
High Speed, Rail-to-Rail Output
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Op Amps with Ultralow Power-Down
FEATURES
Ultralow power-down current: 150 nA/amplifier maximum
Low quiescent current: 2.4 mA/amplifier
High speed
175 MHz, −3 dB bandwidth
220 V/μs slew rate
85 ns settling time to 0.1%
Excellent video specifications
0.1 dB flatness: 14 MHz
Differential gain: 0.12%
Differential phase: 0.09°
Single-supply operation: 2.7 V to 6 V
Rail-to-rail output
Output swings to within 80 mV of either rail
Low voltage offset: 0.6 mV
APPLICATIONS
Portable multimedia players
Video cameras
Digital still cameras
Consumer video
Clock buffers
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-21 are low price, high speed, voltage
feedbacks rail-to-rail output op amps with ultralow powerdown. Despite their low price, the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
provide excellent overall performance and versatility. The
175 MHz, −3 dB bandwidth and 220 V/μs slew rate make these
amplifiers well-suited for many general-purpose, high speed
applications.
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 are designed to operate at supply
voltages as low as 2.7 V and up to 6 V at 2.4 mA of supply
current per amplifier. In power-down mode, the supply current
is less than 150 nA, ideal for battery-powered applications.
The ADA4850 family provides users with a true single-supply
capability, allowing input signals to extend 200 mV below the
negative rail and to within 2.2 V of the positive rail. The output
of the amplifier can swing within 80 mV of either supply rail.
With its combination of low price, excellent differential gain
(0.12%), differential phase (0.09°), and 0.1 dB flatness out to
14 MHz, these amplifiers are ideal for video applications.
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 are designed to work in the
extended temperature range of −40°C to +125°C.
ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
ADA4850-1
1POWER DOWN
NC
2
–IN
3
4+IN
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 1. 8-Lead, 3 mm × 3 mm LFCSP
NC
16
ADA4850-2
1
1V
OUT
2–IN1
3+IN1
4–V
S
5
NC
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 2. 16-Lead, 3 mm × 3 mm LFCSP
2
1
0
–1
–2
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–4
G = +1
= 5V
V
S
–5
= 1kΩ
R
L
= 0.1V p-p
V
OUT
–6
1 10010 1000
FREQUENCY (MHz)
1
Patents pending.
Figure 3. Small Signal Frequency Response
PD2
NC
PD1
13
14
15
8
7
6
NC
NC
NC
+V
8
OUTPUT
7
NC
6
–V
5
12 +V
11 V
OUT
10 –IN2
9 +IN2
S
S
05320-106
S
2
05320-043
05320-054
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2005–2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Pin Configurations ........................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Specifications with +3 V Supply................................................. 3
Specifications with +5 V Supply................................................. 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
REVISION HISTORY
12/07—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changes to Applications .................................................................. 1
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 14
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 14
4/05—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Added ADA4850-1.............................................................Universal
Added 8-Lead LFCSP.........................................................Universal
Changes to Features.......................................................................... 1
Changes to General Description .................................................... 1
Changes to Figure 3.......................................................................... 1
Changes to Table 1............................................................................ 3
Changes to Table 2............................................................................ 4
Changes to Power-Down Pins Section and Table 5 ................... 13
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 14
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 14
2/05—Revision 0: Initial Version
ESD Caution...................................................................................5
Typical Performance Characteristics..............................................6
Circuit Description......................................................................... 12
Headroom and Overdrive Recovery Considerations............ 12
Operating the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 on Bipolar
Supplies........................................................................................ 13
Power-Down Pins....................................................................... 13
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 14
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 14
Rev. B | Page 2 of 16
ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS WITH +3 V SUPPLY
