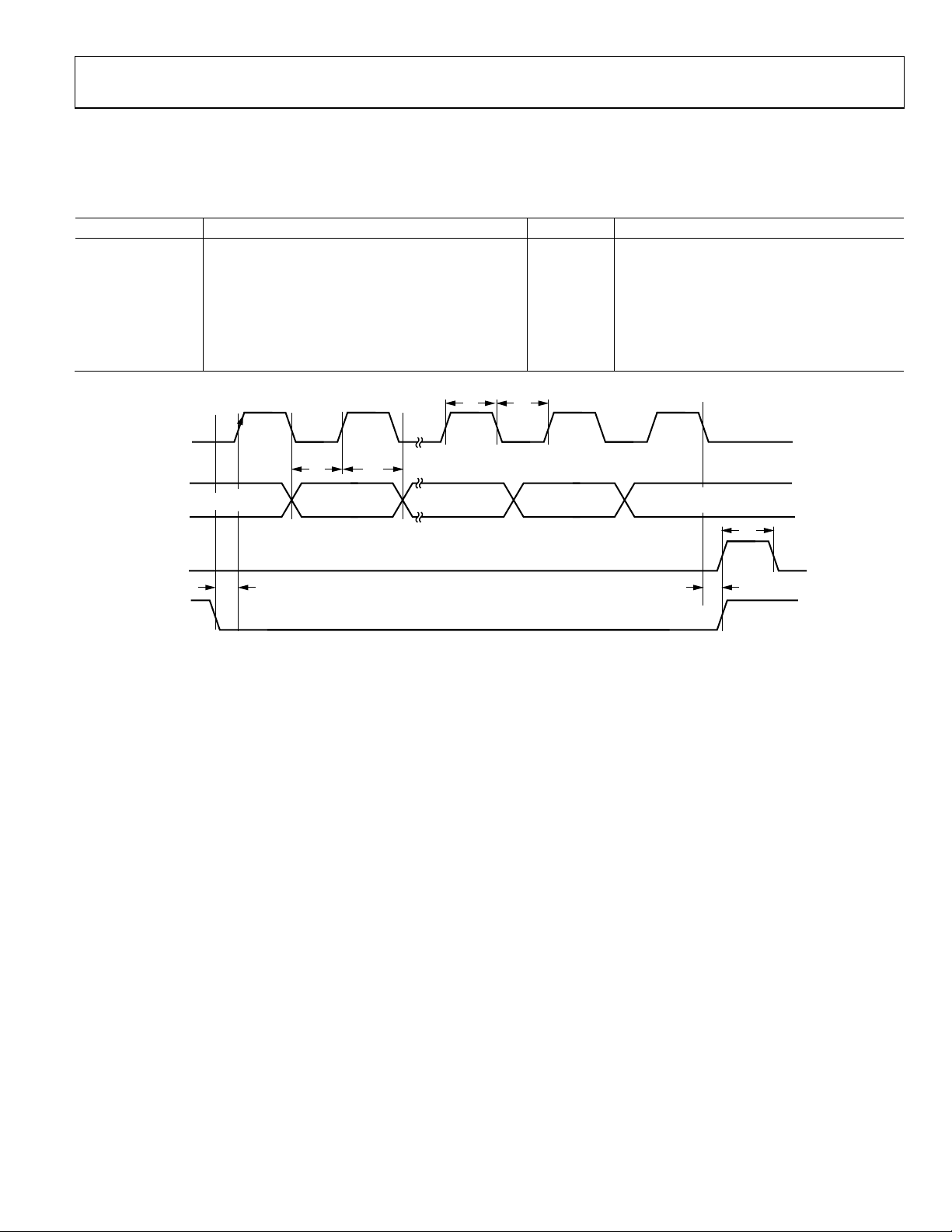
Data Sheet ADF4151
CLK
DATA
LE
LE
DB31 (MSB) DB30
DB1 (LSB)
(CONTROL BIT C2)
DB2 (LSB)
(CONTROL BIT C3)
DB0 (LSB)
(CONTROL BIT C1)
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
7
t
6
t
4
t
5
10265-002
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD1, AVDD2 = DVDD = SD
Operating temperature range is −40°C to +85°C.
Table 2.
Parameter Limit (B Version) Unit Test Conditions/Comments
t1 20 ns min LE setup time
t2 10 ns min DATA to CLK setup time
t3 10 ns min DATA to CLK hold time
t4 25 ns min CLK high duration
t5 25 ns min CLK low duration
t6 10 ns min CLK to LE setup time
t7 20 ns min LE pulse width
= 3.3 V ± 10%; VP = AVDD to 5 . 5 V; A
VDD
GND
= D
= 0 V; TA = T
GND
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Figure 2. Timing Diagram
Rev. B | Page 5 of 28
ADF4151 Data Sheet
Peak Temperature
260°C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
AVDD1, AVDD2 to GND1 −0.3 V to +3.9 V
AVDD1, AVDD2 to DVDD −0.3 V to +0.3 V
VP to AVDD1, AVDD2 −0.3 V to +5.8 V
Digital I/O Voltage to GND1 −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Analog I/O Voltage to GND1 −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
REFIN to GND1 −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +125°C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
LFCSP θJA Thermal Impedance
(Paddle-Soldered) 27.3°C/W
Reflow Soldering
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
TRANSISTOR COUNT
36685 (CMOS) and 967 (bipolar)
ESD CAUTION
Time at Peak Temperature 40 sec
1
GND = A
GND
= D
GND
= 0 V.
Rev. B | Page 6 of 28
Data Sheet ADF4151
1
CLK
2
DATA
3
LE
4
CE
5
SW
6
7
24
23
NC
22
21
20
19
18
17
8
SDV
DD
ADF4151
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
9
A
GND
10
11
REF
IN
12
D
GND
13
DV
DD
141516
3231302928
SD
GND
27
26
25
PIN 1
INDICATOR
V
P
CP
OUT
CP
GND
MUXOUT
R
SET
NC
RF
IN
+
RF
IN
−
NC
NC
NC
D
GND
LD
A
GND
A
GND
A
GND
NC
AV
DD
2
AV
DD
2
AV
DD
1
NOTES
1. NC = NO CONNE CT. DO NOT CONNECT TO THIS PIN.
2. THE LFCSP HAS AN EXPO S E D P ADDLE THAT MUST
BE CONNECTED TO GND.
10265-003
5
SW
Fast Lock Switch. Make a connection to this pin from the loop filter when using the fast lock mode.
8
CP
Charge Pump Ground. This is the ground return pin for CP
.
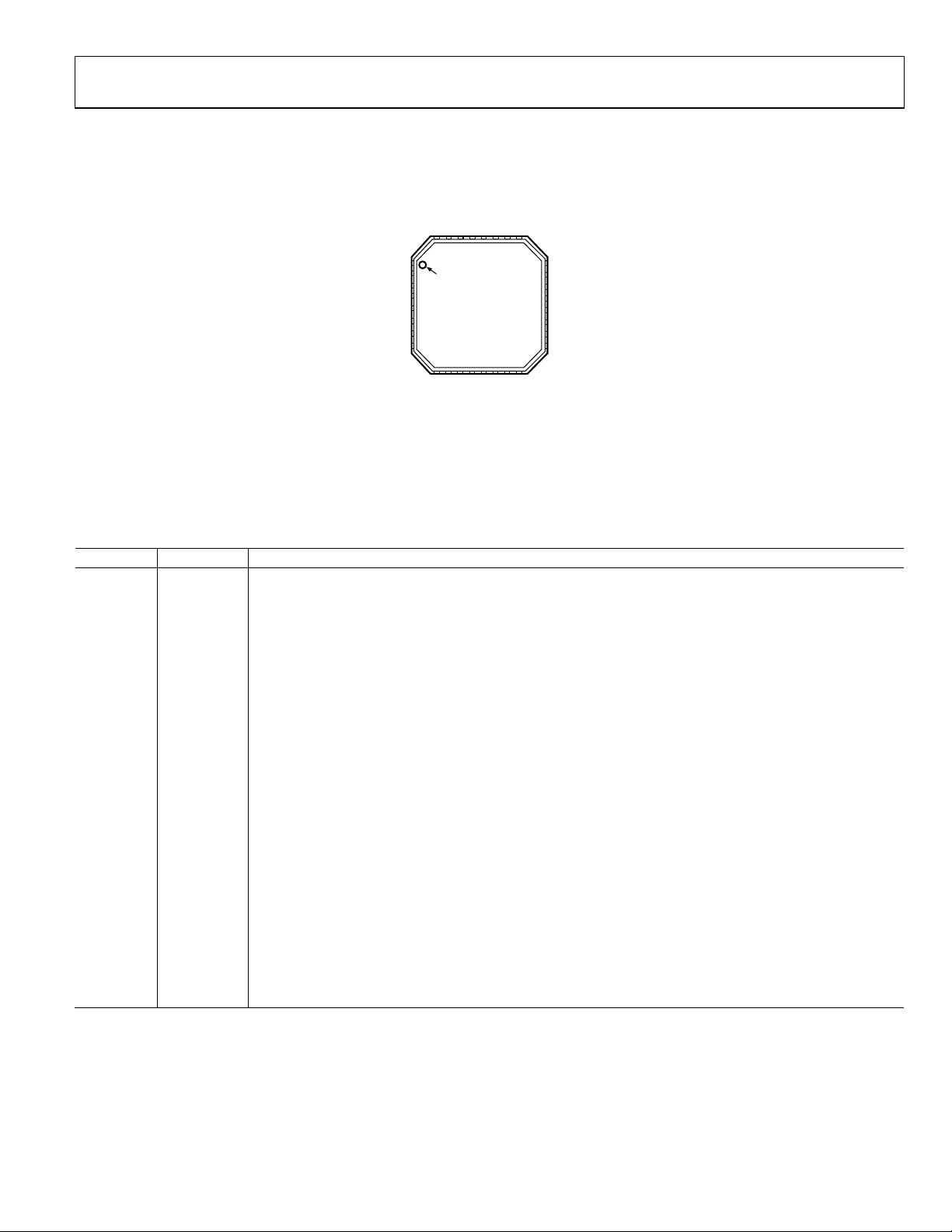
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 CLK Serial Clock Input. Data is clocked into the 32-bit shift register on the CLK rising edge. This input is a high
impedance CMOS input.
