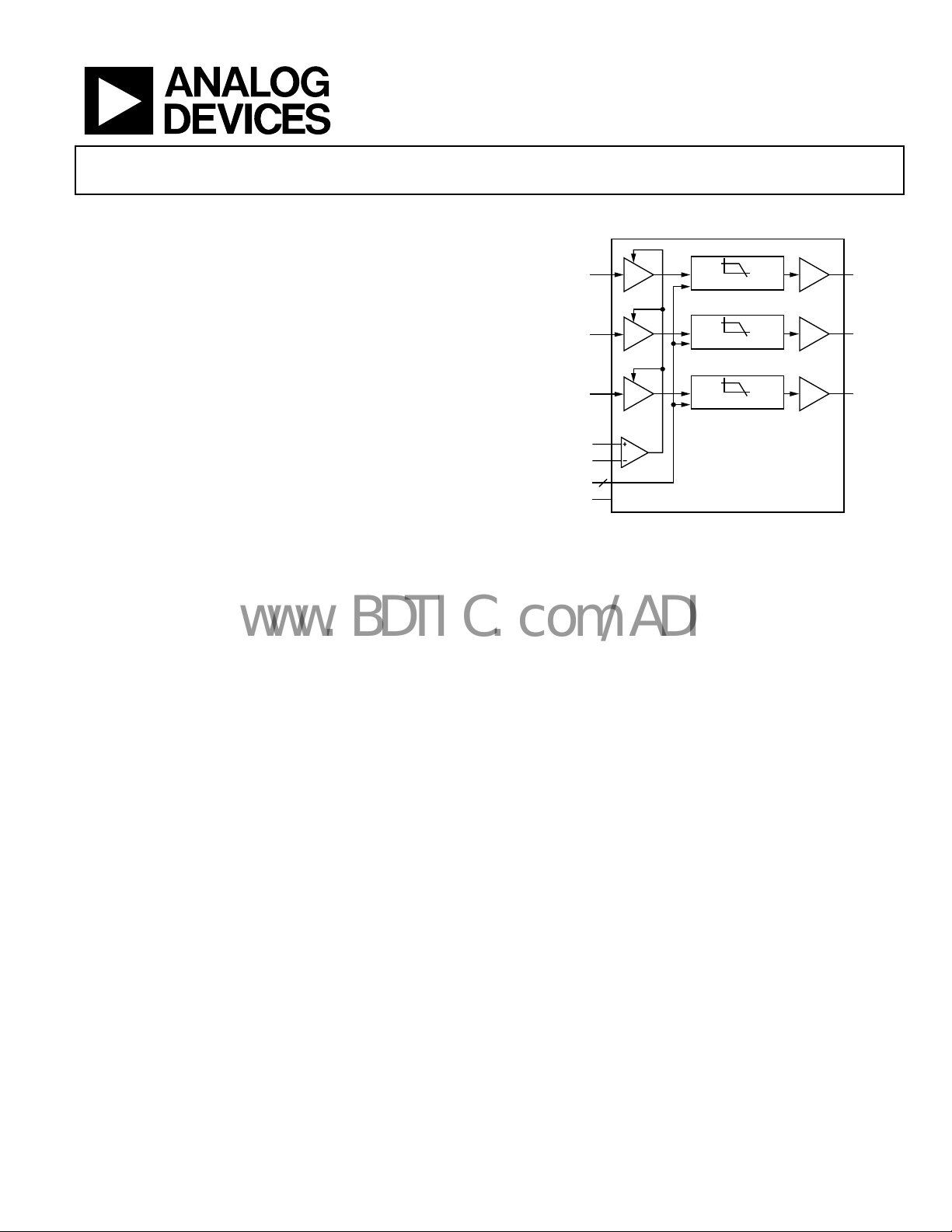
Integrated Triple Video Filter with Selectable
T
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
Sixth-order adjustable video filters
36 MHz, 18 MHz, and 9 MHz
Many video standards supported: RGB, YPbPr, YUV, SD, Y/C
Ideal for 720p and 1080i resolutions
−1 dB bandwidth of 31.5 MHz for HD
Low quiescent power
Only 265 mW for 3 channels on 5 V supply
Disable feature cuts supply current to 10 μA
DC output offset adjust: ±0.5 V, input referred
Fixed throughput gain of ×2
Excellent video specifications
Wide supply range: +4.5 V to ±5 V
Rail-to-rail output
Output can swing 4.5 V p-p on single 5 V supply
Small packaging: 20-lead QSOP
APPLICATIONS
Set-top boxes
DVD players and recorders
Personal video recorders
HDTVs
Projectors
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Cutoff Frequencies for RGB, HD/SD
ADA4412-3
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Y/G IN
Pb/B IN
Pr/R IN
LEVEL1
LEVEL2
CUTOFF S E LECT
DISABLE
×1
×1
×1
DC
OFFSET
2
36MHz, 18MHz, 9MHz
36MHz, 18MHz, 9MHz
36MHz, 18MHz, 9MHz
ADA4412-3
Figure 1.
×2
×2
×2
Y/G OUT
Pb/B OU
Pr/R OUT
05528-001
The ADA4412-3 is a comprehensive filtering solution designed
to give designers the flexibility to easily filter and drive various
video signals, including high definition video. Cutoff frequencies of the sixth-order video filters range from 9 MHz to
36 MHz and can be selected by two logic pins to obtain four
filter combinations that are tuned for RGB, high definition, and
standard definition video signals. The ADA4412-3 has a rail-torail output that can swing 4.5 V p-p on a single 5 V supply.