TA = 25°C, RF = 0 Ω for G = +1, RF = 1 kΩ for G > +1, RL = 1 kΩ, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth G = +1, VO = 0.1 V p-p 160 MHz
G = +2, VO = 0.5 V p-p, RL = 150 Ω 45 MHz
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = +2, VO = 0.5 V p-p, RL = 150 Ω 14 MHz
Slew Rate G = +2, VO = 1 V step 110 V/μs
Settling Time to 0.1% G = +2, VO = 1 V step, RL = 150 Ω 80 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion (dBc) HD2/HD3 fC = 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, G = +3, RL = 150 Ω −72/−77 dBc
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 10 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.5 pA/√Hz
Differential Gain G = +3, NTSC, RL = 150 Ω, VO = 2 V p-p 0.2 %
Differential Phase G = +3, NTSC, RL = 150 Ω, VO = 2 V p-p 0.2 Degrees
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.6 4.1 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 4 μV/°C
Input Bias Current 2.4 4.4 μA
Input Bias Current Drift 4 nA/°C
Input Bias Offset Current 30 nA
Open-Loop Gain VO = 0.25 V to 0.75 V 78 100 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Differential/common-mode 0.5/5.0 MΩ
Input Capacitance 1.2 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range −0.2 to +0.8 V
Input Overdrive Recovery Time (Rise/Fall) VIN = +3.5 V to −0.5 V, G = +1 60/50 ns
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio VCM = 0.5 V −76 −108 dB
POWER-DOWN
Power-Down Input Voltage Power-down ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 <0.7/<0.6 V
Enabled ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 >0.8/>1.7 V
Turn-Off Time 0.7 μs
Turn-On Time 60 ns
Power-Down Bias Current/ Power Down Pin
Enabled Power-down = 3 V 37 55 μA
Power-Down Power-down = 0 V 0.01 0.2 μA
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Overdrive Recovery Time (Rise/Fall) VIN = +0.7 V to −0.1 V, G = +5 70/100 ns
Output Voltage Swing 0.06 to 2.83 0.03 to 2.92 V
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 105/74 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range
Quiescent Current/Amplifier 2.4 2.8 mA
Quiescent Current (Power-Down)/Amplifier 15 150 nA
Positive Power Supply Rejection +VS = +3 V to +4 V, −VS = 0 V −83 −100 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection +VS = +3 V, −VS = 0 V to –1 V −83 −102 dB
1
For operation on bipolar supplies, see the Operating the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 on Bipolar Supplies section.
1
2.7 6 V
Rev. B | Page 3 of 16
ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS WITH +5 V SUPPLY
TA = 25°C, RF = 0 Ω for G = +1, RF = 1 kΩ for G > +1, RL = 1 kΩ, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth G = +1, VO = 0.1 V p-p 175 MHz
G = +1, VO = 0.5 V p-p 110 MHz
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = +2, VO = 1.4 V p-p, RL = 150 Ω 9 MHz
Slew Rate G = +2, VO = 4 V step 220 V/μs
G = +2, VO = 2 V step 160 V/μs
Settling Time to 0.1% G = +2, VO = 1 V step, RL = 150 Ω 85 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion (dBc) HD2/HD3 fC = 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, G = +2, RL = 150 Ω −81/−86 dBc
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 10 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.5 pA/√Hz
Differential Gain G = +3, NTSC, RL = 150 Ω 0.12 %
Differential Phase G = +3, NTSC, RL = 150 Ω 0.09 Degrees
Crosstalk (RTI)–ADA4850-2 f = 4.5 MHz, RL = 150 Ω, VO = 2 V p-p 60 dB
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.6 4.2 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 4 μV/°C
Input Bias Current 2.3 4.2 μA
Input Bias Current Drift 4 nA/°C
Input Bias Offset Current 30 nA
Open-Loop Gain VO = 2.25 V to 2.75 V 83 105 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Differential/common-mode 0.5/5.0 MΩ
Input Capacitance 1.2 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range −0.2 to +2.8 V
Input Overdrive Recovery Time (Rise/Fall) VIN = +5.5 V to −0.5 V, G = +1 50/40 ns
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio VCM = 2.0 V −85 −110 dB
POWER-DOWN
Power-Down Input Voltage Power-down ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 <0.7/<0.6 V
Enabled ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 >0.8/>1.7 V
Turn-Off Time 0.7 μs
Turn-On Time 50 ns
Power-Down Bias Current/Power Down Pin
Enabled Power-down = 5 V 0.05 0.13 mA
Power-Down Power-down = 0 V 0.02 0.2 μA
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Overdrive Recovery Time (Rise/Fall) VIN = +1.1 V to −0.1 V, G = +5 60/70 ns
Output Voltage Swing 0.14 to 4.83 0.07 to 4.92 V
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 118/94 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range
Quiescent Current/Amplifier 2.5 2.9 mA
Quiescent Current (Power-Down)/Amplifier 15 150 nA
Positive Power Supply Rejection +VS = +5 V to +6 V, −VS = 0 V −84 −100 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection +VS = +5 V, −VS = −0 V to −1 V −84 −102 dB
1
For operation on bipolar supplies, see the Operating the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 on Bipolar Supplies section.
