Page 1

Low Noise, 1 GHz
A
–V
A
–V
A
FEATURES
High speed
−3 dB bandwidth (G = 1, R
Slew rate: 870 V/μs
0.1% settling time: 9 ns
Low input bias current: 2 pA
Low input capacitance
Common-mode capacitance: 1.3 pF
Differential-mode capacitance: 0.1 pF
Low noise
4 nV/√Hz @ 100 kHz
2.5 fA/√Hz @ 100 kHz
Low distortion
−90 dBc @ 10 MHz (G = 1, R
Offset voltage: 2 mV maximum
High output current: 40 mA
Supply current per amplifier: 19 mA
Power-down supply current per amplifier: 1.5 mA
APPLICATIONS
Photodiode amplifiers
Data acquisition front ends
Instrumentation
Filters
ADC drivers
CCD output buffers
= 100 Ω): 1050 MHz
L
= 1 kΩ)
L
FastFET Op Amps
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
DA4817-1
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
1PD
2FB
3–IN
4+IN
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 1. 8-Lead LFCSP (CP-8-2)
DA4817-1
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
1
FB
–IN
2
+IN
3
4
S
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 2. 8-Lead SOIC (RD-8-1)
DA4817-2
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
FB1
PD1
16
15
1–IN1
2+IN1
3NC
4
S2
8+V
S
7OUT
6NC
5–V
S
07756-001
8
PD
+V
7
S
OUT
6
NC
5
07756-002
S1
OUT1
+V
14
13
12 –V
S1
11 NC
10 +IN2
9–IN2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADA4817-1 (single) and ADA4817-2 (dual) FastFET™
amplifiers are unity-gain stable, ultrahigh speed voltage
feedback amplifiers with FET inputs. These amplifiers were
developed with the Analog Devices, Inc., proprietary eXtra Fast
Complementary Bipolar (XFCB) process, which allows the
amplifiers to achieve ultralow noise (4 nV/√Hz; 2.5 fA/√Hz)
as well as very high input impedances.
With 1.3 pF of input capacitance, low noise (4 nV/√Hz), low
offset voltage (2 mV maximum), and 1050 MHz −3 dB bandwidth, the ADA4817-1/ADA4871-2 are ideal for data acquisition
front ends as well as wideband transimpedance applications,
such as photodiode preamps.
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
8
7
5
6
S2
D2
FB2
P
+V
OUT2
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 3. 16-Lead LFSCP (CP-16-4)
07756-003
With a wide supply voltage range from 5 V to 10 V and the
ability to operate on either single or dual supplies, the
ADA4817-1/ ADA4817-2 are designed to work in a variety of
applications including active filtering and ADC driving.
The ADA4817-1 is available in a 3 mm × 3 mm, 8-lead LFCSP and
8-lead SOIC, and the ADA4817-2 is available in a 4 mm × 4 mm,
16-lead LFCSP. These packages feature a low distortion pinout
that improves second harmonic distortion and simplifies circuit
board layout. They also feature an exposed paddle that provides a
low thermal resistance path to the printed circuit board (PCB).
This enables more efficient heat transfer and increases reliability.
These products are rated to work over the extended industrial
temperature range (−40°C to +105°C).
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2008–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Connection Diagrams ...................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
±5 V Operation ............................................................................. 3
5 V Operation ............................................................................... 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
Maximum Safe Power Dissipation ............................................. 5
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 5
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Test Circuits ..................................................................................... 13
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 14
Closed-Loop Frequency Response ........................................... 14
Noninverting Closed-Loop Frequency Response .................. 14
Inverting Closed-Loop Frequency Response ............................. 14
Wideband Operation ................................................................. 15
Driving Capacitive Loads .......................................................... 15
Thermal Considerations ............................................................ 15
Power-Down Operation ............................................................ 15
Capacitive Feedback ................................................................... 16
Higher Frequency Attenuation ................................................. 16
Layout, Grounding, and Bypassing Considerations .................. 17
Signal Routing ............................................................................. 17
Power Supply Bypassing ............................................................ 17
Grounding ................................................................................... 17
Exposed Paddle ........................................................................... 17
Leakage Currents ........................................................................ 18
Input Capacitance ...................................................................... 18
Input-to-Input/Output Coupling ............................................. 18
Applications Information .............................................................. 19
Low Distortion Pinout ............................................................... 19
Wideband Photodiode Preamp ................................................ 19
High Speed JFET Input Instrumentation Amplifier.............. 21
Active Low-Pass Filter (LPF) .................................................... 22
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 24
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 25
REVISION HISTORY
3/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Added 8-Lead SOIC Package ............................................ Universal
Changes to Features Section and General Description Section . 1
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 3
Changes to Table 2 ............................................................................ 4
Changes to Figure 4 .......................................................................... 5
Changes to Figure 9, Figure 11, and Figure 12 ............................. 8
Changes to Figure 21, Figure 22, and Figure 24 ......................... 10
Changes to Figure 33 ...................................................................... 12
Added Figure 34; Renumbered Sequentially .............................. 12
Changes to Thermal Considerations Section and Power-Down
Operation Section ........................................................................... 15
Changes to Capacitive Feedback Section and Figure 46 ........... 16
Added Higher Frequency Attenuation Section, Figure 47,
Figure 48, and Figure 49; Renumbered Sequentially ................. 16
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 24
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 25
11/08—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 28
Page 3
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
SPECIFICATIONS
±5 V OPERATION
TA = 25°C, +VS = 5 V, −VS = −5 V, G = 1, RF = 348 Ω for G > 1, RL = 100 Ω to ground, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth V
V
V
Gain Bandwidth Product V
Full Power Bandwidth VIN = 3.3 V p-p, G = 2 60 MHz
0.1 dB Flatness V
Slew Rate V
Settling Time to 0.1% V
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion (HD2/HD3) f = 1 MHz, V
f = 10 MHz, V
f = 50 MHz, V
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 4 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.5 fA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.4 2 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 7 μV/°C
Input Bias Current
T
Input Bias Offset Current 1 pA
Open-Loop Gain 62 65 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Common mode 500 GΩ
Input Capacitance Common mode 1.3 pF
Differential mode 0.1 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range −VS to +VS − 2.8 V
Common-Mode Rejection VCM = ±0.5 V −77 −90 dB
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Overdrive Recovery Time VIN = ±2.5 V, G = 2 8 ns
Output Voltage Swing
R
Linear Output Current 1% output error 40 mA
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 100/170 mA
POWER-DOWN
PD Pin Voltage
Powered down <+VS − 3 V
Turn-On/Turn-Off Time 0.3/1 μs
Input Leakage Current
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 5 10 V
Quiescent Current per Amplifier 19 21 mA
Powered Down Quiescent Current 1.5 3 mA
Positive Power Supply Rejection +VS = 4.5 V to 5.5 V, −VS = −5 V −67 −72 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection +VS = 5 V, −VS = −4.5 V to −5.5 V −67 −72 dB
= 0.1 V p-p 1050 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 200 MHz
OUT
= 0.1 V p-p, G = 2 390 MHz
OUT
= 0.1 V p-p ≥410 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, RL = 100 Ω, G = 2 60 MHz
OUT
= 4 V step 870 V/μs
OUT
= 2 V step, G = 2 9 ns
OUT
= 2 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −113/−117 dBc
OUT
= 2 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −90/−94 dBc
OUT
= 2 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −64/−66 dBc
OUT
2 20 pA
to T
MIN
= 1 kΩ
L
Enabled >+V
PD
PD
100 pA
MAX
V
V
= +VS
= −VS
Rev. A | Page 3 of 28
−V
+V
−V
+V
S
S
S
S
+ 1.5 to
− 1.5
+ 1.1 to
− 1.1
+ 1.4 to
−V
S
+V
− 1.3
S
−V
+ 1 to
S
− 1
+V
S
− 1 V
S
0.3 3 μA
34 61 μA
Page 4

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
5 V OPERATION
TA = 25°C, +VS = 3 V, −VS = −2 V, G = 1, RF = 348 Ω for G > 1, RL = 100 Ω to ground, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
–3 dB Bandwidth V
V
V
Full Power Bandwidth VIN = 1 V p-p, G = 2 95 MHz
0.1 dB Flatness V
Slew Rate V
Settling Time to 0.1% V
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
Harmonic Distortion (HD2/HD3) f = 1 MHz, V
f = 10 MHz, V
f = 50 MHz, V
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 4 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 2.5 fA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.5 2.3 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 7 μV/°C
Input Bias Current
T
Input Bias Offset Current 1 pA
Open-Loop Gain 61 63 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance Common mode 500 GΩ
Input Capacitance Common mode 1.3 pF
Differential mode 0.1 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range −VS to +VS − 2.9 V
Common-Mode Rejection VCM = ±0.25 V −72 −83 dB
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Overdrive Recovery Time VIN = ±1.25 V, G = 2 13 ns
Output Voltage Swing RL = 100 Ω
R
Linear Output Current 1% output error 20 mA
Short-Circuit Current Sinking/sourcing 40/130 mA
POWER-DOWN
PD Pin Voltage
Powered down <+VS − 3 V
Turn-On/Turn-Off Time 0.2/0.7 μs
Input Leakage Current
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 5 10 V
Quiescent Current per Amplifier 14 16 mA
Powered Down Quiescent Current 1.5 2.8 mA
Positive Power Supply Rejection +VS = 4.75 V to 5.25 V, −VS = 0 V −66 −71 dB
Negative Power Supply Rejection +VS = 5 V, −VS = −0.25 V to +0.25 V −63 −69 dB
= 0.1 V p-p 500 MHz
OUT
= 1 V p-p 160 MHz
OUT
= 0.1 V p- p, G = 2 280 MHz
OUT
= 1 V p-p, G = 2 32 MHz
OUT
= 2 V step 320 V/μs
OUT
= 1 V step, G = 2 11 ns
OUT
= 1 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −87/−88 dBc
OUT
= 1 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −68/−66 dBc
OUT
= 1 V p-p, RL = 1 kΩ −57/−55 dBc
OUT
2 20 pA
to T
MIN
= 1 kΩ
L
Enabled >+V
PD
PD
100 pA
MAX
V
V
= +VS
= −VS
−V
+V
−V
+V
S
S
S
S
+ 1.3 to
− 1.3
+ 1 to
− 1.1
+ 1 to
−V
S
+V
− 1.2
S
−V
+ 0.9 to
S
− 1
+V
S
− 1 V
S
0.2 3 μA
31 53 μA
Rev. A | Page 4 of 28
Page 5