The ADA4412-3 includes an output offset voltage adjustment
fe
ature. Output voltage offset is continuously adjustable over an
input-referred range of ±500 mV by applying a differential
voltage to an independent offset control input.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The ADA4412-3 can operate on a single +5 V supply as
ell as on ±5 V supplies. Single-supply operation is ideal in
w
applications where power consumption is critical. The disable
feature allows for further power conservation by reducing the
supply current to typically 10 µA when a particular device is not
in use.
Dual-supply operation is best for applications where the
ne
gative-going video signal excursions must swing at or below
ground while maintaining excellent video performance. The
output buffers have the ability to drive two 75 Ω doubly
terminated cables that are either dc-coupled or ac-coupled.
The ADA4412-3 is available in a 20-lead QSOP and is rated for
peration over the extended industrial temperature range of
o
−40°C to +85°C.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 © 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications..................................................................................... 10
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration And Function Descriptions............................ 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 7
Theory of Operation ........................................................................ 9
REVISION HISTORY
7/05—Revision 0: Initial Version
Overview ..................................................................................... 10
Disable ......................................................................................... 10
Cutoff Frequency Selection ....................................................... 10
Output DC Offset Control........................................................ 10
Input and Output Coupling ...................................................... 11
Printed Circuit Board Layout ................................................... 11
Video Encoder Reconstruction Filter...................................... 11
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 13
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 13
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 16
ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