1
2.7 6 V
Rev. B | Page 4 of 16
ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
(
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 12.6 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 4
Power Down Pin Voltage (−VS + 6) V
Common-Mode Input Voltage (−VS − 0.5 ) V to (+VS + 0.5) V
Differential Input Voltage +VS to −V
S
Storage Temperature −65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature Range
300°C
(Soldering 10 sec)
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for the device soldered in the circuit board for
surface-mount packages.
Table 4.
Package Type θ
JA
16-Lead LFCSP 91 °C/W
8-Lead LFCSP 80 °C/W
Maximum Power Dissipation
The maximum safe power dissipation for the ADA4850-1/
ADA4850-2 is limited by the associated rise in junction
temperature (T
) on the die. At approximately 150°C, which
J
is the glass transition temperature, the plastic changes its
properties. Even temporarily exceeding this temperature limit
may change the stresses that the package exerts on the die,
permanently shifting the parametric performance of the
ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2. Exceeding a junction temperature
of 150°C for an extended period of time can result in changes
in silicon devices, potentially causing degradation or loss of
functionality.
Unit
The power dissipated in the package (P
cent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the die due
to the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 drive at the output. The
quiescent power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
times the quiescent current (I
P
= Quiescent Power + (Tota l Dr i ve P o w er − Load Power)
D
⎛
()
D
⎜
IVP
SS
⎜
⎝
).
S
V
V
OUTS
×+×=
R
2
RMS output voltages should be considered. If R
to −V
, as in single-supply operation, the total drive power is
S
V
× I
. If the rms signal levels are indeterminate, consider
S
OUT
the worst case, when V
()
D
IVP
SS
= VS/4 for RL to midsupply.
OUT
2
)
4V
/
S
+×=
R
L
In single-supply operation with R
case is V
= VS/2.
OUT
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
Also, more metal directly in contact with the package leads and
exposed paddle from metal traces through holes, ground, and
power planes reduce θ
.
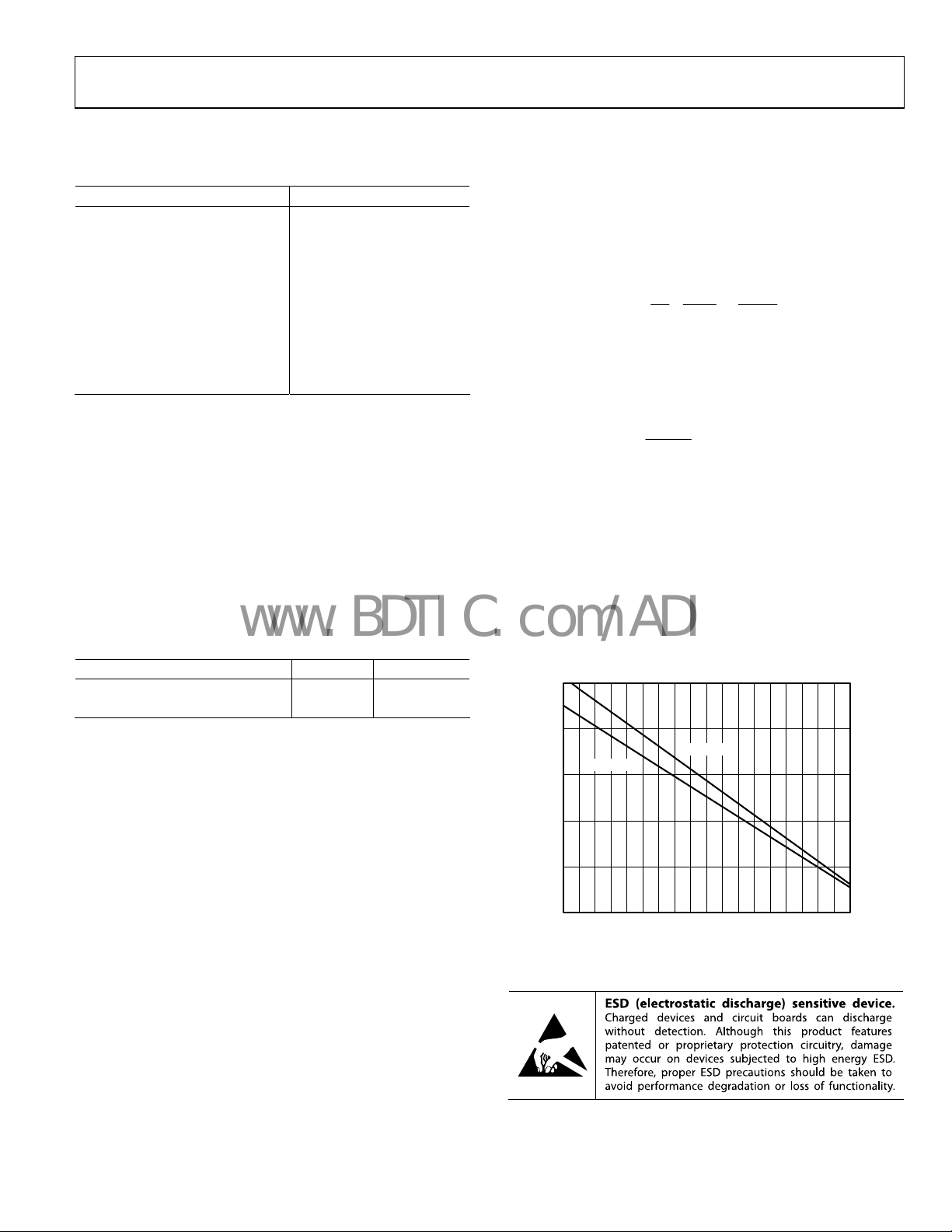
JA
Figure 4 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
ackage vs. the ambient temperature for the LFCSP (91°C/W)
p
package on a JEDEC standard 4-layer board. θ
approximations.
2.5
2.0
LFCSP-8
LFCSP-16
1.5
1.0
0.5
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0
–55 125–45–35–25–15–5 5 152535455565758595105115
Figure 4. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature for a 4-Layer Board
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
) is the sum of the quies-
D
⎞
⎟
⎟
L
⎠
referenced to −VS, the worst
L
2
V
OUT
−
R
L
is referenced
L
values are
JA
)
S
.
JA
05320-055
Rev. B | Page 5 of 16
ESD CAUTION

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
TA = 25°C, RF = 0 Ω for G = +1, RF = 1 kΩ for G > +1, RL = 1 kΩ, unless otherwise noted.