2 D ATA Serial Data Input. The serial data is loaded, MSB first, with the three LSBs as the control bits. This input is a high
impedance CMOS input.
3 LE Load Enable, CMOS Input. When LE goes high, the data stored in the shift register is loaded into the register
that is selected by the three LSBs.
4 CE Chip Enable. A logic low on this pin powers down the device and puts the charge pump into three-state
mode. Taking the pin high powers up the device depending on the status of the power-down bits.
6 VP Charge Pump Power Supply. This pin should be greater than or equal to AVDD. In systems where AVDDx is 3 V, it
can be set to 5.5 V and used to drive a VCO with a tuning range of up to 5.5 V.
7 CP
9, 11, 18,
Charge Pump Output. When enabled, this provides ±ICP to the external loop filter. The output of the loop filter
OUT
GND
A
Analog Ground. This is a ground return pin for AVDD1 and AVDD2.
GND
is connected to V
to drive the external VCO.
TUNE
21
10 AVDD1 Analog Power Supply. This pin ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane
12, 13, 19,
are to be placed as close as possible to this pin. AV
NC No connect. Do not connect to this pin.
DD
20, 23, 24
14 RFIN+ Input to the RF Input. This small signal input is ac-coupled to the external VCO.
15 RFIN− Complementary Input to the RF Input. This pin must be decoupled to the ground plane with a small bypass
16, 17 AVDD2 Analog Power Supply. This pin ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane
capacitor, typically 100 pF.
are to be placed as close as possible to this pin. AV
Rev. B | Page 7 of 28
DD
OUT
must have the same value as DVDD.
x must have the same value as DVDD.
ADF4151 Data Sheet
SET
CP
R
I
22.95
=
28
DVDD
Digital Power Supply. This pin should be the same voltage as AVDD. Decoupling capacitors to the ground plane
Multiplexer Output. This multiplexer output allows either the lock detect, the scaled RF, or the scaled reference
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
22 R
25 LD Lock Detect Output Pin. This pin outputs a logic high to indicate PLL lock; a logic low output indicates loss of PLL
26, 27 D
29 REFIN Reference Input. This is a CMOS input with a nominal threshold of VDD/2 and a dc equivalent input resistance
30 MUXOUT
31 SD
32 SDVDD Power Supply Pin for the Digital Σ-Δ Modulator. Should be the same voltage as AVDDx. Decoupling capacitors
EP The exposed pad must be connected to GND.
Connecting a resistor between this pin and GND sets the charge pump output current. The nominal voltage
SET
bias at the R
pin is 0.49 V. The relationship between ICP and R
SET
SET
is
where:
R
= 5.1 kΩ.
SET
= 4.5 mA.
I
CP
lock.
Digital Ground. Ground return path for DVDD.
GND
should be placed as close as possible to this pin.
of 100 kΩ. This input can be driven from a TTL or CMOS crystal oscillator, or it can be ac-coupled.
frequency to be accessed externally.
Digital Sigma-Delta (Σ-Δ) Modulator Ground. Ground return path for the Σ-Δ modulator.
GND
to the ground plane are to be placed as close as possible to this pin.
Rev. B | Page 8 of 28
Data Sheet ADF4151
0
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
POWER (dBm)
FREQUENCY ( GHz)
–40°C
+25°C
+85°C
10265-004
6.0
–6.0
–5.5
–5.0
–4.5
–4.0
–3.5
–3.0
–2.5
–2.0
–1.5
–1.0
–0.5
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 5.04.54.0
I
CP
(mA)
VCP (V)
0.28mA
0.28mA
0.56mA
0.56mA
1.13mA
1.13mA
2.25mA
2.25mA
4.5mA
4.5mA
SOURCE SINK
10265-005
–90
–100
–99
–98
–97
–96
–95
–94
–93
–92
–91
2.60 2.61 2.62 2.63 2.64 2.65 2.66 2.67 2.68 2.702.69
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY ( GHz)
LOW NOISE MODE
LOW SP UR M ODE
10265-006
6.0
–6.0
–5.5
–5.0
–4.5
–4.0
–3.5
–3.0
–2.5
–2.0
–1.5
–1.0
–0.5
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 5.04.54.0
I
CP
MISMATCH ( %)
V
CP
(V)
ICP = 0.28mA
ICP = 0.56mA
ICP = 1.13mA
ICP = 2.25mA
ICP = 4.5mA
10265-007
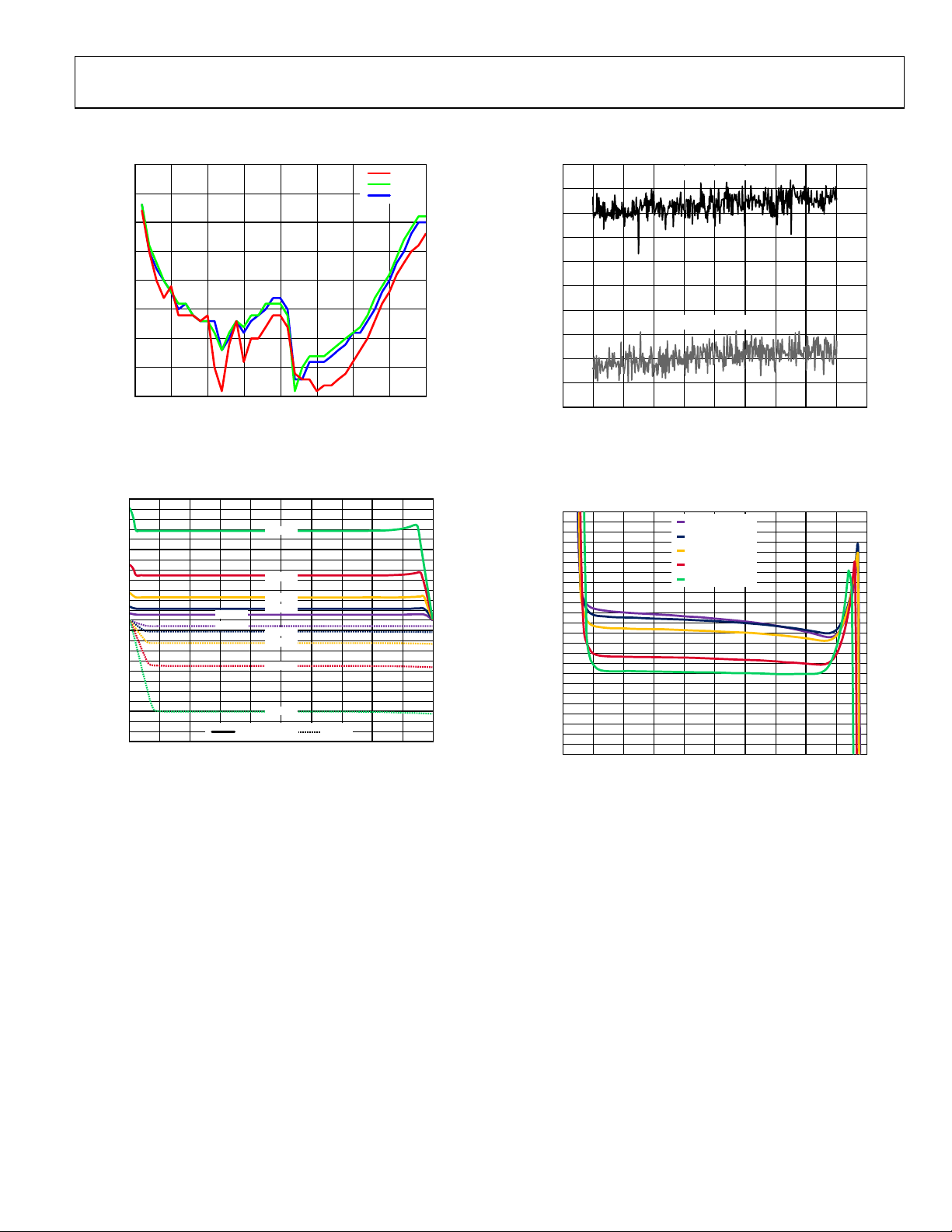
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 4. RF Input Sensitivity
Figure 5. Charge Pump Output Characteristics, VP = 5 V, Selected ICP Values
Between 0.28 mA (Min) and 4.5 mA (Max), R
= 5.1 kΩ
SET
Figure 6. In-Band Phase Noise Measured at 10 kHz Offset
for Low Noise Mode and Low Spur Mode,
PFD = 25 MHz, PLL Loop Bandwidth = 50 kHz
Figure 7. Charge Pump Output Mismatch vs. VCP , Selected ICP Values Between
0.28 mA (Min) and 4.5 mA (Max), R
= 5.1 kΩ
SET
Rev. B | Page 9 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-008
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-009
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-010
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-011
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-012
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
10265-013
Figure 8. Integer-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance;
Low Noise Mode; VCO
= 1750 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz,
OUT
PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter Bandwidth = 50 kHz
Figure 9. Fractional-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance; Low Noise Mode;
VCO
= 1755.2 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz, PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter
OUT
Bandwidth = 50 kHz, Channel Spacing = 200 kHz, FRAC = 26, MOD = 125
