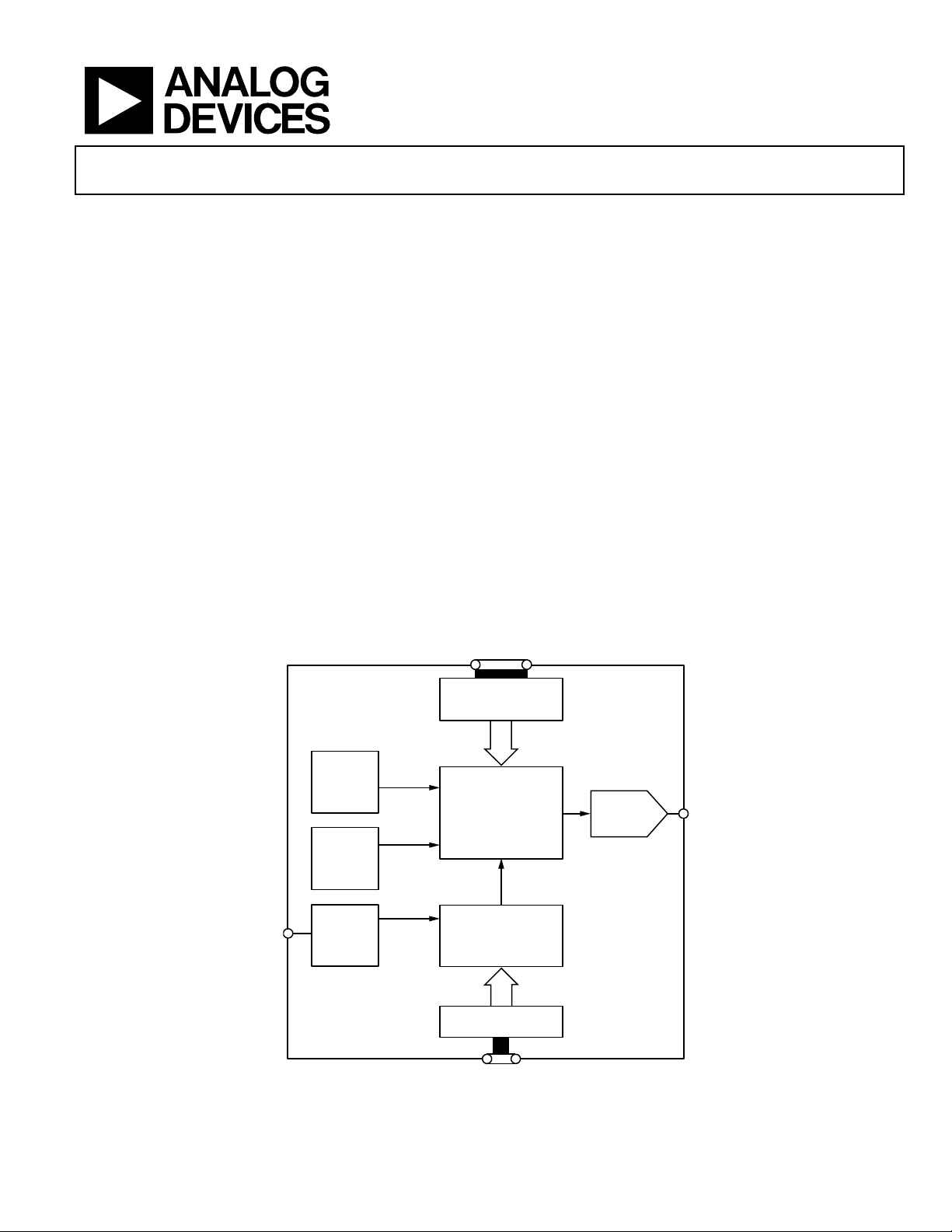
Direct Digital Synthesizer
AD9910
Rev. D
Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007–2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
14-BIT DAC
1GSPS DDS CO RE
LINEAR
RAMP
GENERATOR
1024-
ELEMENT
RAM
HIGH SPEED PARALLEL
DATA INTERFACE
TIMINGAND CONTROL
SERIAL CONTROL
DATA PORT
REFCLK
MULTIPLIER
06479-001
AD9910
Data Sheet
FEATURES
1 GSPS internal clock speed (up to 400 MHz analog output)
Integrated 1 GSPS, 14-bit DAC
0.23 Hz or better frequency resolution
Phase noise ≤ −125 dBc/Hz @ 1 kHz offset (400 MHz carrier)
Excellent dynamic performance with
>80 dB narrow-band SFDR
Serial input/output (I/O) control
Automatic linear or arbitrary frequency, phase, and
amplitude sweep capability
8 frequency and phase offset profiles
Sin(x)/(x) correction (inverse sinc filter)
1.8 V and 3.3 V power supplies
Software and hardware controlled power-down
100-lead TQFP_EP package
Integrated 1024 word × 32-bit RAM
PLL REFCLK multiplier
Parallel datapath interface
Internal oscillator can be driven by a single crystal
Phase modulation capability
Amplitude modulation capability
Multichip synchronization
1 GSPS, 14-Bit, 3.3 V CMOS
APPLICATIONS
Agile local oscillator (LO) frequency synthesis
Programmable clock generators
FM chirp source for radar and scanning systems
Test and measurement equipment
Acousto-optic device drivers
Polar modulators
Fast frequency hopping
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Information furnishe d by
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com

AD9910 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
External PLL Loop Filter Components ............................... 27
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 4
General Description ......................................................................... 5
Specifications ..................................................................................... 6
Electrical Specifications ............................................................... 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 9
Equivalent Circuits ....................................................................... 9
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 9
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ........................... 10
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 13
Application Circuits ....................................................................... 16
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 17
Single Tone Mode ....................................................................... 17
RAM Modulation Mode ............................................................ 18
PLL Lock Indication .................................................................. 27
Output Shift Keying (OSK) ....................................................... 27
Manual OSK ............................................................................ 27
Automatic OSK ....................................................................... 28
Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) ............................................... 28
DRG Overview ....................................................................... 28
DRG Slope Control ................................................................ 30
DRG Limit Control ................................................................ 30
DRG Accumulator Clear ....................................................... 30
Normal Ramp Generation .................................................... 30
No-Dwell Ramp Generation ................................................. 32
DROVER Pin .......................................................................... 32
RAM Control .............................................................................. 33
RAM Overview....................................................................... 33
Load/Retrieve RAM Operation ............................................ 33
Digital Ramp Modulation Mode .............................................. 19
Parallel Data Port Modulation Mode ....................................... 20
Parallel Data Clock (PDCLK) ............................................... 20
Transmit Enable (TxENABLE) ............................................. 21
Mode Priority .............................................................................. 22
Functional Block Detail ................................................................. 23
DDS Core ..................................................................................... 23
14-Bit DAC Output .................................................................... 23
Auxiliary DAC ........................................................................ 24
Inverse Sinc Filter ....................................................................... 24
Clock Input (REF_CLK/
REF_CLK/
Crystal Driven REF_CLK/
Direct Driven REF_CLK/
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Multiplier .................................. 25
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
Overview ........................................... 24
) ........................................ 24
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
.................................. 25
.................................... 25
RAM Playback Operation (Waveform Generation) .......... 33
RAM_SWP_OVR (RAM Sweep Over) Pin ........................ 34
Overview of RAM Playback Modes .................................... 34
RAM Direct Switch Mode ..................................................... 34
RAM Direct Switch Mode with Zero Crossing .................. 35
RAM Ramp-Up Mode ........................................................... 35
RAM Ramp-Up Internal Profile Control Mode ................ 36
Internal Profile Control Continuous Waveform Timing
Diagram ................................................................................... 38
RAM Bidirectional Ramp Mode .......................................... 38
RAM Continuous Bidirectional Ramp Mode .................... 39
RAM Continuous Recirculate Mode ................................... 41
Additional Features ........................................................................ 42
Profiles ......................................................................................... 42
I/O_UPDATE, SYNC_CLK, and System Clock
Relationships ............................................................................... 42
PLL Charge Pump .................................................................. 26
Rev. D | Page 2 of 64
Automatic I/O Update ............................................................... 43