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
(
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
P
= Quiescent Power + (Total Drive Power – Load Power) (1)
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 10.6 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 4
Common-Mode Input Voltage −VS − 0.5 V to +VS + 0.5 V
Differential Input Voltage
±V
S
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +105°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for a device soldered in the circuit board for the
surface-mount packages.
Table 4.
Package Type θJA θ
LFCSP_VD (ADA4817-1) 94 29 °C/W
SOIC_N_EP (ADA4817-1) 79 29 °C/W
LFSCP_VQ (ADA4817-2) 64 14 °C/W
Unit
JC
D
⎛
()
D
⎜
IVP
SS
⎜
⎝
V
2
⎞
V
OUTS
⎟
×+×= (2)
⎟
R
L
⎠
Consider RMS output voltages. If R
in single-supply operation, the total drive power is V
2
V
OUT
–
R
L
is referenced to −VS, as
L
× I
S
OUT
. If
the rms signal levels are indeterminate, consider the worst-case
scenario, when V
()
D
In single-supply operation with R
case situation is V
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
= VS/4 for RL to midsupply.
OUT
2
)
V
4/
S
IVP
+×=
SS
OUT
= VS/2.
(3)
R
L
referenced to −VS, the worst-
L
.
JA
More metal directly in contact with the package leads and
exposed paddle from metal traces, throughholes, ground,
and power planes also reduces θ
.
JA
Figure 4 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
package vs. the ambient temperature for the exposed paddle
LFCSP_VD (single 94°C/W), SOIC_N_EP (single 79°C/W)
and LFCSP_VQ (dual 64°C/W) package on a JEDEC standard
4-layer board. θ
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
values are approximations.
JA
ADA4817-2, LFCS P
ADA4817-1, SOIC
MAXIMUM SAFE POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum safe power dissipation for the ADA4817-1/
ADA4817-2 are limited by the associated rise in junction
temperature (T
the glass transition temperature), the properties of the plastic
change. Even temporarily exceeding this temperature limit may
change the stresses that the package exerts on the die, permanently
shifting the parametric performance of the ADA4817-x. Exceeding
a junction temperature of 175°C for an extended period can result
in changes in silicon devices, potentially causing degradation or
loss of functionality.
The power dissipated in the package (P
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
die due to the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 drive at the output.
The quiescent power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
multiplied by the quiescent current (I
) on the die. At approximately 150°C (which is
J
) is the sum of the
D
).
S
Rev. A | Page 5 of 28
1.5
ADA4817-1, LFCS P
1.0
MAXIMUM POW ER DISSIPAT ION (W)
0.5
0
–40
–30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 4. Maximum Safe Power Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature for
a 4-Layer Board
07756-008
ESD CAUTION
)
S
Page 6
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
A
A
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DA4817-1
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
1PD
2FB
3–IN
4+IN
NC = NO CONNECT
NOTES
1. EXPOSE D PAD CAN BE CONNECTED
TO GROUND PLANE OR NEGATIVE
SUPPLY PLANE.
8+V
S
7OUT
6NC
5–V
S
07756-005
Figure 5. ADA4817-1 Pin Configuration (8-Lead LFCSP)
Table 5. ADA4817-1 Pin Function Descriptions (8-Lead LFCSP)
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1
PD
Power-Down. Do not leave floating.
2 FB Feedback Pin.
3 −IN Inverting Input.
4 +IN Noninverting Input.
5 −VS Negative Supply.
6 NC No Connect.
7 OUT Output.
8 +VS Positive Supply.
Exposed pad (EPAD) Exposed Pad. Can be connected to GND, −VS plane, or left floating.
DA4817-1
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
1
FB
2
–IN
+IN
3
–V
4
S
NC = NO CONNECT
NOTES
1. EXPOSED PAD CAN BE CONNECTED
TO GROUND PLANE O R NEGATIVE
SUPPLY PLANE.
8
PD
7
+V
S
OUT
6
NC
5
07756-006
Figure 6. ADA4817-1 Pin Configuration (8-Lead SOIC)
Table 6. ADA4817-1 Pin Function Descriptions (8-Lead SOIC)
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 FB Feedback Pin.
2 −IN Inverting Input.
3 +IN Noninverting Input.
4 −VS Negative Supply.
5 NC No Connect.
6 OUT Output.
7 +VS Positive Supply.
8
PD
Power-Down. Do not leave floating.
Exposed pad (EPAD) Exposed Pad. Can be connected to GND, −VS plane, or left floating.
Rev. A | Page 6 of 28
Page 7
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
A
DA4817-2
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
S1
OUT1
FB1
PD1
+V
14
13
16
15
1–IN1
2+IN1
3NC
4–V
S2
5
6
S2
+V
OUT2
NOTES
1. EXPOSED PAD CAN BE CONNECTED
SUPPLY PLANE.
NC = NO CONNECT
TO THE GROUND PLANE OR NEGATIVE
12 –V
S1
11 NC
10 +IN2
9–IN2
8
7
FB2
PD2
07756-107
Figure 7. ADA4817-2 Pin Configuration (16-Lead LFCSP)
Table 7. 16-Lead LFCSP Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 −IN1 Inverting Input 1.
2 +IN1 Noninverting Input 1.
3, 11 NC No Connect.
4 −VS2 Negative Supply 2.
5 OUT2 Output 2.
6 +VS2 Positive Supply 2.
7
PD2
Power-Down 2. Do not leave floating.
8 FB2 Feedback Pin 2.
9 −IN2 Inverting Input 2.
10 +IN2 Noninverting Input 2.
12 −VS1 Negative Supply 1.
13 OUT1 Output 1.
14 +VS1 Positive Supply 1.
15
PD1
Power-Down 1. Do not leave floating.
16 FB1 Feedback Pin 1.
Exposed pad (EPAD) Exposed Pad. Can be connected to GND, −VS plane, or left floating.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 28
Page 8

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
TA = 25°C, VS = ±5 V, G = 1, (RF = 348 Ω for G > 1), RL = 100 Ω to ground, small signal V
unless noted otherwise.
6
G=1, SINGLEG=1,DUAL
3
0
G = 2
6
3
0
= 100 mV p-p, large signal V
OUT
G=1, SINGLE
G = 2
= 2 V p-p,
OUT
G = 1, DUAL
–3
–6
–9
NORMALIZED CLOSED-LO OP GAIN (dB)
–12
100k 10G
1M 10M 100M 1G
G=5
FREQUENCY (Hz)
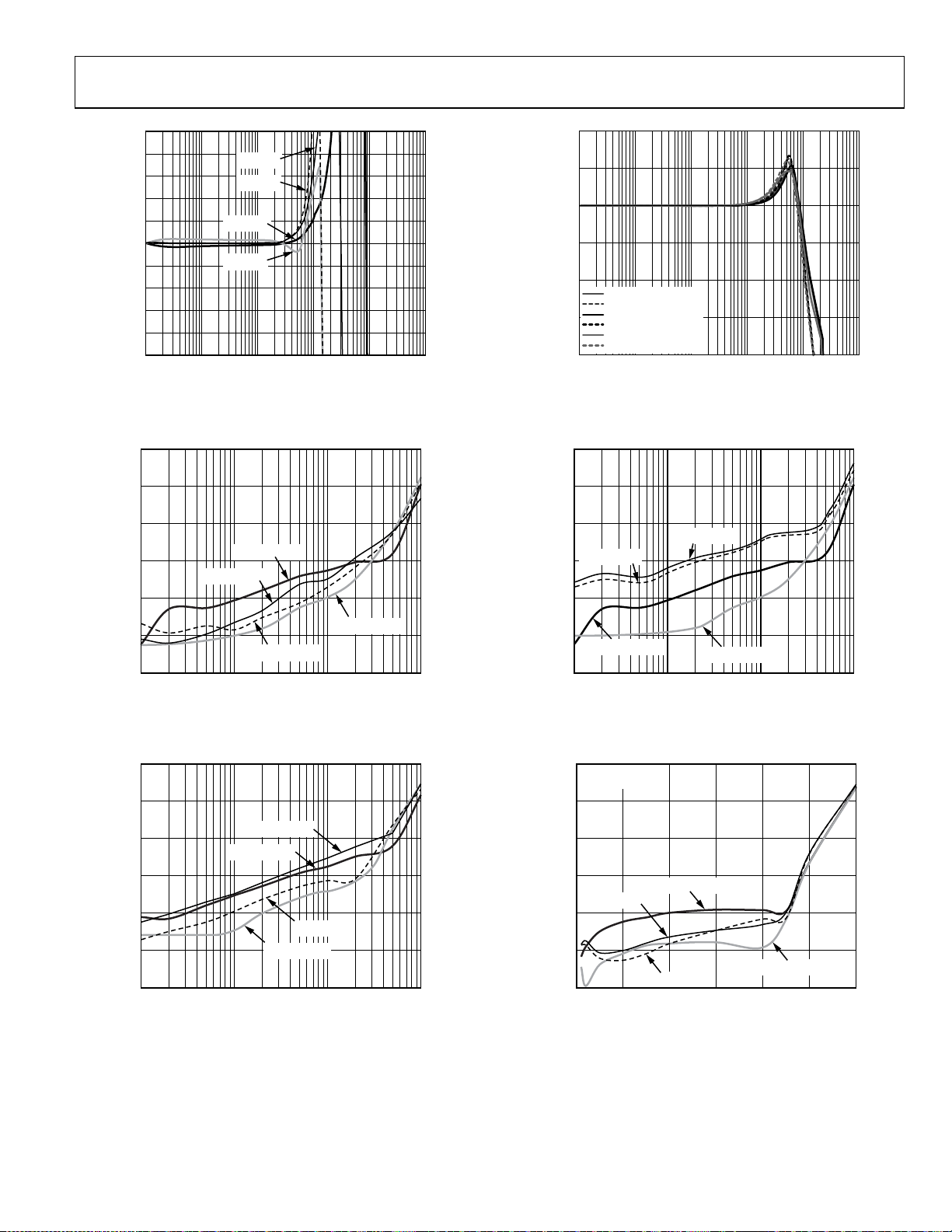
Figure 8. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Gains (LFCSP)
6
3
0
–3
–6
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–9
–12
100k 10G
1M 10M 100M 1G
Figure 9. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various Supplies
= 10V, SOIC
V
S
VS= 10V, LFCSP
VS=5V, LFCSP
VS= 5V, SOIC
FREQUENCY (Hz)
–3
–6
–9
NORMALIZED CLOSED-LO OP GAIN (dB)
–12
100k 10G
07756-066
1M 10M 100M 1G
G = 5
FREQUENCY (Hz)
07756-009
Figure 11. Large Signal Frequency Response for Various Gains
6
3
VS= 10V
0
–3
–6
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–9
V
= 1V p-p
OUT
–12
100k 10G
07756-007
1M 10M 100M 1G
Figure 12. Large Signal Frequency Response for Various Supplies
VS=5V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
07756-010
9
6
3
0
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–6
G = 2
R
=274
F
–9
100k 10G
1M 10M 100M 1G
CL=6.6pF
CL=4.4pF
CL=0pF
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 10. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various C
CL=2.2pF
07756-068
L
Rev. A | Page 8 of 28
9
RF= 348
6
3
0
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–6
G = 2
–9
100k 10G
1M 10M 100M 1G
RF= 200
FREQUENCY (Hz)
RF=274
Figure 13. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various RF
07756-011
Page 9
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
–
–
–
–
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
NORMALIZE D CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–0.4
–0.5
100k 10G
G=2,SS
G=2,LS
G=1, SS
G = 1, LS
1M 10M 100M 1G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
07756-012
Figure 14. 0.1 dB Flatness Frequency Response vs. Gain and Output Voltage
6
3
0
–3
–6
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–12
TA = +25°C, SING LE
T
= +25°C, DUAL
A
T
= –40°C, SING LE
–9
A
T
= –40°C, DUAL
A
T
= +105°C, SI NGLE
A
T
= +105°C, DUAL
A
100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 17. Small Signal Frequency Response vs. Temperature
07756-036
20
–40
–60
–80
–100
DISTORT ION (dBc)
–120
–140
100k 100M
Figure 15. Distortion vs. Frequency for Various Loads, V
20
–40
–60
–80
–100
DISTORT ION (dBc)
–120
–140
100k 100M
HD2, RL = 100
HD2, RL = 1k
HD3, RL = 100
HD3, RL = 1k
1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
OUT
HD2, VS = 5V
HD2, VS = 10V
HD3, VS = 5V
HD3, VS = 10V
1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 16. Distortion vs. Frequency for Various Supplies, G = 2, V
= 2 V p-p
= 2 V p-p
OUT
20
–40
–60
HD3, VS = 5V
–80
–100
DISTORT ION (dBc)
–120
–140
07756-014
HD2, VS = 10V
100k 100M
Figure 18. Distortion vs. Frequency for Various Supplies, V
20
f
= 1MHz
C
–40
–60
–80
HD2, RL = 1k
–100
DISTORT ION (dBc)
–120
–140
06
07756-016
12345
HD2, VS = 5V
HD3, VS = 10V
1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
HD2, RL = 100
HD3, RL = 1k
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V p-p)
HD3, RL = 100
= 2 V p-p
OUT
07756-013
07756-017
Figure 19. Distortion vs. Output Voltage for Various Loads
Rev. A | Page 9 of 28
Page 10