Figure 11. Integer-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance;
Low Noise Mode; VCO
= 900 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz,
OUT
PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter Bandwidth = 20 kHz
Figure 12. Fractional-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance; Low Noise Mode;
VCO
= 905.2 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz, PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter
OUT
Bandwidth= 20 kHz, Channel Spacing = 200 kHz, FRAC = 26, MOD = 125
Figure 10. Fractional-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance; Low Spur Mode;
VCO
= 1755.2 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz, PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter
OUT
Bandwidth = 50 kHz, Channel Spacing = 200 kHz, FRAC = 26, MOD = 125
Figure 13. Fractional-N Phase Noise and Spur Performance; Low Spur Mode;
VCO
= 905.2 MHz, REFIN = 100 MHz, PFD = 25 MHz, Loop Filter Bandwidth
OUT
= 20 kHz, Channel Spacing = 200 kHz, FRAC = 26, MOD = 125
Rev. B | Page 10 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
BUFFER
TO R COUNT E R
REF
IN
100kΩ
NC
SW2
SW3
NO
NC
SW1
POWER-DOWN
CONTROL
10265-014
THIRD-ORDER
FRACTIONAL
INTERPOLATOR
FRAC
VALUE
MOD
REG
INT
REG
RF N DIVIDE R
N = INT + F RAC/MOD
FROM
VCO OUTPUT/
OUTPUT DIVIDERS
TO PFD
N COUNTER
10265-015
U3
CLR2
Q2D2
U2
DOWN
UP
HIGH
HIGH
CP
–IN
+IN
CHARGE
PUMP
DELAY
CLR1
Q1D1
U1
10265-016
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
REFERENCE INPUT SECTION
The reference input stage is shown in Figure 14. SW1 and SW2
are normally closed switches. SW3 is normally open. When
power-down is initiated, SW3 is closed and SW1 and SW2 are
opened. This ensures that there is no loading of the REF
on power-down.
IN
pin
Figure 14. Reference Input Stage
RF N DIVIDER
The RF N divider allows a division ratio in the PLL feedback
path. Division ratio is determined by the INT, F RAC , and MOD
values, which build up this divider.
INT, FRAC, MOD, AND R COUNTER RELATIONSHIP
The INT, FRAC, and MOD values, in conjunction with the R
counter, make it possible to generate output frequencies that
are spaced by fractions of the PFD frequency. See the RF
Synthesizer—A Worked Example section for more
information. The RF VCO frequency (RF
RF
= f
OUT
× (INT + (FRAC/MOD)) (1)
PFD
where:
RF
is the output frequency of the external voltage controlled
OUT
oscillator (VCO).
INT is the preset divide ratio of the binary 16-bit counter
(23 to 32,767 for 4/5 prescaler, 75 to 65,535 for 8/9 prescaler).
FRAC is the numerator of the fractional division (0 to MOD − 1).
MOD is the preset fractional modulus (2 to 4095 for low noise
mode, 50 to 4095 for low spur mode).
f
= REFIN × [(1 + D)/(R × (1 + T))] (2)
PFD
where:
REF
is the reference input frequency.
IN
D is the REF
doubler bit.
IN
R is the preset divide ratio of the binary 10–bit programmable
reference counter (1 to 1023).
T is the REF
divide-by-2 bit (0 or 1).
IN
) equation is
OUT
Figure 15. RF INT Divider
INT N MODE
If the FRAC = 0 and DB8 in Register 2 (LDF) is set to 1, the
synthesizer operates in integer-N mode. The DB8 in Register 2
(LDF) should be set to 1 to get integer-N digital lock detect.
Additionally, lower phase noise is possible if the antibacklash
pulse width is reduced to 3 ns. This mode is not valid for
fractional-N applications.
R COUNTER
The 10-bit R counter allows the input reference frequency
(REF
) to be divided down to produce the reference clock
IN
to the PFD. Division ratios from 1 to 1023 are allowed.
PHASE FREQUENCY DETECTOR (PFD) AND CHARGE PUMP
The phase frequency detector (PFD) takes inputs from the R
counter and N counter and produces an output proportional to
the phase and frequency difference between them. Figure 16 is
a simplified schematic of the phase frequency detector. The PFD
includes a programmable delay element that sets the width of
the antibacklash pulse, which can be either 6 ns (default, for
fractional-N applications) or 3 ns (for integer-N mode). This
pulse ensures that there is no dead zone in the PFD transfer
function and gives a consistent reference spur level.
Figure 16. PFD Simplified Schematic
Rev. B | Page 11 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
D
GND
DV
DD
CONTROL
MUX
MUXOUT
ANALOG L OCK DETECT
DIGITAL LOCK DETECT
R COUNTER OUTPUT
N COUNTER OUTPUT
DGND
RESERVED
THREE-STATE-OUTPUT
DV
DD
R COUNTER INP UT
10265-017
MUXOUT AND LOCK DETECT
The output multiplexer on the ADF4151 allows the user
to access various internal points on the chip. The state of
MUXOUT is controlled by M3, M2, and M1 (for details, see
Figure 21). Figure 17 shows the MUXOUT section in block
diagram form.
Figure 17. MUXOUT Schematic
INPUT SHIFT REGISTERS
The ADF4151 digital section includes a 10-bit RF R counter,
a 16-bit RF N counter, a 12-bit FRAC counter, and a 12-bit
modulus counter. Data is clocked into the 32-bit shift register
on each rising edge of CLK. The data is clocked in MSB first.
Data is transferred from the shift register to one of six latches
on the rising edge of LE. The destination latch is determined
by the state of the three control bits (C3, C2, and C1) in the
shift register. There are three LSBs: DB2, DB1, and DB0, as
shown in Figure 2. The truth table for these bits is shown in
Tabl e 5. Figure 18 shows a summary of how the latches are
programmed.