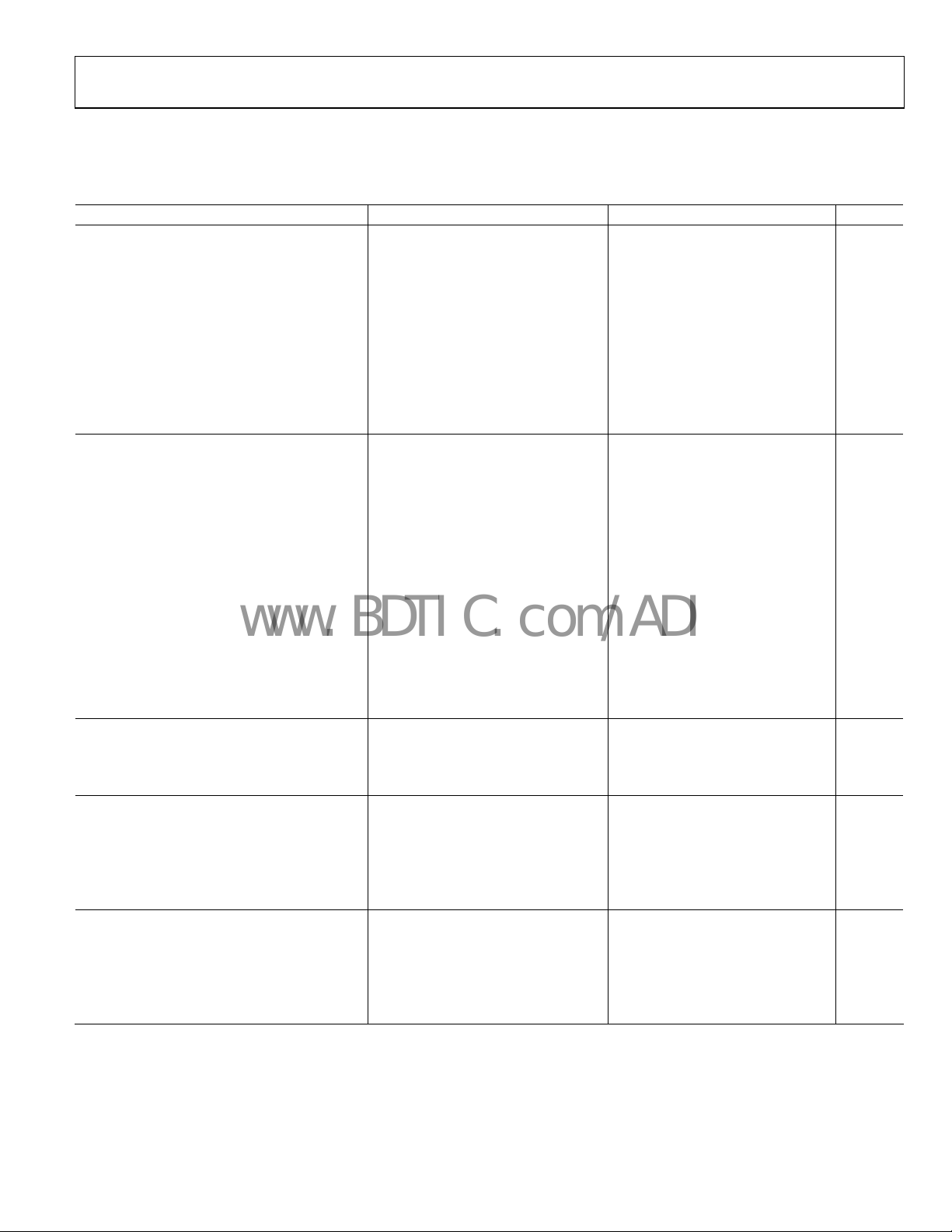
SPECIFICATIONS
VS = 5 V, @ TA = 25°C, VO = 1.4 V p-p, RL = 150 Ω, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
OVERALL PERFORMANCE
Offset Error Input referred, all channels 9 23 mV
Offset Adjust Range Input referred ±500 mV
Input Voltage Range, All Inputs VS− − 0.1 VS+ − 2.0 V
Output Voltage Swing, All Outputs Positive swing VS+ − 0.30 VS+ − 0.20 V
Negative swing VS− + 0.10 VS− + 0.15 V
Linear Output Current per Channel 30 mA
Integrated Voltage Noise, Referred to Input All channels 0.50 mV rms
Filter Input Bias Current All channels 6.6 μA
Total Harmonic Distortion at 1 MHz FC = 36 MHz, FC = 18 MHz/FC = 9 MHz 0.01/0.04 %
Gain Error Magnitude 0.09 0.49 dB
FILTER DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−1 dB Bandwidth Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 26.5 31.5 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 13.5 15.5 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 6.5 8.0 MHz
−3 dB Bandwidth Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 34 37 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 16 19 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 8 9 MHz
Out-of-Band Rejection f = 75 MHz −31 −43 dB
Crosstalk f = 5 MHz, FC = 36 MHz −62 dB
Propagation Delay f = 5 MHz, FC = 36 MHz 19 ns
Group Delay Variation Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 7 ns
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 14 ns
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 27 ns
Differential Gain NTSC, FC = 9 MHz 0.16 %
Differential Phase NTSC, FC = 9 MHz 0.05 Degrees
CUTOFF CONTROL INPUT PERFORMANCE
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Bias Current 10 15 μA
DISABLE PERFORMANCE
DISABLE Assert Voltage VS+ − 0.5 V
DISABLE Assert Time 100 ns
DISABLE Deassert Time 130 ns
DISABLE Input Bias Current 12 μA
Input-to-Output Isolation—Disabled f = 10 MHz 90 dB
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 4.5 12 V
Quiescent Current 53 56 mA
Quiescent Current—Disabled 10 150 μA
PSRR, Positive Supply All channels 64 70 dB
PSRR, Negative Supply All channels 58 60 dB
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 16
ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
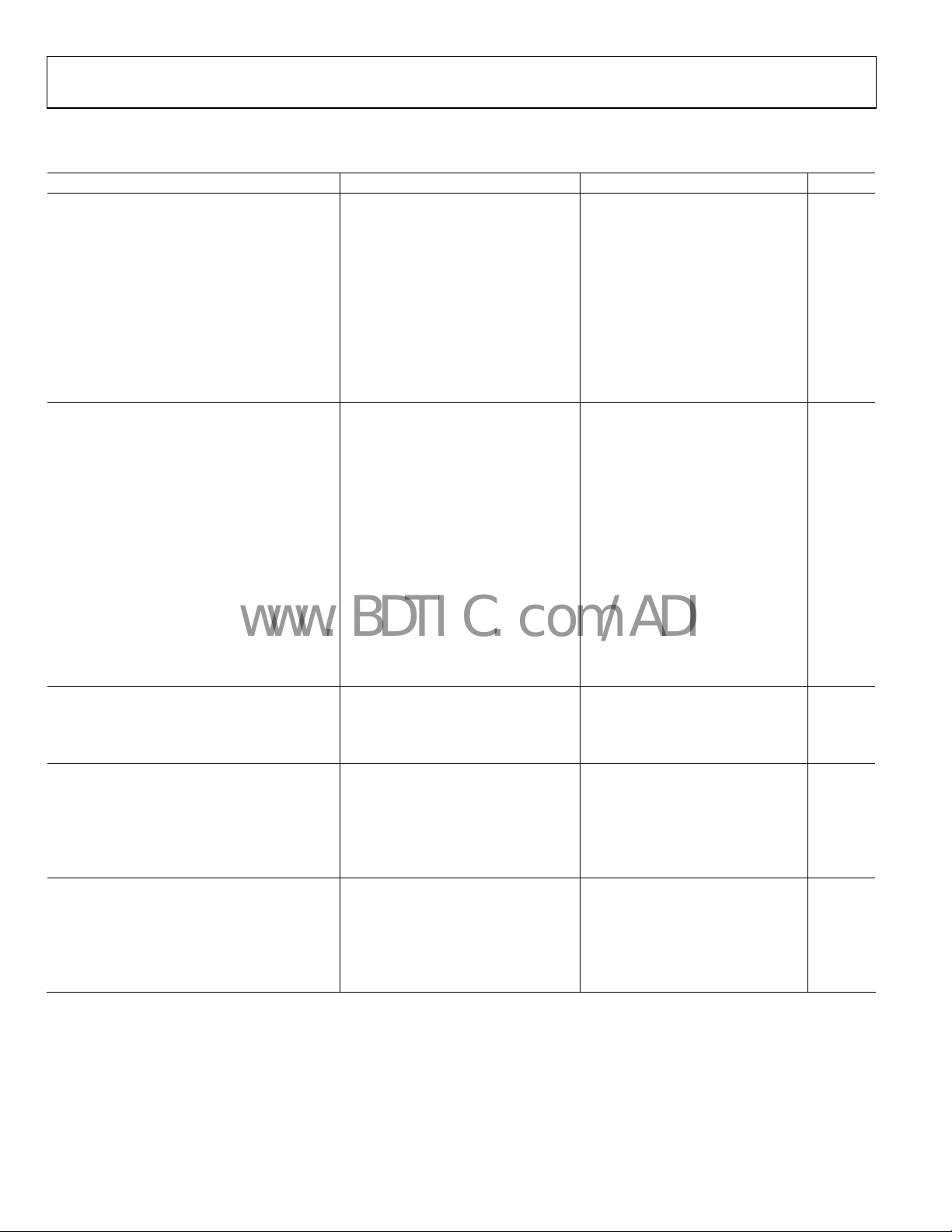
VS = ±5 V, @ TA = 25°C, VO = 1.4 V p-p, RL = 150 Ω, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
