High Voltage, Low Noise, Low Distortion,
Unity Gain Stable, High Speed Op Amp
ADA4898-1
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
FEATURES
Ultralow noise
0.9 nV/√Hz
2.4 pA/√Hz
1.2 nV/√Hz @10 Hz
Ultralow distortion: −93 dBc at 500 kHz
Wide supply voltage range: ±5 V to ±16 V
High speed
−3 dB bandwidth: 65 MHz (G = +1)
Slew rate: 55 V/µs
Unity gain stable
Low input offset voltage: 150 µV maximum
Low input offset voltage drift: 1 V/°C
Low input bias current: −0.1 µA
Low input bias current drift: 2 nA/°C
Supply current: 8 mA
Power-down feature
APPLICATIONS
Instrumentation
Active filters
DAC buffers
SAR ADC drivers
Optoelectronics
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
NC
1
–IN
2
+IN
3
–V
S
4
PD
8
+V
S
7
OUT
6
NC
5
NC = NO CONNECT
ADA4898-1
07037-001
Figure 1. 8-Lead SOIC_N_EP (RD-8)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADA4898-1 is an ultralow noise and distortion, unity gain
stable, voltage feedback op amp that is ideal for use in 16-bit
and 18-bit systems with power supplies from ±5 V to ±16 V.
The ADA4898-1 features a linear, low noise input stage and internal
compensation that achieves high slew rates and low noise.
With the wide supply voltage range, low offset voltage, and wide
bandwidth, the ADA4898-1 is designed to work in the most
demanding applications. The ADA4898-1 also features an input
bias current cancellation mode that reduces input bias current
by a factor of 60.
The ADA4898-1 is available in an 8-lead SOIC package that
features an exposed metal paddle on its underside that improves
heat transfer to the ground plane. This is a significant improvement
over traditional plastic packages. The ADA4898-1 is rated to
work over the extended automotive temperature range of
−40°C to +105°C.
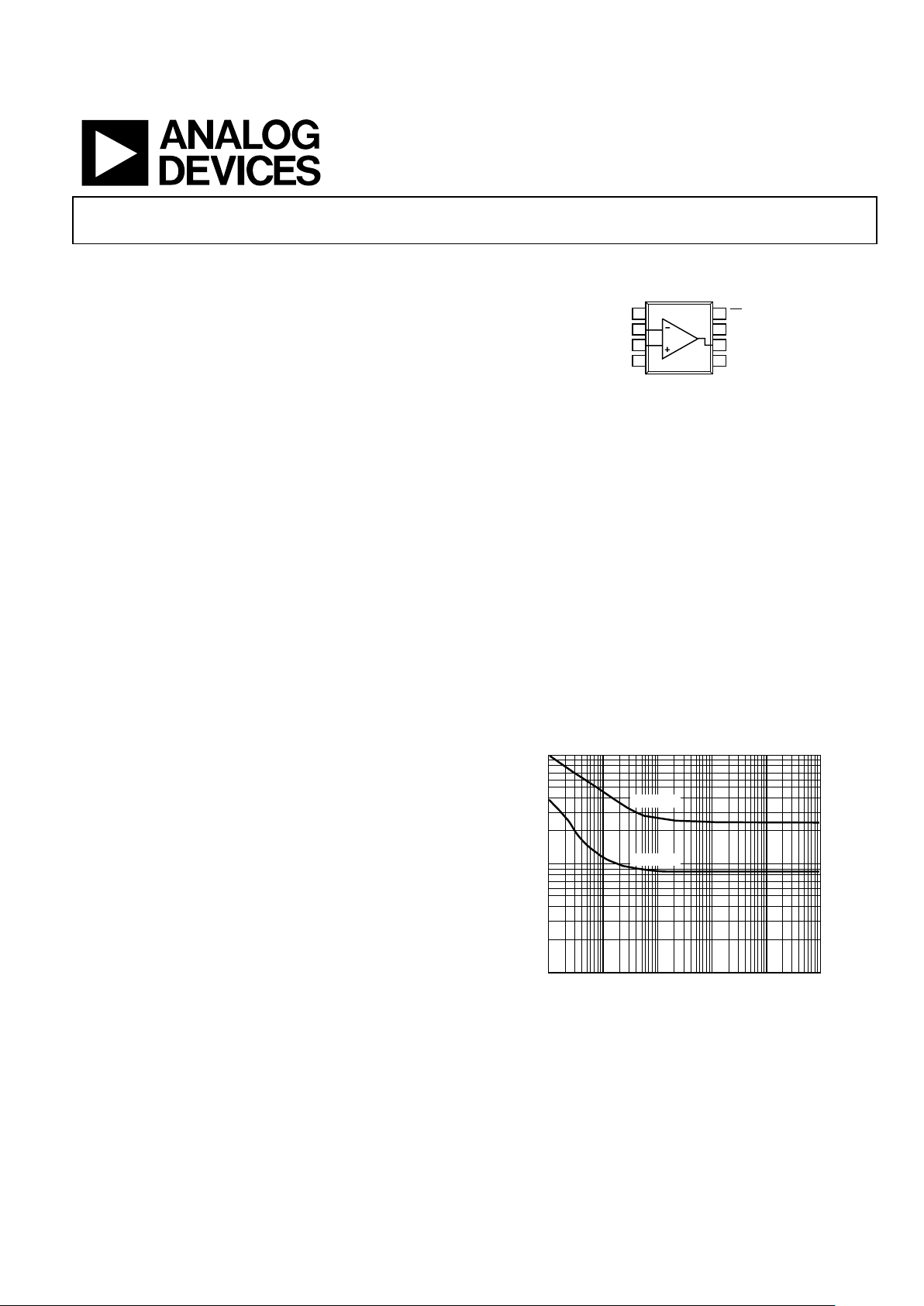
07037-002
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VOLTAGE NOISE (nV/√Hz)
CURRENT NOISE (p A/√Hz)
1
0.1
1
10
0.1
1
10
10 100 1k 10k 100k
CURRENT
VOLTAGE
Figure 2. Input Voltage Noise and Current Noise vs. Frequency

ADA4898-1
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 16
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Connection Diagram .......................................................................1
General Description......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications with ±15 V Supply................................................... 3
Specifications with ±5 V Supply..................................................... 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
Maximum Power Dissipation .....................................................5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
Typical Performance Characteristics............................................. 7
Test C irc uits ..................................................................................... 12
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 13
PD
(Power Down) Pin............................................................... 13
Current Noise Measurement .................................................... 13
Applications Information.............................................................. 14
Higher Feedback Gain Operation............................................ 14
Recommended Values for Various Gains................................ 14
Noise ............................................................................................ 15