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
0.15
0.10
0.05
= 0.5pF
DUAL, C
F
SINGLE, NO C
F
SINGLE
0.15
0.10
0.05
DUAL, C
= 0.5pF
F
SINGLE, NO C
F
SINGLE
0
–0.05
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–0.10
G = 2
–0.15
TIME (5ns/DIV)
Figure 20. Small Signal Transient Response
0.075
0.050
0.025
0
–0.025
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–0.050
–0.075
R
= 0
F
R
= 100
L
V
= ±5V
S
G = +1
TIME (5ns/DIV)
DUAL, LFCSP
SINGLE, LFCSP
SINGLE, SOIC
Figure 21. Small Signal Transient Response vs. Package
6
2 × V
IN
4
2
0
–2
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (V)
–4
G = 2
–6
TIME (10n s/DIV)
Figure 22. Output Overdrive Recovery
DUAL
V
OUT
0
–0.05
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–0.10
VS = 5V
07756-018
–0.15
G = 2
TIME (5ns/DIV)
DUAL
07756-021
Figure 23. Small Signal Transient Response
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–1.0
–1.5
07756-022
RF = 0
R
= 100
L
V
= ±5V
S
G = +1
TIME (5ns/DIV)
Figure 24. Large Signal Transient Response
SINGLE,SOIC
DUAL, LFCSP
SINGLE, LFCSP
07756-024
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
–0.1
SETTLING TIME (%)
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
07756-019
–0.5
TIME (5ns/DIV)
Figure 25. 0.1% Short-Term Settling Time
SETTLING TIME
07756-023
Rev. A | Page 10 of 28
Page 11
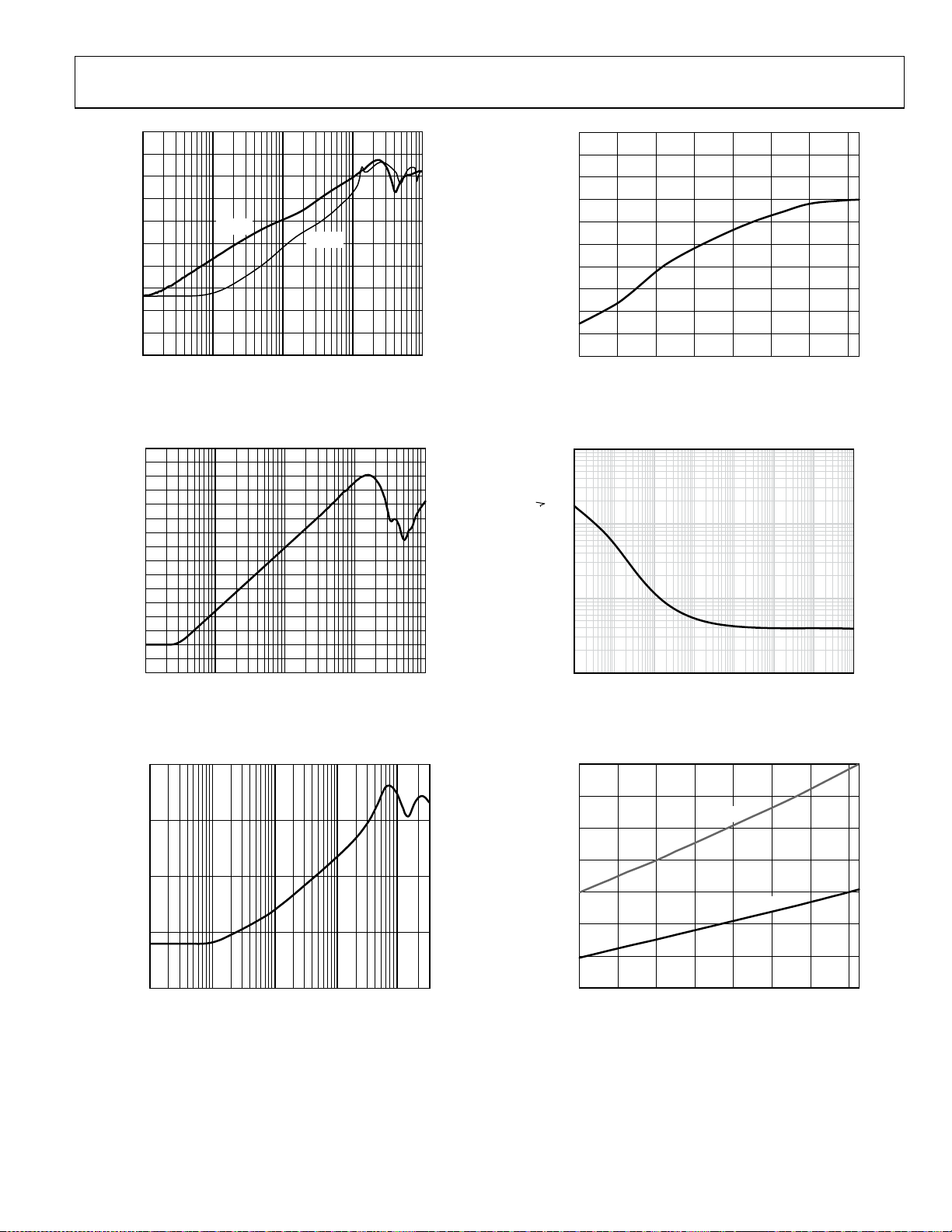
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
–
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
PSRR (dB)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
100k 1G
–PSRR
+PSRR
1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 26. PSRR vs. Frequency
20
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
CMRR (dB)
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
100k 1M 10M 100M 1G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 27. CMRR vs. Frequency
07756-032
07756-029
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
–0.1
–0.2
OFFSET VOLTAGE (mV)
–0.3
–0.4
–0.5
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 29. Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
1000
100
10
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE (nV/ Hz)
1
10 100M
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 30. Input Voltage Noise
07756-037
07756-026
100
10
1
OUTPUT IM PEDANCE ()
0.1
0.01
100k 1G100M10M1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 28. Output Impedance vs. Frequency
07756-030
Figure 31. Quiescent Current vs. Temperature for Various Supply Voltages
Rev. A | Page 11 of 28
24
22
20
18
16
14
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
12
10
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
VS
V
5
±
=
+
5
V
V
=
S
07756-033
Page 12
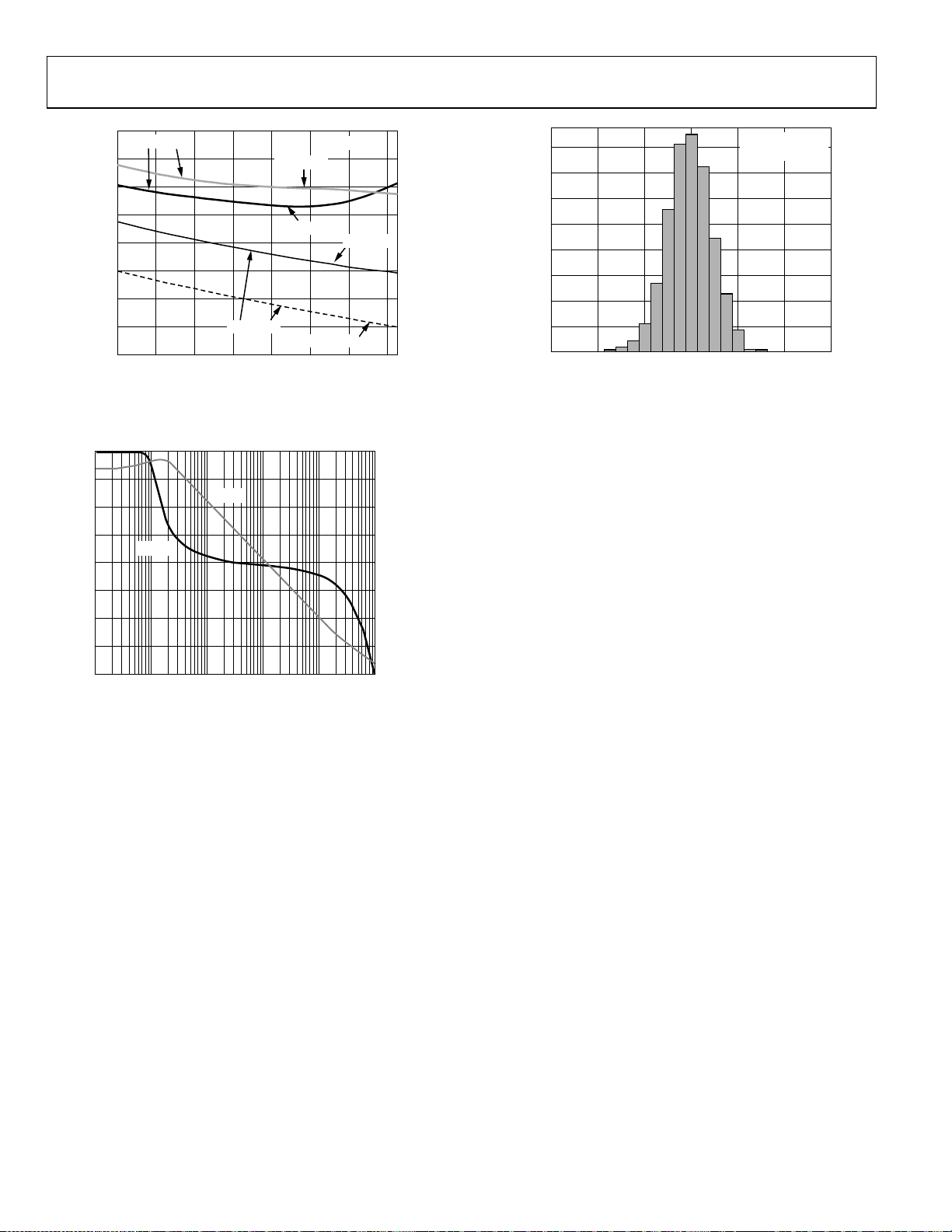
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
1.6
VS = ±5V
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1.0
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE (V)
0.9
0.8
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 8 0 100
VS = +5V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
-
–VS + V
+VS – V
OUT
OUT
–VS + V
Figure 32. Output Saturation Voltage vs. Temperature
RL = 100
+VS – V
OUT
OUT
800
700
600
500
400
300
NUMBER OF HIT S
200
100
07756-034
0
–1.5 –1.0 –0.5 0 0.5 1.0 1.5
VOS (mV)
Figure 34. Input Offset Voltage Histogram
N: 4197
MEAN: –0.0248457
SD: 0.245658
07756-025
70
60
50
40
30
GAIN (dB)
20
10
0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G
PHASE
GAIN
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 33. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
0
–45
–90
–135
–180–10
PHASE (Degrees)
07756-015
Rev. A | Page 12 of 28
Page 13