Data Sheet AD9910
Power-Down Control ................................................................. 43
SDO—Serial Data Out ........................................................... 48
Synchronization of Multiple Devices ............................................ 44
Power Supply Partitioning ............................................................. 47
3.3 V Supplies .............................................................................. 47
DVDD_I/O (3.3 V) (Pin 11, Pin 15, Pin 21, Pin 28, Pin 45,
Pin 56, and Pin 66) .................................................................. 47
AVDD (3.3 V) (Pin 74 to Pin 77 and Pin 83) ...................... 47
1.8 V Supplies .............................................................................. 47
DVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 17, Pin 23, Pin 30, Pin 47, Pin 57, and
Pin 64) ...................................................................................... 47
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 3)............................................................. 47
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 6)............................................................. 47
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 89 and Pin 92) ....................................... 47
Serial Programming ........................................................................ 48
Control Interface—Serial I/O .................................................... 48
General Serial I/O Operation .................................................... 48
Instruction Byte ........................................................................... 48
Instruction Byte Information Bit Map ................................. 48
Serial I/O Port Pin Descriptions ............................................... 48
SCLK—Serial Clock................................................................ 48
CS
—Chip Select Bar ............................................................... 48
SDIO—Serial Data Input/Output ......................................... 48
I/O_RESET—Input/Output Reset ........................................ 49
I/O_UPDATE—Input/Output Update ................................ 49
Serial I/O Timing Diagrams ...................................................... 49
MSB/LSB Transfers ..................................................................... 49
Register Map and Bit Descriptions ............................................... 50
Register Bit Descriptions............................................................ 55
Control Function Register 1 (CFR1)—Address 0x00 ........ 55
Control Function Register 2 (CFR2)—Address 0x01 ........ 57
Control Function Register 3 (CFR3)—Address 0x02 ........ 58
Auxiliary DAC Control Register—Address 0x03 ............... 58
I/O Update Rate Register—Address 0x04 ........................... 59
Frequency Tuning Word Register (FTW)—Address 0x07 ..... 59
Phase Offset Word Register (POW)—Address 0x08 ......... 59
Amplitude Scale Factor Register (ASF)—Address 0x09 .... 59
Multichip Sync Register—Address 0x0A ............................. 60
Digital Ramp Limit Register—Address 0x0B...................... 60
Digital Ramp Step Size Register—Address 0x0C ............... 60
Digital Ramp Rate Register—Address 0x0D ....................... 60
Profile Registers ...................................................................... 61
Outline Dimensions ........................................................................ 62
Ordering Guide ........................................................................... 62
Rev. D | Page 3 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
REVISION HISTORY
5/12—Rev. C to Rev. D
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 8
Changes to Table 3 .......................................................................... 12
Changes to Figure 39 ...................................................................... 31
Changes to Synchronization of Multiple Devices Section ........ 45
Changes to Table 18 ........................................................................ 55
Changes to Table 20 ........................................................................ 58
Changes to Table 26 ........................................................................ 60
8/10—Rev. B to Rev. C
Changes to XTAL_SEL Input Parameter in Table 1 ..................... 8
Changes to Table 2 ............................................................................ 9
Changes to Transmit Enable (TxENABLE) Section .................. 21
12/08—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changes to Figure 2 .......................................................................... 5
Changes to I/O_UPDATE Pulse Width Parameter and
Minimum Profile Toggle Period Parameter in Table 1 ................ 7
Added XTAL_SEL Input Parameter in Table 1............................. 8
Changes to Table 3 .......................................................................... 11
Changes to Figure 20 ...................................................................... 16
Changes to Figure 22 ...................................................................... 17
Changes to Figure 23 ...................................................................... 18
Changes to Figure 24 ...................................................................... 19
Changes to Figure 25 ...................................................................... 20
Changes to REF_CLK/
Changes to Crystal Driven REF_CLK/
Changes to PLL Lock Indication Section and Output Shift
Keying (OSK) Section .................................................................... 27
Changes to DRG Slope Control Section and Normal Ramp
Generation Section ......................................................................... 30
Changes to Drover Pin Section ..................................................... 32
Changes to Figure 43 ...................................................................... 35
Changes to Figure 45 and Internal Profile Control Continuous
Waveform Timing Diagram Section ............................................ 38
Changes to Figure 47 ...................................................................... 40
Changes to Figure 48 ...................................................................... 41
REF_CLK
Overview Section ................. 24
REF_CLK
Section ........ 25
Deleted I/O_UPDATE Pin Section .............................................. 41
Changes to Profiles Section ........................................................... 42
Added I/O_UPDATE, SYNC_CLK, and System Clock
Relationships Section ..................................................................... 42
Added Figure 49; Renumbered Sequentially .............................. 42
Changes to Synchronization of Multiple Devices Section ........ 44
Changes to DVDD (1.8V) (Pin 17, Pin 23, Pin 30, Pin 47,
Pin 57, and Pin 64) Section and AVDD (1.8V) (Pin 89 and
Pin 92) Section ................................................................................ 47
Changes to Control Interface—Serial I/O Section .................... 48
Changes to Table 17 ....................................................................... 50
Changes to Table 19 ....................................................................... 57
Changes to Table 20 and Table 21 ................................................ 58
2/08—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Features .......................................................................... 1
Changes to REFCLK Multiplier Specification in Table 1 ............. 5
Changes to Minimum Setup Time to SYNC_CLK ....................... 6
Changes to I/O Update/Profile[2:0] Timing Characteristics ...... 6
Changes to TxENABLE/Data Setup Time (to PDCLK) and
TxENABLE/Data Hold Time (to PDCLK) .................................... 6
Changes to Miscellaneous Timing Characteristics ....................... 6
Changes to Table 3 .......................................................................... 10
Changes to Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13,
and Figure 14 ................................................................................... 12
Changes to Figure 30 and Table 7................................................. 24
Changes to Automatic I/O Update Section................................. 41
Added Table 16, Renumbered Sequentially ................................ 41
Changes to Figure 49 to Figure 53 ................................................ 43
Added Power Supply Partitioning Section .................................. 46
Changes to General Serial I/O Operation Section ..................... 47
Changes to Table 17 ....................................................................... 49
Changes to Table 19 ....................................................................... 56
Changes to Table 20 ....................................................................... 57
Added Table 32 ............................................................................... 60
5/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. D | Page 4 of 64
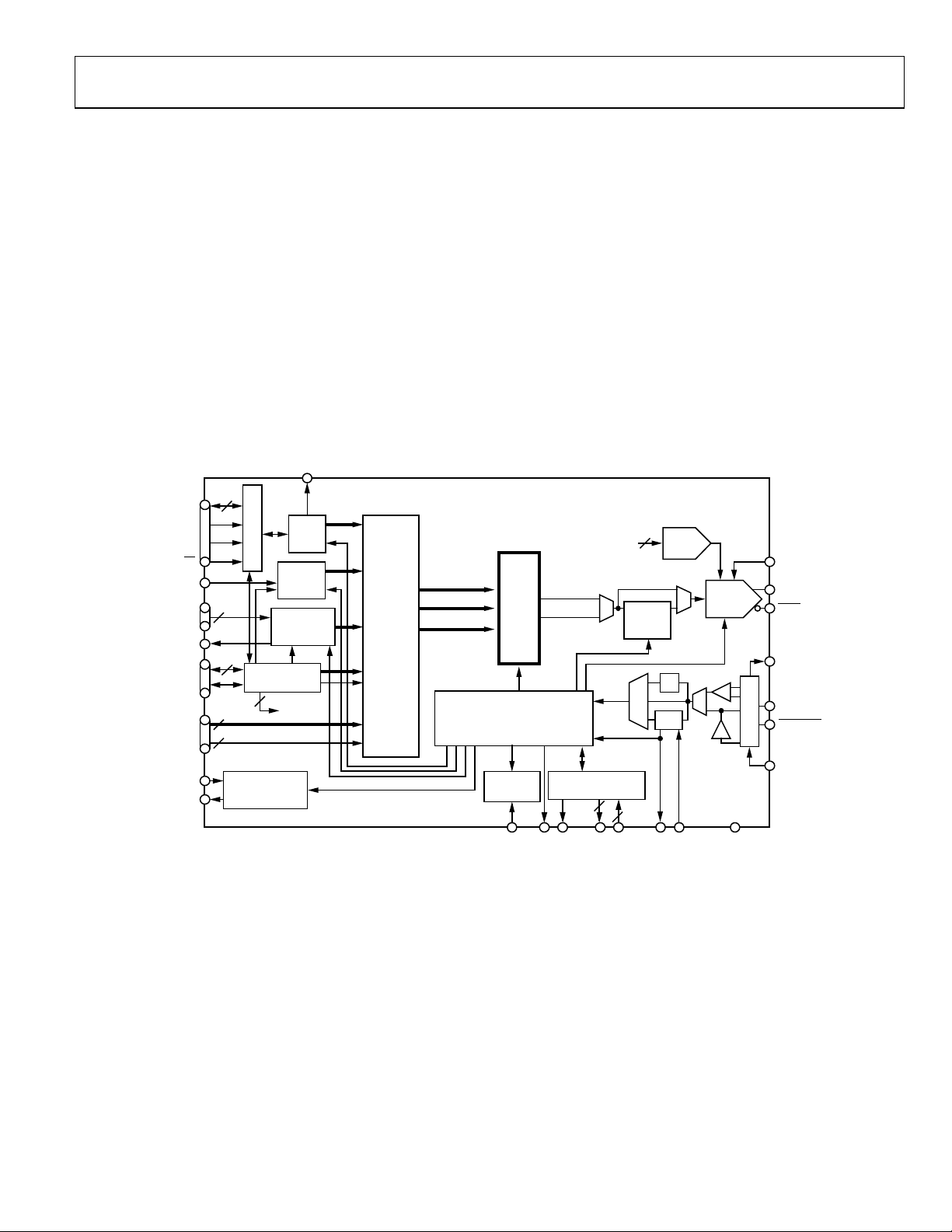
Data Sheet AD9910
06479-002
16
PARALLEL
INPUT
PDCLK
SCLK
SDIO
I/O_RESET
PROFILE[2:0]
I/O_UPDATE
RAM
POWER-
DOWN
CONTROL
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
CS
TxENABLE
DAC FSC
OSK
RAM_SWP_OVR
A
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
AMPLIT UDE ( A)
FREQUENCY (ω)
PHASE (θ)
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
8
DAC FSC
8
2
DRCTL
DRHOLD
DROVER
2
MULTICHIP
SYNCHRONIZATION
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMINGAND
CONTROL
SERIAL I/O PORT
2
AD9910
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
SHIFT
KEYING
DATA
ROUTE
AND
PARTITION
CONTROL
3
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
AND CONTROL
ω
Acos (ωt + θ)
Asin (ωt + θ)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC_CLK
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
DAC
14-BIT
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9910 is a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) featuring
an integrated 14-bit DAC and supporting sample rates up to
1 GSPS. The AD9910 employs an advanced, proprietary DDS
technology that provides a significant reduction in power consumption without sacrificing performance. The DDS/DAC
combination forms a digitally programmable, high frequency,
analog output synthesizer capable of generating a frequency
agile sinusoidal waveform at frequencies up to 400 MHz.
The user has access to the three signal control parameters that
control the DDS: frequency, phase, and amplitude. The DDS
provides fast frequency hopping and frequency tuning resolution with its 32-bit accumulator. With a 1 GSPS sample rate, the
tuning resolution is ~0.23 Hz. The DDS also enables fast phase
and amplitude switching capability.
The AD9910 is controlled by programming its internal control
registers via a serial I/O port. The AD9910 includes an integrated
static RAM to support various combinations of frequency, phase,
and/or amplitude modulation. The AD9910 also supports a user
defined, digitally controlled, digital ramp mode of operation. In
this mode, the frequency, phase, or amplitude can be varied
linearly over time. For more advanced modulation functions, a
high speed parallel data input port is included to enable direct
frequency, phase, amplitude, or polar modulation.
The AD9910 is specified to operate over the extended industrial
temperature range (see the Absolute Maximum Ratings section
for details).
Figure 2. Detailed Block Diagram
Rev. D | Page 5 of 64
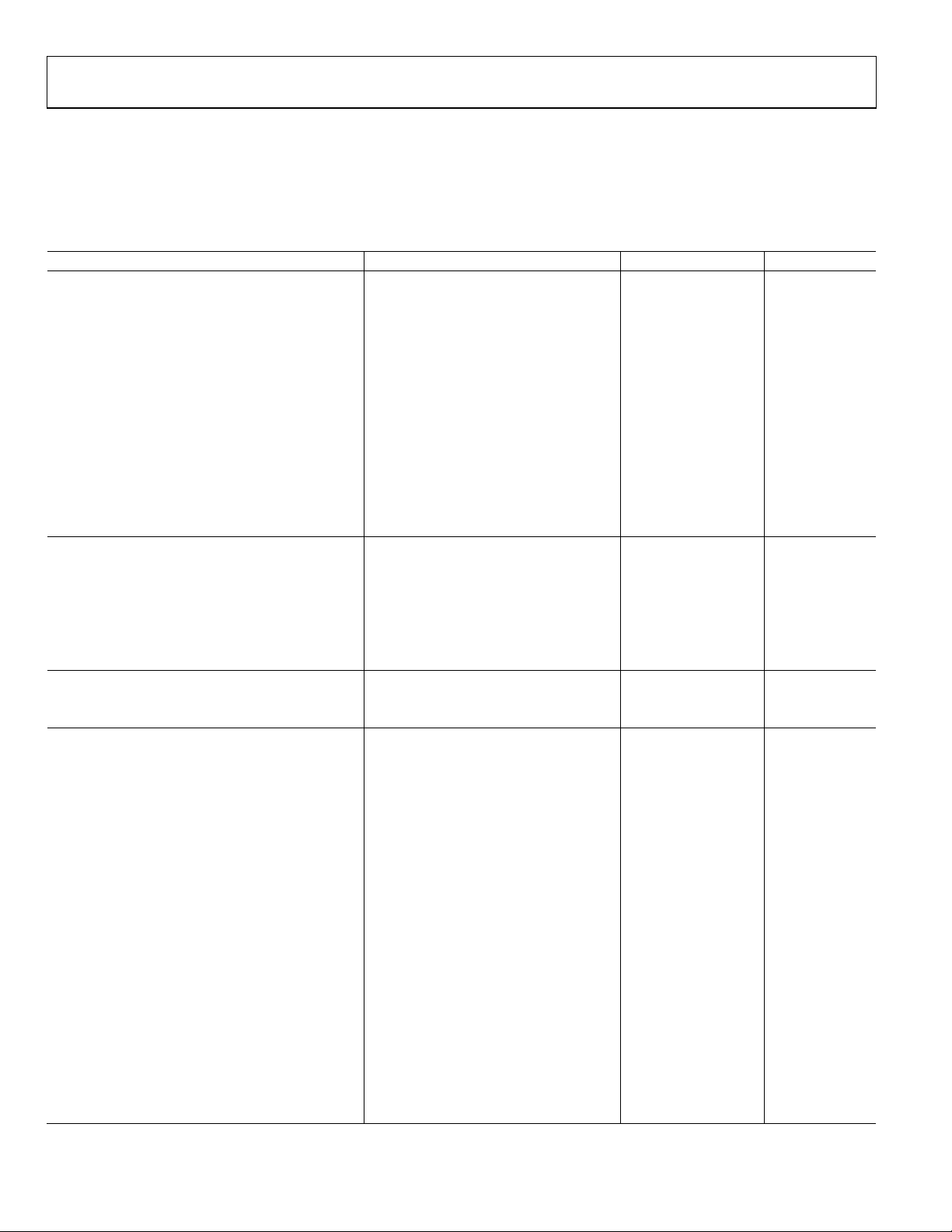
AD9910 Data Sheet
REFCLK Input Level
Single-ended
50 1000
mV p-p
Differential
100 2000
mV p-p
OUT
Enabled @ 20×
−140
dBc/Hz
±12.5 kHz
–95 dBc
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD (1.8 V) and DVDD (1.8 V) = 1.8 V ± 5%, AVDD (3.3 V) = 3.3 V ± 5%, DVDD_I/O (3.3 V) = 3.3 V ± 5%, T = 25°C, R
I
= 20 mA, external reference clock frequency = 1000 MHz with reference clock (REFCLK) multiplier disabled, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
REFCLK INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Frequency Range
REFCLK Multiplier Disabled 60 1000 MHz
Enabled 3.2 60 MHz
Maximum REFCLK Input Divider Frequency Full temperature range 1500 1900 MHz
Minimum REFCLK Input Divider Frequency Full temperature range 25 35 MHz
External Crystal 25 MHz
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Input Impedance Differential 2.8 kΩ
Single-ended 1.4 kΩ
Duty Cycle REFCLK multiplier disabled 45 55 %
REFCLK multiplier enabled 40 60 %
= 10 kΩ,
SET
REFCLK MULTIPLIER VCO CHARACTERISTICS
VCO Gain (KV) @ Center Frequency VCO range Setting 0 429 MHz/V
VCO range Setting 1 500 MHz/V
VCO range Setting 2 555 MHz/V
VCO range Setting 3 750 MHz/V
VCO range Setting 4 789 MHz/V
VCO range Setting 51 850 MHz/V
REFCLK_OUT CHARACTERISTICS
Maximum Capacitive Load 20 pF
Maximum Frequency 25 MHz
DAC OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Full-Scale Output Current 8.6 20 31.6 mA
Gain Error −10 +10 % FS
Output Offset 2.3 µA
Differential Nonlinearity 0.8 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 1.5 LSB
Output Capacitance 5 pF
Residual Phase Noise @ 1 kHz offset, 20 MHz A
REFCLK Multiplier Disabled −152 dBc/Hz
Enabled @ 100× −140 dBc/Hz
Voltage Compliance Range −0.5 +0.5 V
Wideband SFDR See the Typical Performance
Characteristics section
Narrow-Band SFDR
50.1 MHz Analog Output ±500 kHz –87 dBc
±125 kHz –87 dBc
±12.5 kHz –96 dBc
101.3 MHz Analog Output ±500 kHz –87 dBc
±125 kHz –87 dBc
Rev. D | Page 6 of 64
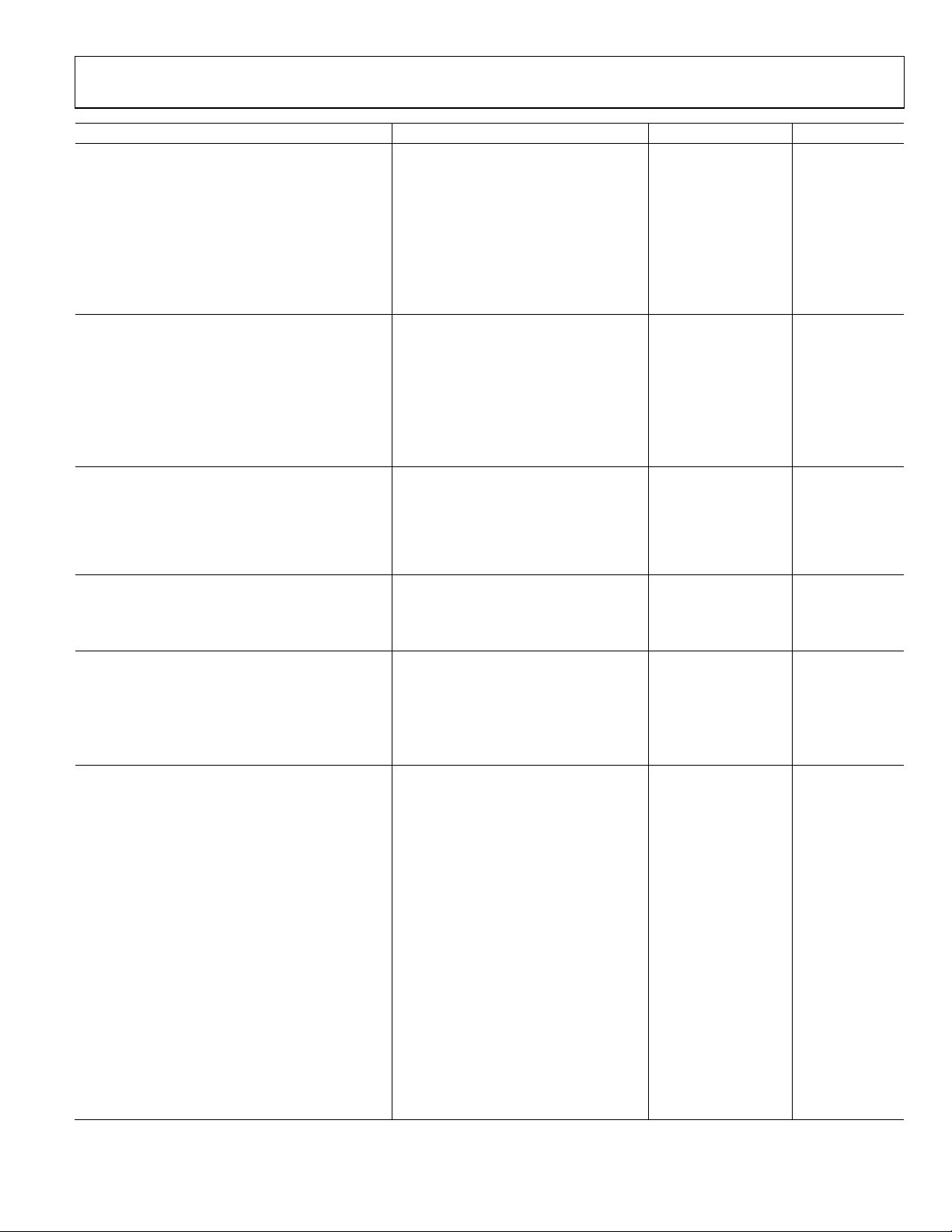
Data Sheet AD9910
±125 kHz
–86 dBc
Maximum SCLK Rise/Fall Time
2 ns
Minimum Setup Time to SYNC_CLK
ns
Minimum Hold Time to SYNC_CLK
0 ns
I/O_UPDATE Pulse Width
High
>1
SYNC_CLK cycle
Minimum Profile Toggle Period
2 SYNC_CLK cycles
Wake-Up Time2
Fast Recovery
8 SYSCLK cycles3
Full Sleep Mode
REFCLK multiplier enabled
1 ms
REFCLK multiplier disabled
150
μs
Frequency, Phase-to-DAC Output
Matched latency enabled/disabled
91 SYSCLK cycles3
Parameter Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
201.1 MHz Analog Output ±500 kHz –87 dBc
±125 kHz –87 dBc
±12.5 kHz –91 dBc
301.1 MHz Analog Output ±500 kHz –86 dBc
±12.5 kHz –88 dBc
401.3 MHz Analog Output ±500 kHz –84 dBc
±125 kHz –84 dBc
±12.5 kHz –85 dBc
SERIAL PORT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Maximum SCLK Frequency 70 Mbps
Minimum SCLK Clock Pulse Width Low 4 ns
High 4 ns
Minimum Data Setup Time to SCLK 5 ns
Minimum Data Hold Time to SCLK 0 ns
Maximum Data Valid Time in Read Mode 11 ns
I/O_UPDATE/PROFILE[2:0] TIMING
CHARACTERISTICS
1.75
TxENABLE and 16-BIT PARALLEL (DATA) BUS TIMING
Maximum PDCLK Frequency 250 MHz
TxENABLE/Data Setup Time (to PDCLK) 1.75 ns
TxENABLE/Data Hold Time (to PDCLK) 0 ns
MISCELLANEOUS TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Minimum Reset Pulse Width High 5 SYSCLK cycles3
DATA LATENCY (PIPELINE DELAY )
Data Latency, Single Tone or Using Profiles
Frequency, Phase, Amplitude-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled and OSK
enabled
Frequency, Phase-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled and OSK
disabled
Matched latency disabled 79 SYSCLK cycles3
Amplitude-to-DAC Output Matched latency disabled 47 SYSCLK cycles3
Data Latency Using RAM Mode
Frequency, Phase-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled/disabled 94 SYSCLK cycles3
Amplitude-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled 106 SYSCLK cycles3
Matched latency disabled 58 SYSCLK cycles3
Data Latency, Sweep Mode
Amplitude-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled 91 SYSCLK cycles3
Matched latency disabled 47 SYSCLK cycles3
Data Latency, 16-Bit Input Modulation Mode
Frequency, Phase-to-DAC Output Matched latency enabled 103 SYSCLK cycles3
Matched latency disabled 91 SYSCLK cycles3
91 SYSCLK cycles3
79 SYSCLK cycles3
Rev. D | Page 7 of 64
AD9910 Data Sheet
Logic 0 Current
90
150
µA
CMOS LOGIC OUTPUTS
1 mA load
AVDD
AVDD
DVDD
DVDD
Full Sleep Mode
19
40
mW
Parameter Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
CMOS LOGIC INPUTS
Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Logic 1 Current 90 150 µA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
XTAL_SEL INPUT
Logic 1 Voltage 1.25 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.6 V
Input Capacitance 2 pF
Logic 1 Voltage 2.8 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.4 V
POWER SUPPLY CURRENT
I
(1.8 V) 110 mA
I
(3.3 V) 29 mA
I
(1.8 V) 222 mA
I
(3.3 V) 11 mA
TOTAL POWER CONSUMPTION
Single Tone Mode 715 950 mW
Rapid Power-Down Mode 330 450 mW
1
The gain value for VCO range Setting 5 is measured at 1000 MHz.
2
Wake-up time refers to the recovery time from a power-down state. The longest time required is for the reference clock multiplier PLL to relock to the reference. The
wake-up time assumes that the recommended PLL loop filter values are used.
3
SYSCLK cycle refers to the actual clock frequency used on-chip by the DDS. If the reference clock multiplier is used to multiply the external reference clock frequency,
the SYSCLK frequency is the external frequency multiplied by the reference clock multiplication factor. If the reference clock multiplier is not used, the SYSCLK
frequency is the same as the external reference clock frequency.
Rev. D | Page 8 of 64
Data Sheet AD9910
Digital Output Current
5 mA
Lead Temperature (10 sec Soldering)
300°C
06479-003
MUST TERMINATE OUTPUTSTO AGND
FOR CURRENT FLOW. DO NOT EXCEED
THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE COMPLIANCE
RATING.
IOUT IOUT
DAC OUTPUTS
AVDD
AVOID OVERDRIVING DIGITAL INPUTS.
FORWARD BIASING ESD DIODES M AY
COUPLE DIGITAL NOISE ONTO POWER
PINS.
DIGITAL INPUTS
INPUT
DVDD_I/O
06479-055
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
AVDD (1.8V), DVDD (1.8V) Supplies 2 V
AVDD (3.3V), DVDD_I/O (3.3V) Supplies 4 V
Digital Input Voltage −0.7 V to +4 V
XTAL_SEL −0.7 V TO +2.2 V
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
θJA 22°C/W
θJC 2.8°C/W
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
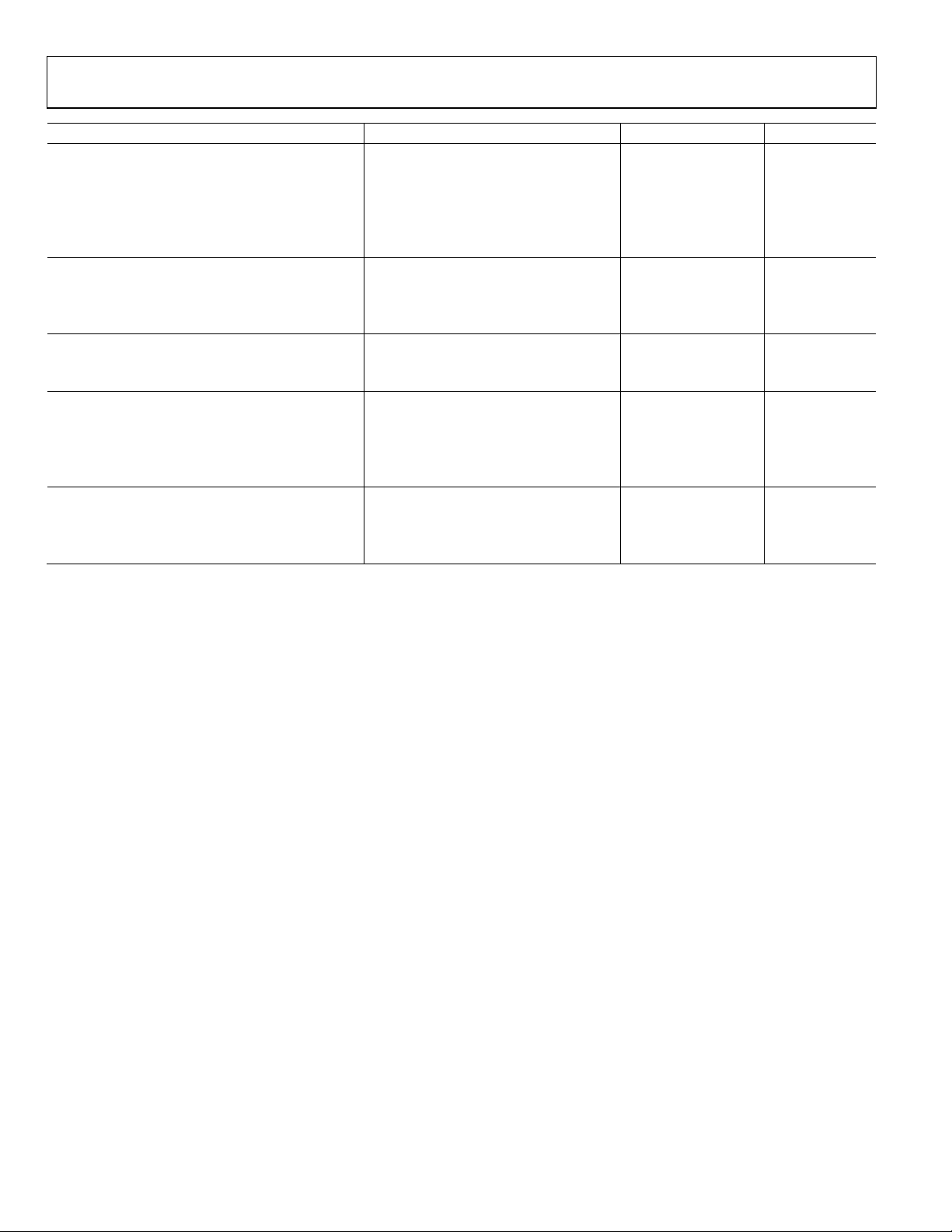
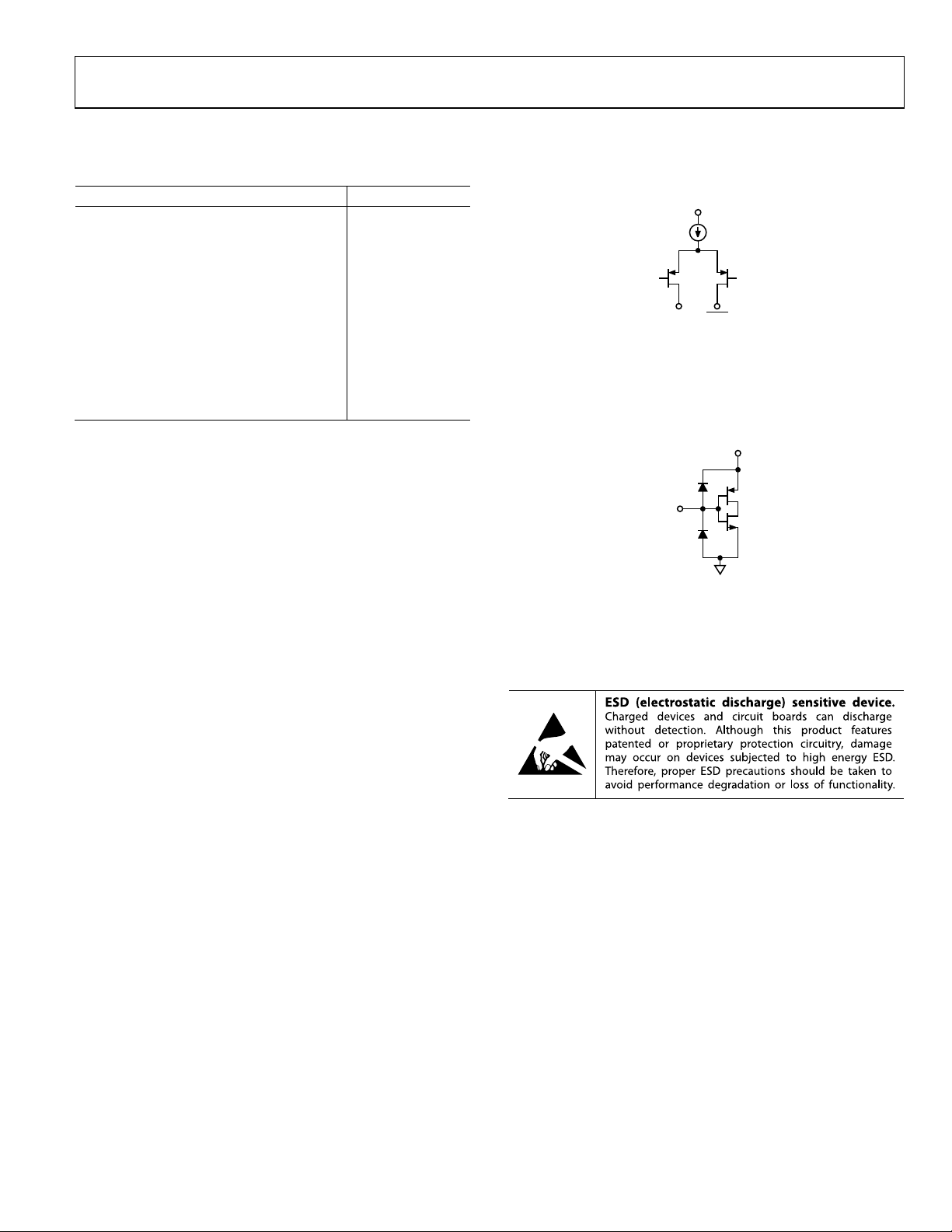
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
Figure 3. Equivalent Input Circuit
Figure 4. Equivalent Output Circuit
ESD CAUTION
Rev. D | Page 9 of 64
AD9910 Data Sheet
2627282930
55
54
53
52
51
TQFP-100 ( E _PAD)
TOP VIEW
(Not to S cal e)
AD9910
D14
D13
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
5
4
3
2
7
6
9
8
1
11
10
16
15
14
13
18
17
20
19
22
21
12
24
23
25
32
33
343536
38
39
40
414243
4445464748
49
50
31
37
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7D6D5
D4
PDCLK
TxENABLE
DGND
D3D2D1
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DVDD (1.8V)
D0
F1
F0
80
IOUT79AGND78AGND77AVDD (3.3V)76AVDD (3.3V)
75
AVDD (3.3V)
74
AVDD (3.3V)
73
AGND
72
NC
71
I/O_RESET
70
CS
69
SCLK
68
SDO
67
SDIO
66
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
65
DGND
64
DVDD (1.8V)
63
DRHOLD
62
DRCTL
61
DROVER
60
OSK
59
I/O_UPDATE
58
DGND
57
DVDD (1.8V)
56
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
SYNC_CLK
PROFILE0
PROFILE1
PROFILE2
DGND
100
99989796959493
929190
89
88
8786858483
82
81
NCNCNCNCAGND
XTAL_SEL
REFCLK_OUTNCAVDD (1.8V)
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
AVDD (1.8V)
AGNDNCNC
AGND
DAC_RSET
AVDD (3.3V)
AGND
IOUT
NC
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
AVDD (1.8V)
AGND
AGND
AVDD (1.8V)
SYNC_IN+
SYNC_IN–
SYNC_OUT+
SYNC_OUT–
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
DGND
MASTER_RESET
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
EXT_PWR_DWN
PLL_LOCK
NC
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
RAM_SWP_OVR
D15
06479-004
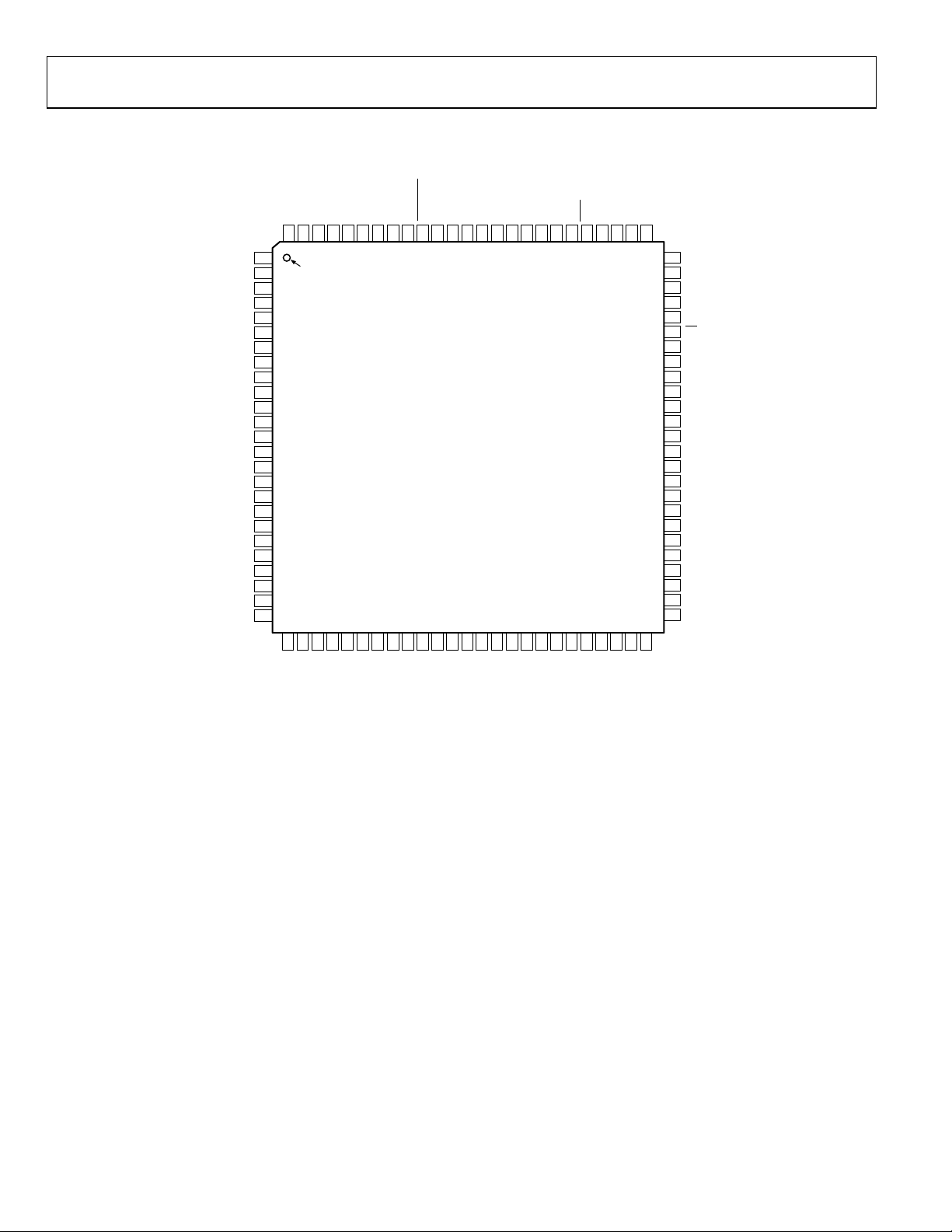
PIN 1
INDICATOR
NOTES:
1. EXPOSED PAD SHOULD BE SOLDERED TO GROUND.
2. NC = NO CONNEC T.
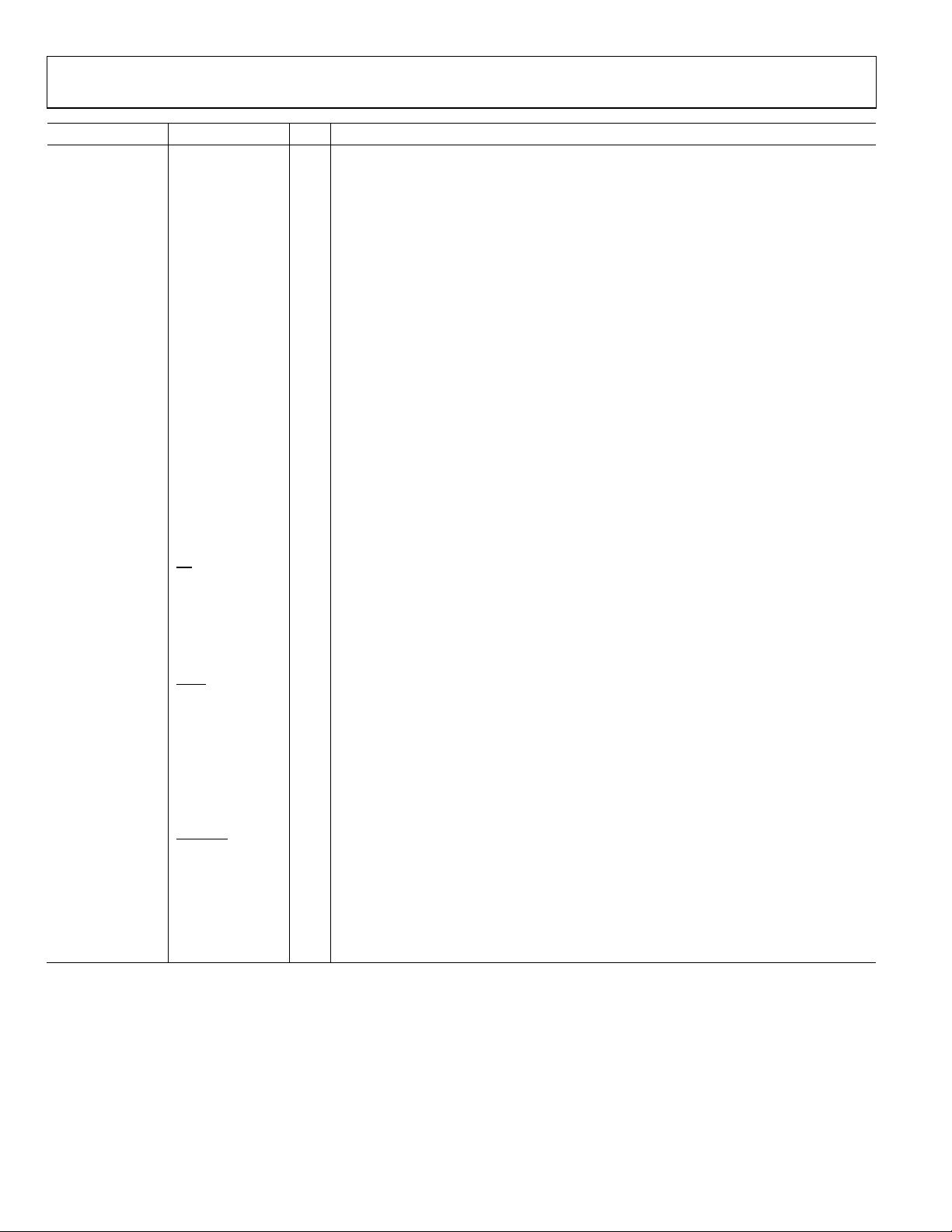
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Figure 5. Pin Configuration
Rev. D | Page 10 of 64
Data Sheet AD9910
7
SYNC_IN+
I
Synchronization Signal (LVDS), Digital Input (Rising Edge Active). The synchronization
18
EXT_PWR_DWN
I
External Power-Down, Digital Input (Active High). A high level on this pin initiates the
41
TxENABLE
I
Transmit Enable. Digital input (active high). In burst mode communications, a high on this
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic I/O1 Description
1, 20, 72, 86, 87,
93, 97 to 100
2 PLL_LOOP_FILTER I PLL Loop Filter Compensation Pin. See the External PLL Loop Filter Components section for
3, 6, 89, 92 AVDD (1.8V) I Analog Core VDD, 1.8 V Analog Supplies.
74 to 77, 83 AVDD (3.3V) I Analog DAC VDD, 3.3 V Analog Supplies.
17, 23, 30, 47,
57, 64
11, 15, 21, 28, 45,
56, 66
4, 5, 73, 78, 79, 82,
85, 88, 96
13, 16, 22, 29, 46,
51, 58, 65
8 SYNC_IN− I Synchronization Signal (LVDS), Digital Input. The synchronization signal from the external
9 SYNC_OUT+ O Synchronization Signal (LVDS), Digital Output (Rising Edge Active). The synchronization
10 SYNC_OUT− O Synchronization Signal (LVDS), Digital Output. The synchronization signal from the internal
12 SYNC_SMP_ERR O Synchronization Sample Error, Digital Output (Active High). Sync sample error: a high on
14 MASTER_RESET I Master Reset, Digital Input (Active High). Master reset: clears all memory elements and sets
NC Not Connected. Allow device pins to float.
details.
DVDD (1.8V) I Digital Core VDD, 1.8 V Digital Supplies.
DVDD_I/O (3.3V) I Digital Input/Output VDD, 3.3 V Digital Supplies.
AGND I Analog Ground.
DGND I Digital Ground.
signal from the external master to synchronize internal subclocks. See the Synchronization
of Multiple Devices section for details.
master to synchronize internal subclocks. See the Synchronization of Multiple Devices
section for details.
signal from the internal device subclocks to synchronize external slave devices. See the
Synchronization of Multiple Devices section for details.
device subclocks to synchronize external slave devices. See the Synchronization of Multiple
Devices section for details.
this pin indicates that the AD9910 did not receive a valid sync signal on SYNC_IN+/SYNC_IN−.
registers to default values.
currently programmed power-down mode. See the Power-Down Control section for
further details. If unused, connect to ground.
19 PLL_LOCK O Clock Multiplier PLL Lock, Digital Output (Active High). A high on this pin indicates that the
Clock Multiplier PLL has acquired lock to the reference clock input.
24 RAM_SWP_OVR O RAM Sweep Over, Digital Output (Active High). A high on this pin indicates that the RAM
sweep profile has completed.
25 to 27, 31 to 39,
42 to 44, 48
49, 50 F[1:0] I Modulation Format Pins. Digital input to determine the modulation format.
40 PDCLK O Parallel Data Clock. This is the digital output (clock). The parallel data clock provides a
52 to 54 PROFILE[2:0] I Profile Select Pins. Digital inputs (active high). Use these pins to select one of eight
55 SYNC_CLK O Output Clock Divided-By-Four. A digital output (clock). Many of the digital inputs on the
D[15:0] I Parallel Input Bus (Active High).
timing signal for aligning data at the parallel inputs.
pin indicates new data for transmission. In continuous mode, this pin remains high.
phase/frequency profiles for the DDS. Changing the state of one of these pins transfers the
current contents of all I/O buffers to the corresponding registers. State changes should be
set up on the SYNC_CLK pin.
chip, such as I/O_UPDATE and PROFILE[2:0], need to be set up on the rising edge of this signal.
Rev. D | Page 11 of 64
AD9910 Data Sheet
62
DRCTL
I
Digital Ramp Control. Digital input (active high). This pin controls the slope polarity of the
a Clock. Digital clock (rising edge on write, falling edge on read). This pin provides
Pin No. Mnemonic I/O1 Description
59 I/O_UPDATE I/O Input/Output Update. Digital input (active high). A high on this pin transfers the contents
of the I/O buffers to the corresponding internal registers.
60 OSK I Output Shift Keying. Digital input (active high). When the OSK features are placed in either
manual or automatic mode, this pin controls the OSK function. In manual mode, it toggles
the multiplier between 0 (low) and the programmed amplitude scale factor (high). In
automatic mode, a low sweeps the amplitude down to zero, a high sweeps the amplitude
up to the amplitude scale factor.
61 DROVER O Digital Ramp Over. Digital output (active high). This pin switches to Logic 1 whenever the
digital ramp generator reaches its programmed upper or lower limit.
digital ramp generator. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for more details. If
not using the digital ramp generator, connect this pin to Logic 0.
63 DRHOLD I Digital Ramp Hold. Digital input (active high). This pin stalls the digital ramp generator in
its present state. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for more details. If not
using a digital ramp generator, connect this pin to Logic 0.
67 SDIO I/O Serial Data Input/Output. Digital input/output (active high). This pin can be either unidirec-
tional or bidirectional (default), depending on the configuration settings. In bidirectional serial
port mode, this pin acts as the serial data input and output. In unidirectional mode, it is an
input only.
68 SDO O Serial Data Output. Digital output (active high). This pin is only active in unidirectional
serial data mode. In this mode, it functions as the output. In bidirectional mode, this pin is
not operational and should be left floating.
69 SCLK I Serial Dat
the serial data clock for the control data path. Write operations to the AD9910 use the
rising edge. Readback operations from the AD9910 use the falling edge.
70
71 I/O_RESET I Input/Output Reset. Digital input (active high). This pin can be used when a serial I/O
80
81 IOUT O Open-Drain DAC Output Source. Analog output (current mode). Connect through a 50 Ω
84 DAC_RSET O Analog Reference Pin. This pin programs the DAC output full-scale reference current.
90 REF_CLK I Reference Clock Input. Analog input. When the internal oscillator is engaged, this pin can
91
94 REFCLK_OUT O Crystal Output. Analog output. See the REF_CLK/ Overview section for more details.
95 XTAL_SEL I Crystal Select (1.8 V Logic). Analog input (active high). Driving the XTAL_SEL pin high,
EPAD Exposed Paddle
1
I = input, O = output.
I Chip Select. Digital input (active low). This pin allows the AD9910 to operate on a common
CS
O Open-Drain DAC Complementary Output Source. Analog output (current mode). Connect
IOUT
REF_CLK
(EPAD)
I Reference Clock Input. Analog input. See the REF_CLK/ Overview section for more details.
serial bus for the control data path. Bringing this pin low enables the AD9910 to detect
serial clock rising/falling edges. Bringing this pin high causes the AD9910 to ignore input
on the serial data pins.
communication cycle fails (see the I/O_RESET—Input/Output Reset section for details).
When not used, connect this pin to ground.
through a 50 Ω resistor to AGND.
resistor to AGND.
Attach a 10 kΩ resistor to AGND.
be driven by either an external oscillator or connected to a crystal. See the REF_CLK/ Overview
section for more details.
the AVDD (1.8V) pin enables the internal oscillator to be used with a crystal resonator.
If unused, connect it to AGND.
The EPAD should be soldered to ground.
Rev. D | Page 12 of 64
Data Sheet AD9910
–50
–55
–60
–65
–75
–70
06479-034
SFDR (dBc)
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz )
SFDR WITHOUT PLL
SFDR WITH PLL
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
400 450300250 350200150100500
06479-046
SFDR (dBc)
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz )
–75
–70
–65
–60
–55
–45
–50
LOW SUPPLY
HIGH SUPPLY
400 450300250 350200150100500
06479-047
SFDR (dBc)
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz )
–75
–70
–65
–60
–55
–50
–40°C
+85°C
START 0Hz
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
–50
–40
–30
–20
–10
0
50MHz/DIV ST OP 500MHz
06479-035
1
SFDR (dBc)
0
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
–50
–40
–30
–20
–10
START 0Hz 50MHz/DIV ST OP 500MHz
06479-036
1
SFDR (dBc)
06479-037
START 0Hz
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
–50
–40
–30
–20
–10
0
50MHz/DIV ST OP 500MHz
1
SFDR (dBc)
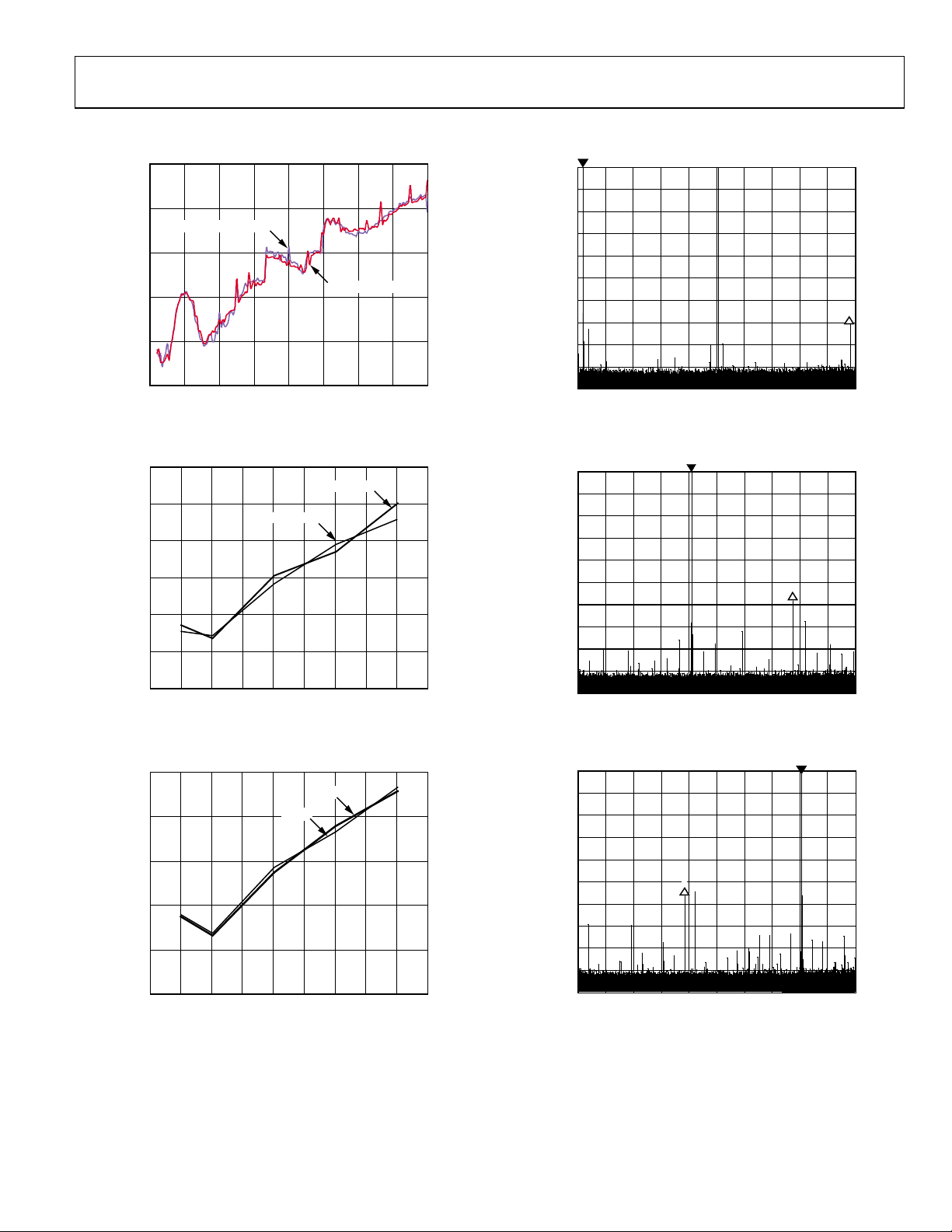
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 6. Wideband SFDR vs. Output Frequency
(PLL with Reference Clock = 15.625 MHz × 64)
Figure 7. Wideband SFDR vs. Output Frequency and Supply (±5%),
REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 9. Wideband SFDR at 10 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 10. Wideband SFDR at 204 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 8. Wideband SFDR vs. Output Frequency and Temperature,
REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 11. Wideband SFDR at 403 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Rev. D | Page 13 of 64
AD9910 Data Sheet
06479-038
CENTER 10.32MHz
–120
–108
–96
–84
–72
–60
–48
–36
–24
–12
0
2.5kHz/DIV SPAN 25kHz
1
SFDR (dBc)
06479-039
CENTER 204.36MHz
–120
–108
–96
–84
–72
–60
–48
–36
–24
–12
0
2.5kHz/DIV SPAN 25kHz
1
SFDR (dBc)
06479-040
CENTER 403.78MHz
–120
–108
–96
–84
–72
–60
–48
–36
–24
–12
0
2.5kHz/DIV SPAN 25kHz
1
SFDR (dBc)
–90
–100
–120
–110
–140
–150
–130
–170
–160
10 100 1k
10k 100k 100M1M 10M
06479-042
MAGNITUDE ( dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
f
OUT
= 20.1MHz
f
OUT
= 98.6MHz
f
OUT
= 201.1MHz
f
OUT
= 397.8MHz
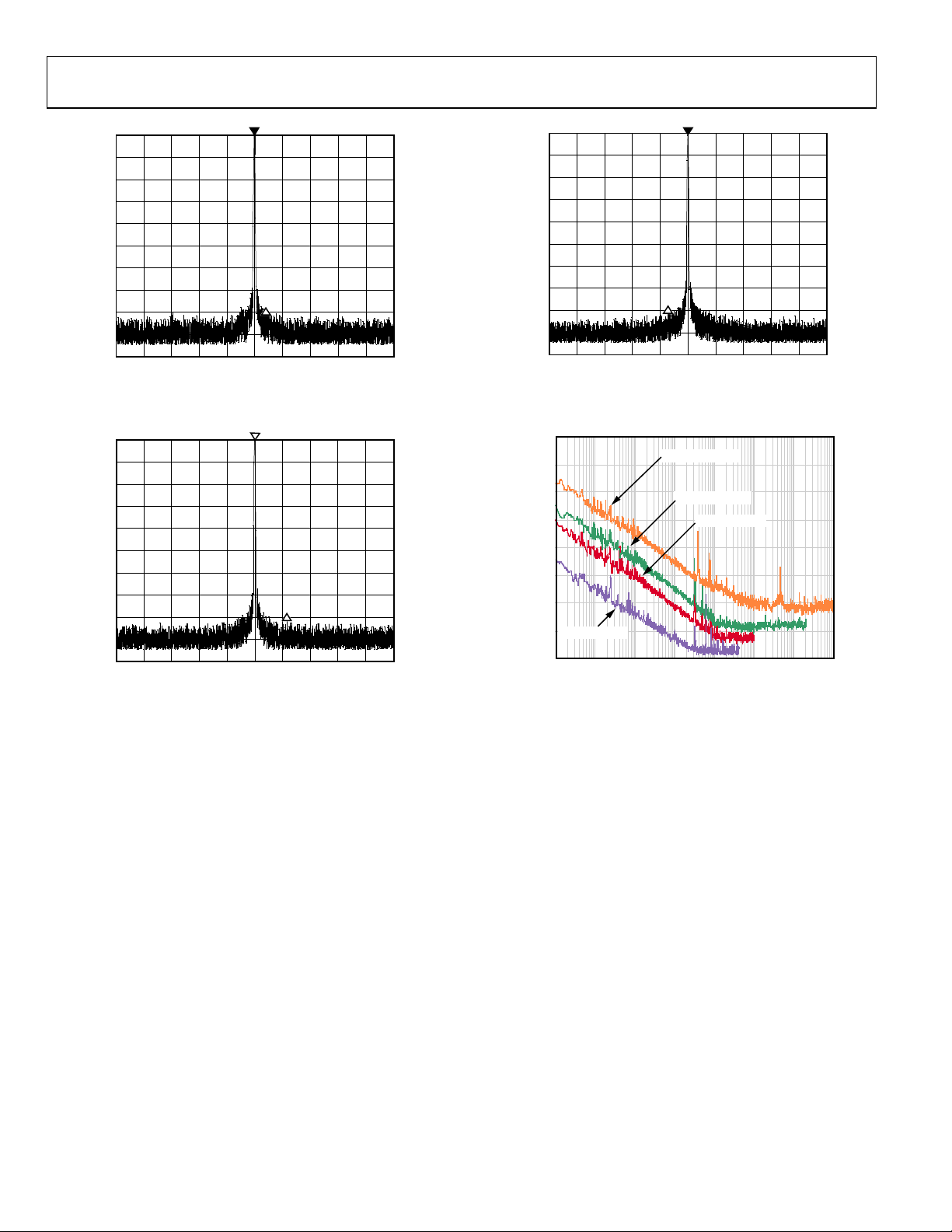
Figure 12. Narrow-Band SFDR at 10.32 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 13. Narrow-Band SFDR at 204.36 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 14. Narrow-Band SFDR at 403.78 MHz, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 15. Residual Phase Noise Plot, 1 GHz Operation with PLL Disabled
Rev. D | Page 14 of 64
Data Sheet AD9910
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–160
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
100M
06479-043
MAGNITUDE ( dBc/ Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
f
OUT
= 20.1MHz
f
OUT
= 397.8MHz
f
OUT
= 98.6MHz
f
OUT
= 201.1MHz
400
450
300
250
350
200
150
100
50
0
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
06479-044
POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
SYSTEM CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz)
DVDD 3.3V
AVDD 3.3V
AVDD 1.8V
DVDD 1.8V
400
450
300
250
350
200
150
100
50
0
400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
06479-045
POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
SYSTEM CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz)
DVDD 1.8V
AVDD 1.8V
AVDD 3.3V
DVDD 3.3V
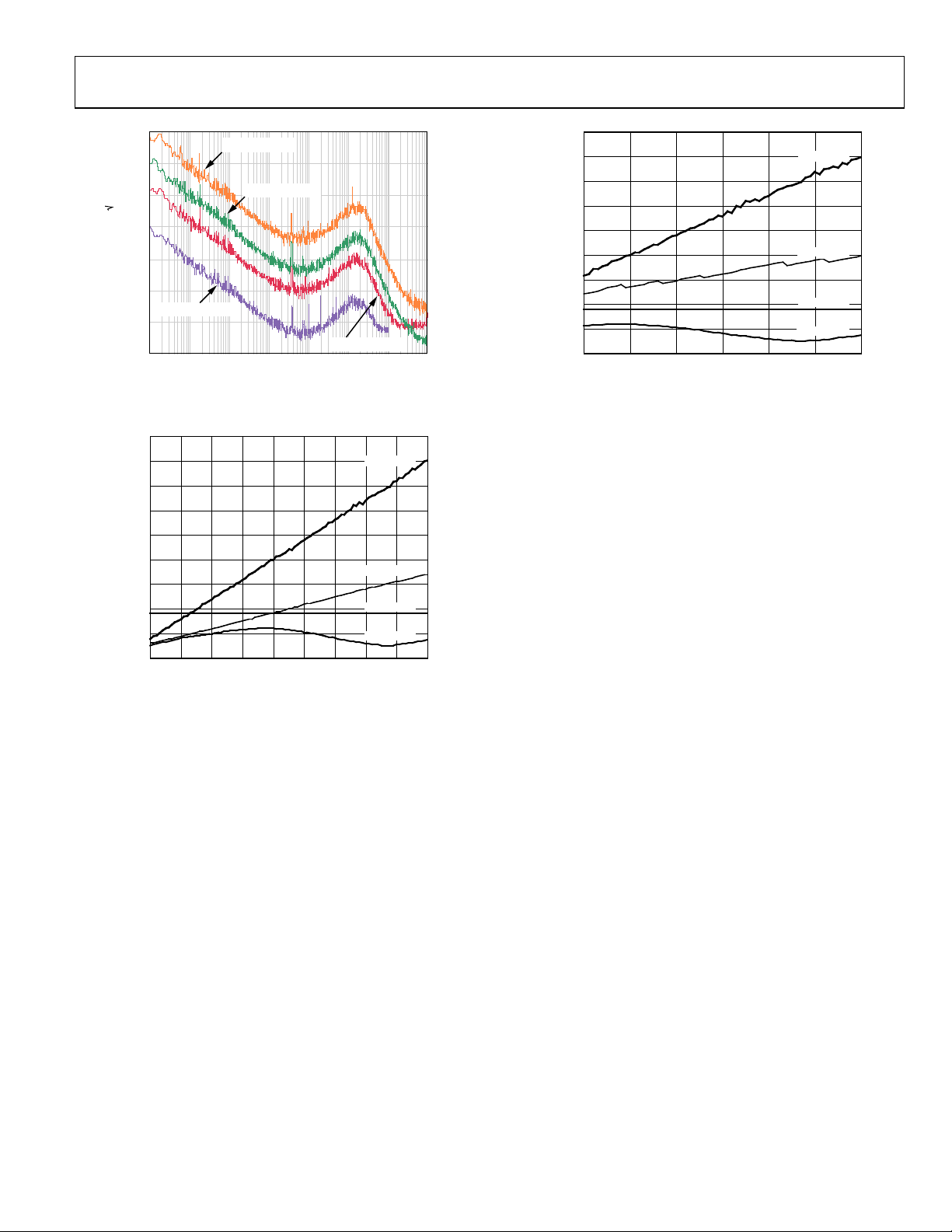
1 GHz Operation Using a 50 MHz Reference Clock with 20× PLL Multiplier
Figure 16. Residual Phase Noise,
Figure 17. Power Dissipation vs. System Clock Frequency (PLL Disabled)
Figure 18. Power Dissipation vs. System Clock Frequency (PLL Enabled)
Rev. D | Page 15 of 64
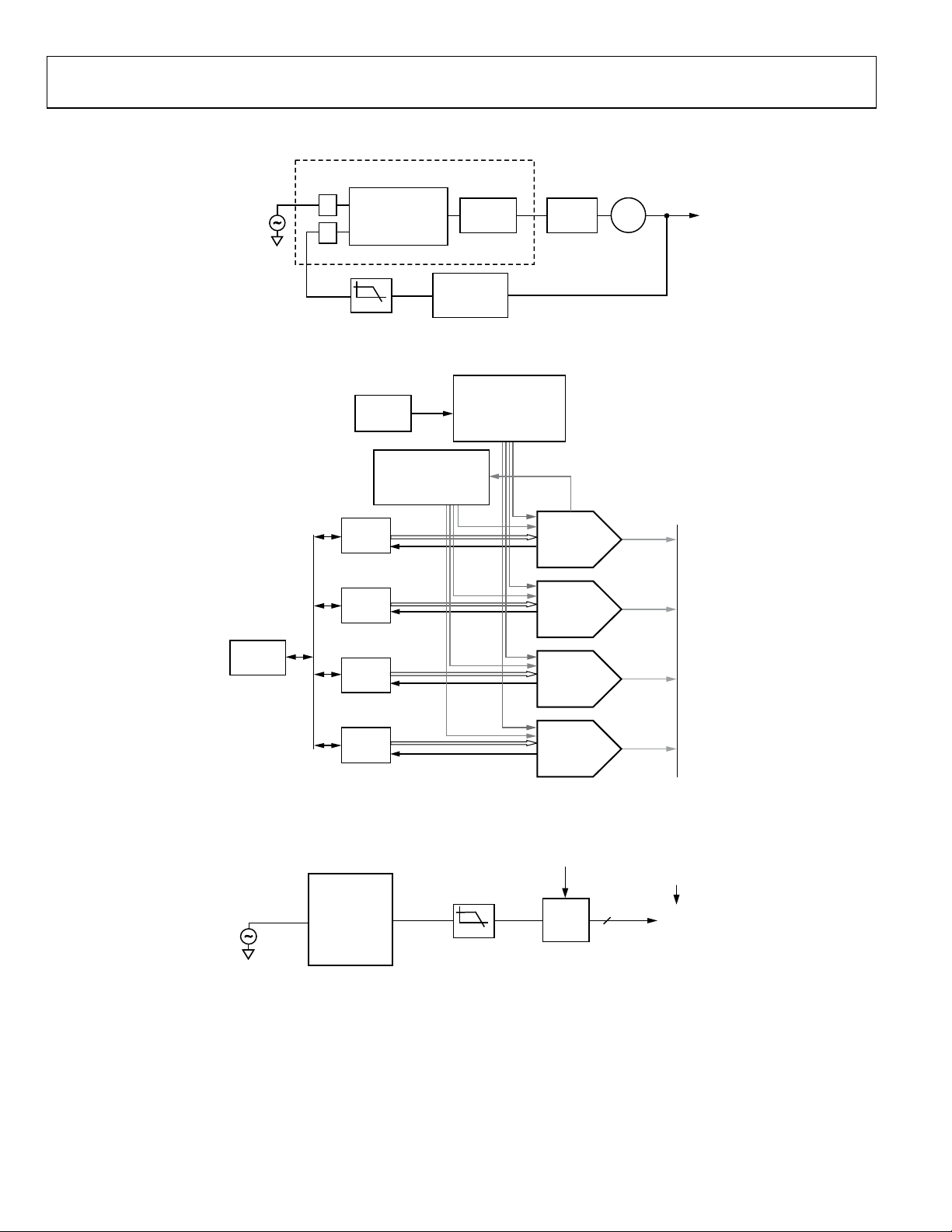
AD9910 Data Sheet
LOOP
FILTER
PHASE
COMPARATOR
VCO
AD9910
REF_CLK
REFERENCE
CHARGE
PUMP
AD9510,AD9511, ADF4106
÷
÷
06479-056
LPF
AD9910
(SLAVE 1)
AD9910
(MASTER)
CLOCK
SOURCE
AD9910
(SLAVE 2)
AD9910
(SLAVE 3)
FPGA
DATA
SYNC_CLK
REF_CLK
SYNC_CLK
SYNC_CLK
FPGA
DATA
FPGA
DATA
DATA
FPGA
SYNC_CLK
C1
S1
C2
S2
C3
S3
C4
S4
A1
A2
A4
A3
A_END
CENTRAL
CONTROL
AD9510
CLOCK DISTRIBUTOR
WITH
DELAY EQUALIZATION
SYNC_OUT
AD9510
SYNCHRONIZATION
DELAY EQUALIZATION
06479-058
AD9910
REFCLK
n
PROGRAMMABLE 1 TO 32
DIVIDER AND DELAYADJUST
CLOCK OUT P UT
SELECTION(S)
n = DEPENDENT ON PRODUCT SELECTIO N.
AD9515
AD9514
AD9513
AD9512
LVPECL
LVDS
CMOS
CH 2
06479-057
LPF
APPLICATION CIRCUITS
Figure 19. DDS in PLL Feedback Locking to Reference, Offering Fine Frequency and Delay Adjust Tuning
Figure 20. Synchronizing Multiple Devices to Increase Channel Capacity Using the AD9510 as a Clock Distributor for the Reference and Synchronization Clock
Figure 21. Clock Generation Circuit Using the AD9512/AD9513/AD9514/AD9515 Series of Clock Distribution Chips
Rev. D | Page 16 of 64
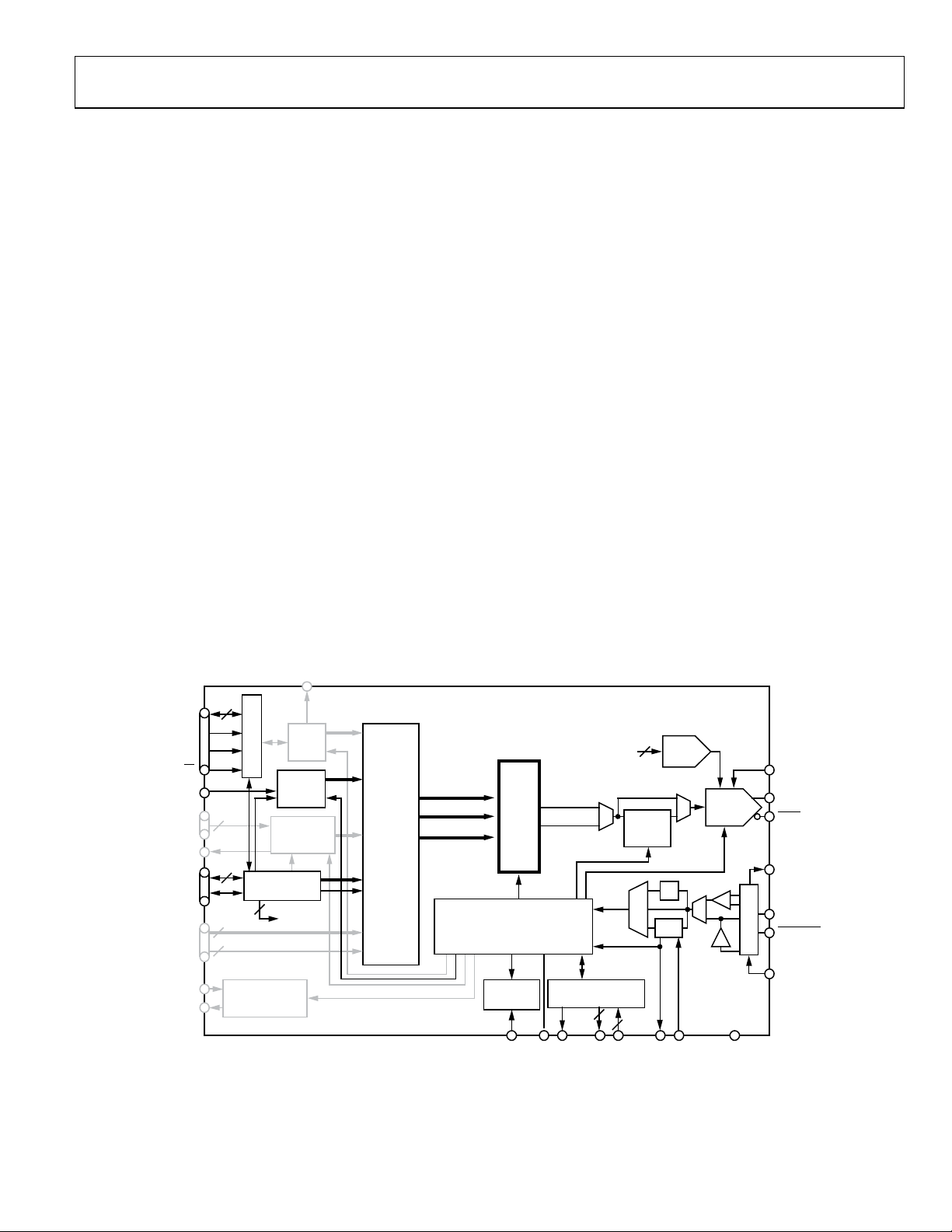
Data Sheet AD9910
06479-005
16
PARALLEL
INPUT
PDCLK
SCLK
SDIO
I/O_RESET
PROFILE[2:0]
I/O_UPDATE
RAM
POWER-
DOWN
CONTROL
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
CS
TxENABLE
DAC FSC
OSK
A
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
AMPLIT UDE ( A)
FREQUENCY (ω)
PHASE (θ)
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
8
DAC FSC
8
2
2
MULTICHIP
SYNCHRONIZATION
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMINGAND
CONTROL
SERIAL I/O PORT
2
AD9910
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
SHIFT
KEYING
DATA
ROUTE
AND
PARTITION
CONTROL
3
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
AND CONTROL
ω
Acos (ωt + θ)
Asin (ωt + θ)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
14-BIT
DDS
RAM_SWP_OVR
DRCTL
DRHOLD
DROVER
SYNC_CLK
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9910 has four modes of operation.
• Single tone
• RAM modulation
• Digital ramp modulation
• Parallel data port modulation
The modes relate to the data source used to supply the DDS
with its signal control parameters: frequency, phase, or amplitude. The partitioning of the data into different combinations
of frequency, phase, and amplitude is handled automatically
based on the mode and/or specific control bits.
In single tone mode, the DDS signal control parameters come
directly from the programming registers associated with the
serial I/O port. In RAM modulation mode, the DDS signal
control parameters are stored in the internal RAM and played
back upon command. In digital ramp modulation mode, the
DDS signal control parameters are delivered by a digital ramp
generator. In parallel data port modulation mode, the DDS
signal control parameters are driven directly into the parallel port.
A separate output shift keying (OSK) function is also available.
This function employs a separate digital linear ramp generator
that only affects the amplitude parameter of the DDS. The OSK
function has priority over the other data sources that can drive
the DDS amplitude parameter. As such, no other data source
can drive the DDS amplitude when the OSK function is enabled.
Although the various modes (including the OSK function) are
described independently, they can be enabled simultaneously.
This provides an unprecedented level of flexibility for generating
complex modulation schemes. However, to avoid multiple data
sources from driving the same DDS signal control parameter,
the device has a built-in priority protocol (see Ta b l e 5 in the
Mode Priority section).
SINGLE TONE MODE
In single tone mode, the DDS signal control parameters are
supplied directly from the programming registers. A profile is
an independent register that contains the DDS signal control
parameters. Eight profile registers are available.
The various modulation modes generally operate on only one of
the DDS signal control parameters (two in the case of the polar
modulation format). The unmodulated DDS signal control
parameters are stored in their appropriate programming
registers and automatically route to the DDS based on the
selected mode.
Each profile is independently accessible. Use the three external
profile pins (PROFILE[2:0]) to select the desired profile. A
change in the state of the profile pins with the next rising edge
on SYNC_CLK updates the DDS with the parameters specified
by the selected profile.
Figure 22. Single Tone Mode
Rev. D | Page 17 of 64
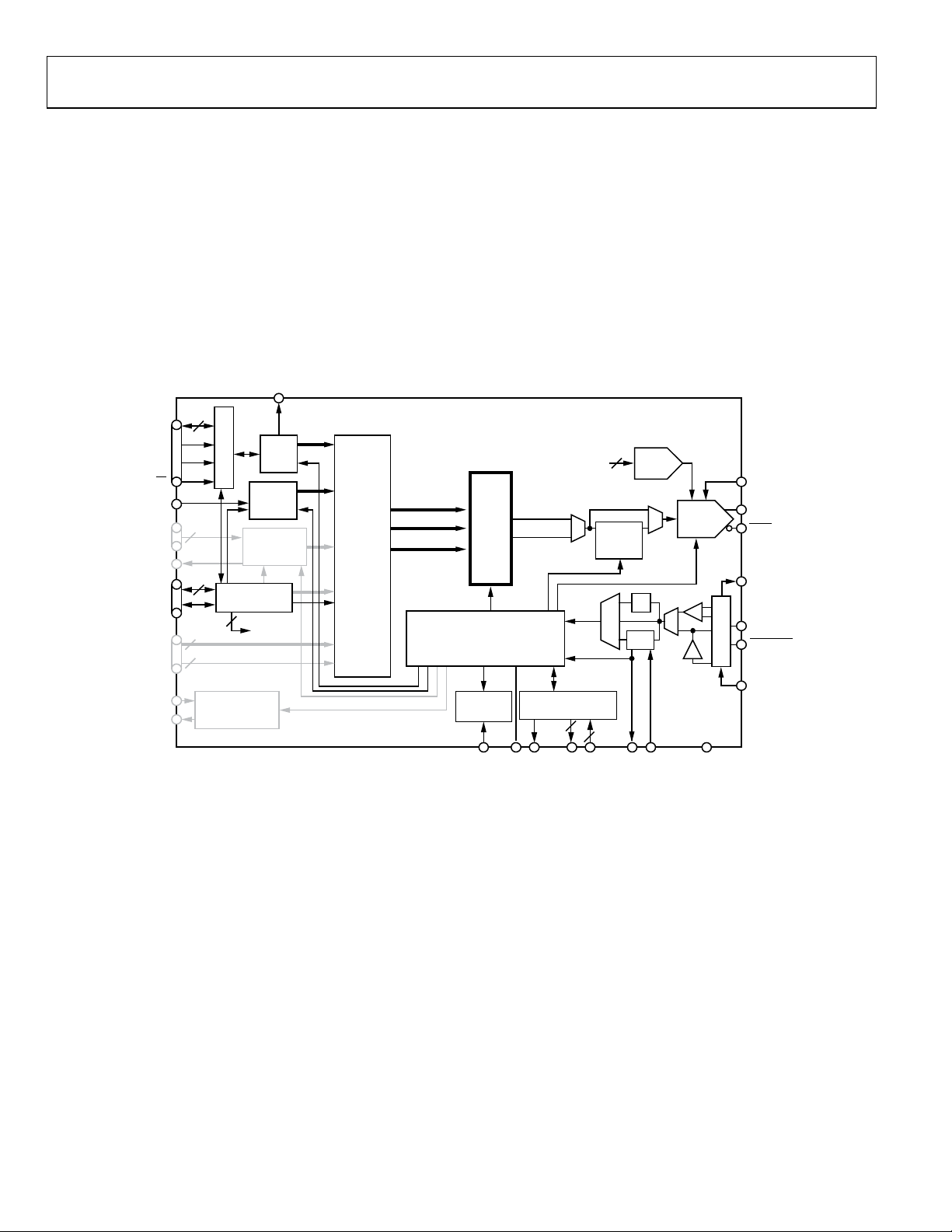
AD9910 Data Sheet
06479-006
16
PARALLEL
INPUT
PDCLK
SCLK
SDIO
I/O_RESET
PROFILE[2:0]
I/O_UPDATE
RAM
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
CS
TxENABLE
DAC FSC
OSK
A
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
AMPLIT UDE ( A)
FREQUENCY (ω)
PHASE (θ)
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
8
DAC FSC
8
2
2
MULTICHIP
SYNCHRONIZATION
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMINGAND
CONTROL
SERIAL I/O PORT
2
AD9910
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
SHIFT
KEYING
DATA
ROUTE
AND
PARTITION
CONTROL
3
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
AND CONTROL
ω
Acos (ωt + θ)
Asin (ωt + θ)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
14-BIT
RAM_SWP_OVR
DRCTL
DRHOLD
DROVER
SYNC_CLK
POWER-
DOWN
CONTROL
RAM MODULATION MODE
The RAM modulation mode (see Figure 23) is activated via the
RAM enable bit and assertion of the I/O_UPDAT E pin (or a
profile change). In this mode, the modulated DDS signal control
parameters are supplied directly from RAM.
The RAM consists of 32-bit words and is 1024 words deep.
Coupled with a sophisticated internal state machine, the RAM
provides a very flexible method for generating arbitrary, time
dependent waveforms. A programmable timer controls the rate
at which words are extracted from the RAM for delivery to the
DDS. Thus, the programmable timer establishes a sample rate at
which 32-bit samples are supplied to the DDS.
The selection of the specific DDS signal control parameters that
serve as the destination for the RAM samples is also programmable
through eight independent RAM profile registers. Select a particular profile using the three external profile pins (PROFILE[2:0]).
A change in the state of the profile pins with the next rising
edge on SYNC_CLK activates the selected RAM profile.
In RAM modulation mode, the ability to generate a time dependent amplitude, phase, or frequency signal enables modulation
of any one of the parameters controlling the DDS carrier signal.
Furthermore, a polar modulation format is available that partitions
each RAM sample into a magnitude and phase component; 16 bits
are allocated to phase and 14 bits are allocated to magnitude.
Figure 23. RAM Modulation Mode
Rev. D | Page 18 of 64
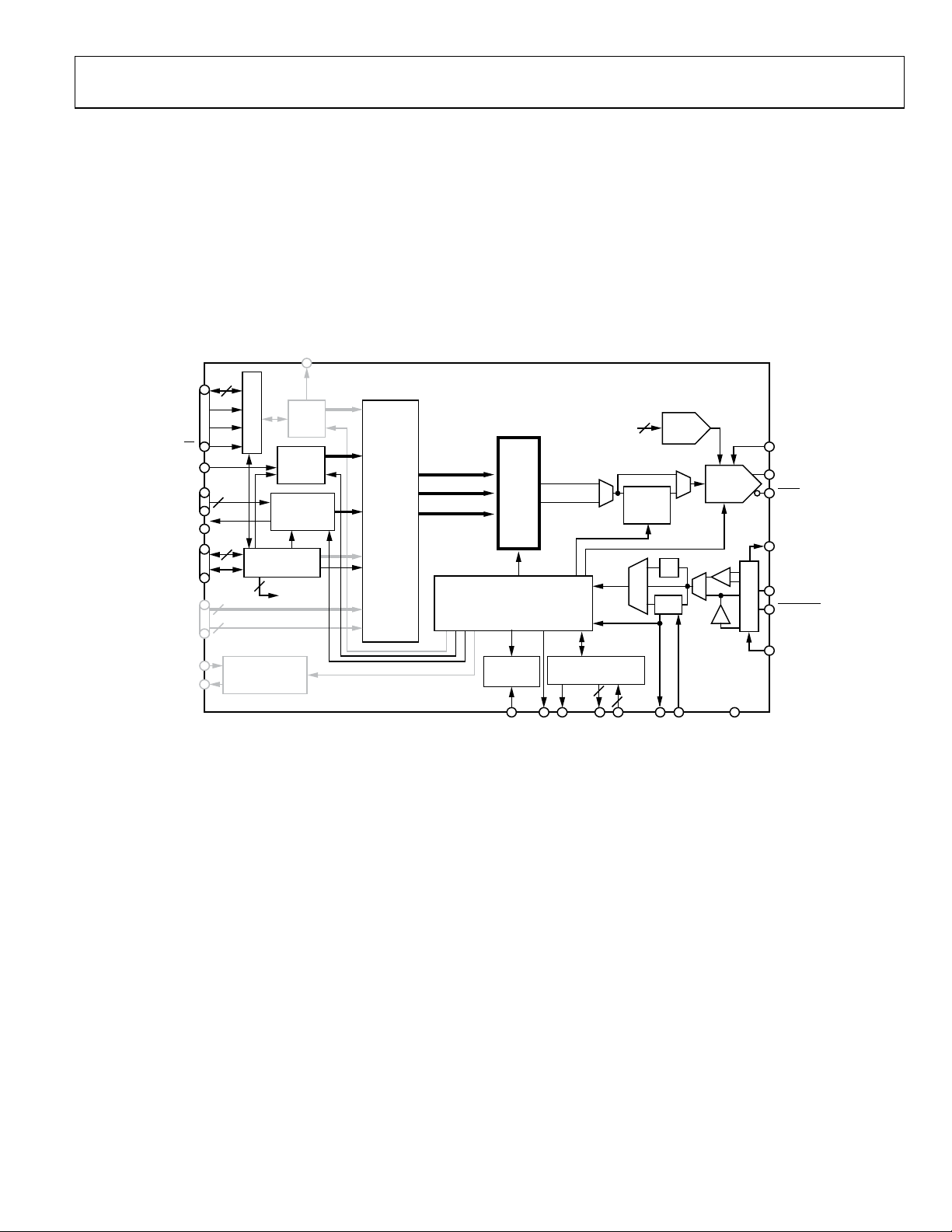
Data Sheet AD9910
06479-007
16
PARALLEL
INPUT
PDCLK
SCLK
SDIO
I/O_RESET
PROFILE[2:0]
I/O_UPDATE
RAM
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
CS
TxENABLE
DAC FSC
OSK
A
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
AMPLIT UDE ( A)
FREQUENCY (ω)
PHASE (θ)
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
8
DAC FSC
8
2
2
MULTICHIP
SYNCHRONIZATION
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMINGAND
CONTROL
SERIAL I/O PORT
2
AD9910
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
SHIFT
KEYING
DATA
ROUTE
AND
PARTITION
CONTROL
3
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
AND CONTROL
ω
Acos (ωt + θ)
Asin (ωt + θ)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
14-BIT
RAM_SWP_OVR
DRCTL
DRHOLD
DROVER
SYNC_CLK
POWER-
DOWN
CONTROL
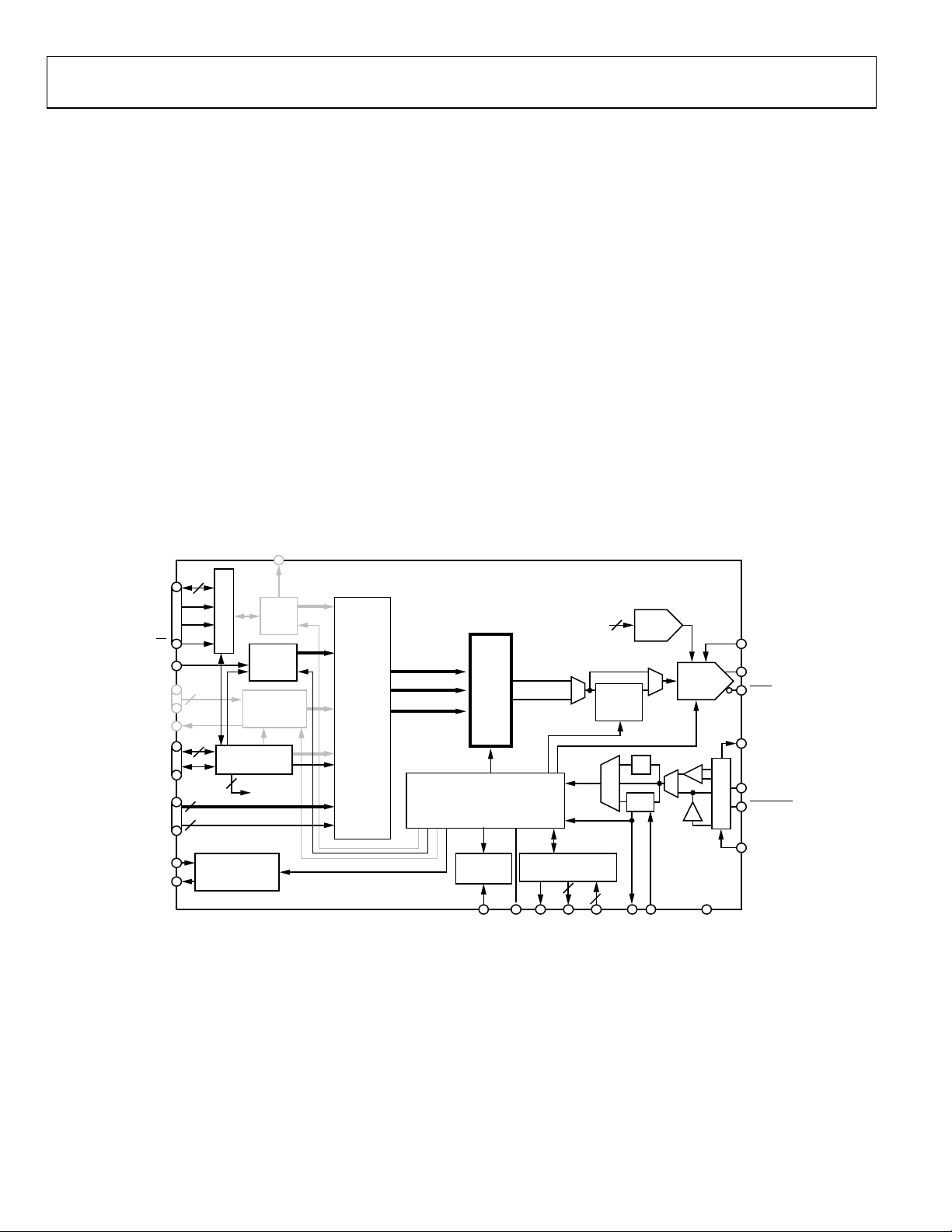
DIGITAL RAMP MODULATION MODE
In digital ramp modulation mode (see Figure 24), the modulated
DDS signal control parameter is supplied directly from the
digital ramp generator (DRG). The ramp generation parameters
are controlled through the serial I/O port.
The ramp generation parameters allow the user to control both
the rising and falling slopes of the ramp. The upper and lower
boundaries of the ramp, the step size and step rate of the rising
portion of the ramp, and the step size and step rate of the falling
portion of the ramp are all programmable.
The ramp is digitally generated with 32-bit output resolution.
The 32-bit output of the DRG can be programmed to represent
frequency, phase, or amplitude. When programmed to represent
frequency, all 32 bits are used. However, when programmed to
represent phase or amplitude, only the 16 MSBs or 14 MSBs,
respectively, are used.
The ramp direction (rising or falling) is externally controlled by
the DRCTL pin. An additional pin (DRHOLD) allows the user
to suspend the ramp generator in its present state.
Figure 24. Digital Ramp Modulation Mode
Rev. D | Page 19 of 64
AD9910 Data Sheet
06479-008
16
PARALLEL
INPUT
PDCLK
SCLK
SDIO
I/O_RESET
PROFILE[2:0]
I/O_UPDATE
RAM
POWER-
DOWN
CONTROL
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
CS
TxENABLE
DAC FSC
OSK
A
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
AMPLIT UDE ( A)
FREQUENCY (ω)
PHASE (θ)
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
8
DAC FSC
8
2
2
MULTICHIP
SYNCHRONIZATION
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMINGAND
CONTROL
SERIAL I/O PORT
2
AD9910
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
OUTPUT
SHIFT
KEYING
DATA
ROUTE
AND
PARTITION
CONTROL
3
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
AND CONTROL
ω
Acos (ωt + θ)
Asin (ωt + θ)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
DAC
14-BIT
RAM_SWP_OVR
DRCTL
DRHOLD
DROVER
SYNC_CLK
PARALLEL DATA PORT MODULATION MODE
In parallel data port modulation mode (see Figure 25), the
modulated DDS signal control parameter(s) are supplied
directly from the 18-bit parallel data port.
The data port is partitioned into two sections. The 16 MSBs make
up a 16-bit data-word (D[15:0] pins) and the two LSBs make up
a 2-bit destination word (F[1:0] pins). The destination word
defines how the 16-bit data-word is applied to the DDS signal
control parameters. Table 4 defines the relationship between the
destination bits, the partitioning of the 16-bit data-word, and
the destination of the data (in terms of the DDS signal control
parameters). Formatting of the 16-bit data-word is unsigned
binary, regardless of the destination.
When the destination bits indicate that the data-word is destined
as a DDS frequency parameter, the 16-bit data-word serves as
an offset to the 32-bit frequency tuning word in the FTW register. This means that the 16-bit data-word must somehow be
properly aligned with the 32-bit word in the FTW register. This
is accomplished by means of the 4-bit FM gain word in the
programming registers. The FM gain word allows the user to
apply a weighting factor to the 16-bit data-word. In the default
state (0), the 16-bit data-word and the 32-bit word in the FTW
register are LSB aligned. Each increment in the value of the FM
gain word shifts the 16-bit data-word to the left relative to the
32-bit word in the FTW register, increasing the influence of the
16-bit data-word on the frequency defined by the FTW register
by a factor of two. The FM gain word effectively controls the
frequency range spanned by the data-word.
Parallel Data Clock (PDCLK)
The AD9910 generates a clock signal on the PDCLK pin that
runs at ¼ of the DAC sample rate (the sample rate of the parallel data port). PDCLK serves as a data clock for the parallel
port. By default, each rising edge of PDCLK is used to latch the
18 bits of user-supplied data into the data port. The edge polarity
can be changed through the PDCLK invert bit. Furthermore,
the PDCLK output signal can be switched off using the PDCLK
enable bit. However, even though the output signal is switched
off, it continues to operate internally using the internal PDCLK
timing to capture the data at the parallel port. Note that PDCLK
is Logic 0 when disabled.
Figure 25. Parallel Data Port Modulation Mode
Rev. D | Page 20 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
−14
06479-009
FALSE
TRUE
TxENABLE
(BURST)
TxENABLE
(CLOCK)
WORD1WORD2WORD3WORD4WORD
N – 4
WORD
N
PDCLK
PARALLEL
DATA PORT
t
DS
t
DS
t
DH
t
DH
Table 4. Parallel Port Destination Bits
F[1:0] D[15:0] Parameter(s) Comments
00 D[15:2] 14-bit amplitude
parameter (unsigned
integer)
01 D[15:0] 16-bit phase parameter
(unsigned integer)
10 D[15:0] 32-bit frequency
parameter (unsigned
integer)
11 D[15:8] 8-bit amplitude
(unsigned integer)
D[7:0] 8-bit phase (unsigned
integer)
Amplitude scales from 0 to 1 − 2
Phase offset ranges from 0 to 2π(1 − 2
. D[1:0] are not used.
−16
) radians.
The alignment of the 16-bit data-word with the 32-bit frequency parameter is controlled
by a 4-bit FM gain word in the programming registers.
The MSB of the data-word amplitude aligns with the MSB of the DDS 14-bit amplitude
parameter. The six LSBs of the DDS amplitude parameter are assigned from Bits[5:0] of the
ASF register. The resulting 14-bit word scales the amplitude from 0 to 1 − 2
−14
.
The MSB of the data-word phase aligns with the MSB of the 16-bit phase parameter of
the DDS. The eight LSBs of the DDS phase parameter are assigned from Bits[7:0] of the
POW register. The resulting 16-bit word offsets the phase from 0 to 2π(1 − 2
−16
) radians.
Transmit Enable (TxENABLE)
The AD9910 also accepts a user-generated signal applied to the
TxENABLE pin that acts as a gate for the user-supplied data. By
default, TxENABLE is considered true for Logic 1 and false for
Logic 0. However, the logical behavior of this pin can be reversed
using the TxENABLE invert bit. When TxENABLE is true, the
device latches data into the device on the expected edge of PDCLK
(based on the PDCLK invert bit). When TxENABLE is false,
even though the PDCLK may continue to operate, the device
ignores the data supplied to the port. Furthermore, when the
TxENABLE pin is held false, the device internally clears the
16-bit data-words, or it retains the last value present on the data
port prior to TxENABLE switching to the false state (based on
the setting of the data assembler hold last value bit).
Alternatively, instead of operating the TxENABLE pin as a gate,
the user can drive the TxENABLE pin with a clock signal
operating at the parallel port data rate. When driven by a clock
signal, the transition from the false to true state must meet the
required setup and hold time on each cycle to ensure proper
operation. The TxENABLE and PDCLK timing is shown in
Figure 26.
Figure 26. PDCLK and TxENABLE Timing Diagram
Rev. D | Page 21 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
MODE PRIORITY
The three different modulation modes generate frequency,
phase, and/or amplitude data destined for the DDS signal
control parameters. In addition, the OSK function generates
amplitude data destined for the DDS. Each of these functions is
independently invoked using the appropriate control bit via the
serial I/O port.
The ability to activate each of these functions independently
makes it possible to have multiple data sources attempting to
Table 5. Data Source Priority
DDS Signal Control Parameters
Frequency Phase Amplitude
Priority
Highest
Priority
DRG DRG enabled and
Parallel data
FTW register RAM enabled and
FTW in active
FTW in active
FTW in active
Lowest
Priority
Data Source Conditions Data Source Conditions Data Source Conditions
RAM RAM enabled and
data destination is
frequency
data destination is
frequency
Parallel data port
port and FTW
register
single tone
profile register
single tone
profile register
single tone
profile register
POW in active
enabled and data
destination is
frequency
data destination is
phase, amplitude,
or polar
DRG enabled and
data destination is
phase or amplitude
Parallel data port
enabled and data
destination is
phase, amplitude,
or polar
None POW in active
RAM RAM enabled and
DRG DRG enabled and
Parallel data port Parallel data port
Parallel data port
concatenated with
the POW register
LSBs
POW register RAM enabled and
POW in active
single tone profile
register
single tone profile
register
single tone profile
register
drive the same DDS signal control parameter. To av oi d contention,
the AD9910 has a built-in priority system. Table 5 summarizes
the priority for each of the DDS signal control parameters. The
rows of Ta b l e 5 list data sources for a particular DDS signal control parameter in descending order of precedence. For example,
if both the RAM and the parallel port are enabled and both are
programmed for frequency as the destination, then the DDS
frequency parameter is driven by the RAM and not the parallel
data port.
OSK generator OSK enabled (auto
data destination is
phase or polar
ASF register OSK enabled
data destination is
phase
RAM RAM enabled and
enabled and data
destination is
phase
Parallel data port
enabled and data
destination is polar
destination is
frequency or
amplitude
DRG enabled and
data destination is
frequency or
amplitude
Parallel data port
enabled and data
destination is
frequency or
amplitude
None No amplitude
DRG DRG enabled and
Parallel data port Parallel data port
Parallel data port
concatenated with
the ASF register
LSBs
ASF in active single
tone profile
register
scaling
mode)
(manual mode)
data destination is
amplitude or polar
data destination is
amplitude
enabled and data
destination is
amplitude
Parallel data port
enabled and data
destination is
polar
Enable amplitude
scale from single
tone profiles bit
(CFR2[24]) set
None
Rev. D | Page 22 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
06479-010
DDS_CLK
32 19
FREQUENCY
CONTROL
ANGLE-TO-
AMPLITUDE
CONVERSION
(SINE OR
COSINE)
PHASE
OFFSET
CONTROL
TO DAC
(MSBs)
D Q
R
ACCUMULATOR
RESET
32
16
MSB ALIG NE D
AMPLITUDE
CONTROL
14
DDS SIGNAL CONTROL PARAM E TERS
16
1419
32
32
14
14
32-BIT
ACCUMULATOR
SYSCLK
OUT
f
FTW
f
=
32
2
=
SYSCLK
OUT
f
f
FTW
32
2round
SYSCLK
OUT
f
FTW
f
−=
32
2
1
=
16
16
2
360
2
2
Δ
POW
POW
π
θ
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DETAIL
DDS CORE
The direct digital synthesizer (DDS) block generates a reference
signal (sine or cosine based on CFR1[16], the select DDS sine
output bit). The parameters of the reference signal (frequency,
phase, and amplitude) are applied to the DDS at its frequency,
phase offset, and amplitude control inputs, as shown in Figure 27.
The output frequency (f
frequency tuning word (FTW) at the frequency control input to
the DDS. The relationship among f
where FTW is a 32-bit integer ranging in value from 0 to
2,147,483,647 (2
full 32-bit range. This range constitutes frequencies from dc to
Nyquist (that is, ½ f
The FTW required to generate a desired value of f
by solving Equation 1 for FTW, as given in Equation 2.
where the round(x) function rounds the argument (the value of
x) to the nearest integer. This is required because the FTW is
constrained to be an integer value. For example, for f
41 MHz and f
(0x556AAAAB).
Programming an FTW greater than 2
image that appears at a frequency given by
The relative phase of the DDS signal can be digitally controlled
by means of a 16-bit phase offset word (POW). The phase offset
is applied prior to the angle-to-amplitude conversion block
internal to the DDS core. The relative phase offset (Δθ) is given by
31
− 1), which represents the lower half of the
SYSCLK
Figure 27. DDS Block Diagram
) of the AD9910 is controlled by the
OUT
, FTW, and f
OUT
SYSCLK
is given by
(1)
).
SYSCLK
is found
OUT
(2)
=
OUT
= 122.88 MHz, then FTW = 1,433,053,867
31
produces an aliased
(for FTW ≥ 231)
Rev. D | Page 23 of 64
where the upper quantity is for the phase offset expressed as
radian units and the lower quantity as degrees. To find the POW
value necessary to develop an arbitrary Δθ, solve the previous
equation for POW and round the result (in a manner similar
to that described previously for finding an arbitrary FTW).
The relative amplitude of the DDS signal can be digitally scaled
(relative to full scale) by means of a 14-bit amplitude scale
factor (ASF). The amplitude scale value is applied at the output
of the angle-to-amplitude conversion block internal to the DDS
core. The amplitude scale is given by
ASF
14
ScaleAmplitude
2
=
log20
(3)
ASF
14
2
where the upper quantity is amplitude expressed as a fraction of
full scale and the lower quantity is expressed in decibels relative
to full scale. To find the ASF value necessary for a particular
scale factor, solve Equation 3 for ASF and round the result (in
a manner similar to that described previously for finding an
arbitrary FTW).
When the AD9910 is programmed to modulate any of the DDS
signal control parameters, the maximum modulation sample
rate is ¼ f
images at multiples of ¼ f
. This means that the modulation signal exhibits
SYSCLK
. The impact of these images
SYSCLK
must be considered when using the device as a modulator.
14-BIT DAC OUTPUT
The AD9910 incorporates an integrated 14-bit, current output
DAC. The output current is delivered as a balanced signal using
two outputs. The use of balanced outputs reduces the potential
amount of common-mode noise present at the DAC output,
offering the advantage of an increased signal-to-noise ratio. An
external resistor (R
and AGND establishes the reference current. The full-scale
output current of the DAC (I
of the reference current (see the Auxiliary DAC section). The
recommended value of R
Attention should be paid to the load termination to keep the
output voltage within the specified compliance range; voltages
developed beyond this range cause excessive distortion and can
damage the DAC output circuitry.
) connected between the DAC_RSET pin
SET
) is produced as a scaled version
OUT
is 10 kΩ.
SET