Table 5. C3, C2, and C1 Truth Table
Control Bits
C3 C2 C1 Register
0 0 0 Register 0 (R0)
0 0 1 Register 1 (R1)
0 1 0 Register 2 (R2)
0 1 1 Register 3 (R3)
1 0 0 Register 4 (R4)
1 0 1 Register 5 (R5)
PROGRAM MODES
Figure 19 through Figure 24 show how the program modes are
to be set up in the ADF4151.
A number of settings in the ADF4151 are double buffered.
These include the modulus value, phase value, R counter
value, reference doubler, reference divide-by-2, and current
setting. This means that two events must occur before the
part uses a new value of any of the double-buffered settings.
First, the new value is latched into the device by writing to the
appropriate register. Second, a new write must be performed
on Register R0. For example, any time the modulus value is
updated, Register R0 must be written to, thus ensuring that the
modulus value is loaded correctly.
Rev. B | Page 12 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
DB31
DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0
N16 N15 N14 N13 N12 N11 N10 N9
RESERVED
16-BIT INTEGER VALUE ( INT) 12-BIT F RACTIONAL VALUE ( FRAC)
CONTROL
BITS
N8 N7 N6 N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 F12 F11 F10 F9 F8 F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 C3(0) C2(0) C1(0)
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 PH1 PR1 P12 P11 P10 P9
12-BIT PHASE VALUE (PHASE)
12-BIT MODULUS VALUE ( MOD)
CONTROL
BITS
P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 M12 M11 M10 M9 M8 M7 M6 M5 M4 M3 M2 M1 C3(0) C2(0) C1(1)
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 L2 L1 M3 M2 M1 RD2 RD1 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 0 CP4 CP3 CP2 CP1 U6 U5 U4 U3 U2 U1 C3(0) C2(1) C1(0)
CSR
RDIV2
REFERENCE
DOUBLER
CHARGE
PUMP
CURRENT
SETTING
10-BIT R COUNTER
CONTROL
BITS
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F3 F2 0 0 F1 0 C2 C1 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 C3(0) C2(1) C1(1)
CONTROL
BITS
12-BIT CL OCK DIVIDER VALUE
LDP
PD
POLARITY
POWER-DOWN
CP THREE-
STATE
COUNTER
RESET
CLK
DIV
MODE
DBR
1
1
DBR = DOUBLE BUF FERED REGIS TER—BUFFERE D BY THE WRIT E TO REGIS TER 0.
RESERVED
LDF
RESERVED
ABP
CHARGE
CANCEL
RESERVED
REGISTER 4
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C3(1) C2(0) C1(0)
CONTROL
BITS
RESERVED
LD PIN
MODE
REGISTER 0
REGISTER 1
REGISTER 2
REGISTER 3
REGISTER 5
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 D15 D14 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C3(1) C2(0) C1(1)
CONTROL
BITS
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
DBR
1
DBR
1
DBR
1
DBR
1
DBR
1
RESERVED
PRESCALER
LOW
NOISE AND
LOW SPUR
MODES
MUXOUT
PHASE ADJUST
RESERVED
10265-018
REGISTER MAPS
Figure 18. Register Summary
Rev. B | Page 13 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
N16 N15 ... N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 INTEGER VALUE (I NT )
0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 NOT ALLOWED
0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 1 NOT ALLOWED
0 0 ... 0 0 0 1 0 NOT ALLOWED
. . ... . . . . . ...
0 0 ... 1 0 1 1 0 NOT ALLOWED
0 0 ... 1 0 1 1 1 23
0 0 ... 1 1 0 0 0 24
. . ... . . . . . ...
1 1 ... 1 1 1 0 1 65533
1 1 ... 1 1 1 1 0 65534
1 1 ... 1 1 1 1 1 65535
F12 F11 .......... F2 F1 FRACTIONAL VALUE ( FRAC)
0 0 .......... 0 0 0
0 0 .......... 0 1 1
0 0 .......... 1 0 2
0 0 .......... 1 1 3
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
1 1 .......... 0 0 4092
1 1 .......... 0 1 4093
1 1 .......... 1 0 4094
1 1 ......... 1 1 4095
DB31
DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0
N16 N15 N14 N13 N12 N11 N10 N9
RESERVED
16-BIT INTEGER VALUE ( INT) 12-BIT F RACTIONAL VALUE (F RAC)
CONTROL
BITS
N8 N7 N6 N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 F12 F11 F10 F9 F8 F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 C3(0) C2(0) C1(0)
INTmin = 75 WITH PRES CALER = 8/9
10265-019
P12 P11 .......... P2 P1 PHASE VALUE (PHASE)
0 0 .......... 0 0 0
0 0 .......... 0 1 1 (RE COMMENDED)
0 0 .......... 1 0 2
0 0 .......... 1 1 3
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
1 1 .......... 0 0 4092
1 1 .......... 0 1 4093
1 1 .......... 1 0 4094
1 1 .......... 1 1 4095
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 PH1 PR1 P12 P11 P10 P9
12-BIT PHASE VALUE (PHASE) 12-BIT MODULUS VALUE (MOD)
CONTROL
BITS
P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 M12 M11 M10 M9 M8 M7 M6 M5 M4 M3 M2 M1 C3(0) C2(0) C1(1)
RESERVED
M12 M11 ..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
M2 M1 INTERPO LAT OR MODULUS ( MOD)
0 0 1 0 2
0 0 1 1 3
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
1 1 0 0 4092
1 1 0 1 4093
1 1 1 0 4094
1 1 1 1 4095
PRESCALER
PHASE ADJUST
P1 PRESCALER
0 4/5
1 8/9
PH1 PHASE ADJUST
0 OFF
1 ON
DBR DBR
10265-020
Figure 19. Register 0 (R0)
Figure 20. Register 1 (R1)
Rev. B | Page 14 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
RD2
REFERENCE
DOUBLER
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
RD1 REF ERENCE DIVIDE BY 2
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
CP4 CP3 CP2 CP1
ICP (mA)
5.1kΩ
0 0 0 0 0.28
0 0 0 1 0.56
0 0 1 0 0.84
0 0 1 1 1.13
0 1 0 0 1.41
0 1 0 1 1.69
0 1 1 0 1.97
0 1 1 1 2.25
1 0 0 0 2.53
1 0 0 1 2.81
1 0 1 0 3.09
1 0 1 1 3.38
1 1 0 0 3.66
1 1 0 1 3.94
1 1 1 0 4.22
1 1 1 1 4.5
R10 R9 ..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
R2 R1 R DIVIDER (R)
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 2
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
1 1 0 0 1020
1 1 0 1 1021
1 1 1 0 1022
1 1 1 1 1023
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 L2 L1 M3 M2 M1 RD2 RD1 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 0 CP4 CP3 CP2 CP1 U6 U5 U4 U3 U2 U1 C3(0) C2(1) C1(0)
RDIV2 DBR
REFERENCE
DOUBLER DBR
CHARGE
PUMP
CURRENT
SETTING
10-BIT R COUNTER DBR
CONTROL
BITS
LDP
PD
POLARITY
POWER-DOWN
CP THREE-
STATE
COUNTER
RESET
LDF
MUXOUT
RESERVED
U5 LDP
0 10ns
1 6ns
U4 PD POLARIT Y
0 NEGATIVE
1 POSITIVE
U3 POWER-DOWN
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
U2
CP
THREE-STATE
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
U1
COUNTER
RESET
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
U6 LDF
0 FRAC-N
1 INT-N
RESERVED
M3 M2 M1 OUTPUT
0 0 0 THREE-STATE OUTPUT
0 0 1 DV
DD
0 1 0 DGND
0 1 1 R DIVIDER OUTPUT
1 0 0 N DIVIDER OUTPUT
1 0 1 ANALOG LOCK DET ECT
1 1 0 DIGITAL LOCK DETECT
1 1 1 RESERVED
L1 L2 NOISE MODE
0 0 LOW NOISE MODE
0 1 RESERVED
1 0 RESERVED
1 1 LOW SPUR MODE
LOW
NOISE AND
LOW SPUR
MODES
10265-021
Figure 21. Register 2 (R2)
Rev. B | Page 15 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
C2 C1 CLOCK DIVIDER MODE
0 0 CLOCK DIVI DER OFF
0 1 FAST LOCK ENABLE
1 0 RESYNC ENABLE
1 1 RESERVED
D12 D11 .......... D2 D1 CL OCK DIVIDER VALUE
0 0 .......... 0 0 0
0 0 .......... 0 1 1
0 0 .......... 1 0 2
0 0 .......... 1 1 3
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
. . .......... . . .