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
TEST CIRCUITS
The output feedback pins are used for ease of layout as shown in Figure 35 to Figure 40.
+
+
S
10µF
+
0.1µF
V
IN
49.9
10µF
+
–V
0.1µF
S
Figure 35. G = 1 Configuration
+
S
10µF
+
AC
49.9
R
L
0.1µF
–V
S
Figure 36. Positive Power Supply Rejection
V
0.1µF
OUT
R
G
V
OUT
R
L
7756-147
V
IN
49.9
Figure 38. Noninverting Gain Configuration
10µF
07756-145
Figure 39. Negative Power Supply Rejection
10µF
10µF
+
+
AC
S
+
R
F
+
–V
S
0.1µF
0.1µF
V
OUT
R
L
0.1µF
–V
S
S
0.1µF
V
OUT
R
49.9
L
7756-141
07756-148
+
+
S
10µF
+
R
R
F
G
V
IN
49.9
10µF
+
0.1µF
R
SNUB
0.1µF
–V
S
Figure 37. Capacitive Load Configuration
0.1µF
1k
V
C
OUT
R
L
L
7756-142
IN
53.6
1k
1k
Figure 40. Common-Mode Rejection
10µF
1k
10µF
+
S
+
0.1µF
0.1µF
V
OUT
R
L
0.1µF
–V
S
7756-146
Rev. A | Page 13 of 28
Page 14