AD9910 Data Sheet
+=
96
1
4.86 CODE
R
I
SET
OUT
1
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
0 0.1 0.2 0.40.3 0.5
06479-011
(dB)
FREQUENCY RE LATIVE T O DAC SAMPLE RAT E
INVERSE
SINC
SINC
–2.8
–2.9
–3.0
–3.1
0 0.1 0.2 0.40.3 0.5
06479-012
(dB)
FREQUENCY RE LATIVE T O DAC SAMPLE RAT E
COMPENSATED RESPONSE
Auxiliary DAC
An 8-bit auxiliary DAC controls the full-scale output current of
the main DAC (I
register map location sets I
). An 8-bit code word stored in the appropriate
OUT
according to the following equation:
OUT
where R
is the value of the R
SET
resistor (in ohms) and CODE
SET
is the 8-bit value supplied to the auxiliary DAC (default is 127).
For example, with R
= 10,000 Ω and CODE = 127, then I
SET
OUT
=
20.07 mA.
INVERSE SINC FILTER
The sampled carrier data stream is the input to the digital-to-
Figure 28. Sinc and Inverse Sinc Responses
analog converter (DAC) integrated into the AD9910. The
DAC output spectrum is shaped by the characteristic sin(x)/x
(or sinc) envelope, due to the intrinsic zero-order hold effect
associated with DAC generated signals. The sinc envelope
can be compensated for because its shape is well known. This
envelope restoration function is provided by the inverse sinc
filter preceding the DAC. The inverse sinc filter is implemented
as a digital FIR filter. It has a response characteristic that very
nearly matches the inverse of the sinc envelope. The response
of the inverse sinc filter is shown in Figure 28 (with the sinc
envelope for comparison).
The inverse sinc filter is enabled using CFR1[22]. The filter tap
coefficients are given in Tab l e 6. The filter operates by distorting
the data prior to its arrival at the DAC in such a way as to
compensate for the sinc envelope that otherwise distorts the
spectrum.
When the inverse sinc filter is enabled, it introduces a ~3.0 dB
insertion loss. The inverse sinc compensation is effective for output
frequencies up to approximately 40% of the DAC sample rate.
Table 6. Inverse Sinc Filter Tap Coefficients
Tap No. Tap Value
1, 7 −35
2, 6 +134
3, 5 −562
4 +6729
Figure 29. DAC Response with Inverse Sinc Compensation
CLOCK INPUT (REF_CLK/
REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
Overview
REF_CLK
)
The AD9910 supports a number of options for producing the
internal SYSCLK signal (that is, the DAC sample clock) via the
REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
input pins. The REF_CLK input can be
driven directly from a differential or single-ended source, or it
can accept a crystal connected across the two input pins. There
is also an internal phase-locked loop (PLL) multiplier that can
be independently enabled. A block diagram of the REF_CLK
functionality is shown in Figure 30. The various input configurations are controlled by the XTAL_SEL pin and the control bits
In Figure 28, the sinc envelope introduces a frequency dependent
attenuation that can be as much as 4 dB at the Nyquist frequency
(½ of the DAC sample rate). Without the inverse sinc filter, the
DAC output suffers from the frequency dependent droop of
the sinc envelope. The inverse sinc filter effectively flattens the
droop to within ±0.05 dB, as shown in Figure 29, which shows
the corrected sinc response with the inverse sinc filter enabled.
Rev. D | Page 24 of 64
in the CFR3 register. Figure 30 also shows how the CFR3 control
bits are associated with specific functional blocks.