1 1 .......... 0 0 4092
1 1 .......... 0 1 4093
1 1 .......... 1 0 4094
1 1 .......... 1 1 4095
CSR
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F1 0 C2 C1 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 C3(0) C2(1) C1(1)
CONTROL
BITS12-BIT CL OCK DIVIDER VALUE
CLK
DIV
MODE
RESERVED
F1
CYCLE SLIP
REDUCTION
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
RESERVED
0
0
RESERVED
F3 F2
F2
CHARGE
CANCELLATION
0 DISABLED
1 ENABLED
F3
ANTIBACKLASH
PULSE WIDTH
0 6ns (FRAC-N)
1 3ns (INT_N)
CHARGE
CANCEL
ABP
10265-022
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C3(1) C2(0) C1(0)
CONTROL
BITS
RESERVED
10265-023
LD PIN
MODE
DB31 DB30 DB29 DB28 DB27 DB26 DB25 DB24 DB23 DB22 DB21 DB20 DB19 DB18 DB17 DB16 DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 D15 D14 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C3(1) C2(0) C1(1)
CONTROL
BITSRESERVEDRESERVED
D15 D1 4 LO CK DETECT PIN OPERATION
0 0 LOW
0 1 DIGIT AL L OCK DETECT
1 0 LOW
1 1 HIGH
10265-024
Figure 22. Register 3 (R3)
Figure 23. Register 4 (R4)
Figure 24. Register 5 (R5)
Rev. B | Page 16 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
REGISTER 0
Control Bits
With Bits[C3:C1] set to 0, 0, 0, Register 0 is programmed.
Figure 19 shows the input data format for programming this
register.
16-Bit Integer Value (INT)
These 16 bits set the INT value, which determines the integer
part of the feedback division factor. They are used in Equation 1
(see the INT, FRAC, MOD, and R Counter Relationship
section). All integer values from 23 to 32,767 are allowed for 4/5
prescaler. For 8/9 prescaler, the minimum integer value is 75, and
the maximum value is 65,535.
12-Bit Fractional Value (FRAC)
The 12 FRAC bits set the numerator of the fraction that is input
to the Σ-Δ modulator. This, along with INT, specifies the new
frequency channel that the synthesizer locks to, as shown in the
RF Synthesizer—A Worked Example section. FRAC values from
0 to MOD − 1 cover channels over a frequency range equal to
the PFD reference frequency.
REGISTER 1
Control Bits
With Bits[C3:C1] set to 0, 0, 1, Register 1 is programmed.
Figure 20 shows the input data format for programming
this register.
Phase Adjust
The phase adjust bit, enabled by programming a 1 to DB28,
permits adjustments to the output phase of a given output
frequency. If enabled, it does not perform a phase resync
function on updating R0. If set to 0, the phase resync (if
enabled in R3, Bits[DB16:DB15]) occurs on every update
of R0.
Prescaler Value
The dual modulus prescaler (P/P + 1), along with the INT,
FRAC, and MOD counters, determines the overall division
ratio from the VCO output to the PFD input.
Operating at CML levels, it takes the clock from the VCO
output and divides it down for the counters. It is based on a
synchronous 4/5 core. When set to 4/5, the maximum RF
frequency allowed is 3 GHz. Therefore, when operating the
ADF4151 above 3 GHz, this must be set to 8/9. The prescaler
limits the INT value, where:
P = 4/5, N
P = 8/9, N
In the ADF4151, PR1 in Register 1 sets the prescaler values.
MIN
MIN
= 23
= 75
12-Bit Phase Value (PHASE)
These bits control what is loaded as the phase word. The word
must be less than the MOD value programmed in Register 1.
The word is used to program the RF output phase from 0° to
360° with a resolution of 360°/MOD. See the Phase Resync
section for more information. In most applications, the phase
relationship between the RF signal and the reference is not
important. In such applications, the phase value can be used to
optimize the fractional and subfractional spur levels. See the
Spur Consistency and Fractional Spur Optimization section for
more information.
If neither the phase resync nor the spurious optimization
functions are being used, it is recommended that the phase
word be set to 1.
12-Bit Modulus Value (MOD)
This programmable register sets the fractional modulus. This
is the ratio of the PFD frequency to the channel step resolution
on the RF output. See the RF Synthesizer—A Worked Example
section for more information.
REGISTER 2
Control Bits
With Bits[C3:C1] set to 0, 1, 0, Register 2 is programmed.
Figure 21 shows the input data format for programming
this register.
Low Noise and Spur Modes
The noise modes on the ADF4151 are controlled by DB30 and
DB29 in Register 2 (see Figure 21). The noise modes allow the
user to optimize a design either for improved spurious performance or for improved phase noise performance.
When the lowest spur setting is chosen, dither is enabled. This
randomizes the fractional quantization noise so it resembles
white noise rather than spurious noise. As a result, the part is
optimized for improved spurious performance. This operation
would normally be used when the PLL closed-loop bandwidth
is wide, for fast locking applications. (Wide-loop bandwidth is
seen as a loop bandwidth greater than 1/10 of the RF
step resolution (f
)). A wide loop filter does not attenuate the
RES
spurs to the same level as a narrow-loop bandwidth.
For best noise performance, use the lowest noise setting option.
As well as disabling the dither, it also ensures that the charge
pump is operating in an optimum region for noise performance.
This setting is extremely useful where a narrow-loop filter
bandwidth is available. The synthesizer ensures extremely low
noise, and the filter attenuates the spurs. The typical performance
characteristics give the user an idea of the trade-off in a typical
W-CDMA setup for the different noise and spur settings.
channel
OUT
Rev. B | Page 17 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
MUXOUT
The on-chip multiplexer is controlled by Bits[DB28:DB26] (see
Figure 21).
Reference Doubler
Setting DB25 to 0 feeds the REFIN signal directly to the 10-bit
R counter, disabling the doubler. Setting this bit to 1 multiplies
the REF
10-bit R counter. When the doubler is disabled, the REF
frequency by a factor of 2 before feeding into the
IN
IN
falling edge is the active edge at the PFD input to the fractional
synthesizer. When the doubler is enabled, both the rising and
falling edges of REF
become active edges at the PFD input.
IN
When the doubler is enabled and the lowest spur mode is
chosen, the in-band phase noise performance is sensitive to the
REF
duty cycle. The phase noise degradation can be as much
IN
as 5 dB for the REF
duty cycles outside a 45% to 55% range.
IN
The phase noise is insensitive to the REFIN duty cycle in the
lowest noise mode. The phase noise is insensitive to the REF
IN
duty cycle when the doubler is disabled.
When the doubler is enabled, the maximum allowable REF
IN
frequency is 30 MHz.
RDIV2
Setting the DB24 bit to 1 inserts a divide-by-2 toggle flip-flop
between the R counter and PFD, which extends the maximum
REFIN input rate. This function allows a 50% duty cycle signal
to appear at the PFD input, which is necessary for cycle slip
reduction.
10-Bit R Counter
The 10-bit R counter allows the input reference frequency
(REF
) to be divided down to produce the reference clock to
IN
the PFD. Division ratios from 1 to 1023 are allowed.
Current Setting
Bits[DB12:DB9] set the charge pump current setting. This
should be set to the charge pump current that the loop filter
is designed with (see Figure 21).
LDF
Setting DB8 to 1 enables integer-N digital lock detect, when
the FRAC part of the divider is zero; setting DB8 to 0 enables
fractional-N digital lock detect.
Lock Detect Precision (LDP)
When DB7 is set to 0, the fractional-N digital lock detect is
activated. In this case after setting DB7 to 0, 40 consecutive PFD
cycles of 10 ns must occur before digital lock detect is set. When
DB7 is programmed to 1, 40 consecutive reference cycles of 6 ns
must occur before digital lock detect goes high. Setting DB8
(LDF) to 1 causes the activation of the integer-N digital lock
detect. In this case, after setting DB7 (LDP) to 0, five
consecutive cycles of 10 ns must occur before digital lock detect
is set. When DB7 is set to 1, five consecutive cycles of 6 ns must
occ u r. Recommended settings of both the LDP and LDF bits are
shown in Tab l e 6.
Table 6. Recommended LDF/LDP Bit Settings
DB8
Mode
Integer-N 1 1
Fractional-N Low Noise Mode 0 1
Fractional-N Low Spur Mode 0 0
(LDF)
DB7
(LDP)
Phase Detector Polarity
DB6 sets the phase detector polarity. When a passive loop filter
or noninverting active loop filter is used, set this bit to 1. If an
active filter with an inverting characteristic is used, this bit
should be set to 0.