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
(
)
×π−
THEORY OF OPERATION
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 are voltage feedback operational
amplifiers that combine new architecture for FET input operational
amplifiers with the eXtra Fast Complementary Bipolar (XFCB)
process from Analog Devices, resulting in an outstanding
combination of speed and low noise. The innovative high speed
FET input stage handles common-mode signals from the negative
supply to within 2.7 V of the positive rail. This stage is combined
with an H-bridge to attain a 870 V/s slew rate and low distortion,
in addition to 4 nV/√Hz input voltage noise. The amplifier
features a high speed output stage capable of driving heavy loads
sourcing and sinking up to 40 mA of linear current. Supply current
and offset current are laser trimmed for optimum performance.
These specifications make the ADA4817-1/ ADA4817-2 a great
choice for high speed instrumentation and high resolution data
acquisition systems. Its low noise, picoamp input current, precision
offset, and high speed make them superb preamps for fast photodiode applications.
CLOSED-LOOP FREQUENCY RESPONSE
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 are classic voltage feedback
amplifiers with an open-loop frequency response that can be
approximated as the integrator response shown in Figure 43. Basic
closed-loop frequency response for inverting and noninverting
configurations can be derived from the schematics shown in
Figure 41 and Figure 42.
R
F
R
G
A
V
E
V
IN
Figure 41. Noninverting Configuration
R
F
R
V
G
IN
V
A
E
Figure 42. Inverting Configuration
V
OUT
07756-044
V
OUT
07756-045
NONINVERTING CLOSED-LOOP FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Solving for the transfer function,
RRf
V
O
=
()
V
where f
F
I
is the frequency where the amplifier’s open-loop
CROSSOVER
gain equals 0 dB.
At dc,
V +
F
O
=
V
R
I
2
2
RR
G
(5)
G
+×π
F
GCROSSOVER
(4)
RfSRR
××π++
GCROSSOVERG
Rev. A | Page 14 of 28
Closed-loop −3 dB frequency
R
G
ff
CROSSOVER
−
3dB
×=
(6)
RR
+
F
G
INVERTING CLOSED-LOOP FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Solving for the transfer function,
V
O
V
I
At dc
=
2
CROSSOVER
()
F
V
O
V
I
2
R
F
−=
(8)
R
G
Solve for closed-loop −3 dB frequency by,
ff
CROSSOVER
−3
dB
80
60
40
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (A) (dB)
20
0
0.1 1000
A = (2 ×
Figure 43. Open-Loop Gain vs. Frequency and Basic Connections
R
×=
+
F
f
CROSSOVER
1 10010
FREQUENCY (MHz)
The closed-loop bandwidth is inversely proportional to the noise
gain of the op amp circuit, (R
accurate for noise gains above 2. The actual bandwidth of circuits
with noise gains at or below 2 is higher than those predicted
with this model due to the influence of other poles in the
frequency response of the real op amp.
Figure 44 shows a voltage feedback amplifier’s dc errors. For
both inverting and noninverting configurations,
⎛
G
()
OUT
⎜
RIerrorV
×=
S
b
⎜
⎝
(10)
–
+V
R
G
V
IN
Figure 44. Voltage Feedback Amplifier’s DC Errors
OS
R
S
Rf
×
F
G
(9)
RR
G
)/s
+ RG)/RG. This simple model is
F
⎞
RR
+
F
⎟
⎟
R
G
⎠
R
F
I
b
–
I
b
+
(7)
RfSRR
××π++
GCROSSOVERG
f
CROSSOVER
+×−
F
b
−+
A
= 410MHz
⎛
⎜
VRI
OS
⎜
⎝
V
OUT
⎞
RR
+
F
G
⎟
⎟
R
G
⎠
07756-047
07756-046
Page 15
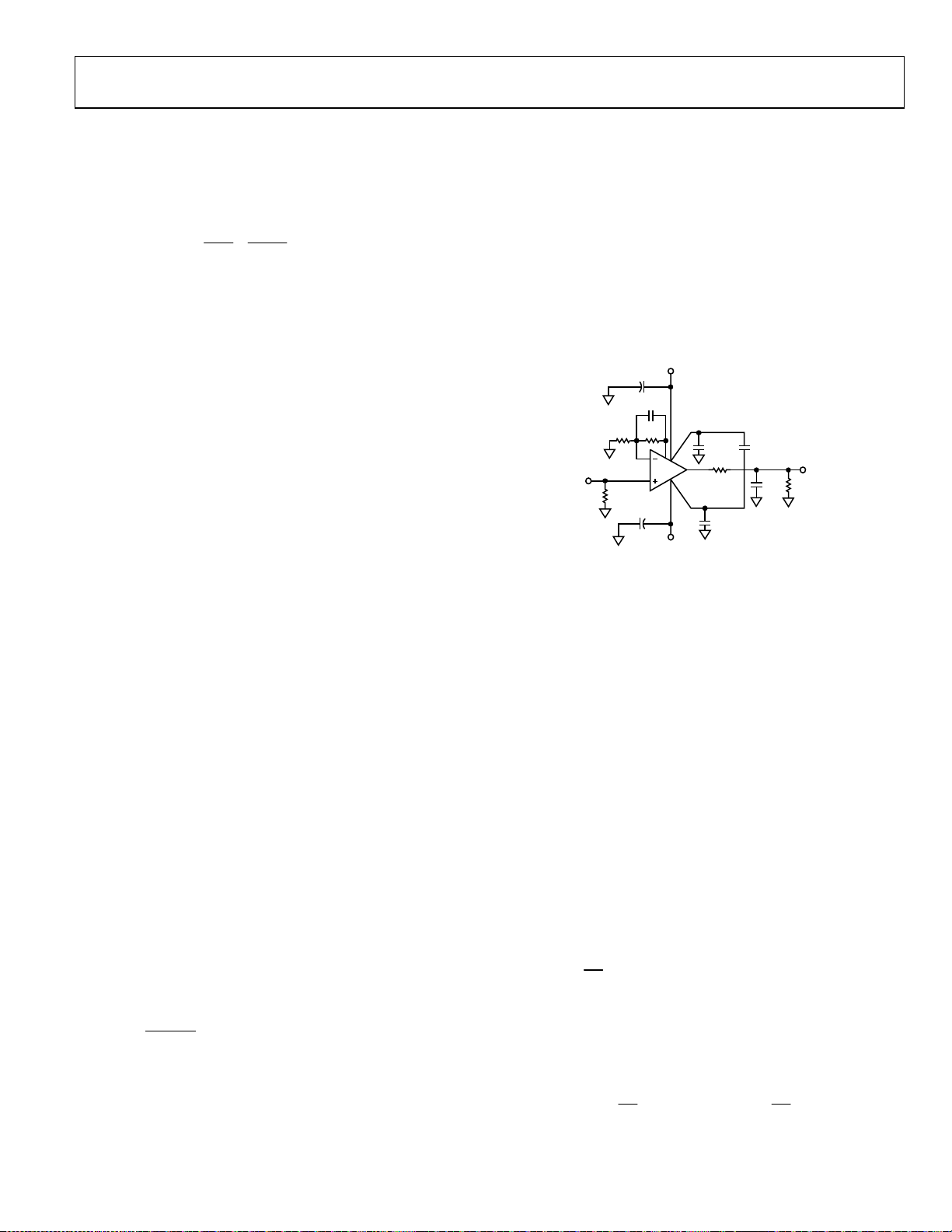
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
V
The voltage error due to Ib+ and Ib– is minimized if RS = RF || RG
(though with the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 input currents in the
picoamp range, this is likely not a concern). To include commonmode effects and power supply rejection effects, total V
can be
OS
modeled by
nom
V
PSR
VV
OSOS
++=
CMS
(11)
CMR
V
where:
V
is the offset voltage specified at nominal conditions.
OS
nom
V
is the change in power supply from nominal conditions.
S
PSR is the power supply rejection.
is the change in common-mode voltage from nominal
ΔV
CM
conditions.
CMR is the common-mode rejection.
WIDEBAND OPERATION
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 provides excellent performance as
a high speed buffer. Figure 41 shows the circuit used for wideband
characterization for high gains. The impedance at the summing
junction (R
|| RG) forms a pole in the loop response of the amp-
F
lifier with the amplifier’s input capacitance of 1.3 pF. This pole
can cause peaking and ringing if its frequency is too low. Feedback resistances of 100 Ω to 400 Ω are recommended because
they minimize the peaking and they do not degrade the
performance of the output stage. Peaking in the frequency
response can also be compensated for with a small feedback
capacitor (C
) in parallel with the feedback resistor, or a series
F
resistor in the noninverting input, as shown in Figure 45.
The distortion performance depends on a number of variables:
•
The closed-loop gain of the application
•
Whether it is inverting or noninverting
•
Amplifier loading
•
Signal frequency and amplitude
•
Board layout
The best performance is usually obtained in the G + 1
configuration with no feedback resistance, big output
load resistors, and small board parasitic capacitances.
DRIVING CAPACITIVE LOADS
In general, high speed amplifiers have a difficult time driving
capacitive loads. This is particularly true in low closed-loop
gains, where the phase margin is the lowest. The difficulty
arises because the load capacitance, C
output resistance, R
, of the amplifier. The pole can be described
O
by the following equation:
1
= (12)
f
P
2π
CR
L
O
If this pole occurs too close to the unity-gain crossover point,
the phase margin degrades. This is due to the additional phase
loss associated with the pole.
, forms a pole with the
L
Note that such capacitance introduces significant peaking in the
frequency response. Larger capacitance values can be driven but
must use a snubbing resistor (R
as shown in Figure 45. Adding a small series resistor, R
) at the output of the amplifier,
SNUB
SNUB
, creates
a zero that cancels the pole introduced by the load capacitance.
Typical values for R
can range from 10 Ω to 50 Ω. The value is
SNUB
typically based on the circuit requirements. Figure 45 also shows
another way to reduce the effect of the pole created by the capacitive
) by placing a capacitor (CF) in the feedback loop parallel
load (C
L
to the feedback resistor Typical capacitor values can range from
0.5 pF to 2 pF. Figure 46 shows the effect of adding a feedback
capacitor to the frequency response.
+
S
10µF
+
C
F
R
R
F
V
IN
G
49.9
10µF
+
Figure 45. R
SNUB
0.1µF
0.1µF
R
SNUB
0.1µF
–V
S
or CF Used to Reduce Peaking
C
L
V
OUT
R
L
7756-143
THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
With 10 V power supplies and 19 mA quiescent current, the
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 dissipate 190 mW with no load. This
implies that in the LFCSP, whose thermal resistance is 94°C/W for
the ADA4817-1 and 64°C/W for the ADA4817-2, the junction
temperature is typically almost 25° higher than the ambient temperature. The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 are designed to maintain a
constant bandwidth over temperature; therefore, an initial ramp up
of the current consumption during warm-up is expected. The V
OS
temperature drift is below 8 µV/°C; therefore, it can change up to
0.3 mV due to warm-up effects for an ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
in a LFCSP on 10 V. The input bias current increases by a factor
of 1.7 for every 10°C rise in temperature.
Heavy loads increase power dissipation and raise the chip
junction temperature as described in the Absolute Maximum
Ratings section. Take care not to exceed the rated power
dissipation of the package.
POWER-DOWN OPERATION
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 are equipped with separate powerdown pins (
to reduce the quiescent supply current when an amplifier is
inactive from 19 mA to below 2 mA. The power-down threshold
levels are derived from the voltage applied to the +V
supply application, the enable voltage is greater than +4 V, and in a
+3 V, −2 V supply application, the enable voltage is greater than
+2 V. However, the amplifier is powered down whenever the
voltage applied to
connect it to the positive supply to ensure proper start-up.
) for each amplifier. This allows the user the ability
PD
pin. In ±5 V
S
is 3 V below +VS. If the PD pin is not used,
PD
Rev. A | Page 15 of 28
Page 16
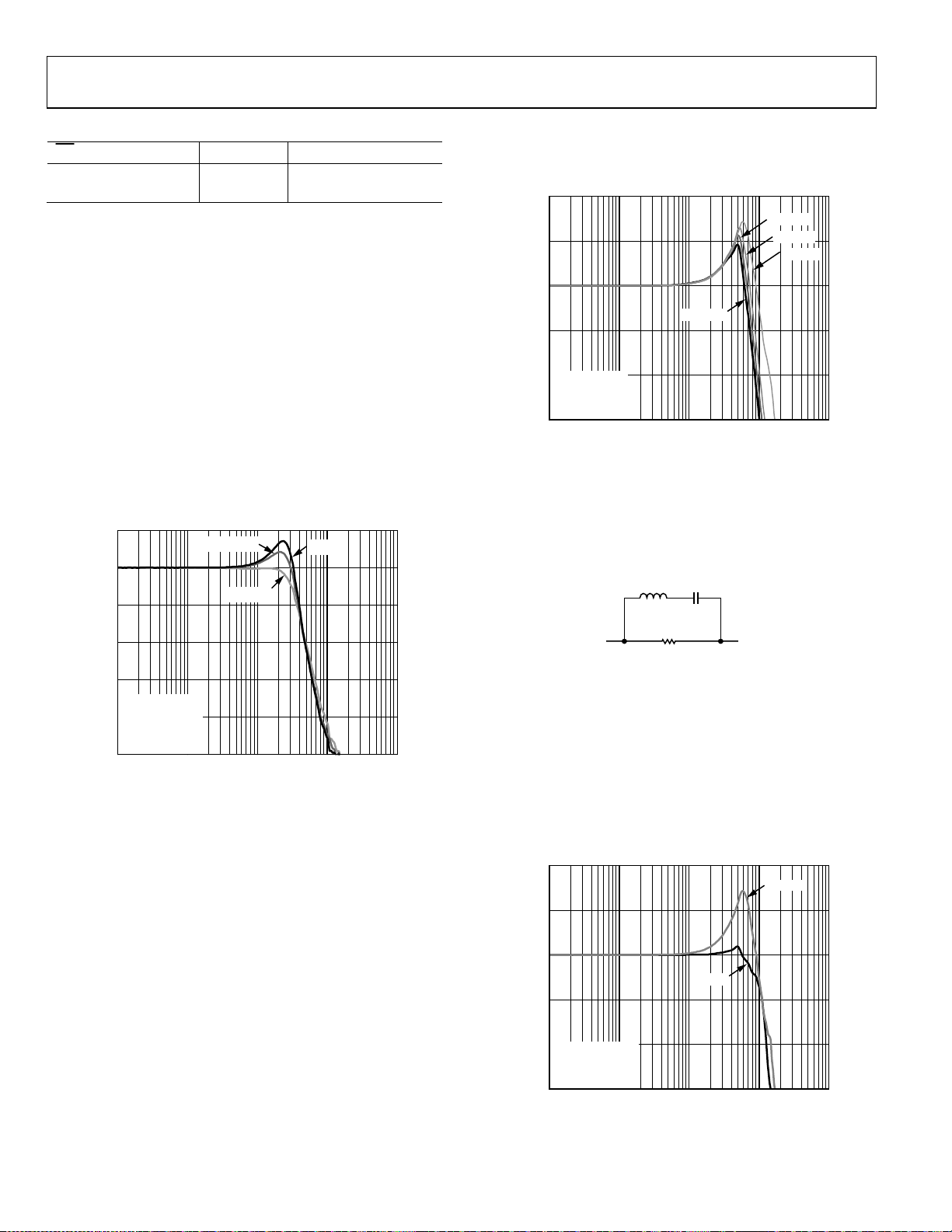
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
Table 8. Power-Down Voltage Control
Pin ±5 V +3 V, −2 V
PD
Not active
>4 V >2 V
Active <2 V <0 V
CAPACITIVE FEEDBACK
Due to package variations and pin-to-pin parasitics between the
single and the dual models, the ADA4817-2 has a little more
peaking then the ADA4817-1, especially at a gain of 2. The best
way to tame the peaking is to place a feedback capacitor across
the feedback resistor. Figure 46 shows the small signal frequency
response of the ADA4817-2 at a gain of 2 vs. C
. At first, no CF
F
was used to show the peaking, but then two other values of
0.5 pF and 1 pF were used to show how to reduce the peaking or
even eliminate it. As shown in Figure 46, if the power consumption
is a factor in the system, then using a larger feedback capacitor
is acceptable as long as a feedback capacitor is used across it to
control the peaking. However, if power consumption is not an
issue, then a lower value feedback resistor, such as 200 Ω, would
not require any additional feedback capacitance to maintain
flatness and lower peaking.
9
6
3
0
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
RF = 348
G = 2
–6
V
= 10V
S
V
= 100mV p-p
OUT
R
= 100
L
–9
1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
Figure 46. Small Signal Frequency Response vs. Feedback Capacitor
C
= 0.5pF
F
= 1pF
C
F
FREQUENCY (Hz)
(ADA4817-2)
NO C
F
07756-049
HIGHER FREQUENCY ATTENUATION
There is another package variation problem between the SOIC
and the LFCSP package. The SOIC package shows approximately
1 dB to 1.5 dB of additional peaking at a gain of 1. This is due to
the parasitic in the SOIC package, which is not recommended
for very high frequency parts that exceed 1 GHz. A good approach
to reducing the peaking is to place a resistor, R
the noninverting input. This creates a first-order pole formed
and CIN, the common-mode input capacitance.
by R
S
, in series with
S
Figure 47 shows the higher frequency attenuation, which
reduces the peaking but also reduces the −3 dB bandwidth.
6
RS= 75
= 50
R
3
0
RS= 100
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–6
RL = 100
V
= ±5V
S
V
= 0.1V p-p
OUT
G = 1
–9
1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 47. Small Signal Frequency Response for Various R
S
R
S
= 0
(SOIC)
S
07756-247
As shown in Figure 47, the peaking dropped by almost 2 dB
when R
= 0 Ω to RS = 100 Ω, and in return, the −3 dB bandwidth
S
dropped from 1 GHz to 700 MHz. To maintain the −3 dB
bandwidth and to reduce peaking, an RLC circuit is recommended
instead of R
, as shown in Figure 48.
S
L
10nH
R
120
Figure 48. RLC Circuit
C
2pF
07756-248
The R in parallel to the series LC forms a notch that can be
shaped to compensate for the peaking produced by the amplifier.
The result is a smooth 1 GHz −3 dB bandwidth, 250 MHz 0.1 dB
flatness, and less than 1 dB of peaking. This circuit should be
placed in the path of the noninverting input when the ADA4817-x
is used at a gain of 1. The RLC values may need tweaking
depending on the source impedance and the flatness and bandwidth required. Figure 49 shows the frequency response after the
RLC circuit is in place.
6
NO RLC
3
0
RLC
–3
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–6
RL = 100
V
= 10V
S
V
= 100mV p-p
OUT
G = 1
–9
1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 49. Frequency Response with RLC Circuit
07756-249
Rev. A | Page 16 of 28
Page 17