Data Sheet AD9910
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
PLL
VCO
SELECT
DIVIDE
CHARGE
PUMP
OUTIN
PLL_LOOP_FILTERENABLE
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
DRV0
CFR3
[29:28]
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
REFCLK
INPUT
SELECT
LOGIC
SYSCLK
I
CP
CFR3
[21:19]
N
CFR3
[7:1]
VCO SEL
CFR3
[26:24]
÷2
REFCLK
INPUT DIV IDER BYPASS
CFR3[15]
PLL ENABL E
CFR3
[8]
REFCLK
INPUT DIV IDER
RESETB
CFR3[14]
94
95
2
90
91
0
1
0
1
2
2
7
3
0
1
06479-013
06479-014
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
39pF39pF
XTAL
90
91
06479-015
TERMINATION
REF_CLK
DIFFERE NTIAL SOURCE ,
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT
SINGLE - E NDE D S OURCE,
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT
SINGLE - E NDE D S OURCE,
SINGLE - E NDE D INPUT
90
91
0.1µF
0.1µF
PECL,
LVPECL,
OR
LVDS
DRIVER
REF_CLK
90
91
50Ω
0.1µF
0.1µF
BALUN
(1:1)
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
90
91
0.1µF
0.1µF
50Ω
Figure 30. REF_CLK Block Diagram
The PLL enable bit is used to choose between the PLL path or
the direct input path. When the direct input path is selected,
the REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
pins must be driven by an external
signal source (single-ended or differential). Input frequencies
up to 2 GHz are supported. For input frequencies greater than
1 GHz, the input divider must be enabled for proper operation
of the device.
When the PLL is enabled, a buffered clock signal is available at
the REFCLK_OUT pin. This clock signal is the same frequency
as the REF_CLK input. This is especially useful when a crystal
is connected because it gives the user a replica of the crystal
clock for driving other external devices. The REFCLK_OUT has
programmable drive capability. This is controlled by two bits, as
listed in Table 7.
Figure 31. Crystal Connection Diagram
Direct Driven REF_CLK/
When driving the REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
inputs directly from a
signal source, either single-ended or differential signals can be
used. With a differential signal source, the REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
pins are driven with complementary signals and ac-coupled with
0.1 µF capacitors. With a single-ended signal source, either a
single-ended-to-differential conversion can be employed or the
REF_CLK input can be driven single-ended directly. In either
case, 0.1 µF capacitors are used to ac couple both REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
pins to avoid disturbing the internal dc bias voltage
of ~1.35 V. See Figure 32 for more details.
The REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
input resistance is ~2.5 kΩ differential
(~1.2 kΩ single-ended). Most signal sources have relatively low
output impedances. The REF_CLK/
REF_CLK
input resistance
is relatively high; therefore, its effect on the termination impedance
is negligible and can usually be chosen to be the same as the
output impedance of the signal source. The bottom two examples
in
Figure 32 assume a signal source with a 50 Ω output
impedance.
Table 7. REFCLK_OUT Buffer Control
DRV0 Bits (CFR3[29:28]) REFCLK_OUT Buffer
00 Disabled (tristate)
01 Low output current
10 Medium output current
11 High output current
Crystal Driven REF_CLK/
When using a crystal at the REF_CLK/
resonant frequency should be approximately 25 MHz. Figure 31
shows the recommended circuit configuration. The internal
oscillator works with fundamental mode crystals only. Crystal
operation is enabled by a Logic 1 (1.8 V logic required) on the
XTAL_SEL pin.
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
input, the
Figure 32. Direct Connection Diagram
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Multiplier
An internal phase-locked loop (PLL) provides the option to use
a reference clock frequency that is significantly lower than the
system clock frequency. The PLL supports a wide range of
programmable frequency multiplication factors (12× to 127×)
Rev. D | Page 25 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
06479-059
VCO0
VCO1
VCO2
VCO3
VCO4
VCO5
395 495 595 695 795 895 995
f
LOW
= 400
f
HIGH
= 460
f
LOW
= 455
f
HIGH
= 530
f
LOW
= 530
f
HIGH
= 615
f
LOW
= 760
f
HIGH
= 875
f
LOW
= 920
f
HIGH
= 1030
f
LOW
= 650
f
HIGH
= 790
(MHz)
335 435 535 635 735 835 935 1035 1135
VCO0
VCO1
VCO2
VCO3
VCO4
VCO5
06479-060
f
LOW
= 370
f
HIGH
= 510
f
LOW
= 420
f
HIGH
= 590
f
LOW
= 500
f
HIGH
= 700
f
LOW
= 700
f
HIGH
= 950
f
LOW
= 820
f
HIGH
= 1150
f
LOW
= 600
f
HIGH
= 880
(MHz)
as well as a programmable charge pump current and external
loop filter components (connected via the PLL_LOOP_FILTER
pin). These features add an extra layer of flexibility to the PLL,
allowing optimization of phase noise performance and
flexibility in frequency plan development. The PLL is also
equipped with a PLL_LOCK pin.
The PLL output frequency range (f
range of 420 MHz ≤ f
≤ 1 GHz by the internal VCO. In
SYSCLK
) is constrained to the
SYSCLK
addition, the user must program the VCO to one of six operating
ranges such that f
falls within the specified range. Figure 33
SYSCLK
and Figure 34 summarize these VCO ranges.
Figure 33 shows the boundaries of the VCO frequency ranges
over the full range of temperature and supply voltage variation
for all devices from the available population. The implication is
that multiple devices chosen at random from the population and
operated under widely varying conditions may require different
values to be programmed into CFR3[26:24] to operate at the
same frequency. For example, Part A chosen randomly from the
population, operating at an ambient temperature of −10°C with
a system clock frequency of 900 MHz may require CFR3[26:24] to
be set to 100b, whereas Part B chosen randomly from the
population, operating at an ambient temperature of 90°C with a
system clock frequency of 900 MHz may require CFR3[26:24]
to be set to 101b. If a frequency plan is chosen such that the
system clock frequency operates within one set of boundaries
(as shown in Figure 33), the required value in CFR3[26:24] is
consistent from part to part.
Figure 34 shows the boundaries of the VCO frequency ranges
over the full range of temperature and supply voltage variation
for an individual device selected from the population. Figure 34
shows that the VCO frequency ranges for a single device always
overlap when operated over the full range of conditions.
If a user wants to retain a single default value for CFR3[26:24],
a frequency that falls into one of the ranges found in Figure 33
should be selected. Additionally, for any given individual device,
the VCO frequency ranges overlap, meaning that any given
device exhibits no gaps in its frequency coverage across VCO
ranges over the full range of conditions.
Figure 34. Typical VCO Ranges
Table 8. VCO Range Bit Settings
VCO SEL Bits (CFR3[26:24]) VCO Range
000 VCO0
001 VCO1
010 VCO2
011 VCO3
100 VCO4
101 VCO5
110 PLL bypassed
111 PLL bypassed
PLL Charge Pump
The charge pump current (ICP) is programmable to provide the
user with additional flexibility to optimize the PLL performance.
Tabl e 9 lists the bit settings vs. the nominal charge pump current.
Table 9. PLL Charge Pump Current
ICP Bits (CFR3[21:19]) Charge Pump Current, ICP (μA)
000 212
001 237
010 262
011 287
100 312
101 337
110 363
111 387
Figure 33. VCO Ranges Including Atypical Wafer Process Skew
Rev. D | Page 26 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
PFD CP
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
VCO
÷N
PLL OUT
PLL IN
AVDD
REFCLK PL L
2
R1
C1
C2
06479-016
( )
+=
φKK
Nfπ
R1
VD
OL
sin
1
1
( )
( )
2
2
tan
OL
VD
fπN
φKK
C1 =
( )
( )
( )
−
=
φ
φ
fπN
KK
C2
OL
VD
cos
sin1
2
2
06479-017
OSK ENABLE
AMPLIT UDE S CALE FACTOR
(ASF[15:2])
AMPLIT UDE RAM P RATE
(ASF[31:16])
AMPLITUDE STEP SIZE
(ASF[1:0])
MANUAL OSK EX TERNAL
AUTO OSK E NABLE
OSK
DDS CLOCK
TO DDS
AMPLITUDE
CONTROL
PARAMETER
60
LOAD ARR AT I /O_UPDATE
OSK
CONTROLLER
14
16
14
2
External PLL Loop Filter Components
The PLL_LOOP_FILTER pin provides a connection interface to
attach the external loop filter components. The ability to use
custom loop filter components gives the user more flexibility to
optimize the PLL performance. The PLL and external loop filter
components are shown in Figure 35.
PLL LOCK INDICATION
When the PLL is in use, the PLL_LOCK pin provides an active
high indication that the PLL has locked to the REFCLK input
signal. Note that the PLL_LOCK pin is a latched output. When the
PLL is bypassed, the pin may remain at Logic 1. The PLL_LOCK
pin can be cleared by setting the PFD reset bit. The PFD reset
bit must be cleared for normal operation.
OUTPUT SHIFT KEYING (OSK)
The OSK function (see Figure 36) allows the user to control the
output signal amplitude of the DDS. Both a manual and an
automatic mode are available under program control. The
amplitude data generated by the OSK block has priority over
any other functional block that is programmed to deliver
amplitude data to the DDS. Therefore, the OSK data source,
when enabled, overrides all other amplitude data sources.
In the prevailing literature, this configuration yields a thirdorder, Type II PLL. To calculate the loop filter component
values, begin with the feedback divider value (N), the gain of
the phase detector (K
the programmed VCO SEL bit settings (see Table 1 for K
loop filter component values depend on the desired open-loop
bandwidth (f
where:
K
is equal to the programmed value of ICP.
D
K
is taken from Table 1.
V
Ensure that proper units are used for the variables in Equation 4
through Equation 6. I
as appears in Tab l e 9; K
megahertz per volts (MHz/V) as listed in Tabl e 1; the loop
bandwidth (f
must be in radians.
For example, suppose the PLL is programmed such that I
287 μA, K
bandwidth and phase margin are 50 kHz and 45°, respectively,
then the loop filter component values are R1 = 52.85 Ω, C1 =
145.4 nF, and C2 = 30.11 nF.
Figure 35. REFCLK PLL External Loop Filter
), and the gain of the VCO (KV) based on
D
) and phase margin (φ), as follows:
OL
(4)
(5)
(6)
must be in amps, not microamps (μA)
CP
must be in hertz per volts (Hz/V), not
V
) must be in hertz (Hz); the phase margin (φ)
OL
= 625 MHz/V, and N = 25. If the desired loop
V
). The
V
=
CP
Rev. D | Page 27 of 64
Figure 36. OSK Block Diagram
The operation of the OSK function is governed by two CFR1
register bits (OSK enable and select auto OSK), the external
OSK pin, and the entire 32 bits of the ASF register. The primary
control for the OSK block is the OSK Enable bit. When the OSK
function is disabled, the OSK input controls are ignored and the
internal clocks shut down.
When the OSK function is enabled, automatic or manual
operation is selected using the select auto OSK bit. A Logic 0
indicates manual mode (default).
Manual OSK
In manual mode, output amplitude is varied by successive write
operations to the amplitude scale factor portion of the ASF
register. The rate at which amplitude changes can be applied to
the output signal is limited by the speed of the serial I/O port.
In manual mode, the OSK pin functionality depends on the
state of the manual OSK external control bit. When the OSK
pin is Logic 0, the output amplitude is forced to 0; otherwise,
the output amplitude is set by the amplitude scale factor value.