Power-Down (PD)
DB5 provides the programmable power-down mode. Setting this
bit to 1 performs a power-down. Setting this bit to 0 returns the
synthesizer to normal operation. When in software power-down
mode, the part retains all information in its registers. Only if the
supply voltages are removed are the register contents lost.
When a power-down is activated, the following events occur:
• The synthesizer counters are forced to their load state
conditions.
• The charge pump is forced into three-state mode.
• The digital lock detect circuitry is reset.
• The RF
buffers are disabled.
OUT
• The input register remains active and capable of loading
and latching data.
Charge Pump (CP) Three-State
DB4 puts the charge pump into three-state mode when
programmed to 1. It should be set to 0 for normal operation.
Counter Reset
DB3 is the R counter and N counter reset bit for the ADF4151.
When this bit is 1, the RF synthesizer N counter and R counter
are held in reset. For normal operation, this bit should be set to 0.
Rev. B | Page 18 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
REGISTER 3
Control Bits
With Bits[C3:C1] set to 0, 1, 1, Register 3 is programmed.
Figure 22 shows the input data format for programming
this register.
Antibacklash Pulse Width
Setting DB22 to 0 sets the PFD antibacklash pulse width to 6 ns.
This is the recommended mode for fractional-N use. By setting
this bit to 1, the 3 ns pulse width is used and results in a phase
noise and spur improvement in integer-N operation. For
fractional-N mode it is not recommended to use this smaller
setting.
Charge Cancellation Mode Pulse Width
Setting DB21 to 1 enables charge pump charge cancellation.
This has the effect of reducing PFD spurs in integer-N mode.
In fractional-N mode, this bit should not be used. This results
in a phase noise and fractional spur improvement.
Cycle Slip Reduction (CSR) Enable
Setting DB18 to 1 enables cycle slip reduction. This is a method
for improving lock times. Note that the signal at the phase frequency detector (PFD) must have a 50% duty cycle for cycle slip
reduction to work. The charge pump current setting must also
be set to a minimum. See the Cycle Slip Reduction for Faster
Lock Times section for more information.
Clock Divider Mode
Bits[DB16:DB15] must be set to 1, 0 to activate phase resync or
0, 1 to activate fast lock. Setting Bits[DB16:DB15] to 0, 0
disables the clock divider. See Figure 22.
12-Bit Clock Divider Value
The 12-bit clock divider value sets the timeout counter for
activation of phase resync. See the Phase Resync section for
more information. It also sets the timeout counter for fast lock.
See the Fast Lock Timer and Register Sequences section for
more information.
REGISTER 4
Control Bits
With Bits[C3: C1] set to 1, 0, 0, Register 4 is programmed.
Figure 23 shows the input data format for programming this
register.
This register is reserved and has to be programmed with the
values as shown in Figure 23. Bits[DB31:DB24] and [DB22:DB3]
must be programmed to 0, while Bit DB23 must be set to 1.
REGISTER 5
Control Bits
With Bits[C3:C1] set to 1, 0, 1, Register 5 is programmed.
Figure 24 shows the input data form for programming this
register.
Lock Detect PIN Operation
Bits[DB23:DB22] set the operation of the lock detect pin (see
Figure 24).
INITIALIZATION SEQUENCE
The following sequence of registers is the correct sequence for
initial power up of the ADF4151 after the correct application
of voltages to the supply pins:
1. Register 5
2. Register 4
3. Register 3
4. Register 2
5. Register 1
6. Register 0
Rev. B | Page 19 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
f
PFD
PFD VCO
N
DIVIDER
RF
OUT
10265-025
RF SYNTHESIZER—A WORKED EXAMPLE
The following is an example of how to program the ADF4151
synthesizer:
RF
= [INT + (FRAC/MOD)] × [f
OUT
where:
RF
is the RF frequency output.
OUT
INT is the integer division factor.
FRAC is the fractionality.
MOD is the modulus.
RF Divider is the output divider that divides down the VCO
frequ e nc y.
f
= REFIN × [(1 + D)/(R × (1 + T))] (4)
PFD
where:
REF
is the reference frequency input.
IN
D is the RF REF
doubler bit.
IN
R is the RF reference division factor.
T is the reference divide-by-2 bit (0 or 1).
For example, in a UMTS system, where 2112.6 MHz RF
frequency output (RF
frequency input (REF
resolution (f
RESOUT
) is required, a 10 MHz reference
OUT
) is available, and a 200 kHz channel
IN
) is required on the RF output. A 2.1 GHz
VCO is suitable to cover the required fractional frequency of
2112.6 MHz.
Figure 25. Loop Closed Before Output Divider
A channel resolution (f
) of 200 kHz is required at the output
RES
of the VC O.
MOD = REF
IN/fRES
MOD = 10 MHz/200 kHz = 50
From Equation 4
= [10 MHz × (1 + 0)/1] = 10 MHz (5)
f
PFD
2112.6 MHz = 10 MHz × (INT + FRAC/50) (6)
where:
INT = 211
FRAC = 13
]/RF Divider (3)
PFD
MODULUS
The choice of modulus (MOD) depends on the reference signal
(REF
) available and the channel resolution (f
IN
the RF output. For example, a GSM system with 13 MHz REF
) required at
RES
IN
sets the modulus to 65. This means that the RF output resolution
(f
) is the 200 kHz (13 MHz/65) necessary for GSM. With dither
RES
off, the fractional spur interval depends on the modulus values
chosen (see Tabl e 7).
REFERENCE DOUBLER AND REFERENCE DIVIDER
The reference doubler on chip allows the input reference signal
to be doubled. This is useful for increasing the PFD comparison
frequency. Making the PFD frequency higher improves the
noise performance of the system. Doubling the PFD frequency
usually improves noise performance by 3 dB. It is important
to note that the PFD cannot operate above maximum value (see
Tabl e 1) due to a limitation in the speed of the Σ-Δ circuit of the
N-divider.
The reference divide-by-2 divides the reference signal by 2,
resulting in a 50% duty cycle PFD frequency. This is necessary
for the correct operation of the cycle slip reduction (CSR)
function. See the Cycle Slip Reduction for Faster Lock Times
section for more information.
12-BIT PROGRAMMABLE MODULUS
Unlike most other fractional-N PLLs, the ADF4151 allows the
user to program the modulus over a 12-bit range. This means
that the user can set up the part in many different configurations
for the application, when combined with the reference doubler
and the 10-bit R counter.
For example, consider an application that requires 1.75 GHz RF
and 200 kHz channel step resolution. The system has a 13 MHz
reference signal.
One possible setup is feeding the 13 MHz directly to the PFD
and programming the modulus to divide by 65. This results in
the required 200 kHz resolution.
Another possible setup is using the reference doubler to create
26 MHz from the 13 MHz input signal. The 26 MHz is then fed
into the PFD, programming the modulus to divide by 130. This
also results in 200 kHz resolution and offers superior phase
noise performance over the previous setup.
The programmable modulus is also very useful for multistandard applications. If a dual-mode phone requires PDC
and GSM 1800 standards, the programmable modulus is a
great benefit. PDC requires 25 kHz channel step resolution,
whereas GSM 1800 requires 200 kHz channel step resolution.
Rev. B | Page 20 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
A 13 MHz reference signal can be fed directly to the PFD, and
the modulus can be programmed to 520 when in PDC mode
(13 MHz/520 = 25 kHz).
The modulus needs to be reprogrammed to 65 for GSM 1800
operation (13 MHz/65 = 200 kHz).
It is important that the PFD frequency remain constant (13 MHz).
This allows the user to design one loop filter for both setups
without running into stability issues. It is important to remember that the ratio of the RF frequency to the PFD frequency
principally affects the loop filter design, not the actual channel
spacing.
CYCLE SLIP REDUCTION FOR FASTER LOCK TIMES
As outlined in the Low Noise and Spur Mode section, the
ADF4151 contains a number of features that allow optimization
for noise performance. However, in fast locking applications,
the loop bandwidth generally needs to be wide, and, therefore,
the filter does not provide much attenuation of the spurs. If
the cycle slip reduction feature is enabled, the narrow-loop
bandwidth is maintained for spur attenuation but faster lock
times are still possible.
Cycle Slips
Cycle slips occur in integer-N/fractional-N synthesizers when
the loop bandwidth is narrow compared to the PFD frequency.