Circuit Considerations .............................................................. 15
PCB Layout ................................................................................. 15
Power Supply Bypassing............................................................ 15
Grounding................................................................................... 15
Outline Dimensions .......................................................................16
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 16
REVISION HISTORY
5/08—Revision 0: Initial Release
ADA4898-1
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 16
SPECIFICATIONS WITH ±15 V SUPPLY
TA = 25°C, G = +1, RF = 0 Ω, RG open, RL = 1 kΩ to GND (for G > 1, RF = 100 Ω), unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth V
OUT
= 100 mV p-p 65 MHz
V
OUT
= 2 V p-p 14 MHz
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = +2, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p 3.3 MHz
Slew Rate V
OUT
= 5 V step 55 V/μs
Settling Time to 0.1% V
OUT
= 5 V step 85 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion SFDR f = 100 kHz, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p −116 dBc
f = 500 kHz, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p −93 dBc
f = 1 MHz, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p −79 dBc
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 0.9 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.4 pA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 20 110 μV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 1 μV/°C
Input Bias Current
−0.1 −0.4 μA
Input Bias Offset Current 0.03 0.3 μA
Input Bias Current Drift 2 nA/°C
Open-Loop Gain V
OUT
= ±5 V 99 103 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Differential mode 5 kΩ
Common mode 30 MΩ
Input Capacitance Differential mode 0.8 pF
Common mode 2.2 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range ±11 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio VCM = ±2 V −103 −126 dB
PD (Power Down) PIN
PD Input Voltages
Chip powered down ≤−14 V
Chip enabled ≥−13 V
Input Leakage Current
PD = +VS
−0.1 μA
PD = −VS
−0.2 μA
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing RL = 1 kΩ −11.4 to +12.1 −11.7 to +12.2 V
R
L
= None ±12.76 ±12.82 V
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 150 mA
Off Isolation
f = 1 MHz,
PD = −V
S
80 dB
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range ±4.5 ±16.5 V
Quiescent Current
PD = +V
S
8.1 mA
PD = −V
S
0.1 mA
Positive Power Supply Rejection Ratio +VS = 15 V to 17 V, −VS = −15 V −98 −107 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection Ratio +VS = 15 V, −VS = −15 V to −17 V −100 −114 dB

ADA4898-1
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 16
SPECIFICATIONS WITH ±5 V SUPPLY
TA = 25°C, G = +1, RF = 0 Ω, RG open, RL = 1 kΩ to GND (for G > 1, RF = 100 Ω), unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth V
OUT
= 100 mV p-p 57 MHz
V
OUT
= 2 V p-p 12 MHz
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = +2, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p 3 MHz
Slew Rate V
OUT
= 2 V step 50 V/μs
Settling Time to 0.1% V
OUT
= 2 V step 90 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion SFDR f = 500 kHz, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p −95 dBc
f = 1 MHz, V
OUT
= 2 V p-p −78 dBc