1
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
NORMALIZED CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–6
1 10 100
G = +10
FREQUENCY (MHz)
G = +2
VS = 5V
= 150Ω
R
L
V
OUT
= 0.1V p-p
Figure 5. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Gains
2
1
0
–1
–2
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–4
VS = 5V
G = +1
–5
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
–6
1 10010 1000
RL = 1kΩ
FREQUENCY (MHz)
RL = 150Ω
Figure 6. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Loads
3
2
1
0
–1
–2
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–4
G = +1
= 150Ω
R
–5
L
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
–6
1 10010 1000
FREQUENCY (MHz)
VS = 5V
V
= 3V
S
Figure 7. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Supplies
G = –1
05320-044
05320-045
05320-046
4
G = +1
V
= 5V
3
S
R
= 1kΩ
L
V
= 0.1V p-p
2
OUT
1
0
–1
–2
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–4
–5
–6
1 10010 300
FREQUENCY (MHz)
1pF
0pF
6pF
Figure 8. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Capacitor Loads
6.2
6.1
6.0
5.9
5.8
GAIN (dB)
5.7
5.6
5.5
5.4
VS = 5V, V
100k 100M
= 5V, V
V
S
OUT
VS = 3V, V
= 2V p-p
= 1.4V p-p
OUT
= 0.5V p-p
OUT
VS = 5V, V
1M 10M
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VS = 5V
G = +2
R
= 150Ω
L
Figure 9. 0.1 dB Flatness Response
1
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–5
–6
–7
1 10010 1000
= 150Ω
R
L
= 1kΩ
R
L
FREQUENCY (MHz)
VS = 5V
G = +1
V
OUT
= 0.5V p-p
Figure 10. Large Frequency Response for Various Loads
05320-007
05320-047
05320-048
Rev. B | Page 6 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
3
VS = 3V
G = +1
2
R
= 1kΩ
L
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
1
0
–1
–2
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–3
–4
+25°C
–40°C
+125°C
+85°C
300
G = +2
V
= 5V
S
R
= 1kΩ
L
250
200
150
100
SLEW RATE (V/μs)
50
NEGATIVE SLEW RATE
POSITIVE SLEW RATE
–5
1 1000
10 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 11. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Temperatures
3
VS = 5V
G = +1
2
R
= 1kΩ
L
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
1
0
–1
–2
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–3
–4
–5
1 1000
+25°C
–40°C
10 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
+125°C
+85°C
Figure 12. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Temperatures
140
120
100
80
60
PHASE
VS = 5V
0
–30
–60
–90
–120
05320-057
05320-098
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE STEP (V)
Figure 14. Slew Rate vs. Output Voltage
10k
1k
A)
μ
100
10
SUPPLY CURRENT (
1
0.1
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
0
VS = 3V, 5V, ADA4850-2
VS = 3V, 5V, ADA4850-1 ENABLE
VS = 3V, 5V, ADA4850-1 POWER DOWN
POWER-DOWN VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 15. Supply Current vs. Power-Down Voltage
–40
G = +2
V
= 5V
S
R
= 150Ω
L
–50
V
= 2V p-p
OUT
–60
V
2 TO V
OUT
1
OUT
–70
5.0
5.0
05320-024
05320-036
40
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB)
20
0
–20
GAIN
100k10k100 1k10 1M 10M 100M 1G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
–150
–180
–210
–240
OPEN-LOOP PHASE (Degrees)
05320-012
Figure 13. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
Rev. B | Page 7 of 16
–80
CROSSTALK (dB)
–90
–100
V
1 TO V
OUT
1M100k 10M 100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
OUT
2
Figure 16. Crosstalk vs. Frequency
05320-037

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
–50
40
G = +1
V
= 5V
S
V
= 500mV p-p
OUT
2.575
2.550
G = +1
V
= 5V
S
R
= 150Ω
L
10pF
0pF
–60
R
= 1kΩ HD2
–70
–80
–90
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
–100
–110
0.1 100
L
RL = 150Ω HD2
= 1kΩ HD3
R
L
R
= 150Ω HD3
L
110
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 17. Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency for Various Loads
50
G = +2
V
= 5V
S
R
= 1kΩ
L
–60
–70
V
OUT
–80
–90
–100
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
–110
–120
0.1 100
V
= 200mV p-p
HD2
= 500mV p-p
OUT
HD2
V
= 200mV p-p
OUT
HD3
V
= 500mV p-p
OUT
HD3
110
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 18. Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency for Various V
0.65
G = +2
R
= 1kΩ
L
V
= 5V
S
0.60
OUT
05320-102
05320-103
2.525
2.500
2.475
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
2.450
2.425
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
TIME (ns)
Figure 20. Small Signal Transient Response for Capacitive Load
3.25
G = +2
R
= 1kΩ
L
V
= 5V
S
3.00
2.75
2.50
2.25
2.00
OUTPUT VOLTAGE FOR 5V SUPPLY (V)
1.75
500 100 150 200
TIME (ns)
Figure 21. Large Signal Transient Response