AD9910 Data Sheet
DIGITAL RAMP LIMIT REGISTER
DRCTL
DDS CLOCK
DRHOLD
DROVER
DIGITAL RAMP RATE REGISTER
DIGITAL RAMP STEP REGISTER
06479-018
TO DDS
SIGNAL
CONTROL
PARAMETER
DIGIT AL RAMP ENABLE
DROVER PIN ACTIVE
LOAD LRR AT I/O_UPDATE
CLEAR DIGITAL
RAMP ACCUMULATOR
AUTOCLEAR DIGITAL
RAMP ACCUMULATOR
64
64
DIGITAL RAMP DESTINATION
2
DIGITAL RAMP NO-DWELL
2
32
32
DIGITAL
RAMP
GENERATOR
62 61 63
Automatic OSK
In automatic mode, the OSK function automatically generates a
linear amplitude vs. time profile (or amplitude ramp). The amplitude ramp is controlled via three parameters: the maximum
amplitude scale factor, the amplitude step size, and the time
interval between steps. The amplitude ramp parameters reside
in the 32-bit ASF register and are programmed via the serial
I/O port. The time interval between amplitude steps is set via
the 16-bit amplitude ramp rate portion of the ASF register
(Bits[31:16]). The maximum amplitude scale factor is set via the
14-bit amplitude scale factor in the ASF register (Bits[15:2]). The
amplitude step size is set via the 2-bit amplitude step size
portion of the ASF register (Bits[1:0]). Additionally, the
direction of the ramp (positive or negative slope) is controlled
by the external OSK pin.
The step interval is controlled by a 16-bit programmable timer
that is clocked at a rate of ¼ f
. The period of the timer sets
SYSCLK
the time interval between amplitude steps. The step time interval
(Δt) is given by
Mt4
f
SYSCLK
Δ =
where M is the 16-bit number stored in the amplitude ramp rate
(ARR) portion of the ASF register. For example, if f
SYSCLK
=
750 MHz and M = 23218 (0x5AB2), then Δt ≈ 123.8293 μs.
The output of the OSK function is a 14-bit unsigned data bus
that controls the amplitude parameter of the DDS (as long as
the OSK enable bit is set). When the OSK pin is set, the OSK
output value starts at 0 (zero) and increments by the programmed amplitude step size until it reaches the programmed
maximum amplitude value. When the OSK pin is cleared, the
OSK output starts at its present value and decrements by the
programmed amplitude step size until it reaches 0 (zero).
The OSK output does not necessarily attain the maximum
amplitude value if the OSK pin is switched to Logic 0 before the
maximum value is reached. Nor does the OSK output necessarily
reach a value of 0 if the OSK pin is switched to Logic 1 before
the 0 value is reached.
Table 10. OSK Amplitude Step Size
Amplitude Step Size Bits (ASF[1:0]) Amplitude Step Size
00 1
01 2
10 4
11 8
As mentioned previously, a 16-bit programmable timer controls
the step interval. Normally, this timer is loaded with the programmed timing value whenever the timer expires, initiating a
new timing cycle. However, there are three events that can cause
reloading of the timer to have its timing value reloaded prior to
the timer expiring. One such event occurs when the select auto
OSK bit transitions from cleared to set, followed by an I/O update.
A second such event is a change of state in the OSK pin. The
third is dependent on the status of the load ARR @ I/O update
bit. If this bit is cleared, then no action occurs; otherwise, when
the I/O_UPDATE pin is asserted (or a profile change occurs),
the timer is reset to its initial starting point.
DIGITAL RAMP GENERATOR (DRG)
DRG Overview
To sweep phase, frequency, or amplitude from a defined start
point to a defined endpoint, a completely digital, digital ramp
generator is included in the AD9910. The DRG makes use of
nine control register bits, three external pins, two 64-bit
registers, and one 32-bit register (see Figure 37).
The OSK output is initialized to 0 (zero) at power-up and reset
whenever the OSK enable bit or the select auto OSK bit is cleared.
The amplitude step size of the OSK output is set by the amplitude
step size bits in the ASF register according to Table 10. The step
size refers to the LSB weight of the 14-bit OSK output. Regardless
of the programmed step size, the OSK output does not exceed
the maximum amplitude value programmed into the ASF
register.
Figure 37. Digital Ramp Block Diagram
Rev. D | Page 28 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
Digital Ramp
(CFR2[21:20])
DDS Signal
Parameter
DDS Parameter
DDS CLOCK
D Q
R
LOWER
LIMIT
0
1
DECREMENT STEP SIZE
PRESET
Q
DRCTL
LOAD
CLEAR DIGITAL RAMP ACCUMULATOR
AUTOCLEAR DIGITAL RAM P ACC
.
NO DWELL
LIMIT CONTROL
DIGIT AL RAMP ACCUMULATOR
INCREMENT STEP SIZE
32
32
0
1
NEGATIVE SLOPE RATE
POSITIVE SLOPE RATE
16
16
32
16
62
DRHOLD
63
32
32
LOAD
CONTROL
LOGIC
LOAD LRR AT I/O_UPDATE
DIGITAL
RAMP
TIMER
ACCUMULATOR
RESET
CONTROL
LOGIC
NO-DWELL
CONTROL
2
3232
TO DDS
SIGNAL
CONTROL
PARAMETER
UPPER
LIMIT
32
06479-019
The primary control for the DRG is the digital ramp enable bit.
When disabled, the other DRG input controls are ignored and the
internal clocks are shut down to conserve power.
The output of the DRG is a 32-bit unsigned data bus that can be
routed to any one of the three DDS signal control parameters, as
controlled by the two digital ramp destination bits in Control
Function Register 2 according to Table 11. The 32-bit output
bus is MSB-aligned with the 32-bit frequency parameter, the
16-bit phase parameter, or the 14-bit amplitude parameter, as
defined by the destination bits. When the destination is phase
or amplitude, the unused LSBs are ignored.
Table 11. Digital Ramp Destination
The ramp characteristics of the DRG are fully programmable. This
includes the upper and lower ramp limits, and independent control
of the step size and step rate for both the positive and negative slope
characteristics of the ramp. A detailed block diagram of the DRG is
shown in Figure 38.
The direction of the ramping function is controlled by the
DRCTL pin. A Logic 0 on this pin causes the DRG to ramp
with a negative slope, whereas a Logic 1 causes the DRG to
ramp with a positive slope.
The DRG also supports a hold feature controlled via the DRHOLD
pin. When this pin is set to Logic 1, the DRG is stalled at its last
state; otherwise, the DRG operates normally.
Destination Bits
Control
Bits Assigned to
00 Frequency 31:0
01 Phase 31:16
1x1 Amplitude 31:18
1
x = Don’t care.
The DDS signal control parameters that are not the destination of
the DRG are taken from the active profile.
Figure 38. Digital Ramp Generator Detail
Rev. D | Page 29 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
SYSCLK
f
Pt4
Δ =+
SYSCLK
f
Nt4
Δ =−
SYSCLK
f
M
StepFrequency
=
32
2
31
2
M
StepPhase
π
=
29
2
45M
StepPhase =
FS
I
M
StepAmplitude
=
32
2
DRG Slope Control
The core of the DRG is a 32-bit accumulator clocked by a
programmable timer. The time base for the timer is the DDS
clock, which operates at ¼ f
. The timer establishes the
SYSCLK
interval between successive updates of the accumulator. The
positive (+Δt) and negative (−Δt) slope step intervals are
independently programmable as given by
where P and N are the two 16-bit values stored in the 32-bit digital
ramp rate register and control the step interval. N defines the step
interval of the negative slope portion of the ramp. P defines the step
interval of the positive slope portion of the ramp.
The step size of the positive (STEP
) and negative (STEPN) slope
P
portions of the ramp are 32-bit values programmed into the 64-bit
digital ramp step size register. Program each of the step sizes as an
unsigned integer (the hardware automatically interprets STEP
N
as
a negative value). The relationship between the 32-bit step size
values and actual units of frequency, phase, or amplitude depend
on the digital ramp destination bits. Calculate the actual frequency,
phase, or amplitude step size by substituting STEP
or STEPP
N
for M in the following equations as required:
(radians)
(degrees)
Note that the frequency units are the same as those used to
represent f
the same as those used to represent I
(MHz, for example). The amplitude units are
SYSCLK
, the full-scale output
FS
current of the DAC (mA, for example).
The phase and amplitude step size equations yield the average
step size. Although the step size accumulates with 32-bit precision,
the phase or amplitude destination exhibits only 16 or 14 bits,
respectively. Therefore, at the destination, the actual phase or
amplitude step is the accumulated 32-bit value truncated to 16
or 14 bits, respectively.
As described previously, the step interval is controlled by a
16-bit programmable timer. There are three events that can
cause this timer to be reloaded prior to its expiration. One event
occurs when the digital ramp enable bit transitions from cleared
to set, followed by an I/O update. A second event is a change of
state in the DRCTL pin. The third event is enabled using the load
LRR @ I/O update bit (see the Register Map and Bit Descriptions
section for details).
DRG Limit Control
The ramp accumulator is followed by limit control logic that
enforces an upper and lower boundary on the output of the
ramp generator. Under no circumstances does the output of the
DRG exceed the programmed limit values while the DRG is
enabled. The limits are set through the 64-bit digital ramp limit
register. Note that the upper limit value must be greater than the
lower limit value to ensure normal operation.
DRG Accumulator Clear
The ramp accumulator can be cleared (that is, reset to 0) under
program control. When the ramp accumulator is cleared, it forces
the DRG output to the lower limit programmed into the digital
ramp limit register.
With the limit control block embedded in the feedback path of the
accumulator, resetting the accumulator is equivalent to presetting it
to the lower limit value.
Normal Ramp Generation
Normal ramp generation implies that both no-dwell bits are
cleared (see the No-Dwell Ramp Generation section for details).
In Figure 39, a sample ramp waveform is depicted with the
required control signals. The top trace is the DRG output.
The next trace down is the status of the DROVER output pin
(assuming that the DROVER pin active bit is set). The remaining
traces are control bits and control pins. The pertinent ramp
parameters are also identified (upper and lower limits plus step
size and Δt for the positive and negative slopes). Along the
bottom, circled numbers identify specific events. These events
are referred to by number (Event 1 and so on) in the following
paragraphs.
In this particular example, the positive and negative slopes of
the ramp are different to demonstrate the flexibility of the DRG.
The parameters of both slopes can be programmed to make the
positive and negative slopes the same.
Rev. D | Page 30 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
DRG OUTPUT
LOWER LIMIT
UPPER LIMIT
DRCTL
DRHOLD
AUTOCLEAR DIGITAL
RAMP ACCUMULATOR
CLEAR DIGITAL
RAMP ACCUMULATOR
I/O_UPDATE
POSITIVE
STEP SIZE
NEGATIVE
STEP SIZE
P DDS CLOCK CYCLES N DDS CLOCK CYCLE S
1 DDS CLOCK CYCL E
DIGIT AL RAMP ENABLE
DROVER
06479-020
CLEAR
RELEASE
AUTO
CLEAR
–Δ
t
+Δ
t
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
101112
13
Event 1—The digital ramp enable bit is set, which has no effect
on the DRG output because the bit is not effective until an I/O
update.
Event 2—An I/O update registers the enable bit. If DRCTL = 1
is in effect at this time (the gray portion of the DRCTL trace),
then the DRG output immediately begins a positive slope (the
gray portion of the DRG output trace). Otherwise, if DRCTL =
0, the DRG output is initialized to the lower limit.
Event 3—DRCTL transitions to a Logic 1 to initiate a positive
slope at the DRG output. In this example, the DRCTL pin is
held long enough to cause the DRG to reach its programmed
upper limit. The DRG remains at the upper limit until the ramp
accumulator is cleared, DRCTL = 0, or the upper limit is
reprogrammed to a higher value. In the last case, the DRG
immediately resumes its previous positive slope profile.
Event 4—DRCTL transitions to a Logic 0 to initiate a negative
slope at the DRG output. In this example, the DRCTL pin is
held long enough to cause the DRG to reach its programmed
lower limit. The DRG remains at the lower limit until DRCTL = 1,
or until the lower limit is reprogrammed to a lower value. In the
latter case, the DRG immediately resumes its previous negative
slope profile.
Event 5—DRCTL transitions to a Logic 1 for the second time,
initiating a second positive slope.
Event 6—The positive slope profile is interrupted by DRHOLD
transitioning to a Logic 1. This stalls the ramp accumulator and
freezes the DRG output at its last value.
Figure 39. Normal Ramp Generation
Event 7—DRHOLD transitions to a Logic 0, releasing the ramp
accumulator and reinstating the previous positive slope profile.
Event 8—The clear digital ramp accumulator bit is set, which
has no effect on the DRG because the bit is not effective until an
I/O update is issued.
Event 9—An I/O update registers that the clear digital ramp
accumulator bit is set, resetting the ramp accumulator and
forcing the DRG output to the programmed lower limit. The
DRG output remains at the lower limit until the clear condition
is removed.
Event 10—The clear digital ramp accumulator bit is cleared,
which has no effect on the DRG output because the bit is not
effective until an I/O update is issued.
Event 11—An I/O update registers that the clear digital ramp
accumulator bit is cleared, releasing the ramp accumulator, and
the previous positive slope profile restarts.
Event 12—The autoclear digital ramp accumulator bit is set,
which has no effect on the DRG output because the bit is not
effective until an I/O update is issued.
Event 13—An I/O update registers that the autoclear digital
ramp accumulator bit is set, resetting the ramp accumulator.
However, with an automatic clear, the ramp accumulator is only
held reset for a single DDS clock cycle. This forces the DRG
output to the lower limit, but the ramp accumulator is immediately made available for normal operation. In this example, the
DRCTL pin remains a Logic 1; therefore, the DRG output
restarts the previous positive ramp profile.
Rev. D | Page 31 of 64