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
LAYOUT, GROUNDING, AND BYPASSING CONSIDERATIONS
Laying out the PCB is usually the last step in the design process
and often proves to be one of the most critical. A brilliant design
can be rendered useless because of poor layout. Because the
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 can operate into the RF frequency
spectrum, high frequency board layout considerations must
be taken into account. The PCB layout, signal routing, power
supply bypassing, and grounding all must be addressed to
ensure optimal performance.
SIGNAL ROUTING
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 feature the new low distortion
pinout with a dedicated feedback pin that allows a compact
layout. The dedicated feedback pin reduces the distance from
the output to the inverting input, which greatly simplifies the
routing of the feedback network.
When laying out the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 as a unity-gain
amplifier, it is recommended that a short, but wide, trace be
placed between the dedicated feedback pins, and the inverting
input to the amplifier be used to minimize stray parasitic
inductance.
To minimize parasitic inductances, use ground planes under
high frequency signal traces. However, remove the ground
plane from under the input and output pins to minimize the
formation of parasitic capacitors, which degrades phase margin.
Signals that are susceptible to noise pickup should be run on
the internal layers of the PCB, which can provide maximum
shielding.
POWER SUPPLY BYPASSING
Power supply bypassing is a critical aspect of the PCB design
process. For best performance, the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
power supply pins need to be properly bypassed.
A parallel connection of capacitors from each of the power
supply pins to ground works best. Paralleling different values
and sizes of capacitors helps to ensure that the power supply
pins see a low ac impedance across a wide band of frequencies.
This is important for minimizing the coupling of noise into the
amplifier. Starting directly at the power supply pins, place the
smallest value and sized component on the same side of the
board as the amplifier, and as close as possible to the amplifier,
and connect it to the ground plane. Repeat this process for the
next largest value capacitor. It is recommended that a 0.1 µF
ceramic, 0508 case be used for the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2.
The 0508 offers low series inductance and excellent high
frequency performance. The 0.1 µF provides low impedance at
high frequencies. Place a 10 µF electrolytic capacitor in parallel
with the 0.1 µF. The 10 µF capacitor provides low ac impedance
at low frequencies. Smaller values of electrolytic capacitors can
be used depending on the circuit requirements. Additional
smaller value capacitors help to provide a low impedance path
for unwanted noise out to higher frequencies but are not always
necessary.
Rev. A | Page 17 of 28
Placement of the capacitor returns (grounds) is also important.
Returning the capacitors’ grounds close to the amplifier load is
critical for distortion performance. Keeping the capacitors distance
short but equal from the load is optimal for performance.
In some cases, bypassing between the two supplies can help
to improve PSRR and to maintain distortion performance in
crowded or difficult layouts. This is another option to improve
performance.
Minimizing the trace length and widening the trace from the
capacitors to the amplifier reduces the trace inductance. A series
inductance with the parallel capacitance can form a tank circuit,
which can introduce high frequency ringing at the output. This
additional inductance can also contribute to increased distortion
due to high frequency compression at the output. The use of
vias should be minimized in the direct path to the amplifier power
supply pins because vias can introduce parasitic inductance, which
can lead to instability. When required to use vias, choose multiple
large diameter vias because this lowers the equivalent parasitic
inductance.
GROUNDING
The use of ground and power planes is encouraged as a method
of providing low impedance returns for power supply and signal
currents. Ground and power planes can also help to reduce stray
trace inductance and to provide a low thermal path for the
amplifier. Do not use ground and power planes under any of
the pins. The mounting pads and the ground or power planes
can form a parasitic capacitance at the input of the amplifier. Stray
capacitance on the inverting input and the feedback resistor form
a pole, which degrades the phase margin, leading to instability.
Excessive stray capacitance on the output also forms a pole,
which degrades phase margin.
EXPOSED PADDLE
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 feature an exposed paddle, which
lowers the thermal resistance by 25% compared to a standard
SOIC plastic package. The exposed paddle of the ADA4817-1/
ADA4817-2 floats internally which provides the maximum
flexibility and ease of use. It can be connected to the ground plane
or to the negative power supply plane. In cases where thermal
heating is not an issue, the exposed pad can be left floating.
The use of thermal vias or heat pipes can also be incorporated
into the design of the mounting pad for the exposed paddle.
These additional vias help to lower the overall junction-toambient temperature (θ
the surface to which the exposed paddle of the amplifier is
soldered can greatly reduce the overall thermal resistance seen
by the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2.
). Using a heavier weight copper on
JA
Page 18

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
LEAKAGE CURRENTS
Poor PCB layout, contaminants, and the board insulator
material can create leakage currents that are much larger than
the input bias current of the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2. Any
voltage differential between the inputs and nearby runs sets
up leakage currents through the PCB insulator, for example, 1 V/
100 GΩ = 10 pA. Similarly, any contaminants, such as skin oils
on the board, can create significant leakage. To reduce leakage
significantly, put a guard ring (shield) around the inputs and
input leads that are driven to the same voltage potential as the
inputs. This way there is no voltage potential between the inputs
and surrounding area to set up any leakage currents. For the
guard ring to be completely effective, it must be driven by a
relatively low impedance source and should completely
surround the input leads on all sides (above and below)
while using a multilayer board.
Another effect that can cause leakage currents is the charge
absorption of the insulator material itself. Minimizing the amount
of material between the input leads and the guard ring helps to
reduce the absorption. In addition, low absorption materials,
such as Teflon® or ceramic, can be necessary in some instances.
INPUT CAPACITANCE
Along with bypassing and ground, high speed amplifiers can be
sensitive to parasitic capacitance between the inputs and ground. A
few picofarads of capacitance reduces the input impedance at high
frequencies, in turn increasing the gain of the amplifier, causing
peaking of the frequency response or even oscillations if severe
enough. It is recommended that the external passive components
connected to the input pins be placed as close as possible to the
inputs to avoid parasitic capacitance. The ground and power
planes must be kept at a small distance from the input pins on
all layers of the board.
INPUT-TO-INPUT/OUTPUT COUPLING
To minimize capacitive coupling between the inputs and outputs,
the output signal traces should not be parallel with the inputs.
In addition, the input traces should not be close to each other. A
minimum of 7 mils between the two inputs is recommended.
Rev. A | Page 18 of 28
Page 19