OVERALL PERFORMANCE
Offset Error Input referred, all channels 10 25 mV
Offset Adjust Range Input referred ±500 mV
Input Voltage Range, All Inputs VS− − 0.1 VS+ − 2.0 V
Output Voltage Swing, All Outputs Positive swing VS+ − 0.33 VS+ − 0.24 V
Negative swing VS− + 0.24 VS− + 0.33 V
Linear Output Current per Channel 30 mA
Integrated Voltage Noise, Referred to Input All channels 0.50 mV rms
Filter Input Bias Current All channels 6.3 μA
Total Harmonic Distortion at 1 MHz FC = 36 MHz, FC = 18 MHz/FC = 9 MHz 0.01/0.03 %
Gain Error Magnitude 0.04 0.50 dB
FILTER DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−1 dB Bandwidth Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 30.0 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 15.5 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 8.0 MHz
−3 dB Bandwidth Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 34 36 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 17 19 MHz
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 8 9 MHz
Out-of-Band Rejection f = 75 MHz −31 −42 dB
Crosstalk f = 5 MHz, FC = 36 MHz −62 dB
Propagation Delay f = 5 MHz, FC = 36 MHz 19 ns
Group Delay Variation Cutoff frequency select = 36 MHz 7 ns
Cutoff frequency select = 18 MHz 12 ns
Cutoff frequency select = 9 MHz 24 ns
Differential Gain NTSC, FC = 9 MHz 0.04 %
Differential Phase NTSC, FC = 9 MHz 0.16 Degrees
CUTOFF CONTROL INPUT PERFORMANCE
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Bias Current 10 15 μA
DISABLE PERFORMANCE
DISABLE Assert Voltage VS+ − 0.5 V
DISABLE Assert Time 75 ns
DISABLE Deassert Time 125 ns
DISABLE Input Bias Current 35 μA
Input-to-Output Isolation—Disabled f = 10 MHz 90 dB
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 4.5 12 V
Quiescent Current 57 60 mA
Quiescent Current—Disabled 10 150 μA
PSRR, Positive Supply All channels 66 74 dB
PSRR, Negative Supply All channels 59 62 dB
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 16
ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
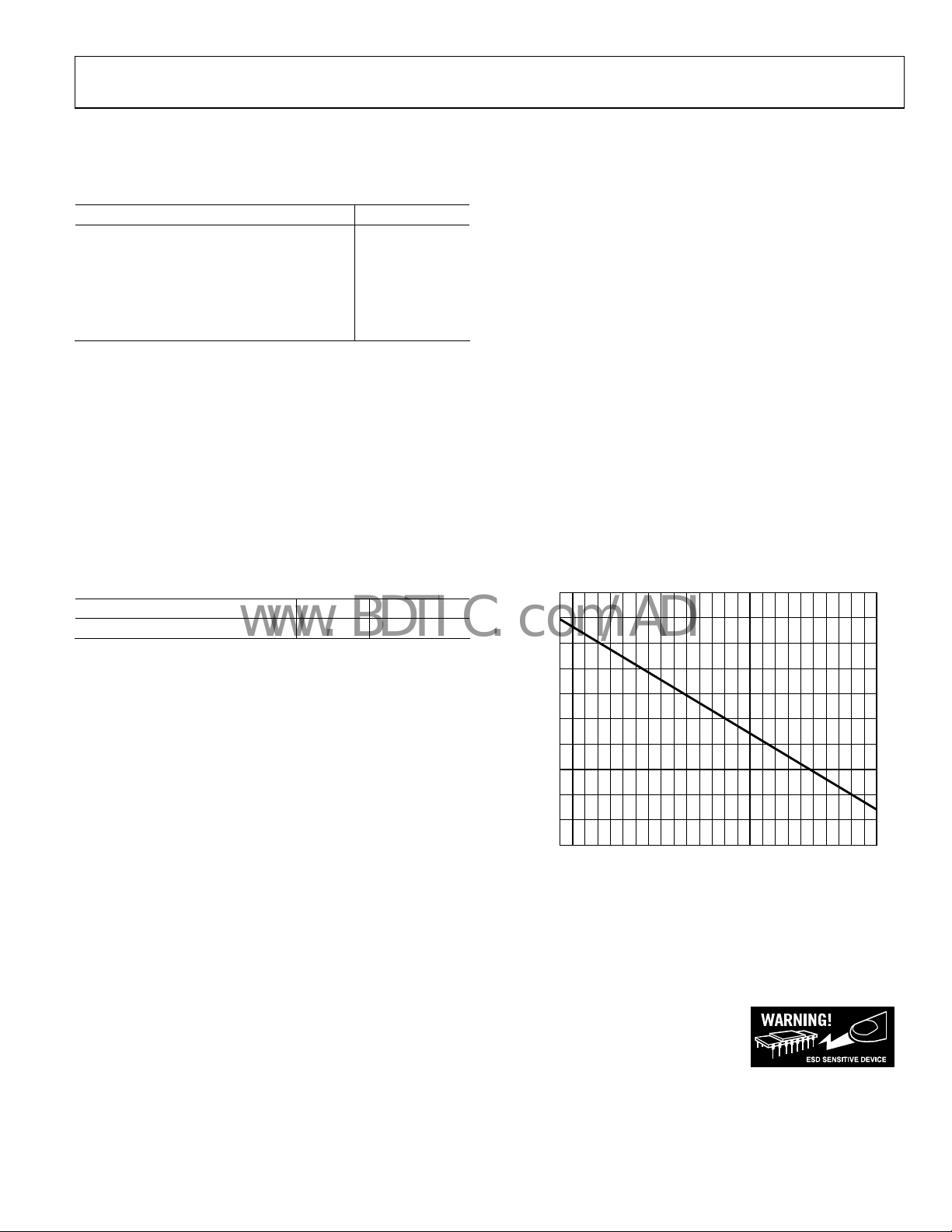
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 12 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 2
Storage Temperature –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range –40°C to +85°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for device soldered in circuit board for surface-mount
packages.