UPPER LIMIT
P DDS CLOCK CYCLES
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DRG OUTPUT
LOWER LIMIT
DRCTL
POSITIVE
STEP SIZE
DROVER
+Δ
t
06479-021
AD9910 Data Sheet
No-Dwell Ramp Generation
The two no-dwell bits in Control Function Register 2 add to the
flexibility of the DRG capabilities. During normal ramp generation,
when the DRG output reaches the programmed upper or lower
limit, it simply remains at the limit until the operating parameters
dictate otherwise. However, during no-dwell operation, the DRG
output does not necessarily remain at the limit. For example, if the
digital ramp no-dwell high bit is set when the DRG reaches the
upper limit, it automatically (and immediately) snaps to the lower
limit (that is, it does not ramp back to the lower limit; it jumps to
the lower limit). Likewise, when the digital ramp no-dwell low bit is
set, and the DRG reaches the lower limit, it automatically (and
immediately) snaps to the upper limit.
During no-dwell operation, the DRCTL pin is monitored for state
transitions only; that is, the static logic level is immaterial.
During no-dwell high operation, a positive transition of the
DRCTL pin initiates a positive slope ramp, which continues
uninterrupted (regardless of any further activity on the DRCTL
pin) until the upper limit is reached.
During no-dwell low operation, a negative transition of the DRCTL
pin initiates a negative slope ramp, which continues uninterrupted
(regardless of any further activity on the DRCTL pin) until the
lower limit is reached.
Setting both no-dwell bits invokes a continuous ramping mode
of operation; that is, the DRG output automatically oscillates
between the two limits using the programmed slope parameters.
Furthermore, the function of the DRCTL pin is slightly different.
Instead of controlling the initiation of the ramp sequence, it
only serves to change the direction of the ramp; that is, if the
DRG output is in the midst of a positive slope and the DRCTL
pin transitions from Logic 1 to Logic 0, then the DRG immediately switches to the negative slope parameters and resumes
oscillation between the limits. Likewise, if the DRG output is in
the midst of a negative slope and the DRCTL pin transitions from
Logic 0 to Logic 1, the DRG immediately switches to the positive
slope parameters and resumes oscillation between the limits.
When both no-dwell bits are set, the DROVER signal produces a
positive pulse (two cycles of the DDS clock) each time the DRG
output reaches either of the programmed limits (assuming that the
DROVER pin active bit is set).
A no-dwell high DRG output waveform is shown in Figure 40.
The waveform diagram assumes that the digital ramp no-dwell
high bit is set and has been registered by an I/O update. The
status of the DROVER pin is also shown with the assumption
that the DROVER pin active bit has been set.
Rev. D | Page 32 of 64
The circled numbers in Figure 40 indicate specific events, which
are explained as follows:
Event 1—Indicates the instant that an I/O update registers that the
digital ramp enable bit has been set.
Event 2—DRCTL transitions to a Logic 1, initiating a positive
slope at the DRG output.
Event 3—DRCTL transition to a Logic 0, which has no effect on
the DRG output.
Event 4—Because the digital ramp no-dwell high bit is set,
the moment that the DRG output reaches the upper limit, it
immediately switches to the lower limit, where it remains
until the next Logic 0 to Logic 1 transition of DRCTL.
Event 5—DRCTL transitions from Logic 0 to Logic 1, which
restarts a positive slope ramp.
Event 6 and Event 7—DRCTL transitions are ignored until the
DRG output reaches the programmed upper limit.
Event 8—Because the digital ramp no-dwell high bit is set, the
moment that the DRG output reaches the upper limit, it immediately switches to the lower limit, where it remains until the next
Logic 0 to Logic 1 transition of DRCTL.
Operation with the digital ramp no-dwell low bit set (instead of the
digital ramp no-dwell high bit) is similar, except that the DRG
output ramps in the negative direction on a Logic 1 to Logic 0
transition of DRCTL and jumps to the upper limit upon reaching
the lower limit.
DROVER Pin
The DROVER pin provides an external signal to indicate the status
of the DRG. Specifically, when the DRG output is at either of the
programmed limits, the DROVER pin is Logic 1; otherwise, it is
Logic 0. In the special case of both no-dwell bits set, the DROVER
pin pulses positive for two DDS clock cycles each time the DRG
output reaches either of the programmed limits.
Figure 40. No-Dwell High Ramp Generation

RAM
ADDRESS
DATA
Q
SCLK
I/O_RESET
SDIO
CS
PROFILE
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
ADDRESS CLOCK
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
STATE
MACHINE
UP/DOWN
COUNTER
SERIAL
I/O
PORT
2
32
10
10
U/D
3
06479-022
Data Sheet AD9910
RAM CONTROL
RAM Overview
The AD9910 makes use of a 1024 × 32-bit RAM. The RAM has
two fundamental modes of operation: data load/retrieve mode
and playback mode. Data load/retrieve mode is active when the
RAM data is being loaded or read back via the serial I/O port.
Playback mode is active when the RAM enable contents are
routed to one of the internal data destinations.
Depending on the specific playback mode, the user can
partition the RAM with up to eight independent time domain
waveforms. These waveforms drive the DDS signal control
parameters, allowing for frequency, phase, amplitude, or polar
modulated signals.
RAM operations are enabled by setting the RAM enable bit in
Control Function Register 1; an I/O update (or a profile change)
is necessary to enact any change to the state of this bit.
Waveforms are generated using eight RAM profile control
registers that are accessed via the three profile pins. Each profile
contains the following:
• 10-bit waveform start address word
• 10-bit waveform end address word
• 16-bit address step rate control word
• 3-bit RAM mode control word
• No-dwell high bit
• Zero-crossing bit
The user must ensure that the end address is greater than the
start address.
Each profile defines the number of samples and the sample rate
for a given waveform. In conjunction with an internal state
machine, the RAM contents are delivered to the appropriate
DDS signal control parameter(s) at the specified rate. Furthermore, the state machine can control the order in which samples
are extracted from RAM (forward/reverse), facilitating efficient
generation of time symmetric waveforms.
Load/Retrieve RAM Operation
It is strongly recommended that RAM enable = 0 when
performing RAM load/retrieve operations. Loading or
retrieving the contents of the RAM requires a three-step
process.
1. Program the RAM Profile 0 through RAM Profile 7 control
registers with the start and end addresses that are to define
the boundaries of each independent waveform.
2. Drive the appropriate logic levels on the profile pins to
select the desired RAM profile.
3. Write to (or read from) the
appropriate number of RAM words as specified by the
selected RAM profile control register (see the Serial
Programming section for details). Figure 41 is a block
diagram showing the functional components used for RAM
data load/retrieve operation.
During RAM load/retrieve operations, the state machine controls
an up/down counter to step through the required RAM locations. The counter synchronizes with the serial I/O port so that
the serial/parallel conversion of the 32-bit words is correctly
timed with the generation of the appropriate RAM address to
properly execute the desired read or write operation.
Figure 41. RAM Data Load/Retrieve Operation
The RAM profiles are completely independent; it is possible
to define overlapping address ranges. Doing so causes data
that has been written to overlapped address locations to be
overwritten by the most recent write operation.
Multiple waveforms can be loaded into RAM by treating them
as a single waveform, that is, a time-domain concatenation of all
the waveforms. This is done by programming one of the RAM
profiles with a start and end address spanning the entire range
of the concatenated waveforms. Then the single concatenated
waveform is written into RAM via the serial I/O port using the
same RAM profile that was programmed with the start and end
addresses. The RAM profiles must then be programmed with
the proper start and end addresses associated with each
individual waveform.
RAM Playback Operation (Waveform Generation)
When the RAM has been loaded with the desired waveform
data, it can then be used for waveform generation during play
back. RAM playback requires that RAM enable = 1. To p l ay back
RAM data, select the desired waveform using the PROFILE[2:0]
pins. The selected profile directs the internal state machine by
defining the RAM address range occupied by the waveform, the
rate at which samples are to be extracted from the RAM
(playback rate), the mode of operation, and whether to use the
no-dwell feature. Figure 42 is a block diagram showing the
functional components used for RAM playback operation.
Rev. D | Page 33 of 64
RAM (Address 0x16) the

AD9910 Data Sheet
RAM
ADDRESS
DATA
Q
PROFILE
DDS CLOCK
RAM
PROFILE
REGISTERS
STATE
MACHINE
UP/DOWN
COUNTER
32
10
2
3
16
10
10
U/D
3
06479-023
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
ADDRESS RAMP RATE
NO DWELL
RAM MODE
TO DDS
SIGNAL
CONTROL
PARAMETER
M
f
M
f
RatePlayback
SYSCLKDDSCLOCK
4
==
SYSCLK
f
M
RatePlayback
t41Δ ==
The RAM playback destination bits affect specific DDS signal
control parameters. The parameters that are not affected by the
RAM playback destination bits are controlled by the FTW, P O W,
and/or ASF registers.
RAM_SWP_OVR (RAM Sweep Over) Pin
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin provides an active high external
signal that indicates the end of a playback sequence. The
operation of this pin varies with the RAM operating mode
as detailed in the following sections. When RAM enable = 0,
Figure 42. RAM Playback Operation
During playback, the state machine uses an up/down counter to
step through the specified address locations. The clock rate of
this counter defines the playback rate, that is, the sample rate of
the generated waveform. The clocking of the counter is controlled
by a 16-bit programmable timer that is internal to the state
machine. This timer is clocked by the DDS clock, and its time
interval is set by the 16-bit address step rate value stored in the
selected RAM profile register.
The address step rate value determines the playback rate. For
example, if M is the 16-bit value of the address step rate for a
specific RAM profile, then the playback rate for that profile is
given by
The sample interval (Δt) associated with the playback rate is
therefore given by
this pin is forced to a Logic 0.
Overview of RAM Playback Modes
The RAM can operate in any one of five different playback modes.
• Direct switch
• Ramp-up
• Bidirectional ramp
• Continuous bidirectional ramp
• Continuous recirculate
The mode is selected via the 3-bit RAM mode control word
located in each of the RAM profile registers. Thus, the RAM
operating mode is profile dependent. The RAM profile mode
control bits are detailed in Table 13.
Table 13. RAM Operating Modes
RAM Profile
Mode Control Bits RAM Operating Mode
000, 101, 110, 111 Direct switch
001 Ramp-up
010 Bidirectional ramp
011 Continuous bidirectional ramp
100 Continuous recirculate
RAM data entry/retrieval via the I/O port takes precedence
over playback operation. An I/O operation targeting the RAM
during playback interrupts any waveform in progress.
The 32-bit words output by the RAM during playback route to
the DDS signal control parameters according to two RAM
playback destination bits in Control Function Register 1. The
32-bit words are partitioned based on Tabl e 12.
Table 12. RAM Playback Destination
RAM Playback
Destination Bits
CFR1[30:29]
00 Frequency 31:0
01 Phase 31:16
10 Amplitude 31:18
11 Polar (phase
When the destination is phase, amplitude, or polar, the unused
LSBs are ignored.
DDS Signal
Control
Parameter
and amplitude)
Bits Assigned to
DDS Parameters
31:16 (phase)
15:2 (amplitude)
RAM Direct Switch Mode
In direct switch mode, the RAM is not used as a waveform generator. I nstead, when a RAM profile is selected via the PROFILE[2:0]
pins, only a single 32-bit word is routed to the DDS to be applied
to the signal control parameter(s). This 32-bit word is the data
stored in the RAM at the location given by the 10-bit waveform
start address of the selected profile.
In direct switch mode, the RAM_SWP_OVR pin is always
Logic 0, and the no-dwell high bit is ignored.
Direct switch mode enables up to eight-level FSK, PSK, or ASK
modulation; the type of modulation is determined by the RAM
playback destination bits (frequency for FSK and so on). Each
RAM profile is associated with a specific value of frequency,
phase, or amplitude. Each unique waveform start address value
in each RAM profile allows access of the 32-bit word stored in
that particular RAM location. In this way, the profile pins
implement the shift-keying function, modulating the DDS
output as desired.
Rev. D | Page 34 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
06479-024
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
1
M DDS CLOCK CYCLES
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
NO-DWELL
HIGH = 0
NO-DWELL
HIGH = 1
1
RAM ADDRESS
RAM ADDRESS
RAM_SWP_OVER
I/O_UPDATE
1 2 3
Δ
t
Note that two-level modulation can be accomplished by using
only one of the three profile pins to toggle between two different parameter values. Likewise, four-level modulation can be
accomplished by using only two of the three profile pins. There
is no restriction on which profile pins are used.
RAM Direct Switch Mode with Zero Crossing
The zero-crossing function (enabled with the zero-crossing bit)
is a special feature that is only available in RAM direct switch
mode. The zero-crossing function is only valid if the RAM
playback destination bits specify phase as the DDS signal
control parameter.
Enabling zero-crossing causes the DDS to delay the application
of a new phase value until such time as the DDS phase accumulator rolls over from full scale to 0 (the point at which the DDS
phase accumulator represents a phase angle that is at the 360° to
0° transition point). This can be a very beneficial feature when
the DDS is programmed to generate a sine wave (using the
select DDS sine output bit) because the zero-crossing point of
phase for a sine wave corresponds with the zero-crossing point
of amplitude.
Ramp-Up Timing Diagram
A graphic representation of the ramp-up mode appears in
Figure 43, showing both normal and no-dwell operation.
The two upper traces show the progression of the RAM address
from the waveform start address to the waveform end address
for the selected profile. The address value advances by one with
each timeout of the timer internal to the state machine. The
timer period (Δt) is determined by the address ramp rate value
for the selected profile. The two upper traces are differentiated
by the state of the no-dwell high bit.
In the case of binary phase shift keying (BPSK), the zerocrossing feature allows the AD9910 to perform the 180° phase
jumps associated with BPSK with only a minimal instantaneous
change in amplitude. This avoids the spectral splatter that
frequently accompanies BPSK modulation.
Although the intent of the zero-crossing feature is for use with
the DDS sine output enabled, it can be used with a cosine
output. In this case, the phase values extracted from RAM are
registered at the DDS when the output amplitude is at its peak
positive value.
RAM Ramp-Up Mode
In ramp-up mode, upon assertion of an I/O update or a change
of profile, the RAM begins operating as a waveform generator
using the parameters programmed into the selected RAM
profile register. Data is extracted from RAM over the specified
address range and at the specified rate contained in the waveform start address, waveform end address, and address ramp
rate values of the selected RAM profile. The data is delivered
to the specified DDS signal control parameter(s) based on the
RAM playback destination bits.
The internal state machine begins extracting data from the
RAM at the waveform start address and continues to extract
data until it reaches the waveform end address. Upon reaching
this address, it either remains at the waveform end address or
returns to the waveform start address as defined by the no-dwell
high bit. Then the state machine halts, and the RAM_SWP_OVR
pin goes high.
Rev. D | Page 35 of 64
Figure 43. Ramp-Up Timing Diagram
The circled numbers in Figure 43 indicate specific events,
explained as follows:
Event 1—An I/O update or profile change occurs. This event
initializes the state machine to the waveform start address and
sets the RAM_SWP_OVR pin to Logic 0.
Event 2—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
value for the selected profile. The RAM_SWP_OVR pin
switches to Logic 1. This marks the end of the waveform
generation sequence for normal operation.
Event 3—The state machine switches to the waveform start
address. This marks the end of the waveform generation
sequence for no-dwell operation.
Changing profiles resets the RAM_SWP_OVR pin to Logic 0,
automatically terminates the current waveform, and initiates the
newly selected waveform.

AD9910 Data Sheet
Internal Profile Control Bits (CFR1[20:17])
Waveform Type
Internal Profile Control Description
0111
Burst
Execute Profile 0 to Profile 7, then halt.
RAM Ramp-Up Internal Profile Control Mode
Table 14. RAM Internal Profile Control Modes
0000 Internal profile control disabled.
0001 Burst Execute Profile 0, then Profile 1, then halt.
0010 Burst Execute Profile 0 to Profile 2, then halt.
0011 Burst Execute Profile 0 to Profile 3, then halt.
0100 Burst Execute Profile 0 to Profile 4, then halt.
0101 Burst Execute Profile 0 to Profile 5, then halt.
0110 Burst Execute Profile 0 to Profile 6, then halt.
1000 Continuous Execute Profile 0, then Profile 1, continuously.
1001 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 2, continuously.
1010 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 3, continuously.
1011 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 4, continuously.
1100 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 5, continuously.
1101 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 6, continuously.
1110 Continuous Execute Profile 0 to Profile 7, continuously.
1111 Invalid.
Ramp up internal profile control mode is invoked via the four
internal profile control bits (rather than through the RAM
profile mode control bits in the RAM profile registers).
If any of the internal profile control bits is set, then the RAM
profile mode control bits of the RAM profile registers are
ignored. The no-dwell high bit is ignored in this mode. The
internal profile control mode is identical to ramp-up mode
except that profile switching is done automatically and
internally; the state of the PROFILE[2:0] pins is ignored.
Profiles cycle according to Table 14.
There are two types of waveform generation types available
under internal profile control: burst waveforms and continuous
waveforms. With both types, the state machine begins with the
waveform specified by the waveform start address, waveform
end address, and address ramp rate in Profile 0. After reaching
the waveform end address of Profile 0, the state machine automatically advances to the next profile and initiates the specified
waveform as defined by the new profile parameters. After the
state machine reaches the waveform end address of the new
profile, it advances to the next profile. This action continues
until the state machine reaches the waveform end address of
the last profile, as governed by the internal profile control bits in
Control Function Register 1 (CFR1) per Tab l e 14.
At this point, the next course of action depends on whether the
waveform type is burst or continuous. For burst waveforms, the
state machine halts operation after reaching the waveform end
address of the final profile. For continuous waveforms, the state
machine automatically jumps to Profile 0 and continues the
automatic waveform generation by sequentially advancing
through the profiles. This process continues indefinitely until
the internal profile control bits are reprogrammed and an I/O
update is asserted.
A burst waveform timing diagram is exemplified in Figure 44.
The diagram assumes that the internal profile control bits in
Register CFR1 are programmed as 0010, the start address in
RAM Profile 1 is greater than the end address in RAM Profile 0,
and that the start address in RAM Profile 2 is greater than the
end address in RAM Profile 1. However, the block of RAM
associated with each profile can be chosen arbitrarily based on
the waveform start address and waveform end address for each
profile. Furthermore, the example shows how different Δt
values associated with each profile can be used.
Rev. D | Page 36 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
RAM_SWP_OVER
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS 0
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S 0
1
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS 1
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S 1
1
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S 2
1
RAM PROFILE 0 1 2
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS 2
RAM
ADDRESS
I/O_UPDATE
Δ
t
0
Δ
t
1
Δ
t
2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
06479-025
Figure 44. Internal Profile Control Timing Diagram (Burst)
The gray bar across the top indicates the time interval over
which the designated profile is in effect. The circled numbers
indicate specific events as follows:
Event 1—An I/O update registers the internal profile control bits
(in Control Function Register 1) as 0010. The RAM_SWP_OVR
pin is set to Logic 0. The state machine is initialized to the
waveform start address of RAM Profile 0 and begins incrementing through the address range for RAM Profile 0 at intervals of
Δt
(as specified by the address step rate for RAM Profile 0).
0
Event 2—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
of RAM Profile 0, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin generates a
positive pulse spanning two DDS clock cycles.
Event 3—Having reached the waveform end address of RAM
Profile 0, the next expiration of the internal timer causes the
state machine to advance to RAM Profile 1. The state machine
is initialized to the waveform start address of RAM Profile 1
and begins incrementing through the address range for RAM
Profile 1 at intervals of Δt
.
1
Event 4—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
of RAM Profile 1, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin generates a
positive pulse spanning two DDS clock cycles.
Event 5—Having reached the waveform end address of RAM
Profile 1, the next expiration of the internal timer causes the
state machine to advance to RAM Profile 2. The state machine
initializes to the waveform start address of RAM Profile 2 and
begins incrementing through the address range for RAM
Profile 2 at intervals of Δt
.
2
Event 6—The state machine reaches the waveform end address of
RAM Profile 2, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin generates a positive
pulse spanning two DDS clock cycles.
Event 7—Having reached the waveform end address of RAM
Profile 2, the next expiration of the internal timer causes the
state machine to halt and marks completion of the burst
waveform generation process.
Rev. D | Page 37 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
WAVEFO RM S TART
ADDRESS 0
WAVEFORM END
ADDRESS 0
WAVEFO RM S TART
ADDRESS 1
WAVEFORM END
ADDRESS 1
06479-026
1
RAM_SWP_OVER
RAM PROFILE
RAM
ADDRESS
I/O_UPDATE
0 1 0
0
1
1
1 2
3 4
5
6
7 8
9
10 11
Δ
t
0
Δ
t
1
1
Internal Profile Control Continuous Waveform Timing Diagram
An example of an internal profile control continuous waveform
timing diagram is shown in Figure 45. The diagram assumes that
the internal profile control bits (in Control Function Register 1)
are programmed as 1000. It also assumes that the start address in
RAM Profile 1 is greater than the end address in RAM Profile 0.
The gray bar across the top indicates the time interval over
which the designated profile is in effect. The circled numbers
indicate specific events.
Event 1—An I/O update registers that the internal profile
control bits (in Control Function Register 1) are programmed
to 1000. The RAM_SWP_OVR pin is set to Logic 0. The state
machine is initialized to the waveform start address of RAM
Profile 0 and begins incrementing through the address range for
RAM Profile 0 at intervals of Δt
step rate for RAM Profile 0).
Event 2—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
of RAM Profile 0, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin generates a
positive pulse spanning two DDS clock cycles.
Event 3—Having reached the waveform end address of RAM
Profile 0, the next expiration of the internal timer causes the
state machine to advance to RAM Profile 1. The state machine
is initialized to the waveform start address of RAM Profile 1
and begins incrementing through the address range for RAM
Profile 1 at intervals of Δt
Event 4—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
of RAM Profile 1, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin generates a
positive pulse spanning two DDS clock cycles.
Event 5—Having reached the waveform end address of RAM
Profile 1, the next expiration of the internal timer causes the
state machine to jump back to RAM Profile 0. The state
machine initializes to the waveform start address of RAM
.
1
Figure 45. Internal Profile Control Timing Diagram (Continuous)
(as specified by the address
0
Profile 0 and begins incrementing through the address range for
RAM Profile 0 at intervals of Δt
Event 5 to Event 11—These events repeat indefinitely until the
internal profile control bits are reprogrammed and an I/O
update is asserted.
RAM Bidirectional Ramp Mode
In bidirectional ramp mode, upon assertion of an I/O update,
the RAM begins operating as a waveform generator using the
parameters programmed only into RAM Profile 0 (unlike ramp
up mode, which uses all eight profiles). Data is extracted from
RAM over the specified address range and at the specified rate
contained in the waveform start address, waveform end address,
and address ramp rate values of the selected RAM profile. The
data is delivered to the specified DDS signal control parameter(s)
based on the RAM playback destination bits.
The PROFILE[2:1] pins are ignored by the internal logic in this
mode. When a RAM profile programmed to operate in this
mode is selected, no other RAM profiles can be selected until the
active RAM profile is reprogrammed with a different RAM
operating mode. The no-dwell high bit is ignored in this mode.
With the bidirectional ramp mode activated via an I/O update
or profile change, the internal state machine readies to extract
data from the RAM at the waveform start address. Data extraction begins when PROFILE0 is Logic 1, which instructs the state
machine to begin incrementing through the address range. As
long as the PROFILE0 pin remains Logic 1, the state machine
continues to extract data until it reaches the waveform end
address. At this point, the state machine halts until the PROFILE0
pin is Logic 0, instructing the state machine to begin decrementing
through the address range. As long as the PROFILE0 pin is
Logic 0, the state machine continues to extract data until it
reaches the waveform start address. At this point, the state
machine halts until the PROFILE0 pin is Logic 1.
Rev. D | Page 38 of 64
.
0