2.875
G = +1
R
= 1kΩ
L
2.750
0.875
0.750
05320-020
05320-050
0.55
0.50
0.45
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.40
0.35
500 100 150 200
TIME (ns)
05320-019
Figure 19. Small Signal Transient Response for Various Supplies
Rev. B | Page 8 of 16
2.625
2.500
OUTPUT VOLTAGE FOR 5V SUPPLY (V)
2.375
2.250
2.125
= 3V
V
S
500 100 150 200
TIME (ns)
VS = 5V
Figure 22. Large Signal Transient Response for Various Supplies
0.625
0.500
0.375
0.250
0.125
OUTPUT VOLTAGE FOR 3V SUPPLY (V)
05320-049

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
6
5
V
4
DISABLE
3
2
VOLTAGE (V)
1
0
–1
03015 45
V
OUT
TIME (μs)
Figure 23. Enable/Disable Time
G = +2
V
= 5V
S
f
= 400kHz
IN
05320-025
1000
100
10
VOLTAGE NOISE (nV/ Hz)
1
100k10k100 1k10 1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 26. Voltage Noise vs. Frequency
05320-059
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
INPUT AND OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.5
0
–0.5
0 1000
OUTPUT
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
INPUT
TIME (ns)
Figure 24. Input Overdrive Recovery
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
INPUT AND OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
–0.5
0 1000
5 × INPUT
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Figure 25. Output Ove
OUTPUT
TIME (ns)
rdrive Recovery
G = +1
V
= 5V
S
R
= 150Ω
L
f = 1MHz
G = +5
V
= 3V
S
R
= 150Ω
L
f = 1MHz
05320-058
05320-060
100
10
CURRENT NOISE (pA/ Hz)
1
100k10k100 1k10 1M 10M 100M 1G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 27. Current Noise vs. Frequency
350
VS = 5V
N = 1720
300
x = 450μV
σ = 750μV
250
200
COUNT
150
100
50
0
–4 4
–3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3
V
(mV)
OFFSET
Figure 28. Input Offset Voltage Distribution
05320-095
05320-065
Rev. B | Page 9 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
400
380
360
340
320
V)
μ
(
300
OS
V
280
260
240
220
200
–1.0 3.5
VS = 5V
–0.5 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
VCM (V)
Figure 29. Input Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode Voltage
05320-063
–1.2
+I
B
–1.4
–1.6
VS = 5V
–1.8
–2.0
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (μA)
–2.2
–2.4
–40
–25–105203550658095110
TEMPERATURE (°C)
VS = 3V
–I
B
125
Figure 32. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature for Various Supplies
05320-092
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE (V)
0
05
5 1015202530354045
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
VS = 3V
+V
SAT
–V
SAT
VS = 5V
0
05320-064
Figure 30. Output Saturation Voltage vs. Load Current
(
Voltage Differential from Rails)
–30
–32
–34
–36
–38
–40
–42
–44
POWER-DOWN PIN BIAS CURRENT (μA)
–46
–25–105203550658095110
–40 125
VS = 3V
VS = 5V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
05320-091
Figure 31. Power-Down Bias Current vs. Temperature for Various Supplies
95
VS = 5V
R
= 1k
L
90
85
80
75
70
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE (mV)
65
–40 125
–25–105203550658095110
Figure 33. Output Saturation Voltage vs. Temperature
4.9
4.8
4.7
4.6
4.5
4.4
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
4.3
4.2
–40
Figure 34. Current vs. Temperature for Various Supplies
Ω
+VS– V
OUT
–VS– V
OUT
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Voltage Differential from Rails)
(
VS = 5V
VS = 3V
–25–105203550658095110
TEMPERATURE (°C)
125
05320-062
05320-090
Rev. B | Page 10 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
COMMON-MODE REJECTION (dB)
–20
VS = 5V
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
1k
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
CHANNEL 1
CHANNEL 2
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 37. Common-Mode Rejection (CMR) vs. Frequency
0
VS = 5V
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION (dB)
–100
–110
100
Figure 35. Power Supply Rejecti
0.7
0.6
+PSR
FREQUENCY (Hz)
on (PSR) vs. Frequency
–PSR
1M100k1k 10k 10M 100M
05320-094
05320-034
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE (mV)
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
–0.1
–25–105203550658095110
–40
VS = 5V
VS = 3V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 36. Input Offset Voltage vs. Temperature for Various Supplies
05320-093
125
Rev. B | Page 11 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 feature a high slew rate input
stage that is a true single-supply topology, capable of sensing
signals at or below the negative supply rail. The rail-to-rail
output stage can swing to within 80 mV of either supply rail
when driving light loads and within 0.17 V when driving 150 Ω.