Table 4. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θ
20-Lead QSOP 83 °C/W
JA
Maximum Power Dissipation
The maximum safe power dissipation in the ADA4412-3
package is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature
(T
) on the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass
J
transition temperature, the plastic changes its properties.
Even temporarily exceeding this temperature limit may change
the stresses that the package exerts on the die, permanently
shifting the parametric performance of the ADA4412-3.
Exceeding a junction temperature of 150°C for an extended
period can result in changes in the silicon devices potentially
causing failure.
Unit
The power dissipated in the package (P
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
package due to the load drive for all outputs. The quiescent
power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
quiescent current (I
depends on the particular application. For each output, the
power due to load drive is calculated by multiplying the load
current by the associated voltage drop across the device. The
power dissipated due to all of the loads is equal to the sum of
the power dissipations due to each individual load. RMS
voltages and currents must be used in these calculations.
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
In addition, more metal directly in contact with the package
leads from metal traces, through-holes, ground, and power
planes reduces the θ
Figure 2 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
ackage vs. the ambient temperature for the 20-lead QSOP
p
(83°C/W) on a JEDEC standard 4-layer board. θ
approximations.
2.5
2.3
2.1
1.9
1.7
1.5
WATTS
1.3
1.1
0.9
0.7
0.5
–40 –20 0 20 40 60
Figure 2. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature for a 4-Layer Board
). The power dissipated due to load drive
S
.
JA
AMBIENT TEMP E R A TURE (°C)
) is the sum of the
D
) times the
S
values are
JA
.
JA
80
05528-002
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 16

ADA4412-3
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
LEVEL1
DISABLE
F_SEL_
F_SEL_B
1
2
3
Y/G
4
GND
Pb/B
GND
Pr/R
GND
Figure 3. 20-Lead QSOP Pin
ADA4412-3
5
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
6
7
8
9
10
NC = NO CONNECT
20
LEVEL2
19
VCC
18
Y/G_OUT
17
VEE
16
Pb/B_OUT
15
VEE
14
Pr/R_OUT
13
VCC
12
NC
11
DGND
Configuration
05528-003
Table 5. 20-Lead QSOP Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Name Description
1 LEVEL1 DC Level Adjust Pin 1
2 DISABLE Disable/Power Down
3 Y/G Y/G Video Input
4 GND Signal Ground Reference
5 Pb/B Pb/B Video Input
6 GND Signal Ground Reference
7 Pr/R Pr/R Video Input
8 F_SEL_A Filter Cutoff Select Input A
9 F_SEL_B Filter Cutoff Select Input B
10 GND Signal Ground Reference
11 DGND Digital Ground Reference
12 NC No Internal Connection
13 VCC Positive Power Supply
14 Pr/R_OUT Pr/R Video Output
15 VEE Negative Power Supply
16 Pb/B_OUT Pb/B Video Output
17 VEE Negative Power Supply
18 Y/G_OUT Y/G Video Output
19 VCC Positive Power Supply
20 LEVEL2 DC Level Adjust Pin 2
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 16

ADA4412-3
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Unless otherwise noted, RL = 150 , VO = 1.4 V p-p, VS = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
9
6
3
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
–24
GAIN (dB)
–27
–30
–33
–36
–39
–42
–45
–48
1 10 100
Figure 4. Frequency Response vs. Po
FC = 9MHz
FC = 18MHz
BLACK LINE: VS = +5V
GRAY LINE: V
= ±5V
S
FREQUENCY (MHz)
wer Supply and Cutoff Frequency
FC = 36MHz
05528-004
9
6
3
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
–24
GAIN (dB)
–27
–30
–33
–36
–39
–42
–45
–48
110100
FC = 9MHz
FC = 18MHz
–40°C
+25°C
+85°C
FREQUENCY (MHz)
FC = 36MHz
Figure 7. Frequency Response vs. Temperature and Cutoff Frequency
05528-007
6.5
6.0
5.5
FC = 9MHz
5.0
4.5
GAIN (dB)
4.0
BLACK LINE: VS = +5V
GRAY LINE: V
3.5
3.0
1 10 100
Figure 5. Frequency Response F
9
6
3
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
–24
GAIN (dB)
–27
–30
–33
BLACK LINE:
–36
V
–39
OUT
GRAY LINE:
–42
V
OUT
–45
–48
110100
FC = 18MHz
S
FC = 9MHz
FC = 18MHz
= 100mV p- p
= 2V p-p
= ±5V
FREQUENCY (MHz)