Data Sheet AD9910
06479-027
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
1
PROFILE0
RAM ADRESS
RAM_SWP_OVER
I/O_UPDATE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Δ
t
Δ
t
M DDS CLOCK CYCLES
Figure 46. Bidirectional Ramp Timing Diagram
If the PROFILE0 pin changes states before the state machine
reaches the programmed start or end address, the internal timer
is restarted and the direction of the address counter is reversed.
Figure 46 is a graphic representation of the bidirectional ramp
mode. It shows the action of the state machine in response to
the PROFILE0 pin and the response of the RAM_SWP_OVR pin.
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin switches to Logic 1 when the state
machine reaches the waveform end address. It remains Logic 1
until the state machine reaches the waveform start address and
the PROFILE0 pin transitions from Logic 0 to Logic 1.
The circled numbers in Figure 46 indicate specific events as
follows:
Event 1—An I/O update or profile change activates the RAM
bidirectional ramp mode. The state machine initializes to the
waveform start address, and the RAM_SWP_OVR pin is set to
Logic 0.
Event 2—Pin PROFILE0 switches to Logic 1. The state machine
begins incrementing the RAM address counter.
Event 3—Pin PROFILE0 remains at Logic 1 long enough for the
state machine to reach the waveform end address. The RAM_
SWP_OVR pin switches to Logic 1 accordingly.
Event 4—Pin PROFILE0 switches to Logic 0. The state machine
begins decrementing the RAM address counter. The RAM_
SWP_OVR pin remains at Logic 1.
Event 5—Pin PROFILE0 switches to Logic 1. The state machine
resets its internal timer and reverses the direction of the RAM
address counter (that is, it starts to increment). There is no
change of the RAM_SWP_OVR state because the waveform
start address has not yet been reached.
Event 6—Pin PROFILE0 switches to Logic 0. The state machine
resets its internal timer and again reverses the direction of the RAM
address counter. The RAM_SWP_OVR state does not change.
Event 7—Pin PROFILE0 remains at Logic 0 long enough for the
state machine to reach the waveform start address. There is no
change in the RAM_SWP_OVR state.
Event 8—Pin PROFILE0 switches to Logic 1. The state machine
resets its internal timer and begins incrementing the RAM
address counter. The RAM_SWP_OVR pin switches to Logic 0
because both the waveform start address was reached and the
PROFILE0 pin transitioned from Logic 0 to Logic 1.
RAM Continuous Bidirectional Ramp Mode
In continuous bidirectional ramp mode, upon assertion of an
I/O update or a change of profile, the RAM begins operating
as a waveform generator using the parameters programmed
into the RAM profile designated by the PROFILEx pins. Data is
extracted from RAM over the specified address range and at the
specified rate contained in the waveform start address, waveform
end address, and address ramp rate values of the selected RAM
profile. The data is delivered to the specified DDS signal control
parameter(s) based on the RAM playback destination bits. The
no-dwell high bit is ignored in this mode.
With the continuous bidirectional ramp mode activated via an
I/O update or profile change, the internal state machine begins
extracting data from the RAM at the waveform start address and
incrementing the address counter until it reaches the waveform
end address. At this point, the state machine automatically reverses
the direction of the address counter and begins decrementing
through the address range. Whenever one of the terminal
addresses is reached, the state machine reverses the address
counter; the process continues indefinitely.
Rev. D | Page 39 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
1
Δ
t
Δ
t
RAM ADRESS
RAM_SWP_OVER
I/O_UPDATE
M DDS CLOCK CYCLES
1
2 3
06479-028
Figure 47. Continuous Bidirectional Ramp Timing Diagram
A change in state of the PROFILE pins aborts the current waveform, and the newly selected RAM profile is used to initiate a
new waveform.
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin switches to Logic 1 when the state
machine reaches the waveform end address, then returns to
Logic 0 at the waveform start address, toggling each time one
of these addresses is reached.
A graphic representation of the continuous bidirectional ramp
mode is shown in Figure 47. The circled numbers indicate specific
events as follows:
Event 1—An I/O update or profile change has activated the RAM
continuous bidirectional ramp mode. The state machine initializes
to the waveform start address. The RAM_SWP_OVR pin resets to
Logic 0. The state machine begins incrementing through the
specified address range.
Event 2—The state machine reaches the waveform end address.
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin toggles to Logic 1.
Event 3—The state machine reaches the waveform start address.
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin toggles to Logic 0.
The continuous bidirectional ramp continues indefinitely until
the mode is changed.
Rev. D | Page 40 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
06479-029
WAVEFO RM S TART ADDRESS
WAVEFO RM E ND ADDRE S S
1
1 2
3
4
5
RAM ADRESS
RAM_SWP_OVER
I/O_UPDATE
M DDS CLOCK CYCLES
Δ
t
Figure 48. Continuous Recirculate Timing Diagram
RAM Continuous Recirculate Mode
The continuous recirculate mode mimics the ramp-up mode,
except that when the state machine reaches the waveform end
address, the next timeout of the internal timer causes the state
machine to jump to the waveform start address. The waveform
repeats until an I/O update or profile change.
The no-dwell high bit is ignored in this mode.
A profile pin state change aborts the current waveform, and the
newly selected RAM profile is used to initiate a new waveform.
The RAM_SWP_OVR pin pulses high for two DDS clock cycles
when the state machine reaches the waveform end address.
Continuous recirculate mode is graphically represented in
Figure 48. The circled numbers indicate specific events as
follows:
Event 1—An I/O update or profile change occurs. This event
initializes the state machine to the waveform start address and
sets the RAM_SWP_OVR pin to Logic 0.
Event 2—The state machine reaches the waveform end address
value for the selected profile. The RAM_SWP_OVR pin toggles
to Logic 1 for two DDS clock cycles.
Event 3—The state machine switches to the waveform start
address and continues to increment the address counter.
Event 4—The state machine again reaches the waveform end
address value for the selected profile, and the RAM_SWP_OVR
pin toggles to Logic 1 for two DDS clock cycles.
Event 5—The state machine switches to the waveform start
address and continues to increment the address counter.
Event 4 and Event 5—These events repeat until an I/O update is
issued or a change in profile is made.
Rev. D | Page 41 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
010
2
SYNC_CLK
SYSCLK
A B
N N + 1
N – 1
DATA IN
REGISTERS
DATA IN
I/O BUFFERS
N
N + 1 N + 2
I/O_UPDATE
THE DEVICE RE GISTERS AN I/O UPDATE AT POINT A. THE DATA IS TRANSFERRED FROM THE ASYNCHRO NOUSLY LO ADE D I/O BUFF E RS AT POINT B.
06479-061
ADDITIONAL FEATURES
PROFILES
The AD9910 supports the use of profiles, which consist of a group
of eight registers containing pertinent operating parameters for
a particular operating mode. Profiles enable rapid switching
between parameter sets. Profile parameters are programmed via
the serial I/O port. Once programmed, a specific profile is
activated by means of three external pins (PROFILE[2:0]). A
particular profile is activated by providing the appropriate logic
levels to the profile control pins per Tabl e 15.
Table 15. Profile Control Pins
PROFILE[2:0] Active Profile
000 0
001 1
011 3
100 4
101 5
110 6
111 7
There are two different parameter sets that the eight profile
registers can control depending on the operating mode of the
device. When RAM enable = 0, the profile parameters follow
the single tone profile format detailed in the Register Map and
Bit Descriptions section. When RAM enable = 1, they follow
the RAM profile format.
As an example of the use of profiles, consider an application for
implementing basic two-tone frequency shift keying (FSK). FSK
uses the binary data in a serial bit stream to select between two
different frequencies: a mark frequency (Logic 1) and a space
frequency (Logic 0). To accommodate FSK, the device operates
in single tone mode. The Single Tone Profile 0 register is programmed with the appropriate frequency tuning word for a
space. The S i n gle To n e Profile 1 register is programmed with
the appropriate frequency tuning word for a mark. Then, with
the PROFILE1 and PROFILE2 pins tied to Logic 0, the PROFILE0
pin is connected to the serial bit stream. In this way, the logic
state of the PROFILE0 pin causes the appropriate mark and
space frequencies to be generated in accordance with the binary
digits of the bit stream.
The profile pins must meet setup and hold times to the rising
edge of SYNC_CLK.
I/O_UPDATE, SYNC_CLK, AND SYSTEM CLOCK RELATIONSHIPS
The I/O_UPDATE pin is used to transfer data from the serial
I/O buffer to the active registers in the device. Data in the buffer
is inactive.
SYNC_CLK is a rising edge active signal. It is derived from the
system clock and a divide-by-4 frequency divider. SYNC_CLK,
which is externally provided, can be used to synchronize external
hardware to the AD9910 internal clocks.
I/O_UPDATE initiates the start of a buffer transfer. It can be
sent synchronously or asynchronously relative to the SYNC_CLK.
If the setup time between these signals is met, then constant
latency (pipeline) to the DAC output exists. For example, if
repetitive changes to phase offset via the SPI port is desired,
the latency of those changes to the DAC output is constant;
otherwise, a time uncertainty of one SYNC_CLK period is
present.
By default, the I/O_UPDATE pin is an input that serves as a
strobe signal to allow synchronous update of the device operating parameters. A rising edge on I/O_UPDATE initiates transfer
of the register contents to the internal workings of the device.
Alternatively, the transfer of programmed data from the programming registers to the internal hardware can be accomplished by
changing the state of the PROFILE[2:0] pins.
The timing diagram shown in Figure 49 depicts when the data
in the buffer is transferred to the active registers.
Figure 49. I/O_UPDATE Transferring Data from I/O Buffer to Active Registers
Rev. D | Page 42 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
B
f
f
A
SYSCLK
UPDATEOI2_/
2
+
=
AUTOMATIC I/O UPDATE
The AD9910 offers an option whereby the I/O update function
is asserted automatically rather than relying on an external signal
supplied by the user. This feature is enabled by setting the internal
I/O update active bit in Control Function Register 2 (CFR2).
When this feature is active, the I/O_UPDATE pin becomes an
output pin. It generates an active high pulse each time an internal I/O update occurs. The pulse width is determine by the I/O
update rate control bits (CFR2[15:14]). Table 16 approximates the
pulse width setting.
Table 16. Pulse Width Setting
I/O Update Rate Control Bits
(CFR2[15:14])
00 12 SYSCLKs
01 24 SYSCLKs
10 48 SYSCLKs
11 96 SYSCLKs
This I/O update strobe can be used to notify an external
controller that the device has generated an I/O update
internally.
The repetition rate of the internal I/O update is programmed
via the serial I/O port. There are two parameters that control
the repetition rate. The first consists of the two I/O update rate
control bits in CFR2. The second is the 32-bit word in the I/O
update rate register that sets the range of an internal counter.
The I/O update rate control bits establish a divide-by-1, -2, -4,
or -8 of a clock signal that runs at ¼ f
divider clocks the aforementioned 32-bit internal counter. The
repetition rate of the I/O update is given by
where:
A is the value of the 2-bit word comprising the I/O update rate
control bits.
B is the value of the 32-bit word stored in the I/O update rate
register.
I/O Update Pulse Width
. The output of the
SYSCLK
POWER-DOWN CONTROL
The AD9910 offers the ability to independently power down
four specific sections of the device. Power-down functionality
applies to the following:
• Digital core
• DAC
• Auxiliary DAC
• Input REFCLK clock circuitry
A power-down of the digital core disables the ability to update
the serial I/O port. However, the digital power-down bit can
still be cleared via the serial port to prevent the possibility of a
nonrecoverable state.
Software power-down is controlled via four independent powerdown bits in Control Function Register 1 (CFR1). Software
control requires that the EXT_PWR_DWN pin be forced to a
Logic 0 state. In this case, setting the desired power-down bits
(via the serial I/O port) powers down the associated functional
block, whereas clearing the bits restores the function.
Alternatively, all four functions can be simultaneously powered
down via external hardware control through the EXT_PWR_DWN
pin. When this pin is forced to Logic 1, all four circuit blocks are
powered down regardless of the state of the power-down bits;
that is, the independent power-down bits in CFR1 are ignored
and overridden when EXT_PWR_DWN is Logic 1.
Based on the state of the external power-down control bit, the
EXT_PWR_DWN pin produces either a full power-down or a
fast recovery power-down. The fast recovery power-down mode
maintains power to the DAC bias circuitry and the PLL, VCO,
and input clock circuitry. Although the fast recovery powerdown does not conserve as much power as the full power-down,
it allows the device to awaken very quickly from the powerdown state.
The default value of A is 0, and the value of B is 0xFFFF. If B is
programmed to 0x0003 or less, the I/O_UPDATE pin no longer
pulses but assumes a static Logic 1 state.
Rev. D | Page 43 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
06479-050
SYNC
GENERATOR
REF_CLK
5
SYSCLK
INTERNAL
CLOCKS
5
4
SYNC
RECEIVER
SYNC
GENERATOR
ENABLE
SYNC
GENERATOR
DELAY
SYNC
POLARITY
90
91
9
10
REF_CLK
INPUT
CIRCUITRY
7
8
12
SYNC_IN+
REF_CLK
SYNC_IN–
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC
VALIDATION
DELAY
SYNC
TIMING
VALIDATION
DISABLE
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SETUP AND
HOLD VALIDATION
SYNC
RECEIVER
ENABLE
SYNC
RECEIVER
DELAY
INPUT DEL AY
AND EDGE
DETECTION
SYNC_OUT+
SYNC_OUT–
SYSCLK
SYNC
GENERATOR
ENABLE
SYNC
GENERATOR
DELAY
SYNC
POLARITY
SYNC_OUT+
SYNC_OUT–
0
1
D Q
R
PROGAMMABLE
DELAY
÷16
5
9
10
9
10
LVDS
DRIVER
06479-051
16
f
SYNCHRONIZATION OF MULTIPLE DEVICES
Multiple devices are synchronized when their clock states match
and they transition between states simultaneously. Clock
synchronization allows the user to asynchronously program
multiple devices but synchronously activate the programming by
applying a coincident I/O update to all devices
The function of the synchronization logic in the AD9910 is to
force the internal clock generator to a predefined state coincident
with an external synchronization signal applied to the SYNC_INx
pins. If all devices are forced to the same clock state in synchronization with the same external signal, then the devices are, by
definition, synchronized. Figure 50 is a block diagram of the
synchronization function. The synchronization logic is divided
into two independent blocks: a sync generator and a sync receiver,
both of which use the local SYSCLK signal for internal timing.
The sync generator block is shown in Figure 51. It is activated
via the sync generator enable bit. It allows for one AD9910 in a
group to function as a master timing source with the remaining
devices slaved to the master.
Figure 51. Sync Generator Diagram
The sync generator produces a clock signal that appears at the
SYNC_OUTx pins. This clock is delivered by an LVDS driver
and exhibits a 50% duty cycle. The clock has a fixed frequency
given by
SYSCLK
f =
_
OUTSYNC
Figure 50. Synchronization Circuit Block Diagram
The synchronization mechanism relies on the premise that the
REFCLK signal appearing at each device is edge aligned with all
others as a result of the external REFCLK distribution system
(see Figure 53).
The clock at the SYNC_OUTx pins synchronizes with either the
rising or falling edge of the internal SYSCLK signal, as determined
by the sync generator polarity bit. Because the SYNC_OUTx signal
is synchronized with the internal SYSCLK of the master device,
the master device SYSCLK serves as the reference timing source
for all slave devices. The user can adjust the output delay of the
SYNC_OUTx signal in steps of ~75 ps by programming the 5-bit
output sync generator delay word via the serial I/O port. The
programmable output delay facilitates added edge timing
flexibility to the overall synchronization mechanism.
The sync receiver block (shown in Figure 52) is activated via the
sync receiver enable bit (0x0A[27]). The sync receiver consists
of three subsections: the input delay and edge detection block,
the internal clock generator block, and the setup and hold
validation block.
The clock generator block remains operational even if the sync
receiver is not enabled.
Rev. D | Page 44 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
LVDS
RECEIVER
PROGAMMABLE
DELAY
5
INTERNAL
CLOCKS
CLOCK
STATE
SYNC PULSE
SYSCLK
SETUP AND HOLD
VALIDATION
4
Q0
RESET
Qn
DELAYED SYNC- IN SIGNAL
SYNC
RECEIVER
DELAY
SYNC
RECEIVER
ENABLE
SYNC_SMP_ERR
7
8
12
RISING EDGE
DETECTOR
AND
STROBE
GENERATOR
SYNC
TIMING
VALIDATION
DISABLE
SYNC
VALIDATION
DELAY
06479-052
CLOCK
GENERATOR
•
•
•
•
•
•
SYNC_IN+
SYNC_IN–
SYNCINSYNC
OUT
REF_CLK
AD9910
NUMBER 1
MASTER DEVICE
FPGA
DATA
FPGA
DATA
FPGA
DATA
EDGE
ALIGNED
AT REF_CLK
INPUTS
EDGE
ALIGNED
AT SYNC_IN
INPUTS.
PDCLK
SYNCINSYNC
OUT
REF_CLK
AD9910
NUMBER 2
PDCLK
SYNCINSYNC
OUT
REF_CLK
AD9910
NUMBER 3
PDCLK
(FOR EXAMPLE AD951x)
CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
AND
DELAY EQUALIZATION
SYNCHRONIZATION
DISTRIBUTION AND
DELAY EQUALIZATION
(FOR EXAMPLE AD951x)
06479-053
CLOCK
SOURCE
Figure 52. Sync Receiver Diagram
Figure 53. Multichip Synchronization Example
The sync receiver accepts a periodic clock signal at the SYNC_
INx pins. This signal is assumed to originate from an LVDScompatible driver. The user can delay the SYNC_INx signal in
steps of ~75 ps by programming the 5-bit input sync receiver
delay word in the multichip sync register. The signal at the
output of the programmable delay is referred to as the delayed
SYNC_INx signal.
Note that an internal 100 Ω LVDS termination resistor exists
across both SYNC_IN inputs.
The edge detection logic generates a sync pulse having a duration of one SYSCLK cycle with a repetition rate equal to the
frequency of the signal applied to the SYNC_INx pins. The
sync pulse is generated as a result of sampling the rising edge
Rev. D | Page 45 of 64
of the delayed SYNC_INx signal with the rising edge of the
local SYSCLK. The sync pulse is routed to the internal clock
generator, which behaves as a presettable counter clocked at the
SYSCLK rate. The sync pulse presets the counter to a predefined
state (programmable via the 6-bit sync state preset value word
in the multichip sync register). The predefined state is only active
for a single SYSCLK cycle, after which the clock generator resumes
cycling through its state sequence at the SYSCLK rate. This
unique state presetting mechanism gives the user the flexibility
to synchronize devices with specific relative clock state offsets
(by assigning a different sync state preset value word to each
device).
Multiple device synchronization is accomplished by providing
each AD9910 with a SYNC_INx signal that is edge aligned

AD9910 Data Sheet
SYNC
PULSE
SYSCLK
DELAY
DELAY
CHECK LOGIC
4
SYNC VALIDATION
DELAY
4
4
SYNC_SMP_ERR
SYNC RECEIVER
12
SYNC TIMING VALIDATION DISABLE
SETUP
VALIDATION
HOLD
VALIDATION
D
Q
12
SETUP AND HOLD VALIDATION
TO
CLOCK
GENERATION
LOGIC
FROM
SYNC
RECEIVER
DELAY
LOGIC
D Q
D Q
RISING EDGE
DETECTOR
AND STROBE
GENERATOR
06479-054
across all the devices. If the SYNC_INx signal is edge aligned at all
devices, and all devices have the same sync receiver delay and
sync state preset value, then they all have matching clock states
(that is, they are synchronized). This concept is shown in
Figure 53, in which three AD9910 devices are synchronized,
with one device operating as a master timing unit and the
others as slave units.
The master device must have its SYNC_INx pins included as part
of the synchronization distribution and delay equalization mechanism in order for it to be synchronized with the slave units.
The synchronization mechanism begins with the clock distribution and delay equalization block, which is used to ensure that
all devices receive an edge-aligned REFCLK signal. However,
even though the REFCLK signal is edge aligned among all devices,
this alone does not guarantee that the clock state of each internal
clock generator is coordinated with the others. This is the role
of the synchronization and delay equalization block. This block
accepts the SYNC_OUTx signal generated by the master device
and redistributes it to the SYNC_INx input of the slave units (as
well as feeding it back to the master). The goal of the redistributed
SYNC_OUT x signal from the master device is to deliver an
edge-aligned SYNC_INx signal to all of the sync receivers.
Assuming that all devices share the same REFCLK edge (due to
the clock distribution and delay equalization block), and all
devices share the same SYNC_INx edge (due to the synchronization and delay equalization block), then all devices should
generate an internal sync pulse in unison (assuming that they
all have the same sync receiver delay value). With the further
stipulation that all devices have the same sync state preset value,
then the synchronized sync pulses cause all of the devices to
assume the same predefined clock state simultaneously; that is,
the internal clocks of all devices become fully synchronized.
The synchronization mechanism depends on the reliable generation of a sync pulse by the edge detection block in the sync
receiver. Generation of a valid sync pulse, however, requires
proper sampling of the rising edge of the delayed SYNC_INx signal
with the rising edge of the local SYSCLK. If the edge timing of
these signals fails to meet the setup or hold time requirements
of the internal latches in the edge detection circuitry, then the
proper generation of the sync pulse is in jeopa rdy. The setup
and hold validation block (see Figure 54) gives the user a means
to validate that proper edge timing exists between the two signals.
The setup and hold validation block can be disabled via the
sync timing validation disable bit in Control Function Register 2.
The validation block makes use of a user-specified time window
(programmable in increments of ~75 ps via the 4-bit sync
validation delay word in the multichip sync register). The setup
validation and hold validation circuits use latches identical to
those in the rising edge detector and strobe generator. The
programmable time window is used to skew the timing between
the rising edges of the local SYSCLK signal and the rising edges
of the delayed SYNC_INx signal. If either the hold or setup
validation circuits fail to detect a valid edge sample, the condition
is indicated externally via the SYNC_SMP_ERR pin (active high).
The user must choose a sync validation delay value that is a
reasonable fraction of the SYSCLK period. For example, if the
SYSCLK frequency is 1 GHz (1 ns period), then a reasonable
value is 4 (300 ps). Choosing too large a value can cause the
SYNC_SMP_ERR pin to generate false error signals. Choosing
too small a value may cause instability.
Figure 54. Sync Timing Validation Block
Rev. D | Page 46 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
POWER SUPPLY PARTITIONING
The AD9910 features multiple power supplies, and their power
consumption varies with its configuration. This section covers
which power supplies can be grouped together and how the
power consumption of each block varies with frequency.
The values quoted in this section are for comparison only. Refer
to Tab l e 1 for exact values. With each group, use 0.1 μF or 0.01 μF
bypass capacitors in parallel with a 10 μF capacitor.
The recommendations here are for typical applications, for
which there are four groups of power supplies: 3.3 V digital,
3.3 V analog, 1.8 V digital, and 1.8 V analog.
Applications demanding the highest performance may require
additional power supply isolation.
3.3 V SUPPLIES
DVDD_I/O (3.3 V) (Pin 11, Pin 15, Pin 21, Pin 28, Pin 45, Pin 56, and Pin 66)
These 3.3 V supplies can be grouped together. The power
consumption on these pins varies dynamically with serial port
activity.
1.8 V SUPPLIES
DVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 17, Pin 23, Pin 30, Pin 47, Pin 57, and Pin 64)
These pins can be grouped together. Their current consumption
increases linearly with the system clock frequency. See Figure 17
and Figure 18 for typical current consumption curves. There is
also a slight (~5%) increase as f
400 MHz.
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 3)
This 1.8 V supply powers the REFCLK multiplier (PLL) and
consumes about 7 mA. For applications demanding the highest
performance with the PLL enabled, this supply should be
isolated from other 1.8 V AVDD supplies with a separate
regulator. For less demanding applications, this supply can be
run off the same regulator as Pin 89 and Pin 92 with a ferrite
bead to isolate Pin 3 from Pin 89 and Pin 92.
The loop filter for the PLL should directly connect to Pin 3. If
the PLL is bypassed, Pin 3 should still be powered, but isolation
is not critical.
increases from 50 MHz to
OUT
AVDD (3.3 V) (Pin 74 to Pin 77 and Pin 83)
These are 3.3 V DAC power supplies that typically consume
about 28 mA. At a minimum, a ferrite bead should be used to
isolate these from other 3.3 V supplies, with a separate regulator
being ideal. The current consumption of these supplies consist
mainly of biasing current and do not vary with frequency.
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 6)
This pin can be grouped together with the DVDD 1.8 V supply
pins. For the highest performance, a ferrite bead should be used
for isolation, with a separate regulator being ideal.
AVDD (1.8 V) (Pin 89 and Pin 92)
This 1.8 V supply for the REFCLK input consumes about
15 mA. These pins can run off the supply of Pin 3 with a ferrite
bead to isolate Pin 3 from Pin 89 and Pin 92. At a minimum, a
ferrite bead should be used to isolate these from other 1.8 V
supplies. However, for applications demanding the highest
performance, a separate regulator is recommended.
Rev. D | Page 47 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
SERIAL PROGRAMMING
CONTROL INTERFACE—SERIAL I/O
The AD9910 serial port is a flexible, synchronous serial communications port allowing easy interface to many industry-standard
microcontrollers and microprocessors. The serial I/O is compatible
with most synchronous transfer formats.
The interface allows read/write access to all registers that configure
the AD9910. MSB-first or LSB-first transfer formats are supported.
In addition, the serial interface port can be configured as a single
pin input/output (SDIO) allowing a 2-wire interface, or it can
be configured as two unidirectional pins for input/output
(SDIO/SDO) enabling a 3-wire interface. Two optional pins
(I/O_RESET and
systems with the AD9910.
CS
) enable greater flexibility for designing
GENERAL SERIAL I/O OPERATION
There are two phases to a serial communications cycle. The first
is the instruction phase to write the instruction byte into the
AD9910. The instruction byte contains the address of the register
to be accessed (see the Register Map and Bit Descriptions
section) and defines whether the upcoming data transfer is a
write or read operation.
For a write cycle, Phase 2 represents the data transfer between
the serial port controller to the serial port buffer. The number
of bytes transferred is a function of the register being accessed.
For example, when accessing the Control Function Register 2
(Address 0x01), Phase 2 requires that four bytes be transferred.
Each bit of data is registered on each corresponding rising edge
of SCLK. The serial port controller expects that all bytes of the
register be accessed; otherwise, the serial port controller is put
out of sequence for the next communication cycle. However,
one way to write fewer bytes than required is to use the I/O_RESET
pin feature. The I/O_RESET pin function can be used to abort
an I/O operation and reset the pointer of the serial port controller. After an I/O reset, the next byte is the instruction byte.
Note that every completed byte written prior to an I/O reset is
preserved in the serial port buffer. Partial bytes written are not
preserved. At the completion of any communication cycle, the
AD9910 serial port controller expects the next eight rising
SCLK edges to be the instruction byte for the next communication cycle.
After a write cycle, the programmed data resides in the serial
port buffer and is inactive. I/O_UPDATE transfers data from
the serial port buffer to active registers. The I/O update can be
sent either after each communication cycle or when all serial
operations are complete. In addition, a change in profile pins
can initiate an I/O update.
For a read cycle, Phase 2 is the same as the write cycle with the
following differences: data is read from the active registers, not
the serial port buffer, and data is driven out on the falling edge
of SCLK.
Rev. D | Page 48 of 64
Note that to read back any profile register (0x0E to 0x15), the
three external profile pins must be used. For example, if the
profile register is Profile 5 (0x13), then the PROFILE[0:2] pins
must equal 101.This is not required to write to profile registers.
INSTRUCTION BYTE
The instruction byte contains the following information as
shown in the instruction byte information bit map.
Instruction Byte Information Bit Map
MSB LSB
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W X X A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
R/W—Bit 7 of the instruction byte determines whether a read
or write data transfer occurs after the instruction byte write.
Logic 1 indicates a read operation. Cleared indicates a write
operation.
X, X—Bit 6 and Bit 5 of the instruction byte are don’t cares.
A4, A3, A2, A1, A0—Bit 4, Bit 3, Bit 2, Bit 1, and Bit 0 of the
instruction byte determine which register is accessed during the
data transfer portion of the communications cycle.
SERIAL I/O PORT PIN DESCRIPTIONS
SCLK—Serial Clock
The serial clock pin is used to synchronize data to and from the
AD9910 and to run the internal state machines.
CS
—Chip Select Bar
CS
is an active low input that allows more than one device on
the same serial communications line. The SDO and SDIO pins
go to a high impedance state when this input is high. If driven
high during any communications cycle, that cycle is suspended
CS
until
systems that maintain control of SCLK.
SDIO—Serial Data Input/Output
Data is always written into the AD9910 on this pin. However,
this pin can be used as a bidirectional data line. Bit 1 of CFR1
Register Address 0x00 controls the configuration of this pin.
The default is cleared, which configures the SDIO pin as
bidirectional.
SDO—Serial Data Out
Data is read from this pin for protocols that use separate lines
for transmitting and receiving data. When the AD9910 operates
in single bidirectional I/O mode, this pin does not output data
and is set to a high impedance state.
is reactivated low. Chip select (CS) can be tied low in