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 0.9 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.4 pA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 30 150 μV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 1 μV/°C
Input Bias Current −0.1 −0.4 μA
Input Bias Offset Current 0.01 0.3 μA
Input Bias Current Drift 2 nA/°C
Open-Loop Gain V
OUT
= ±1 V 90 94 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Differential mode 5 kΩ
Common mode 30 MΩ
Input Capacitance Differential mode 0.8 pF
Common mode 2.2 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range −3 to +2.5 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio VCM = ±1 V −102 −120 dB
PD (Power Down) PIN
PD Input Voltages
Chip powered down ≤−4 V
Chip enabled ≥−3 V
Input Leakage Current
PD = +VS
0.1 μA
PD = −VS
−2 μA
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing RL = 1 kΩ ±3.12 ±3.17 V
R
L
= None ±3.3 ±3.34 V
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 150 mA
Off Isolation
f = 1 MHz,
PD = −V
S
80 dB
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range ±4.5 ±16.5 V
Quiescent Current
PD = +V
S
7.7 mA
PD = −V
S
0.1 mA
Positive Power Supply Rejection Ratio +VS = 5 V to 7 V, −VS = −5 V −95 −100 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection Ratio +VS = 5 V, −VS = −5 V to −7 V −97 −104 dB
ADA4898-1
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 16
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 36 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 3
Differential Mode Input Voltage ±1.5 V
Common-Mode Input Voltage ±11.4 V
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +105°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for a device soldered in the circuit board with its
exposed paddle soldered to a pad on the PCB surface that is
thermally connected to a copper plane, with zero airflow.
Table 4.
Package Type θJAθJCUnit
8-Lead SOIC with EP on Four-Layer Board 47 29
°C/W
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum safe power dissipation in the ADA4898-1
package is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature
(T
J
) on the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass
transition temperature, the plastic changes its properties. Even
temporarily exceeding this temperature limit can change the
stresses that the package exerts on the die, permanently shifting
the parametric performance of the ADA4898-1. Exceeding a
junction temperature of 150°C for an extended period can
result in changes in the silicon devices, potentially causing
failure.
The power dissipated in the package (P
D
) is the sum of the
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
package due to the output load drive. The quiescent power is
the voltage between the supply pins (V
S
) times the quiescent
current (I
S
). The power dissipated due to the load drive depends
upon the particular application. For each output, the power due
to load drive is calculated by multiplying the load current by the
associated voltage drop across the device. RMS voltages and
currents must be used in these calculations.
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
JA
. In
addition, more metal directly in contact with the package leads
from metal traces, through holes, ground, and power planes
reduces the θ
JA
. The exposed paddle on the underside of the
package must be soldered to a pad on the PCB surface that is
thermally connected to a copper plane to achieve the specified θ
JA
.