latness vs. Cutoff Frequency
FREQUENCY ( MHz)
FC = 36MHz
FC = 36MHz
Figure 6. Frequency Response vs. Output Amplitude and Cutoff Frequency
100
90
80
FC = 9MHz
70
60
50
FC = 18MHz
40
GROUP DELAY (ns)
30
20
05528-005
FC = 36MHz
10
110
FREQUENCY ( M Hz )
Figure 8. Group Delay vs. Frequency, Po
40
R
= 300
SOURCE
Y AND Pr SOURCE CHA NNE LS
Pb RECEPTOR CHANNEL
–50
–60
FC = 9MHz
–70
–80
–90
CROSSTALK REFERRE D TO INPUT (dB)
05528-006
–100
0.1 1 10 100
Ω
FC = 18MHz
FC = 36MHz
FREQUENC Y ( M Hz )
Figure 9. Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk vs. Frequency and Cuto
BLACK LINE: VS = +5V
GRAY LINE : V
= ±5V
S
100
wer Supply, and Cutoff Frequency
ff Frequency
05527-008
05528-009
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
5
5
–5
–15
–25
–35
PSRR (dB)
–45
–55
–65
–75
0.1 1 10 100
FC = 9MHz
FC = 36MHz
FREQUENCY ( M Hz)
Figure 10. Positive Supply PSRR vs. Frequency
3.5
2 ×
INPUT
3.3
3.1
2.9
2.7
2.5
2.3
2.1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1.9
1.7
1.5
OUTPUT
0.5% (70ns)
ERROR
1% (58ns)
FC = 18MHz
and Cutoff Frequency
50ns/DIV
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
–2.5
–5
–15
–25
–35
PSRR (dB)
–45
–55
–65
05528-011
–75
0.1 1 10 100
Figure 13. Negative Supply PSRR vs. Frequen
6
5
4
3
ERROR (%)
05528-010
2
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1
0
–1
= 36MHz
F
C
F
C
= 9MHz
FC = 9MHz
FC = 18MHz
FC = 18MHz
FC = 36MHz
FREQUENCY ( M Hz)
2× INPUT
cy and Cutoff Frequency
200ns/DIV
05528-013
05528-014
3.5
3.3
3.1
F
= 36MHz
C
2.9
2.7
= 18MHz
F
C
2.5
2.3
2.1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1.9
1.7
1.5
Figure 12. Transient Respo
Figure 11. Settling Time
FC = 9MHz
100ns/DIV
nse vs. Cutoff Frequency
NETWORK
ANALYZE R Tx
05528-012
MINIMUM - LOSS M ATCHING NETWOR K LOSS CALIBRATE D OUT
Figure 14. Overdrive Recove
ry vs. Cutoff Frequency
= 150Ω
R
L
50Ω 118Ω
DUT
50Ω 86.6Ω
NETWORK
ANALYZE R Rx
50Ω
Figure 15. Basic Test Circuit for Swept Frequency Measurements
05528-051
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
THEORY OF OPERATION
The ADA4412-3 is an integrated video filtering and driving
solution that offers variable bandwidth to meet the needs of a
number of different video resolutions. There are three filters
targeted for use with component video signals. The filters
have selectable bandwidths that correspond to the popular
component video standards. Each filter has a sixth-order
Butterworth response that includes group delay optimization.
The group delay variation from 1 MHz to 36 MHz in the
36 MHz section is 7 ns, which produces a fast settling pulse
response.
The ADA4412-3 is designed to opera
ments. The supply range is 5 V to 12 V, single supply or dual
supply, and requires a relatively low nominal quiescent current
of 15 mA per channel. In single-supply applications, the PSRR
is greater than 60 dB, providing excellent rejection in systems
with supplies that are noisy or under-regulated. In applications
where power consumption is critical, the part can be powered
down to draw typically 10 µA by pulling the DISABLE pin to
the most positive rail. The ADA4412-3 is also well-suited for
high encoding frequency applications because it maintains a
stop-band attenuation of over 40 dB to 400 MHz.
The ADA4412-3 is intended to take dc-coupled inputs
rom an encoder or other ground referenced video signals.
f
The ADA4412-3 input is high impedance. No minimum or
maximum input termination is required, though input
terminations above 1 kΩ can degrade crosstalk performance
at high frequencies. No clamping is provided internally. For
applications where dc restoration is required, dual supplies
work best. Using a termination resistance of less than a few
hundred ohms to ground on the inputs and suitably adjusting
the level-shifting circuitry provides precise placement of the
output voltage.
te in many video environ-
For single-supply applications (V
range extends from 100 mV below ground to within 2.0 V of
the most positive supply. Each filter input includes level-shifting
circuitry. The level-shifting circuitry adds a dc component to
ground-referenced input signals so that they can be reproduced
accurately without the output buffers hitting the negative rail.