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
LOW DISTORTION PINOUT
The ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 feature a new low distortion
pinout from Analog Devices. The new pinout provides two
advantages over the traditional pinout. The first advantage is
improved second harmonic distortion performance, which is
accomplished by the physical separation of the noninverting
input pin and the negative power supply pin. The second
advantage is the simplification of the layout due to the dedicated
feedback pin and easy routing of the gain set resistor back to
the inverting input pin. This allows a compact layout, which
helps to minimize parasitics and increase stability.
The designer does not need to use the dedicated feedback pin to
provide feedback for the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2. The output
pin of the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 can still be used to provide
feedback to the inverting input of the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2.
WIDEBAND PHOTODIODE PREAMP
The wide bandwidth and low noise of the ADA4817-1/
ADA4817-2 make it an ideal choice for transimpedance
amplifiers, such as those used for signal conditioning with
high speed photodiodes. Figure 50 shows an I/V converter
with an electrical model of a photodiode. The basic transfer
function is
RI
×
S
F
(13)
RsC
FF
R
and CF sets the signal bandwidth.
F
C
F
R
F
RSH= 1011
C
M
C
D
C
M
V
OUT
07756-048
OUT
PHOTO
=
+
1
V
where:
I
is the output current of the photodiode.
PHOTO
The parallel combination of
I
PHOTO
C
V
B
Figure 50. Wideband Photodiode Preamp
The stable bandwidth attainable with this preamp is a function
, the gain bandwidth product of the amplifier, and the total
of R
F
capacitance at the summing junction of the amplifier, including the
photodiode capacitance (C
R
and the total capacitance produce a pole in the amplifier’s
F
) and the amplifier input capacitance.
S
loop transmission that can result in peaking and instability.
Adding C
creates a zero in the loop transmission that compen-
F
sates for the effect of the pole and reduces the signal bandwidth.
It can be shown that the signal bandwidth obtained with a 45°
phase margin (f
=
f
)45(
) is defined by
(45)
f
CR
F
S
(14)
)(2
CCCR
++××π
DM
where:
f
is the amplifier crossover frequency.
CR
R
is the feedback resistor.
F
C
is the source capacitance including the photodiode and the
S
board parasitic.
C
is the common-mode capacitance of the amplifier.
M
C
is the differential capacitance of the amplifier.
D
The value of C
C
F
that produces f
F
S
=
2
CCC
++
DM
fR
××π
F
CR
The frequency response shows less peaking if bigger C
can be shown to be
(45)
(15)
values
F
are used.
The preamplifier output noise over frequency is shown in
Figure 51.
f
=
1
2
f
=
2
2
f
=
3
(CF + CS + CM + CD)/C
RF NOISE
f
VOLTAGE NOISE (nV/ Hz)
VEN
2
f
1
NOISE DUE TO AMPLIFIER
Figure 51. Photodiode Voltage Noise Contributions
1
RF (CF + CS + CM + CD)
1
RFC
F
f
CR
VEN (CF + CS + CM + CD)/C
FREQUENCY (Hz)
F
f
F
3
07756-043
Rev. A | Page 19 of 28
Page 20
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
The pole in the loop transmission translates to a zero in the
noise gain of the amplifier, leading to an amplification of the
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
MAGNITUDE (dB)
10
5
G = 63V/V
= 100
R
L
0
= 10V
V
S
= 6V p-p
V
OUT
–5
0.1 1 10 100 1000
Figure 52. Photodiode Preamp Frequency Response
FREQUENCY (MHz)
The loop transmission zero introduced by C
limits the
F
amplification. The noise gain bandwidth extends past the preamp signal bandwidth and is eventually rolled off by the decreasing
loop gain of the amplifier. The current equivalent noise from the
inverting terminal is typically negligible for most applications.
The innovative architecture used in the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
makes balancing both inputs unnecessary, as opposed to traditional
FET input amplifiers. Therefore, minimizing the impedance
seen from the noninverting terminal to ground at all frequencies
is critical for optimal noise performance.
Integrating the square of the output voltage noise spectral density
07756-051
over frequency and then taking the square root allows users
to obtain the total rms output noise of the preamp. Table 9
summarizes approximations for the amplifier and feedback
and source resistances. Noise components for an example
preamp with R
= 50 kΩ, CS = 30 pF, and CF = 0.5 pF
F
(bandwidth of about 6.4 MHz) are also listed.
input voltage noise over frequency.
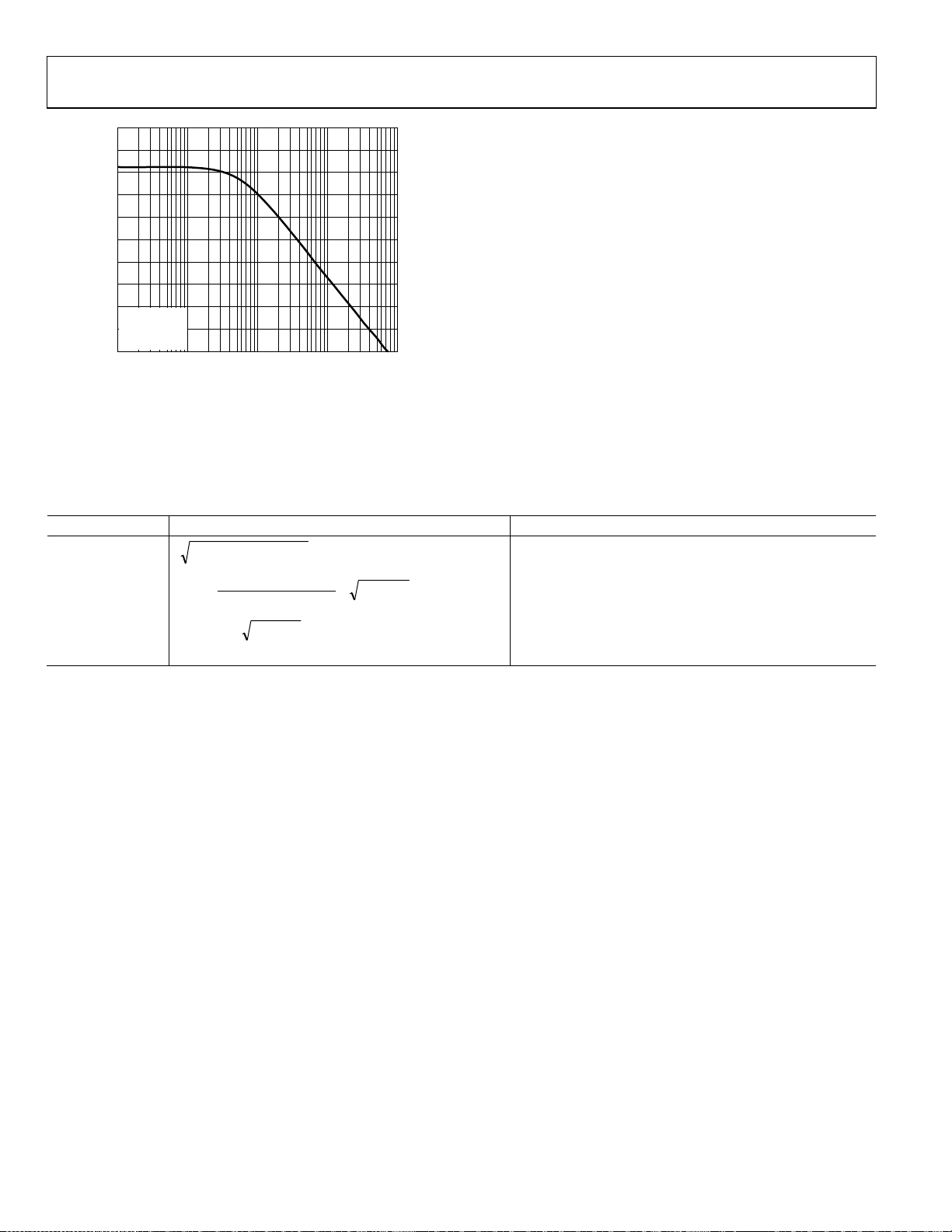
Table 9. RMS Noise Contributions of Photodiode Preamp
Contributor Expression RMS Noise with RF = 50 kΩ, CS = 30 pF, CF = 0.5 pF
RF
VEN Amp
IEN Amp
57.14
××× fRkT
2
F
× f
VEN
C
F
F
57.12××× fRIEN
+++
CCCC
FDMS
57.13××
94 μV
777.5 μV
0.4 μV
783 μV (total)
Rev. A | Page 20 of 28
Page 21
ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
(
δ−δ
V
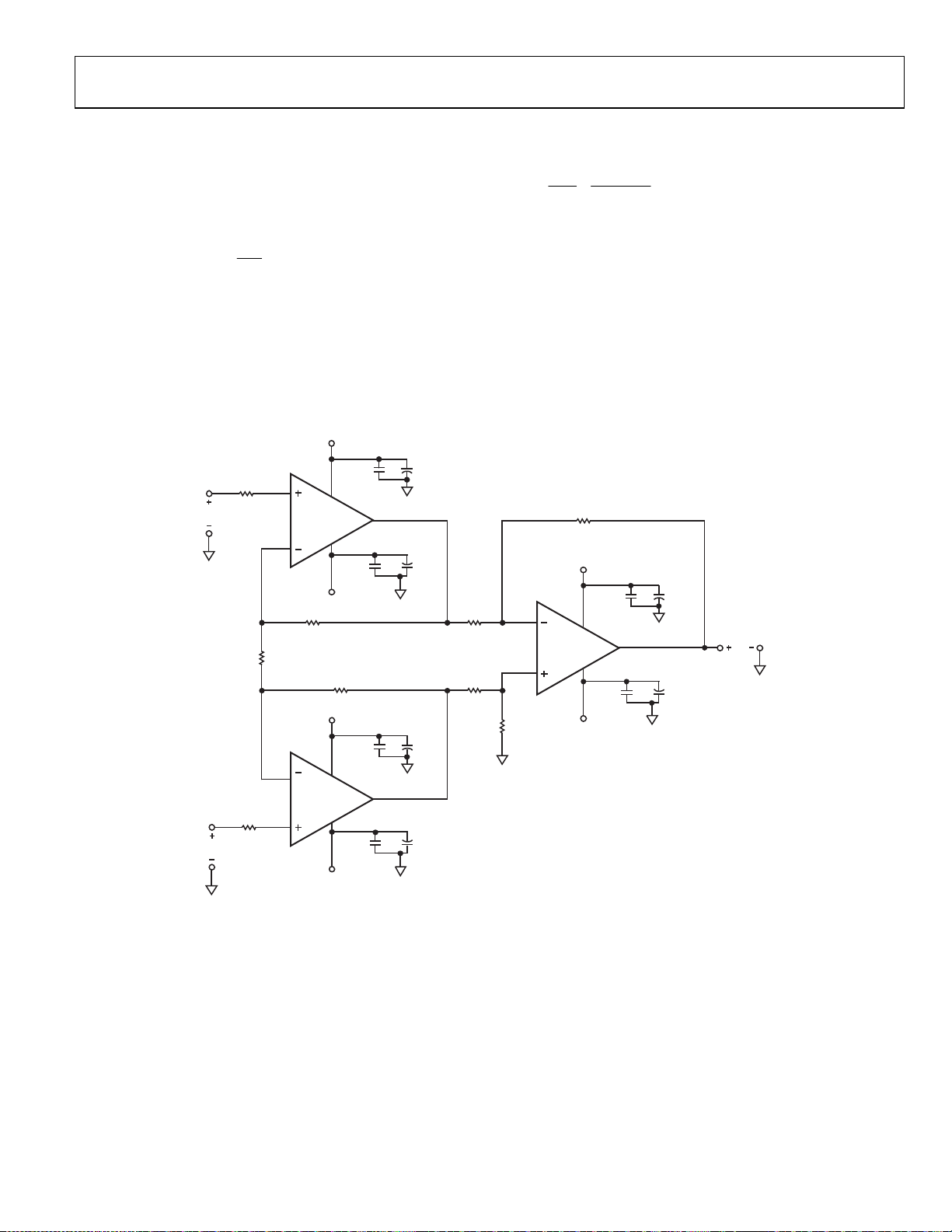
HIGH SPEED JFET INPUT INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
Figure 53 shows an example of a high speed instrumentation
amplifier with a high input impedance using the ADA4817-1/
ADA4817-2. The dc transfer function is
⎛
()
OUT
⎜
VVV
PN
⎜
⎝
For G = 1, it is recommended that the feedback resistors for the
two preamps be set to 0 Ω and the gain resistor be open. The
system bandwidth for G = 1 is 400 MHz. For gains higher than 2,
the bandwidth is set by the preamp, and it can be approximated by
In-amp
= (fCR × RG)/(2 × RF)
−3 dB
⎞
R
2
F
(16)
⎟
1
+−=
⎟
R
G
⎠
CC
Common-mode rejection of the in-amp is primarily determined by
the match of resistor ratios, R1:R2 to R3:R4. It can be estimated by
V
O
=
V
CM
()
)
21
(17)
211
δδ+
The summing junction impedance for the preamps is equal
|| 0.5(RG). Keep this value relatively low to improve the
to R
F
bandwidth response like in the previous example.
R
S1
V
N
R
R
S2
V
P
G
ADA4817-2
U1
V
EE
R
= 500
F
R
= 500
F
V
CC
ADA4817-2
U2
V
EE
10µF0.1µF
R2
350
V
10µF0.1µF
R1
350
R3
350
R4
350
10µF0.1µF
10µF0.1µF
CC
ADA4817-1
V
EE
10µF0.1µF
V
O
10µF0.1µF
07756-050
Figure 53. High Speed Instrumentation Amplifier
Rev. A | Page 21 of 28
Page 22