The phase error at the PFD inputs accumulates too fast for the
PLL to correct, and the charge pump temporarily pumps in the
wrong direction. This slows down the lock time dramatically.
The ADF4151 contains a cycle slip reduction feature that
extends the linear range of the PFD, allowing faster lock
times without modifications to the loop filter circuitry.
When the circuitry detects that a cycle slip is about to occur,
it turns on an extra charge pump current cell. This outputs a
constant current to the loop filter or removes a constant
current from the loop filter (depending on whether the VCO
tuning voltage needs to increase or decrease to acquire the
new frequency). The effect is that the linear range of the PFD
is increased. Loop stability is maintained because the current
is constant and is not a pulsed current.
If the phase error increases again to a point where another cycle
slip is likely, the ADF4151 turns on another charge pump cell.
This continues until the ADF4151 detects that the VCO
frequency has gone past the desired frequency. The extra charge
pump cells are turned off one by one until all the extra charge
pump cells have been disabled and the frequency is settled with
the original loop filter bandwidth.
Up to seven extra charge pump cells can be turned on. In most
applications, it is enough to eliminate cycle slips altogether,
giving much faster lock times.
Setting Bit DB18 in the Register 3 to 1 enables cycle slip
reduction. Note that the PFD requires a 45% to 55% duty
cycle for CSR to operate correctly.
SPURIOUS OPTIMIZATION AND FAST LOCK
Narrow-loop bandwidths can filter unwanted spurious signals,
but these usually have a long lock time. A wider loop bandwidth
achieves faster lock times, but a wider loop bandwidth may lead
to increased spurious signals inside the loop bandwidth.
The fast lock feature can achieve the same fast lock time as the
wider bandwidth, but with the advantage of a narrow final loop
bandwidth to keep spurs low.
FAST LOCK TIMER AND REGISTER SEQUENCES
If the fast lock mode is used, a timer value must be loaded into
the PLL to determine the duration of the wide bandwidth mode.
When Bits[DB16:DB15] in Register 3 are set to 0, 1 (fast
lock enable), the timer value is loaded by the 12-bit clock
divider value. The following sequence must be programmed
to use fast lock:
1. Initialization sequence (see the Initialization Sequence
section); occurs only once after powering up the part.
2. Load Register 3 by setting Bits[DB16:DB15] to 0, 1 and
the chosen fast lock timer value, Bits[DB14:DB3]. Note that
the length of time the PLL remains in wide bandwidth is
equal to the fast lock timer/f
PFD
.
Rev. B | Page 21 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
ADF4151
CP
OUT
SW
C1
C2
R2
R1
R1A
C3
VCO
10265-026
ADF4151
CP
OUT
SW
C1
C2
R2
R1R1A
C3
VCO
10265-027
If MOD is divisible by 2, but not 3
2 × MOD
Channel step/2
If MOD is divisible by 3, but not 2
3 × MOD
Channel step/3
FAST LOCK—AN EXAMPLE
If a PLL has a reference frequency of 13 MHz, a f
and a required lock time of 50 µs, the PLL is set to wide bandwidth
for 40 µs. This example assumes a modulus of 65 for channel
spacing of 200 kHz.
If the time period set for the wide bandwidth is 40 µs, then
Fast Lock Timer Value = Time In Wide Bandwidth × f
Fast Lock Timer Value = 40 µs × 13 MHz/65 = 8
Therefore, 8 must be loaded into the clock divider value in
Register 3 in Step 1 of the sequence described in the Fast Lock
Timer and Register Sequences section.
of 13 MHz
PFD
PFD
/MOD
FAST LOCK—LOOP FILTER TOPOLOGY
To use fast lock mode, the damping resistor in the loop filter
is reduced to ¼ of its value while in wide bandwidth mode. To
achieve the wider loop filter bandwidth, the charge pump
current increases by a factor of 16. To maintain loop stability,
the damping resistor must be reduced a factor of ¼. To enable
fast lock, the SW pin is shorted to the GND pin by setting
Bits[DB16:DB15] in Register 3 to values 0, 1. The following two
topologies are available:
• The damping resistor (R1) is divided into two values (R1
and R1A) that have a ratio of 1:3 (see Figure 26).
• An extra resistor (R1A) is connected directly from SW,
as shown in Figure 27. The extra resistor is calculated
such that the parallel combination of an extra resistor
and the damping resistor (R1) is reduced to ¼ of the
original value of R1 (see Figure 27).
Figure 26. Fast Lock Loop Filter Topology—Topology 1
SPUR MECHANISMS
This section describes the three different spur mechanisms that
arise with a fractional-N synthesizer and how to minimize them
in the ADF4151.
Fractional Spurs
The fractional interpolator in the ADF4151 is a third-order Σ-Δ
modulator (SDM) with a modulus (MOD) that is programmable
to any integer value from 2 to 4095. In low spur mode (dither
enabled), the minimum allowable value of MOD is 50. The
SDM is clocked at the PFD reference rate (f
output frequencies to be synthesized at a channel step resolution
of f
/MOD.
PFD
In low noise mode (dither off ), the quantization noise from the
Σ-Δ modulator appears as fractional spurs. The interval between
spurs is f
/L, where L is the repeat length of the code sequence
PFD
in the digital Σ-Δ modulator. For the third-order modulator
used in the ADF4151, the repeat length depends on the value
of MOD, as listed in Table 7.
Table 7. Fractional Spurs with Dither Off
Repeat
Condition (Dither Off)
Length Spur Interval
If MOD is divisible by 6 6 × MOD Channel step/6
Otherwise MOD Channel step
In low spur mode (dither on), the repeat length is extended to
21
2
cycles, regardless of the value of MOD, which makes the
quantization error spectrum look like broadband noise. This
may degrade the in-band phase noise at the PLL output by as
much as 10 dB. For lowest noise, dither off is a better choice,
particularly when the final loop bandwidth is low enough to
attenuate even the lowest frequency fractional spur.
Integer Boundary Spurs
Another mechanism for fractional spur creation is the interactions
between the RF VCO frequency and the reference frequency.
When these frequencies are not integer related (the point of a
fractional-N synthesizer) spur sidebands appear on the VCO
output spectrum at an offset frequency that corresponds to the
beat note or difference frequency between an integer multiple of
the reference and the VCO frequency. These spurs are attenuated
by the loop filter and are more noticeable on channels close to
integer multiples of the reference where the difference frequency
can be inside the loop bandwidth; therefore, the name integer
boundary spurs.
) that allows PLL
PFD
Figure 27. Fast Lock Loop Filter Topology—Topology 2
Rev. B | Page 22 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
10265-028
LE
PHASE
FREQUENCY
SYNC
(INTERNAL)
–100 0 100 200 1000
300 400 500 600 700 800 900
TIME (µs)
PLL SETTLES TO
CORRECT PHASE
AFTER RESYNC
t
SYNC
LAST CYCLE SLIP
PLL SETTLES TO
INCORRECT PHASE
Reference Spurs
Reference spurs are generally not a problem in fractional-N
synthesizers because the reference offset is far outside the loop
bandwidth. However, any reference feedthrough mechanism
that bypasses the loop can cause a problem. Feedthrough of low
levels of on-chip reference switching noise, through the RF
IN
pin back to the VCO, can result in reference spur levels as high
as −90 dBc. PCB layout must ensure adequate isolation between
VCO traces and the input reference to avoid a possible
feedthrough path on the board.
SPUR CONSISTENCY AND FRACTIONAL SPUR OPTIMIZATION
With dither off, the fractional spur pattern due to the quantization noise of the SDM also depends on the particular phase
word with which the modulator is seeded.
The phase word can be varied to optimize the fractional and
subfractional spur levels on any particular frequency. Thus, a
look-up table of phase values corresponding to each frequency
can be constructed for use when programming the ADF4151.
If a look-up table is not used, keep the phase word at a constant
value to ensure consistent spur levels on any particular frequency.
PHASE RESYNC
The output of a fractional-N PLL can settle to any one of the
MOD phase offsets with respect to the input reference, where
MOD is the fractional modulus. The phase resync feature in the
ADF4151 produces a consistent output phase offset with respect
to the input reference. This is necessary in applications where the
output phase and frequency are important, such as digital beam
forming. See the Phase Programmability section for how to
program a specific RF output phase when using phase resync.
Phase resync is enabled by setting Bit DB16, Bit DB15 in
Register 3 to 1, 0. When phase resync is enabled, an internal
timer generates sync signals at intervals of t
given by the
SYNC
following formula:
t
= CLK_DIV_VALUE × MOD × t
SYNC
PFD
where:
CLK_DIV_VALUE is the decimal value programmed in
Bits[DB14:DB3] of Register 3 and can be any integer in the
range of 1 to 4095.