Because the filters have negative rail input and rail-to-rail
output, dc level shifting is generally not necessary, unless
accuracy greater than that of the saturated output of the driver
is required at the most negative edge. This varies with load but
is typically 100 mV in a dc-coupled, single-supply application. If
ac coupling is used, the saturated output level is higher because
the drivers have to sink more current on the low side. If dual
supplies are used (V
dual-supply applications, the level-shifting circuitry can be used
to take a ground referenced signal and put the blanking level at
ground while the sync level is below ground.
The output drivers on the ADA4412-3 have rail-to-rail output
apabilities with 6 dB gain. Each output is capable of driving
c
two ac- or dc-coupled, 75 Ω source-terminated loads. If a large
dc output level is required while driving two loads, ac coupling
should be used to limit the power dissipation.
< GND), no level shifting is required. In
S−
= GND), the input voltage
S−
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 16

ADA4412-3
(
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATIONS
OVERVIEW
With its high impedance inputs and high output drive, the
ADA4412-3 is ideally suited to video reconstruction and
antialias filtering applications. The high impedance inputs give
designers flexibility with regard to how the input signals are
terminated. Devices with DAC current source outputs that feed
the ADA4412-3 can be loaded in whatever resistance provides
the best performance, and devices with voltage outputs can be
optimally terminated as well. The ADA4412-3 outputs can each
drive up to two source-terminated 75 Ω loads and can therefore
directly drive the outputs from set-top boxes, DVD players, and
the like without the need for a separate output buffer.
Binary control inputs are provided to select the filter cutoff
requency. These inputs are compatible with 3 V and 5 V TTL
f
and CMOS logic levels referenced to GND. The disable feature
is asserted by pulling the DISABLE pin to the positive supply.
OUTPUT DC OFFSET CONTROL
The LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs work as a differential, inputreferred output offset control. In other words, the output offset
voltage of a given channel is equal to the difference in voltage
between the LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs multiplied by the
overall filter gain. This relationship is expressed in Equation 1.
OS
LEVEL1 and LE
inputs, and the factor of 2 reflects the gain of ×2 in the output
stage.
For example, setting LEVEL1 to 300 mV and LEVEL2 to 0 V
s
hifts the offset voltages at the ADA4412-3 outputs to 600 mV.
This particular setting can be used in most single-supply
applications to keep the output swings safely above the negative
supply rail.
)
VEL2 are the voltages applied to the respective
−= (1)
)(2)( LEVEL2LEVEL1OUTV
The LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs comprise a differential input
tha
t controls the dc level at the output pins.
DISABLE
The ADA4412-3 includes a disable feature that can be used
to save power when a particular device is not in use. As
indicated in the Overview section, the disable feature is
a
sserted by pulling the DISABLE pin to the positive supply.
The DISABLE pin also functions as a reference level for the
logic inputs and therefore must be connected to ground when
the device is not disabled.
Tabl e 6 summarizes the disable feature operation.
Table 6. DISABLE Function
DISABLE Pin Connection Status
V
S+
GND Enabled
Disabled
CUTOFF FREQUENCY SELECTION
Four combinations of cutoff frequencies are provided for the
video signals. The cutoff frequencies have been selected to
correspond with the most commonly deployed component
video scanning systems. Selection between the cutoff frequency
combinations is controlled by the logic signals applied to the
F_SEL_A and F_SEL_B inputs.
equency selection.
fr
Table 7. Filter Cutoff Frequency Selection
F_SEL_A F_SEL_B Y/G Cutoff Pb/B Cutoff Pr/R Cutoff
0 0 36 MHz 36 MHz 36 MHz
0 1 36 MHz 18 MHz 18 MHz
1 0 18 MHz 18 MHz 18 MHz
1 1 9 MHz 9 MHz 9 MHz
Tabl e 7 summarizes cutoff
The maximum differential voltage that can be applied across the
VEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs is ±500 mV. From a single-ended
LE
standpoint, the LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs have the same
range as the filter inputs. See the
VEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs must each be bypassed to
The LE
GND with a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor.
In single-supply applications, a positive output offset must be
a
pplied to keep the negative-most excursions of the output
signals above the specified minimum output swing limit.
Figure 16 and Figure 17 illustrate several ways to use the
LE
VEL1 and LEVEL2 inputs. Figure 16 shows examples of how
o generate fully adjustable LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 voltages from
t
±5 V and single +5 V supplies. These circuits show a general
case, but a more practical approach is to fix one voltage and
vary the other.
a 600 mV o
Although the LEVEL2 input could simply be connected to
GND,
Figure 17 includes bypassed resistive voltage dividers for
eac
h input so that the input levels can be changed, if necessary.
Additionally, many in-circuit testers require that I/O signals not
be tied directly to the supplies or GND. DNP indicates do not
populate.
Figure 17 illustrates an effective way to produce
utput offset voltage in a single-supply application.
Specifications for the limits.