High speed performance is maintained at supply voltages as low
as 2.7 V.
HEADROOM AND OVERDRIVE RECOVERY CONSIDERATIONS
Input
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 are designed for use in low
voltage systems. To obtain optimum performance, it is useful
to understand the behavior of the amplifier as input and output
signals approach the amplifier’s headroom limits. The input
common-mode voltage range extends 200 mV below the
negative supply voltage or ground for single-supply operation
to within 2.2 V of the positive supply voltage. Therefore, in a
gain of +3, the ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 can provide full railto-rail output swing for supply voltage as low as 3.3 V, assuming
the input signal swing is from −V
Exceeding the headroom limit is not a concern for any inverting
ga
in on any supply voltage, as long as the reference voltage at
the amplifier’s positive input lies within the amplifier’s input
common-mode range.
The input stage sets the headroom limit for signals when the
a
mplifier is used in a gain of +1 for signals approaching the
positive rail. For high speed signals, however, there are other
considerations.
v
oltage for a unity-gain follower. As the common-mode voltage
Figure 38 shows −3 dB bandwidth vs. dc input
approaches the positive supply, the bandwidth begins to drop
when within 2 V of +V
. This can manifest itself in increased
S
distortion or settling time.
2
1
0
–1
–2
GAIN (dB)
–3
–4
VS = 5V
G = +1
R
= 1k
Ω
L
–5
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
–6
0.1 1000
1 10 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 38. Unity-Gain Follow
Frequency for Various Input Common-Mode
(or ground) to 1.1 V.
S
VCM = 3V
V
= 3.1V
CM
V
= 3.2V
CM
V
= 3.3V
CM
er Bandwidth vs.
05320-096
Higher frequency signals require more headroom than the
lower frequencies to maintain distortion performance. Figure 39
i
llustrates how the rising edge settling time for the amplifier
configured as a unity-gain follower stretches out as the top of
a 1 V step input approaches and exceeds the specified input
common-mode voltage limit.
3.6
VS = 5V
3.4
G = +1
R
= 1k
Ω
L
3.2
3.0
2.8
2.6
2.4
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
2.2
2.0
1.8
0 100
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
V
STEP
V
= 2.1V TO 3.1V
STEP
V
STEP
V
STEP
TIME (ns)
= 2V TO 3V
= 2.2V TO 3.2V
= 2.3V TO 3.3V
= 2.4V TO 3.4V
V
STEP
Figure 39. Pulse Response, Input Headroom Limits
The recovery time from input voltages 2.2 V or closer to the
positive supply is approximately 50 ns, which is limited by the
settling artifacts caused by transistors in the input stage coming
out of saturation.
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 do not exhibit phase reversal, even
f
or input voltages beyond the voltage supply rails. Going more than
0.6 V beyond the power supplies turns on protection diodes at the
input stage, which greatly increase the current draw of the devices.
Output
For signals approaching the negative supply and inverting gain,
and high positive gain configurations, the headroom limit is the
output stage. The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 amplifiers use a
common-emitter output stage. This output stage maximizes the
available output range, limited by the saturation voltage of the
output transistors. The saturation voltage increases with drive
current, due to the output transistor collector resistance.