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
ACTIVE LOW-PASS FILTER (LPF)
Active filters are used in many applications such as antialiasing
filters and high frequency communication IF strips.
With a 410 MHz gain bandwidth product and high slew rate,
the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 is an ideal candidate for active
filters. Moreover, thanks to the low input bias current provided
by the FET stage, the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2 eliminate any dc
errors. Figure 54 shows the frequency response of 90 MHz and
45 MHz LPFs. In addition to the bandwidth requirements, the slew
rate must be capable of supporting the full power bandwidth of the
filter. In this case, a 90 MHz bandwidth with a 2 V p-p output
swing requires at least 870 V/µs. This performance is achievable
at 90 MHz only because of the wide bandwidth and high slew
rate of the ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2.
The circuit shown in Figure 55 is a 4-pole, Sallen-Key, low-pass
filter (LPF). The filter comprises two identical cascaded SallenKey LPF sections, each with a fixed gain of G = 2. The net gain
of the filter is equal to G = 4 or 12 dB. The actual gain shown in
Figure 54 is 12 dB. This does not take into account the output
voltage being divided in half by the series matching termination
resistor, R
Setting the resistors equal to each other greatly simplifies the
design equations for the Sallen-Key filter. To achieve 90 MHz
the value of R should be set to 182 Ω. However, if the value of R
is doubled, the corner frequency is cut in half to 45 MHz. This
would be an easy way to tune the filter by simply multiplying
the value of R (182 Ω) by the ratio of 90 MHz and the new
corner frequency in megahertz. Figure 54 shows the output of
each stage of the filter and the two different filters corresponding
to R = 182 Ω and R = 365 Ω. It is not recommended to increase
the corner frequency beyond 90 MHz due to bandwidth and
slew rate limitations unless unity-gain stages are acceptable.
, and the load resistor.
T
+IN1
R
T
49.9
C1
3.9pF
10µF
+5V
0.1µF
R
R
5.6pF
U1
C2
R2
348
–5V
10µF
0.1µF
R1
348
Figure 55. 4-Pole Sallen-Key Low-Pass Filter (ADA4817-2)
OUT1
Resistor values are kept low for minimal noise contribution,
offset voltage, and optimal frequency response. Due to the low
capacitance values used in the filter circuit, the PCB layout and
minimization of parasitics is critical. A few picofarads can detune
the corner frequency, f
, of the filter. The capacitor values shown
c
in Figure 55 actually incorporate some stray PCB capacitance.
Capacitor selection is critical for optimal filter performance.
Capacitors with low temperature coefficients, such as NPO
ceramic capacitors and silver mica, are good choices for filter
elements.
15
12
9
6
3
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
MAGNITUDE (d B)
–24
–27
–30
–33
–36
–39
–42
100k 1G
OUT2, f = 90MHz
OUT1, f = 90MHz
OUT1, f = 45MHz
OUT2, f = 45MHz
1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 54. Low-Pass Filter Response
C3
3.9pF
10µF
+5V
0.1µF
R4
348
U2
–5V
10µF
0.1µF
R3
348
R
T
49.9
OUT2
07756-054
R
R
5.6pF
C4
07756-062
Rev. A | Page 22 of 28
Page 23

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
0.15
0.10
0.05
VOLTAGE (V)
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
0
90MHz
45MHz
TIME (5ns/DIV)
Figure 56. Small Signal Transient Response (Low-Pass Filter)
1.2
0.8
0.4
0
VOLTAGE (V)
–0.4
–0.8
–1.2
07756-063
Figure 57. Large Signal Transient Response (Low-Pass Filter)
90MHz
45MHz
TIME (5ns/DIV)
07756-064
Rev. A | Page 23 of 28
Page 24

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
3.25
3.00 SQ
INDICATOR
0.90 MAX
0.85 NOM
SEATING
PLANE
PIN 1
12° MAX
2.75
TOP
VIEW
0.70 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
2.95
2.75 SQ
2.55
0.05 MAX
0.01 NOM
0.20 REF
0.60 MAX
Figure 58. 8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VD]
3 mm × 3 mm Body, Very Thin, Dual Lead (CP-8-2)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
5.00 (0.197)
4.90 (0.193)
4.00 (0.157)
3.90 (0.154)
3.80 (0.150)
4.80 (0.189)
85
TOP VIEW
6.20 (0.244)
6.00 (0.236)
41
5.80 (0.228)
0.60 MAX
5
EXPOSED
PA D
(BOTTOM VIEW)
0.50
0.40
0.30
2.29 (0.090)
4
FOR PROPER CONNECTION O F
THE EXPOSE D PAD, REFER T O
THE PIN CONF IGURATIO N AND
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIO NS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
FOR PROPER CONNECTION O F
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONF IGURATIO N AND
FUNCTION DES CRIPTIONS
SECTION O F THIS DAT A SHEET.
2.29 (0.090)
0.50
BSC
8
1.60
1.45
1.30
1
1.89
1.74
1.59
PIN 1
INDICATOR
90308-B
BOTTOM VIEW
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
(PINS UP)
8°
0°
0.50 (0.020)
0.25 (0.010)
45°
1.27 (0.050)
0.40 (0.016)
072808-A
1.75 (0.069)
1.35 (0.053)
0.10 (0.004)
MAX
COPLANARITY
0.10
1.27 (0.05)
BSC
1.65 (0.065)
1.25 (0.049)
SEATING
0.51 (0.020)
0.31 (0.012)
CONTROLL ING DIMENSI ONS ARE IN MILLIMET ER; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-O FF MIL LIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRI ATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
PLANE
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-A A
Figure 59. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package with Exposed Pad [SOIC_N_EP]
(RD-8-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Rev. A | Page 24 of 28
Page 25

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
4.00
BSC SQ
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VGGC
0.35
0.30
0.25
3.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.60 MAX
0.65 BSC
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.75
0.60
0.50
0.08
0.60 MAX
(BOTTO M VIEW )
16
13
12
9
8
5
1.95 BSC
FOR PROPER CO NNECTION O F
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONF IGURATIO N AND
FUNCTION DES CRIPTIONS
SECTION O F THIS DAT A SHEET.
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1
4
5
2
.
2
0
1
.
2
9
.
1
5
0.25 MIN
Q
S
072808-A
Figure 60.16-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
4 mm × 4 mm Body, Very Thin Quad (CP-16-4)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option Ordering Quantity Branding
ADA4817-1ACPZ-R21 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead LFCSP_VD CP-8-2 250 H1F
ADA4817-1ACPZ-RL1 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead LFCSP_VD CP-8-2 5,000 H1F
ADA4817-1ACPZ-R71 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead LFCSP_VD CP-8-2 1,500 H1F
ADA4817-1ARDZ1 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead SOIC_N_EP RD-8-1 1
ADA4817-1ARDZ-RL1 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead SOIC_N_EP RD-8-1 2,500
ADA4817-1ARDZ-R71 –40°C to +105°C 8-Lead SOIC_N_EP RD-8-1 1,000
ADA4817-2ACPZ-R21 –40°C to +105°C 16-Lead LFCSP_VQ CP-16-4 250
ADA4817-2ACPZ-RL1 –40°C to +105°C 16-Lead LFCSP_VQ CP-16-4 5,000
ADA4817-2ACPZ-R71 –40°C to +105°C 16-Lead LFCSP_VQ CP-16-4 1,500
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
Rev. A | Page 25 of 28
Page 26

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 26 of 28
Page 27

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 27 of 28
Page 28

ADA4817-1/ADA4817-2
NOTES
©2008–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D07756-0-3/09(A)
Rev. A | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...