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 16

ADA4412-3
A
Ω
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
+5V
9.53kΩ
1kΩ
9.53kΩ
–5V
+5V
9.09kΩ
1kΩ
Figure 16. Generating Fully Adjusta
DUAL SUPPLY
9.53kΩ
LEVEL1
0.1μF
SINGLE SUPPLY
LEVEL1
0.1μF
9.53kΩ
9.09kΩ
+5V
1kΩ
–5V
+5V
1kΩ
ble Output Offsets
0.1μF
0.1μF
LEVEL2
LEVEL2
05528-018
+5V
10kΩ
LEVEL1
634Ω
Figure 17. Flexible Circuits to Set the LEVEL1 and LEVEL2 Inputs to
Obt
0.1μF
ain a 600 mV Output Offset on a Single Supply
DNP
0Ω
+5V
DNP
LEVEL2
05528-019
INPUT AND OUTPUT COUPLING
Inputs to the ADA4412-3 are normally dc-coupled. Ac coupling
the inputs is not recommended; however, if ac coupling is
necessary, suitable circuitry must be provided following the ac
coupling element to provide proper dc level and bias currents at
the ADA4412-3 input stages. The ADA4412-3 outputs can be
either ac- or dc-coupled.
When driving single ac-coupled loads in standard 75 Ω video
dis
tribution systems, 220 µF coupling capacitors are
recommended for use on all but the chrominance signal output.
Since the chrominance signal is a narrow-band modulated
carrier, it has no low frequency content and can therefore be
coupled with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
There are two ac coupling options when driving two loads from
o
ne output. One simply uses the same value capacitor on the
second load, while the other is to use a common coupling
capacitor that is at least twice the value used for the single load
(see
Figure 18 and Figure 19).
When driving two parallel 150 Ω loads (75 Ω effective load),
t
he 3 dB bandwidth of the filters typically varies from that of
the filters with a single 150 Ω load. For the 9 MHz and 18 MHz
filters, the typical variation is within ±1.0%; for the 36 MHz
filters, the typical variation is within ±2.5%.
75
220μF
470μF
75Ω
220μF
75Ω
75Ω
75Ω
ds with One Common Coupling Capacitor
DA4412-3
Figure 18. Driving Two AC-Coupled Loads with Two Coupling Capacitors
ADA4412-3
Figure 19. Driving Two AC-Coupled Loa
CABLE
CABLE
75Ω
CABLE
75Ω
CABLE
75Ω
75Ω
75Ω
75Ω
75Ω
05528-020
05528-021
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD LAYOUT
As with all high speed applications, attention to printed
circuit board layout is of paramount importance. Standard high
speed layout practices should be adhered to when designing
with the ADA4412-3. A solid ground plane is recommended,
and surface-mount, ceramic power supply decoupling
capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the supply
pins. All of the ADA4412-3 GND pins should be connected to
the ground plane with traces that are as short as possible.
Controlled impedance traces of the shortest length possible
should be used to connect to the signal I/O pins and should not
pass over any voids in the ground plane. A 75 Ω impedance
level is typically used in video applications. All signal outputs of
the ADA4412-3 should include series termination resistors
when driving transmission lines.
When the ADA4412-3 receives its inputs from a device
th current outputs, the required load resistor value for
wi
the output current is often different from the characteristic
impedance of the signal traces. In this case, if the interconnections are sufficiently short (<< 0.1 wavelength), the trace does
not have to be terminated in its characteristic impedance.
Traces of 75 can be used in this instance, provided their
lengths are an inch or two at the most. This is easily achieved
because the ADA4412-3 and the device feeding it are usually
adjacent to each other, and connections can be made that are
less than one inch in length.
VIDEO ENCODER RECONSTRUCTION FILTER
The ADA4412-3 is easily applied as a reconstruction filter at the
DAC outputs of a video encoder. Figure 20 illustrates how to use
e ADA4412-3 in this type of application with an ADV7322 video
th
encoder in a single-supply application with ac-coupled outputs.
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
5V
(ANALOG)
0.1μF
0.1μF
0Ω
0.1μF
10kΩDNP
634Ω
0.1μF
1
20
2
13
VCC
LEVEL1
LEVEL2
ADA4412-3
DISABLE
19
VCC
VIDEO ENCODER
VIDEO
DAC
OUTPUTS
ADV7322
CUTOFF
FREQUENCY
SELECT
INPUT
R
L
R
L
R
L
8
9
3
5
7
F_SEL_A
F_SEL_B
Y/G
Pb/B
Pr/R
GND
4, 6, 10
DGND
Y/G_OUT
Pb/B_OUT
Pr/R_OUT
VEE
11
15, 17
Figure 20. The ADA4412-3 Applied as a Single-Supply Reconstruction Filter Following the ADV7322
220μF
75Ω
18
220μF
75Ω
16
220μF
75Ω
14
05528-024
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.341
BSC
PIN 1
0.010
0.004
COPLANARITY
0.004
20 11
1
0.065
0.049
0.025
BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-137-AD
Figure 21. 20-Lead Shrink Small Outline Package [QSOP]
Dimensions shown in inches
0.069
0.053
0.012
0.008
(R
10
Q-20)
0.154
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
0.236
BSC
0.010
0.006
8°
0°
0.050
0.016
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Order Quantity Package Option
ADA4412-3ARQZ
ADA4412-3ARQZ-R7
ADA4412-3ARQZ-RL
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
1
1
–40°C to +85°C 20-Lead QSOP 1 RQ-20
–40°C to +85°C 20-Lead QSOP 1,000 RQ-20
–40°C to +85°C 20-Lead QSOP 2,500 RQ-20
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 16

ADA4412-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
© 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05528–0–7/05(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...