Data Sheet AD9910
I
7
SDIO
INSTRUCTION CYCLE DATA TRANSFER CYCLE
SCLK
CS
I
6
I
5
I
4
I
3I2
I
1
I
0
D
7
D
6
D5D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1D0
06479-030
D
O7
INSTRUCTION CYCLE DATA TRANSFE R CY CLE
DON'T CARE
I
7
I
6
I
5
I
4I3
I
2I1I0
SDIO
SCLK
CS
SDO
D
O6
D
O5
D
O4
D
O3DO2
D
O1DO0
06479-031
I
7
SDIO
INSTRUCTION CYCLE DATA TRANSFER CYCLE
SCLK
CS
I
6
I5I4I3I
2
I1I
0
D
7
D
6
D5D4D
3
D2D
1
D
0
06479-032
I
7
SDIO
INSTRUCTION CYCLE DATA TRANSFER CYCLE
SCLK
CS
I
6I5I4I3I2I1I0
DO7DO6DO5DO4DO3DO2DO1D
O0
06479-033
I/O_RESET—Input/Output Reset
I/O_RESET synchronizes the I/O port state machines without
affecting the contents of the addressable registers. An active
high input on the I/O_RESET pin causes the current communication cycle to abort. After I/O_RESET returns low (Logic 0),
another communication cycle can begin, starting with the
instruction byte write.
I/O_UPDATE—Input/Output Update
The I/O_UPDATE initiates the transfer of written data from
the I/O port buffer to active registers. I/O_UPDATE is active
on the rising edge, and its pulse width must be greater than one
SYNC_CLK period. It is either an input or output pin depending
on the programming of the internal I/O update active bit.
SERIAL I/O TIMING DIAGRAMS
Figure 55 through Figure 58 provide basic examples of the timing
relationships between the various control signals of the serial
I/O port. Most of the bits in the register map are not transferred
to their internal destinations until assertion of an I/O update,
which is not included in the timing diagrams that follow.
MSB/LSB TRANSFERS
The AD9910 serial port can support both most significant bit
(MSB) first or least significant bit (LSB) first data formats. This
functionality is controlled by Bit 0 in Control Function Register 1
(0x00). The default format is MSB first. If LSB first is active, all
data, including the instruction byte, must follow LSB-first convention. Note that the highest number found in the bit range column
for each register is the MSB, and the lowest number is the LSB
for that register (see the Register Map and Bit Descriptions
section and Table 17).
Figure 55. Serial Port Write Timing, Clock Stall Low
Figure 56. 3-Wire Serial Port Read Timing, Clock Stall Low
Figure 57. Serial Port Write Timing, Clock Stall High
Figure 58. 2-Wire Serial Port Read Timing, Clock Stall High
Rev. D | Page 49 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
7:0
N[6:0]
Open
0x00
7:0
I/O update rate[7:0]
0xFF
REGISTER MAP AND BIT DESCRIPTIONS
Table 17. Register Map
Register
Name
(Serial
Address)
CFR1—
Control
Function
Register 1
(0x00)
CFR2—
Control
Function
Register 2
(0x01)
CFR3—
Control
Function
Register 3
(0x02)
Bit Range
(Internal
Address)
31:24 RAM
23:16 Manual
15:8 Load LRR
7:0 Digital
31:24 Open Enable
23:16 Internal
15:8 I/O update rate control Open PDCLK
7:0 Matched
31:24 Open DRV0[1:0] Open VCO SEL[2:0] 0x1F
23:16 Open ICP[2:0] Open 0x3F
15:8 REFCLK
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
enable
OSK
external
control
@ I/O
update
powerdown
I/O
update
active
latency
enable
input
divider
bypass
RAM playback
destination
Inverse
sinc filter
enable
Autoclear
digital
ramp
accumulator
DAC
powerdown
SYNC_CLK
enable
Data
assembler
hold last
value
REFCLK
input
divider
ResetB
Open Internal profile control Select DDS
Autoclear
phase
accumulator
REFCLK
input
powerdown
Digital ramp destination Digital
Sync
timing
validation
disable
Clear
digital
ramp
accumulator
Aux DAC
powerdown
Parallel
data port
enable
Open PFD reset Open PLL enable 0x40
Clear
phase
accumulator
External
powerdown
control
ramp
enable
enable
Open 0x00
sine output
Load ARR
@ I/O
update
Open SDIO input
Digital
ramp
no-dwell
high
PDCLK
invert
OSK
enable
only
Digital
ramp
no-dwell
low
TxEnable
invert
FM gain 0x20
Select auto
OSK
LSB first 0x00
amplitude
scale from
single tone
profiles
Read
effective
FTW
Open 0x08
Default
Value
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x40
1
Auxiliary
DAC
Control
(0x03)
I/O Update
Rate (0x04)
FTW—
Frequency
Tuning
Word
(0x07)
31:24 Open 0x00
23:16 Open 0x00
15:8 Open 0x00
7:0 FSC[7:0] 0x7F
31:24 I/O update rate[31:24] 0xFF
23:16 I/O update rate[23:16] 0xFF
15:8 I/O update rate[15:8] 0xFF
31:24 Frequency tuning word[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency tuning word[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency tuning word[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency tuning word[7:0] 0x00
Rev. D | Page 50 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
7:0
Phase offset word[7:0]
0x00
7:0
Input sync receiver delay[4:0]
Open
0x00
23:16
Digital ramp lower limit[23:16]
N/A
23:16
Digital ramp increment step size[23:16]
N/A
47:40
Phase Offset Word 0[15:8]
0x00
Register
Name
(Serial
Address)
POW—
Phase Offset
Word (0x08)
ASF—
Amplitude
Scale
Factor
(0x09)
Multichip
Sync (0x0A)
Bit Range
(Internal
Address)
15:8 Phase offset word[15:8] 0x00
31:24 Amplitude ramp rate[15:8] 0x00
23:16 Amplitude ramp rate[7:0] 0x00
15:8 Amplitude scale factor[13:6] 0x00
7:0 Amplitude scale factor[5:0] Amplitude step size[1:0]
31:24 Sync validation delay[3:0] Sync
23:16 Sync state preset value[5:0] Open 0x00
15:8 Output sync generator delay[4:0] Open 0x00
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
receiver
enable
Sync
generator
enable
Sync
generator
polarity
Open 0x00
Default
Value
(Hex)
0x00
1
Digital
Ramp Limit
(0x0B)
Digital
Ramp Step
Size (0x0C)
Digital
Ramp Rate
(0x0D)
Single Tone
Profile 0
(0x0E)
63:56 Digital ramp upper limit[31:24] N/A
55:48 Digital ramp upper limit[23:16] N/A
47:40 Digital ramp upper limit[15:8] N/A
39:32 Digital ramp upper limit[7:0] N/A
31:24 Digital ramp lower limit[31:24] N/A
15:8 Digital ramp lower limit[15:8] N/A
7:0 Digital ramp lower limit[7:0] N/A
63:56 Digital ramp decrement step size[31:24] N/A
55:48 Digital ramp decrement step size[23:16] N/A
47:40 Digital ramp decrement step size[15:8] N/A
39:32 Digital ramp decrement step size[7:0] N/A
31:24 Digital ramp increment step size[31:24] N/A
15:8 Digital ramp increment step size[15:8] N/A
7:0 Digital ramp increment step size[7:0] N/A
31:24 Digital ramp negative slope rate [15:8] N/A
23:16 Digital ramp negative slope rate[7:0] N/A
15:8 Digital ramp positive slope rate[15:8] N/A
7:0 Digital ramp positive slope rate[7:0] N/A
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 0[13:8] 0x08
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 0[7:0] 0xB5
39:32 Phase Offset Word 0[7:0] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 0[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 0[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency Tuning Word 0[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 0[7:0] 0x00
Rev. D | Page 51 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
55:48
RAM Profile 0 address step rate[15:8]
0x00
7:0
Open
No-dwell
Open
Zero-
RAM Profile 0 mode control[2:0]
0x00
39:32
Phase Offset Word 1[7:0]
0x00
31:24
RAM Profile 1 waveform
Open
0x00
15:8
Frequency Tuning Word 2[15:8]
0x00
23:16
RAM Profile 2 waveform start address[9:2]
0x00
Register
Name
(Serial
Address)
RAM
Profile 0
(0x0E)
Bit Range
(Internal
Address)
63:56 Open 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 0 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 0 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24 RAM Profile 0 waveform
23:16 RAM Profile 0 waveform start address[9:2] 0x00
15:8 RAM Profile 0 waveform
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
Open 0x00
end address[1:0]
Open 0x00
start address[1:0]
Default
Value
(Hex)
1
Single Tone
Profile 1
(0x0F)
RAM
Profile 1
(0x0F)
Single Tone
Profile 2
(0x10)
high
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 1[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 1[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 1[15:8] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 1[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 1[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency Tuning Word 1[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 1[7:0] 0x00
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 1 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 1 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 1 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
end address[1:0]
23:16 RAM Profile 1 waveform start address[9:2] 0x00
15:8 RAM Profile 1 waveform
7:0 Open No-dwell
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 2[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 2[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 2[15:8] 0x00
39:32 Phase Offset Word 2[7:0] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 2[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 2[23:16] 0x00
start address[1:0]
Open Zero-
high
crossing
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 1 mode control[2:0] 0x00
crossing
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 2[7:0] 0x00
RAM
Profile 2
(0x10)
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 2 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 2 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 2 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24 RAM Profile 2 waveform
15:8 RAM Profile 2 waveform
7:0 Open No-dwell
end address[1:0]
start address[1:0]
high
Open Zero-
Rev. D | Page 52 of 64
Open 0x00
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 2 mode control[2:0] 0x00
crossing

Data Sheet AD9910
55:48
Amplitude Scale Factor 3[7:0]
0x00
47:40
RAM Profile 3 address step rate[7:0]
0x00
23:16
RAM Profile 3 waveform start address[9:2]
0x00
31:24
Frequency Tuning Word 4[31:24]
0x00
15:8
Frequency Tuning Word 5[15:8]
0x00
Register
Name
(Serial
Address)
Single Tone
Profile 3
(0x11)
RAM
Profile 3
(0x11)
Bit Range
(Internal
Address)
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 3[13:8] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 3[15:8] 0x00
39:32 Phase Offset Word 3[7:0] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 3[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 3[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency Tuning Word 3[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 3[7:0] 0x00
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 3 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 3 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
RAM Profile 3 waveform
end address[1:0]
Open 0x00
Default
Value
(Hex)
1
Single Tone
Profile 4
(0x12)
RAM
Profile 4
(0x12)
Single Tone
Profile 5
(0x13)
15:8
7:0
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 4[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 4[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 4[15:8] 0x00
39:32 Phase Offset Word 4[7:0] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 4[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency Tuning Word 4[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 4[7:0] 0x00
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 4 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 4 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 4 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24 RAM Profile 4 waveform
23:16 RAM Profile 4 waveform start address[9:2] 0x00
15:8 RAM Profile 4 waveform
7:0 Open No-dwell
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 5[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 5[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 5[15:8] 0x00
39:32 Phase Offset Word 5[7:0] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 5[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 5[23:16] 0x00
RAM Profile 3 waveform
start address[1:0]
Open No-dwell
end address[1:0]
start address[1:0]
high
high
Open Zero-
crossing
Open Zero-
crossing
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 3 mode control[2:0]
Open 0x00
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 4 mode control[2:0] 0x00
0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 5[7:0] 0x00
Rev. D | Page 53 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
55:48
RAM Profile 5 address step rate[15:8]
0x00
Open
No-dwell
Open
Zero-
RAM Profile 5 mode control[2:0]
0x00
39:32
Phase Offset Word 6[7:0]
0x00
31:24
RAM Profile 6 waveform
Open
0x00
15:8
Frequency Tuning Word 7[15:8]
0x00
23:16
RAM Profile 7 waveform start address[9:2]
0x00
RAM (0x16)
31:0
RAM word[31:0]
0x00
Register
Name
(Serial
Address)
RAM
Profile 5
(0x13)
Single Tone
Profile 6
(0x14)
RAM
Profile 6
(0x14)
Bit Range
(Internal
Address)
63:56 Open 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 5 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 5 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24
23:16 RAM Profile 5 waveform start address[9:2] 0x00
15:8
7:0
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 6[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 6[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 6[15:8] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 6[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 6[23:16] 0x00
15:8 Frequency Tuning Word 6[15:8] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 6[7:0] 0x00
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 6 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 6 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 6 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
RAM Profile 5 waveform
end address[1:0]
RAM Profile 5 waveform
start address[1:0]
high
crossing
Open 0x00
Open 0x00
Default
Value
(Hex)
1
Single Tone
Profile 7
(0x15)
RAM
Profile 7
(0x15)
end address[1:0]
23:16 RAM Profile 6 waveform start address[9:2] 0x00
15:8 AM Profile 6 waveform
7:0 Open No-dwell
63:56 Open Amplitude Scale Factor 7[13:8] 0x00
55:48 Amplitude Scale Factor 7[7:0] 0x00
47:40 Phase Offset Word 7[15:8] 0x00
39:32 Phase Offset Word 7[7:0] 0x00
31:24 Frequency Tuning Word 7[31:24] 0x00
23:16 Frequency Tuning Word 7[23:16] 0x00
7:0 Frequency Tuning Word 7[7:0] 0x00
63:56 Open 0x00
55:48 RAM Profile 7 address step rate[15:8] 0x00
47:40 RAM Profile 7 address step rate[7:0] 0x00
39:32 RAM Profile 7 waveform end address[9:2] 0x00
31:24
15:8
7:0
start address[1:0]
RAM Profile 7 waveform
end address[1:0]
RAM Profile 7 waveform
start address[1:0]
Open No-dwell
high
high
Open Zero-
crossing
Open Zero-
crossing
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 6 mode control[2:0] 0x00
Open 0x00
Open 0x00
RAM Profile 7 mode control[2:0] 0x00
1
N/A = not applicable.
Rev. D | Page 54 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
REGISTER BIT DESCRIPTIONS
The serial I/O port registers span an address range of 0 to 23
(0x00 to 0x16 in hexadecimal notation). This represents a total
of 24 registers. However, two of these registers are unused,
yielding a total of 22 available registers. The unused registers are
Register 5 and Register 6 (0x05 and 0x06, respectively).
The number of bytes assigned to the registers varies. That is, the
registers are not of uniform depth; each contains the number of
bytes necessary for its particular function. Additionally, the
registers are assigned names according to their functionality. In
some cases, a register is given a mnemonic descriptor. For
example, the register at Serial Address 0x00 is named Control
Function Register 1 and is assigned the mnemonic CFR1.
The following section provides a detailed description of each bit
in the AD9910 register map. For cases in which a group of bits
serves a specific function, the entire group is considered a
binary word and described in aggregate.
Control Function Register 1 (CFR1)—Address 0x00
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
This section is organized in sequential order of the serial addresses
of the registers. Each subheading includes the register name and
optional register mnemonic (in parentheses). Also given is the
serial address in hexadecimal format and the number of bytes
assigned to the register.
Following each subheading is a table containing the individual
bit descriptions for that particular register. The location of the
bit(s) in the register is indicated by a single number or a pair of
numbers separated by a colon; that is, a pair of numbers (A:B)
indicates a range of bits from the most significant (A) to the
least significant (B). For example, 5:2 implies Bit Position 5
down to Bit Position 2, inclusive, with Bit 0 identifying the LSB
of the register.
Unless otherwise stated, programmed bits are not transferred to
their internal destinations until the assertion of the I/O_UPDAT E
pin or a profile change.
Table 18. Bit Description for CFR1
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31 RAM enable 0 = disables RAM functionality (default).
1 = enables RAM functionality (required for both load/retrieve and playback operation).
30:29 RAM playback destination See Table 12 for details; default is 00b.
28:24 Open
23 Manual OSK external
0 = OSK pin inoperative (default).
1 = OSK pin enabled for manual OSK control (see Output Shift Keying (OSK) section for
22 Inverse sinc filter enable 0 = inverse sinc filter bypassed (default).
1 = inverse sinc filter active.
21 Open
20:17 Internal profile control Ineffective unless CFR1[31] = 1. These bits are effective without the need for an I/O update.
16 Select DDS sine output 0 = cosine output of the DDS is selected (default).
1 = sine output of the DDS is selected.
15 Load LRR @ I/O update Ineffective unless CFR2[19] = 1.
0 = normal operation of the digital ramp timer (default).
1 = digital ramp timer loaded any time I/O_UPDATE is asserted or a PROFILE[2:0] change
14 Autoclear digital ramp
13 Autoclear phase
control
accumulator
accumulator
Ineffective unless CFR1[9:8] = 10b.
details).
See Table 14 for details. Default is 0000b.
occurs.
0 = normal operation of the DRG accumulator (default).
1 = the ramp accumulator is reset for one cycle of the DDS clock after which the accumula-
tor automatically resumes normal operation. As long as this bit remains set, the ramp
accumulator is momentarily reset each time an I/O_UPDATE is asserted or a PROFILE[2:0]
change occurs. This bit is synchronized with either an I/O _UPDATE or a PROFILE[2:0]
change and the next rising edge of SYNC_CLK.
0 = normal operation of the DDS phase accumulator (default).
1 = synchronously resets the DDS phase accumulator anytime I/O_UPDATE is asserted or a
profile change occurs.
Rev. D | Page 55 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
11
Clear phase accumulator
0 = normal operation of the DDS phase accumulator (default).
1 = DAC clock signals and bias circuits are disabled.
5
REFCLK input power-down
This bit is effective without the need for an I/O update.
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
12 Clear digital ramp
accumulator
1 = asynchronous, static reset of the DDS phase accumulator.
10 Load ARR @ I/O update Ineffective unless CFR1[9:8] = 11b.
0 = normal operation of the OSK amplitude ramp rate timer (default).
1 = OSK amplitude ramp rate timer reloaded anytime I/O_UPDATE is asserted or a
9 OSK enable The output shift keying enable bit.
0 = OSK disabled (default).
1 = OSK enabled.
8 Select auto OSK Ineffective unless CFR1[9] = 1.
0 = manual OSK enabled (default).
1 = automatic OSK enabled.
7 Digital power-down This bit is effective without the need for an I/O update.
0 = clock signals to the digital core are active (default).
1 = clock signals to the digital core are disabled.
6 DAC power-down 0 = DAC clock signals and bias circuits are active (default).
0 = normal operation of the DRG accumulator (default).
1 = asynchronous, static reset of the DRG accumulator. The ramp accumulator remains reset
as long as this bit remains set. This bit is synchronized with either an I/O_UPDATE or a
PROFILE[2:0] change and the next rising edge of SYNC_CLK.
PROFILE[2:0] change occurs.
0 = REFCLK input circuits and PLL are active (default).
1 = REFCLK input circuits and PLL are disabled.
4 Auxiliary DAC power-down 0 = auxiliary DAC clock signals and bias circuits are active (default).
1 = auxiliary DAC clock signals and bias circuits are disabled.
3 External power-down
1 = assertion of the EXT_PWR_DWN pin affects fast recovery power-down.
2 Open
1 SDIO input only 0 = configures the SDIO pin for bidirectional operation; 2-wire serial programming
1 = configures the serial data I/O pin (SDIO) as an input only pin; 3-wire serial
0 LSB first 0 = configures the serial I/O port for MSB-first format (default).
1 = configures the serial I/O port for LSB-first format.
control
0 = assertion of the EXT_PWR_DWN pin affects full power-down (default).
mode (default).
programming mode.
Rev. D | Page 56 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
1 = the internal PDCLK signal appears at the PDCLK pin (default).
Control Function Register 2 (CFR2)—Address 0x01
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 19. Bit Descriptions for CFR2
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:25 Open
24 Enable amplitude scale
0 = the amplitude scaler is bypassed and shut down for power conservation (default).
1 = the amplitude is scaled by the ASF from the active profile.
23 Internal I/O update active This bit is effective without the need for an I/O update.
22 SYNC_CLK enable 0 = the SYNC_CLK pin is disabled; static Logic 0 output.
1 = the SYNC_CLK pin generates a clock signal at ¼ f
21:20 Digital ramp destination See Table 11 for details. Default is 00b. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for
19 Digital ramp enable 0 = disables digital ramp generator functionality (default).
1 = enables digital ramp generator functionality.
18 Digital ramp no-dwell high See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for details.
0 = disables no-dwell high functionality (default).
1 = enables no-dwell high functionality.
17 Digital ramp no-dwell low See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for details.
0 = disables no-dwell low functionality (default).
1 = enables no-dwell low functionality.
16 Read effective FTW 0 = a serial I/O port read operation of the FTW register reports the contents of the FTW
1 = a serial I/O port read operation of the FTW register reports the actual 32-bit word
15:14 I/O update rate control Ineffective unless CFR2[23] = 1. Sets the prescale ratio of the divider that clocks the auto I/O
00 = divide-by-1 (default).
01 = divide-by-2.
10 = divide-by-4.
11 = divide-by-8.
13:12 Open
11 PDCLK enable 0 = the PDCLK pin is disabled and forced to a static Logic 0 state; the internal clock signal
from single tone profiles
Ineffective if CFR2[19 ] = 1 or CFR1[31] = 1 or CFR1[9] = 1.
0 = serial I/O programming is synchronized with the external assertion of the
I/O_UPDATE pin, which is configured as an input pin (default).
1 = serial I/O programming is synchronized with an internally generated I/O update
signal (the internally generated signal appears at the I/O_UPDATE pin, which is
configured as an output pin).
; used for synchronization of the
serial I/O port (default).
details.
register (default).
appearing at the input to the DDS phase accumulator.
update timer as follows:
continues to operate and provide timing to the data assembler.
SYSCLK
10 PDCLK invert 0 = normal PDCLK polarity; Q-data associated with Logic 1, I-data with Logic 0 (default).
1 = inverted PDCLK polarity.
9 TxEnable invert 0 = no inversion.
1 = inversion.
8 Open
7 Matched latency enable 0 = simultaneous application of amplitude, phase, and frequency changes to the DDS
arrive at the output in the order listed (default).
1 = simultaneous application of amplitude, phase, and frequency changes to the DDS
arrive at the output simultaneously.
Rev. D | Page 57 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
23:22
Open
14
REFCLK input divider ResetB
0 = input divider is reset.
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
6 Data assembler hold last
value
1 = the data assembler of the parallel data port internally forces the last value received
5 Sync timing validation
disable
1 = the SYNC_SMP_ERR pin is forced to a static Logic 0 condition (default).
4 Parallel data port enable See the Parallel Data Port Modulation Mode section for more details.
0 = disables parallel data port modulation functionality (default).
1 = enables parallel data port modulation functionality.
3:0 FM gain See the Parallel Data Port Modulation Mode section for more details. Default is 0000b.
Control Function Register 3 (CFR3)—Address 0x02
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 20. Bit Descriptions for CFR3
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:30 Open
29:28 DRV0 Controls the REFCLK_OUT pin (see Table 7 for details); default is 01b.
27 Open
26:24 VCO SEL Selects the frequency band of the REFCLK PLL VCO (see Table 8 for details); default is 111b.
Ineffective unless CFR2[4] = 1.
0 = the data assembler of the parallel data port internally forces zeros on the data path
and ignores the signals on the D[15:0] and F[1:0] pins while the TxENABLE pin is Logic 0
(default). This implies that the destination of the data at the parallel data port is
amplitude when TxENABLE is Logic 0.
on the D[15:0] and F[1:0] pins while the TxENABLE pin is Logic 1.
0 = enables the SYNC_SMP_ERR pin to indicate (active high) detection of a synchronization
pulse sampling error.
21:19 ICP Selects the charge pump current in the REFCLK PLL (see Table 9 for details); default is 111b.
18:16 Open
15 REFCLK input divider bypass 0 = input divider is selected (default).
1 = input divider is bypassed.
1 = input divider operates normally (default).
13:11 Open
10 PFD reset 0 = normal operation (default).
1 = phase detector disabled.
9 Open
8 PLL enable 0 = REFCLK PLL bypassed (default).
1 = REFCLK PLL enabled.
7:1 N This 7-bit number is the divide modulus of the REFCLK PLL feedback divider; default is
0000000b.
0 Open
Auxiliary DAC Control Register—Address 0x03
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 21. Bit Descriptions for DAC Control Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:8 Open
7:0 FSC This 8-bit number controls the full-scale output current of the main DAC (see the Auxiliary
DAC section); default is 0x7F.
Rev. D | Page 58 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
I/O Update Rate Register—Address 0x04
Four bytes are assigned to this register. This register is effective without the need for an I/O update.
Table 22. Bit Descriptions for I/O Update Rate Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:0 I/O update rate Ineffective unless CFR2[23] = 1. This 32-bit number controls the automatic I/O update
rate (see the Automatic I/O Update section for details); default is 0xFFFFFFFF.
Frequency Tuning Word Register (FTW)—Address 0x07
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 23. Bit Descriptions for FTW Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:0 Frequency tuning word 32-bit frequency tuning word.
Phase Offset Word Register (POW)—Address 0x08
Two bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 24. Bit Descriptions for POW Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
15:0 Phase offset word 16-bit phase offset word.
Amplitude Scale Factor Register (ASF)—Address 0x09
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 25. Bit Descriptions for ASF Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:16 Amplitude ramp rate 16-bit amplitude ramp rate value. Effective only if CFR1[9:8] = 11b; see the Output Shift
Keying (OSK) section for details.
15:2 Amplitude scale factor 14-bit amplitude scale factor.
1:0 Amplitude step size Effective only if CFR1[9:8] = 11b; see the Output Shift Keying (OSK) section for details.
Rev. D | Page 59 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
25
Sync generator polarity
0 = synchronization clock generator coincident with the rising edge of SYSCLK (default).
15:11
Output sync generator
This 5-bit number sets the output delay (in ~75 ps increments) of the sync generator.
Bit(s)
Mnemonic
Description
Multichip Sync Register—Address 0x0A
Four bytes are assigned to this register.
Table 26. Multichip Sync Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:28 Sync validation delay This 4-bit number sets the timing skew (in ~75ps increments) between SYSCLK and the
delayed SYNC_INx signal for the sync validation block in the sync receiver. Default is 0000b.
27 Sync receiver enable 0 = synchronization clock receiver disabled (default).
1 = synchronization clock receiver enabled.
26 Sync generator enable 0 = synchronization clock generator disabled (default).
1 = synchronization clock generator enabled.
1 = synchronization clock generator coincident with the falling edge of SYSCLK.
24 Open
23:18 Sync state preset value This 6-bit number is the state that the internal clock generator assumes when it receives a
sync pulse. Default is 000000b.
17:16 Open
delay
10:8 Open
7:3 Input sync receiver delay This 5-bit number sets the input delay (in ~75 ps increments) of the sync receiver. Default is
2:0 Open
Default is 00000b.
00000b.
Digital Ramp Limit Register—Address 0x0B
Eight bytes are assigned to this register. This register is only effective if CFR2[19] = 1. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for
details.
Table 27. Bit Descriptions for Digital Ramp Limit Register
63:32 Digital ramp upper limit 32-bit digital ramp upper limit value.
31:0 Digital ramp lower limit 32-bit digital ramp lower limit value.
Digital Ramp Step Size Register—Address 0x0C
Eight bytes are assigned to this register. This register is only effective if CFR2[19] = 1. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for
details.
Table 28. Bit Descriptions for Digital Ramp Step Size Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
63:32 Digital ramp decrement
step size
31:0 Digital ramp increment
step size
32-bit digital ramp decrement step size value.
32-bit digital ramp increment step size value.
Digital Ramp Rate Register—Address 0x0D
Four bytes are assigned to this register. This register is only effective if CFR2[19] = 1. See the Digital Ramp Generator (DRG) section for
details.
Table 29. Bit Descriptions for Digital Ramp Rate Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:16 Digital ramp negative slope
rate
15:0 Digital ramp positive slope
rate
16-bit digital ramp negative slope value that defines the time interval between decrement
values.
16-bit digital ramp positive slope value that defines the time interval between increment
values.
Rev. D | Page 60 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
13:6
Open
Profile Registers
There are eight consecutive serial I/O addresses (Address 0x0E
to Address 0x015) dedicated to device profiles. All eight profile
registers are either single tone profiles or RAM profiles. RAM
profiles are in effect when CFR1[31] = 1. Single tone profiles are
in effect when CFR1[31] = 0, CFR2[19] = 0, and CFR2[4] = 0.
Profile 0 to Profile 7, Single Tone Registers—Address 0x0E to Address 0x15
Eight bytes are assigned to each register.
Table 30. Bit Descriptions for Profile 0 to Profile 7 Single Tone Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
63:62 Open
61:48 Amplitude scale factor This 14-bit number controls the DDS output amplitude.
47:32 Phase offset word This 16-bit number controls the DDS phase offset.
31:0 Frequency tuning word This 32-bit number controls the DDS frequency.
RAM Profile 0 to RAM Profile 7, Control Registers—Address 0x0E to Address 0x15
Eight bytes are assigned to each register.
In normal operation, the active profile register is selected using
the external PROFILE[2:0] pins. However, in the specific case
when CFR1[31] = 1 and CFR1[20:17] ≠ 0000b, the active profile
is selected automatically (see the RAM Ramp-Up Internal
Profile Control Mode section).
Table 31. Bit Descriptions for Profile 0 to Profile 7 RAM Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
63:56 Open
55:40 Address step rate 16-bit address step rate value.
39:30 Waveform end address 10-bit waveform end address.
29:24 Open
23:14 Waveform start address 10-bit waveform start address.
5 No-dwell high Effective only when the RAM mode is in ramp-up.
0 = when the RAM state machine reaches the end address, it halts.
1 = when the RAM state machines reaches the end address, it jumps to the start address
and halts.
4 Open
3 Zero-crossing Effective only when in RAM mode, direct switch.
0 = zero-crossing function disabled.
1 = zero-crossing function enabled.
2:0 RAM mode control See Table 13 for details.
RAM Register—Address 0x16
Four bytes are assigned to the RAM register.
Table 32. Bit Descriptions for RAM Register
Bit(s) Mnemonic Description
31:0 RAM word The start and end addresses in the RAM Profile 0 to RAM Profile 7 control registers define
the number of 32-bit words (1 minimum, 1024 maximum) to be written to the RAM register.
Rev. D | Page 61 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-026-AED-HD
1
25
26 50
76
100
75
51
14.00 BSC SQ
16.00 BSC SQ
0.75
0.60
0.45
1.20
MAX
1.05
1.00
0.95
0.20
0.09
0.08 MAX
COPLANARITY
VIEW A
ROTATED 90° CCW
SEATING
PLANE
0° MIN
7°
3.5°
0°
0.15
0.05
VIEW A
PIN 1
TOP VIEW
(PINS DO W N)
0.27
0.22
0.17
0.50 BSC
LEAD PIT CH
1
25
2650
76 100
75
51
BOTTOM VIEW
(PINS UP)
5.00 SQ
EXPOSED
PAD
042209-A
FOR PROP E R CONNECTION OF
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CO NFIGURATI ON AND
FUNCTIO N DE S CRIPTIONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Figure 59. 100-Lead Thin Quad Flat Package, Exposed Pad [TQFP_EP]
(SV-100-4)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9910BSVZ –40°C to +85°C 100-Lead Thin Quad Flat Package, Exposed Pad [TQFP_EP] SV-100-4
AD9910BSVZ-REEL –40°C to +85°C 100-Lead Thin Quad Flat Package, Exposed Pad [TQFP_EP] SV-100-4
AD9910/PCBZ Evaluation Board
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
Rev. D | Page 62 of 64

Data Sheet AD9910
NOTES
Rev. D | Page 63 of 64

AD9910 Data Sheet
©2007–2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
NOTES
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D06479-0-5/12(D)
Rev. D | Page 64 of 64
 Loading...
Loading...