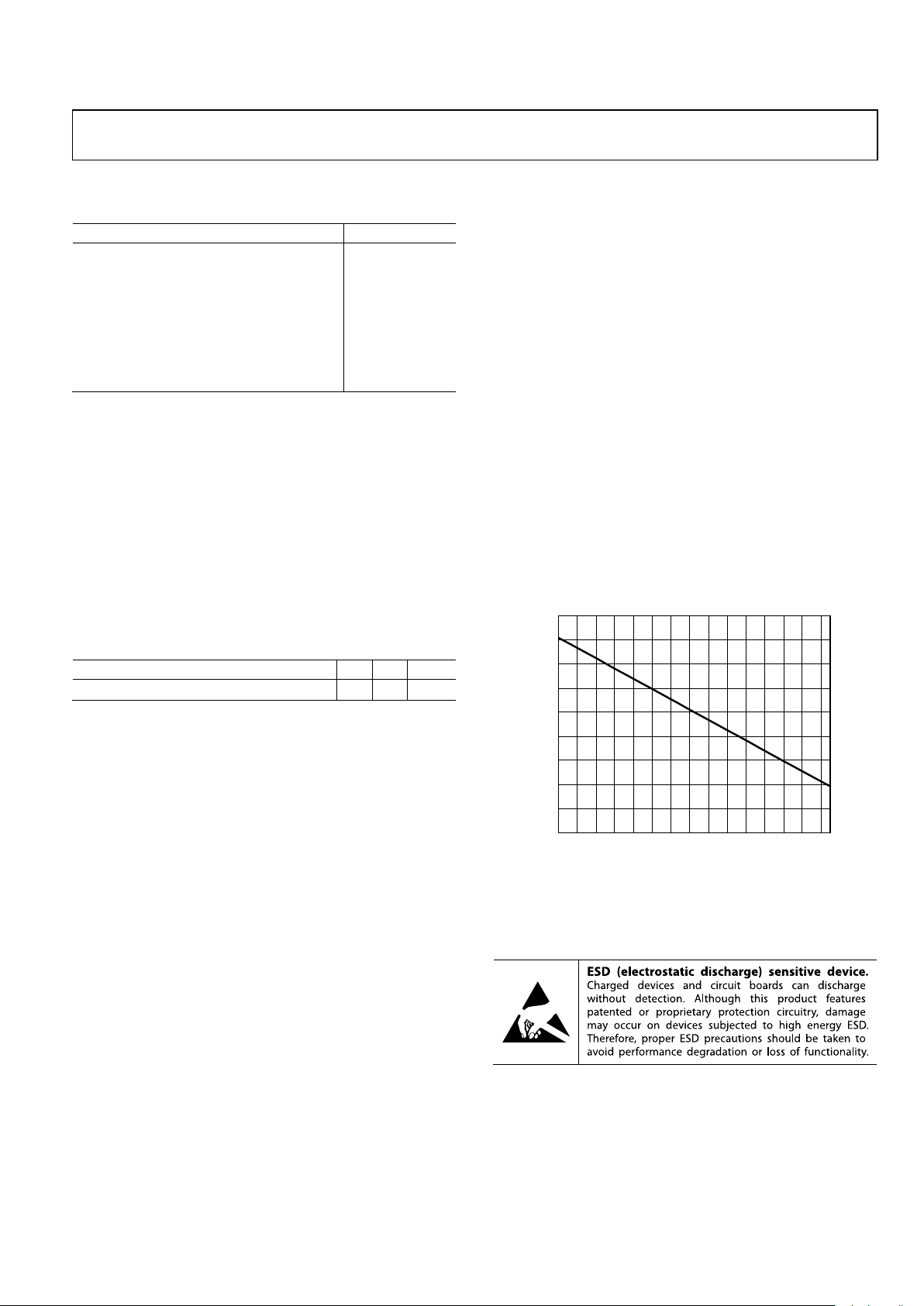
Figure 3 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
package vs. the ambient temperature for the 8-lead SOIC_EP
(47°C/W) on a JEDEC standard four-layer board, with its
underside paddle soldered to a pad that is thermally connected
to a PCB plane. θ
JA
values are approximations.
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
07037-003
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATIO N (W)
0 2040608010010 30 50 70 90–40 –20–30 –10
Figure 3. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature
ESD CAUTION
 Loading...
Loading...