As the saturation point of the output stage is approached, the
utput signal shows increasing amounts of compression and
o
clipping. As in the input headroom case, higher frequency signals
require a bit more headroom than the lower frequency signals.
Output overload recovery is typically within 40 ns after the
a
mplifier’s input is brought to a nonoverloading value.
05320-061
Rev. B | Page 12 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 40 shows the output recovery transients for the amplifier
recovering from a saturated output from the top and bottom
supplies to a point at midsupply.
6.5
V
= +2.5V TO 0V
5.5
4.5
3.5
INPUT
2.5
VOLTAGE
EDGES
1.5
0.5
INPUT AND OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–0.5
–1.5
0 100
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Figure 40. Overload Recovery
OUT
V
TIME (ns)
= –2.5V TO 0V
OUT
VS = 5V
G = –1
R
= 1k
L
Ω
05320-042
OPERATING THE ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 ON BIPOLAR SUPPLIES
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 can operate on bipolar supplies
p to ±5 V. The only restriction is that the voltage between −V
u
and the POWER DOWN pin must not exceed 6 V. Voltage
differences greater than 6 V can cause permanent damage to the
amplifier. For example, when operating on ±5 V supplies, the
POWER DOWN pin must not exceed +1 V.
POWER-DOWN PINS
The ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2 feature an ultralow power-down
mode that lowers the supply current to less than 150 nA. When
a power-down pin is brought to within 0.6 V of the negative
supply, the amplifier is powered down.
ower-down pins functionality. To ensure proper operation, the
p
power-down pins (PD1, PD2) should not be left floating.
Table 5. Power-Down Pins Functionality
3 V and 5 V
Supply Voltage
ADA4850-1 ADA4850-2
Power Down 0 V to 0.7 V 0 V to 0.6 V
Enabled 0.8 to +V
Table 5 outlines the
S
1.7 V to +V
S
S
Rev. B | Page 13 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
R
R
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
INDICATOR
0.90 MAX
0.85 NOM
SEATING
PLANE
INDICATO
0.90
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
3.25
3.00 SQ
PIN 1
12° MAX
2.75
TOP
VIEW
0.70 MAX
0.65TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
2.95
2.75 SQ
2.55
0.05 MAX
0.01 NOM
0.20 REF
0.60 MAX
Figure 41. 8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VD]
3
mm × 3 mm Body, Very Thin, Dual Lead
Dimensions shown in millimeters
3.00
BSC SQ
PIN 1
12° MAX
TOP
VIEW
0.30
0.23
0.18
*
COMPLIANT
EXCEPT FOR EXPOSED PAD DIMENSION.
2.75
BSC SQ
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
TO
JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VEED-2
Figure 42. 16-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
3
mm × 3 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-16-3)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
0.50
0.40
0.30
(CP-8-2)
0.45
0.60 MAX
0.50
BSC
1.50 REF
0.60 MAX
5
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTT OM VIEW)
4
13
12
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
9
8
0.50
BSC
8
1.60
1.45
1.30
1
16
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1.89
1.74
1.59
61507-B
0.50
0.40
0.30
1
4
5
N
I
P
D
N
I
*
1.65
1.50 SQ
1.35
0.25 MIN
1
O
T
C
I
A
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option Branding
ADA4850-1YCPZ-R2
ADA4850-1YCPZ-RL
ADA4850-1YCPZ-RL7
ADA4850-2YCPZ-R2
ADA4850-2YCPZ-RL
ADA4850-2YCPZ-RL7
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VD) CP-8-2 HWB
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VD) CP-8-2 HWB
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VD) CP-8-2 HWB
1
−40°C to +125°C 16-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-16-3 HTB
1
−40°C to +125°C 16-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-16-3 HTB
1
−40°C to +125°C 16-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-16-3 HTB
Rev. B | Page 14 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. B | Page 15 of 16

ADA4850-1/ADA4850-2
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
©2005–2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05320-0-12/07(B)
Rev. B | Page 16 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...