MOD is the modulus value programmed in Bits[DB14:DB3] of
Register 1 (R1).
t
is the PFD reference period.
PFD
When a new frequency is programmed, the second sync pulse
after the LE rising edge is used to resynchronize the output
phase to the reference. The t
time must be programmed to
SYNC
a value that is at least as long as the worst-case lock time. This
guarantees that the phase resync occurs after the last cycle slip
in the PLL settling transient.
In the example shown in Figure 28, the PFD reference is
25 MHz and MOD is 125 for a 200 kHz channel spacing. t
SYNC
is set to 400 µs by programming the clock divider value,
CLK_DIV_VALUE, to 80.
Figure 28. Phase Resync Example
Phase Programmability
The phase word in Register 1 controls the RF output phase. As
this word is swept from 0 to MOD, the RF output phase sweeps
over a 360° range in steps of 360°/MOD.
Rev. B | Page 23 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
10265-029
AD9788
TxDAC
REFIO
FSADJ
OUT2_N
OUT1_P
OUT1_N
OUT2_P
2kΩ
LOW-PASS
FILTER
LOW-PASS
FILTER
2700pF 1200pF
39nF
680Ω
360Ω
IBBP
IBBN
QBBP
QBBN
LOIP
LOIN
SPI-CO M P ATIBLE SERIAL BUS
ADF4151
CP
GND
A
GND
A
GND
SD
GND
1nF1nF
4.7kΩ
R
SET
LE
DATA
CLK
REF
IN
FREF
IN
CP
OUT
AV
DD
2 AV
DD
2 CE MUXOUT
V
CC
VCO
OUT
VCO
V
TUNE
1716
AV
DD
1
10
29
1
2
3
22
8 11 18 31
V
DD
LOCK
DETECT
51Ω
51Ω51Ω
51Ω51Ω
25
30
LD
7
D
VDD
28
32
6
SDV
DD
V
P
5
SW
4
ADL5375
RFOUT
QUADRATURE
PHASE
SPLITTER
DSOP
RF
IN–
RF
IN+
15
14
1nF
1nF
100pF
100pF
V
VCO
18Ω
100pF
18Ω
18Ω
MODULATED
DIGITAL
DATA
V
P
9
A
GND
A
GND
21
D
GND
27
D
GND
26
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
DIRECT CONVERSION MODULATOR
Direct conversion architectures are increasingly being used to
implement base station transmitters. Figure 29 shows how Analog
Devices, Inc., parts can be used to implement such a system.
The circuit block diagram shows the AD9788 TxDAC® being
used with the ADL5375. The use of dual integrated DACs, such
as the AD9788 with its specified ±0.02 dB and ±0.004 dB gain
and offset matching characteristics, ensures minimum error
contribution (over temperature) from this portion of the
signal chain. The signal for the I channel of the quadrature
modulator is taken from the OUT1 differential outputs of the
AD9788, and the OUT2 differential outputs provide the signal
for the Q channel of the quadrature modulator ADL5375.
The local oscillator (LO) is implemented using the ADF4151.
The low-pass filter was designed using ADIsimPLL™ for a channel
spacing of 200 kHz and a closed-loop bandwidth of 35 kHz.
The LO ports of the ADL5375 can be driven from the VCO
output. To ensure that all three RF ports (VCO output, RF
IN
and
LOIP) are connected to 50 Ω impedance, the matching network
of three 18 Ω resistors must be placed as in Figure 29. AC
coupling of the RF signal is implemented by the capacitors
connected in serial with the 18 Ω resistors . It is possible, as
well, to use a balun to convert from a single-ended LO input to
the differential LO inputs for the ADL5375.
If the I and Q inputs are driven in quadrature by 2 V p-p
signals, the resulting output power from the modulator is
approximately 2 dBm.
Figure 29. Direct Conversion Modulator
Rev. B | Page 24 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
ADuC812
ADF4151
CLK
DATA
LE
CE
MUXOUT
(LOCK DET E CT)
SCLOCK
MOSI
I/O PORTS
10265-030
ADSP-BF527
ADF4151
CLK
DATA
LE
CE
MUXOUT
(LOCK DET E CT)
SCLK
MOSI
GPIO
I/O FLAGS
10265-031
INTERFACING
The ADF4151 has a simple SPI-compatible serial interface
for writing to the device. CLK, DATA, and LE control the data
transfer. When LE goes high, the 32 bits that have been clocked
into the appropriate register on each rising edge of CLK are
transferred to the appropriate latch. See Figure 2 for the timing
diagram and Table 5 for the register address table.
ADuC812 Interface
Figure 30 shows the interface between the ADF4151 and the
ADuC812 MicroConverter®. Because the ADuC812 is based
on an 8051 core, this interface can be used with any 8051-based
microcontroller. The MicroConverter is set up for SPI master
mode with CPHA = 0. To initiate the operation, the I/O port
driving LE is brought low. Each latch of the ADF4151 needs a
32-bit word, which is accomplished by writing four 8-bit bytes
from the MicroConverter to the device. When the fourth byte
has been written, the LE input should be brought high to
complete the transfer.
Blackfin BF527 Interface
Figure 31 shows the interface between the ADF4151 and the
Blackfin ADSP-BF527 digital signal processor (DSP). The
ADF4151 needs a 32-bit serial word for each latch write. The
easiest way to accomplish this using the Blackfin family is to use
the autobuffered transmit mode of operation with alternate
framing. This provides a means for transmitting an entire block
of serial data before an interrupt is generated. Set up the word
length for eight bits and use four memory locations for each
32-bit word. To program each 32-bit latch, store the four 8-bit
bytes, enable the autobuffered mode, and write to the transmit
register of the DSP. This last operation initiates the autobuffer
transfer. As in the microcontroller case, just make sure that the
clock speeds are within the maximum limits outlined in Table 2.
Figure 30. ADuC812 to ADF4151 Interface
I/O port lines on the ADuC812 are also used to control powerdown (CE input) and detect lock (MUXOUT configured as
lock detect and polled by the port input). When operating in
the described mode, the maximum SCLOCK rate of the
ADuC812 is 4 MHz. This means that the maximum rate at
which the output frequency can be changed is 125 kHz.
Figure 31. ADSP-BF527 to ADF4151 Interface
PCB DESIGN GUIDELINES FOR CHIP SCALE PACKAGE
The lands on the chip scale package (CP-32-7) are rectangular.
The PCB pad for these must be 0.1 mm longer than the package
land length and 0.05 mm wider than the package land width.
The land is to be centered on the pad. This ensures that the
solder joint size is maximized. The bottom of the chip scale
package has a central thermal pad.
The thermal pad on the PCB must be at least as large as the
exposed pad. On the PCB, there is to be a minimum clearance
of 0.25 mm between the thermal pad and the inner edges of the
pad pattern. This ensures that shorting is avoided.
Thermal vias can be used on the PCB thermal pad to improve
the thermal performance of the package. If vias are used, they
are to be incorporated in the thermal pad at 1.2 mm pitch grid.
The via diameter must be between 0.3 mm and 0.33 mm, and
the via barrel must be plated with one ounce copper to plug
the via.
Rev. B | Page 25 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
COMPLIANT TO JE DE C S TANDARDS MO-220- WHHD.
112408-A
1
0.50
BSC
BOTTOM VIEWTOP VIEW
PIN 1
INDICATOR
32
9
16
17
24
25
8
EXPOSED
PAD
PIN 1
INDICATOR
3.25
3.10 SQ
2.95
SEATING
PLANE
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
COPLANARITY
0.08
0.30
0.25
0.18
5.10
5.00 SQ
4.90
0.80
0.75
0.70
FOR PRO P E R CONNECTIO N OF
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONFIGURATION AND
FUNCTION DESCRIPT IONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.25 MIN
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Figure 32. 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_WQ]
5 mm × 5 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-32-7)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADF4151BCPZ −40°C to +85°C 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_WQ] CP-32-7
ADF4151BCPZ-RL7 −40°C to +85°C 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_WQ] CP-32-7
EVAL-ADF4151EB1Z Evaluation Board
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
Rev. B | Page 26 of 28

Data Sheet ADF4151
NOTES
Rev. B | Page 27 of 28

ADF4151 Data Sheet
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
NOTES
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D10265-0-12/11(B)
Rev. B | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...